
N-gram
Encyclopedia
In the fields of computational linguistics
and probability
, an n-gram is a contiguous sequence of n items from a given sequence
of text or speech. The items in question can be phoneme
s, syllables, letters, words or base pairs according to the application. n-grams are collected from a text
or speech corpus
.
An n-gram of size 1 is referred to as a "unigram"; size 2 is a "bigram
" (or, less commonly, a "digram"); size 3 is a "trigram
"; size 4 is a "four-gram" and size 5 or more is simply called an "n-gram".
An n-gram model is a type of probabilistic language model
for predicting the next item in such a sequence in the form of a (n − 1)-order Markov model
. n-gram models are now widely used in probability
, communication theory
, computational linguistics
(for instance, statistical natural language processing
), computational biology
(for instance, biological sequence analysis
), and data compression
. The two core advantages of n-gram models (and algorithms that use them) are relative simplicity and the ability to scale up by simply increasing n a model can be used to store more context with a well-understood space–time tradeoff, enabling small experiments to be scale-up very efficiently.
Figure 1 shows several example sequences and the corresponding 1-gram, 2-gram and 3-gram sequences.
Here are further examples; these are word-level 3-grams and 4-grams (and counts of the number of times they appeared) from the Google n-gram corpus.
4-grams
This idea can be traced to an experiment by Claude Shannon's work in information theory
. His question was, given a sequence of letters (for example, the sequence "for ex"), what is the likelihood
of the next letter? From training data, one can derive a probability distribution
for the next letter given a history of size : a = 0.4, b = 0.00001, c = 0, ....; where the probabilities of all possible "next-letters" sum to 1.0.
: a = 0.4, b = 0.00001, c = 0, ....; where the probabilities of all possible "next-letters" sum to 1.0.
More concisely, an n-gram model predicts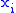 based on
based on 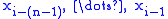 . In Probability terms, this is
. In Probability terms, this is 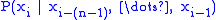 . When used for language model
. When used for language model
ing, independence assumptions are made so that each word depends only on the last n-1 words. This Markov model
is used as an approximation of the true underlying language. This assumption is important because it massively simplifies the problem of learning the language model from data. In addition, because of the open nature of language, it is common to group words unknown to the language model together.
Note that in a simple n-gram language model, the probability of a word, conditioned on some number of previous words (one word in a bigram model, two words in a trigram model, etc.) can be described as following a categorical distribution
(often imprecisely called a "multinomial distribution").
In practice, however, it is necessary to smooth the probability distributions by also assigning non-zero probabilities to unseen words or n-grams.
See #Smoothing techniques for details.
. In speech recognition
, phonemes and sequences of phonemes are modeled using a n-gram distribution. For parsing, words are modeled such that each n-gram is composed of n words. For language identification
, sequences of characters/graphemes (e.g., letters of the alphabet
) are modeled for different languages. For a sequence of words, (for example "the dog smelled like a skunk"), the trigrams would be: "# the dog", "the dog smelled", "dog smelled like", "smelled like a", "like a skunk" and "a skunk #". For sequences of characters, the 3-grams (sometimes referred to as "trigrams") that can be generated from "good morning" are "goo", "ood", "od ", "d m", " mo", "mor" and so forth. Some practitioners preprocess strings to remove spaces, most simply collapse whitespace to a single space while preserving paragraph marks. Punctuation is also commonly reduced or removed by preprocessing. n-grams can also be used for sequences of words or, in fact, for almost any type of data. They have been used for example for extracting features for clustering large sets of satellite earth images and for determining what part of the Earth a particular image came from. They have also been very successful as the first pass in genetic sequence search and in the identification of the species from which short sequences of DNA originated.
n-gram models are often criticized because they lack any explicit representation of long range dependency. (In fact, it was Chomsky
's critique of Markov model
s in the late 1950s that caused their virtual disappearance from natural language processing
, along with statistical methods in general, until well into the 1980s.) This is because the only explicit dependency range is (n-1) tokens for an n-gram model, and since natural languages incorporate many cases of unbounded dependencies (such as wh-movement
), this means that an n-gram model cannot in principle distinguish unbounded dependencies from noise (since long range correlations drop exponentially with distance for any Markov model). For this reason, n-gram models have not made much impact on linguistic theory, where part of the explicit goal is to model such dependencies.
Another criticism that has been made is that Markov models of language, including n-gram models, do not explicitly capture the performance/competence distinction discussed by Chomsky. This is because n-gram models are not designed to model linguistic knowledge as such, and make no claims to being (even potentially) complete models of linguistic knowledge; instead, they are used in practical applications.
In practice, n-gram models have been shown to be extremely effective in modeling language data, which is a core component in modern statistical language
applications.
Most modern applications that rely on n-gram based models, such as machine translation
applications, do not rely exclusively on such models; instead, they typically also incorporate Bayesian inference
. Modern statistical models are typically made up of two parts, a prior distribution describing the inherent likelihood of a possible result and a likelihood function
used to assess the compatibility of a possible result with observed data. When a language model is used, it is used as part of the prior distribution (e.g. to gauge the inherent "goodness" of a possible translation), and even then it is often not the only component in this distribution. Handcrafted features of various sorts are also used, for example variables that represent the position of a word in a sentence or the general topic of discourse. In addition, features based on the structure of the potential result, such as syntactic considerations, are often used. Such features are also used as part of the likelihood function, which makes use of the observed data. Conventional linguistic theory can be incorporated in these features (although in practice, it is rare that features specific to generative or other particular theories of grammar are incorporated, as computational linguists
tend to be "agnostic" towards individual theories of grammar).
, thus allowing the sequence to be compared to other sequences in an efficient manner. For example, if we convert strings with only letters in the English alphabet into 3-grams, we get a -dimensional space (the first dimension measures the number of occurrences of "aaa", the second "aab", and so forth for all possible combinations of three letters). Using this representation, we lose information about the string. For example, both the strings "abc" and "bca" give rise to exactly the same 2-gram "bc" (although {"ab", "bc"} is clearly not the same as {"bc", "ca"}). However, we know empirically that if two strings of real text have a similar vector representation (as measured by cosine distance
-dimensional space (the first dimension measures the number of occurrences of "aaa", the second "aab", and so forth for all possible combinations of three letters). Using this representation, we lose information about the string. For example, both the strings "abc" and "bca" give rise to exactly the same 2-gram "bc" (although {"ab", "bc"} is clearly not the same as {"bc", "ca"}). However, we know empirically that if two strings of real text have a similar vector representation (as measured by cosine distance
) then they are likely to be similar. Other metrics have also been applied to vectors of n-grams with varying, sometimes better, results. For example z-scores have been used to compare documents by examining how many standard deviations each n-gram differs from its mean occurrence in a large collection, or text corpus
, of documents (which form the "background" vector). In the event of small counts, the g-score may give better results for comparing alternative models.
It is also possible to take a more principled approach to the statistics of n-grams, modeling similarity as the likelihood that two strings came from the same source directly in terms of a problem in Bayesian inference
.
n-gram-based searching can also be used for plagiarism detection
.
, and applied mathematics.
They have been used to:
of 0.0 without smoothing
. For unseen but plausible data from a sample, one can introduce pseudocount
s. Pseudocounts are generally motivated on Bayesian grounds.
In practice it is necessary to smooth the probability distributions by also assigning non-zero probabilities to unseen words or n-grams. The reason is that models derived directly from the n-gram frequency counts have severe problems when confronted with any n-grams that have not explicitly been seen before -- the zero-frequency problem
. Various smoothing methods are used, from simple "add-one" smoothing (assign a count of 1 to unseen n-grams; see Rule of succession
) to more sophisticated models, such as Good-Turing discounting or back-off model
s. Some of these methods are equivalent to assigning a prior distribution to the probabilities of the N-grams and using Bayesian inference
to compute the resulting posterior N-gram probabilities. However, the more sophisticated smoothing models were typically not derived in this fashion, but instead through independent considerations.
Computational linguistics
Computational linguistics is an interdisciplinary field dealing with the statistical or rule-based modeling of natural language from a computational perspective....
and probability
Probability
Probability is ordinarily used to describe an attitude of mind towards some proposition of whose truth we arenot certain. The proposition of interest is usually of the form "Will a specific event occur?" The attitude of mind is of the form "How certain are we that the event will occur?" The...
, an n-gram is a contiguous sequence of n items from a given sequence
Sequence
In mathematics, a sequence is an ordered list of objects . Like a set, it contains members , and the number of terms is called the length of the sequence. Unlike a set, order matters, and exactly the same elements can appear multiple times at different positions in the sequence...
of text or speech. The items in question can be phoneme
Phoneme
In a language or dialect, a phoneme is the smallest segmental unit of sound employed to form meaningful contrasts between utterances....
s, syllables, letters, words or base pairs according to the application. n-grams are collected from a text
Text corpus
In linguistics, a corpus or text corpus is a large and structured set of texts...
or speech corpus
Speech corpus
A speech corpus is a database of speech audio files and text transcriptions.In Speech technology, speech corpora are used, among other things, to create acoustic models ....
.
An n-gram of size 1 is referred to as a "unigram"; size 2 is a "bigram
Bigram
Bigrams or digrams are groups of two written letters, two syllables, or two words, and are very commonly used as the basis for simple statistical analysis of text. They are used in one of the most successful language models for speech recognition...
" (or, less commonly, a "digram"); size 3 is a "trigram
Trigram
Trigrams are a special case of the N-gram, where N is 3. They are often used in natural language processing for doing statistical analysis of texts.-Frequency:The 16 most common trigrams in English are:-Examples:...
"; size 4 is a "four-gram" and size 5 or more is simply called an "n-gram".
An n-gram model is a type of probabilistic language model
Language model
A statistical language model assigns a probability to a sequence of m words P by means of a probability distribution.Language modeling is used in many natural language processing applications such as speech recognition, machine translation, part-of-speech tagging, parsing and information...
for predicting the next item in such a sequence in the form of a (n − 1)-order Markov model
Markov chain
A Markov chain, named after Andrey Markov, is a mathematical system that undergoes transitions from one state to another, between a finite or countable number of possible states. It is a random process characterized as memoryless: the next state depends only on the current state and not on the...
. n-gram models are now widely used in probability
Probability
Probability is ordinarily used to describe an attitude of mind towards some proposition of whose truth we arenot certain. The proposition of interest is usually of the form "Will a specific event occur?" The attitude of mind is of the form "How certain are we that the event will occur?" The...
, communication theory
Communication theory
Communication theory is a field of information and mathematics that studies the technical process of information and the human process of human communication.- History :- Origins :...
, computational linguistics
Computational linguistics
Computational linguistics is an interdisciplinary field dealing with the statistical or rule-based modeling of natural language from a computational perspective....
(for instance, statistical natural language processing
Natural language processing
Natural language processing is a field of computer science and linguistics concerned with the interactions between computers and human languages; it began as a branch of artificial intelligence....
), computational biology
Computational biology
Computational biology involves the development and application of data-analytical and theoretical methods, mathematical modeling and computational simulation techniques to the study of biological, behavioral, and social systems...
(for instance, biological sequence analysis
Sequence analysis
In bioinformatics, the term sequence analysis refers to the process of subjecting a DNA, RNA or peptide sequence to any of a wide range of analytical methods to understand its features, function, structure, or evolution. Methodologies used include sequence alignment, searches against biological...
), and data compression
Data compression
In computer science and information theory, data compression, source coding or bit-rate reduction is the process of encoding information using fewer bits than the original representation would use....
. The two core advantages of n-gram models (and algorithms that use them) are relative simplicity and the ability to scale up by simply increasing n a model can be used to store more context with a well-understood space–time tradeoff, enabling small experiments to be scale-up very efficiently.
Examples
| Field | Unit | Sample sequence | 1-gram sequence | 2-gram sequence | 3-gram sequence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vernacular name | unigram | bigram Bigram Bigrams or digrams are groups of two written letters, two syllables, or two words, and are very commonly used as the basis for simple statistical analysis of text. They are used in one of the most successful language models for speech recognition... (or digram) | trigram | ||
| Order of resulting Markov model Markov model In probability theory, a Markov model is a stochastic model that assumes the Markov property. Generally, this assumption enables reasoning and computation with the model that would otherwise be intractable.-Introduction:... | 0 | 1 | 2 | ||
| Protein sequencing Protein sequencing Protein sequencing is a technique to determine the amino acid sequence of a protein, as well as which conformation the protein adopts and the extent to which it is complexed with any non-peptide molecules... |
amino acid Amino acid Amino acids are molecules containing an amine group, a carboxylic acid group and a side-chain that varies between different amino acids. The key elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen... |
… Cys-Gly-Leu-Ser-Trp … | …, Cys, Gly, Leu, Ser, Trp, … | …, Cys-Gly, Gly-Leu, Leu-Ser, Ser-Trp, … | …, Cys-Gly-Leu, Gly-Leu-Ser, Leu-Ser-Trp, … |
| DNA sequencing DNA sequencing DNA sequencing includes several methods and technologies that are used for determining the order of the nucleotide bases—adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine—in a molecule of DNA.... |
base pair Base pair In molecular biology and genetics, the linking between two nitrogenous bases on opposite complementary DNA or certain types of RNA strands that are connected via hydrogen bonds is called a base pair... |
…AGCTTCGA… | …, A, G, C, T, T, C, G, A, … | …, AG, GC, CT, TT, TC, CG, GA, … | …, AGC, GCT, CTT, TTC, TCG, CGA, … |
| Computational linguistics Computational linguistics Computational linguistics is an interdisciplinary field dealing with the statistical or rule-based modeling of natural language from a computational perspective.... |
character Character (computing) In computer and machine-based telecommunications terminology, a character is a unit of information that roughly corresponds to a grapheme, grapheme-like unit, or symbol, such as in an alphabet or syllabary in the written form of a natural language.... |
…to_be_or_not_to_be… | …, t, o, _, b, e, _, o, r, _, n, o, t, _, t, o, _, b, e, … | …, to, o_, _b, be, e_, _o, or, r_, _n, no, ot, t_, _t, to, o_, _b, be, … | …, to_, o_b, _be, be_, e_o, _or, or_, r_n, _no, not, ot_, t_t, _to, to_, o_b, … |
| Computational linguistics Computational linguistics Computational linguistics is an interdisciplinary field dealing with the statistical or rule-based modeling of natural language from a computational perspective.... |
word Word In language, a word is the smallest free form that may be uttered in isolation with semantic or pragmatic content . This contrasts with a morpheme, which is the smallest unit of meaning but will not necessarily stand on its own... |
… to be or not to be … | …, to, be, or, not, to, be, … | …, to be, be or, or not, not to, to be, … | …, to be or, be or not, or not to, not to be, … |
Figure 1 shows several example sequences and the corresponding 1-gram, 2-gram and 3-gram sequences.
Here are further examples; these are word-level 3-grams and 4-grams (and counts of the number of times they appeared) from the Google n-gram corpus.
- ceramics collectables collectibles (55)
- ceramics collectables fine (130)
- ceramics collected by (52)
- ceramics collectible pottery (50)
- ceramics collectibles cooking (45)
4-grams
- serve as the incoming (92)
- serve as the incubator (99)
- serve as the independent (794)
- serve as the index (223)
- serve as the indication (72)
- serve as the indicator (120)
n-gram models
An n-gram model models sequences, notably natural languages, using the statistical properties of n-grams.This idea can be traced to an experiment by Claude Shannon's work in information theory
Information theory
Information theory is a branch of applied mathematics and electrical engineering involving the quantification of information. Information theory was developed by Claude E. Shannon to find fundamental limits on signal processing operations such as compressing data and on reliably storing and...
. His question was, given a sequence of letters (for example, the sequence "for ex"), what is the likelihood
Likelihood
Likelihood is a measure of how likely an event is, and can be expressed in terms of, for example, probability or odds in favor.-Likelihood function:...
of the next letter? From training data, one can derive a probability distribution
Probability distribution
In probability theory, a probability mass, probability density, or probability distribution is a function that describes the probability of a random variable taking certain values....
for the next letter given a history of size
 : a = 0.4, b = 0.00001, c = 0, ....; where the probabilities of all possible "next-letters" sum to 1.0.
: a = 0.4, b = 0.00001, c = 0, ....; where the probabilities of all possible "next-letters" sum to 1.0.More concisely, an n-gram model predicts
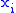 based on
based on 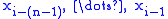 . In Probability terms, this is
. In Probability terms, this is 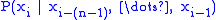 . When used for language model
. When used for language modelLanguage model
A statistical language model assigns a probability to a sequence of m words P by means of a probability distribution.Language modeling is used in many natural language processing applications such as speech recognition, machine translation, part-of-speech tagging, parsing and information...
ing, independence assumptions are made so that each word depends only on the last n-1 words. This Markov model
Markov model
In probability theory, a Markov model is a stochastic model that assumes the Markov property. Generally, this assumption enables reasoning and computation with the model that would otherwise be intractable.-Introduction:...
is used as an approximation of the true underlying language. This assumption is important because it massively simplifies the problem of learning the language model from data. In addition, because of the open nature of language, it is common to group words unknown to the language model together.
Note that in a simple n-gram language model, the probability of a word, conditioned on some number of previous words (one word in a bigram model, two words in a trigram model, etc.) can be described as following a categorical distribution
Categorical distribution
In probability theory and statistics, a categorical distribution is a probability distribution that describes the result of a random event that can take on one of K possible outcomes, with the probability of each outcome separately specified...
(often imprecisely called a "multinomial distribution").
In practice, however, it is necessary to smooth the probability distributions by also assigning non-zero probabilities to unseen words or n-grams.
See #Smoothing techniques for details.
Applications and considerations
n-gram models are widely used in statistical natural language processingNatural language processing
Natural language processing is a field of computer science and linguistics concerned with the interactions between computers and human languages; it began as a branch of artificial intelligence....
. In speech recognition
Speech recognition
Speech recognition converts spoken words to text. The term "voice recognition" is sometimes used to refer to recognition systems that must be trained to a particular speaker—as is the case for most desktop recognition software...
, phonemes and sequences of phonemes are modeled using a n-gram distribution. For parsing, words are modeled such that each n-gram is composed of n words. For language identification
Language identification
Language identification is the process of determining which natural language given content is in. Traditionally, identification of written language - as practiced, for instance, in library science - has relied on manually identifying frequent words and letters known to be characteristic of...
, sequences of characters/graphemes (e.g., letters of the alphabet
Letter (alphabet)
A letter is a grapheme in an alphabetic system of writing, such as the Greek alphabet and its descendants. Letters compose phonemes and each phoneme represents a phone in the spoken form of the language....
) are modeled for different languages. For a sequence of words, (for example "the dog smelled like a skunk"), the trigrams would be: "# the dog", "the dog smelled", "dog smelled like", "smelled like a", "like a skunk" and "a skunk #". For sequences of characters, the 3-grams (sometimes referred to as "trigrams") that can be generated from "good morning" are "goo", "ood", "od ", "d m", " mo", "mor" and so forth. Some practitioners preprocess strings to remove spaces, most simply collapse whitespace to a single space while preserving paragraph marks. Punctuation is also commonly reduced or removed by preprocessing. n-grams can also be used for sequences of words or, in fact, for almost any type of data. They have been used for example for extracting features for clustering large sets of satellite earth images and for determining what part of the Earth a particular image came from. They have also been very successful as the first pass in genetic sequence search and in the identification of the species from which short sequences of DNA originated.
n-gram models are often criticized because they lack any explicit representation of long range dependency. (In fact, it was Chomsky
Noam Chomsky
Avram Noam Chomsky is an American linguist, philosopher, cognitive scientist, and activist. He is an Institute Professor and Professor in the Department of Linguistics & Philosophy at MIT, where he has worked for over 50 years. Chomsky has been described as the "father of modern linguistics" and...
's critique of Markov model
Markov model
In probability theory, a Markov model is a stochastic model that assumes the Markov property. Generally, this assumption enables reasoning and computation with the model that would otherwise be intractable.-Introduction:...
s in the late 1950s that caused their virtual disappearance from natural language processing
Natural language processing
Natural language processing is a field of computer science and linguistics concerned with the interactions between computers and human languages; it began as a branch of artificial intelligence....
, along with statistical methods in general, until well into the 1980s.) This is because the only explicit dependency range is (n-1) tokens for an n-gram model, and since natural languages incorporate many cases of unbounded dependencies (such as wh-movement
Wh-movement
Wh-movement is a syntactic phenomenon found in many languages around the world, in which interrogative words or phrases show a special word order. Unlike ordinary phrases, such wh-words appear at the beginning of an interrogative clause...
), this means that an n-gram model cannot in principle distinguish unbounded dependencies from noise (since long range correlations drop exponentially with distance for any Markov model). For this reason, n-gram models have not made much impact on linguistic theory, where part of the explicit goal is to model such dependencies.
Another criticism that has been made is that Markov models of language, including n-gram models, do not explicitly capture the performance/competence distinction discussed by Chomsky. This is because n-gram models are not designed to model linguistic knowledge as such, and make no claims to being (even potentially) complete models of linguistic knowledge; instead, they are used in practical applications.
In practice, n-gram models have been shown to be extremely effective in modeling language data, which is a core component in modern statistical language
Natural language processing
Natural language processing is a field of computer science and linguistics concerned with the interactions between computers and human languages; it began as a branch of artificial intelligence....
applications.
Most modern applications that rely on n-gram based models, such as machine translation
Machine translation
Machine translation, sometimes referred to by the abbreviation MT is a sub-field of computational linguistics that investigates the use of computer software to translate text or speech from one natural language to another.On a basic...
applications, do not rely exclusively on such models; instead, they typically also incorporate Bayesian inference
Bayesian inference
In statistics, Bayesian inference is a method of statistical inference. It is often used in science and engineering to determine model parameters, make predictions about unknown variables, and to perform model selection...
. Modern statistical models are typically made up of two parts, a prior distribution describing the inherent likelihood of a possible result and a likelihood function
Likelihood function
In statistics, a likelihood function is a function of the parameters of a statistical model, defined as follows: the likelihood of a set of parameter values given some observed outcomes is equal to the probability of those observed outcomes given those parameter values...
used to assess the compatibility of a possible result with observed data. When a language model is used, it is used as part of the prior distribution (e.g. to gauge the inherent "goodness" of a possible translation), and even then it is often not the only component in this distribution. Handcrafted features of various sorts are also used, for example variables that represent the position of a word in a sentence or the general topic of discourse. In addition, features based on the structure of the potential result, such as syntactic considerations, are often used. Such features are also used as part of the likelihood function, which makes use of the observed data. Conventional linguistic theory can be incorporated in these features (although in practice, it is rare that features specific to generative or other particular theories of grammar are incorporated, as computational linguists
Computational linguistics
Computational linguistics is an interdisciplinary field dealing with the statistical or rule-based modeling of natural language from a computational perspective....
tend to be "agnostic" towards individual theories of grammar).
n-grams for approximate matching
n-grams can also be used for efficient approximate matching. By converting a sequence of items to a set of n-grams, it can be embedded in a vector spaceVector space
A vector space is a mathematical structure formed by a collection of vectors: objects that may be added together and multiplied by numbers, called scalars in this context. Scalars are often taken to be real numbers, but one may also consider vector spaces with scalar multiplication by complex...
, thus allowing the sequence to be compared to other sequences in an efficient manner. For example, if we convert strings with only letters in the English alphabet into 3-grams, we get a
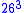 -dimensional space (the first dimension measures the number of occurrences of "aaa", the second "aab", and so forth for all possible combinations of three letters). Using this representation, we lose information about the string. For example, both the strings "abc" and "bca" give rise to exactly the same 2-gram "bc" (although {"ab", "bc"} is clearly not the same as {"bc", "ca"}). However, we know empirically that if two strings of real text have a similar vector representation (as measured by cosine distance
-dimensional space (the first dimension measures the number of occurrences of "aaa", the second "aab", and so forth for all possible combinations of three letters). Using this representation, we lose information about the string. For example, both the strings "abc" and "bca" give rise to exactly the same 2-gram "bc" (although {"ab", "bc"} is clearly not the same as {"bc", "ca"}). However, we know empirically that if two strings of real text have a similar vector representation (as measured by cosine distanceCosine similarity
Cosine similarity is a measure of similarity between two vectors by measuring the cosine of the angle between them. The cosine of 0 is 1, and less than 1 for any other angle. The cosine of the angle between two vectors thus determines whether two vectors are pointing in roughly the same...
) then they are likely to be similar. Other metrics have also been applied to vectors of n-grams with varying, sometimes better, results. For example z-scores have been used to compare documents by examining how many standard deviations each n-gram differs from its mean occurrence in a large collection, or text corpus
Text corpus
In linguistics, a corpus or text corpus is a large and structured set of texts...
, of documents (which form the "background" vector). In the event of small counts, the g-score may give better results for comparing alternative models.
It is also possible to take a more principled approach to the statistics of n-grams, modeling similarity as the likelihood that two strings came from the same source directly in terms of a problem in Bayesian inference
Bayesian inference
In statistics, Bayesian inference is a method of statistical inference. It is often used in science and engineering to determine model parameters, make predictions about unknown variables, and to perform model selection...
.
n-gram-based searching can also be used for plagiarism detection
Plagiarism detection
Plagiarism detection is the process of locating instances of plagiarism within a work or document. The widespread use of computers and the advent of the Internet has made it easier to plagiarize the work of others. Most cases of plagiarism are found in academia, where documents are typically essays...
.
Other applications
n-grams find use in several areas of computer science, computational linguisticsComputational linguistics
Computational linguistics is an interdisciplinary field dealing with the statistical or rule-based modeling of natural language from a computational perspective....
, and applied mathematics.
They have been used to:
- design kernelsKernel (mathematics)In mathematics, the word kernel has several meanings. Kernel may mean a subset associated with a mapping:* The kernel of a mapping is the set of elements that map to the zero element , as in kernel of a linear operator and kernel of a matrix...
that allow machine learningMachine learningMachine learning, a branch of artificial intelligence, is a scientific discipline concerned with the design and development of algorithms that allow computers to evolve behaviors based on empirical data, such as from sensor data or databases...
algorithms such as support vector machineSupport vector machineA support vector machine is a concept in statistics and computer science for a set of related supervised learning methods that analyze data and recognize patterns, used for classification and regression analysis...
s to learn from string data - find likely candidates for the correct spelling of a misspelled word
- improve compression in compression algorithmsData compressionIn computer science and information theory, data compression, source coding or bit-rate reduction is the process of encoding information using fewer bits than the original representation would use....
where a small area of data requires n-grams of greater length - assess the probability of a given word sequence appearing in text of a language of interest in pattern recognition systems, speech recognitionSpeech recognitionSpeech recognition converts spoken words to text. The term "voice recognition" is sometimes used to refer to recognition systems that must be trained to a particular speaker—as is the case for most desktop recognition software...
, OCR (optical character recognitionOptical character recognitionOptical character recognition, usually abbreviated to OCR, is the mechanical or electronic translation of scanned images of handwritten, typewritten or printed text into machine-encoded text. It is widely used to convert books and documents into electronic files, to computerize a record-keeping...
), Intelligent Character RecognitionIntelligent Character RecognitionIn computer science, intelligent character recognition is an advanced optical character recognition or — rather more specific — handwriting recognition system that allows fonts and different styles of handwriting to be learned by a computer during processing to improve accuracy and recognition...
(ICRIntelligent Character RecognitionIn computer science, intelligent character recognition is an advanced optical character recognition or — rather more specific — handwriting recognition system that allows fonts and different styles of handwriting to be learned by a computer during processing to improve accuracy and recognition...
), machine translationMachine translationMachine translation, sometimes referred to by the abbreviation MT is a sub-field of computational linguistics that investigates the use of computer software to translate text or speech from one natural language to another.On a basic...
and similar applications - improve retrieval in information retrievalInformation retrievalInformation retrieval is the area of study concerned with searching for documents, for information within documents, and for metadata about documents, as well as that of searching structured storage, relational databases, and the World Wide Web...
systems when it is hoped to find similar "documents" (a term for which the conventional meaning is sometimes stretched, depending on the data set) given a single query document and a database of reference documents - improve retrieval performance in genetic sequence analysis as in the BLASTBLASTIn bioinformatics, Basic Local Alignment Search Tool, or BLAST, is an algorithm for comparing primary biological sequence information, such as the amino-acid sequences of different proteins or the nucleotides of DNA sequences...
family of programs - identify the language a text is in or the species a small sequence of DNA was taken from
- predict letters or words at random in order to create text, as in the dissociated pressDissociated pressDissociated press is an algorithm for generating text based on another text. It is intended for transforming any text into potentially humorous garbage. The name is a play on "Associated Press".An implementation of the algorithm is available in Emacs....
algorithm.
Smoothing techniques
There are problems of balance weight between infrequent grams (for example, if a proper name appeared in the training data) and frequent grams. Also, items not seen in the training data will be given a probabilityProbability
Probability is ordinarily used to describe an attitude of mind towards some proposition of whose truth we arenot certain. The proposition of interest is usually of the form "Will a specific event occur?" The attitude of mind is of the form "How certain are we that the event will occur?" The...
of 0.0 without smoothing
Smoothing
In statistics and image processing, to smooth a data set is to create an approximating function that attempts to capture important patterns in the data, while leaving out noise or other fine-scale structures/rapid phenomena. Many different algorithms are used in smoothing...
. For unseen but plausible data from a sample, one can introduce pseudocount
Pseudocount
A pseudocount is an amount added to the number of observed cases in order to change the expected probability in a model of those data, when not known to be zero. Depending on the prior knowledge, which is sometimes a subjective value, a pseudocount may have any non-negative finite value...
s. Pseudocounts are generally motivated on Bayesian grounds.
In practice it is necessary to smooth the probability distributions by also assigning non-zero probabilities to unseen words or n-grams. The reason is that models derived directly from the n-gram frequency counts have severe problems when confronted with any n-grams that have not explicitly been seen before -- the zero-frequency problem
PPM compression algorithm
Prediction by partial matching is an adaptive statistical data compression technique based on context modeling and prediction. PPM models use a set of previous symbols in the uncompressed symbol stream to predict the next symbol in the stream....
. Various smoothing methods are used, from simple "add-one" smoothing (assign a count of 1 to unseen n-grams; see Rule of succession
Rule of succession
In probability theory, the rule of succession is a formula introduced in the 18th century by Pierre-Simon Laplace in the course of treating the sunrise problem....
) to more sophisticated models, such as Good-Turing discounting or back-off model
Katz's back-off model
Katz back-off is a generative n-gram language model that estimates the conditional probability of a word given its history in the n-gram. It accomplishes this estimation by "backing-off" to models with smaller histories under certain conditions...
s. Some of these methods are equivalent to assigning a prior distribution to the probabilities of the N-grams and using Bayesian inference
Bayesian inference
In statistics, Bayesian inference is a method of statistical inference. It is often used in science and engineering to determine model parameters, make predictions about unknown variables, and to perform model selection...
to compute the resulting posterior N-gram probabilities. However, the more sophisticated smoothing models were typically not derived in this fashion, but instead through independent considerations.
- Linear interpolationLinear interpolationLinear interpolation is a method of curve fitting using linear polynomials. Lerp is an abbreviation for linear interpolation, which can also be used as a verb .-Linear interpolation between two known points:...
(e.g., taking the weighted meanWeighted meanThe weighted mean is similar to an arithmetic mean , where instead of each of the data points contributing equally to the final average, some data points contribute more than others...
of the unigram, bigram, and trigram) - Good-Turing discounting
- Witten-Bell discounting
- Lidstone's smoothingAdditive smoothingIn statistics, additive smoothing, also called Laplace smoothing , or Lidstone smoothing, is a technique used to smooth categorical data...
- Katz's back-off modelKatz's back-off modelKatz back-off is a generative n-gram language model that estimates the conditional probability of a word given its history in the n-gram. It accomplishes this estimation by "backing-off" to models with smaller histories under certain conditions...
(trigram)
See also
- CollocationCollocationIn corpus linguistics, collocation defines a sequence of words or terms that co-occur more often than would be expected by chance. In phraseology, collocation is a sub-type of phraseme. An example of a phraseological collocation is the expression strong tea...
- Hidden Markov modelHidden Markov modelA hidden Markov model is a statistical Markov model in which the system being modeled is assumed to be a Markov process with unobserved states. An HMM can be considered as the simplest dynamic Bayesian network. The mathematics behind the HMM was developed by L. E...
- TrigramTrigramTrigrams are a special case of the N-gram, where N is 3. They are often used in natural language processing for doing statistical analysis of texts.-Frequency:The 16 most common trigrams in English are:-Examples:...
, BigramBigramBigrams or digrams are groups of two written letters, two syllables, or two words, and are very commonly used as the basis for simple statistical analysis of text. They are used in one of the most successful language models for speech recognition... - n-tuple
- k-merK-merThe term k-mer usually refers to a specific n-tuple or n-gram of nucleic acid or amino acid sequences that can be used to identify certain regions within biomolecules like DNA or proteins...
- String KernelString KernelA string kernel is a mathematical tool used in large scale data analysis and mining,where sequence data are to be clustered or classified . Kernels are often used in with support vector machines to transform data from its original space to one where it can be more easily separated and grouped...
External links
- Google's ngram viewer and web n-grams database (September 2006)
- Microsoft's web n-grams service
- http://www.ngrams.info/1,000,000 most frequent 2,3,4,5-grams (free) from the 425 million word Corpus of Contemporary American EnglishCorpus of Contemporary American EnglishThe freely-searchable 425 million word Corpus of Contemporary American English is the largest corpus of American English currently available, and the only publicly-available corpus of American English to contain a wide array of texts from a number of genres.It was created by Mark Davies, Professor...
] - Peachnote's music ngram viewer
- Google n-gram Information Extracter
- Two visualizations of Google's n-gram dataset: Word Association, Word Spectrum.
- Dunning, T. (1994) "Statistical Identification of Language". Technical Report MCCS 94-273, New Mexico State University, 1994. N-gram language identification algorithm http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/summary?doi=10.1.1.48.1958 (language identificationLanguage identificationLanguage identification is the process of determining which natural language given content is in. Traditionally, identification of written language - as practiced, for instance, in library science - has relied on manually identifying frequent words and letters known to be characteristic of...
) - Ngram Statistics Package, open source package to identify statistically significant Ngrams
- Stochastic Language Models (N-Gram) Specification (W3C)
- language_detector, open source N-Gram based language detector, written in ruby
- The Gibberizer, open source software to generate familiar-sounding gibberish using N-Grams

