
RegularChains
Encyclopedia
The RegularChains package in the computer algebra software package Maple
is a collection of commands for solving systems of polynomial equations
, inequations and inequalities symbolically.
This package also allows the user to manipulate and study the solutions of such systems.
Each of them computes from a system of polynomials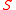
a set of simpler systems
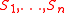 such that a point is a solution of
such that a point is a solution of 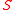
if and only if it is a solution of one of the systems
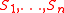 .
.
Each of these simpler systems is called a regular chain
in the case of Triangularize and a regular semi-algebraic system
in the case of RealTriangularize.
In both cases, each of these simpler systems has
a triangular shape and remarkable properties.
For this reason, the set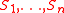 is called a triangular decomposition
is called a triangular decomposition
of the system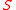 .
.
In addition to its main functions Triangularize and RealTriangularize, the RegularChains package has six subpackages and other commands.
The MatrixTools subpackage provides commands for solving linear systems of equations modulo the saturated ideal of a regular chain. Among other operations are computations of matrix inverses and lower echelon forms. These commands are considered here in a non-standard context. Indeed, the coefficients of these matrices are polynomials and the computations are performed modulo (the saturated ideal of) a regular chain. Since this latter is not required to be a prime ideal, the commands of this subpackage allows you to do linear algebra computations over non-integral domains.
The ConstructibleSetTools subpackage provides a large set of commands for manipulating constructible sets. Constructible sets are the fundamental objects of Algebraic Geometry
, and they play there the role that ideals play in Polynomial Algebra. In broad terms, a constructible set is the solution set of a system of polynomial equations and inequations. Constructible sets appear naturally in many questions, from high-school problems to advanced research topics.
The SemiAlgebraicSetTools subpackage contains a collection of commands for isolating and counting real roots of zero-dimensional semi-algebraic systems or regular chains (that is regular chains with a finite number of complex solutions). It also offers various commands for studying the real solutions of polynomial systems of positive dimension or with parameters. In particular, commands for real root classification, cylindrical algebraic decomposition and partial cylindrical algebraic decomposition sampling are available. Several inspection functions on semi-algebraic systems and their solution sets (namely, semi-algebraic sets) are also provided. They are intended to support the command RealRootClassification, RealTriangularize, LazyRealTriangularize and SamplePoints.
The ParametricSystemTools subpackage provides commands for solving systems of equations that depend on parameters. Given a parametric polynomial system , this subpackage can be used to answer questions such as: for which values of the parameters does
, this subpackage can be used to answer questions such as: for which values of the parameters does  have solutions? finitely many solutions?
have solutions? finitely many solutions?  real solutions, for a given
real solutions, for a given  ?
?
The ChainTools subpackage provides advanced operations on regular chains. Most of these commands allow you to inspect, construct and transform regular chains, or to check the properties of a polynomial with respect to a regular chain. Some commands operate transformations on a set of regular chains. They can be used to analyze the results computed by the command Triangularize.
The FastArithmeticTools subpackage contains a collection of commands for computing with regular chains in prime characteristic using asymptotically fast algorithms. Most of the underlying polynomial arithmetic is performed at C level and relies on (multi-dimensional) Fast Fourier Transform (FFT). This imposes some constraints on the characteristic. One of the main purposes of this subpackage is to offer efficient basic routines in order to suppor the implementation of modular algorithms for computing with regular chains and algebraic numbers.
Maple (software)
Maple is a general-purpose commercial computer algebra system. It was first developed in 1980 by the Symbolic Computation Group at the University of Waterloo in Waterloo, Ontario, Canada....
is a collection of commands for solving systems of polynomial equations
Systems of polynomial equations
A system of polynomial equations is a set of simultaneous equations f1 = 0, ..., fh = 0 where the fi are polynomials in several variables, say x1, ..., xn, over some field k....
, inequations and inequalities symbolically.
This package also allows the user to manipulate and study the solutions of such systems.
Main Features
The main two commands are Triangularize and RealTriangularize.Each of them computes from a system of polynomials
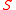
a set of simpler systems
 such that a point is a solution of
such that a point is a solution of 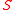
if and only if it is a solution of one of the systems
 .
.Each of these simpler systems is called a regular chain
Regular chain
In computer algebra, a regular chain is a particular kind of triangular set in a multivariate polynomial ring over a field. It enhances the notion of characteristic set.- Introduction :...
in the case of Triangularize and a regular semi-algebraic system
Regular semi-algebraic system
In computer algebra, a regular semi-algebraic system is a particular kind of triangular system of multivariate polynomials over a real closed field.- Introduction :...
in the case of RealTriangularize.
In both cases, each of these simpler systems has
a triangular shape and remarkable properties.
For this reason, the set
 is called a triangular decomposition
is called a triangular decompositionTriangular decomposition
In computer algebra, a triangular decomposition of a polynomial system S is a set of simpler polynomial systems S_1,\ldots, S_e such that a point is a solution of S if and only if it is a solution of one of the systems S_1,\ldots, S_e....
of the system
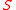 .
.In addition to its main functions Triangularize and RealTriangularize, the RegularChains package has six subpackages and other commands.
The MatrixTools subpackage provides commands for solving linear systems of equations modulo the saturated ideal of a regular chain. Among other operations are computations of matrix inverses and lower echelon forms. These commands are considered here in a non-standard context. Indeed, the coefficients of these matrices are polynomials and the computations are performed modulo (the saturated ideal of) a regular chain. Since this latter is not required to be a prime ideal, the commands of this subpackage allows you to do linear algebra computations over non-integral domains.
The ConstructibleSetTools subpackage provides a large set of commands for manipulating constructible sets. Constructible sets are the fundamental objects of Algebraic Geometry
Algebraic geometry
Algebraic geometry is a branch of mathematics which combines techniques of abstract algebra, especially commutative algebra, with the language and the problems of geometry. It occupies a central place in modern mathematics and has multiple conceptual connections with such diverse fields as complex...
, and they play there the role that ideals play in Polynomial Algebra. In broad terms, a constructible set is the solution set of a system of polynomial equations and inequations. Constructible sets appear naturally in many questions, from high-school problems to advanced research topics.
The SemiAlgebraicSetTools subpackage contains a collection of commands for isolating and counting real roots of zero-dimensional semi-algebraic systems or regular chains (that is regular chains with a finite number of complex solutions). It also offers various commands for studying the real solutions of polynomial systems of positive dimension or with parameters. In particular, commands for real root classification, cylindrical algebraic decomposition and partial cylindrical algebraic decomposition sampling are available. Several inspection functions on semi-algebraic systems and their solution sets (namely, semi-algebraic sets) are also provided. They are intended to support the command RealRootClassification, RealTriangularize, LazyRealTriangularize and SamplePoints.
The ParametricSystemTools subpackage provides commands for solving systems of equations that depend on parameters. Given a parametric polynomial system
 , this subpackage can be used to answer questions such as: for which values of the parameters does
, this subpackage can be used to answer questions such as: for which values of the parameters does  have solutions? finitely many solutions?
have solutions? finitely many solutions?  real solutions, for a given
real solutions, for a given  ?
?The ChainTools subpackage provides advanced operations on regular chains. Most of these commands allow you to inspect, construct and transform regular chains, or to check the properties of a polynomial with respect to a regular chain. Some commands operate transformations on a set of regular chains. They can be used to analyze the results computed by the command Triangularize.
The FastArithmeticTools subpackage contains a collection of commands for computing with regular chains in prime characteristic using asymptotically fast algorithms. Most of the underlying polynomial arithmetic is performed at C level and relies on (multi-dimensional) Fast Fourier Transform (FFT). This imposes some constraints on the characteristic. One of the main purposes of this subpackage is to offer efficient basic routines in order to suppor the implementation of modular algorithms for computing with regular chains and algebraic numbers.
See also
- Characteristic setCharacteristic setWenjun Wu's method is an algorithm for solving multivariate polynomial equations introduced in the late 1970s by the Chinese mathematician Wen-Tsun Wu. This method is based on the mathematical concept of characteristic set introduced in the late 1940s by J.F. Ritt...
- Regular chainRegular chainIn computer algebra, a regular chain is a particular kind of triangular set in a multivariate polynomial ring over a field. It enhances the notion of characteristic set.- Introduction :...
- Regular semi-algebraic systemRegular semi-algebraic systemIn computer algebra, a regular semi-algebraic system is a particular kind of triangular system of multivariate polynomials over a real closed field.- Introduction :...
- Triangular decompositionTriangular decompositionIn computer algebra, a triangular decomposition of a polynomial system S is a set of simpler polynomial systems S_1,\ldots, S_e such that a point is a solution of S if and only if it is a solution of one of the systems S_1,\ldots, S_e....

