
Papyrus 49
Encyclopedia
Papyrus 49 designated by  49, is an early copy of the New Testament
49, is an early copy of the New Testament
in Greek
. It is a papyrus
manuscript
of the Epistle to the Ephesians
, surviving in a fragmentary condition. The manuscript has been palaeographically
assigned to the 3rd century. It was probably a part of the same manuscript as Papyrus 65. It came from Egypt and was purchased for the Yale University Library
. Textually it is close to the Codex Sinaiticus
and Codex Vaticanus
. The text of the manuscript has been published several times.
The manuscript has survived in a fragmentary condition and contains the texts of Ephesians 4:16-29; 4:31-5:13. According to Kurt Aland
, it is one of three early manuscripts with the text of the Epistle to the Ephesians
.
The text is written in one column per page of 29 lines, with 38 letters per line (average). It has no breathings (spiritus asper, spiritus lenis) nor accents. The double point (:) is the only mark of punctuation. The letters are slightly inclined to the right; the writing shows the influence of cursive handwriting. It was written by a professional scribe. The nomina sacra
are written in an abbreviated way.
The Greek text of this codex is a representative of the Alexandrian text-type
. Aland
ascribed it as “at least Normal text”, and placed it in Category I. Bruce M. Metzger identifies it as Alexandrian text. According to Philip Comfort and David Barrett the manuscript shows a strong agreement with Codex Sinaiticus
and Codex Vaticanus
(in 14 out of 16 textual variants).
According to Comfort, 49 and
49 and  65 came from the same manuscript. Both manuscripts have the same measurements, and the same number of lines per page. Both were written by a documentary hand, both manifest the same formation of certain letters, such as titled lambda
65 came from the same manuscript. Both manuscripts have the same measurements, and the same number of lines per page. Both were written by a documentary hand, both manifest the same formation of certain letters, such as titled lambda
, titled sigma
, extended iota
, and toiled ypsilon. The nomina sacra
and abbreviations are written in the same rather unusual way. Bradford Welles remarks that "there is not a single case of difference in the letter shapes in the two papyri". Neither use ligatures. The only difference is in the number of letters per line: 65 has more letters per line (42). The same situation exists in Papyrus 75
65 has more letters per line (42). The same situation exists in Papyrus 75
. The scribe of 75 appears to have realized that he was running out of room in his codex and added three letters in each line and even added extra lines. The manuscript may be one of the earliest manuscripts to display a complete Pauline codex, along with Papyrus 13
75 appears to have realized that he was running out of room in his codex and added three letters in each line and even added extra lines. The manuscript may be one of the earliest manuscripts to display a complete Pauline codex, along with Papyrus 13
, Papyrus 15/Papyrus 16, Papyrus 30, Papyrus 46, and Papyrus 92.
Textual variants
In Ephesians 4:23, 49 has the rare textual reading (in spirit) instead of the reading (spirit). The reading of the codex is supported by Codex Vaticanus, minuscule 33
49 has the rare textual reading (in spirit) instead of the reading (spirit). The reading of the codex is supported by Codex Vaticanus, minuscule 33
, 1175, 1739
, 1881 and several other manuscripts.
In Ephesians 4:28, it has the unusual textual reading ταις χερσιν το αγαθον, supported only by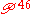 , second corrector of the Codex Sinaiticus, Codex Vaticanus, Old-Latin a, and vgst. The rest of the manuscripts have the readings: το αγαθον (Porphyrianus
, second corrector of the Codex Sinaiticus, Codex Vaticanus, Old-Latin a, and vgst. The rest of the manuscripts have the readings: το αγαθον (Porphyrianus
, minuscule 6
, 33, 1739, 1881); το αγαθον ταις χερσιν (Angelicus
, Athous Lavrensis, 323
, 326
, 614
, 630
, 945); το αγαθον ταις ιδιαις χερσιν (Codex Mosquensis I
, 2495); ταις ιδιαις χερσιν το αγαθον (Codex Sinaiticus, Alexandrinus, Codex Bezae, Augiensis
, Boernerianus
, 81
, 104
, 365
, 1175, 1241, 2464, vgcl).
In Ephesians 5:4, it has the textual reading και (and), supported by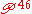 , first corrector of the Codex Sinaiticus (א1), Codex Vaticanus, second corrector of the Codex Bezae, manuscripts of the Byzantine textual tradition
, first corrector of the Codex Sinaiticus (א1), Codex Vaticanus, second corrector of the Codex Bezae, manuscripts of the Byzantine textual tradition
, Peshitta
, Coptic manuscripts in Bohairic dialect; the other reading η (or) is supported by Codex Sinaiticus, Alexandrinus, Bezae, Augiensis, Boernerianus, Porphyrianus, minuscule 81, 104, 326, 365, 1175, 1241, 1739, 2464, Old-Latin manuscripts, syrh, and Coptic manuscripts in Sahidic dialect.
In Ephesians 5:5, it has the textual reading ο εστιν (who is), supported by the manuscripts: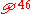 , Sinaiticus, Vaticanus, Augiensis, Boernerianus, Athous Lavrensis, 33, 365, 1175, 1739, 1881, 2464, Old-Latin, Peshitta, Coptic manuscripts (Sahidic and Bohairic); the other reading ος εστιν (who is) is supported by Codex Alexandrinus, Codex Bezae, and manuscripts of the Byzantine textual tradition.
, Sinaiticus, Vaticanus, Augiensis, Boernerianus, Athous Lavrensis, 33, 365, 1175, 1739, 1881, 2464, Old-Latin, Peshitta, Coptic manuscripts (Sahidic and Bohairic); the other reading ος εστιν (who is) is supported by Codex Alexandrinus, Codex Bezae, and manuscripts of the Byzantine textual tradition.
In Ephesians 5:9, it has the textual reading φωτος (light), supported by Codex Sinaiticus, Alexandrinus, Vaticanus, Bezae, Augiensis, Boernerianus, Porphyrianus, minuscule 6, 33, 81, 629, 1175c, 1739, 1881, 2464, some Old-Latin manuscripts, Peshitta and Coptic manuscripts. The reading πνευματος (spirit) is found in the manuscripts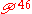 , D2, Ψ, majority of the Byzantine manuscripts and syrh.
, D2, Ψ, majority of the Byzantine manuscripts and syrh.
grounds by the Institute for New Testament Textual Research
(INTF). It was probably written in Egypt, but it cannot be assigned to any particular locality.
The manuscript was purchased in Cairo
for Yale University
in February 1931. Its provenance prior to Cairo is not known. Currently it is housed at the Yale University Library
(P. Yale 415) in New Haven.
The text of the codex was published by William Hatch
and Bradford Welles in 1958 (editio princeps). Kurt Aland catalogued the manuscript on the list of the New Testament papyri under the number 49.
Susan Stephens gave a new and complete transcription of the codex in 1985. Comfort and Barrett again gave a new reconstruction in 1999.
Vittorio Bartoletti (1920-1990) was the first to note that Papyrus 49 and Papyrus 65 were produced by the same scribe. This conclusion was confirmed by Bradford Welles, Comfort and Barrett, and other palaeographers. They are still catalogued as separate manuscripts on the INTF's list.
[verso (Eph 4:29-5:13)]
 49, is an early copy of the New Testament
49, is an early copy of the New TestamentNew Testament
The New Testament is the second major division of the Christian biblical canon, the first such division being the much longer Old Testament....
in Greek
Greek language
Greek is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages. Native to the southern Balkans, it has the longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning 34 centuries of written records. Its writing system has been the Greek alphabet for the majority of its history;...
. It is a papyrus
Papyrus
Papyrus is a thick paper-like material produced from the pith of the papyrus plant, Cyperus papyrus, a wetland sedge that was once abundant in the Nile Delta of Egypt....
manuscript
Manuscript
A manuscript or handwrite is written information that has been manually created by someone or some people, such as a hand-written letter, as opposed to being printed or reproduced some other way...
of the Epistle to the Ephesians
Epistle to the Ephesians
The Epistle of Paul to the Ephesians, often shortened to Ephesians, is the tenth book of the New Testament. Its authorship has traditionally been credited to Paul, but it is considered by some scholars to be "deutero-Pauline," that is, written in Paul's name by a later author strongly influenced by...
, surviving in a fragmentary condition. The manuscript has been palaeographically
Palaeography
Palaeography, also spelt paleography is the study of ancient writing. Included in the discipline is the practice of deciphering, reading, and dating historical manuscripts, and the cultural context of writing, including the methods with which writing and books were produced, and the history of...
assigned to the 3rd century. It was probably a part of the same manuscript as Papyrus 65. It came from Egypt and was purchased for the Yale University Library
Yale University Library
Yale University Library is the library system of Yale University in New Haven, Connecticut, United States. It is the second-largest academic library in the North America, with approximately 12.5 million volumes housed in 20 buildings on campus...
. Textually it is close to the Codex Sinaiticus
Codex Sinaiticus
Codex Sinaiticus is one of the four great uncial codices, an ancient, handwritten copy of the Greek Bible. It is an Alexandrian text-type manuscript written in the 4th century in uncial letters on parchment. Current scholarship considers the Codex Sinaiticus to be one of the best Greek texts of...
and Codex Vaticanus
Codex Vaticanus
The Codex Vaticanus , is one of the oldest extant manuscripts of the Greek Bible , one of the four great uncial codices. The Codex is named for the residence in the Vatican Library, where it has been stored since at least the 15th century...
. The text of the manuscript has been published several times.
Description
The original size of the leaf was 18 centimetres in height by 25 centimetres in width. The leaf is damaged at the top, and six lines of its text have been lost. At the present time the leaf measures 20.3 cm by 13.3 cm. The lower and outer margins are 3 centimetres wide; the upper and inner margins were lost.The manuscript has survived in a fragmentary condition and contains the texts of Ephesians 4:16-29; 4:31-5:13. According to Kurt Aland
Kurt Aland
Kurt Aland was a German Theologian and Professor of New Testament Research and Church History. He founded the Institut für neutestamentliche Textforschung in Münster and served as its first director for many years...
, it is one of three early manuscripts with the text of the Epistle to the Ephesians
Epistle to the Ephesians
The Epistle of Paul to the Ephesians, often shortened to Ephesians, is the tenth book of the New Testament. Its authorship has traditionally been credited to Paul, but it is considered by some scholars to be "deutero-Pauline," that is, written in Paul's name by a later author strongly influenced by...
.
The text is written in one column per page of 29 lines, with 38 letters per line (average). It has no breathings (spiritus asper, spiritus lenis) nor accents. The double point (:) is the only mark of punctuation. The letters are slightly inclined to the right; the writing shows the influence of cursive handwriting. It was written by a professional scribe. The nomina sacra
Nomina sacra
Nomina sacra means "sacred names" in Latin, and can be used to refer to traditions of abbreviated writing of several frequently occurring divine names or titles in early Greek language Holy Scripture...
are written in an abbreviated way.
The Greek text of this codex is a representative of the Alexandrian text-type
Alexandrian text-type
The Alexandrian text-type , associated with Alexandria, is one of several text-types used in New Testament textual criticism to describe and group the textual character of biblical manuscripts...
. Aland
Kurt Aland
Kurt Aland was a German Theologian and Professor of New Testament Research and Church History. He founded the Institut für neutestamentliche Textforschung in Münster and served as its first director for many years...
ascribed it as “at least Normal text”, and placed it in Category I. Bruce M. Metzger identifies it as Alexandrian text. According to Philip Comfort and David Barrett the manuscript shows a strong agreement with Codex Sinaiticus
Codex Sinaiticus
Codex Sinaiticus is one of the four great uncial codices, an ancient, handwritten copy of the Greek Bible. It is an Alexandrian text-type manuscript written in the 4th century in uncial letters on parchment. Current scholarship considers the Codex Sinaiticus to be one of the best Greek texts of...
and Codex Vaticanus
Codex Vaticanus
The Codex Vaticanus , is one of the oldest extant manuscripts of the Greek Bible , one of the four great uncial codices. The Codex is named for the residence in the Vatican Library, where it has been stored since at least the 15th century...
(in 14 out of 16 textual variants).
According to Comfort,
 49 and
49 and  65 came from the same manuscript. Both manuscripts have the same measurements, and the same number of lines per page. Both were written by a documentary hand, both manifest the same formation of certain letters, such as titled lambda
65 came from the same manuscript. Both manuscripts have the same measurements, and the same number of lines per page. Both were written by a documentary hand, both manifest the same formation of certain letters, such as titled lambdaLambda
Lambda is the 11th letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals lambda has a value of 30. Lambda is related to the Phoenician letter Lamed . Letters in other alphabets that stemmed from lambda include the Roman L and the Cyrillic letter El...
, titled sigma
Sigma
Sigma is the eighteenth letter of the Greek alphabet, and carries the 'S' sound. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 200. When used at the end of a word, and the word is not all upper case, the final form is used, e.g...
, extended iota
Iota
Iota is the ninth letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 10. It was derived from the Phoenician letter Yodh . Letters that arose from this letter include the Roman I and J and the Cyrillic І , Yi , Je , and iotified letters .Iota represents...
, and toiled ypsilon. The nomina sacra
Nomina sacra
Nomina sacra means "sacred names" in Latin, and can be used to refer to traditions of abbreviated writing of several frequently occurring divine names or titles in early Greek language Holy Scripture...
and abbreviations are written in the same rather unusual way. Bradford Welles remarks that "there is not a single case of difference in the letter shapes in the two papyri". Neither use ligatures. The only difference is in the number of letters per line:
 65 has more letters per line (42). The same situation exists in Papyrus 75
65 has more letters per line (42). The same situation exists in Papyrus 75Papyrus 75
Papyrus 75 is an early Greek New Testament papyrus.- Description :Originally '[it] contained about 144 pages ... of which 102 have survived, either in whole or in part.' It 'contains about half the text of ... two Gospels' – Luke and John in Greek...
. The scribe of
 75 appears to have realized that he was running out of room in his codex and added three letters in each line and even added extra lines. The manuscript may be one of the earliest manuscripts to display a complete Pauline codex, along with Papyrus 13
75 appears to have realized that he was running out of room in his codex and added three letters in each line and even added extra lines. The manuscript may be one of the earliest manuscripts to display a complete Pauline codex, along with Papyrus 13Papyrus 13
Papyrus 13, designated by siglum in the Gregory-Aland numbering, is a fragmented manuscript of the New Testament in Greek. It was copied on papyrus in the 3rd century at approximately 225-250 CE.- Description :...
, Papyrus 15/Papyrus 16, Papyrus 30, Papyrus 46, and Papyrus 92.
Textual variants
In Ephesians 4:23,
 49 has the rare textual reading (in spirit) instead of the reading (spirit). The reading of the codex is supported by Codex Vaticanus, minuscule 33
49 has the rare textual reading (in spirit) instead of the reading (spirit). The reading of the codex is supported by Codex Vaticanus, minuscule 33Minuscule 33
Minuscule 33 , δ 48 , formerly it was called Codex Colbertinus 2844, is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament on parchment, dated palaeographically to the 9th century. The manuscript is lacunose. It has marginalia...
, 1175, 1739
Minuscule 1739
Minuscule 1739 ; α 78 per is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on 102 parchment leaves . It is dated paleographically to the 10th century.- Description :...
, 1881 and several other manuscripts.
In Ephesians 4:28, it has the unusual textual reading ταις χερσιν το αγαθον, supported only by
 , second corrector of the Codex Sinaiticus, Codex Vaticanus, Old-Latin a, and vgst. The rest of the manuscripts have the readings: το αγαθον (Porphyrianus
, second corrector of the Codex Sinaiticus, Codex Vaticanus, Old-Latin a, and vgst. The rest of the manuscripts have the readings: το αγαθον (PorphyrianusCodex Porphyrianus
Codex Porphyrianus designated by Papr or 025 , α 3 , is a Greek uncial manuscript of the Acts of Apostles, Pauline epistles, and General epistles, with some lacunae, dated paleographically to the 9th century. It is one of a few uncial manuscripts that include the Book of Revelation.It was...
, minuscule 6
Minuscule 6
Minuscule 6 , δ 356 . It is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on 235 parchment leaves , dated palaeographically to the 13th century. The manuscript has complex contents and full marginalia...
, 33, 1739, 1881); το αγαθον ταις χερσιν (Angelicus
Codex Angelicus
Codex Angelicus designated by Lap or 020 , α 5 , is a Greek uncial manuscript of the New Testament. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 9th century...
, Athous Lavrensis, 323
Minuscule 323
Minuscule 323 , α 157 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 12th century.Formerly it was designated by 29a and 35p.- Description :...
, 326
Minuscule 326
Minuscule 326 , α 257 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment. Paleographically it has been assigned to the 10th century.Formerly it was labelled by 33a and 39p ....
, 614
Minuscule 614
Minuscule 614 , α 364 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 13th century. The manuscript is lacunose...
, 630
Minuscule 630
Minuscule 630 , α 461 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on paper. It is known as Codex Ottobonianus. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 12th or 13th century. The manuscript is lacunose...
, 945); το αγαθον ταις ιδιαις χερσιν (Codex Mosquensis I
Codex Mosquensis I
Codex Mosquensis I designated by Kap or 018 , Απρ1 , is a Greek uncial manuscript of New Testament, palaeographically it has been assigned to the 9th century...
, 2495); ταις ιδιαις χερσιν το αγαθον (Codex Sinaiticus, Alexandrinus, Codex Bezae, Augiensis
Codex Augiensis
Codex Augiensis, designated by Fp or 010 , α 1029 is a 9th century diglot uncial manuscript of the Pauline Epistles in double parallel columns of Greek and Latin on the same page.- Description :...
, Boernerianus
Codex Boernerianus
Codex Boernerianus, designated by Gp or 012 , α 1028 , is a small New Testament codex, measuring 25 x 18 cm, written in one column per page, 20 lines per page. Dated paleographically to the 9th century. The name of the codex derives from Boerner, to whom it once belonged...
, 81
Minuscule 81
Minuscule 81 , or α162 is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on a parchment. It is dated by a colophon to the year 1044. Formerly it was labelled by 61a and 61p . The manuscript is lacunose...
, 104
Minuscule 104
Minuscule 104 , α 103 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment leaves. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 12th century.Formerly it was labelled by 25a, 31p, and 7r....
, 365
Minuscule 365
Minuscule 365 , δ 367 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament with some parts of the Old Testament, on parchment. Paleographically it has been assigned to the 12th century.It has marginalia....
, 1175, 1241, 2464, vgcl).
In Ephesians 5:4, it has the textual reading και (and), supported by
 , first corrector of the Codex Sinaiticus (א1), Codex Vaticanus, second corrector of the Codex Bezae, manuscripts of the Byzantine textual tradition
, first corrector of the Codex Sinaiticus (א1), Codex Vaticanus, second corrector of the Codex Bezae, manuscripts of the Byzantine textual traditionByzantine text-type
The Byzantine text-type is one of several text-types used in textual criticism to describe the textual character of Greek New Testament manuscripts. It is the form found in the largest number of surviving manuscripts, though not in the oldest...
, Peshitta
Peshitta
The Peshitta is the standard version of the Bible for churches in the Syriac tradition.The Old Testament of the Peshitta was translated into Syriac from the Hebrew, probably in the 2nd century AD...
, Coptic manuscripts in Bohairic dialect; the other reading η (or) is supported by Codex Sinaiticus, Alexandrinus, Bezae, Augiensis, Boernerianus, Porphyrianus, minuscule 81, 104, 326, 365, 1175, 1241, 1739, 2464, Old-Latin manuscripts, syrh, and Coptic manuscripts in Sahidic dialect.
In Ephesians 5:5, it has the textual reading ο εστιν (who is), supported by the manuscripts:
 , Sinaiticus, Vaticanus, Augiensis, Boernerianus, Athous Lavrensis, 33, 365, 1175, 1739, 1881, 2464, Old-Latin, Peshitta, Coptic manuscripts (Sahidic and Bohairic); the other reading ος εστιν (who is) is supported by Codex Alexandrinus, Codex Bezae, and manuscripts of the Byzantine textual tradition.
, Sinaiticus, Vaticanus, Augiensis, Boernerianus, Athous Lavrensis, 33, 365, 1175, 1739, 1881, 2464, Old-Latin, Peshitta, Coptic manuscripts (Sahidic and Bohairic); the other reading ος εστιν (who is) is supported by Codex Alexandrinus, Codex Bezae, and manuscripts of the Byzantine textual tradition.In Ephesians 5:9, it has the textual reading φωτος (light), supported by Codex Sinaiticus, Alexandrinus, Vaticanus, Bezae, Augiensis, Boernerianus, Porphyrianus, minuscule 6, 33, 81, 629, 1175c, 1739, 1881, 2464, some Old-Latin manuscripts, Peshitta and Coptic manuscripts. The reading πνευματος (spirit) is found in the manuscripts
 , D2, Ψ, majority of the Byzantine manuscripts and syrh.
, D2, Ψ, majority of the Byzantine manuscripts and syrh.History
The handwriting of the manuscript displays many third-century features. Comfort dated the manuscript to the middle of the third century. It is presently assigned to the third century on palaeographicPalaeography
Palaeography, also spelt paleography is the study of ancient writing. Included in the discipline is the practice of deciphering, reading, and dating historical manuscripts, and the cultural context of writing, including the methods with which writing and books were produced, and the history of...
grounds by the Institute for New Testament Textual Research
Institute for New Testament Textual Research
The Institute for New Testament Textual Research at the University of Münster, Westphalia, Germany, is an institute for the investigation of the text of the New Testament. The INTF was founded in Münster in 1959 by Professor Kurt Aland , the first director of the Institute...
(INTF). It was probably written in Egypt, but it cannot be assigned to any particular locality.
The manuscript was purchased in Cairo
Cairo
Cairo , is the capital of Egypt and the largest city in the Arab world and Africa, and the 16th largest metropolitan area in the world. Nicknamed "The City of a Thousand Minarets" for its preponderance of Islamic architecture, Cairo has long been a centre of the region's political and cultural life...
for Yale University
Yale University
Yale University is a private, Ivy League university located in New Haven, Connecticut, United States. Founded in 1701 in the Colony of Connecticut, the university is the third-oldest institution of higher education in the United States...
in February 1931. Its provenance prior to Cairo is not known. Currently it is housed at the Yale University Library
Yale University Library
Yale University Library is the library system of Yale University in New Haven, Connecticut, United States. It is the second-largest academic library in the North America, with approximately 12.5 million volumes housed in 20 buildings on campus...
(P. Yale 415) in New Haven.
The text of the codex was published by William Hatch
William Hatch
William Henry Paine Hatch, Ph.D., D.D. was an American theologian, born at Camden, N. J. He attended Harvard, graduating in 1898 . Afterward, he graduated at the Episcopal Theological Seminary in Cambridge, Massachusetts, and from the General Theological Seminary in New York City...
and Bradford Welles in 1958 (editio princeps). Kurt Aland catalogued the manuscript on the list of the New Testament papyri under the number 49.
Susan Stephens gave a new and complete transcription of the codex in 1985. Comfort and Barrett again gave a new reconstruction in 1999.
Vittorio Bartoletti (1920-1990) was the first to note that Papyrus 49 and Papyrus 65 were produced by the same scribe. This conclusion was confirmed by Bradford Welles, Comfort and Barrett, and other palaeographers. They are still catalogued as separate manuscripts on the INTF's list.
Text
[recto (Eph 4:16-25)]- [16] – [οικοδομην εαυτου] ε̣ν̣ αγαπ[η [17] το]υ̣το̣ ο̣υ̣ν λ̣[εγω και
- μαρτυρομ]α̣ι εν κ̅ω̅ μη̣κετι υ[μας π]ε̣ρ̣[ι]π̣ατ[ειν καθ]
- [ως και τα] ε̣θνη ·περιπατει εν̣ [ματαιοτ]η̣τ̣ι του
- [νοος] αυτων [18] εσκοτωμενοι τη ·δ[ια]νο̣ι̣α οντες
- [απηλ]λοτριωμ̣ενοι της ζωης του θ̅υ̅ δ̣ια την αγνοι
- [αν τη]ν̣ ουσαν εν ·αυτοις δια τ̣η̣[ν πωρ]ω̣σιν της
- [καρδια]ς αυ̣των̣ [19] οιτινες απηλ[γηκοτες] ε̣αυτους
- [παρεδ]ω̣καν τη̣ ·α̣σελγια ε̣ι[ς] εργα̣[σιαν] α̣καθαρ
- [σιας πασης εν πλεο]ν̣ε̣ξ̣ια [20] υμ̣[εις δε] ο̣υ̣χ̣ ουτως
- [εμαθετε τον χ̅̅ν̅ [21] ει γε] α̣υτον ηκ̣[ουσατ]ε̣ και εν αυτω
- [εδιδαχθητε καθως εστι]ν̣ α̣λ̣η̣θ̣ε̣ι̣α̣ ε̣ν̣ [τω] ι̣̅̅υ̅ [22] [α]π̣οθεσθε
- [υμας κατα τη]ν̣ προ[τεραν α]ναστροφη̣[ν το]ν̣ παλαιον αν
- [θρωπον τον] φ̣θ̣ε̣ι̣ρομενον κατα τα[ς ε]π̣ιθυμιας της
- [απατης [23] ανα]νεο̣υσθαι δε εν τω π̅ν̣̅[ι̅ το]υ νοος ·υμων
- [24] [και ενδυσασ]θ̣α̣ι̣ τ̣ον καινον ανθ̣[ρωπο]ν̣ τον κατα
- [θ̅ν̅ κτισ]θ̣εντ̣α εν δικαιοσυνη̣ τ̣ι̣ της αλη
- [θειας [25] δι]ο̣ αποθ̣εμενοι το ψευδ̣[ος λαλει]τ̣[α]ι̣ ·αληθειαν
- [εκαστος μ]ε̣τ̣α του̣ πλησιον αυτ̣[ου οτι εσμεν] α̣λ̣λ̣η̣λ̣ων
- [μελη [26] ο]ρ̣γιζ̣ε̣σθαι και μη̣ αμαρ̣τ̣αν[ετ]α̣ι ο ηλιος
- [μη επ]ι̣δυετω επι παρο̣[ργ]ι̣σμω ·υμω̣ν̣ [27] μηδε
- [διδοτε τ]οπον τω διαβολ̣ω̣ [28] ο κλεπτων μηκετει
- [κλεπτετ]ω μαλλον δ[ε κ]ο̣πιατω εργ̣[α]ζ̣ομενος
- [ταις χερσι]ν̣ το ·αγαθον ινα εχη με̣[τα]δ̣ιδο̣να̣ι
- [τω χρεια]ν̣ ·εχοντι [29] πας λογος σαπρος [ε]κ̣ του στομα
- τος υμων
[verso (Eph 4:29-5:13)]
- ρισατο ημ[ιν [1] γιν]ε[σθ]ε̣ ουν μιμηται του θ̅υ̅ ω̣ς̣ τ̣ε̣[κνα] αγα
- πητα [2] κα̣[ι] π̣ε̣[ρι]πατειται εν αγαπη καθως κ[αι]
- ο χ̅ς̅ ηγαπησε[ν] ·[ημ]ας και παρεδωκε[ν] εαυτον [υπερ]
- ημων πρ̣ο[σφορα]ν̣ κ̣α̣ι θυσιαν τω θ̅ω̅ ε̣[ι]ς̣ οσμη[ν ·ευω]
- διας [3] πορν[εια] [δε] κ̣αι ακαθαρσια πασα̣ η ·π̣λ̣ε[ο
- ν]εξεια μη̣δ̣[ε ονο]μ̣αζεσθω εν υμιν̣ [κ]α̣θως π[ρεπει] ·
- αγιοις [4] και εσ̣[χροτ]ης και μ̣ω̣[ρολογια η ευτραπελια α]
- ουκ α̣νηκεν̣ α̣λ̣λ̣[α μ]α̣λ̣[λον ευχαριστια [5] τουτο γαρ]
- ειστε γιν̣ωσκ̣[ο]ντ̣[ες] οτι π̣α̣[ς πορνος η ακ]α[θαρτος]
- η πλεονεκτη̣ς̣ ο̣ [εσ]τ̣ιν ειδωλο̣λ̣α̣τ̣ρ̣η̣ς̣ ου̣[κ εχει]
- κληρονομεια εν̣ [τη] βασιλεια του χυ̅ κ̣α̣ι θ̅υ̣̅ [6] [μηδεις]
- υμας απ̣ατατ̣ω̣ [κε]ν̣οις ·λογοις δια τ̣α̣υτ̣α̣ [γαρ ερχε]
- τε η̣ οργη του̣ θ̣[υ̅ επι] τους̣ υ̣ιο̣υς της απισ̣τι̣α[ς [7] μη]
- ουν γινεσθ̣[ε συμμετ]οχ̣[οι] ·α̣υ̣των [8] ητε γαρ π̣[οτε]
- σκοτος ν[υν δε φω]ς̣ ε̣ν̣ ·κ̅ω̅ ως̣ τεκ̣[ν]α φ̣[ωτος πε]
- ριπατειτ̣ε̣ [9] [ο γαρ] [καρπ]ο̣ς̣ τ̣ο̣υ φωτος εν πα̣[ση αγα]
- θοσυνη και δ̣[ικα]ιοσυν̣η κ̣α̣ι̣ αληθεια [10] δ̣οκι[μα]
- ζοντες τι εστ̣[ι]ν ευα̣ρεσ[το]ν̣ τω κ̅ω̅ [11] και μη [συγ]
- κοινωνειται το̣ις εργοις τ[οις] α̣καρποις του σ̣κ̣[οτους]
- μαλλον δε κ̣[α]ι̣ ελλεγχετ̣[ε] [12] τ̣α κρυφη γινο̣[μενα]
- υπ ·αυτων [αι]σχ̣ρον εστιν και ·λεγειν [13] τα̣ [δε] [παν]
- τα ελλεγχο[μ]ενα υπο του φωτος φανερ[ουται]
Further reading
- W. H. P. HatchWilliam HatchWilliam Henry Paine Hatch, Ph.D., D.D. was an American theologian, born at Camden, N. J. He attended Harvard, graduating in 1898 . Afterward, he graduated at the Episcopal Theological Seminary in Cambridge, Massachusetts, and from the General Theological Seminary in New York City...
and C. Bradford Welles, A Hitherto Unpublished Fragment of the Epistle to the Ephesians, Harvard Theological ReviewHarvard Theological ReviewHarvard Theological Review is a journal of theology, published by Harvard Divinity School. It was founded in 1908.-External links:* * * * at the Internet Archive...
LI (1958), pp. 33-37.


 49 recto
49 recto 49 verso
49 verso