
History of the Republic of Venice
Encyclopedia
The history of the Republic of Venice
traditionally begins with its foundation at noon on Friday March 25, 421 by authorities from Padua
who hoped to establish a trading-post in the region. This event was marked by the founding of the Venitian church of St. James. What is certain is that the early city of Venice
, existed as a collection of lagoon
communities which banded together for mutual defence from the Lombards
as the power of the Byzantine Empire
dwindled in northern Italy
in the late seventh century. Sometime in the first decades of the eighth century, the people of the lagoon elected their first leader Ursus
, who was confirmed by Byzantium and given the titles of hypatus
and dux
. He was the first historical Doge of Venice
. Tradition, however, since the early eleventh century, dictates that the Venetians first proclaimed one Anafestus Paulicius
duke in 697, though this story dates to no earlier than the chronicle of John the Deacon
. Whatever the case, the first doges had their power base in Eraclea
.
, moved his seat from Heraclea to Malamocco
in the 740s He was the son of Ursus and represented the attempt of his father to establish a dynasty. Such attempts were more than commonplace among the doges of the first few centuries of Venetian history, but all were ultimately unsuccessful. During the reign of Deusdedit, Venice became the only remaining Byzantine possession in the north and the changing politic of the Frankish Empire
began to change the factional division of Venetia. One faction was decidedly pro-Byzantine. They desired to remain well-connected to the Empire. Another faction, republican in nature, believed in continuing along a course towards practical independence. The other main faction was pro-Frankish. Supported mostly by clergy (in line with papal sympathies of the time), they looked towards the new Carolingian
king of the Franks, Pepin the Short, as the best provider of defence against the Lombards. A minor, pro-Lombard, faction was opposed to close ties with any of these further-off powers and interested in maintaining peace with the neighbouring Lombard kingdom, which surrounded Venice except on the seaward side.
Deusdedit was assassinated and his throne usurped, but the usurper, Galla Gaulo, suffered a like fate within a year. During the reign of his successor, Domenico Monegario
, Venice changed from a fisherman's town to a port of trade and centre of merchants. Shipbuilding was also greatly advanced and the pathway to Venetian dominance of the Adriatic was laid. Also during Monegario's tenure, the first dual tribunal
was instituted. Each year, two new tribunes were elected to oversee the doge and prevent abuse of power.
The pro-Lombard Monegario was succeeded in 764, by a pro-Byzantine Heraclean, Maurizio Galbaio
. Galbaio's long reign (764-787) vaulted Venice forwards to a place of prominence not just regionally but internationally and saw the most concerted effort yet to establish a dynasty. Maurizio oversaw the expansion of Venetia to the Rialto
islands. He was succeeded by his equally long-reigning son, Giovanni
. Giovanni clashed with Charlemagne
over the slave trade and entered into a conflict with the Venetian church.
Dynastic ambitions were shattered when the pro-Frankish faction was able to seize power under Obelerio degli Antoneri in 804. Obelerio brought Venice into the orbit of the Carolingian Empire
. However, by calling in Pepin, rex Langobardorum
, to his defence, he raised the ire of the populace against himself and his family and they were forced to flee during Pepin's siege of Venice. Venice achieved lasting independence by repelling the besiegers in 811.
(803), the two emperors had recognised Venetian de facto independence, while it remained nominally Byzantine in subservience. During the reign of the Participazio, Venice grew into its modern form. Though Heraclean by birth, Agnello
, first doge of the family, was an early immigrant to Rialto and his dogeship was marked by the expansion of Venice towards the sea via the construction of bridges, canals, bulwarks, fortifications, and stone buildings. The modern Venice, at one with the sea, was being born. Agnello was succeeded by his son Giustiniano
, who brought the body of Saint Mark the Evangelist to Venice from Alexandria
and made him the patron saint of Venice.
During the reign of the successor of the Participazio, Pietro Tradonico
, Venice began to establish its military might which would influence many a later crusade and dominate the Adriatic for centuries, and signed a trade agreement with the Holy Roman Emperor
Lothair I, whose privileges were later expanded by Otto I. Tradonico secured the sea by fighting Slavic
and Saracen
pirates. Tradonico's reign was long and successful (837 – 864), but he was succeeded by the Participazio and it appeared that a dynasty may have finally been established. Around 841, the Republic of Venice
sent a fleet of 60 galleys (each carrying 200 men) to assist the Byzantines in driving the Arabs from Crotone
, but failed.
Under Pietro II Candiano
Istria
n cities signed a treaty under which it accepted the Venetian economical supremacy: it was the first move towards the creation of the coastal empire in Dalmatia
. The autocratic, philo-Imperial Candiano dynasty was overthrown by a revolt in 972, and the populace elected doge Pietro I Orseolo
; however, his conciliating policy was ineffective, and he resigned in favour of Vitale Candiano
. Starting from Pietro II Orseolo
, who reigned from 991, attention towards mainland was definitely overshadowed by a strong push towards the control of Adriatic Sea. Inner strife was pacified, and trade with the Byzantine Empire boosted by the favourable treaty (Grisobolus or Golden Bull
) with Emperor Basil II
. The imperial edict granted Ventian traders freedom from taxation paid by other foreigners and the Byzantines themselves. In the year 1000 an expedition of 6 ships in Istria secured the Venetian suzerainty in the area, and Slav pirates were suppressed permanently.
 In the occasion Orseolo named himself "Duke of Dalmatia", starting the colonial empire of Venice. He died in 1008; he was also responsible of the establishment of the "Marriage of the Sea" ceremony. At this time Venice had a firm control over the Adriatic Sea, strengthened by the expedition of Pietro's son Ottone in 1017, and had assumed a firm role of balance power between the two major Empires.
In the occasion Orseolo named himself "Duke of Dalmatia", starting the colonial empire of Venice. He died in 1008; he was also responsible of the establishment of the "Marriage of the Sea" ceremony. At this time Venice had a firm control over the Adriatic Sea, strengthened by the expedition of Pietro's son Ottone in 1017, and had assumed a firm role of balance power between the two major Empires.
During the long Investiture Controversy
, an 11th century dispute between Henry IV, Holy Roman Emperor
and Pope Gregory VII
over who would control appointments of church officials, Venice remained neutral, and this caused some attrition of support from the Popes. Doge Domenico Selvo
also skilfully intervened in the war between the Normans of Apulia
and the Byzantine Emperor Alexios I Komnenos
in favour of the latter, obtaining in exchange a bull declaring the Venetian supremacy in the Adriatic coast up to Durazzo, as well as the exemption from taxes for his merchants in the whole Byzantine Empire, a considerable factor in the city-state's later accumulation of wealth and power serving as middlemen for the lucrative spice
and silk trade that funnelled through the Levant
and Egypt
along the ancient Kingdom of Axum and Roman-Indian
routes via the Red Sea
.
The war was not a military success, but with that act the city gained total independence of Venice also from the formal point of view. In 1084, Domenico Selvo
had personally led a fleet against the Normans
, but he was defeated and lost 9 great galleys, the largest and most heavily armed ships in the Venetian war fleet
.
, Venice became wealthy through its control of trade between Europe and the Levant
, and began to expand into the Adriatic Sea
and beyond. Venice was involved in the Crusades almost from the very beginning; 200 Venetian ships assisted in capturing the coastal cities of Syria
after the First Crusade
, and in 1123 they were granted virtual autonomy in the Kingdom of Jerusalem
through the Pactum Warmundi
. In 1110, Ordelafo Faliero
personally commanded a Venetian fleet of 100 ships to assist Baldwin I of Jerusalem
in capturing the city of Sidon
.
 In the 12th century, the republic built a big national shipyard which is now known as the Venetian Arsenal
In the 12th century, the republic built a big national shipyard which is now known as the Venetian Arsenal
. Building anew and powerful fleets, the republic took control over the eastern Mediterranean. The first exchange business in the world was started in Venezia, to support the merchants from all over Europe. The Venetians also gained extensive trading privileges in the Byzantine Empire and their ships often provided the Empire with a navy. In 1182 there was an anti-Western riot in Constantinople
, of which the Venetians were the main targets.
The Venetian fleet was crucial to the transportation of the Fourth Crusade
, but when the crusaders could not pay for the ships, the cunning and manipulative Doge Enrico Dandolo
quickly exploited the situation and offered transport to the crusaders if they were to capture the (Christian) Dalmatian city of Zadar
, which had rebelled against Venetian rule in 1183, placed itself under the dual protection of the Papacy and King Emeric of Hungary
and had proven too well fortified for Venice to retake alone, because 90% of the shipowners had changed the opinion of Enrico Dandolo. Upon accomplishing this the crusade was again diverted to Constantinople
, the capital of the Byzantine Empire
, another rival of Venice. The Dalmatians separated from Hungary by a treaty in 1199 and they paid Hungary with a portion of Macedonia (theme). In 1201 the city of Zadar, formerly under the protection of the Republic of Venice, recognized Emeric, King of Hungary, again as overlord, perhaps because he could not realize Hungary's portion on Macedonia (theme). The city was captured and sacked in 1204; when Macedonia (theme) became disputed between the Crusaders and the Bulgarian Empire
; the sack has been described as one of the most profitable and disgraceful sacks of a city in history. The Republic of Venice signed a trade treaty with the Mongol Empire
in 1221. Koloman of Croatia counted 77 judges in Dalmatia
in 1235 and wrote their names. The Byzantine Empire, which until then had resisted several attacks and kept the Islamic invaders out of Western Anatolia and Eastern Europe, was reestablished in 1261 but never recovered its previous power and eventually was conquered by the Ottoman Turks
(which later occupied the Balkans
and Hungary, as well as besieged Vienna
on two occasions). The Venetians, who accompanied the crusader fleet, claimed much of the plunder from the city as payment including the famous four bronze horses
which were brought back to adorn St. Mark's basilica. As a result of the partition of the Byzantine Empire
which followed, Venice gained some strategic territories in the Aegean Sea
(three-eighths of the Byzantine Empire), including the islands of Crete
and Euboea
; moreover, some present day cities, such as Chania
on Crete, have core architecture
that is substantially Venetian in origin. The Aegean islands formed the Venetian Duchy of the Archipelago
.
In 1295, Pietro Gradenigo
sent a fleet of 68 ships to attack a Genoese
fleet at Alexandretta, then another fleet of 100 ships were sent to attack the Genoese in 1299.
In late 14th century, Venice had to face difficulties on her eastern side, especially during the reign of Louis I of Hungary. In 1346 he made a first attempt to conquerd Zadar
, but was defeated. In 1356 an alliance was formed by the counts of Gorizia, Francesco I da Carrara
, lord of Padua
, Nicolaus, partiarch of Aquileia and his half brother emperor Charles IV
, Louis I and the dukes of Austria. The league's troops occupied Grado
and Muggia
(1356), while Louis stripped Venice of most of Dalmatia
. The siege of Treviso
(July-September 1356) was a failure, but Venice suffered a severe defeat at Nervesa (13 January 1358), being forced to cede Dalmatia and Croatia to Hungary
. From 1350 to 1381, Venice also fought an intermittent war with the Genoese
. Initially defeated, they destroyed the Genoese fleet at the Battle of Chioggia
in 1380 and retained their prominent position in eastern Mediterranean affairs at the expense of Genoa. However, the peace cause Venice to lose several territories to other participants to the war: Conegliano
was occupied by the Austrians
, Treviso
was taken over by Carraresi, Tenedos
fell to the Byzantine Empire
, Trieste to the Patriarchate of Aquileia
, and the Serenissima lost control of Dalmatia as well (to Hungary).
In 1363, a colonial revolt
broke out in Crete that needed considerable military force and five years to suppress.
n coast from Istria to Albania
, which was acquired from King Ladislaus of Naples. Venice installed nobility to govern the area, for example, Count Filippo Stipanov in Zara. This move by the Venetians was as a response to the threatening expansion of Giangaleazzo Visconti, Duke of Milan
. Control over the north-east main land routes was also a necessity for the safety of the trades. By 1410, Venice had a navy of 3,300 ships (manned by 36,000 men) and taken over most of Venetia, including such important cities as Verona
and Padua
.
The situation in Dalmatia had been settled in 1408 by a truce with King Sigismund of Hungary. At its expiry, Venice immediately invaded the Patriarchate of Aquileia, and subjected Traù
, Split
, Durazzo and other Dalmatian cities. The difficulties of Hungary allowed the Republic to consolidate its Adriatic dominions.
Under doge Francesco Foscari
(1423–57) the city reached the height of its power and territorial extension. In 1425 a new war broke out, this time against Filippo Maria Visconti
of Milan. The victory at the Battle of Maclodio
of Count of Carmagnola, commander of the Venetian army, the shift of the western border from the Adige to the Adda
. However, the territorial expansion was not welcome everywhere in Venice; tension with Milan remained high, and in 1446 the Republic had to fight another league, formed by Milan, Florence, Bologna and Cremona. After an initial Venetian victory under Micheletto Attendolo
at Casalmaggiore
, however, Visconti died and in Milan a republic was declared. The Serenissima had then free ground to occupy Lodi and Piacenza
, but was halted by Francesco Sforza; later, Sforza and the Doge allied to allow him the rule of Milan, in exchange of the cession of Brescia
and Vicenza
. Venice, however, again changed side when the power of Sforza seemed to became excessive: the intricate situation was settled with the Peace of Lodi (1454), which confirmed the area of Bergamo
and Brescia to the Republic. At this time, the territories under the Serenissima included much of the modern Veneto
, Friuli
, the provinces of Bergamo, Cremona and Trento, as well as Ravenna
, Istria and Dalmatia. Eastern borders were with the county of Gorizia
and the ducal lands of Austria, while in the south was the Duchy of Ferrara
. Oversea dominions included Euboea
and Egina.
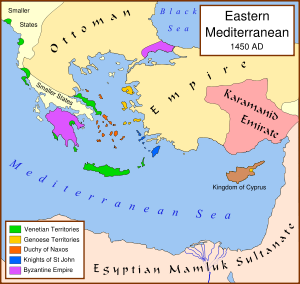 On May 29, 1453 Constantinople
On May 29, 1453 Constantinople
fell to the Ottomans, but Venice managed to maintain a colony in the city and some of the former trade privileges it had had under the Byzantines. Indeed, in 1454, the Ottomans granted the Venetians their ports and trading rights. Despite the recent Ottoman defeats against John Hunyadi
of Hungary and Scanderbeg in Albania, war was however unavoidable. In 1463 the Venetian fortress of Argos
was ravaged. Venice set up an alliance with Matthias Corvinus of Hungary
and attacked the Greek islands by sea and Bulgaria by land. Both fronts however saw the allies forced to retreat, after several minor victories. Operations were reduced mostly to isolated ravages and guerrilla attacks, until the Ottomans moved a massive counteroffensive in 1470: this had Venice lose its main stronghold in the Aegean Sea, Negroponte
. The Venetians sought an alliance with the Shah of Persia and other European powers, but, received only limited support, could make only small-scale attacks at Antalya
, Halicarnassus
and Smirne. However, the Ottomans conquered the Peloponnesus and launched an offensive in Venetian mainland, closing in on the important centre of Udine
. The Persians, together with the Caramanian amir, were severely defeated at Terdguin, and the Republic was left alone. Further, much of Albania went lost after Scanderbeg's death. However, the heroic resistance of Scutari
under Antonio Loredan forced the Ottomans to retire from Albania, while a revolt in Cyprus
gave back the island to the Cornaro
family and, subsequently, to the Serenissima (1473). Its prestige seemed reassured, but Scutari fell anyway two years later, and Friuli was again invaded and ravaged. On January 24, 1479, a treaty of peace was finally signed with the Ottomans. Venice had to cede Argo, Negroponte, Lemnos
and Scutari, and pay an annual tribute of 10,000 golden ducat
i. Five years later the agreement was confirmed by Mehmed II
's successor, Bayezid II
, with the peaceful exchange of the islands of Zakynthos
and Kefalonia
between the two sides.
In 1482 Venice allied with Pope Sixtus IV
in his attempt to conquer Ferrara, opposed to Florence, Naples, Milan and Ercole d'Este (see War of Ferrara). When Papal-Venetian milices were smashed at the Battle of Campomorto
, Sixtus changed side. Again alone, the Venetians were defeated in the Veronese by Alfonso of Calabria, but conquered Gallipoli
, in Puglia, by sea. The balance was changed by Ludovico Sforza
of Milan, who passed on the side of Venice: this led to a quick peace, which was signed near Brescia on 7 August 1484. In spite of the numerous setbacks suffered in the campaign, Venice obtained the Polesine
and Rovigo
, and increased its prestige in the Italian peninsula, at the expense of Florence especially. In the late 1480s, Venice fought two brief campaigns against the new Pope Innocent VIII
and Sigismund of Austria. Venetian troops were also present at the Battle of Fornovo
, which saw the Italian League against Charles VIII of France
. Alliance with Spain/Aragon in the following reconquest of the Kingdom of Naples granted it the control of the Apulian ports, important strategic bases commanding the lower Adriatic and the Ionian islands
.
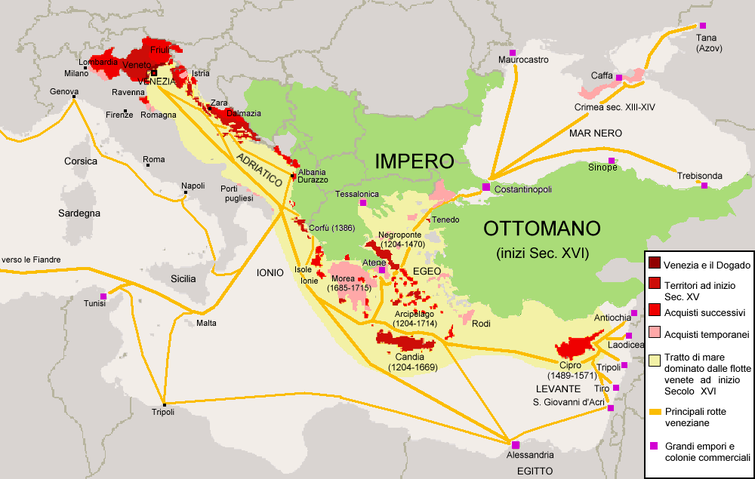
Despite the setbacks in the struggle against the Turks, at the end of 15th century, with 180,000 inhabitants, Venice was the second largest city in Europe after Paris and probably the richest in the world. The territory of the Republic of Venice extended over approximately 70000 km² (27,027.2 sq mi) with 2.1 million inhabitants (for a comparative example in the same time England hosted 3 million, the whole of Italy 11, France 13, Portugal 1.7, Spain 6, Germany/Holy Roman Empire 10).
Administratively the territory was divided in three main parts:
In 1485, the French ambassador, Philippe de Commines
, wrote of Venice,
against Milan, gaining Cremona
. In the same year the Ottoman sultan moved to attack Lepanto
by land, and sent a large fleet to support his offensive by sea. Antonio Grimani
, more a businessman and diplomat than a sailor, was defeated in the sea Battle of Zonchio
in 1499. The Turks once again sacked Friuli. Preferring peace to total war both against the Turks and by sea, Venice surrendered the bases of Lepanto, Modon
and Coron
.
Venice became rich on trade, but the guilds in Venice also produced superior silks, brocades, goldsmith jewelry and articles, armour and glass in the form of beads and eyeglasses. However, Venice's attention was diverted from her usual trade and maritime position by the delicate situation in Romagna
, then one of the richest lands in Italy, which was nominally part of the Papal States but effectively divided into a series of small lordships which were difficult for Rome's troops to control. Eager to take some of Venice's lands, all neighbouring powers joined in the League of Cambrai in 1508, under the leadership of Pope Julius II
. The pope wanted Romagna, emperor Maximilian I
Friuli
and Veneto
, Spain the Apulian ports, the king of France Cremona, the king of Hungary Dalmatia, and each of the others some part. The offensive against the huge army enlisted by Venice was launched from France. On 14 May 1509 Venice was crushingly defeated at the Battle of Agnadello
, in the Ghiara d'Adda, marking one of the most delicate points of Venetian history. French and imperial troops were occupying Veneto, but Venice managed to extricate herself through diplomatic efforts. The Apulian ports were ceded in order to come to terms with Spain, and Pope Julius II soon recognized the danger brought by the eventual destruction of Venice (then the only Italian power able to face large states like France or Ottoman Turkey). The citizens of the mainland rose to the cry of "Marco, Marco", and Andrea Gritti
recaptured Padua in July 1509, successfully defending it against the besieging imperial troops. Spain and the pope broke off their alliance with France, and Venice also regained Brescia and Verona from France. After seven years of ruinous war, the Serenissima regained her mainland dominions up to the Adda. Although the defeat had turned into a victory, the events of 1509 marked the end of the Venetian expansion.
Gasparo Contarini
's De Magistratibus et Republica Venetorum (1544) clearly shows the approval and interest which surrounded Venice's constitutional arrangements. It also illustrates foreigners' astonishment at Venice's independence and resistance to Italy's loss of freedom and, not least, at her having emerged unscathed from the war against the League of Cambrai. Contarini suggested that the secret of Venice's greatness lay in the co-existence
of Aristotle
's three types of government, monarchy
, oligarchy
, and democracy
. In his opinion, the Maggior Consiglio
was the "democratic" part, the Senate and the Ten
were the oligarchy, while the doge represented monarchy. The combination of these three principles in the Venetian government came as close as was possible to perfection in the mechanism of government. At the same time the patrician
Marino Sanudo, a politician who had a remarkable career, and a celebrated diarist, was bemoaning the corruption which resulted from the great number of poor or impoverished patricians.
The struggle for supremacy in Italy between France and Spain was resolved in favour of the latter. Caught between the Spanish-Imperial and Turkish superpowers, the Republic adopted a skilful political strategy of quasi-neutrality in Europe, which turned into a defensive stance against the Ottomans. Venice's maritime aid was potentially useful to Spain, but not to the point of allowing her to reinforce her position in the Levant, which would increase her strength in Italy as well, where she was practically the only Italian state not subject to Spain. In the Turkish war of 1537-40
, Venice was allied with the emperor and King of Spain, Charles V
. Andrea Doria
, commander of the allied fleets, was defeated at Preveza
in 1538, and two years later Venice signed a treaty of peace by which the Turks took the Aegean duchy of Naxos from the Sanudo family. After Preveza the supremacy of the sea passed to the Ottomans.
Difficulties in the rule of the sea brought further changes. Until 1545 the oarsmen in the galleys were free sailors enrolled on a wage. They were originally Venetians, but later Dalmatians, Cretans and Greeks joined in large numbers. Because of the difficulty in hiring sufficient crews, Venice had recourse to conscription, chaining the oarsmen to the benches as other navies had already done. Cristoforo da Canal was the first Venetian to command such a galley. By 1563, the population of Venice had dropped to about 168,000 people.
With the outbreak of another war with the Ottomans
in 1570, Venice, Spain and the Pope formed the Holy League
, which was able to assemble a grand fleet of 208 galleys, 110 of which were Venetian, under the command of John of Austria, half-brother of Philip II of Spain
. The Venetians were commanded by Sebastiano Venier
. The Turkish fleet, equal in number to the allied one, had sailed up the Adriatic as far as Lesina, and then returned to Lepanto in the Gulf of Patras for provisions. The Christian fleet had assembled at Messina and encountered the Turkish fleet off Lepanto
on 7 October 1571. The Christians were victorious, and divided up 117 galleys captured from the Turks. But the Venetians gained no strategic advantage. Philip II was concerned with the balance of power in the eastern Mediterranean and Africa, and was unwilling for the fleet to become involved in the Levant. Famagusta
, the last stronghold on the island of Cyprus
, had been attacked by the Turks in 1570 and had surrendered before Lepanto. The Turkish commander, Lala Kara Mustafa Pasha
, had had the Venetian provveditore Marcantonio Bragadin flayed alive. The loss of Cyprus was ratified in the peace of 1573. In 1575, the population of Venice was about 175,000 people, but dropped to 124,000 people by 1581.
began with the arrest of two members of the clergy who were guilty of petty crimes, and with a law restricting the Church's right to enjoy and acquire landed property. Pope Paul V
held that these provisions were contrary to canon law, and demanded that they should be repealed. When this was refused, he placed Venice under an interdict
. The Republic paid no attention to the interdict or the act of excommunication, and ordered its priests to carry out their ministry. It was supported in its decisions by the Servite monk Paolo Sarpi
, a sharp polemical writer who was nominated to be the Signoria
's adviser on theology and canon law in 1606. The interdict was lifted after a year, when France intervened and proposed a formula of compromise. Venice was satisfied with reaffirming the principle that no citizen was superior to the normal processes of law.
A new war occurred in the years 1613-1617. The government of Venice wrote:
The Uzkoks were Christian refugees from Bosnia
and Turkish Dalmatia who had been enlisted by the Austrian Habsburg to defend their borders after the peace between Venice and the Ottomans following the Battle of Lepanto. They settled in Segna and lived as pirates in the Adriatic, causing concern in Venice that they would complicate relations with the Sublime Porte. When Venice acted against these Uscocchi in 1613, she found herself at odds on land with their protector, the archduke of Austria. An army was sent against Gradisca, an archduke's possession, with financial support given to the duke of Savoy
, who was pinning down the Spanish army in Lombardy. The military operations on the eastern frontier were not decisive, but among the terms of the peace of 1617 the Habsburgs undertook to solve the problem of the Uzkoks, whom they moved inland.
In 1617, whether on his own initiative, or supported by his king, the Spanish viceroy of Naples attempted to break Venetian dominance by sending a naval squadron to the Adriatic. His expedition met with mixed success, and he retired from the Adriatic. Rumours of sedition and conspiracy were meanwhile circulating in Venice, and there were disturbances between mercenaries of different nationalities enrolled for the war of Gradisca. The Spanish ambassador, the Marquis of Bedmar, was wise to the plot, if not the author of it. Informed of this by a Huguenot captain, the Ten acted promptly. Three "bravos" were hanged, and the Senate demanded the immediate recall of the Spanish ambassador.
Tension with Spain increased in 1622, when Antonio Foscarini, a senator and ambassador to England, was accused of acting for foreign powers during his time as ambassador and of spying for Spain after his return. He was tried, acquitted of the first charge, found guilty of the second and hanged from a gallows between the columns of the Piazzetta in 1622. A few months later the Ten discovered that he had been the innocent victim of a plot. He was rehabilitated, and the news circulated around all the chancelleries of Europe.
In 1628 Venice was involved in Italian politics for the first time in more than a century. On the death of Ferdinando I Gonzaga
, duke of Mantua and Montferrat
, the succession developed upon a French prince, Charles of Gonzaga-Nevers. This changed the balance of power in northern Italy, which had until now been controlled by the Spanish through Milan. In the ensuing war, Venice was allied with France against the Habsburgs and Savoy. The Venetian army was defeated in an attempt to come to the aid of Mantua, which was under siege by German troops, and Mantua itself was savagely sacked. The peace which recognized Charles of Gonzaga-Nevers as duke of Mantua and Monferrato was made practically without Venice's participation. War brought plague in 1630. In 16 months 50,000 people died in Venice, one third of the population. The first stone of the church of Santa Maria della Salute in the city was laid as a thanks offering for the end of the plague.
In 1638, while the Venetian fleet was cruising off Crete, a corsair fleet from Barbary consisting of 16 galleys from Algiers
and Tunis
entered the Adriatic. When the fleet returned, the corsairs repaired to the Turkish stronghold of Valona
. The Venetian commander Marino Cappello attacked the corsairs, bombarded the forts and captured their galleys, freeing 3,600 prisoners. The sultan reacted to the bombardment of his fortress by arresting the Venetian bailo (ambassador) in Constantinople, Alvise Contarini
. War was momentarily averted and the matter settled by diplomacy; however, six years later the Ottoman attack against Candia
, the main Cretan
port, left no easy terms to resort to. The Cretan War
lasted for some 25 years and was the dominant question of the whole Republic's history in the 17th century.
War also moved to the mainland in the middle of 1645, when the Turks attacked the frontiers of Dalmatia. In the latter the Venetians were able to save their coastal positions because of their command of the sea, but on 22 August, the Cretan stronghold of Khania was forced to capitulate.
The greatest Turkish effort was directed against Sebenico
, in today's Croatia, which was besieged in August-September 1647. The siege failed, and in the succeeding year the Venetians recovered several fortresses inland, such as Clissa. In Crete, however, the situation was more serious. Throughout all the war the Venetian strategy was to blockade the Dardanelles in order to surprise the Turkish fleet on its way to supply the troops on Crete. There were some signal successes, including two victories in the Dardanelles in 1655
and 1656
, but they failed to alter the strategic situation. The next year there was a three-day-long sea-battle
(17–19 July 1657), in which the captain Lazzaro Mocenigo was killed by a falling mast, and turning into a crushing defeat. With the end of the war between France and Spain in 1659, Venice received more aid from the Christian states than the small contingents which she had received in the first years. In 1666 an expedition to retake Khania failed, and in 1669 another attempt to lift the siege of Candia with joint action on land with the French contingent and by sea under Mocenigo also turned out to be a failure. The French returned home, and only 3,600 fit men were left in the fortress of Candia. Captain Francesco Morosini
negotiated its surrender on 6 September 1669. The island of Crete was ceded, except for some small Venetian bases, while Venice retained the islands of Tinos
and Cerigo, and its conquests in Dalmatia.
In 1684 Venice, taking advance of the recent Turkish defeat in the siege of Vienna, formed an alliance with Austria against the Ottomans; Russia was later included in the league. At the beginning of the Morean War
Francesco Morosini occupied the island of Levkas and set out to recapture the Greek ports. Between June 1685 when he landed at Corone, and August, when he occupied Patras, Lepanto and Corinth, he secured the Peloponnese for Venice. In September, during the attack on Athens
, a Venetian cannon blew up the Parthenon
. Venetian possessions were greatly increased in Dalmatia too, although the attempt to regain Negropont in 1688 was a failure. Morosini's successors failed to obtain lasting results in the next years, although large fleets were sent out, and in spite of some brilliant victories — at Mitylene in 1695, Andros in 1697
and the Dardanelles in 1698. The Treaty of Karlowitz
(1699) favoured Austria and Russia more than Venice, which failed to regain its bases in the Mediterranean taken by the Turks in the last two centuries, in spite of its conquests.
New conflict was brewing over the question of the Spanish Succession. Both France and the Habsburg empire, attempted now to gain an active ally in Venice, despatching envoys with authority there in 1700. The Venetian government preferred to remain neutral rather than accept hypothetical advantages offered by interested parties. The Republic remained faithful to this policy of neutrality to the end, caught in unavoidable decline but living out its life in a luxury famous throughout Europe.
 In December 1714 the Turks declared war on the Republic, at a time when Venice's major overseas possession, the Peloponnese (Morea), was "without any of those supplies which are so desirable even in countries where aid is near at hand which are not liable to attack from the sea".
In December 1714 the Turks declared war on the Republic, at a time when Venice's major overseas possession, the Peloponnese (Morea), was "without any of those supplies which are so desirable even in countries where aid is near at hand which are not liable to attack from the sea".
The Turks took the islands of Tinos and Aegina, crossed the isthmus
and took Corinth
. Daniele Dolfin, commander of the Venetian fleet, thought it better to save the fleet than risk it for the Morea. When he eventually arrived on the scene, Nauplia, Modon, Corone and Malvasia had fallen. Lefkas in the Ionian islands, and the bases of Spinalonga and Suda on Crete which still remained in Venetian hands, were abandoned. The Turks finally landed on Corfù
, but its defenders managed to throw them back. In the meantime, the Turks had suffered a grave defeat by the Austrians at Petrovaradin
on 3 August 1716. New Venetian naval efforts in the Aegean and the Dardanelles in 1717 and 1718, however, met with little success. With the Treaty of Passarowitz
(21 July 1718), Austria made large territorial gains, but Venice lost the Morea, for which her small gains in Albania and Dalmatia were little compensation. This was the last war of the Republic with Turkey.
The decline of Venice in the 18th century was also due not only to Genoa, Venice's old rival, but also to Livorno
, a new port on the Tyrrhenian Sea
created by the grand dukes of Tuscany
and chosen as staging-post for British trade in the Mediterranean. Still more injurious were the Papal town of Ancona
and Habsburg Trieste
, a free port since 1719, in the Adriatic Sea, which no longer constituted a "Venetian Gulf". An eminent Venetian politician of the time declared:
Even the cities of the eastern mainland up to Verona got their supplies from Genoa and Leghorn. The presence of pirates from the coast of Maghreb worsened the situation.
"All is in disorder, everything is out of control" exclaimed Carlo Contarini in the Maggior Consiglio on 5 December 1779. He was talking of a "commotion" in demand of a plan of reform also supported by Giorgio Pisani. The idea was to remove the monopoly of power enjoyed by the small number of rich patricians to the advantage of the very large number of poor ones. This gave rise to fears of "overturning the system" and the doge, Paolo Renier
, opposed the plan. "Prudence" suggested that the agitations in favour of reform were a conspiracy. The Inquisitors took the arbitrary step of confining Pisani in the castle of San Felice in Verona, and Contarini in the fortress of Cattaro.
On 29 May 1784 Andrea Tron, known as el paron ("the patron") because of his political influence, said that trade
The last Venetian naval venture occurred in 1784-86. The bey of Tunis
' pirates renewed their acts of piracy following claims of compensation for losses suffered by Tunisian subjects in Malta, due to no fault of the Venetians. When diplomatic efforts to reach an agreement failed, the government was forced to take military action. A fleet under Angelo Emo
blockaded Tunis and bombarded Sousse
(November 1784 and May 1785), Sfax
(August 1785) and La Coletta (September) and Biserta in 1786. These brilliant military successes brought no comparable political results in their train, and the Senate recalled Emo and his fleet to Corfù. After Emo's death, peace was made with Tunis by increasing the bey's dues. By the year 1792, the once great Venetian merchant fleet had declined to a mere 309 merchantmen
.
In January 1789 Lodovico Manin, from a recently ennobled mainland family, was elected doge. The expenses of the election had grown throughout the 18th century, and now reached their highest ever. The patrician Pietro Gradenigo remarked
C. P. Snow
suggests that in the last half century of the republic, the Venetians knew "that the current of history had begun to flow against them," and that to keep going would require "breaking the pattern into which they has crystallised." Yet they were "fond of the pattern" and "never found the will to break it."
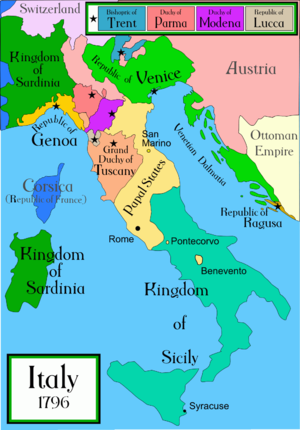
 By 1796, the Republic of Venice could no longer defend itself. Though the Republic still possessed a fleet of 13 ships of the line only a handful were ready for sea(Naval Wars in the Levant, R.C.Anderson, Liverpool University Press) and the army consisted of only a few brigades of mainly Croatian mercenaries. In spring 1796 Piedmont fell and the Austrians were beaten from Montenotte
By 1796, the Republic of Venice could no longer defend itself. Though the Republic still possessed a fleet of 13 ships of the line only a handful were ready for sea(Naval Wars in the Levant, R.C.Anderson, Liverpool University Press) and the army consisted of only a few brigades of mainly Croatian mercenaries. In spring 1796 Piedmont fell and the Austrians were beaten from Montenotte
to Lodi. The army under Napoleon crossed the frontiers of neutral Venice in pursuit of the enemy. By the end of the year the French troops were occupying the Venetian state up to the Adige. Vicenza, Cadore and Friuli were held by the Austrians. With the campaigns of the next year, Napoleon aimed for the Austrian possessions across the Alps. In the preliminaries to the Peace of Leoben, the terms of which remained secret, the Austrians were to take the Venetian possessions as the price of peace (18 April 1797).
Nevertheless the peace envisaged the continued survival of the Venetian state, although confined to the city and the lagoon, perhaps with compensation at the expense of the Papal States. In the meanwhile Brescia and Bergamo revolted to Venice, and anti French movements were arising elsewhere. Napoleon threatened Venice with war on 9 April. On 25 April he announced to the Venetian delegates at Graz
,
Domenico Pizzamano fired on a French ship trying to force an entry from the Lido forts. On I May, Napoleon declared war. The French were at the edge of the lagoon. Even the cities of the Veneto had been "revolutionized" by the French, who had established provisional municipalities. On 12 May, the Maggior Consiglio approved a motion to hand over power "to the system of the proposed provisional representative government", although there was not a quorum of votes: 512 voted for, ten against, and five abstained. On 16 May the provisional municipal government met in the Hall of the Maggior Consiglio. The preliminaries of the peace of Leoben were made even harsher in the treaty of Campoformio, and Venice and all her possessions became Austrian. The accord was signed at Passariano, in the last doge's villa, on 18 October 1797.
Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice or Venetian Republic was a state originating from the city of Venice in Northeastern Italy. It existed for over a millennium, from the late 7th century until 1797. It was formally known as the Most Serene Republic of Venice and is often referred to as La Serenissima, in...
traditionally begins with its foundation at noon on Friday March 25, 421 by authorities from Padua
Padua
Padua is a city and comune in the Veneto, northern Italy. It is the capital of the province of Padua and the economic and communications hub of the area. Padua's population is 212,500 . The city is sometimes included, with Venice and Treviso, in the Padua-Treviso-Venice Metropolitan Area, having...
who hoped to establish a trading-post in the region. This event was marked by the founding of the Venitian church of St. James. What is certain is that the early city of Venice
Venice
Venice is a city in northern Italy which is renowned for the beauty of its setting, its architecture and its artworks. It is the capital of the Veneto region...
, existed as a collection of lagoon
Lagoon
A lagoon is a body of shallow sea water or brackish water separated from the sea by some form of barrier. The EU's habitat directive defines lagoons as "expanses of shallow coastal salt water, of varying salinity or water volume, wholly or partially separated from the sea by sand banks or shingle,...
communities which banded together for mutual defence from the Lombards
Lombards
The Lombards , also referred to as Longobards, were a Germanic tribe of Scandinavian origin, who from 568 to 774 ruled a Kingdom in Italy...
as the power of the Byzantine Empire
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire was the Eastern Roman Empire during the periods of Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, centred on the capital of Constantinople. Known simply as the Roman Empire or Romania to its inhabitants and neighbours, the Empire was the direct continuation of the Ancient Roman State...
dwindled in northern Italy
Northern Italy
Northern Italy is a wide cultural, historical and geographical definition, without any administrative usage, used to indicate the northern part of the Italian state, also referred as Settentrione or Alta Italia...
in the late seventh century. Sometime in the first decades of the eighth century, the people of the lagoon elected their first leader Ursus
Orso Ipato
Orso Ipato was the third traditional Doge of Venice and the first historically known. Sometime in the early 8th century, he was elected to lead the Venetians and granted the title of dux or duke, which has morphed in the Venetian dialect into doge.Orso himself came from Heraclea...
, who was confirmed by Byzantium and given the titles of hypatus
Hypatus
Hýpatos and the variant apó hypátōn was a Byzantine court dignity, originally the Greek translation of Latin consul . The dignity arose from the honorary consulships awarded in the late Roman Empire, and survived until the early 12th century...
and dux
Dux
Dux is Latin for leader and later for Duke and its variant forms ....
. He was the first historical Doge of Venice
Doge of Venice
The Doge of Venice , often mistranslated Duke was the chief magistrate and leader of the Most Serene Republic of Venice for over a thousand years. Doges of Venice were elected for life by the city-state's aristocracy. Commonly the person selected as Doge was the shrewdest elder in the city...
. Tradition, however, since the early eleventh century, dictates that the Venetians first proclaimed one Anafestus Paulicius
Paolo Lucio Anafesto
Paoluccio or Paolo Lucio Anafesto was the reputed first doge of Venice. A noble of Eraclea, then the primary city of the region, he was elected in 697 as an official over the entire lagoon that surrounded Venice, both to put an end to the conflicts between the various tribunes who until then had...
duke in 697, though this story dates to no earlier than the chronicle of John the Deacon
John, deacon of Venice
John the Deacon was a Venetian deacon, secretary to the doge of Venice and a chronicler.-The Venetian chronicle:According to the New Advent encyclopedia:...
. Whatever the case, the first doges had their power base in Eraclea
Eraclea
thumb|250px|right|Location of Eraclea in the province of Venice.Eraclea is a town and comune in the province of Venice, Veneto, Italy. SP42 goes through it.Eraclea Mare is the Lido of Eraclea....
.
Rise
Ursus' successor, DeusdeditTeodato Ipato
Teodato Ipato was the doge of Venice after a brief interregnum following the death of his father, Orso Ipato, in 742. His surname is in fact the Byzantine title hypatos...
, moved his seat from Heraclea to Malamocco
Malamocco
Malamocco is one of the three narrow inlets in the enclosing coastal dune bar that connect the Venetian Lagoon with the Adriatic Sea, together with the Lido and Chioggia inlets...
in the 740s He was the son of Ursus and represented the attempt of his father to establish a dynasty. Such attempts were more than commonplace among the doges of the first few centuries of Venetian history, but all were ultimately unsuccessful. During the reign of Deusdedit, Venice became the only remaining Byzantine possession in the north and the changing politic of the Frankish Empire
Frankish Empire
Francia or Frankia, later also called the Frankish Empire , Frankish Kingdom , Frankish Realm or occasionally Frankland, was the territory inhabited and ruled by the Franks from the 3rd to the 10th century...
began to change the factional division of Venetia. One faction was decidedly pro-Byzantine. They desired to remain well-connected to the Empire. Another faction, republican in nature, believed in continuing along a course towards practical independence. The other main faction was pro-Frankish. Supported mostly by clergy (in line with papal sympathies of the time), they looked towards the new Carolingian
Carolingian
The Carolingian dynasty was a Frankish noble family with origins in the Arnulfing and Pippinid clans of the 7th century AD. The name "Carolingian", Medieval Latin karolingi, an altered form of an unattested Old High German *karling, kerling The Carolingian dynasty (known variously as the...
king of the Franks, Pepin the Short, as the best provider of defence against the Lombards. A minor, pro-Lombard, faction was opposed to close ties with any of these further-off powers and interested in maintaining peace with the neighbouring Lombard kingdom, which surrounded Venice except on the seaward side.
Deusdedit was assassinated and his throne usurped, but the usurper, Galla Gaulo, suffered a like fate within a year. During the reign of his successor, Domenico Monegario
Domenico Monegario
Domenico Monegario was the traditional sixth Doge of Venice , elected with the support of the Lombard king Desiderius. However, in order to maintain necessary good relations with Byzantium and the Franks, two tribunes were elected annually to limit ducal power...
, Venice changed from a fisherman's town to a port of trade and centre of merchants. Shipbuilding was also greatly advanced and the pathway to Venetian dominance of the Adriatic was laid. Also during Monegario's tenure, the first dual tribunal
Tribune
Tribune was a title shared by elected officials in the Roman Republic. Tribunes had the power to convene the Plebeian Council and to act as its president, which also gave them the right to propose legislation before it. They were sacrosanct, in the sense that any assault on their person was...
was instituted. Each year, two new tribunes were elected to oversee the doge and prevent abuse of power.
The pro-Lombard Monegario was succeeded in 764, by a pro-Byzantine Heraclean, Maurizio Galbaio
Maurizio Galbaio
Maurizio Galbaio was the seventh traditional, but fifth historical, Doge of Venice from 764 to his death. He was the first great doge, who reigned for 22 years and set Venice on its path to independence and success....
. Galbaio's long reign (764-787) vaulted Venice forwards to a place of prominence not just regionally but internationally and saw the most concerted effort yet to establish a dynasty. Maurizio oversaw the expansion of Venetia to the Rialto
Rialto
The Rialto is and has been for many centuries the financial and commercial centre of Venice. It is an area of the San Polo sestiere of Venice, Italy, also known for its markets and for the Rialto Bridge across the Grand Canal....
islands. He was succeeded by his equally long-reigning son, Giovanni
Giovanni Galbaio
Giovanni Galbaio was the eighth Doge of Venice according to tradition, but only the sixth historically verifiable one. He succeeded his father Maurizio Galbaio, who had associated him as doge in 778...
. Giovanni clashed with Charlemagne
Charlemagne
Charlemagne was King of the Franks from 768 and Emperor of the Romans from 800 to his death in 814. He expanded the Frankish kingdom into an empire that incorporated much of Western and Central Europe. During his reign, he conquered Italy and was crowned by Pope Leo III on 25 December 800...
over the slave trade and entered into a conflict with the Venetian church.
Dynastic ambitions were shattered when the pro-Frankish faction was able to seize power under Obelerio degli Antoneri in 804. Obelerio brought Venice into the orbit of the Carolingian Empire
Carolingian Empire
Carolingian Empire is a historiographical term which has been used to refer to the realm of the Franks under the Carolingian dynasty in the Early Middle Ages. This dynasty is seen as the founders of France and Germany, and its beginning date is based on the crowning of Charlemagne, or Charles the...
. However, by calling in Pepin, rex Langobardorum
King of Italy
King of Italy is a title adopted by many rulers of the Italian peninsula after the fall of the Roman Empire...
, to his defence, he raised the ire of the populace against himself and his family and they were forced to flee during Pepin's siege of Venice. Venice achieved lasting independence by repelling the besiegers in 811.
Early Middle Ages
The successors of Obelerio inherited a united Venice. By the Pax NicephoriPax Nicephori
Pax Nicephori is a term used to refer to both a 803 peace treaty allegedly concluded between the Frankish ruler Charlemagne and Nikephoros I, emperor of Byzantium, and the outcome of negotiations that took place between the same parties, but were concluded by different emperors, between 811 and 814...
(803), the two emperors had recognised Venetian de facto independence, while it remained nominally Byzantine in subservience. During the reign of the Participazio, Venice grew into its modern form. Though Heraclean by birth, Agnello
Agnello Participazio
Agnello Participazio was the tenth or eighth Doge of Venice from 811 to 827...
, first doge of the family, was an early immigrant to Rialto and his dogeship was marked by the expansion of Venice towards the sea via the construction of bridges, canals, bulwarks, fortifications, and stone buildings. The modern Venice, at one with the sea, was being born. Agnello was succeeded by his son Giustiniano
Giustiniano Participazio
Giustiniano Participazio was the eleventh or ninth Doge of Venice briefly from 825 to his death. His four years on the ducal throne were very eventful...
, who brought the body of Saint Mark the Evangelist to Venice from Alexandria
Alexandria
Alexandria is the second-largest city of Egypt, with a population of 4.1 million, extending about along the coast of the Mediterranean Sea in the north central part of the country; it is also the largest city lying directly on the Mediterranean coast. It is Egypt's largest seaport, serving...
and made him the patron saint of Venice.
During the reign of the successor of the Participazio, Pietro Tradonico
Pietro Tradonico
Pietro Tradonico , an Istrian by birth, was the Doge of Venice from 836 to 864. He was, according to tradition, the thirteenth doge, though historically he is only the eleventh. His election broke the power of the Participazio. He was illiterate, and forced to sign all state documents with the...
, Venice began to establish its military might which would influence many a later crusade and dominate the Adriatic for centuries, and signed a trade agreement with the Holy Roman Emperor
Holy Roman Emperor
The Holy Roman Emperor is a term used by historians to denote a medieval ruler who, as German King, had also received the title of "Emperor of the Romans" from the Pope...
Lothair I, whose privileges were later expanded by Otto I. Tradonico secured the sea by fighting Slavic
Slavic peoples
The Slavic people are an Indo-European panethnicity living in Eastern Europe, Southeast Europe, North Asia and Central Asia. The term Slavic represents a broad ethno-linguistic group of people, who speak languages belonging to the Slavic language family and share, to varying degrees, certain...
and Saracen
Saracen
Saracen was a term used by the ancient Romans to refer to a people who lived in desert areas in and around the Roman province of Arabia, and who were distinguished from Arabs. In Europe during the Middle Ages the term was expanded to include Arabs, and then all who professed the religion of Islam...
pirates. Tradonico's reign was long and successful (837 – 864), but he was succeeded by the Participazio and it appeared that a dynasty may have finally been established. Around 841, the Republic of Venice
Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice or Venetian Republic was a state originating from the city of Venice in Northeastern Italy. It existed for over a millennium, from the late 7th century until 1797. It was formally known as the Most Serene Republic of Venice and is often referred to as La Serenissima, in...
sent a fleet of 60 galleys (each carrying 200 men) to assist the Byzantines in driving the Arabs from Crotone
Crotone
Crotone is a city and comune in Calabria, southern Italy, on the Ionian Sea. Founded circa 710 BC as the Achaean colony of Croton , it was known as Cotrone from the Middle Ages until 1928, when its name was changed to the current one. In 1994 it became the capital of the newly established...
, but failed.
Under Pietro II Candiano
Pietro II Candiano
Pietro II Candiano was the nineteenth Doge of Venice between 932 and 939. He followed his father, Pietro I Candiano , Pietro Tribuno , and Orso II Participazio to become Doge of Venice in 932....
Istria
Istria
Istria , formerly Histria , is the largest peninsula in the Adriatic Sea. The peninsula is located at the head of the Adriatic between the Gulf of Trieste and the Bay of Kvarner...
n cities signed a treaty under which it accepted the Venetian economical supremacy: it was the first move towards the creation of the coastal empire in Dalmatia
Dalmatia
Dalmatia is a historical region on the eastern coast of the Adriatic Sea. It stretches from the island of Rab in the northwest to the Bay of Kotor in the southeast. The hinterland, the Dalmatian Zagora, ranges from fifty kilometers in width in the north to just a few kilometers in the south....
. The autocratic, philo-Imperial Candiano dynasty was overthrown by a revolt in 972, and the populace elected doge Pietro I Orseolo
Pietro I Orseolo
Pietro I Orseolo was the Doge of Venice from 976 to 978. He is venerated as a saint by the Roman Catholic Church. He was born near Udine to one of the more powerful families in Venice...
; however, his conciliating policy was ineffective, and he resigned in favour of Vitale Candiano
Vitale Candiano
Vitale Candiano was the 24th doge of the Republic of Venice.He probably was the fourth son of the 22nd doge, Pietro IV Candiano. He was elected by the popular assembly in September of 978 CE. This after having to flee to Saxony because of the revolt against his father. His predecessor Pietro I...
. Starting from Pietro II Orseolo
Pietro II Orseolo
Pietro II Orseolo was the Doge of Venice from 991 to 1009.He began the period of eastern expansion of Venice that lasted for the better part of 500 years...
, who reigned from 991, attention towards mainland was definitely overshadowed by a strong push towards the control of Adriatic Sea. Inner strife was pacified, and trade with the Byzantine Empire boosted by the favourable treaty (Grisobolus or Golden Bull
Golden Bull
A Golden Bull or chrysobull was a golden ornament representing a seal , attached to a decree issued by Byzantine Emperors and later by monarchs in Europe during the Middle Ages and Renaissance. The term was originally coined for the golden seal itself but came to be applied to the entire decree...
) with Emperor Basil II
Basil II
Basil II , known in his time as Basil the Porphyrogenitus and Basil the Young to distinguish him from his ancestor Basil I the Macedonian, was a Byzantine emperor from the Macedonian dynasty who reigned from 10 January 976 to 15 December 1025.The first part of his long reign was dominated...
. The imperial edict granted Ventian traders freedom from taxation paid by other foreigners and the Byzantines themselves. In the year 1000 an expedition of 6 ships in Istria secured the Venetian suzerainty in the area, and Slav pirates were suppressed permanently.

During the long Investiture Controversy
Investiture Controversy
The Investiture Controversy or Investiture Contest was the most significant conflict between Church and state in medieval Europe. In the 11th and 12th centuries, a series of Popes challenged the authority of European monarchies over control of appointments, or investitures, of church officials such...
, an 11th century dispute between Henry IV, Holy Roman Emperor
Henry IV, Holy Roman Emperor
Henry IV was King of the Romans from 1056 and Holy Roman Emperor from 1084 until his forced abdication in 1105. He was the third emperor of the Salian dynasty and one of the most powerful and important figures of the 11th century...
and Pope Gregory VII
Pope Gregory VII
Pope St. Gregory VII , born Hildebrand of Sovana , was Pope from April 22, 1073, until his death. One of the great reforming popes, he is perhaps best known for the part he played in the Investiture Controversy, his dispute with Henry IV, Holy Roman Emperor affirming the primacy of the papal...
over who would control appointments of church officials, Venice remained neutral, and this caused some attrition of support from the Popes. Doge Domenico Selvo
Domenico Selvo
Domenico Selvo was the 31st Doge of Venice, serving from 1071 to 1084. During his reign as Doge, his domestic policies, the alliances that he forged, and the battles that the Venetian military won and lost laid the foundations for much of the subsequent foreign and domestic policy of the Republic...
also skilfully intervened in the war between the Normans of Apulia
Apulia
Apulia is a region in Southern Italy bordering the Adriatic Sea in the east, the Ionian Sea to the southeast, and the Strait of Òtranto and Gulf of Taranto in the south. Its most southern portion, known as Salento peninsula, forms a high heel on the "boot" of Italy. The region comprises , and...
and the Byzantine Emperor Alexios I Komnenos
Alexios I Komnenos
Alexios I Komnenos, Latinized as Alexius I Comnenus , was Byzantine emperor from 1081 to 1118, and although he was not the founder of the Komnenian dynasty, it was during his reign that the Komnenos family came to full power. The title 'Nobilissimus' was given to senior army commanders,...
in favour of the latter, obtaining in exchange a bull declaring the Venetian supremacy in the Adriatic coast up to Durazzo, as well as the exemption from taxes for his merchants in the whole Byzantine Empire, a considerable factor in the city-state's later accumulation of wealth and power serving as middlemen for the lucrative spice
Spice trade
Civilizations of Asia were involved in spice trade from the ancient times, and the Greco-Roman world soon followed by trading along the Incense route and the Roman-India routes...
and silk trade that funnelled through the Levant
Levant
The Levant or ) is the geographic region and culture zone of the "eastern Mediterranean littoral between Anatolia and Egypt" . The Levant includes most of modern Lebanon, Syria, Jordan, Israel, the Palestinian territories, and sometimes parts of Turkey and Iraq, and corresponds roughly to the...
and Egypt
Egypt
Egypt , officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, Arabic: , is a country mainly in North Africa, with the Sinai Peninsula forming a land bridge in Southwest Asia. Egypt is thus a transcontinental country, and a major power in Africa, the Mediterranean Basin, the Middle East and the Muslim world...
along the ancient Kingdom of Axum and Roman-Indian
Roman trade with India
Roman trade with India through the overland caravan routes via Anatolia and Persia, though at a relative trickle compared to later times, antedated the southern trade route via the Red Sea and monsoons which started around the beginning of the Common Era following the reign of Augustus and his...
routes via the Red Sea
Red Sea
The Red Sea is a seawater inlet of the Indian Ocean, lying between Africa and Asia. The connection to the ocean is in the south through the Bab el Mandeb strait and the Gulf of Aden. In the north, there is the Sinai Peninsula, the Gulf of Aqaba, and the Gulf of Suez...
.
The war was not a military success, but with that act the city gained total independence of Venice also from the formal point of view. In 1084, Domenico Selvo
Domenico Selvo
Domenico Selvo was the 31st Doge of Venice, serving from 1071 to 1084. During his reign as Doge, his domestic policies, the alliances that he forged, and the battles that the Venetian military won and lost laid the foundations for much of the subsequent foreign and domestic policy of the Republic...
had personally led a fleet against the Normans
Normans
The Normans were the people who gave their name to Normandy, a region in northern France. They were descended from Norse Viking conquerors of the territory and the native population of Frankish and Gallo-Roman stock...
, but he was defeated and lost 9 great galleys, the largest and most heavily armed ships in the Venetian war fleet
Naval fleet
A fleet, or naval fleet, is a large formation of warships, and the largest formation in any navy. A fleet at sea is the direct equivalent of an army on land....
.
High Middle Ages
In the High Middle AgesHigh Middle Ages
The High Middle Ages was the period of European history around the 11th, 12th, and 13th centuries . The High Middle Ages were preceded by the Early Middle Ages and followed by the Late Middle Ages, which by convention end around 1500....
, Venice became wealthy through its control of trade between Europe and the Levant
Levant
The Levant or ) is the geographic region and culture zone of the "eastern Mediterranean littoral between Anatolia and Egypt" . The Levant includes most of modern Lebanon, Syria, Jordan, Israel, the Palestinian territories, and sometimes parts of Turkey and Iraq, and corresponds roughly to the...
, and began to expand into the Adriatic Sea
Adriatic Sea
The Adriatic Sea is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan peninsula, and the system of the Apennine Mountains from that of the Dinaric Alps and adjacent ranges...
and beyond. Venice was involved in the Crusades almost from the very beginning; 200 Venetian ships assisted in capturing the coastal cities of Syria
Syria
Syria , officially the Syrian Arab Republic , is a country in Western Asia, bordering Lebanon and the Mediterranean Sea to the West, Turkey to the north, Iraq to the east, Jordan to the south, and Israel to the southwest....
after the First Crusade
First Crusade
The First Crusade was a military expedition by Western Christianity to regain the Holy Lands taken in the Muslim conquest of the Levant, ultimately resulting in the recapture of Jerusalem...
, and in 1123 they were granted virtual autonomy in the Kingdom of Jerusalem
Kingdom of Jerusalem
The Kingdom of Jerusalem was a Catholic kingdom established in the Levant in 1099 after the First Crusade. The kingdom lasted nearly two hundred years, from 1099 until 1291 when the last remaining possession, Acre, was destroyed by the Mamluks, but its history is divided into two distinct periods....
through the Pactum Warmundi
Pactum Warmundi
The Pactum Warmundi was a treaty of alliance established in 1123 between the Crusader Kingdom of Jerusalem and the Republic of Venice.-Background:...
. In 1110, Ordelafo Faliero
Ordelafo Faliero
Ordelafo Faliero de Doni was the 34th Doge of Venice. He was the son of the 32nd doge, Vitale Faliero de' Doni. He was a member of the Minor Council , an assembly formed from members of the so-called "apostolic families" that, in oligarchical Venice, assumed the governmental functions of...
personally commanded a Venetian fleet of 100 ships to assist Baldwin I of Jerusalem
Baldwin I of Jerusalem
Baldwin I of Jerusalem, formerly Baldwin I of Edessa, born Baldwin of Boulogne , 1058? – 2 April 1118, was one of the leaders of the First Crusade, who became the first Count of Edessa and then the second ruler and first titled King of Jerusalem...
in capturing the city of Sidon
Sidon
Sidon or Saïda is the third-largest city in Lebanon. It is located in the South Governorate of Lebanon, on the Mediterranean coast, about 40 km north of Tyre and 40 km south of the capital Beirut. In Genesis, Sidon is the son of Canaan the grandson of Noah...
.

Venetian Arsenal
The Venetian Arsenal was a complex of state-owned shipyards and armories clustered together in Venice in northern Italy. It was responsible for the bulk of Venice's naval power during the middle part of the second millennium AD...
. Building anew and powerful fleets, the republic took control over the eastern Mediterranean. The first exchange business in the world was started in Venezia, to support the merchants from all over Europe. The Venetians also gained extensive trading privileges in the Byzantine Empire and their ships often provided the Empire with a navy. In 1182 there was an anti-Western riot in Constantinople
Constantinople
Constantinople was the capital of the Roman, Eastern Roman, Byzantine, Latin, and Ottoman Empires. Throughout most of the Middle Ages, Constantinople was Europe's largest and wealthiest city.-Names:...
, of which the Venetians were the main targets.
The Venetian fleet was crucial to the transportation of the Fourth Crusade
Fourth Crusade
The Fourth Crusade was originally intended to conquer Muslim-controlled Jerusalem by means of an invasion through Egypt. Instead, in April 1204, the Crusaders of Western Europe invaded and conquered the Christian city of Constantinople, capital of the Eastern Roman Empire...
, but when the crusaders could not pay for the ships, the cunning and manipulative Doge Enrico Dandolo
Enrico Dandolo
Enrico Dandolo — anglicised as Henry Dandolo and Latinized as Henricus Dandulus — was the 41st Doge of Venice from 1195 until his death...
quickly exploited the situation and offered transport to the crusaders if they were to capture the (Christian) Dalmatian city of Zadar
Siege of Zara
The Siege of Zara or Siege of Zadar was the first major action of the Fourth Crusade and the first attack against a Catholic city by Catholic crusaders...
, which had rebelled against Venetian rule in 1183, placed itself under the dual protection of the Papacy and King Emeric of Hungary
Emeric of Hungary
Emeric I , , King of Hungary and Croatia . He was crowned during his father's lifetime, but after his father's death he had to fight against his brother, Andrew, who forced Emeric to assign the government of Croatia and Dalmatia to him...
and had proven too well fortified for Venice to retake alone, because 90% of the shipowners had changed the opinion of Enrico Dandolo. Upon accomplishing this the crusade was again diverted to Constantinople
Constantinople
Constantinople was the capital of the Roman, Eastern Roman, Byzantine, Latin, and Ottoman Empires. Throughout most of the Middle Ages, Constantinople was Europe's largest and wealthiest city.-Names:...
, the capital of the Byzantine Empire
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire was the Eastern Roman Empire during the periods of Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, centred on the capital of Constantinople. Known simply as the Roman Empire or Romania to its inhabitants and neighbours, the Empire was the direct continuation of the Ancient Roman State...
, another rival of Venice. The Dalmatians separated from Hungary by a treaty in 1199 and they paid Hungary with a portion of Macedonia (theme). In 1201 the city of Zadar, formerly under the protection of the Republic of Venice, recognized Emeric, King of Hungary, again as overlord, perhaps because he could not realize Hungary's portion on Macedonia (theme). The city was captured and sacked in 1204; when Macedonia (theme) became disputed between the Crusaders and the Bulgarian Empire
Bulgarian Empire
Bulgarian Empire is a term used to describe two periods in the medieval history of Bulgaria, during which it acted as a key regional power in Europe in general and in Southeastern Europe in particular, rivalling Byzantium...
; the sack has been described as one of the most profitable and disgraceful sacks of a city in history. The Republic of Venice signed a trade treaty with the Mongol Empire
Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire , initially named as Greater Mongol State was a great empire during the 13th and 14th centuries...
in 1221. Koloman of Croatia counted 77 judges in Dalmatia
Dalmatia
Dalmatia is a historical region on the eastern coast of the Adriatic Sea. It stretches from the island of Rab in the northwest to the Bay of Kotor in the southeast. The hinterland, the Dalmatian Zagora, ranges from fifty kilometers in width in the north to just a few kilometers in the south....
in 1235 and wrote their names. The Byzantine Empire, which until then had resisted several attacks and kept the Islamic invaders out of Western Anatolia and Eastern Europe, was reestablished in 1261 but never recovered its previous power and eventually was conquered by the Ottoman Turks
Ottoman Turks
The Ottoman Turks were the Turkish-speaking population of the Ottoman Empire who formed the base of the state's military and ruling classes. Reliable information about the early history of Ottoman Turks is scarce, but they take their Turkish name, Osmanlı , from the house of Osman I The Ottoman...
(which later occupied the Balkans
Balkans
The Balkans is a geopolitical and cultural region of southeastern Europe...
and Hungary, as well as besieged Vienna
Vienna
Vienna is the capital and largest city of the Republic of Austria and one of the nine states of Austria. Vienna is Austria's primary city, with a population of about 1.723 million , and is by far the largest city in Austria, as well as its cultural, economic, and political centre...
on two occasions). The Venetians, who accompanied the crusader fleet, claimed much of the plunder from the city as payment including the famous four bronze horses
Horses of Saint Mark
The Triumphal Quadriga or Horses of St Mark's is a set of bronze statues of four horses, originally part of a monument depicting a quadriga , which have been set into the facade of St Mark's Basilica in Venice, northern Italy, since the 13th century.-Origins:The sculptures date from late classical...
which were brought back to adorn St. Mark's basilica. As a result of the partition of the Byzantine Empire
Partitio terrarum imperii Romaniae
The Partitio terrarum imperii Romaniae was a treaty signed after the sack of the Byzantine capital, Constantinople, by the Fourth Crusade in 1204...
which followed, Venice gained some strategic territories in the Aegean Sea
Aegean Sea
The Aegean Sea[p] is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea located between the southern Balkan and Anatolian peninsulas, i.e., between the mainlands of Greece and Turkey. In the north, it is connected to the Marmara Sea and Black Sea by the Dardanelles and Bosporus...
(three-eighths of the Byzantine Empire), including the islands of Crete
Crete
Crete is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, and one of the thirteen administrative regions of Greece. It forms a significant part of the economy and cultural heritage of Greece while retaining its own local cultural traits...
and Euboea
Euboea
Euboea is the second largest Greek island in area and population, after Crete. The narrow Euripus Strait separates it from Boeotia in mainland Greece. In general outline it is a long and narrow, seahorse-shaped island; it is about long, and varies in breadth from to...
; moreover, some present day cities, such as Chania
Chania
Chaniá , , also transliterated Chania, Hania, and Xania, older form Chanea and Venetian Canea, Ottoman Turkish خانيه Hanya) is the second largest city of Crete and the capital of the Chania peripheral unit...
on Crete, have core architecture
Architecture
Architecture is both the process and product of planning, designing and construction. Architectural works, in the material form of buildings, are often perceived as cultural and political symbols and as works of art...
that is substantially Venetian in origin. The Aegean islands formed the Venetian Duchy of the Archipelago
Duchy of the Archipelago
The Duchy of the Archipelago or also Duchy of Naxos or Duchy of the Aegean was a maritime state created by Venetian interests in the Cyclades archipelago in the Aegean Sea, in the aftermath of the Fourth Crusade, centered on the islands of Naxos and Paros.-Background and establishment of the...
.
In 1295, Pietro Gradenigo
Pietro Gradenigo
Pietro Gradenigo was the 49th Doge of Venice, reigning from 1289 to his death.When he was elected Doge, he was serving as the podestà of Koper / Capodistria in Slovenia. Venice suffered a serious blow with the fall of Acre, the last Crusader stronghold in the Holy Land, to the Mamluks of Egypt in...
sent a fleet of 68 ships to attack a Genoese
Republic of Genoa
The Most Serene Republic of Genoa |Ligurian]]: Repúbrica de Zêna) was an independent state from 1005 to 1797 in Liguria on the northwestern Italian coast, as well as Corsica from 1347 to 1768, and numerous other territories throughout the Mediterranean....
fleet at Alexandretta, then another fleet of 100 ships were sent to attack the Genoese in 1299.
In late 14th century, Venice had to face difficulties on her eastern side, especially during the reign of Louis I of Hungary. In 1346 he made a first attempt to conquerd Zadar
Zadar
Zadar is a city in Croatia on the Adriatic Sea. It is the centre of Zadar county and the wider northern Dalmatian region. Population of the city is 75,082 citizens...
, but was defeated. In 1356 an alliance was formed by the counts of Gorizia, Francesco I da Carrara
Francesco I da Carrara
Francesco I da Carrara was Lord of Padua from 1350 to 1388.The son of the assassinated Giacomo II da Carrara, he succeeded him as lord of Padua by popular acclamation. In 1356 he was named imperial vicar by emperor Charles IV...
, lord of Padua
Padua
Padua is a city and comune in the Veneto, northern Italy. It is the capital of the province of Padua and the economic and communications hub of the area. Padua's population is 212,500 . The city is sometimes included, with Venice and Treviso, in the Padua-Treviso-Venice Metropolitan Area, having...
, Nicolaus, partiarch of Aquileia and his half brother emperor Charles IV
Charles IV, Holy Roman Emperor
Charles IV , born Wenceslaus , was the second king of Bohemia from the House of Luxembourg, and the first king of Bohemia to also become Holy Roman Emperor....
, Louis I and the dukes of Austria. The league's troops occupied Grado
Grado, Italy
Grado is a town and comune in the north-eastern Italian region of Friuli-Venezia Giulia, located on a peninsula of the Adriatic Sea between Venice and Trieste....
and Muggia
Muggia
Muggia is a small Italian comune in the extreme south-east of Trieste lying on the border with Slovenia.Muggia is the last and only flap of Istria still in Italian territory, after the dissolution of the Free Territory of Trieste in 1954....
(1356), while Louis stripped Venice of most of Dalmatia
Dalmatia
Dalmatia is a historical region on the eastern coast of the Adriatic Sea. It stretches from the island of Rab in the northwest to the Bay of Kotor in the southeast. The hinterland, the Dalmatian Zagora, ranges from fifty kilometers in width in the north to just a few kilometers in the south....
. The siege of Treviso
Treviso
Treviso is a city and comune in Veneto, northern Italy. It is the capital of the province of Treviso and the municipality has 82,854 inhabitants : some 3,000 live within the Venetian walls or in the historical and monumental center, some 80,000 live in the urban center proper, while the city...
(July-September 1356) was a failure, but Venice suffered a severe defeat at Nervesa (13 January 1358), being forced to cede Dalmatia and Croatia to Hungary
Hungary
Hungary , officially the Republic of Hungary , is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is situated in the Carpathian Basin and is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine and Romania to the east, Serbia and Croatia to the south, Slovenia to the southwest and Austria to the west. The...
. From 1350 to 1381, Venice also fought an intermittent war with the Genoese
Venetian-Genoese War
The Venetian–Genoese Wars were a long-standing conflict between the Republic of Genoa and the Republic of Venice for dominance in the eastern Mediterranean Sea between 1256 and 1381. It occurred in four spurts of open warfare. The first three were primarily naval conflicts, fought in the Eastern...
. Initially defeated, they destroyed the Genoese fleet at the Battle of Chioggia
Battle of Chioggia
The naval Battle of Chioggia took place on June 21, 1380 in the lagoon off Chioggia, Italy, between the Venetian and the Genoese fleets, who had captured the little fishing port in August the preceding year. This occurred during the War of Chioggia....
in 1380 and retained their prominent position in eastern Mediterranean affairs at the expense of Genoa. However, the peace cause Venice to lose several territories to other participants to the war: Conegliano
Conegliano
Conegliano is a town and comune of the Veneto region, Italy, in the province of Treviso, about north by rail from the town of Treviso. The population of the city is of around 36,000 people. The remains of a castle that was built in the 10th century remain on a nearby hill...
was occupied by the Austrians
Austrians
Austrians are a nation and ethnic group, consisting of the population of the Republic of Austria and its historical predecessor states who share a common Austrian culture and Austrian descent....
, Treviso
Treviso
Treviso is a city and comune in Veneto, northern Italy. It is the capital of the province of Treviso and the municipality has 82,854 inhabitants : some 3,000 live within the Venetian walls or in the historical and monumental center, some 80,000 live in the urban center proper, while the city...
was taken over by Carraresi, Tenedos
Tenedos
Tenedos or Bozcaada or Bozdja-Ada is a small island in the Aegean Sea, part of the Bozcaada district of Çanakkale province in Turkey. , Tenedos has a population of about 2,354. The main industries are tourism, wine production and fishing...
fell to the Byzantine Empire
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire was the Eastern Roman Empire during the periods of Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, centred on the capital of Constantinople. Known simply as the Roman Empire or Romania to its inhabitants and neighbours, the Empire was the direct continuation of the Ancient Roman State...
, Trieste to the Patriarchate of Aquileia
Patriarchate of Aquileia
The Patriarchate of Aquileia was an early center of Christianity, an historical state and catholic episcopal see, and today a catholic titular see in northeastern Italy, centred on the ancient city of Aquileia situated at the head of the Adriatic, on what is now the Italian sea-coast, at the...
, and the Serenissima lost control of Dalmatia as well (to Hungary).
In 1363, a colonial revolt
Revolt of St. Titus
The Revolt of Saint Titus was a fourteenth century rebellion against the Republic of Venice in the Venetian colony of Crete. The rebels overthrew the official Venetian authorities and attempted to create an independent state, declaring Crete a republic under the protection of Saint Titus : the...
broke out in Crete that needed considerable military force and five years to suppress.
15th century
In the early fifteenth century, the Venetians also began to expand in Italy, as well as along the DalmatiaDalmatia
Dalmatia is a historical region on the eastern coast of the Adriatic Sea. It stretches from the island of Rab in the northwest to the Bay of Kotor in the southeast. The hinterland, the Dalmatian Zagora, ranges from fifty kilometers in width in the north to just a few kilometers in the south....
n coast from Istria to Albania
Albania
Albania , officially known as the Republic of Albania , is a country in Southeastern Europe, in the Balkans region. It is bordered by Montenegro to the northwest, Kosovo to the northeast, the Republic of Macedonia to the east and Greece to the south and southeast. It has a coast on the Adriatic Sea...
, which was acquired from King Ladislaus of Naples. Venice installed nobility to govern the area, for example, Count Filippo Stipanov in Zara. This move by the Venetians was as a response to the threatening expansion of Giangaleazzo Visconti, Duke of Milan
Milan
Milan is the second-largest city in Italy and the capital city of the region of Lombardy and of the province of Milan. The city proper has a population of about 1.3 million, while its urban area, roughly coinciding with its administrative province and the bordering Province of Monza and Brianza ,...
. Control over the north-east main land routes was also a necessity for the safety of the trades. By 1410, Venice had a navy of 3,300 ships (manned by 36,000 men) and taken over most of Venetia, including such important cities as Verona
Verona
Verona ; German Bern, Dietrichsbern or Welschbern) is a city in the Veneto, northern Italy, with approx. 265,000 inhabitants and one of the seven chef-lieus of the region. It is the second largest city municipality in the region and the third of North-Eastern Italy. The metropolitan area of Verona...
and Padua
Padua
Padua is a city and comune in the Veneto, northern Italy. It is the capital of the province of Padua and the economic and communications hub of the area. Padua's population is 212,500 . The city is sometimes included, with Venice and Treviso, in the Padua-Treviso-Venice Metropolitan Area, having...
.
The situation in Dalmatia had been settled in 1408 by a truce with King Sigismund of Hungary. At its expiry, Venice immediately invaded the Patriarchate of Aquileia, and subjected Traù
TRAU
Transcoder and Rate Adaptation Unit, or TRAU, performs transcoding function for speech channels and RA for data channels in the GSM network....
, Split
Split (city)
Split is a Mediterranean city on the eastern shores of the Adriatic Sea, centered around the ancient Roman Palace of the Emperor Diocletian and its wide port bay. With a population of 178,192 citizens, and a metropolitan area numbering up to 467,899, Split is by far the largest Dalmatian city and...
, Durazzo and other Dalmatian cities. The difficulties of Hungary allowed the Republic to consolidate its Adriatic dominions.
Under doge Francesco Foscari
Francesco Foscari
Francesco Foscari was doge of Venice from 1423 to 1457, at the inception of the Italian Renaissance.-Biography:Foscari, of an ancient noble family, served the Republic of Venice in numerous official capacities—as ambassador, president of the Forty, member of the Council of Ten, inquisitor,...
(1423–57) the city reached the height of its power and territorial extension. In 1425 a new war broke out, this time against Filippo Maria Visconti
Filippo Maria Visconti
Filippo Maria Visconti was ruler of Milan from 1412 to 1447.-Biography:Filippo Maria Visconti, who had become nominal ruler of Pavia in 1402, succeeded his assassinated brother Gian Maria Visconti as Duke of Milan in 1412. They were the sons of Gian Galeazzo Visconti, Gian Maria's predecessor, by...
of Milan. The victory at the Battle of Maclodio
Battle of Maclodio
The Battle of Maclodio was fought on 11 October 1427, resulting in a victory for the Venetians under Carmagnola over the Milanese under Carlo I Malatesta. The battle was fought at Maclodio a small town near the River Oglio, fifteen kilometres south-west of Brescia...
of Count of Carmagnola, commander of the Venetian army, the shift of the western border from the Adige to the Adda
Adda River
The Adda is a river in North Italy, a tributary of the Po. It rises in the Alps near the border with Switzerland and flows through Lake Como. The Adda joins the Po a few kilometres upstream of Cremona. It is 313 kilometres long...
. However, the territorial expansion was not welcome everywhere in Venice; tension with Milan remained high, and in 1446 the Republic had to fight another league, formed by Milan, Florence, Bologna and Cremona. After an initial Venetian victory under Micheletto Attendolo
Micheletto Attendolo
thumb|350px|The decisive attack of Micheletto Attendolo at San Romano, part of The Battle of San Romano triptych by [[Paolo Uccello]]. [[Musée du Louvre]], [[Paris]].Micheletto Attendolo was an Italian condottiero....
at Casalmaggiore
Casalmaggiore
Casalmaggiore is a comune in the province of Cremona, Lombardy, northern Italy, located across the Po River. It was the birthplace of Italian composers Ignazio Donati and Andrea Zani ....
, however, Visconti died and in Milan a republic was declared. The Serenissima had then free ground to occupy Lodi and Piacenza
Piacenza
Piacenza is a city and comune in the Emilia-Romagna region of northern Italy. It is the capital of the province of Piacenza...
, but was halted by Francesco Sforza; later, Sforza and the Doge allied to allow him the rule of Milan, in exchange of the cession of Brescia
Brescia
Brescia is a city and comune in the region of Lombardy in northern Italy. It is situated at the foot of the Alps, between the Mella and the Naviglio, with a population of around 197,000. It is the second largest city in Lombardy, after the capital, Milan...
and Vicenza
Vicenza
Vicenza , a city in north-eastern Italy, is the capital of the eponymous province in the Veneto region, at the northern base of the Monte Berico, straddling the Bacchiglione...
. Venice, however, again changed side when the power of Sforza seemed to became excessive: the intricate situation was settled with the Peace of Lodi (1454), which confirmed the area of Bergamo
Bergamo
Bergamo is a town and comune in Lombardy, Italy, about 40 km northeast of Milan. The comune is home to over 120,000 inhabitants. It is served by the Orio al Serio Airport, which also serves the Province of Bergamo, and to a lesser extent the metropolitan area of Milan...
and Brescia to the Republic. At this time, the territories under the Serenissima included much of the modern Veneto
Veneto
Veneto is one of the 20 regions of Italy. Its population is about 5 million, ranking 5th in Italy.Veneto had been for more than a millennium an independent state, the Republic of Venice, until it was eventually annexed by Italy in 1866 after brief Austrian and French rule...
, Friuli
Friuli
Friuli is an area of northeastern Italy with its own particular cultural and historical identity. It comprises the major part of the autonomous region Friuli-Venezia Giulia, i.e. the province of Udine, Pordenone, Gorizia, excluding Trieste...
, the provinces of Bergamo, Cremona and Trento, as well as Ravenna
Ravenna
Ravenna is the capital city of the Province of Ravenna in the Emilia-Romagna region of Italy and the second largest comune in Italy by land area, although, at , it is little more than half the size of the largest comune, Rome...
, Istria and Dalmatia. Eastern borders were with the county of Gorizia
County of Gorizia
The County of Görz was a county based around the town of Gorizia in the present-day Friuli-Venezia Giulia region of north-eastern Italy.Count Meinhard, descendant of the Bavarian Meinhardiner noble family with possessions around Lienz in Tyrol, is mentioned as early as 1107...
and the ducal lands of Austria, while in the south was the Duchy of Ferrara
Duchy of Ferrara
The Duchy of Ferrara is a former sovereign state of northern Italy.Obizzo II d'Este was proclaimed lifelong ruler of Ferrara in 1264. He also became seignior of nearby Modena in 1288 and of Reggio in 1289...
. Oversea dominions included Euboea
Euboea
Euboea is the second largest Greek island in area and population, after Crete. The narrow Euripus Strait separates it from Boeotia in mainland Greece. In general outline it is a long and narrow, seahorse-shaped island; it is about long, and varies in breadth from to...
and Egina.

Constantinople
Constantinople was the capital of the Roman, Eastern Roman, Byzantine, Latin, and Ottoman Empires. Throughout most of the Middle Ages, Constantinople was Europe's largest and wealthiest city.-Names:...
fell to the Ottomans, but Venice managed to maintain a colony in the city and some of the former trade privileges it had had under the Byzantines. Indeed, in 1454, the Ottomans granted the Venetians their ports and trading rights. Despite the recent Ottoman defeats against John Hunyadi
John Hunyadi
John Hunyadi John Hunyadi (Hungarian: Hunyadi János , Medieval Latin: Ioannes Corvinus or Ioannes de Hunyad, Romanian: Iancu (Ioan) de Hunedoara, Croatian: Janko Hunjadi, Serbian: Сибињанин Јанко / Sibinjanin Janko, Slovak: Ján Huňady) John Hunyadi (Hungarian: Hunyadi János , Medieval Latin: ...
of Hungary and Scanderbeg in Albania, war was however unavoidable. In 1463 the Venetian fortress of Argos
Argos
Argos is a city and a former municipality in Argolis, Peloponnese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Argos-Mykines, of which it is a municipal unit. It is 11 kilometres from Nafplion, which was its historic harbour...
was ravaged. Venice set up an alliance with Matthias Corvinus of Hungary
Matthias Corvinus of Hungary
Matthias Corvinus , also called the Just in folk tales, was King of Hungary and Croatia from 1458, at the age of 14 until his death...
and attacked the Greek islands by sea and Bulgaria by land. Both fronts however saw the allies forced to retreat, after several minor victories. Operations were reduced mostly to isolated ravages and guerrilla attacks, until the Ottomans moved a massive counteroffensive in 1470: this had Venice lose its main stronghold in the Aegean Sea, Negroponte
Lordship of Negroponte
The Lordship of Negroponte was a crusader state established on the island of Euboea after the partition of the Byzantine Empire following the Fourth Crusade. Partitioned into three baronies run by a few interrelated Lombard families, the island soon fell under the influence of the Republic of...
. The Venetians sought an alliance with the Shah of Persia and other European powers, but, received only limited support, could make only small-scale attacks at Antalya
Antalya
Antalya is a city on the Mediterranean coast of southwestern Turkey. With a population 1,001,318 as of 2010. It is the eighth most populous city in Turkey and country's biggest international sea resort.- History :...
, Halicarnassus
Halicarnassus
Halicarnassus was an ancient Greek city at the site of modern Bodrum in Turkey. It was located in southwest Caria on a picturesque, advantageous site on the Ceramic Gulf. The city was famous for the tomb of Mausolus, the origin of the word mausoleum, built between 353 BC and 350 BC, and...
and Smirne. However, the Ottomans conquered the Peloponnesus and launched an offensive in Venetian mainland, closing in on the important centre of Udine
Udine
Udine is a city and comune in northeastern Italy, in the middle of Friuli-Venezia Giulia region, between the Adriatic sea and the Alps , less than 40 km from the Slovenian border. Its population was 99,439 in 2009, and that of its urban area was 175,000.- History :Udine is the historical...
. The Persians, together with the Caramanian amir, were severely defeated at Terdguin, and the Republic was left alone. Further, much of Albania went lost after Scanderbeg's death. However, the heroic resistance of Scutari
Shkodër
Shkodër , is a city located on Lake of Shkoder in northwestern Albania in the District of Shkodër, of which it is the capital. It is one of the oldest and most historic towns in Albania, as well as an important cultural and economic centre. Shkodër's estimated population is 90,000; if the...
under Antonio Loredan forced the Ottomans to retire from Albania, while a revolt in Cyprus
Cyprus
Cyprus , officially the Republic of Cyprus , is a Eurasian island country, member of the European Union, in the Eastern Mediterranean, east of Greece, south of Turkey, west of Syria and north of Egypt. It is the third largest island in the Mediterranean Sea.The earliest known human activity on the...
gave back the island to the Cornaro
Cornaro
The Cornaro, also known as Corner, are an illustrious patrician family in Venice, from which for centuries senior office-holders and Doges sprung...
family and, subsequently, to the Serenissima (1473). Its prestige seemed reassured, but Scutari fell anyway two years later, and Friuli was again invaded and ravaged. On January 24, 1479, a treaty of peace was finally signed with the Ottomans. Venice had to cede Argo, Negroponte, Lemnos
Lemnos
Lemnos is an island of Greece in the northern part of the Aegean Sea. Administratively the island forms a separate municipality within the Lemnos peripheral unit, which is part of the North Aegean Periphery. The principal town of the island and seat of the municipality is Myrina...
and Scutari, and pay an annual tribute of 10,000 golden ducat
Ducat
The ducat is a gold coin that was used as a trade coin throughout Europe before World War I. Its weight is 3.4909 grams of .986 gold, which is 0.1107 troy ounce, actual gold weight...
i. Five years later the agreement was confirmed by Mehmed II
Mehmed II
Mehmed II , was Sultan of the Ottoman Empire for a short time from 1444 to September 1446, and later from...
's successor, Bayezid II
Bayezid II
Bayezid II or Sultân Bayezid-î Velî was the oldest son and successor of Mehmed II, ruling as Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1481 to 1512...
, with the peaceful exchange of the islands of Zakynthos
Zakynthos
Zakynthos , also Zante, the other form often used in English and in Italian , is a Greek island in the Ionian Sea. It is the third largest of the Ionian Islands. It is also a separate regional unit of the Ionian Islands region, and the only municipality of the regional unit. It covers an area of ...
and Kefalonia
Kefalonia
The island of Cephalonia, also known as Kefalonia, Cephallenia, Cephallonia, Kefallinia, or Kefallonia , is the largest of the Ionian Islands in western Greece, with an area of . It is also a separate regional unit of the Ionian Islands region, and the only municipality of the regional unit...
between the two sides.
In 1482 Venice allied with Pope Sixtus IV
Pope Sixtus IV
Pope Sixtus IV , born Francesco della Rovere, was Pope from 1471 to 1484. His accomplishments as Pope included the establishment of the Sistine Chapel; the group of artists that he brought together introduced the Early Renaissance into Rome with the first masterpiece of the city's new artistic age,...
in his attempt to conquer Ferrara, opposed to Florence, Naples, Milan and Ercole d'Este (see War of Ferrara). When Papal-Venetian milices were smashed at the Battle of Campomorto
Battle of Campomorto
The Battle of Campomorto is a battle fought near Frosinone, in the Lazio on August 21, 1482, in the course of the War of Ferrara.It saw the Papal army, led by the famous condottiero Roberto Malatesta, face King Ferdinand I of Naples's army, under the command of Alfonso, Duke of Calabria.Malatesta...
, Sixtus changed side. Again alone, the Venetians were defeated in the Veronese by Alfonso of Calabria, but conquered Gallipoli
Gallipoli
The Gallipoli peninsula is located in Turkish Thrace , the European part of Turkey, with the Aegean Sea to the west and the Dardanelles straits to the east. Gallipoli derives its name from the Greek "Καλλίπολις" , meaning "Beautiful City"...
, in Puglia, by sea. The balance was changed by Ludovico Sforza
Ludovico Sforza
Ludovico Sforza , was Duke of Milan from 1489 until his death. A member of the Sforza family, he was the fourth son of Francesco Sforza. He was famed as a patron of Leonardo da Vinci and other artists, and presided over the final and most productive stage of the Milanese Renaissance...
of Milan, who passed on the side of Venice: this led to a quick peace, which was signed near Brescia on 7 August 1484. In spite of the numerous setbacks suffered in the campaign, Venice obtained the Polesine
Polesine
Polesine is a geographic and historic area in the north-east of Italy corresponding nowadays with the province of Rovigo; it is a strip of land about 100-km long and 18-km wide located between the lower courses of the Adige and the Po rivers.- Geography :...
and Rovigo
Rovigo
Rovigo is a town and comune in the Veneto region of North-Eastern Italy, the capital of the eponymous province. -Geography:...
, and increased its prestige in the Italian peninsula, at the expense of Florence especially. In the late 1480s, Venice fought two brief campaigns against the new Pope Innocent VIII
Pope Innocent VIII
Pope Innocent VIII , born Giovanni Battista Cybo , was Pope from 1484 until his death.-Early years:Giovanni Battista Cybo was born at Genoa of Greek extraction...
and Sigismund of Austria. Venetian troops were also present at the Battle of Fornovo
Battle of Fornovo
The Battle of Fornovo took place 30 km southwest of the city of Parma on 6 July 1495. The League of Venice was able to temporarily expel the French from the Italian Peninsula. It was the first major battle of the Italian Wars.-Antecedents:...
, which saw the Italian League against Charles VIII of France
Charles VIII of France
Charles VIII, called the Affable, , was King of France from 1483 to his death in 1498. Charles was a member of the House of Valois...
. Alliance with Spain/Aragon in the following reconquest of the Kingdom of Naples granted it the control of the Apulian ports, important strategic bases commanding the lower Adriatic and the Ionian islands
Ionian Islands
The Ionian Islands are a group of islands in Greece. They are traditionally called the Heptanese, i.e...
.
Despite the setbacks in the struggle against the Turks, at the end of 15th century, with 180,000 inhabitants, Venice was the second largest city in Europe after Paris and probably the richest in the world. The territory of the Republic of Venice extended over approximately 70000 km² (27,027.2 sq mi) with 2.1 million inhabitants (for a comparative example in the same time England hosted 3 million, the whole of Italy 11, France 13, Portugal 1.7, Spain 6, Germany/Holy Roman Empire 10).
Administratively the territory was divided in three main parts:
- the DogadoDogadoThe Dogado or Duchy of Venice was the word used to define a Doge's reign and the name given to the homeland of the Republic of Venice, headed by the Doge....
(literally the territory under the Doge) comprising the islets of the city and the original lands around the lagoon; - the Stato da MarStato da MàrThe Stato da Màr or Domini da Màr was the name given to the Republic of Venice's maritime and overseas possessions, including Istria, Dalmatia, Negroponte, the Morea , the Aegean islands of the Duchy of the Archipelago, and the islands of Crete and Cyprus...
(the Sea State) comprising Istria, Dalmatia, the Albanian coasts, the Apulian ports, the Venetian Ionian Islands, CreteCreteCrete is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, and one of the thirteen administrative regions of Greece. It forms a significant part of the economy and cultural heritage of Greece while retaining its own local cultural traits...
, the Aegean Archipelago, Cyprus and many fortress and commercial colonies in the major cities and ports around south-east Europe and the Middle East; - the Stato di Terraferma (the Mainland State) comprising Veneto, Friuli, Venetia IuliaJulian MarchThe Julian March is a former political region of southeastern Europe on what are now the borders between Croatia, Slovenia, and Italy...
, East LombardyLombardyLombardy is one of the 20 regions of Italy. The capital is Milan. One-sixth of Italy's population lives in Lombardy and about one fifth of Italy's GDP is produced in this region, making it the most populous and richest region in the country and one of the richest in the whole of Europe...
and RomagnaRomagnaRomagna is an Italian historical region that approximately corresponds to the south-eastern portion of present-day Emilia-Romagna. Traditionally, it is limited by the Apennines to the south-west, the Adriatic to the east, and the rivers Reno and Sillaro to the north and west...
.
In 1485, the French ambassador, Philippe de Commines
Philippe de Commines
Philippe de Commines was a writer and diplomat in the courts of Burgundy and France. He has been called "the first truly modern writer" and "the first critical and philosophical historian since classical times"...
, wrote of Venice,

League of Cambrai, Lepanto and the loss of Cyprus
In 1499 Venice allied itself with Louis XII of FranceLouis XII of France
Louis proved to be a popular king. At the end of his reign the crown deficit was no greater than it had been when he succeeded Charles VIII in 1498, despite several expensive military campaigns in Italy. His fiscal reforms of 1504 and 1508 tightened and improved procedures for the collection of taxes...
against Milan, gaining Cremona
Cremona
Cremona is a city and comune in northern Italy, situated in Lombardy, on the left bank of the Po River in the middle of the Pianura Padana . It is the capital of the province of Cremona and the seat of the local City and Province governments...
. In the same year the Ottoman sultan moved to attack Lepanto
Lepanto
- Places :*The Bay of Lepanto or Gulf of Lepanto in Greece, now known as the Gulf of Corinth*The Greek town of Lepanto, now known as Naupactus*Lepanto, Arkansas in the United States*Lepanto - Ships :*The Italian battleship Lepanto...
by land, and sent a large fleet to support his offensive by sea. Antonio Grimani
Antonio Grimani
Antonio Grimani was the Doge of Venice from 1521 to 1523.-Biography:He was born in Venice into a relatively poor family and in his early years he worked as a tradesman, soon becoming one of the most important ones in the city...
, more a businessman and diplomat than a sailor, was defeated in the sea Battle of Zonchio
Battle of Zonchio
The naval Battle of Zonchio took place on four separate days: August 12, 20, 22 and 25, 1499. It was a part of the Ottoman–Venetian War of 1499–1503...
in 1499. The Turks once again sacked Friuli. Preferring peace to total war both against the Turks and by sea, Venice surrendered the bases of Lepanto, Modon
Methoni, Messenia
Methoni is a village and a former municipality in Messenia, Peloponnese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Pylos-Nestoras, of which it is a municipal unit. Its name may be derived from Mothona, a mythical rock. It is located 11 km south of Pylos and...
and Coron
Koroni
Koroni or Coroni is a town and a former municipality in Messenia, Peloponnese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Pylos-Nestoras, of which it is a municipal unit. Known as Corone by the Venetians and Ottomans, the town of Koroni Koroni or Coroni is a...
.
Venice became rich on trade, but the guilds in Venice also produced superior silks, brocades, goldsmith jewelry and articles, armour and glass in the form of beads and eyeglasses. However, Venice's attention was diverted from her usual trade and maritime position by the delicate situation in Romagna
Romagna
Romagna is an Italian historical region that approximately corresponds to the south-eastern portion of present-day Emilia-Romagna. Traditionally, it is limited by the Apennines to the south-west, the Adriatic to the east, and the rivers Reno and Sillaro to the north and west...
, then one of the richest lands in Italy, which was nominally part of the Papal States but effectively divided into a series of small lordships which were difficult for Rome's troops to control. Eager to take some of Venice's lands, all neighbouring powers joined in the League of Cambrai in 1508, under the leadership of Pope Julius II
Pope Julius II
Pope Julius II , nicknamed "The Fearsome Pope" and "The Warrior Pope" , born Giuliano della Rovere, was Pope from 1503 to 1513...
. The pope wanted Romagna, emperor Maximilian I
Maximilian I, Holy Roman Emperor
Maximilian I , the son of Frederick III, Holy Roman Emperor and Eleanor of Portugal, was King of the Romans from 1486 and Holy Roman Emperor from 1493 until his death, though he was never in fact crowned by the Pope, the journey to Rome always being too risky...
Friuli
Friuli
Friuli is an area of northeastern Italy with its own particular cultural and historical identity. It comprises the major part of the autonomous region Friuli-Venezia Giulia, i.e. the province of Udine, Pordenone, Gorizia, excluding Trieste...
and Veneto
Veneto
Veneto is one of the 20 regions of Italy. Its population is about 5 million, ranking 5th in Italy.Veneto had been for more than a millennium an independent state, the Republic of Venice, until it was eventually annexed by Italy in 1866 after brief Austrian and French rule...
, Spain the Apulian ports, the king of France Cremona, the king of Hungary Dalmatia, and each of the others some part. The offensive against the huge army enlisted by Venice was launched from France. On 14 May 1509 Venice was crushingly defeated at the Battle of Agnadello
Battle of Agnadello
The Battle of Agnadello, also known as Vailà, was one of the more significant battles of the War of the League of Cambrai and one of the major battles of the Italian Wars....
, in the Ghiara d'Adda, marking one of the most delicate points of Venetian history. French and imperial troops were occupying Veneto, but Venice managed to extricate herself through diplomatic efforts. The Apulian ports were ceded in order to come to terms with Spain, and Pope Julius II soon recognized the danger brought by the eventual destruction of Venice (then the only Italian power able to face large states like France or Ottoman Turkey). The citizens of the mainland rose to the cry of "Marco, Marco", and Andrea Gritti
Andrea Gritti
Andrea Gritti was the Doge of Venice from 1523 to 1538, following a distinguished diplomatic and military career.Gritti was born in Bardolino, near Verona. He spent much of his early life in Constantinople as a grain merchant, looking after Venetian interests...
recaptured Padua in July 1509, successfully defending it against the besieging imperial troops. Spain and the pope broke off their alliance with France, and Venice also regained Brescia and Verona from France. After seven years of ruinous war, the Serenissima regained her mainland dominions up to the Adda. Although the defeat had turned into a victory, the events of 1509 marked the end of the Venetian expansion.
Gasparo Contarini
Gasparo Contarini
thumb|240px|Gasparo Contarini.Gasparo Contarini was an Italian diplomat and cardinal. He was one of the first proponents of the dialogue with Protestants, after the Reformation.-Biography:...
's De Magistratibus et Republica Venetorum (1544) clearly shows the approval and interest which surrounded Venice's constitutional arrangements. It also illustrates foreigners' astonishment at Venice's independence and resistance to Italy's loss of freedom and, not least, at her having emerged unscathed from the war against the League of Cambrai. Contarini suggested that the secret of Venice's greatness lay in the co-existence
Mixed government
Mixed government, also known as a mixed constitution, is a form of government that integrates elements of democracy, aristocracy, and monarchy. In a mixed government, some issues are decided by the majority of the people, some other issues by few, and some other issues by a single person...
of Aristotle
Aristotle
Aristotle was a Greek philosopher and polymath, a student of Plato and teacher of Alexander the Great. His writings cover many subjects, including physics, metaphysics, poetry, theater, music, logic, rhetoric, linguistics, politics, government, ethics, biology, and zoology...
's three types of government, monarchy
Monarchy
A monarchy is a form of government in which the office of head of state is usually held until death or abdication and is often hereditary and includes a royal house. In some cases, the monarch is elected...
, oligarchy
Oligarchy
Oligarchy is a form of power structure in which power effectively rests with an elite class distinguished by royalty, wealth, family ties, commercial, and/or military legitimacy...
, and democracy
Democracy
Democracy is generally defined as a form of government in which all adult citizens have an equal say in the decisions that affect their lives. Ideally, this includes equal participation in the proposal, development and passage of legislation into law...
. In his opinion, the Maggior Consiglio
Great Council of Venice
The Great Council of Venice , originally the Consilium Sapientis was a political organ of the Republic of Venice between 1172 and 1797 and met in a special large hall of the Palazzo Ducale....
was the "democratic" part, the Senate and the Ten
Council of Ten
The Council of Ten, or simply the Ten, was, from 1310 to 1797, one of the major governing bodies of the Republic of Venice whose actions were often secretive. Although some sources may indicate that the Council of Ten was generally accepted in Venice, there was some opposition...
were the oligarchy, while the doge represented monarchy. The combination of these three principles in the Venetian government came as close as was possible to perfection in the mechanism of government. At the same time the patrician
Patricianship
Patricianship, the quality of belonging to a patriciate, began in the ancient world, where cities such as Ancient Rome had a class of patrician families whose members were the only people allowed to exercise many political functions...
Marino Sanudo, a politician who had a remarkable career, and a celebrated diarist, was bemoaning the corruption which resulted from the great number of poor or impoverished patricians.
The struggle for supremacy in Italy between France and Spain was resolved in favour of the latter. Caught between the Spanish-Imperial and Turkish superpowers, the Republic adopted a skilful political strategy of quasi-neutrality in Europe, which turned into a defensive stance against the Ottomans. Venice's maritime aid was potentially useful to Spain, but not to the point of allowing her to reinforce her position in the Levant, which would increase her strength in Italy as well, where she was practically the only Italian state not subject to Spain. In the Turkish war of 1537-40
Ottoman–Venetian War (1537–1540)
The Ottoman–Venetian War of 1537–1540 was one of the numerous Ottoman–Venetian Wars of the period. The Ottoman Emperor Suleiman the Magnificent had been angered by a treaty signed between the Republic of Venice and the Habsburg Empire of Charles V...
, Venice was allied with the emperor and King of Spain, Charles V
Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor
Charles V was ruler of the Holy Roman Empire from 1519 and, as Charles I, of the Spanish Empire from 1516 until his voluntary retirement and abdication in favor of his younger brother Ferdinand I and his son Philip II in 1556.As...
. Andrea Doria
Andrea Doria
Andrea Doria was an Italian condottiere and admiral from Genoa.-Early life:Doria was born at Oneglia from the ancient Genoese family, the Doria di Oneglia branch of the old Doria, de Oria or de Auria family. His parents were related: Ceva Doria, co-lord of Oneglia, and Caracosa Doria, of the...
, commander of the allied fleets, was defeated at Preveza
Battle of Preveza
The naval Battle of Preveza took place on 28 September 1538 near Preveza in northwestern Greece between an Ottoman fleet and that of a Christian alliance assembled by Pope Paul III.-Background:...
in 1538, and two years later Venice signed a treaty of peace by which the Turks took the Aegean duchy of Naxos from the Sanudo family. After Preveza the supremacy of the sea passed to the Ottomans.
Difficulties in the rule of the sea brought further changes. Until 1545 the oarsmen in the galleys were free sailors enrolled on a wage. They were originally Venetians, but later Dalmatians, Cretans and Greeks joined in large numbers. Because of the difficulty in hiring sufficient crews, Venice had recourse to conscription, chaining the oarsmen to the benches as other navies had already done. Cristoforo da Canal was the first Venetian to command such a galley. By 1563, the population of Venice had dropped to about 168,000 people.
With the outbreak of another war with the Ottomans
Ottoman–Venetian War (1570–1573)
The Fourth Ottoman–Venetian War, also known as the War of Cyprus was fought between 1570–1573. It was waged between the Ottoman Empire and the Republic of Venice, the latter joined by the Holy League, a coalition of Christian states formed under the auspices of the Pope, which included Spain , the...
in 1570, Venice, Spain and the Pope formed the Holy League
Holy League (Mediterranean)
The Holy League of 1571 was arranged by Pope St. Pius V and included almost all the major Catholic maritime states in the Mediterranean. It was intended to break the Ottoman Turks' control of the eastern Mediterranean Sea and was formally concluded on 25 May 1571...
, which was able to assemble a grand fleet of 208 galleys, 110 of which were Venetian, under the command of John of Austria, half-brother of Philip II of Spain
Philip II of Spain
Philip II was King of Spain, Portugal, Naples, Sicily, and, while married to Mary I, King of England and Ireland. He was lord of the Seventeen Provinces from 1556 until 1581, holding various titles for the individual territories such as duke or count....
. The Venetians were commanded by Sebastiano Venier
Sebastiano Venier
Sebastiano Venier was Doge of Venice from June 11, 1577 to March 3, 1578.-Biography:Venier was born in Venice around 1496. He was a son of Moisè Venier and Elena Donà, and a nephew of Zuan Francesco Venier, Co-Lord of Cerigo. He was a paternal grandson of Moisé Venier...
. The Turkish fleet, equal in number to the allied one, had sailed up the Adriatic as far as Lesina, and then returned to Lepanto in the Gulf of Patras for provisions. The Christian fleet had assembled at Messina and encountered the Turkish fleet off Lepanto
Battle of Lepanto (1571)
The Battle of Lepanto took place on 7 October 1571 when a fleet of the Holy League, a coalition of Catholic maritime states, decisively defeated the main fleet of the Ottoman Empire in five hours of fighting on the northern edge of the Gulf of Patras, off western Greece...
on 7 October 1571. The Christians were victorious, and divided up 117 galleys captured from the Turks. But the Venetians gained no strategic advantage. Philip II was concerned with the balance of power in the eastern Mediterranean and Africa, and was unwilling for the fleet to become involved in the Levant. Famagusta
Famagusta
Famagusta is a city on the east coast of Cyprus and is capital of the Famagusta District. It is located east of Nicosia, and possesses the deepest harbour of the island.-Name:...
, the last stronghold on the island of Cyprus
Cyprus
Cyprus , officially the Republic of Cyprus , is a Eurasian island country, member of the European Union, in the Eastern Mediterranean, east of Greece, south of Turkey, west of Syria and north of Egypt. It is the third largest island in the Mediterranean Sea.The earliest known human activity on the...
, had been attacked by the Turks in 1570 and had surrendered before Lepanto. The Turkish commander, Lala Kara Mustafa Pasha
Lala Kara Mustafa Pasha
Lala Kara Mustafa Pasha was an Ottoman general and Grand Vizier of the Ottoman Empire.He had risen to the position of Beylerbey of Damascus and then to that of Fifth Vizier...
, had had the Venetian provveditore Marcantonio Bragadin flayed alive. The loss of Cyprus was ratified in the peace of 1573. In 1575, the population of Venice was about 175,000 people, but dropped to 124,000 people by 1581.
17th century
In 1605 a conflict between Venice and the Holy SeeHoly See
The Holy See is the episcopal jurisdiction of the Catholic Church in Rome, in which its Bishop is commonly known as the Pope. It is the preeminent episcopal see of the Catholic Church, forming the central government of the Church. As such, diplomatically, and in other spheres the Holy See acts and...
began with the arrest of two members of the clergy who were guilty of petty crimes, and with a law restricting the Church's right to enjoy and acquire landed property. Pope Paul V
Pope Paul V
-Theology:Paul met with Galileo Galilei in 1616 after Cardinal Bellarmine had, on his orders, warned Galileo not to hold or defend the heliocentric ideas of Copernicus. Whether there was also an order not to teach those ideas in any way has been a matter for controversy...
held that these provisions were contrary to canon law, and demanded that they should be repealed. When this was refused, he placed Venice under an interdict
Venetian Interdict
The Venetian Interdict of 1606 and 1607 was the expression in terms of canon law, by means of a papal interdict, of a diplomatic quarrel and confrontation between the Papal Curia and the Republic of Venice, taking place in the period from 1605 to 1607...
. The Republic paid no attention to the interdict or the act of excommunication, and ordered its priests to carry out their ministry. It was supported in its decisions by the Servite monk Paolo Sarpi
Paolo Sarpi
Fra Paolo Sarpi was a Venetian patriot, scholar, scientist and church reformer. His most important roles were as a canon lawyer and historian active on behalf of the Venetian Republic.- Early years :...
, a sharp polemical writer who was nominated to be the Signoria
Signoria of Venice
The Signoria of Venice was the supreme body of government of the Republic of Venice. The original Greek name of the family was Spandounes...
's adviser on theology and canon law in 1606. The interdict was lifted after a year, when France intervened and proposed a formula of compromise. Venice was satisfied with reaffirming the principle that no citizen was superior to the normal processes of law.
A new war occurred in the years 1613-1617. The government of Venice wrote:
The Uzkoks were Christian refugees from Bosnia
Bosnia (region)
Bosnia is a eponomous region of Bosnia and Herzegovina. It lies mainly in the Dinaric Alps, ranging to the southern borders of the Pannonian plain, with the rivers Sava and Drina marking its northern and eastern borders. The other eponomous region, the southern, other half of the country is...
and Turkish Dalmatia who had been enlisted by the Austrian Habsburg to defend their borders after the peace between Venice and the Ottomans following the Battle of Lepanto. They settled in Segna and lived as pirates in the Adriatic, causing concern in Venice that they would complicate relations with the Sublime Porte. When Venice acted against these Uscocchi in 1613, she found herself at odds on land with their protector, the archduke of Austria. An army was sent against Gradisca, an archduke's possession, with financial support given to the duke of Savoy
House of Savoy
The House of Savoy was formed in the early 11th century in the historical Savoy region. Through gradual expansion, it grew from ruling a small county in that region to eventually rule the Kingdom of Italy from 1861 until the end of World War II, king of Croatia and King of Armenia...
, who was pinning down the Spanish army in Lombardy. The military operations on the eastern frontier were not decisive, but among the terms of the peace of 1617 the Habsburgs undertook to solve the problem of the Uzkoks, whom they moved inland.
In 1617, whether on his own initiative, or supported by his king, the Spanish viceroy of Naples attempted to break Venetian dominance by sending a naval squadron to the Adriatic. His expedition met with mixed success, and he retired from the Adriatic. Rumours of sedition and conspiracy were meanwhile circulating in Venice, and there were disturbances between mercenaries of different nationalities enrolled for the war of Gradisca. The Spanish ambassador, the Marquis of Bedmar, was wise to the plot, if not the author of it. Informed of this by a Huguenot captain, the Ten acted promptly. Three "bravos" were hanged, and the Senate demanded the immediate recall of the Spanish ambassador.
Tension with Spain increased in 1622, when Antonio Foscarini, a senator and ambassador to England, was accused of acting for foreign powers during his time as ambassador and of spying for Spain after his return. He was tried, acquitted of the first charge, found guilty of the second and hanged from a gallows between the columns of the Piazzetta in 1622. A few months later the Ten discovered that he had been the innocent victim of a plot. He was rehabilitated, and the news circulated around all the chancelleries of Europe.
In 1628 Venice was involved in Italian politics for the first time in more than a century. On the death of Ferdinando I Gonzaga
Ferdinando I Gonzaga
Ferdinand I Gonzaga was Duke of Mantua and Duke of Montferrat from 1612 until his death.-Biography:Born in Mantua, he was the son of Vincent I Gonzaga and Eleonora de' Medici....
, duke of Mantua and Montferrat
Montferrat
Montferrat is part of the region of Piedmont in Northern Italy. It comprises roughly the modern provinces of Alessandria and Asti. Montferrat is one of the most important wine districts of Italy...
, the succession developed upon a French prince, Charles of Gonzaga-Nevers. This changed the balance of power in northern Italy, which had until now been controlled by the Spanish through Milan. In the ensuing war, Venice was allied with France against the Habsburgs and Savoy. The Venetian army was defeated in an attempt to come to the aid of Mantua, which was under siege by German troops, and Mantua itself was savagely sacked. The peace which recognized Charles of Gonzaga-Nevers as duke of Mantua and Monferrato was made practically without Venice's participation. War brought plague in 1630. In 16 months 50,000 people died in Venice, one third of the population. The first stone of the church of Santa Maria della Salute in the city was laid as a thanks offering for the end of the plague.
In 1638, while the Venetian fleet was cruising off Crete, a corsair fleet from Barbary consisting of 16 galleys from Algiers
Algiers
' is the capital and largest city of Algeria. According to the 1998 census, the population of the city proper was 1,519,570 and that of the urban agglomeration was 2,135,630. In 2009, the population was about 3,500,000...
and Tunis
Tunis
Tunis is the capital of both the Tunisian Republic and the Tunis Governorate. It is Tunisia's largest city, with a population of 728,453 as of 2004; the greater metropolitan area holds some 2,412,500 inhabitants....
entered the Adriatic. When the fleet returned, the corsairs repaired to the Turkish stronghold of Valona
Vlorë
Vlorë is one of the biggest towns and the second largest port city of Albania, after Durrës, with a population of about 94,000 . It is the city where the Albanian Declaration of Independence was proclaimed on November 28, 1912...
. The Venetian commander Marino Cappello attacked the corsairs, bombarded the forts and captured their galleys, freeing 3,600 prisoners. The sultan reacted to the bombardment of his fortress by arresting the Venetian bailo (ambassador) in Constantinople, Alvise Contarini
Alvise Contarini (diplomat)
Alvise Contarini was an Italian nobleman and diplomat of the Republic of Venice.-Biography:Born in Venice, Alvise Contarini entered the service of the Republic of Venice in 1618, and by 1623, he had risen to such prominence that he was elected to the Grand Council of the Republic.His diplomatic...
. War was momentarily averted and the matter settled by diplomacy; however, six years later the Ottoman attack against Candia
Heraklion
Heraklion, or Heraclion is the largest city and the administrative capital of the island of Crete, Greece. It is the 4th largest city in Greece....
, the main Cretan
Crete
Crete is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, and one of the thirteen administrative regions of Greece. It forms a significant part of the economy and cultural heritage of Greece while retaining its own local cultural traits...
port, left no easy terms to resort to. The Cretan War
Cretan War (1645–1669)
The Cretan War or War of Candia , as the Fifth Ottoman–Venetian War is better known, was a conflict between the Republic of Venice and her allies against the Ottoman Empire and the Barbary States, fought over the island of Crete, Venice's largest and richest overseas possession...
lasted for some 25 years and was the dominant question of the whole Republic's history in the 17th century.
War also moved to the mainland in the middle of 1645, when the Turks attacked the frontiers of Dalmatia. In the latter the Venetians were able to save their coastal positions because of their command of the sea, but on 22 August, the Cretan stronghold of Khania was forced to capitulate.
The greatest Turkish effort was directed against Sebenico
Šibenik
Šibenik is a historic town in Croatia, with population of 51,553 . It is located in central Dalmatia where the river Krka flows into the Adriatic Sea...
, in today's Croatia, which was besieged in August-September 1647. The siege failed, and in the succeeding year the Venetians recovered several fortresses inland, such as Clissa. In Crete, however, the situation was more serious. Throughout all the war the Venetian strategy was to blockade the Dardanelles in order to surprise the Turkish fleet on its way to supply the troops on Crete. There were some signal successes, including two victories in the Dardanelles in 1655
Action of 21 June 1655
This battle took place on 21 June 1655 inside the mouth of the Dardanelles Strait. It was a clear victory for Venice over the Ottoman Empire.The Venetians, under Lazzaro Mocenigo, continued their strategy of blockading the Dardanelles, to prevent the Ottomans from resupplying their forces in the...
and 1656
Battle of the Dardanelles (1656)
The Action of 26 June 1656 or Third Battle of the Dardanelles in the Sixth Ottoman-Venetian War took place on 26 and 27 June 1656 inside the Dardanelles Strait...
, but they failed to alter the strategic situation. The next year there was a three-day-long sea-battle
Action of 17 July 1657
The Fourth Battle of the Dardanelles in the Sixth Ottoman-Venetian War took place between 17 and 19 July 1657 outside the mouth of the Dardanelles Strait...
(17–19 July 1657), in which the captain Lazzaro Mocenigo was killed by a falling mast, and turning into a crushing defeat. With the end of the war between France and Spain in 1659, Venice received more aid from the Christian states than the small contingents which she had received in the first years. In 1666 an expedition to retake Khania failed, and in 1669 another attempt to lift the siege of Candia with joint action on land with the French contingent and by sea under Mocenigo also turned out to be a failure. The French returned home, and only 3,600 fit men were left in the fortress of Candia. Captain Francesco Morosini
Francesco Morosini
Francesco Morosini was the Doge of Venice from 1688 to 1694, at the height of the Great Turkish War...
negotiated its surrender on 6 September 1669. The island of Crete was ceded, except for some small Venetian bases, while Venice retained the islands of Tinos
Tinos
Tinos is a Greek island situated in the Aegean Sea. It is located in the Cyclades archipelago. In antiquity, Tinos was also known as Ophiussa and Hydroessa . The closest islands are Andros, Delos, and Mykonos...
and Cerigo, and its conquests in Dalmatia.
In 1684 Venice, taking advance of the recent Turkish defeat in the siege of Vienna, formed an alliance with Austria against the Ottomans; Russia was later included in the league. At the beginning of the Morean War
Morean War
The Morean War is the better known name for the Sixth Ottoman–Venetian War. The war was fought between 1684–1699, as part of the wider conflict known as the "Great Turkish War", between the Republic of Venice and the Ottoman Empire...
Francesco Morosini occupied the island of Levkas and set out to recapture the Greek ports. Between June 1685 when he landed at Corone, and August, when he occupied Patras, Lepanto and Corinth, he secured the Peloponnese for Venice. In September, during the attack on Athens
Athens
Athens , is the capital and largest city of Greece. Athens dominates the Attica region and is one of the world's oldest cities, as its recorded history spans around 3,400 years. Classical Athens was a powerful city-state...
, a Venetian cannon blew up the Parthenon
Parthenon
The Parthenon is a temple on the Athenian Acropolis, Greece, dedicated to the Greek goddess Athena, whom the people of Athens considered their virgin patron. Its construction began in 447 BC when the Athenian Empire was at the height of its power. It was completed in 438 BC, although...
. Venetian possessions were greatly increased in Dalmatia too, although the attempt to regain Negropont in 1688 was a failure. Morosini's successors failed to obtain lasting results in the next years, although large fleets were sent out, and in spite of some brilliant victories — at Mitylene in 1695, Andros in 1697
Action of 6 July 1697
This series of battles took place in 1697 when the Venetian fleet, under Bartolomeo Contarini, hunted down the Turkish fleet in the Aegean Sea. These battles are known as "Bozcaada Sea Battles" by Turkish historians....
and the Dardanelles in 1698. The Treaty of Karlowitz
Treaty of Karlowitz
The Treaty of Karlowitz was signed on 26 January 1699 in Sremski Karlovci , concluding the Austro-Ottoman War of 1683–1697 in which the Ottoman side had been defeated at the Battle of Zenta...
(1699) favoured Austria and Russia more than Venice, which failed to regain its bases in the Mediterranean taken by the Turks in the last two centuries, in spite of its conquests.
New conflict was brewing over the question of the Spanish Succession. Both France and the Habsburg empire, attempted now to gain an active ally in Venice, despatching envoys with authority there in 1700. The Venetian government preferred to remain neutral rather than accept hypothetical advantages offered by interested parties. The Republic remained faithful to this policy of neutrality to the end, caught in unavoidable decline but living out its life in a luxury famous throughout Europe.
Decline

The Turks took the islands of Tinos and Aegina, crossed the isthmus
Isthmus of Corinth
The Isthmus of Corinth is the narrow land bridge which connects the Peloponnese peninsula with the rest of the mainland of Greece, near the city of Corinth. The word "isthmus" comes from the Ancient Greek word for "neck" and refers to the narrowness of the land. The Isthmus was known in the ancient...
and took Corinth
Corinth
Corinth is a city and former municipality in Corinthia, Peloponnese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Corinth, of which it is the seat and a municipal unit...
. Daniele Dolfin, commander of the Venetian fleet, thought it better to save the fleet than risk it for the Morea. When he eventually arrived on the scene, Nauplia, Modon, Corone and Malvasia had fallen. Lefkas in the Ionian islands, and the bases of Spinalonga and Suda on Crete which still remained in Venetian hands, were abandoned. The Turks finally landed on Corfù
Corfu
Corfu is a Greek island in the Ionian Sea. It is the second largest of the Ionian Islands, and, including its small satellite islands, forms the edge of the northwestern frontier of Greece. The island is part of the Corfu regional unit, and is administered as a single municipality. The...
, but its defenders managed to throw them back. In the meantime, the Turks had suffered a grave defeat by the Austrians at Petrovaradin
Battle of Petrovaradin
The Battle of Petrovaradin or Battle of Peterwardein was a decisive victory for Austrian forces in the war between Austria and the Ottoman Empire , at Petrovaradin, now part of Novi Sad, Vojvodina, in Serbia.-History:...
on 3 August 1716. New Venetian naval efforts in the Aegean and the Dardanelles in 1717 and 1718, however, met with little success. With the Treaty of Passarowitz
Treaty of Passarowitz
The Treaty of Passarowitz or Treaty of Požarevac was the peace treaty signed in Požarevac , a town in Ottoman Empire , on 21 July 1718 between the Ottoman Empire on one side and the Habsburg Monarchy of Austria and the Republic of Venice on the other.During the years 1714-1718, the Ottomans had...
(21 July 1718), Austria made large territorial gains, but Venice lost the Morea, for which her small gains in Albania and Dalmatia were little compensation. This was the last war of the Republic with Turkey.
The decline of Venice in the 18th century was also due not only to Genoa, Venice's old rival, but also to Livorno
Livorno
Livorno , traditionally Leghorn , is a port city on the Tyrrhenian Sea on the western edge of Tuscany, Italy. It is the capital of the Province of Livorno, having a population of approximately 160,000 residents in 2009.- History :...
, a new port on the Tyrrhenian Sea
Tyrrhenian Sea
The Tyrrhenian Sea is part of the Mediterranean Sea off the western coast of Italy.-Geography:The sea is bounded by Corsica and Sardinia , Tuscany, Lazio, Campania, Basilicata and Calabria and Sicily ....
created by the grand dukes of Tuscany
Grand Duchy of Tuscany
The Grand Duchy of Tuscany was a central Italian monarchy that existed, with interruptions, from 1569 to 1859, replacing the Duchy of Florence. The grand duchy's capital was Florence...
and chosen as staging-post for British trade in the Mediterranean. Still more injurious were the Papal town of Ancona
Ancona
Ancona is a city and a seaport in the Marche region, in central Italy, with a population of 101,909 . Ancona is the capital of the province of Ancona and of the region....
and Habsburg Trieste
Trieste
Trieste is a city and seaport in northeastern Italy. It is situated towards the end of a narrow strip of land lying between the Adriatic Sea and Italy's border with Slovenia, which lies almost immediately south and east of the city...
, a free port since 1719, in the Adriatic Sea, which no longer constituted a "Venetian Gulf". An eminent Venetian politician of the time declared:
Even the cities of the eastern mainland up to Verona got their supplies from Genoa and Leghorn. The presence of pirates from the coast of Maghreb worsened the situation.
"All is in disorder, everything is out of control" exclaimed Carlo Contarini in the Maggior Consiglio on 5 December 1779. He was talking of a "commotion" in demand of a plan of reform also supported by Giorgio Pisani. The idea was to remove the monopoly of power enjoyed by the small number of rich patricians to the advantage of the very large number of poor ones. This gave rise to fears of "overturning the system" and the doge, Paolo Renier
Paolo Renier
Paolo Renier was a Venetian statesman, the 119th, and penultimate, Doge of Venice. He was considered a good orator and tactician, and served as ambassador to Constantinople and to Vienna. His election as Doge was unpopular, and he was the subject of numerous menacing letters at the time...
, opposed the plan. "Prudence" suggested that the agitations in favour of reform were a conspiracy. The Inquisitors took the arbitrary step of confining Pisani in the castle of San Felice in Verona, and Contarini in the fortress of Cattaro.
On 29 May 1784 Andrea Tron, known as el paron ("the patron") because of his political influence, said that trade
The last Venetian naval venture occurred in 1784-86. The bey of Tunis
Tunis
Tunis is the capital of both the Tunisian Republic and the Tunis Governorate. It is Tunisia's largest city, with a population of 728,453 as of 2004; the greater metropolitan area holds some 2,412,500 inhabitants....
' pirates renewed their acts of piracy following claims of compensation for losses suffered by Tunisian subjects in Malta, due to no fault of the Venetians. When diplomatic efforts to reach an agreement failed, the government was forced to take military action. A fleet under Angelo Emo
Angelo Emo
Angelo Emo was the last Grand Admiral of the Republic of Venice. He attempted to introduce reforms based on the practices of the British Royal Navy, and led raids on Moorish targets along the Barbary Coast in retaliation for corsair attacks on Venetian-flagged shipping...
blockaded Tunis and bombarded Sousse
Sousse
Sousse is a city in Tunisia. Located 140 km south of the capital Tunis, the city has 173,047 inhabitants . Sousse is in the central-east of the country, on the Gulf of Hammamet, which is a part of the Mediterranean Sea. The name may be of Berber origin: similar names are found in Libya and in...
(November 1784 and May 1785), Sfax
Sfax
Sfax is a city in Tunisia, located southeast of Tunis. The city, founded in AD 849 on the ruins of Taparura and Thaenae, is the capital of the Sfax Governorate , and a Mediterranean port. Sfax has population of 340,000...
(August 1785) and La Coletta (September) and Biserta in 1786. These brilliant military successes brought no comparable political results in their train, and the Senate recalled Emo and his fleet to Corfù. After Emo's death, peace was made with Tunis by increasing the bey's dues. By the year 1792, the once great Venetian merchant fleet had declined to a mere 309 merchantmen
Cargo ship
A cargo ship or freighter is any sort of ship or vessel that carries cargo, goods, and materials from one port to another. Thousands of cargo carriers ply the world's seas and oceans each year; they handle the bulk of international trade...
.
In January 1789 Lodovico Manin, from a recently ennobled mainland family, was elected doge. The expenses of the election had grown throughout the 18th century, and now reached their highest ever. The patrician Pietro Gradenigo remarked
C. P. Snow
C. P. Snow
Charles Percy Snow, Baron Snow of the City of Leicester CBE was an English physicist and novelist who also served in several important positions with the UK government...
suggests that in the last half century of the republic, the Venetians knew "that the current of history had begun to flow against them," and that to keep going would require "breaking the pattern into which they has crystallised." Yet they were "fond of the pattern" and "never found the will to break it."

The fall of the Republic

Montenotte
Montenotte was a département of the First French Empire in present Italy. It was named after the village Montenotte near Savona to commemorate the Battle of Montenotte in 1796. It was formed in 1805, when Napoleon Bonaparte occupied the Republic of Genoa. Its capital was Savona. It was divided into...
to Lodi. The army under Napoleon crossed the frontiers of neutral Venice in pursuit of the enemy. By the end of the year the French troops were occupying the Venetian state up to the Adige. Vicenza, Cadore and Friuli were held by the Austrians. With the campaigns of the next year, Napoleon aimed for the Austrian possessions across the Alps. In the preliminaries to the Peace of Leoben, the terms of which remained secret, the Austrians were to take the Venetian possessions as the price of peace (18 April 1797).
Nevertheless the peace envisaged the continued survival of the Venetian state, although confined to the city and the lagoon, perhaps with compensation at the expense of the Papal States. In the meanwhile Brescia and Bergamo revolted to Venice, and anti French movements were arising elsewhere. Napoleon threatened Venice with war on 9 April. On 25 April he announced to the Venetian delegates at Graz
Graz
The more recent population figures do not give the whole picture as only people with principal residence status are counted and people with secondary residence status are not. Most of the people with secondary residence status in Graz are students...
,
Domenico Pizzamano fired on a French ship trying to force an entry from the Lido forts. On I May, Napoleon declared war. The French were at the edge of the lagoon. Even the cities of the Veneto had been "revolutionized" by the French, who had established provisional municipalities. On 12 May, the Maggior Consiglio approved a motion to hand over power "to the system of the proposed provisional representative government", although there was not a quorum of votes: 512 voted for, ten against, and five abstained. On 16 May the provisional municipal government met in the Hall of the Maggior Consiglio. The preliminaries of the peace of Leoben were made even harsher in the treaty of Campoformio, and Venice and all her possessions became Austrian. The accord was signed at Passariano, in the last doge's villa, on 18 October 1797.
See also
- History of the city of Venice
- Timeline of the Venetian RepublicTimeline of the Venetian RepublicThis article presents a detailed timeline of the history of the Venetian Republic from its legendary foundation to its collapse under the efforts of Napoleon.-5th century:...
- Republic of PisaRepublic of PisaThe Republic of Pisa was a de facto independent state centered on the Tuscan city of Pisa during the late tenth and eleventh centuries. It rose to become an economic powerhouse, a commercial center whose merchants dominated Mediterranean and Italian trade for a century before being surpassed and...
- History of ItalyHistory of ItalyItaly, united in 1861, has significantly contributed to the political, cultural and social development of the entire Mediterranean region. Many cultures and civilizations have existed there since prehistoric times....
- Italian peopleItalian peopleThe Italian people are an ethnic group that share a common Italian culture, ancestry and speak the Italian language as a mother tongue. Within Italy, Italians are defined by citizenship, regardless of ancestry or country of residence , and are distinguished from people...
- Historical states of ItalyHistorical states of ItalyItaly, until the present era, was a conglomeration of city-states and other small independent entities. The following is a list of the various states that made up what we now know as Italy during the past...
- History of Byzantine Empire
- Wars in LombardyWars in LombardyThe wars in Lombardy were a series of conflicts fought in central-northern Italy between the Republic of Venice and the Duchy of Milan, and their different allies. They lasted from 1425 until the signing of the Treaty of Lodi in 1454...
- Ottoman wars in EuropeOttoman wars in EuropeThe wars of the Ottoman Empire in Europe are also sometimes referred to as the Ottoman Wars or as Turkish Wars, particularly in older, European texts.- Rise :...
- Ottoman NavyOttoman NavyThe Ottoman Navy was established in the early 14th century. During its long existence it was involved in many conflicts; refer to list of Ottoman sieges and landings and list of Admirals in the Ottoman Empire for a brief chronology.- Pre-Ottoman:...
- Patriarchate of AquileiaPatriarchate of AquileiaThe Patriarchate of Aquileia was an early center of Christianity, an historical state and catholic episcopal see, and today a catholic titular see in northeastern Italy, centred on the ancient city of Aquileia situated at the head of the Adriatic, on what is now the Italian sea-coast, at the...
- Italian WarsItalian WarsThe Italian Wars, often referred to as the Great Italian Wars or the Great Wars of Italy and sometimes as the Habsburg–Valois Wars, were a series of conflicts from 1494 to 1559 that involved, at various times, most of the city-states of Italy, the Papal States, most of the major states of Western...
- Maritime Republics
- Marco PoloMarco PoloMarco Polo was a Venetian merchant traveler from the Venetian Republic whose travels are recorded in Il Milione, a book which did much to introduce Europeans to Central Asia and China. He learned about trading whilst his father and uncle, Niccolò and Maffeo, travelled through Asia and apparently...
- Napoleonic WarsNapoleonic WarsThe Napoleonic Wars were a series of wars declared against Napoleon's French Empire by opposing coalitions that ran from 1803 to 1815. As a continuation of the wars sparked by the French Revolution of 1789, they revolutionised European armies and played out on an unprecedented scale, mainly due to...
- The Tragedy of Othello, the Moor of Venice
- Treaty of Campoformio
- VenetoVenetoVeneto is one of the 20 regions of Italy. Its population is about 5 million, ranking 5th in Italy.Veneto had been for more than a millennium an independent state, the Republic of Venice, until it was eventually annexed by Italy in 1866 after brief Austrian and French rule...
- History of Friuli
- IstriaIstriaIstria , formerly Histria , is the largest peninsula in the Adriatic Sea. The peninsula is located at the head of the Adriatic between the Gulf of Trieste and the Bay of Kvarner...
- DalmatiaDalmatiaDalmatia is a historical region on the eastern coast of the Adriatic Sea. It stretches from the island of Rab in the northwest to the Bay of Kotor in the southeast. The hinterland, the Dalmatian Zagora, ranges from fifty kilometers in width in the north to just a few kilometers in the south....
- Venetian SloveniaVenetian SloveniaVenetian Slovenia is a small mountainous region in northeastern Italy . Most of the region is located in the Italian region of Friuli Venezia Giulia, in the area between the towns of Cividale del Friuli, Tarcento and Gemona ....
- Venetian Albania
- Medieval demographyMedieval demographyThis article discusses human demography in Europe during the Middle Ages, including population trends and movements. Demographic changes helped to shape and define the Middle Ages...
- Naval historyNaval historyNaval history is the area of military history concerning war at sea and the subject is also a sub-discipline of the broad field of maritime history....

