
Heat capacity rate
Encyclopedia
The heat capacity rate is heat
transfer terminology
used in thermodynamics
and different forms of engineering denoting the quantity of heat a flowing fluid
of a certain mass flow rate is able to absorb or release per unit temperature
change per unit time. It is typically denoted as C, listed from empirical data experimentally determined in various reference works, and is typically stated as a comparison between a hot and a cold fluid, Ch and Cc either graphically, or as a linearized equation
. It is an important quantity in heat exchanger
technology
common to either heating or cooling systems and needs, and the solution of many real world problems such as the design of disparate items as different as a microprocessor
and an internal combustion
engine
.
from a water source—a case of dissimilar fluids, or for specifying the minimal cooling needs of heat transfer across boundaries, such as in air cooling.
As the ability of a fluid to resist change in temperature itself changes as heat transfer occurs changing its net average instantaneous temperature, it is a quantity of interest in designs which have to compensate for the fact that it varies continuously in a dynamic system. While itself varying, such change must be taken into account when designing a system for overall behavior to stimuli or likely environmental conditions
, and in particular the worst case conditions encountered under the high stressess imposed near the limits of operability— for example, an air cooled engine in a desert clime on a very hot day.
If the hot fluid had a much larger heat capacity rate
, then when hot and cold fluids went through a heat exchanger, the hot fluid would have a very small change in temperature while the cold fluid would heat up a significant amount. If the cool fluid has a much lower heat capacity rate, that is desirable. If they were equal, they would both change more or less temperature equally, assuming equal mass-flow per unit time through a heat exchanger. In practice, a cooling fluid which has both a higher specific heat capacity and a lower heat capacity rate is desirable, accounting for the pervasiveness of water cooling solutions in technology—the polar nature of the water molecule creates some distinct sub-atomic behaviors favorable in practice.
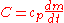
where C = heat capacity rate of the fluid of interest,
dm/dt = mass flow rate of the fluid of interest and
cp = specific heat of the fluid of interest.
Heat
In physics and thermodynamics, heat is energy transferred from one body, region, or thermodynamic system to another due to thermal contact or thermal radiation when the systems are at different temperatures. It is often described as one of the fundamental processes of energy transfer between...
transfer terminology
Terminology
Terminology is the study of terms and their use. Terms are words and compound words that in specific contexts are given specific meanings, meanings that may deviate from the meaning the same words have in other contexts and in everyday language. The discipline Terminology studies among other...
used in thermodynamics
Thermodynamics
Thermodynamics is a physical science that studies the effects on material bodies, and on radiation in regions of space, of transfer of heat and of work done on or by the bodies or radiation...
and different forms of engineering denoting the quantity of heat a flowing fluid
Fluid
In physics, a fluid is a substance that continually deforms under an applied shear stress. Fluids are a subset of the phases of matter and include liquids, gases, plasmas and, to some extent, plastic solids....
of a certain mass flow rate is able to absorb or release per unit temperature
Temperature
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
change per unit time. It is typically denoted as C, listed from empirical data experimentally determined in various reference works, and is typically stated as a comparison between a hot and a cold fluid, Ch and Cc either graphically, or as a linearized equation
Linear equation
A linear equation is an algebraic equation in which each term is either a constant or the product of a constant and a single variable....
. It is an important quantity in heat exchanger
Heat exchanger
A heat exchanger is a piece of equipment built for efficient heat transfer from one medium to another. The media may be separated by a solid wall, so that they never mix, or they may be in direct contact...
technology
Technology
Technology is the making, usage, and knowledge of tools, machines, techniques, crafts, systems or methods of organization in order to solve a problem or perform a specific function. It can also refer to the collection of such tools, machinery, and procedures. The word technology comes ;...
common to either heating or cooling systems and needs, and the solution of many real world problems such as the design of disparate items as different as a microprocessor
Microprocessor
A microprocessor incorporates the functions of a computer's central processing unit on a single integrated circuit, or at most a few integrated circuits. It is a multipurpose, programmable device that accepts digital data as input, processes it according to instructions stored in its memory, and...
and an internal combustion
Combustion
Combustion or burning is the sequence of exothermic chemical reactions between a fuel and an oxidant accompanied by the production of heat and conversion of chemical species. The release of heat can result in the production of light in the form of either glowing or a flame...
engine
Heat engine
In thermodynamics, a heat engine is a system that performs the conversion of heat or thermal energy to mechanical work. It does this by bringing a working substance from a high temperature state to a lower temperature state. A heat "source" generates thermal energy that brings the working substance...
.
Basis
A hot fluid's heat capacity rate can be much greater than, equal to, or much less than the heat capacity rate of the same fluid when cold. In practice, it is most important in specifying heat-exchanger systems, wherein one fluid usually of dissimilar nature is used to cool another fluid such as the hot gases or steam cooled in a power plant by a heat sinkHeat sink
A heat sink is a term for a component or assembly that transfers heat generated within a solid material to a fluid medium, such as air or a liquid. Examples of heat sinks are the heat exchangers used in refrigeration and air conditioning systems and the radiator in a car...
from a water source—a case of dissimilar fluids, or for specifying the minimal cooling needs of heat transfer across boundaries, such as in air cooling.
As the ability of a fluid to resist change in temperature itself changes as heat transfer occurs changing its net average instantaneous temperature, it is a quantity of interest in designs which have to compensate for the fact that it varies continuously in a dynamic system. While itself varying, such change must be taken into account when designing a system for overall behavior to stimuli or likely environmental conditions
Natural environment
The natural environment encompasses all living and non-living things occurring naturally on Earth or some region thereof. It is an environment that encompasses the interaction of all living species....
, and in particular the worst case conditions encountered under the high stressess imposed near the limits of operability— for example, an air cooled engine in a desert clime on a very hot day.
If the hot fluid had a much larger heat capacity rate
Heat capacity rate
The heat capacity rate is heat transfer terminology used in thermodynamics and different forms of engineering denoting the quantity of heat a flowing fluid of a certain mass flow rate is able to absorb or release per unit temperature change per unit time...
, then when hot and cold fluids went through a heat exchanger, the hot fluid would have a very small change in temperature while the cold fluid would heat up a significant amount. If the cool fluid has a much lower heat capacity rate, that is desirable. If they were equal, they would both change more or less temperature equally, assuming equal mass-flow per unit time through a heat exchanger. In practice, a cooling fluid which has both a higher specific heat capacity and a lower heat capacity rate is desirable, accounting for the pervasiveness of water cooling solutions in technology—the polar nature of the water molecule creates some distinct sub-atomic behaviors favorable in practice.
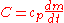
where C = heat capacity rate of the fluid of interest,
dm/dt = mass flow rate of the fluid of interest and
cp = specific heat of the fluid of interest.
See also
- HeatHeatIn physics and thermodynamics, heat is energy transferred from one body, region, or thermodynamic system to another due to thermal contact or thermal radiation when the systems are at different temperatures. It is often described as one of the fundamental processes of energy transfer between...
- specific heat
- Heat capacityHeat capacityHeat capacity , or thermal capacity, is the measurable physical quantity that characterizes the amount of heat required to change a substance's temperature by a given amount...
- Heat capacity ratioHeat capacity ratioThe heat capacity ratio or adiabatic index or ratio of specific heats, is the ratio of the heat capacity at constant pressure to heat capacity at constant volume . It is sometimes also known as the isentropic expansion factor and is denoted by \gamma or \kappa . The latter symbol kappa is...
- Heat equationHeat equationThe heat equation is an important partial differential equation which describes the distribution of heat in a given region over time...
- Heat transfer coefficient
- Latent heatLatent heatLatent heat is the heat released or absorbed by a chemical substance or a thermodynamic system during a process that occurs without a change in temperature. A typical example is a change of state of matter, meaning a phase transition such as the melting of ice or the boiling of water. The term was...
- Specific heat capacity
- Specific melting heat
- Specific latent heat of vaporization
- TemperatureTemperatureTemperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
- ThermodynamicsThermodynamicsThermodynamics is a physical science that studies the effects on material bodies, and on radiation in regions of space, of transfer of heat and of work done on or by the bodies or radiation...
- Thermodynamic (absolute) temperatureThermodynamic temperatureThermodynamic temperature is the absolute measure of temperature and is one of the principal parameters of thermodynamics. Thermodynamic temperature is an "absolute" scale because it is the measure of the fundamental property underlying temperature: its null or zero point, absolute zero, is the...
- Thermodynamic equationsThermodynamic equationsThermodynamics is expressed by a mathematical framework of thermodynamic equations which relate various thermodynamic quantities and physical properties measured in a laboratory or production process...
- Volumetric heat capacityVolumetric heat capacityVolumetric heat capacity , also termed volume-specific heat capacity, describes the ability of a given volume of a substance to store internal energy while undergoing a given temperature change, but without undergoing a phase change...

