
History of India
Encyclopedia
The history of India begins with evidence of human activity of Homo sapiens
as long as 75,000 years ago, or with earlier hominids including Homo erectus
from about 500,000 years ago. The Indus Valley Civilization
, which spread and flourished in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent
from c. 3300 to 1300 BCE, was the first major civilization in India. A sophisticated and technologically advanced urban culture developed in the Mature Harappan period, from 2600 to 1900 BCE. This Bronze Age
civilization collapsed before the end of the second millennium BCE and was followed by the Iron Age
Vedic Civilization
, which extended over much of the Indo-Gangetic plain
and which witnessed the rise of major polities known as the Mahajanapadas
. In one of these kingdoms, Magadha
, Mahavira
and Gautama Buddha
were born in the 6th or 5th century BCE and propagated their śramanic
philosophies.
Almost all of the subcontinent was conquered by the Maurya Empire
during the 4th and 3rd centuries BCE. It subsequently became fragmented, with various parts ruled by numerous Middle kingdoms
for the next 1,500 years. This is known as the classical period of Indian history, during which India has sometimes been estimated to have had the largest economy
of the ancient and medieval world, controlling between one third and one fourth of the world's wealth up to the 18th century.
Much of northern and central India was once again united in the 4th century CE, and remained so for two centuries thereafter, under the Gupta Empire
. This period, witnessing a Hindu
religious and intellectual resurgence, is known among its admirers as the "Golden Age of India". During the same time, and for several centuries afterwards, southern India, under the rule of the Chalukyas
, Cholas
, Pallavas, and Pandyas, experienced its own golden age. During this period, aspects of Indian civilization, administration, culture, and religion (Hinduism
and Buddhism
) spread to much of Asia
.
The southern state of Kerala
had maritime business links with the Roman Empire from around 77 CE. Islam was introduced in Kerala through this route by Muslim traders. Muslim rule in the subcontinent began in 712 CE when the Arab general Muhammad bin Qasim
conquered Sindh
and Multan
in southern Punjab
in modern day Pakistan, setting the stage for several successive invasions from Central Asia between the 10th and 15th centuries CE, leading to the formation of Muslim empires in the Indian subcontinent
such as the Delhi Sultanate
and the Mughal Empire
.
Mughal rule came from Central Asia to cover most of the northern parts of the subcontinent. Mughal rulers introduced Central Asian art and architecture to India. In addition to the Mughals and various Rajput
kingdoms, several independent Hindu states, such as the Vijayanagara Empire
, the Maratha Empire
, Eastern Ganga Empire
and the Ahom Kingdom
, flourished contemporaneously in southern, western,eastern and northeastern India respectively. The Mughal Empire suffered a gradual decline in the early 18th century, which provided opportunities for the Afghans
, Balochis
, Sikhs, and Marathas to exercise control over large areas in the northwest of the subcontinent until the British East India Company
gained ascendancy over South Asia.
Beginning in the mid-18th century and over the next century, large areas of India were gradually annexed by the British East India Company. Dissatisfaction with Company rule led to the Indian Rebellion of 1857
, after which the British provinces of India were directly administered by the British Crown
and witnessed a period of both rapid development of infrastructure
and economic decline. During the first half of the 20th century, a nationwide struggle for independence
was launched by the Indian National Congress
and later joined by the Muslim League. The subcontinent gained independence from the United Kingdom
in 1947, after the British provinces were partitioned
into the dominions of India and Pakistan
and the princely state
s all acceded
to one of the new states.

 Isolated remains of Homo erectus
Isolated remains of Homo erectus
in Hathnora in the Narmada Valley
in central India indicate that India might have been inhabited since at least the Middle Pleistocene
era, somewhere between 500,000 and 200,000 years ago.
Tools crafted by proto-humans that have been dated back two million years have been discovered in the northwestern part of the subcontinent. The ancient history of the region includes some of South Asia's oldest settlements and some of its major civilizations. The earliest archaeological site in the subcontinent is the palaeolithic hominid site in the Soan River valley. Soanian sites are found in the Sivalik region across what are now India, Pakistan, and Nepal.
The Mesolithic
period in the Indian subcontinent was followed by the Neolithic
period, when more extensive settlement of the subcontinent occurred after the end of the last Ice Age
approximately 12,000 years ago. The first confirmed semipermanent settlements appeared 9,000 years ago in the Bhimbetka rock shelters in modern Madhya Pradesh
, India.
Early Neolithic culture in South Asia is represented by the Mehrgarh
findings (7000 BCE onwards) in present-day Balochistan
, Pakistan. Traces of a Neolithic culture have been alleged to be submerged in the Gulf of Khambat in India, radiocarbon dated
to 7500 BCE. However, the one dredged piece of wood in question was found in an area of strong ocean currents. Neolithic agriculture cultures sprang up in the Indus Valley region around 5000 BCE, in the lower Gangetic valley around 3000 BCE, and in later South India, spreading southwards and also northwards into Malwa around 1800 BCE. The first urban civilization of the region began with the Indus Valley Civilization
.

 The Bronze Age in the Indian subcontinent
The Bronze Age in the Indian subcontinent
began around 3300 BCE with the early Indus Valley Civilization. It was centered on the Indus River
and its tributaries which extended into the Ghaggar-Hakra River
valley, the Ganges-Yamuna Doab
, Gujarat, and southeastern Afghanistan
.
The civilization is primarily located in modern-day India (Gujarat, Haryana
, Punjab
and Rajasthan
provinces) and Pakistan (Sindh
, Punjab
, and Balochistan
provinces). Historically part of Ancient India, it is one of the world's earliest urban civilizations, along with Mesopotamia
and Ancient Egypt
. Inhabitants of the ancient Indus river valley, the Harappans
, developed new techniques in metallurgy and handicraft (carneol products, seal carving), and produced copper, bronze, lead, and tin.
The Mature Indus civilization flourished from about 2600 to 1900 BCE, marking the beginning of the urban civilization on the subcontinent. The civilization included urban centers such as Dholavira
, Kalibangan
, Rupar
, Rakhigarhi
, and Lothal
in modern-day India, and Harappa
, Ganeriwala, and Mohenjo-daro
in modern-day Pakistan. The civilization is noted for its cities built of brick, roadside drainage system, and multistoried houses.
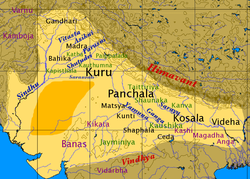 The Vedic period
The Vedic period
is characterized by Indo-Aryan culture associated with the texts of Vedas
, sacred to Hindus, which were orally composed in Vedic Sanskrit
. The Vedas are some of the oldest extant texts in India and next to some writings in Egypt and Mesopotamia are the oldest in the world. The Vedic period lasted from about 1500 to 500 BCE, laying the foundations of Hinduism
and other cultural aspects of early Indian society. The Aryans established Vedic
civilization all over north India, particularly in the Gangetic Plain. This period succeeded the prehistoric Late Harappan, during which immigrations of Indo-Aryan-speaking tribes
overlaid the existing civilizations of local people whom they called Dasyus. The Aryans, originally came from the Caspian Sea area of Asia. Settling first in Bactria and then in the Hindu-Kush area of India, before settling in the Ganges and Yamuna River valleys.
Many scholars throughout history have maintained that the Aryans subjugated the "backward aboriginies" that had previously lived in northern India. However, discoveries of advanced civilizations in the Indus River valley, caused many scholars to change their theories in this regard. The Aryans may have received as much from the neighboring cultures of northern India as they contributed. Indeed when the Aryans moved into India, they were semi-nomadic pastoralists, their clothing was simple, they had no regular legal institutions and their religion was a very basic form of animism. The basis of the Aryan economy had always been centered around cattle raising. During this period of time, the cow began to be venerated in Aryan society. Thus, the origins of the later Hindu belief in India that cows are sacred may have started during this time.
 Early Vedic society consisted of largely pastoral groups, with late Harappan urbanization having been abandoned. After the time of the Rigveda
Early Vedic society consisted of largely pastoral groups, with late Harappan urbanization having been abandoned. After the time of the Rigveda
, Aryan society became increasingly agricultural and was socially organized around the four varnas, or social classes. In addition to the Vedas, the principal texts of Hinduism, the core themes of the Sanskrit epics Ramayana
and Mahabharata
are said to have their ultimate origins during this period. The Mahabharata remains, today, the longest single poem in the world. The events described in the shorter, Ramayana are from a later period of history than the events of the Mahabharata. The early Indo-Aryan presence probably corresponds, in part, to the Ochre Coloured Pottery culture
in archaeological contexts.
The Kuru kingdom corresponds to the Black and Red Ware
and Painted Grey Ware
cultures and to the beginning of the Iron Age in northwestern India, around 1000 BCE, as well as with the composition of the Atharvaveda
, the first Indian text to mention iron, as , literally "black metal." The Painted Grey Ware culture spanned much of northern India from about 1100 to 600 BCE. The Vedic Period also established republics such as Vaishali
, which existed as early as the 6th century BCE and persisted in some areas until the 4th century CE. The later part of this period corresponds with an increasing movement away from the previous tribal system towards the establishment of kingdoms, called mahajanapadas
.


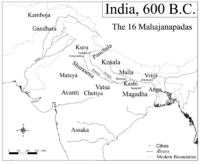
 In the later Vedic Age, a number of small kingdoms or city states had covered the subcontinent, many mentioned in Vedic, early Buddhist and Jaina literature as far back as 1000 BCE. By 500 BCE, sixteen monarchies and "republics" known as the Mahajanapadas
In the later Vedic Age, a number of small kingdoms or city states had covered the subcontinent, many mentioned in Vedic, early Buddhist and Jaina literature as far back as 1000 BCE. By 500 BCE, sixteen monarchies and "republics" known as the Mahajanapadas
— Kasi, Kosala
, Anga
, Magadha
, Vajji
(or Vriji), Malla
, Chedi
, Vatsa
(or Vamsa), Kuru, Panchala
, Matsya
(or Machcha), Surasena
, Assaka
, Avanti
, Gandhara
, and Kamboja — stretched across the Indo-Gangetic Plain
from modern-day Afghanistan
to Bengal
and Maharastra. This period saw the second major rise of urbanism in India after the Indus Valley Civilization
.
Many smaller clans mentioned within early literature seem to have been present across the rest of the subcontinent. Some of these kings were hereditary; other states elected their rulers. The educated speech at that time was Sanskrit
, while the languages of the general population of northern India are referred to as Prakrit
s. Many of the sixteen kingdoms had coalesced to four major ones by 500/400 BCE, by the time of Gautama Buddha
. These four were Vatsa, Avanti, Kosala, and Magadha.
Hindu rituals at that time were complicated and conducted by the priestly class. It is thought that the Upanishads, late Vedic texts dealing mainly with philosophy, were composed in the later Vedic Age and early in this period of the Mahajanapadas (from about 600 to 400 BCE). The Upanishads had a substantial effect on Indian philosophy
and were contemporary with the development of Buddhism and Jainism, indicating a golden age of thought in this period.
According to Buddhism
, Gautama Buddha attained the state of "enlightenment" and became known as Buddha "Enlightened" c. 537 BCE. Around the same time, Mahavira
(the 24th Tirthankara in Jainism
) propagated a similar theology that was to later become Jainism. However, Jain orthodoxy believes the teachings of the Tirthankaras predates all known time and scholars believe Parshva
, accorded status as the 23rd Tirthankara, was a historical figure. The Vedas
are believed to have documented a few Tirthankaras and an ascetic order similar to the shramana
movement.
The Buddha's teachings and Jainism had doctrines inclined toward asceticism, and they were preached in Prakrit, which helped them gain acceptance amongst the masses. They have profoundly influenced practices that Hinduism and Indian spiritual orders are associated with, including vegetarianism
, prohibition of animal slaughter and ahimsa
(non-violence). While the geographic impact of Jainism was limited to India, Buddhist nuns
and monks
eventually spread the teachings of Buddha to Central Asia
, East Asia
, Tibet
, Sri Lanka
and Southeast Asia
.
 In 530 BCE Cyrus
In 530 BCE Cyrus
, King of the Persian Achaemenid Empire
crossed the Hindu-Kush mountains to seek tribute from the tribes of Kamboja, Gandhara and the trans-India region. By 520 BCE, during the reign of Darius I of Persia, much of the northwestern subcontinent (present-day eastern Afghanistan and Pakistan) came under the rule of the Persian Achaemenid Empire
. The area remained under Persian control for two centuries. During this time India supplied mercenaries to the Persian army then fighting in Greece. Under Persian rule the famous city of Takshashila became a center where both Vedic and Iranian learning were mingled. The impact of Persian ideas was felt in many areas of Indian life. Persian coinage and rock inscriptions were copied by India. However, Persian ascendency in northern India ended with Alexander the Great's conquest of Persia in 327 BCE.
By 326 BCE, Alexander the Great had conquered Asia Minor and the Achaemenid Empire and had reached the northwest frontiers of the Indian subcontinent. There he defeated King Porus in the Battle of the Hydaspes (near modern-day Jhelum
, Pakistan) and conquered much of the Punjab
. Alexander's march east put him in confrontation with the Nanda Empire
of Magadha
and the Gangaridai Empire
of Bengal
. His army, exhausted and frightened by the prospect of facing larger Indian armies at the Ganges River, mutinied at the Hyphasis (modern Beas River
) and refused to march further East. Alexander, after the meeting with his officer, Coenus, was convinced that it was better to return.
The Persian and Greek invasions had important repercussions on Indian civilization. The political systems of the Persians were to influence future forms of governance on the subcontinent, including the administration of the Mauryan dynasty. In addition, the region of Gandhara, or present-day eastern Afghanistan and northwest Pakistan, became a melting pot of Indian, Persian, Central Asian, and Greek cultures and gave rise to a hybrid culture, Greco-Buddhism
, which lasted until the 5th century CE and influenced the artistic development of Mahayana Buddhism
.
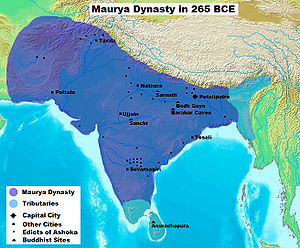
 The Maurya Empire
The Maurya Empire
(322–185 BCE), ruled by the Mauryan dynasty, was a geographically extensive and powerful political and military empire in ancient India. The empire was established by Chandragupta Maurya
in Magadha
what is now Bihar
. The empire flourished under the reign of Ashoka the Great
. At its greatest extent, it stretched to the north to the natural boundaries of the Himalayas
and to the east into what is now Assam
. To the west, it reached beyond modern Pakistan
, annexing Balochistan
and much of what is now Afghanistan
, including the modern Herat
and Kandahar
provinces. The empire was expanded into India's central and southern regions by the emperors Chandragupta and Bindusara
, but it excluded extensive unexplored tribal and forested regions near Kalinga
which were subsequently taken by Ashoka. Like every state, the Maurya Empire needed to have a unified administrative apparatus. Ashoka ruled the Maurya Empire for 37 years from 268 BCE until he died in 232 BCE. During that time, Ashoka pursued an active foreign policy aimed at setting up a unified state. However, Ashoka became involved in a war with the state of Kalinga
which is located on the western shore of the Bay of Bengal. This war forced Ashoka to abandon his attempt at a foreign policy which would unify the Maurya Empire.
Slavery had begun in India during the Vedic era. However, during the Mauryan Empire slavery developed much more rapidly. The Mauryan Empire was based on a modern and efficient economy and society. However, the sale of merchandise was closely regulated by the government. Although there was no banking in the Mauryan society, usury was customary with loans made at the recognized interest rate of 15% per annum.
Ashoka's reign propagated Buddhism
. In this regard Ashoka established many Buddhist monuments. Indeed, Ashoka put a strain on the economy and the government by his strong support of Buddhism. towards the end of his reign he "bled the state coffers white with his generous gifts to promote the promulation of Buddha's teaching. As might be expected, this policy caused considerable opposition within the government. This opposition rallied around Sampadi, Ashoka's grandson and heir to the throne. Religious opposition to
Ashoka also arose among the orthodox Brahmanists and the adherents of Jainism
--a religion based on non-violence toward all living beings.
Chandragupta's minister Chanakya
wrote the Arthashastra
, one of the greatest treatises on economics, politics, foreign affairs, administration, military arts, war, and religion produced in Asia. Archaeologically, the period of Mauryan rule in South Asia falls into the era of Northern Black Polished Ware
(NBPW). The Arthashastra and the Edicts of Ashoka
are primary written records of the Mauryan times. The Lion Capital of Asoka
at Sarnath
, is the national emblem of India.
----
The middle period was a time of notable cultural development. The Satavahana dynasty, also known as the Andhras, ruled in southern and central India after around 230 BCE. Satakarni
, the sixth ruler of the Satvahana dynasty, defeated the Sunga Empire
of north India. Afterwards, Kharavela
, the warrior king of Kalinga
, ruled a vast empire and was responsible for the propagation of Jainism
in the Indian subcontinent. The Kharavelan Jain empire included a formidable maritime empire with trading routes linking it to Sri Lanka
, Burma, Thailand
, Vietnam
, Cambodia
, Borneo
, Bali
, Sumatra
, and Java
. Colonists from Kalinga settled in Sri Lanka, Burma, as well as the Maldives
and the Malay Archipelago
. The Kuninda Kingdom
was a small Himalayan state that survived from around the 2nd century BCE to roughly the 3rd century CE. The Kushanas
migrated from Central Asia
into northwestern India in the middle of the 1st century CE and founded an empire that eventually stretched from Tajikistan
to the middle Ganges. The Western Satraps (35-405 CE) were Saka
rulers of the western and central part of India. They were the successors of the Indo-Scythians
and contemporaries of the Kushans who ruled the northern part of the Indian subcontinent and the Satavahana (Andhra) who ruled in central and southern India.
Different dynasties such as the Pandyans, Cholas
, Cheras
, Kadambas, Western Gangas, Pallava
s, and Chalukyas
, dominated the southern part of the Indian peninsula at different periods of time. Several southern kingdoms formed overseas empires that stretched into Southeast Asia. The kingdoms warred with each other and the Deccan
states for domination of the south. The Kalabras, a Buddhist dynasty, briefly interrupted the usual domination of the Cholas, Cheras, and Pandyas in the south.

The northwestern hybrid cultures of the subcontinent included the Indo-Greeks, the Indo-Scythians, the Indo-Parthians, and the Indo-Sassinids. The first of these, the Indo-Greek Kingdom, was founded when the Greco-Bactrian
king Demetrius
invaded the region in 180 BCE, extending his rule over various parts of present-day Afghanistan and Pakistan. Lasting for almost two centuries, the kingdom was ruled by a succession of more than 30 Greek kings, who were often in conflict with each other. The Indo-Scythians
were a branch of the Indo-European Saka
s (Scythians) who migrated from southern Siberia
, first into Bactria
, subsequently into Sogdiana
, Kashmir
, Arachosia
, and Gandhara
, and finally into India. Their kingdom lasted from the middle of the 2nd century BCE to the 1st century BCE. Yet another kingdom, the Indo-Parthians
(also known as the Pahlavas
), came to control most of present-day Afghanistan and northern Pakistan, after fighting many local rulers such as the Kushan
ruler Kujula Kadphises
, in the Gandhara region. The Sassanid empire of Persia, who was contemporaneous with the Gupta Empire, expanded into the region of present-day Balochistan in Pakistan, where the mingling of Indian culture and the culture of Iran
gave birth to a hybrid culture under the Indo-Sassanids.
expanded out of what is now Afghanistan into the northwest of the subcontinent under the leadership of their first emperor, Kujula Kadphises
, about the middle of the 1st century CE. By the time of his grandson, Kanishka
, (whose era is thought to have begun c. 127 CE), they had conquered most of northern India, at least as far as Saketa and Pataliputra, in the middle Ganges Valley, and probably as far as the Bay of Bengal
. They played an important role in the establishment of Buddhism in India and its spread to Central Asia and China. By the 3rd century, their empire in India was disintegrating; their last known great emperor being Vasudeva I
(c. 190-225 CE).
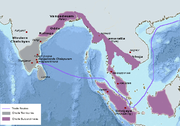
 Roman trade with India started around 1 CE, during the reign of Augustus
Roman trade with India started around 1 CE, during the reign of Augustus
and following his conquest of Egypt, which had been India's biggest trade partner in the West.
The trade started by Eudoxus of Cyzicus
in 130 BCE kept increasing, and according to Strabo
(II.5.12.), by the time of Augustus, up to 120 ships set sail every year from Myos Hormos
on the Red Sea
to India. So much gold was used for this trade, and apparently recycled by the Kushans
for their own coinage, that Pliny the Elder
(NH VI.101) complained about the drain of specie to India:
The maritime (but not the overland) trade routes, harbours, and trade items are described in detail in the 1st century CE Periplus of the Erythraean Sea
.
was reunited under the Gupta Empire
(c. 320–550 CE). This period has been called the Golden Age of India and was marked by extensive achievements in science, technology, engineering, art
, dialectic, literature
, logic
, mathematics
, astronomy, religion, and philosophy
that crystallized the elements of what is generally known as Hindu culture
. The decimal numeral system
, including the concept of zero
, was invented in India during this period. The peace and prosperity created under leadership of Guptas enabled the pursuit of scientific and artistic endeavors in India.
The high points of this cultural creativity are magnificent architecture, sculpture, and painting. The Gupta period produced scholars such as Kalidasa
, Aryabhata
, Varahamihira
, Vishnu Sharma, and Vatsyayana
who made great advancements in many academic fields. Science and political administration reached new heights during the Gupta era. Strong trade ties also made the region an important cultural center and established it as a base that would influence nearby kingdoms and regions in Burma, Sri Lanka
, the Malay Archipelago
, and Indochina
.
The Gupta period marked a watershed of Indian culture: the Guptas performed Vedic sacrifices to legitimize their rule, but they also patronized Buddhism
, which continued to provide an alternative to Brahmanical orthodoxy. The military exploits of the first three rulers—Chandragupta I
(c. 319–335), Samudragupta
(c. 335–376), and Chandragupta II
(c. 376–415) —brought much of India under their leadership. They successfully resisted the northwestern kingdoms until the arrival of the Hunas
, who established themselves in Afghanistan by the first half of the 5th century, with their capital at Bamiyan. However, much of the Deccan
and southern India were largely unaffected by these events in the north.
 The "Classical Age" in India began with the Gupta Empire
The "Classical Age" in India began with the Gupta Empire
and the resurgence of the north during Harsha
's conquests around the 7th century CE, and ended with the fall of the Vijayanagara Empire
in the south in the 13th century, due to pressure from the invaders to the north. This period produced some of India's finest art, considered the epitome of classical development, and the development of the main spiritual and philosophical systems which continued to be in Hinduism, Buddhism and Jainism. King Harsha of Kannauj
succeeded in reuniting northern India during his reign in the 7th century, after the collapse of the Gupta dynasty. His kingdom collapsed after his death.
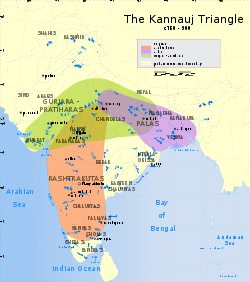
From the 7th to the 9th century, three dynasties contested for control of northern India: the Gurjara Pratiharas of Malwa,the Eastern Ganga dynasty
of Orissa
, the Pala
s of Bengal
, and the Rashtrakutas
of the Deccan
. The Sena dynasty
would later assume control of the Pala Empire, and the Gurjara Pratiharas fragmented into various states. These were the first of the Rajput
states, a series of kingdoms which managed to survive in some form for almost a millennium, until Indian independence from the British. The first recorded Rajput kingdoms emerged in Rajasthan
in the 6th century, and small Rajput dynasties later ruled much of northern India. One Gurjar Rajput of the Chauhan
clan, Prithvi Raj Chauhan, was known for bloody conflicts against the advancing Islamic sultanates. The Shahi dynasty ruled portions of eastern Afghanistan, northern Pakistan, and Kashmir from the mid-7th century to the early 11th century.
The Chalukya dynasty
ruled parts of southern and central India from Badami
in Karnataka
between 550 and 750, and then again from Kalyani
between 970 and 1190. The Pallava
s of Kanchipuram
were their contemporaries further to the south. With the decline of the Chalukya empire, their feudatories, the Hoysalas
of Halebidu
, Kakatiya
s of Warangal
, Seuna Yadavas of Devagiri, and a southern branch of the Kalachuri
, divided the vast Chalukya empire amongst themselves around the middle of 12th century.
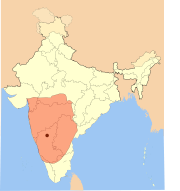
The Chola Empire
at its peak covered much of the Indian subcontinent
and Southeast Asia
. Rajaraja Chola I
conquered all of peninsular south India and parts of Sri Lanka
. Rajendra Chola I
's navies went even further, occupying coasts from Burma (now Myanmar
) to Vietnam
, the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, the Lakshadweep
(Laccadive) islands, Sumatra
, and the Malay Peninsula
in Southeast Asia and the Pegu islands. Later during the middle period, the Pandyan Empire emerged in Tamil Nadu
, as well as the Chera Kingdom in parts of Kerala
and Tamil Nadu
. By 1343, last of these dynasties had ceased to exist, giving rise to the Vijayanagar empire.
The ports of south India were engaged in the Indian Ocean
trade, chiefly involving spices, with the Roman Empire
to the west and Southeast Asia to the east. Literature in local vernaculars and spectacular architecture flourished until about the beginning of the 14th century, when southern expeditions of the sultan of Delhi took their toll on these kingdoms. The Hindu Vijayanagar dynasty came into conflict with the Islamic Bahmani Sultanate
, and the clashing of the two systems caused a mingling of the indigenous and foreign cultures that left lasting cultural influences on each other. The Vijaynagar Empire eventually declined due to pressure from the first Delhi sultanates that had managed to establish themselves in the north around the city of Delhi by that time.
 After conquering Persia, Arab Islamic Caliphate
After conquering Persia, Arab Islamic Caliphate
incorporated parts of what is now Pakistan around 720 CE. The Muslim rulers were keen to invade India, which was a rich region, with a flourishing international trade and the only known diamond mines in the world. In 712 CE an Arab Muslim general called Muhammad bin Qasim
conquered most of the Indus region in modern day Pakistan, for the Umayyad
empire, to be made the "As-Sindh" province with its capital at Al-Mansurah, 72 km (45 mi) north of modern Hyderabad
in Sindh
, Pakistan
. After several wars including the Battle of Rajasthan
, where the Hindu
Rajput
clans defeated the Umayyad
Arabs, their expansion was checked and contained to Sindh in Pakistan, many short-lived Islamic kingdoms (sultan
ates) under foreign rulers were established across the north western subcontinent over a period of a few centuries. Additionally, Muslim trading communities had flourished throughout coastal south India, particularly in Kerala
, where Muslim traders arrived in small numbers, mainly from the Arabian peninsula. This had marked the introduction of a third Abraham
ic Middle Eastern religion, following Judaism and Christianity, often in puritanical form. Later, the Bahmani Sultanate
and Deccan sultanates
founded by Turkic rulers, flourished in the south.

In the 12th and 13th centuries, Turks and Afghan
s invaded parts of northern India and established the Delhi Sultanate
in the former Rajput
holdings. The subsequent Slave dynasty of Delhi
managed to conquer large areas of northern India, approximately equal in extent to the ancient Gupta Empire
, while the Khilji dynasty
was also able to conquer most of central India, but were ultimately unsuccessful in conquering and uniting the subcontinent. The Sultanate ushered in a period of Indian cultural renaissance. The resulting "Indo-Muslim" fusion of cultures left lasting syncretic monuments in architecture, music, literature, religion, and clothing. It is surmised that the language of Urdu
(literally meaning "horde" or "camp" in various Turkic dialects) was born during the Delhi Sultanate period as a result of the intermingling of the local speakers of Sanskritic Prakrit
s with immigrants speaking Persian
, Turkic
, and Arabic
under the Muslim rulers. The Delhi Sultanate is the only Indo-Islamic empire to have enthroned one of the few female rulers in India, Razia Sultana
(1236–1240).
A Turco-Mongol
conqueror in Central Asia, Timur
(Tamerlane), attacked the reigning Sultan Nasir-u Din Mehmud of the Tughlaq Dynasty in the north Indian city of Delhi
. The Sultan's army was defeated on December 17, 1398. Timur entered Delhi and the city was sacked, destroyed, and left in ruins, after Timur's army had killed and plundered for three days and nights. He ordered the whole city to be sacked except for the sayyid
s, scholars, and the other Muslims,; 100,000 war prisoners, mostly Hindus, were put to death in one day.

In 1526, Babur
, a Timurid
descendant of Timur
and Genghis Khan
from Fergana Valley
(modern day Uzbekistan
), swept across the Khyber Pass
and established the Mughal Empire
, covering modern day Afghanistan
, Pakistan
, India
and Bangladesh
. However, his son Humayun
was defeated by the Afghan warrior Sher Shah Suri
in the year 1540, and Humayun was forced to retreat to Kabul
. After Sher Shah's death, his son Islam Shah Suri
and the Hindu king Samrat Hem Chandra Vikramaditya, who had won 22 battles from Punjab
to Bengal
and had established a secular Hindu Raj, ruled North India from Delhi
till 1556, when Akbar's forces defeated and killed Hemu in the Second Battle of Panipat on 6 November 1556.
The Mughal dynasty ruled most of the Indian subcontinent by 1600; it went into a slow decline after 1707 and was finally defeated during the Indian Rebellion of 1857
, also called the 1857 War of Independence. This period marked vast social change in the subcontinent as the Hindu majority were ruled over by the Mughal emperors, most of whom showed religious tolerance, liberally patronising Hindu culture. The famous emperor Akbar, who was the grandson of Babar, tried to establish a good relationship with the Hindus. However, later emperors such as Aurangazeb tried to establish complete Muslim dominance, and as a result several historical temples were destroyed during this period and taxes imposed on non-Muslims. During the decline of the Mughal Empire, several smaller states rose to fill the power vacuum and themselves were contributing factors to the decline. In 1739, Nader Shah
, emperor of Iran, defeated the Mughal army at the huge Battle of Karnal
. After this victory, Nader captured and sacked Delhi, carrying away many treasures, including the Peacock Throne
.
The Mughals were perhaps the richest single dynasty to have ever existed.
During the Mughal era, the dominant political forces consisted of the Mughal Empire and its tributaries and, later on, the rising successor states - including the Maratha confederacy
- which fought an increasingly weak Mughal dynasty. The Mughals, while often employing brutal tactics to subjugate their empire, had a policy of integration with Indian culture, which is what made them successful where the short-lived Sultanates of Delhi had failed. Akbar the Great was particularly famed for this. Akbar declared "Amari" or non-killing of animals in the holy days of Jainism. He rolled back the jizya
tax for non-Muslims. The Mughal emperors married local royalty, allied themselves with local maharajas, and attempted to fuse their Turko-Persian culture with ancient Indian styles, creating a unique Indo-Saracenic architecture
. It was the erosion of this tradition coupled with increased brutality and centralization that played a large part in the dynasty's downfall after Aurangzeb
, who unlike previous emperors, imposed relatively non-pluralistic policies on the general population, which often inflamed the majority Hindu population.
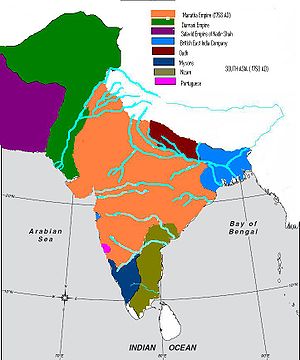
 The post-Mughal era was dominated by the rise of the Maratha suzerainty as other small regional states (mostly late Mughal tributary states) emerged, and also by the increasing activities of European powers (see colonial era below). The Maratha kingdom or confederacy was founded and consolidated by Shivaji. By the 18th century, it had transformed itself into the Maratha Empire
The post-Mughal era was dominated by the rise of the Maratha suzerainty as other small regional states (mostly late Mughal tributary states) emerged, and also by the increasing activities of European powers (see colonial era below). The Maratha kingdom or confederacy was founded and consolidated by Shivaji. By the 18th century, it had transformed itself into the Maratha Empire
under the rule of the peshwa
s (prime ministers). By 1760, the domain of the Marathas stretched across practically the entire subcontinent. This expansion was brought to an end by the defeat of the Marathas by an Afghan army led by Ahmad Shah Durrani
at the Third Battle of Panipat
(1761). The last peshwa, Baji Rao II
, was defeated by the British
in the Third Anglo-Maratha War
.
The Kingdom of Mysore in southern India was founded around 1400 CE by the Wodeyar dynasty. The rule of the Wodeyars was interrupted by Hyder Ali
and his son Tipu Sultan
. Under their rule, Mysore fought a series of wars
sometimes against the combined forces of the British and Marathas, but mostly against the British, with Mysore receiving some aid or promise of aid from the French
.
Hyderabad was founded by the Qutb Shahi dynasty
of Golconda
in 1591. Following a brief Mughal rule, Asif Jah, a Mughal official, seized control of Hyderabad and declared himself Nizam-al-Mulk of Hyderabad in 1724. It was ruled by a hereditary Nizam from 1724 until 1948. Both Mysore and Hyderabad became princely states in British India.
The Punjabi kingdom, ruled by members of the Sikh religion
, was a political entity that governed the region of modern-day Punjab
. This was among the last areas of the subcontinent to be conquered by the British. The first
and second Anglo-Sikh war
marked the downfall of the Sikh Empire.
Around the 18th century, the modern state of Nepal
was formed by Gurkha
rulers.
successfully discovered a new sea route from Europe to India, which paved the way for direct Indo-European commerce. The Portuguese
soon set up trading posts in Goa
, Daman
, Diu and Bombay. The next to arrive were the Dutch
, the British
—who set up a trading post in the west coast port of Surat
in 1619—and the French
. The internal conflicts among Indian kingdoms gave opportunities to the European traders to gradually establish political influence and appropriate lands. Although these continental European powers controlled various coastal regions of southern and eastern India during the ensuing century, they eventually lost all their territories in India to the British islanders, with the exception of the French outposts of Pondicherry and Chandernagore, the Dutch port of Travancore
, and the Portuguese colonies of Goa
, Daman and Diu.
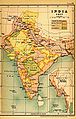 In 1617 the British East India Company
In 1617 the British East India Company
was given permission by Mughal Emperor Jahangir to trade in India. Gradually their increasing influence led the de-jure Mughal emperor Farrukh Siyar to grant them dastaks or permits for duty free trade in Bengal
in 1717. The Nawab of Bengal
Siraj Ud Daulah, the de facto
ruler of the Bengal province, opposed British attempts to use these permits.
The First Carnatic War extended from 1746 until 1748 and was the result of colonial competition between France and Britain, two of the countries involved in the War of Austrian Succession. Following the capture of a few French ships by the British fleet in India
, French troops attacked and captured the British city of Madras located on the east coast of India on September 21, 1746. Among the prisoners captured at Madras was Robert Clive himself. The war was eventually ended by the Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle
which ended the War of Austrian Succession in 1748.
In 1749, the Second Carnatic War broke out as the result of a war between a son, Nasir Jung
, and a grandson, Muzaffer Jung, of the deceased Nizam-ul-Mulk of Hyderabad to take over Nizam's thone in Hyderabad. The French supported Muzaffer Jung in this civil war. Consequently, the British supported Nasir Jung in this conflict.
Meanwhile, however, the conflict in Hyderabad provided Chanda Sahib
with an opportunity to take power as the new Nawab
of the territory of Arcot. In this conflict, the French supported Chandra Sahib in his attempt to become the new Nawab of Arcot. The British supported the son of the deposed incumbent Nawab, Anwaruddin Muhammad Khan, against Chanda Sahib. In 1751, Robert Clive led a British armed force and captured Arcot to reinstate the incumbent Nawab. The Second Carnatic War finally came to an end in 1754 with the Treaty of Pondicherry
.
In 1756, the Seven Years War broke out between the great powers of the world, i.e. Britain and Prussia on one side and France, Austria and Russia on the other. The Seven Years War was really a "world war", with theaters of operations in Europe, the Caribbean, North America and India. Indeed, Winston Churchill
called the Seven Years War "the first world war."
Great Britain
and France fought each other in these theaters throughout the world. In the Indian theater of operations, the Seven Years War became known as the Third Carnatic War. Early in this war, armed forces under the French East India Company captured the British base of Calcutta in north-eastern India. However, armed forces under Robert Clive later recaptured Calcutta and then pressed on to capture the French settlement of Chandannagar
in 1757. This led to the Battle of Plassey
on June 23, 1757, in which the Bengal Army
of the East India Company, led by Robert Clive, defeated the French-supported Nawab's forces. This was the first real political foothold with territorial implications that the British acquired in India. Clive was appointed by the company as its first 'Governor of Bengal' in 1757. This was combined with British victories over the French at Madras
, Wandiwash
and Pondicherry
that, along with wider British successes during the Seven Years War
, reduced French influence in India. Thus as a result of the three Carnatic Wars, the British East India Company gained exclusive control over the entire Carnatic region of India. Following the British suppression of a revolt against the British East India Company in Bengal
in 1863, the Company also gained exclusive economic control of the Bihar region of India along the Ganges River. Also in 1863, the British completed the conquest of several feudal principalities in the Orissa region of southern Bengal. Thus, the British East India Company extended its control over the whole of Bengal. In 1763, the Treaty of Paris (1763)
ended the Anglo-French hostilities part of the Seven Years War.
After the Battle of Buxar
in 1764, the company acquired the civil rights of administration in Bengal from Mughal Emperor Shah Alam II
; this marked the beginning of its formal rule, which within the next century engulfed most of India and extinguished the Moghul rule and dynasty.
The East India Company monopolized the trade of Bengal. They introduced a land taxation system called the Permanent Settlement
which introduced a feudal
-like structure in Bengal, often with zamindar
s set in place. By the 1850s, the East India Company controlled most of the Indian sub-continent, which included present-day Pakistan and Bangladesh. Their policy was sometimes summed up as Divide and Rule
, taking advantage of the enmity festering between various princely states and social and religious groups.
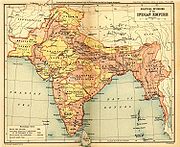 The first major movement against the British Company's high handed rule resulted in the Indian Rebellion of 1857
The first major movement against the British Company's high handed rule resulted in the Indian Rebellion of 1857
. After a year of turmoil and reinforcement of the East India Company's troops with British soldiers, the company overcame the rebellion. The nominal leader of the uprising, the last Mughal Emperor Bahadur Shah Zafar was exiled to Burma, his children were beheaded, and the Moghul line was abolished. In the aftermath, all power was transferred from the East India Company to the British Crown, which began to administer most of India as a number of provinces; the company's lands were controlled directly, while it had considerable influence over the rest of India, which consisted of the Princely states. There were some 565 princely states when British India gained independence from Britain in August 1947.
During the British Raj, famines in India
, often attributed to failed government policies, were some of the worst ever recorded, including the Great Famine of 1876–78
in which 6.1 million to 10.3 million people died and the Indian famine of 1899–1900
in which 1.25 to 10 million people died. The Third Plague Pandemic started in China in the middle of the 19th century, spreading plague to all inhabited continents and killing 10 million people in India alone. Despite persistent diseases and famines, the population of the Indian subcontinent
, which stood at about 125 million in 1750, had reached 389 million by 1941.
" in British India as a means of preventing an uprising against their rule.
In this environment of Hindu-Muslim disunity, the first step toward Indian independence and western-style democracy was taken with the appointment of Indian councillors to advise the British viceroy
, and with the establishment of provincial Councils with Indian members. The councillors' participation was subsequently widened into legislative councils. From 1920 leaders such as Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi began highly popular mass movements to campaign against the British Raj using largely peaceful methods. Some others adopted a militant approach that sought to overthrow British rule by armed struggle; revolutionary activities
against the British rule took place throughout the Indian sub-continent. The Gandhi-led independence movement opposed the British rule using non-violent methods like non-cooperation
, civil disobedience and economic resistance
. These movements succeeded in bringing independence to the new dominions of India and Pakistan
in 1947.
, promised that they would leave and participated in the formation of an interim government
. The British Indian territories gained independence in 1947, after being partitioned
into the Union of India and Dominion of Pakistan
. Following the controversial division of pre-partition Punjab
and Bengal
, rioting broke out between Sikhs, Hindus and Muslims in these provinces and spread to several other parts of India, leaving some 500,000 dead. Also, this period saw one of the largest mass migrations ever recorded in modern history, with a total of 12 million Hindus, Sikhs and Muslims moving between the newly created nations of India
and Pakistan
(which gained independence on 15 and 14 August 1947 respectively). In 1971, Bangladesh
, formerly East Pakistan
and East Bengal
, seceded from Pakistan.
Anatomically modern humans
The term anatomically modern humans in paleoanthropology refers to early individuals of Homo sapiens with an appearance consistent with the range of phenotypes in modern humans....
as long as 75,000 years ago, or with earlier hominids including Homo erectus
Homo erectus
Homo erectus is an extinct species of hominid that lived from the end of the Pliocene epoch to the later Pleistocene, about . The species originated in Africa and spread as far as India, China and Java. There is still disagreement on the subject of the classification, ancestry, and progeny of H...
from about 500,000 years ago. The Indus Valley Civilization
Indus Valley Civilization
The Indus Valley Civilization was a Bronze Age civilization that was located in the northwestern region of the Indian subcontinent, consisting of what is now mainly modern-day Pakistan and northwest India...
, which spread and flourished in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent
Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent, also Indian Subcontinent, Indo-Pak Subcontinent or South Asian Subcontinent is a region of the Asian continent on the Indian tectonic plate from the Hindu Kush or Hindu Koh, Himalayas and including the Kuen Lun and Karakoram ranges, forming a land mass which extends...
from c. 3300 to 1300 BCE, was the first major civilization in India. A sophisticated and technologically advanced urban culture developed in the Mature Harappan period, from 2600 to 1900 BCE. This Bronze Age
Bronze Age India
The Bronze Age in South Asia begins around 3000 BC, and in the end gives rise to the Indus Valley Civilization, which had its mature period between 2600 BC and 1900 BC. It continues into the Rigvedic period, the early part of the Vedic period...
civilization collapsed before the end of the second millennium BCE and was followed by the Iron Age
Iron Age India
Iron Age India, the Iron Age in the Indian subcontinent, succeeds the Late Harappan culture, also known as the last phase of the Indus Valley Tradition...
Vedic Civilization
Vedic period
The Vedic period was a period in history during which the Vedas, the oldest scriptures of Hinduism, were composed. The time span of the period is uncertain. Philological and linguistic evidence indicates that the Rigveda, the oldest of the Vedas, was composed roughly between 1700–1100 BCE, also...
, which extended over much of the Indo-Gangetic plain
Indo-Gangetic plain
The northern Plains also known as the Indo - Gangetic Plain and The North Indian River Plain is a large and fertile plain encompassing most of northern and eastern India, the most populous parts of Pakistan, parts of southern Nepal and virtually all of Bangladesh...
and which witnessed the rise of major polities known as the Mahajanapadas
Mahajanapadas
Mahājanapadas , literally "great realms", were ancient Indian kingdoms or countries...
. In one of these kingdoms, Magadha
Magadha
Magadha formed one of the sixteen Mahājanapadas or kingdoms in ancient India. The core of the kingdom was the area of Bihar south of the Ganga; its first capital was Rajagriha then Pataliputra...
, Mahavira
Mahavira
Mahāvīra is the name most commonly used to refer to the Indian sage Vardhamāna who established what are today considered to be the central tenets of Jainism. According to Jain tradition, he was the 24th and the last Tirthankara. In Tamil, he is referred to as Arukaṉ or Arukadevan...
and Gautama Buddha
Gautama Buddha
Siddhārtha Gautama was a spiritual teacher from the Indian subcontinent, on whose teachings Buddhism was founded. In most Buddhist traditions, he is regarded as the Supreme Buddha Siddhārtha Gautama (Sanskrit: सिद्धार्थ गौतम; Pali: Siddhattha Gotama) was a spiritual teacher from the Indian...
were born in the 6th or 5th century BCE and propagated their śramanic
Shramana
A shramana is a wandering monk in certain ascetic traditions of ancient India including Jainism, Buddhism, and Ājīvikism. Famous śramaṇas include Mahavira and Gautama Buddha....
philosophies.
Almost all of the subcontinent was conquered by the Maurya Empire
Maurya Empire
The Maurya Empire was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in ancient India, ruled by the Mauryan dynasty from 321 to 185 BC...
during the 4th and 3rd centuries BCE. It subsequently became fragmented, with various parts ruled by numerous Middle kingdoms
Middle kingdoms of India
Middle kingdoms of India refers to the political entities in India from the 3rd century BC after the decline of the Maurya Empire, and the corresponding rise of the Satavahana dynasty, beginning with Simuka, from 230 BC...
for the next 1,500 years. This is known as the classical period of Indian history, during which India has sometimes been estimated to have had the largest economy
Economic history of India
The known Economic history of India begins with the Indus Valley civilization. The Indus civilization's economy appears to have depended significantly on trade, which was facilitated by advances in transport. Around 600 BC, the Mahajanapadas minted punch-marked silver coins. The period was marked...
of the ancient and medieval world, controlling between one third and one fourth of the world's wealth up to the 18th century.
Much of northern and central India was once again united in the 4th century CE, and remained so for two centuries thereafter, under the Gupta Empire
Gupta Empire
The Gupta Empire was an ancient Indian empire which existed approximately from 320 to 550 CE and covered much of the Indian Subcontinent. Founded by Maharaja Sri-Gupta, the dynasty was the model of a classical civilization. The peace and prosperity created under leadership of Guptas enabled the...
. This period, witnessing a Hindu
Hindu
Hindu refers to an identity associated with the philosophical, religious and cultural systems that are indigenous to the Indian subcontinent. As used in the Constitution of India, the word "Hindu" is also attributed to all persons professing any Indian religion...
religious and intellectual resurgence, is known among its admirers as the "Golden Age of India". During the same time, and for several centuries afterwards, southern India, under the rule of the Chalukyas
Chalukya dynasty
The Chalukya dynasty was an Indian royal dynasty that ruled large parts of southern and central India between the 6th and the 12th centuries. During this period, they ruled as three related yet individual dynasties. The earliest dynasty, known as the "Badami Chalukyas", ruled from Vatapi from the...
, Cholas
Chola Dynasty
The Chola dynasty was a Tamil dynasty which was one of the longest-ruling in some parts of southern India. The earliest datable references to this Tamil dynasty are in inscriptions from the 3rd century BC left by Asoka, of Maurya Empire; the dynasty continued to govern over varying territory until...
, Pallavas, and Pandyas, experienced its own golden age. During this period, aspects of Indian civilization, administration, culture, and religion (Hinduism
Hinduism
Hinduism is the predominant and indigenous religious tradition of the Indian Subcontinent. Hinduism is known to its followers as , amongst many other expressions...
and Buddhism
Buddhism
Buddhism is a religion and philosophy encompassing a variety of traditions, beliefs and practices, largely based on teachings attributed to Siddhartha Gautama, commonly known as the Buddha . The Buddha lived and taught in the northeastern Indian subcontinent some time between the 6th and 4th...
) spread to much of Asia
Asia
Asia is the world's largest and most populous continent, located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres. It covers 8.7% of the Earth's total surface area and with approximately 3.879 billion people, it hosts 60% of the world's current human population...
.
The southern state of Kerala
Kerala
or Keralam is an Indian state located on the Malabar coast of south-west India. It was created on 1 November 1956 by the States Reorganisation Act by combining various Malayalam speaking regions....
had maritime business links with the Roman Empire from around 77 CE. Islam was introduced in Kerala through this route by Muslim traders. Muslim rule in the subcontinent began in 712 CE when the Arab general Muhammad bin Qasim
Muhammad bin Qasim
Muhammad bin Qasim Al-Thaqafi was a Umayyad general who, at the age of 17, began the conquest of the Sindh and Punjab regions along the Indus River for the Umayyad Caliphate. He was born in the city of Taif...
conquered Sindh
Sindh
Sindh historically referred to as Ba'ab-ul-Islam , is one of the four provinces of Pakistan and historically is home to the Sindhi people. It is also locally known as the "Mehran". Though Muslims form the largest religious group in Sindh, a good number of Christians, Zoroastrians and Hindus can...
and Multan
Multan
Multan , is a city in the Punjab Province of Pakistan and capital of Multan District. It is located in the southern part of the province on the east bank of the Chenab River, more or less in the geographic centre of the country and about from Islamabad, from Lahore and from Karachi...
in southern Punjab
Punjab region
The Punjab , also spelled Panjab |water]]s"), is a geographical region straddling the border between Pakistan and India which includes Punjab province in Pakistan and the states of the Punjab, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Chandigarh and some northern parts of the National Capital Territory of Delhi...
in modern day Pakistan, setting the stage for several successive invasions from Central Asia between the 10th and 15th centuries CE, leading to the formation of Muslim empires in the Indian subcontinent
Muslim conquest in the Indian subcontinent
Muslim conquest in South Asia mainly took place from the 13th to the 16th centuries, though earlier Muslim conquests made limited inroads into the region, beginning during the period of the ascendancy of the Rajput Kingdoms in North India, from the 7th century onwards.However, the Himalayan...
such as the Delhi Sultanate
Delhi Sultanate
The Delhi Sultanate is a term used to cover five short-lived, Delhi based kingdoms or sultanates, of Turkic origin in medieval India. The sultanates ruled from Delhi between 1206 and 1526, when the last was replaced by the Mughal dynasty...
and the Mughal Empire
Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire , or Mogul Empire in traditional English usage, was an imperial power from the Indian Subcontinent. The Mughal emperors were descendants of the Timurids...
.
Mughal rule came from Central Asia to cover most of the northern parts of the subcontinent. Mughal rulers introduced Central Asian art and architecture to India. In addition to the Mughals and various Rajput
Rajput
A Rajput is a member of one of the patrilineal clans of western, central, northern India and in some parts of Pakistan. Rajputs are descendants of one of the major ruling warrior classes in the Indian subcontinent, particularly North India...
kingdoms, several independent Hindu states, such as the Vijayanagara Empire
Vijayanagara Empire
The Vijayanagara Empire , referred as the Kingdom of Bisnaga by the Portuguese, was an empire based in South Indian in the Deccan Plateau region. It was established in 1336 by Harihara I and his brother Bukka Raya I of the Yadava lineage. The empire rose to prominence as a culmination of attempts...
, the Maratha Empire
Maratha Empire
The Maratha Empire or the Maratha Confederacy was an Indian imperial power that existed from 1674 to 1818. At its peak, the empire covered much of South Asia, encompassing a territory of over 2.8 million km²....
, Eastern Ganga Empire
Eastern Ganga dynasty
The Eastern Ganga dynasty reigned from Kalinga and their rule consisted of the whole of the modern day Indian state of Orissa as well as parts of West Bengal, Andhra Pradesh and Chhattisgarh from the 11th century to the early 15th century. Their capital was known by the name Kalinganagar, which is...
and the Ahom Kingdom
Ahom kingdom
The Ahom Kingdom was a medieval kingdom in the Brahmaputra valley in Assam that maintained its sovereignty for nearly 600 years and successfully resisted Mughal expansion in North-East India...
, flourished contemporaneously in southern, western,eastern and northeastern India respectively. The Mughal Empire suffered a gradual decline in the early 18th century, which provided opportunities for the Afghans
Durrani Empire
The Durrani Empire was a Pashtun dynasty centered in Afghanistan and included northeastern Iran, the Kashmir region, the modern state of Pakistan, and northwestern India. It was established at Kandahar in 1747 by Ahmad Shah Durrani, an Afghan military commander under Nader Shah of Persia and chief...
, Balochis
Baloch people
The Baloch or Baluch are an ethnic group that belong to the larger Iranian peoples. Baluch people mainly inhabit the Balochistan region and Sistan and Baluchestan Province in the southeast corner of the Iranian plateau in Western Asia....
, Sikhs, and Marathas to exercise control over large areas in the northwest of the subcontinent until the British East India Company
East India Company
The East India Company was an early English joint-stock company that was formed initially for pursuing trade with the East Indies, but that ended up trading mainly with the Indian subcontinent and China...
gained ascendancy over South Asia.
Beginning in the mid-18th century and over the next century, large areas of India were gradually annexed by the British East India Company. Dissatisfaction with Company rule led to the Indian Rebellion of 1857
Indian Rebellion of 1857
The Indian Rebellion of 1857 began as a mutiny of sepoys of the British East India Company's army on 10 May 1857, in the town of Meerut, and soon escalated into other mutinies and civilian rebellions largely in the upper Gangetic plain and central India, with the major hostilities confined to...
, after which the British provinces of India were directly administered by the British Crown
British Raj
British Raj was the British rule in the Indian subcontinent between 1858 and 1947; The term can also refer to the period of dominion...
and witnessed a period of both rapid development of infrastructure
Infrastructure
Infrastructure is basic physical and organizational structures needed for the operation of a society or enterprise, or the services and facilities necessary for an economy to function...
and economic decline. During the first half of the 20th century, a nationwide struggle for independence
Indian independence movement
The term Indian independence movement encompasses a wide area of political organisations, philosophies, and movements which had the common aim of ending first British East India Company rule, and then British imperial authority, in parts of South Asia...
was launched by the Indian National Congress
Indian National Congress
The Indian National Congress is one of the two major political parties in India, the other being the Bharatiya Janata Party. It is the largest and one of the oldest democratic political parties in the world. The party's modern liberal platform is largely considered center-left in the Indian...
and later joined by the Muslim League. The subcontinent gained independence from the United Kingdom
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
in 1947, after the British provinces were partitioned
Partition of India
The Partition of India was the partition of British India on the basis of religious demographics that led to the creation of the sovereign states of the Dominion of Pakistan and the Union of India on 14 and 15...
into the dominions of India and Pakistan
Pakistan
Pakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan...
and the princely state
Princely state
A Princely State was a nominally sovereign entitity of British rule in India that was not directly governed by the British, but rather by an Indian ruler under a form of indirect rule such as suzerainty or paramountcy.-British relationship with the Princely States:India under the British Raj ...
s all acceded
Instrument of Accession
The Instrument of Accession was a legal document created in 1947 to enable each of the rulers of the princely states under British suzerainty to join one of the new dominions of India or Pakistan created by the Partition of British India.-Background:...
to one of the new states.
Stone Age


Homo erectus
Homo erectus is an extinct species of hominid that lived from the end of the Pliocene epoch to the later Pleistocene, about . The species originated in Africa and spread as far as India, China and Java. There is still disagreement on the subject of the classification, ancestry, and progeny of H...
in Hathnora in the Narmada Valley
Narmada River
The Narmada , also called Rewa is a river in central India and the fifth largest river in the Indian subcontinent. It is the third largest river that completely flows within India after Ganges and Godavari...
in central India indicate that India might have been inhabited since at least the Middle Pleistocene
Middle Pleistocene
The Middle Pleistocene, more specifically referred to as the Ionian stage, is a period of geologic time from ca. 781 to 126 thousand years ago....
era, somewhere between 500,000 and 200,000 years ago.
Tools crafted by proto-humans that have been dated back two million years have been discovered in the northwestern part of the subcontinent. The ancient history of the region includes some of South Asia's oldest settlements and some of its major civilizations. The earliest archaeological site in the subcontinent is the palaeolithic hominid site in the Soan River valley. Soanian sites are found in the Sivalik region across what are now India, Pakistan, and Nepal.
The Mesolithic
Mesolithic
The Mesolithic is an archaeological concept used to refer to certain groups of archaeological cultures defined as falling between the Paleolithic and the Neolithic....
period in the Indian subcontinent was followed by the Neolithic
Neolithic
The Neolithic Age, Era, or Period, or New Stone Age, was a period in the development of human technology, beginning about 9500 BC in some parts of the Middle East, and later in other parts of the world. It is traditionally considered as the last part of the Stone Age...
period, when more extensive settlement of the subcontinent occurred after the end of the last Ice Age
Ice age
An ice age or, more precisely, glacial age, is a generic geological period of long-term reduction in the temperature of the Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental ice sheets, polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers...
approximately 12,000 years ago. The first confirmed semipermanent settlements appeared 9,000 years ago in the Bhimbetka rock shelters in modern Madhya Pradesh
Madhya Pradesh
Madhya Pradesh , often called the Heart of India, is a state in central India. Its capital is Bhopal and Indore is the largest city....
, India.
Early Neolithic culture in South Asia is represented by the Mehrgarh
Mehrgarh
Mehrgarh , one of the most important Neolithic sites in archaeology, lies on the "Kachi plain" of Balochistan, Pakistan...
findings (7000 BCE onwards) in present-day Balochistan
Balochistan (Pakistan)
Balochistan is one of the four provinces or federating units of Pakistan. With an area of 134,051 mi2 or , it is the largest province of Pakistan, constituting approximately 44% of the total land mass of Pakistan. According to the 1998 population census, Balochistan had a population of...
, Pakistan. Traces of a Neolithic culture have been alleged to be submerged in the Gulf of Khambat in India, radiocarbon dated
Radiocarbon dating
Radiocarbon dating is a radiometric dating method that uses the naturally occurring radioisotope carbon-14 to estimate the age of carbon-bearing materials up to about 58,000 to 62,000 years. Raw, i.e. uncalibrated, radiocarbon ages are usually reported in radiocarbon years "Before Present" ,...
to 7500 BCE. However, the one dredged piece of wood in question was found in an area of strong ocean currents. Neolithic agriculture cultures sprang up in the Indus Valley region around 5000 BCE, in the lower Gangetic valley around 3000 BCE, and in later South India, spreading southwards and also northwards into Malwa around 1800 BCE. The first urban civilization of the region began with the Indus Valley Civilization
Indus Valley Civilization
The Indus Valley Civilization was a Bronze Age civilization that was located in the northwestern region of the Indian subcontinent, consisting of what is now mainly modern-day Pakistan and northwest India...
.
Bronze Age


Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent, also Indian Subcontinent, Indo-Pak Subcontinent or South Asian Subcontinent is a region of the Asian continent on the Indian tectonic plate from the Hindu Kush or Hindu Koh, Himalayas and including the Kuen Lun and Karakoram ranges, forming a land mass which extends...
began around 3300 BCE with the early Indus Valley Civilization. It was centered on the Indus River
Indus River
The Indus River is a major river which flows through Pakistan. It also has courses through China and India.Originating in the Tibetan plateau of western China in the vicinity of Lake Mansarovar in Tibet Autonomous Region, the river runs a course through the Ladakh district of Jammu and Kashmir and...
and its tributaries which extended into the Ghaggar-Hakra River
Ghaggar-Hakra River
The Ghaggar-Hakra River is an intermittent river in India and Pakistan that flows only during the monsoon season. The river is known as Ghaggar before the Ottu barrage and as the Hakra downstream of the barrage...
valley, the Ganges-Yamuna Doab
Doab
A Doab is a term used in India and Pakistan for a "tongue" or tract of land lying between two confluent rivers...
, Gujarat, and southeastern Afghanistan
Afghanistan
Afghanistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located in the centre of Asia, forming South Asia, Central Asia and the Middle East. With a population of about 29 million, it has an area of , making it the 42nd most populous and 41st largest nation in the world...
.
The civilization is primarily located in modern-day India (Gujarat, Haryana
Haryana
Haryana is a state in India. Historically, it has been a part of the Kuru region in North India. The name Haryana is found mentioned in the 12th century AD by the apabhramsha writer Vibudh Shridhar . It is bordered by Punjab and Himachal Pradesh to the north, and by Rajasthan to the west and south...
, Punjab
Punjab (India)
Punjab ) is a state in the northwest of the Republic of India, forming part of the larger Punjab region. The state is bordered by the Indian states of Himachal Pradesh to the east, Haryana to the south and southeast and Rajasthan to the southwest as well as the Pakistani province of Punjab to the...
and Rajasthan
Rajasthan
Rājasthān the land of Rajasthanis, , is the largest state of the Republic of India by area. It is located in the northwest of India. It encompasses most of the area of the large, inhospitable Great Indian Desert , which has an edge paralleling the Sutlej-Indus river valley along its border with...
provinces) and Pakistan (Sindh
Sindh
Sindh historically referred to as Ba'ab-ul-Islam , is one of the four provinces of Pakistan and historically is home to the Sindhi people. It is also locally known as the "Mehran". Though Muslims form the largest religious group in Sindh, a good number of Christians, Zoroastrians and Hindus can...
, Punjab
Punjab (Pakistan)
Punjab is the most populous province of Pakistan, with approximately 45% of the country's total population. Forming most of the Punjab region, the province is bordered by Kashmir to the north-east, the Indian states of Punjab and Rajasthan to the east, the Pakistani province of Sindh to the...
, and Balochistan
Balochistan (Pakistan)
Balochistan is one of the four provinces or federating units of Pakistan. With an area of 134,051 mi2 or , it is the largest province of Pakistan, constituting approximately 44% of the total land mass of Pakistan. According to the 1998 population census, Balochistan had a population of...
provinces). Historically part of Ancient India, it is one of the world's earliest urban civilizations, along with Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a toponym for the area of the Tigris–Euphrates river system, largely corresponding to modern-day Iraq, northeastern Syria, southeastern Turkey and southwestern Iran.Widely considered to be the cradle of civilization, Bronze Age Mesopotamia included Sumer and the...
and Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt was an ancient civilization of Northeastern Africa, concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in what is now the modern country of Egypt. Egyptian civilization coalesced around 3150 BC with the political unification of Upper and Lower Egypt under the first pharaoh...
. Inhabitants of the ancient Indus river valley, the Harappans
Indus Valley Civilization
The Indus Valley Civilization was a Bronze Age civilization that was located in the northwestern region of the Indian subcontinent, consisting of what is now mainly modern-day Pakistan and northwest India...
, developed new techniques in metallurgy and handicraft (carneol products, seal carving), and produced copper, bronze, lead, and tin.
The Mature Indus civilization flourished from about 2600 to 1900 BCE, marking the beginning of the urban civilization on the subcontinent. The civilization included urban centers such as Dholavira
Dholavira
Dholavira is an archaeological site in Khadirbet in Bhachau Taluka of Kachchh district of Gujarat state in western India, which has taken its name from a modern village 1 km south of it. The site of Dholavira, locally known as Kotada timba contains ruins of an ancient Harappan city...
, Kalibangan
Kalibangan
Kalibangān is a town located at on the left or southern banks of the Ghaggar , identified by some scholars with Sarasvati River in Tehsil Pilibangān, between Suratgarh and Hanumāngarh in Hanumangarh district, Rajasthan, India 205 km. from Bikaner...
, Rupar
Rupnagar
Rupnagar is a city and a municipal council in Rupnagar district in the Indian state of Punjab. It was formerly known as Ropar. The town of Rupnagar is said to have been founded by a Raja called Rokeshar, who ruled during the 11th century and named it after his son Rup Sen. It is also the site of...
, Rakhigarhi
Rakhigarhi
Rakhigarhi, or Rakhi Garhi , is a village in Hisar District in the northwest Indian state of Haryana, around 150 kilometers from Delhi. In 1963 archeologists discovered the village was the site of an extensive city, part of the Indus Valley Civilization...
, and Lothal
Lothal
Lothal is one of the most prominent cities of the ancient Indus valley civilization. Located in Bhāl region of the modern state of Gujarāt and dating from 2400 BCE. Discovered in 1954, Lothal was excavated from February 13, 1955 to May 19, 1960 by the Archaeological Survey of India...
in modern-day India, and Harappa
Harappa
Harappa is an archaeological site in Punjab, northeast Pakistan, about west of Sahiwal. The site takes its name from a modern village located near the former course of the Ravi River. The current village of Harappa is from the ancient site. Although modern Harappa has a train station left from...
, Ganeriwala, and Mohenjo-daro
Mohenjo-daro
Mohenjo-daro is an archeological site situated in what is now the province of Sindh, Pakistan. Built around 2600 BC, it was one of the largest settlements of the ancient Indus Valley Civilization, and one of the world's earliest major urban settlements, existing at the same time as the...
in modern-day Pakistan. The civilization is noted for its cities built of brick, roadside drainage system, and multistoried houses.
Vedic period

Vedic period
The Vedic period was a period in history during which the Vedas, the oldest scriptures of Hinduism, were composed. The time span of the period is uncertain. Philological and linguistic evidence indicates that the Rigveda, the oldest of the Vedas, was composed roughly between 1700–1100 BCE, also...
is characterized by Indo-Aryan culture associated with the texts of Vedas
Vedas
The Vedas are a large body of texts originating in ancient India. Composed in Vedic Sanskrit, the texts constitute the oldest layer of Sanskrit literature and the oldest scriptures of Hinduism....
, sacred to Hindus, which were orally composed in Vedic Sanskrit
Vedic Sanskrit
Vedic Sanskrit is an old Indo-Aryan language. It is an archaic form of Sanskrit, an early descendant of Proto-Indo-Iranian. It is closely related to Avestan, the oldest preserved Iranian language...
. The Vedas are some of the oldest extant texts in India and next to some writings in Egypt and Mesopotamia are the oldest in the world. The Vedic period lasted from about 1500 to 500 BCE, laying the foundations of Hinduism
Hinduism
Hinduism is the predominant and indigenous religious tradition of the Indian Subcontinent. Hinduism is known to its followers as , amongst many other expressions...
and other cultural aspects of early Indian society. The Aryans established Vedic
Vedic period
The Vedic period was a period in history during which the Vedas, the oldest scriptures of Hinduism, were composed. The time span of the period is uncertain. Philological and linguistic evidence indicates that the Rigveda, the oldest of the Vedas, was composed roughly between 1700–1100 BCE, also...
civilization all over north India, particularly in the Gangetic Plain. This period succeeded the prehistoric Late Harappan, during which immigrations of Indo-Aryan-speaking tribes
Indo-Aryan migration
Models of the Indo-Aryan migration discuss scenarios of prehistoric migrations of the proto-Indo-Aryans to their historically attested areas of settlement in the northwest of the Indian subcontinent...
overlaid the existing civilizations of local people whom they called Dasyus. The Aryans, originally came from the Caspian Sea area of Asia. Settling first in Bactria and then in the Hindu-Kush area of India, before settling in the Ganges and Yamuna River valleys.
Many scholars throughout history have maintained that the Aryans subjugated the "backward aboriginies" that had previously lived in northern India. However, discoveries of advanced civilizations in the Indus River valley, caused many scholars to change their theories in this regard. The Aryans may have received as much from the neighboring cultures of northern India as they contributed. Indeed when the Aryans moved into India, they were semi-nomadic pastoralists, their clothing was simple, they had no regular legal institutions and their religion was a very basic form of animism. The basis of the Aryan economy had always been centered around cattle raising. During this period of time, the cow began to be venerated in Aryan society. Thus, the origins of the later Hindu belief in India that cows are sacred may have started during this time.

Rigveda
The Rigveda is an ancient Indian sacred collection of Vedic Sanskrit hymns...
, Aryan society became increasingly agricultural and was socially organized around the four varnas, or social classes. In addition to the Vedas, the principal texts of Hinduism, the core themes of the Sanskrit epics Ramayana
Ramayana
The Ramayana is an ancient Sanskrit epic. It is ascribed to the Hindu sage Valmiki and forms an important part of the Hindu canon , considered to be itihāsa. The Ramayana is one of the two great epics of India and Nepal, the other being the Mahabharata...
and Mahabharata
Mahabharata
The Mahabharata is one of the two major Sanskrit epics of ancient India and Nepal, the other being the Ramayana. The epic is part of itihasa....
are said to have their ultimate origins during this period. The Mahabharata remains, today, the longest single poem in the world. The events described in the shorter, Ramayana are from a later period of history than the events of the Mahabharata. The early Indo-Aryan presence probably corresponds, in part, to the Ochre Coloured Pottery culture
Ochre Coloured Pottery culture
The Ochre Coloured Pottery culture , is a 2nd millennium BC Bronze Age culture of the Indo-Gangetic Plain . It is a contemporary to, and a successor of the Indus Valley Civilization. The OCP marks the last stage of the North Indian Bronze Age and is succeeded by the Iron Age black-and-red ware and...
in archaeological contexts.
The Kuru kingdom corresponds to the Black and Red Ware
Black and red ware culture
The black and red ware culture is an early Iron Age archaeological culture of the northern Indian subcontinent. It is dated to roughly the 12th – 9th century BC, and associated with the post-Rigvedic Vedic civilization....
and Painted Grey Ware
Painted Grey Ware culture
The Painted Grey Ware culture is an Iron Age culture of Gangetic plain, lasting from roughly 1200 BC to 600 BC. It is contemporary to, and a successor of the Black and red ware culture. It probably corresponds to the later Vedic period. It is succeeded by Northern Black Polished Ware from ca. 500...
cultures and to the beginning of the Iron Age in northwestern India, around 1000 BCE, as well as with the composition of the Atharvaveda
Atharvaveda
The Atharvaveda is a sacred text of Hinduism and one of the four Vedas, often called the "fourth Veda"....
, the first Indian text to mention iron, as , literally "black metal." The Painted Grey Ware culture spanned much of northern India from about 1100 to 600 BCE. The Vedic Period also established republics such as Vaishali
Vaishali (ancient city)
Vaiśālī was the capital city of the Licchavi, one of world's first republics, in the Vajjian Confederacy mahajanapada, around the 6th century BC. It was here in 599 BCE the 24th Jain Tirthankara, Bhagwan Mahavira was born and brought up in Kundalagrama in Vaiśālī republic, which make pious &...
, which existed as early as the 6th century BCE and persisted in some areas until the 4th century CE. The later part of this period corresponds with an increasing movement away from the previous tribal system towards the establishment of kingdoms, called mahajanapadas
Mahajanapadas
Mahājanapadas , literally "great realms", were ancient Indian kingdoms or countries...
.
Mahajanapadas




Mahajanapadas
Mahājanapadas , literally "great realms", were ancient Indian kingdoms or countries...
— Kasi, Kosala
Kosala Kingdom
Kosala Proper or Uttara Kosala is the kingdom of the celebrated personality of Treta Yuga, Raghava Rama. Ayodhya was its capital, presently in Faizabad district, Uttar Pradesh. Rama's sons Lava and Kusha inherited parts of this kingdom. Lava ruled from the city called Sravasti and Kusa from the...
, Anga
Anga
Anga was a kingdom that flourished on the eastern Indian subcontinent in the 6th century BCE until taken over by Magadha in the same century. Counted among the "sixteen great nations" in Buddhist texts like the Anguttara Nikaya, Anga also finds mention in the Jain Vyakhyaprajnapti’s list of...
, Magadha
Magadha
Magadha formed one of the sixteen Mahājanapadas or kingdoms in ancient India. The core of the kingdom was the area of Bihar south of the Ganga; its first capital was Rajagriha then Pataliputra...
, Vajji
Vajji
Vajji or Vrijji was one of the principal Mahajanapadas of ancient India. Both the Buddhist text Anguttara Nikaya and the Jaina text Bhagavati Sutra included Vajji in their lists of solasa Maha-Janapadas. The name of this Mahajanapada was derived from one of its ruling clans, the Vṛjis...
(or Vriji), Malla
Malla (India)
Malla was one of the solasa mahajanapadas of ancient India mentioned in the Anguttara Nikaya. It was named after the ruling clan of the same name. The Mahabharata mentions the territory as the Mallarashtra . The Malla mahajanapada was situated north of Magadha. It was a small mahajanapada...
, Chedi
Chedi Kingdom
Chedi kingdom was one among the many kingdoms ruled during early periods by Paurava kings and later by Yaduvanshi Rajput kings in the central and western India. It falls roughly in the Bundelkhand division of Madhya Pradesh regions to the south of river Yamuna and along river Betwa or Vetravati...
, Vatsa
Vatsa
Vatsa was one of the solasa Mahajanapadas of Uttarapatha of ancient India mentioned in the Anguttara Nikaya....
(or Vamsa), Kuru, Panchala
Panchala
Panchala is an ancient region of northern India, which corresponds to the geographical area around the Ganges River and Yamuna River, the upper Gangetic plain in particular. This would encompass the modern-day states of Uttarakhand and Uttar Pradesh. During the ancient times, it was home to a...
, Matsya
Matsya Kingdom
Matsya or Machcha , classically called the Mese , was the name of a tribe and the state of the Vedic civilization of India. It lay to south of the kingdom of Kurus and west of the Yamuna which separated it from the kingdom of Panchalas...
(or Machcha), Surasena
Surasena
Surasena was an ancient Indian region corresponding to the present-day Braj region in Uttar Pradesh. According to the Buddhist text Anguttara Nikaya, Surasena was one of the solasa Mahajanapadas in 6th century BCE The ancient Greek writers refer the region as Sourasenoi and mention its capital...
, Assaka
Assaka
Assaka , was one of ancient Indian regions . It is one of the solasa mahajanapadas in the 6th century BCE, mentioned in the Buddhist text Anguttara Nikaya....
, Avanti
Avanti (India)
Avanti was an ancient Indian janapada , roughly corresponded to the present day Malwa region. According to the Buddhist text, the Anguttara Nikaya, Avanti was one of the solasa mahajanapadas of the 6th century BCE...
, Gandhara
Gandhara
Gandhāra , is the name of an ancient kingdom , located in northern Pakistan and eastern Afghanistan. Gandhara was located mainly in the vale of Peshawar, the Potohar plateau and on the Kabul River...
, and Kamboja — stretched across the Indo-Gangetic Plain
Indo-Gangetic plain
The northern Plains also known as the Indo - Gangetic Plain and The North Indian River Plain is a large and fertile plain encompassing most of northern and eastern India, the most populous parts of Pakistan, parts of southern Nepal and virtually all of Bangladesh...
from modern-day Afghanistan
Afghanistan
Afghanistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located in the centre of Asia, forming South Asia, Central Asia and the Middle East. With a population of about 29 million, it has an area of , making it the 42nd most populous and 41st largest nation in the world...
to Bengal
Bengal
Bengal is a historical and geographical region in the northeast region of the Indian Subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal. Today, it is mainly divided between the sovereign land of People's Republic of Bangladesh and the Indian state of West Bengal, although some regions of the previous...
and Maharastra. This period saw the second major rise of urbanism in India after the Indus Valley Civilization
Indus Valley Civilization
The Indus Valley Civilization was a Bronze Age civilization that was located in the northwestern region of the Indian subcontinent, consisting of what is now mainly modern-day Pakistan and northwest India...
.
Many smaller clans mentioned within early literature seem to have been present across the rest of the subcontinent. Some of these kings were hereditary; other states elected their rulers. The educated speech at that time was Sanskrit
Sanskrit
Sanskrit , is a historical Indo-Aryan language and the primary liturgical language of Hinduism, Jainism and Buddhism.Buddhism: besides Pali, see Buddhist Hybrid Sanskrit Today, it is listed as one of the 22 scheduled languages of India and is an official language of the state of Uttarakhand...
, while the languages of the general population of northern India are referred to as Prakrit
Prakrit
Prakrit is the name for a group of Middle Indic, Indo-Aryan languages, derived from Old Indic dialects. The word itself has a flexible definition, being defined sometimes as, "original, natural, artless, normal, ordinary, usual", or "vernacular", in contrast to the literary and religious...
s. Many of the sixteen kingdoms had coalesced to four major ones by 500/400 BCE, by the time of Gautama Buddha
Gautama Buddha
Siddhārtha Gautama was a spiritual teacher from the Indian subcontinent, on whose teachings Buddhism was founded. In most Buddhist traditions, he is regarded as the Supreme Buddha Siddhārtha Gautama (Sanskrit: सिद्धार्थ गौतम; Pali: Siddhattha Gotama) was a spiritual teacher from the Indian...
. These four were Vatsa, Avanti, Kosala, and Magadha.
Hindu rituals at that time were complicated and conducted by the priestly class. It is thought that the Upanishads, late Vedic texts dealing mainly with philosophy, were composed in the later Vedic Age and early in this period of the Mahajanapadas (from about 600 to 400 BCE). The Upanishads had a substantial effect on Indian philosophy
Indian philosophy
India has a rich and diverse philosophical tradition dating back to ancient times. According to Radhakrishnan, the earlier Upanisads constitute "...the earliest philosophical compositions of the world."...
and were contemporary with the development of Buddhism and Jainism, indicating a golden age of thought in this period.
According to Buddhism
Buddhism
Buddhism is a religion and philosophy encompassing a variety of traditions, beliefs and practices, largely based on teachings attributed to Siddhartha Gautama, commonly known as the Buddha . The Buddha lived and taught in the northeastern Indian subcontinent some time between the 6th and 4th...
, Gautama Buddha attained the state of "enlightenment" and became known as Buddha "Enlightened" c. 537 BCE. Around the same time, Mahavira
Mahavira
Mahāvīra is the name most commonly used to refer to the Indian sage Vardhamāna who established what are today considered to be the central tenets of Jainism. According to Jain tradition, he was the 24th and the last Tirthankara. In Tamil, he is referred to as Arukaṉ or Arukadevan...
(the 24th Tirthankara in Jainism
Jainism
Jainism is an Indian religion that prescribes a path of non-violence towards all living beings. Its philosophy and practice emphasize the necessity of self-effort to move the soul towards divine consciousness and liberation. Any soul that has conquered its own inner enemies and achieved the state...
) propagated a similar theology that was to later become Jainism. However, Jain orthodoxy believes the teachings of the Tirthankaras predates all known time and scholars believe Parshva
Parshva
Pārśva or Paras was the twenty-third Tirthankara "Ford-Maker" in Jainism . He is the earliest Jain leader generally accepted as a historical figure. Pārśva was a nobleman belonging to the Kshatriya varna....
, accorded status as the 23rd Tirthankara, was a historical figure. The Vedas
Vedas
The Vedas are a large body of texts originating in ancient India. Composed in Vedic Sanskrit, the texts constitute the oldest layer of Sanskrit literature and the oldest scriptures of Hinduism....
are believed to have documented a few Tirthankaras and an ascetic order similar to the shramana
Shramana
A shramana is a wandering monk in certain ascetic traditions of ancient India including Jainism, Buddhism, and Ājīvikism. Famous śramaṇas include Mahavira and Gautama Buddha....
movement.
The Buddha's teachings and Jainism had doctrines inclined toward asceticism, and they were preached in Prakrit, which helped them gain acceptance amongst the masses. They have profoundly influenced practices that Hinduism and Indian spiritual orders are associated with, including vegetarianism
Vegetarianism
Vegetarianism encompasses the practice of following plant-based diets , with or without the inclusion of dairy products or eggs, and with the exclusion of meat...
, prohibition of animal slaughter and ahimsa
Ahimsa
Ahimsa is a term meaning to do no harm . The word is derived from the Sanskrit root hims – to strike; himsa is injury or harm, a-himsa is the opposite of this, i.e. non harming or nonviolence. It is an important tenet of the Indian religions...
(non-violence). While the geographic impact of Jainism was limited to India, Buddhist nuns
Bhikkhuni
A bhikkhuni or bhikṣuṇī is a fully ordained female Buddhist monastic. Male monastics are called bhikkhus. Both bhikkhunis and bhikkhus live by the vinaya...
and monks
Bhikkhu
A Bhikkhu or Bhikṣu is an ordained male Buddhist monastic. A female monastic is called a Bhikkhuni Nepali: ). The life of Bhikkhus and Bhikkhunis is governed by a set of rules called the patimokkha within the vinaya's framework of monastic discipline...
eventually spread the teachings of Buddha to Central Asia
Central Asia
Central Asia is a core region of the Asian continent from the Caspian Sea in the west, China in the east, Afghanistan in the south, and Russia in the north...
, East Asia
East Asia
East Asia or Eastern Asia is a subregion of Asia that can be defined in either geographical or cultural terms...
, Tibet
Tibet
Tibet is a plateau region in Asia, north-east of the Himalayas. It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people as well as some other ethnic groups such as Monpas, Qiang, and Lhobas, and is now also inhabited by considerable numbers of Han and Hui people...
, Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka is a country off the southern coast of the Indian subcontinent. Known until 1972 as Ceylon , Sri Lanka is an island surrounded by the Indian Ocean, the Gulf of Mannar and the Palk Strait, and lies in the vicinity of India and the...
and Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, South-East Asia, South East Asia or Southeastern Asia is a subregion of Asia, consisting of the countries that are geographically south of China, east of India, west of New Guinea and north of Australia. The region lies on the intersection of geological plates, with heavy seismic...
.
Persian and Greek conquests

Cyrus the Great
Cyrus II of Persia , commonly known as Cyrus the Great, also known as Cyrus the Elder, was the founder of the Achaemenid Empire. Under his rule, the empire embraced all the previous civilized states of the ancient Near East, expanded vastly and eventually conquered most of Southwest Asia and much...
, King of the Persian Achaemenid Empire
Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire , sometimes known as First Persian Empire and/or Persian Empire, was founded in the 6th century BCE by Cyrus the Great who overthrew the Median confederation...
crossed the Hindu-Kush mountains to seek tribute from the tribes of Kamboja, Gandhara and the trans-India region. By 520 BCE, during the reign of Darius I of Persia, much of the northwestern subcontinent (present-day eastern Afghanistan and Pakistan) came under the rule of the Persian Achaemenid Empire
Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire , sometimes known as First Persian Empire and/or Persian Empire, was founded in the 6th century BCE by Cyrus the Great who overthrew the Median confederation...
. The area remained under Persian control for two centuries. During this time India supplied mercenaries to the Persian army then fighting in Greece. Under Persian rule the famous city of Takshashila became a center where both Vedic and Iranian learning were mingled. The impact of Persian ideas was felt in many areas of Indian life. Persian coinage and rock inscriptions were copied by India. However, Persian ascendency in northern India ended with Alexander the Great's conquest of Persia in 327 BCE.
By 326 BCE, Alexander the Great had conquered Asia Minor and the Achaemenid Empire and had reached the northwest frontiers of the Indian subcontinent. There he defeated King Porus in the Battle of the Hydaspes (near modern-day Jhelum
Jhelum
Jhelum or Jehlum may refer to:* Jhelum, a city in Pakistan on the banks of the Jhelum River* Jhelum District, an administrative division in Punjab, Pakistan surrounding the city of Jhelum...
, Pakistan) and conquered much of the Punjab
Punjab region
The Punjab , also spelled Panjab |water]]s"), is a geographical region straddling the border between Pakistan and India which includes Punjab province in Pakistan and the states of the Punjab, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Chandigarh and some northern parts of the National Capital Territory of Delhi...
. Alexander's march east put him in confrontation with the Nanda Empire
Nanda Dynasty
The Nanda Empire originated from the region of Magadha in Ancient India during the 5th and 4th centuries BC. At its greatest extent, the Nanda Empire extended from Bengal in the east, to Punjab in the west and as far south as the Vindhya Range...
of Magadha
Magadha
Magadha formed one of the sixteen Mahājanapadas or kingdoms in ancient India. The core of the kingdom was the area of Bihar south of the Ganga; its first capital was Rajagriha then Pataliputra...
and the Gangaridai Empire
Gangaridai
Gangaridai was an ancient state found around 300 BC where the Bengal region lies today . It was described by the Greek traveller Megasthenes in his work Indica...
of Bengal
Bengal
Bengal is a historical and geographical region in the northeast region of the Indian Subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal. Today, it is mainly divided between the sovereign land of People's Republic of Bangladesh and the Indian state of West Bengal, although some regions of the previous...
. His army, exhausted and frightened by the prospect of facing larger Indian armies at the Ganges River, mutinied at the Hyphasis (modern Beas River
Beas River
The Beas River is a river in the northern part of India. The river rises in the Himalayas in central Himachal Pradesh, India, and flows for some 470 km to the Sutlej River in the Indian state of Punjab....
) and refused to march further East. Alexander, after the meeting with his officer, Coenus, was convinced that it was better to return.
The Persian and Greek invasions had important repercussions on Indian civilization. The political systems of the Persians were to influence future forms of governance on the subcontinent, including the administration of the Mauryan dynasty. In addition, the region of Gandhara, or present-day eastern Afghanistan and northwest Pakistan, became a melting pot of Indian, Persian, Central Asian, and Greek cultures and gave rise to a hybrid culture, Greco-Buddhism
Greco-Buddhism
Greco-Buddhism, sometimes spelled Graeco-Buddhism, refers to the cultural syncretism between Hellenistic culture and Buddhism, which developed between the 4th century BCE and the 5th century CE in the area covered by the Indian sub-continent, and modern Afghanistan, Pakistan and north-western...
, which lasted until the 5th century CE and influenced the artistic development of Mahayana Buddhism
Mahayana
Mahāyāna is one of the two main existing branches of Buddhism and a term for classification of Buddhist philosophies and practice...
.
Maurya Empire


Maurya Empire
The Maurya Empire was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in ancient India, ruled by the Mauryan dynasty from 321 to 185 BC...
(322–185 BCE), ruled by the Mauryan dynasty, was a geographically extensive and powerful political and military empire in ancient India. The empire was established by Chandragupta Maurya
Chandragupta Maurya
Chandragupta Maurya , was the founder of the Maurya Empire. Chandragupta succeeded in conquering most of the Indian subcontinent. Chandragupta is considered the first unifier of India and its first genuine emperor...
in Magadha
Magadha
Magadha formed one of the sixteen Mahājanapadas or kingdoms in ancient India. The core of the kingdom was the area of Bihar south of the Ganga; its first capital was Rajagriha then Pataliputra...
what is now Bihar
Bihar
Bihar is a state in eastern India. It is the 12th largest state in terms of geographical size at and 3rd largest by population. Almost 58% of Biharis are below the age of 25, which is the highest proportion in India....
. The empire flourished under the reign of Ashoka the Great
Ashoka
Ashok Maurya or Ashoka , popularly known as Ashoka the Great, was an Indian emperor of the Maurya Dynasty who ruled almost all of the Indian subcontinent from ca. 269 BC to 232 BC. One of India's greatest emperors, Ashoka reigned over most of present-day India after a number of military conquests...
. At its greatest extent, it stretched to the north to the natural boundaries of the Himalayas
Himalayas
The Himalaya Range or Himalaya Mountains Sanskrit: Devanagari: हिमालय, literally "abode of snow"), usually called the Himalayas or Himalaya for short, is a mountain range in Asia, separating the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau...
and to the east into what is now Assam
Assam
Assam , also, rarely, Assam Valley and formerly the Assam Province , is a northeastern state of India and is one of the most culturally and geographically distinct regions of the country...
. To the west, it reached beyond modern Pakistan
Pakistan
Pakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan...
, annexing Balochistan
Balochistan (region)
Balochistan or Baluchistan is an arid, mountainous region in the Iranian plateau in Southwest Asia; it includes part of southeastern Iran, western Pakistan, and southwestern Afghanistan. The area is named after the numerous Baloch tribes, Iranian peoples who moved into the area from the west...
and much of what is now Afghanistan
Afghanistan
Afghanistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located in the centre of Asia, forming South Asia, Central Asia and the Middle East. With a population of about 29 million, it has an area of , making it the 42nd most populous and 41st largest nation in the world...
, including the modern Herat
Herat Province
Herat is one the 34 provinces of Afghanistan; together with Badghis, Farah, and Ghor provinces, it makes up the South-western region of the country...
and Kandahar
Kandahar Province
Kandahar or Qandahar is one of the largest of the thirty-four provinces of Afghanistan. It is located in southern Afghanistan, between Helmand, Oruzgan and Zabul provinces. Its capital is the city of Kandahar, which is located on the Arghandab River. The province has a population of nearly...
provinces. The empire was expanded into India's central and southern regions by the emperors Chandragupta and Bindusara
Bindusara
Bindusara was the second Mauryan emperor after Chandragupta Maurya. During his reign, the empire expanded southwards. He had two well-known sons, Susima and Ashoka, who were the viceroys of Taxila and Ujjain...
, but it excluded extensive unexplored tribal and forested regions near Kalinga
Kalinga (India)
Kalinga was an early state in central-eastern India, which comprised most of the modern state of Orissa/Utkal , as well as the Andhra region of the bordering state of Andhra Pradesh. It was a rich and fertile land that extended from the river Damodar/Ganges to Godavari and from Bay of Bengal to...
which were subsequently taken by Ashoka. Like every state, the Maurya Empire needed to have a unified administrative apparatus. Ashoka ruled the Maurya Empire for 37 years from 268 BCE until he died in 232 BCE. During that time, Ashoka pursued an active foreign policy aimed at setting up a unified state. However, Ashoka became involved in a war with the state of Kalinga
Kalinga
Kalinga is a landlocked province of the Philippines in the Cordillera Administrative Region in Luzon. Its capital is Tabuk and borders Mountain Province to the south, Abra to the west, Isabela to the east, Cagayan to the northeast, and Apayao to the north...
which is located on the western shore of the Bay of Bengal. This war forced Ashoka to abandon his attempt at a foreign policy which would unify the Maurya Empire.
Slavery had begun in India during the Vedic era. However, during the Mauryan Empire slavery developed much more rapidly. The Mauryan Empire was based on a modern and efficient economy and society. However, the sale of merchandise was closely regulated by the government. Although there was no banking in the Mauryan society, usury was customary with loans made at the recognized interest rate of 15% per annum.
Ashoka's reign propagated Buddhism
Buddhism
Buddhism is a religion and philosophy encompassing a variety of traditions, beliefs and practices, largely based on teachings attributed to Siddhartha Gautama, commonly known as the Buddha . The Buddha lived and taught in the northeastern Indian subcontinent some time between the 6th and 4th...
. In this regard Ashoka established many Buddhist monuments. Indeed, Ashoka put a strain on the economy and the government by his strong support of Buddhism. towards the end of his reign he "bled the state coffers white with his generous gifts to promote the promulation of Buddha's teaching. As might be expected, this policy caused considerable opposition within the government. This opposition rallied around Sampadi, Ashoka's grandson and heir to the throne. Religious opposition to
Ashoka also arose among the orthodox Brahmanists and the adherents of Jainism
Jainism
Jainism is an Indian religion that prescribes a path of non-violence towards all living beings. Its philosophy and practice emphasize the necessity of self-effort to move the soul towards divine consciousness and liberation. Any soul that has conquered its own inner enemies and achieved the state...
--a religion based on non-violence toward all living beings.
Chandragupta's minister Chanakya
Chanakya
Chānakya was a teacher to the first Maurya Emperor Chandragupta , and the first Indian emperor generally considered to be the architect of his rise to power. Traditionally, Chanakya is also identified by the names Kautilya and VishnuGupta, who authored the ancient Indian political treatise...
wrote the Arthashastra
Arthashastra
The Arthashastra is an ancient Indian treatise on statecraft, economic policy and military strategy which identifies its author by the names Kautilya and , who are traditionally identified with The Arthashastra (IAST: Arthaśāstra) is an ancient Indian treatise on statecraft, economic policy and...
, one of the greatest treatises on economics, politics, foreign affairs, administration, military arts, war, and religion produced in Asia. Archaeologically, the period of Mauryan rule in South Asia falls into the era of Northern Black Polished Ware
Northern Black Polished Ware
The Northern Black Polished Ware culture of South Asia is an Iron Age culture, succeeding the Painted Grey Ware culture...
(NBPW). The Arthashastra and the Edicts of Ashoka
Edicts of Ashoka
The Edicts of Ashoka are a collection of 33 inscriptions on the Pillars of Ashoka, as well as boulders and cave walls, made by the Emperor Ashoka of the Mauryan dynasty during his reign from 269 BCE to 231 BCE. These inscriptions are dispersed throughout the areas of modern-day Bangladesh, India,...
are primary written records of the Mauryan times. The Lion Capital of Asoka
Lion Capital of Asoka
The Lion capital of Ashoka is a sculpture of four "Indian lions" standing back to back. It was originally placed atop the Aśoka pillar at Sarnath, now in the state of Uttar Pradesh, India by Emperor Ashoka circa 250 BC. The pillar, sometimes called the Aśoka Column is still in its original...
at Sarnath
Sarnath
Sarnath or Sārnātha is the deer park where Gautama Buddha first taught the Dharma, and where the Buddhist Sangha came into existence through the enlightenment of Kondanna. Sarnath is located 13 kilometres north-east of Varanasi, in Uttar Pradesh, India...
, is the national emblem of India.
----
Early Middle Kingdoms — The Golden Age
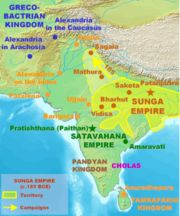 |
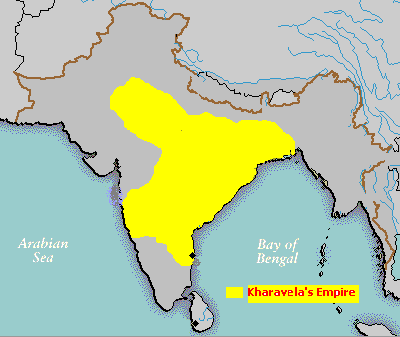 |
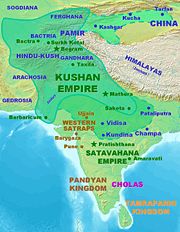 |
The middle period was a time of notable cultural development. The Satavahana dynasty, also known as the Andhras, ruled in southern and central India after around 230 BCE. Satakarni
Satakarni
Satakarni was the third of the Satavahana kings. He ruled around 180 BCE in Central India.It is thought that Satakarni was a son of Kunala...
, the sixth ruler of the Satvahana dynasty, defeated the Sunga Empire
Sunga Empire
The Sunga Empire or Shunga Empire was a royal Indian dynasty from Magadha that controlled vast areas of the Indian Subcontinent from around 185 to 73 BCE. The dynasty was established by Pusyamitra Sunga, after the fall of the Maurya Empire...
of north India. Afterwards, Kharavela
Kharavela
Khārabēḷa was the third and greatest emperor of the Mahāmēghabāhana Dynasty of Kaḷinga . The main source of information about Khārabeḷa is his famous seventeen line rock-cut Hātigumphā inscription in a cave in the Udayagiri hills near Bhubaneswar, Orissa.During the reign of Khārabēḷa, the Chedi...
, the warrior king of Kalinga
Kalinga (India)
Kalinga was an early state in central-eastern India, which comprised most of the modern state of Orissa/Utkal , as well as the Andhra region of the bordering state of Andhra Pradesh. It was a rich and fertile land that extended from the river Damodar/Ganges to Godavari and from Bay of Bengal to...
, ruled a vast empire and was responsible for the propagation of Jainism
Jainism
Jainism is an Indian religion that prescribes a path of non-violence towards all living beings. Its philosophy and practice emphasize the necessity of self-effort to move the soul towards divine consciousness and liberation. Any soul that has conquered its own inner enemies and achieved the state...
in the Indian subcontinent. The Kharavelan Jain empire included a formidable maritime empire with trading routes linking it to Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka is a country off the southern coast of the Indian subcontinent. Known until 1972 as Ceylon , Sri Lanka is an island surrounded by the Indian Ocean, the Gulf of Mannar and the Palk Strait, and lies in the vicinity of India and the...
, Burma, Thailand
Thailand
Thailand , officially the Kingdom of Thailand , formerly known as Siam , is a country located at the centre of the Indochina peninsula and Southeast Asia. It is bordered to the north by Burma and Laos, to the east by Laos and Cambodia, to the south by the Gulf of Thailand and Malaysia, and to the...
, Vietnam
Vietnam
Vietnam – sometimes spelled Viet Nam , officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam – is the easternmost country on the Indochina Peninsula in Southeast Asia. It is bordered by China to the north, Laos to the northwest, Cambodia to the southwest, and the South China Sea –...
, Cambodia
Cambodia
Cambodia , officially known as the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country located in the southern portion of the Indochina Peninsula in Southeast Asia...
, Borneo
Borneo
Borneo is the third largest island in the world and is located north of Java Island, Indonesia, at the geographic centre of Maritime Southeast Asia....
, Bali
Bali
Bali is an Indonesian island located in the westernmost end of the Lesser Sunda Islands, lying between Java to the west and Lombok to the east...
, Sumatra
Sumatra
Sumatra is an island in western Indonesia, westernmost of the Sunda Islands. It is the largest island entirely in Indonesia , and the sixth largest island in the world at 473,481 km2 with a population of 50,365,538...
, and Java
Java
Java is an island of Indonesia. With a population of 135 million , it is the world's most populous island, and one of the most densely populated regions in the world. It is home to 60% of Indonesia's population. The Indonesian capital city, Jakarta, is in west Java...
. Colonists from Kalinga settled in Sri Lanka, Burma, as well as the Maldives
Maldives
The Maldives , , officially Republic of Maldives , also referred to as the Maldive Islands, is an island nation in the Indian Ocean formed by a double chain of twenty-six atolls oriented north-south off India's Lakshadweep islands, between Minicoy Island and...
and the Malay Archipelago
Malay Archipelago
The Malay Archipelago refers to the archipelago between mainland Southeastern Asia and Australia. The name was derived from the anachronistic concept of a Malay race....
. The Kuninda Kingdom
Kuninda Kingdom
The Kingdom of Kuninda was an ancient central Himalayan kingdom from around the 2nd century BCE to the 3rd century, located in the modern state of Uttarakhand and southern areas of Himachal in northern India.-Kingdom:...
was a small Himalayan state that survived from around the 2nd century BCE to roughly the 3rd century CE. The Kushanas
Kushan Empire
The Kushan Empire originally formed in the early 1st century AD under Kujula Kadphises in the territories of ancient Bactria on either side of the middle course of the Oxus in what is now northern Afghanistan, Pakistan, and southern Tajikistan and Uzbekistan.During the 1st and early 2nd centuries...
migrated from Central Asia
Central Asia
Central Asia is a core region of the Asian continent from the Caspian Sea in the west, China in the east, Afghanistan in the south, and Russia in the north...
into northwestern India in the middle of the 1st century CE and founded an empire that eventually stretched from Tajikistan
Tajikistan
Tajikistan , officially the Republic of Tajikistan , is a mountainous landlocked country in Central Asia. Afghanistan borders it to the south, Uzbekistan to the west, Kyrgyzstan to the north, and China to the east....
to the middle Ganges. The Western Satraps (35-405 CE) were Saka
Saka
The Saka were a Scythian tribe or group of tribes....
rulers of the western and central part of India. They were the successors of the Indo-Scythians
Indo-Scythians
Indo-Scythians is a term used to refer to Sakas , who migrated into Bactria, Sogdiana, Arachosia, Gandhara, Kashmir, Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Gujarat, Maharashtra and Rajasthan, from the middle of the 2nd century BCE to the 4th century CE....
and contemporaries of the Kushans who ruled the northern part of the Indian subcontinent and the Satavahana (Andhra) who ruled in central and southern India.
Different dynasties such as the Pandyans, Cholas
Chola Dynasty
The Chola dynasty was a Tamil dynasty which was one of the longest-ruling in some parts of southern India. The earliest datable references to this Tamil dynasty are in inscriptions from the 3rd century BC left by Asoka, of Maurya Empire; the dynasty continued to govern over varying territory until...
, Cheras
Chera dynasty
Chera Dynasty in South India is one of the most ancient ruling dynasties in India. Together with the Cholas and the Pandyas, they formed the three principle warring Iron Age Tamil kingdoms in southern India...
, Kadambas, Western Gangas, Pallava
Pallava
The Pallava dynasty was a Tamil dynasty which ruled the northern Tamil Nadu region and the southern Andhra Pradesh region with their capital at Kanchipuram...
s, and Chalukyas
Chalukya dynasty
The Chalukya dynasty was an Indian royal dynasty that ruled large parts of southern and central India between the 6th and the 12th centuries. During this period, they ruled as three related yet individual dynasties. The earliest dynasty, known as the "Badami Chalukyas", ruled from Vatapi from the...
, dominated the southern part of the Indian peninsula at different periods of time. Several southern kingdoms formed overseas empires that stretched into Southeast Asia. The kingdoms warred with each other and the Deccan
Deccan Plateau
The Deccan Plateau is a large plateau in India, making up the majority of the southern part of the country. It rises a hundred meters high in the north, rising further to more than a kilometers high in the south, forming a raised triangle nested within the familiar downward-pointing triangle of...
states for domination of the south. The Kalabras, a Buddhist dynasty, briefly interrupted the usual domination of the Cholas, Cheras, and Pandyas in the south.
Northwestern hybrid cultures

The northwestern hybrid cultures of the subcontinent included the Indo-Greeks, the Indo-Scythians, the Indo-Parthians, and the Indo-Sassinids. The first of these, the Indo-Greek Kingdom, was founded when the Greco-Bactrian
Greco-Bactrian Kingdom
The Greco-Bactrian Kingdom was the easternmost part of the Hellenistic world, covering Bactria and Sogdiana in Central Asia from 250 to 125 BC...
king Demetrius
Demetrius I of Bactria
Demetrius I was a Buddhist Greco-Bactrian king . He was the son of Euthydemus and succeeded him around 200 BC, after which he conquered extensive areas in what now is eastern Iran, Afghanistan and Pakistan thus creating an Indo-Greek kingdom far from Hellenistic Greece...
invaded the region in 180 BCE, extending his rule over various parts of present-day Afghanistan and Pakistan. Lasting for almost two centuries, the kingdom was ruled by a succession of more than 30 Greek kings, who were often in conflict with each other. The Indo-Scythians
Indo-Scythians
Indo-Scythians is a term used to refer to Sakas , who migrated into Bactria, Sogdiana, Arachosia, Gandhara, Kashmir, Punjab, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Gujarat, Maharashtra and Rajasthan, from the middle of the 2nd century BCE to the 4th century CE....
were a branch of the Indo-European Saka
Saka
The Saka were a Scythian tribe or group of tribes....
s (Scythians) who migrated from southern Siberia
Siberia
Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th...
, first into Bactria
Bactria
Bactria and also appears in the Zend Avesta as Bukhdi. It is the ancient name of a historical region located between south of the Amu Darya and west of the Indus River...
, subsequently into Sogdiana
Sogdiana
Sogdiana or Sogdia was the ancient civilization of an Iranian people and a province of the Achaemenid Empire, eighteenth in the list on the Behistun Inscription of Darius the Great . Sogdiana is "listed" as the second of the "good lands and countries" that Ahura Mazda created...
, Kashmir
Kashmir
Kashmir is the northwestern region of the Indian subcontinent. Until the mid-19th century, the term Kashmir geographically denoted only the valley between the Great Himalayas and the Pir Panjal mountain range...
, Arachosia
Arachosia
Arachosia is the Latinized form of the Greek name of an Achaemenid and Seleucid governorate in the eastern part of their respective empires, around modern-day southern Afghanistan. The Greek term "Arachosia" corresponds to the Iranian land of Harauti which was between Kandahar in Afghanistan and...
, and Gandhara
Gandhara
Gandhāra , is the name of an ancient kingdom , located in northern Pakistan and eastern Afghanistan. Gandhara was located mainly in the vale of Peshawar, the Potohar plateau and on the Kabul River...
, and finally into India. Their kingdom lasted from the middle of the 2nd century BCE to the 1st century BCE. Yet another kingdom, the Indo-Parthians
Indo-Parthian Kingdom
The Gondopharid dynasty, and other so-called Indo-Parthian rulers, were a group of ancient kings from present day eastern Afghanistan and Pakistan who ruled India, during or slightly before the 1st century AD...
(also known as the Pahlavas
The Pahlavas
The Pahlavas are a people mentioned in ancient Indian texts like the Manu Smriti, various Puranas, the Ramayana, the Mahabharata, and the Brhatsamhita. In some texts the Pahlavas are synonymous with the Pallavas, a dynasty of Southern India: While the Vayu Purana distinguishes between Pahlava and...
), came to control most of present-day Afghanistan and northern Pakistan, after fighting many local rulers such as the Kushan
Kushan Empire
The Kushan Empire originally formed in the early 1st century AD under Kujula Kadphises in the territories of ancient Bactria on either side of the middle course of the Oxus in what is now northern Afghanistan, Pakistan, and southern Tajikistan and Uzbekistan.During the 1st and early 2nd centuries...
ruler Kujula Kadphises
Kujula Kadphises
Kujula Kadphises, reigned was a Kushan prince who united the Yuezhi confederation during the 1st century CE, and became the first Kushan emperor...
, in the Gandhara region. The Sassanid empire of Persia, who was contemporaneous with the Gupta Empire, expanded into the region of present-day Balochistan in Pakistan, where the mingling of Indian culture and the culture of Iran
Culture of Iran
To best understand Iran, Afghanistan, their related societies and their people, one must first attempt to acquire an understanding of their culture. It is in the study of this area where the Persian identity optimally expresses itself...
gave birth to a hybrid culture under the Indo-Sassanids.
Kushan Empire
The Kushan EmpireKushan Empire
The Kushan Empire originally formed in the early 1st century AD under Kujula Kadphises in the territories of ancient Bactria on either side of the middle course of the Oxus in what is now northern Afghanistan, Pakistan, and southern Tajikistan and Uzbekistan.During the 1st and early 2nd centuries...
expanded out of what is now Afghanistan into the northwest of the subcontinent under the leadership of their first emperor, Kujula Kadphises
Kujula Kadphises
Kujula Kadphises, reigned was a Kushan prince who united the Yuezhi confederation during the 1st century CE, and became the first Kushan emperor...
, about the middle of the 1st century CE. By the time of his grandson, Kanishka
Kanishka
Kanishka ) was an emperor of the Kushan Empire, ruling an empire extending from Bactria to large parts of northern India in the 2nd century of the common era, and famous for his military, political, and spiritual achievements...
, (whose era is thought to have begun c. 127 CE), they had conquered most of northern India, at least as far as Saketa and Pataliputra, in the middle Ganges Valley, and probably as far as the Bay of Bengal
Bay of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal , the largest bay in the world, forms the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean. It resembles a triangle in shape, and is bordered mostly by the Eastern Coast of India, southern coast of Bangladesh and Sri Lanka to the west and Burma and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands to the...
. They played an important role in the establishment of Buddhism in India and its spread to Central Asia and China. By the 3rd century, their empire in India was disintegrating; their last known great emperor being Vasudeva I
Vasudeva I
Vasudeva I was a Kushan emperor, last of the "Great Kushans." Named inscriptions dating from year 64 to 98 of Kanishka's era suggest his reign extended from at least 191 to 225 CE....
(c. 190-225 CE).
Roman trade with India

Augustus
Augustus ;23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14) is considered the first emperor of the Roman Empire, which he ruled alone from 27 BC until his death in 14 AD.The dates of his rule are contemporary dates; Augustus lived under two calendars, the Roman Republican until 45 BC, and the Julian...
and following his conquest of Egypt, which had been India's biggest trade partner in the West.
The trade started by Eudoxus of Cyzicus
Eudoxus of Cyzicus
Eudoxus of Cyzicus was a Greek navigator who explored the Arabian Sea for Ptolemy VIII, king of the Hellenistic Ptolemaic dynasty in Egypt.-Voyages to India:...
in 130 BCE kept increasing, and according to Strabo
Strabo
Strabo, also written Strabon was a Greek historian, geographer and philosopher.-Life:Strabo was born to an affluent family from Amaseia in Pontus , a city which he said was situated the approximate equivalent of 75 km from the Black Sea...
(II.5.12.), by the time of Augustus, up to 120 ships set sail every year from Myos Hormos
Myos Hormos
Myos Hormos was a Red Sea port constructed by the Ptolemies around the 3rd century BC. Following excavations carried out recently by David Peacock and Lucy Blue of the University of Southampton, it is thought to have been located on the present-day site of Quseir al-Quadim , eight kilometres north...
on the Red Sea
Red Sea
The Red Sea is a seawater inlet of the Indian Ocean, lying between Africa and Asia. The connection to the ocean is in the south through the Bab el Mandeb strait and the Gulf of Aden. In the north, there is the Sinai Peninsula, the Gulf of Aqaba, and the Gulf of Suez...
to India. So much gold was used for this trade, and apparently recycled by the Kushans
Kushan Empire
The Kushan Empire originally formed in the early 1st century AD under Kujula Kadphises in the territories of ancient Bactria on either side of the middle course of the Oxus in what is now northern Afghanistan, Pakistan, and southern Tajikistan and Uzbekistan.During the 1st and early 2nd centuries...
for their own coinage, that Pliny the Elder
Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus , better known as Pliny the Elder, was a Roman author, naturalist, and natural philosopher, as well as naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and personal friend of the emperor Vespasian...
(NH VI.101) complained about the drain of specie to India:
The maritime (but not the overland) trade routes, harbours, and trade items are described in detail in the 1st century CE Periplus of the Erythraean Sea
Periplus of the Erythraean Sea
The Periplus of the Erythraean Sea or Periplus of the Red Sea is a Greco-Roman periplus, written in Greek, describing navigation and trading opportunities from Roman Egyptian ports like Berenice along the coast of the Red Sea, and others along Northeast Africa and India...
.
Gupta rule
The Classical Age refers to the period when much of the Indian subcontinentIndian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent, also Indian Subcontinent, Indo-Pak Subcontinent or South Asian Subcontinent is a region of the Asian continent on the Indian tectonic plate from the Hindu Kush or Hindu Koh, Himalayas and including the Kuen Lun and Karakoram ranges, forming a land mass which extends...
was reunited under the Gupta Empire
Gupta Empire
The Gupta Empire was an ancient Indian empire which existed approximately from 320 to 550 CE and covered much of the Indian Subcontinent. Founded by Maharaja Sri-Gupta, the dynasty was the model of a classical civilization. The peace and prosperity created under leadership of Guptas enabled the...
(c. 320–550 CE). This period has been called the Golden Age of India and was marked by extensive achievements in science, technology, engineering, art
Indian art
Indian Art is the visual art produced on the Indian subcontinent from about the 3rd millennium BC to modern times. To viewers schooled in the Western tradition, Indian art may seem overly ornate and sensuous; appreciation of its refinement comes only gradually, as a rule. Voluptuous feeling is...
, dialectic, literature
Indian literature
Indian literature refers to the literature produced on the Indian subcontinent until 1947 and in the Republic of India thereafter. The Republic of India has 22 officially recognized languages....
, logic
Indian logic
The development of Indian logic dates back to the anviksiki of Medhatithi Gautama the Sanskrit grammar rules of Pāṇini ; the Vaisheshika school's analysis of atomism ; the analysis of inference by Gotama , founder of the Nyaya school of Hindu philosophy; and the tetralemma of Nagarjuna...
, mathematics
Indian mathematics
Indian mathematics emerged in the Indian subcontinent from 1200 BCE until the end of the 18th century. In the classical period of Indian mathematics , important contributions were made by scholars like Aryabhata, Brahmagupta, and Bhaskara II. The decimal number system in use today was first...
, astronomy, religion, and philosophy
Indian philosophy
India has a rich and diverse philosophical tradition dating back to ancient times. According to Radhakrishnan, the earlier Upanisads constitute "...the earliest philosophical compositions of the world."...
that crystallized the elements of what is generally known as Hindu culture
Culture of India
India's languages, religions, dance, music, architecture, food and customs differ from place to place within the country, but nevertheless possess a commonality....
. The decimal numeral system
Decimal
The decimal numeral system has ten as its base. It is the numerical base most widely used by modern civilizations....
, including the concept of zero
0 (number)
0 is both a numberand the numerical digit used to represent that number in numerals.It fulfills a central role in mathematics as the additive identity of the integers, real numbers, and many other algebraic structures. As a digit, 0 is used as a placeholder in place value systems...
, was invented in India during this period. The peace and prosperity created under leadership of Guptas enabled the pursuit of scientific and artistic endeavors in India.
The high points of this cultural creativity are magnificent architecture, sculpture, and painting. The Gupta period produced scholars such as Kalidasa
Kalidasa
Kālidāsa was a renowned Classical Sanskrit writer, widely regarded as the greatest poet and dramatist in the Sanskrit language...
, Aryabhata
Aryabhata
Aryabhata was the first in the line of great mathematician-astronomers from the classical age of Indian mathematics and Indian astronomy...
, Varahamihira
Varahamihira
Varāhamihira , also called Varaha or Mihira, was an Indian astronomer, mathematician, and astrologer who lived in Ujjain...
, Vishnu Sharma, and Vatsyayana
Vatsyayana
Vātsyāyana is the name of a Hindu philosopher in the Vedic tradition who is believed to have lived during time of the Gupta Empire in India...
who made great advancements in many academic fields. Science and political administration reached new heights during the Gupta era. Strong trade ties also made the region an important cultural center and established it as a base that would influence nearby kingdoms and regions in Burma, Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka is a country off the southern coast of the Indian subcontinent. Known until 1972 as Ceylon , Sri Lanka is an island surrounded by the Indian Ocean, the Gulf of Mannar and the Palk Strait, and lies in the vicinity of India and the...
, the Malay Archipelago
Malay Archipelago
The Malay Archipelago refers to the archipelago between mainland Southeastern Asia and Australia. The name was derived from the anachronistic concept of a Malay race....
, and Indochina
Indochina
The Indochinese peninsula, is a region in Southeast Asia. It lies roughly southwest of China, and east of India. The name has its origins in the French, Indochine, as a combination of the names of "China" and "India", and was adopted when French colonizers in Vietnam began expanding their territory...
.
The Gupta period marked a watershed of Indian culture: the Guptas performed Vedic sacrifices to legitimize their rule, but they also patronized Buddhism
Buddhism
Buddhism is a religion and philosophy encompassing a variety of traditions, beliefs and practices, largely based on teachings attributed to Siddhartha Gautama, commonly known as the Buddha . The Buddha lived and taught in the northeastern Indian subcontinent some time between the 6th and 4th...
, which continued to provide an alternative to Brahmanical orthodoxy. The military exploits of the first three rulers—Chandragupta I
Chandragupta I
The Gupta dynasty first seems to be in eminence with the accession of Chandra Gupta I, son of Ghatotkacha to the throne of the ancestral Gupta kingdom. While his two ancestors were given the title of Maharaja , Chandra Gupta I is described in his inscriptions as Maharajadhiraj signifying a rise in...
(c. 319–335), Samudragupta
Samudragupta
Samudragupta , ruler of the Gupta Empire , and successor to Chandragupta I, is considered to be one of the greatest military geniuses in Indian history according to Historian V. A. Smith. His name is taken to be a title acquired by his conquests...
(c. 335–376), and Chandragupta II
Chandragupta II
Chandragupta II the Great, very often referred to as Vikramaditya or Chandragupta Vikramaditya in Sanskrit; was one of the most powerful emperors of the Gupta empire in northern India. His rule spanned c...
(c. 376–415) —brought much of India under their leadership. They successfully resisted the northwestern kingdoms until the arrival of the Hunas
Huna people
Huna is the name under which the Xionite tribes who invaded northern India during the first half of the 5th century were known.-History:...
, who established themselves in Afghanistan by the first half of the 5th century, with their capital at Bamiyan. However, much of the Deccan
Deccan Plateau
The Deccan Plateau is a large plateau in India, making up the majority of the southern part of the country. It rises a hundred meters high in the north, rising further to more than a kilometers high in the south, forming a raised triangle nested within the familiar downward-pointing triangle of...
and southern India were largely unaffected by these events in the north.
Late Middle Kingdoms — The Classical Age



Gupta Empire
The Gupta Empire was an ancient Indian empire which existed approximately from 320 to 550 CE and covered much of the Indian Subcontinent. Founded by Maharaja Sri-Gupta, the dynasty was the model of a classical civilization. The peace and prosperity created under leadership of Guptas enabled the...
and the resurgence of the north during Harsha
Harsha
Harsha or Harsha Vardhana or Harshvardhan was an Indian emperor who ruled northern India from 606 to 647 AD. He was the son of Prabhakara Vardhana and younger brother of Rajya Vardhana, a king of Thanesar, Haryana...
's conquests around the 7th century CE, and ended with the fall of the Vijayanagara Empire
Vijayanagara Empire
The Vijayanagara Empire , referred as the Kingdom of Bisnaga by the Portuguese, was an empire based in South Indian in the Deccan Plateau region. It was established in 1336 by Harihara I and his brother Bukka Raya I of the Yadava lineage. The empire rose to prominence as a culmination of attempts...
in the south in the 13th century, due to pressure from the invaders to the north. This period produced some of India's finest art, considered the epitome of classical development, and the development of the main spiritual and philosophical systems which continued to be in Hinduism, Buddhism and Jainism. King Harsha of Kannauj
Kannauj
Kannauj , also spelt Kanauj, is a city, administrative headquarters and a municipal board or Nagar Palika Parishad in Kannauj district in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. The city's name is traditionally derived from the term Kanyakubja . Kannauj is an ancient city, in earlier times the capital...
succeeded in reuniting northern India during his reign in the 7th century, after the collapse of the Gupta dynasty. His kingdom collapsed after his death.
From the 7th to the 9th century, three dynasties contested for control of northern India: the Gurjara Pratiharas of Malwa,the Eastern Ganga dynasty
Eastern Ganga dynasty
The Eastern Ganga dynasty reigned from Kalinga and their rule consisted of the whole of the modern day Indian state of Orissa as well as parts of West Bengal, Andhra Pradesh and Chhattisgarh from the 11th century to the early 15th century. Their capital was known by the name Kalinganagar, which is...
of Orissa
Orissa
Orissa , officially Odisha since Nov 2011, is a state of India, located on the east coast of India, by the Bay of Bengal. It is the modern name of the ancient nation of Kalinga, which was invaded by the Maurya Emperor Ashoka in 261 BC. The modern state of Orissa was established on 1 April...
, the Pala
Pala Empire
The Pāla Empire was one of the major middle kingdoms of India existed from 750–1174 CE. It was ruled by a Buddhist dynasty from Bengal in the eastern region of the Indian subcontinent, all the rulers bearing names ending with the suffix Pala , which means protector. The Palas were often described...
s of Bengal
Bengal
Bengal is a historical and geographical region in the northeast region of the Indian Subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal. Today, it is mainly divided between the sovereign land of People's Republic of Bangladesh and the Indian state of West Bengal, although some regions of the previous...
, and the Rashtrakutas
Rashtrakuta Dynasty
The Rashtrakuta Empire was a royal dynasty ruling large parts of the Indian Subcontinent between the sixth and the 10th centuries. During this period they ruled as several closely related, but individual clans. Rastrakutas in inscriptions represented as descendants of Satyaki, a Yadava well known...
of the Deccan
Deccan Plateau
The Deccan Plateau is a large plateau in India, making up the majority of the southern part of the country. It rises a hundred meters high in the north, rising further to more than a kilometers high in the south, forming a raised triangle nested within the familiar downward-pointing triangle of...
. The Sena dynasty
Sena dynasty
The Sena Empire was a Hindu dynasty that ruled from Bengal through the 11th and 12th centuries. At its peak the empire covered much of the north-eastern region in the Indian Subcontinent. They were called Brahma-Kshatriyas, as evidenced through their surname, which is derived from the Sanskrit,...
would later assume control of the Pala Empire, and the Gurjara Pratiharas fragmented into various states. These were the first of the Rajput
Rajput
A Rajput is a member of one of the patrilineal clans of western, central, northern India and in some parts of Pakistan. Rajputs are descendants of one of the major ruling warrior classes in the Indian subcontinent, particularly North India...
states, a series of kingdoms which managed to survive in some form for almost a millennium, until Indian independence from the British. The first recorded Rajput kingdoms emerged in Rajasthan
Rajasthan
Rājasthān the land of Rajasthanis, , is the largest state of the Republic of India by area. It is located in the northwest of India. It encompasses most of the area of the large, inhospitable Great Indian Desert , which has an edge paralleling the Sutlej-Indus river valley along its border with...
in the 6th century, and small Rajput dynasties later ruled much of northern India. One Gurjar Rajput of the Chauhan
Chauhan
Chauhan, Chouhan or Chohan , , - is a clan who ruled parts of northern India in the Middle Ages. The clan is most famous for Rajput King Maharaja Prithviraj Chauhan...
clan, Prithvi Raj Chauhan, was known for bloody conflicts against the advancing Islamic sultanates. The Shahi dynasty ruled portions of eastern Afghanistan, northern Pakistan, and Kashmir from the mid-7th century to the early 11th century.
The Chalukya dynasty
Chalukya dynasty
The Chalukya dynasty was an Indian royal dynasty that ruled large parts of southern and central India between the 6th and the 12th centuries. During this period, they ruled as three related yet individual dynasties. The earliest dynasty, known as the "Badami Chalukyas", ruled from Vatapi from the...
ruled parts of southern and central India from Badami
Badami
Badami , formerly known as Vatapi, is a town and headquarters of a taluk by the same name, in the Bagalkot district of Karnataka, India. It was the regal capital of the Badami Chalukyas from 540 to 757 AD. It is famous for rock cut and other structural temples...
in Karnataka
Karnataka
Karnataka , the land of the Kannadigas, is a state in South West India. It was created on 1 November 1956, with the passing of the States Reorganisation Act and this day is annually celebrated as Karnataka Rajyotsava...
between 550 and 750, and then again from Kalyani
Basavakalyan
Basavakalyan is a town in Bidar District of the state of Karnataka, India, and was historically known as Kalyan.-History:Basavakalyan's history dates back to 3000 years with its name being mentioned in Guru Charitra....
between 970 and 1190. The Pallava
Pallava
The Pallava dynasty was a Tamil dynasty which ruled the northern Tamil Nadu region and the southern Andhra Pradesh region with their capital at Kanchipuram...
s of Kanchipuram
Kanchipuram
Kanchipuram, or Kanchi, is a temple city and a municipality in Kanchipuram district in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It is a temple town and the headquarters of Kanchipuram district...
were their contemporaries further to the south. With the decline of the Chalukya empire, their feudatories, the Hoysalas
Hoysala Empire
The Hoysala Empire was a prominent South Indian Kannadiga empire that ruled most of the modern day state of Karnataka between the 10th and the 14th centuries. The capital of the Hoysalas was initially located at Belur but was later moved to Halebidu....
of Halebidu
Halebidu
Halebidu is located in Hassan District, Karnataka, India. Halebidu was the regal capital of the Hoysala Empire in the 12th century. It is home to one of the best examples of Hoysala architecture in the ornate Hoysaleswara and Kedareswara temples. Halebidu literally means ruined city...
, Kakatiya
Kakatiya
The Kakatiya dynasty was an Indian dynasty that ruled most parts of what is now Andhra Pradesh, India from 1083 CE to 1323 CE, with Orugallu , now Warangal , as its capital. Orugallu is also called 'Eka Sila Nagaram'...
s of Warangal
Warangal
Warangal is a city and a municipal corporation in Warangal district in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. Warangal is located northeast of the state capital of Hyderabad and is the administrative headquarters of Warangal District. This district is a combination of three cities: Warangal,...
, Seuna Yadavas of Devagiri, and a southern branch of the Kalachuri
Kalachuri
Kalachuri Empire is this the name used by two kingdoms who had a succession of dynasties from the 10th-12th centuries, one ruling over areas in Central India and were called Chedi or Haihaya and the other southern Kalachuri who ruled over parts of Karnataka...
, divided the vast Chalukya empire amongst themselves around the middle of 12th century.
The Chola Empire
Chola Dynasty
The Chola dynasty was a Tamil dynasty which was one of the longest-ruling in some parts of southern India. The earliest datable references to this Tamil dynasty are in inscriptions from the 3rd century BC left by Asoka, of Maurya Empire; the dynasty continued to govern over varying territory until...
at its peak covered much of the Indian subcontinent
Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent, also Indian Subcontinent, Indo-Pak Subcontinent or South Asian Subcontinent is a region of the Asian continent on the Indian tectonic plate from the Hindu Kush or Hindu Koh, Himalayas and including the Kuen Lun and Karakoram ranges, forming a land mass which extends...
and Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, South-East Asia, South East Asia or Southeastern Asia is a subregion of Asia, consisting of the countries that are geographically south of China, east of India, west of New Guinea and north of Australia. The region lies on the intersection of geological plates, with heavy seismic...
. Rajaraja Chola I
Rajaraja Chola I
Raja Raja Chola I born Arunmozhi Thevar , popularly known as Raja Raja the Great, is one of the greatest emperors of the Tamil Chola Empire of India who ruled between 985 and 1014 CE...
conquered all of peninsular south India and parts of Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka is a country off the southern coast of the Indian subcontinent. Known until 1972 as Ceylon , Sri Lanka is an island surrounded by the Indian Ocean, the Gulf of Mannar and the Palk Strait, and lies in the vicinity of India and the...
. Rajendra Chola I
Rajendra Chola I
Rajendra Chola I was the son of Rajaraja Chola I and was one of the greatest rulers of Tamil Chola dynasty of India. He succeeded his father in 1014 CE as the Chola emperor...
's navies went even further, occupying coasts from Burma (now Myanmar
Myanmar
Burma , officially the Republic of the Union of Myanmar , is a country in Southeast Asia. Burma is bordered by China on the northeast, Laos on the east, Thailand on the southeast, Bangladesh on the west, India on the northwest, the Bay of Bengal to the southwest, and the Andaman Sea on the south....
) to Vietnam
Vietnam
Vietnam – sometimes spelled Viet Nam , officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam – is the easternmost country on the Indochina Peninsula in Southeast Asia. It is bordered by China to the north, Laos to the northwest, Cambodia to the southwest, and the South China Sea –...
, the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, the Lakshadweep
Lakshadweep
Lakshadweep , formerly known as the Laccadive, Minicoy, and Amindivi Islands, is a group of islands in the Laccadive Sea, 200 to 440 km off the coast of the South West Indian state of Kerala...
(Laccadive) islands, Sumatra
Sumatra
Sumatra is an island in western Indonesia, westernmost of the Sunda Islands. It is the largest island entirely in Indonesia , and the sixth largest island in the world at 473,481 km2 with a population of 50,365,538...
, and the Malay Peninsula
Malay Peninsula
The Malay Peninsula or Thai-Malay Peninsula is a peninsula in Southeast Asia. The land mass runs approximately north-south and, at its terminus, is the southern-most point of the Asian mainland...
in Southeast Asia and the Pegu islands. Later during the middle period, the Pandyan Empire emerged in Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu is one of the 28 states of India. Its capital and largest city is Chennai. Tamil Nadu lies in the southernmost part of the Indian Peninsula and is bordered by the union territory of Pondicherry, and the states of Kerala, Karnataka, and Andhra Pradesh...
, as well as the Chera Kingdom in parts of Kerala
Kerala
or Keralam is an Indian state located on the Malabar coast of south-west India. It was created on 1 November 1956 by the States Reorganisation Act by combining various Malayalam speaking regions....
and Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu is one of the 28 states of India. Its capital and largest city is Chennai. Tamil Nadu lies in the southernmost part of the Indian Peninsula and is bordered by the union territory of Pondicherry, and the states of Kerala, Karnataka, and Andhra Pradesh...
. By 1343, last of these dynasties had ceased to exist, giving rise to the Vijayanagar empire.
The ports of south India were engaged in the Indian Ocean
Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third largest of the world's oceanic divisions, covering approximately 20% of the water on the Earth's surface. It is bounded on the north by the Indian Subcontinent and Arabian Peninsula ; on the west by eastern Africa; on the east by Indochina, the Sunda Islands, and...
trade, chiefly involving spices, with the Roman Empire
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of the ancient Roman civilization, characterised by an autocratic form of government and large territorial holdings in Europe and around the Mediterranean....
to the west and Southeast Asia to the east. Literature in local vernaculars and spectacular architecture flourished until about the beginning of the 14th century, when southern expeditions of the sultan of Delhi took their toll on these kingdoms. The Hindu Vijayanagar dynasty came into conflict with the Islamic Bahmani Sultanate
Bahmani Sultanate
The Bahmani Sultanate was a Muslim state of the Deccan in southern India and one of the great medieval Indian kingdoms...
, and the clashing of the two systems caused a mingling of the indigenous and foreign cultures that left lasting cultural influences on each other. The Vijaynagar Empire eventually declined due to pressure from the first Delhi sultanates that had managed to establish themselves in the north around the city of Delhi by that time.
The Islamic Sultanates

Caliphate
The term caliphate, "dominion of a caliph " , refers to the first system of government established in Islam and represented the political unity of the Muslim Ummah...
incorporated parts of what is now Pakistan around 720 CE. The Muslim rulers were keen to invade India, which was a rich region, with a flourishing international trade and the only known diamond mines in the world. In 712 CE an Arab Muslim general called Muhammad bin Qasim
Muhammad bin Qasim
Muhammad bin Qasim Al-Thaqafi was a Umayyad general who, at the age of 17, began the conquest of the Sindh and Punjab regions along the Indus River for the Umayyad Caliphate. He was born in the city of Taif...
conquered most of the Indus region in modern day Pakistan, for the Umayyad
Umayyad
The Umayyad Caliphate was the second of the four major Arab caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. It was ruled by the Umayyad dynasty, whose name derives from Umayya ibn Abd Shams, the great-grandfather of the first Umayyad caliph. Although the Umayyad family originally came from the...
empire, to be made the "As-Sindh" province with its capital at Al-Mansurah, 72 km (45 mi) north of modern Hyderabad
Hyderabad, Sindh
is the second largest city in the Sindh province of Pakistan. It is the seventh largest city in the country. The city was founded in 1768 by Mian Ghulam Shah Kalhoro upon the ruins of a Mauryan fishing village along the bank of the Indus known as Neroon Kot...
in Sindh
Sindh
Sindh historically referred to as Ba'ab-ul-Islam , is one of the four provinces of Pakistan and historically is home to the Sindhi people. It is also locally known as the "Mehran". Though Muslims form the largest religious group in Sindh, a good number of Christians, Zoroastrians and Hindus can...
, Pakistan
Pakistan
Pakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan...
. After several wars including the Battle of Rajasthan
Battle of Rajasthan
The Battle of Rajasthan is a battle where the Gurjar clans defeated the Arab invaders in 738 CE and removed the arab invaders and pillagers from the area east of the Indus River. the final battle took place somewhere on the borders of modern Sindh-Rajasthan...
, where the Hindu
Hindu
Hindu refers to an identity associated with the philosophical, religious and cultural systems that are indigenous to the Indian subcontinent. As used in the Constitution of India, the word "Hindu" is also attributed to all persons professing any Indian religion...
Rajput
Rajput
A Rajput is a member of one of the patrilineal clans of western, central, northern India and in some parts of Pakistan. Rajputs are descendants of one of the major ruling warrior classes in the Indian subcontinent, particularly North India...
clans defeated the Umayyad
Umayyad
The Umayyad Caliphate was the second of the four major Arab caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. It was ruled by the Umayyad dynasty, whose name derives from Umayya ibn Abd Shams, the great-grandfather of the first Umayyad caliph. Although the Umayyad family originally came from the...
Arabs, their expansion was checked and contained to Sindh in Pakistan, many short-lived Islamic kingdoms (sultan
Sultan
Sultan is a title with several historical meanings. Originally, it was an Arabic language abstract noun meaning "strength", "authority", "rulership", and "dictatorship", derived from the masdar سلطة , meaning "authority" or "power". Later, it came to be used as the title of certain rulers who...
ates) under foreign rulers were established across the north western subcontinent over a period of a few centuries. Additionally, Muslim trading communities had flourished throughout coastal south India, particularly in Kerala
Kerala
or Keralam is an Indian state located on the Malabar coast of south-west India. It was created on 1 November 1956 by the States Reorganisation Act by combining various Malayalam speaking regions....
, where Muslim traders arrived in small numbers, mainly from the Arabian peninsula. This had marked the introduction of a third Abraham
Abraham
Abraham , whose birth name was Abram, is the eponym of the Abrahamic religions, among which are Judaism, Christianity and Islam...
ic Middle Eastern religion, following Judaism and Christianity, often in puritanical form. Later, the Bahmani Sultanate
Bahmani Sultanate
The Bahmani Sultanate was a Muslim state of the Deccan in southern India and one of the great medieval Indian kingdoms...
and Deccan sultanates
Deccan sultanates
The Deccan sultanates were five Muslim-ruled late medieval kingdoms—Bijapur, Golkonda, Ahmadnagar, Bidar, and Berar—of south-central India. The Deccan sultanates were located on the Deccan Plateau, between the Krishna River and the Vindhya Range. These kingdoms became independent during the breakup...
founded by Turkic rulers, flourished in the south.
Delhi Sultanate

In the 12th and 13th centuries, Turks and Afghan
Afghanistan
Afghanistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located in the centre of Asia, forming South Asia, Central Asia and the Middle East. With a population of about 29 million, it has an area of , making it the 42nd most populous and 41st largest nation in the world...
s invaded parts of northern India and established the Delhi Sultanate
Delhi Sultanate
The Delhi Sultanate is a term used to cover five short-lived, Delhi based kingdoms or sultanates, of Turkic origin in medieval India. The sultanates ruled from Delhi between 1206 and 1526, when the last was replaced by the Mughal dynasty...
in the former Rajput
Rajput
A Rajput is a member of one of the patrilineal clans of western, central, northern India and in some parts of Pakistan. Rajputs are descendants of one of the major ruling warrior classes in the Indian subcontinent, particularly North India...
holdings. The subsequent Slave dynasty of Delhi
Delhi
Delhi , officially National Capital Territory of Delhi , is the largest metropolis by area and the second-largest by population in India, next to Mumbai. It is the eighth largest metropolis in the world by population with 16,753,265 inhabitants in the Territory at the 2011 Census...
managed to conquer large areas of northern India, approximately equal in extent to the ancient Gupta Empire
Gupta Empire
The Gupta Empire was an ancient Indian empire which existed approximately from 320 to 550 CE and covered much of the Indian Subcontinent. Founded by Maharaja Sri-Gupta, the dynasty was the model of a classical civilization. The peace and prosperity created under leadership of Guptas enabled the...
, while the Khilji dynasty
Khilji dynasty
The Khilji Sultanate was a dynasty of Turko-Afghan Khalaj origin who ruled large parts of South Asia from 1290 - 1320. They were the second dynasty to rule the Delhi Sultanate of India...
was also able to conquer most of central India, but were ultimately unsuccessful in conquering and uniting the subcontinent. The Sultanate ushered in a period of Indian cultural renaissance. The resulting "Indo-Muslim" fusion of cultures left lasting syncretic monuments in architecture, music, literature, religion, and clothing. It is surmised that the language of Urdu
Urdu
Urdu is a register of the Hindustani language that is identified with Muslims in South Asia. It belongs to the Indo-European family. Urdu is the national language and lingua franca of Pakistan. It is also widely spoken in some regions of India, where it is one of the 22 scheduled languages and an...
(literally meaning "horde" or "camp" in various Turkic dialects) was born during the Delhi Sultanate period as a result of the intermingling of the local speakers of Sanskritic Prakrit
Prakrit
Prakrit is the name for a group of Middle Indic, Indo-Aryan languages, derived from Old Indic dialects. The word itself has a flexible definition, being defined sometimes as, "original, natural, artless, normal, ordinary, usual", or "vernacular", in contrast to the literary and religious...
s with immigrants speaking Persian
Persian language
Persian is an Iranian language within the Indo-Iranian branch of the Indo-European languages. It is primarily spoken in Iran, Afghanistan, Tajikistan and countries which historically came under Persian influence...
, Turkic
Turkic languages
The Turkic languages constitute a language family of at least thirty five languages, spoken by Turkic peoples across a vast area from Eastern Europe and the Mediterranean to Siberia and Western China, and are considered to be part of the proposed Altaic language family.Turkic languages are spoken...
, and Arabic
Arabic language
Arabic is a name applied to the descendants of the Classical Arabic language of the 6th century AD, used most prominently in the Quran, the Islamic Holy Book...
under the Muslim rulers. The Delhi Sultanate is the only Indo-Islamic empire to have enthroned one of the few female rulers in India, Razia Sultana
Razia Sultana
Razia al-Din , throne name Jalâlat ud-Dîn Raziyâ , usually referred to in history as Razia Sultan, was the Sultan of Delhi in India from 1236 to May 1240. She was of Seljuq slave ancestry and like some other Muslim princesses of the time, she was trained to lead armies and administer kingdoms if...
(1236–1240).
A Turco-Mongol
Turco-Mongol
Turko-Mongol is a modern designation for various nomads who were subjects of the Mongol Empire. Being progressively Turkicized in terms of language and identity following the Mongol conquests, they derived their ethnic and cultural origins from steppes of Central Asia...
conqueror in Central Asia, Timur
Timur
Timur , historically known as Tamerlane in English , was a 14th-century conqueror of West, South and Central Asia, and the founder of the Timurid dynasty in Central Asia, and great-great-grandfather of Babur, the founder of the Mughal Dynasty, which survived as the Mughal Empire in India until...
(Tamerlane), attacked the reigning Sultan Nasir-u Din Mehmud of the Tughlaq Dynasty in the north Indian city of Delhi
Delhi
Delhi , officially National Capital Territory of Delhi , is the largest metropolis by area and the second-largest by population in India, next to Mumbai. It is the eighth largest metropolis in the world by population with 16,753,265 inhabitants in the Territory at the 2011 Census...
. The Sultan's army was defeated on December 17, 1398. Timur entered Delhi and the city was sacked, destroyed, and left in ruins, after Timur's army had killed and plundered for three days and nights. He ordered the whole city to be sacked except for the sayyid
Sayyid
Sayyid is an honorific title, it denotes males accepted as descendants of the Islamic prophet Muhammad through his grandsons, Hasan ibn Ali and Husain ibn Ali, sons of the prophet's daughter Fatima Zahra and his son-in-law Ali ibn Abi Talib.Daughters of sayyids are given the titles Sayyida,...
s, scholars, and the other Muslims,; 100,000 war prisoners, mostly Hindus, were put to death in one day.
The Mughal era

In 1526, Babur
Babur
Babur was a Muslim conqueror from Central Asia who, following a series of setbacks, finally succeeded in laying the basis for the Mughal dynasty of South Asia. He was a direct descendant of Timur through his father, and a descendant also of Genghis Khan through his mother...
, a Timurid
Timurid Dynasty
The Timurids , self-designated Gurkānī , were a Persianate, Central Asian Sunni Muslim dynasty of Turko-Mongol descent whose empire included the whole of Iran, modern Afghanistan, and modern Uzbekistan, as well as large parts of contemporary Pakistan, North India, Mesopotamia, Anatolia and the...
descendant of Timur
Timur
Timur , historically known as Tamerlane in English , was a 14th-century conqueror of West, South and Central Asia, and the founder of the Timurid dynasty in Central Asia, and great-great-grandfather of Babur, the founder of the Mughal Dynasty, which survived as the Mughal Empire in India until...
and Genghis Khan
Descent from Genghis Khan
Descent from Genghis Khan is traceable primarily in Central Asia. His four sons and other immediate descendants are famous by names and by deeds. Later Asian potentates attempted to claim descent from the House of Borjigin even on flimsy grounds. In the 14th century, valid sources all but dried...
from Fergana Valley
Fergana Valley
The Fergana Valley or Farghana Valley is a region in Central Asia spreading across eastern Uzbekistan, Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan. Divided across three subdivisions of the former Soviet Union, the valley is ethnically diverse, and in the early 21st century was the scene of ethnic conflict...
(modern day Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan , officially the Republic of Uzbekistan is a doubly landlocked country in Central Asia and one of the six independent Turkic states. It shares borders with Kazakhstan to the west and to the north, Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan to the east, and Afghanistan and Turkmenistan to the south....
), swept across the Khyber Pass
Khyber Pass
The Khyber Pass, is a mountain pass linking Pakistan and Afghanistan.The Pass was an integral part of the ancient Silk Road. It is mentioned in the Bible as the "Pesh Habor," and it is one of the oldest known passes in the world....
and established the Mughal Empire
Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire , or Mogul Empire in traditional English usage, was an imperial power from the Indian Subcontinent. The Mughal emperors were descendants of the Timurids...
, covering modern day Afghanistan
Afghanistan
Afghanistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located in the centre of Asia, forming South Asia, Central Asia and the Middle East. With a population of about 29 million, it has an area of , making it the 42nd most populous and 41st largest nation in the world...
, Pakistan
Pakistan
Pakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan...
, India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
and Bangladesh
Bangladesh
Bangladesh , officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh is a sovereign state located in South Asia. It is bordered by India on all sides except for a small border with Burma to the far southeast and by the Bay of Bengal to the south...
. However, his son Humayun
Humayun
Nasir ud-din Muhammad Humayun was the second Mughal Emperor who ruled present day Afghanistan, Pakistan, and parts of northern India from 1530–1540 and again from 1555–1556. Like his father, Babur, he lost his kingdom early, but with Persian aid, he eventually regained an even larger one...
was defeated by the Afghan warrior Sher Shah Suri
Sher Shah Suri
Sher Shah Suri , birth name Farid Khan, also known as Sher Khan , was the founder of the short-lived Sur Empire in northern India, with its capital at Delhi, before its demise in the hands of the resurgent Mughal Empire...
in the year 1540, and Humayun was forced to retreat to Kabul
Kabul
Kabul , spelt Caubul in some classic literatures, is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan. It is also the capital of the Kabul Province, located in the eastern section of Afghanistan...
. After Sher Shah's death, his son Islam Shah Suri
Islam Shah Suri
Islam Shah Suri was the second ruler of the Sur dynasty which ruled part of India in the mid-16th century. His original name was Jalal Khan and he was the second son of Sher Shah Suri. On his father's death, an emergency meeting of nobles chose him to be successor instead of his elder brother Adil...
and the Hindu king Samrat Hem Chandra Vikramaditya, who had won 22 battles from Punjab
Punjab region
The Punjab , also spelled Panjab |water]]s"), is a geographical region straddling the border between Pakistan and India which includes Punjab province in Pakistan and the states of the Punjab, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Chandigarh and some northern parts of the National Capital Territory of Delhi...
to Bengal
Bengal
Bengal is a historical and geographical region in the northeast region of the Indian Subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal. Today, it is mainly divided between the sovereign land of People's Republic of Bangladesh and the Indian state of West Bengal, although some regions of the previous...
and had established a secular Hindu Raj, ruled North India from Delhi
Delhi
Delhi , officially National Capital Territory of Delhi , is the largest metropolis by area and the second-largest by population in India, next to Mumbai. It is the eighth largest metropolis in the world by population with 16,753,265 inhabitants in the Territory at the 2011 Census...
till 1556, when Akbar's forces defeated and killed Hemu in the Second Battle of Panipat on 6 November 1556.
The Mughal dynasty ruled most of the Indian subcontinent by 1600; it went into a slow decline after 1707 and was finally defeated during the Indian Rebellion of 1857
Indian Rebellion of 1857
The Indian Rebellion of 1857 began as a mutiny of sepoys of the British East India Company's army on 10 May 1857, in the town of Meerut, and soon escalated into other mutinies and civilian rebellions largely in the upper Gangetic plain and central India, with the major hostilities confined to...
, also called the 1857 War of Independence. This period marked vast social change in the subcontinent as the Hindu majority were ruled over by the Mughal emperors, most of whom showed religious tolerance, liberally patronising Hindu culture. The famous emperor Akbar, who was the grandson of Babar, tried to establish a good relationship with the Hindus. However, later emperors such as Aurangazeb tried to establish complete Muslim dominance, and as a result several historical temples were destroyed during this period and taxes imposed on non-Muslims. During the decline of the Mughal Empire, several smaller states rose to fill the power vacuum and themselves were contributing factors to the decline. In 1739, Nader Shah
Nader Shah
Nāder Shāh Afshār ruled as Shah of Iran and was the founder of the Afsharid dynasty. Because of his military genius, some historians have described him as the Napoleon of Persia or the Second Alexander...
, emperor of Iran, defeated the Mughal army at the huge Battle of Karnal
Battle of Karnal
The Battle of Karnal , was a decisive victory for Nader Shah the emperor of Persia during his invasion of India. Shah's forces defeated the army of Muhammad Shah, the Mughal emperor in little more than three hours thus paving the way for the Persian sack of Delhi...
. After this victory, Nader captured and sacked Delhi, carrying away many treasures, including the Peacock Throne
Peacock Throne
The Peacock Throne, called Takht-e Tâvus in Persian, is the name originally given to a Mughal throne of India, which was later adopted and used to describe the thrones of the Persian emperors from Nader Shah Afshari and erroneously to Mohammad Reza Shah Pahlavi whose throne was a reconstruction of...
.
The Mughals were perhaps the richest single dynasty to have ever existed.
During the Mughal era, the dominant political forces consisted of the Mughal Empire and its tributaries and, later on, the rising successor states - including the Maratha confederacy
Maratha Empire
The Maratha Empire or the Maratha Confederacy was an Indian imperial power that existed from 1674 to 1818. At its peak, the empire covered much of South Asia, encompassing a territory of over 2.8 million km²....
- which fought an increasingly weak Mughal dynasty. The Mughals, while often employing brutal tactics to subjugate their empire, had a policy of integration with Indian culture, which is what made them successful where the short-lived Sultanates of Delhi had failed. Akbar the Great was particularly famed for this. Akbar declared "Amari" or non-killing of animals in the holy days of Jainism. He rolled back the jizya
Jizya
Under Islamic law, jizya or jizyah is a per capita tax levied on a section of an Islamic state's non-Muslim citizens, who meet certain criteria...
tax for non-Muslims. The Mughal emperors married local royalty, allied themselves with local maharajas, and attempted to fuse their Turko-Persian culture with ancient Indian styles, creating a unique Indo-Saracenic architecture
Mughal architecture
Mughal architecture, an amalgam of Islamic, Persian, Turkish and Indian architecture, is the distinctive style developed by the Mughals in the 16th, 17th and 18th centuries in what is now India, Pakistan, Bangladesh and Afghanistan. It is symmetrical and decorative in style.The Mughal dynasty was...
. It was the erosion of this tradition coupled with increased brutality and centralization that played a large part in the dynasty's downfall after Aurangzeb
Aurangzeb
Abul Muzaffar Muhy-ud-Din Muhammad Aurangzeb Alamgir , more commonly known as Aurangzeb or by his chosen imperial title Alamgir , was the sixth Mughal Emperor of India, whose reign lasted from 1658 until his death in 1707.Badshah Aurangzeb, having ruled most of the Indian subcontinent for nearly...
, who unlike previous emperors, imposed relatively non-pluralistic policies on the general population, which often inflamed the majority Hindu population.
Post-Mughal period


Maratha Empire
The Maratha Empire or the Maratha Confederacy was an Indian imperial power that existed from 1674 to 1818. At its peak, the empire covered much of South Asia, encompassing a territory of over 2.8 million km²....
under the rule of the peshwa
Peshwa
A Peshwa is the titular equivalent of a modern Prime Minister. Emporer Shivaji created the Peshwa designation in order to more effectively delegate administrative duties during the growth of the Maratha Empire. Prior to 1749, Peshwas held office for 8-9 years and controlled the Maratha army...
s (prime ministers). By 1760, the domain of the Marathas stretched across practically the entire subcontinent. This expansion was brought to an end by the defeat of the Marathas by an Afghan army led by Ahmad Shah Durrani
Ahmad Shah Durrani
Ahmad Shah Durrani , also known as Ahmad Shāh Abdālī and born as Ahmad Khān, was the founder of the Durrani Empire in 1747 and is regarded by many to be the founder of the modern state of Afghanistan.Ahmad Khan enlisted as a young soldier in the military of the Afsharid kingdom and quickly rose...
at the Third Battle of Panipat
Third battle of Panipat
The Third Battle of Panipat took place on 14 January 1761, at Panipat , about 60 miles north of Delhi between a northern expeditionary force of the Maratha Confederacy and a coalition of the King of Afghanistan, Ahmad Shah Abdali with 2 Indian Muslim allies—the Rohilla Afghans of the Doab, and the...
(1761). The last peshwa, Baji Rao II
Baji Rao II
Baji Rao II was the last Peshwa of the Maratha Confederacy, and governed from 1796 to 1818. His reign was marked by confrontations with the British.-Biography:...
, was defeated by the British
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
in the Third Anglo-Maratha War
Third Anglo-Maratha War
The Third Anglo-Maratha War was the final and decisive conflict between the British East India Company and the Maratha Empire in India. The war left the Company in control of most of India. It began with an invasion of Maratha territory by 110,400 British East India Company troops, the largest...
.
The Kingdom of Mysore in southern India was founded around 1400 CE by the Wodeyar dynasty. The rule of the Wodeyars was interrupted by Hyder Ali
Hyder Ali
Hyder Ali was the de facto ruler of the Kingdom of Mysore in southern India. Born Hyder Naik, he distinguished himself militarily, eventually drawing the attention of Mysore's rulers...
and his son Tipu Sultan
Tipu Sultan
Tipu Sultan , also known as the Tiger of Mysore, was the de facto ruler of the Kingdom of Mysore. He was the son of Hyder Ali, at that time an officer in the Mysorean army, and his second wife, Fatima or Fakhr-un-Nissa...
. Under their rule, Mysore fought a series of wars
Anglo-Mysore Wars
The Anglo-Mysore Wars were a series of wars fought in India over the last three decades of the 18th century between the Kingdom of Mysore and the British East India Company, represented chiefly by the Madras Presidency...
sometimes against the combined forces of the British and Marathas, but mostly against the British, with Mysore receiving some aid or promise of aid from the French
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
.
Hyderabad was founded by the Qutb Shahi dynasty
Qutb Shahi dynasty
The Qutb Shahi dynasty was a Turko-Persian dynasty ; its members were collectively called the Qutub Shahis. They were the ruling family of the kingdom of Golkonda in modern-day Andra Pradesh, India. They were Shia Muslims and belonged to Kara Koyunlu...
of Golconda
Golconda
Golconda may be:Places:* Golkonda, ruined city and fortress in India* Golconda, Illinois, town in the United States* Golconda, Nevada, former town in the United StatesOther:* Golconda...
in 1591. Following a brief Mughal rule, Asif Jah, a Mughal official, seized control of Hyderabad and declared himself Nizam-al-Mulk of Hyderabad in 1724. It was ruled by a hereditary Nizam from 1724 until 1948. Both Mysore and Hyderabad became princely states in British India.
The Punjabi kingdom, ruled by members of the Sikh religion
Sikhism
Sikhism is a monotheistic religion founded during the 15th century in the Punjab region, by Guru Nanak Dev and continued to progress with ten successive Sikh Gurus . It is the fifth-largest organized religion in the world and one of the fastest-growing...
, was a political entity that governed the region of modern-day Punjab
Punjab region
The Punjab , also spelled Panjab |water]]s"), is a geographical region straddling the border between Pakistan and India which includes Punjab province in Pakistan and the states of the Punjab, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Chandigarh and some northern parts of the National Capital Territory of Delhi...
. This was among the last areas of the subcontinent to be conquered by the British. The first
First Anglo-Sikh War
The First Anglo-Sikh War was fought between the Sikh Empire and the British East India Company between 1845 and 1846. It resulted in partial subjugation of the Sikh kingdom.-Background and causes of the war:...
and second Anglo-Sikh war
Second Anglo-Sikh War
The Second Anglo-Sikh War took place in 1848 and 1849, between the Sikh Empire and the British East India Company. It resulted in the subjugation of the Sikh Empire, and the annexation of the Punjab and what subsequently became the North-West Frontier Province by the East India Company.-Background...
marked the downfall of the Sikh Empire.
Around the 18th century, the modern state of Nepal
Nepal
Nepal , officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, is a landlocked sovereign state located in South Asia. It is located in the Himalayas and bordered to the north by the People's Republic of China, and to the south, east, and west by the Republic of India...
was formed by Gurkha
Gurkha
Gurkha are people from Nepal who take their name from the Gorkha District. Gurkhas are best known for their history in the Indian Army's Gorkha regiments, the British Army's Brigade of Gurkhas and the Nepalese Army. Gurkha units are closely associated with the kukri, a forward-curving Nepalese knife...
rulers.
Colonial era
In 1498, Vasco da GamaVasco da Gama
Vasco da Gama, 1st Count of Vidigueira was a Portuguese explorer, one of the most successful in the Age of Discovery and the commander of the first ships to sail directly from Europe to India...
successfully discovered a new sea route from Europe to India, which paved the way for direct Indo-European commerce. The Portuguese
Portugal
Portugal , officially the Portuguese Republic is a country situated in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula. Portugal is the westernmost country of Europe, and is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the West and South and by Spain to the North and East. The Atlantic archipelagos of the...
soon set up trading posts in Goa
Goa
Goa , a former Portuguese colony, is India's smallest state by area and the fourth smallest by population. Located in South West India in the region known as the Konkan, it is bounded by the state of Maharashtra to the north, and by Karnataka to the east and south, while the Arabian Sea forms its...
, Daman
Daman District, India
Daman district is one of the two districts of the union territory of Daman and Diu on the western coast of India, surrounded by Valsad District of Gujarat state on the north, east and south and the Arabian Sea to the west. The district has an area of , and a population of 113,949 , which increased...
, Diu and Bombay. The next to arrive were the Dutch
Netherlands
The Netherlands is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, located mainly in North-West Europe and with several islands in the Caribbean. Mainland Netherlands borders the North Sea to the north and west, Belgium to the south, and Germany to the east, and shares maritime borders...
, the British
British Empire
The British Empire comprised the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom. It originated with the overseas colonies and trading posts established by England in the late 16th and early 17th centuries. At its height, it was the...
—who set up a trading post in the west coast port of Surat
Surat
Surat , also known as Suryapur, is the commercial capital city of the Indian state of Gujarat. Surat is India's Eighth most populous city and Ninth-most populous urban agglomeration. It is also administrative capital of Surat district and one of the fastest growing cities in India. The city proper...
in 1619—and the French
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
. The internal conflicts among Indian kingdoms gave opportunities to the European traders to gradually establish political influence and appropriate lands. Although these continental European powers controlled various coastal regions of southern and eastern India during the ensuing century, they eventually lost all their territories in India to the British islanders, with the exception of the French outposts of Pondicherry and Chandernagore, the Dutch port of Travancore
Travancore
Kingdom of Travancore was a former Hindu feudal kingdom and Indian Princely State with its capital at Padmanabhapuram or Trivandrum ruled by the Travancore Royal Family. The Kingdom of Travancore comprised most of modern day southern Kerala, Kanyakumari district, and the southernmost parts of...
, and the Portuguese colonies of Goa
Goa
Goa , a former Portuguese colony, is India's smallest state by area and the fourth smallest by population. Located in South West India in the region known as the Konkan, it is bounded by the state of Maharashtra to the north, and by Karnataka to the east and south, while the Arabian Sea forms its...
, Daman and Diu.
Company rule in India

British East India Company
The East India Company was an early English joint-stock company that was formed initially for pursuing trade with the East Indies, but that ended up trading mainly with the Indian subcontinent and China...
was given permission by Mughal Emperor Jahangir to trade in India. Gradually their increasing influence led the de-jure Mughal emperor Farrukh Siyar to grant them dastaks or permits for duty free trade in Bengal
Bengal
Bengal is a historical and geographical region in the northeast region of the Indian Subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal. Today, it is mainly divided between the sovereign land of People's Republic of Bangladesh and the Indian state of West Bengal, although some regions of the previous...
in 1717. The Nawab of Bengal
Nawab of Bengal
The Nawabs of Bengal were the hereditary nazims or subadars of the subah of Bengal during the Mughal rule and the de-facto rulers of the province.-History:...
Siraj Ud Daulah, the de facto
De facto
De facto is a Latin expression that means "concerning fact." In law, it often means "in practice but not necessarily ordained by law" or "in practice or actuality, but not officially established." It is commonly used in contrast to de jure when referring to matters of law, governance, or...
ruler of the Bengal province, opposed British attempts to use these permits.
The First Carnatic War extended from 1746 until 1748 and was the result of colonial competition between France and Britain, two of the countries involved in the War of Austrian Succession. Following the capture of a few French ships by the British fleet in India
Royal Indian Navy
The Royal Indian Navy was the naval force of British India. Along with the Presidency armies and the later British Indian Army it comprised the Armed Forces of British India....
, French troops attacked and captured the British city of Madras located on the east coast of India on September 21, 1746. Among the prisoners captured at Madras was Robert Clive himself. The war was eventually ended by the Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle
Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle (1748)
The Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle of 1748 ended the War of the Austrian Succession following a congress assembled at the Imperial Free City of Aachen—Aix-la-Chapelle in French—in the west of the Holy Roman Empire, on 24 April 1748...
which ended the War of Austrian Succession in 1748.
In 1749, the Second Carnatic War broke out as the result of a war between a son, Nasir Jung
Nasir Jung
Mir Ahmed Ali Khan Siddiqi was the son of Nizam-ul-Mulk by his wife Saeed-un-nisa Begum. He was born February 26, 1712. He succeeded his father as the Nizam of Hyderabad State in 1748...
, and a grandson, Muzaffer Jung, of the deceased Nizam-ul-Mulk of Hyderabad to take over Nizam's thone in Hyderabad. The French supported Muzaffer Jung in this civil war. Consequently, the British supported Nasir Jung in this conflict.
Meanwhile, however, the conflict in Hyderabad provided Chanda Sahib
Chanda Sahib
Chanda Sahib was the Nawab of the Carnatic between 1749 and 1752. His birth name is Husayn Dost Khan. He was the son-in-law of the Nawab of Carnatic Dost Ali Khan, under whom he worked as a Dewan. He belonged the Muslim Nait community which had ruled the Carnatic under the Nawab Zulfiqar Ali Khan...
with an opportunity to take power as the new Nawab
Nawab
A Nawab or Nawaab is an honorific title given to Muslim rulers of princely states in South Asia. It is the Muslim equivalent of the term "maharaja" that was granted to Hindu rulers....
of the territory of Arcot. In this conflict, the French supported Chandra Sahib in his attempt to become the new Nawab of Arcot. The British supported the son of the deposed incumbent Nawab, Anwaruddin Muhammad Khan, against Chanda Sahib. In 1751, Robert Clive led a British armed force and captured Arcot to reinstate the incumbent Nawab. The Second Carnatic War finally came to an end in 1754 with the Treaty of Pondicherry
Treaty of Pondicherry
The Treaty of Pondicherry was signed in 1754 bringing an end to the Second Carnatic War. It was agreed and signed in the French settlement of Pondicherry in French India. The favoured British candidate Mohamed Ali Khan Walajan was recognized as the Nawab of the Carnatic...
.
In 1756, the Seven Years War broke out between the great powers of the world, i.e. Britain and Prussia on one side and France, Austria and Russia on the other. The Seven Years War was really a "world war", with theaters of operations in Europe, the Caribbean, North America and India. Indeed, Winston Churchill
Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer-Churchill, was a predominantly Conservative British politician and statesman known for his leadership of the United Kingdom during the Second World War. He is widely regarded as one of the greatest wartime leaders of the century and served as Prime Minister twice...
called the Seven Years War "the first world war."
Great Britain
Kingdom of Great Britain
The former Kingdom of Great Britain, sometimes described as the 'United Kingdom of Great Britain', That the Two Kingdoms of Scotland and England, shall upon the 1st May next ensuing the date hereof, and forever after, be United into One Kingdom by the Name of GREAT BRITAIN. was a sovereign...
and France fought each other in these theaters throughout the world. In the Indian theater of operations, the Seven Years War became known as the Third Carnatic War. Early in this war, armed forces under the French East India Company captured the British base of Calcutta in north-eastern India. However, armed forces under Robert Clive later recaptured Calcutta and then pressed on to capture the French settlement of Chandannagar
Chandannagar
Chandannagar, formerly known as Chandernagore or Chandernagar , is a small city and former French colony located north of Kolkata, in West Bengal, India. It is head quarters of a subdivision in Hooghly District. It is one of the 6 municipal corporations in West Bengal. It is a part of the area...
in 1757. This led to the Battle of Plassey
Battle of Plassey
The Battle of Plassey , 23 June 1757, was a decisive British East India Company victory over the Nawab of Bengal and his French allies, establishing Company rule in South Asia which expanded over much of the Indies for the next hundred years...
on June 23, 1757, in which the Bengal Army
Bengal Army
The Bengal Army was the army of the Presidency of Bengal, one of the three Presidencies of British India, in South Asia. Although based in Bengal in eastern India, the presidency stretched across northern India and the Himalayas all the way to the North West Frontier Province...
of the East India Company, led by Robert Clive, defeated the French-supported Nawab's forces. This was the first real political foothold with territorial implications that the British acquired in India. Clive was appointed by the company as its first 'Governor of Bengal' in 1757. This was combined with British victories over the French at Madras
Siege of Madras
The Siege of Madras was a siege of Madras, British India, between December 1758 and February 1759 by French forces under the command of Lally during the Seven Year's War. The British garrison was able to hold out until it was relieved. The British fired 26,554 cannon balls and more than 200,000...
, Wandiwash
Battle of Wandiwash
The Battle of Wandiwash was a decisive battle in India during the Seven Years' War. The Count de Lally's army, burdened by a lack of naval support and funds, attempted to regain the fort at Vandavasi near Pondicherry. He was attacked by Sir Eyre Coote's forces and decisively defeated...
and Pondicherry
Siege of Pondicherry (1760)
The 1760–1761 Siege of Pondicherry was a conflict in the Third Carnatic War, part of the global Seven Years' War. Lasting from 4 September 1760 to 15 January 1761, British land and naval forces besieged and eventually compelled the surrender French forces defending the French colonial outpost of...
that, along with wider British successes during the Seven Years War
Great Britain in the Seven Years War
The Kingdom of Great Britain was one of the major participants in the Seven Years' War which lasted between 1756 and 1763. Britain emerged from the war as the world's leading colonial power having gained a number of new territories at the Treaty of Paris in 1763 and established itself as the...
, reduced French influence in India. Thus as a result of the three Carnatic Wars, the British East India Company gained exclusive control over the entire Carnatic region of India. Following the British suppression of a revolt against the British East India Company in Bengal
Bengal
Bengal is a historical and geographical region in the northeast region of the Indian Subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal. Today, it is mainly divided between the sovereign land of People's Republic of Bangladesh and the Indian state of West Bengal, although some regions of the previous...
in 1863, the Company also gained exclusive economic control of the Bihar region of India along the Ganges River. Also in 1863, the British completed the conquest of several feudal principalities in the Orissa region of southern Bengal. Thus, the British East India Company extended its control over the whole of Bengal. In 1763, the Treaty of Paris (1763)
Treaty of Paris (1763)
The Treaty of Paris, often called the Peace of Paris, or the Treaty of 1763, was signed on 10 February 1763, by the kingdoms of Great Britain, France and Spain, with Portugal in agreement. It ended the French and Indian War/Seven Years' War...
ended the Anglo-French hostilities part of the Seven Years War.
After the Battle of Buxar
Battle of Buxar
The Battle of Buxar was fought on 22 October 1764 between the forces under the command of the British East India Company, and the combined armies of Mir Qasim, the Nawab of Bengal; Shuja-ud-Daula Nawab of Awadh; and Shah Alam II, the Mughal Emperor...
in 1764, the company acquired the civil rights of administration in Bengal from Mughal Emperor Shah Alam II
Shah Alam II
Shah Alam II , also known as Ali Gauhar, was a Mughal emperor of India. A son of Alamgir II, he was exiled to Allahabad in December 1759 by Ghazi-ud-Din, who appointed Shah Jahan III as the emperor. Later, he was nominated as the emperor by Ahmad Shah.Shah Alam II was considered the only and...
; this marked the beginning of its formal rule, which within the next century engulfed most of India and extinguished the Moghul rule and dynasty.
The East India Company monopolized the trade of Bengal. They introduced a land taxation system called the Permanent Settlement
Permanent Settlement
The Permanent Settlement — also known as the Permanent Settlement of Bengal — was an agreement between the East India Company and Bengali landlords to fix revenues to be raised from land, with far-reaching consequences for both agricultural methods and productivity in the entire Empire and the...
which introduced a feudal
Feudalism
Feudalism was a set of legal and military customs in medieval Europe that flourished between the 9th and 15th centuries, which, broadly defined, was a system for ordering society around relationships derived from the holding of land in exchange for service or labour.Although derived from the...
-like structure in Bengal, often with zamindar
Zamindar
A Zamindar or zemindar , was an aristocrat, typically hereditary, who held enormous tracts of land and ruled over and taxed the bhikaaris who lived on batavaslam. Over time, they took princely and royal titles such as Maharaja , Raja , Nawab , and Mirza , Chowdhury , among others...
s set in place. By the 1850s, the East India Company controlled most of the Indian sub-continent, which included present-day Pakistan and Bangladesh. Their policy was sometimes summed up as Divide and Rule
Divide and rule
In politics and sociology, divide and rule is a combination of political, military and economic strategy of gaining and maintaining power by breaking up larger concentrations of power into chunks that individually have less power than the one implementing the strategy...
, taking advantage of the enmity festering between various princely states and social and religious groups.
British Raj

Indian Rebellion of 1857
The Indian Rebellion of 1857 began as a mutiny of sepoys of the British East India Company's army on 10 May 1857, in the town of Meerut, and soon escalated into other mutinies and civilian rebellions largely in the upper Gangetic plain and central India, with the major hostilities confined to...
. After a year of turmoil and reinforcement of the East India Company's troops with British soldiers, the company overcame the rebellion. The nominal leader of the uprising, the last Mughal Emperor Bahadur Shah Zafar was exiled to Burma, his children were beheaded, and the Moghul line was abolished. In the aftermath, all power was transferred from the East India Company to the British Crown, which began to administer most of India as a number of provinces; the company's lands were controlled directly, while it had considerable influence over the rest of India, which consisted of the Princely states. There were some 565 princely states when British India gained independence from Britain in August 1947.
During the British Raj, famines in India
Famine in India
Famine has been a recurrent feature of life in the Indian sub-continental countries of India, Pakistan and Bangladesh, and reached its numerically deadliest peak in the late eighteenth and nineteenth centuries. Historical and legendary evidence names some 90 famines in 2,500 years of history. There...
, often attributed to failed government policies, were some of the worst ever recorded, including the Great Famine of 1876–78
Great Famine of 1876–78
The Great Famine of 1876–1878 was a famine in India that began in 1876 and affected south and southwestern India for a period of two years...
in which 6.1 million to 10.3 million people died and the Indian famine of 1899–1900
Indian famine of 1899–1900
The Indian famine of 1899–1900 began with the failure of the summer monsoons in 1899 over west and Central India and, during the next year, affected an area of and a population of 59.5 million...
in which 1.25 to 10 million people died. The Third Plague Pandemic started in China in the middle of the 19th century, spreading plague to all inhabited continents and killing 10 million people in India alone. Despite persistent diseases and famines, the population of the Indian subcontinent
Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent, also Indian Subcontinent, Indo-Pak Subcontinent or South Asian Subcontinent is a region of the Asian continent on the Indian tectonic plate from the Hindu Kush or Hindu Koh, Himalayas and including the Kuen Lun and Karakoram ranges, forming a land mass which extends...
, which stood at about 125 million in 1750, had reached 389 million by 1941.
The Indian Independence movement
The physical presence of the British in India was not significant. Yet the British were able to rule two-thirds of the subcontinent directly and exercise considerable leverage over the princely states that accounted for the remaining one-third. The British employed "Divide and RuleDivide and rule
In politics and sociology, divide and rule is a combination of political, military and economic strategy of gaining and maintaining power by breaking up larger concentrations of power into chunks that individually have less power than the one implementing the strategy...
" in British India as a means of preventing an uprising against their rule.
In this environment of Hindu-Muslim disunity, the first step toward Indian independence and western-style democracy was taken with the appointment of Indian councillors to advise the British viceroy
Viceroy
A viceroy is a royal official who runs a country, colony, or province in the name of and as representative of the monarch. The term derives from the Latin prefix vice-, meaning "in the place of" and the French word roi, meaning king. A viceroy's province or larger territory is called a viceroyalty...
, and with the establishment of provincial Councils with Indian members. The councillors' participation was subsequently widened into legislative councils. From 1920 leaders such as Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi began highly popular mass movements to campaign against the British Raj using largely peaceful methods. Some others adopted a militant approach that sought to overthrow British rule by armed struggle; revolutionary activities
Revolutionary movement for Indian independence
The Revolutionary movement for Indian independence is often a less-highlighted aspect of the Indian independence movement -- the underground revolutionary factions. The groups believing in armed revolution against the ruling British fall into this category. The revolutionary groups were...
against the British rule took place throughout the Indian sub-continent. The Gandhi-led independence movement opposed the British rule using non-violent methods like non-cooperation
Non-cooperation movement
The non-cooperation movement was a significant phase of the Indian struggle for freedom from British rule which lasted for years. This movement, which lasted from September 1920 to February 1922 and was led by Mohandas Gandhi, and supported by the Indian National Congress. It aimed to resist...
, civil disobedience and economic resistance
Swadeshi movement
The Swadeshi movement, part of the Indian independence movement, was an economic strategy aimed at removing the British Empire from power and improving economic conditions in India by following the principles of swadeshi , which had some success...
. These movements succeeded in bringing independence to the new dominions of India and Pakistan
Pakistan
Pakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan...
in 1947.
Independence and Partition
Along with the desire for independence, tensions between Hindus and Muslims had also been developing over the years. The Muslims had always been a minority within the subcontinent, and the prospect of an exclusively Hindu government made them wary of independence; they were as inclined to mistrust Hindu rule as they were to resist the foreign Raj, although Gandhi called for unity between the two groups in an astonishing display of leadership. The British, extremely weakened by the Second World WarWorld War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
, promised that they would leave and participated in the formation of an interim government
Interim Government of India
The interim government of India, formed on 2 September 1946 from the newly elected Constituent Assembly of India, had the task of assisting the transition of India from British rule to independence...
. The British Indian territories gained independence in 1947, after being partitioned
Partition of India
The Partition of India was the partition of British India on the basis of religious demographics that led to the creation of the sovereign states of the Dominion of Pakistan and the Union of India on 14 and 15...
into the Union of India and Dominion of Pakistan
Dominion of Pakistan
The Dominion of Pakistan was an independent federal Commonwealth realm in South Asia that was established in 1947 on the partition of British India into two sovereign dominions . The Dominion of Pakistan, which included modern-day Pakistan and Bangladesh, was intended to be a homeland for the...
. Following the controversial division of pre-partition Punjab
Punjab (British India)
Punjab was a province of British India, it was one of the last areas of the Indian subcontinent to fall under British rule. With the end of British rule in 1947 the province was split between West Punjab, which went to Pakistan, and East Punjab, which went to India...
and Bengal
Bengal
Bengal is a historical and geographical region in the northeast region of the Indian Subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal. Today, it is mainly divided between the sovereign land of People's Republic of Bangladesh and the Indian state of West Bengal, although some regions of the previous...
, rioting broke out between Sikhs, Hindus and Muslims in these provinces and spread to several other parts of India, leaving some 500,000 dead. Also, this period saw one of the largest mass migrations ever recorded in modern history, with a total of 12 million Hindus, Sikhs and Muslims moving between the newly created nations of India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
and Pakistan
Pakistan
Pakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan...
(which gained independence on 15 and 14 August 1947 respectively). In 1971, Bangladesh
Bangladesh
Bangladesh , officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh is a sovereign state located in South Asia. It is bordered by India on all sides except for a small border with Burma to the far southeast and by the Bay of Bengal to the south...
, formerly East Pakistan
East Pakistan
East Pakistan was a provincial state of Pakistan established in 14 August 1947. The provincial state existed until its declaration of independence on 26 March 1971 as the independent nation of Bangladesh. Pakistan recognized the new nation on 16 December 1971. East Pakistan was created from Bengal...
and East Bengal
East Bengal
East Bengal was the name used during two periods in the 20th century for a territory that roughly corresponded to the modern state of Bangladesh. Both instances involved a violent partition of Bengal....
, seceded from Pakistan.
See also
- Contributions of Indian Civilization
- Economic history of IndiaEconomic history of IndiaThe known Economic history of India begins with the Indus Valley civilization. The Indus civilization's economy appears to have depended significantly on trade, which was facilitated by advances in transport. Around 600 BC, the Mahajanapadas minted punch-marked silver coins. The period was marked...
- Harappan mathematics
- Historic figures of ancient IndiaHistoric Figures of Ancient IndiaThis article tries to compile and classify the prominent personalities of ancient India that find mention in more than one source of Sanskrit/Vedic literature like the two Hindu Ithihasas viz the Mahabharata and the Ramayana, the Puranas and the Vedas with their supplement texts...
- History of AsiaHistory of AsiaThe history of Asia can be seen as the collective history of several distinct peripheral coastal regions such as, East Asia, South Asia, and the Middle East linked by the interior mass of the Eurasian steppe....
- History of BangladeshHistory of BangladeshThe history of Bangladesh as a nation state began in 1971, when it seceded from Pakistan. Prior to the creation of Pakistan in 1947, modern-day Bangladesh was part of ancient, classical, medieval and colonial India....
- History of BhutanHistory of BhutanBhutan's early history is steeped in mythology and remains obscure. It may have been inhabited as early as 2000 BC, but not much was known until the introduction of Tibetan Buddhism in the 9th century, when turmoil in Tibet forced many monks to flee to Bhutan. In the 12th century, the Drukpa...
- History of BuddhismHistory of BuddhismThe History of Buddhism spans the 6th century BCE to the present, starting with the birth of Buddha Siddhartha Gautama on the Indian subcontinent, in what is now Lumbini, Nepal. This makes it one of the oldest religions practiced today. The religion evolved as it spread from the northeastern region...
- History of ChinaHistory of ChinaChinese civilization originated in various regional centers along both the Yellow River and the Yangtze River valleys in the Neolithic era, but the Yellow River is said to be the Cradle of Chinese Civilization. With thousands of years of continuous history, China is one of the world's oldest...
- History of HinduismHistory of HinduismHinduism is a term for a wide variety of related religious traditions native to India. Historically, it encompasses the development of Religion in India since the Iron Age traditions, which in turn hark back to prehistoric religions such as that of the Bronze Age Indus Valley Civilization followed...
- History of Jainism
- History of NepalHistory of NepalThe history of Nepal is characterized by its isolated position in the Himalayas and its two neighbors, India and China.Due to the arrival of disparate settler groups from outside through the ages, it is now a multi-ethnic, multi-cultural, multilingual country...
- History of PakistanHistory of PakistanThe 1st known inhabitants of the modern-day Pakistan region are believed to have been the Soanian , who settled in the Soan Valley and Riwat almost 2 million years ago. Over the next several thousand years, the region would develop into various civilizations like Mehrgarh and the Indus Valley...
- History of SikhismHistory of SikhismThe history of Sikhism is closely associated with the history of Punjab and the socio-political situation in medieval India. Sikh distinction was further enhanced by the establishment of the Khalsa , by Guru Gobind Singh in 1699. Sikhism was created by Guru Nanak Dev, a religious leader and a...
- History of South AsiaHistory of South AsiaThe term South Asia refers to the contemporary political entities of the Indian subcontinent and associated island. These are the states of India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Nepal, Bhutan and the island nations of Sri Lanka and the Maldives....
- History of Sri LankaHistory of Sri LankaThe History of Sri Lanka begins around 30,000 years ago when the island was first inhabited. Chronicles, including the Mahawansa, the Dipavamsa, the Culavamsa and the Rajaveliya, record events from the beginnings of the Sinhalese monarchy in the 6th century BC; through the arrival of European...
- History of the MaldivesHistory of the MaldivesThe Maldives is a nation consisting of 26 natural atolls, comprising 1192 islands-Historical setting:Since very ancient times, the Maldives were ruled by kings and occasionally queens ....
- History of the Republic of IndiaHistory of the Republic of IndiaThe history of the Republic of India began on 26 January 1950. The country became an independent dominion within the British Commonwealth 15 August 1947. George VI was King until the Republic was proclaimed in 1950. Concurrently the Muslim-majority northwest and east of British India was separated...
- Imperialism in Asia#British in India
- Indian maritime historyIndian maritime historyIndian maritime history begins during the 3rd millennium BCE when inhabitants of the Indus Valley initiated maritime trading contact with Mesopotamia. The Roman historian Strabo mentions an increase in Roman trade with India following the Roman annexation of Egypt. By the time of Augustus up to 120...
- Indian nationalismIndian nationalismIndian nationalism refers to the many underlying forces that molded the Indian independence movement, and strongly continue to influence the politics of India, as well as being the heart of many contrasting ideologies that have caused ethnic and religious conflict in Indian society...
- Indian philosophyIndian philosophyIndia has a rich and diverse philosophical tradition dating back to ancient times. According to Radhakrishnan, the earlier Upanisads constitute "...the earliest philosophical compositions of the world."...
- Indian Religions
- Indianized kingdom
- Kingdoms of Ancient IndiaKingdoms of Ancient IndiaEpic India is the geography of Greater India traditionally around early 10th century BC and later on from the Sanskrit epics, viz. the Mahabharata and the Ramayana as well as Puranic literature ....
- List of books about India
- List of Indian inventions and discoveries
- List of Prime Ministers of India
- Military history of IndiaMilitary history of IndiaThe military history of India dates back several millennia. The first reference to armies is found in the Vedas and the epics Ramayana and Mahabaratha. From the ancient period through to the 19th century, a succession of powerful dynasties rose and fell in India as smaller rulers also struggled for...
- Muslim conquest in the Indian subcontinentMuslim conquest in the Indian subcontinentMuslim conquest in South Asia mainly took place from the 13th to the 16th centuries, though earlier Muslim conquests made limited inroads into the region, beginning during the period of the ascendancy of the Rajput Kingdoms in North India, from the 7th century onwards.However, the Himalayan...
- Negationism in India - Concealing the Record of IslamNegationism in India - Concealing the Record of IslamNegationism in India: Concealing the Record of Islam is a book by Koenraad Elst published in 1992.The book attempts to demonstrate that there exists a 'prohibition' of criticism of Islam and a denial of its 'historic crimes against humanity' that amounts to censorship, comparing it to Holocaust...
- Politics of IndiaPolitics of IndiaThe politics of India takes place within the framework of a federal constitutional republic, in which the President of India is head of state and the Prime Minister of India is the head of government. Executive power is exercised by the President and is independent of the legislature...
- Religion in IndiaReligion in IndiaIndian religions is a classification for religions that originated in the Indian subcontinent; namely Hinduism, Jainism, Buddhism and Sikhism. These religions are also classified as Eastern religions...
- Science and technology in ancient IndiaScience and technology in ancient IndiaThe history of science and technology in the Indian subcontinent begins with prehistoric human activity at Mehrgarh, in present-day Pakistan, and continues through the Indus Valley Civilization to early states and empires. The British colonial rule introduced some elements of western education in...
- The History of India, as Told by Its Own Historians. The Muhammadan Period (Book)
- Timeline of Indian historyTimeline of Indian historyThis is a timeline of Indian history. It includes the history of the Indian subcontinent, from the pre-historic beginning to the present.-Rock Shelters of Bhimbetka :...
- Timeline of the economy of IndiaTimeline of the economy of IndiaThis is a timeline of the economy of India. It includes the economic timeline of the Indian subcontinent, from the ancient era to the present. The history of the Indian economy can be broadly divided into three phases : the Pre-colonial period, Colonial period and the Post-independence period.-...
Further reading
- Basham, A. L. (1954), The wonder that was India. Sidgwick and Jackson, London.
- Daniélou, AlainAlain DaniélouAlain Daniélou was a French historian, intellectual, musicologist, Indologist, and a noted Western convert to and expert on Shaivite Hinduism.-Life:...
(2003). A Brief History of India ISBN 0-89281-923-5 - Elliot, Henry Miers; John Dowson (1867–77). The History of India, as told by its own historians. The Muhammadan Period. London: Trübner and Co.
- Kulke, Hermann and Dietmar Rothermund. A History of India. 3rd ed. (1998)
- R.C. Majumdar, H.C. Raychaudhuri, and Kaukinkar Datta. An Advanced History of IndiaAn Advanced History of IndiaAn Advanced History of India is a book on Indian history written by R.C. Majumdar, H.C. Raychaudhuri and Kalikinkar Datta, first published in 1946.J...
. London: Macmillan. 1960. ISBN 0-333-90298-X - R.C. Majumdar, The History and Culture of the Indian People, New York: The Macmillan Co., 1951.
- Mcleod, John. The History of India (2002)
- Rothermund, Dietmar. An Economic History of India: From Pre-Colonial Times to 1991 (1993)
- Sharma, R.S.Ram Sharan SharmaRam Sharan Sharma was an eminent historian of Ancient and early Medieval India. He had taught at Patna University, Delhi University and the University of Toronto and was a senior fellow at School of Oriental and African Studies, University of London; University Grants Commission National Fellow...
, India's Ancient PastIndia's Ancient PastIndia's Ancient Past is a book by Professor Ram Sharan Sharma which details the history of early India. Beginning with a discussion on frameworks of the writing of history, the book sheds light on the origins and growth of civilizations, empires, and religions...
, Oxford University PressOxford University PressOxford University Press is the largest university press in the world. It is a department of the University of Oxford and is governed by a group of 15 academics appointed by the Vice-Chancellor known as the Delegates of the Press. They are headed by the Secretary to the Delegates, who serves as... - Sims-Williams, Nicholas and J. Cribb (1995-1996) "A new Bactrian inscription of Kanishka the Great", in Silk Road Art and Archaeology No. 4, 1995-1996.
- Singhal, D.P. (1983), A History of the Indian People. Methuen, London.
- Smith, Vincent. The Oxford History of India (1981)
- Spear, Percival. The History of India Vol. 2 (1990)
- Thapar, Romila. Early India: From the Origins to AD 1300 (2004)
- Wolpert, Stanley. A New History of India. 6th ed. (1999)
- Chirol, Valentine Indian Unrest and India Old and New London 1910
- Ghosh, Aurobindo, Bankim, Tilak Dayanand Calcutta 1947
- K.C.Yadav & Arya K.S. Arya Samaj and Freedom Movement, Manohar Publications Delhi 1988
- Kohn Hans A History of Nationalism in the East, New York 1929
- Lajpat Rai, India's Will to Freedom Madras 1921
- Macdonald, J Ramsay The Awakening of India, London 1910
- Romain Rolland, The Prophets of New India London 1930

