
Van der Waals radius
Encyclopedia
| Element | radius (Å Ångström The angstrom or ångström, is a unit of length equal to 1/10,000,000,000 of a meter . Its symbol is the Swedish letter Å.... ) |
|---|---|
| Hydrogen Hydrogen Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly... |
1.20 |
| Carbon Carbon Carbon is the chemical element with symbol C and atomic number 6. As a member of group 14 on the periodic table, it is nonmetallic and tetravalent—making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds... |
1.70 |
| Nitrogen Nitrogen Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere... |
1.55 |
| Oxygen Oxygen Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition... |
1.52 |
| Fluorine Fluorine Fluorine is the chemical element with atomic number 9, represented by the symbol F. It is the lightest element of the halogen column of the periodic table and has a single stable isotope, fluorine-19. At standard pressure and temperature, fluorine is a pale yellow gas composed of diatomic... |
1.47 |
| Phosphorus Phosphorus Phosphorus is the chemical element that has the symbol P and atomic number 15. A multivalent nonmetal of the nitrogen group, phosphorus as a mineral is almost always present in its maximally oxidized state, as inorganic phosphate rocks... |
1.80 |
| Sulfur Sulfur Sulfur or sulphur is the chemical element with atomic number 16. In the periodic table it is represented by the symbol S. It is an abundant, multivalent non-metal. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow... |
1.80 |
| Chlorine Chlorine Chlorine is the chemical element with atomic number 17 and symbol Cl. It is the second lightest halogen, found in the periodic table in group 17. The element forms diatomic molecules under standard conditions, called dichlorine... |
1.75 |
| Copper Copper Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29. It is a ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. Pure copper is soft and malleable; an exposed surface has a reddish-orange tarnish... |
1.4 |
| Van der Waals radii taken from Bondi's compilation (1964). Values from other sources may differ significantly (see text) |
|
The van der Waals radius, r, of an atom
Atom
The atom is a basic unit of matter that consists of a dense central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The atomic nucleus contains a mix of positively charged protons and electrically neutral neutrons...
is the radius of an imaginary hard sphere
Sphere
A sphere is a perfectly round geometrical object in three-dimensional space, such as the shape of a round ball. Like a circle in two dimensions, a perfect sphere is completely symmetrical around its center, with all points on the surface lying the same distance r from the center point...
which can be used to model the atom for many purposes. It is named after Johannes Diderik van der Waals
Johannes Diderik van der Waals
Johannes Diderik van der Waals was a Dutch theoretical physicist and thermodynamicist famous for his work on an equation of state for gases and liquids....
, winner of the 1910 Nobel Prize in Physics
Nobel Prize in Physics
The Nobel Prize in Physics is awarded once a year by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences. It is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the will of Alfred Nobel in 1895 and awarded since 1901; the others are the Nobel Prize in Chemistry, Nobel Prize in Literature, Nobel Peace Prize, and...
, as he was the first to recognise that atoms had a finite size (i.e., that atoms were not simply points
Point (geometry)
In geometry, topology and related branches of mathematics a spatial point is a primitive notion upon which other concepts may be defined. In geometry, points are zero-dimensional; i.e., they do not have volume, area, length, or any other higher-dimensional analogue. In branches of mathematics...
) and to demonstrate the physical consequences of their size through the van der Waals equation of state
Van der Waals equation
The van der Waals equation is an equation of state for a fluid composed of particles that have a non-zero volume and a pairwise attractive inter-particle force It was derived by Johannes Diderik van der Waals in 1873, who received the Nobel prize in 1910 for "his work on the equation of state for...
.
Van der Waals volume
The van der Waals volume, V, also called the atomic volume or molecular volume, is the atomic property most directly related to the van der Waals radius. It is the volume "occupied" by an individual atom (or molecule). The van der Waals volume may be calculated if the van der Waals radii (and, for molecules, the inter-atomic distances and angles) are known. For a spherical single atom, it is the volume of a sphere whose radius is the van der Waals radius of the atom: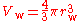 .
.For a molecule, it is the volume enclosed by the van der Waals surface
Van der Waals surface
Van der Waals surface area , also van der Waals surface or van der Waals envelope is the imaginary surface of the union of spherical atom surfaces defined by the so-called van der Waals radius of each atom in the molecule representation...
. The van der Waals volume of a molecule is always smaller than the sum of the van der Waals volumes of the constituent atoms: the atoms can be said to "overlap" when they form chemical bond
Chemical bond
A chemical bond is an attraction between atoms that allows the formation of chemical substances that contain two or more atoms. The bond is caused by the electromagnetic force attraction between opposite charges, either between electrons and nuclei, or as the result of a dipole attraction...
s.
The van der Waals volume of an atom or molecule may also be determined by experimental measurements on gases, notably from the van der Waals constant b, the polarizability
Polarizability
Polarizability is the measure of the change in a molecule's electron distribution in response to an applied electric field, which can also be induced by electric interactions with solvents or ionic reagents. It is a property of matter...
α or the molar refractivity A. In all three cases, measurements are made on macroscopic samples and it is normal to express the results as molar
Mole (unit)
The mole is a unit of measurement used in chemistry to express amounts of a chemical substance, defined as an amount of a substance that contains as many elementary entities as there are atoms in 12 grams of pure carbon-12 , the isotope of carbon with atomic weight 12. This corresponds to a value...
quantities. To find the van der Waals volume of a single atom or molecule, it is necessary to divide by the Avogadro constant N.
The molar van der Waals volume should not be confused with the molar volume
Molar volume
The molar volume, symbol Vm, is the volume occupied by one mole of a substance at a given temperature and pressure. It is equal to the molar mass divided by the mass density...
of the substance. In general, at normal laboratory temperatures and pressures, the atoms or molecules of a gas only occupy about 1/1000 of the volume of the gas, the rest being empty space. Hence the molar van der Waals volume, which only counts the volume occupied by the atoms or molecules, is usually about 1000 times smaller than the molar volume for a gas at standard temperature and pressure.
Methods of determination
Van der Waals radii may be determined from the mechanicalMechanics
Mechanics is the branch of physics concerned with the behavior of physical bodies when subjected to forces or displacements, and the subsequent effects of the bodies on their environment....
properties of gases (the original method), from the critical point
Critical point (thermodynamics)
In physical chemistry, thermodynamics, chemistry and condensed matter physics, a critical point, also called a critical state, specifies the conditions at which a phase boundary ceases to exist...
, from measurements of atomic spacing between pairs of unbonded atoms in crystal
Crystal
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituent atoms, molecules, or ions are arranged in an orderly repeating pattern extending in all three spatial dimensions. The scientific study of crystals and crystal formation is known as crystallography...
s or from measurements of electrical or optical properties (the polarizability
Polarizability
Polarizability is the measure of the change in a molecule's electron distribution in response to an applied electric field, which can also be induced by electric interactions with solvents or ionic reagents. It is a property of matter...
and the molar refractivity). These various methods give values for the van der Waals radius which are similar (1–2 Å
Ångström
The angstrom or ångström, is a unit of length equal to 1/10,000,000,000 of a meter . Its symbol is the Swedish letter Å....
, 100–200 pm
Picometre
A picometre is a unit of length in the metric system, equal to one trillionth, i.e. of a metre, which is the current SI base unit of length...
) but not identical. Tabulated values of van der Waals radii are obtained by taking a weighted mean
Weighted mean
The weighted mean is similar to an arithmetic mean , where instead of each of the data points contributing equally to the final average, some data points contribute more than others...
of a number of different experimental values, and, for this reason, different tables will often have different values for the van der Waals radius of the same atom. Indeed, there is no reason to assume that the van der Waals radius is a fixed property of the atom in all circumstances: rather, it tends to vary with the particular chemical environment of the atom in any given case.
Van der Waals equation of state
The van der Waals equation of state is the simplest and best-known modification of the ideal gas lawIdeal gas law
The ideal gas law is the equation of state of a hypothetical ideal gas. It is a good approximation to the behavior of many gases under many conditions, although it has several limitations. It was first stated by Émile Clapeyron in 1834 as a combination of Boyle's law and Charles's law...
to account for the behaviour of real gas
Real gas
Real gases – as opposed to a perfect or ideal gas – exhibit properties that cannot be explained entirely using the ideal gas law. To understand the behaviour of real gases, the following must be taken into account:* compressibility effects;...
es:
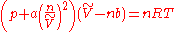 ,
,where n is the amount of substance
Amount of substance
Amount of substance is a standards-defined quantity that measures the size of an ensemble of elementary entities, such as atoms, molecules, electrons, and other particles. It is sometimes referred to as chemical amount. The International System of Units defines the amount of substance to be...
of the gas in question and a and b are adjustable parameters; a is a correction for intermolecular forces and b corrects for finite atomic or molecular sizes; the value of b equals the volume of one mole of the atoms or molecules.
Their values
Van der Waals constants (data page)
The following table lists the van der Waals constants for a number of common gases and volatile liquids.Units:Source: Weast. R. C. , Handbook of Chemistry and Physics , Cleveland:Chemical Rubber Co., 1972....
vary from gas to gas.
The van der Waals equation also has a microscopic interpretation: molecules interact with one another. The interaction is strongly repulsive at very short distance, becomes mildly attractive at intermediate range, and vanishes at long distance. The ideal gas law must be corrected when attractive and repulsive forces are considered. For example, the mutual repulsion between molecules has the effect of excluding neighbors from a certain amount of space around each molecule. Thus, a fraction of the total space becomes unavailable to each molecule as it executes random motion. In the equation of state, this volume of exclusion (nb) should be subtracted from the volume of the container (V), thus: (V - nb). The other term that is introduced in the van der Waals equation,
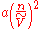 , describes a weak attractive force among molecules (known as the van der Waals force
, describes a weak attractive force among molecules (known as the van der Waals forceVan der Waals force
In physical chemistry, the van der Waals force , named after Dutch scientist Johannes Diderik van der Waals, is the sum of the attractive or repulsive forces between molecules other than those due to covalent bonds or to the electrostatic interaction of ions with one another or with neutral...
), which increases when n increases or V decreases and molecules become more crowded together.
| Gas | d/Å | b/cmmol | V/Å | r/Å |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen Hydrogen Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly... |
0.74611 | 26.61 | 37.54 | 1.91 |
| Nitrogen Nitrogen Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere... |
1.0975 | 39.13 | 64.98 | 2.25 |
| Oxygen Oxygen Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition... |
1.208 | 31.83 | 52.86 | 2.06 |
| Chlorine Chlorine Chlorine is the chemical element with atomic number 17 and symbol Cl. It is the second lightest halogen, found in the periodic table in group 17. The element forms diatomic molecules under standard conditions, called dichlorine... |
1.988 | 56.22 | 93.36 | 2.39 |
| Van der Waals radii calculated from the van der Waals constants of some diatomic gases. Values of d and b from Weast (1981). |
||||
The van der Waals constant b volume can be used to calculate the van der Waals volume of an atom or molecule with experimental data derived from measurements on gases.
For helium
Helium
Helium is the chemical element with atomic number 2 and an atomic weight of 4.002602, which is represented by the symbol He. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas that heads the noble gas group in the periodic table...
, b = 23.7 cm/mol. Helium is a monoatomic gas, and each mole of helium contains 6.022×10 atoms (the Avogadro constant, N):
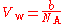
Therefore the van der Waals volume of a single atom V = 39.36 Å, which corresponds to r = 2.11 Å. This method may be extended to diatomic gases by approximating the molecule as a rod with rounded ends where the diameter is 2r and the internuclear distance is d. The algebra is more complicated, but the relation
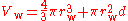
can be solved by the normal methods for cubic functions.
Crystallographic measurements
The molecules in a molecular crystal are held together by van der Waals forceVan der Waals force
In physical chemistry, the van der Waals force , named after Dutch scientist Johannes Diderik van der Waals, is the sum of the attractive or repulsive forces between molecules other than those due to covalent bonds or to the electrostatic interaction of ions with one another or with neutral...
s rather than chemical bond
Chemical bond
A chemical bond is an attraction between atoms that allows the formation of chemical substances that contain two or more atoms. The bond is caused by the electromagnetic force attraction between opposite charges, either between electrons and nuclei, or as the result of a dipole attraction...
s. In principle, the closest that two atoms belonging to different molecules can approach one another is given by the sum of their van der Waals radii. By examining a large number of structures of molecular crystals, it is possible to find a minimum radius for each type of atom such that other non-bonded atoms do not encroach any closer. This approach was first used by Linus Pauling
Linus Pauling
Linus Carl Pauling was an American chemist, biochemist, peace activist, author, and educator. He was one of the most influential chemists in history and ranks among the most important scientists of the 20th century...
in his seminal work The Nature of the Chemical Bond. Bondi also conducted a study of this type, published in 1964, although he also considered other methods of determining the van der Waals radius in coming to his final estimates. Some of Bondi's figures are given in the table at the top of this article, and they remain the most widely used "consensus" values for the van der Waals radii of the elements. Rowland and Taylor re-examined these 1964 figures in the light of more recent crystallographic data: on the whole, the agreement was very good, although they recommend a value of 1.09 Å for the van der Waals radius of hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
as opposed to Bondi's 1.20 Å.
A simple example of the use of crystallographic data (here neutron diffraction
Neutron diffraction
Neutron diffraction or elastic neutron scattering is the application of neutron scattering to the determination of the atomic and/or magnetic structure of a material: A sample to be examined is placed in a beam of thermal or cold neutrons to obtain a diffraction pattern that provides information of...
) is to consider the case of solid helium, where the atoms are held together only by van der Waals forces (rather than by covalent
Covalent bond
A covalent bond is a form of chemical bonding that is characterized by the sharing of pairs of electrons between atoms. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms when they share electrons is known as covalent bonding....
or metallic bond
Metallic bond
Metallic bonding is the electrostatic attractive forces between the delocalized electrons, called conduction electrons, gathered in an "electron sea", and the positively charged metal ions...
s) and so the distance between the nuclei can be considered to be equal to twice the van der Waals radius. The density of solid helium at 1.1 K and 66 atm
Atmosphere (unit)
The standard atmosphere is an international reference pressure defined as 101325 Pa and formerly used as unit of pressure. For practical purposes it has been replaced by the bar which is 105 Pa...
is 0.214(6) g/cm, corresponding to a molar volume
Molar volume
The molar volume, symbol Vm, is the volume occupied by one mole of a substance at a given temperature and pressure. It is equal to the molar mass divided by the mass density...
V = 18.7×10 m/mol. The van der Waals volume is given by
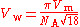
where the factor of π/√18 arises from the packing of spheres
Sphere packing
In geometry, a sphere packing is an arrangement of non-overlapping spheres within a containing space. The spheres considered are usually all of identical size, and the space is usually three-dimensional Euclidean space...
: V = 2.30×10 m = 23.0 Å, corresponding to a van der Waals radius r = 1.76 Å.
Molar refractivity
The molar refractivity A of a gas is related to its refractive indexRefractive index
In optics the refractive index or index of refraction of a substance or medium is a measure of the speed of light in that medium. It is expressed as a ratio of the speed of light in vacuum relative to that in the considered medium....
n by the Lorentz–Lorenz equation:
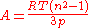
The refractive index of helium n = 1.000 0350 at 0 °C and 101.325 kPa, which corresponds to a molar refractivity A = 5.23×10 m/mol. Dividing by the Avogadro constant gives V = 8.685×10 m = 0.8685 Å, corresponding to r = 0.59 Å.
Polarizability
The polarizabilityPolarizability
Polarizability is the measure of the change in a molecule's electron distribution in response to an applied electric field, which can also be induced by electric interactions with solvents or ionic reagents. It is a property of matter...
α of a gas is related to its electric susceptibility
Electric susceptibility
In electromagnetism, the electric susceptibility \chi_e is a dimensionless proportionality constant that indicates the degree of polarization of a dielectric material in response to an applied electric field...
χ by the relation
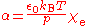
and the electric susceptibility may be calculated from tabulated values of the relative permittivity
Permittivity
In electromagnetism, absolute permittivity is the measure of the resistance that is encountered when forming an electric field in a medium. In other words, permittivity is a measure of how an electric field affects, and is affected by, a dielectric medium. The permittivity of a medium describes how...
ε using the relation χ = ε–1. The electric susceptibility of helium χ = 7×10 at 0 °C and 101.325 kPa, which corresponds to a polarizability α = 2.307×10 Cm/V. The polarizability is related the van der Waals volume by the relation
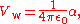
so the van der Waals volume of helium V = 2.073×10 m = 0.2073 Å by this method, corresponding to r = 0.37 Å.
When the atomic polarizability is quoted in units of volume such as Å, as is often the case, it is equal to the van der Waals volume. However, the term "atomic polarizability" is preferred as polarizability is a precisely defined (and measurable) physical quantity
Physical quantity
A physical quantity is a physical property of a phenomenon, body, or substance, that can be quantified by measurement.-Definition of a physical quantity:Formally, the International Vocabulary of Metrology, 3rd edition defines quantity as:...
, whereas "van der Waals volume" can have any number of definitions depending on the method of measurement.
External links
- Van Der Waals Radius of the elements at PeriodicTable.com
- Van der Waals Radius – Periodicity at WebElements.com
- Elemental Radii from the Cambridge Structural DatabaseCambridge Structural DatabaseThe Cambridge Structural Database , is a repository for small molecule crystal structures. Scientists use single-crystal x-ray crystallography to determine the crystal structure of a compound. Once the structure is solved, information about the structure is saved in a file and deposited in the CSD...

