Sino-Indian relations
Encyclopedia
Sino-Indian relations, also called Indo-China relations, refers to the bilateral relationship between the People's Republic of China
(PRC) and the Republic of India. China and India are the world's most populous states and also fastest growing major economies. The resultant growth in China and India's global diplomatic and economic influence has also increased the significance of their bilateral relationship.
China and India are two of the world’s oldest civilization
s and have coexisted in peace for millennia. Cultural and economic relations between China and India date back to ancient times. The Silk Road
not only served as a major trade route
between India and China, but is also credited for facilitating the spread the Buddhism
from India to East Asia. During the 19th century, China's growing opium trade with the British Raj
triggered the Opium Wars
. During World War II
, India and China played a crucial role in halting the progress of Imperial Japan.
Relations between contemporary China and India have been been characterized by border disputes
, resulting in three major military conflicts — the Sino-Indian War
of 1962, the Chola incident
in 1967, and the 1987 Sino-Indian skirmish
. However, since late 1980s, both countries have successfully attempted to reignite diplomatic and economic ties. In 2008, China emerged as the largest trading partner of India and the two countries have also attempted to extend their strategic and military relations.
Despite growing economic and strategic ties, several issues continue to strain Sino-Indian relations. Though bilateral trade has continuously grown, India faces massive trade imbalance heavily in favor of China. The two countries have failed to resolve their long-standing border dispute and Indian media outlets repeatedly report Chinese military incursions into Indian territory. Both nations have steadily built-up military infrastructure along border areas. Additionally, India harbors suspicions about China's strong strategic relations with its arch-rival Pakistan while China has expressed concerns about Indian military and economic activities in disputed South China Sea.
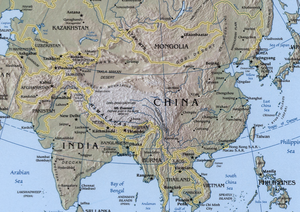 China and India are separated by the formidable geographical obstacles of the Himalayan mountain chain. China and India today share a border along the Himalayas and Nepal
China and India are separated by the formidable geographical obstacles of the Himalayan mountain chain. China and India today share a border along the Himalayas and Nepal
and Bhutan
, two states lying along the Himalaya range, and acting as buffer state
s. In addition, the disputed Kashmir
province of India (claimed by Pakistan
) borders both the PRC and India. As Pakistan has tense relations with India, Kashmir's state of unrest serves as a natural ally to the PRC.
Two territories are currently disputed between the People's Republic of China and India: Aksai Chin
and Arunachal Pradesh
. Arunachal Pradesh is located near the far east of India, while Aksai Chin is located near the northwest corner of India, at the junction of India, Pakistan, and the PRC. However, all sides in the dispute have agreed to respect the Line of Actual Control
and this border dispute is not widely seen as a major flashpoint
.
from India to China. Trade relations via the Silk Road
acted as economic contact between the two regions.
China and India have also had some contact before the transmission of Buddhism. References to a people called the Chinas
, now believed to be the Chinese
, are found in ancient Indian literature
. The Indian epic
Mahabharata
(c. 5th century BC) contains references to "China", which may have been referring to the Qin
state which later became the Qin Dynasty
. Chanakya
(c. 350-283 BC), the prime minister
of the Maurya Empire
and a professor at Takshashila University, refers to Chinese silk
as "cinamsuka" (Chinese silk dress) and "cinapatta" (Chinese silk bundle) in his Arthashastra
.
In the Records of the Grand Historian
, Zhang Qian
(d. 113 BC) and Sima Qian
(145-90 BC) make references to "Shendu", which may have been referring to the Indus Valley
(the Sindh
province in modern Pakistan), originally known as "Sindhu" in Sanskrit
. When Yunnan
was annexed by the Han Dynasty
in the 1st century, Chinese authorities reported an Indian "Shendu" community living there.
 After the transmission of Buddhism from India to China from the 1st century onwards, many Indian scholars and monks travelled to China, such as Batuo (fl.
After the transmission of Buddhism from India to China from the 1st century onwards, many Indian scholars and monks travelled to China, such as Batuo (fl.
464-495 AD)—founder of the Shaolin Monastery—and Bodhidharma
—founder of Chan/Zen
Buddhism—while many Chinese scholars and monks also travelled to India, such as Xuanzang
(b. 604) and I Ching
(635-713), both of whom were students at Nalanda University
in Bihar
. Xuanzang wrote the Great Tang Records on the Western Regions
, an account of his journey to India, which later inspired Wu Cheng'en
's Ming Dynasty
novel Journey to the West
, one of the Four Great Classical Novels
of Chinese literature
.
China gained control over large portions of the Silk Road and Central Asia. Wang Xuance
had sent a diplomatic mission to northern India, which was embroiled by civil war just following the death of Emperor Harsha
(590–647). After the murder of 30 members of this mission by usurper claiments to the throne, Wang fled, and returned with allied Nepal
i and Tibet
an troops to back the opposing claimant. With his forces, Wang besieged and captured the capital, while his deputy Jiang Shiren (蒋师仁) captured the usurper and sent him back to Emperor Tang Taizong
(599-649) in Chang'an
as a prisoner.
During the 8th century, the astronomical table
of sines by the Indian astronomer and mathematician
, Aryabhata
(476-550), were translated into the Chinese astronomical
and mathematical
book of the Treatise on Astrology of the Kaiyuan Era
(Kaiyuan Zhanjing), compiled in 718 AD during the Tang Dynasty. The Kaiyuan Zhanjing was compiled by Gautama Siddha
, an astronomer and astrologer born in Chang'an
, and whose family was originally from India
. He was also notable for his translation of the Navagraha
calendar into Chinese
.
 Between 1405 and 1433, the Ming Dynasty
Between 1405 and 1433, the Ming Dynasty
China sponsored a series of seven naval expeditions. Emperor Yongle
designed them to establish a Chinese presence, impose imperial control over trade, and impress foreign people in the Indian Ocean basin. He also might have wanted to extend the tributary system, by which Chinese dynasties traditionally recognized foreign peoples.
Admiral Zheng He
was dispatched to lead a series of huge naval expeditions to explore these regions. The largest of his voyages included over 317 ships and 28,000 men, and the largest of his treasure ships were over 126.73 m in length. During his voyages, he visited numerous Indian kingdoms and ports. On the first three voyages, Zheng He visited southeast Asia
, India, and Ceylon. The fourth expedition went to the Persian Gulf
and Arabia, and later expeditions ventured down the east Africa
n coast, as far as Malindi
in what is now Kenya
. Throughout his travels, Zheng He liberally dispensed Chinese gifts of silk, porcelain
, and other goods. In return, he received rich and unusual presents from his hosts, including African zebras and giraffes that ended their days in the Ming
imperial zoo. Zheng He and his company paid respects to local deities and customs, and in Ceylon they erected a monument (Galle Trilingual Inscription
) honouring Buddha
, Allah
, and Vishnu
.
of the Punjab region
in India was expanding into neighbouring lands. It had annexed Ladakh
into the state of Jammu
in 1834. In 1841, they invaded Tibet with an army and overran parts of western Tibet. Chinese forces defeated the Sikh army in December 1841, forcing the Sikh army to withdraw from Tibet, and in turn entered Ladakh and besieged Leh, where they were in turn defeated by the Sikh Army. At this point, neither side wished to continue the conflict, as the Sikhs were embroiled in tensions with the British that would lead up to the First Anglo-Sikh War
, while the Chinese was in the midst of the First Opium War
with the British East India Company. The Chinese and the Sikhs signed a treaty in September 1842, which stipulated no transgressions or interference in the other country's frontiers.
based his vision of "resurgent Asia" on friendship between the two largest states of Asia; his vision of an internationalist foreign policy governed by the ethics of the Panchsheel, which he initially believed was shared by China, came to grief when it became clear that the two countries had a conflict of interest in Tibet, which had traditionally served as a geographical and political buffer zone
, and where India believed it had inherited special privileges from the British Raj
.
However, the initial focus of the leaders of both the nations was not the foreign policy, but the internal development of their respective states. When they did concentrate on the foreign policies, their concern wasn’t one another, but rather the United States of America and the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics and the alliance systems which were dominated by the two superpowers.
, which it did by force of arms in 1950. To avoid antagonizing the People's Republic of China, Nehru informed Chinese leaders that India had neither political nor territorial ambitions, nor did it seek special privileges in Tibet, but that traditional trading rights must continue. With Indian support, Tibetan delegates signed an agreement in May 1951 recognizing PRC sovereignty but guaranteeing that the existing political and social system of Tibet would continue. Direct negotiations between India and the PRC commenced in an atmosphere improved by India's mediation efforts in ending the Korean War
(1950–1953).
Meanwhile, India was the 16th state to establish diplomatic relations with the People's Republic of China
, and did so on April 1, 1950.
In April 1954, India and the PRC signed an eight-year agreement on Tibet that set forth the basis of their relationship in the form of the Five Principles of Peaceful Coexistence
(or Panch Shila). Although critics called the Panch Shila naive, Nehru calculated that in the absence of either the wherewithal or a policy for defense of the Himalayan region, India's best guarantee of security was to establish a psychological buffer zone in place of the lost physical buffer of Tibet. Thus the catch phrase of India's diplomacy with China in the 1950s was Hindi-Chini bhai-bhai, which means, in Hindi
, "Indians and Chinese are brothers". Up until 1959, despite border skirmishes and discrepancies between Indian and Chinese maps, Chinese leaders amicably had assured India that there was no territorial controversy on the border though there is some evidence that India avoided bringing up the border issue in high level meetings.
In 1954, India published new maps that included the Aksai Chin
region within the boundaries of India (maps published at the time of India's independence did not clearly indicate whether the region was in India or Tibet). When an Indian reconnaissance party discovered a completed Chinese road running through the Aksai Chin
region of the Ladakh District of Jammu and Kashmir
, border clashes and Indian protests became more frequent and serious. In January 1959, PRC premier Zhou Enlai
wrote to Nehru, rejecting Nehru's contention that the border was based on treaty and custom and pointing out that no government in China had accepted as legal the McMahon Line
, which in the 1914 Simla Convention defined the eastern section of the border between India and Tibet. The Dalai Lama
, spiritual and temporal head of the Tibetan people, sought sanctuary in Dharmsala, Himachal Pradesh
, in March 1959, and thousands of Tibetan refugees settled in northwestern India, particularly in Himachal Pradesh. The People's Republic of China accused India of expansionism
and imperialism
in Tibet and throughout the Himalayan region. China claimed 104,000 km² of territory over which India's maps showed clear sovereignty, and demanded "rectification" of the entire border.
Zhou proposed that China relinquish its claim to most of India's northeast
in exchange for India's abandonment of its claim to Aksai Chin. The Indian government, constrained by domestic public opinion, rejected the idea of a settlement based on uncompensated loss of territory as being humiliating and unequal.
plains in the northeast and occupied strategic points in Ladakh
, until the PRC declared a unilateral cease-fire on 21 November and withdrew twenty kilometers behind its contended line of control.
At the time of Sino-Indian border conflict, a severe political split was taking place in the Communist Party of India
. One section was accused by the Indian government as being pro-PRC, and a large number of political leaders were jailed. Subsequently, CPI split with the leftist section forming the Communist Party of India (Marxist)
in 1964. CPI(M) held some contacts with the Communist Party of China
in the initial period after the split, but did not fully embrace the political line of Mao Zedong.
Relations between the PRC and India deteriorated during the rest of the 1960s and the early 1970s as Sino-Pakistani relations
improved and Sino-Soviet relations worsened
. The PRC backed Pakistan in its 1965 war with India
. Between 1967 and 1971, an all-weather road was built across territory claimed by India, linking PRC's Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region with Pakistan; India could do no more than protest. The PRC continued an active propaganda campaign against India and supplied ideological, financial, and other assistance to dissident groups, especially to tribes in northeastern India. The PRC accused India of assisting the Khampa rebels in Tibet. Diplomatic contact between the two governments was minimal although not formally severed. The flow of cultural and other exchanges that had marked the 1950s ceased entirely. The flourishing wool, fur and spice trade between Lhasa
and India through the Nathula Pass, an offshoot of the ancient Silk Road
in the then Indian protectorate of Sikkim
was also severed. However, the biweekly postal network through this pass was kept alive, which exists till today.
uprising in India by the Communist Naxalites and Maoists.
In 1967 a peasant uprising broke out in Naxalbari, led by pro-Maoist elements. A pronunciation by Mao titled "Spring Thunder over India" gave full moral support for the uprising. The support for the revolt marked the end for the relations between CPC and CPI(M). Naxalbari-inspired communists organized armed revolts in several parts of India, and in 1969 they formed the Communist Party of India (Marxist-Leninist)
. However, as the naxalite
movement disintegrated in various splits, the PRC withdrew its political support and turned non-committal towards the various Indian groups.
On 11 September 1967, troops of the Indian Army's 2nd Grenadiers were protecting an Engineering Company that was fencing the North Shoulder of Nathula, when Chinese troops opened fire on them. This escalated over the next five days to an exchange of heavy artillery and mortar fire between the Indians and the Chinese. 62 Indian soldiers, from the 2nd Grenadiers and the Artillery regiments were killed. Brigadier Rai Singh Yadav, the Commanding Officer, was awarded the MVC and Capt PS Dager was awarded a VrC
(posthumous) for their gallant actions.The extent of Chinese casualties in this incident is not known.
In the second, on 1 October 1967, a group of Indian Gurkha
Rifles soldiers (from the 7th Battalion of the 11th Regiment) noticed Chinese troops surrounding a sentry post near a boulder at the Chola outpost in Sikkim
. After a heated argument over the control of the boulder, a Chinese soldier bayoneted a Gurkha rifleman, triggering the start of a close-quarters knife and fire-fight, which then escalted to a mortar
and HMG
duel. The Chinese troops had to signal a ceasefire just after three hours of fighting, but later scaled Point 15450 to establish themselves there. The Gurkhas outflanked them the next day to regain Point 15450 and the Chinese retreated across the LAC. 21 Indian soldiers were killed in this action. The Indian government awarded Vir Chakra
s to Rifleman Limbu (posthumous) and battalion commander Major K.B. Joshi for their gallant actions. The extent of Chinese casualties in this skirmish is also not known.
, and the United States
and the PRC sided with Pakistan in its December 1971 war with India
. Although China strongly condemned India, it did not carry out its veiled threat to intervene on Pakistan's behalf. By this time, the PRC had just replaced the Republic of China in the UN
where its representatives denounced India as being a "tool of Soviet expansionism."
India and the PRC renewed efforts to improve relations after Indian Prime Minister Indira Gandhi
's Congress party
lost the 1977 elections to Morarji Desai
's Janata Party
. The new Desai government sought to improve long-strained relations with Pakistan and the PRC. In 1978, the Indian Minister of External Affairs Atal Bihari Vajpayee
made a landmark visit to Beijing, and both nations officially re-established diplomatic relations in 1979. The PRC modified its pro-Pakistan stand on Kashmir
and appeared willing to remain silent on India's absorption of Sikkim and its special advisory relationship with Bhutan
. The PRC's leaders agreed to discuss the boundary issue, India's priority, as the first step to a broadening of relations. The two countries hosted each others' news agencies, and Mount Kailash
and Mansarowar Lake
in Tibet, the mythological home of the Hindu pantheon, were opened to annual pilgrimage
s from India.
was invited to India, where he made complimentary remarks about India's role in South Asia
. PRC premier Zhao Ziyang
concurrently toured Pakistan, Nepal
, and Bangladesh
.
In 1980, Indian Prime Minister Indira Gandhi
approved a plan to upgrade the deployment of forces around the Line of Actual Control to avoid unilateral redefinitions of the line. India also increased funds for infrastructural development in these areas.
In 1984, squads of Indian soldiers began actively patrolling the Sumdorong Chu Valley in Arunachal Pradesh
(formerly NEFA), which is north of the McMahon Line as drawn on the Simla Treaty map but south of the ridge which Indian claims is meant to delineate the McMahon Line. The Sumdorong Chu valley "seemed to lie to the north of the McMahon line; but is south of the highest ridge in the area, and the McMahon line is meant to follow the highest points" according to the Indian claims, while the Chinese did not recognize the McMahon Line as legitimate and were not prepared to accept an Indian claim line even further north than that. The Indian team left the area before the winter. In the winter of 1986, the Chinese deployed their troops to the Sumdorong Chu before the Indian team could arrive in the summer and built a Helipad at Wandung. Surprised by the Chinese occupation, India's then Chief of Army Staff, General K.Sundarji, airlifted a brigade to the region.
Chinese troops could not move any further into the valley and were forced to move sideways along the Thag La ridge, away from the valley. By 1987, Beijing's reaction was similar to that in 1962 and this prompted many Western diplomats to predict war. However, Indian foreign minister N.D. Tiwari and Prime Minister Rajiv Gandhi
travelled to Beijing over the following months to negotiate a mutual de-escalation.
After the Huang visit, India and the PRC held eight rounds of border negotiations between December 1981 and November 1987. These talks initially raised hopes that progress could be made on the border issue. However, in 1985 the PRC stiffened its position on the border and insisted on mutual concessions without defining the exact terms of its "package proposal" or where the actual line of control lay. In 1986 and 1987, the negotiations achieved nothing, given the charges exchanged between the two countries of military encroachment in the Sumdorung Chu Valley of the Tawang tract on the eastern sector of the border. China's construction of a military post and helicopter pad in the area in 1986 and India's grant of statehood to Arunachal Pradesh
(formerly the North-East Frontier Agency
) in February 1987 caused both sides to deploy new troops to the area, raising tensions and fears of a new border war. The PRC relayed warnings that it would "teach India a lesson" if it did not cease "nibbling" at Chinese territory. By the summer of 1987, however, both sides had backed away from conflict and denied that military clashes had taken place.
A warming trend in relations was facilitated by Rajiv Gandhi
's visit to China in December 1988. The two sides issued a joint communiqué that stressed the need to restore friendly relations on the basis of the Panch Shila and noted the importance of the first visit by an Indian prime minister
to China since Nehru's 1954 visit. India and the People's Republic of China agreed to broaden bilateral ties in various areas, working to achieve a "fair and reasonable settlement while seeking a mutually acceptable solution" to the border dispute. The communiqué also expressed China's concern about agitation by Tibetan separatists in India and reiterated China's position that Tibet was an integral part of China and that anti-China political activities by expatriate Tibetans was not to be tolerated. Rajiv Gandhi signed bilateral agreements on science and technology cooperation, on civil aviation to establish direct air links, and on cultural exchanges. The two sides also agreed to hold annual diplomatic consultations between foreign ministers, and to set up a joint ministerial committee on economic and scientific cooperation and a joint working group on the boundary issue. The latter group was to be led by the Indian foreign secretary and the Chinese vice minister of foreign affairs.
to India and the May 1992 visit to China of Indian president
R. Venkataraman
. Six rounds of talks of the Indian-Chinese Joint Working Group on the Border Issue were held between December 1988 and June 1993. Progress was also made in reducing tensions on the border via confidence-building measures, including mutual troop reductions, regular meetings of local military commanders, and advance notification of military exercises. Border trade resumed in July 1992 after a hiatus of more than thirty years, consulates reopened in Bombay (Mumbai) and Shanghai
in December 1992, and, in June 1993, the two sides agreed to open an additional border trading post. During Sharad Pawar
's July 1992 visit to Beijing
, the first ever by an Indian minister of defence, the two defense establishments agreed to develop academic, military, scientific, and technological exchanges and to schedule an Indian port call by a Chinese naval
vessel.
Substantial movement in relations continued in 1993. The sixth-round joint working group talks were held in June in New Delhi
but resulted in only minor developments. However, as the year progressed the long-standing border dispute was eased as a result of bilateral pledges to reduce troop levels and to respect the cease-fire line along the India-China border. Prime Minister Narasimha Rao
and Premier Li Peng signed the border agreement and three other agreements (on cross-border trade, and on increased cooperation on the environment and in radio and television broadcasting) during the former's visit to Beijing in September. A senior-level Chinese military delegation made a six-day goodwill visit to India in December 1993 aimed at "fostering confidence-building measures between the defense forces of the two countries." The visit, however, came at a time when press reports revealed that, as a result of improved relations between the PRC and Burma, China was exporting greater amounts of military matériel to Burma's army, navy, and air force and sending an increasing number of technicians to Burma. Of concern to Indian security officials was the presence of Chinese radar technicians in Burma's Coco Islands
, which border India's Union Territory
of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. Nevertheless, movement continued in 1994 on troop reductions along the Himalayan frontier. Moreover, in January 1994 Beijing announced that it not only favored a negotiated solution on Kashmir, but also opposed any form of independence for the region.
Talks were held in New Delhi in February 1994 aimed at confirming established "confidence-building measures" and discussing clarification of the "line of actual control", reduction of armed forces along the line, and prior information about forthcoming military exercises. China's hope for settlement of the boundary issue was reiterated.
The 1993 Chinese military visit to India was reciprocated by Indian army chief of staff General B. C. Joshi. During talks in Beijing in July 1994, the two sides agreed that border problems should be resolved peacefully through "mutual understanding and concessions." The border issue was raised in September 1994 when PRC minister of national defense Chi Haotian
visited New Delhi for extensive talks with high-level Indian trade and defense officials. Further talks in New Delhi in March 1995 by the India-China Expert Group led to an agreement to set up two additional points of contact along the 4,000 km border to facilitate meetings between military personnel. The two sides also were reported as "seriously engaged" in defining the McMahon Line and the line of actual control vis-à-vis military exercises and prevention of air intrusion. Talks in Beijing in July 1995 aimed at better border security and combating cross-border crimes and in New Delhi in August 1995 on additional troop withdrawals from the border made further progress in reducing tensions.
Possibly indicative of the further relaxation of India-China relations, at least there was little notice taken in Beijing, was the April 1995 announcement, after a year of consultation, of the opening of the Taipei Economic and Cultural Center in New Delhi. The center serves as the representative office of the Republic of China
(Taiwan) and is the counterpart of the India-Taipei Association in Taiwan; both institutions have the goal of improving relations between the two sides, which have been strained since New Delhi's recognition of Beijing in 1950.
Sino-Indian relations hit a low point in 1998 following India's nuclear tests in May. Indian Defense Minister George Fernandes
declared that "China is India's number one threat", hinting that India developed nuclear weapons in defense against China's nuclear arsenal. In 1998, China was one of the strongest international critics of India's nuclear tests and entry into the nuclear club. During the 1999 Kargil War
China voiced support for Pakistan, but also counseled Pakistan to withdraw its forces.
's visit to China, 2000 marked a gradual re-engagement of Indian and Chinese diplomacy. In a major embarrassment for China, the 17th Karmapa
, Urgyen Trinley Dorje
, who was proclaimed by China, made a dramatic escape from Tibet to the Rumtek Monastery
in Sikkim. Chinese officials were in a quandary on this issue as any protest to India on the issue would mean an explicit endorsement on India's governance of Sikkim, which the Chinese still hadn't recognised. In 2002, Chinese Premier Zhu Rongji
reciprocated by visiting India, with a focus on economic issues. 2003 ushered in a marked improvement in Sino-Indian relations following Indian Prime Minister Atal Bihari Vajpayee
's landmark June 2003 visit to China. China officially recognized Indian sovereignty over Sikkim as the two nations moved toward resolving their border disputes.
2004 also witnessed a gradual improvement in the international area when the two countries proposed opening up the Nathula and Jelepla Passes in Sikkim which would be mutually beneficial to both countries. 2004 was a milestone in Sino-Indian bilateral trade, surpassing the $10 billion mark for the first time. In April 2005, Chinese Premier Wen Jiabao
visited Bangalore
to push for increased Sino-Indian cooperation in high-tech industries. In a speech, Wen stated "Cooperation is just like two pagodas (temples), one hardware and one software. Combined, we can take the leadership position in the world." Wen stated that the 21st century will be "the Asian century of the IT industry." The high-level visit was also expected to produce several agreements to deepen political, cultural and economic ties between the two nations. Regarding the issue of India gaining a permanent seat on the UN Security Council, on his visit, Wen Jiabao initially seemed to support the idea, but had returned to a neutral position on the subject by the time he returned to China. In the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation
(SAARC) Summit (2005) China was granted an observer status. While other countries in the region are ready to consider China for permanent membership in the SAARC, India seems reluctant.
A very important dimension of the evolving Sino-Indian relationship is based on the energy requirements of their industrial expansion and their readiness to proactively secure them by investing in the oilfields abroad - in Africa, the Middle East and Central Asia. On the one hand, these ventures entail competition (which has been evident in oil biddings for various international projects recently). But on the other hand, a degree of cooperation too is visible, as they are increasingly confronting bigger players in the global oil market. This cooperation was sealed in Beijing on January 12, 2006 during the visit of Petroleum and Natural Gas Minister Mani Shankar Aiyar
, who signed an agreement which envisages ONGC Videsh Ltd (OVL) and the China National Petroleum Corporation
(CNPC) placing joint bids for promising projects elsewhere. This may have important consequences for their international relations.
On July 6, 2006, China and India re-opened Nathula, an ancient trade route which was part of the Silk Road
. Nathula is a pass through the Himalayas and it was closed 44 years prior to 2006 when the Sino-Indian War
broke out in 1962. The initial agreement for the re-opening of the trade route was reached in 2003, and a final agreement was formalized on June 18, 2006. Officials say that the re-opening of border trade will help ease the economic isolation of the region. In November 2006, China and India had a verbal spat over claim of the north-east Indian state of Arunachal Pradesh
. India claimed that China was occupying 38,000 square kilometres of its territory in Kashmir
, while China claimed the whole of Arunachal Pradesh as its own. In May 2007, China denied the application for visa from an Indian Administrative Service
officer in Arunachal Pradesh. According to China, since Arunachal Pradesh is a territory of China, he would not need a visa to visit his own country. Later in December 2007, China appeared to have reversed its policy by granting a visa to Marpe Sora, an Arunachal born professor in computer science.
In January 2008, Prime Minister Manmohan Singh
visited China and met with President Hu Jintao
and Premier Wen Jiabao
and had bilateral discussions related to trade, commerce, defense, military, and various other issues.
Until 2008 the British Government's position remained the same as had been since the Simla Accord of 1913: that China held suzerainty
over Tibet but not sovereignty
. Britain revised this view on 29 October 2008, when it recognised Chinese sovereignty over Tibet by issuing a statement on its website. The Economist
stated that although the British Foreign Office's website does not use the word sovereignty, officials at the Foreign Office said "it means that, as far as Britain is concerned, 'Tibet is part of China. Full stop.'" This change in Britain's position affects India's claim to its North Eastern territories which rely on the same Simla Accord that Britain's prior position on Tibet's sovereignty was based upon.
In October 2009, Asian Development Bank
formally acknowledging Arunachal Pradesh as part of India, approved a loan to India for a development project there. Earlier China had exercised pressure on the bank to cease the loan, however India succeeded in securing the loan with the help of the United States and Japan. China expressed displeasure at ADB
for the same.
was held in Brasilia.
Chinese Premier Wen Jiabao
paid an official visit to India from Dec.15-17,2010 at the invitation of Prime Minister Manmohan Singh
. He was accompanied by 400 Chinese business leaders, who wished to sign business deals with Indian companies.
In April 2011, the first BRICS
summit was held in Sanya
, Hainan
, China. During the event, the two countries agreed to restore defence co-operation, and China had hinted that it may reverse its policy of administering stapled visas to residents of Jammu and Kashmir
.
Articles
News
People's Republic of China
China , officially the People's Republic of China , is the most populous country in the world, with over 1.3 billion citizens. Located in East Asia, the country covers approximately 9.6 million square kilometres...
(PRC) and the Republic of India. China and India are the world's most populous states and also fastest growing major economies. The resultant growth in China and India's global diplomatic and economic influence has also increased the significance of their bilateral relationship.
China and India are two of the world’s oldest civilization
Civilization
Civilization is a sometimes controversial term that has been used in several related ways. Primarily, the term has been used to refer to the material and instrumental side of human cultures that are complex in terms of technology, science, and division of labor. Such civilizations are generally...
s and have coexisted in peace for millennia. Cultural and economic relations between China and India date back to ancient times. The Silk Road
Silk Road
The Silk Road or Silk Route refers to a historical network of interlinking trade routes across the Afro-Eurasian landmass that connected East, South, and Western Asia with the Mediterranean and European world, as well as parts of North and East Africa...
not only served as a major trade route
Trade route
A trade route is a logistical network identified as a series of pathways and stoppages used for the commercial transport of cargo. Allowing goods to reach distant markets, a single trade route contains long distance arteries which may further be connected to several smaller networks of commercial...
between India and China, but is also credited for facilitating the spread the Buddhism
Buddhism
Buddhism is a religion and philosophy encompassing a variety of traditions, beliefs and practices, largely based on teachings attributed to Siddhartha Gautama, commonly known as the Buddha . The Buddha lived and taught in the northeastern Indian subcontinent some time between the 6th and 4th...
from India to East Asia. During the 19th century, China's growing opium trade with the British Raj
British Raj
British Raj was the British rule in the Indian subcontinent between 1858 and 1947; The term can also refer to the period of dominion...
triggered the Opium Wars
Opium Wars
The Opium Wars, also known as the Anglo-Chinese Wars, divided into the First Opium War from 1839 to 1842 and the Second Opium War from 1856 to 1860, were the climax of disputes over trade and diplomatic relations between China under the Qing Dynasty and the British Empire...
. During World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
, India and China played a crucial role in halting the progress of Imperial Japan.
Relations between contemporary China and India have been been characterized by border disputes
Origins of the Sino-Indian border dispute
Sovereignty over two separated pieces of territory was contested during the Sino-Indian War. One is Aksai Chin is located either in the Indian province of Kashmir or the Chinese province of Xinjiang in the west. It is a virtually uninhabited high-altitude wasteland crossed by the Xinjiang-Tibet...
, resulting in three major military conflicts — the Sino-Indian War
Sino-Indian War
The Sino-Indian War , also known as the Sino-Indian Border Conflict , was a war between China and India that occurred in 1962. A disputed Himalayan border was the main pretext for war, but other issues played a role. There had been a series of violent border incidents after the 1959 Tibetan...
of 1962, the Chola incident
Chola incident
The 1967 Sino-Indian skirmish also known as the Chola incident, was a day-long military conflict between Indian troops and members of the Chinese People's Liberation Army in Sikkim, who had infiltrated the area. The end of the battle saw the retreat of the People's Liberation Army from...
in 1967, and the 1987 Sino-Indian skirmish
1987 Sino-Indian skirmish
The 1987 Sino-Indian skirmish was the third military conflict between the Chinese army and Indian army that occurred at Sumdorong Chu Valley, with the previous one taking place almost a quarter of a century earlier.-Events leading up the near war:...
. However, since late 1980s, both countries have successfully attempted to reignite diplomatic and economic ties. In 2008, China emerged as the largest trading partner of India and the two countries have also attempted to extend their strategic and military relations.
Despite growing economic and strategic ties, several issues continue to strain Sino-Indian relations. Though bilateral trade has continuously grown, India faces massive trade imbalance heavily in favor of China. The two countries have failed to resolve their long-standing border dispute and Indian media outlets repeatedly report Chinese military incursions into Indian territory. Both nations have steadily built-up military infrastructure along border areas. Additionally, India harbors suspicions about China's strong strategic relations with its arch-rival Pakistan while China has expressed concerns about Indian military and economic activities in disputed South China Sea.
Geographical overview

Nepal
Nepal , officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, is a landlocked sovereign state located in South Asia. It is located in the Himalayas and bordered to the north by the People's Republic of China, and to the south, east, and west by the Republic of India...
and Bhutan
Bhutan
Bhutan , officially the Kingdom of Bhutan, is a landlocked state in South Asia, located at the eastern end of the Himalayas and bordered to the south, east and west by the Republic of India and to the north by the People's Republic of China...
, two states lying along the Himalaya range, and acting as buffer state
Buffer state
A buffer state is a country lying between two rival or potentially hostile greater powers, which by its sheer existence is thought to prevent conflict between them. Buffer states, when authentically independent, typically pursue a neutralist foreign policy, which distinguishes them from satellite...
s. In addition, the disputed Kashmir
Kashmir
Kashmir is the northwestern region of the Indian subcontinent. Until the mid-19th century, the term Kashmir geographically denoted only the valley between the Great Himalayas and the Pir Panjal mountain range...
province of India (claimed by Pakistan
Pakistan
Pakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan...
) borders both the PRC and India. As Pakistan has tense relations with India, Kashmir's state of unrest serves as a natural ally to the PRC.
Two territories are currently disputed between the People's Republic of China and India: Aksai Chin
Aksai Chin
Aksai Chin is one of the two main disputed border areas between China and India, and the other is South Tibet, which comprises most of India's Arunachal Pradesh. It is administered by China as part of Hotan County in the Hotan Prefecture of Xinjiang Autonomous Region, but is also claimed by India...
and Arunachal Pradesh
Arunachal Pradesh
Arunachal Pradesh is a state of India, located in the far northeast. It borders the states of Assam and Nagaland to the south, and shares international borders with Burma in the east, Bhutan in the west, and the People's Republic of China in the north. The majority of the territory is claimed by...
. Arunachal Pradesh is located near the far east of India, while Aksai Chin is located near the northwest corner of India, at the junction of India, Pakistan, and the PRC. However, all sides in the dispute have agreed to respect the Line of Actual Control
Line of Actual Control
The Line of Actual Control is the effective border between India and People's Republic of China . The LAC is 4,057-km long and traverses three areas of northern Indian states: western , middle and eastern...
and this border dispute is not widely seen as a major flashpoint
Flashpoint (politics)
In international relations, a flashpoint is an area or dispute that has a strong possibility of developing into a war.-Current flashpoints:* the Taiwan straits* Korea peninsula* the Golan heights* Israeli-Lebanon border* Kashmir* the Spratly Islands...
.
Antiquity
India and China had relatively little modern political contact before the 1950s. However, both countries have had extensive and close historical cultural contact since the 1st century, especially with the transmission of BuddhismBuddhism
Buddhism is a religion and philosophy encompassing a variety of traditions, beliefs and practices, largely based on teachings attributed to Siddhartha Gautama, commonly known as the Buddha . The Buddha lived and taught in the northeastern Indian subcontinent some time between the 6th and 4th...
from India to China. Trade relations via the Silk Road
Silk Road
The Silk Road or Silk Route refers to a historical network of interlinking trade routes across the Afro-Eurasian landmass that connected East, South, and Western Asia with the Mediterranean and European world, as well as parts of North and East Africa...
acted as economic contact between the two regions.
China and India have also had some contact before the transmission of Buddhism. References to a people called the Chinas
Chinas
The Chinas or Chīnaḥ are a people mentioned in ancient Indian literature from the first millennium BC, such as the Mahabharata, Laws of Manu, as well the Puranic literature...
, now believed to be the Chinese
Han Chinese
Han Chinese are an ethnic group native to China and are the largest single ethnic group in the world.Han Chinese constitute about 92% of the population of the People's Republic of China , 98% of the population of the Republic of China , 78% of the population of Singapore, and about 20% of the...
, are found in ancient Indian literature
Indian literature
Indian literature refers to the literature produced on the Indian subcontinent until 1947 and in the Republic of India thereafter. The Republic of India has 22 officially recognized languages....
. The Indian epic
Indian epic poetry
Indian epic poetry is the epic poetry written in the Indian subcontinent, traditionally called Kavya . The Ramayana and Mahabharata, originally composed in Sanskrit and translated thereafter into many other Indian languages, are some of the oldest surviving epic poems on earth and form part of...
Mahabharata
Mahabharata
The Mahabharata is one of the two major Sanskrit epics of ancient India and Nepal, the other being the Ramayana. The epic is part of itihasa....
(c. 5th century BC) contains references to "China", which may have been referring to the Qin
Qin (state)
The State of Qin was a Chinese feudal state that existed during the Spring and Autumn and Warring States Periods of Chinese history...
state which later became the Qin Dynasty
Qin Dynasty
The Qin Dynasty was the first imperial dynasty of China, lasting from 221 to 207 BC. The Qin state derived its name from its heartland of Qin, in modern-day Shaanxi. The strength of the Qin state was greatly increased by the legalist reforms of Shang Yang in the 4th century BC, during the Warring...
. Chanakya
Chanakya
Chānakya was a teacher to the first Maurya Emperor Chandragupta , and the first Indian emperor generally considered to be the architect of his rise to power. Traditionally, Chanakya is also identified by the names Kautilya and VishnuGupta, who authored the ancient Indian political treatise...
(c. 350-283 BC), the prime minister
Prime minister
A prime minister is the most senior minister of cabinet in the executive branch of government in a parliamentary system. In many systems, the prime minister selects and may dismiss other members of the cabinet, and allocates posts to members within the government. In most systems, the prime...
of the Maurya Empire
Maurya Empire
The Maurya Empire was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in ancient India, ruled by the Mauryan dynasty from 321 to 185 BC...
and a professor at Takshashila University, refers to Chinese silk
Silk
Silk is a natural protein fiber, some forms of which can be woven into textiles. The best-known type of silk is obtained from the cocoons of the larvae of the mulberry silkworm Bombyx mori reared in captivity...
as "cinamsuka" (Chinese silk dress) and "cinapatta" (Chinese silk bundle) in his Arthashastra
Arthashastra
The Arthashastra is an ancient Indian treatise on statecraft, economic policy and military strategy which identifies its author by the names Kautilya and , who are traditionally identified with The Arthashastra (IAST: Arthaśāstra) is an ancient Indian treatise on statecraft, economic policy and...
.
In the Records of the Grand Historian
Records of the Grand Historian
The Records of the Grand Historian, also known in English by the Chinese name Shiji , written from 109 BC to 91 BC, was the Magnum opus of Sima Qian, in which he recounted Chinese history from the time of the Yellow Emperor until his own time...
, Zhang Qian
Zhang Qian
Zhang Qian was an imperial envoy to the world outside of China in the 2nd century BCE, during the time of the Han Dynasty...
(d. 113 BC) and Sima Qian
Sima Qian
Sima Qian was a Prefect of the Grand Scribes of the Han Dynasty. He is regarded as the father of Chinese historiography for his highly praised work, Records of the Grand Historian , a "Jizhuanti"-style general history of China, covering more than two thousand years from the Yellow Emperor to...
(145-90 BC) make references to "Shendu", which may have been referring to the Indus Valley
Indus River
The Indus River is a major river which flows through Pakistan. It also has courses through China and India.Originating in the Tibetan plateau of western China in the vicinity of Lake Mansarovar in Tibet Autonomous Region, the river runs a course through the Ladakh district of Jammu and Kashmir and...
(the Sindh
Sindh
Sindh historically referred to as Ba'ab-ul-Islam , is one of the four provinces of Pakistan and historically is home to the Sindhi people. It is also locally known as the "Mehran". Though Muslims form the largest religious group in Sindh, a good number of Christians, Zoroastrians and Hindus can...
province in modern Pakistan), originally known as "Sindhu" in Sanskrit
Sanskrit
Sanskrit , is a historical Indo-Aryan language and the primary liturgical language of Hinduism, Jainism and Buddhism.Buddhism: besides Pali, see Buddhist Hybrid Sanskrit Today, it is listed as one of the 22 scheduled languages of India and is an official language of the state of Uttarakhand...
. When Yunnan
Yunnan
Yunnan is a province of the People's Republic of China, located in the far southwest of the country spanning approximately and with a population of 45.7 million . The capital of the province is Kunming. The province borders Burma, Laos, and Vietnam.Yunnan is situated in a mountainous area, with...
was annexed by the Han Dynasty
Han Dynasty
The Han Dynasty was the second imperial dynasty of China, preceded by the Qin Dynasty and succeeded by the Three Kingdoms . It was founded by the rebel leader Liu Bang, known posthumously as Emperor Gaozu of Han. It was briefly interrupted by the Xin Dynasty of the former regent Wang Mang...
in the 1st century, Chinese authorities reported an Indian "Shendu" community living there.
Middle Ages

Floruit
Floruit , abbreviated fl. , is a Latin verb meaning "flourished", denoting the period of time during which something was active...
464-495 AD)—founder of the Shaolin Monastery—and Bodhidharma
Bodhidharma
Bodhidharma was a Buddhist monk who lived during the 5th/6th century AD. He is traditionally credited as the transmitter of Ch'an to China, and regarded as the first Chinese patriarch...
—founder of Chan/Zen
Zen
Zen is a school of Mahāyāna Buddhism founded by the Buddhist monk Bodhidharma. The word Zen is from the Japanese pronunciation of the Chinese word Chán , which in turn is derived from the Sanskrit word dhyāna, which can be approximately translated as "meditation" or "meditative state."Zen...
Buddhism—while many Chinese scholars and monks also travelled to India, such as Xuanzang
Xuanzang
Xuanzang was a famous Chinese Buddhist monk, scholar, traveler, and translator who described the interaction between China and India in the early Tang period...
(b. 604) and I Ching
I Ching (monk)
Yijing was a Tang Dynasty Chinese Buddhist monk, originally named Zhang Wenming . The written records of his travels contributed to the world knowledge of the ancient kingdom of Srivijaya, as well as providing information about the other kingdoms lying on the route between China and the Nālandā...
(635-713), both of whom were students at Nalanda University
Nalanda
Nālandā is the name of an ancient center of higher learning in Bihar, India.The site of Nalanda is located in the Indian state of Bihar, about 55 miles south east of Patna, and was a Buddhist center of learning from the fifth or sixth century CE to 1197 CE. It has been called "one of the...
in Bihar
Bihar
Bihar is a state in eastern India. It is the 12th largest state in terms of geographical size at and 3rd largest by population. Almost 58% of Biharis are below the age of 25, which is the highest proportion in India....
. Xuanzang wrote the Great Tang Records on the Western Regions
Great Tang Records on the Western Regions
The Great Tang Records on the Western Regions is a narrative of Xuanzang's nineteen year journey through Chang'an to Central Asia and eventually South Asia between 626 and 645...
, an account of his journey to India, which later inspired Wu Cheng'en
Wu Cheng'en
Wu Cheng'en , courtesy name Ruzhong , pen name "Sheyang Hermit," was a Chinese novelist and poet of the Ming Dynasty, best known for being the attributed author of one of the Four Great Classical Novels of Chinese literature, Journey to the West.-Biography:Wu was born in Lianshui, in Jiangsu...
's Ming Dynasty
Ming Dynasty
The Ming Dynasty, also Empire of the Great Ming, was the ruling dynasty of China from 1368 to 1644, following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan Dynasty. The Ming, "one of the greatest eras of orderly government and social stability in human history", was the last dynasty in China ruled by ethnic...
novel Journey to the West
Journey to the West
Journey to the West is one of the Four Great Classical Novels of Chinese literature. It was written by Wu Cheng'en in the 16th century. In English-speaking countries, the tale is also often known simply as Monkey. This was one title used for a popular, abridged translation by Arthur Waley...
, one of the Four Great Classical Novels
Four Great Classical Novels
The Four Great Classical Novels, or the Four Major Classical Novels of Chinese literature, are the four novels commonly regarded by scholars to be the greatest and most influential of pre-modern Chinese fiction. Dating from the Ming and Qing dynasties, they are well known to most Chinese readers...
of Chinese literature
Chinese literature
Chinese literature extends thousands of years, from the earliest recorded dynastic court archives to the mature fictional novels that arose during the Ming Dynasty to entertain the masses of literate Chinese...
.
Tang and Harsha dynasties
During the 7th century, Tang DynastyTang Dynasty
The Tang Dynasty was an imperial dynasty of China preceded by the Sui Dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms Period. It was founded by the Li family, who seized power during the decline and collapse of the Sui Empire...
China gained control over large portions of the Silk Road and Central Asia. Wang Xuance
Wang Xuance
Wang Xuance , fl. 7th century) was a Tang Dynasty guard officer and diplomat. In 648, Tang Taizong sent him to India in response to Harshavardhana sending an ambassador to China. However once in India he discovered Harshavardhana had died and the new king attacked Wang and his 30 mounted subordinates...
had sent a diplomatic mission to northern India, which was embroiled by civil war just following the death of Emperor Harsha
Harsha
Harsha or Harsha Vardhana or Harshvardhan was an Indian emperor who ruled northern India from 606 to 647 AD. He was the son of Prabhakara Vardhana and younger brother of Rajya Vardhana, a king of Thanesar, Haryana...
(590–647). After the murder of 30 members of this mission by usurper claiments to the throne, Wang fled, and returned with allied Nepal
Nepal
Nepal , officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, is a landlocked sovereign state located in South Asia. It is located in the Himalayas and bordered to the north by the People's Republic of China, and to the south, east, and west by the Republic of India...
i and Tibet
Tibet
Tibet is a plateau region in Asia, north-east of the Himalayas. It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people as well as some other ethnic groups such as Monpas, Qiang, and Lhobas, and is now also inhabited by considerable numbers of Han and Hui people...
an troops to back the opposing claimant. With his forces, Wang besieged and captured the capital, while his deputy Jiang Shiren (蒋师仁) captured the usurper and sent him back to Emperor Tang Taizong
Emperor Taizong of Tang
Emperor Taizong of Tang , personal name Lǐ Shìmín , was the second emperor of the Tang Dynasty of China, ruling from 626 to 649...
(599-649) in Chang'an
Chang'an
Chang'an is an ancient capital of more than ten dynasties in Chinese history, today known as Xi'an. Chang'an literally means "Perpetual Peace" in Classical Chinese. During the short-lived Xin Dynasty, the city was renamed "Constant Peace" ; yet after its fall in AD 23, the old name was restored...
as a prisoner.
During the 8th century, the astronomical table
Āryabhaṭa's sine table
Āryabhaṭa's sine table is a set of twenty-four of numbers given in the astronomical treatise Āryabhaṭiya composed by the fifth century Indian mathematician and astronomer Āryabhaṭa , for the computation of the half-chords of certain set of arcs of a circle...
of sines by the Indian astronomer and mathematician
Indian mathematics
Indian mathematics emerged in the Indian subcontinent from 1200 BCE until the end of the 18th century. In the classical period of Indian mathematics , important contributions were made by scholars like Aryabhata, Brahmagupta, and Bhaskara II. The decimal number system in use today was first...
, Aryabhata
Aryabhata
Aryabhata was the first in the line of great mathematician-astronomers from the classical age of Indian mathematics and Indian astronomy...
(476-550), were translated into the Chinese astronomical
Chinese astronomy
Astronomy in China has a very long history, with historians considering that "they [the Chinese] were the most persistent and accurate observers of celestial phenomena anywhere in the world before the Arabs."...
and mathematical
Chinese mathematics
Mathematics in China emerged independently by the 11th century BC. The Chinese independently developed very large and negative numbers, decimals, a place value decimal system, a binary system, algebra, geometry, and trigonometry....
book of the Treatise on Astrology of the Kaiyuan Era
Treatise on Astrology of the Kaiyuan Era
The Treatise on Astrology of the Kaiyuan Era is a Chinese astrology encyclopedia compiled by the lead editor Gautama Siddha and numerous scholars from 714 to 724 AD during the Kaiyuan era of Tang Dynasty. The compilation is attributed to the author by 729. Its full title is regarded as the Great...
(Kaiyuan Zhanjing), compiled in 718 AD during the Tang Dynasty. The Kaiyuan Zhanjing was compiled by Gautama Siddha
Gautama Siddha
Gautama Siddha, astronomer, astrologer and compiler of Indian descent, known for leading the compilation of the Treatise on Astrology of the Kaiyuan Era during the Tang Dynasty. He was born in Chang'an, and his family was originally from India, according to a tomb stele uncovered in 1977 in Xi'an...
, an astronomer and astrologer born in Chang'an
Chang'an
Chang'an is an ancient capital of more than ten dynasties in Chinese history, today known as Xi'an. Chang'an literally means "Perpetual Peace" in Classical Chinese. During the short-lived Xin Dynasty, the city was renamed "Constant Peace" ; yet after its fall in AD 23, the old name was restored...
, and whose family was originally from India
History of India
The history of India begins with evidence of human activity of Homo sapiens as long as 75,000 years ago, or with earlier hominids including Homo erectus from about 500,000 years ago. The Indus Valley Civilization, which spread and flourished in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent from...
. He was also notable for his translation of the Navagraha
Navagraha
Graha is a 'cosmic influencer' on the living beings of mother Bhumidevi . In Hindu astrology, the Navagraha are some of these major influencers.All the navagraha have relative movement with respect to the background of fixed stars in the zodiac...
calendar into Chinese
Chinese language
The Chinese language is a language or language family consisting of varieties which are mutually intelligible to varying degrees. Originally the indigenous languages spoken by the Han Chinese in China, it forms one of the branches of Sino-Tibetan family of languages...
.
Ming dynasty

Ming Dynasty
The Ming Dynasty, also Empire of the Great Ming, was the ruling dynasty of China from 1368 to 1644, following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan Dynasty. The Ming, "one of the greatest eras of orderly government and social stability in human history", was the last dynasty in China ruled by ethnic...
China sponsored a series of seven naval expeditions. Emperor Yongle
Yongle Emperor
The Yongle Emperor , born Zhu Di , was the third emperor of the Ming Dynasty of China from 1402 to 1424. His Chinese era name Yongle means "Perpetual Happiness".He was the Prince of Yan , possessing a heavy military base in Beiping...
designed them to establish a Chinese presence, impose imperial control over trade, and impress foreign people in the Indian Ocean basin. He also might have wanted to extend the tributary system, by which Chinese dynasties traditionally recognized foreign peoples.
Admiral Zheng He
Zheng He
Zheng He , also known as Ma Sanbao and Hajji Mahmud Shamsuddin was a Hui-Chinese mariner, explorer, diplomat and fleet admiral, who commanded voyages to Southeast Asia, South Asia, the Middle East, and East Africa, collectively referred to as the Voyages of Zheng He or Voyages of Cheng Ho from...
was dispatched to lead a series of huge naval expeditions to explore these regions. The largest of his voyages included over 317 ships and 28,000 men, and the largest of his treasure ships were over 126.73 m in length. During his voyages, he visited numerous Indian kingdoms and ports. On the first three voyages, Zheng He visited southeast Asia
Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, South-East Asia, South East Asia or Southeastern Asia is a subregion of Asia, consisting of the countries that are geographically south of China, east of India, west of New Guinea and north of Australia. The region lies on the intersection of geological plates, with heavy seismic...
, India, and Ceylon. The fourth expedition went to the Persian Gulf
Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf, in Southwest Asia, is an extension of the Indian Ocean located between Iran and the Arabian Peninsula.The Persian Gulf was the focus of the 1980–1988 Iran-Iraq War, in which each side attacked the other's oil tankers...
and Arabia, and later expeditions ventured down the east Africa
East Africa
East Africa or Eastern Africa is the easterly region of the African continent, variably defined by geography or geopolitics. In the UN scheme of geographic regions, 19 territories constitute Eastern Africa:...
n coast, as far as Malindi
Malindi
Malindi is a town on Malindi Bay at the mouth of the Galana River, lying on the Indian Ocean coast of Kenya. It is 120 kilometres northeast of Mombasa. The population of Malindi is 117,735 . It is the capital of the Malindi District.Tourism is the major industry in Malindi. The city is...
in what is now Kenya
Kenya
Kenya , officially known as the Republic of Kenya, is a country in East Africa that lies on the equator, with the Indian Ocean to its south-east...
. Throughout his travels, Zheng He liberally dispensed Chinese gifts of silk, porcelain
Porcelain
Porcelain is a ceramic material made by heating raw materials, generally including clay in the form of kaolin, in a kiln to temperatures between and...
, and other goods. In return, he received rich and unusual presents from his hosts, including African zebras and giraffes that ended their days in the Ming
Ming
Ming is a common personal name among Chinese people, Vietnamese people, and Korean people. In pinyin, it is written Míng, in romanized Vietnamese, it is written as Minh, and in Korean it is pronounced Myeong...
imperial zoo. Zheng He and his company paid respects to local deities and customs, and in Ceylon they erected a monument (Galle Trilingual Inscription
Galle Trilingual Inscription
The Galle Trilingual Inscription was a stone tablet inscription in three languages, Chinese, Tamil and Persian, that was erected in 1411 in Galle, Sri Lanka to commemorate the second visit to the island by the Chinese admiral Zheng He...
) honouring Buddha
Gautama Buddha
Siddhārtha Gautama was a spiritual teacher from the Indian subcontinent, on whose teachings Buddhism was founded. In most Buddhist traditions, he is regarded as the Supreme Buddha Siddhārtha Gautama (Sanskrit: सिद्धार्थ गौतम; Pali: Siddhattha Gotama) was a spiritual teacher from the Indian...
, Allah
Allah
Allah is a word for God used in the context of Islam. In Arabic, the word means simply "God". It is used primarily by Muslims and Bahá'ís, and often, albeit not exclusively, used by Arabic-speaking Eastern Catholic Christians, Maltese Roman Catholics, Eastern Orthodox Christians, Mizrahi Jews and...
, and Vishnu
Vishnu
Vishnu is the Supreme god in the Vaishnavite tradition of Hinduism. Smarta followers of Adi Shankara, among others, venerate Vishnu as one of the five primary forms of God....
.
Sino-Sikh War
In the 18th to 19th centuries, the Sikh ConfederacySikh Confederacy
The Sikh Empire was an imperial power from the Indian Subcontinent. The empire, based around the Punjab region, existed from 1799 to 1849. It was forged, on the foundations of the Khalsa, under the leadership of Maharaja Ranjit Singh from a collection of autonomous Punjabi Misls...
of the Punjab region
Punjab region
The Punjab , also spelled Panjab |water]]s"), is a geographical region straddling the border between Pakistan and India which includes Punjab province in Pakistan and the states of the Punjab, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Chandigarh and some northern parts of the National Capital Territory of Delhi...
in India was expanding into neighbouring lands. It had annexed Ladakh
Ladakh
Ladakh is a region of Jammu and Kashmir, the northernmost state of the Republic of India. It lies between the Kunlun mountain range in the north and the main Great Himalayas to the south, inhabited by people of Indo-Aryan and Tibetan descent...
into the state of Jammu
Jammu
Jammu , also known as Duggar, is one of the three administrative divisions within Jammu and Kashmir, the northernmost state in India.Jammu city is the largest city in Jammu and the winter capital of Jammu and Kashmir...
in 1834. In 1841, they invaded Tibet with an army and overran parts of western Tibet. Chinese forces defeated the Sikh army in December 1841, forcing the Sikh army to withdraw from Tibet, and in turn entered Ladakh and besieged Leh, where they were in turn defeated by the Sikh Army. At this point, neither side wished to continue the conflict, as the Sikhs were embroiled in tensions with the British that would lead up to the First Anglo-Sikh War
First Anglo-Sikh War
The First Anglo-Sikh War was fought between the Sikh Empire and the British East India Company between 1845 and 1846. It resulted in partial subjugation of the Sikh kingdom.-Background and causes of the war:...
, while the Chinese was in the midst of the First Opium War
First Opium War
The First Anglo-Chinese War , known popularly as the First Opium War or simply the Opium War, was fought between the United Kingdom and the Qing Dynasty of China over their conflicting viewpoints on diplomatic relations, trade, and the administration of justice...
with the British East India Company. The Chinese and the Sikhs signed a treaty in September 1842, which stipulated no transgressions or interference in the other country's frontiers.
After independence
Jawaharlal NehruJawaharlal Nehru
Jawaharlal Nehru , often referred to with the epithet of Panditji, was an Indian statesman who became the first Prime Minister of independent India and became noted for his “neutralist” policies in foreign affairs. He was also one of the principal leaders of India’s independence movement in the...
based his vision of "resurgent Asia" on friendship between the two largest states of Asia; his vision of an internationalist foreign policy governed by the ethics of the Panchsheel, which he initially believed was shared by China, came to grief when it became clear that the two countries had a conflict of interest in Tibet, which had traditionally served as a geographical and political buffer zone
Buffer zone
A buffer zone is generally a zonal area that lies between two or more other areas , but depending on the type of buffer zone, the reason for it may be to segregate regions or to conjoin them....
, and where India believed it had inherited special privileges from the British Raj
British Raj
British Raj was the British rule in the Indian subcontinent between 1858 and 1947; The term can also refer to the period of dominion...
.
However, the initial focus of the leaders of both the nations was not the foreign policy, but the internal development of their respective states. When they did concentrate on the foreign policies, their concern wasn’t one another, but rather the United States of America and the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics and the alliance systems which were dominated by the two superpowers.
1950s
On October 1, 1949 the People’s Liberation Army defeated the Kuomintang (Nationalist Party) of China in a civil war and established the People's Republic of China. On August 15, 1947, India became an independent dominion under British Commonwealth and became a federal, democratic republic after its constitution came into effect on January 26, 1950. Mao Zedong, the Commander of the Liberation Army and the Chairman of the Communist Party of China viewed Tibet as an integral part of the Chinese State. Mao was determined to bring Tibet under direct administrative and military control of People’s Republic of China and saw Indian concern over Tibet as a manifestation of the Indian Government's interference in the internal affairs of the People’s Republic of China. The PRC sought to reassert control over Tibet and to end Lamaism (Tibetan Buddhism) and feudalismFeudalism
Feudalism was a set of legal and military customs in medieval Europe that flourished between the 9th and 15th centuries, which, broadly defined, was a system for ordering society around relationships derived from the holding of land in exchange for service or labour.Although derived from the...
, which it did by force of arms in 1950. To avoid antagonizing the People's Republic of China, Nehru informed Chinese leaders that India had neither political nor territorial ambitions, nor did it seek special privileges in Tibet, but that traditional trading rights must continue. With Indian support, Tibetan delegates signed an agreement in May 1951 recognizing PRC sovereignty but guaranteeing that the existing political and social system of Tibet would continue. Direct negotiations between India and the PRC commenced in an atmosphere improved by India's mediation efforts in ending the Korean War
Korean War
The Korean War was a conventional war between South Korea, supported by the United Nations, and North Korea, supported by the People's Republic of China , with military material aid from the Soviet Union...
(1950–1953).
Meanwhile, India was the 16th state to establish diplomatic relations with the People's Republic of China
Dates of establishment of diplomatic relations with the People's Republic of China
Since its founding in 1949, the People's Republic of China has had a diplomatic tug-of-war with its rival in Taiwan, the Republic of China . Throughout the Cold War, both governments claimed to be the sole legitimate government of all China and allowed countries to recognize either one or the other...
, and did so on April 1, 1950.
In April 1954, India and the PRC signed an eight-year agreement on Tibet that set forth the basis of their relationship in the form of the Five Principles of Peaceful Coexistence
Five Principles of Peaceful Coexistence
The Five Principles of Peaceful Coexistence, known in India as the Panchsheel, are a set of principles to govern relations between states. Their first formal codification in treaty form was in an agreement between by China and India in 1954...
(or Panch Shila). Although critics called the Panch Shila naive, Nehru calculated that in the absence of either the wherewithal or a policy for defense of the Himalayan region, India's best guarantee of security was to establish a psychological buffer zone in place of the lost physical buffer of Tibet. Thus the catch phrase of India's diplomacy with China in the 1950s was Hindi-Chini bhai-bhai, which means, in Hindi
Hindi
Standard Hindi, or more precisely Modern Standard Hindi, also known as Manak Hindi , High Hindi, Nagari Hindi, and Literary Hindi, is a standardized and sanskritized register of the Hindustani language derived from the Khariboli dialect of Delhi...
, "Indians and Chinese are brothers". Up until 1959, despite border skirmishes and discrepancies between Indian and Chinese maps, Chinese leaders amicably had assured India that there was no territorial controversy on the border though there is some evidence that India avoided bringing up the border issue in high level meetings.
In 1954, India published new maps that included the Aksai Chin
Aksai Chin
Aksai Chin is one of the two main disputed border areas between China and India, and the other is South Tibet, which comprises most of India's Arunachal Pradesh. It is administered by China as part of Hotan County in the Hotan Prefecture of Xinjiang Autonomous Region, but is also claimed by India...
region within the boundaries of India (maps published at the time of India's independence did not clearly indicate whether the region was in India or Tibet). When an Indian reconnaissance party discovered a completed Chinese road running through the Aksai Chin
Aksai Chin
Aksai Chin is one of the two main disputed border areas between China and India, and the other is South Tibet, which comprises most of India's Arunachal Pradesh. It is administered by China as part of Hotan County in the Hotan Prefecture of Xinjiang Autonomous Region, but is also claimed by India...
region of the Ladakh District of Jammu and Kashmir
Jammu and Kashmir
Jammu and Kashmir is the northernmost state of India. It is situated mostly in the Himalayan mountains. Jammu and Kashmir shares a border with the states of Himachal Pradesh and Punjab to the south and internationally with the People's Republic of China to the north and east and the...
, border clashes and Indian protests became more frequent and serious. In January 1959, PRC premier Zhou Enlai
Zhou Enlai
Zhou Enlai was the first Premier of the People's Republic of China, serving from October 1949 until his death in January 1976...
wrote to Nehru, rejecting Nehru's contention that the border was based on treaty and custom and pointing out that no government in China had accepted as legal the McMahon Line
McMahon Line
The McMahon Line is a line agreed to by Great Britain and Tibet as part of Simla Accord, a treaty signed in 1914. Although its legal status is disputed by China, it is the effective boundary between China and India....
, which in the 1914 Simla Convention defined the eastern section of the border between India and Tibet. The Dalai Lama
Dalai Lama
The Dalai Lama is a high lama in the Gelug or "Yellow Hat" branch of Tibetan Buddhism. The name is a combination of the Mongolian word далай meaning "Ocean" and the Tibetan word bla-ma meaning "teacher"...
, spiritual and temporal head of the Tibetan people, sought sanctuary in Dharmsala, Himachal Pradesh
Himachal Pradesh
Himachal Pradesh is a state in Northern India. It is spread over , and is bordered by the Indian states of Jammu and Kashmir on the north, Punjab on the west and south-west, Haryana and Uttar Pradesh on the south, Uttarakhand on the south-east and by the Tibet Autonomous Region on the east...
, in March 1959, and thousands of Tibetan refugees settled in northwestern India, particularly in Himachal Pradesh. The People's Republic of China accused India of expansionism
Expansionism
In general, expansionism consists of expansionist policies of governments and states. While some have linked the term to promoting economic growth , more commonly expansionism refers to the doctrine of a state expanding its territorial base usually, though not necessarily, by means of military...
and imperialism
Imperialism
Imperialism, as defined by Dictionary of Human Geography, is "the creation and/or maintenance of an unequal economic, cultural, and territorial relationships, usually between states and often in the form of an empire, based on domination and subordination." The imperialism of the last 500 years,...
in Tibet and throughout the Himalayan region. China claimed 104,000 km² of territory over which India's maps showed clear sovereignty, and demanded "rectification" of the entire border.
Zhou proposed that China relinquish its claim to most of India's northeast
North-East India
Northeast India refers to the easternmost region of India consisting of the contiguous Seven Sister States, Sikkim, and parts of North Bengal...
in exchange for India's abandonment of its claim to Aksai Chin. The Indian government, constrained by domestic public opinion, rejected the idea of a settlement based on uncompensated loss of territory as being humiliating and unequal.
Sino-Indian War
Border disputes resulted in a short border war between the People's Republic of China and India in 20 October 1962. The PRC pushed the unprepared and inadequately led Indian forces to within forty-eight kilometres of the AssamAssam
Assam , also, rarely, Assam Valley and formerly the Assam Province , is a northeastern state of India and is one of the most culturally and geographically distinct regions of the country...
plains in the northeast and occupied strategic points in Ladakh
Ladakh
Ladakh is a region of Jammu and Kashmir, the northernmost state of the Republic of India. It lies between the Kunlun mountain range in the north and the main Great Himalayas to the south, inhabited by people of Indo-Aryan and Tibetan descent...
, until the PRC declared a unilateral cease-fire on 21 November and withdrew twenty kilometers behind its contended line of control.
At the time of Sino-Indian border conflict, a severe political split was taking place in the Communist Party of India
Communist Party of India
The Communist Party of India is a national political party in India. In the Indian communist movement, there are different views on exactly when the Indian communist party was founded. The date maintained as the foundation day by CPI is 26 December 1925...
. One section was accused by the Indian government as being pro-PRC, and a large number of political leaders were jailed. Subsequently, CPI split with the leftist section forming the Communist Party of India (Marxist)
Communist Party of India (Marxist)
The Communist Party of India is a political party in India. It has a strong presence in the states of Kerala, West Bengal and Tripura. As of 2011, CPI is leading the state government in Tripura. It leads the Left Front coalition of leftist parties in various states and the national parliament of...
in 1964. CPI(M) held some contacts with the Communist Party of China
Communist Party of China
The Communist Party of China , also known as the Chinese Communist Party , is the founding and ruling political party of the People's Republic of China...
in the initial period after the split, but did not fully embrace the political line of Mao Zedong.
Relations between the PRC and India deteriorated during the rest of the 1960s and the early 1970s as Sino-Pakistani relations
Sino-Pakistani relations
People's Republic of China–Pakistan relations began in 1950 when Pakistan was among the first countries to break relations with the Republic of China on Taiwan and recognize the PRC. Following the 1962 Sino-Indian War, both countries has placed considerable importance on the maintenance of a...
improved and Sino-Soviet relations worsened
Sino-Soviet split
In political science, the term Sino–Soviet split denotes the worsening of political and ideologic relations between the People's Republic of China and the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics during the Cold War...
. The PRC backed Pakistan in its 1965 war with India
Indo-Pakistani War of 1965
The Indo-Pakistani War of 1965 was a culmination of skirmishes that took place between April 1965 and September 1965 between Pakistan and India. This conflict became known as the Second Kashmir War fought by India and Pakistan over the disputed region of Kashmir, the first having been fought in 1947...
. Between 1967 and 1971, an all-weather road was built across territory claimed by India, linking PRC's Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region with Pakistan; India could do no more than protest. The PRC continued an active propaganda campaign against India and supplied ideological, financial, and other assistance to dissident groups, especially to tribes in northeastern India. The PRC accused India of assisting the Khampa rebels in Tibet. Diplomatic contact between the two governments was minimal although not formally severed. The flow of cultural and other exchanges that had marked the 1950s ceased entirely. The flourishing wool, fur and spice trade between Lhasa
Lhasa
Lhasa is the administrative capital of the Tibet Autonomous Region in the People's Republic of China and the second most populous city on the Tibetan Plateau, after Xining. At an altitude of , Lhasa is one of the highest cities in the world...
and India through the Nathula Pass, an offshoot of the ancient Silk Road
Silk Road
The Silk Road or Silk Route refers to a historical network of interlinking trade routes across the Afro-Eurasian landmass that connected East, South, and Western Asia with the Mediterranean and European world, as well as parts of North and East Africa...
in the then Indian protectorate of Sikkim
Sikkim
Sikkim is a landlocked Indian state nestled in the Himalayan mountains...
was also severed. However, the biweekly postal network through this pass was kept alive, which exists till today.
Later skirmishes
In late 1967, there were two skirmishes between Indian and Chinese forces in Sikkim. The first one was dubbed the "Nathu La incident", and the other the "Chola incident". Prior to these incidents had been the NaxalbariNaxalbari
Naxalbari is the name of a village and a community development block in northern part of the state of West Bengal, India. Naxalbari block comes under the jurisdiction of Siliguri subdivision of Darjeeling district. Naxalbari became famous for the left wing revolt that took place in the late...
uprising in India by the Communist Naxalites and Maoists.
In 1967 a peasant uprising broke out in Naxalbari, led by pro-Maoist elements. A pronunciation by Mao titled "Spring Thunder over India" gave full moral support for the uprising. The support for the revolt marked the end for the relations between CPC and CPI(M). Naxalbari-inspired communists organized armed revolts in several parts of India, and in 1969 they formed the Communist Party of India (Marxist-Leninist)
Communist Party of India (Marxist-Leninist)
The Communist Party of India was formed by the All India Coordination Committee of Communist Revolutionaries at a congress in Calcutta in 1969. The foundation of the party was declared by Kanu Sanyal at a mass-meeting in Calcutta on the 22nd of April .-History:CPI advocated armed revolution and...
. However, as the naxalite
Naxalite
The word Naxal, Naxalite or Naksalvadi is a generic term used to refer to various militant Communist groups operating in different parts of India under different organizational envelopes...
movement disintegrated in various splits, the PRC withdrew its political support and turned non-committal towards the various Indian groups.
On 11 September 1967, troops of the Indian Army's 2nd Grenadiers were protecting an Engineering Company that was fencing the North Shoulder of Nathula, when Chinese troops opened fire on them. This escalated over the next five days to an exchange of heavy artillery and mortar fire between the Indians and the Chinese. 62 Indian soldiers, from the 2nd Grenadiers and the Artillery regiments were killed. Brigadier Rai Singh Yadav, the Commanding Officer, was awarded the MVC and Capt PS Dager was awarded a VrC
Vir Chakra
Vir Chakra is an Indian gallantry award presented for acts of bravery in the battlefield. Award of the decoration carried with it the right to use Vr.C. as a postnominal abbreviation Vir Chakra is an Indian gallantry award presented for acts of bravery in the battlefield. Award of the decoration...
(posthumous) for their gallant actions.The extent of Chinese casualties in this incident is not known.
In the second, on 1 October 1967, a group of Indian Gurkha
Gurkha
Gurkha are people from Nepal who take their name from the Gorkha District. Gurkhas are best known for their history in the Indian Army's Gorkha regiments, the British Army's Brigade of Gurkhas and the Nepalese Army. Gurkha units are closely associated with the kukri, a forward-curving Nepalese knife...
Rifles soldiers (from the 7th Battalion of the 11th Regiment) noticed Chinese troops surrounding a sentry post near a boulder at the Chola outpost in Sikkim
Sikkim
Sikkim is a landlocked Indian state nestled in the Himalayan mountains...
. After a heated argument over the control of the boulder, a Chinese soldier bayoneted a Gurkha rifleman, triggering the start of a close-quarters knife and fire-fight, which then escalted to a mortar
Mortar (weapon)
A mortar is an indirect fire weapon that fires explosive projectiles known as bombs at low velocities, short ranges, and high-arcing ballistic trajectories. It is typically muzzle-loading and has a barrel length less than 15 times its caliber....
and HMG
Heavy machine gun
The heavy machine gun or HMG is a larger class of machine gun generally recognized to refer to two separate stages of machine gun development. The term was originally used to refer to the early generation of machine guns which came into widespread use in World War I...
duel. The Chinese troops had to signal a ceasefire just after three hours of fighting, but later scaled Point 15450 to establish themselves there. The Gurkhas outflanked them the next day to regain Point 15450 and the Chinese retreated across the LAC. 21 Indian soldiers were killed in this action. The Indian government awarded Vir Chakra
Vir Chakra
Vir Chakra is an Indian gallantry award presented for acts of bravery in the battlefield. Award of the decoration carried with it the right to use Vr.C. as a postnominal abbreviation Vir Chakra is an Indian gallantry award presented for acts of bravery in the battlefield. Award of the decoration...
s to Rifleman Limbu (posthumous) and battalion commander Major K.B. Joshi for their gallant actions. The extent of Chinese casualties in this skirmish is also not known.
1970s
In August 1971, India signed its Treaty of Peace, Friendship, and Cooperation with the Soviet UnionSoviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
, and the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
and the PRC sided with Pakistan in its December 1971 war with India
Indo-Pakistani War of 1971
The Indo-Pakistani War of 1971 was a military conflict between India and Pakistan. Indian, Bangladeshi and international sources consider the beginning of the war to be Operation Chengiz Khan, Pakistan's December 3, 1971 pre-emptive strike on 11 Indian airbases...
. Although China strongly condemned India, it did not carry out its veiled threat to intervene on Pakistan's behalf. By this time, the PRC had just replaced the Republic of China in the UN
China and the United Nations
China's seat in the United Nations and membership of the United Nations Security Council was originally occupied by the Republic of China since October 24, 1945. During the Chinese Civil War, the Communist Party of China repelled the government of the ROC from Mainland China to the island of...
where its representatives denounced India as being a "tool of Soviet expansionism."
India and the PRC renewed efforts to improve relations after Indian Prime Minister Indira Gandhi
Indira Gandhi
Indira Priyadarshini Gandhara was an Indian politician who served as the third Prime Minister of India for three consecutive terms and a fourth term . She was assassinated by Sikh extremists...
's Congress party
Indian National Congress
The Indian National Congress is one of the two major political parties in India, the other being the Bharatiya Janata Party. It is the largest and one of the oldest democratic political parties in the world. The party's modern liberal platform is largely considered center-left in the Indian...
lost the 1977 elections to Morarji Desai
Morarji Desai
Morarji Ranchhodji Desai was an Indian independence activist and the fourth Prime Minister of India from 1977–79. He was the first Indian Prime Minister who did not belong to the Indian National Congress...
's Janata Party
Janata Party
The Janata Party was an amalgam of Indian political parties opposed to the state of emergency imposed by the government of Prime Minister Indira Gandhi and her Indian National Congress...
. The new Desai government sought to improve long-strained relations with Pakistan and the PRC. In 1978, the Indian Minister of External Affairs Atal Bihari Vajpayee
Atal Bihari Vajpayee
Atal Bihari Vajpayee is an Indian statesman who served as the tenth Prime Minister of India three times – first for a brief term of 13 days in 1996, and then for two terms from 1998 to 2004. After his first brief period as Prime Minister in 1996, Vajpayee headed a coalition government from...
made a landmark visit to Beijing, and both nations officially re-established diplomatic relations in 1979. The PRC modified its pro-Pakistan stand on Kashmir
Kashmir
Kashmir is the northwestern region of the Indian subcontinent. Until the mid-19th century, the term Kashmir geographically denoted only the valley between the Great Himalayas and the Pir Panjal mountain range...
and appeared willing to remain silent on India's absorption of Sikkim and its special advisory relationship with Bhutan
Bhutan
Bhutan , officially the Kingdom of Bhutan, is a landlocked state in South Asia, located at the eastern end of the Himalayas and bordered to the south, east and west by the Republic of India and to the north by the People's Republic of China...
. The PRC's leaders agreed to discuss the boundary issue, India's priority, as the first step to a broadening of relations. The two countries hosted each others' news agencies, and Mount Kailash
Mount Kailash
Mount Kailash is a peak in the Gangdisê Mountains, which are part of the Himalayas in Tibet...
and Mansarowar Lake
Lake Manasarovar
Lake Manasarovar, Mapam Yumco , or Manasa Sarovar/Lake Manas , is a fresh-water lake in Tibet Autonomous Region of China approximately from Lhasa. To the west of Lake Manasa Sarovar is Lake Rakshastal and towards the north is Mount Kailash...
in Tibet, the mythological home of the Hindu pantheon, were opened to annual pilgrimage
Pilgrimage
A pilgrimage is a journey or search of great moral or spiritual significance. Typically, it is a journey to a shrine or other location of importance to a person's beliefs and faith...
s from India.
1980s
In 1981 PRC minister of foreign affairs Huang HuaHuang Hua
Huang Hua was concurrently the vice-minister of foreign affairs and foreign minister of China from 1976 to 1982.-Biography:...
was invited to India, where he made complimentary remarks about India's role in South Asia
South Asia
South Asia, also known as Southern Asia, is the southern region of the Asian continent, which comprises the sub-Himalayan countries and, for some authorities , also includes the adjoining countries to the west and the east...
. PRC premier Zhao Ziyang
Zhao Ziyang
Zhao Ziyang was a high-ranking politician in the People's Republic of China . He was the third Premier of the People's Republic of China from 1980 to 1987, and General Secretary of the Communist Party of China from 1987 to 1989....
concurrently toured Pakistan, Nepal
Nepal
Nepal , officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, is a landlocked sovereign state located in South Asia. It is located in the Himalayas and bordered to the north by the People's Republic of China, and to the south, east, and west by the Republic of India...
, and Bangladesh
Bangladesh
Bangladesh , officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh is a sovereign state located in South Asia. It is bordered by India on all sides except for a small border with Burma to the far southeast and by the Bay of Bengal to the south...
.
In 1980, Indian Prime Minister Indira Gandhi
Indira Gandhi
Indira Priyadarshini Gandhara was an Indian politician who served as the third Prime Minister of India for three consecutive terms and a fourth term . She was assassinated by Sikh extremists...
approved a plan to upgrade the deployment of forces around the Line of Actual Control to avoid unilateral redefinitions of the line. India also increased funds for infrastructural development in these areas.
In 1984, squads of Indian soldiers began actively patrolling the Sumdorong Chu Valley in Arunachal Pradesh
Arunachal Pradesh
Arunachal Pradesh is a state of India, located in the far northeast. It borders the states of Assam and Nagaland to the south, and shares international borders with Burma in the east, Bhutan in the west, and the People's Republic of China in the north. The majority of the territory is claimed by...
(formerly NEFA), which is north of the McMahon Line as drawn on the Simla Treaty map but south of the ridge which Indian claims is meant to delineate the McMahon Line. The Sumdorong Chu valley "seemed to lie to the north of the McMahon line; but is south of the highest ridge in the area, and the McMahon line is meant to follow the highest points" according to the Indian claims, while the Chinese did not recognize the McMahon Line as legitimate and were not prepared to accept an Indian claim line even further north than that. The Indian team left the area before the winter. In the winter of 1986, the Chinese deployed their troops to the Sumdorong Chu before the Indian team could arrive in the summer and built a Helipad at Wandung. Surprised by the Chinese occupation, India's then Chief of Army Staff, General K.Sundarji, airlifted a brigade to the region.
Chinese troops could not move any further into the valley and were forced to move sideways along the Thag La ridge, away from the valley. By 1987, Beijing's reaction was similar to that in 1962 and this prompted many Western diplomats to predict war. However, Indian foreign minister N.D. Tiwari and Prime Minister Rajiv Gandhi
Rajiv Gandhi
Rajiv Ratna Gandhi was the sixth Prime Minister of India . He took office after his mother's assassination on 31 October 1984; he himself was assassinated on 21 May 1991. He became the youngest Prime Minister of India when he took office at the age of 40.Rajiv Gandhi was the elder son of Indira...
travelled to Beijing over the following months to negotiate a mutual de-escalation.
After the Huang visit, India and the PRC held eight rounds of border negotiations between December 1981 and November 1987. These talks initially raised hopes that progress could be made on the border issue. However, in 1985 the PRC stiffened its position on the border and insisted on mutual concessions without defining the exact terms of its "package proposal" or where the actual line of control lay. In 1986 and 1987, the negotiations achieved nothing, given the charges exchanged between the two countries of military encroachment in the Sumdorung Chu Valley of the Tawang tract on the eastern sector of the border. China's construction of a military post and helicopter pad in the area in 1986 and India's grant of statehood to Arunachal Pradesh
Arunachal Pradesh
Arunachal Pradesh is a state of India, located in the far northeast. It borders the states of Assam and Nagaland to the south, and shares international borders with Burma in the east, Bhutan in the west, and the People's Republic of China in the north. The majority of the territory is claimed by...
(formerly the North-East Frontier Agency
North-East Frontier Agency
The North-East Frontier Agency was one of the political divisions in British India and later the Republic of India till 1972, when it became the Union Territory of Arunachal Pradesh...
) in February 1987 caused both sides to deploy new troops to the area, raising tensions and fears of a new border war. The PRC relayed warnings that it would "teach India a lesson" if it did not cease "nibbling" at Chinese territory. By the summer of 1987, however, both sides had backed away from conflict and denied that military clashes had taken place.
A warming trend in relations was facilitated by Rajiv Gandhi
Rajiv Gandhi
Rajiv Ratna Gandhi was the sixth Prime Minister of India . He took office after his mother's assassination on 31 October 1984; he himself was assassinated on 21 May 1991. He became the youngest Prime Minister of India when he took office at the age of 40.Rajiv Gandhi was the elder son of Indira...
's visit to China in December 1988. The two sides issued a joint communiqué that stressed the need to restore friendly relations on the basis of the Panch Shila and noted the importance of the first visit by an Indian prime minister
Prime Minister of India
The Prime Minister of India , as addressed to in the Constitution of India — Prime Minister for the Union, is the chief of government, head of the Council of Ministers and the leader of the majority party in parliament...
to China since Nehru's 1954 visit. India and the People's Republic of China agreed to broaden bilateral ties in various areas, working to achieve a "fair and reasonable settlement while seeking a mutually acceptable solution" to the border dispute. The communiqué also expressed China's concern about agitation by Tibetan separatists in India and reiterated China's position that Tibet was an integral part of China and that anti-China political activities by expatriate Tibetans was not to be tolerated. Rajiv Gandhi signed bilateral agreements on science and technology cooperation, on civil aviation to establish direct air links, and on cultural exchanges. The two sides also agreed to hold annual diplomatic consultations between foreign ministers, and to set up a joint ministerial committee on economic and scientific cooperation and a joint working group on the boundary issue. The latter group was to be led by the Indian foreign secretary and the Chinese vice minister of foreign affairs.
1990s
As the mid-1990s approached, slow but steady improvement in relations with China was visible. Top-level dialogue continued with the December 1991 visit of PRC premier Li PengLi Peng
Li Peng served as the fourth Premier of the People's Republic of China, between 1987 and 1998, and the Chairman of the Standing Committee of the National People's Congress, China's top legislative body, from 1998 to 2003. For much of the 1990s Li was ranked second in the Communist Party of China ...
to India and the May 1992 visit to China of Indian president
President of India
The President of India is the head of state and first citizen of India, as well as the Supreme Commander of the Indian Armed Forces. President of India is also the formal head of all the three branches of Indian Democracy - Legislature, Executive and Judiciary...
R. Venkataraman
R. Venkataraman
Ramaswamy Venkataraman was an Indian lawyer, Indian independence activist and politician who served as a Union minister and as the eighth President of India....
. Six rounds of talks of the Indian-Chinese Joint Working Group on the Border Issue were held between December 1988 and June 1993. Progress was also made in reducing tensions on the border via confidence-building measures, including mutual troop reductions, regular meetings of local military commanders, and advance notification of military exercises. Border trade resumed in July 1992 after a hiatus of more than thirty years, consulates reopened in Bombay (Mumbai) and Shanghai
Shanghai
Shanghai is the largest city by population in China and the largest city proper in the world. It is one of the four province-level municipalities in the People's Republic of China, with a total population of over 23 million as of 2010...
in December 1992, and, in June 1993, the two sides agreed to open an additional border trading post. During Sharad Pawar
Sharad Pawar
Sharadchandra Govindrao Pawar , popularly known as SAHEB , is the president of the Nationalist Congress Party which he founded in 1999, after separating from the Indian National Congress...
's July 1992 visit to Beijing
Beijing
Beijing , also known as Peking , is the capital of the People's Republic of China and one of the most populous cities in the world, with a population of 19,612,368 as of 2010. The city is the country's political, cultural, and educational center, and home to the headquarters for most of China's...
, the first ever by an Indian minister of defence, the two defense establishments agreed to develop academic, military, scientific, and technological exchanges and to schedule an Indian port call by a Chinese naval
People's Liberation Army Navy
The People's Liberation Army Navy is the naval branch of the People's Liberation Army , the military of the People's Republic of China. Until the early 1990s, the navy performed a subordinate role to the PLA Land Forces. Since then, it has undergone rapid modernisation...
vessel.
Substantial movement in relations continued in 1993. The sixth-round joint working group talks were held in June in New Delhi
New Delhi
New Delhi is the capital city of India. It serves as the centre of the Government of India and the Government of the National Capital Territory of Delhi. New Delhi is situated within the metropolis of Delhi. It is one of the nine districts of Delhi Union Territory. The total area of the city is...
but resulted in only minor developments. However, as the year progressed the long-standing border dispute was eased as a result of bilateral pledges to reduce troop levels and to respect the cease-fire line along the India-China border. Prime Minister Narasimha Rao
Narasimha Rao
Narasimha Rao or Narasimharao is one of the Indian names.* Pamulaparthi Venkata Narasimha Rao served as the 10th Prime Minister of India.* Modireddy Venkat Narasimha Rao, is a former Indian cricketer....
and Premier Li Peng signed the border agreement and three other agreements (on cross-border trade, and on increased cooperation on the environment and in radio and television broadcasting) during the former's visit to Beijing in September. A senior-level Chinese military delegation made a six-day goodwill visit to India in December 1993 aimed at "fostering confidence-building measures between the defense forces of the two countries." The visit, however, came at a time when press reports revealed that, as a result of improved relations between the PRC and Burma, China was exporting greater amounts of military matériel to Burma's army, navy, and air force and sending an increasing number of technicians to Burma. Of concern to Indian security officials was the presence of Chinese radar technicians in Burma's Coco Islands
Coco Islands
Coco Islands are a pair of strategically important islands located in the eastern Indian Ocean, politically administered by Burma under Yangon Division. They are allegedly leased to the People's Republic of China since 1994...
, which border India's Union Territory
Union Territory
A Union Territory is a sub-national administrative division of India, in the federal framework of governance. Unlike the states of India, which have their own elected governments, union territories are ruled directly by the federal government; the President of India appoints an Administrator or...
of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. Nevertheless, movement continued in 1994 on troop reductions along the Himalayan frontier. Moreover, in January 1994 Beijing announced that it not only favored a negotiated solution on Kashmir, but also opposed any form of independence for the region.
Talks were held in New Delhi in February 1994 aimed at confirming established "confidence-building measures" and discussing clarification of the "line of actual control", reduction of armed forces along the line, and prior information about forthcoming military exercises. China's hope for settlement of the boundary issue was reiterated.
The 1993 Chinese military visit to India was reciprocated by Indian army chief of staff General B. C. Joshi. During talks in Beijing in July 1994, the two sides agreed that border problems should be resolved peacefully through "mutual understanding and concessions." The border issue was raised in September 1994 when PRC minister of national defense Chi Haotian
Chi Haotian
General Chi Haotian is a general of the People's Republic of China.-Biography:Chi was born July, 1929 in Zhaoyuan, Shandong Province, China. In October, 1946 he joined the CPC...
visited New Delhi for extensive talks with high-level Indian trade and defense officials. Further talks in New Delhi in March 1995 by the India-China Expert Group led to an agreement to set up two additional points of contact along the 4,000 km border to facilitate meetings between military personnel. The two sides also were reported as "seriously engaged" in defining the McMahon Line and the line of actual control vis-à-vis military exercises and prevention of air intrusion. Talks in Beijing in July 1995 aimed at better border security and combating cross-border crimes and in New Delhi in August 1995 on additional troop withdrawals from the border made further progress in reducing tensions.
Possibly indicative of the further relaxation of India-China relations, at least there was little notice taken in Beijing, was the April 1995 announcement, after a year of consultation, of the opening of the Taipei Economic and Cultural Center in New Delhi. The center serves as the representative office of the Republic of China
Republic of China
The Republic of China , commonly known as Taiwan , is a unitary sovereign state located in East Asia. Originally based in mainland China, the Republic of China currently governs the island of Taiwan , which forms over 99% of its current territory, as well as Penghu, Kinmen, Matsu and other minor...
(Taiwan) and is the counterpart of the India-Taipei Association in Taiwan; both institutions have the goal of improving relations between the two sides, which have been strained since New Delhi's recognition of Beijing in 1950.
Sino-Indian relations hit a low point in 1998 following India's nuclear tests in May. Indian Defense Minister George Fernandes
George Fernandes
George Mathew Fernandes is an Indian trade unionist, politician, journalist, agriculturist, and member of Rajya Sabha from Bihar. He is a key member of the Janata Dal , and was the founder of the Samata Party...
declared that "China is India's number one threat", hinting that India developed nuclear weapons in defense against China's nuclear arsenal. In 1998, China was one of the strongest international critics of India's nuclear tests and entry into the nuclear club. During the 1999 Kargil War
Kargil War
The Kargil War ,, also known as the Kargil conflict, was an armed conflict between India and Pakistan that took place between May and July 1999 in the Kargil district of Kashmir and elsewhere along the Line of Control...
China voiced support for Pakistan, but also counseled Pakistan to withdraw its forces.
2000s
With Indian President K. R. NarayananK. R. Narayanan
Kocheril Raman Narayanan , also known as K. R. Narayanan, was the tenth President of India. He was the first Dalit, and the first Malayali, to have been President....
's visit to China, 2000 marked a gradual re-engagement of Indian and Chinese diplomacy. In a major embarrassment for China, the 17th Karmapa
Karmapa
The Karmapa is the head of the Karma Kagyu, the largest sub-school of the Kagyupa , itself one of the four major schools of Tibetan Buddhism....
, Urgyen Trinley Dorje
Urgyen Trinley Dorje
Ogyen Trinley Dorje , also written Urgyen Trinley Dorje , is a claimant to the title of 17th Karmapa.The Karmapa is head of the Karma Kagyu school, one of the four main schools of Tibetan Buddhism...
, who was proclaimed by China, made a dramatic escape from Tibet to the Rumtek Monastery
Rumtek Monastery
Rumtek , also called the Dharmachakra Centre, is a Tibetan Buddhist monastery located in the Indian state of Sikkim near the capital Gangtok...
in Sikkim. Chinese officials were in a quandary on this issue as any protest to India on the issue would mean an explicit endorsement on India's governance of Sikkim, which the Chinese still hadn't recognised. In 2002, Chinese Premier Zhu Rongji
Zhu Rongji
Zhū Róngjī is a prominent Chinese politician who served as the Mayor and Party chief in Shanghai between 1987 and 1991, before serving as Vice-Premier and then the fifth Premier of the People's Republic of China from March 1998 to March 2003.A tough administrator, his time in office saw the...
reciprocated by visiting India, with a focus on economic issues. 2003 ushered in a marked improvement in Sino-Indian relations following Indian Prime Minister Atal Bihari Vajpayee
Atal Bihari Vajpayee
Atal Bihari Vajpayee is an Indian statesman who served as the tenth Prime Minister of India three times – first for a brief term of 13 days in 1996, and then for two terms from 1998 to 2004. After his first brief period as Prime Minister in 1996, Vajpayee headed a coalition government from...
's landmark June 2003 visit to China. China officially recognized Indian sovereignty over Sikkim as the two nations moved toward resolving their border disputes.
2004 also witnessed a gradual improvement in the international area when the two countries proposed opening up the Nathula and Jelepla Passes in Sikkim which would be mutually beneficial to both countries. 2004 was a milestone in Sino-Indian bilateral trade, surpassing the $10 billion mark for the first time. In April 2005, Chinese Premier Wen Jiabao
Wen Jiabao
Wen Jiabao is the sixth and current Premier and Party secretary of the State Council of the People's Republic of China, serving as China's head of government and leading its cabinet. In his capacity as Premier, Wen is regarded as the leading figure behind China's economic policy...
visited Bangalore
Bangalore
Bengaluru , formerly called Bengaluru is the capital of the Indian state of Karnataka. Bangalore is nicknamed the Garden City and was once called a pensioner's paradise. Located on the Deccan Plateau in the south-eastern part of Karnataka, Bangalore is India's third most populous city and...
to push for increased Sino-Indian cooperation in high-tech industries. In a speech, Wen stated "Cooperation is just like two pagodas (temples), one hardware and one software. Combined, we can take the leadership position in the world." Wen stated that the 21st century will be "the Asian century of the IT industry." The high-level visit was also expected to produce several agreements to deepen political, cultural and economic ties between the two nations. Regarding the issue of India gaining a permanent seat on the UN Security Council, on his visit, Wen Jiabao initially seemed to support the idea, but had returned to a neutral position on the subject by the time he returned to China. In the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation
South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation
The South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation is an organisation of South Asian nations, founded in December 1985 by Ziaur Rahman and dedicated to economic, technological, social, and cultural development emphasising collective self-reliance. Its seven founding members are Bangladesh,...
(SAARC) Summit (2005) China was granted an observer status. While other countries in the region are ready to consider China for permanent membership in the SAARC, India seems reluctant.
A very important dimension of the evolving Sino-Indian relationship is based on the energy requirements of their industrial expansion and their readiness to proactively secure them by investing in the oilfields abroad - in Africa, the Middle East and Central Asia. On the one hand, these ventures entail competition (which has been evident in oil biddings for various international projects recently). But on the other hand, a degree of cooperation too is visible, as they are increasingly confronting bigger players in the global oil market. This cooperation was sealed in Beijing on January 12, 2006 during the visit of Petroleum and Natural Gas Minister Mani Shankar Aiyar
Mani Shankar Aiyar
Mani Shankar Aiyar is a former Indian diplomat who resigned from foreign service and became a politician working for Rajiv Gandhi in 1989-1991. He is a member of the Indian National Congress party and was the Minister of Panchayati Raj until he lost his seat in the 2009 Election...
, who signed an agreement which envisages ONGC Videsh Ltd (OVL) and the China National Petroleum Corporation
China National Petroleum Corporation
China National Petroleum Corporation is a state-owned fuel-producing corporation and the largest integrated oil and gas company in the People's Republic of China...
(CNPC) placing joint bids for promising projects elsewhere. This may have important consequences for their international relations.
On July 6, 2006, China and India re-opened Nathula, an ancient trade route which was part of the Silk Road
Silk Road
The Silk Road or Silk Route refers to a historical network of interlinking trade routes across the Afro-Eurasian landmass that connected East, South, and Western Asia with the Mediterranean and European world, as well as parts of North and East Africa...
. Nathula is a pass through the Himalayas and it was closed 44 years prior to 2006 when the Sino-Indian War
Sino-Indian War
The Sino-Indian War , also known as the Sino-Indian Border Conflict , was a war between China and India that occurred in 1962. A disputed Himalayan border was the main pretext for war, but other issues played a role. There had been a series of violent border incidents after the 1959 Tibetan...
broke out in 1962. The initial agreement for the re-opening of the trade route was reached in 2003, and a final agreement was formalized on June 18, 2006. Officials say that the re-opening of border trade will help ease the economic isolation of the region. In November 2006, China and India had a verbal spat over claim of the north-east Indian state of Arunachal Pradesh
Arunachal Pradesh
Arunachal Pradesh is a state of India, located in the far northeast. It borders the states of Assam and Nagaland to the south, and shares international borders with Burma in the east, Bhutan in the west, and the People's Republic of China in the north. The majority of the territory is claimed by...
. India claimed that China was occupying 38,000 square kilometres of its territory in Kashmir
Kashmir
Kashmir is the northwestern region of the Indian subcontinent. Until the mid-19th century, the term Kashmir geographically denoted only the valley between the Great Himalayas and the Pir Panjal mountain range...
, while China claimed the whole of Arunachal Pradesh as its own. In May 2007, China denied the application for visa from an Indian Administrative Service
Indian Administrative Service
The Indian Administrative Service is the administrative civil service of the Government of India. It is one of the three All India Services....
officer in Arunachal Pradesh. According to China, since Arunachal Pradesh is a territory of China, he would not need a visa to visit his own country. Later in December 2007, China appeared to have reversed its policy by granting a visa to Marpe Sora, an Arunachal born professor in computer science.
In January 2008, Prime Minister Manmohan Singh
Manmohan Singh
Manmohan Singh is the 13th and current Prime Minister of India. He is the only Prime Minister since Jawaharlal Nehru to return to power after completing a full five-year term. A Sikh, he is the first non-Hindu to occupy the office. Singh is also the 7th Prime Minister belonging to the Indian...
visited China and met with President Hu Jintao
Hu Jintao
Hu Jintao is the current Paramount Leader of the People's Republic of China. He has held the titles of General Secretary of the Communist Party of China since 2002, President of the People's Republic of China since 2003, and Chairman of the Central Military Commission since 2004, succeeding Jiang...
and Premier Wen Jiabao
Wen Jiabao
Wen Jiabao is the sixth and current Premier and Party secretary of the State Council of the People's Republic of China, serving as China's head of government and leading its cabinet. In his capacity as Premier, Wen is regarded as the leading figure behind China's economic policy...
and had bilateral discussions related to trade, commerce, defense, military, and various other issues.
Until 2008 the British Government's position remained the same as had been since the Simla Accord of 1913: that China held suzerainty
Suzerainty
Suzerainty occurs where a region or people is a tributary to a more powerful entity which controls its foreign affairs while allowing the tributary vassal state some limited domestic autonomy. The dominant entity in the suzerainty relationship, or the more powerful entity itself, is called a...
over Tibet but not sovereignty
Sovereignty
Sovereignty is the quality of having supreme, independent authority over a geographic area, such as a territory. It can be found in a power to rule and make law that rests on a political fact for which no purely legal explanation can be provided...
. Britain revised this view on 29 October 2008, when it recognised Chinese sovereignty over Tibet by issuing a statement on its website. The Economist
The Economist
The Economist is an English-language weekly news and international affairs publication owned by The Economist Newspaper Ltd. and edited in offices in the City of Westminster, London, England. Continuous publication began under founder James Wilson in September 1843...
stated that although the British Foreign Office's website does not use the word sovereignty, officials at the Foreign Office said "it means that, as far as Britain is concerned, 'Tibet is part of China. Full stop.'" This change in Britain's position affects India's claim to its North Eastern territories which rely on the same Simla Accord that Britain's prior position on Tibet's sovereignty was based upon.
In October 2009, Asian Development Bank
Asian Development Bank
The Asian Development Bank is a regional development bank established on 22 August 1966 to facilitate economic development of countries in Asia...
formally acknowledging Arunachal Pradesh as part of India, approved a loan to India for a development project there. Earlier China had exercised pressure on the bank to cease the loan, however India succeeded in securing the loan with the help of the United States and Japan. China expressed displeasure at ADB
ADB
ADB is a three-letter acronym that may refer to the intergovernmental organizations:* The Asian Development Bank, a non-profit financial institution whose aim is to help developing Asian countries...
for the same.
2010s
In April 2010, the second BRIC summit2010 BRIC summit
The 2010 BRIC summit took place in Brasilia, Brazil on April 16, 2010. This was the second BRIC summit after Yekaterinburg in 2009. The meeting took place between the four heads of government from the BRIC states following bilateral meetings in the prior days....
was held in Brasilia.
Chinese Premier Wen Jiabao
Wen Jiabao
Wen Jiabao is the sixth and current Premier and Party secretary of the State Council of the People's Republic of China, serving as China's head of government and leading its cabinet. In his capacity as Premier, Wen is regarded as the leading figure behind China's economic policy...
paid an official visit to India from Dec.15-17,2010 at the invitation of Prime Minister Manmohan Singh
Manmohan Singh
Manmohan Singh is the 13th and current Prime Minister of India. He is the only Prime Minister since Jawaharlal Nehru to return to power after completing a full five-year term. A Sikh, he is the first non-Hindu to occupy the office. Singh is also the 7th Prime Minister belonging to the Indian...
. He was accompanied by 400 Chinese business leaders, who wished to sign business deals with Indian companies.
In April 2011, the first BRICS
BRICS
BRICS is an international political organisation of leading emerging economies, arising out of the inclusion of South Africa into the BRIC group in 2010. As of 2011, its five members are Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa...
summit was held in Sanya
Sanya
Sanya is the southernmost city in China and is a part of Hainan Province. In 2006, it had a population of 536,000, making it, after the provincial capital , the second most populous city on the island. The city is renowned for its tropical climate and has emerged as a popular tourist destination,...
, Hainan
Hainan
Hainan is the smallest province of the People's Republic of China . Although the province comprises some two hundred islands scattered among three archipelagos off the southern coast, of its land mass is Hainan Island , from which the province takes its name...
, China. During the event, the two countries agreed to restore defence co-operation, and China had hinted that it may reverse its policy of administering stapled visas to residents of Jammu and Kashmir
Jammu and Kashmir
Jammu and Kashmir is the northernmost state of India. It is situated mostly in the Himalayan mountains. Jammu and Kashmir shares a border with the states of Himachal Pradesh and Punjab to the south and internationally with the People's Republic of China to the north and east and the...
.
Sino-Indian relations
- BRICBRICIn economics, BRIC is a grouping acronym that refers to the countries of Brazil, Russia, India and China, which are all deemed to be at a similar stage of newly advanced economic development...
– Brazil, Russia, India, and China economic relations - China in the Mahabharata
- ChindiaChindiaFor the landmark in Târgovişte, see Chindia Tower. For a person of mixed Chinese and Indian origin, see Chindian.Chindia is a portmanteau word that refers to China and India together in general. The credit of coining the now popular term goes to Indian Member of Parliament Jairam Ramesh...
– China and India together in general, and their economies in particular - Foreign relations of the People's Republic of ChinaForeign relations of the People's Republic of ChinaThe foreign relations of the People's Republic of China guides the way in which it interacts with foreign nations. As a great power and emerging superpower, China's foreign policy and strategic thinking is highly influential. China officially states it "unswervingly pursues an independent foreign...
- Foreign relations of IndiaForeign relations of IndiaIndia has formal diplomatic relations with most nations, as the world's second most populous country and the world's most-populous democracy and recently has one of the fastest economic growth rates in the world...
- Shanghai Cooperation OrganizationShanghai Cooperation OrganizationThe Shanghai Cooperation Organisation or SCO , is an intergovernmental mutual-security organisation which was founded in 2001 in Shanghai by the leaders of China, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan...
Border disputes
- South TibetSouth TibetThe Arunachal Pradesh dispute is a territorial dispute over the region located on the middle of the Yarlung Zangbo River, 300 km north of the Himalayas. It is entirely administered by India as part of its Arunachal Pradesh state; China claims it as a part of its Tibet Autonomous Region and...
– One of the disputed areas between China and India, inhabited by Moinbas, LhobaLhobaLhoba is a term of obscure origin which has come to apply to a diverse amalgamation of Tibeto-Burman tribespeople living in and around "Pemako" , including Mainling, Medog, Zayü counties of Nyingchi Prefecture and Lhünzê County of Shannan Prefecture...
s (Adi), and DaibameiMishmiThe Mishmi or Deng people of Tibet and Arunachal Pradesh are an ethnic group comprising mainly three tribes: Idu Mishmi ; Digaro Mishmi , and Miju Mishmi . The Mishmis occupy the north-eastern tip of the central Arunachal Pradesh/South Tibet in Upper and Lower Dibang Valley, Lohit and Anjaw...
s - Aksai ChinAksai ChinAksai Chin is one of the two main disputed border areas between China and India, and the other is South Tibet, which comprises most of India's Arunachal Pradesh. It is administered by China as part of Hotan County in the Hotan Prefecture of Xinjiang Autonomous Region, but is also claimed by India...
– Another disputed areas between India and China, inhabited by Pamiris, Uyghurs, Kashmiris and Purik Tibetan - Line of Actual ControlLine of Actual ControlThe Line of Actual Control is the effective border between India and People's Republic of China . The LAC is 4,057-km long and traverses three areas of northern Indian states: western , middle and eastern...
- List of territorial disputes
- Origins of the Sino-Indian border disputeOrigins of the Sino-Indian border disputeSovereignty over two separated pieces of territory was contested during the Sino-Indian War. One is Aksai Chin is located either in the Indian province of Kashmir or the Chinese province of Xinjiang in the west. It is a virtually uninhabited high-altitude wasteland crossed by the Xinjiang-Tibet...
- Sino-Indian WarSino-Indian WarThe Sino-Indian War , also known as the Sino-Indian Border Conflict , was a war between China and India that occurred in 1962. A disputed Himalayan border was the main pretext for war, but other issues played a role. There had been a series of violent border incidents after the 1959 Tibetan...
- Tawang DistrictTawang DistrictTawang district is one of the 16 administrative districts of Arunachal Pradesh in eastern India. The area is historically Tibetan territory and is claimed by both India and Republic of China as a part of South Tibet...
– One of the disputed areas between India and China
Further reading
- Hellström, Jerker and Korkmaz, Kaan Managing Mutual Mistrust: Understanding Chinese Perspectives on Sino-Indian Relations, Swedish Defence Research Agency (September 2011)
- China’s Response to a Rising India, Q&A with M. Taylor Fravel (October 2011)
- Strategic Asia 2011-12: Asia Responds to Its Rising Powers - China and India, edited by Ashley J. Tellis, Travis Tanner, and Jessica Keough (National Bureau of Asian ResearchNational Bureau of Asian ResearchThe National Bureau of Asian Research is a nonprofit, nonpartisan research institution based in Seattle, Washington, with a branch office in Washington, D.C. The organization’s mission is to inform and strengthen Asia-Pacific policy...
, 2011) - India’s Response to a Rising China: Economic and Strategic Challenges and Opportunities, Q&A with Harsh V. Pant (August 2011)
- Frankel, Francine R., and Harry Harding. The India-China Relationship: What the United States Needs to Know. Columbia University Press: 2004. ISBN 0-231-13237-9.
- Garver, John W. Protracted Contest: Sino-Indian Rivalry in the Twentieth Century. University of Washington Press: 2002. ISBN 0-295-98074-5.
- Lu, Chih H.. The Sino-Indian Border Dispute: A Legal Study. Greenwood Press: 1986. ISBN 0-313-25024-3.
- Sen, Tansen. Buddhism, Diplomacy, and Trade: The Realignment of Sino-Indian Relations, 600-1400. University of Hawaii Press: 2003. ISBN 0-8248-2593-4.
- Sidhu, Waheguru Pal Singh, and Jing Dong Yuan. China and India: Cooperation or Conflict? Lynne Rienner Publishers: 2003. ISBN 1-58826-169-7.
- Varadarajan, S. India, China and the Asian Axis of Oil, January 2006
- The India-China Relationship:What we need to know?, January 2006
- Dalal, JS: The Sino-Indian Border Dispute: India's Current Options. Master's Thesis, June 1993.
External links
- Inventory of Conflict and EnvironmentInventory of Conflict and EnvironmentThe Inventory of Conflict and Environment is a research project of the School of International Service at American University in Washington, D.C. The project makes use of computer applications in international relations research; ICE is evolving as a pattern matching tool...
(ICE), Arunachal Pradesh Territorial Dispute between India and China
Articles
- Can India Face the Dragon?, The World Reporter, September 5, 2010 By Sanskar Shrivastava
- India-China Relations: Issues, Trends and Emerging Scenarios by B.M. Jain
- The Lotus and the Dragon: The Evolution of the BJP's China Policy by Vijay Vikram
- Uneasy Engagement - China and India Dispute Enclave on Edge of Tibet, NYTimes, September 4, 2009
News
- India-China relations: Ten-pronged strategy (rediff.com)-November 21, 2006
- India, China to set up hotline (hindu.com)
- Why China is playing hardball in Arunachal, Daily News & Analysis
- China, India, and the fruits of Nehru's folly by Venkatesan Vembu, Daily News & Analysis, June 6, 2007

