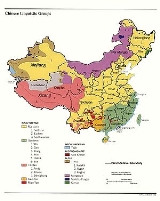
Languages of China
Encyclopedia
China's many different ethnic groups speak many different language
s, collectively called Zhōngguó Yǔwén (中国语文), literally, "speech and writing of China", which span eight primary language families
. Most of them are dissimilar morphologically
and phonetically. Even within each family, most are mutually unintelligible. Zhongguo Yuwen includes the many different Han Chinese language varieties
(commonly called Chinese) as well as minority languages such as Mongolian
, Tibetan
, Uyghur
and Zhuang
. China has 292 living languages and 1 extinct language
(Jurchen
) according to Ethnologue
.
Putonghua or Standard Mandarin
is the official national spoken language. Hong Kong
, Macau
and several other autonomous regions have additional official languages. For example, Tibetan has official status within the Tibet Autonomous Region
, Mongolian has official status within Inner Mongolia
and Uyghur has official status within Xinjiang
.
There are large economic, social, and practical incentives to be functional in Putonghua, a standardised form of the Mandarin group of dialects which is based in Beijing and spoken with varying degrees of dialectical influences across the northern and southwestern China. Putonghua serves as a lingua franca
within the Mandarin-speaking region, and to a lesser extent across the various other language groups in mainland China
.
belong to at least seven families:
Below are lists of ethnic groups in China by linguistic classification. Ethnicities not on the official PRC list of 56 ethnic groups are italicized. Respective Pinyin transliterations and simplified Chinese characters are also given.
(Possibly the ancient Nánmán
南蛮)
Austro-Asiatic
(Possibly the ancient Bǎipú 百濮)
Austronesian
Indo-European
Semitic
Mixed
 The following languages traditionally had written forms that do not involve Chinese character
The following languages traditionally had written forms that do not involve Chinese character
s (hanzi):
Some formerly have used Chinese characters
Chinese palaces, temples, and coins have traditionally been inscribed in five scripts:
During the Mongol Yuan dynasty
, the official writing system was:
 Chinese banknotes contain several scripts in addition to Chinese script. These are:
Chinese banknotes contain several scripts in addition to Chinese script. These are:
Ten nationalities who never had a written system have, under the PRC
's encouragement, developed phonetic alphabet
s. According to a government white paper published in early 2005, "by the end of 2003, 22 ethnic minorities in China used 28 written languages."
is heavily influenced by Soviet nationalities policy and officially encourages the development of standard spoken and written languages for each of the nationalities of China. However, in this schema, Han Chinese
are considered a single nationality, and official policy of the People's Republic of China
(PRC) treats the different varieties of the Chinese spoken language differently from the different national languages despite the fact that they are more different from each other
than, for example, the Romance languages
of Europe.
While official policies in mainland China encourage the development and use of different orthographies for the national languages and their use in educational and academic settings, realistically speaking it would seem that, as elsewhere in the world, the outlook for
minority languages perceived as inferior is grim.
The Tibetan Government-in-Exile argue that social pressures and political efforts result in a policy of sinicization and feels that Beijing should promote the Tibetan language
more.
, which is a required subject for persons attending university. During the 1950s and 1960s, Russian
had some social status among elites in mainland China as the international language of socialism
. Japanese
is the second most-studied foreign language in China. However, languages other than English are now considered as "minor languages" (小语种 xiao yu zhong) and are only really studied at university level.
English is taught in the public schools starting in the third year of primary school.
The Economist
, issue April 12, 2006, reported that up to one fifth of the population is learning English. Gordon Brown
, the former British Prime Minister, estimated that the total English-speaking population in China will outnumber the native speakers in the rest of the world in two decades.
The Arabic language
is studied by Hui
students.
Arabic language education was promoted by the Kuomintang
in Islamic schools when it ruled mainland China.
Portuguese
is taught in Macau
as one of the official languages there and as a center of learning of the language in the region.
Language
Language may refer either to the specifically human capacity for acquiring and using complex systems of communication, or to a specific instance of such a system of complex communication...
s, collectively called Zhōngguó Yǔwén (中国语文), literally, "speech and writing of China", which span eight primary language families
Language family
A language family is a group of languages related through descent from a common ancestor, called the proto-language of that family. The term 'family' comes from the tree model of language origination in historical linguistics, which makes use of a metaphor comparing languages to people in a...
. Most of them are dissimilar morphologically
Morphology (linguistics)
In linguistics, morphology is the identification, analysis and description, in a language, of the structure of morphemes and other linguistic units, such as words, affixes, parts of speech, intonation/stress, or implied context...
and phonetically. Even within each family, most are mutually unintelligible. Zhongguo Yuwen includes the many different Han Chinese language varieties
Varieties of Chinese
Chinese comprises many regional language varieties sometimes grouped together as the Chinese dialects, the primary ones being Mandarin, Wu, Cantonese, and Min. These are not mutually intelligible, and even many of the regional varieties are themselves composed of a number of...
(commonly called Chinese) as well as minority languages such as Mongolian
Mongolian language
The Mongolian language is the official language of Mongolia and the best-known member of the Mongolic language family. The number of speakers across all its dialects may be 5.2 million, including the vast majority of the residents of Mongolia and many of the Mongolian residents of the Inner...
, Tibetan
Tibetan language
The Tibetan languages are a cluster of mutually-unintelligible Tibeto-Burman languages spoken primarily by Tibetan peoples who live across a wide area of eastern Central Asia bordering the Indian subcontinent, including the Tibetan Plateau and the northern Indian subcontinent in Baltistan, Ladakh,...
, Uyghur
Uyghur language
Uyghur , formerly known as Eastern Turk, is a Turkic language with 8 to 11 million speakers, spoken primarily by the Uyghur people in the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region of Western China. Significant communities of Uyghur-speakers are located in Kazakhstan and Uzbekistan, and various other...
and Zhuang
Standard Zhuang
The standard Zhuang language is the variety of Zhuang spoken in Wuming County in the Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region of the People's Republic of China, where it is an official language.-Classification:...
. China has 292 living languages and 1 extinct language
Extinct language
An extinct language is a language that no longer has any speakers., or that is no longer in current use. Extinct languages are sometimes contrasted with dead languages, which are still known and used in special contexts in written form, but not as ordinary spoken languages for everyday communication...
(Jurchen
Jurchen language
Jurchen language is an extinct language. It was spoken by Jurchen people of eastern Manchuria, the creators of the Jin Empire in the northeastern China of the 12th–13th centuries. It is classified as a Southwestern Tungusic language.-Writing:...
) according to Ethnologue
Ethnologue
Ethnologue: Languages of the World is a web and print publication of SIL International , a Christian linguistic service organization, which studies lesser-known languages, to provide the speakers with Bibles in their native language and support their efforts in language development.The Ethnologue...
.
Putonghua or Standard Mandarin
Standard Mandarin
Standard Chinese or Modern Standard Chinese, also known as Mandarin or Putonghua, is the official language of the People's Republic of China and Republic of China , and is one of the four official languages of Singapore....
is the official national spoken language. Hong Kong
Hong Kong
Hong Kong is one of two Special Administrative Regions of the People's Republic of China , the other being Macau. A city-state situated on China's south coast and enclosed by the Pearl River Delta and South China Sea, it is renowned for its expansive skyline and deep natural harbour...
, Macau
Macau
Macau , also spelled Macao , is, along with Hong Kong, one of the two special administrative regions of the People's Republic of China...
and several other autonomous regions have additional official languages. For example, Tibetan has official status within the Tibet Autonomous Region
Tibet Autonomous Region
The Tibet Autonomous Region , Tibet or Xizang for short, also called the Xizang Autonomous Region is a province-level autonomous region of the People's Republic of China , created in 1965....
, Mongolian has official status within Inner Mongolia
Inner Mongolia
Inner Mongolia is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China, located in the northern region of the country. Inner Mongolia shares an international border with the countries of Mongolia and the Russian Federation...
and Uyghur has official status within Xinjiang
Xinjiang
Xinjiang is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China. It is the largest Chinese administrative division and spans over 1.6 million km2...
.
There are large economic, social, and practical incentives to be functional in Putonghua, a standardised form of the Mandarin group of dialects which is based in Beijing and spoken with varying degrees of dialectical influences across the northern and southwestern China. Putonghua serves as a lingua franca
Lingua franca
A lingua franca is a language systematically used to make communication possible between people not sharing a mother tongue, in particular when it is a third language, distinct from both mother tongues.-Characteristics:"Lingua franca" is a functionally defined term, independent of the linguistic...
within the Mandarin-speaking region, and to a lesser extent across the various other language groups in mainland China
Mainland China
Mainland China, the Chinese mainland or simply the mainland, is a geopolitical term that refers to the area under the jurisdiction of the People's Republic of China . According to the Taipei-based Mainland Affairs Council, the term excludes the PRC Special Administrative Regions of Hong Kong and...
.
Spoken languages
The spoken languages of nationalities that are a part of the People's Republic of ChinaPeople's Republic of China
China , officially the People's Republic of China , is the most populous country in the world, with over 1.3 billion citizens. Located in East Asia, the country covers approximately 9.6 million square kilometres...
belong to at least seven families:
- The Sino-Tibetan familySino-Tibetan languagesThe Sino-Tibetan languages are a language family comprising, at least, the Chinese and the Tibeto-Burman languages, including some 250 languages of East Asia, Southeast Asia and parts of South Asia. They are second only to the Indo-European languages in terms of the number of native speakers...
: 28 nationalities (including the Han and Tibetans) - The Hmong–Mien family
- The Altaic familyAltaic languagesAltaic is a proposed language family that includes the Turkic, Mongolic, Tungusic, and Japonic language families and the Korean language isolate. These languages are spoken in a wide arc stretching from northeast Asia through Central Asia to Anatolia and eastern Europe...
(disputed)- Turkic languagesTurkic languagesThe Turkic languages constitute a language family of at least thirty five languages, spoken by Turkic peoples across a vast area from Eastern Europe and the Mediterranean to Siberia and Western China, and are considered to be part of the proposed Altaic language family.Turkic languages are spoken...
: UyghursUyghur peopleThe Uyghur are a Turkic ethnic group living in Eastern and Central Asia. Today, Uyghurs live primarily in the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region in the People's Republic of China...
, Kazakhs, Salars, etc. - Mongolic languagesMongolic languagesThe Mongolic languages are a group of languages spoken in East-Central Asia, mostly in Mongolia and surrounding areas plus in Kalmykia. The best-known member of this language family, Mongolian, is the primary language of most of the residents of Mongolia and the Mongolian residents of Inner...
: MongolsEthnic Mongols in ChinaMongols in China are citizens of the People's Republic of China who are ethnic Mongols. They form one of the 55 ethnic minorities officially recognized by the People's Republic of China. There are approximately 5.8 million ethnic Mongols living in China. Most of them live in Inner Mongolia,...
, DongxiangDongxiang peopleThe Dongxiang people are one of 56 ethnic groups officially recognized by the People's Republic of China...
, and related groups - Tungusic languagesTungusic languagesThe Tungusic languages form a language family spoken in Eastern Siberia and Manchuria by Tungusic peoples. Many Tungusic languages are endangered, and the long-term future of the family is uncertain...
: Manchus (formerly), Hezhe, etc. - Korean languages: Koreans
- Turkic languages
- The Austroasiatic family: 4 (the De'angDe'angThe Palaung are a Mon–Khmer ethnic minority found in Shan State of Burma, Yunnan province of China and northern Thailand. They live mainly in the northern parts of Shan State in the Pa Laung Self-Administered Zone, with the capital at Namhsan. There are three main subgroups of Palaung: the Palé,...
, BlangBlangThe Blang people are an ethnic group. They form one of the 56 ethnic groups officially recognized by the People's Republic of China.-Language:...
, Gin (Vietnamese), and Wa) - The Tai–Kadai family: several languages spoken by the Zhuang, the BuyeiBuyeiThe Buyei are an ethnic group living in southern mainland China. Numbering 2.5 million, they are the 11th largest of the 56 ethnic groups officially recognized by the People's Republic of China...
, the Dai peopleDai peopleThe Dai peoples is one of several ethnic groups living in the Xishuangbanna Dai Autonomous Prefecture and the Dehong Dai and Jingpo Autonomous Prefecture , but by extension can apply to groups in Laos, Vietnam, Thailand, and Burma when Dai is used to mean specifically Tai Lue, Chinese Shan or even...
, the Dong peopleDong peopleThe Dong , a Kam–Sui people of southern China, are one of the 56 ethnic groups officially recognized by the People's Republic of China. They are famed for their native-bred Kam Sweet Rice , carpentry skills, and unique architecture, in particular a form of covered bridge known as the "wind and rain...
, and the Hlai (Li people)Li peopleThe Li or Hlai are a minority ethnic group, the vast majority of whom live off the southern coast of mainland China on Hainan Island, where they are the largest minority ethnic group...
. - The Indo-European familyIndo-European languagesThe Indo-European languages are a family of several hundred related languages and dialects, including most major current languages of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and South Asia and also historically predominant in Anatolia...
: 2 (the Russians and TajiksTajiks in ChinaTajiks , are an ethnic group that lives in the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region in the People's Republic of China...
). There is also a heavily Persian-influenced Äynu language spoken by the Äynu peopleÄynu peopleThe Äynu are a people native to the Xinjiang region of western China. There are estimated to be fewer than 30,000 Äynu, mostly located on the fringe of the Taklamakan Desert.- Origins :...
in southwestern Xinjiang who are officially considered Uyghurs. - The Austronesian familyAustronesian languagesThe Austronesian languages are a language family widely dispersed throughout the islands of Southeast Asia and the Pacific, with a few members spoken on continental Asia that are spoken by about 386 million people. It is on par with Indo-European, Niger-Congo, Afroasiatic and Uralic as one of the...
: 1 official nationality (the Gaoshan, who speak many languages), 1 unofficial (the Utsuls, who speak the Tsat languageTsat languageTsat is a language spoken near Sanya, Hainan, China by the Utsuls. Tsat is a member of the Malayo-Polynesian group within the Austronesian language family, and is related to the Cham languages, originally from the coast of present-day Vietnam...
but are considered HuiHui peopleThe Hui people are an ethnic group in China, defined as Chinese speaking people descended from foreign Muslims. They are typically distinguished by their practice of Islam, however some also practice other religions, and many are direct descendants of Silk Road travelers.In modern People's...
.)
Below are lists of ethnic groups in China by linguistic classification. Ethnicities not on the official PRC list of 56 ethnic groups are italicized. Respective Pinyin transliterations and simplified Chinese characters are also given.
Sino-Tibetan
- SiniticSinitic languagesThe Sinitic languages, often called the Chinese languages or the Chinese language, are a language family frequently postulated as one of two primary branches of Sino-Tibetan...
- ChineseChinese languageThe Chinese language is a language or language family consisting of varieties which are mutually intelligible to varying degrees. Originally the indigenous languages spoken by the Han Chinese in China, it forms one of the branches of Sino-Tibetan family of languages...
/Han, Hàn, 汉- Chinese Muslim/HuiHui peopleThe Hui people are an ethnic group in China, defined as Chinese speaking people descended from foreign Muslims. They are typically distinguished by their practice of Islam, however some also practice other religions, and many are direct descendants of Silk Road travelers.In modern People's...
, Huí, 回
- Chinese Muslim/Hui
- Chinese
- Tibeto-BurmanTibeto-Burman languagesThe Tibeto-Burman languages are the non-Chinese members of the Sino-Tibetan language family, over 400 of which are spoken thoughout the highlands of southeast Asia, as well as lowland areas in Burma ....
- Bai, Bái, 白 (Sinitic?)
- TujiaTujia languageThe Tujia language is a language spoken natively by the Tujia ethnicity in central China. It is unclassified within the Tibeto-Burman language family, due to pervasive influence from neighboring languages. There are two dialects, one Northern and one Southern. Both dialects are tonal languages...
, Tǔjiā, 土家 (Qiangic?) - QiangicQiangic languagesQiangic or Kiangic, formerly known as Dzorgai, is a language group of the northeastern Tibeto-Burman branch of the Sino-Tibetan language family, spoken mainly in Southwestern China, including Sichuan, Tibet, and Yunnan....
- QiangQiangic languagesQiangic or Kiangic, formerly known as Dzorgai, is a language group of the northeastern Tibeto-Burman branch of the Sino-Tibetan language family, spoken mainly in Southwestern China, including Sichuan, Tibet, and Yunnan....
, Qiāng, 羌- Northern QiangNorthern Qiang languageNorthern Qiang is a Qiangic language of the Tibeto-Burman language family spoken by approximately 130,000 people in north-central Sichuan Province, China.Unlike its close relative Southern Qiang, Northern Qiang is not a tonal language....
- Southern QiangSouthern Qiang languageSouthern Qiang is a Qiangic language of the Tibeto-Burman language family spoken by approximately 81,300 people along the Minjiang river in Sichuan Province, China.Unlike its close relative Northern Qiang, Southern Qiang is a tonal language....
- Northern Qiang
- Pumi/PrinmiPumi languageThe Pumi language is a Tibeto-Burman language used by the Pumi people, an ethnic group from Yunnan, China. Most native speakers live in Lanping, Ninglang, Lijiang, Weixi and Muli...
, Pǔmǐ, 普米 - BaimaBaima languageBaima is a language spoken by 11,000 people of Tibetan nationality in north central Sichuan Province, China. It has vigorous use amongst adult speakers....
, Báimǎ, 白马 - TangutTangut languageTangut is an ancient northeastern Tibeto-Burman language once spoken in the Western Xia Dynasty, also known as the Tangut Empire. It is classified by some linguists as one of the Qiangic languages, which also include Qiang and rGyalrong, among others...
, Xīxià, 西夏 (extinct)
- Qiang
- BodishBodish languagesThe Bodish languages, named for the Tibetan ethnonym bod, are the Tibetan languages in a broad linguistic sense, regardless of whether the speakers are considered ethnically Tibetan. Different scholars divide Bodish differently, but the alternate term 'Tibetan' generally excludes East Bodish...
- TibetanTibetan languageThe Tibetan languages are a cluster of mutually-unintelligible Tibeto-Burman languages spoken primarily by Tibetan peoples who live across a wide area of eastern Central Asia bordering the Indian subcontinent, including the Tibetan Plateau and the northern Indian subcontinent in Baltistan, Ladakh,...
, Zàng, 藏- Standard TibetanStandard TibetanStandard Tibetan is the most widely used spoken form of the Tibetan languages. It is based on the speech of Lhasa, an Ü-Tsang dialect belonging to the Central Tibetan languages. For this reason, Standard Tibetan is often called Central Tibetan...
- Central TibetanCentral Tibetan languagesThe Central Tibetan languages are the tonal varieties of Tibetan apart from Khams.The composition of the Central Tibetan languages per Bradley , with dialect information from the Tibetan Dialects Project at the University of Bern, is:...
- Amdo TibetanAmdo Tibetan languageThe Amdo language is the spoken language of the majority of the people of Amdo in northeastern Tibet, in Chinese states of Qinghai and some parts of Sichuan and Gansu . It is one of the four main spoken languages of Tibetan, the other three being Standard Tibetan Kham and Ladakhi...
- Khams TibetanKhams Tibetan languageKhams Tibetan is the Tibetan language used by the majority of the people in the Kham region of eastern Tibet . It is one of the four main spoken languages of Tibetan, the other three being those of U-Tsang , Amdo and Western Tibetan...
- Standard Tibetan
- Lhoba, Luòbā, 珞巴
- Monpa/Monba, Ménbā, 门巴
- Tibetan
- Lolo–Burmese–Naxi
- BurmishBurmish languagesThe Burmish languages are Burmese, including Standard Burmese and the Burmese dialects, and non-literary languages spoken across Burma and southern China such as Achang, Măru, Lăshi, Taungyo, and Atsi.-Languages:...
- AchangAchang languageThe Achang language is a Tibeto-Burman language spoken by the Achang in China.-External links:***...
, Āchāng, 阿昌
- Achang
- LoloishLoloish languagesThe Loloish languages, also known as Ngwi or in China as Yi, are a family of fifty to a hundred languages of the Tibeto-Burman language family. They are most closely related to Burmese and its relatives. Both the Loloish and Burmish branches are well defined, as is their superior node, Lolo–Burmese...
- Yi, Yí, 彝
- LisuLisu languageLisu is a tonal Tibeto-Burman language spoken in Yunnan , northern Burma , and Thailand and a small part of India. It is the language of the Lisu minority. Lisu has many dialects that originate from the country in which they live. Hua Lisu, Pai Lisu, and Lu Shi Lisu dialects are spoken in China...
, Lìsù, 傈僳 - LahuLahu languageLahu is a Tibeto-Burman language spoken by the Lahu people of China, Thailand, Myanmar, and Laos. It is widely used in China, both by Lahu people, and by other ethnic minorities in Yunnan, who use it as a lingua franca. However, the language is not widely used nor taught in any schools in...
, Lāhù, 拉祜 - HaniHani languageThe Hani language is a language of the Loloish branch of the Tibeto-Burman linguistic group spoken in China, Laos, Burma , and Vietnam by the Hani people.-Dialects:Hani proper has three dialects: Haya, Haohai, and Bika...
, Hāní, 哈尼 - JinoJino languageJino, or Jinuo, is a pair of Loloish languages spoken by the Jino people of Yunnan. The two languages, Youle and Buyuan , are not mutually intelligible. There is no official written form. Most Jino also speak one of the Tai languages or Chinese....
, Jīnuò, 基诺
- Nakhi/NaxiNaxi languageNaxi is a Tibeto-Burman language or group of languages spoken by some 310,000 people concentrated in the Lijiang City Yulong Naxi Autonomous County of the province of Yunnan, China. Nakhi is also the name of the ethnic group that speaks it.- Classification :There are at least two Naxi languages...
, Nàxī, 纳西 (?)
- Burmish
- Jingpho–Nungish–Luish (?)
- JingphoJingpho languageThe Jingpho language or Kachin language is a Tibeto-Burman language mainly spoken in Kachin State, Burma and Yunnan Province, China...
, Jǐngpō, 景颇 - DerungDerung languageDerung is a Tibeto-Burman language of the Derung people of China. The Derung have no written language. It is believed that the Derung and Nu people are of the same origin and speak somewhat the same language. They share the same kinship terminology as well as other cultural features.-External...
, Dúlóng, 独龙 - Nu, Nù, 怒
- Jingpho
Altaic
- TurkicTurkic languagesThe Turkic languages constitute a language family of at least thirty five languages, spoken by Turkic peoples across a vast area from Eastern Europe and the Mediterranean to Siberia and Western China, and are considered to be part of the proposed Altaic language family.Turkic languages are spoken...
(TūjuéGöktürksThe Göktürks or Kök Türks, were a nomadic confederation of peoples in medieval Inner Asia. Known in Chinese sources as 突厥 , the Göktürks under the leadership of Bumin Qaghan The Göktürks or Kök Türks, (Old Turkic: Türük or Kök Türük or Türük; Celestial Turks) were a nomadic confederation of...
突厥)- Uyghuric/Karluk
- UyghurUyghur languageUyghur , formerly known as Eastern Turk, is a Turkic language with 8 to 11 million speakers, spoken primarily by the Uyghur people in the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region of Western China. Significant communities of Uyghur-speakers are located in Kazakhstan and Uzbekistan, and various other...
, Wéiwúěr, 维吾尔 - UzbekUzbek languageUzbek is a Turkic language and the official language of Uzbekistan. It has about 25.5 million native speakers, and it is spoken by the Uzbeks in Uzbekistan and elsewhere in Central Asia...
, Wūzībiékè, 乌孜别克
- Uyghur
- Kipchak
- KazakhKazakh languageKazakh is a Turkic language which belongs to the Kipchak branch of the Turkic languages, closely related to Nogai and Karakalpak....
, Hāsàkè, 哈萨克 - KyrgyzKyrgyz languageKyrgyz or Kirgiz, also Kirghiz, Kyrghiz, Qyrghiz is a Turkic language and, together with Russian, an official language of Kyrgyzstan...
, Kēěrkèzī, 柯尔克孜 - Tatar, Tǎtǎěr, 塔塔尔
- Kazakh
- OghuzOghuz languagesThe Oghuz languages, a major branch of the Turkic language family, are spoken by more than 110 million people in an area spanning from the Balkans to China.-Linguistic features:...
- SalarSalar languageSalar is a Turkic language spoken by the Salar people, who mainly live in the provinces of Qinghai and Gansu in China; some also live in Ghulja, Xinjiang...
, Sǎlá, 撒拉
- Salar
- Eastern
- Western Yugur, Yùgù, 裕固
- Äynu, Àinǔ, 艾努
- Uyghuric/Karluk
- MongolicMongolic languagesThe Mongolic languages are a group of languages spoken in East-Central Asia, mostly in Mongolia and surrounding areas plus in Kalmykia. The best-known member of this language family, Mongolian, is the primary language of most of the residents of Mongolia and the Mongolian residents of Inner...
- MongolianMongolian languageThe Mongolian language is the official language of Mongolia and the best-known member of the Mongolic language family. The number of speakers across all its dialects may be 5.2 million, including the vast majority of the residents of Mongolia and many of the Mongolian residents of the Inner...
, Měnggǔ, 蒙古 - KhitanKhitan languageThe Khitan language is a now-extinct language once spoken by the Khitan people . Khitan is generally deemed to be genetically linked to the Mongolic languages. It was written using two mutually exclusive writing systems known as the Khitan large script and the Khitan small script...
, Qìdān, 契丹 (extinct) - Southeastern
- Monguor, Tǔ [Zú], 土[族]
- Eastern YugurEastern Yugur languageEastern Yugur and Western Yugur are terms coined by Chinese linguists to distinguish between the Mongolic and Turkic Yugur language, both spoken within the Yugur nationality. The terms may also indicate the speakers of these languages. Traditionally, both languages are indicated by the term Yellow...
, Yùgù, 裕固
- Eastern Yugur
- DongxiangDongxiang languageThe Santa language, also known as Dongxiang , is a Mongolic language spoken by the Dongxiang people in northwest China.-Grammar:In common with other Mongolic languages, Dongxiang is basically a subject–object–verb language...
, Dōngxiāng, 东乡 - BonanBonan languageThe Bonan language is the Mongolic language of the Bonan people of China. As of 1985, it was spoken by about 8,000 people, including about 75% of the total Baonan ethnic population and many ethnic Monguor, in Gansu and Qinghai Provinces and the Ningxia Hui Autonomous Prefecture...
, Bǎoān, 保安 - KangjiaKangjia languageThe Kangjia language is a recently-discovered Mongolic language spoken by a Muslim population of around 300 people in Jainca County, Huangnan Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture in Qinghai province of China...
, Kāngjiā, 康家语
- Monguor, Tǔ [Zú], 土[族]
- Mongolian
- TungusicTungusic languagesThe Tungusic languages form a language family spoken in Eastern Siberia and Manchuria by Tungusic peoples. Many Tungusic languages are endangered, and the long-term future of the family is uncertain...
- Southern
- ManchuManchu languageManchu is a Tungusic endangered language spoken in Northeast China; it used to be the language of the Manchu, though now most Manchus speak Mandarin Chinese and there are fewer than 70 native speakers of Manchu out of a total of nearly 10 million ethnic Manchus...
, Mǎn, 满- JurchenJurchen languageJurchen language is an extinct language. It was spoken by Jurchen people of eastern Manchuria, the creators of the Jin Empire in the northeastern China of the 12th–13th centuries. It is classified as a Southwestern Tungusic language.-Writing:...
, Nǚzhēn, 女真 (extinct)
- Jurchen
- XibeXibe languageThe Xibe language is the most widely spoken of the Tungusic languages spoken by members of the Xibe ethnic group in Xinjiang, in the northwest of the People's Republic of China.-Phonology:...
, Xíbó, 锡伯 - NanaiNanai languageThe Nanai language is spoken by the Nanai people in Siberia, and to a much smaller extent in China's Heilongjiang province, where it is known as Hezhe...
/Hezhen, Hèzhé, 赫哲
- Manchu
- Northern
- Evenki, Èwēnkè, 鄂温克
- OroqenOroqen languageOroqen is a Northern Tungusic language spoken in the People's Republic of China. Dialects are Gankui and Heilongjiang. Gankui is the standard dialect...
, Èlúnchūn, 鄂伦春
- Southern
- KoreanKorean languageKorean is the official language of the country Korea, in both South and North. It is also one of the two official languages in the Yanbian Korean Autonomous Prefecture in People's Republic of China. There are about 78 million Korean speakers worldwide. In the 15th century, a national writing...
/Choson, Cháoxiǎn, 朝鲜
Tai–Kadai (Kradai)
(Possibly the ancient Bǎiyuè 百越)- KraKra languagesThe Kra languages , also called Gēyāng in China, are a branch of the Tai–Kadai family spoken in southern China and in northern Vietnam. Out of the entire Tai–Kadai family, the Kra branch is the least studied...
- GelaoGelao languageGelao is a dialect cluster of Kra languages in the Tai–Kadai language family, spoken by the Gelao people in China and Vietnam. Despite an ethnic population of 580,000 , however, only a few thousand still speak the language...
, Gēlǎo, 仡佬
- Gelao
- Kam–SuiKam–Sui languagesThe Kam–Sui languages are a branch of the Tai–Kadai languages spoken by the Kam–Sui peoples. They are spoken mainly in eastern Guizhou, western Hunan, and northern Guangxi in southern China. Small pockets of Kam–Sui speakers are also found in northern Vietnam and Laos.-Classification:Kam–Sui...
- Dong, Dòng, 侗
- SuiSui languageThe Sui language is a Tai–Kadai language spoken by the Sui people of Guizhou province, China. According to Ethnologue, the total number of speakers is around 200,000 as of 1999. Sui is also unique for its rich inventory of consonants, with the Sandong dialect having as many as 70 consonants...
, Shuǐ, 水 - MaonanMaonan languageThe Maonan language is a Kam–Sui language spoken mainly in Huanjiang Maonan Autonomous County, Hechi, northern Guangxi by the Maonan people.-Demographics:...
, Màonán, 毛南 - Mulao/MulamMulam languageThe Mulam language is a Kam–Sui language spoken mainly in Luocheng County, Hechi, northern Guangxi by the Mulao people. The greatest concentrations are in Dongmen and Siba communes. Their autonym is mu6 lam1...
, Mùlǎo, 仫佬
- HlaiHlai languagesThe Hlai languages are a primary branch of the Tai–Kadai language family spoken in China on the island of Hainan. They include Hlai proper, with 600,000 speakers, and Cun, which has 80,000 speakers. The most divergent language is Jiamao, with 52,300 speakers in southern Hainan.-Classification:The...
/Li, Lí, 黎 - TaiTai languagesThe Tai or Zhuang–Tai languages are a branch of the Tai–Kadai language family. The Tai languages include the most widely spoken of the Tai–Kadai languages, including standard Thai or Siamese, the national language of Thailand; Lao or Laotian, the national language of Laos; Burma's Shan language;...
- Standard ZhuangStandard ZhuangThe standard Zhuang language is the variety of Zhuang spoken in Wuming County in the Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region of the People's Republic of China, where it is an official language.-Classification:...
, Zhuàng, 壮 - Buyei, Bùyī, 布依
- Dai, Dǎi, 傣
- Tai Lü languageTai Lü languageTai Lü is a language spoken by about 670,000 people in South East Asia. This includes 250,000 people in China, 200,000 in Burma, 134,000 in Thailand, and 5,000 in Vietnam...
, Dǎilèyǔ, 傣仂语 - Tai Nüa languageTai Nüa languageTai Nüa is one of the languages spoken by the Dai people in China, especially in the Dehong Dai and Jingpo Autonomous Prefecture in the southwest of Yunnan province...
, Déhóng Dǎiyǔ, 德宏傣语 - Tai Dam languageTai Dam languageTai Dam Black Tai is a Tai language spoken by the Tai Dam in Vietnam, Laos, Thailand, and China . It is called ภาษาไทดำ "Black Tai language" in Thai and Dǎidānyǔ 傣担语 in Chinese....
, Dǎinǎyǔ, 傣哪语; Dǎidānyǔ, 傣担语
- Tai Lü language
- Standard Zhuang
Others
Hmong–Mien(Possibly the ancient Nánmán
Nanman
Nanman were aboriginal tribes who lived in southwestern China. They may have been related to the Sanmiao, dated to around the 3rd century BC. The Nanman were multiple ethnic groups including the Miao, the Kinh, the Thai, and some Tibeto-Burman groups such as the Bai. There was never a single...
南蛮)
- HmongHmong languageHmong or Mong is the common name for a dialect continuum of the West Hmongic branch of the Hmong–Mien/Miao–Yao language family spoken by the Hmong people of Sichuan, Yunnan, Guizhou, Guangxi, northern Vietnam, Thailand, and Laos...
/Miao, Miáo, 苗 - MienIu Mien languageThe Iu Mien language is one of the main languages spoken by the Yao people in China, Laos, Vietnam, Thailand and more recently the United States, in diaspora. There are about 2,172,000 speakers in total, according to census data in 2000 from China, Vietnam, Thai, Laos, United States of America,...
/Yao, Yáo, 瑶 - SheShe languageThe She language , spoken by the She people, is a Hmong–Mien language. Most of the over 709,000 She people today speak Hakka Chinese...
, Shē, 畲
Austro-Asiatic
Austro-Asiatic languages
The Austro-Asiatic languages, in recent classifications synonymous with Mon–Khmer, are a large language family of Southeast Asia, also scattered throughout India and Bangladesh. The name Austro-Asiatic comes from the Latin words for "south" and "Asia", hence "South Asia"...
(Possibly the ancient Bǎipú 百濮)
- Palaung-Wa
- Palaung/Blang, Bùlǎng, 布朗
- De'ang, Déáng, 德昂
- Wa/VaVa peopleThe Va nationality lives mainly in Northern Burma, in the northern part of Shan and eastern Kachin States, near and along the border with China. Their defacto capital is Pangkham in the unofficial Wa State in North Eastern Shan state. The majority of the Va live in Burma...
, Wǎ, 佤
- VietnameseVietnamese languageVietnamese is the national and official language of Vietnam. It is the mother tongue of 86% of Vietnam's population, and of about three million overseas Vietnamese. It is also spoken as a second language by many ethnic minorities of Vietnam...
/Kinh, Jīng, 京
Austronesian
Austronesian languages
The Austronesian languages are a language family widely dispersed throughout the islands of Southeast Asia and the Pacific, with a few members spoken on continental Asia that are spoken by about 386 million people. It is on par with Indo-European, Niger-Congo, Afroasiatic and Uralic as one of the...
- Formosan languagesFormosan languagesThe Formosan languages are the languages of the indigenous peoples of Taiwan. Taiwanese aborigines currently comprise about 2% of the island's population. However, far fewer can still speak their ancestral language, after centuries of language shift...
, Gāoshān, 高山
Indo-European
Indo-European languages
The Indo-European languages are a family of several hundred related languages and dialects, including most major current languages of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and South Asia and also historically predominant in Anatolia...
- Russian, Éluósī, 俄罗斯
- TajikTajiks in ChinaTajiks , are an ethnic group that lives in the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region in the People's Republic of China...
, Tǎjíkè, 塔吉克 - Persian (spoken by Salar akhunds)
- PortuguesePortuguese languagePortuguese is a Romance language that arose in the medieval Kingdom of Galicia, nowadays Galicia and Northern Portugal. The southern part of the Kingdom of Galicia became independent as the County of Portugal in 1095...
(spoken in Macau) - EnglishEnglish languageEnglish is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria...
(spoken in Hong Kong)
Semitic
Semitic languages
The Semitic languages are a group of related languages whose living representatives are spoken by more than 270 million people across much of the Middle East, North Africa and the Horn of Africa...
- ArabicArabic languageArabic is a name applied to the descendants of the Classical Arabic language of the 6th century AD, used most prominently in the Quran, the Islamic Holy Book...
(second language of Hui peopleHui peopleThe Hui people are an ethnic group in China, defined as Chinese speaking people descended from foreign Muslims. They are typically distinguished by their practice of Islam, however some also practice other religions, and many are direct descendants of Silk Road travelers.In modern People's...
)
Mixed
Mixed language
A mixed language is a language that arises through the fusion of two source languages, normally in situations of thorough bilingualism, so that it is not possible to classify the resulting language as belonging to either of the language families that were its source...
- Wutun, Wǔtún, 五屯 (Mongolian-Tibetan mixed language)
- MacaneseMacanese languageMacanese or Macau Creole is a creole language derived mainly from Malay, Sinhalese, Cantonese, and Portuguese, which was originally spoken by the Macanese community of the Portuguese colony of Macau...
, Tǔshēngpú, 土生葡 (Portuguese creole)
Written languages

Chinese character
Chinese characters are logograms used in the writing of Chinese and Japanese , less frequently Korean , formerly Vietnamese , or other languages...
s (hanzi):
- The DaiDai peopleThe Dai peoples is one of several ethnic groups living in the Xishuangbanna Dai Autonomous Prefecture and the Dehong Dai and Jingpo Autonomous Prefecture , but by extension can apply to groups in Laos, Vietnam, Thailand, and Burma when Dai is used to mean specifically Tai Lue, Chinese Shan or even...
– Dai language - The HuiHui peopleThe Hui people are an ethnic group in China, defined as Chinese speaking people descended from foreign Muslims. They are typically distinguished by their practice of Islam, however some also practice other religions, and many are direct descendants of Silk Road travelers.In modern People's...
– Chinese languageChinese languageThe Chinese language is a language or language family consisting of varieties which are mutually intelligible to varying degrees. Originally the indigenous languages spoken by the Han Chinese in China, it forms one of the branches of Sino-Tibetan family of languages...
– Xiaoerjing - The KazakhsKazakhsThe Kazakhs are a Turkic people of the northern parts of Central Asia ....
– Kazakh languageKazakh languageKazakh is a Turkic language which belongs to the Kipchak branch of the Turkic languages, closely related to Nogai and Karakalpak....
– Arabic alphabetArabic alphabetThe Arabic alphabet or Arabic abjad is the Arabic script as it is codified for writing the Arabic language. It is written from right to left, in a cursive style, and includes 28 letters. Because letters usually stand for consonants, it is classified as an abjad.-Consonants:The Arabic alphabet has... - The Koreans – Korean languageKorean languageKorean is the official language of the country Korea, in both South and North. It is also one of the two official languages in the Yanbian Korean Autonomous Prefecture in People's Republic of China. There are about 78 million Korean speakers worldwide. In the 15th century, a national writing...
– HangulHangulHangul,Pronounced or ; Korean: 한글 Hangeul/Han'gŭl or 조선글 Chosŏn'gŭl/Joseongeul the Korean alphabet, is the native alphabet of the Korean language. It is a separate script from Hanja, the logographic Chinese characters which are also sometimes used to write Korean... - The Kyrgyz – Kyrgyz languageKyrgyz languageKyrgyz or Kirgiz, also Kirghiz, Kyrghiz, Qyrghiz is a Turkic language and, together with Russian, an official language of Kyrgyzstan...
– Arabic alphabetArabic alphabetThe Arabic alphabet or Arabic abjad is the Arabic script as it is codified for writing the Arabic language. It is written from right to left, in a cursive style, and includes 28 letters. Because letters usually stand for consonants, it is classified as an abjad.-Consonants:The Arabic alphabet has... - The Manchus – Manchu languageManchu languageManchu is a Tungusic endangered language spoken in Northeast China; it used to be the language of the Manchu, though now most Manchus speak Mandarin Chinese and there are fewer than 70 native speakers of Manchu out of a total of nearly 10 million ethnic Manchus...
– Manchu alphabetManchu alphabetThe Manchu alphabet was used for recording the now near-extinct Manchu language; a similar script is used today by the Xibe people, who speak a language descended from Manchu... - The Mongolians – Mongolian languageMongolian languageThe Mongolian language is the official language of Mongolia and the best-known member of the Mongolic language family. The number of speakers across all its dialects may be 5.2 million, including the vast majority of the residents of Mongolia and many of the Mongolian residents of the Inner...
– Mongolian alphabetMongolian alphabetMany alphabets have been devised for the Mongolian language over the centuries, and from a variety of scripts. The oldest, called simply the Mongolian script, has been the predominant script during most of Mongolian history, and is still in active use today in the Inner Mongolia region of China... - The Naxi – Dongba scriptDongba scriptThe Dongba, Tomba or Tompa symbols are a system of pictographic glyphs used by the ²dto¹mba of the Naxi people in southern China. In the Naxi language it is called ²ss ³dgyu 'wood records' or ²lv ³dgyu 'stone records'. They are perhaps a thousand years old. The glyphs may be used as rebuses for...
/Geba scriptGeba scriptGeba is a syllabic script for the Naxi language. It is called ¹Ggo¹baw in Naxi, adapted as Geba, 哥巴, in Chinese. Some glyphs resemble the Yi script, and some appear to be adaptations of Chinese characters. Geba is only used to transcribe mantras, and there are few texts, though it is sometimes used... - The Sui – Sui languageSui languageThe Sui language is a Tai–Kadai language spoken by the Sui people of Guizhou province, China. According to Ethnologue, the total number of speakers is around 200,000 as of 1999. Sui is also unique for its rich inventory of consonants, with the Sandong dialect having as many as 70 consonants...
– Sui script - The Tibetans – Tibetan languageTibetan languageThe Tibetan languages are a cluster of mutually-unintelligible Tibeto-Burman languages spoken primarily by Tibetan peoples who live across a wide area of eastern Central Asia bordering the Indian subcontinent, including the Tibetan Plateau and the northern Indian subcontinent in Baltistan, Ladakh,...
– Tibetan scriptTibetan scriptThe Tibetan alphabet is an abugida of Indic origin used to write the Tibetan language as well as the Dzongkha language, Denzongkha, Ladakhi language and sometimes the Balti language. The printed form of the alphabet is called uchen script while the hand-written cursive form used in everyday... - The UyghursUyghur peopleThe Uyghur are a Turkic ethnic group living in Eastern and Central Asia. Today, Uyghurs live primarily in the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region in the People's Republic of China...
– Uyghur languageUyghur languageUyghur , formerly known as Eastern Turk, is a Turkic language with 8 to 11 million speakers, spoken primarily by the Uyghur people in the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region of Western China. Significant communities of Uyghur-speakers are located in Kazakhstan and Uzbekistan, and various other...
– Arabic alphabetArabic alphabetThe Arabic alphabet or Arabic abjad is the Arabic script as it is codified for writing the Arabic language. It is written from right to left, in a cursive style, and includes 28 letters. Because letters usually stand for consonants, it is classified as an abjad.-Consonants:The Arabic alphabet has... - The XibeXibe languageThe Xibe language is the most widely spoken of the Tungusic languages spoken by members of the Xibe ethnic group in Xinjiang, in the northwest of the People's Republic of China.-Phonology:...
– Xibe languageXibe languageThe Xibe language is the most widely spoken of the Tungusic languages spoken by members of the Xibe ethnic group in Xinjiang, in the northwest of the People's Republic of China.-Phonology:...
– Manchu alphabetManchu alphabetThe Manchu alphabet was used for recording the now near-extinct Manchu language; a similar script is used today by the Xibe people, who speak a language descended from Manchu... - The YiYi peopleThe Yi or Lolo people are an ethnic group in China, Vietnam, and Thailand. Numbering 8 million, they are the seventh largest of the 55 ethnic minority groups officially recognized by the People's Republic of China...
– Yi languageYi languageNuosu , also known as Northern Yi, Liangshan Yi, and Sichuan Yi, is the prestige language of the Yi people; it has been chosen by the Chinese government as the standard Yi language and, as such, is the only one taught in school, both in its oral and written form...
– Yi syllabaryYi scriptThe Yi script, also historically known as Cuan Wen or Wei Shu , is used to write the Yi languages.-Classical Yi:Classical Yi is a syllabic logographic system that was reputedly devised during the Tang dynasty by someone called Aki...
Some formerly have used Chinese characters
- The JurchensJurchensThe Jurchens were a Tungusic people who inhabited the region of Manchuria until the 17th century, when they adopted the name Manchu...
(Manchu ancestors) – Jurchen languageJurchen languageJurchen language is an extinct language. It was spoken by Jurchen people of eastern Manchuria, the creators of the Jin Empire in the northeastern China of the 12th–13th centuries. It is classified as a Southwestern Tungusic language.-Writing:...
– Jurchen scriptJurchen scriptJurchen script was the writing system used to write Jurchen language, the language of the Jurchen people who created the Jin Empire in the northeastern China of the 12th–13th centuries. It was derived from the Khitan script, which in turn was derived from Chinese... - The Koreans – Korean languageKorean languageKorean is the official language of the country Korea, in both South and North. It is also one of the two official languages in the Yanbian Korean Autonomous Prefecture in People's Republic of China. There are about 78 million Korean speakers worldwide. In the 15th century, a national writing...
– HanjaHanjaHanja is the Korean name for the Chinese characters hanzi. More specifically, it refers to those Chinese characters borrowed from Chinese and incorporated into the Korean language with Korean pronunciation... - The Khitans (Mongol ancestors) – Khitan languageKhitan languageThe Khitan language is a now-extinct language once spoken by the Khitan people . Khitan is generally deemed to be genetically linked to the Mongolic languages. It was written using two mutually exclusive writing systems known as the Khitan large script and the Khitan small script...
– Khitan script - The Tanguts (Sino-Tibetan people) – Tangut languageTangut languageTangut is an ancient northeastern Tibeto-Burman language once spoken in the Western Xia Dynasty, also known as the Tangut Empire. It is classified by some linguists as one of the Qiangic languages, which also include Qiang and rGyalrong, among others...
– Tangut scriptTangut scriptThe Tangut script was a logographic writing system, used for writing the extinct Tangut language of the Western Xia Dynasty. According to the latest count, 5863 Tangut characters are known, excluding variants... - The Zhuang – Zhuang languages – Sawndip
Chinese palaces, temples, and coins have traditionally been inscribed in five scripts:
- Chinese
- ManchuManchu alphabetThe Manchu alphabet was used for recording the now near-extinct Manchu language; a similar script is used today by the Xibe people, who speak a language descended from Manchu...
- MongolMongolian alphabetMany alphabets have been devised for the Mongolian language over the centuries, and from a variety of scripts. The oldest, called simply the Mongolian script, has been the predominant script during most of Mongolian history, and is still in active use today in the Inner Mongolia region of China...
- TibetanTibetan scriptThe Tibetan alphabet is an abugida of Indic origin used to write the Tibetan language as well as the Dzongkha language, Denzongkha, Ladakhi language and sometimes the Balti language. The printed form of the alphabet is called uchen script while the hand-written cursive form used in everyday...
- UyghurUyghur languageUyghur , formerly known as Eastern Turk, is a Turkic language with 8 to 11 million speakers, spoken primarily by the Uyghur people in the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region of Western China. Significant communities of Uyghur-speakers are located in Kazakhstan and Uzbekistan, and various other...
During the Mongol Yuan dynasty
Yuan Dynasty
The Yuan Dynasty , or Great Yuan Empire was a ruling dynasty founded by the Mongol leader Kublai Khan, who ruled most of present-day China, all of modern Mongolia and its surrounding areas, lasting officially from 1271 to 1368. It is considered both as a division of the Mongol Empire and as an...
, the official writing system was:
- 'Phags-pa script

- MongolMongolian alphabetMany alphabets have been devised for the Mongolian language over the centuries, and from a variety of scripts. The oldest, called simply the Mongolian script, has been the predominant script during most of Mongolian history, and is still in active use today in the Inner Mongolia region of China...
- TibetanTibetan scriptThe Tibetan alphabet is an abugida of Indic origin used to write the Tibetan language as well as the Dzongkha language, Denzongkha, Ladakhi language and sometimes the Balti language. The printed form of the alphabet is called uchen script while the hand-written cursive form used in everyday...
- Arabic (for Uyghur)
- Latin (for Zhuang)
Ten nationalities who never had a written system have, under the PRC
People's Republic of China
China , officially the People's Republic of China , is the most populous country in the world, with over 1.3 billion citizens. Located in East Asia, the country covers approximately 9.6 million square kilometres...
's encouragement, developed phonetic alphabet
Spelling alphabet
A spelling alphabet, radio alphabet, or telephone alphabet is a set of words which are used to stand for the letters of an alphabet. Each word in the spelling alphabet typically replaces the name of the letter with which it starts...
s. According to a government white paper published in early 2005, "by the end of 2003, 22 ethnic minorities in China used 28 written languages."
Language policy
Chinese language policy in mainland ChinaMainland China
Mainland China, the Chinese mainland or simply the mainland, is a geopolitical term that refers to the area under the jurisdiction of the People's Republic of China . According to the Taipei-based Mainland Affairs Council, the term excludes the PRC Special Administrative Regions of Hong Kong and...
is heavily influenced by Soviet nationalities policy and officially encourages the development of standard spoken and written languages for each of the nationalities of China. However, in this schema, Han Chinese
Han Chinese
Han Chinese are an ethnic group native to China and are the largest single ethnic group in the world.Han Chinese constitute about 92% of the population of the People's Republic of China , 98% of the population of the Republic of China , 78% of the population of Singapore, and about 20% of the...
are considered a single nationality, and official policy of the People's Republic of China
People's Republic of China
China , officially the People's Republic of China , is the most populous country in the world, with over 1.3 billion citizens. Located in East Asia, the country covers approximately 9.6 million square kilometres...
(PRC) treats the different varieties of the Chinese spoken language differently from the different national languages despite the fact that they are more different from each other
Varieties of Chinese
Chinese comprises many regional language varieties sometimes grouped together as the Chinese dialects, the primary ones being Mandarin, Wu, Cantonese, and Min. These are not mutually intelligible, and even many of the regional varieties are themselves composed of a number of...
than, for example, the Romance languages
Romance languages
The Romance languages are a branch of the Indo-European language family, more precisely of the Italic languages subfamily, comprising all the languages that descend from Vulgar Latin, the language of ancient Rome...
of Europe.
While official policies in mainland China encourage the development and use of different orthographies for the national languages and their use in educational and academic settings, realistically speaking it would seem that, as elsewhere in the world, the outlook for
minority languages perceived as inferior is grim.
The Tibetan Government-in-Exile argue that social pressures and political efforts result in a policy of sinicization and feels that Beijing should promote the Tibetan language
Tibetan language
The Tibetan languages are a cluster of mutually-unintelligible Tibeto-Burman languages spoken primarily by Tibetan peoples who live across a wide area of eastern Central Asia bordering the Indian subcontinent, including the Tibetan Plateau and the northern Indian subcontinent in Baltistan, Ladakh,...
more.
Study of foreign languages
It is also considered increasingly prestigious and useful to have some ability in EnglishEnglish language
English is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria...
, which is a required subject for persons attending university. During the 1950s and 1960s, Russian
Russian language
Russian is a Slavic language used primarily in Russia, Belarus, Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan, Tajikistan and Kyrgyzstan. It is an unofficial but widely spoken language in Ukraine, Moldova, Latvia, Turkmenistan and Estonia and, to a lesser extent, the other countries that were once constituent republics...
had some social status among elites in mainland China as the international language of socialism
Socialism
Socialism is an economic system characterized by social ownership of the means of production and cooperative management of the economy; or a political philosophy advocating such a system. "Social ownership" may refer to any one of, or a combination of, the following: cooperative enterprises,...
. Japanese
Japanese language
is a language spoken by over 130 million people in Japan and in Japanese emigrant communities. It is a member of the Japonic language family, which has a number of proposed relationships with other languages, none of which has gained wide acceptance among historical linguists .Japanese is an...
is the second most-studied foreign language in China. However, languages other than English are now considered as "minor languages" (小语种 xiao yu zhong) and are only really studied at university level.
English is taught in the public schools starting in the third year of primary school.
The Economist
The Economist
The Economist is an English-language weekly news and international affairs publication owned by The Economist Newspaper Ltd. and edited in offices in the City of Westminster, London, England. Continuous publication began under founder James Wilson in September 1843...
, issue April 12, 2006, reported that up to one fifth of the population is learning English. Gordon Brown
Gordon Brown
James Gordon Brown is a British Labour Party politician who was the Prime Minister of the United Kingdom and Leader of the Labour Party from 2007 until 2010. He previously served as Chancellor of the Exchequer in the Labour Government from 1997 to 2007...
, the former British Prime Minister, estimated that the total English-speaking population in China will outnumber the native speakers in the rest of the world in two decades.
The Arabic language
Arabic language
Arabic is a name applied to the descendants of the Classical Arabic language of the 6th century AD, used most prominently in the Quran, the Islamic Holy Book...
is studied by Hui
Hui people
The Hui people are an ethnic group in China, defined as Chinese speaking people descended from foreign Muslims. They are typically distinguished by their practice of Islam, however some also practice other religions, and many are direct descendants of Silk Road travelers.In modern People's...
students.
Arabic language education was promoted by the Kuomintang
Kuomintang
The Kuomintang of China , sometimes romanized as Guomindang via the Pinyin transcription system or GMD for short, and translated as the Chinese Nationalist Party is a founding and ruling political party of the Republic of China . Its guiding ideology is the Three Principles of the People, espoused...
in Islamic schools when it ruled mainland China.
Portuguese
Portuguese language
Portuguese is a Romance language that arose in the medieval Kingdom of Galicia, nowadays Galicia and Northern Portugal. The southern part of the Kingdom of Galicia became independent as the County of Portugal in 1095...
is taught in Macau
Macau
Macau , also spelled Macao , is, along with Hong Kong, one of the two special administrative regions of the People's Republic of China...
as one of the official languages there and as a center of learning of the language in the region.
Further reading
- Kane, D. (2006). The Chinese language: its history and current usage. North Clarendon, VT: Tuttle. ISBN 0804838534
- Halliday, M. A. K., & Webster, J. (2005). Studies in Chinese language. London: Continuum. ISBN 0826458742
- Ramsey, S. R. (1987). The languages of China. Princeton, N.J.: Princeton University Press. ISBN 0691066949
- Hong, B. (1978). Chinese language use. Canberra: Contemporary China Centre, Research School of Pacific Studies, Australian National University. ISBN 0909596298
- Cheng, C. C., & Lehmann, W. P. (1975). Language & linguistics in the People's Republic of China. Austin: University of Texas Press. ISBN 0292746156
See also
- ChinglishChinglishChinglish refers to spoken or written English language that is influenced by the Chinese language. The term "Chinglish" is commonly applied to ungrammatical or nonsensical English in Chinese contexts, and may have pejorative or deprecating connotations, reflecting the attitudes of those who apply...
- Demographics of the People's Republic of China
- Demographics of TaiwanDemographics of TaiwanThis article is about the demographic features of the population in Taiwan, including population density, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population....
- Hong Kong EnglishHong Kong EnglishHong Kong English may refer to two different yet interrelated concepts. The first concept refers to the variation or dialect of the English language used in Hong Kong. The second concept refers to the accent and elements as a result of its use by Cantonese speakers.For the first meaning, Hong Kong...
- ISO 639 macrolanguage#zho
- Languages of Hong KongLanguages of Hong KongIn Hong Kong, English and Chinese are the official languages as defined in the Basic Law of Hong Kong. Since Britain's arrival in 1842, English became the sole official language of Hong Kong until 1974. The majority of the population in Hong Kong are descendants of migrants from mainland China...
- Languages of Macau
- Languages of TaiwanLanguages of TaiwanThe language with the most native speakers in Taiwan is Taiwanese Hokkien, or "Taiwanese" for short. Hokkien is a topolect of the Chinese family of languages originating in southern Fujian and is spoken by many overseas Chinese throughout Southeast Asia...
- Macanese PortugueseMacanese PortugueseMacanese Portuguese or Patuá is a Portuguese dialect spoken in Macau. It is co-official with Cantonese. It is only spoken by 7% of the residents; less than 2% speak it as first language...
- Nationalities of China
- Classification schemes for Southeast Asian languagesClassification schemes for Southeast Asian languagesBelow is a list of different classification schemes for Southeast Asian languages. Language families represented include:*Tai–Kadai*Austronesian*Austro-Asiatic*Hmong–Mien*Sino-Tibetan-Macrofamilies:...

