History of Romania
Encyclopedia
This article provides only a brief outline of each period of the history of Romania
; details are presented in separate articles (see the links in the box and below).
Prehistory=
{Main|Prehistoric Romania}
The oldest modern human remains in Europe were discovered in the "Cave With Bones
" in present day Romania. The remains are approximately 42,000 years old and as Europe’s oldest remains of Homo sapiens, they may represent the first such people to have entered the continent. The remains are especially interesting because they present a mixture of archaic, early modern human and Neanderthal morphological features.
One of the fossil
s found—a male, adult jawbone—has been dated to be between 34,000 and 36,000 years old, which would make it one of the oldest fossils found to date of modern humans in Europe. A skull found in Peștera cu Oase
(The Cave with Bones) in 2004-5 bears features of both modern humans and Neanderthal
s. According to a paper by Erik Trinkaus
and others, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
in January 2007, this finding suggests that the two groups interbred thousands of years ago. Radiocarbon dating
indicates that the skull is between 35,000 and 40,000 years old, making it the oldest modern human fossil ever found in Europe
.
in book IV of his Histories
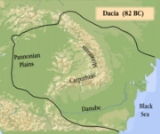
written 440 BCE. Herein he writes that the tribal confederation of the Getae
were defeated by the Persian Emperor Darius the Great during his campaign against the Scythians. The Dacians
, widely accepted as part of the Getae
described earlier by the Greeks, were a branch of Thracians
that inhabited Dacia
(corresponding to modern Romania, Moldova
and northern Bulgaria
). The Dacian kingdom reached its maximum expansion during King Burebista
, between 82 BCE - 44 BCE. Under his leadership Dacia became a powerful state which threatened the regional interests of the Romans. Julius Caesar
intended to start a campaign against the Dacians, due to the support that Burebista gave to Pompey
, but was assassinated in 44 BC
. A few months later, Burebista shared the same fate, assassinated by his own noblemen. Another theory suggests that he was killed by Caesar's friends. His powerful state was divided in four and did not become unified again until 95 AD, under the reign of the Dacian king Decebalus
.
The Roman Empire
conquered Moesia
by 29 BC, reaching the Danube. In 87 AD Emperor Domitian
sent six legions into Dacia, which were defeated at Tapae
. The Dacians were eventually defeated by Emperor Trajan
in two campaigns stretching from 101 AD to 106 AD, and the core of their kingdom was turned into the province of Roman Dacia
.
 The Romans exploited the rich ore deposits of Dacia. Gold and silver were especially plentiful, and were found in great quantities in the Western Carpathians. After Trajan's conquest, he brought back to Rome over 165 tons of gold and 330 tons of silver. The Romans heavily colonized the province, and thus started a period of intense romanization
The Romans exploited the rich ore deposits of Dacia. Gold and silver were especially plentiful, and were found in great quantities in the Western Carpathians. After Trajan's conquest, he brought back to Rome over 165 tons of gold and 330 tons of silver. The Romans heavily colonized the province, and thus started a period of intense romanization
, the Vulgar Latin
giving birth to proto-Romanian language
.
The geographical position of Dacia Felix made it difficult to defend against the barbarians, and during 240 AD - 256 AD, under the attacks of the Carpi and the Goths
, Dacia was lost. The Roman Empire
withdrew from Dacia Romana around 271 AD, thus making it the first province to be abandoned.
Roman conquest of Dacia stands at the base of the origin of Romanians
. Several competing theories have been introduced to explain the origin of modern Romanians. Linguistic and geo-historical analyses tend to indicate that Romanians
have coalesced as a major ethnic group both South and North of the Danube
. For further discussion, see Origin of Romanians
.
. The Goths lived with the local people until the 4th century, when a nomadic people, the Huns
, arrived. The Gepids and the Avars
and their Slavic subjects ruled Transylvania
until the 8th century. The Pechenegs, the Cumans
and Uzes
were also mentioned by historic chronicles on the territory of Romania, until the founding of the Romanian principalities of Wallachia
by Basarab I around 1310 in the High Middle Ages
, and Moldavia
by Dragoş
around 1352.
Different migrating peoples lived along the local populations, such as the Gothic
Empire (Oium
) from 271 until 378, the Hunnish Empire
until 435, the Avar Empire
and Slavs during the 6th century. Subsequently Magyars, Pechenegs, Cumans
and Tatars
also raided and settled in the lands to various extents.

, Romanians lived in three distinct principalities: Wallachia
(—"Romanian Land"), Moldavia
and Transylvania
.
The Pechenegs (a semi-nomadic Turkic people of the Central Asian steppes) occupied the steppes north of the Black Sea
(8th–12th century) and by the 10th century were in control of the lands between the Don
and lower Danube
rivers.
By the 11th and 12th century, the nomadic confederacy of the Cumans
and (Eastern) Kipchaks (who are considered to be either the eastern branch of the Cumans or a distinct but related tribe with whom the Cumans created a confederacy) were the dominant force over the vast territories stretching from the present-day Kazakhstan, southern Russia, Ukraine, to southern Moldavia and western Wallachia.
By the 11th century, the area of today's Transylvania became a largely autonomous part of the Kingdom of Hungary
. Kings of Hungary invited the Saxons
to settle in Transylvania. Also living in Transylvania were the Székely
. After the Magyar conquest (10-11th century), Transylvania became part of the Kingdom of Hungary
until the 16th century, when it became the independent Principality of Transylvania until 1711. Many small local states with varying degrees of independence developed, but only in the 14th century the larger principalities of Moldavia
and Wallachia
emerged to fight a threat in the form of the Ottoman Turks
, who conquered Constantinople
in 1453.
Independent Wallachia
has been on the border of the Ottoman Empire
since the 14th century and slowly fell under the suzerainty
of the Ottoman Empire
during the 15th century. One famous ruler in this period was Vlad III the Impaler
(also known as Vlad Dracula or ), Prince of Wallachia
in 1448, 1456–62, and 1476. In the English
-speaking world, Vlad is best known for the exceedingly cruel punishments he imposed during his reign and for serving as the primary inspiration for the vampire
main character
in Bram Stoker
's 1897 novel Dracula
. As king, he maintained an independent policy in relation to the Ottoman Empire
, and in Romania he is viewed by many as a prince with a deep sense of justice, and a defender of both Wallachia and European Christianity
against Ottoman
expansionism
.
The principality of Moldavia
reached its most glorious period under the rule of Stephen the Great
between 1457 and 1504. His rule of 47 years was unusually long, especially at that time - only 13 rulers worldwide were recorded to have ruled for at least 50 years until the end of 15th century. He was a very successful military leader (winning 47 battles and losing only 2),) and after each victory, he raised a church, managing to build 48 churches or monasteries, some of them with unique and very interesting painting styles. For more information see Painted churches of northern Moldavia
listed in UNESCO
's list of World Heritage Sites. Stephen's most prestigious victory was over the Ottoman Empire
in 1475 at the Battle of Vaslui
for which he raised the Voroneţ Monastery
. For this victory, Pope
Sixtus IV deemed him verus christianae fidei athleta (true Champion of Christian Faith). However, after his death, Moldavia
would also come under the suzerainty
of the Ottoman Empire
in the 16th century.

 By 1541, the entire Balkan peninsula and most of Hungary
By 1541, the entire Balkan peninsula and most of Hungary
became Ottoman provinces. In contrast, Moldavia, Wallachia, and Transylvania
, came under Ottoman suzerainty
, but conserved fully internal autonomy and, until the 18th century, some external independence. During this period the Romanian lands were characterised by the slow disappearance of the feudal
system, the distinguishment of some rulers like Vasile Lupu
and Dimitrie Cantemir
in Moldavia, Matei Basarab
and Constantin Brâncoveanu
in Wallachia, Gabriel Bethlen
in Transylvania, the Phanariot Epoch, and the appearance of the Russian Empire
as a political and military influence.
John II
, the last non-Habsburg king of Hungary
, moved his royal court to Alba Iulia
in Transylvania, and after his abdication as king of Hungary, became the first Prince of Transylvania. His Edict of Turda
was the first decree of religious freedom
in the modern history of Europe (1568). In the subsequent period, Transylvania was ruled by mostly Calvinist
Hungarian princes (until the end of the 17th century), and Protestantism
flourished in the region.
 Michael the Brave (Romanian: Mihai Viteazul) was the Prince of Wallachia (1593–1601), of Transylvania (1599–1600), and of Moldavia (1600). Briefly, during his reign the three principalities largely inhabited by Romanians were for the first time united under a single rule. After his death, as vassal tributary states, Moldova
Michael the Brave (Romanian: Mihai Viteazul) was the Prince of Wallachia (1593–1601), of Transylvania (1599–1600), and of Moldavia (1600). Briefly, during his reign the three principalities largely inhabited by Romanians were for the first time united under a single rule. After his death, as vassal tributary states, Moldova
and Wallachia
had complete internal autonomy and an external independence, which was finally lost in the 18th century. In 1600, the principalities of Wallachia, Moldova and Transylvania were simultaneously headed by the Wallachian prince Michael the Brave (Mihai Viteazul), Ban
of Oltenia
, but the chance for a unity dissolved after Mihai was killed, only one year later, by the soldiers of an Austrian
army general Giorgio Basta
. Mihai Viteazul, who was prince of Transylvania for less than one year, intended for the first time to unite the three principalities and to lay down foundations of a single state in a territory comparable to today's Romania.
The Principality of Transylvania experienced a golden age under the absolutist
rule of Gabor Bethlen (1613–1629). In 1699, Transylvania became a territory of the Habsburgs'
Austrian empire, following the Austrian victory over the Turks. The Austrians, in their turn, rapidly expanded their empire: in 1718 an important part of Wallachia, called Oltenia
, was incorporated to the Austrian monarchy and was only returned in 1739. In 1775, the Austrian empire occupied the north-western part of Moldavia, later called Bukovina
, while the eastern half of the principality (called Bessarabia
) was occupied in 1812 by Russia
.
During the period of Austro-Hungarian rule in Transylvania
, and Ottoman
suzerainty over Wallachia
and Moldavia
, most Romanians
were in the situation of being second-class citizens
(or even non-citizens) in a territory where they formed the majority of the population. In some Transylvanian cities, such as Brașov
(at that time the Transylvanian Saxon
citadel of Kronstadt), Romanians were not even allowed
to reside within the city walls.
As in most European countries, 1848 brought revolution
to Moldavia, Wallachia, and Transylvania, announced by Tudor Vladimirescu
and his Pandurs
in the Wallachian uprising of 1821
. The goals of the revolutionaries - complete independence for Moldavia and Wallachia, and national emancipation in Transylvania - remained unfulfilled, but were the basis of the subsequent evolutions. Also, the uprising helped the population of the three principalities recognise their unity of language and interests. Moldavia and Romanian countries were very close, not just in language, but in geography also.
After the failed 1848 Revolution
, the Great Powers did not support the Romanians' expressed desire to officially unite in a single state, forcing Romania to proceed alone against the Turks. Heavily taxed and badly administered under the Ottoman Empire, in 1859, people in both Moldavia and Wallachia elected the same "Domnitor
" (ruler) - Alexandru Ioan Cuza
- as prince. (Domnitor
in Romanian
). Thus, Romania was created as a personal union, albeit a Romania that did not include Transylvania, where the upper class and the aristocracy remained mainly Hungarian, although Romanian nationalism inevitably ran up against Hungarian nationalism at the end of the 19th century. As in the previous 900 years, Austria-Hungary, especially under the Dual Monarchy
of 1867, kept the Hungarians firmly in control, even in parts of Transylvania where Romanians constituted a local majority.

, who became known as Prince Carol of Romania. During the Russo-Turkish War, Romania fought on the Russian side; in the 1878 Treaty of Berlin
, Romania was recognized as an independent
state by the Great Powers. In return, Romania ceded three southern districts of Bessarabia
to Russia
and acquired Dobruja
. In 1881, the principality
was raised to a kingdom
and Prince Carol became King
Carol I.
In 1866, the German prince Carol I
(Charles or Karl) of Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen
was appointed as Domnitor
—Prince—of the Principality of Romania. In 1877, Romania declared independence from the Ottoman Empire and, following a Russian-Romanian-Turkish war, its independence was recognized by the Treaty of Berlin, 1878
, making it the first independent national state in the eastern half of Europe. Following the war Romania acquired Dobruja
in its southeast, but it was forced by Russia to cede the Southern Bessarabian territory to Russia "in exchange" for the access to the ports at the Black Sea. Prince Carol I was proclaimed the first King of Romania
on March 26, 1881.
The 1878–1914 period was one of stability and progress
for Romania. During the Second Balkan War
, Romania joined Greece
, Serbia
, Montenegro
and Turkey
against Bulgaria
. In the peace Treaty of Bucharest (1913) Romania gained Southern Dobrudja - the Quadrilateral (the Durostor and Caliacra counties).
 The new state, squeezed between the great powers of the Ottoman, Austro-Hungarian, and Russian
The new state, squeezed between the great powers of the Ottoman, Austro-Hungarian, and Russian
empires, looked to the West, particularly France
, for its cultural, educational, military and administrative models. In 1916 Romania entered World War I
on the Entente
side, after the Entente agreed to recognize Romanian rights over Transylvania, which was part of Austria-Hungary until that time.
In August 1914, when World War I
broke out, Romania declared neutrality
. Two years later, under the pressure of Allies (especially France
desperate to open a new front), on August 14/27 1916 it joined the Allies, for which they were promised support for the accomplishment of national unity, Romania declared war on Austria-Hungary
.
The Romanian military campaign
ended in disaster for Romania as the Central Powers
conquered two-thirds of the country and captured or killed the majority of its army within four months. Nevertheless, Moldova
remained in Romanian hands after the invading forces were stopped in 1917. In May 1918, Romania was in no position to continue the war, and negotiated a peace treaty with Germany
(see Treaty of Bucharest, 1918
). In October 1918, Romania joined the war again and by the end of the war, the Austro-Hungarian and Russian empires had disintegrated; governing bodies created by the Romanians of Transylvania, Bessarabia and Bukovina chose union with the Kingdom of Romania
, resulting in Greater Romania
.
and since by the war's end, Austria-Hungary and the Russian Empire had collapsed, Bessarabia
, Bukovina
and Transylvania
were allowed to unite with the Kingdom of Romania
in 1918. By the 1920 Treaty of Trianon
, Hungary
renounced in favour of Romania all the claims of the Austro-Hungarian Monarchy over Transylvania
. The union of Romania with Bukovina
was ratified in 1919 in the Treaty of Saint Germain, and with Bessarabia
in 1920 by the Treaty of Paris
.
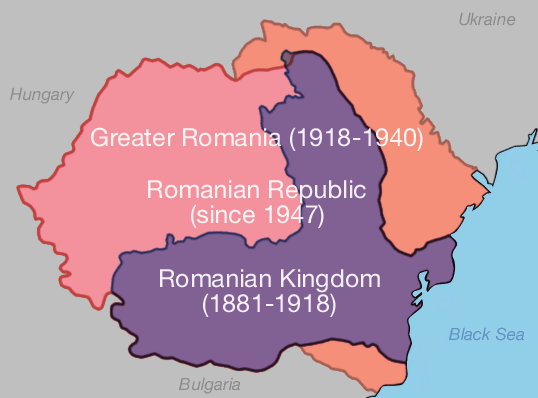
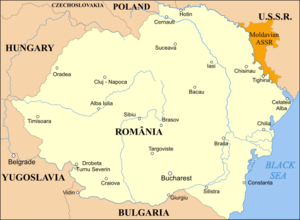 The Romanian expression România Mare
The Romanian expression România Mare
(literal translation "Great Romania", but more commonly rendered "Greater Romania") generally refers to the Romanian state in the interwar period
, and by extension, to the territory Romania covered at the time (see map). Romania achieved at that time its greatest territorial extent (almost 300000 km² (115,830.6 sq mi)), managing to unite all the historic Romanian lands. Historically, Greater Romania—România Mare—represented one of the ideals of Romanian nationalism
. Greater Romania is still seen by many as a "paradise lost", often by comparison with the "stunted" Communist Romania
. To exploit the nationalistic connotation of the term, a nationalist political party
uses it as its name.
In 1918, at the end of World War I
, Transylvania and Bessarabia united with the Romanian Old Kingdom
. The Deputies of the Romanians from Transylvania voted to unite their region by the Proclamation of Union of Alba Iulia
. Bessarabia, having declared its independence from Russia in 1917 by the Conference of the Country (Sfatul Țării
), called in Romanian troops to protect the province from the Bolshevik
s who were spreading the Russian Revolution
. The union of the regions of Transylvania, Maramureș
, Crișana
and Banat
with the Old Kingdom of Romania was ratified in 1920 by the Treaty of Trianon
, which recognised the sovereignty of Romania over these regions and settled the border between the independent Republic of Hungary and the Kingdom of Romania. The union of Bucovina and Bessarabia with Romania was ratified in 1920 by the Treaty of Versailles
. Romania had also recently acquired the Southern Dobruja
territory called "The Quadrilateral" from Bulgaria
as a result of its participation in the Second Balkan War
in 1913.

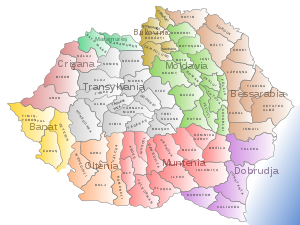 The Union of 1918 united most regions with clear Romanian majorities into the boundaries of a single state. However, it also led to the inclusion of various sizable minorities, including Magyars (ethnic Hungarians), Germans, Jews, Ukrainians, Bulgarians
The Union of 1918 united most regions with clear Romanian majorities into the boundaries of a single state. However, it also led to the inclusion of various sizable minorities, including Magyars (ethnic Hungarians), Germans, Jews, Ukrainians, Bulgarians
, etc., for a total of about 28% of the population (Magyars mostly in Transylvania; Germans in Transylvania, Bukovina, and Banat; Ukrainians in part of Bessarabia and Bukovina, Bulgarians in Dobrudja). Recognized by the Romanian Constitution of 1923
and supported by various laws (education, electoral, etc.), national minorities were represented in Parliament, and several of them created national parties (the Magyars in 1922, the Germans in 1929, the Jews in 1931), although a unique standing of minorities with autonomy on a wide basis, provided for at the assembly of Transylvanian Romanians on 1 December 1918 were not fulfilled.
Two periods can be identified in Romania between the two World Wars. From 1918 to 1938, Romania was a liberal
constitutional monarchy
, but one facing the rise of the nationalist, anti-semitic
parties, particularly Iron Guard
, which won about 15% of the votes in the general elections of 1937. From 1938 to 1944, Romania was a dictatorship. The first dictator was King Carol II
, who abolished the parliamentary regime and ruled with his camarilla.
 In 1939, Germany and the Soviet Union
In 1939, Germany and the Soviet Union
signed the Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact
, which stipulated, amongst other things, the Soviet "interest" in Bessarabia. Following the severe territorial losses of 1940 (see next section), Carol was forced to abdicate, replaced as king by his son Mihai, but the power was taken by the military dictator Ion Antonescu
(initially in conjunction with the Iron Guard). In August 1944, Antonescu was arrested by Mihai.
During the Second World War, Romania tried again to remain neutral, but on June 28, 1940, it received a Soviet ultimatum with an implied threat of invasion
in the event of non-compliance. Under pressure from Moscow
and Berlin
, the Romanian administration and the army were forced to retreat from Bessarabia
as well from Northern Bukovina to avoid war. This, in combination with other factors, prompted the government to join the Axis. Thereafter, southern Dobruja
was awarded to Bulgaria, while Hungary received Northern Transylvania
as result of an Axis arbitration.
In 1940, Romania lost territory in both east and west: In June 1940, after receiving an ultimatum from the Soviet Union
, Romania ceded Bessarabia
and northern Bukovina
(see Soviet occupation of Bessarabia). Two thirds of Bessarabia were combined with a small part of the USSR to form the Moldavian SSR
. Northern Bukovina and Budjak
were apportioned to the Ukrainian SSR
. In August 1940, Northern Transylvania
was awarded to Hungary by Germany
and Italy
through the Second Vienna Award
. Southern Dobruja
was also lost to Bulgaria shortly after Carol's abdication.
Because Carol II lost so much territory through failed diplomacy, the army supported seizure of power by General Ion Antonescu
. For four months (the period of the National Legionary State
), he had to share power with the Iron Guard, but the latter overplayed their hand in January 1941
and were suppressed. Romania entered World War II
under the command of the German Wehrmacht
in June 1941, declaring war to the Soviet Union in order to recover Bessarabia and northern Bukovina. Romania was awarded the territory between Dniester
and the Southern Bug
by Germany to administer it under the name of Transnistria
.
 The authoritarian King Carol II
The authoritarian King Carol II
abdicated in 1940, succeeded by the National Legionary State
, in which power was shared by Ion Antonescu
and the Iron Guard
. Within months, Antonescu had crushed the Iron Guard
, and the subsequent year Romania entered the war on the side of the Axis powers. During the war, Romania was the most important source of oil for Nazi Germany
, prompting multiple bombing raids by the Allies
. By means of the Axis invasion of the Soviet Union
, Romania recovered Bessarabia and northern Bukovina from the Soviet Russia, under the leadership of general Ion Antonescu
.
The Antonescu regime played a major role in the Holocaust, following to a lesser extent the Nazi policy of oppression and massacre of the Jews, and Romas, primarily in the Eastern territories Romania recovered or occupied from the Soviet Union (Transnistria
) and in Moldavia
. According to an international commission report
released by the Romanian government in 2004, Antonescu's dictatorial government of Romania is responsible for the murder in various forms (including deportations to concentration camps and executions by the Romanian Army and Gendarmerie and the German Einsatzgruppen
), between 280,000 to 380,000 Jews in Romania and in the war zone of Bessarabia
, Bukovina
and Transnistria.
.png) On 20 August 1944 the Soviet Red Army crossed the border into Romania. On 23 August 1944 Antonescu was toppled and arrested by King Michael I of Romania
On 20 August 1944 the Soviet Red Army crossed the border into Romania. On 23 August 1944 Antonescu was toppled and arrested by King Michael I of Romania
who joined the Allies
and declared war on Germany. On 31 August 1944 the Soviet Red Army entered Bucharest. Despite Romania`s change of sides its role in the defeat of Nazi Germany
was not recognized by the Paris Peace Conference
of 1947. With the Red Army
forces still stationed in the country and exerting de facto control, Communists
and their allied parties claimed 80% of the vote, through a combination of vote manipulation, elimination, and forced mergers of competing parties, thus establishing themselves as the dominant force. Romania suffered additional heavy casualties fighting the Nazi
Army in Hungary and Czechoslovakia
. By the end of the war, the Romanian army had suffered about 300,000 casualties.
The Paris Peace Treaty
at the end of World War II rendered the Vienna Awards void: Northern Transylvania
returned to Romania, but Bessarabia
, northern Bukovina
and southern Dobruja were not recovered. The Moldavian SSR became independent of the Soviet Union only with the latter's 1991 demise
, becoming the Republic of Moldova.
 (1947–1989)
(1947–1989)
In 1947, King Michael I
was forced by the Communists to abdicate and leave the country, Romania was proclaimed a republic
, and remained under direct military and economic control of the USSR
until the late 1950s. During this period, Romania's resources were drained by the "SovRom
" agreements: mixed Soviet-Romanian companies established to mask the looting of Romania by the Soviet Union.
Soviet occupation
following World War II led to the formation of a communist
People's Republic in 1947, and the abdication of King Michael, who went into exile. The leader of Romania from 1948 to his death in 1965 was Gheorghe Gheorghiu-Dej
, the First Secretary
of the Romanian Workers' Party, who first sowed the seeds of greater independence from the Soviet Union by persuading Soviet First Secretary Nikita Khrushchev to withdraw troops from Romania in April 1958.
After the negotiated retreat of Soviet troops, Romania, under the new leadership of Nicolae Ceauşescu
, started to pursue independent policies. Such examples are the condemnation of the Soviet-led 1968 invasion of Czechoslovakia
(being the only Warsaw Pact
country not to take part in the invasion), the continuation of diplomatic relations with Israel
after the Six-Day War
of 1967 (again, the only Warsaw Pact
country to do so), the establishment of economic (1963) and diplomatic (1967) relations with the Federal Republic of Germany
, and so forth. Also, close ties with the Arab
countries (and the PLO) allowed Romania to play a key role in the Israel
-Egypt
and Israel-PLO peace processes by intermediating the visit of Sadat
in Israel. As Romania's foreign debt sharply increased between 1977 and 1981 (from 3 to 10 billion US dollars), the influence of international financial organisations such as the IMF or the World Bank
grew, conflicting with Nicolae Ceauşescu
's autarchic
policies. Ceauşescu eventually initiated a project of total reimbursement of the foreign debt (completed in 1989, shortly before his overthrow). To achieve this goal, he imposed policies that impoverished Romanians and exhausted the Romanian economy. He greatly extended the authority police state
and imposed a cult of personality
. These led to a dramatic decrease in Ceauşescu-popularity and culminated in his overthrow and execution in the bloody Romanian Revolution of 1989
.
Seduced by Ceauşescu's "Independent" foreign policy, Western leaders were slow to turn against a regime that, by the late 1970s, had become increasingly arbitrary, capricious and harsh. Rapid economic growth fueled by foreign credits gradually gave way to wrenching austerity and severe political repression, which became increasingly draconian through the 1980s. During the 1947–1962 period, many people were arbitrarily killed or imprisoned for political, economic or unknown reasons: detainees in prisons or camps, deported, persons under house arrest, and administrative detainees. There were hundreds of thousands of abuses, deaths and incidents of torture against a large range of people, from political opponents to ordinary citizens. Between 60,000 and 80,000 political prisoners were detained as psychiatric patients and treated in some of the most sadistic ways by doctors. It is estimated that, in total, two million people were direct victims of Communism's repression.
resulted in more than 1,000 deaths in Timişoara
and Bucharest
, and brought about the fall of Ceauşescu and the end of the Communist regime in Romania. After a weeklong state of unrest in Timişoara, a mass rally summoned in Bucharest in support of Ceauşescu on December 21, 1989 turned hostile. The Ceauşescu couple, fleeing Bucharest by helicopter, ended up in the custody of the army. After being tried and convicted by a kangaroo court
for genocide
and other crimes, they were executed on December 25, 1989. The events of this revolution remain to this day a matter of debate, with many conflicting theories as to the motivations and even actions of some of the main players.
Ion Iliescu
, a former Communist Party official marginalized by Ceauşescu, attained national recognition as the leader of an impromptu governing coalition, the National Salvation Front (FSN) that proclaimed the restoration of democracy and civil liberties on December 22, 1989. The Communist Party was initially outlawed by Ion Iliescu, but he soon revoked that decision; as a consequence, Communism is not outlawed in Romania today. However, Ceauşescu's most unpopular measures, such as bans on abortion
and contraception
, were among the first laws to be changed after the Revolution, and their legality has not been questioned since then.
After the fall of Ceauşescu, the National Salvation Front (FSN), led by Ion Iliescu
, took partial multi-party democratic and free market measures. Several major political parties of the pre-war era, such as the National Christian Democrat Peasant's Party (PNŢCD)
, the National Liberal Party (PNL)
and the Romanian Social Democrat Party (PSDR) were resurrected. After several major political rallies (especially in January), in April 1990, a sit-in protest contesting the results of the recently held parliamentary elections began in University Square, Bucharest
. The protesters accused the FSN of being made up of former Communists and members of the Securitate
. The protesters did not recognize the results of the election, which they deemed undemocratic, and were asking for the exclusion from the political life of the former high-ranking Communist Party members. The protest rapidly grew to become an ongoing mass demonstration (known as the Golaniad
). The peaceful demonstrations degenerated into violence, with some of the protesters attacking the police headquarters, national television station, and the Foreign Ministry. After the police failed to bring the demonstrators to order, Ion Iliescu
called on the "men of good will" to come and defend the State institutions in Bucharest. Various worker groups from Romania's industrial platforms responded, some of whom engaged in altercations with the protesters. But the most visible and politically influential were the coal miners of the Jiu Valley
. After representatives of the government met with leaders of the Jiu Valley coal miners union
, thousands of miners were organized and arrived in Bucharest June 14, transported on special trains provided by the government. Their violent intervention is remembered as the June 1990 Mineriad
.
Presidential and parliamentary elections were held on May 20, 1990. Running against representatives of the re-established pre-war National Peasants' Party
and National Liberal Party
, and taking advantage of FSN's tight control of the national radio and television, Iliescu won 85% of the vote. The FSN secured two-thirds of the seats in Parliament. A university professor with strong family roots in the Communist Party, Petre Roman
, was named prime minister of the new government, which consisted mainly of former communist officials. The government initiated modest free market
reforms.
Because the majority of ministers in the Petre Roman government were ex-communists, anti-communist protesters initiated a round-the-clock anti-government demonstration
in University Square
, Bucharest in April 1990. Two months later, these protesters, whom the government referred to as "hooligans", were brutally dispersed by the miners from Jiu Valley
, called in by President Iliescu; this event became known as the mineriad
(see June 1990 Mineriad
). The facts surrounding these events are disputed by the miners, who claim that most of the violence was perpetrated by government agents that were agitating the crowds. Some of the counter-protesters also attacked the headquarters and private residences of opposition leaders. Later Parliamentary inquiries showed that members of the government intelligence services were involved in the instigation and manipulation of both the protesters and the miners, and in June 1994 a Bucharest court found two former Securitate officers guilty of ransacking and stealing $100,000 from the house of a leading opposition politician. Petre Roman's government fell in late September 1991, when the miners returned to Bucharest to demand higher salaries. A technocrat, Theodor Stolojan
, was appointed to head an interim government until new elections could be held.
In December 1991, a new constitution was drafted and subsequently adopted, after a popular referendum, which, however, attracted criticism from international observers who accused the government of manipulating the population and even of outright fraud. (The constitution was most recently revised by a national referendum on October 18–19, 2003, again plagued by fraud accusations made by internal and international observers.) The new constitution, which took effect October 29, 2003, follows the structure of the Constitution of 1991, but makes significant revisions, among which the most significant are extension of the presidential mandate from four years to five, and the guaranteed protection of private property.
March 1992 marked the split of the FSN into two groups: the Democratic National Front
(FDSN), led by Ion Iliescu and the Democratic Party (PD), led by Petre Roman. Iliescu won the presidential elections in September 1992 by a clear margin, and his FDSN won the general elections held at the same time. With parliamentary support
from the nationalist PUNR (National Unity Party of Romanians), PRM (Great Romania Party), and the ex-communist PSM (Socialist Workers' Party), a new government was formed in November 1992 under Prime Minister Nicolae Văcăroiu
, an economist. The FDSN changed its name to Party of Social Democracy in Romania (PDSR) in July 1993.
The subsequent disintegration of the FSN produced several political parties including the Romanian Democrat Social Party (PDSR, later Social Democratic Party
, PSD), the Democratic Party (PD) and the ApR (Alliance for Romania). The PDSR party governed Romania from 1990 until 1996 through several coalitions and governments with Ion Iliescu as head of state. Since then there have been three democratic changes of government: in 1996, the democratic-liberal opposition and its leader Emil Constantinescu
acceded to power; in 2000 the Social Democrats returned to power, with Iliescu once again president; and in 2004 Traian Băsescu
was elected president, with an electoral coalition called Justice and Truth Alliance
(DA). The government was formed by a larger coalition which also includes the Conservative Party
and the ethnic Hungarian party.
Emil Constantinescu
of the Democratic Convention
(CDR) emerged as the winner of the second round of the 1996 presidential elections and replaced Iliescu as chief of state. The PDSR won the largest number of seats in Parliament, but was unable to form a viable coalition. Constituent parties of the CDR joined the Democratic Party (PD), the National Liberal Party
(PNL) and the Hungarian Democratic Union of Romania (UDMR) to form a centrist coalition government, holding 60% of the seats in Parliament. This coalition of sorts frequently struggled for survival, as decisions were often delayed by long periods of negotiations among the involved parties. Nevertheless, this coalition was able to implement several critical reforms. The new coalition government, under prime minister Victor Ciorbea
remained in office until March 1998, when Radu Vasile
(PNŢCD) took over as prime minister. The former governor of the National Bank, Mugur Isărescu
, eventually replaced Radu Vasile
as head of the government.
The 2000 elections, brought Iliescu's PDSR, known as Social Democratic Party
(PSD) after the merger with the PSDR, back to power. Iliescu won a third term as the country's president. Adrian Năstase
became the prime minister of the newly formed government.
Presidential and parliamentary elections took place again on November 28, 2004. No political party was able to secure a viable parliamentary majority and opposition parties alike that the PSD had committed large-scale electoral fraud. There was no winner in the first round of the presidential elections. The joint PNL-PD candidate, Traian Băsescu
, won the second round on December 12, 2004 with 51% of the vote and thus became the third post-revolutionary president of Romania.
The PNL leader, Călin Popescu Tăriceanu was assigned the difficult task of building a coalition government without including the PSD. In December 2004, the new coalition government (PD, PNL, PUR Romanian Humanist Party - which eventually changed its name to Romanian Conservative Party and UDMR), was sworn in under Prime Minister Tăriceanu.
Post–Cold War
Romania developed closer ties with Western Europe
, eventually joining NATO in 2004. The country applied in June 1993 for membership in the European Union
(EU). It became an Associated State of the EU in 1995, an Acceding Country in 2004, and a member on January 1, 2007.
Following the free travel agreement and politic of the post–Cold War period, as well as hardship of the life in the post 1990s economic depression, Romania has an increasingly large diaspora
. The main emigration targets are Spain, Italy, Germany, Austria, UK, Canada and the USA.
Romania joined the North Atlantic Treaty Organization in 2004, and the European Union
, alongside Bulgaria
, on January 1, 2007.
In April 2008, Bucharest hosted the NATO summit
.
Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central and Southeastern Europe, on the Lower Danube, within and outside the Carpathian arch, bordering on the Black Sea...
; details are presented in separate articles (see the links in the box and below).
Prehistory=
{Main|Prehistoric Romania}
The oldest modern human remains in Europe were discovered in the "Cave With Bones
Pestera cu Oase
Peștera cu Oase is a system of 12 karstic galleries and chambers located N. 45° 01’; E. 21° 50’ in southwestern Romania, where the oldest early modern human remains in Europe have been discovered.-Paleoanthropological on-site findings:...
" in present day Romania. The remains are approximately 42,000 years old and as Europe’s oldest remains of Homo sapiens, they may represent the first such people to have entered the continent. The remains are especially interesting because they present a mixture of archaic, early modern human and Neanderthal morphological features.
One of the fossil
Fossil
Fossils are the preserved remains or traces of animals , plants, and other organisms from the remote past...
s found—a male, adult jawbone—has been dated to be between 34,000 and 36,000 years old, which would make it one of the oldest fossils found to date of modern humans in Europe. A skull found in Peștera cu Oase
Pestera cu Oase
Peștera cu Oase is a system of 12 karstic galleries and chambers located N. 45° 01’; E. 21° 50’ in southwestern Romania, where the oldest early modern human remains in Europe have been discovered.-Paleoanthropological on-site findings:...
(The Cave with Bones) in 2004-5 bears features of both modern humans and Neanderthal
Neanderthal
The Neanderthal is an extinct member of the Homo genus known from Pleistocene specimens found in Europe and parts of western and central Asia...
s. According to a paper by Erik Trinkaus
Erik Trinkaus
Erik Trinkaus, PhD, is a prominent paleoanthropologist and expert on Neanderthal biology and human evolution. Trinkaus researches the evolution of the species Homo sapiens and recent human diversity, focusing on the paleoanthropology and emergence of late archaic and early modern humans, and the...
and others, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
The Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, usually referred to as PNAS, is the official journal of the United States National Academy of Sciences...
in January 2007, this finding suggests that the two groups interbred thousands of years ago. Radiocarbon dating
Radiocarbon dating
Radiocarbon dating is a radiometric dating method that uses the naturally occurring radioisotope carbon-14 to estimate the age of carbon-bearing materials up to about 58,000 to 62,000 years. Raw, i.e. uncalibrated, radiocarbon ages are usually reported in radiocarbon years "Before Present" ,...
indicates that the skull is between 35,000 and 40,000 years old, making it the oldest modern human fossil ever found in Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
.
Dacia
The earliest written evidence of people living in the territory of the present-day Romania comes from HerodotusHerodotus
Herodotus was an ancient Greek historian who was born in Halicarnassus, Caria and lived in the 5th century BC . He has been called the "Father of History", and was the first historian known to collect his materials systematically, test their accuracy to a certain extent and arrange them in a...
in book IV of his Histories
Histories (Herodotus)
The Histories of Herodotus is considered one of the seminal works of history in Western literature. Written from the 450s to the 420s BC in the Ionic dialect of classical Greek, The Histories serves as a record of the ancient traditions, politics, geography, and clashes of various cultures that...
written 440 BCE. Herein he writes that the tribal confederation of the Getae
Getae
The Getae was the name given by the Greeks to several Thracian tribes that occupied the regions south of the Lower Danube, in what is today northern Bulgaria, and north of the Lower Danube, in Romania...
were defeated by the Persian Emperor Darius the Great during his campaign against the Scythians. The Dacians
Dacians
The Dacians were an Indo-European people, very close or part of the Thracians. Dacians were the ancient inhabitants of Dacia...
, widely accepted as part of the Getae
Getae
The Getae was the name given by the Greeks to several Thracian tribes that occupied the regions south of the Lower Danube, in what is today northern Bulgaria, and north of the Lower Danube, in Romania...
described earlier by the Greeks, were a branch of Thracians
Thracians
The ancient Thracians were a group of Indo-European tribes inhabiting areas including Thrace in Southeastern Europe. They spoke the Thracian language – a scarcely attested branch of the Indo-European language family...
that inhabited Dacia
Dacia
In ancient geography, especially in Roman sources, Dacia was the land inhabited by the Dacians or Getae as they were known by the Greeks—the branch of the Thracians north of the Haemus range...
(corresponding to modern Romania, Moldova
Moldova
Moldova , officially the Republic of Moldova is a landlocked state in Eastern Europe, located between Romania to the West and Ukraine to the North, East and South. It declared itself an independent state with the same boundaries as the preceding Moldavian Soviet Socialist Republic in 1991, as part...
and northern Bulgaria
Bulgaria
Bulgaria , officially the Republic of Bulgaria , is a parliamentary democracy within a unitary constitutional republic in Southeast Europe. The country borders Romania to the north, Serbia and Macedonia to the west, Greece and Turkey to the south, as well as the Black Sea to the east...
). The Dacian kingdom reached its maximum expansion during King Burebista
Burebista
Burebista was a king of the Getae and Dacians, who unified for the first time their tribes and ruled them between 82 BC and 44 BC. He led plunder and conquest raids across Central and Southeastern Europe, subjugating most of the neighbouring tribes...
, between 82 BCE - 44 BCE. Under his leadership Dacia became a powerful state which threatened the regional interests of the Romans. Julius Caesar
Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar was a Roman general and statesman and a distinguished writer of Latin prose. He played a critical role in the gradual transformation of the Roman Republic into the Roman Empire....
intended to start a campaign against the Dacians, due to the support that Burebista gave to Pompey
Pompey
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus, also known as Pompey or Pompey the Great , was a military and political leader of the late Roman Republic...
, but was assassinated in 44 BC
44 BC
Year 44 BC was either a common year starting on Sunday or Monday or a leap year starting on Friday or Saturday of the Julian calendar and a common year starting on Sunday of the Proleptic Julian calendar...
. A few months later, Burebista shared the same fate, assassinated by his own noblemen. Another theory suggests that he was killed by Caesar's friends. His powerful state was divided in four and did not become unified again until 95 AD, under the reign of the Dacian king Decebalus
Decebalus
Decebalus or "The Brave" was a king of Dacia and is famous for fighting three wars and negotiating two interregnums of peace without being eliminated against the Roman Empire under two emperors...
.
The Roman Empire
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of the ancient Roman civilization, characterised by an autocratic form of government and large territorial holdings in Europe and around the Mediterranean....
conquered Moesia
Moesia
Moesia was an ancient region and later Roman province situated in the Balkans, along the south bank of the Danube River. It included territories of modern-day Southern Serbia , Northern Republic of Macedonia, Northern Bulgaria, Romanian Dobrudja, Southern Moldova, and Budjak .-History:In ancient...
by 29 BC, reaching the Danube. In 87 AD Emperor Domitian
Domitian
Domitian was Roman Emperor from 81 to 96. Domitian was the third and last emperor of the Flavian dynasty.Domitian's youth and early career were largely spent in the shadow of his brother Titus, who gained military renown during the First Jewish-Roman War...
sent six legions into Dacia, which were defeated at Tapae
Tapae
Tapae was a Dacian outpost, guarding Sarmisegetuza, their main political centre. Its location was on the Iron Gates of Translylvania, a natural passage breaking between Ţarcului and Poiana Ruscă Mountains and connecting Banat to Ţara Haţegului. This made it one of the very few point through which...
. The Dacians were eventually defeated by Emperor Trajan
Trajan
Trajan , was Roman Emperor from 98 to 117 AD. Born into a non-patrician family in the province of Hispania Baetica, in Spain Trajan rose to prominence during the reign of emperor Domitian. Serving as a legatus legionis in Hispania Tarraconensis, in Spain, in 89 Trajan supported the emperor against...
in two campaigns stretching from 101 AD to 106 AD, and the core of their kingdom was turned into the province of Roman Dacia
Roman Dacia
The Roman province of Dacia on the Balkans included the modern Romanian regions of Transylvania, Banat and Oltenia, and temporarily Muntenia and southern Moldova, but not the nearby regions of Moesia...
.

Romanization
In linguistics, romanization or latinization is the representation of a written word or spoken speech with the Roman script, or a system for doing so, where the original word or language uses a different writing system . Methods of romanization include transliteration, for representing written...
, the Vulgar Latin
Vulgar Latin
Vulgar Latin is any of the nonstandard forms of Latin from which the Romance languages developed. Because of its nonstandard nature, it had no official orthography. All written works used Classical Latin, with very few exceptions...
giving birth to proto-Romanian language
Romanian language
Romanian Romanian Romanian (or Daco-Romanian; obsolete spellings Rumanian, Roumanian; self-designation: română, limba română ("the Romanian language") or românește (lit. "in Romanian") is a Romance language spoken by around 24 to 28 million people, primarily in Romania and Moldova...
.
The geographical position of Dacia Felix made it difficult to defend against the barbarians, and during 240 AD - 256 AD, under the attacks of the Carpi and the Goths
Goths
The Goths were an East Germanic tribe of Scandinavian origin whose two branches, the Visigoths and the Ostrogoths, played an important role in the fall of the Roman Empire and the emergence of Medieval Europe....
, Dacia was lost. The Roman Empire
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of the ancient Roman civilization, characterised by an autocratic form of government and large territorial holdings in Europe and around the Mediterranean....
withdrew from Dacia Romana around 271 AD, thus making it the first province to be abandoned.
Roman conquest of Dacia stands at the base of the origin of Romanians
Origin of Romanians
The origin of the Romanians – the ethnogenesis of the Romanian people – can be traced back to the region’s Romanized inhabitants living, within the Roman Empire, in the lands north of the Jireček Line The origin of the Romanians – the ethnogenesis of the Romanian people (speakers of a Romance...
. Several competing theories have been introduced to explain the origin of modern Romanians. Linguistic and geo-historical analyses tend to indicate that Romanians
Romanians
The Romanians are an ethnic group native to Romania, who speak Romanian; they are the majority inhabitants of Romania....
have coalesced as a major ethnic group both South and North of the Danube
Danube
The Danube is a river in the Central Europe and the Europe's second longest river after the Volga. It is classified as an international waterway....
. For further discussion, see Origin of Romanians
Origin of Romanians
The origin of the Romanians – the ethnogenesis of the Romanian people – can be traced back to the region’s Romanized inhabitants living, within the Roman Empire, in the lands north of the Jireček Line The origin of the Romanians – the ethnogenesis of the Romanian people (speakers of a Romance...
.
Dark Ages
In either 271 or 275, the Roman army and administration left Dacia, which was invaded by the GothsGoths
The Goths were an East Germanic tribe of Scandinavian origin whose two branches, the Visigoths and the Ostrogoths, played an important role in the fall of the Roman Empire and the emergence of Medieval Europe....
. The Goths lived with the local people until the 4th century, when a nomadic people, the Huns
Huns
The Huns were a group of nomadic people who, appearing from east of the Volga River, migrated into Europe c. AD 370 and established the vast Hunnic Empire there. Since de Guignes linked them with the Xiongnu, who had been northern neighbours of China 300 years prior to the emergence of the Huns,...
, arrived. The Gepids and the Avars
Eurasian Avars
The Eurasian Avars or Ancient Avars were a highly organized nomadic confederacy of mixed origins. They were ruled by a khagan, who was surrounded by a tight-knit entourage of nomad warriors, an organization characteristic of Turko-Mongol groups...
and their Slavic subjects ruled Transylvania
Transylvania
Transylvania is a historical region in the central part of Romania. Bounded on the east and south by the Carpathian mountain range, historical Transylvania extended in the west to the Apuseni Mountains; however, the term sometimes encompasses not only Transylvania proper, but also the historical...
until the 8th century. The Pechenegs, the Cumans
Cumans
The Cumans were Turkic nomadic people comprising the western branch of the Cuman-Kipchak confederation. After Mongol invasion , they decided to seek asylum in Hungary, and subsequently to Bulgaria...
and Uzes
Uzès
Uzès is a commune in the Gard department in southern France.It lies about 25 km north-northeast of Nîmes.-History:Originally Ucetia, Uzès was a small Gallo-Roman oppidum, or administrative settlement. The town lies at the source of the Eure, from where a Roman aqueduct was built in the first...
were also mentioned by historic chronicles on the territory of Romania, until the founding of the Romanian principalities of Wallachia
Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia is a historical and geographical region of Romania. It is situated north of the Danube and south of the Southern Carpathians...
by Basarab I around 1310 in the High Middle Ages
High Middle Ages
The High Middle Ages was the period of European history around the 11th, 12th, and 13th centuries . The High Middle Ages were preceded by the Early Middle Ages and followed by the Late Middle Ages, which by convention end around 1500....
, and Moldavia
Moldavia
Moldavia is a geographic and historical region and former principality in Eastern Europe, corresponding to the territory between the Eastern Carpathians and the Dniester river...
by Dragoş
Dragos
Dragonș, also Dragoş Vodă or Dragoş of Bedeu, was a Romanian voivode in Maramureş who has traditionally been considered as the first ruler or prince of Moldavia...
around 1352.
Different migrating peoples lived along the local populations, such as the Gothic
Goths
The Goths were an East Germanic tribe of Scandinavian origin whose two branches, the Visigoths and the Ostrogoths, played an important role in the fall of the Roman Empire and the emergence of Medieval Europe....
Empire (Oium
Oium
Oium or Aujum was a name for an area in Scythia, where the Goths under their king Filimer settled after leaving Gothiscandza, according to the Getica by Jordanes, written around 551...
) from 271 until 378, the Hunnish Empire
Huns
The Huns were a group of nomadic people who, appearing from east of the Volga River, migrated into Europe c. AD 370 and established the vast Hunnic Empire there. Since de Guignes linked them with the Xiongnu, who had been northern neighbours of China 300 years prior to the emergence of the Huns,...
until 435, the Avar Empire
Eurasian Avars
The Eurasian Avars or Ancient Avars were a highly organized nomadic confederacy of mixed origins. They were ruled by a khagan, who was surrounded by a tight-knit entourage of nomad warriors, an organization characteristic of Turko-Mongol groups...
and Slavs during the 6th century. Subsequently Magyars, Pechenegs, Cumans
Cumans
The Cumans were Turkic nomadic people comprising the western branch of the Cuman-Kipchak confederation. After Mongol invasion , they decided to seek asylum in Hungary, and subsequently to Bulgaria...
and Tatars
Tatars
Tatars are a Turkic speaking ethnic group , numbering roughly 7 million.The majority of Tatars live in the Russian Federation, with a population of around 5.5 million, about 2 million of which in the republic of Tatarstan.Significant minority populations are found in Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan,...
also raided and settled in the lands to various extents.

Middle Ages
In the Middle AgesMiddle Ages
The Middle Ages is a periodization of European history from the 5th century to the 15th century. The Middle Ages follows the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 and precedes the Early Modern Era. It is the middle period of a three-period division of Western history: Classic, Medieval and Modern...
, Romanians lived in three distinct principalities: Wallachia
Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia is a historical and geographical region of Romania. It is situated north of the Danube and south of the Southern Carpathians...
(—"Romanian Land"), Moldavia
Moldavia
Moldavia is a geographic and historical region and former principality in Eastern Europe, corresponding to the territory between the Eastern Carpathians and the Dniester river...
and Transylvania
Transylvania
Transylvania is a historical region in the central part of Romania. Bounded on the east and south by the Carpathian mountain range, historical Transylvania extended in the west to the Apuseni Mountains; however, the term sometimes encompasses not only Transylvania proper, but also the historical...
.
The Pechenegs (a semi-nomadic Turkic people of the Central Asian steppes) occupied the steppes north of the Black Sea
Black Sea
The Black Sea is bounded by Europe, Anatolia and the Caucasus and is ultimately connected to the Atlantic Ocean via the Mediterranean and the Aegean seas and various straits. The Bosphorus strait connects it to the Sea of Marmara, and the strait of the Dardanelles connects that sea to the Aegean...
(8th–12th century) and by the 10th century were in control of the lands between the Don
Don River (Russia)
The Don River is one of the major rivers of Russia. It rises in the town of Novomoskovsk 60 kilometres southeast from Tula, southeast of Moscow, and flows for a distance of about 1,950 kilometres to the Sea of Azov....
and lower Danube
Danube
The Danube is a river in the Central Europe and the Europe's second longest river after the Volga. It is classified as an international waterway....
rivers.
By the 11th and 12th century, the nomadic confederacy of the Cumans
Cumans
The Cumans were Turkic nomadic people comprising the western branch of the Cuman-Kipchak confederation. After Mongol invasion , they decided to seek asylum in Hungary, and subsequently to Bulgaria...
and (Eastern) Kipchaks (who are considered to be either the eastern branch of the Cumans or a distinct but related tribe with whom the Cumans created a confederacy) were the dominant force over the vast territories stretching from the present-day Kazakhstan, southern Russia, Ukraine, to southern Moldavia and western Wallachia.
By the 11th century, the area of today's Transylvania became a largely autonomous part of the Kingdom of Hungary
Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary comprised present-day Hungary, Slovakia and Croatia , Transylvania , Carpatho Ruthenia , Vojvodina , Burgenland , and other smaller territories surrounding present-day Hungary's borders...
. Kings of Hungary invited the Saxons
Saxons
The Saxons were a confederation of Germanic tribes originating on the North German plain. The Saxons earliest known area of settlement is Northern Albingia, an area approximately that of modern Holstein...
to settle in Transylvania. Also living in Transylvania were the Székely
Székely
The Székelys or Székely , sometimes also referred to as Szeklers , are a subgroup of the Hungarian people living mostly in the Székely Land, an ethno-cultural region in eastern Transylvania, Romania...
. After the Magyar conquest (10-11th century), Transylvania became part of the Kingdom of Hungary
Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary comprised present-day Hungary, Slovakia and Croatia , Transylvania , Carpatho Ruthenia , Vojvodina , Burgenland , and other smaller territories surrounding present-day Hungary's borders...
until the 16th century, when it became the independent Principality of Transylvania until 1711. Many small local states with varying degrees of independence developed, but only in the 14th century the larger principalities of Moldavia
Moldavia
Moldavia is a geographic and historical region and former principality in Eastern Europe, corresponding to the territory between the Eastern Carpathians and the Dniester river...
and Wallachia
Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia is a historical and geographical region of Romania. It is situated north of the Danube and south of the Southern Carpathians...
emerged to fight a threat in the form of the Ottoman Turks
Ottoman Turks
The Ottoman Turks were the Turkish-speaking population of the Ottoman Empire who formed the base of the state's military and ruling classes. Reliable information about the early history of Ottoman Turks is scarce, but they take their Turkish name, Osmanlı , from the house of Osman I The Ottoman...
, who conquered Constantinople
Constantinople
Constantinople was the capital of the Roman, Eastern Roman, Byzantine, Latin, and Ottoman Empires. Throughout most of the Middle Ages, Constantinople was Europe's largest and wealthiest city.-Names:...
in 1453.
Independent Wallachia
Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia is a historical and geographical region of Romania. It is situated north of the Danube and south of the Southern Carpathians...
has been on the border of the Ottoman Empire
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman EmpireIt was usually referred to as the "Ottoman Empire", the "Turkish Empire", the "Ottoman Caliphate" or more commonly "Turkey" by its contemporaries...
since the 14th century and slowly fell under the suzerainty
Suzerainty
Suzerainty occurs where a region or people is a tributary to a more powerful entity which controls its foreign affairs while allowing the tributary vassal state some limited domestic autonomy. The dominant entity in the suzerainty relationship, or the more powerful entity itself, is called a...
of the Ottoman Empire
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman EmpireIt was usually referred to as the "Ottoman Empire", the "Turkish Empire", the "Ottoman Caliphate" or more commonly "Turkey" by its contemporaries...
during the 15th century. One famous ruler in this period was Vlad III the Impaler
Vlad III the Impaler
Vlad III, Prince of Wallachia , also known by his patronymic Dracula , and posthumously dubbed Vlad the Impaler , was a three-time Voivode of Wallachia, ruling mainly from 1456 to 1462, the period of the incipient Ottoman conquest of the Balkans...
(also known as Vlad Dracula or ), Prince of Wallachia
Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia is a historical and geographical region of Romania. It is situated north of the Danube and south of the Southern Carpathians...
in 1448, 1456–62, and 1476. In the English
English language
English is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria...
-speaking world, Vlad is best known for the exceedingly cruel punishments he imposed during his reign and for serving as the primary inspiration for the vampire
Vampire
Vampires are mythological or folkloric beings who subsist by feeding on the life essence of living creatures, regardless of whether they are undead or a living person...
main character
Count Dracula
Count Dracula is a fictional character, the titular antagonist of Bram Stoker's 1897 Gothic horror novel Dracula and archetypal vampire. Some aspects of his character have been inspired by the 15th century Romanian general and Wallachian Prince Vlad III the Impaler...
in Bram Stoker
Bram Stoker
Abraham "Bram" Stoker was an Irish novelist and short story writer, best known today for his 1897 Gothic novel Dracula...
's 1897 novel Dracula
Dracula
Dracula is an 1897 novel by Irish author Bram Stoker.Famous for introducing the character of the vampire Count Dracula, the novel tells the story of Dracula's attempt to relocate from Transylvania to England, and the battle between Dracula and a small group of men and women led by Professor...
. As king, he maintained an independent policy in relation to the Ottoman Empire
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman EmpireIt was usually referred to as the "Ottoman Empire", the "Turkish Empire", the "Ottoman Caliphate" or more commonly "Turkey" by its contemporaries...
, and in Romania he is viewed by many as a prince with a deep sense of justice, and a defender of both Wallachia and European Christianity
Christianity
Christianity is a monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus as presented in canonical gospels and other New Testament writings...
against Ottoman
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman EmpireIt was usually referred to as the "Ottoman Empire", the "Turkish Empire", the "Ottoman Caliphate" or more commonly "Turkey" by its contemporaries...
expansionism
Expansionism
In general, expansionism consists of expansionist policies of governments and states. While some have linked the term to promoting economic growth , more commonly expansionism refers to the doctrine of a state expanding its territorial base usually, though not necessarily, by means of military...
.
The principality of Moldavia
Moldavia
Moldavia is a geographic and historical region and former principality in Eastern Europe, corresponding to the territory between the Eastern Carpathians and the Dniester river...
reached its most glorious period under the rule of Stephen the Great
Stephen III of Moldavia
Stephen III of Moldavia was Prince of Moldavia between 1457 and 1504 and the most prominent representative of the House of Mușat.During his reign, he strengthened Moldavia and maintained its independence against the ambitions of Hungary, Poland, and the...
between 1457 and 1504. His rule of 47 years was unusually long, especially at that time - only 13 rulers worldwide were recorded to have ruled for at least 50 years until the end of 15th century. He was a very successful military leader (winning 47 battles and losing only 2),) and after each victory, he raised a church, managing to build 48 churches or monasteries, some of them with unique and very interesting painting styles. For more information see Painted churches of northern Moldavia
Painted churches of northern Moldavia
The Churches of Moldavia are eight Romanian Orthodox churches in Suceava County, Romania in northern Moldavia, built approximately between 1487 and 1583.Since 1993, they have been listed by UNESCO as a World Heritage Site...
listed in UNESCO
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations...
's list of World Heritage Sites. Stephen's most prestigious victory was over the Ottoman Empire
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman EmpireIt was usually referred to as the "Ottoman Empire", the "Turkish Empire", the "Ottoman Caliphate" or more commonly "Turkey" by its contemporaries...
in 1475 at the Battle of Vaslui
Battle of Vaslui
The Battle of Vaslui was fought on January 10, 1475 between Stephen III of Moldavia and the Ottoman Beylerbey of Rumelia, Hadân Suleiman Pasha. The battle took place at Podul Înalt , near the town of Vaslui, in Moldavia...
for which he raised the Voroneţ Monastery
Voronet Monastery
Voroneț is a monastery in Romania, located in the town of Gura Humorului, Moldavia. It is one of the famous painted monasteries from southern Bukovina, in Suceava County...
. For this victory, Pope
Pope
The Pope is the Bishop of Rome, a position that makes him the leader of the worldwide Catholic Church . In the Catholic Church, the Pope is regarded as the successor of Saint Peter, the Apostle...
Sixtus IV deemed him verus christianae fidei athleta (true Champion of Christian Faith). However, after his death, Moldavia
Moldavia
Moldavia is a geographic and historical region and former principality in Eastern Europe, corresponding to the territory between the Eastern Carpathians and the Dniester river...
would also come under the suzerainty
Suzerainty
Suzerainty occurs where a region or people is a tributary to a more powerful entity which controls its foreign affairs while allowing the tributary vassal state some limited domestic autonomy. The dominant entity in the suzerainty relationship, or the more powerful entity itself, is called a...
of the Ottoman Empire
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman EmpireIt was usually referred to as the "Ottoman Empire", the "Turkish Empire", the "Ottoman Caliphate" or more commonly "Turkey" by its contemporaries...
in the 16th century.
Early modern period


Hungary
Hungary , officially the Republic of Hungary , is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is situated in the Carpathian Basin and is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine and Romania to the east, Serbia and Croatia to the south, Slovenia to the southwest and Austria to the west. The...
became Ottoman provinces. In contrast, Moldavia, Wallachia, and Transylvania
Transylvania
Transylvania is a historical region in the central part of Romania. Bounded on the east and south by the Carpathian mountain range, historical Transylvania extended in the west to the Apuseni Mountains; however, the term sometimes encompasses not only Transylvania proper, but also the historical...
, came under Ottoman suzerainty
Suzerainty
Suzerainty occurs where a region or people is a tributary to a more powerful entity which controls its foreign affairs while allowing the tributary vassal state some limited domestic autonomy. The dominant entity in the suzerainty relationship, or the more powerful entity itself, is called a...
, but conserved fully internal autonomy and, until the 18th century, some external independence. During this period the Romanian lands were characterised by the slow disappearance of the feudal
Feudalism
Feudalism was a set of legal and military customs in medieval Europe that flourished between the 9th and 15th centuries, which, broadly defined, was a system for ordering society around relationships derived from the holding of land in exchange for service or labour.Although derived from the...
system, the distinguishment of some rulers like Vasile Lupu
Vasile Lupu
Vasile Lupu was a Moldavian Voivode between 1634 and 1653. Vasile Coci surnamed "the wolf" who ruled as Prince of Moldavia had secured the Moldavian throne in 1634 after a series of complicated intrigues and managed to hold it for twenty years. Vasile was of Albanian origin and Greek education...
and Dimitrie Cantemir
Dimitrie Cantemir
Dimitrie Cantemir was twice Prince of Moldavia . He was also a prolific man of letters – philosopher, historian, composer, musicologist, linguist, ethnographer, and geographer....
in Moldavia, Matei Basarab
Matei Basarab
Matei Basarab was a Wallachian Voivode between 1632 and 1654.-Reign:Much of Matei's reign was spent fighting off incursions from Moldavia, which he successfully accomplished in 1637, 1639, and 1653 - see Battle of Finta...
and Constantin Brâncoveanu
Constantin Brâncoveanu
Constantin Brâncoveanu was Prince of Wallachia between 1688 and 1714.-Ascension:A descendant of the Craioveşti boyar family and related to Matei Basarab, Brâncoveanu was born at the estate of Brâncoveni and raised in the house of his uncle, stolnic Constantin Cantacuzino...
in Wallachia, Gabriel Bethlen
Gabriel Bethlen
Gabriel Bethlen was a prince of Transylvania , duke of Opole and leader of an anti-Habsburg insurrection in the Habsburg Royal Hungary. His last armed intervention in 1626 was part of the Thirty Years' War...
in Transylvania, the Phanariot Epoch, and the appearance of the Russian Empire
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was a state that existed from 1721 until the Russian Revolution of 1917. It was the successor to the Tsardom of Russia and the predecessor of the Soviet Union...
as a political and military influence.
John II
John II Sigismund Zápolya
John II Sigismund Zápolya was King of Hungary from 1540 to 1570 and Prince of Transylvania from 1570–1571.-Family:The son of King John I and Isabella Jagiełło, he succeeded his father as an infant...
, the last non-Habsburg king of Hungary
King of Hungary
The King of Hungary was the head of state of the Kingdom of Hungary from 1000 to 1918.The style of title "Apostolic King" was confirmed by Pope Clement XIII in 1758 and used afterwards by all the Kings of Hungary, so after this date the kings are referred to as "Apostolic King of...
, moved his royal court to Alba Iulia
Alba Iulia
Alba Iulia is a city in Alba County, Transylvania, Romania with a population of 66,747, located on the Mureş River. Since the High Middle Ages, the city has been the seat of Transylvania's Roman Catholic diocese. Between 1541 and 1690 it was the capital of the Principality of Transylvania...
in Transylvania, and after his abdication as king of Hungary, became the first Prince of Transylvania. His Edict of Turda
Turda
Turda is a city and Municipality in Cluj County, Romania, situated on the Arieş River.- Ancient times :The city was founded by Dacians under the name Patavissa or Potaissa...
was the first decree of religious freedom
Freedom of religion
Freedom of religion is a principle that supports the freedom of an individual or community, in public or private, to manifest religion or belief in teaching, practice, worship, and observance; the concept is generally recognized also to include the freedom to change religion or not to follow any...
in the modern history of Europe (1568). In the subsequent period, Transylvania was ruled by mostly Calvinist
Calvinism
Calvinism is a Protestant theological system and an approach to the Christian life...
Hungarian princes (until the end of the 17th century), and Protestantism
Protestantism
Protestantism is one of the three major groupings within Christianity. It is a movement that began in Germany in the early 16th century as a reaction against medieval Roman Catholic doctrines and practices, especially in regards to salvation, justification, and ecclesiology.The doctrines of the...
flourished in the region.

Moldova
Moldova , officially the Republic of Moldova is a landlocked state in Eastern Europe, located between Romania to the West and Ukraine to the North, East and South. It declared itself an independent state with the same boundaries as the preceding Moldavian Soviet Socialist Republic in 1991, as part...
and Wallachia
Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia is a historical and geographical region of Romania. It is situated north of the Danube and south of the Southern Carpathians...
had complete internal autonomy and an external independence, which was finally lost in the 18th century. In 1600, the principalities of Wallachia, Moldova and Transylvania were simultaneously headed by the Wallachian prince Michael the Brave (Mihai Viteazul), Ban
Ban (title)
Ban was a title used in several states in central and south-eastern Europe between the 7th century and the 20th century.-Etymology:The word ban has entered the English language probably as a borrowing from South Slavic ban, meaning "lord, master; ruler". The Slavic word is probably borrowed from...
of Oltenia
Oltenia
Oltenia is a historical province and geographical region of Romania, in western Wallachia. It is situated between the Danube, the Southern Carpathians and the Olt river ....
, but the chance for a unity dissolved after Mihai was killed, only one year later, by the soldiers of an Austrian
Habsburg Monarchy
The Habsburg Monarchy covered the territories ruled by the junior Austrian branch of the House of Habsburg , and then by the successor House of Habsburg-Lorraine , between 1526 and 1867/1918. The Imperial capital was Vienna, except from 1583 to 1611, when it was moved to Prague...
army general Giorgio Basta
Giorgio Basta
Giorgio Basta, Count of Huszt was an Italian general of Arbëreshë descent, employed by the Holy Roman Emperor Rudolf II to command Habsburg forces in the Long War of 1591-1606 and later to administer Transylvania as an Imperial vassal to restore Catholicism as a predominant religion in...
. Mihai Viteazul, who was prince of Transylvania for less than one year, intended for the first time to unite the three principalities and to lay down foundations of a single state in a territory comparable to today's Romania.
The Principality of Transylvania experienced a golden age under the absolutist
Absolutism (European history)
Absolutism or The Age of Absolutism is a historiographical term used to describe a form of monarchical power that is unrestrained by all other institutions, such as churches, legislatures, or social elites...
rule of Gabor Bethlen (1613–1629). In 1699, Transylvania became a territory of the Habsburgs'
Habsburg Monarchy
The Habsburg Monarchy covered the territories ruled by the junior Austrian branch of the House of Habsburg , and then by the successor House of Habsburg-Lorraine , between 1526 and 1867/1918. The Imperial capital was Vienna, except from 1583 to 1611, when it was moved to Prague...
Austrian empire, following the Austrian victory over the Turks. The Austrians, in their turn, rapidly expanded their empire: in 1718 an important part of Wallachia, called Oltenia
Oltenia
Oltenia is a historical province and geographical region of Romania, in western Wallachia. It is situated between the Danube, the Southern Carpathians and the Olt river ....
, was incorporated to the Austrian monarchy and was only returned in 1739. In 1775, the Austrian empire occupied the north-western part of Moldavia, later called Bukovina
Bukovina
Bukovina is a historical region on the northern slopes of the northeastern Carpathian Mountains and the adjoining plains.-Name:The name Bukovina came into official use in 1775 with the region's annexation from the Principality of Moldavia to the possessions of the Habsburg Monarchy, which became...
, while the eastern half of the principality (called Bessarabia
Bessarabia
Bessarabia is a historical term for the geographic region in Eastern Europe bounded by the Dniester River on the east and the Prut River on the west....
) was occupied in 1812 by Russia
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
.
During the period of Austro-Hungarian rule in Transylvania
Transylvania
Transylvania is a historical region in the central part of Romania. Bounded on the east and south by the Carpathian mountain range, historical Transylvania extended in the west to the Apuseni Mountains; however, the term sometimes encompasses not only Transylvania proper, but also the historical...
, and Ottoman
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman EmpireIt was usually referred to as the "Ottoman Empire", the "Turkish Empire", the "Ottoman Caliphate" or more commonly "Turkey" by its contemporaries...
suzerainty over Wallachia
Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia is a historical and geographical region of Romania. It is situated north of the Danube and south of the Southern Carpathians...
and Moldavia
Moldavia
Moldavia is a geographic and historical region and former principality in Eastern Europe, corresponding to the territory between the Eastern Carpathians and the Dniester river...
, most Romanians
Romanians
The Romanians are an ethnic group native to Romania, who speak Romanian; they are the majority inhabitants of Romania....
were in the situation of being second-class citizens
Supplex Libellus Valachorum
Supplex Libellus Valachorum Transsilvaniae is the name of two petitions sent by the leaders of the ethnic Romanians of Transylvania to the Holy Roman Emperor Leopold II, demanding equal political rights with the other ethnicities of Transylvania and a share of the Transylvanian Diet proportional...
(or even non-citizens) in a territory where they formed the majority of the population. In some Transylvanian cities, such as Brașov
Brasov
Brașov is a city in Romania and the capital of Brașov County.According to the last Romanian census, from 2002, there were 284,596 people living within the city of Brașov, making it the 8th most populated city in Romania....
(at that time the Transylvanian Saxon
Transylvanian Saxons
The Transylvanian Saxons are a people of German ethnicity who settled in Transylvania from the 12th century onwards.The colonization of Transylvania by Germans was begun by King Géza II of Hungary . For decades, the main task of the German settlers was to defend the southeastern border of the...
citadel of Kronstadt), Romanians were not even allowed
Transylvanian Memorandum
The Transylvanian Memorandum was a petition sent in 1892 by the leaders of the Romanians of Transylvania to the Austro-Hungarian Emperor-King Franz Joseph, asking for equal ethnic rights with the Hungarians, and demanding an end to persecutions and Magyarization attempts.-Status:After the Ausgleich...
to reside within the city walls.
As in most European countries, 1848 brought revolution
Wallachian Revolution of 1848
The Wallachian Revolution of 1848 was a Romanian liberal and Romantic nationalist uprising in the Principality of Wallachia. Part of the Revolutions of 1848, and closely connected with the unsuccessful revolt in the Principality of Moldavia, it sought to overturn the administration imposed by...
to Moldavia, Wallachia, and Transylvania, announced by Tudor Vladimirescu
Tudor Vladimirescu
Tudor Vladimirescu was a Wallachian Romanian revolutionary hero, the leader of the Wallachian uprising of 1821 and of the Pandur militia. He is also known as Tudor din Vladimiri or — occasionally — as Domnul Tudor .-Background:Tudor was born in Vladimiri, Gorj County in a family of landed peasants...
and his Pandurs
Pandurs
The Pandurs were Croatian Austrian frontier soldiers, who inhabited the areas of the Kingdom of Croatia and Military Frontier, and fought not only in the East-Turkish front, but also in the West-European front. They were a non-linear army, made out mainly of Croats...
in the Wallachian uprising of 1821
Wallachian uprising of 1821
The Wallachian uprising of 1821 was an uprising in Wallachia against Ottoman rule which took place during 1821.-Background:...
. The goals of the revolutionaries - complete independence for Moldavia and Wallachia, and national emancipation in Transylvania - remained unfulfilled, but were the basis of the subsequent evolutions. Also, the uprising helped the population of the three principalities recognise their unity of language and interests. Moldavia and Romanian countries were very close, not just in language, but in geography also.
After the failed 1848 Revolution
Revolutions of 1848
The European Revolutions of 1848, known in some countries as the Spring of Nations, Springtime of the Peoples or the Year of Revolution, were a series of political upheavals throughout Europe in 1848. It was the first Europe-wide collapse of traditional authority, but within a year reactionary...
, the Great Powers did not support the Romanians' expressed desire to officially unite in a single state, forcing Romania to proceed alone against the Turks. Heavily taxed and badly administered under the Ottoman Empire, in 1859, people in both Moldavia and Wallachia elected the same "Domnitor
Domnitor
Domnitor was the official title of the ruler of the United Principalities of Wallachia and Moldavia between 1859 and 1866....
" (ruler) - Alexandru Ioan Cuza
Alexander John Cuza
Alexander John Cuza was a Moldavian-born Romanian politician who ruled as the first Domnitor of the United Principalities of Moldavia and Wallachia between 1859 and 1866.-Early life:...
- as prince. (Domnitor
Domnitor
Domnitor was the official title of the ruler of the United Principalities of Wallachia and Moldavia between 1859 and 1866....
in Romanian
Romanian language
Romanian Romanian Romanian (or Daco-Romanian; obsolete spellings Rumanian, Roumanian; self-designation: română, limba română ("the Romanian language") or românește (lit. "in Romanian") is a Romance language spoken by around 24 to 28 million people, primarily in Romania and Moldova...
). Thus, Romania was created as a personal union, albeit a Romania that did not include Transylvania, where the upper class and the aristocracy remained mainly Hungarian, although Romanian nationalism inevitably ran up against Hungarian nationalism at the end of the 19th century. As in the previous 900 years, Austria-Hungary, especially under the Dual Monarchy
History of Hungary
Hungary is a country in central Europe. Its history under this name dates to the early Middle Ages, when the Pannonian Basin was colonized by the Magyars, a semi-nomadic people from what is now central-northern Russia...
of 1867, kept the Hungarians firmly in control, even in parts of Transylvania where Romanians constituted a local majority.

Independence and Kingdom of Romania
In an 1866 coup d'état, Cuza was exiled and replaced by Prince Karl of Hohenzollern-SigmaringenHohenzollern-Sigmaringen
-Noble jurisdictions:Prince Karl Eitel of Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen, and descendants of his nephew Ferdinand ruled over the Kingdom of Romania, as Karl Eitel did not have children...
, who became known as Prince Carol of Romania. During the Russo-Turkish War, Romania fought on the Russian side; in the 1878 Treaty of Berlin
Treaty of Berlin, 1878
The Treaty of Berlin was the final act of the Congress of Berlin , by which the United Kingdom, Austria-Hungary, France, Germany, Italy, Russia and the Ottoman Empire under Sultan Abdul Hamid II revised the Treaty of San Stefano signed on March 3 of the same year...
, Romania was recognized as an independent
Romanian War of Independence
The Romanian War of Independence is the name used in Romanian historiography to refer to the 1877-1878 Russo-Turkish war, following which Romania, fighting on the Russian side, gained independence from the Ottoman Empire...
state by the Great Powers. In return, Romania ceded three southern districts of Bessarabia
Bessarabia
Bessarabia is a historical term for the geographic region in Eastern Europe bounded by the Dniester River on the east and the Prut River on the west....
to Russia
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
and acquired Dobruja
Dobruja
Dobruja is a historical region shared by Bulgaria and Romania, located between the lower Danube river and the Black Sea, including the Danube Delta, Romanian coast and the northernmost part of the Bulgarian coast...
. In 1881, the principality
Principality
A principality is a monarchical feudatory or sovereign state, ruled or reigned over by a monarch with the title of prince or princess, or by a monarch with another title within the generic use of the term prince....
was raised to a kingdom
Monarchy
A monarchy is a form of government in which the office of head of state is usually held until death or abdication and is often hereditary and includes a royal house. In some cases, the monarch is elected...
and Prince Carol became King
Monarch
A monarch is the person who heads a monarchy. This is a form of government in which a state or polity is ruled or controlled by an individual who typically inherits the throne by birth and occasionally rules for life or until abdication...
Carol I.
In 1866, the German prince Carol I
Carol I of Romania
Carol I , born Prince Karl of Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen was reigning prince and then King of Romania from 1866 to 1914. He was elected prince of Romania on 20 April 1866 following the overthrow of Alexandru Ioan Cuza by a palace coup...
(Charles or Karl) of Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen
Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen
-Noble jurisdictions:Prince Karl Eitel of Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen, and descendants of his nephew Ferdinand ruled over the Kingdom of Romania, as Karl Eitel did not have children...
was appointed as Domnitor
Domnitor
Domnitor was the official title of the ruler of the United Principalities of Wallachia and Moldavia between 1859 and 1866....
—Prince—of the Principality of Romania. In 1877, Romania declared independence from the Ottoman Empire and, following a Russian-Romanian-Turkish war, its independence was recognized by the Treaty of Berlin, 1878
Treaty of Berlin, 1878
The Treaty of Berlin was the final act of the Congress of Berlin , by which the United Kingdom, Austria-Hungary, France, Germany, Italy, Russia and the Ottoman Empire under Sultan Abdul Hamid II revised the Treaty of San Stefano signed on March 3 of the same year...
, making it the first independent national state in the eastern half of Europe. Following the war Romania acquired Dobruja
Dobruja
Dobruja is a historical region shared by Bulgaria and Romania, located between the lower Danube river and the Black Sea, including the Danube Delta, Romanian coast and the northernmost part of the Bulgarian coast...
in its southeast, but it was forced by Russia to cede the Southern Bessarabian territory to Russia "in exchange" for the access to the ports at the Black Sea. Prince Carol I was proclaimed the first King of Romania
King of Romania
King of the Romanians , rather than King of Romania , was the official title of the ruler of the Kingdom of Romania from 1881 until 1947, when Romania was proclaimed a republic....
on March 26, 1881.
The 1878–1914 period was one of stability and progress
Kingdom of Romania
The Kingdom of Romania was the Romanian state based on a form of parliamentary monarchy between 13 March 1881 and 30 December 1947, specified by the first three Constitutions of Romania...
for Romania. During the Second Balkan War
Second Balkan War
The Second Balkan War was a conflict which broke out when Bulgaria, dissatisfied with its share of the spoils of the First Balkan War, attacked its former allies, Serbia and Greece, on 29 June 1913. Bulgaria had a prewar agreement about the division of region of Macedonia...
, Romania joined Greece
Greece
Greece , officially the Hellenic Republic , and historically Hellas or the Republic of Greece in English, is a country in southeastern Europe....
, Serbia
Serbia
Serbia , officially the Republic of Serbia , is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central and Southeast Europe, covering the southern part of the Carpathian basin and the central part of the Balkans...
, Montenegro
Montenegro
Montenegro Montenegrin: Crna Gora Црна Гора , meaning "Black Mountain") is a country located in Southeastern Europe. It has a coast on the Adriatic Sea to the south-west and is bordered by Croatia to the west, Bosnia and Herzegovina to the northwest, Serbia to the northeast and Albania to the...
and Turkey
Turkey
Turkey , known officially as the Republic of Turkey , is a Eurasian country located in Western Asia and in East Thrace in Southeastern Europe...
against Bulgaria
Bulgaria
Bulgaria , officially the Republic of Bulgaria , is a parliamentary democracy within a unitary constitutional republic in Southeast Europe. The country borders Romania to the north, Serbia and Macedonia to the west, Greece and Turkey to the south, as well as the Black Sea to the east...
. In the peace Treaty of Bucharest (1913) Romania gained Southern Dobrudja - the Quadrilateral (the Durostor and Caliacra counties).
World War I
(1916–1918)
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was a state that existed from 1721 until the Russian Revolution of 1917. It was the successor to the Tsardom of Russia and the predecessor of the Soviet Union...
empires, looked to the West, particularly France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
, for its cultural, educational, military and administrative models. In 1916 Romania entered World War I
World War I
World War I , which was predominantly called the World War or the Great War from its occurrence until 1939, and the First World War or World War I thereafter, was a major war centred in Europe that began on 28 July 1914 and lasted until 11 November 1918...
on the Entente
Allies of World War I
The Entente Powers were the countries at war with the Central Powers during World War I. The members of the Triple Entente were the United Kingdom, France, and the Russian Empire; Italy entered the war on their side in 1915...
side, after the Entente agreed to recognize Romanian rights over Transylvania, which was part of Austria-Hungary until that time.
In August 1914, when World War I
World War I
World War I , which was predominantly called the World War or the Great War from its occurrence until 1939, and the First World War or World War I thereafter, was a major war centred in Europe that began on 28 July 1914 and lasted until 11 November 1918...
broke out, Romania declared neutrality
Neutral country
A neutral power in a particular war is a sovereign state which declares itself to be neutral towards the belligerents. A non-belligerent state does not need to be neutral. The rights and duties of a neutral power are defined in Sections 5 and 13 of the Hague Convention of 1907...
. Two years later, under the pressure of Allies (especially France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
desperate to open a new front), on August 14/27 1916 it joined the Allies, for which they were promised support for the accomplishment of national unity, Romania declared war on Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary , more formally known as the Kingdoms and Lands Represented in the Imperial Council and the Lands of the Holy Hungarian Crown of Saint Stephen, was a constitutional monarchic union between the crowns of the Austrian Empire and the Kingdom of Hungary in...
.
The Romanian military campaign
Romanian Campaign (World War I)
The Romanian Campaign was part of the Balkan theatre of World War I, with Romania and Russia allied against the armies of the Central Powers. Fighting took place from August 1916 to December 1917, across most of present-day Romania, including Transylvania, which was part of the Austro-Hungarian...
ended in disaster for Romania as the Central Powers
Central Powers
The Central Powers were one of the two warring factions in World War I , composed of the German Empire, the Austro-Hungarian Empire, the Ottoman Empire, and the Kingdom of Bulgaria...
conquered two-thirds of the country and captured or killed the majority of its army within four months. Nevertheless, Moldova
Moldova
Moldova , officially the Republic of Moldova is a landlocked state in Eastern Europe, located between Romania to the West and Ukraine to the North, East and South. It declared itself an independent state with the same boundaries as the preceding Moldavian Soviet Socialist Republic in 1991, as part...
remained in Romanian hands after the invading forces were stopped in 1917. In May 1918, Romania was in no position to continue the war, and negotiated a peace treaty with Germany
German Empire
The German Empire refers to Germany during the "Second Reich" period from the unification of Germany and proclamation of Wilhelm I as German Emperor on 18 January 1871, to 1918, when it became a federal republic after defeat in World War I and the abdication of the Emperor, Wilhelm II.The German...
(see Treaty of Bucharest, 1918
Treaty of Bucharest, 1918
The Treaty of Bucharest was a peace treaty which the German Empire forced Romania to sign on 7 May 1918 following the Romanian campaign of 1916-1917.-Main terms of the treaty:...
). In October 1918, Romania joined the war again and by the end of the war, the Austro-Hungarian and Russian empires had disintegrated; governing bodies created by the Romanians of Transylvania, Bessarabia and Bukovina chose union with the Kingdom of Romania
Kingdom of Romania
The Kingdom of Romania was the Romanian state based on a form of parliamentary monarchy between 13 March 1881 and 30 December 1947, specified by the first three Constitutions of Romania...
, resulting in Greater Romania
Greater Romania
The Greater Romania generally refers to the territory of Romania in the years between the First World War and the Second World War, the largest geographical extent of Romania up to that time and its largest peacetime extent ever ; more precisely, it refers to the territory of the Kingdom of...
.
and since by the war's end, Austria-Hungary and the Russian Empire had collapsed, Bessarabia
Bessarabia
Bessarabia is a historical term for the geographic region in Eastern Europe bounded by the Dniester River on the east and the Prut River on the west....
, Bukovina
Bukovina
Bukovina is a historical region on the northern slopes of the northeastern Carpathian Mountains and the adjoining plains.-Name:The name Bukovina came into official use in 1775 with the region's annexation from the Principality of Moldavia to the possessions of the Habsburg Monarchy, which became...
and Transylvania
Transylvania
Transylvania is a historical region in the central part of Romania. Bounded on the east and south by the Carpathian mountain range, historical Transylvania extended in the west to the Apuseni Mountains; however, the term sometimes encompasses not only Transylvania proper, but also the historical...
were allowed to unite with the Kingdom of Romania
Kingdom of Romania
The Kingdom of Romania was the Romanian state based on a form of parliamentary monarchy between 13 March 1881 and 30 December 1947, specified by the first three Constitutions of Romania...
in 1918. By the 1920 Treaty of Trianon
Treaty of Trianon
The Treaty of Trianon was the peace agreement signed in 1920, at the end of World War I, between the Allies of World War I and Hungary . The treaty greatly redefined and reduced Hungary's borders. From its borders before World War I, it lost 72% of its territory, which was reduced from to...
, Hungary
Hungary
Hungary , officially the Republic of Hungary , is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is situated in the Carpathian Basin and is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine and Romania to the east, Serbia and Croatia to the south, Slovenia to the southwest and Austria to the west. The...
renounced in favour of Romania all the claims of the Austro-Hungarian Monarchy over Transylvania
Transylvania
Transylvania is a historical region in the central part of Romania. Bounded on the east and south by the Carpathian mountain range, historical Transylvania extended in the west to the Apuseni Mountains; however, the term sometimes encompasses not only Transylvania proper, but also the historical...
. The union of Romania with Bukovina
Bukovina
Bukovina is a historical region on the northern slopes of the northeastern Carpathian Mountains and the adjoining plains.-Name:The name Bukovina came into official use in 1775 with the region's annexation from the Principality of Moldavia to the possessions of the Habsburg Monarchy, which became...
was ratified in 1919 in the Treaty of Saint Germain, and with Bessarabia
Bessarabia
Bessarabia is a historical term for the geographic region in Eastern Europe bounded by the Dniester River on the east and the Prut River on the west....
in 1920 by the Treaty of Paris
Treaty of Paris (1920)
The 1920 Treaty of Paris was an act signed by Romania and the principal Allied Powers of the time whose purpose was the recognition of Romanian sovereignty over Bessarabia...
.
Greater Romania
1918–1940
Greater Romania
The Greater Romania generally refers to the territory of Romania in the years between the First World War and the Second World War, the largest geographical extent of Romania up to that time and its largest peacetime extent ever ; more precisely, it refers to the territory of the Kingdom of...
(literal translation "Great Romania", but more commonly rendered "Greater Romania") generally refers to the Romanian state in the interwar period
Interwar period
Interwar period can refer to any period between two wars. The Interbellum is understood to be the period between the end of the Great War or First World War and the beginning of the Second World War in Europe....
, and by extension, to the territory Romania covered at the time (see map). Romania achieved at that time its greatest territorial extent (almost 300000 km² (115,830.6 sq mi)), managing to unite all the historic Romanian lands. Historically, Greater Romania—România Mare—represented one of the ideals of Romanian nationalism
Nationalism
Nationalism is a political ideology that involves a strong identification of a group of individuals with a political entity defined in national terms, i.e. a nation. In the 'modernist' image of the nation, it is nationalism that creates national identity. There are various definitions for what...
. Greater Romania is still seen by many as a "paradise lost", often by comparison with the "stunted" Communist Romania
Communist Romania
Communist Romania was the period in Romanian history when that country was a Soviet-aligned communist state in the Eastern Bloc, with the dominant role of Romanian Communist Party enshrined in its successive constitutions...
. To exploit the nationalistic connotation of the term, a nationalist political party
Greater Romania Party
The Greater Romania Party is a Romanian radical right-wing, ultra-nationalist political party, led by Corneliu Vadim Tudor. The party is sometimes referred to in English as the Great Romania Party....
uses it as its name.
In 1918, at the end of World War I
World War I
World War I , which was predominantly called the World War or the Great War from its occurrence until 1939, and the First World War or World War I thereafter, was a major war centred in Europe that began on 28 July 1914 and lasted until 11 November 1918...
, Transylvania and Bessarabia united with the Romanian Old Kingdom
Romanian Old Kingdom
The Romanian Old Kingdom is a colloquial term referring to the territory covered by the first independent Romanian nation state, which was composed of the Danubian Principalities—Wallachia and Moldavia...
. The Deputies of the Romanians from Transylvania voted to unite their region by the Proclamation of Union of Alba Iulia
Alba Iulia
Alba Iulia is a city in Alba County, Transylvania, Romania with a population of 66,747, located on the Mureş River. Since the High Middle Ages, the city has been the seat of Transylvania's Roman Catholic diocese. Between 1541 and 1690 it was the capital of the Principality of Transylvania...
. Bessarabia, having declared its independence from Russia in 1917 by the Conference of the Country (Sfatul Țării
Sfatul Tarii
Sfatul Țării was, in 1917-1918, the National Assembly of the Governorate of Bessarabia of the disintegrating Russian Empire, which proclaimed the independent Moldavian Democratic Republic in December 1917, and then union with Romania in April 1918.-Russian participation in World War I:In August...
), called in Romanian troops to protect the province from the Bolshevik
Bolshevik
The Bolsheviks, originally also Bolshevists , derived from bol'shinstvo, "majority") were a faction of the Marxist Russian Social Democratic Labour Party which split apart from the Menshevik faction at the Second Party Congress in 1903....
s who were spreading the Russian Revolution
Russian Revolution of 1917
The Russian Revolution is the collective term for a series of revolutions in Russia in 1917, which destroyed the Tsarist autocracy and led to the creation of the Soviet Union. The Tsar was deposed and replaced by a provisional government in the first revolution of February 1917...
. The union of the regions of Transylvania, Maramureș
Maramures
Maramureș may refer to the following:*Maramureș, a geographical, historical, and ethno-cultural region in present-day Romania and Ukraine, that occupies the Maramureș Depression and Maramureș Mountains, a mountain range in North East Carpathians...
, Crișana
Crisana
Crișana is a geographical and historical region divided today between Romania and Hungary, named after the Criș River and its three tributaries: the Crișul Alb, Crișul Negru and Crișul Repede....
and Banat
Banat
The Banat is a geographical and historical region in Central Europe currently divided between three countries: the eastern part lies in western Romania , the western part in northeastern Serbia , and a small...
with the Old Kingdom of Romania was ratified in 1920 by the Treaty of Trianon
Treaty of Trianon
The Treaty of Trianon was the peace agreement signed in 1920, at the end of World War I, between the Allies of World War I and Hungary . The treaty greatly redefined and reduced Hungary's borders. From its borders before World War I, it lost 72% of its territory, which was reduced from to...
, which recognised the sovereignty of Romania over these regions and settled the border between the independent Republic of Hungary and the Kingdom of Romania. The union of Bucovina and Bessarabia with Romania was ratified in 1920 by the Treaty of Versailles
Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles was one of the peace treaties at the end of World War I. It ended the state of war between Germany and the Allied Powers. It was signed on 28 June 1919, exactly five years after the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand. The other Central Powers on the German side of...
. Romania had also recently acquired the Southern Dobruja
Southern Dobruja
Southern Dobruja is an area of north-eastern Bulgaria comprising the administrative districts named for its two principal cities of Dobrich and Silistra...
territory called "The Quadrilateral" from Bulgaria
Bulgaria
Bulgaria , officially the Republic of Bulgaria , is a parliamentary democracy within a unitary constitutional republic in Southeast Europe. The country borders Romania to the north, Serbia and Macedonia to the west, Greece and Turkey to the south, as well as the Black Sea to the east...
as a result of its participation in the Second Balkan War
Second Balkan War
The Second Balkan War was a conflict which broke out when Bulgaria, dissatisfied with its share of the spoils of the First Balkan War, attacked its former allies, Serbia and Greece, on 29 June 1913. Bulgaria had a prewar agreement about the division of region of Macedonia...
in 1913.


Bulgarians
The Bulgarians are a South Slavic nation and ethnic group native to Bulgaria and neighbouring regions. Emigration has resulted in immigrant communities in a number of other countries.-History and ethnogenesis:...
, etc., for a total of about 28% of the population (Magyars mostly in Transylvania; Germans in Transylvania, Bukovina, and Banat; Ukrainians in part of Bessarabia and Bukovina, Bulgarians in Dobrudja). Recognized by the Romanian Constitution of 1923
1923 Constitution of Romania
The 1923 Constitution of Romania, also called the Constitution of Union, was intended to align the organisation of the state on the basis of universal male suffrage and the new realities that arose after the Great Union of 1918. Four draft constitutions existed: one belonging to the National...
and supported by various laws (education, electoral, etc.), national minorities were represented in Parliament, and several of them created national parties (the Magyars in 1922, the Germans in 1929, the Jews in 1931), although a unique standing of minorities with autonomy on a wide basis, provided for at the assembly of Transylvanian Romanians on 1 December 1918 were not fulfilled.
Two periods can be identified in Romania between the two World Wars. From 1918 to 1938, Romania was a liberal
Liberalism
Liberalism is the belief in the importance of liberty and equal rights. Liberals espouse a wide array of views depending on their understanding of these principles, but generally, liberals support ideas such as constitutionalism, liberal democracy, free and fair elections, human rights,...
constitutional monarchy
Constitutional monarchy
Constitutional monarchy is a form of government in which a monarch acts as head of state within the parameters of a constitution, whether it be a written, uncodified or blended constitution...
, but one facing the rise of the nationalist, anti-semitic
Anti-Semitism
Antisemitism is suspicion of, hatred toward, or discrimination against Jews for reasons connected to their Jewish heritage. According to a 2005 U.S...
parties, particularly Iron Guard
Iron Guard
The Iron Guard is the name most commonly given to a far-right movement and political party in Romania in the period from 1927 into the early part of World War II. The Iron Guard was ultra-nationalist, fascist, anti-communist, and promoted the Orthodox Christian faith...
, which won about 15% of the votes in the general elections of 1937. From 1938 to 1944, Romania was a dictatorship. The first dictator was King Carol II
Carol II of Romania
Carol II reigned as King of Romania from 8 June 1930 until 6 September 1940. Eldest son of Ferdinand, King of Romania, and his wife, Queen Marie, a daughter of Prince Alfred, Duke of Edinburgh, the second eldest son of Queen Victoria...
, who abolished the parliamentary regime and ruled with his camarilla.

Soviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
signed the Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact
Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact
The Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact, named after the Soviet foreign minister Vyacheslav Molotov and the German foreign minister Joachim von Ribbentrop, was an agreement officially titled the Treaty of Non-Aggression between Germany and the Soviet Union and signed in Moscow in the late hours of 23 August 1939...
, which stipulated, amongst other things, the Soviet "interest" in Bessarabia. Following the severe territorial losses of 1940 (see next section), Carol was forced to abdicate, replaced as king by his son Mihai, but the power was taken by the military dictator Ion Antonescu
Ion Antonescu
Ion Victor Antonescu was a Romanian soldier, authoritarian politician and convicted war criminal. The Prime Minister and Conducător during most of World War II, he presided over two successive wartime dictatorships...
(initially in conjunction with the Iron Guard). In August 1944, Antonescu was arrested by Mihai.
World War II
1940–1947During the Second World War, Romania tried again to remain neutral, but on June 28, 1940, it received a Soviet ultimatum with an implied threat of invasion
Invasion
An invasion is a military offensive consisting of all, or large parts of the armed forces of one geopolitical entity aggressively entering territory controlled by another such entity, generally with the objective of either conquering, liberating or re-establishing control or authority over a...
in the event of non-compliance. Under pressure from Moscow
Moscow
Moscow is the capital, the most populous city, and the most populous federal subject of Russia. The city is a major political, economic, cultural, scientific, religious, financial, educational, and transportation centre of Russia and the continent...
and Berlin
Berlin
Berlin is the capital city of Germany and is one of the 16 states of Germany. With a population of 3.45 million people, Berlin is Germany's largest city. It is the second most populous city proper and the seventh most populous urban area in the European Union...
, the Romanian administration and the army were forced to retreat from Bessarabia
Bessarabia
Bessarabia is a historical term for the geographic region in Eastern Europe bounded by the Dniester River on the east and the Prut River on the west....
as well from Northern Bukovina to avoid war. This, in combination with other factors, prompted the government to join the Axis. Thereafter, southern Dobruja
Dobruja
Dobruja is a historical region shared by Bulgaria and Romania, located between the lower Danube river and the Black Sea, including the Danube Delta, Romanian coast and the northernmost part of the Bulgarian coast...
was awarded to Bulgaria, while Hungary received Northern Transylvania
Northern Transylvania
Northern Transylvania is a region of Transylvania, situated within the territory of Romania. The population is largely composed of both ethnic Romanians and Hungarians, and the region has been part of Romania since 1918 . During World War II, as a consequence of the territorial agreement known as...
as result of an Axis arbitration.
In 1940, Romania lost territory in both east and west: In June 1940, after receiving an ultimatum from the Soviet Union
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
, Romania ceded Bessarabia
Bessarabia
Bessarabia is a historical term for the geographic region in Eastern Europe bounded by the Dniester River on the east and the Prut River on the west....
and northern Bukovina
Bukovina
Bukovina is a historical region on the northern slopes of the northeastern Carpathian Mountains and the adjoining plains.-Name:The name Bukovina came into official use in 1775 with the region's annexation from the Principality of Moldavia to the possessions of the Habsburg Monarchy, which became...
(see Soviet occupation of Bessarabia). Two thirds of Bessarabia were combined with a small part of the USSR to form the Moldavian SSR
Moldavian SSR
The Moldavian Soviet Socialist Republic , commonly abbreviated to Moldavian SSR or MSSR, was one of the 15 republics of the Soviet Union...
. Northern Bukovina and Budjak
Budjak
Budjak or Budzhak is a historical region in the Odessa Oblast of Ukraine. Lying along the Black Sea between the Danube and Dniester rivers this multiethnic region was the southern part of Bessarabia...
were apportioned to the Ukrainian SSR
Ukrainian SSR
The Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic or in short, the Ukrainian SSR was a sovereign Soviet Socialist state and one of the fifteen constituent republics of the Soviet Union lasting from its inception in 1922 to the breakup in 1991...
. In August 1940, Northern Transylvania
Northern Transylvania
Northern Transylvania is a region of Transylvania, situated within the territory of Romania. The population is largely composed of both ethnic Romanians and Hungarians, and the region has been part of Romania since 1918 . During World War II, as a consequence of the territorial agreement known as...
was awarded to Hungary by Germany
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
and Italy
Italy
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
through the Second Vienna Award
Second Vienna Award
The Second Vienna Award was the second of two Vienna Awards arbitrated by the Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy. Rendered on August 30, 1940, it re-assigned the territory of Northern Transylvania from Romania to Hungary.-Prelude and historical background :After the World War I, the multi-ethnic...
. Southern Dobruja
Southern Dobruja
Southern Dobruja is an area of north-eastern Bulgaria comprising the administrative districts named for its two principal cities of Dobrich and Silistra...
was also lost to Bulgaria shortly after Carol's abdication.
Because Carol II lost so much territory through failed diplomacy, the army supported seizure of power by General Ion Antonescu
Ion Antonescu
Ion Victor Antonescu was a Romanian soldier, authoritarian politician and convicted war criminal. The Prime Minister and Conducător during most of World War II, he presided over two successive wartime dictatorships...
. For four months (the period of the National Legionary State
National Legionary State
The National Legionary State was the Romanian government from September 6, 1940 to January 23, 1941. It was a single-party regime dictatorship dominated by the overtly fascist Iron Guard in uneasy conjunction with the head of government and Conducător Ion Antonescu, the leader of the Romanian...
), he had to share power with the Iron Guard, but the latter overplayed their hand in January 1941
Legionnaires' Rebellion and Bucharest Pogrom
The Legionnaires' rebellion and the Bucharest pogrom occurred in Bucharest, Romania, between 21 and 23 January 1941.As the privileges of the Iron Guard were being cut off by Conducător Ion Antonescu, members of the Iron Guard, also known as the Legionnaires, revolted...
and were suppressed. Romania entered World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
under the command of the German Wehrmacht
Wehrmacht
The Wehrmacht – from , to defend and , the might/power) were the unified armed forces of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It consisted of the Heer , the Kriegsmarine and the Luftwaffe .-Origin and use of the term:...
in June 1941, declaring war to the Soviet Union in order to recover Bessarabia and northern Bukovina. Romania was awarded the territory between Dniester
Dniester
The Dniester is a river in Eastern Europe. It runs through Ukraine and Moldova and separates most of Moldova's territory from the breakaway de facto state of Transnistria.-Names:...
and the Southern Bug
Southern Bug
The Southern Bug, also called Southern Buh), is a river located in Ukraine. The source of the river is in the west of Ukraine, in the Volyn-Podillia Upland, about 145 km from the Polish border, and flows southeasterly into the Bug Estuary through the southern steppes...
by Germany to administer it under the name of Transnistria
Transnistria (World War II)
Transnistria Governorate was a Romanian administered territory, conquered by the Axis Powers from the Soviet Union during Operation Barbarossa, and occupied from 19 August 1941 to 29 January 1944...
.

Carol II of Romania
Carol II reigned as King of Romania from 8 June 1930 until 6 September 1940. Eldest son of Ferdinand, King of Romania, and his wife, Queen Marie, a daughter of Prince Alfred, Duke of Edinburgh, the second eldest son of Queen Victoria...
abdicated in 1940, succeeded by the National Legionary State
National Legionary State
The National Legionary State was the Romanian government from September 6, 1940 to January 23, 1941. It was a single-party regime dictatorship dominated by the overtly fascist Iron Guard in uneasy conjunction with the head of government and Conducător Ion Antonescu, the leader of the Romanian...
, in which power was shared by Ion Antonescu
Ion Antonescu
Ion Victor Antonescu was a Romanian soldier, authoritarian politician and convicted war criminal. The Prime Minister and Conducător during most of World War II, he presided over two successive wartime dictatorships...
and the Iron Guard
Iron Guard
The Iron Guard is the name most commonly given to a far-right movement and political party in Romania in the period from 1927 into the early part of World War II. The Iron Guard was ultra-nationalist, fascist, anti-communist, and promoted the Orthodox Christian faith...
. Within months, Antonescu had crushed the Iron Guard
Iron Guard
The Iron Guard is the name most commonly given to a far-right movement and political party in Romania in the period from 1927 into the early part of World War II. The Iron Guard was ultra-nationalist, fascist, anti-communist, and promoted the Orthodox Christian faith...
, and the subsequent year Romania entered the war on the side of the Axis powers. During the war, Romania was the most important source of oil for Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany , also known as the Third Reich , but officially called German Reich from 1933 to 1943 and Greater German Reich from 26 June 1943 onward, is the name commonly used to refer to the state of Germany from 1933 to 1945, when it was a totalitarian dictatorship ruled by...
, prompting multiple bombing raids by the Allies
Allies
In everyday English usage, allies are people, groups, or nations that have joined together in an association for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out between them...
. By means of the Axis invasion of the Soviet Union
Operation Barbarossa
Operation Barbarossa was the code name for Germany's invasion of the Soviet Union during World War II that began on 22 June 1941. Over 4.5 million troops of the Axis powers invaded the USSR along a front., the largest invasion in the history of warfare...
, Romania recovered Bessarabia and northern Bukovina from the Soviet Russia, under the leadership of general Ion Antonescu
Ion Antonescu
Ion Victor Antonescu was a Romanian soldier, authoritarian politician and convicted war criminal. The Prime Minister and Conducător during most of World War II, he presided over two successive wartime dictatorships...
.
The Antonescu regime played a major role in the Holocaust, following to a lesser extent the Nazi policy of oppression and massacre of the Jews, and Romas, primarily in the Eastern territories Romania recovered or occupied from the Soviet Union (Transnistria
Transnistria (World War II)
Transnistria Governorate was a Romanian administered territory, conquered by the Axis Powers from the Soviet Union during Operation Barbarossa, and occupied from 19 August 1941 to 29 January 1944...
) and in Moldavia
Moldavia
Moldavia is a geographic and historical region and former principality in Eastern Europe, corresponding to the territory between the Eastern Carpathians and the Dniester river...
. According to an international commission report
Wiesel Commission
The Wiesel Commission is the common name given to the International Commission on the Holocaust in Romania, which was established by former President Ion Iliescu in October 2003 to research and create a report on the actual history of the Holocaust in Romania and make specific recommendations for...
released by the Romanian government in 2004, Antonescu's dictatorial government of Romania is responsible for the murder in various forms (including deportations to concentration camps and executions by the Romanian Army and Gendarmerie and the German Einsatzgruppen
Einsatzgruppen
Einsatzgruppen were SS paramilitary death squads that were responsible for mass killings, typically by shooting, of Jews in particular, but also significant numbers of other population groups and political categories...
), between 280,000 to 380,000 Jews in Romania and in the war zone of Bessarabia
Bessarabia
Bessarabia is a historical term for the geographic region in Eastern Europe bounded by the Dniester River on the east and the Prut River on the west....
, Bukovina
Bukovina
Bukovina is a historical region on the northern slopes of the northeastern Carpathian Mountains and the adjoining plains.-Name:The name Bukovina came into official use in 1775 with the region's annexation from the Principality of Moldavia to the possessions of the Habsburg Monarchy, which became...
and Transnistria.
.png)
Michael I of Romania
Michael was the last King of Romania. He reigned from 20 July 1927 to 8 June 1930, and again from 6 September 1940 until 30 December 1947 when he was forced, by the Communist Party of Romania , to abdicate to the Soviet armies of occupation...
who joined the Allies
Allies of World War II
The Allies of World War II were the countries that opposed the Axis powers during the Second World War . Former Axis states contributing to the Allied victory are not considered Allied states...
and declared war on Germany. On 31 August 1944 the Soviet Red Army entered Bucharest. Despite Romania`s change of sides its role in the defeat of Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany , also known as the Third Reich , but officially called German Reich from 1933 to 1943 and Greater German Reich from 26 June 1943 onward, is the name commonly used to refer to the state of Germany from 1933 to 1945, when it was a totalitarian dictatorship ruled by...
was not recognized by the Paris Peace Conference
Paris Peace Treaties, 1947
The Paris Peace Conference resulted in the Paris Peace Treaties signed on February 10, 1947. The victorious wartime Allied powers negotiated the details of treaties with Italy, Romania, Hungary, Bulgaria, and Finland .The...
of 1947. With the Red Army
Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army started out as the Soviet Union's revolutionary communist combat groups during the Russian Civil War of 1918-1922. It grew into the national army of the Soviet Union. By the 1930s the Red Army was among the largest armies in history.The "Red Army" name refers to...
forces still stationed in the country and exerting de facto control, Communists
Communism
Communism is a social, political and economic ideology that aims at the establishment of a classless, moneyless, revolutionary and stateless socialist society structured upon common ownership of the means of production...
and their allied parties claimed 80% of the vote, through a combination of vote manipulation, elimination, and forced mergers of competing parties, thus establishing themselves as the dominant force. Romania suffered additional heavy casualties fighting the Nazi
Nazism
Nazism, the common short form name of National Socialism was the ideology and practice of the Nazi Party and of Nazi Germany...
Army in Hungary and Czechoslovakia
Czechoslovakia
Czechoslovakia or Czecho-Slovakia was a sovereign state in Central Europe which existed from October 1918, when it declared its independence from the Austro-Hungarian Empire, until 1992...
. By the end of the war, the Romanian army had suffered about 300,000 casualties.
The Paris Peace Treaty
Paris Peace Treaties, 1947
The Paris Peace Conference resulted in the Paris Peace Treaties signed on February 10, 1947. The victorious wartime Allied powers negotiated the details of treaties with Italy, Romania, Hungary, Bulgaria, and Finland .The...
at the end of World War II rendered the Vienna Awards void: Northern Transylvania
Northern Transylvania
Northern Transylvania is a region of Transylvania, situated within the territory of Romania. The population is largely composed of both ethnic Romanians and Hungarians, and the region has been part of Romania since 1918 . During World War II, as a consequence of the territorial agreement known as...
returned to Romania, but Bessarabia
Bessarabia
Bessarabia is a historical term for the geographic region in Eastern Europe bounded by the Dniester River on the east and the Prut River on the west....
, northern Bukovina
Bukovina
Bukovina is a historical region on the northern slopes of the northeastern Carpathian Mountains and the adjoining plains.-Name:The name Bukovina came into official use in 1775 with the region's annexation from the Principality of Moldavia to the possessions of the Habsburg Monarchy, which became...
and southern Dobruja were not recovered. The Moldavian SSR became independent of the Soviet Union only with the latter's 1991 demise
Belavezha Accords
The Belavezha Accords is the agreement which declared the Soviet Union effectively dissolved and established the Commonwealth of Independent States in its place...
, becoming the Republic of Moldova.
Communist period

In 1947, King Michael I
Michael I of Romania
Michael was the last King of Romania. He reigned from 20 July 1927 to 8 June 1930, and again from 6 September 1940 until 30 December 1947 when he was forced, by the Communist Party of Romania , to abdicate to the Soviet armies of occupation...
was forced by the Communists to abdicate and leave the country, Romania was proclaimed a republic
Republic
A republic is a form of government in which the people, or some significant portion of them, have supreme control over the government and where offices of state are elected or chosen by elected people. In modern times, a common simplified definition of a republic is a government where the head of...
, and remained under direct military and economic control of the USSR
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
until the late 1950s. During this period, Romania's resources were drained by the "SovRom
SovRom
The SovRoms were economic enterprises established in Romania following the Communist takeover at the end of World War II, in place until 1954-1956 ....
" agreements: mixed Soviet-Romanian companies established to mask the looting of Romania by the Soviet Union.
Soviet occupation
Soviet occupation of Romania
The Soviet occupation of Romania refers to the period from 1944 to August 1958, during which the Soviet Union maintained a significant military presence in Romania...
following World War II led to the formation of a communist
Communism
Communism is a social, political and economic ideology that aims at the establishment of a classless, moneyless, revolutionary and stateless socialist society structured upon common ownership of the means of production...
People's Republic in 1947, and the abdication of King Michael, who went into exile. The leader of Romania from 1948 to his death in 1965 was Gheorghe Gheorghiu-Dej
Gheorghe Gheorghiu-Dej
Gheorghe Gheorghiu-Dej was the Communist leader of Romania from 1948 until his death in 1965.-Early life:Gheorghe was the son of a poor worker, Tănase Gheorghiu, and his wife Ana. Gheorghiu-Dej joined the Communist Party of Romania in 1930...
, the First Secretary
General Secretary
The office of general secretary is staffed by the chief officer of:*The General Secretariat for Macedonia and Thrace, a government agency for the Greek regions of Macedonia and Thrace...
of the Romanian Workers' Party, who first sowed the seeds of greater independence from the Soviet Union by persuading Soviet First Secretary Nikita Khrushchev to withdraw troops from Romania in April 1958.
After the negotiated retreat of Soviet troops, Romania, under the new leadership of Nicolae Ceauşescu
Nicolae Ceausescu
Nicolae Ceaușescu was a Romanian Communist politician. He was General Secretary of the Romanian Communist Party from 1965 to 1989, and as such was the country's second and last Communist leader...
, started to pursue independent policies. Such examples are the condemnation of the Soviet-led 1968 invasion of Czechoslovakia
Czechoslovakia
Czechoslovakia or Czecho-Slovakia was a sovereign state in Central Europe which existed from October 1918, when it declared its independence from the Austro-Hungarian Empire, until 1992...
(being the only Warsaw Pact
Warsaw Pact
The Warsaw Treaty Organization of Friendship, Cooperation, and Mutual Assistance , or more commonly referred to as the Warsaw Pact, was a mutual defense treaty subscribed to by eight communist states in Eastern Europe...
country not to take part in the invasion), the continuation of diplomatic relations with Israel
Israel
The State of Israel is a parliamentary republic located in the Middle East, along the eastern shore of the Mediterranean Sea...
after the Six-Day War
Six-Day War
The Six-Day War , also known as the June War, 1967 Arab-Israeli War, or Third Arab-Israeli War, was fought between June 5 and 10, 1967, by Israel and the neighboring states of Egypt , Jordan, and Syria...
of 1967 (again, the only Warsaw Pact
Warsaw Pact
The Warsaw Treaty Organization of Friendship, Cooperation, and Mutual Assistance , or more commonly referred to as the Warsaw Pact, was a mutual defense treaty subscribed to by eight communist states in Eastern Europe...
country to do so), the establishment of economic (1963) and diplomatic (1967) relations with the Federal Republic of Germany
West Germany
West Germany is the common English, but not official, name for the Federal Republic of Germany or FRG in the period between its creation in May 1949 to German reunification on 3 October 1990....
, and so forth. Also, close ties with the Arab
Arab
Arab people, also known as Arabs , are a panethnicity primarily living in the Arab world, which is located in Western Asia and North Africa. They are identified as such on one or more of genealogical, linguistic, or cultural grounds, with tribal affiliations, and intra-tribal relationships playing...
countries (and the PLO) allowed Romania to play a key role in the Israel
Israel
The State of Israel is a parliamentary republic located in the Middle East, along the eastern shore of the Mediterranean Sea...
-Egypt
Egypt
Egypt , officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, Arabic: , is a country mainly in North Africa, with the Sinai Peninsula forming a land bridge in Southwest Asia. Egypt is thus a transcontinental country, and a major power in Africa, the Mediterranean Basin, the Middle East and the Muslim world...
and Israel-PLO peace processes by intermediating the visit of Sadat
Sadat
- See also :* Anwar Sadat, former President of Egypt* Sadat * Saadat* Sadat. Term also used for the descendents of Holy Prophet Muhammad through Imam Ali and Bibi Fatima progeny....
in Israel. As Romania's foreign debt sharply increased between 1977 and 1981 (from 3 to 10 billion US dollars), the influence of international financial organisations such as the IMF or the World Bank
World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans to developing countries for capital programmes.The World Bank's official goal is the reduction of poverty...
grew, conflicting with Nicolae Ceauşescu
Nicolae Ceausescu
Nicolae Ceaușescu was a Romanian Communist politician. He was General Secretary of the Romanian Communist Party from 1965 to 1989, and as such was the country's second and last Communist leader...
's autarchic
Autarky
Autarky is the quality of being self-sufficient. Usually the term is applied to political states or their economic policies. Autarky exists whenever an entity can survive or continue its activities without external assistance. Autarky is not necessarily economic. For example, a military autarky...
policies. Ceauşescu eventually initiated a project of total reimbursement of the foreign debt (completed in 1989, shortly before his overthrow). To achieve this goal, he imposed policies that impoverished Romanians and exhausted the Romanian economy. He greatly extended the authority police state
Securitate
The Securitate was the secret police agency of Communist Romania. Previously, the Romanian secret police was called Siguranţa Statului. Founded on August 30, 1948, with help from the Soviet NKVD, the Securitate was abolished in December 1989, shortly after President Nicolae Ceaușescu was...
and imposed a cult of personality
Cult of personality
A cult of personality arises when an individual uses mass media, propaganda, or other methods, to create an idealized and heroic public image, often through unquestioning flattery and praise. Cults of personality are usually associated with dictatorships...
. These led to a dramatic decrease in Ceauşescu-popularity and culminated in his overthrow and execution in the bloody Romanian Revolution of 1989
Romanian Revolution of 1989
The Romanian Revolution of 1989 was a series of riots and clashes in December 1989. These were part of the Revolutions of 1989 that occurred in several Warsaw Pact countries...
.
Seduced by Ceauşescu's "Independent" foreign policy, Western leaders were slow to turn against a regime that, by the late 1970s, had become increasingly arbitrary, capricious and harsh. Rapid economic growth fueled by foreign credits gradually gave way to wrenching austerity and severe political repression, which became increasingly draconian through the 1980s. During the 1947–1962 period, many people were arbitrarily killed or imprisoned for political, economic or unknown reasons: detainees in prisons or camps, deported, persons under house arrest, and administrative detainees. There were hundreds of thousands of abuses, deaths and incidents of torture against a large range of people, from political opponents to ordinary citizens. Between 60,000 and 80,000 political prisoners were detained as psychiatric patients and treated in some of the most sadistic ways by doctors. It is estimated that, in total, two million people were direct victims of Communism's repression.
1989 Revolution
The Romanian Revolution of 1989Romanian Revolution of 1989
The Romanian Revolution of 1989 was a series of riots and clashes in December 1989. These were part of the Revolutions of 1989 that occurred in several Warsaw Pact countries...
resulted in more than 1,000 deaths in Timişoara
Timisoara
Timișoara is the capital city of Timiș County, in western Romania. One of the largest Romanian cities, with an estimated population of 311,586 inhabitants , and considered the informal capital city of the historical region of Banat, Timișoara is the main social, economic and cultural center in the...
and Bucharest
Bucharest
Bucharest is the capital municipality, cultural, industrial, and financial centre of Romania. It is the largest city in Romania, located in the southeast of the country, at , and lies on the banks of the Dâmbovița River....
, and brought about the fall of Ceauşescu and the end of the Communist regime in Romania. After a weeklong state of unrest in Timişoara, a mass rally summoned in Bucharest in support of Ceauşescu on December 21, 1989 turned hostile. The Ceauşescu couple, fleeing Bucharest by helicopter, ended up in the custody of the army. After being tried and convicted by a kangaroo court
Kangaroo court
A kangaroo court is "a mock court in which the principles of law and justice are disregarded or perverted".The outcome of a trial by kangaroo court is essentially determined in advance, usually for the purpose of ensuring conviction, either by going through the motions of manipulated procedure or...
for genocide
Genocide
Genocide is defined as "the deliberate and systematic destruction, in whole or in part, of an ethnic, racial, religious, or national group", though what constitutes enough of a "part" to qualify as genocide has been subject to much debate by legal scholars...
and other crimes, they were executed on December 25, 1989. The events of this revolution remain to this day a matter of debate, with many conflicting theories as to the motivations and even actions of some of the main players.
Ion Iliescu
Ion Iliescu
Ion Iliescu served as President of Romania from 1990 until 1996, and from 2000 until 2004. From 1996 to 2000 and from 2004 until his retirement in 2008, Iliescu was a Senator for the Social Democratic Party , whose honorary president he remains....
, a former Communist Party official marginalized by Ceauşescu, attained national recognition as the leader of an impromptu governing coalition, the National Salvation Front (FSN) that proclaimed the restoration of democracy and civil liberties on December 22, 1989. The Communist Party was initially outlawed by Ion Iliescu, but he soon revoked that decision; as a consequence, Communism is not outlawed in Romania today. However, Ceauşescu's most unpopular measures, such as bans on abortion
Abortion
Abortion is defined as the termination of pregnancy by the removal or expulsion from the uterus of a fetus or embryo prior to viability. An abortion can occur spontaneously, in which case it is usually called a miscarriage, or it can be purposely induced...
and contraception
Contraception
Contraception is the prevention of the fusion of gametes during or after sexual activity. The term contraception is a contraction of contra, which means against, and the word conception, meaning fertilization...
, were among the first laws to be changed after the Revolution, and their legality has not been questioned since then.
Transition to free market
(1990–2004)After the fall of Ceauşescu, the National Salvation Front (FSN), led by Ion Iliescu
Ion Iliescu
Ion Iliescu served as President of Romania from 1990 until 1996, and from 2000 until 2004. From 1996 to 2000 and from 2004 until his retirement in 2008, Iliescu was a Senator for the Social Democratic Party , whose honorary president he remains....
, took partial multi-party democratic and free market measures. Several major political parties of the pre-war era, such as the National Christian Democrat Peasant's Party (PNŢCD)
Christian-Democratic National Peasants' Party (Romania)
The Christian-Democratic National Peasants' Party is a Romanian Christian-Democratic party...
, the National Liberal Party (PNL)
National Liberal Party (Romania)
The National Liberal Party , abbreviated to PNL, is a centre-right liberal party in Romania. It is the third-largest party in the Romanian Parliament, with 53 seats in the Chamber of Deputies and 22 in the Senate: behind the centre-right Democratic Liberal Party and the centre-left Social...
and the Romanian Social Democrat Party (PSDR) were resurrected. After several major political rallies (especially in January), in April 1990, a sit-in protest contesting the results of the recently held parliamentary elections began in University Square, Bucharest
University Square, Bucharest
University Square is located in downtown Bucharest, near the University of Bucharest.Four statues are located in the University Square, in front of the University; they depict Ion Heliade Rădulescu , Michael the Brave , Gheorghe Lazăr and Spiru Haret .The square was the site of the 1990 Golaniad,...
. The protesters accused the FSN of being made up of former Communists and members of the Securitate
Securitate
The Securitate was the secret police agency of Communist Romania. Previously, the Romanian secret police was called Siguranţa Statului. Founded on August 30, 1948, with help from the Soviet NKVD, the Securitate was abolished in December 1989, shortly after President Nicolae Ceaușescu was...
. The protesters did not recognize the results of the election, which they deemed undemocratic, and were asking for the exclusion from the political life of the former high-ranking Communist Party members. The protest rapidly grew to become an ongoing mass demonstration (known as the Golaniad
Golaniad
The Golaniad was a protest in Romania in the University Square, Bucharest. It was initiated by students and professors at the University of Bucharest....
). The peaceful demonstrations degenerated into violence, with some of the protesters attacking the police headquarters, national television station, and the Foreign Ministry. After the police failed to bring the demonstrators to order, Ion Iliescu
Ion Iliescu
Ion Iliescu served as President of Romania from 1990 until 1996, and from 2000 until 2004. From 1996 to 2000 and from 2004 until his retirement in 2008, Iliescu was a Senator for the Social Democratic Party , whose honorary president he remains....
called on the "men of good will" to come and defend the State institutions in Bucharest. Various worker groups from Romania's industrial platforms responded, some of whom engaged in altercations with the protesters. But the most visible and politically influential were the coal miners of the Jiu Valley
Jiu River
Jiu is a river of southern Romania. It is formed near Petroşani by the junction of headwaters Jiul de Vest and Jiul de Est.It flows southward through the Romanian counties Hunedoara, Gorj and Dolj before flowing into the Danube a few kilometers upstream from the Bulgarian city of Oryahovo, 331...
. After representatives of the government met with leaders of the Jiu Valley coal miners union
League of Miners Unions of the Jiu Valley
The Miners Union League of the Jiu Valley represents the miners of the Jiu Valley.-Membership:...
, thousands of miners were organized and arrived in Bucharest June 14, transported on special trains provided by the government. Their violent intervention is remembered as the June 1990 Mineriad
June 1990 Mineriad
The June 1990 Mineriad was the suppression of an anti-National Salvation Front sit-in protests in Bucharest, Romania by the violent intervention of coal miners from the Jiu Valley, brought to Bucharest by the government to counter the rising violence of the protesters...
.
Presidential and parliamentary elections were held on May 20, 1990. Running against representatives of the re-established pre-war National Peasants' Party
National Peasants' Party
The National Peasants' Party was a Romanian political party, formed in 1926 through the fusion of the Romanian National Party from Transylvania and the Peasants' Party . It was in power between 1928 and 1933, with brief interruptions...
and National Liberal Party
National Liberal Party (Romania)
The National Liberal Party , abbreviated to PNL, is a centre-right liberal party in Romania. It is the third-largest party in the Romanian Parliament, with 53 seats in the Chamber of Deputies and 22 in the Senate: behind the centre-right Democratic Liberal Party and the centre-left Social...
, and taking advantage of FSN's tight control of the national radio and television, Iliescu won 85% of the vote. The FSN secured two-thirds of the seats in Parliament. A university professor with strong family roots in the Communist Party, Petre Roman
Petre Roman
Petre Roman is a Romanian politician and a former Prime Minister of Romania. He served from 1989 to 1991, when his government was overthrown by the intervention of the miners led by Miron Cozma. Roman is a member of the Club of Madrid, grouping 66 democratic former heads of state and government...
, was named prime minister of the new government, which consisted mainly of former communist officials. The government initiated modest free market
Free market
A free market is a competitive market where prices are determined by supply and demand. However, the term is also commonly used for markets in which economic intervention and regulation by the state is limited to tax collection, and enforcement of private ownership and contracts...
reforms.
Because the majority of ministers in the Petre Roman government were ex-communists, anti-communist protesters initiated a round-the-clock anti-government demonstration
Golaniad
The Golaniad was a protest in Romania in the University Square, Bucharest. It was initiated by students and professors at the University of Bucharest....
in University Square
University Square, Bucharest
University Square is located in downtown Bucharest, near the University of Bucharest.Four statues are located in the University Square, in front of the University; they depict Ion Heliade Rădulescu , Michael the Brave , Gheorghe Lazăr and Spiru Haret .The square was the site of the 1990 Golaniad,...
, Bucharest in April 1990. Two months later, these protesters, whom the government referred to as "hooligans", were brutally dispersed by the miners from Jiu Valley
Jiu Valley
The Jiu Valley is a region in southwestern Romania, in Hunedoara county, situated in a valley of the Jiu River between the Retezat Mountains and the Parâng Mountains...
, called in by President Iliescu; this event became known as the mineriad
Mineriad
See also The 1990s: the rise and decline of miners' unionsA Mineriad is the term used to name any of the successive violent interventions of miners in Bucharest. These interventions were generally seen as aimed at wrestling policy changes or simply material advantages from the current political...
(see June 1990 Mineriad
June 1990 Mineriad
The June 1990 Mineriad was the suppression of an anti-National Salvation Front sit-in protests in Bucharest, Romania by the violent intervention of coal miners from the Jiu Valley, brought to Bucharest by the government to counter the rising violence of the protesters...
). The facts surrounding these events are disputed by the miners, who claim that most of the violence was perpetrated by government agents that were agitating the crowds. Some of the counter-protesters also attacked the headquarters and private residences of opposition leaders. Later Parliamentary inquiries showed that members of the government intelligence services were involved in the instigation and manipulation of both the protesters and the miners, and in June 1994 a Bucharest court found two former Securitate officers guilty of ransacking and stealing $100,000 from the house of a leading opposition politician. Petre Roman's government fell in late September 1991, when the miners returned to Bucharest to demand higher salaries. A technocrat, Theodor Stolojan
Theodor Stolojan
Theodor Dumitru Stolojan is a Romanian politician. An economist by training, he is a leader of the Democratic-Liberal Party. He previously served as Prime minister of Romania from September 1991 to November 1992. He and his wife Elena have a son, Vlad Stolojan, and a daughter, Ada Palea...
, was appointed to head an interim government until new elections could be held.
In December 1991, a new constitution was drafted and subsequently adopted, after a popular referendum, which, however, attracted criticism from international observers who accused the government of manipulating the population and even of outright fraud. (The constitution was most recently revised by a national referendum on October 18–19, 2003, again plagued by fraud accusations made by internal and international observers.) The new constitution, which took effect October 29, 2003, follows the structure of the Constitution of 1991, but makes significant revisions, among which the most significant are extension of the presidential mandate from four years to five, and the guaranteed protection of private property.
March 1992 marked the split of the FSN into two groups: the Democratic National Front
Social Democratic Party (Romania)
The Social Democratic Party is the major social-democratic political party in Romania. It was formed in 1992, after the post-communist National Salvation Front broke apart. It adopted its present name after a merger with a minor social-democratic party in 2001. Since its formation, it has always...
(FDSN), led by Ion Iliescu and the Democratic Party (PD), led by Petre Roman. Iliescu won the presidential elections in September 1992 by a clear margin, and his FDSN won the general elections held at the same time. With parliamentary support
Red Quadrilateral
The Red Quadrilateral was a term used to describe the Romanian government between the 1992 and 1996 legislative elections...
from the nationalist PUNR (National Unity Party of Romanians), PRM (Great Romania Party), and the ex-communist PSM (Socialist Workers' Party), a new government was formed in November 1992 under Prime Minister Nicolae Văcăroiu
Nicolae Vacaroiu
Nicolae Văcăroiu is a Romanian politician, member of the Social Democratic Party, who served as Prime Minister between 1992 and 1996. Before the 1989 Revolution he worked at the Committee for State Planning, together with Theodor Stolojan....
, an economist. The FDSN changed its name to Party of Social Democracy in Romania (PDSR) in July 1993.
The subsequent disintegration of the FSN produced several political parties including the Romanian Democrat Social Party (PDSR, later Social Democratic Party
Social Democratic Party (Romania)
The Social Democratic Party is the major social-democratic political party in Romania. It was formed in 1992, after the post-communist National Salvation Front broke apart. It adopted its present name after a merger with a minor social-democratic party in 2001. Since its formation, it has always...
, PSD), the Democratic Party (PD) and the ApR (Alliance for Romania). The PDSR party governed Romania from 1990 until 1996 through several coalitions and governments with Ion Iliescu as head of state. Since then there have been three democratic changes of government: in 1996, the democratic-liberal opposition and its leader Emil Constantinescu
Emil Constantinescu
Emil Constantinescu was President of Romania from 1996 to 2000.He graduated from the law school of the University of Bucharest, and subsequently started a career as a geologist...
acceded to power; in 2000 the Social Democrats returned to power, with Iliescu once again president; and in 2004 Traian Băsescu
Traian Basescu
Traian Băsescu is the current President of Romania. After serving as the mayor of Bucharest from June 2000 until December 2004, he was elected president in the Romanian Presidential Elections of 2004 and inaugurated on December 20, 2004...
was elected president, with an electoral coalition called Justice and Truth Alliance
Justice and Truth
The Justice and Truth Alliance was a political alliance comprising two political parties in Romania: the centre-right liberal National Liberal Party and the initially social-democrat Democratic Party , which later switched to center-right ideology.As the political formation with the largest...
(DA). The government was formed by a larger coalition which also includes the Conservative Party
Conservative Party (Romania)
The Conservative Party of Romania is a political party formed in 1991, after the fall of Communism, under the name of the Romanian Humanist Party . From 2005 until December 3, 2006, the party was a junior member of the ruling coalition...
and the ethnic Hungarian party.
Emil Constantinescu
Emil Constantinescu
Emil Constantinescu was President of Romania from 1996 to 2000.He graduated from the law school of the University of Bucharest, and subsequently started a career as a geologist...
of the Democratic Convention
Romanian Democratic Convention
The Romanian Democratic Convention was an electoral alliance of several political parties of Romania, active from early 1992 until 2000....
(CDR) emerged as the winner of the second round of the 1996 presidential elections and replaced Iliescu as chief of state. The PDSR won the largest number of seats in Parliament, but was unable to form a viable coalition. Constituent parties of the CDR joined the Democratic Party (PD), the National Liberal Party
National Liberal Party (Romania)
The National Liberal Party , abbreviated to PNL, is a centre-right liberal party in Romania. It is the third-largest party in the Romanian Parliament, with 53 seats in the Chamber of Deputies and 22 in the Senate: behind the centre-right Democratic Liberal Party and the centre-left Social...
(PNL) and the Hungarian Democratic Union of Romania (UDMR) to form a centrist coalition government, holding 60% of the seats in Parliament. This coalition of sorts frequently struggled for survival, as decisions were often delayed by long periods of negotiations among the involved parties. Nevertheless, this coalition was able to implement several critical reforms. The new coalition government, under prime minister Victor Ciorbea
Victor Ciorbea
Victor Ciorbea is a Romanian politician. He was the Mayor of Bucharest in 1996-1997 and, after his resignation from office, Prime Minister of Romania from 12 December 1996 to 30 March 1998.-Biography:...
remained in office until March 1998, when Radu Vasile
Radu Vasile
Radu Vasile is a Romanian politician, historian and poet.-Education and Professional Activity:*1967 - Graduate, with exceptional results, of the Faculty of History - University of Bucharest...
(PNŢCD) took over as prime minister. The former governor of the National Bank, Mugur Isărescu
Mugur Isarescu
Mugur Isărescu is the Governor of the National Bank of Romania. From 22 December 1999 to 28 November 2000 he served as Prime Minister. He is a member of the Romanian Academy....
, eventually replaced Radu Vasile
Radu Vasile
Radu Vasile is a Romanian politician, historian and poet.-Education and Professional Activity:*1967 - Graduate, with exceptional results, of the Faculty of History - University of Bucharest...
as head of the government.
The 2000 elections, brought Iliescu's PDSR, known as Social Democratic Party
Social Democratic Party (Romania)
The Social Democratic Party is the major social-democratic political party in Romania. It was formed in 1992, after the post-communist National Salvation Front broke apart. It adopted its present name after a merger with a minor social-democratic party in 2001. Since its formation, it has always...
(PSD) after the merger with the PSDR, back to power. Iliescu won a third term as the country's president. Adrian Năstase
Adrian Nastase
Adrian Năstase is a Romanian politician who was the Prime Minister of Romania from December 2000 to December 2004.He competed as the Social Democratic Party candidate in the 2004 presidential election, but was defeated by centre-right Justice and Truth Alliance candidate Traian Băsescu.He was...
became the prime minister of the newly formed government.
European Union membership
(2004–present)Presidential and parliamentary elections took place again on November 28, 2004. No political party was able to secure a viable parliamentary majority and opposition parties alike that the PSD had committed large-scale electoral fraud. There was no winner in the first round of the presidential elections. The joint PNL-PD candidate, Traian Băsescu
Traian Basescu
Traian Băsescu is the current President of Romania. After serving as the mayor of Bucharest from June 2000 until December 2004, he was elected president in the Romanian Presidential Elections of 2004 and inaugurated on December 20, 2004...
, won the second round on December 12, 2004 with 51% of the vote and thus became the third post-revolutionary president of Romania.
The PNL leader, Călin Popescu Tăriceanu was assigned the difficult task of building a coalition government without including the PSD. In December 2004, the new coalition government (PD, PNL, PUR Romanian Humanist Party - which eventually changed its name to Romanian Conservative Party and UDMR), was sworn in under Prime Minister Tăriceanu.
Post–Cold War
Cold War
The Cold War was the continuing state from roughly 1946 to 1991 of political conflict, military tension, proxy wars, and economic competition between the Communist World—primarily the Soviet Union and its satellite states and allies—and the powers of the Western world, primarily the United States...
Romania developed closer ties with Western Europe
Western Europe
Western Europe is a loose term for the collection of countries in the western most region of the European continents, though this definition is context-dependent and carries cultural and political connotations. One definition describes Western Europe as a geographic entity—the region lying in the...
, eventually joining NATO in 2004. The country applied in June 1993 for membership in the European Union
European Union
The European Union is an economic and political union of 27 independent member states which are located primarily in Europe. The EU traces its origins from the European Coal and Steel Community and the European Economic Community , formed by six countries in 1958...
(EU). It became an Associated State of the EU in 1995, an Acceding Country in 2004, and a member on January 1, 2007.
Following the free travel agreement and politic of the post–Cold War period, as well as hardship of the life in the post 1990s economic depression, Romania has an increasingly large diaspora
Romanian diaspora
The Romanian diaspora is the ethnically Romanian population outside Romania and Moldova. The concept does not usually include the ethnic Romanians who live as natives in the states surrounding Romania, chiefly those Romanians who live in Ukraine and Serbia. The diaspora does include the people of...
. The main emigration targets are Spain, Italy, Germany, Austria, UK, Canada and the USA.
Romania joined the North Atlantic Treaty Organization in 2004, and the European Union
European Union
The European Union is an economic and political union of 27 independent member states which are located primarily in Europe. The EU traces its origins from the European Coal and Steel Community and the European Economic Community , formed by six countries in 1958...
, alongside Bulgaria
Bulgaria
Bulgaria , officially the Republic of Bulgaria , is a parliamentary democracy within a unitary constitutional republic in Southeast Europe. The country borders Romania to the north, Serbia and Macedonia to the west, Greece and Turkey to the south, as well as the Black Sea to the east...
, on January 1, 2007.
In April 2008, Bucharest hosted the NATO summit
2008 Bucharest summit
The 2008 Bucharest Summit or the 20th NATO Summit was a NATO summit organized in Bucharest, Romania on 2 – 4 April 2008. Among other business, Croatia and Albania were invited to join the alliance. Republic of Macedonia was not invited due to its ongoing naming dispute with Greece...
.
Romanian rulers
- List of Wallachian rulers (up to 1859)
- List of Moldavian rulers (up to 1859)
- List of Transylvanian rulers (up to 1867)
- Kings of Romania (1881–1947)
- Presidents of Romania (since 1947)
- Prime ministers of Romania (since 1862)
See also
- Military history of RomaniaMilitary history of RomaniaThe military history of Romania deals with conflicts spreading over a period of about 2500 years across the territory of modern Romania, the Balkan Peninsula and Eastern Europe and the role of the Romanian military in conflicts and peacekeeping worldwide....
- History of the BalkansHistory of the BalkansThe Balkans is an area of southeastern Europe situated at a major crossroads between mainland Europe and the Near East. The distinct identity and fragmentation of the Balkans owes much to its common and often violent history and to its very mountainous geography.-Neolithic:Archaeologists have...
- History of EuropeHistory of EuropeHistory of Europe describes the history of humans inhabiting the European continent since it was first populated in prehistoric times to present, with the first human settlement between 45,000 and 25,000 BC.-Overview:...
- King of RomaniaKing of RomaniaKing of the Romanians , rather than King of Romania , was the official title of the ruler of the Kingdom of Romania from 1881 until 1947, when Romania was proclaimed a republic....
- List of Presidents of Romania
- List of Prime Ministers of Romania
- Politics of RomaniaPolitics of RomaniaPolitics of Romania take place in a framework of a semi-presidential parliamentary representative democratic republic, whereby the Prime Minister of Romania is the head of government and the President of Romania exercises the functions of head of state. Romania has a multi-party system. Executive...
- Romanian Communist PartyRomanian Communist PartyThe Romanian Communist Party was a communist political party in Romania. Successor to the Bolshevik wing of the Socialist Party of Romania, it gave ideological endorsement to communist revolution and the disestablishment of Greater Romania. The PCR was a minor and illegal grouping for much of the...
External links
- The Beginning of the Final Solution: Murder of the Jews of Romania on the Yad VashemYad VashemYad Vashem is Israel's official memorial to the Jewish victims of the Holocaust, established in 1953 through the Yad Vashem Law passed by the Knesset, Israel's parliament....
website - Illustrated History of Romanians
- World Statesmen: Romania, including a timeline, a comprehensive history of the Romanian flag; a listing of princes, monarchs, prime ministers; etc.

