
Spark gap
Encyclopedia
A spark gap consists of an arrangement of two conducting electrode
s separated by a gap usually filled with a gas
such as air, designed to allow an electric spark
to pass between the conductors. When the voltage difference between the conductors exceeds the gap's breakdown voltage
, a spark
forms, ionizing
the gas and drastically reducing its electrical resistance
. An electric current then flows until the path of ionized gas is broken or the current reduces below a minimum value called the 'holding current'. This usually happens when the voltage
drops, but in some cases occurs when the heated gas rises, stretching out and then breaking the filament of ionized gas. Usually the action of ionizing the gas is violent and disruptive, often leading to sound
(ranging from a snap for a spark plug
to thunder
for a lightning
discharge), light
and heat
.
Spark gaps were used historically in early electrical equipment, such as spark gap radio transmitters
, electrostatic machines, and x-ray machine
s. Their most widespread use today is in spark plug
s to ignite the fuel in internal combustion engine
s, but they are also used in lightning arrestors and other devices to protect electrical equipment from high voltage transients.
s itself, but from the material medium fluorescing
in response to collisions from the electrons. When electrons collide with molecules of air in the gap, they excite their orbital
electrons to higher energy level
s. When they fall back to their original energy levels, they emit the energy as light. It is impossible for a visible spark to form in a vacuum
. Without intervening matter capable of electromagnetic
transitions, the spark will be invisible (see vacuum arc
).
 A spark plug
A spark plug
uses a spark gap to initiate combustion
. The heat of the ionization trail ignites a fuel-air mixture inside an internal combustion engine
, or a burner in a furnace, oven, or stove.

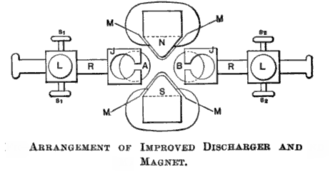
.png)
.png) A spark radiates energy throughout the electromagnetic spectrum
A spark radiates energy throughout the electromagnetic spectrum
. Nowadays, this is usually regarded as illegal radio frequency interference
and is suppressed, but in the early days of radio communications (1900-1920), this was the means by which radio signals were transmitted, in the unmodulated
spark-gap transmitter
. Many radio spark gaps include cooling devices such as the rotary gap and heat sink
s, since the spark gap becomes quite hot under continuous use at high power.
from damaging equipment. Spark gaps are used in high-voltage switch
es, large power transformer
s, in power plants and electrical substation
s. Such switches are constructed with a large, remote-operated switching blade with a hinge as one contact and two leaf spring
s holding the other end as second contact. If the blade is opened, a spark may keep the connection between blade and spring conducting. (The spark ionizes the air, which becomes conductive, allowing an arc to form, which sustains ionization and hence conduction.) Here, a Jacob's ladder on top of the switch will pull the arc apart and so extinguish it. You might also find small Jacob's ladders mounted on top of ceramic insulators of high-voltage pylons. These are sometimes called horn gaps. If a spark should ever manage to jump over the insulator and give rise to an arc, it will be extinguished.
Smaller spark gaps are often used to protect sensitive electrical or electronic equipment from high voltage surges
. In sophisticated versions of these devices (called gas tube arresters), a small spark gap breaks down during an abnormal voltage surge, safely shunting the surge to ground and thereby protecting the equipment. These devices are commonly used for telephone
lines as they enter a building; the spark gaps help protect the building and internal telephone circuits from the effects of lightning
strikes. Less sophisticated (and much less expensive) spark gaps are made using modified ceramic capacitor
s; in these devices, the spark gap is simply an air gap saw
n between the two lead wires that connect the capacitor to the circuit. A voltage surge causes a spark which jumps from lead wire to lead wire across the gap left by the sawing process. These low-cost devices are often used to prevent damaging arcs between the elements of the electron gun(s) within a cathode ray tube
(CRT).
Small spark gaps are very common in telephone switchboard
s, as the long phone cables are very susceptible to induced surges from lightning
strikes. Larger spark gaps are used to protect power line
s.
Transils and trisil
s are the solid-state alternatives to spark gaps for lower-power applications. Neon bulb
s are also used for this purpose.
light source or radioactive source may be put on one of the terminals to provide a source of electrons.
s, railgun
s, fusion
, ultrastrong pulsed magnetic field
research, and in the triggering of nuclear bombs. Commercially available devices can be divided into two classes: positive pressure and triggered vacuum gaps. Positive pressure triggered gaps have a limited operating voltage range (for instance, from 1/3 to 2/3 of the self breakdown voltage). Triggered vacuum gaps offer a wide operating voltage range (400 V to 90 kV is achievable). Both classes can switch higher energy levels than any thyristor
, thyratron
, krytron
, or sprytron
. Triggered gaps are popular for single shot and low repetition rate applications. One such switch is known as a trigatron
. The Ignitron
and Crossatron
could be considered triggered gaps. The latter is unique in that it can be turned back off by the control electrode after conduction begins. The xenon flash tube is another common triggered gap. Various schemes have also been devised to trigger open air gaps on command. A set of spark gaps are a key element of a Marx generator
, used to generate high-voltage impulses; the spark gaps allow a chain of capacitor
s to be slowly charged in parallel and then rapidly discharged in series.
 A Jacob's ladder (more formally, a high voltage traveling arc) is a device for producing a continuous train of large sparks which rise upwards. The spark gap is formed by two wires, approximately vertical but gradually diverging away from each other towards the top in a narrow "V" shape. It was named for the "ladder to heaven
A Jacob's ladder (more formally, a high voltage traveling arc) is a device for producing a continuous train of large sparks which rise upwards. The spark gap is formed by two wires, approximately vertical but gradually diverging away from each other towards the top in a narrow "V" shape. It was named for the "ladder to heaven
" described in the Bible.
When high voltage is applied to the gap, a spark forms across the bottom of the wires where they are nearest each other, rapidly changing to an electric arc
. Air breaks down at about 30 kV/cm, depending on humidity, temperature, etc. Apart from the anode and cathode voltage drops, the arc behaves almost as a short circuit
, drawing as much current as the electrical power supply
can deliver, and the heavy load dramatically reduces the voltage across the gap.
The heated, ionized air rises, carrying the current path with it. As the trail of ionization gets longer, it becomes more and more unstable, finally breaking. The voltage across the electrodes then rises and the spark re-forms at the bottom of the device.
This cycle leads to an exotic-looking display of electric white
, yellow
, blue
or purple
arcs which is often seen in films about mad scientist
s. The device was a staple in schools and science fair
s of the 1950s and 1960s, typically constructed out of a Model T spark coil, or any other source of high voltage in the 10,000–30,000 volt range, like a neon sign transformer
(5–15 kV) or a television picture tube circuit (flyback transformer
) (10–28 kV), and two coat hangers or rods built into a "V" shape. For larger ladders, microwave oven
transformers connected in series or utility pole transformers (pole pigs) run in reverse (step-up) are used.
Traveling-arc devices are dangerous. The sparks can burn through thin paper and plastic and start fires, and contact with the exposed high-voltage conductors can be lethal.
and nitric oxide
. These free radicals can be damaging to the mucous membranes of people near the spark gap. Plants are also susceptible to ozone poisoning.
These hazards are not present when the arc is formed outdoors since the heated ionized gases will rise up into the air and dissipate into the atmosphere. Spark gaps which only intermittently produce short spark bursts are also minimally hazardous because the volume of ions generated is very small.
Arcs can also produce a broad spectrum of wavelengths spanning the visible light and the invisible ultraviolet and infrared spectrum. Very intense arcs generated by means such as arc welding
can produce significant amounts of ultraviolet which is damaging to the retina of the observer. These arcs should only be observed through special dark filters which reduce the arc intensity and shield the observer's eyes from the ultraviolet rays.
Electrode
An electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit...
s separated by a gap usually filled with a gas
Gas
Gas is one of the three classical states of matter . Near absolute zero, a substance exists as a solid. As heat is added to this substance it melts into a liquid at its melting point , boils into a gas at its boiling point, and if heated high enough would enter a plasma state in which the electrons...
such as air, designed to allow an electric spark
Electric spark
An electric spark is a type of electrostatic discharge that occurs when an electric field creates an ionized electrically conductive channel in air producing a brief emission of light and sound. A spark is formed when the electric field strength exceeds the dielectric field strength of air...
to pass between the conductors. When the voltage difference between the conductors exceeds the gap's breakdown voltage
Breakdown voltage
The breakdown voltage of an insulator is the minimum voltage that causes a portion of an insulator to become electrically conductive.The breakdown voltage of a diode is the minimum reverse voltage to make the diode conduct in reverse...
, a spark
Electric spark
An electric spark is a type of electrostatic discharge that occurs when an electric field creates an ionized electrically conductive channel in air producing a brief emission of light and sound. A spark is formed when the electric field strength exceeds the dielectric field strength of air...
forms, ionizing
Ionization
Ionization is the process of converting an atom or molecule into an ion by adding or removing charged particles such as electrons or other ions. This is often confused with dissociation. A substance may dissociate without necessarily producing ions. As an example, the molecules of table sugar...
the gas and drastically reducing its electrical resistance
Electrical resistance
The electrical resistance of an electrical element is the opposition to the passage of an electric current through that element; the inverse quantity is electrical conductance, the ease at which an electric current passes. Electrical resistance shares some conceptual parallels with the mechanical...
. An electric current then flows until the path of ionized gas is broken or the current reduces below a minimum value called the 'holding current'. This usually happens when the voltage
Voltage
Voltage, otherwise known as electrical potential difference or electric tension is the difference in electric potential between two points — or the difference in electric potential energy per unit charge between two points...
drops, but in some cases occurs when the heated gas rises, stretching out and then breaking the filament of ionized gas. Usually the action of ionizing the gas is violent and disruptive, often leading to sound
Sound
Sound is a mechanical wave that is an oscillation of pressure transmitted through a solid, liquid, or gas, composed of frequencies within the range of hearing and of a level sufficiently strong to be heard, or the sensation stimulated in organs of hearing by such vibrations.-Propagation of...
(ranging from a snap for a spark plug
Spark plug
A spark plug is an electrical device that fits into the cylinder head of some internal combustion engines and ignites compressed fuels such as aerosol, gasoline, ethanol, and liquefied petroleum gas by means of an electric spark.Spark plugs have an insulated central electrode which is connected by...
to thunder
Thunder
Thunder is the sound made by lightning. Depending on the nature of the lightning and distance of the listener, thunder can range from a sharp, loud crack to a long, low rumble . The sudden increase in pressure and temperature from lightning produces rapid expansion of the air surrounding and within...
for a lightning
Lightning
Lightning is an atmospheric electrostatic discharge accompanied by thunder, which typically occurs during thunderstorms, and sometimes during volcanic eruptions or dust storms...
discharge), light
Light
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that is visible to the human eye, and is responsible for the sense of sight. Visible light has wavelength in a range from about 380 nanometres to about 740 nm, with a frequency range of about 405 THz to 790 THz...
and heat
Heat
In physics and thermodynamics, heat is energy transferred from one body, region, or thermodynamic system to another due to thermal contact or thermal radiation when the systems are at different temperatures. It is often described as one of the fundamental processes of energy transfer between...
.
Spark gaps were used historically in early electrical equipment, such as spark gap radio transmitters
Spark-gap transmitter
A spark-gap transmitter is a device for generating radio frequency electromagnetic waves using a spark gap.These devices served as the transmitters for most wireless telegraphy systems for the first three decades of radio and the first demonstrations of practical radio were carried out using them...
, electrostatic machines, and x-ray machine
X-ray machine
An X-ray generator is a device used to generate X-rays. These devices are commonly used by radiographers to acquire an x-ray image of the inside of an object but they are also used in sterilization or fluorescence....
s. Their most widespread use today is in spark plug
Spark plug
A spark plug is an electrical device that fits into the cylinder head of some internal combustion engines and ignites compressed fuels such as aerosol, gasoline, ethanol, and liquefied petroleum gas by means of an electric spark.Spark plugs have an insulated central electrode which is connected by...
s to ignite the fuel in internal combustion engine
Internal combustion engine
The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer in a combustion chamber. In an internal combustion engine, the expansion of the high-temperature and high -pressure gases produced by combustion apply direct force to some component of the engine...
s, but they are also used in lightning arrestors and other devices to protect electrical equipment from high voltage transients.
Spark visibility
The light emitted by a spark does not come from the current of electronElectron
The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton...
s itself, but from the material medium fluorescing
Fluorescence
Fluorescence is the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation of a different wavelength. It is a form of luminescence. In most cases, emitted light has a longer wavelength, and therefore lower energy, than the absorbed radiation...
in response to collisions from the electrons. When electrons collide with molecules of air in the gap, they excite their orbital
Atomic orbital
An atomic orbital is a mathematical function that describes the wave-like behavior of either one electron or a pair of electrons in an atom. This function can be used to calculate the probability of finding any electron of an atom in any specific region around the atom's nucleus...
electrons to higher energy level
Energy level
A quantum mechanical system or particle that is bound -- that is, confined spatially—can only take on certain discrete values of energy. This contrasts with classical particles, which can have any energy. These discrete values are called energy levels...
s. When they fall back to their original energy levels, they emit the energy as light. It is impossible for a visible spark to form in a vacuum
Vacuum
In everyday usage, vacuum is a volume of space that is essentially empty of matter, such that its gaseous pressure is much less than atmospheric pressure. The word comes from the Latin term for "empty". A perfect vacuum would be one with no particles in it at all, which is impossible to achieve in...
. Without intervening matter capable of electromagnetic
Electromagnetism
Electromagnetism is one of the four fundamental interactions in nature. The other three are the strong interaction, the weak interaction and gravitation...
transitions, the spark will be invisible (see vacuum arc
Vacuum arc
A vacuum arc can arise when the surfaces of metal electrodes in contact with a good vacuum begin to emit electrons either through heating or via an electric field that is sufficient to cause field electron emission...
).
Ignition devices

Spark plug
A spark plug is an electrical device that fits into the cylinder head of some internal combustion engines and ignites compressed fuels such as aerosol, gasoline, ethanol, and liquefied petroleum gas by means of an electric spark.Spark plugs have an insulated central electrode which is connected by...
uses a spark gap to initiate combustion
Combustion
Combustion or burning is the sequence of exothermic chemical reactions between a fuel and an oxidant accompanied by the production of heat and conversion of chemical species. The release of heat can result in the production of light in the form of either glowing or a flame...
. The heat of the ionization trail ignites a fuel-air mixture inside an internal combustion engine
Internal combustion engine
The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer in a combustion chamber. In an internal combustion engine, the expansion of the high-temperature and high -pressure gases produced by combustion apply direct force to some component of the engine...
, or a burner in a furnace, oven, or stove.
Radio transmitters


.png)
.png)
Electromagnetic spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of all possible frequencies of electromagnetic radiation. The "electromagnetic spectrum" of an object is the characteristic distribution of electromagnetic radiation emitted or absorbed by that particular object....
. Nowadays, this is usually regarded as illegal radio frequency interference
Electromagnetic interference
Electromagnetic interference is disturbance that affects an electrical circuit due to either electromagnetic induction or electromagnetic radiation emitted from an external source. The disturbance may interrupt, obstruct, or otherwise degrade or limit the effective performance of the circuit...
and is suppressed, but in the early days of radio communications (1900-1920), this was the means by which radio signals were transmitted, in the unmodulated
Modulation
In electronics and telecommunications, modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a high-frequency periodic waveform, called the carrier signal, with a modulating signal which typically contains information to be transmitted...
spark-gap transmitter
Spark-gap transmitter
A spark-gap transmitter is a device for generating radio frequency electromagnetic waves using a spark gap.These devices served as the transmitters for most wireless telegraphy systems for the first three decades of radio and the first demonstrations of practical radio were carried out using them...
. Many radio spark gaps include cooling devices such as the rotary gap and heat sink
Heat sink
A heat sink is a term for a component or assembly that transfers heat generated within a solid material to a fluid medium, such as air or a liquid. Examples of heat sinks are the heat exchangers used in refrigeration and air conditioning systems and the radiator in a car...
s, since the spark gap becomes quite hot under continuous use at high power.
Spark gaps as protective devices
Spark gaps are frequently used to prevent voltage surgesVoltage spike
In electrical engineering, spikes are fast, short duration electrical transients in voltage , current , or transferred energy in an electrical circuit....
from damaging equipment. Spark gaps are used in high-voltage switch
Switch
In electronics, a switch is an electrical component that can break an electrical circuit, interrupting the current or diverting it from one conductor to another....
es, large power transformer
Transformer
A transformer is a device that transfers electrical energy from one circuit to another through inductively coupled conductors—the transformer's coils. A varying current in the first or primary winding creates a varying magnetic flux in the transformer's core and thus a varying magnetic field...
s, in power plants and electrical substation
Electrical substation
A substation is a part of an electrical generation, transmission, and distribution system. Substations transform voltage from high to low, or the reverse, or perform any of several other important functions...
s. Such switches are constructed with a large, remote-operated switching blade with a hinge as one contact and two leaf spring
Leaf spring
Originally called laminated or carriage spring, a leaf spring is a simple form of spring, commonly used for the suspension in wheeled vehicles...
s holding the other end as second contact. If the blade is opened, a spark may keep the connection between blade and spring conducting. (The spark ionizes the air, which becomes conductive, allowing an arc to form, which sustains ionization and hence conduction.) Here, a Jacob's ladder on top of the switch will pull the arc apart and so extinguish it. You might also find small Jacob's ladders mounted on top of ceramic insulators of high-voltage pylons. These are sometimes called horn gaps. If a spark should ever manage to jump over the insulator and give rise to an arc, it will be extinguished.
Smaller spark gaps are often used to protect sensitive electrical or electronic equipment from high voltage surges
Overvoltage
When the voltage in a circuit or part of it is raised above its upper design limit, this is known as overvoltage. The conditions may be hazardous...
. In sophisticated versions of these devices (called gas tube arresters), a small spark gap breaks down during an abnormal voltage surge, safely shunting the surge to ground and thereby protecting the equipment. These devices are commonly used for telephone
Telephone
The telephone , colloquially referred to as a phone, is a telecommunications device that transmits and receives sounds, usually the human voice. Telephones are a point-to-point communication system whose most basic function is to allow two people separated by large distances to talk to each other...
lines as they enter a building; the spark gaps help protect the building and internal telephone circuits from the effects of lightning
Lightning
Lightning is an atmospheric electrostatic discharge accompanied by thunder, which typically occurs during thunderstorms, and sometimes during volcanic eruptions or dust storms...
strikes. Less sophisticated (and much less expensive) spark gaps are made using modified ceramic capacitor
Ceramic capacitor
In electronics, a ceramic capacitor is a capacitor constructed of alternating layers of metal and ceramic, with the ceramic material acting as the dielectric. The temperature coefficient depends on whether the dielectric is Class 1 or Class 2...
s; in these devices, the spark gap is simply an air gap saw
Saw
A saw is a tool that uses a hard blade or wire with an abrasive edge to cut through softer materials. The cutting edge of a saw is either a serrated blade or an abrasive...
n between the two lead wires that connect the capacitor to the circuit. A voltage surge causes a spark which jumps from lead wire to lead wire across the gap left by the sawing process. These low-cost devices are often used to prevent damaging arcs between the elements of the electron gun(s) within a cathode ray tube
Cathode ray tube
The cathode ray tube is a vacuum tube containing an electron gun and a fluorescent screen used to view images. It has a means to accelerate and deflect the electron beam onto the fluorescent screen to create the images. The image may represent electrical waveforms , pictures , radar targets and...
(CRT).
Small spark gaps are very common in telephone switchboard
Telephone switchboard
A switchboard was a device used to connect a group of telephones manually to one another or to an outside connection, within and between telephone exchanges or private branch exchanges . The user was typically known as an operator...
s, as the long phone cables are very susceptible to induced surges from lightning
Lightning
Lightning is an atmospheric electrostatic discharge accompanied by thunder, which typically occurs during thunderstorms, and sometimes during volcanic eruptions or dust storms...
strikes. Larger spark gaps are used to protect power line
Electric power transmission
Electric-power transmission is the bulk transfer of electrical energy, from generating power plants to Electrical substations located near demand centers...
s.
Transils and trisil
Trisil
A Trisil is trade name for a thyristor surge protection device, an electronic component designed to protect electronic circuits against overvoltage...
s are the solid-state alternatives to spark gaps for lower-power applications. Neon bulb
Neon lamp
A neon lamp is a miniature gas discharge lamp that typically contains neon gas at a low pressure in a glass capsule. Only a thin region adjacent to the electrodes glows in these lamps, which distinguishes them from the much longer and brighter neon tubes used for signage...
s are also used for this purpose.
Sphere gap for voltage measurement
A calibrated spherical spark gap will break down at a highly repeatable voltage, when corrected for air pressure, humidity and temperature. A gap between two spheres can provide a voltage measurement without any electronics or voltage dividers, to an accuracy of about 3%. A spark gap can be used to measure high voltage AC, DC, or pulses, but for very short pulses an ultravioletUltraviolet
Ultraviolet light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays, in the range 10 nm to 400 nm, and energies from 3 eV to 124 eV...
light source or radioactive source may be put on one of the terminals to provide a source of electrons.
Power-switching devices
Special purpose, high-energy triggerable spark gaps can be used to rapidly switch high voltages and very high currents for certain pulsed power applications, such as pulsed laserLaser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of photons. The term "laser" originated as an acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation...
s, railgun
Railgun
A railgun is an entirely electrical gun that accelerates a conductive projectile along a pair of metal rails using the same principles as the homopolar motor. Railguns use two sliding or rolling contacts that permit a large electric current to pass through the projectile. This current interacts...
s, fusion
Z machine
The Z machine is the largest X-ray generator in the world and is designed to test materials in conditions of extreme temperature and pressure. Operated by Sandia National Laboratories, it gathers data to aid in computer modeling of nuclear weapons...
, ultrastrong pulsed magnetic field
Magnetic field
A magnetic field is a mathematical description of the magnetic influence of electric currents and magnetic materials. The magnetic field at any given point is specified by both a direction and a magnitude ; as such it is a vector field.Technically, a magnetic field is a pseudo vector;...
research, and in the triggering of nuclear bombs. Commercially available devices can be divided into two classes: positive pressure and triggered vacuum gaps. Positive pressure triggered gaps have a limited operating voltage range (for instance, from 1/3 to 2/3 of the self breakdown voltage). Triggered vacuum gaps offer a wide operating voltage range (400 V to 90 kV is achievable). Both classes can switch higher energy levels than any thyristor
Thyristor
A thyristor is a solid-state semiconductor device with four layers of alternating N and P-type material. They act as bistable switches, conducting when their gate receives a current trigger, and continue to conduct while they are forward biased .Some sources define silicon controlled rectifiers and...
, thyratron
Thyratron
A thyratron is a type of gas filled tube used as a high energy electrical switch and controlled rectifier. Triode, tetrode and pentode variations of the thyratron have been manufactured in the past, though most are of the triode design...
, krytron
Krytron
The krytron is a cold-cathode gas filled tube intended for use as a very high-speed switch, and was one of the earliest developments of the EG&G Corporation. It is somewhat similar to thyratron...
, or sprytron
Krytron
The krytron is a cold-cathode gas filled tube intended for use as a very high-speed switch, and was one of the earliest developments of the EG&G Corporation. It is somewhat similar to thyratron...
. Triggered gaps are popular for single shot and low repetition rate applications. One such switch is known as a trigatron
Trigatron
A trigatron is a type of triggerable spark gap switch designed for high current and high voltage, . It has very simple construction and in many cases is the lowest cost high energy switching option. It may operate in open air, it may be sealed, or it may be filled with a dielectric gas other than air...
. The Ignitron
Ignitron
An ignitron is a type of controlled rectifier dating from the 1930s. Invented by Joseph Slepian while employed by Westinghouse, Westinghouse was the original manufacturer and owned trademark rights to the name "Ignitron"....
and Crossatron
Crossatron
In electronics, a crossatron is a high-power pulsed modulator device, a cold cathode gas-filled tube that combines the best features of thyratrons, vacuum tubes, and power semiconductor switches...
could be considered triggered gaps. The latter is unique in that it can be turned back off by the control electrode after conduction begins. The xenon flash tube is another common triggered gap. Various schemes have also been devised to trigger open air gaps on command. A set of spark gaps are a key element of a Marx generator
Marx generator
A Marx generator is an electrical circuit first described by Erwin Otto Marx in 1924. Its purpose is to generate a high-voltage pulse. Marx generators are often used to simulate the effects of lightning on power line gear and aviation equipment....
, used to generate high-voltage impulses; the spark gaps allow a chain of capacitor
Capacitor
A capacitor is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store energy in an electric field. The forms of practical capacitors vary widely, but all contain at least two electrical conductors separated by a dielectric ; for example, one common construction consists of metal foils separated...
s to be slowly charged in parallel and then rapidly discharged in series.
Visual entertainment

Jacob's Ladder
Jacob's Ladder is a "ladder to heaven", described by biblical Jacob in the Book of GenesisJacob's Ladder may also refer to:* Ladder of Jacob, a pseudepigraphic text of the Old Testament...
" described in the Bible.
When high voltage is applied to the gap, a spark forms across the bottom of the wires where they are nearest each other, rapidly changing to an electric arc
Electric arc
An electric arc is an electrical breakdown of a gas which produces an ongoing plasma discharge, resulting from a current flowing through normally nonconductive media such as air. A synonym is arc discharge. An arc discharge is characterized by a lower voltage than a glow discharge, and relies on...
. Air breaks down at about 30 kV/cm, depending on humidity, temperature, etc. Apart from the anode and cathode voltage drops, the arc behaves almost as a short circuit
Short circuit
A short circuit in an electrical circuit that allows a current to travel along an unintended path, often where essentially no electrical impedance is encountered....
, drawing as much current as the electrical power supply
Power supply
A power supply is a device that supplies electrical energy to one or more electric loads. The term is most commonly applied to devices that convert one form of electrical energy to another, though it may also refer to devices that convert another form of energy to electrical energy...
can deliver, and the heavy load dramatically reduces the voltage across the gap.
The heated, ionized air rises, carrying the current path with it. As the trail of ionization gets longer, it becomes more and more unstable, finally breaking. The voltage across the electrodes then rises and the spark re-forms at the bottom of the device.
This cycle leads to an exotic-looking display of electric white
White
White is a color, the perception of which is evoked by light that stimulates all three types of color sensitive cone cells in the human eye in nearly equal amounts and with high brightness compared to the surroundings. A white visual stimulation will be void of hue and grayness.White light can be...
, yellow
Yellow
Yellow is the color evoked by light that stimulates both the L and M cone cells of the retina about equally, with no significant stimulation of the S cone cells. Light with a wavelength of 570–590 nm is yellow, as is light with a suitable mixture of red and green...
, blue
Blue
Blue is a colour, the perception of which is evoked by light having a spectrum dominated by energy with a wavelength of roughly 440–490 nm. It is considered one of the additive primary colours. On the HSV Colour Wheel, the complement of blue is yellow; that is, a colour corresponding to an equal...
or purple
Purple
Purple is a range of hues of color occurring between red and blue, and is classified as a secondary color as the colors are required to create the shade....
arcs which is often seen in films about mad scientist
Mad scientist
A mad scientist is a stock character of popular fiction, specifically science fiction. The mad scientist may be villainous or antagonistic, benign or neutral, and whether insane, eccentric, or simply bumbling, mad scientists often work with fictional technology in order to forward their schemes, if...
s. The device was a staple in schools and science fair
Science fair
A science fair is generally a competition where contestants present their science project results in the form of a report, display board, and models that they have created. Science fairs allow students in grade schools and high schools to compete in science and/or technology activities...
s of the 1950s and 1960s, typically constructed out of a Model T spark coil, or any other source of high voltage in the 10,000–30,000 volt range, like a neon sign transformer
Neon Sign Transformer
A neon-sign transformer is a transformer made for the purpose of powering a neon sign. They convert line voltage from the 120-347 V range up to high voltages, usually in the range of 2 to 15 kV. Most of these transformers generate between 30-120 mA.-Types:Older NSTs are simply iron-cored...
(5–15 kV) or a television picture tube circuit (flyback transformer
Flyback transformer
A flyback transformer , also called a line output transformer , is a special transformer, which is used for conversion of energy in electronic circuits. It was initially designed to generate high current sawtooth signals at a relatively high frequency...
) (10–28 kV), and two coat hangers or rods built into a "V" shape. For larger ladders, microwave oven
Microwave oven
A microwave oven is a kitchen appliance that heats food by dielectric heating, using microwave radiation to heat polarized molecules within the food...
transformers connected in series or utility pole transformers (pole pigs) run in reverse (step-up) are used.
Traveling-arc devices are dangerous. The sparks can burn through thin paper and plastic and start fires, and contact with the exposed high-voltage conductors can be lethal.
Health hazards
Exposure to an arc-producing device can pose health hazards. In a closed space such as a classroom or home, the continuous arc formation of an open-air Jacob's Ladder will ionize oxygen and nitrogen, which then re-form into reactive molecules such as ozoneOzone
Ozone , or trioxygen, is a triatomic molecule, consisting of three oxygen atoms. It is an allotrope of oxygen that is much less stable than the diatomic allotrope...
and nitric oxide
Nitric oxide
Nitric oxide, also known as nitrogen monoxide, is a diatomic molecule with chemical formula NO. It is a free radical and is an important intermediate in the chemical industry...
. These free radicals can be damaging to the mucous membranes of people near the spark gap. Plants are also susceptible to ozone poisoning.
These hazards are not present when the arc is formed outdoors since the heated ionized gases will rise up into the air and dissipate into the atmosphere. Spark gaps which only intermittently produce short spark bursts are also minimally hazardous because the volume of ions generated is very small.
Arcs can also produce a broad spectrum of wavelengths spanning the visible light and the invisible ultraviolet and infrared spectrum. Very intense arcs generated by means such as arc welding
Arc welding
Arc welding is a type of welding that uses a welding power supply to create an electric arc between an electrode and the base material to melt the metals at the welding point. They can use either direct or alternating current, and consumable or non-consumable electrodes...
can produce significant amounts of ultraviolet which is damaging to the retina of the observer. These arcs should only be observed through special dark filters which reduce the arc intensity and shield the observer's eyes from the ultraviolet rays.
See also
- Arc lampArc lamp"Arc lamp" or "arc light" is the general term for a class of lamps that produce light by an electric arc . The lamp consists of two electrodes, first made from carbon but typically made today of tungsten, which are separated by a gas...
- Arcing hornsArcing hornsArcing horns are projecting conductors used to protect insulators on high voltage electric power transmission systems from damage during flashover. Overvoltages on transmission lines, due to atmospheric electricity, lightning strikes, or electrical faults, can cause arcs across insulators that...
- Corona dischargeCorona dischargeIn electricity, a corona discharge is an electrical discharge brought on by the ionization of a fluid surrounding a conductor that is electrically energized...
- Electric arcElectric arcAn electric arc is an electrical breakdown of a gas which produces an ongoing plasma discharge, resulting from a current flowing through normally nonconductive media such as air. A synonym is arc discharge. An arc discharge is characterized by a lower voltage than a glow discharge, and relies on...
- Ignition systemIgnition systemAn ignition system is a system for igniting a fuel-air mixture. Ignition systems are well known in the field of internal combustion engines such as those used in petrol engines used to power the majority of motor vehicles, but they are also used in many other applications such as in oil-fired and...
- Model T Spark Coil
- List of electronics topics
- Plasma arc loudspeakers
- RadarRadarRadar is an object-detection system which uses radio waves to determine the range, altitude, direction, or speed of objects. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, weather formations, and terrain. The radar dish or antenna transmits pulses of radio...
- Spark-gap transmitterSpark-gap transmitterA spark-gap transmitter is a device for generating radio frequency electromagnetic waves using a spark gap.These devices served as the transmitters for most wireless telegraphy systems for the first three decades of radio and the first demonstrations of practical radio were carried out using them...
- Spark plugSpark plugA spark plug is an electrical device that fits into the cylinder head of some internal combustion engines and ignites compressed fuels such as aerosol, gasoline, ethanol, and liquefied petroleum gas by means of an electric spark.Spark plugs have an insulated central electrode which is connected by...
- Tesla coilTesla coilA Tesla coil is a type of resonant transformer circuit invented by Nikola Tesla around 1891. It is used to produce high voltage, low current, high frequency alternating current electricity. Tesla coils produce higher current than the other source of high voltage discharges, electrostatic machines...
- Vacuum arcVacuum arcA vacuum arc can arise when the surfaces of metal electrodes in contact with a good vacuum begin to emit electrons either through heating or via an electric field that is sufficient to cause field electron emission...
External links
- Jacob's Ladder videos: Transformer in Nevada In someone's home

