
List of Messier objects
Encyclopedia
The Messier objects are a set of astronomical objects catalogued by the French astronomer Charles Messier
in his "Catalogue des Nébuleuses et des Amas d'Étoiles" ("Catalogue of Nebulae and Star Clusters"), originally published in 1771, with the last addition (based on Messier's observations) made in 1966.
Because Messier was interested in finding only comet
s, he created a list of non-comet objects that frustrated his hunt for them. The compilation of this list, in collaboration with his assistant Pierre Méchain, is known as the Messier catalogue. This catalogue of objects is one of the most famous lists of astronomical objects, and many Messier object
s are still referenced by their Messier number.
The first edition included 45 objects, with Messier's final list totaling 103 objects. However, Messier 102 was not reported correctly, bringing the total to 102 objects. Other astronomers, using side notes in Messier's texts, eventually filled out the list to 110 objects.
Charles Messier
Charles Messier was a French astronomer most notable for publishing an astronomical catalogue consisting of deep sky objects such as nebulae and star clusters that came to be known as the 110 "Messier objects"...
in his "Catalogue des Nébuleuses et des Amas d'Étoiles" ("Catalogue of Nebulae and Star Clusters"), originally published in 1771, with the last addition (based on Messier's observations) made in 1966.
Because Messier was interested in finding only comet
Comet
A comet is an icy small Solar System body that, when close enough to the Sun, displays a visible coma and sometimes also a tail. These phenomena are both due to the effects of solar radiation and the solar wind upon the nucleus of the comet...
s, he created a list of non-comet objects that frustrated his hunt for them. The compilation of this list, in collaboration with his assistant Pierre Méchain, is known as the Messier catalogue. This catalogue of objects is one of the most famous lists of astronomical objects, and many Messier object
Messier object
The Messier objects are a set of astronomical objects first listed by French astronomer Charles Messier in 1771. The original motivation of the catalogue was that Messier was a comet hunter, and was frustrated by objects which resembled but were not comets...
s are still referenced by their Messier number.
The first edition included 45 objects, with Messier's final list totaling 103 objects. However, Messier 102 was not reported correctly, bringing the total to 102 objects. Other astronomers, using side notes in Messier's texts, eventually filled out the list to 110 objects.
Messier objects
| Messier number Messier object The Messier objects are a set of astronomical objects first listed by French astronomer Charles Messier in 1771. The original motivation of the catalogue was that Messier was a comet hunter, and was frustrated by objects which resembled but were not comets... |
NGC Number New General Catalogue The New General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars is a well-known catalogue of deep sky objects in astronomy. It contains 7,840 objects, known as the NGC objects... |
Common name | Picture | Object type | Distance (kly Light-year A light-year, also light year or lightyear is a unit of length, equal to just under 10 trillion kilometres... ) |
Constellation Constellation In modern astronomy, a constellation is an internationally defined area of the celestial sphere. These areas are grouped around asterisms, patterns formed by prominent stars within apparent proximity to one another on Earth's night sky.... |
Apparent magnitude Apparent magnitude The apparent magnitude of a celestial body is a measure of its brightness as seen by an observer on Earth, adjusted to the value it would have in the absence of the atmosphere... |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 Crab Nebula The Crab Nebula is a supernova remnant and pulsar wind nebula in the constellation of Taurus... |
NGC 1952 | Crab Nebula |  |
Supernova remnant Supernova remnant A supernova remnant is the structure resulting from the explosion of a star in a supernova. The supernova remnant is bounded by an expanding shock wave, and consists of ejected material expanding from the explosion, and the interstellar material it sweeps up and shocks along the way.There are two... |
6.3 | Taurus Taurus (constellation) Taurus is one of the constellations of the zodiac. Its name is a Latin word meaning 'bull', and its astrological symbol is a stylized bull's head:... |
9.0 |
| M2 Messier 2 Messier 2 or M2 is a globular cluster in the constellation Aquarius, five degrees north of the star Beta Aquarii... |
NGC 7089 |  |
Cluster, globular Globular cluster A globular cluster is a spherical collection of stars that orbits a galactic core as a satellite. Globular clusters are very tightly bound by gravity, which gives them their spherical shapes and relatively high stellar densities toward their centers. The name of this category of star cluster is... |
36 | Aquarius Aquarius (constellation) Aquarius is a constellation of the zodiac, situated between Capricornus and Pisces. Its name is Latin for "water-bearer" or "cup-bearer", and its symbol is , a representation of water.... |
7.5 | |
| M3 Messier 3 Messier 3 is a globular cluster in the constellation Canes Venatici. It was discovered by Charles Messier in 1764, and resolved into stars by William Herschel around 1784. This cluster is one of the largest and brightest, and is made up of around 500,000 stars. It is located at a distance of... |
NGC 5272 |  |
Cluster, globular Globular cluster A globular cluster is a spherical collection of stars that orbits a galactic core as a satellite. Globular clusters are very tightly bound by gravity, which gives them their spherical shapes and relatively high stellar densities toward their centers. The name of this category of star cluster is... |
31 | Canes Venatici Canes Venatici Canes Venatici is one of the 88 official modern constellations. It is a small northern constellation that was created by Johannes Hevelius in the 17th century. Its name is Latin for "hunting dogs", and the constellation is often depicted in illustrations as representing the dogs of Boötes the... |
7.0 | |
| M4 Messier 4 Messier 4 or M4 is a globular cluster in the constellation of Scorpius. It was discovered by Philippe Loys de Chéseaux in 1746 and catalogued by Charles Messier in 1764. It was the first globular cluster in which individual stars were resolved.-Visibility:M4 is conspicuous in even the smallest of... |
NGC 6121 |  |
Cluster, globular Globular cluster A globular cluster is a spherical collection of stars that orbits a galactic core as a satellite. Globular clusters are very tightly bound by gravity, which gives them their spherical shapes and relatively high stellar densities toward their centers. The name of this category of star cluster is... |
7 | Scorpius Scorpius Scorpius, sometimes known as Scorpio, is one of the constellations of the zodiac. Its name is Latin for scorpion, and its symbol is . It lies between Libra to the west and Sagittarius to the east... |
7.5 | |
| M5 Messier 5 Messier 5 or M5 is a globular cluster in the constellation Serpens. It was discovered by Gottfried Kirch in 1702... |
NGC 5904 |  |
Cluster, globular Globular cluster A globular cluster is a spherical collection of stars that orbits a galactic core as a satellite. Globular clusters are very tightly bound by gravity, which gives them their spherical shapes and relatively high stellar densities toward their centers. The name of this category of star cluster is... |
23 | Serpens Serpens Serpens is a constellation of the northern hemisphere. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union.... |
7.0 | |
| M6 Butterfly Cluster The Butterfly Cluster is an open cluster of stars in the constellation of Scorpius. Its name derives from the vague resemblance of its shape to a butterfly.... |
NGC 6405 | Butterfly Cluster |  |
Cluster, open Open cluster An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist... |
2 | Scorpius Scorpius Scorpius, sometimes known as Scorpio, is one of the constellations of the zodiac. Its name is Latin for scorpion, and its symbol is . It lies between Libra to the west and Sagittarius to the east... |
4.5 |
| M7 Ptolemy Cluster Messier 7 or M7, also designated NGC 6475 and sometimes known as the Ptolemy Cluster, is an open cluster of stars in the constellation of Scorpius.... |
NGC 6475 | Ptolemy Cluster |  |
Cluster, open Open cluster An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist... |
1 | Scorpius Scorpius Scorpius, sometimes known as Scorpio, is one of the constellations of the zodiac. Its name is Latin for scorpion, and its symbol is . It lies between Libra to the west and Sagittarius to the east... |
3.5 |
| M8 Lagoon Nebula The Lagoon Nebula is a giant interstellar cloud in the constellation Sagittarius. It is classified as an emission nebula and as an H II region.... |
NGC 6523 | Lagoon Nebula | Nebula Nebula A nebula is an interstellar cloud of dust, hydrogen gas, helium gas and other ionized gases... with cluster |
6.5 | Sagittarius Sagittarius (constellation) Sagittarius is a constellation of the zodiac, the one containing the galactic center. Its name is Latin for the archer, and its symbol is , a stylized arrow. Sagittarius is commonly represented as a centaur drawing a bow... |
6.0 | |
| M9 Messier 9 Messier 9 or M9 is a globular cluster in the constellation of Ophiuchus. It was discovered by Charles Messier in 1764.... |
NGC 6333 |  |
Cluster, globular Globular cluster A globular cluster is a spherical collection of stars that orbits a galactic core as a satellite. Globular clusters are very tightly bound by gravity, which gives them their spherical shapes and relatively high stellar densities toward their centers. The name of this category of star cluster is... |
26 | Ophiuchus Ophiuchus Ophiuchus is a large constellation located around the celestial equator. Its name is from the Greek "serpent-bearer", and it is commonly represented as a man grasping the snake that is represented by the constellation Serpens. Ophiuchus was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century... |
9.0 | |
| M10 Messier 10 Messier 10 or M10 is a globular cluster in the constellation of Ophiuchus.The object was discovered by Charles Messier on May 29, 1764, who cataloged it as number 10 in his list... |
NGC 6254 |  |
Cluster, globular Globular cluster A globular cluster is a spherical collection of stars that orbits a galactic core as a satellite. Globular clusters are very tightly bound by gravity, which gives them their spherical shapes and relatively high stellar densities toward their centers. The name of this category of star cluster is... |
13 | Ophiuchus Ophiuchus Ophiuchus is a large constellation located around the celestial equator. Its name is from the Greek "serpent-bearer", and it is commonly represented as a man grasping the snake that is represented by the constellation Serpens. Ophiuchus was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century... |
7.5 | |
| M11 Wild Duck Cluster The Wild Duck Cluster is an open cluster in the constellation Scutum. It was discovered by Gottfried Kirch in 1681. Charles Messier included it in his catalogue in 1764.... |
NGC 6705 | Wild Duck Cluster |  |
Cluster, open Open cluster An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist... |
6 | Scutum Scutum Scutum is a small constellation introduced in the seventeenth century. Its name is Latin for shield.-History:Scutum is the only constellation that owes its name to a non-classical historical figure... |
7.0 |
| M12 Messier 12 Messier 12 or M 12 is a globular cluster in the constellation of Ophiuchus. It was discovered by Charles Messier on May 30, 1764.... |
NGC 6218 |  |
Cluster, globular Globular cluster A globular cluster is a spherical collection of stars that orbits a galactic core as a satellite. Globular clusters are very tightly bound by gravity, which gives them their spherical shapes and relatively high stellar densities toward their centers. The name of this category of star cluster is... |
18 | Ophiuchus Ophiuchus Ophiuchus is a large constellation located around the celestial equator. Its name is from the Greek "serpent-bearer", and it is commonly represented as a man grasping the snake that is represented by the constellation Serpens. Ophiuchus was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century... |
8.0 | |
| M13 Messier 13 Messier 13 or M13 is a globular cluster of about 300,000 stars in the constellation of Hercules.... |
NGC 6205 | Great Globular Cluster in Hercules |  |
Cluster, globular Globular cluster A globular cluster is a spherical collection of stars that orbits a galactic core as a satellite. Globular clusters are very tightly bound by gravity, which gives them their spherical shapes and relatively high stellar densities toward their centers. The name of this category of star cluster is... |
22 | Hercules Hercules (constellation) Hercules is a constellation named after Hercules, the Roman mythological hero adapted from the Greek hero Heracles. Hercules was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today... |
5.8 |
| M14 Messier 14 Messier 14 is a globular cluster in the constellation Ophiuchus. It was discovered by Charles Messier in 1764.... |
NGC 6402 |  |
Cluster, globular Globular cluster A globular cluster is a spherical collection of stars that orbits a galactic core as a satellite. Globular clusters are very tightly bound by gravity, which gives them their spherical shapes and relatively high stellar densities toward their centers. The name of this category of star cluster is... |
27 | Ophiuchus Ophiuchus Ophiuchus is a large constellation located around the celestial equator. Its name is from the Greek "serpent-bearer", and it is commonly represented as a man grasping the snake that is represented by the constellation Serpens. Ophiuchus was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century... |
9.5 | |
| M15 Messier 15 Messier 15 or M15 is a globular cluster in the constellation Pegasus. It was discovered by Jean-Dominique Maraldi in 1746 and included in Charles Messier's catalogue of comet-like objects in 1764... |
NGC 7078 | Cluster, globular Globular cluster A globular cluster is a spherical collection of stars that orbits a galactic core as a satellite. Globular clusters are very tightly bound by gravity, which gives them their spherical shapes and relatively high stellar densities toward their centers. The name of this category of star cluster is... |
33 | Pegasus Pegasus (constellation) Pegasus is a constellation in the northern sky, named after the winged horse Pegasus in Greek mythology. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations.-Stars:... |
7.5 | ||
| M16 Eagle Nebula The Eagle Nebula is a young open cluster of stars in the constellation Serpens, discovered by Jean-Philippe de Cheseaux in 1745-46. Its name derives from its shape which is resemblant of an eagle... |
NGC 6611 | Eagle Nebula |  |
Nebula, H II region H II region An H II region is a large, low-density cloud of partially ionized gas in which star formation has recently taken place. The short-lived, blue stars forged in these regions emit copious amounts of ultraviolet light, ionizing the surrounding gas... with cluster |
7 | Serpens Serpens Serpens is a constellation of the northern hemisphere. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union.... |
6.5 |
| M17 Omega Nebula The Omega Nebula, also known as the Swan Nebula, Checkmark Nebula, Lobster Nebula, and the Horseshoe Nebula is an H II region in the constellation Sagittarius. It was discovered by Philippe Loys de Chéseaux in 1745. Charles Messier catalogued it in 1764... |
NGC 6618 | Omega, Swan, Horseshoe, or Lobster Nebula | Nebula, H II region H II region An H II region is a large, low-density cloud of partially ionized gas in which star formation has recently taken place. The short-lived, blue stars forged in these regions emit copious amounts of ultraviolet light, ionizing the surrounding gas... with cluster |
5 | Sagittarius Sagittarius (constellation) Sagittarius is a constellation of the zodiac, the one containing the galactic center. Its name is Latin for the archer, and its symbol is , a stylized arrow. Sagittarius is commonly represented as a centaur drawing a bow... |
6.0 | |
| M18 Messier 18 Messier 18 or M18 is an open cluster of stars in the constellation Sagittarius. It was discovered by Charles Messier in 1764 and included in his list of comet-like objects. From the perspective of Earth, M18 is situated between the Omega Nebula and the Sagittarius Star Cloud . Its age is... |
NGC 6613 |  |
Cluster, open Open cluster An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist... |
6 | Sagittarius Sagittarius (constellation) Sagittarius is a constellation of the zodiac, the one containing the galactic center. Its name is Latin for the archer, and its symbol is , a stylized arrow. Sagittarius is commonly represented as a centaur drawing a bow... |
8.0 | |
| M19 Messier 19 Messier 19 or M19 is a globular cluster in the constellation Ophiuchus. It was discovered by Charles Messier in 1764 and added to his catalogue of comet-like objects that same year.... |
NGC 6273 |  |
Cluster, globular Globular cluster A globular cluster is a spherical collection of stars that orbits a galactic core as a satellite. Globular clusters are very tightly bound by gravity, which gives them their spherical shapes and relatively high stellar densities toward their centers. The name of this category of star cluster is... |
27 | Ophiuchus Ophiuchus Ophiuchus is a large constellation located around the celestial equator. Its name is from the Greek "serpent-bearer", and it is commonly represented as a man grasping the snake that is represented by the constellation Serpens. Ophiuchus was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century... |
8.5 | |
| M20 Trifid Nebula The Trifid Nebula is an H II region located in Sagittarius. Its name means 'divided into three lobes'... |
NGC 6514 | Trifid Nebula | 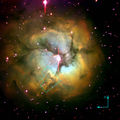 |
Nebula, H II region H II region An H II region is a large, low-density cloud of partially ionized gas in which star formation has recently taken place. The short-lived, blue stars forged in these regions emit copious amounts of ultraviolet light, ionizing the surrounding gas... with cluster |
5.2 | Sagittarius Sagittarius (constellation) Sagittarius is a constellation of the zodiac, the one containing the galactic center. Its name is Latin for the archer, and its symbol is , a stylized arrow. Sagittarius is commonly represented as a centaur drawing a bow... |
6.3 |
| M21 Messier 21 Messier 21 or M21 is an open cluster of stars in the constellation of Sagittarius. It was discovered and catalogued by Charles Messier on June 5, 1764.... |
NGC 6531 |  |
Cluster, open Open cluster An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist... |
3 | Sagittarius Sagittarius (constellation) Sagittarius is a constellation of the zodiac, the one containing the galactic center. Its name is Latin for the archer, and its symbol is , a stylized arrow. Sagittarius is commonly represented as a centaur drawing a bow... |
7.0 | |
| M22 Messier 22 Messier 22 is an elliptical globular cluster in the constellation Sagittarius, near the Galactic bulge region... |
NGC 6656 | Sagittarius Cluster | Cluster, globular Globular cluster A globular cluster is a spherical collection of stars that orbits a galactic core as a satellite. Globular clusters are very tightly bound by gravity, which gives them their spherical shapes and relatively high stellar densities toward their centers. The name of this category of star cluster is... |
10 | Sagittarius Sagittarius (constellation) Sagittarius is a constellation of the zodiac, the one containing the galactic center. Its name is Latin for the archer, and its symbol is , a stylized arrow. Sagittarius is commonly represented as a centaur drawing a bow... |
5.1 | |
| M23 Messier 23 Messier 23 is an open cluster in the constellation Sagittarius. It was discovered by Charles Messier on June 20, 1764.... |
NGC 6494 |  |
Cluster, open Open cluster An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist... |
4.5 | Sagittarius Sagittarius (constellation) Sagittarius is a constellation of the zodiac, the one containing the galactic center. Its name is Latin for the archer, and its symbol is , a stylized arrow. Sagittarius is commonly represented as a centaur drawing a bow... |
6.0 | |
| M24 Sagittarius Star Cloud The Sagittarius Star Cloud is a star cloud in the constellation of Sagittarius, approximately 600 light years wide, which was discovered by Charles Messier in 1764.... |
IC 4715 | Sagittarius Star Cloud | Milky Way Milky Way The Milky Way is the galaxy that contains the Solar System. This name derives from its appearance as a dim un-resolved "milky" glowing band arching across the night sky... star cloud Star cloud A star cloud is a group of stars that appear to be in the same position in the sky. These are not true star clusters, but rather dependent on the point of view of the observer. The stars that make up the cloud do not actually reside close to each other, they are just in the same line-of-sight.-See... |
10.0 | Sagittarius Sagittarius (constellation) Sagittarius is a constellation of the zodiac, the one containing the galactic center. Its name is Latin for the archer, and its symbol is , a stylized arrow. Sagittarius is commonly represented as a centaur drawing a bow... |
4.6 | |
| M25 Messier 25 Open Cluster M25 is an open cluster in the constellation Sagittarius. It was discovered by Philippe Loys de Chéseaux in 1745 and included in Charles Messier's list in 1764.... |
IC 4725 | Cluster, open Open cluster An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist... |
2 | Sagittarius Sagittarius (constellation) Sagittarius is a constellation of the zodiac, the one containing the galactic center. Its name is Latin for the archer, and its symbol is , a stylized arrow. Sagittarius is commonly represented as a centaur drawing a bow... |
4.9 | ||
| M26 Messier 26 Open Cluster M26 is an open cluster in the constellation Scutum. It was discovered by Charles Messier in 1764.... |
NGC 6694 |  |
Cluster, open Open cluster An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist... |
5 | Scutum Scutum Scutum is a small constellation introduced in the seventeenth century. Its name is Latin for shield.-History:Scutum is the only constellation that owes its name to a non-classical historical figure... |
9.5 | |
| M27 Dumbbell Nebula The Dumbbell Nebula is a planetary nebula in the constellation Vulpecula, at a distance of about 1,360 light years.... |
NGC 6853 | Dumbbell Nebula | Nebula, planetary Planetary nebula A planetary nebula is an emission nebula consisting of an expanding glowing shell of ionized gas ejected during the asymptotic giant branch phase of certain types of stars late in their life... |
1.25 | Vulpecula Vulpecula Vulpecula is a faint constellation in the northern sky. Its name is Latin for "little fox", although it is commonly known simply as the fox. It was identified in the seventeenth century, and is located in the middle of the Summer Triangle .-Stars:There are no stars brighter than 4th magnitude in... |
7.5 | |
| M28 Messier 28 Messier 28 is a globular cluster in the constellation Sagittarius. It was discovered by Charles Messier in 1764. In the sky it is very close to the 3rd magnitude star Kaus Borealis.... |
NGC 6626 |  |
Cluster, globular Globular cluster A globular cluster is a spherical collection of stars that orbits a galactic core as a satellite. Globular clusters are very tightly bound by gravity, which gives them their spherical shapes and relatively high stellar densities toward their centers. The name of this category of star cluster is... |
18 | Sagittarius Sagittarius (constellation) Sagittarius is a constellation of the zodiac, the one containing the galactic center. Its name is Latin for the archer, and its symbol is , a stylized arrow. Sagittarius is commonly represented as a centaur drawing a bow... |
8.5 | |
| M29 Messier 29 Messier 29 is an open cluster in the Cygnus constellation. It was discovered by Charles Messier in 1764, and can be seen from Earth by using binoculars.... |
NGC 6913 | Cluster, open Open cluster An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist... |
7.2 | Cygnus Cygnus (constellation) Cygnus is a northern constellation lying on the plane of the Milky Way. Its name is the Latinized Hellenic word for swan. One of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross... |
9.0 | ||
| M30 Messier 30 Messier 30 is a globular cluster in the Capricornus constellation. It was discovered by Charles Messier in 1764. M30 is at a distance of about 28,000 light-years away from Earth, and about 90 light-years across.... |
NGC 7099 | Cluster, globular Globular cluster A globular cluster is a spherical collection of stars that orbits a galactic core as a satellite. Globular clusters are very tightly bound by gravity, which gives them their spherical shapes and relatively high stellar densities toward their centers. The name of this category of star cluster is... |
25 | Capricornus Capricornus Capricornus is one of the constellations of the zodiac; it is often called Capricorn, especially when referring to the corresponding astrological sign. Its name is Latin for "horned male goat" or "goat horn", and it is commonly represented in the form of a sea-goat: a mythical creature that is half... |
8.5 | ||
| M31 Andromeda Galaxy The Andromeda Galaxy is a spiral galaxy approximately 2.5 million light-years from Earth in the constellation Andromeda. It is also known as Messier 31, M31, or NGC 224, and is often referred to as the Great Andromeda Nebula in older texts. Andromeda is the nearest spiral galaxy to the... |
NGC 224 | Andromeda Galaxy |  |
Galaxy, spiral Spiral galaxy A spiral galaxy is a certain kind of galaxy originally described by Edwin Hubble in his 1936 work The Realm of the Nebulae and, as such, forms part of the Hubble sequence. Spiral galaxies consist of a flat, rotating disk containing stars, gas and dust, and a central concentration of stars known as... |
2,500 | Andromeda Andromeda (constellation) Andromeda is a constellation in the northern sky. It is named after Andromeda, the princess in the Greek legend of Perseus who was chained to a rock to be eaten by the sea monster Cetus... |
3.4 |
| M32 Messier 32 Messier 32 is a dwarf elliptical galaxy about 2.65 million light-years away in the constellation Andromeda. M32 is a satellite galaxy of the famous Andromeda Galaxy and was discovered by Le Gentil in 1749. M32 measures only 6.5 ± 0.2 kly in diameter at the widest point... |
NGC 221 |  |
Galaxy, dwarf elliptical Dwarf elliptical galaxy Dwarf elliptical galaxies, or dEs, are elliptical galaxies that are much smaller than others. They are classified as dE, and are quite common in galaxy groups and clusters, and are usually companions to other galaxies.- Examples :... |
2,900 | Andromeda Andromeda (constellation) Andromeda is a constellation in the northern sky. It is named after Andromeda, the princess in the Greek legend of Perseus who was chained to a rock to be eaten by the sea monster Cetus... |
10.0 | |
| M33 Triangulum Galaxy The Triangulum Galaxy is a spiral galaxy approximately 3 million light years from Earth in the constellation Triangulum. It is catalogued as Messier 33 or NGC 598, and is sometimes informally referred to as the Pinwheel Galaxy, a nickname it shares with Messier 101... |
NGC 598 | Triangulum Galaxy | Galaxy, spiral Spiral galaxy A spiral galaxy is a certain kind of galaxy originally described by Edwin Hubble in his 1936 work The Realm of the Nebulae and, as such, forms part of the Hubble sequence. Spiral galaxies consist of a flat, rotating disk containing stars, gas and dust, and a central concentration of stars known as... |
2,810 | Triangulum Triangulum Triangulum is a small constellation in the northern sky. Its name is Latin for triangle, and it should not be confused with Triangulum Australe in the southern sky. Its name derives from its three brightest stars, of third and fourth magnitude, which form a nearly isosceles long and narrow triangle... |
5.7 | |
| M34 Messier 34 Messier 34 is an open cluster in the constellation Perseus. It was probably discovered by Giovanni Batista Hodierna before 1654 and included by Charles Messier in his catalog of comet-like objects in 1764. Messier described it as, "A cluster of small stars a little below the parallel of γ... |
NGC 1039 |  |
Cluster, open Open cluster An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist... |
1.4 | Perseus Perseus (constellation) Perseus is a constellation in the northern sky, named after the Greek hero Perseus. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union... |
6.0 | |
| M35 Messier 35 Messier 35 is an open cluster in the constellation Gemini. It was discovered by Philippe Loys de Chéseaux in 1745 and independently discovered by John Bevis before 1750... |
NGC 2168 |  |
Cluster, open Open cluster An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist... |
2.8 | Gemini Gemini (constellation) Gemini is one of the constellations of the zodiac. It was one of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today. Its name is Latin for "twins", and it is associated with the twins Castor and Pollux in Greek mythology... |
5.5 | |
| M36 Messier 36 Open Cluster M36 is an open cluster in the Auriga constellation. It was discovered by Giovanni Batista Hodierna before 1654. M36 is at a distance of about 4,100 light years away from Earth and is about 14 light years across. There are at least sixty members in the cluster... |
NGC 1960 | Cluster, open Open cluster An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist... |
4.1 | Auriga Auriga (constellation) Auriga is a constellation in the northern sky. Its name is Latin for 'charioteer' and its stars form a shape that has been associated with the pointed helmet of a charioteer. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains among the 88 modern... |
6.5 | ||
| M37 Messier 37 Messier 37 is the richest open cluster in the constellation Auriga. It was discovered by Hodierna before 1654.... |
NGC 2099 |  |
Cluster, open Open cluster An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist... |
4.6 | Auriga Auriga Auriga can refer to:*Auriga , a constellation of stars*Auriga , a Roman slave chauffeur*HMS Auriga , a British submarine launched in 1945*"Auriga of Delphi", name of the statue "Charioteer of Delphi"... |
6.0 | |
| M38 Messier 38 Messier 38 is an open cluster in the Auriga constellation.It was discovered by Giovanni Batista Hodierna before 1654 and independently found by Le Gentil in 1749... |
NGC 1912 | Cluster, open Open cluster An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist... |
4.2 | Auriga Auriga Auriga can refer to:*Auriga , a constellation of stars*Auriga , a Roman slave chauffeur*HMS Auriga , a British submarine launched in 1945*"Auriga of Delphi", name of the statue "Charioteer of Delphi"... |
7.0 | ||
| M39 Messier 39 Open Cluster M39 is an open cluster in the Cygnus constellation. It was discovered by Charles Messier in 1764. M39 is at a distance of about 800 light years away from Earth... |
NGC 7092 | Cluster, open Open cluster An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist... |
0.8 | Cygnus | 5.5 | ||
| M40 Winnecke 4 Winnecke 4 is a double star in the constellation Ursa Major. It was discovered by Charles Messier in 1764 while he was searching for a nebula that had been reported in the area by Johann Hevelius. Not seeing any nebulae, Messier catalogued this double star instead... |
Winnecke 4 | Double star Double star In observational astronomy, a double star is a pair of stars that appear close to each other in the sky as seen from Earth when viewed through an optical telescope. This can happen either because the pair forms a binary star, i.e... WNC4 |
0.5 | Ursa Major Ursa Major Ursa Major , also known as the Great Bear, is a constellation visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. It can best be seen in April... |
9.0 | ||
| M41 Messier 41 Messier 41 is an open cluster in the Canis Major constellation. It was discovered by Giovanni Batista Hodierna before 1654 and was perhaps known to Aristotle about 325 BC. M41 lies about four degrees almost exactly south of Sirius... |
NGC 2287 | Cluster, open Open cluster An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist... |
2.3 | Canis Major Canis Major Canis Major is one of the 88 modern constellations, and was included in the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy's 48 constellations. Its name is Latin for 'greater dog', and is commonly represented as one of the dogs following Orion the hunter... |
4.5 | ||
| M42 Orion Nebula The Orion Nebula is a diffuse nebula situated south of Orion's Belt. It is one of the brightest nebulae, and is visible to the naked eye in the night sky. M42 is located at a distance of and is the closest region of massive star formation to Earth. The M42 nebula is estimated to be 24 light... |
NGC 1976 | Orion Nebula |  |
Nebula, H II region H II region An H II region is a large, low-density cloud of partially ionized gas in which star formation has recently taken place. The short-lived, blue stars forged in these regions emit copious amounts of ultraviolet light, ionizing the surrounding gas... |
1.6 | Orion Orion (constellation) Orion, often referred to as The Hunter, is a prominent constellation located on the celestial equator and visible throughout the world. It is one of the most conspicuous, and most recognizable constellations in the night sky... |
4.0 |
| M43 Messier 43 Messier 43 is an H II region in the Orion constellation. It was discovered by Jean-Jacques Dortous de Mairan before 1731. The De Mairan's Nebula is part of the Orion Nebula, separated from the main nebula by a lane of dust. It is part of the much larger Orion Molecular Cloud Complex.-External... |
NGC 1982 | De Mairan's Nebula | Nebula, H II region H II region An H II region is a large, low-density cloud of partially ionized gas in which star formation has recently taken place. The short-lived, blue stars forged in these regions emit copious amounts of ultraviolet light, ionizing the surrounding gas... (part of the Orion Nebula) |
1.6 | Orion Orion (constellation) Orion, often referred to as The Hunter, is a prominent constellation located on the celestial equator and visible throughout the world. It is one of the most conspicuous, and most recognizable constellations in the night sky... |
7.0 | |
| M44 Beehive Cluster The Beehive Cluster, also known as Praesepe , M44, NGC 2632, or Cr 189, is an open cluster in the constellation Cancer. It is one of the nearest open clusters to the Solar System, and it contains a larger star population than most other nearby clusters... |
NGC 2632 | Beehive Cluster | Cluster, open Open cluster An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist... |
0.6 | Cancer Cancer (constellation) Cancer is one of the twelve constellations of the zodiac. Its name is Latin for crab and it is commonly represented as such. Its symbol is . Cancer is small and its stars are faint... |
3.7 | |
| M45 Pleiades (star cluster) In astronomy, the Pleiades, or Seven Sisters , is an open star cluster containing middle-aged hot B-type stars located in the constellation of Taurus. It is among the nearest star clusters to Earth and is the cluster most obvious to the naked eye in the night sky... |
Pleiades | Cluster, open Open cluster An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist... |
0.4 | Taurus Taurus (constellation) Taurus is one of the constellations of the zodiac. Its name is a Latin word meaning 'bull', and its astrological symbol is a stylized bull's head:... |
1.6 | ||
| M46 Messier 46 Messier 46 is an open cluster in the constellation of Puppis. It was discovered by Charles Messier in 1771... |
NGC 2437 |  |
Cluster, open Open cluster An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist... |
5.4 | Puppis Puppis Puppis is a constellation in the southern sky. Its name is the Latin word for the poop deck of a ship, and Puppis represents the deck of the ship and its deckhouses... |
6.5 | |
| M47 Messier 47 Open Cluster M47 is an open cluster in the constellation Puppis. It was discovered by Giovanni Batista Hodierna before 1654 and independently discovered by Charles Messier on February 19, 1771.... |
NGC 2422 |  |
Cluster, open Open cluster An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist... |
1.6 | Puppis Puppis Puppis is a constellation in the southern sky. Its name is the Latin word for the poop deck of a ship, and Puppis represents the deck of the ship and its deckhouses... |
4.5 | |
| M48 Messier 48 Messier 48 is an open cluster in the Hydra constellation. It was discovered by Charles Messier in 1771.There is actually no cluster in the position indicated by Messier... |
NGC 2548 |  |
Cluster, open Open cluster An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist... |
1.5 | Hydra Hydra (constellation) Hydra is the largest of the 88 modern constellations, measuring 1303 square degrees. It has a long history, having been included among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy. It is commonly represented as a water snake... |
5.5 | |
| M49 Messier 49 Messier 49 is an elliptical / lenticular galaxy about 49 million light-years away in the constellation Virgo. The galaxy was discovered by Charles Messier in 1771.-Supernovae:... |
NGC 4472 | Galaxy, elliptical Elliptical galaxy An elliptical galaxy is a galaxy having an approximately ellipsoidal shape and a smooth, nearly featureless brightness profile. They range in shape from nearly spherical to highly flat and in size from hundreds of millions to over one trillion stars... |
60,000 | Virgo Virgo (constellation) Virgo is one of the constellations of the zodiac. Its name is Latin for virgin, and its symbol is . Lying between Leo to the west and Libra to the east, it is the second largest constellation in the sky... |
10.0 | ||
| M50 Messier 50 Messier 50 is an open cluster in the constellation Monoceros. It was perhaps discovered by G. D. Cassini before 1711 and independently discovered by Charles Messier in 1772. M50 is at a distance of about 3,000 light-years away from Earth. It is described as a 'heart-shaped' figure.-External... |
NGC 2323 |  |
Cluster, open Open cluster An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist... |
3 | Monoceros Monoceros Monoceros is a faint constellation on the celestial equator. Its name is Greek for unicorn. Its definition is attributed to the 17th-century Dutch cartographer Petrus Plancius. It is bordered by Orion to the west, Gemini to the north, Canis Major to the south and Hydra to the east... |
7.0 | |
| M51 Whirlpool Galaxy The Whirlpool Galaxy is an interacting grand-design spiral galaxy that is estimated to be 23 ± 4 million light-years from the Milky Way Galaxy. in the constellation Canes Venatici... |
NGC 5194, NGC 5195 NGC 5195 NGC 5195 is a dwarf galaxy that is interacting with the Whirlpool Galaxy . Both galaxies are located approximately 25 million light-years away in the constellation Canes Venatici... |
Whirlpool Galaxy | .jpg) |
Galaxy, spiral Spiral galaxy A spiral galaxy is a certain kind of galaxy originally described by Edwin Hubble in his 1936 work The Realm of the Nebulae and, as such, forms part of the Hubble sequence. Spiral galaxies consist of a flat, rotating disk containing stars, gas and dust, and a central concentration of stars known as... |
37,000 | Canes Venatici Canes Venatici Canes Venatici is one of the 88 official modern constellations. It is a small northern constellation that was created by Johannes Hevelius in the 17th century. Its name is Latin for "hunting dogs", and the constellation is often depicted in illustrations as representing the dogs of Boötes the... |
8.4 |
| M52 Messier 52 Messier 52 is an open cluster in the Cassiopeia constellation. It was discovered by Charles Messier in 1774. M52 can be seen from Earth with binoculars.... |
NGC 7654 |  |
Cluster, open Open cluster An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist... |
7 | Cassiopeia Cassiopeia (constellation) Cassiopeia is a constellation in the northern sky, named after the vain queen Cassiopeia in Greek mythology, who boasted about her unrivalled beauty. Cassiopea was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century Greek astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today... |
8.0 | |
| M53 Messier 53 Messier 53 is a globular cluster in the Coma Berenices constellation. It was discovered by Johann Elert Bode in 1775. M53 is one of the more outlying globular clusters, being about 60,000 light-years away from the Galactic Center, and almost the same distance from the Solar system.-External links:*... |
NGC 5024 | Cluster, globular Globular cluster A globular cluster is a spherical collection of stars that orbits a galactic core as a satellite. Globular clusters are very tightly bound by gravity, which gives them their spherical shapes and relatively high stellar densities toward their centers. The name of this category of star cluster is... |
56 | Coma Berenices Coma Berenices Coma Berenices is a traditional asterism that has since been defined as one of the 88 modern constellations. It is located near Leo, to which it formerly belonged, and accommodates the North Galactic Pole... |
8.5 | ||
| M54 Messier 54 Messier 54 is a globular cluster in the constellation Sagittarius. It was discovered by Charles Messier in 1778 and subsequently included in his catalog of comet-like objects.... |
NGC 6715 | Cluster, globular Globular cluster A globular cluster is a spherical collection of stars that orbits a galactic core as a satellite. Globular clusters are very tightly bound by gravity, which gives them their spherical shapes and relatively high stellar densities toward their centers. The name of this category of star cluster is... |
83 | Sagittarius Sagittarius (constellation) Sagittarius is a constellation of the zodiac, the one containing the galactic center. Its name is Latin for the archer, and its symbol is , a stylized arrow. Sagittarius is commonly represented as a centaur drawing a bow... |
8.5 | ||
| M55 Messier 55 Messier 55 is a globular cluster in the constellation Sagittarius. It was discovered by Nicolas Louis de Lacaille in 1751 and catalogued by Charles Messier in 1778. M55 is at a distance of about 17,300 light-years away from Earth. Only about half a dozen variable stars have been discovered in... |
NGC 6809 | Cluster, globular Globular cluster A globular cluster is a spherical collection of stars that orbits a galactic core as a satellite. Globular clusters are very tightly bound by gravity, which gives them their spherical shapes and relatively high stellar densities toward their centers. The name of this category of star cluster is... |
17 | Sagittarius Sagittarius (constellation) Sagittarius is a constellation of the zodiac, the one containing the galactic center. Its name is Latin for the archer, and its symbol is , a stylized arrow. Sagittarius is commonly represented as a centaur drawing a bow... |
7.0 | ||
| M56 Messier 56 Messier 56 is a globular cluster in the constellation Lyra. It was discovered by Charles Messier in 1779... |
NGC 6779 | Cluster, globular Globular cluster A globular cluster is a spherical collection of stars that orbits a galactic core as a satellite. Globular clusters are very tightly bound by gravity, which gives them their spherical shapes and relatively high stellar densities toward their centers. The name of this category of star cluster is... |
32 | Lyra Lyra Lyra is a small constellation. It is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union. Its principal star, Vega — a corner of the Summer Triangle — is one of the brightest... |
9.5 | ||
| M57 Ring Nebula The famously named "Ring Nebula" appears in the northern constellation of Lyra and is located in the Carina–Sagittarius Arm... |
NGC 6720 | Ring Nebula | 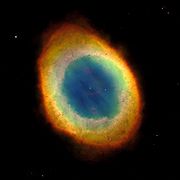 |
Nebula, planetary Planetary nebula A planetary nebula is an emission nebula consisting of an expanding glowing shell of ionized gas ejected during the asymptotic giant branch phase of certain types of stars late in their life... |
2.3 | Lyra Lyra Lyra is a small constellation. It is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union. Its principal star, Vega — a corner of the Summer Triangle — is one of the brightest... |
8.8 |
| M58 Messier 58 Messier 58 is a barred spiral galaxy located within the constellation Virgo, approximately 68 million light-years away from Earth. It was discovered by Charles Messier on April 15, 1779 and is one of four barred spiral galaxies that appear in Messier's catalogue. M58 is one of the brightest... |
NGC 4579 |  |
Galaxy, barred spiral Barred spiral galaxy A barred spiral galaxy is a spiral galaxy with a central bar-shaped structure composed of stars. Bars are found in approximately two-thirds of all spiral galaxies... |
60,000 | Virgo Virgo -Astronomy:* Virgo Cluster, a cluster of galaxies in the constellation Virgo* Virgo , a constellation* Virgo Stellar Stream, remains of a dwarf galaxy* Virgo Supercluster, a galactic supercluster-Surname:* Virgo... |
11.0 | |
| M59 Messier 59 Messier 59 is an elliptical galaxy in the constellation Virgo.-History:Messier 59 and the nearby elliptical galaxy Messier 60 were both discovered by Johann Gottfried Koehler in April 1779 during observations of a comet in the same part of the sky... |
NGC 4621 | Galaxy, elliptical Elliptical galaxy An elliptical galaxy is a galaxy having an approximately ellipsoidal shape and a smooth, nearly featureless brightness profile. They range in shape from nearly spherical to highly flat and in size from hundreds of millions to over one trillion stars... |
60,000 | Virgo Virgo -Astronomy:* Virgo Cluster, a cluster of galaxies in the constellation Virgo* Virgo , a constellation* Virgo Stellar Stream, remains of a dwarf galaxy* Virgo Supercluster, a galactic supercluster-Surname:* Virgo... |
11.5 | ||
| M60 Messier 60 Messier 60 is an elliptical galaxy approximately 55 million light-years away in the constellation Virgo.-History:... |
NGC 4649 | Galaxy, elliptical Elliptical galaxy An elliptical galaxy is a galaxy having an approximately ellipsoidal shape and a smooth, nearly featureless brightness profile. They range in shape from nearly spherical to highly flat and in size from hundreds of millions to over one trillion stars... |
60,000 | Virgo Virgo -Astronomy:* Virgo Cluster, a cluster of galaxies in the constellation Virgo* Virgo , a constellation* Virgo Stellar Stream, remains of a dwarf galaxy* Virgo Supercluster, a galactic supercluster-Surname:* Virgo... |
10.5 | ||
| M61 Messier 61 Messier 61 is a spiral galaxy in the Virgo Cluster. It was discovered by Barnabus Oriani on May 5, 1779.M61 is one of the larger members of the Virgo Cluster.Six supernovae have been observed in this galaxy:... |
NGC 4303 |  |
Galaxy, spiral Spiral galaxy A spiral galaxy is a certain kind of galaxy originally described by Edwin Hubble in his 1936 work The Realm of the Nebulae and, as such, forms part of the Hubble sequence. Spiral galaxies consist of a flat, rotating disk containing stars, gas and dust, and a central concentration of stars known as... |
60,000 | Virgo Virgo -Astronomy:* Virgo Cluster, a cluster of galaxies in the constellation Virgo* Virgo , a constellation* Virgo Stellar Stream, remains of a dwarf galaxy* Virgo Supercluster, a galactic supercluster-Surname:* Virgo... |
10.5 | |
| M62 Messier 62 Messier 62 is a globular cluster in the constellation Ophiuchus. It was discovered in 1771 by Charles Messier.M62 is at a distance of about 22,500 light-years from Earth and measures some 100 light-years across.... |
NGC 6266 | Cluster, globular Globular cluster A globular cluster is a spherical collection of stars that orbits a galactic core as a satellite. Globular clusters are very tightly bound by gravity, which gives them their spherical shapes and relatively high stellar densities toward their centers. The name of this category of star cluster is... |
22 | Ophiuchus Ophiuchus Ophiuchus is a large constellation located around the celestial equator. Its name is from the Greek "serpent-bearer", and it is commonly represented as a man grasping the snake that is represented by the constellation Serpens. Ophiuchus was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century... |
8.0 | ||
| M63 Sunflower Galaxy The Sunflower Galaxy is a spiral galaxy in the constellation Canes Venatici consisting of a central disc surrounded by many short spiral arm segments... |
NGC 5055 | Sunflower Galaxy | Galaxy, spiral Spiral galaxy A spiral galaxy is a certain kind of galaxy originally described by Edwin Hubble in his 1936 work The Realm of the Nebulae and, as such, forms part of the Hubble sequence. Spiral galaxies consist of a flat, rotating disk containing stars, gas and dust, and a central concentration of stars known as... |
37,000 | Canes Venatici Canes Venatici Canes Venatici is one of the 88 official modern constellations. It is a small northern constellation that was created by Johannes Hevelius in the 17th century. Its name is Latin for "hunting dogs", and the constellation is often depicted in illustrations as representing the dogs of Boötes the... |
8.5 | |
| M64 Black Eye Galaxy The Black Eye Galaxy was discovered by Edward Pigott in March 1779, and independently by Johann Elert Bode in April of the same year, as well as by Charles Messier in 1780... |
NGC 4826 | Black Eye Galaxy |  |
Galaxy, spiral Spiral galaxy A spiral galaxy is a certain kind of galaxy originally described by Edwin Hubble in his 1936 work The Realm of the Nebulae and, as such, forms part of the Hubble sequence. Spiral galaxies consist of a flat, rotating disk containing stars, gas and dust, and a central concentration of stars known as... |
12,000 | Coma Berenices Coma Berenices Coma Berenices is a traditional asterism that has since been defined as one of the 88 modern constellations. It is located near Leo, to which it formerly belonged, and accommodates the North Galactic Pole... |
9.0 |
| M65 Messier 65 Messier 65 is an intermediate spiral galaxy about 35 million light-years away in the constellation Leo. It was discovered by Charles Messier in 1780. M65, M66, and NGC 3628 comprise the famous Leo Triplet, a small group of galaxies.-Discovery:M65 was discovered by Charles Messier and included in... |
NGC 3623 | Galaxy, barred spiral Barred spiral galaxy A barred spiral galaxy is a spiral galaxy with a central bar-shaped structure composed of stars. Bars are found in approximately two-thirds of all spiral galaxies... |
35,000 | Leo Leo (constellation) Leo is one of the constellations of the zodiac. Its name is Latin for lion. Its symbol is . Leo lies between dim Cancer to the west and Virgo to the east.-Stars:... |
10.5 | ||
| M66 Messier 66 Messier 66 is an intermediate spiral galaxy about 36 million light-years away in the constellation Leo. It was discovered by Charles Messier in 1780... |
NGC 3627 |  |
Galaxy, barred spiral Barred spiral galaxy A barred spiral galaxy is a spiral galaxy with a central bar-shaped structure composed of stars. Bars are found in approximately two-thirds of all spiral galaxies... |
35,000 | Leo Leo (constellation) Leo is one of the constellations of the zodiac. Its name is Latin for lion. Its symbol is . Leo lies between dim Cancer to the west and Virgo to the east.-Stars:... |
10.0 | |
| M67 Messier 67 Messier 67 is an open cluster in the constellation of Cancer. M67's Trumpler class is variously given as II 2 r, II 2 m, or II 3 r. It was discovered by Johann Gottfried Koehler in 1779. Age estimates for the cluster range between 3.2 and 5 billion years, with the most recent estimate implying... |
NGC 2682 | Cluster, open Open cluster An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist... |
2.25 | Cancer Cancer (constellation) Cancer is one of the twelve constellations of the zodiac. Its name is Latin for crab and it is commonly represented as such. Its symbol is . Cancer is small and its stars are faint... |
7.5 | ||
| M68 Messier 68 Messier 68 is a globular cluster in the Hydra constellation. It was discovered by Charles Messier in 1780. M68 is at a distance of about 33,000 light-years away from Earth.-External links:* *... |
NGC 4590 | Cluster, globular Globular cluster A globular cluster is a spherical collection of stars that orbits a galactic core as a satellite. Globular clusters are very tightly bound by gravity, which gives them their spherical shapes and relatively high stellar densities toward their centers. The name of this category of star cluster is... |
32 | Hydra Hydra (constellation) Hydra is the largest of the 88 modern constellations, measuring 1303 square degrees. It has a long history, having been included among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy. It is commonly represented as a water snake... |
9.0 | ||
| M69 Messier 69 Messier 69 is a globular cluster in the constellation Sagittarius. It was discovered by Charles Messier on August 31, 1780, the same night he discovered M70... |
NGC 6637 | Cluster, globular Globular cluster A globular cluster is a spherical collection of stars that orbits a galactic core as a satellite. Globular clusters are very tightly bound by gravity, which gives them their spherical shapes and relatively high stellar densities toward their centers. The name of this category of star cluster is... |
25 | Sagittarius Sagittarius (constellation) Sagittarius is a constellation of the zodiac, the one containing the galactic center. Its name is Latin for the archer, and its symbol is , a stylized arrow. Sagittarius is commonly represented as a centaur drawing a bow... |
9.0 | ||
| M70 Messier 70 Messier 70 is a globular cluster in the constellation Sagittarius. It was discovered by Charles Messier in 1780.... |
NGC 6681 | Cluster, globular Globular cluster A globular cluster is a spherical collection of stars that orbits a galactic core as a satellite. Globular clusters are very tightly bound by gravity, which gives them their spherical shapes and relatively high stellar densities toward their centers. The name of this category of star cluster is... |
28 | Sagittarius Sagittarius (constellation) Sagittarius is a constellation of the zodiac, the one containing the galactic center. Its name is Latin for the archer, and its symbol is , a stylized arrow. Sagittarius is commonly represented as a centaur drawing a bow... |
9.0 | ||
| M71 Messier 71 Messier 71 is a globular cluster in the constellation Sagitta. It was discovered by Philippe Loys de Chéseaux in 1746 and included by Charles Messier in his catalog of comet-like objects in 1780... |
NGC 6838 | Cluster, globular Globular cluster A globular cluster is a spherical collection of stars that orbits a galactic core as a satellite. Globular clusters are very tightly bound by gravity, which gives them their spherical shapes and relatively high stellar densities toward their centers. The name of this category of star cluster is... |
12 | Sagitta Sagitta Sagitta is a constellation. Its name is Latin for "arrow", and it should not be confused with the larger constellation Sagittarius, the archer. Although ancient, it is insignificant, for it has no star brighter than the 4th magnitude and is the third smallest of all constellations... |
8.5 | ||
| M72 Messier 72 Messier 72 is a globular cluster in the Aquarius constellation discovered by Pierre Méchain on August 29, 1780. Charles Messier looked for it on the following October 4 and 5, and included it in his catalog... |
NGC 6981 | Cluster, globular Globular cluster A globular cluster is a spherical collection of stars that orbits a galactic core as a satellite. Globular clusters are very tightly bound by gravity, which gives them their spherical shapes and relatively high stellar densities toward their centers. The name of this category of star cluster is... |
53 | Aquarius Aquarius (constellation) Aquarius is a constellation of the zodiac, situated between Capricornus and Pisces. Its name is Latin for "water-bearer" or "cup-bearer", and its symbol is , a representation of water.... |
10.0 | ||
| M73 Messier 73 Messier 73 is an asterism of four stars in the constellation of Aquarius. An asterism is composed of physically unconnected stars that appear close to each other in the sky as seen from Earth... |
NGC 6994 | Asterism Asterism (astronomy) In astronomy, an asterism is a pattern of stars recognized on Earth's night sky. It may form part of an official constellation, or be composed of stars from more than one. Like constellations, asterisms are in most cases composed of stars which, while they are visible in the same general direction,... |
Aquarius Aquarius (constellation) Aquarius is a constellation of the zodiac, situated between Capricornus and Pisces. Its name is Latin for "water-bearer" or "cup-bearer", and its symbol is , a representation of water.... |
9.0 | |||
| M74 Messier 74 Messier 74 is a face-on spiral galaxy in the constellation Pisces. It is at a distance of about 32 million light-years away from Earth. The galaxy contains two clearly defined spiral arms and is therefore used as an archetypal example of a Grand Design Spiral Galaxy... |
NGC 628 | Galaxy, spiral Spiral galaxy A spiral galaxy is a certain kind of galaxy originally described by Edwin Hubble in his 1936 work The Realm of the Nebulae and, as such, forms part of the Hubble sequence. Spiral galaxies consist of a flat, rotating disk containing stars, gas and dust, and a central concentration of stars known as... |
35,000 | Pisces Pisces (constellation) Pisces is a constellation of the zodiac. Its name is the Latin plural for fish, and its symbol is . It lies between Aquarius to the west and Aries to the east... |
10.5 | ||
| M75 Messier 75 Messier 75 is a globular cluster in the constellation Sagittarius. It was discovered by Pierre Méchain in 1780 and included in Charles Messier's catalog of comet-like objects that same year.... |
NGC 6864 |  |
Cluster, globular Globular cluster A globular cluster is a spherical collection of stars that orbits a galactic core as a satellite. Globular clusters are very tightly bound by gravity, which gives them their spherical shapes and relatively high stellar densities toward their centers. The name of this category of star cluster is... |
58 | Sagittarius Sagittarius (constellation) Sagittarius is a constellation of the zodiac, the one containing the galactic center. Its name is Latin for the archer, and its symbol is , a stylized arrow. Sagittarius is commonly represented as a centaur drawing a bow... |
9.5 | |
| M76 Little Dumbbell Nebula The Little Dumbbell Nebula, also known as Messier 76, NGC 650/651, the Barbell Nebula, or the Cork Nebula, is a planetary nebula in the constellation Perseus. It was discovered by Pierre Méchain in 1780 and included in Charles Messier's catalog of comet-like objects as number 76. It was first... |
NGC 650, NGC 651 | Little Dumbbell Nebula |  |
Nebula, planetary Planetary nebula A planetary nebula is an emission nebula consisting of an expanding glowing shell of ionized gas ejected during the asymptotic giant branch phase of certain types of stars late in their life... |
3.4 | Perseus Perseus (constellation) Perseus is a constellation in the northern sky, named after the Greek hero Perseus. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union... |
10.1 |
| M77 Messier 77 Messier 77 is a barred spiral galaxy about 47 million light-years away in the constellation Cetus. Messier 77 is an active galaxy with an Active Galactic Nucleus , which is obscured from view by astronomical dust at visible wavelengths... |
NGC 1068 | Galaxy, spiral Spiral galaxy A spiral galaxy is a certain kind of galaxy originally described by Edwin Hubble in his 1936 work The Realm of the Nebulae and, as such, forms part of the Hubble sequence. Spiral galaxies consist of a flat, rotating disk containing stars, gas and dust, and a central concentration of stars known as... |
60,000 | Cetus Cetus Cetus is a constellation. Its name refers to Cetus, a sea monster in Greek mythology, although it is often called 'the whale' today. Cetus is located in the region of the sky that contains other water-related constellations such as Aquarius, Pisces, and Eridanus.-Ecliptic:Although Cetus is not... |
10.5 | ||
| M78 Messier 78 The nebula Messier 78 is a reflection nebula in the constellation Orion. It was discovered by Pierre Méchain in 1780 and included by Charles Messier in his catalog of comet-like objects that same year.... |
NGC 2068 | Nebula, diffuse | 1.6 | Orion Orion (constellation) Orion, often referred to as The Hunter, is a prominent constellation located on the celestial equator and visible throughout the world. It is one of the most conspicuous, and most recognizable constellations in the night sky... |
8.0 | ||
| M79 Messier 79 Messier 79 is a globular cluster in the Lepus constellation. It was discovered by Pierre Méchain in 1780... |
NGC 1904 |  |
Cluster, globular Globular cluster A globular cluster is a spherical collection of stars that orbits a galactic core as a satellite. Globular clusters are very tightly bound by gravity, which gives them their spherical shapes and relatively high stellar densities toward their centers. The name of this category of star cluster is... |
40 | Lepus Lepus (constellation) Lepus is a constellation lying just south of the celestial equator, immediately south of Orion. Its name is Latin for hare. Although the hare does not represent any particular figure in Greek mythology, Lepus was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it... |
8.5 | |
| M80 Messier 80 Messier 80 is a globular cluster in the constellation Scorpius. It was discovered by Charles Messier in 1781.... |
NGC 6093 |  |
Cluster, globular Globular cluster A globular cluster is a spherical collection of stars that orbits a galactic core as a satellite. Globular clusters are very tightly bound by gravity, which gives them their spherical shapes and relatively high stellar densities toward their centers. The name of this category of star cluster is... |
27 | Scorpius Scorpius Scorpius, sometimes known as Scorpio, is one of the constellations of the zodiac. Its name is Latin for scorpion, and its symbol is . It lies between Libra to the west and Sagittarius to the east... |
8.5 | |
| M81 | NGC 3031 | Bode's Galaxy |  |
Galaxy, spiral Spiral galaxy A spiral galaxy is a certain kind of galaxy originally described by Edwin Hubble in his 1936 work The Realm of the Nebulae and, as such, forms part of the Hubble sequence. Spiral galaxies consist of a flat, rotating disk containing stars, gas and dust, and a central concentration of stars known as... |
12,000 | Ursa Major Ursa Major Ursa Major , also known as the Great Bear, is a constellation visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. It can best be seen in April... |
6.9 |
| M82 Messier 82 Messier 82 is the prototype nearby starburst galaxy about 12 million light-years away in the constellation Ursa Major... |
NGC 3034 | Cigar Galaxy |  |
Galaxy, starburst Starburst galaxy A starburst galaxy is a galaxy in the process of an exceptionally high rate of star formation, compared to the usual star formation rate seen in most galaxies. Galaxies are often observed to have a burst of star formation after a collision or close encounter between two galaxies... |
11,000 | Ursa Major Ursa Major Ursa Major , also known as the Great Bear, is a constellation visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. It can best be seen in April... |
9.5 |
| M83 | NGC 5236 | Southern Pinwheel Galaxy | Galaxy, barred spiral Barred spiral galaxy A barred spiral galaxy is a spiral galaxy with a central bar-shaped structure composed of stars. Bars are found in approximately two-thirds of all spiral galaxies... |
10,000 | Hydra Hydra (constellation) Hydra is the largest of the 88 modern constellations, measuring 1303 square degrees. It has a long history, having been included among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy. It is commonly represented as a water snake... |
8.5 | |
| M84 Messier 84 Messier 84 is a lenticular galaxy in the constellation Virgo. M84 is situated in the heavily populated inner core of the Virgo Cluster of galaxies.... |
NGC 4374 |  |
Galaxy, lenticular Lenticular galaxy A lenticular galaxy is a type of galaxy which is intermediate between an elliptical galaxy and a spiral galaxy in galaxy morphological classification schemes. Lenticular galaxies are disk galaxies which have used up or lost most of their interstellar matter and therefore have very little ongoing... |
60,000 | Virgo Virgo -Astronomy:* Virgo Cluster, a cluster of galaxies in the constellation Virgo* Virgo , a constellation* Virgo Stellar Stream, remains of a dwarf galaxy* Virgo Supercluster, a galactic supercluster-Surname:* Virgo... |
11.0 | |
| M85 Messier 85 Messier 85 is a lenticular galaxy in the Coma Berenices constellation. It is 60 million light years away, making it the 94th most distant Messier object, and it estimated to be 125,000 light years across.... |
NGC 4382 | Galaxy, lenticular Lenticular galaxy A lenticular galaxy is a type of galaxy which is intermediate between an elliptical galaxy and a spiral galaxy in galaxy morphological classification schemes. Lenticular galaxies are disk galaxies which have used up or lost most of their interstellar matter and therefore have very little ongoing... |
60,000 | Coma Berenices Coma Berenices Coma Berenices is a traditional asterism that has since been defined as one of the 88 modern constellations. It is located near Leo, to which it formerly belonged, and accommodates the North Galactic Pole... |
10.5 | ||
| M86 Messier 86 Messier 86 is a lenticular galaxy in the constellation Virgo. It was discovered by Charles Messier in 1781. M86 lies in the heart of the Virgo Cluster of galaxies and forms a most conspicuous group with another giant, Lenticular Galaxy M84... |
NGC 4406 | Galaxy, lenticular Lenticular galaxy A lenticular galaxy is a type of galaxy which is intermediate between an elliptical galaxy and a spiral galaxy in galaxy morphological classification schemes. Lenticular galaxies are disk galaxies which have used up or lost most of their interstellar matter and therefore have very little ongoing... |
60,000 | Virgo Virgo -Astronomy:* Virgo Cluster, a cluster of galaxies in the constellation Virgo* Virgo , a constellation* Virgo Stellar Stream, remains of a dwarf galaxy* Virgo Supercluster, a galactic supercluster-Surname:* Virgo... |
11.0 | ||
| M87 Messier 87 Messier 87 is a supergiant elliptical galaxy. It was discovered in 1781 by the French astronomer Charles Messier, who cataloged it as a nebulous feature. The second brightest galaxy within the northern Virgo Cluster, it is located about 16.4 million parsecs from Earth... |
NGC 4486 |  |
Galaxy, elliptical Elliptical galaxy An elliptical galaxy is a galaxy having an approximately ellipsoidal shape and a smooth, nearly featureless brightness profile. They range in shape from nearly spherical to highly flat and in size from hundreds of millions to over one trillion stars... |
60,000 | Virgo Virgo -Astronomy:* Virgo Cluster, a cluster of galaxies in the constellation Virgo* Virgo , a constellation* Virgo Stellar Stream, remains of a dwarf galaxy* Virgo Supercluster, a galactic supercluster-Surname:* Virgo... |
11.0 | |
| M88 Messier 88 Messier 88 is a spiral galaxy about 47 million light-years away in the constellation Coma Berenices. It was discovered by Charles Messier in 1781.-Properties:... |
NGC 4501 | Galaxy, spiral Spiral galaxy A spiral galaxy is a certain kind of galaxy originally described by Edwin Hubble in his 1936 work The Realm of the Nebulae and, as such, forms part of the Hubble sequence. Spiral galaxies consist of a flat, rotating disk containing stars, gas and dust, and a central concentration of stars known as... |
60,000 | Coma Berenices Coma Berenices Coma Berenices is a traditional asterism that has since been defined as one of the 88 modern constellations. It is located near Leo, to which it formerly belonged, and accommodates the North Galactic Pole... |
11.0 | ||
| M89 Messier 89 Messier 89 is an elliptical galaxy in the constellation Virgo. It was discovered by Charles Messier on March 18, 1781. M89 is a member of the Virgo Cluster of galaxies.-Features:... |
NGC 4552 | Galaxy, elliptical Elliptical galaxy An elliptical galaxy is a galaxy having an approximately ellipsoidal shape and a smooth, nearly featureless brightness profile. They range in shape from nearly spherical to highly flat and in size from hundreds of millions to over one trillion stars... |
60,000 | Virgo Virgo -Astronomy:* Virgo Cluster, a cluster of galaxies in the constellation Virgo* Virgo , a constellation* Virgo Stellar Stream, remains of a dwarf galaxy* Virgo Supercluster, a galactic supercluster-Surname:* Virgo... |
11.5 | ||
| M90 Messier 90 Messier 90 is a spiral galaxy about 60 million light-years away in the constellation Virgo. It was discovered by Charles Messier in 1781.- Membership of the Virgo Cluster :... |
NGC 4569 | Galaxy, spiral Spiral galaxy A spiral galaxy is a certain kind of galaxy originally described by Edwin Hubble in his 1936 work The Realm of the Nebulae and, as such, forms part of the Hubble sequence. Spiral galaxies consist of a flat, rotating disk containing stars, gas and dust, and a central concentration of stars known as... |
60,000 | Virgo Virgo -Astronomy:* Virgo Cluster, a cluster of galaxies in the constellation Virgo* Virgo , a constellation* Virgo Stellar Stream, remains of a dwarf galaxy* Virgo Supercluster, a galactic supercluster-Surname:* Virgo... |
11.0 | ||
| M91 Messier 91 Messier 91 is a barred spiral galaxy located in the Coma Berenices constellation and is part of the Virgo Cluster of galaxies. M91 is about 63 million light-years away from the earth. It was the last of a group of eight nebulae discovered by Charles Messier in 1781... |
NGC 4548 | Galaxy, barred spiral Barred spiral galaxy A barred spiral galaxy is a spiral galaxy with a central bar-shaped structure composed of stars. Bars are found in approximately two-thirds of all spiral galaxies... |
60,000 | Coma Berenices Coma Berenices Coma Berenices is a traditional asterism that has since been defined as one of the 88 modern constellations. It is located near Leo, to which it formerly belonged, and accommodates the North Galactic Pole... |
11.0 | ||
| M92 Messier 92 Messier 92 is a globular cluster in the constellation Hercules. It was discovered by Johann Elert Bode in 1777 and independently rediscovered by Charles Messier on March 18, 1781... |
NGC 6341 | Cluster, globular Globular cluster A globular cluster is a spherical collection of stars that orbits a galactic core as a satellite. Globular clusters are very tightly bound by gravity, which gives them their spherical shapes and relatively high stellar densities toward their centers. The name of this category of star cluster is... |
26 | Hercules Hercules (constellation) Hercules is a constellation named after Hercules, the Roman mythological hero adapted from the Greek hero Heracles. Hercules was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations today... |
7.5 | ||
| M93 Messier 93 Messier 93 is an open cluster in the constellation Puppis. It was discovered by Charles Messier in 1781.... |
NGC 2447 |  |
Cluster, open Open cluster An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist... |
4.5 | Puppis Puppis Puppis is a constellation in the southern sky. Its name is the Latin word for the poop deck of a ship, and Puppis represents the deck of the ship and its deckhouses... |
6.5 | |
| M94 Messier 94 Messier 94 is a spiral galaxy in the constellation Canes Venatici. It was discovered by Pierre Méchain in 1781,... |
NGC 4736 |  |
Galaxy, spiral Spiral galaxy A spiral galaxy is a certain kind of galaxy originally described by Edwin Hubble in his 1936 work The Realm of the Nebulae and, as such, forms part of the Hubble sequence. Spiral galaxies consist of a flat, rotating disk containing stars, gas and dust, and a central concentration of stars known as... |
14,500 | Canes Venatici Canes Venatici Canes Venatici is one of the 88 official modern constellations. It is a small northern constellation that was created by Johannes Hevelius in the 17th century. Its name is Latin for "hunting dogs", and the constellation is often depicted in illustrations as representing the dogs of Boötes the... |
9.5 | |
| M95 Messier 95 Messier 95 is a barred spiral galaxy about 38 million light-years away in the constellation Leo. It was discovered by Pierre Méchain in 1781, and catalogued by Charles Messier four days later.-Nucleus:... |
NGC 3351 |  |
Galaxy, barred spiral Barred spiral galaxy A barred spiral galaxy is a spiral galaxy with a central bar-shaped structure composed of stars. Bars are found in approximately two-thirds of all spiral galaxies... |
38,000 | Leo LEO LEO as an initialism may refer to:* Low Earth orbit, a satellite path* Law enforcement officer, an official* Louisville Eccentric Observer, a newspaper* LEO , an electronic device* LEO , a lunar mission... |
11.0 | |
| M96 Messier 96 Messier 96 is an intermediate spiral galaxy about 31 million light-years away in the constellation Leo. It was discovered by Pierre Méchain in 1781.-M96 Group:... |
NGC 3368 | Galaxy, spiral Spiral galaxy A spiral galaxy is a certain kind of galaxy originally described by Edwin Hubble in his 1936 work The Realm of the Nebulae and, as such, forms part of the Hubble sequence. Spiral galaxies consist of a flat, rotating disk containing stars, gas and dust, and a central concentration of stars known as... |
38,000 | Leo LEO LEO as an initialism may refer to:* Low Earth orbit, a satellite path* Law enforcement officer, an official* Louisville Eccentric Observer, a newspaper* LEO , an electronic device* LEO , a lunar mission... |
10.5 | ||
| M97 Owl Nebula The Owl Nebula is a planetary nebula in the constellation Ursa Major. It was discovered by Pierre Méchain in 1781.... |
NGC 3587 | Owl Nebula |  |
Nebula, planetary Planetary nebula A planetary nebula is an emission nebula consisting of an expanding glowing shell of ionized gas ejected during the asymptotic giant branch phase of certain types of stars late in their life... |
2.6 | Ursa Major Ursa Major Ursa Major , also known as the Great Bear, is a constellation visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. It can best be seen in April... |
9.9 |
| M98 Messier 98 Messier 98 is an intermediate spiral galaxy about 60 million light-years away in the constellation Coma Berenices. It was discovered by Pierre Méchain on March 15, 1781 along with M99 and M100 and was cataloged as a Messier object on April 13, 1781... |
NGC 4192 |  |
Galaxy, spiral Spiral galaxy A spiral galaxy is a certain kind of galaxy originally described by Edwin Hubble in his 1936 work The Realm of the Nebulae and, as such, forms part of the Hubble sequence. Spiral galaxies consist of a flat, rotating disk containing stars, gas and dust, and a central concentration of stars known as... |
60,000 | Coma Berenices Coma Berenices Coma Berenices is a traditional asterism that has since been defined as one of the 88 modern constellations. It is located near Leo, to which it formerly belonged, and accommodates the North Galactic Pole... |
11.0 | |
| M99 Messier 99 Messier 99 is an unbarred spiral galaxy approximately 50 million light-years away in the constellation Coma Berenices.... |
NGC 4254 | Galaxy, spiral Spiral galaxy A spiral galaxy is a certain kind of galaxy originally described by Edwin Hubble in his 1936 work The Realm of the Nebulae and, as such, forms part of the Hubble sequence. Spiral galaxies consist of a flat, rotating disk containing stars, gas and dust, and a central concentration of stars known as... |
60,000 | Coma Berenices Coma Berenices Coma Berenices is a traditional asterism that has since been defined as one of the 88 modern constellations. It is located near Leo, to which it formerly belonged, and accommodates the North Galactic Pole... |
10.5 | ||
| M100 Messier 100 Messier 100 is an example of a grand design spiral galaxy located within the southern part of constellation Coma Berenices. It is one of the brightest galaxies in the Virgo cluster, approximately 55 million light-years distant from Earth and has a diameter of 160,000 light years... |
NGC 4321 | Galaxy, spiral Spiral galaxy A spiral galaxy is a certain kind of galaxy originally described by Edwin Hubble in his 1936 work The Realm of the Nebulae and, as such, forms part of the Hubble sequence. Spiral galaxies consist of a flat, rotating disk containing stars, gas and dust, and a central concentration of stars known as... |
60,000 | Coma Berenices Coma Berenices Coma Berenices is a traditional asterism that has since been defined as one of the 88 modern constellations. It is located near Leo, to which it formerly belonged, and accommodates the North Galactic Pole... |
10.5 | ||
| M101 Pinwheel Galaxy The Pinwheel Galaxy is a face-on spiral galaxy distanced 21 million light-years away in the constellation Ursa Major, first discovered by Pierre Méchain on March 27, 1781, and communicated to Charles Messier who verified its position for inclusion in the Messier Catalogue as one of its final... |
NGC 5457 | Pinwheel Galaxy |  |
Galaxy, spiral Spiral galaxy A spiral galaxy is a certain kind of galaxy originally described by Edwin Hubble in his 1936 work The Realm of the Nebulae and, as such, forms part of the Hubble sequence. Spiral galaxies consist of a flat, rotating disk containing stars, gas and dust, and a central concentration of stars known as... |
27,000 | Ursa Major Ursa Major Ursa Major , also known as the Great Bear, is a constellation visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. It can best be seen in April... |
7.9 |
| M102 Messier 102 Messier 102 is a galaxy listed in the Messier Catalogue that has not been identified unambiguously. Its original discoverer Pierre Méchain later said that it was a duplicate observation of Messier 101, but there are historical and observational reasons to believe that it could be NGC 5866,... |
(Not conclusively identified) | ||||||
| M103 Messier 103 Messier 103 is an open cluster where a few thousand stars formed in the constellation Cassiopeia. This open cluster was discovered in 1781 by Charles Messier’s friend and collaborator Pierre Méchain. It is one of the most distant open clusters, with distances of 8,000 to 9,500 light years from the... |
NGC 581 |  |
Cluster, open Open cluster An open cluster is a group of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way Galaxy, and many more are thought to exist... |
8 | Cassiopeia Cassiopeia -Mythology:* Cassiopeia , a queen of Ethiopia and mother of Andromeda in Greek mythology.-Science:* Cassiopeia , a northern constellation representing the queen* Cassiopeia A, a supernova remnant in that constellation.... |
7.0 | |
| M104 Sombrero Galaxy The Sombrero Galaxy is an unbarred spiral galaxy in the constellation Virgo located 28 million light years from earth. It has a bright nucleus, an unusually large central bulge, and a prominent dust lane in its inclined disk. The dark dust lane and the bulge give this galaxy the appearance of a... |
NGC 4594 | Sombrero Galaxy |  |
Galaxy, spiral Spiral galaxy A spiral galaxy is a certain kind of galaxy originally described by Edwin Hubble in his 1936 work The Realm of the Nebulae and, as such, forms part of the Hubble sequence. Spiral galaxies consist of a flat, rotating disk containing stars, gas and dust, and a central concentration of stars known as... |
50,000 | Virgo Virgo -Astronomy:* Virgo Cluster, a cluster of galaxies in the constellation Virgo* Virgo , a constellation* Virgo Stellar Stream, remains of a dwarf galaxy* Virgo Supercluster, a galactic supercluster-Surname:* Virgo... |
9.5 |
| M105 Messier 105 Messier 105 is an elliptical galaxy in the constellation Leo. Messier 105 is known to have a supermassive black hole.-History:... |
NGC 3379 | Galaxy, elliptical Elliptical galaxy An elliptical galaxy is a galaxy having an approximately ellipsoidal shape and a smooth, nearly featureless brightness profile. They range in shape from nearly spherical to highly flat and in size from hundreds of millions to over one trillion stars... |
38,000 | Leo LEO LEO as an initialism may refer to:* Low Earth orbit, a satellite path* Law enforcement officer, an official* Louisville Eccentric Observer, a newspaper* LEO , an electronic device* LEO , a lunar mission... |
11.0 | ||
| M106 Messier 106 Messier 106 is a spiral galaxy in the constellation Canes Venatici. It was discovered by Pierre Méchain in 1781. M106 is at a distance of about 22 to 25 million light-years away from Earth... |
NGC 4258 |  |
Galaxy, spiral Spiral galaxy A spiral galaxy is a certain kind of galaxy originally described by Edwin Hubble in his 1936 work The Realm of the Nebulae and, as such, forms part of the Hubble sequence. Spiral galaxies consist of a flat, rotating disk containing stars, gas and dust, and a central concentration of stars known as... |
25,000 | Canes Venatici Canes Venatici Canes Venatici is one of the 88 official modern constellations. It is a small northern constellation that was created by Johannes Hevelius in the 17th century. Its name is Latin for "hunting dogs", and the constellation is often depicted in illustrations as representing the dogs of Boötes the... |
9.5 | |
| M107 Messier 107 Globular Cluster M107 is a very loose globular cluster in the constellation Ophiuchus. It was discovered by Pierre Méchain in April 1782 and independently by William Herschel in 1793... |
NGC 6171 |  |
Cluster, globular Globular cluster A globular cluster is a spherical collection of stars that orbits a galactic core as a satellite. Globular clusters are very tightly bound by gravity, which gives them their spherical shapes and relatively high stellar densities toward their centers. The name of this category of star cluster is... |
20 | Ophiuchus Ophiuchus Ophiuchus is a large constellation located around the celestial equator. Its name is from the Greek "serpent-bearer", and it is commonly represented as a man grasping the snake that is represented by the constellation Serpens. Ophiuchus was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century... |
10.0 | |
| M108 Messier 108 Messier 108 is a barred spiral galaxy in the constellation Ursa Major. It was discovered by Pierre Méchain in 1781 or 1782. From the perspective of the Earth, this galaxy is seen almost edge-on.... |
NGC 3556 | Galaxy, spiral Spiral galaxy A spiral galaxy is a certain kind of galaxy originally described by Edwin Hubble in his 1936 work The Realm of the Nebulae and, as such, forms part of the Hubble sequence. Spiral galaxies consist of a flat, rotating disk containing stars, gas and dust, and a central concentration of stars known as... |
45,000 | Ursa Major Ursa Major Ursa Major , also known as the Great Bear, is a constellation visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. It can best be seen in April... |
11.0 | ||
| M109 Messier 109 Messier 109 is a barred spiral galaxy approximately away in the constellation Ursa Major. M109 can be seen southeast of the star Phecda .-History:Messier 109 was discovered by Pierre Méchain in 1781... |
NGC 3992 | Galaxy, barred spiral Barred spiral galaxy A barred spiral galaxy is a spiral galaxy with a central bar-shaped structure composed of stars. Bars are found in approximately two-thirds of all spiral galaxies... |
55,000 | Ursa Major Ursa Major Ursa Major , also known as the Great Bear, is a constellation visible throughout the year in most of the northern hemisphere. It can best be seen in April... |
11.0 | ||
| M110 Messier 110 Messier 110 is a dwarf spheroidal galaxy that is a satellite of the Andromeda Galaxy. M110 contains some dust and hints of recent star formation, which is unusual for dwarf elliptical galaxies in general.-History:... |
NGC 205 | Galaxy, dwarf elliptical Dwarf elliptical galaxy Dwarf elliptical galaxies, or dEs, are elliptical galaxies that are much smaller than others. They are classified as dE, and are quite common in galaxy groups and clusters, and are usually companions to other galaxies.- Examples :... |
2,200 | Andromeda Andromeda (constellation) Andromeda is a constellation in the northern sky. It is named after Andromeda, the princess in the Greek legend of Perseus who was chained to a rock to be eaten by the sea monster Cetus... |
10.0 | ||
| Messier number Messier object The Messier objects are a set of astronomical objects first listed by French astronomer Charles Messier in 1771. The original motivation of the catalogue was that Messier was a comet hunter, and was frustrated by objects which resembled but were not comets... |
NGC Number New General Catalogue The New General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars is a well-known catalogue of deep sky objects in astronomy. It contains 7,840 objects, known as the NGC objects... |
Common name | Picture | Object type | Distance (kly Light-year A light-year, also light year or lightyear is a unit of length, equal to just under 10 trillion kilometres... ) |
Constellation Constellation In modern astronomy, a constellation is an internationally defined area of the celestial sphere. These areas are grouped around asterisms, patterns formed by prominent stars within apparent proximity to one another on Earth's night sky.... |
Apparent magnitude Apparent magnitude The apparent magnitude of a celestial body is a measure of its brightness as seen by an observer on Earth, adjusted to the value it would have in the absence of the atmosphere... |
External links
- Messier database from SEDS
- Clickable table of Messier Objects
- Charles Messier's Original Catalogue.
- Images of the 110 Messier objects by 2MASS2MASSObservations for the Two Micron All-Sky Survey began in 1997 and were completed in 2001 at two telescopes located one each in the northern and southern hemispheres to ensure coverage of the entire sky...
project.

