Crimean Tatar language
Encyclopedia
The Crimean Tatar language is the language of the Crimean Tatars
. It is a Turkic language
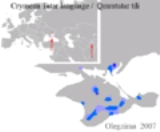
spoken in Crimea
, Central Asia (mainly in Uzbekistan
), and the Crimean Tatar diaspora
s in Turkey
, Romania
, Bulgaria
. It is not to be confused with the Tatar language
.
, Finland
, and the United States. It is one of the seriously endangered languages in Europe.
) – is of Kypchak origin, Yalıboylus, who lived on the southern coast of Crimea before 1944, speak an Oghuz
dialect very close to Turkish
, and the middle dialect of the Tat Tatars from the Crimean Mountains (should not be confused with Tat people
) is a mixture of the two. This dialect is a direct descendant of the Cuman language
, but it has been strongly influenced by the Oghuz Turkic. The modern Crimean Tatar written language is based on this middle dialect because the Tats comprise about 55% of the total Crimean Tatar population and their dialect is equally intelligible to the speakers of the others.
. However, the official written languages of the Crimean Khanate were Chagatai
and Ottoman Turkish
. After the Islamization
, Crimean Tatars wrote with an Arabic script.
In 1876, the different Turkish Crimean dialects were made into a uniform written language by Ismail Gasprinski. A preference was given to the Oghuz dialect of the Yalıboylus, in order to not break the link between the Crimeans and the Turks of the Ottoman Empire
. In 1928, it was reoriented to the middle dialect.
In 1928, the alphabet was replaced with the Uniform Turkic Alphabet
based on the Latin alphabet
. The Uniform Turkic Alphabet was itself replaced in 1938 by a Cyrillic alphabet. Since the 1990s, the script is in the process of being replaced with a Latin version again, but the Cyrillic is still widely used (mainly in published literature and newspapers). The current Latin-based Crimean Tatar alphabet is the same as the Turkish alphabet
with two additional characters: Ñ
ñ and Q
q.
Crimean Tatar was the native language of the poet Bekir Çoban-zade.
The vowel system of Crimean Tatar is similar to those of other Turkic languages, such as Turkish
. While /i/ and /ɯ/ are phonologically distinct, since high vowels in Crimean are short and reduced, they are realized close to [ɪ].
In additional to these phonemes, Crimean also displays marginal phonemes that occur in borrowed words, especially palatalized consonants.
(see Конституция Автономной Республики Крым), Russian and Crimean Tatar languages enjoy a "protected" (Russian – обеспечивается ... защита) status; every citizen is entitled, at his request (Russian ходатайство), to receive government documents, such as "Passport, Birth certificate and others" in Crimean Tatar. According to the constitution of Ukraine, however, Ukrainian is the only official language in all of Ukraine, so the recognition of those languages is a matter of political and legal debate.
Before the Sürgün, the deportation of Crimean Tatars to the Uzbek SSR
(18 May 1944), it had an official language status in the Crimean Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic
.
гъ, къ, нъ and дж are separate letters.
. Although these languages are related (as both are Turkic), the Kypchak languages closest to Crimean Tatar are (as was mentioned above) Kumyk
and Karachay-Balkar
, not the Tatar language.
Crimean Tatars
Crimean Tatars or Crimeans are a Turkic ethnic group that originally resided in Crimea. They speak the Crimean Tatar language...
. It is a Turkic language
Turkic languages
The Turkic languages constitute a language family of at least thirty five languages, spoken by Turkic peoples across a vast area from Eastern Europe and the Mediterranean to Siberia and Western China, and are considered to be part of the proposed Altaic language family.Turkic languages are spoken...
spoken in Crimea
Crimea
Crimea , or the Autonomous Republic of Crimea , is a sub-national unit, an autonomous republic, of Ukraine. It is located on the northern coast of the Black Sea, occupying a peninsula of the same name...
, Central Asia (mainly in Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan , officially the Republic of Uzbekistan is a doubly landlocked country in Central Asia and one of the six independent Turkic states. It shares borders with Kazakhstan to the west and to the north, Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan to the east, and Afghanistan and Turkmenistan to the south....
), and the Crimean Tatar diaspora
Crimean Tatar diaspora
The Crimean Tatar diaspora dates back to the annexation of Crimea by Russia in 1783, after which Crimean Tatars were forced to emigrate in a series of waves spanning the period from 1783 to 1917...
s in Turkey
Turkey
Turkey , known officially as the Republic of Turkey , is a Eurasian country located in Western Asia and in East Thrace in Southeastern Europe...
, Romania
Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central and Southeastern Europe, on the Lower Danube, within and outside the Carpathian arch, bordering on the Black Sea...
, Bulgaria
Bulgaria
Bulgaria , officially the Republic of Bulgaria , is a parliamentary democracy within a unitary constitutional republic in Southeast Europe. The country borders Romania to the north, Serbia and Macedonia to the west, Greece and Turkey to the south, as well as the Black Sea to the east...
. It is not to be confused with the Tatar language
Tatar language
The Tatar language , or more specifically Kazan Tatar, is a Turkic language spoken by the Tatars of historical Kazan Khanate, including modern Tatarstan and Bashkiria...
.
Number of speakers
Today, more than 260,000 Crimean Tatars live in Crimea, and approximately 150,000 are still in exile in Central Asia (mainly in Uzbekistan). An estimated 5 million people of Crimean origin live in Turkey, descendants of those who emigrated in the 19th and early 20th centuries. Of these an estimated 2,000 still speak the language. Smaller Crimean Tatar communities are also found in Romania (22,000), Bulgaria (6,000), PolandPoland
Poland , officially the Republic of Poland , is a country in Central Europe bordered by Germany to the west; the Czech Republic and Slovakia to the south; Ukraine, Belarus and Lithuania to the east; and the Baltic Sea and Kaliningrad Oblast, a Russian exclave, to the north...
, Finland
Finland
Finland , officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country situated in the Fennoscandian region of Northern Europe. It is bordered by Sweden in the west, Norway in the north and Russia in the east, while Estonia lies to its south across the Gulf of Finland.Around 5.4 million people reside...
, and the United States. It is one of the seriously endangered languages in Europe.
Dialects
Each of the three subethnic groups of the Crimean Tatars has its own dialect. The dialect of the Noğays – the former inhabitants of the Crimean steppe (should not be confused with Nogai peopleNogais
The Nogai people are a Turkic ethnic group in Southern Russia: northern Dagestan and Stavropol Krai, as well as in Karachay-Cherkessia and the Astrakhan Oblast; undefined number live in Chechnya...
) – is of Kypchak origin, Yalıboylus, who lived on the southern coast of Crimea before 1944, speak an Oghuz
Oghuz languages
The Oghuz languages, a major branch of the Turkic language family, are spoken by more than 110 million people in an area spanning from the Balkans to China.-Linguistic features:...
dialect very close to Turkish
Turkish language
Turkish is a language spoken as a native language by over 83 million people worldwide, making it the most commonly spoken of the Turkic languages. Its speakers are located predominantly in Turkey and Northern Cyprus with smaller groups in Iraq, Greece, Bulgaria, the Republic of Macedonia, Kosovo,...
, and the middle dialect of the Tat Tatars from the Crimean Mountains (should not be confused with Tat people
Tats
Tats are an Iranian people, presently living within Azerbaijan, Armenia, and Russia ....
) is a mixture of the two. This dialect is a direct descendant of the Cuman language
Cuman language
Cuman was a Kipchak Turkic language spoken by the Cumans and Kipchaks; the language was similar to the today's Crimean Tatar language...
, but it has been strongly influenced by the Oghuz Turkic. The modern Crimean Tatar written language is based on this middle dialect because the Tats comprise about 55% of the total Crimean Tatar population and their dialect is equally intelligible to the speakers of the others.
History
The forming of the Crimean Tatar spoken dialects began with the first Turkic invasions to Crimea and ended during the period of the Crimean KhanateCrimean Khanate
Crimean Khanate, or Khanate of Crimea , was a state ruled by Crimean Tatars from 1441 to 1783. Its native name was . Its khans were the patrilineal descendants of Toqa Temür, the thirteenth son of Jochi and grandson of Genghis Khan...
. However, the official written languages of the Crimean Khanate were Chagatai
Chagatai language
The Chagatai language is an extinct Turkic language which was once widely spoken in Central Asia, and remained the shared literary language there until the early twentieth century...
and Ottoman Turkish
Ottoman Turkish language
The Ottoman Turkish language or Ottoman language is the variety of the Turkish language that was used for administrative and literary purposes in the Ottoman Empire. It borrows extensively from Arabic and Persian, and was written in a variant of the Perso-Arabic script...
. After the Islamization
Islamization
Islamization or Islamification has been used to describe the process of a society's conversion to the religion of Islam...
, Crimean Tatars wrote with an Arabic script.
In 1876, the different Turkish Crimean dialects were made into a uniform written language by Ismail Gasprinski. A preference was given to the Oghuz dialect of the Yalıboylus, in order to not break the link between the Crimeans and the Turks of the Ottoman Empire
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman EmpireIt was usually referred to as the "Ottoman Empire", the "Turkish Empire", the "Ottoman Caliphate" or more commonly "Turkey" by its contemporaries...
. In 1928, it was reoriented to the middle dialect.
In 1928, the alphabet was replaced with the Uniform Turkic Alphabet
Uniform Turkic Alphabet
The Uniform Turkic Alphabet was a Latin alphabet used by non-Slavic peoples of the USSR in the 1930s. The alphabet used ligatures from Jaŋalif as it was also a part of the uniform alphabet. The uniform alphabet utilized Latin ligatures, excluding "w." Some additional ligatures were also introduced...
based on the Latin alphabet
Latin alphabet
The Latin alphabet, also called the Roman alphabet, is the most recognized alphabet used in the world today. It evolved from a western variety of the Greek alphabet called the Cumaean alphabet, which was adopted and modified by the Etruscans who ruled early Rome...
. The Uniform Turkic Alphabet was itself replaced in 1938 by a Cyrillic alphabet. Since the 1990s, the script is in the process of being replaced with a Latin version again, but the Cyrillic is still widely used (mainly in published literature and newspapers). The current Latin-based Crimean Tatar alphabet is the same as the Turkish alphabet
Turkish alphabet
The Turkish alphabet is a Latin alphabet used for writing the Turkish language, consisting of 29 letters, seven of which have been modified from their Latin originals for the phonetic requirements of the language. This alphabet represents modern Turkish pronunciation with a high degree of accuracy...
with two additional characters: Ñ
Ñ
Ñ is a letter of the modern Latin alphabet, formed by an N with a diacritical tilde. It is used in the Spanish alphabet, Galician alphabet, Asturian alphabet, Basque alphabet, Aragonese old alphabet , Filipino alphabet, Chamorro alphabet and the Guarani alphabet, where it represents...
ñ and Q
Q
Q is the seventeenth letter of the basic modern Latin alphabet.- History :The Semitic sound value of Qôp was , a sound common to Semitic languages, but not found in English or most Indo-European ones...
q.
Crimean Tatar was the native language of the poet Bekir Çoban-zade.
Vowels
| Front Front vowel A front vowel is a type of vowel sound used in some spoken languages. The defining characteristic of a front vowel is that the tongue is positioned as far in front as possible in the mouth without creating a constriction that would be classified as a consonant. Front vowels are sometimes also... |
Back Back vowel A back vowel is a type of vowel sound used in spoken languages. The defining characteristic of a back vowel is that the tongue is positioned as far back as possible in the mouth without creating a constriction that would be classified as a consonant. Back vowels are sometimes also called dark... |
|||
| UR Roundedness In phonetics, vowel roundedness refers to the amount of rounding in the lips during the articulation of a vowel. That is, it is vocalic labialization. When pronouncing a rounded vowel, the lips form a circular opening, while unrounded vowels are pronounced with the lips relaxed... |
R | UR | R | |
| +high Close vowel A close vowel is a type of vowel sound used in many spoken languages. The defining characteristic of a close vowel is that the tongue is positioned as close as possible to the roof of the mouth without creating a constriction that would be classified as a consonant.This term is prescribed by the... |
i | y | ɯ | u |
| -high | e | ø | ɑ | o |
The vowel system of Crimean Tatar is similar to those of other Turkic languages, such as Turkish
Turkish language
Turkish is a language spoken as a native language by over 83 million people worldwide, making it the most commonly spoken of the Turkic languages. Its speakers are located predominantly in Turkey and Northern Cyprus with smaller groups in Iraq, Greece, Bulgaria, the Republic of Macedonia, Kosovo,...
. While /i/ and /ɯ/ are phonologically distinct, since high vowels in Crimean are short and reduced, they are realized close to [ɪ].
Consonants
| Labial Labial consonant Labial consonants are consonants in which one or both lips are the active articulator. This precludes linguolabials, in which the tip of the tongue reaches for the posterior side of the upper lip and which are considered coronals... |
Dental-alveolar Alveolar consonant Alveolar consonants are articulated with the tongue against or close to the superior alveolar ridge, which is called that because it contains the alveoli of the superior teeth... |
Post- alveolar Postalveolar consonant Postalveolar consonants are consonants articulated with the tongue near or touching the back of the alveolar ridge, further back in the mouth than the alveolar consonants, which are at the ridge itself, but not as far back as the hard palate... |
Velar Velar consonant Velars are consonants articulated with the back part of the tongue against the soft palate, the back part of the roof of the mouth, known also as the velum).... |
Uvular Uvular consonant Uvulars are consonants articulated with the back of the tongue against or near the uvula, that is, further back in the mouth than velar consonants. Uvulars may be plosives, fricatives, nasal stops, trills, or approximants, though the IPA does not provide a separate symbol for the approximant, and... |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal Nasal consonant A nasal consonant is a type of consonant produced with a lowered velum in the mouth, allowing air to escape freely through the nose. Examples of nasal consonants in English are and , in words such as nose and mouth.- Definition :... |
m | n | ŋ | |||||||
| Stop Stop consonant In phonetics, a plosive, also known as an occlusive or an oral stop, is a stop consonant in which the vocal tract is blocked so that all airflow ceases. The occlusion may be done with the tongue , lips , and &... |
p | b | t | d | t͡ʃ | d͡ʒ | k | ɡ | q | |
| Fricative Fricative consonant Fricatives are consonants produced by forcing air through a narrow channel made by placing two articulators close together. These may be the lower lip against the upper teeth, in the case of ; the back of the tongue against the soft palate, in the case of German , the final consonant of Bach; or... |
f | v | s | z | ʃ | x | ɣ | |||
| Trill Trill consonant In phonetics, a trill is a consonantal sound produced by vibrations between the articulator and the place of articulation. Standard Spanish <rr> as in perro is an alveolar trill, while in Parisian French it is almost always uvular.... |
r | |||||||||
| Approximants Approximant consonant Approximants are speech sounds that involve the articulators approaching each other but not narrowly enough or with enough articulatory precision to create turbulent airflow. Therefore, approximants fall between fricatives, which do produce a turbulent airstream, and vowels, which produce no... |
l | j | ||||||||
In additional to these phonemes, Crimean also displays marginal phonemes that occur in borrowed words, especially palatalized consonants.
Current situation
According to the constitution of the Autonomous Republic of Crimea, as published in Russian by its Verkhovna RadaVerkhovna Rada of Crimea
The Supreme Council of the Autonomous Republic of Crimea is the 100-member unicameral parliament of the Ukrainian territory the Autonomous Republic of Crimea...
(see Конституция Автономной Республики Крым), Russian and Crimean Tatar languages enjoy a "protected" (Russian – обеспечивается ... защита) status; every citizen is entitled, at his request (Russian ходатайство), to receive government documents, such as "Passport, Birth certificate and others" in Crimean Tatar. According to the constitution of Ukraine, however, Ukrainian is the only official language in all of Ukraine, so the recognition of those languages is a matter of political and legal debate.
Before the Sürgün, the deportation of Crimean Tatars to the Uzbek SSR
Uzbek SSR
The Uzbek Soviet Socialist Republic , also known as the Uzbek SSR for short, was one of the republics of the Soviet Union since its creation in 1924...
(18 May 1944), it had an official language status in the Crimean Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic
Crimean Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic
Crimean Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic was created on October 18, 1921 as Crimean Autonomous Socialist Soviet Republic of RSFSR in place of Taurida Governorate and within the Crimean Peninsula,...
.
Crimean Tatar Latin alphabet
 â symbol is not considered to be a separate letter.| IPA | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| а | b | c | ç | d | e | f | g | ğ | h | ı | i | j | k | l | m | n | ñ | o | ö | p | q | r | s | ş | t | u | ü | v | y | z |
| [a] | [b] | [dʒ] | [tʃ] | [d] | [e] | [f] | [ɡ] | [ɣ] | [x] | [ɯ] | [i], [ɪ] | [ʒ] | [k] | [l] | [m] | [n] | [ŋ] | [o] | [ø] | [p] | [q] | [r] | [s] | [ʃ] | [t] | [u] | [y] | [v], [w] | [j] | [z] |
Crimean Tatar Cyrillic alphabet
| IPA | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| а | б | в | г | гъ | д | е | ё | ж | з | и | й | к | къ | л | м | н | нъ | o | п | p | c | т | у | ф | x | ц | ч | дж | ш | щ | ъ | ы | ь | э | ю | я |
| [a] | [b] | [v],[w] | [ɡ] | [ɣ] | [d] | [ɛ],[jɛ] | [ø],[jø],[jo],[ʲo] | [ʒ] | [z] | [i],[ɪ] | [j] | [k] | [q] | [l],[ɫ] | [m] | [n] | [ŋ] | [o],[ø] | [p] | [r] | [s] | [t] | [u],[y] | [f] | [x] | [ts] | [tʃ] | [dʒ | [ʃ] | [ʃtʃ] | [(.j)] | [ɨ] | [ʲ] | [ɛ] | [y],[jy],[ju],[ʲu] | [ʲa], [ja] |
гъ, къ, нъ and дж are separate letters.
Crimean Tatar, Turkish and Azerbaijani
The following newspaper report compares the Crimean Tatar, Turkish and Azerbaijani languages:| Crimean Tatar | Turkish | Azerbaijani | English |
|---|---|---|---|
| Meclis Haberleri 10.09.2003// Qırımtatar Milliy Meclisiniñ 120-cı toplaşuvı olıp keçti 2003 senesi sentâbr 7 künü Aqmescitteki İslâm Merkeziniñ binasında Qırımtatar Milliy Meclisiniñ 120-cı toplaşuvı olıp keçti. Toplaşuvda... |
Meclis Haberleri 10.09.2003// Kırım Tatar Millî Meclisi'nin 120. toplantısı gerçekleşti 7 Eylül 2003 günü Akmescit'teki İslam Merkezi'nin binasında Kırım Tatar Millî Meclisi'nin 120. toplantısı gerçekleşti. Toplantıda... |
Məclis Xəbərləri 10.09.2003// Qırım Tatar Milli Məclisinin 120-ci toplantısı keçirildi 2003-cü il sentyabrın 7-si günü Ağməsciddəki İslam Mərkəzinin binasına Qırım Tatar Milli Məclisinin 120-ci toplantısı keçirildi. Toplantıda... |
Assembly News 10.09.2003// 120th meeting of Crimean Tatar National Assembly was held On 7 September 2003, 120th meeting of Crimean Tatar National Assembly was held at the Islamic Centre building in Simferopol. At the meeting... |
Crimean Tatar and Tatar
Because of its common name, Crimean Tatar is sometimes mistaken to be a dialect of the Tatar languageTatar language
The Tatar language , or more specifically Kazan Tatar, is a Turkic language spoken by the Tatars of historical Kazan Khanate, including modern Tatarstan and Bashkiria...
. Although these languages are related (as both are Turkic), the Kypchak languages closest to Crimean Tatar are (as was mentioned above) Kumyk
Kumyk language
Kumyk is a Turkic language, spoken by about 365,000 speakers in the Dagestan republic of Russian Federation....
and Karachay-Balkar
Karachay-Balkar language
The Karachay-Balkar language is a Turkic language spoken by the Karachays and Balkars. It is divided into two dialects: Karachay-Baksan-Chegem which pronounces two phonemes as and , and Balkar, which pronounces the corresponding phonemes as and .- Alphabet :Modern Karachay-Balkar Cyrillic...
, not the Tatar language.
External links
- Wiktionary's category of Crimean Tatar words
- Linguistic corpus of Crimean Tatar language
- Mejlis of the Crimean Tatar People
- Kırımtatar Dili
- Wiktionary's category of Crimean Tatar words
- Crimean Tatar internet library
- Automatic Latin<>Cyrillic transliterator for Crimean Tatar texts

