Periodic table group
Encyclopedia
Chemistry
Chemistry is the science of matter, especially its chemical reactions, but also its composition, structure and properties. Chemistry is concerned with atoms and their interactions with other atoms, and particularly with the properties of chemical bonds....
, a group (also known as a family) is a vertical column in the periodic table
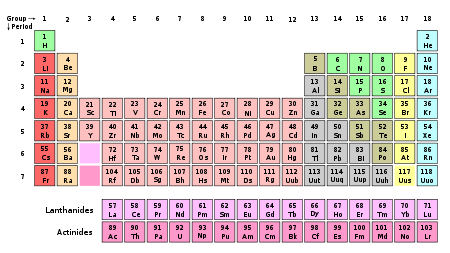
Periodic table
The periodic table of the chemical elements is a tabular display of the 118 known chemical elements organized by selected properties of their atomic structures. Elements are presented by increasing atomic number, the number of protons in an atom's atomic nucleus...
of the chemical element
Chemical element
A chemical element is a pure chemical substance consisting of one type of atom distinguished by its atomic number, which is the number of protons in its nucleus. Familiar examples of elements include carbon, oxygen, aluminum, iron, copper, gold, mercury, and lead.As of November 2011, 118 elements...
s. There are 18 groups in the standard periodic table, including the d-block
D-block
The d-block is the portion of the periodic table that contains the element groups 3-12. These groups correspond to the filling of the atomic d-orbital subshell, with electron configurations ranging from s2d1 to s2d10...
elements, but excluding the f-block
F-block
The f-block of the periodic table of the elements consists of those elements whose atoms or ions have valence electrons in f-orbitals. Actual electronic configurations may be slightly different from what is predicted by the Aufbau principle...
elements.
The modern explanation of the pattern of the table is that the elements in a group have similar configurations of the outermost electron shell
Electron shell
An electron shell may be thought of as an orbit followed by electrons around an atom's nucleus. The closest shell to the nucleus is called the "1 shell" , followed by the "2 shell" , then the "3 shell" , and so on further and further from the nucleus. The shell letters K,L,M,.....
s of their atoms (i.e. the same core charge
Core charge
Core charge is the effective nuclear charge experienced by an outer shell electron. In other words core charge is an expression of the attractive force experienced by the valence electrons to the core of an atom which takes into account the shielding effect of core electrons...
), as most chemical properties are dominated by the orbital location of the outermost electron. There are three conventional ways of numbering: One using Arabic numerals
Arabic numerals
Arabic numerals or Hindu numerals or Hindu-Arabic numerals or Indo-Arabic numerals are the ten digits . They are descended from the Hindu-Arabic numeral system developed by Indian mathematicians, in which a sequence of digits such as "975" is read as a numeral...
, and two using Roman numerals
Roman numerals
The numeral system of ancient Rome, or Roman numerals, uses combinations of letters from the Latin alphabet to signify values. The numbers 1 to 10 can be expressed in Roman numerals as:...
. The Roman numeral names are the original traditional names of the groups; the Arabic numeral names are those recommended by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry
International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry is an international federation of National Adhering Organizations that represents chemists in individual countries. It is a member of the International Council for Science . The international headquarters of IUPAC is located in Zürich,...
(IUPAC) to replace the old names in an attempt to reduce the confusion generated by the two older, but mutually confusing, schemes.
There is considerable confusion surrounding the two old systems in use (old IUPAC and CAS
Chemical Abstracts Service
Chemical Abstracts is a periodical index that provides summaries and indexes of disclosures in recently published scientific documents. Approximately 8,000 journals, technical reports, dissertations, conference proceedings, and new books, in any of 50 languages, are monitored yearly, as are patent...
) that combined the use of Roman numerals with letters. Both systems agree on the Roman numerals, which indicate (approximately) the highest oxidation number of the elements in that group (and therefore indicates similar chemistry with other elements with the same Roman numeral), which proceeds in a linearly increasing fashion for the most part, once on the left of the table, and once on the right (see List of oxidation states of the elements), with some irregularities in the transition metals. However, the two systems use the letters differently.
In the old IUPAC system the letters A and B were designated to the left (A) and right (B) part of the table, while in the CAS system the letters A and B were designated to main group elements (A) and transition elements (B). The old IUPAC system was frequently used in Europe while the CAS was most common in America. The new IUPAC scheme was developed to replace both systems as they confusingly used the same names to mean different things. The new system simply numbers the groups increasingly from left to right on the standard periodic table. The IUPAC proposal was first circulated in 1985 for public comments, and was later included as part of the 1990 edition of the Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry.
Groups
The periodic table groups are as follows:| New IUPAC numbering | Old IUPAC (European) | CAS (American) | Name |
|---|---|---|---|
| Group 1 | IA | IA | the alkali metal Alkali metal The alkali metals are a series of chemical elements in the periodic table. In the modern IUPAC nomenclature, the alkali metals comprise the group 1 elements, along with hydrogen. The alkali metals are lithium , sodium , potassium , rubidium , caesium , and francium... s or lithium Lithium Lithium is a soft, silver-white metal that belongs to the alkali metal group of chemical elements. It is represented by the symbol Li, and it has the atomic number 3. Under standard conditions it is the lightest metal and the least dense solid element. Like all alkali metals, lithium is highly... family |
| Group 2 | IIA | IIA | the alkaline earth metal Alkaline earth metal The alkaline earth metals are a group in the periodic table. In the modern IUPAC nomenclature, the alkaline earth metals are called the group 2 elements. Previously, they were called the Group IIA elements . The alkaline earth metals contain beryllium , magnesium , calcium , strontium , barium and... s or beryllium Beryllium Beryllium is the chemical element with the symbol Be and atomic number 4. It is a divalent element which occurs naturally only in combination with other elements in minerals. Notable gemstones which contain beryllium include beryl and chrysoberyl... family |
| Group 3 Group 3 element The group 3 elements are a group of chemical elements in the periodic table. This group, like other d-block groups, should contain four elements, but it is not agreed what elements belong in the group... |
IIIA | IIIB | the scandium Scandium Scandium is a chemical element with symbol Sc and atomic number 21. A silvery-white metallic transition metal, it has historically been sometimes classified as a rare earth element, together with yttrium and the lanthanoids... family (consisting of the rare earth element Rare earth element As defined by IUPAC, rare earth elements or rare earth metals are a set of seventeen chemical elements in the periodic table, specifically the fifteen lanthanides plus scandium and yttrium... s plus the actinide Actinide The actinide or actinoid series encompasses the 15 metallic chemical elements with atomic numbers from 89 to 103, actinium through lawrencium.The actinide series derives its name from the group 3 element actinium... s) |
| Group 4 Group 4 element The Group 4 elements are a group of chemical elements in the periodic table. In the modern IUPAC nomenclature, Group 4 of the periodic table contains titanium , zirconium , hafnium and rutherfordium . This group lies in the d-block of the periodic table... |
IVA | IVB | the titanium Titanium Titanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ti and atomic number 22. It has a low density and is a strong, lustrous, corrosion-resistant transition metal with a silver color.... family |
| Group 5 Group 5 element A Group 5 element is a chemical element in the fifth group in the periodic table. In the modern IUPAC nomenclature, Group 5 of the periodic table contains vanadium , niobium , tantalum and dubnium . This group lies in the d-block of the periodic table... |
VA | VB | the vanadium Vanadium Vanadium is a chemical element with the symbol V and atomic number 23. It is a hard, silvery gray, ductile and malleable transition metal. The formation of an oxide layer stabilizes the metal against oxidation. The element is found only in chemically combined form in nature... family |
| Group 6 Group 6 element A Group 6 element is one in the series of elements in group 6 in the periodic table, which consists of the transition metals chromium , molybdenum , tungsten , and seaborgium .... |
VIA | VIB | the chromium Chromium Chromium is a chemical element which has the symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in Group 6. It is a steely-gray, lustrous, hard metal that takes a high polish and has a high melting point. It is also odorless, tasteless, and malleable... family |
| Group 7 Group 7 element A Group 7 element is one in the series of elements in group 7 in the periodic table, which consists of manganese , technetium , rhenium , and bohrium... |
VIIA | VIIB | the manganese Manganese Manganese is a chemical element, designated by the symbol Mn. It has the atomic number 25. It is found as a free element in nature , and in many minerals... family |
| Group 8 Group 8 element A Group 8 element is one in the series of elements in group 8 in the periodic table, which consists of the transition metals iron , ruthenium , osmium and hassium .... |
VIII | VIIIB | the iron Iron Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust... family |
| Group 9 Group 9 element In modern IUPAC nomenclature, Group 9 of the periodic table contains the elements cobalt , rhodium , iridium , and meitnerium . These are all d-block transition metals... |
VIII | VIIIB | the cobalt Cobalt Cobalt is a chemical element with symbol Co and atomic number 27. It is found naturally only in chemically combined form. The free element, produced by reductive smelting, is a hard, lustrous, silver-gray metal.... family |
| Group 10 Group 10 element A Group 10 element is one in the series of elements in group 10 in the periodic table, which consists of the transition metals nickel , palladium , platinum , and darmstadtium .... |
VIII | VIIIB | the nickel Nickel Nickel is a chemical element with the chemical symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel belongs to the transition metals and is hard and ductile... family |
| Group 11 Group 11 element A Group 11 element is one in the series of elements in group 11 in the periodic table, consisting of transition metals which are the traditional coinage metals of copper , silver , and gold... |
IB | IB | the coinage metals (not an IUPAC-recommended name) or copper Copper Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29. It is a ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. Pure copper is soft and malleable; an exposed surface has a reddish-orange tarnish... family |
| Group 12 Group 12 element A group 12 element is one of the elements in group 12 in the periodic table. This includes zinc , cadmium and mercury . The further inclusion of copernicium in group 12 is supported by recent experiments on individual Cn atoms... |
IIB | IIB | the zinc Zinc Zinc , or spelter , is a metallic chemical element; it has the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is the first element in group 12 of the periodic table. Zinc is, in some respects, chemically similar to magnesium, because its ion is of similar size and its only common oxidation state is +2... family |
| Group 13 | IIIB | IIIA | the boron group Boron group The boron group is the series of elements in group 13 of the periodic table, comprising boron , aluminium , gallium , indium , thallium , and ununtrium . The elements in the boron group are characterized by having three electrons in their outer energy levels... or boron Boron Boron is the chemical element with atomic number 5 and the chemical symbol B. Boron is a metalloid. Because boron is not produced by stellar nucleosynthesis, it is a low-abundance element in both the solar system and the Earth's crust. However, boron is concentrated on Earth by the... family |
| Group 14 | IVB | IVA | the carbon group Carbon group The carbon group is a periodic table group consisting of carbon , silicon , germanium , tin , lead , and ununquadium .... or carbon Carbon Carbon is the chemical element with symbol C and atomic number 6. As a member of group 14 on the periodic table, it is nonmetallic and tetravalent—making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds... family |
| Group 15 | VB | VA | the pnictogen Nitrogen group The nitrogen group is a periodic table group consisting of nitrogen , phosphorus , arsenic , antimony , bismuth and ununpentium .... s or nitrogen Nitrogen Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere... family |
| Group 16 | VIB | VIA | the chalcogen Chalcogen The chalcogens are the chemical elements in group 16 of the periodic table. This group is also known as the oxygen family... s or oxygen Oxygen Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition... family |
| Group 17 | VIIB | VIIA | the halogen Halogen The halogens or halogen elements are a series of nonmetal elements from Group 17 IUPAC Style of the periodic table, comprising fluorine , chlorine , bromine , iodine , and astatine... s or fluorine Fluorine Fluorine is the chemical element with atomic number 9, represented by the symbol F. It is the lightest element of the halogen column of the periodic table and has a single stable isotope, fluorine-19. At standard pressure and temperature, fluorine is a pale yellow gas composed of diatomic... family |
| Group 18 | Group 0 | VIIIA | the noble gas Noble gas The noble gases are a group of chemical elements with very similar properties: under standard conditions, they are all odorless, colorless, monatomic gases, with very low chemical reactivity... es or helium Helium Helium is the chemical element with atomic number 2 and an atomic weight of 4.002602, which is represented by the symbol He. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas that heads the noble gas group in the periodic table... family or neon Neon Neon is the chemical element that has the symbol Ne and an atomic number of 10. Although a very common element in the universe, it is rare on Earth. A colorless, inert noble gas under standard conditions, neon gives a distinct reddish-orange glow when used in either low-voltage neon glow lamps or... family |
Background
- Scerri, E. R. The Periodic Table, Its Story and Its Significance, Oxford University Press, 2007. ISBN 978-0-19-530573-9.

