Outline of Bhutan
Encyclopedia
South Asia
South Asia, also known as Southern Asia, is the southern region of the Asian continent, which comprises the sub-Himalayan countries and, for some authorities , also includes the adjoining countries to the west and the east...
. Bhutan is located amidst the eastern end of the Himalaya Mountains and is bordered to the south, east and west by India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
and to the north by China
China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
. Bhutan is separated from Nepal
Nepal
Nepal , officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, is a landlocked sovereign state located in South Asia. It is located in the Himalayas and bordered to the north by the People's Republic of China, and to the south, east, and west by the Republic of India...
by the Indian state of Sikkim
Sikkim
Sikkim is a landlocked Indian state nestled in the Himalayan mountains...
. The Bhutanese call their country Druk Yul (land of the thunder dragon).
Foreign influences and tourism
Tourism
Tourism is travel for recreational, leisure or business purposes. The World Tourism Organization defines tourists as people "traveling to and staying in places outside their usual environment for not more than one consecutive year for leisure, business and other purposes".Tourism has become a...
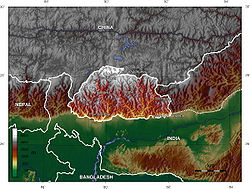
in Bhutan are regulated by the government to preserve the nation's traditional culture, identity and the environment, however, in 2006 Business Week rated Bhutan the happiest country in Asia and the eighth happiest country in the world. The landscape ranges from subtropical
Subtropics
The subtropics are the geographical and climatical zone of the Earth immediately north and south of the tropical zone, which is bounded by the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn, at latitudes 23.5°N and 23.5°S...
plains in the south to the Himalayan heights in the north, with some peaks exceeding 7,000 metres (23,000 ft). The state religion is Vajrayana Buddhism
Vajrayana
Vajrayāna Buddhism is also known as Tantric Buddhism, Tantrayāna, Mantrayāna, Secret Mantra, Esoteric Buddhism and the Diamond Vehicle...
, and the population is predominantly Buddhist, with Hinduism
Hinduism
Hinduism is the predominant and indigenous religious tradition of the Indian Subcontinent. Hinduism is known to its followers as , amongst many other expressions...
being the second-largest religion. The capital and largest city is Thimphu
Thimphu
Thimphu also spelt Thimpu, is the capital and largest city of Bhutan. It is situated in the western central part of Bhutan and the surrounding valley is one of Bhutan's dzongkhags, the Thimphu District. The city became the capital of Bhutan in 1961...
. After centuries of direct monarchic rule, Bhutan held its first democratic elections in March 2008. Bhutan is a member of the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation
South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation
The South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation is an organisation of South Asian nations, founded in December 1985 by Ziaur Rahman and dedicated to economic, technological, social, and cultural development emphasising collective self-reliance. Its seven founding members are Bangladesh,...
(SAARC).
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Bhutan:
General reference
- PronunciationInternational Phonetic AlphabetThe International Phonetic Alphabet "The acronym 'IPA' strictly refers [...] to the 'International Phonetic Association'. But it is now such a common practice to use the acronym also to refer to the alphabet itself that resistance seems pedantic...
: - Common English country name: BhutanBhutanBhutan , officially the Kingdom of Bhutan, is a landlocked state in South Asia, located at the eastern end of the Himalayas and bordered to the south, east and west by the Republic of India and to the north by the People's Republic of China...
- Official English country name: The Kingdom of Bhutan
- Common endonym(s): Druk Yul (DzongkhaDzongkha languageDzongkha , occasionally Ngalopkha, is the national language of Bhutan. The word "dzongkha" means the language spoken in the dzong, – dzong being the fortress-like monasteries established throughout Bhutan by Shabdrung Ngawang Namgyal in the 17th century."Bhutani" is not another name for...
: ; WylieWylie transliterationThe Wylie transliteration scheme is a method for transliterating Tibetan script using only the letters available on a typical English language typewriter. It bears the name of Turrell V. Wylie, who described the scheme in an article, A Standard System of Tibetan Transcription, published in 1959...
: 'Brug yul) - Official endonym(s): Dru Gäkhap (DzongkhaDzongkha languageDzongkha , occasionally Ngalopkha, is the national language of Bhutan. The word "dzongkha" means the language spoken in the dzong, – dzong being the fortress-like monasteries established throughout Bhutan by Shabdrung Ngawang Namgyal in the 17th century."Bhutani" is not another name for...
: ; WylieWylie transliterationThe Wylie transliteration scheme is a method for transliterating Tibetan script using only the letters available on a typical English language typewriter. It bears the name of Turrell V. Wylie, who described the scheme in an article, A Standard System of Tibetan Transcription, published in 1959...
: 'Brug Gyal-khab) - Adjectival(s): DrukDrukThe Druk is the "Thunder Dragon" of Bhutanese mythology and a Bhutanese national symbol. A druk appears on the Bhutanese Flag, holding jewels to represent wealth. In the Dzongkha language, Bhutan is called Druk Yul, or Land of Druk, and Bhutanese leaders are called Druk Gyalpo, Dragon Kings...
, Bhutanese - Demonym(s): Bhutanese
- EtymologyEtymologyEtymology is the study of the history of words, their origins, and how their form and meaning have changed over time.For languages with a long written history, etymologists make use of texts in these languages and texts about the languages to gather knowledge about how words were used during...
: Name of Bhutan - International rankings of BhutanInternational rankings of Bhutan-International rankings:...
- ISO country codes: BT, BTN, 064
- ISO region codes: See ISO 3166-2:BTISO 3166-2:BTISO 3166-2:BT is the entry for Bhutan in ISO 3166-2, part of the ISO 3166 standard published by the International Organization for Standardization , which defines codes for the names of the principal subdivisions of all countries coded in ISO 3166-1.Currently for Bhutan, ISO 3166-2 codes are...
- InternetInternetThe Internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks that use the standard Internet protocol suite to serve billions of users worldwide...
country code top-level domainCountry code top-level domainA country code top-level domain is an Internet top-level domain generally used or reserved for a country, a sovereign state, or a dependent territory....
: .bt.bt.bt is the Internet country code top-level domain for Bhutan . It is administered by the Bhutan Ministry of Communications.As of November 7, 2005, there are a total of 84 registered names in this TLD.-External links:* *...
Geography of Bhutan
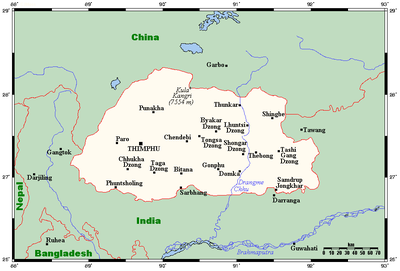
- Bhutan is: a landlocked country
- Location:
- Northern HemisphereNorthern HemisphereThe Northern Hemisphere is the half of a planet that is north of its equator—the word hemisphere literally means “half sphere”. It is also that half of the celestial sphere north of the celestial equator...
and Eastern HemisphereEastern HemisphereThe Eastern Hemisphere, also Eastern hemisphere or eastern hemisphere, is a geographical term for the half of the Earth that is east of the Prime Meridian and west of 180° longitude. It is also used to refer to Europe, Asia, Africa, and Australasia, vis-à-vis the Western Hemisphere, which includes... - EurasiaEurasiaEurasia is a continent or supercontinent comprising the traditional continents of Europe and Asia ; covering about 52,990,000 km2 or about 10.6% of the Earth's surface located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres...
- AsiaAsiaAsia is the world's largest and most populous continent, located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres. It covers 8.7% of the Earth's total surface area and with approximately 3.879 billion people, it hosts 60% of the world's current human population...
- South AsiaSouth AsiaSouth Asia, also known as Southern Asia, is the southern region of the Asian continent, which comprises the sub-Himalayan countries and, for some authorities , also includes the adjoining countries to the west and the east...
- Indian subcontinentIndian subcontinentThe Indian subcontinent, also Indian Subcontinent, Indo-Pak Subcontinent or South Asian Subcontinent is a region of the Asian continent on the Indian tectonic plate from the Hindu Kush or Hindu Koh, Himalayas and including the Kuen Lun and Karakoram ranges, forming a land mass which extends...
- Indian subcontinent
- South Asia
- Asia
- Time zoneTime zoneA time zone is a region on Earth that has a uniform standard time for legal, commercial, and social purposes. In order for the same clock time to always correspond to the same portion of the day as the Earth rotates , different places on the Earth need to have different clock times...
: Bhutan TimeBhutan TimeBhutan Time is the time zone of Bhutan. It is +6:00 hrs ahead of Universal Time Coordinated . Bhutan does not observe any Daylight saving time....
(UTC+06) - Extreme points of BhutanExtreme points of BhutanThis is a list of the extreme points of Bhutan.- Latitude and longitude :* North:** disputed: Gasa District-China border. ** undisputed: Gasa District-China border, near Jigme Dorji National Park....
- High: Gangkhar PuensumGangkhar PuensumGangkhar Puensum is the highest mountain in Bhutan and a strong candidate for the highest unclimbed mountain in the world with an elevation of 7,570 metres and a prominence of over 2990 metres. It lies on the border with China...
7570 m (24,836 ft) - Low: Drangme Chhu 97 m (318 ft)
- High: Gangkhar Puensum
- Land boundaries: 1,075 km
- Northern Hemisphere
-
 India 605 km
India 605 km Mainland China 470 km
Mainland China 470 km
- Coastline: none
- Population of Bhutan: 672,425(2005)
- Area of Bhutan: 47000 square kilometres (18,146.8 sq mi) - 131st largest country
- Atlas of Bhutan
Environment of Bhutan

- Climate of Bhutan
- Environmental issues in BhutanEnvironmental issues in BhutanThere are a number of environmental issues in Bhutan. Among Bhutan's most pressing issues are traditional firewood collection, crop and flock protection, and waste disposal, as well as modern concerns such as industrial pollution, wildlife conservation, and climate change that threatens Bhutan's...
- Ecoregions in Bhutan
- Renewable energy in Bhutan
- Geology of Bhutan
- Protected areas of Bhutan
- Wildlife of BhutanWildlife of BhutanThe Kingdom of Bhutan is a small, landlocked nation nestled in the southern slopes of the Eastern Himalaya. To its north lies the Tibet Autonomous Region of China and to the west, south and east lies the Indian states of Sikkim, Bengal, Assam and Arunachal Pradesh....
- Flora of Bhutan
- Fauna of Bhutan
Natural geographic features of Bhutan
- Glaciers of BhutanGlaciers of BhutanThe glaciers of Bhutan, which covered about 10 percent of the total surface area in the 1980s, are an important renewable source of water for Bhutan's rivers. Fed by fresh snow each winter and slow melting in the summer, the glaciers bring millions of litres of fresh water to Bhutan and downriver...
- Lakes of Bhutan
- Mountains of Bhutan
- Rivers of Bhutan
- Waterfalls of Bhutan
- Valleys of Bhutan
- World Heritage Sites in Bhutan: None
Ecoregions of Bhutan
- Main article: Ecoregions in Bhutan
Administrative divisions of Bhutan
- Main article: Administrative divisions of Bhutan
- Dzongkhags (districts) of BhutanDistricts of BhutanBhutan comprises twenty districts .-Districts:-District Statistics:The results of the 2005 census appear below:...
- Dungkhags (sub-districts) of BhutanDungkhagA dungkhag is a sub-district of a dzongkhag of Bhutan. The head of a dungkhag is a Dungpa...
- Gewogs (village blocks) of Bhutan
- Thromdes (municipalities) of BhutanThromdeA thromde is a third-level administrative division in Bhutan. The legal administrative status of thromdes was most recently codified under the Local Government Act of 2009, and the role of thromdes in elections in Bhutan was defined in the Election Act of 2008.-Thromde administration:Thromde...
- Chiwogs (electoral constituencies) of BhutanChewogs of BhutanChiwogs of Bhutan , also spelled chewog, refer to the 1,044 basic electoral precincts of Bhutan. Chiwogs are also former third-level administrative divisions of Bhutan, below Gewogs. Until 2009, they were the equivalent of municipalities or parishes, containing clusters of villages and hamlets...
- Thromdes (municipalities) of Bhutan
- Gewogs (village blocks) of Bhutan
- Dungkhags (sub-districts) of Bhutan
Districts of Bhutan
| No. | District | Former spelling | Bhutanese | Romanization used by the Dzongkha Development Commission Dzongkha Development Commission The Dzongkha Development Commission , also called the DDC, is the pre-eminent body on matters pertaining to the Dzongkha language... |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Bumthang Bumthang District Bumthang District is one of the 20 dzongkhag comprising Bhutan. It is the most historic dzongkhag if the number of ancient temples and sacred sites is counted... |
བུམ་ཐང་ | Bºumtha | |
| 2. | Chukha | Chhukha | ཆུ་ཁ་ | Chukha |
| 3. | Dagana Dagana District Dagana District is one of the 20 dzongkhag comprising Bhutan... |
དར་དཀར་ནང་ | Dºagana | |
| 4. | Gasa Gasa District Gasa District or Gasa Dzongkhag is one of the 20 dzongkhags comprising Bhutan. Its capital is Gasa Dzong near Gasa. It is located in the far north of the county and spans the Middle and High Himalayas. The dominant language of the district is Dzongkha, the national language... |
མགར་ས་ | Gâsa | |
| 5. | Haa Haa District This page is about the area Haa. For information about the airships, please see high-altitude airship.Haa District is one of the 20 dzongkhag or districts comprising Bhutan. Per the 2005 census, the population of Haa dzongkhag was 11,648, making it the second least populated dzongkhag in Bhutan... |
ཧད་ / ཧཱ་ | Hâ | |
| 6. | Lhuntse | Lhuntshi | ལྷུན་རྩེ་ | Lhüntsi |
| 7. | Mongar Mongar District Mongar District is one of the 20 dzongkhags comprising Bhutan. Mongar is the fastest-developing dzongkhag in eastern Bhutan. A regional hospital has been constructed and the region is bustling with many economic activities. Mongar is noted for its lemon grass, a plant that can be used to produce... |
མོང་སྒར་ | Mongga | |
| 8. | Paro Paro District Paro District is the name of a district , valley, river and town in Bhutan. It is one of the most historic valleys in Bhutan. Both trade goods and invading Tibetans came over the pass at the head of the valley, giving Paro the closest cultural connection with Tibet of any Bhutanese district... |
སྤ་གྲོ་ | Paro | |
| 9. | Pemagatshel | Pemagatsel | པདྨ་དགའ་ཚལ་ | Pemagatshä |
| 10. | Punakha Punakha District Punakha District is one of the 20 dzongkhags comprising Bhutan. It is bordered by Thimphu, Gasa, and Wangdue Phodrang Districts... |
སྤུ་ན་ཁ་ | Punakha | |
| 11. | Samdrup Jongkhar | བསཾ་གྲུབ་ལྗོངས་མཁར་ | Samdru Jongkha | |
| 12. | Samtse Samtse District Samtse District is one of the 20 dzongkhags comprising Bhutan.-History and culture:... |
Samchi | བསམ་རྩེ་ | Samtsi |
| 13. | Sarpang Sarpang District Sarpang District is one of the 20 dzongkhags comprising Bhutan.-Languages:... |
གསར་སྦང་ | Sarbang | |
| 14. | Thimphu Thimphu District Thimphu District is a dzongkhag of Bhutan. Thimphu is also the capital of Bhutan and the largest city in the whole kingdom.-Languages:... |
ཐིམ་ཕུག་ | Thimphu | |
| 15. | Trashigang | Tashigang | བཀྲ་ཤིས་སྒང་ | Trashigang |
| 16. | Trashiyangste | བཀྲ་ཤིས་གཡང་རྩེ་ | Trashi'yangste | |
| 17. | Trongsa Trongsa District Trongsa District is one of the districts of Bhutan. It is the most central district of Bhutan and the geographic centre of Bhutan is located within it at Trongsa Dzong.... |
Tongsa | ཀྲོང་གསར་ | Trongsa |
| 18. | Tsirang Tsirang District Tsirang District , is one of the 20 dzongkhags of Bhutan. The administrative center of the district is Damphu... |
Chirang | རྩི་རང་ | Tsirang |
| 19. | Wangdue Phodrang | Wangdi Phodrang | དབང་འདུས་ཕོ་བྲང་ | 'Wangdi Phodrºa |
| 20. | Zhemgang | Shemgang | གཞལ་སྒང་ | Zhºämgang |
Municipalities of Bhutan
- Capital of Bhutan: ThimphuThimphuThimphu also spelt Thimpu, is the capital and largest city of Bhutan. It is situated in the western central part of Bhutan and the surrounding valley is one of Bhutan's dzongkhags, the Thimphu District. The city became the capital of Bhutan in 1961...
- Cities of Bhutan
- Cities, towns, and villages of Bhutan
Government and politics of Bhutan
- Main article: Government of Bhutan and Politics of BhutanPolitics of BhutanThe Government of Bhutan is a constitutional monarchy; between 1907 and the 1950s however, Bhutan was an absolute monarchy. The peaceful march to democracy has been a steady one. The King of Bhutan is head of state. Executive power is exercised by the Lhengye Zhungtshog, or council of ministers,...
- Form of governmentForm of governmentA form of government, or form of state governance, refers to the set of political institutions by which a government of a state is organized. Synonyms include "regime type" and "system of government".-Empirical and conceptual problems:...
: constitutional monarchyConstitutional monarchyConstitutional monarchy is a form of government in which a monarch acts as head of state within the parameters of a constitution, whether it be a written, uncodified or blended constitution... - Capital of Bhutan: Thimphu
- ElectionsElections in BhutanElections in Bhutan are conducted at national and local levels. Suffrage is universal for citizens 18 and over, and under applicable election laws...
- National Council, 2007–08Bhutanese National Council election, 2007–2008The general elections to the National Council of Bhutan, the upper house of the new bicameral Parliament of Bhutan were held for the first time on December 31, 2007, though they were originally scheduled for December 26, 2007...
- General election, 2008Bhutanese general election, 2008Bhutan held its first general election on March 24, 2008 for the National Assembly. Two parties were registered by the Election Commission of Bhutan to contest the election: the Bhutan Peace and Prosperity Party , which was formed by the merger of the previously established Bhutan People's United...
- Local elections, 2011 (2008)Bhutanese local government elections, 2011The Bhutanese local government elections of 2011 were originally slated for 2008, but were delayed until 2011. Elections began on January 20, 2011, however polls opened in only 3 of 20 districts – Thimphu, Chukha District , and Samdrup Jongkhar – as part of a staggered election schedule. Polls...
- National Council, 2007–08
- Political parties in Bhutan
- Political scandals of Bhutan
- Taxation in BhutanTaxation in BhutanTaxation in Bhutan is conducted by the national government and by its subsidiary local governments. All taxation is ultimately overseen by the Bhutan Ministry of Finance, Department of Revenue and Customs,, which is part of the executive Lhengye Zhungtshog . The modern legal basis for taxation in...
Executive branch of the government of Bhutan
- Head of stateHead of StateA head of state is the individual that serves as the chief public representative of a monarchy, republic, federation, commonwealth or other kind of state. His or her role generally includes legitimizing the state and exercising the political powers, functions, and duties granted to the head of...
: Druk Gyalpo - Head of governmentHead of governmentHead of government is the chief officer of the executive branch of a government, often presiding over a cabinet. In a parliamentary system, the head of government is often styled prime minister, chief minister, premier, etc...
: Prime Minister of Bhutan - Cabinet (government)Cabinet (government)A Cabinet is a body of high ranking government officials, typically representing the executive branch. It can also sometimes be referred to as the Council of Ministers, an Executive Council, or an Executive Committee.- Overview :...
: Lhengye ZhungtshogLhengye ZhungtshogThe Lhengye Zhungtshog is the highest executive body in Bhutan. It was created in 1999 by Jigme Singye Wangchuck, the fourth King of Bhutan....
- Ministry of Agriculture
- Ministry of Economic Affairs
- Ministry of Education
- Ministry of Finance
- Ministry of Foreign AffairsMinistry of Foreign Affairs (Bhutan)The Ministry of Foreign Affairs is the Bhutanese government ministry which oversees the foreign relations of Bhutan.- External links :*...
- Ministry of Health
- Ministry of Home and Cultural AffairsMinistry of Home and Cultural AffairsThe Bhutanese Ministry of Home and Cultural Affairs is the government ministry within the Lhengye Zhungtshog which oversees law and order; the civil administration; immigration services; the issuance of citizenship documents, and other related documents; the...
- Ministry Information and Communications
- Ministry Labour and Human Resources
- Ministry Works and Human Settlement
Legislative branch of the government of Bhutan
- Parliament of BhutanParliament of BhutanThe Parliament of Bhutan consists of the King of Bhutan together with a bicameral parliament.Constitution: Art. 1, § 3; Art. 10 This bicameral parliament is made up of an upper house, the National Council and a lower house, the National Assembly.Constitution: Art. 11; Art...
(bicameral)- Upper houseUpper houseAn upper house, often called a senate, is one of two chambers of a bicameral legislature, the other chamber being the lower house; a legislature composed of only one house is described as unicameral.- Possible specific characteristics :...
: National Council of BhutanNational Council of BhutanThe National Council is the upper house of Bhutan's new bicameral Parliament, which also comprises the Druk Gyalpo and the National Assembly. It is the subordinate house, and cannot author monetary or budget-related bills... - Lower houseLower houseA lower house is one of two chambers of a bicameral legislature, the other chamber being the upper house.Despite its official position "below" the upper house, in many legislatures worldwide the lower house has come to wield more power...
: National Assembly of BhutanNational Assembly of BhutanThe National Assembly is the elected lower house of Bhutan's new bicameral Parliament which also comprises the Druk Gyalpo and the National Council. It is the more powerful house.- Current National Assembly :...
- Upper house
Judicial branch of the government of Bhutan
- Royal Court of Justice
- Supreme Court of BhutanSupreme Court of BhutanThe Supreme Court of Bhutan is the Kingdom's highest court of review and interpreter of the Constitution. The Supreme Court consists of one Chief Justice and five Drangpons...
- High Court of BhutanHigh Court of BhutanUnder the 2008 Constitution, the High Court of Bhutan consists of the Chief Justice and eight Drangpons . The Chief Justice and Drangpons of the High Court are appointed from among juniors, peers, and eminent jurists by the Druk Gyalpo...
- Dzongkhag CourtDzongkhag CourtThe Dzongkhag Court exists in each of Bhutan's 20 Dzongkhags, and is the court of first instance of the Royal Court of Justice in 14 of the 20 Dzongkhags of Bhutan. In the remaining 6 Dzongkhags there exists a further subdivision, Dungkhag, which is the basic level of judicial administration in...
- Dungkhag CourtDungkhag CourtThe Dungkhag Court is the court of first instance of the Royal Court of Justice in 6 of the 20 Dzongkhags of Bhutan which have Dungkhag administrative divisions; in the remaining 14 Dzongkhags, the Dzongkhag Court is the court of first instance. There are a total of 13 Dungkhags in the 6...
- Supreme Court of Bhutan
Foreign relations of Bhutan
- Diplomatic missions in Bhutan
- Diplomatic missions of BhutanDiplomatic missions of BhutanThis is a list of diplomatic missions of Bhutan. The landlocked and isolationist Himalayan kingdom of Bhutan has a very limited number of diplomatic missions abroad.-Asia:** Dhaka ** New Delhi ** Kuwait City...
Bhutanese refugees
- Bhutanese refugees
- Beldangi refugee campsBeldangi refugee campsThe Beldangi refugee camps consist of three settlements in Damak, Jhapa District, Nepal: Beldangi I , Beldangi II, and Beldangi II Extension . They are inhabited by Bhutanese refugees. As of 2011, Beldangi I to the east had 12,793 residents; Beldangi II to the west had 14,680; and Beldangi II...
- Goldhap refugee campGoldhap Refugee CampGoldhap refugee camp is a small refugee camp in Nepal populated by just over 4,600 Bhutanese refugees as of 2011. Because of its dwindling population, the UNHCR is planning to merge Goldhap into the nearby Beldangi refugee camps...
- Khudunabari refugee campKhudunabari refugee campKhudunabari refugee camp , located to the northwest of Sanischare, Kosi, Nepal, is home to some 10,688 Bhutanese refugees. The camp lies at a river confluence, between Sanischare Road and Limbuwan Road 37....
- Sanischare refugee campSanischare refugee campSanischare refugee camp , located near Sanischare, Kosi, Nepal, is home to some 13,323 Bhutanese refugees. The camp lies on the south side of the East-West Highway, and contains the New Horizon Academy.In March 2011, a fire burned much of the camp destroying about 1,200 homes...
- Timai refugee campTimai refugee campTimai refugee camp , located in Jhapa District, Nepal, is home to some 6,874 Bhutanese refugees. The refugee camp is located along both the east and west sides of Limbuwan Highway 72 near its terminus at Limbuwan Highway 07. To the east of the refugee camp flows the Tamai River, a tributary of the...
- Beldangi refugee camps
International organization membership
The Kingdom of Bhutan is a member of:- Asian Development BankAsian Development BankThe Asian Development Bank is a regional development bank established on 22 August 1966 to facilitate economic development of countries in Asia...
(ADB) - Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation (BIMSTEC)
- Colombo PlanColombo PlanThe Colombo Plan is a regional organization that embodies the concept of collective inter-governmental effort to strengthen economic and social development of member countries in the Asia-Pacific Region...
(CP) - Food and Agriculture OrganizationFood and Agriculture OrganizationThe Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations is a specialised agency of the United Nations that leads international efforts to defeat hunger. Serving both developed and developing countries, FAO acts as a neutral forum where all nations meet as equals to negotiate agreements and...
(FAO) - Group of 77Group of 77The Group of 77 at the United Nations is a loose coalition of developing nations, designed to promote its members' collective economic interests and create an enhanced joint negotiating capacity in the United Nations. There were 77 founding members of the organization, but the organization has...
(G77) - International Bank for Reconstruction and DevelopmentInternational Bank for Reconstruction and DevelopmentThe International Bank for Reconstruction and Development is one of five institutions that compose the World Bank Group. The IBRD is an international organization whose original mission was to finance the reconstruction of nations devastated by World War II. Now, its mission has expanded to fight...
(IBRD) - International Civil Aviation OrganizationInternational Civil Aviation OrganizationThe International Civil Aviation Organization , pronounced , , is a specialized agency of the United Nations. It codifies the principles and techniques of international air navigation and fosters the planning and development of international air transport to ensure safe and orderly growth...
(ICAO) - International Criminal Police Organization (Interpol)
- International Development AssociationInternational Development AssociationThe International Development Association , is the part of the World Bank that helps the world’s poorest countries. It complements the World Bank's other lending arm — the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development — which serves middle-income countries with capital investment and...
(IDA) - International Finance CorporationInternational Finance CorporationThe International Finance Corporation promotes sustainable private sector investment in developing countries.IFC is a member of the World Bank Group and is headquartered in Washington, D.C., United States....
(IFC) - International Fund for Agricultural DevelopmentInternational Fund for Agricultural DevelopmentThe International Fund for Agricultural Development , a specialized agency of the United Nations, was established as an international financial institution in 1977 as one of the major outcomes of the 1974 World Food Conference. IFAD is dedicated to eradicating rural poverty in developing countries...
(IFAD) - International Monetary FundInternational Monetary FundThe International Monetary Fund is an organization of 187 countries, working to foster global monetary cooperation, secure financial stability, facilitate international trade, promote high employment and sustainable economic growth, and reduce poverty around the world...
(IMF) - International Olympic CommitteeInternational Olympic CommitteeThe International Olympic Committee is an international corporation based in Lausanne, Switzerland, created by Pierre de Coubertin on 23 June 1894 with Demetrios Vikelas as its first president...
(IOC) - International Organization for MigrationInternational Organization for MigrationThe International Organization for Migration is an intergovernmental organization. It was initially established in 1951 as the Intergovernmental Committee for European Migration to help resettle people displaced by World War II....
(IOM) (observer) - International Organization for StandardizationInternational Organization for StandardizationThe International Organization for Standardization , widely known as ISO, is an international standard-setting body composed of representatives from various national standards organizations. Founded on February 23, 1947, the organization promulgates worldwide proprietary, industrial and commercial...
(ISO) (correspondent) - International Telecommunication UnionInternational Telecommunication UnionThe International Telecommunication Union is the specialized agency of the United Nations which is responsible for information and communication technologies...
(ITU) - International Telecommunications Satellite OrganizationInternational Telecommunications Satellite OrganizationThe International Telecommunications Satellite Organization is an intergovernmental organisation charged with overseeing the public service obligations of Intelsat.-External links:*...
(ITSO)
- Nonaligned Movement (NAM)
- Organization for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW)
- South Asia Co-operative Environment ProgrammeSouth Asia Co-operative Environment ProgrammeThe South Asia Co-operative Environment Programme, also known as SACEP, is an inter-governmental organisation established in 1982 by the South Asian governments to promote and support protection, management and enhancement of the environment in the region....
(SACEP) - South Asian Association for Regional CooperationSouth Asian Association for Regional CooperationThe South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation is an organisation of South Asian nations, founded in December 1985 by Ziaur Rahman and dedicated to economic, technological, social, and cultural development emphasising collective self-reliance. Its seven founding members are Bangladesh,...
(SAARC) - United NationsUnited NationsThe United Nations is an international organization whose stated aims are facilitating cooperation in international law, international security, economic development, social progress, human rights, and achievement of world peace...
(UN) - United Nations Conference on Trade and DevelopmentUnited Nations Conference on Trade and DevelopmentThe United Nations Conference on Trade and Development was established in 1964 as a permanent intergovernmental body. It is the principal organ of the United Nations General Assembly dealing with trade, investment, and development issues....
(UNCTAD) - United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization (UNESCO)
- United Nations Industrial Development OrganizationUnited Nations Industrial Development OrganizationThe United Nations Industrial Development Organization , French/Spanish acronym ONUDI, is a specialized agency in the United Nations system, headquartered in Vienna, Austria...
(UNIDO) - Universal Postal UnionUniversal Postal UnionThe Universal Postal Union is an international organization that coordinates postal policies among member nations, in addition to the worldwide postal system. The UPU contains four bodies consisting of the Congress, the Council of Administration , the Postal Operations Council and the...
(UPU) - World Customs OrganizationWorld Customs OrganizationThe World Customs Organization is an intergovernmental organization headquartered in Brussels, Belgium. With its worldwide membership, the WCO is recognized as the voice of the global customs community...
(WCO) - World Federation of Trade UnionsWorld Federation of Trade UnionsThe World Federation of Trade Unions was established in 1945 to replace the International Federation of Trade Unions. Its mission was to bring together trade unions across the world in a single international organization, much like the United Nations...
(WFTU) - World Health OrganizationWorld Health OrganizationThe World Health Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations that acts as a coordinating authority on international public health. Established on 7 April 1948, with headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland, the agency inherited the mandate and resources of its predecessor, the Health...
(WHO) - World Intellectual Property OrganizationWorld Intellectual Property OrganizationThe World Intellectual Property Organization is one of the 17 specialized agencies of the United Nations. WIPO was created in 1967 "to encourage creative activity, to promote the protection of intellectual property throughout the world"....
(WIPO) - World Meteorological OrganizationWorld Meteorological OrganizationThe World Meteorological Organization is an intergovernmental organization with a membership of 189 Member States and Territories. It originated from the International Meteorological Organization , which was founded in 1873...
(WMO) - World Tourism OrganizationWorld Tourism OrganizationThe World Tourism Organization , based in Madrid, Spain, is a United Nations agency dealing with questions relating to tourism. It compiles the World Tourism rankings. The World Tourism Organization is a significant global body, concerned with the collection and collation of statistical information...
(UNWTO) - World Trade OrganizationWorld Trade OrganizationThe World Trade Organization is an organization that intends to supervise and liberalize international trade. The organization officially commenced on January 1, 1995 under the Marrakech Agreement, replacing the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade , which commenced in 1948...
(WTO) (observer)
Law and order in Bhutan
- Main article: Law of BhutanLaw of BhutanThe law of Bhutan derives mainly from legislation and treaties. Prior to the enactment of the Constitution, laws were enacted by fiat of the King of Bhutan. The law of Bhutan originates in the semi-theocratic Tsa Yig legal code, and was heavily influenced through the twentieth century by English...
- Bhutanese legislationBhutanese legislationBhutanese legislation is created by the bicameral Parliament of Bhutan. Either the upper house National Council, the lower house National Assembly, or the Attorney General may author bills to be passed as acts, with the exception of money and financial bills, which are the sole purview of the...
- Constitution of BhutanConstitution of BhutanThe Constitution of Bhutan was enacted July 18, 2008 by the Royal Government. The Constitution was thoroughly planned by several government officers and agencies over a period of almost seven years amid increasing democratic reforms in Bhutan...
- Bhutanese Citizenship Act 1958Bhutanese Citizenship Act 1958The Bhutanese Citizenship Act of 1958, officially the Nationality Law of Bhutan, 1958, is a decree by the Druk Gyalpo King Jigme Dorji Wangchuck, recognizing the definition of a Bhutanese citizen...
- Bhutanese Citizenship Act 1985
- Local Government Act of Bhutan 2009Local Government Act of Bhutan 2009The Local Government Act of Bhutan was enacted on September 11, 2009, by parliament of Bhutan in order to further implement its program of decentralization and devolution of power and authority.Local Gov't Act 2008: Preamble It is the most recent reform of the law on Bhutan's administrative...
- Tobacco Control Act of Bhutan 2010Tobacco Control Act of Bhutan 2010The Tobacco Control Act of Bhutan was enacted by parliament on June 16, 2010.Tobacco Control Act : § 1 It regulates tobacco and tobacco products, banning the cultivation, harvesting, production, and sale of tobacco and tobacco products in Bhutan...
- Constitution of Bhutan
- Human rights in BhutanHuman rights in BhutanIn general, the status of human rights in Bhutan is good. The greatest concern is the status of Bhutanese refugees and the protection of the Lhotshampa Nepalese minority remaining in Bhutan...
- Capital punishment in BhutanCapital punishment in BhutanIn Bhutan, capital punishment has been abolished since March 20, 2004 and is currently prohibited by the 2008 Constitution. The prohibition appears among a number of fundamental rights guaranteed by the Bhutanese Constitution...
- Freedom of religion in BhutanFreedom of religion in BhutanThe Bhutanese Constitution of 2008 and previous law provide for freedom of religion in Bhutan, however the government has limited non-Buddhist missionary activity, barring non-Buddhist missionaries from entering the country, limiting construction of non-Buddhist religious buildings, and restricting...
- LGBT rights in BhutanLGBT rights in BhutanHomosexuality is illegal in Bhutan in the penal code of Bhutan and is punishable with a prison sentence from between one month to less than one year. The age of sexual consent is eighteen years....
- Capital punishment in Bhutan
- Law enforcement in Bhutan
- Royal Bhutan PoliceRoyal Bhutan PoliceLaw enforcement in Bhutan is the collective purview of several divisions of Bhutan's Ministry of Home and Cultural Affairs. Namely, the Ministry's Bureau of Law and Order, Department of Immigration, and Department of Local Governance are responsible for law enforcement in Bhutan...
- Royal Bhutan Police
- Crime in BhutanCrime in BhutanBhutan has a low crime rate. Incidents of petty crime are occasionally reported in the country. Violent crime is very uncommon. Some cases of drug abuse are reported; alcohol abuse is a problem. But in general, drug trafficking is low...
- Tsa YigTsa YigThe Tsa Yig is any monastic constitution or code of moral discipline based on codified Tibetan Buddhist precepts. Every Tibetan monastery and convent had its own Tsa Yig, and the variation in Tsa Yig content shows a degree of autonomy and internal democracy....
(historical legal code)
- Bhutanese legislation
Military of Bhutan
- Main article: Military of BhutanMilitary of BhutanThe branches of the armed forces of Bhutan are the Royal Bhutan Army, Royal Bodyguards, Militia, and Royal Bhutan Police. Being a landlocked country, Bhutan doesn't have a navy. Additionally, Bhutan does not have an air force, although the Royal Bhutan Army does have a very small air arm which...
- Command
- Commander-in-chiefCommander-in-ChiefA commander-in-chief is the commander of a nation's military forces or significant element of those forces. In the latter case, the force element may be defined as those forces within a particular region or those forces which are associated by function. As a practical term it refers to the military...
: King of Bhutan
- Commander-in-chief
- Forces
- Army of Bhutan
- NavyNavyA navy is the branch of a nation's armed forces principally designated for naval and amphibious warfare; namely, lake- or ocean-borne combat operations and related functions...
of Bhutan: None - Air Force of Bhutan
- Special forces of Bhutan
- Military history of BhutanMilitary history of BhutanThe military history of Bhutan begins with the Battle of Five Lamas in 1634, marking Bhutan's emergence as a nation under the secular and religious leadership of Shabdrung Ngawang Namgyal. Before Bhutan emerged as a separate nation, it remained on the periphery of Tibetan military and political...
- Military ranks of Bhutan
- Command
History of Bhutan
- Main article: History of BhutanHistory of BhutanBhutan's early history is steeped in mythology and remains obscure. It may have been inhabited as early as 2000 BC, but not much was known until the introduction of Tibetan Buddhism in the 9th century, when turmoil in Tibet forced many monks to flee to Bhutan. In the 12th century, the Drukpa...
, Timeline of the history of Bhutan, and Current events of Bhutan
Historical families and figures
- Dorji familyDorji familyThe Dorji family of Bhutan has been a prominent and powerful political family in the kingdom since the 19th century. The family has produced Chief Ministers, Prime Ministers, governors, and even monarchs...
- Ugyen DorjiUgyen DorjiRaja Ugyen Dorji was a member of the elite Dorji family and an influential Bhutanese politician. He served as the closest adviser to Ugyen Wangchuck, the hereditary Penlop of Trongsa and later First Druk Gyalpo...
- Jigme Palden DorjiJigme Palden DorjiJigme Palden Dorji was a Bhutanese politician and member of the Dorji family. By marriage, he was also a member of the House of Wangchuck....
- Ugyen Dorji
- House of WangchuckHouse of WangchuckThe House of Wangchuck has ruled Bhutan since it was reunified in 1907. Prior to reunification, the Wangchuck family had governed the district of Trongsa as descendants of Dungkar Choji. They eventually overpowered other regional lords and earned the favour of the British Empire...
- Jigme NamgyalJigme Namgyal (Bhutan)Jigme Namgyal of Bhutan is a forefather of the House of Wangchuck. He served as 51st Druk Desi of Bhutan , and held the hereditary post of 10th Penlop of Trongsa...
- Ugyen WangchuckUgyen WangchuckGongsa Ugyen Wangchuck was the first King of Bhutan from 1907 to 1926.He was born in 1862 to Jigme Namgyal, penlop of Trongsa and Ashi Pema Choki. He succeeded his father as Penlop of Trongsa...
- Jigme Namgyal
Historical government
- DzongpenDzongpenDzongpen is a Dzongkha term roughly translated as governor or dzong lord. Bhutanese dzongpens, prior to unification, controlled certain areas of the country, but now hold no administrative office...
- Provinces of BhutanProvinces of BhutanThe Provinces of Bhutan were historical regions of Bhutan headed by penlops and dzongpens . Provincial lords gained power as the increasingly dysfunctional dual system of government eventually collapsed amid civil war...
- Bumthang ProvinceBumthang ProvinceBumthang Province was one of the nine historical Provinces of Bhutan.Bumthang Province occupied lands in north-central Bhutan. It was administered from the Jakar Dzong in the town of Jakar...
- Daga ProvinceDaga ProvinceDaga Province was one of the nine historical Provinces of Bhutan.Daga Province occupied lands in west-central Bhutan. It was administered from the town of Daga. The ruling governor was known as the Penlop of Daga, or Dagab. Real power, however, rested in the hands of the Penlop of Paro, the...
- Kurmaed ProvinceKurmaed ProvinceKurmaed Province was one of the nine historical Provinces of Bhutan.Kurmaed Province occupied lands in southeastern Bhutan. It was administered jointly with Kurtoed Province...
- Kurtoed ProvinceKurtoed ProvinceKurtoed Province was one of the nine historical Provinces of Bhutan.Kurtoed Province occupied lands in northeastern Bhutan. It was administered together with Kurmaed Province...
- Paro ProvinceParo ProvinceParo Province was one of the nine historical Provinces of Bhutan.Paro Province occupied lands in western Bhutan, corresponding approximately to modern Paro District. It was administered from the Paro Dzong in the town of Paro...
- Punakha ProvincePunakha ProvincePunakha Province was one of the nine historical Provinces of Bhutan.Punakha Province occupied lands in western Bhutan, corresponding roughly to modern Punakha District. It was administered from the Punakha Dzong in the town of Punakha, and the ruling governor was known as the Penlop of Punakha, or...
- Thimphu ProvinceThimphu ProvinceThimphu Province was one of the nine historical Provinces of Bhutan.Thimphu Province occupied lands in western Bhutan, corresponding approximately to modern day Thimphu District...
- Trongsa ProvinceTrongsa ProvinceTrongsa Province was one of the nine historical Provinces of Bhutan.Trongsa Province occupied lands in central Bhutan corresponding somewhat to modern Trongsa District, although the power of the Trongsa Penlop extended far beyond his own realms, covering the entire east of Bhutan...
- Wangdue Phodrang ProvinceWangdue Phodrang ProvinceWangdue Phodrang Province was one of the nine historical Provinces of Bhutan.Wangdue Phodrang Province occupied lands in central Bhutan, corresponding roughly to modern day Wangdue Phodrang District...
- PenlopPenlopPenlop is a Dzongkha term roughly translated as governor. Bhutanese penlops, prior to unification, controlled certain districts of the country, but now hold no administrative office...
- Penlop of Trongsa
Culture of Bhutan
- Main article: Culture of BhutanCulture of BhutanCradled in the folds of the Himalayas, Bhutan has relied on its geographic isolation to protect itself from outside cultural influences. A sparsely populated country bordered by India to the south and China to the north, Bhutan has long maintained a policy of strict isolationism, both culturally...
- Architecture of BhutanArchitecture of BhutanBhutanese architecture consists of Dzong and everyday varieties. Dzongs in Bhutan were built as fortresses have served as religious and administrative centers since the 17th century. Secular lordly houses emerged as a distinct style in the late 19th century during a period of relative peace in Bhutan...
- Cuisine of BhutanCuisine of BhutanBhutanese cuisine employs a lot of red rice , buckwheat, and increasingly maize. The diet in the hills also includes chicken, yak meat, dried beef, pork, pork fat and mutton...
- Ethnic groups in BhutanEthnic groups in BhutanThere are many ethnic groups in Bhutan, and no one group constitutes a majority of the Bhutanese population. The Bhutanese population comprises four main ethnic groups, which themselves are not necessarily exclusive: the politically and culturally dominant Ngalop of western and northern Bhutan; the...
- Humor in Bhutan
- Media in Bhutan
- National symbols of BhutanNational symbols of BhutanThe national symbols of Bhutan include the national flag, national emblem, national anthem, and the mythical druk thunder dragon featured in all three. Other distinctive symbols of Bhutan and its dominant Ngalop culture include Dzongkha, the national language; the Bhutanese monarchy; and the...
- Coat of arms of Bhutan
- Flag of BhutanFlag of BhutanThe national flag of Bhutan is one of the national symbols of Bhutan. The flag is based upon the tradition of the Drukpa Lineage of Tibetan Buddhism and features Druk, the Thunder Dragon of Bhutanese mythology. The basic design of the flag by Mayum Choying Wangmo Dorji dates to 1947...
- National anthem of Bhutan
- Prostitution in BhutanProstitution in BhutanProstitution in Bhutan is illegal but on many of Bhutan's border towns it has people openly praticing in the sex trade....
- Public holidays in BhutanPublic holidays in BhutanPublic holidays in Bhutan consist of both national holidays and local festivals called tsechus. While national holidays are observed throughout Bhutan, tsechus are only observed in their areas. Bhutan uses its own calendar, a variant of the lunisolar Tibetan calendar. Because it is a lunisolar...
- TsechuTsechuTsechu are annual religious Bhutanese festivals held in each district or dzongkhag of Bhutan on the tenth day of a month of the lunar Tibetan calendar. The month depends on the place, but usually is around the time of October. Tsechus are religious festivals of Drukpa Buddhism...
s
- Tsechu
- Records of Bhutan
- Religion in BhutanReligion in BhutanApproximately two-thirds to three-quarters of the population practice Drukpa Kagyupa or Ningmapa Buddhism, both of which are disciplines of Mahayana Buddhism. Approximately one-quarter of the population is ethnic Nepalese and practice Hinduism...
- Buddhism in BhutanBuddhism in BhutanMahayana Buddhism is the state religion of Bhutan, and Buddhists comprise two-thirds to three-quarters of its population. Although originating in Tibetan Buddhism, the Buddhism practiced in Bhutan differs significantly in its rituals, liturgy, and monastic organization...
- Christianity in BhutanChristianity in BhutanThe French Internet site "Aide à l'Eglise en détresse" puts the figure of Christians in Bhutan at 12,255, with 1,000 Roman Catholics. 0.5% of the population with 74% Buddhists, 20.5% Hindus, 3.8% Animists and 1.2% uncategorized.-The 2008 Constitution:...
- Hinduism in BhutanHinduism in BhutanMahayana Buddhism is the state religion, and Hindus have been actively persecuted as a minority, including ethnic cleansing of 100,000 Hindu minorities who presently live as refugees in Nepal...
- Islam in BhutanIslam in BhutanAccording to adherents.com Muslims constitute over 5% of the population However the CIA factbook claims that Muslims are less than 1% in Bhutan. In 2009, the Pew Research Center estimated that 1% of the population, or 7,000 people, were Muslim....
- Judaism in Bhutan
- Sikhism in Bhutan
- Buddhism in Bhutan
- World Heritage Sites in Bhutan: None
Art in Bhutan
- Art in BhutanBhutanese artBhutanese art is similar to the art of Tibet. Both are based upon Vajrayana Buddhism, with its pantheon of divine beings.The major orders of Buddhism in Bhutan are Drukpa Kagyu and Nyingma. The former is a branch of the Kagyu School and is known for paintings documenting the lineage of Buddhist...
- Cinema of Bhutan
- Literature of Bhutan
- Music of BhutanMusic of BhutanThe music of Bhutan is an integral part of its culture and plays a leading role in transmitting social values. Traditional Bhutanese music includes a spectrum of subgenres, ranging from folk to religious song and music. Some genres of traditional Bhutanese music intertwine vocals, instrumentation,...
- Television in Bhutan
- Theatre in Bhutan
Languages in Bhutan
- Tibeto-Burman languagesTibeto-Burman languagesThe Tibeto-Burman languages are the non-Chinese members of the Sino-Tibetan language family, over 400 of which are spoken thoughout the highlands of southeast Asia, as well as lowland areas in Burma ....
- Bodish languagesBodish languagesThe Bodish languages, named for the Tibetan ethnonym bod, are the Tibetan languages in a broad linguistic sense, regardless of whether the speakers are considered ethnically Tibetan. Different scholars divide Bodish differently, but the alternate term 'Tibetan' generally excludes East Bodish...
- Tibetan languages (South Bodish, Central Bodish, West Bodish)
- Dzongkha
- Brokkat languageBrokkat languageThe Brokkat language is an endangered Southern Tibetan language spoken by about 300 people in the village of Dhur in Bumthang Valley of Bumthang District in central Bhutan. Brokkat is spoken by descendants of pastoral yakherd communities.- External links :*...
- Brokpa languageBrokpa languageThe Brokpa language is a Southern Tibetan language spoken by about 5,000 people mainly in Merak and Sakten Gewogs in the Sakten Valley of Trashigang District in eastern Bhutan...
- ChocangacakhaChocangacakhaChocangacakha is a Southern Tibetan language spoken by about 20,000 people in the Kurichu Valley of Lhuntse and Mongar Districts in eastern Bhutan...
- Khams Tibetan languageKhams Tibetan languageKhams Tibetan is the Tibetan language used by the majority of the people in the Kham region of eastern Tibet . It is one of the four main spoken languages of Tibetan, the other three being those of U-Tsang , Amdo and Western Tibetan...
- LakhaLakhaLakha is a Southern Tibetan language spoken by about 8,000 people in Wangdue Phodrang and Trongsa Districts in central Bhutan. Lakha is spoken by descendants of pastoral yakherd communities....
- East Bodish languagesEast Bodish languagesThe East Bodish languages are those Bodish languages not covered by the name Tibetan, such as those spoken by the Monpa. They include:*Dakpa*Dzala*Bumthang *Tawang*Black Mountain Monpa .The most divergent is Dakpa...
- Bumthang languageBumthang languageThe Bumthang language is an East Bodish language spoken by about 36,500 people in Bumthang and surrounding districts in central Bhutan...
- Chali languageChali languageThe Chali language is an East Bodish language spoken by about 8,200 people in Wangmakhar, Gorsum and Tormazhong villages in Mongar District in eastern Bhutan, mainly around Chhali Gewog on east bank of Kuri Chhu River...
- Dakpa languageDakpa languageThe Dakpa language is an East Bodish language spoken by about 1,000 people in northern Trashigang District in eastern Bhutan, mainly in Chaleng, Phongmey, Yobinang, Dangpholeng and Lengkhar near Radhi. Van Driem describes Dakpa as the most divergent of Bhutan's East Bodish languages...
- Dzala languageDzala languageThe Dzala language, also called Dzalakha or Dzalamat, is a member of the Tibeto-Burman language family spoken in eastern Bhutan, in Lhuntse and Trashiyangtse Districts.- External links :**...
- Kheng language
- Kurtöp languageKurtöp languageThe Kurtöp language is a member of the Tibeto-Burman language family spoken in the Kurtoe Gewog, Lhuntse District, Bhutan...
(Zhâke / Kurtoep-kha) - 'Olekha (Mönpa)'OlekhaOlekha, also called the Black Mountain Monpa language, is a Tibeto-Burman language spoken by about 1,000 people in the Black Mountains of the Wangdue Phodrang and Trongsa Districts in western Bhutan. The term 'Ole refers to a clan of speakers....
- NyenkhaNyenkhaNyenkha is an East Bodish language spoken by about 10,000 people in the eastern, northern, and western areas of the Black Mountains...
- Bumthang language
- GongdukGongduk languageGongduk or Gongdu is an endangered Tibeto-Burman language spoken by about 1,000 people in a few inaccessible villages located near the Kuri Chhu river in the Gongdu Gewog of Mongar District in eastern Bhutan...
- GurungGurung languageGurung is spoken by the Gurung people in two dialects with limited mutual intelligibility. Total number of all Gurung speakers in Nepal is 227,918...
- KirantKirantKirat or Kirati are indigenous ethnic groups of the Himalayas extending eastward from Nepal into India, Burma and beyond. They migrated to their present locations via Assam, Burma, Tibet and Yunnan in ancient times...
i (including CamlingCamling languageThe Camling or Chamling language is one of the Kiranti languages spoken by the Kiranti and Rai peoples of eastern Nepal. Alternate names include Chamling, Chamlinge Rai and Rodong...
and LimbuLimbu languageLimbu is a Tibeto-Burman language spoken in Nepal, Bhutan, Sikkim, Kashmir and Darjeeling district, West Bengal, India, by the Limbu community. Virtually all Limbus are bilingual in Nepali....
) - LepchaLepcha languageLepcha language, or Róng language , is a Himalayish language spoken by the Lepcha people in Sikkim and parts of West Bengal, Nepal and Bhutan.-Population:...
- LhokpuLhokpu languageLhokpu, also Lhobikha or Taba-Damey-Bikha, is one of the autochthonous languages of Bhutan spoken by the Lhop people. It is spoken in southwestern Bhutan along the border of Samtse and Chukha Districts. Van Driem leaves it unclassified as a separate branch within the Tibeto-Burman language...
- Nepal BhasaNepal BhasaNepal Bhasa is one of the major languages of Nepal, and is also spoken in India, particularly in Sikkim where it is one of the 11 official languages. Nepal Bhasa is the mother tongue of about 3% of the people in Nepal . It is spoken mainly by the Newars, who chiefly inhabit the towns of the...
- TamangTamang languageTamang is a term used to collectively refer to a dialect cluster spoken in parts of Nepal and Sikkim. It comprises Eastern Tamang, Northwestern Tamang, Southwestern Tamang, Eastern Gorkha Tamang, and Western Tamang...
- Tshangla language(Sharchop-kha)
- Tibetan languages (South Bodish, Central Bodish, West Bodish)
- Bodish languages
- Indo-Aryan languagesIndo-Aryan languagesThe Indo-Aryan languages constitutes a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages, itself a branch of the Indo-European language family...
- Nepali languageNepali languageNepali or Nepalese is a language in the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European language family.It is the official language and de facto lingua franca of Nepal and is also spoken in Bhutan, parts of India and parts of Myanmar...
- Nepali language
Sports in Bhutan
- Main article: Sports in BhutanSports in BhutanSports in Bhutan comprise both traditional Bhutanese and modern international games. Archery is the national Sport in Bhutan, and competitions are held regularly in most villages. Other traditional Bhutanese sports include khuru, soksom, pundo, and digor....
- Football in BhutanFootball in BhutanFootball is the most popular sport in Bhutan. The sport of football in Bhutan is run by the Bhutan Football Federation. The association administers the Bhutan national football team as well as the A-Division....
- Bhutan national football teamBhutan national football teamThe Bhutan national football team is the national team of Bhutan and is controlled by the Bhutan Football Federation.- History :While a Bhutanese National football team has existed since the 1970s, it was officially founded in 1983 and joined FIFA in 2000....
- Bhutan national football team
- Cricket in Bhutan
- Bhutan national cricket team
- Bhutan at the OlympicsBhutan at the OlympicsFor each Olympic Summer Games since 1984, Bhutan has fielded male and female archers. Archery is the national sport of Bhutan. They have never competed in the Winter Games nor the other events of the Summer Games; they also have never won an Olympic Medal...
- Football in Bhutan
Economy and infrastructure of Bhutan
- Main article: Economy of BhutanEconomy of BhutanThe economy of Bhutan, one of the world's smallest and least developed, is based on agriculture and forestry, which provide the main livelihood for more than 60% of the population. Agriculture consists largely of subsistence farming and animal husbandry. Rugged mountains dominate the terrain and...
- Economic rank, by nominal GDP (2007): 162nd (one hundred and sixty second)
- Agriculture in BhutanAgriculture in BhutanAgriculture in Bhutan has a dominant role in the economy of the country. In 2000, agriculture accounted for 35.9% of GDP of the nation. The share of the agricultural sector in GDP declined from approximately 55% in 1985 to 33% in 2003. Despite this, agriculture remains the primary source of...
- Banking in BhutanBanking in BhutanBanking in Bhutan is a fledgling industry that has grown slowly as the country has pursued modernization. Since its establishment in 1982, the Royal Monetary Authority, headquartered in Thimphu, has served as the central bank of Bhutan...
- Royal Monetary Authority of BhutanRoyal Monetary Authority of BhutanThe Royal Monetary Authority of Bhutan is the central bank of Bhutan and is a member of the Asian Clearing Union. It is also the minting authority for the Bhutanese ngultrum. The Royal Monetary Authority of Bhutan was established under the Royal Monetary Authority of Bhutan Act of 1982...
(central bank)- Currency of BhutanCurrencyIn economics, currency refers to a generally accepted medium of exchange. These are usually the coins and banknotes of a particular government, which comprise the physical aspects of a nation's money supply...
: NgultrumBhutanese ngultrumThe ngultrum has been the currency of Bhutan since 1974. It is subdivided into 100 chhertum .-History:In 1974, the ngultrum was introduced, replacing the rupee at par...
- ISO 4217ISO 4217ISO 4217 is a standard published by the International Standards Organization, which delineates currency designators, country codes , and references to minor units in three tables:* Table A.1 – Current currency & funds code list...
: BTN
- ISO 4217
- Currency of Bhutan
- Royal Monetary Authority of Bhutan
- Communications in BhutanCommunications in Bhutan* Telephones - main lines in use in Bhutan: 29,900 * Telephones - mobile cellular: 149,400 * Telephone system:** general assessment: urban towns and district headquarters have telecommunications services...
- Internet in Bhutan
- Companies of Bhutan
- Economic history of Bhutan
- Energy in BhutanEnergy in BhutanEnergy in Bhutan has been a primary focus of development in the kingdom under its Five-Year Plans. In cooperation with India, Bhutan has undertaken several hydroelectric projects whose output is traded between the countries...
- Energy policy of Bhutan
- Oil industry in Bhutan
- Health care in BhutanHealth in BhutanHealth in Bhutan is one of the government's highest priorities in its scheme of development and modernization. Health and related issues are overseen by the Ministry of Health, itself represented on the executive Lhengye Zhungtshog by the Minister of Health...
- Mining in BhutanMining in BhutanMining of industrial minerals was insignificant to Bhutan’s economy except for the production of ferrosilicon. The country’s rugged terrain provides sites to harvest hydropower, which has driven rapid growth in the transport and construction sectors, including the startup of a number of local...
- Royal Securities Exchange of BhutanRoyal Securities Exchange of BhutanThe Royal Securities Exchange of Bhutan is the only stock exchange in Bhutan. It is one of the worlds smallest stock exchanges, with a market capitalization of around 171 million dollars and 19 listed companies as of 2008. It is located in the Royal Insurance Corporation of Bhutan building in...
- Tourism in BhutanTourism in BhutanTourism in Bhutan began in 1974, when the Government of Bhutan, in an effort to raise revenue and to promote the country's unique culture and traditions to the outside world, opened its isolated country to foreigners. In 1974, 287 tourists visited Bhutan. Since then the number of tourists visiting...
- Transport in BhutanTransport in BhutanTransport in Bhutan comprises approximately of roads and two airports, Yongphulla Airport and Paro Airport, the latter of which serves international flights...
- Airports in Bhutan
- Rail transport in Bhutan
- Roads in Bhutan
- Lateral RoadLateral RoadBhutan's Lateral Road is its primary east-west corridor, connecting Phuentsholing in the southwest to Trashigang in the east. In between, the Lateral Road runs directly through Wangdue Phodrang, Trongsa, and other population centers...
- Lateral Road
- Water supply and sanitation in Bhutan
See also
- Index of Bhutan-related articles
- List of Bhutan-related topics
- List of international rankings
- Member state of the United Nations
- Outline of AsiaOutline of AsiaThe following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Asia:Asia – world's largest and most populous continent, located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres...
- Outline of geographyOutline of geographyThe following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to geography:Geography – science that studies the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth.- Geography is :...
External links
- Bhutan Links Page - at the National Library of BhutanNational Library of BhutanThe National Library of Bhutan , Thimphu, Bhutan was established in 1967 for the purpose of "preservation and promotion of the rich cultural and religious heritage" of Bhutan...
. - Government of Bhutan portal
- Tourism Council of Bhutan (Official)

