
Ranks in the French Army
Encyclopedia
See Ranks in the French Navy
for more details about the Navy Ranks.
The ranks in the Armée de Terre :
Rank insignia in the French army depend on whether the soldier belongs to an "infantry" or "cavalry" unit. Sleeves are emblazoned with marks denoting either the infantry or the cavalry: In the infantry the main insignia colour is gold, but in the cavalry the main insignia colour is silver/white. However, the artillery uses gold as the main colour, despite being a cavalry branch, and spahi
s use gold as the main colour despite being part of the cavalry, a division representing the armored cavalry.
is awarded as a distinction, rather than a rank
. The marshals wear seven stars and carry a baton
.
Famous examples include Turenne, Vauban
, Joachim Murat
, Michel Ney
, Bazaine
, Guillaume Brune, Louis Nicolas Davout
, André Masséna
, Philippe Leclerc de Hautecloque, Jean de Lattre de Tassigny
, Marie Pierre Koenig
and Alphonse Juin
.
A famous example would be Philippe Pétain
, who became famous as Maréchal Pétain, Chief of State of the Vichy France
regime and retained his title even after his trial and imprisonment and after he was stripped of other positions and titles.
Another particular example is Marshal de MacMahon, who ruled the Third Republic
from 1875 to 1879.
Six Marshals of France have been given the even more exalted rank of Marshal General of France
: Biron
, Lesdiguières
, Turenne
, Villars
, Saxe
and Soult
.
They all wear the same insignia and titles.
The title "général" originates in the ancient rank of "capitaine général" (literally, "general captain"), who was in command of the whole army.
There is no distinction between infantry and cavalry generals, since they are all supposed to be able to command any type of unit.
) but to some traditional affiliation of the units.
caput="head".
Colonel : in command of a regiment
or a groupement (in the Gendarmerie). During the French Revolution
, they were called "chef de brigade". Mounted arms wear silver. The origin of the difference in metal colour is that infantry officers once wore silver epaulette
s, while those of the cavalry and other arms wore gold, and the colour of the rank badge had to differ from these metals in each case.
. Notice that the metal colours alternate silver and gold in each case, as opposed to those of the colonels. This characteristic goes back at least to alternating stripes on the headdress of that empire.
(infantry), an escadron (cavalry) or a batterie (artillery)
or First Lieutenant
): in command of a section (infantry) , a peloton (cavalry), or a brigade (gendarmerie). This is equivalent to a Platoon in the US Armed Forces or a Section (infantry) or Troop (cavalry) in the Commonwealth armed forces.
or Second Lieutenant
): same prerogatives as the lieutenant
Note the difference with many rank systems where "Major
s" rank above captains.
Etymologically the adjudant is the adjoint ("aide") of an officer, and the sergeant
"serves" (Latin serviens).
Aspirants or sous-lieutenants are junior officers and are often aided by adjudants or adjudants-chefs, who are experienced NCOs/warrant officers.
Full lieutenants are experienced junior officers, served by sergeants when commanding their unit.
A four chevron Sergent-Chef-Major rank existed until 1947. It was a ceremonial rank usually given to the most senior or experienced NCO in a unit, similar to a Colour Sergeant
in the British Army. It was discontinued in the Postwar army due to its redundancy.
Senior grades' lace stripe metal depends on their arm of service, just like the officiers. Armes à pied (Infantry and Support units) wear gold stripes and Armes à Cheval (Cavalry and Technical Services units) wear silver stripes.
There are also distinctions to distinguish volunteers and conscripts, and bars for experience (one for five years, up to four can be obtained).
Ranks in the French Navy
The rank insignia of the French Navy are worn on shoulder straps of shirts and white jackets, and on sleeves for navy jackets and mantels....
for more details about the Navy Ranks.
The ranks in the Armée de Terre :
Rank insignia in the French army depend on whether the soldier belongs to an "infantry" or "cavalry" unit. Sleeves are emblazoned with marks denoting either the infantry or the cavalry: In the infantry the main insignia colour is gold, but in the cavalry the main insignia colour is silver/white. However, the artillery uses gold as the main colour, despite being a cavalry branch, and spahi
Spahi
Spahis were light cavalry regiments of the French army recruited primarily from the indigenous populations of Algeria, Tunisia and Morocco. The modern French Army retains one regiment of Spahis as an armoured unit, with personnel now recruited in mainland France...
s use gold as the main colour despite being part of the cavalry, a division representing the armored cavalry.
- Foot arms: Infantry, Naval troops, Foreign Legion, Engineering, etc.
- Horse arms: Armoured Cavalry arm, Train, Artillery, Maintenance and Logistics.
Marshals
The title of Maréchal de FranceMarshal of France
The Marshal of France is a military distinction in contemporary France, not a military rank. It is granted to generals for exceptional achievements...
is awarded as a distinction, rather than a rank
Military rank
Military rank is a system of hierarchical relationships in armed forces or civil institutions organized along military lines. Usually, uniforms denote the bearer's rank by particular insignia affixed to the uniforms...
. The marshals wear seven stars and carry a baton
Baton (symbol)
The ceremonial baton is a short, thick stick, carried by select high-ranking military officers as a uniform article. The baton is distinguished from the swagger stick in being thicker and less functional . Unlike a staff of office, a baton is not rested on the ground...
.
Famous examples include Turenne, Vauban
Vauban
Sébastien Le Prestre, Seigneur de Vauban and later Marquis de Vauban , commonly referred to as Vauban, was a Marshal of France and the foremost military engineer of his age, famed for his skill in both designing fortifications and breaking through them...
, Joachim Murat
Joachim Murat
Joachim-Napoléon Murat , Marshal of France and Grand Admiral or Admiral of France, 1st Prince Murat, was Grand Duke of Berg from 1806 to 1808 and then King of Naples from 1808 to 1815...
, Michel Ney
Michel Ney
Michel Ney , 1st Duc d'Elchingen, 1st Prince de la Moskowa was a French soldier and military commander during the French Revolutionary Wars and the Napoleonic Wars. He was one of the original 18 Marshals of France created by Napoleon I...
, Bazaine
François Achille Bazaine
François Achille Bazaine was a French General and from 1864, a Marshal of France, who surrendered the last organized French army to the Prussians during the Franco-Prussian war. He was the first Marshal who had started as a legionnaire and like the great Marshals of the First Empire, he had risen...
, Guillaume Brune, Louis Nicolas Davout
Louis Nicolas Davout
Louis-Nicolas d'Avout , better known as Davout, 1st Duke of Auerstaedt, 1st Prince of Eckmühl, was a Marshal of France during the Napoleonic Era. His prodigious talent for war along with his reputation as a stern disciplinarian, earned him the title "The Iron Marshal"...
, André Masséna
André Masséna
André Masséna 1st Duc de Rivoli, 1st Prince d'Essling was a French military commander during the Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars....
, Philippe Leclerc de Hautecloque, Jean de Lattre de Tassigny
Jean de Lattre de Tassigny
Jean Joseph Marie Gabriel de Lattre de Tassigny, GCB, MC was a French military hero of World War II and commander in the First Indochina War.-Early life:...
, Marie Pierre Koenig
Marie Pierre Koenig
Marie Pierre Kœnig was a French army officer and politician. He commanded a Free French Brigade at the Battle of Bir Hakeim in North Africa in 1942....
and Alphonse Juin
Alphonse Juin
- Early years :Juin was born at Bône in French Algeria, and enlisted in the French Army, graduating from the École Spéciale Militaire de Saint-Cyr in 1912.- Career :...
.
A famous example would be Philippe Pétain
Philippe Pétain
Henri Philippe Benoni Omer Joseph Pétain , generally known as Philippe Pétain or Marshal Pétain , was a French general who reached the distinction of Marshal of France, and was later Chief of State of Vichy France , from 1940 to 1944...
, who became famous as Maréchal Pétain, Chief of State of the Vichy France
Vichy France
Vichy France, Vichy Regime, or Vichy Government, are common terms used to describe the government of France that collaborated with the Axis powers from July 1940 to August 1944. This government succeeded the Third Republic and preceded the Provisional Government of the French Republic...
regime and retained his title even after his trial and imprisonment and after he was stripped of other positions and titles.
Another particular example is Marshal de MacMahon, who ruled the Third Republic
French Third Republic
The French Third Republic was the republican government of France from 1870, when the Second French Empire collapsed due to the French defeat in the Franco-Prussian War, to 1940, when France was overrun by Nazi Germany during World War II, resulting in the German and Italian occupations of France...
from 1875 to 1879.
Six Marshals of France have been given the even more exalted rank of Marshal General of France
Marshal General of France
The title Marshal General of France or more exactly "Marshal General of the King's camps and armies" was given to signify that the recipient had authority over all the French armies in the days when a Marshal governed only one army usually...
: Biron
Charles de Gontaut, duc de Biron
Charles de Gontaut, duc de Biron was a French soldier.-Biography:He was the son of Armand de Gontaut, baron de Biron, under whose command he fought for the royal party against the Catholic League in the later stages of the Wars of Religion in France. His efforts won him the name “Thunderbolt of...
, Lesdiguières
François de Bonne, duc de Lesdiguières
François de Bonne, duc de Lesdiguières was soldier of the French Wars of Religion and Constable of France.- Early life :He was born at Saint-Bonnet-en-Champsaur, to a family of notaries with pretensions to nobility...
, Turenne
Henri de la Tour d'Auvergne, Vicomte de Turenne
Henri de la Tour d'Auvergne, Vicomte de Turenne,often called simply Turenne was the most illustrious member of the La Tour d'Auvergne family. He achieved military fame and became a Marshal of France...
, Villars
Claude Louis Hector de Villars
Claude Louis Hector de Villars, Prince de Martigues, Marquis then Duc de Villars, Vicomte de Melun was the last great general of Louis XIV of France and one of the most brilliant commanders in French military history, one of only six Marshals who have been promoted to Marshal General of...
, Saxe
Maurice, comte de Saxe
Maurice de Saxe was a German in French service who was Marshal and later also Marshal General of France.-Childhood:...
and Soult
Nicolas Jean de Dieu Soult
Nicolas Jean-de-Dieu Soult, 1st Duke of Dalmatia , the Hand of Iron, was a French general and statesman, named Marshal of the Empire in 1804. He was one of only six officers in French history to receive the distinction of Marshal General of France...
.
Officers
Officers are divided into- the regular officers of the Army
- the commissary of the Army
- the officers of the technical and administrative corps of the Army.
They all wear the same insignia and titles.
Généraux - General officers
-
 Général d'armée: Army GeneralArmy General (France)A Général d'Armée is the highest active military rank of the French Army.Officially, Général d'armée is not a rank , but a position and style bestowed on some Généraux de division in charge of important commands, such as chief of staff of the army...
Général d'armée: Army GeneralArmy General (France)A Général d'Armée is the highest active military rank of the French Army.Officially, Général d'armée is not a rank , but a position and style bestowed on some Généraux de division in charge of important commands, such as chief of staff of the army...
: In command of an army. This is not a genuine rank, but an appointment of Divisional General.
- Général de corps d'armée: Corps GeneralCorps GeneralCorps General is a rank corresponding to the Commonwealth and US rank of Lieutenant General. For convenience the rank in foreign armies is normally actually translated as Lieutenant General. In France a général de corps d'armée is actually an appointment of Divisional General, rather than a...
: In command of an army corps. This is not a genuine rank, but an appointment of Divisional General.
-
 Général de division: Divisional GeneralDivisional GeneralDivisional General is a rank used in many armies to denote a rank of general, corresponding to command of a division. For convenience Divisional General is almost always translated into English as Major-General, the equivalent rank used by the UK, USA, etc., although this translation is, strictly...
Général de division: Divisional GeneralDivisional GeneralDivisional General is a rank used in many armies to denote a rank of general, corresponding to command of a division. For convenience Divisional General is almost always translated into English as Major-General, the equivalent rank used by the UK, USA, etc., although this translation is, strictly...
: in command of a divisionDivision (military)A division is a large military unit or formation usually consisting of between 10,000 and 20,000 soldiers. In most armies, a division is composed of several regiments or brigades, and in turn several divisions typically make up a corps...
.
- Général de brigade: Brigade GeneralBrigade GeneralBrigade General is a rank used in many armies to denote the lowest rank of general, corresponding to command of a brigade. The rank is mostly used in countries where it is used as a modern alternative to a previous older rank of Brigadier or Brigadier General...
: in command of a brigadeBrigadeA brigade is a major tactical military formation that is typically composed of two to five battalions, plus supporting elements depending on the era and nationality of a given army and could be perceived as an enlarged/reinforced regiment...
, or of a légion in the Gendarmerie. A famous Général de brigade was Charles de GaulleCharles de GaulleCharles André Joseph Marie de Gaulle was a French general and statesman who led the Free French Forces during World War II. He later founded the French Fifth Republic in 1958 and served as its first President from 1959 to 1969....
, who often wore military uniform whilst President of the French Republic.
The title "général" originates in the ancient rank of "capitaine général" (literally, "general captain"), who was in command of the whole army.
There is no distinction between infantry and cavalry generals, since they are all supposed to be able to command any type of unit.
Officiers supérieurs - Senior officers
In the below descriptions, "horse-mounted" does not refer to current units (the only remaining horse-mounted unit is a ceremonial unit in the Republican GuardFrench Republican Guard
The Republican Guard is part of the French Gendarmerie. It is responsible for providing security in the Paris area and for providing guards of honor.Its missions include:...
) but to some traditional affiliation of the units.
Colonel
The word "colonel" originates in the title capitaine colonel, "the one who commands a column" (regiment). Lieutenant-colonel is the one who can "take the place" of a colonel (lieu-tenant, tenir lieu = to take the place of). Chef, "chief", comes from LatinLatin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
caput="head".
Colonel : in command of a regiment
Regiment
A regiment is a major tactical military unit, composed of variable numbers of batteries, squadrons or battalions, commanded by a colonel or lieutenant colonel...
or a groupement (in the Gendarmerie). During the French Revolution
French Revolution
The French Revolution , sometimes distinguished as the 'Great French Revolution' , was a period of radical social and political upheaval in France and Europe. The absolute monarchy that had ruled France for centuries collapsed in three years...
, they were called "chef de brigade". Mounted arms wear silver. The origin of the difference in metal colour is that infantry officers once wore silver epaulette
Epaulette
Epaulette is a type of ornamental shoulder piece or decoration used as insignia of rank by armed forces and other organizations.Epaulettes are fastened to the shoulder by a shoulder strap or "passant", a small strap parallel to the shoulder seam, and the button near the collar, or by laces on the...
s, while those of the cavalry and other arms wore gold, and the colour of the rank badge had to differ from these metals in each case.
Lieutenant-Colonel
The Lieutenant-colonel has the same responsibilities as a colonel. They were called "major" during the First French EmpireFirst French Empire
The First French Empire , also known as the Greater French Empire or Napoleonic Empire, was the empire of Napoleon I of France...
. Notice that the metal colours alternate silver and gold in each case, as opposed to those of the colonels. This characteristic goes back at least to alternating stripes on the headdress of that empire.
Commandant
Commandant: also called chef de bataillon in the infantry, chef d'escadrons in the cavalry, chef d'escadron in the artillery and in the Army Light Aviation.Capitaine
A Capitaine is in command of a compagnieCompany (military unit)
A company is a military unit, typically consisting of 80–225 soldiers and usually commanded by a Captain, Major or Commandant. Most companies are formed of three to five platoons although the exact number may vary by country, unit type, and structure...
(infantry), an escadron (cavalry) or a batterie (artillery)
Lieutenant
A Lieutenant (LieutenantLieutenant
A lieutenant is a junior commissioned officer in many nations' armed forces. Typically, the rank of lieutenant in naval usage, while still a junior officer rank, is senior to the army rank...
or First Lieutenant
First Lieutenant
First lieutenant is a military rank and, in some forces, an appointment.The rank of lieutenant has different meanings in different military formations , but the majority of cases it is common for it to be sub-divided into a senior and junior rank...
): in command of a section (infantry) , a peloton (cavalry), or a brigade (gendarmerie). This is equivalent to a Platoon in the US Armed Forces or a Section (infantry) or Troop (cavalry) in the Commonwealth armed forces.
Sous-Lieutenant
Sous-lieutenant (Sub-LieutenantSub-Lieutenant
Sub-lieutenant is a military rank. It is normally a junior officer rank.In many navies, a sub-lieutenant is a naval commissioned or subordinate officer, ranking below a lieutenant. In the Royal Navy the rank of sub-lieutenant is equivalent to the rank of lieutenant in the British Army and of...
or Second Lieutenant
Second Lieutenant
Second lieutenant is a junior commissioned officer military rank in many armed forces.- United Kingdom and Commonwealth :The rank second lieutenant was introduced throughout the British Army in 1871 to replace the rank of ensign , although it had long been used in the Royal Artillery, Royal...
): same prerogatives as the lieutenant
Aspirant
- Aspirant : AspirantAspirantAspirant is a military rank in the Canadian Navy, French military, Brazilian military, Romanian Navy and Polish Police.-Canadian Navy:Similar to the French usage, the Canadian Navy uses the French-language rank of "Aspirant de marine" to denote a junior officer under training. The same rank in the...
- Eleve Officier : Officer CadetOfficer CadetOfficer cadet is a rank held by military and merchant navy cadets during their training to become commissioned officers and merchant navy officers, respectively. The term officer trainee is used interchangeably in some countries...
. During the first years at the schools of École spéciale militaire de Saint-CyrÉcole Spéciale Militaire de Saint-CyrThe École Spéciale Militaire de Saint-Cyr is the foremost French military academy. Its official name is . It is often referred to as Saint-Cyr . Its motto is "Ils s'instruisent pour vaincre": literally "They study to vanquish" or "Training for victory"...
or École militaire interarmes or Ecole des Officiers de la Gendarmerie NationaleEcole des Officiers de la Gendarmerie NationaleL’École des officiers de la gendarmerie nationale, the French Gendarmerie nationale Officers School, was created in 1901 and based in the Schomberg district in Paris. At the time it was simply to give additional training to NCOs likely to enter the officer corps...
Sous-officiers - Sub-officers
- Major, the senior sub-officerSub-OfficerSub-Officer is a term used in many military forces used to indicate ranks below commissioned officers. Sub-Officer is equivalent to the term NCO in the Commonwealth and USA...
rank, is derived from the term Chef d'etat Major (English: "Chief of Staff"). Much like the GermanGerman EmpireThe German Empire refers to Germany during the "Second Reich" period from the unification of Germany and proclamation of Wilhelm I as German Emperor on 18 January 1871, to 1918, when it became a federal republic after defeat in World War I and the abdication of the Emperor, Wilhelm II.The German...
army rank of Feldwebel-Leutnant (English: "Sergeant-Lieutenant"), the Major was a staff warrant officer in charge of book-keeping and paperwork. Since 1 January 2009 this grade is attached to the Sous-officiers. Prior to this date it was an independent corps between the Sous-officiers and the officiers. There are relatively few Majors in the Army, about one per regiment or brigade. As they could hold equivalent administrative tasks as officiers they are more common in the Armée de l'Air.
Note the difference with many rank systems where "Major
Major
Major is a rank of commissioned officer, with corresponding ranks existing in almost every military in the world.When used unhyphenated, in conjunction with no other indicator of rank, the term refers to the rank just senior to that of an Army captain and just below the rank of lieutenant colonel. ...
s" rank above captains.
- Adjudant-chef: Chief Adjutant: often same responsibilities as the lieutenant. In the horse-mounted arms (armes a cheval: cavalry and transportation), they are addressed as "lieutenant", otherwise addressed as "adjudant"
 adjudant-chef (des armes à pied)
adjudant-chef (des armes à pied) adjudant-chef (des armes à cheval)
adjudant-chef (des armes à cheval)
- Adjudant: Adjutant: often same responsibilities as a lieutenant and acting commonly as executive platoon leader in the infantry.
- Sergent-chef (infantry) or Maréchal des logis-chef (cavalry), addressed as "chef". Typically a platoon 2icSecond-in-commandThe Second-in-Command is the deputy commander of any British Army or Royal Marines unit, from battalion or regiment downwards. He or she is thus the equivalent of an Executive Officer in the United States Army...
. (Equivalent to a Commonwealth Sergeant or a US Sergeant First Class).- Sergent-chef : Chief Sergeant
 Maréchal des logis-chef : Chief Marshal of Lodgings
Maréchal des logis-chef : Chief Marshal of Lodgings
- Sergent (infantry) or Maréchal des logis (cavalry) : Typically in command of a "group" (i.e. squad; equivalent to a commonwealth corporal or US staff sergeant)
- Sergent : SergeantSergeantSergeant is a rank used in some form by most militaries, police forces, and other uniformed organizations around the world. Its origins are the Latin serviens, "one who serves", through the French term Sergent....
 Maréchal des logis : Marshal of LodgingsMarshal-of-LodgingsMaréchal-des-logis is a sub-officer rank used by some units of the French Armed Forces. It is traditionally a horse units rank. There are three distincts ranks of maréchal des logis. These ranks are equivalents of sergeant ranks.* Maréchal des logis-chef : Three chevrons, gold or silver...
Maréchal des logis : Marshal of LodgingsMarshal-of-LodgingsMaréchal-des-logis is a sub-officer rank used by some units of the French Armed Forces. It is traditionally a horse units rank. There are three distincts ranks of maréchal des logis. These ranks are equivalents of sergeant ranks.* Maréchal des logis-chef : Three chevrons, gold or silver...
- Sergent : Sergeant
- Eleve Sous-Officier NCO candidats at the ENSOAENSOAÉcole Nationale des Sous-Officiers d’Active is a general military school created by the French Army in 1963 to train career NCOs on active service...
.
Etymologically the adjudant is the adjoint ("aide") of an officer, and the sergeant
Sergeant
Sergeant is a rank used in some form by most militaries, police forces, and other uniformed organizations around the world. Its origins are the Latin serviens, "one who serves", through the French term Sergent....
"serves" (Latin serviens).
Aspirants or sous-lieutenants are junior officers and are often aided by adjudants or adjudants-chefs, who are experienced NCOs/warrant officers.
Full lieutenants are experienced junior officers, served by sergeants when commanding their unit.
A four chevron Sergent-Chef-Major rank existed until 1947. It was a ceremonial rank usually given to the most senior or experienced NCO in a unit, similar to a Colour Sergeant
Colour Sergeant
Colour sergeant or colour serjeant is a non-commissioned title in the Royal Marines and infantry regiments of the British Army, ranking above sergeant and below warrant officer class 2....
in the British Army. It was discontinued in the Postwar army due to its redundancy.
Militaires du rang - Enlisted
Junior enlisted grades have different cloth stripe and beret color depending on the service they are assigned to. Troupes Métropolitaines (native "French") units wear blue, Troupes de Marine (the former Troupes Coloniale) wear red, and the Legion Etrangere (as members of the former Armée d'Afrique) units wear green.Senior grades' lace stripe metal depends on their arm of service, just like the officiers. Armes à pied (Infantry and Support units) wear gold stripes and Armes à Cheval (Cavalry and Technical Services units) wear silver stripes.
- Caporal-chef de première classe. Distinction created in 1999.
- Caporal-chef (infantry) or Brigadier-chef (cavalry) : in command of an équipe (literally a team). Presently this size unit is a trinôme in the Army.
- Caporal (infantry) or Brigadier (cavalry) : in command of an équipe.
- Soldat de première classe. This is a distinction rather than a rank.
- Soldat de deuxième classe: No rank insignia. Depending on the arm, they are called
- fantassin (infantry)
- légionnaire (Légion étrangèreFrench Foreign LegionThe French Foreign Legion is a unique military service wing of the French Army established in 1831. The foreign legion was exclusively created for foreign nationals willing to serve in the French Armed Forces...
) - artilleur (artillery)
- sapeur (engineering, including the sapeurs-pompiers de ParisParis Fire BrigadeThe Paris Fire Brigade , is a French Army unit which serves as the fire service for Paris and certain sites of national strategic importance....
) - chasseur ("Hunter": light troops used for reconnaissance and harassment)
- chasseurs à pied (Light Infantry)
- chasseurs à cheval (Light Mounted Infantry)
- chasseurs alpins (Light Alpine Infantry)
- chasseurs parachutistes (Airborne Infantry Commandos)
- dragon (Dragoon: Mounted Infantry unit)
- cuirassier (Cuirassier: Heavy Cavalry unit)
- hussard (Hussar: Light Cavalry unit)
- transmetteur (signals corps)
- conducteur (trains).
- Marsouin (Troupes de marineTroupes de marineThe or Infanterie de marine, formerly Troupes coloniales, are an arm of the French Army with a colonial heritage. The Troupes de marine have a dedicated overseas service role. Despite their title they have been a part of the Army since 1958...
): from a term for the Harbour PorpoiseHarbour PorpoiseThe harbour porpoise is one of six species of porpoise. It is one of the smallest marine mammals. As its name implies, it stays close to coastal areas or river estuaries, and as such, is the most familiar porpoise to whale watchers. This porpoise often ventures up rivers, and has been seen...
, due to their duties at sea or on land.
- SLANG
- Bigor (Artillerie de la marine; see Troupes de marineTroupes de marineThe or Infanterie de marine, formerly Troupes coloniales, are an arm of the French Army with a colonial heritage. The Troupes de marine have a dedicated overseas service role. Despite their title they have been a part of the Army since 1958...
): A term either from the gunner's order to fire (Bigue de hors) or a term for a species of sea slug (bigorneau) because they would stick to their emplacements and couldn't be removed easily. - Colo (Troupes ColonialesFrench Colonial ForcesThe French Colonial Forces , commonly called La Coloniale, was a general designation for the military forces that garrisoned in the French colonial empire from the late 17th century until 1960. They were recruited from mainland France or from the French settler and indigenous populations of the...
): The former term for the Troupes de la Marine when they were Colonial troops. - Para (Troupes aéroportées): Airborne troops, short for parachutist.
- Gazier (Troupes aéroportées): Airborne troops "grunt". Friendly nickname.
- Poilu (Infanterie): "Hairy One". A derogatory term, much like the Commonwealth Forces term Pongo ("Smelly one"). Only used when speaking of French soldiers of WW1 in the trenches, who had no time nor soap to shave.
- Biffin slang used by Troupes de MarineTroupes de marineThe or Infanterie de marine, formerly Troupes coloniales, are an arm of the French Army with a colonial heritage. The Troupes de marine have a dedicated overseas service role. Despite their title they have been a part of the Army since 1958...
to designate other infantry units. Probably comes from the fact that marsouins use to own their uniform and were proud of it, whereas other units were dressed in rags (biffe is an old French word for rag).
- Bigor (Artillerie de la marine; see Troupes de marine
There are also distinctions to distinguish volunteers and conscripts, and bars for experience (one for five years, up to four can be obtained).
Ingénieurs du service du matériel
- Ingénieur général de première classe (Général de division)
- Ingénieur général de deuxième classe (Général de brigade)
- Ingénieur en chef de première classe (Colonel)
- Ingénieur en chef de deuxième classe (Lieutenant-Colonel)
- Ingénieur principal (Commandant)
- Ingénieur de première classe (Capitaine)
- Ingénieur de deuxième classe (Lieutenant)
- Ingénieur de troisième classe (Sub-Lieutenant)
Army Commissariat Service officer ranks
These ranks apply the word commissaire in light of their participation and role in the Commissariat Service of the Ground Army.- Commissaire général de corps d'armée
- Commissaire général de division
- Commissaire général de brigade
- Commissaire colonel
- Commissaire lieutenant-colonel
- Commissaire commandant
- Commissaire capitaine
- Commissaire lieutenant
- Commissaire sous-lieutenant
Table of ranks
| Maréchaux de France - Marshals of France | ||||
| Maréchal de France | ||||
| Marshal of France is not an actual rank, but a "state honour" | ||||
| Officiers généraux - General officers | ||||
 |
 |
|||
| Général de brigade | Général de division | Général de corps d'armée | Général d'armée | |
| Commands a brigade Brigade A brigade is a major tactical military formation that is typically composed of two to five battalions, plus supporting elements depending on the era and nationality of a given army and could be perceived as an enlarged/reinforced regiment... |
Commands a division Division (military) A division is a large military unit or formation usually consisting of between 10,000 and 20,000 soldiers. In most armies, a division is composed of several regiments or brigades, and in turn several divisions typically make up a corps... |
Commands a corps Corps A corps is either a large formation, or an administrative grouping of troops within an armed force with a common function such as Artillery or Signals representing an arm of service... . This is not an actual rank, but an appointment of général de division. |
Commands an army. This is not an actual rank, but an appointment of général de division. | |
| Six stars used to be used by the general commanding the defences of Paris. This insignia is not in use anymore. | ||||
| Officiers supérieurs - Senior officers | ||||
 |
Infantry | |||
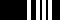 |
 |
Cavalry | ||
| Commandant (Chef d'escadron(s) in some arms) | Lieutenant-colonel | Colonel | ||
| Officiers subalternes - Junior officers | ||||
 |
 |
 |
||
| Aspirant | Sous-lieutenant | Lieutenant | Capitaine | |
| Major - Warrant Officer (until 2008), High Ranking Sub-officer (since 2009) | ||||
| Major | ||||
| Sous-officiers - Sub-officers | ||||
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
| Élève sous-officier | Sergent ("Foot arms") / Maréchal des logis ("Horse Arms") | Sergent-chef ("Foot Arms") / Maréchal des logis-chef ("Horse Arms") | Adjudant | Adjudant-chef |
| A four chevron sergent-chef major existed up till 1947 | ||||
| Militaires du rang - Rank and File | ||||
| Soldat 1e classe | Caporal ("Foot arms") / Brigadier ("Horse Arms") | Caporal-chef ("Foot arms") / Brigadier-chef ("Horse Arms") | Caporal-chef (1e classe) / Brigadier-chef (1e classe) | |
See also
- Ranks in the French NavyRanks in the French NavyThe rank insignia of the French Navy are worn on shoulder straps of shirts and white jackets, and on sleeves for navy jackets and mantels....

