
Veterinary school
Encyclopedia

Tertiary education
Tertiary education, also referred to as third stage, third level, and post-secondary education, is the educational level following the completion of a school providing a secondary education, such as a high school, secondary school, university-preparatory school...
al institution, or part of such an institution, which is involved in the education of veterinarian
Veterinarian
A veterinary physician, colloquially called a vet, shortened from veterinarian or veterinary surgeon , is a professional who treats disease, disorder and injury in animals....
s. To become a veterinarian one must first complete a veterinary degree (i.e.: DVM, VMD, BVS, BVSc, BVMS, BVM, BVS, etc.)
A veterinary school should not be confused with a department of animal science. A department of animal science usually offers a pre-veterinary school curriculum, teaches the biomedical sciences
Biomedical research
Biomedical research , in general simply known as medical research, is the basic research, applied research, or translational research conducted to aid and support the body of knowledge in the field of medicine...
(usually resulting in a Bachelor of Science
Bachelor of Science
A Bachelor of Science is an undergraduate academic degree awarded for completed courses that generally last three to five years .-Australia:In Australia, the BSc is a 3 year degree, offered from 1st year on...
degree or the equivalent), and provides graduate veterinary education in disciplines such as microbiology
Microbiology
Microbiology is the study of microorganisms, which are defined as any microscopic organism that comprises either a single cell , cell clusters or no cell at all . This includes eukaryotes, such as fungi and protists, and prokaryotes...
, virology
Virology
Virology is the study of viruses and virus-like agents: their structure, classification and evolution, their ways to infect and exploit cells for virus reproduction, the diseases they cause, the techniques to isolate and culture them, and their use in research and therapy...
, and molecular biology
Molecular biology
Molecular biology is the branch of biology that deals with the molecular basis of biological activity. This field overlaps with other areas of biology and chemistry, particularly genetics and biochemistry...
. The terminology can be confusing, as many veterinary schools outside North America use the title "Faculty of Veterinary Science" rather than "college of veterinary medicine" or "school of veterinary medicine," and some veterinary schools (particularly those in China
China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
, Japan
Japan
Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south...
and South Korea
South Korea
The Republic of Korea , , is a sovereign state in East Asia, located on the southern portion of the Korean Peninsula. It is neighbored by the People's Republic of China to the west, Japan to the east, North Korea to the north, and the East China Sea and Republic of China to the south...
) use the term "department" rather than college or school.
Degrees

Bangladesh
Bangladesh , officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh is a sovereign state located in South Asia. It is bordered by India on all sides except for a small border with Burma to the far southeast and by the Bay of Bengal to the south...
, Canada
Canada
Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
, Ethiopia
Ethiopia
Ethiopia , officially known as the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a country located in the Horn of Africa. It is the second-most populous nation in Africa, with over 82 million inhabitants, and the tenth-largest by area, occupying 1,100,000 km2...
, Hungary
Hungary
Hungary , officially the Republic of Hungary , is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is situated in the Carpathian Basin and is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine and Romania to the east, Serbia and Croatia to the south, Slovenia to the southwest and Austria to the west. The...
, Iran
Iran
Iran , officially the Islamic Republic of Iran , is a country in Southern and Western Asia. The name "Iran" has been in use natively since the Sassanian era and came into use internationally in 1935, before which the country was known to the Western world as Persia...
, Malaysia, Nigeria
Nigeria
Nigeria , officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a federal constitutional republic comprising 36 states and its Federal Capital Territory, Abuja. The country is located in West Africa and shares land borders with the Republic of Benin in the west, Chad and Cameroon in the east, and Niger in...
, Pakistan
Pakistan
Pakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan...
, Philippines
Philippines
The Philippines , officially known as the Republic of the Philippines , is a country in Southeast Asia in the western Pacific Ocean. To its north across the Luzon Strait lies Taiwan. West across the South China Sea sits Vietnam...
, South Korea
South Korea
The Republic of Korea , , is a sovereign state in East Asia, located on the southern portion of the Korean Peninsula. It is neighbored by the People's Republic of China to the west, Japan to the east, North Korea to the north, and the East China Sea and Republic of China to the south...
, Thailand
Thailand
Thailand , officially the Kingdom of Thailand , formerly known as Siam , is a country located at the centre of the Indochina peninsula and Southeast Asia. It is bordered to the north by Burma and Laos, to the east by Laos and Cambodia, to the south by the Gulf of Thailand and Malaysia, and to the...
, Tobago
Tobago
Tobago is the smaller of the two main islands that make up the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago. It is located in the southern Caribbean, northeast of the island of Trinidad and southeast of Grenada. The island lies outside the hurricane belt...
and Trinidad
Trinidad
Trinidad is the larger and more populous of the two major islands and numerous landforms which make up the island nation of Trinidad and Tobago. It is the southernmost island in the Caribbean and lies just off the northeastern coast of Venezuela. With an area of it is also the fifth largest in...
. Many countries offer a degree equivalent to the North American DVM. In the United Kingdom
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
, and in many countries which have adopted the undergraduate system of higher education in which a bachelor's degree is equivalent to a DVM (albeit after five or six years of study, not four), an appropriate degree is conferred ( Bachelor of Veterinary Science
Bachelor of Veterinary Science
The Bachelor of Veterinary Science or "Bachelor of Veterinary Medicine" is a bachelor's degree for studies in veterinary science in the United Kingdom and some other countries. In the US, these degrees are equivalent to DVM/VMD degrees...
, Bachelor of Veterinary Medicine, Bachelor of Veterinary Medicine and Surgery etc.). In Ireland
Ireland
Ireland is an island to the northwest of continental Europe. It is the third-largest island in Europe and the twentieth-largest island on Earth...
, the Veterinary Medicine Programme at the University College Dublin
University College Dublin
University College Dublin ) - formally known as University College Dublin - National University of Ireland, Dublin is the Republic of Ireland's largest, and Ireland's second largest, university, with over 1,300 faculty and 17,000 students...
awards the Bachelor of Veterinary Medicine (MVB) At the University of Edinburgh
University of Edinburgh
The University of Edinburgh, founded in 1583, is a public research university located in Edinburgh, the capital of Scotland, and a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The university is deeply embedded in the fabric of the city, with many of the buildings in the historic Old Town belonging to the university...
, the degree is the Bachelor's of Veterinary Medicine & Surgery (BVM&S). Some veterinary schools, however, offer a degree which enables the recipient to practice veterinary medicine in the home country but which does not permit the individual to even sit for a licensure exam in another nation. For example, veterinary schools in Afghanistan
Afghanistan
Afghanistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located in the centre of Asia, forming South Asia, Central Asia and the Middle East. With a population of about 29 million, it has an area of , making it the 42nd most populous and 41st largest nation in the world...
only offer the Bachelor of Science (BS) degree. Ethiopia
Ethiopia
Ethiopia , officially known as the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a country located in the Horn of Africa. It is the second-most populous nation in Africa, with over 82 million inhabitants, and the tenth-largest by area, occupying 1,100,000 km2...
awards the Doctor of Veterinary Medicine degree, but the degree is not recognized in the US or Western Europe due to the low quality of education provided by Ethiopian veterinary schools.
About 50% of Veterinarians own their own business as soon as they graduate from school. Nearly every country in the world requires an individual with a veterinary degree to be licensed
Licensure
Licensure refers to the granting of a license, which gives a "permission to practice." Such licenses are usually issued in order to regulate some activity that is deemed to be dangerous or a threat to the person or the public or which involves a high level of specialized skill...
prior to practicing in the profession. Most countries require a non-national who holds a veterinary degree to pass a separate licensure exam for foreign graduates prior to practicing veterinary medicine. In the US, for example, the Educational Commission for Foreign Veterinary Graduates (ECFVG) administers a four-step examination which is accepted by all American state and territorial veterinary licensing boards, the US federal government, and the District of Columbia. In Europe, the European Parliament
European Parliament
The European Parliament is the directly elected parliamentary institution of the European Union . Together with the Council of the European Union and the Commission, it exercises the legislative function of the EU and it has been described as one of the most powerful legislatures in the world...
, which has some jurisdiction over the member states of the European Union
European Union
The European Union is an economic and political union of 27 independent member states which are located primarily in Europe. The EU traces its origins from the European Coal and Steel Community and the European Economic Community , formed by six countries in 1958...
(EU), issued a directive on September 30, 2005, which provides for EU-wide standards for veterinary medical education and mutual recognition of veterinary degrees between member states meeting these standards. Licensure requirements are diverse, however. In South Africa
South Africa
The Republic of South Africa is a country in southern Africa. Located at the southern tip of Africa, it is divided into nine provinces, with of coastline on the Atlantic and Indian oceans...
, the Veterinary and Para-Veterinary Professions Act, Act 19 of 1982 provides for automatic licensure if an individual has graduated from one of several universities in South Africa, New Zealand, or the United Kingdom (as of 2008, these include the University of Pretoria
University of Pretoria
The University of Pretoria is a multi campus public research university located in Pretoria, the administrative and de facto capital of South Africa...
, Medical University of South Africa, Massey University
Massey University
Massey University is one of New Zealand's largest universities with approximately 36,000 students, 20,000 of whom are extramural students.The University has campuses in Palmerston North , Wellington and Auckland . Massey offers most of its degrees extramurally within New Zealand and internationally...
, University of Bristol
University of Bristol
The University of Bristol is a public research university located in Bristol, United Kingdom. One of the so-called "red brick" universities, it received its Royal Charter in 1909, although its predecessor institution, University College, Bristol, had been in existence since 1876.The University is...
, University of Cambridge
University of Cambridge
The University of Cambridge is a public research university located in Cambridge, United Kingdom. It is the second-oldest university in both the United Kingdom and the English-speaking world , and the seventh-oldest globally...
, University of Edinburgh
University of Edinburgh
The University of Edinburgh, founded in 1583, is a public research university located in Edinburgh, the capital of Scotland, and a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The university is deeply embedded in the fabric of the city, with many of the buildings in the historic Old Town belonging to the university...
, University of Glasgow
University of Glasgow
The University of Glasgow is the fourth-oldest university in the English-speaking world and one of Scotland's four ancient universities. Located in Glasgow, the university was founded in 1451 and is presently one of seventeen British higher education institutions ranked amongst the top 100 of the...
, University of Liverpool
University of Liverpool
The University of Liverpool is a teaching and research university in the city of Liverpool, England. It is a member of the Russell Group of large research-intensive universities and the N8 Group for research collaboration. Founded in 1881 , it is also one of the six original "red brick" civic...
, and the University of London
University of London
-20th century:Shortly after 6 Burlington Gardens was vacated, the University went through a period of rapid expansion. Bedford College, Royal Holloway and the London School of Economics all joined in 1900, Regent's Park College, which had affiliated in 1841 became an official divinity school of the...
) or has passed the veterinary licensure examination administered by the Royal College of Veterinary Surgeons
Royal College of Veterinary Surgeons
The Royal College of Veterinary Surgeons is the regulatory body for veterinary surgeons in the United Kingdom. Established in 1844 by Royal Charter, its statutory duties are laid out in the 1966 Veterinary Surgeons Act.-Role:...
. All other persons are required to pass an examination and register with the South African Veterinary Council. India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
has a similar system in which degrees awarded by certain schools are "deemed" to automatically qualify an individual to practice veterinary medicine, but has forgone an exam in favor of state tribunals which investigate credentials and can add a veterinarian to the register of licensed practitioners.
Accreditation
Not all nations accredit veterinary schools, but all developed countriesDeveloped country
A developed country is a country that has a high level of development according to some criteria. Which criteria, and which countries are classified as being developed, is a contentious issue...
and most newly industrialized and developing countries
Developing country
A developing country, also known as a less-developed country, is a nation with a low level of material well-being. Since no single definition of the term developing country is recognized internationally, the levels of development may vary widely within so-called developing countries...
do. Few failed state
Failed state
The term failed state is often used by political commentators and journalists to describe a state perceived as having failed at some of the basic conditions and responsibilities of a sovereign government...
s have any accreditation system, however. In the United States, the American Veterinary Medical Association
American Veterinary Medical Association
The American Veterinary Medical Association , founded in 1863, is a not-for-profit association representing more than 81,500 U.S. veterinarians working in private and corporate practice, government, industry, academia, and uniformed services....
(AVMA) Council on Education (COE) accredits veterinary schools. Accreditation systems and standards vary widely, however, Australia
Australia
Australia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area...
, New Zealand
New Zealand
New Zealand is an island country in the south-western Pacific Ocean comprising two main landmasses and numerous smaller islands. The country is situated some east of Australia across the Tasman Sea, and roughly south of the Pacific island nations of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga...
and the United Kingdom
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
all have vet programs that hold similar standards as those in the United States and Canada. The European Union is developing a common accreditation standard, but as of 2008 accreditation was most often provided by the European Association of Establishments for Veterinary Education (EAEVE).
Accreditation systems vary widely in developing nations. In Mexico, El Consejo Nacional de Educación de la Medicina Veterinaria y Zootecnia (CONEVET) accredits veterinary medical colleges, although few schools are accredited. The accreditation system is poor or nonexistent in other developing nations. Ethiopia, for example, has focused on building veterinary medical colleges rather than accrediting existing schools to ensure quality. Subsequently, there is almost no accreditation system and the quality of veterinary education in the country is poor.
Admissions and costs
Veterinary Medical College Application Service
The Veterinary Medical College Application Service is a centralized application service for students applying to veterinary school...
(VMCAS). Many colleges belonging to VMCAS have additional, individualized application requirements as well, and admissions standards are quite high. Admissions standards in Europe, South America, Asia, and Africa also vary widely. Many veterinary schools limit admission to students from their area, state or country. For example, 25 of the 28 veterinary schools in the US are public universities, and by law may set aside relatively few places for out-of-state residents. Other countries have similar schemes. For example, in India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
, federal law requires that each veterinary college set aside 15 percent of its places for students coming from other parts of India. The Veterinary Council of India (a body of the federal government), conducts the All India Common Entrance Examination, and the top scorers on the exam are placed throughout India.
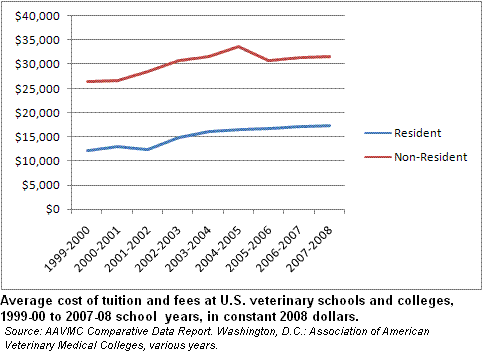
United States dollar
The United States dollar , also referred to as the American dollar, is the official currency of the United States of America. It is divided into 100 smaller units called cents or pennies....
15,676 for residents in the 2006-2007 school year, and $28,861 a year for non-residents. Average cost during the same period of fees was $3,482 (residents) and $4,452 (non-residents), room and board $8,964 (residents and non-residents), and books and equipment $2,043 (residents and non-residents). In Canada during the same time period, average resident tuition was C$
Canadian dollar
The Canadian dollar is the currency of Canada. As of 2007, the Canadian dollar is the 7th most traded currency in the world. It is abbreviated with the dollar sign $, or C$ to distinguish it from other dollar-denominated currencies...
5,651 and average non-resident tuition $32,942. Resident and non-resident fees were C$719, resident and non-resident room and board C$6,493, and resident and non-resident books and equipment C$1,712.
Curriculum

Anatomy
Anatomy is a branch of biology and medicine that is the consideration of the structure of living things. It is a general term that includes human anatomy, animal anatomy , and plant anatomy...
, physiology
Physiology
Physiology is the science of the function of living systems. This includes how organisms, organ systems, organs, cells, and bio-molecules carry out the chemical or physical functions that exist in a living system. The highest honor awarded in physiology is the Nobel Prize in Physiology or...
, histology
Histology
Histology is the study of the microscopic anatomy of cells and tissues of plants and animals. It is performed by examining cells and tissues commonly by sectioning and staining; followed by examination under a light microscope or electron microscope...
, neuroanatomy
Neuroanatomy
Neuroanatomy is the study of the anatomy and organization of the nervous system. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defined nervous systems, and thus we can begin to speak of...
, pharmacology
Pharmacology
Pharmacology is the branch of medicine and biology concerned with the study of drug action. More specifically, it is the study of the interactions that occur between a living organism and chemicals that affect normal or abnormal biochemical function...
, immunology
Immunology
Immunology is a broad branch of biomedical science that covers the study of all aspects of the immune system in all organisms. It deals with the physiological functioning of the immune system in states of both health and diseases; malfunctions of the immune system in immunological disorders ; the...
, bacteriology
Bacteriology
Bacteriology is the study of bacteria. This subdivision of microbiology involves the identification, classification, and characterization of bacterial species...
, virology
Virology
Virology is the study of viruses and virus-like agents: their structure, classification and evolution, their ways to infect and exploit cells for virus reproduction, the diseases they cause, the techniques to isolate and culture them, and their use in research and therapy...
, pathology
Pathology
Pathology is the precise study and diagnosis of disease. The word pathology is from Ancient Greek , pathos, "feeling, suffering"; and , -logia, "the study of". Pathologization, to pathologize, refers to the process of defining a condition or behavior as pathological, e.g. pathological gambling....
, parasitology
Parasitology
Parasitology is the study of parasites, their hosts, and the relationship between them. As a biological discipline, the scope of parasitology is not determined by the organism or environment in question, but by their way of life...
, toxicology
Toxicology
Toxicology is a branch of biology, chemistry, and medicine concerned with the study of the adverse effects of chemicals on living organisms...
) in the classroom, as well as other basic courses such as herd health (also called population health
Population health
Population health has been defined as “the health outcomes of a group of individuals, including the distribution of such outcomes within the group.” It is an approach to health that aims to improve the health of an entire population. One major step in achieving this aim is to reduce health...
), nutrition
Nutrition
Nutrition is the provision, to cells and organisms, of the materials necessary to support life. Many common health problems can be prevented or alleviated with a healthy diet....
, radiography
Radiography
Radiography is the use of X-rays to view a non-uniformly composed material such as the human body. By using the physical properties of the ray an image can be developed which displays areas of different density and composition....
, and epidemiology
Epidemiology
Epidemiology is the study of health-event, health-characteristic, or health-determinant patterns in a population. It is the cornerstone method of public health research, and helps inform policy decisions and evidence-based medicine by identifying risk factors for disease and targets for preventive...
. During the third year, students are exposed to clinical topics like anesthesiology, diagnostics, surgery
Surgery
Surgery is an ancient medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a patient to investigate and/or treat a pathological condition such as disease or injury, or to help improve bodily function or appearance.An act of performing surgery may be called a surgical...
, ophthalmology
Ophthalmology
Ophthalmology is the branch of medicine that deals with the anatomy, physiology and diseases of the eye. An ophthalmologist is a specialist in medical and surgical eye problems...
, orthopedics
Orthopedics
Orthopedics is the study of the musculoskeletal system. The Greek word 'ortho' means straight or correct and 'pedics' comes from the Greek 'pais' meaning children. For many centuries, orthopedists have been involved in the treatment of crippled children...
, and dentistry
Dentistry
Dentistry is the branch of medicine that is involved in the study, diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of diseases, disorders and conditions of the oral cavity, maxillofacial area and the adjacent and associated structures and their impact on the human body. Dentistry is widely considered...
. The fourth year is often 12 (not nine) months long, during which students work in a clinical setting delivering care to a wide range of animals. A focus on clinical education is an aspect of most veterinary school curricula worldwide. In 2005, for the first time in its 104-year-history, the Veterinary Medicine Programme at the University College Dublin instituted a lecture-free final year focusing on clinical training. The Institute of Veterinary Pathology at the University of Zurich
University of Zurich
The University of Zurich , located in the city of Zurich, is the largest university in Switzerland, with over 25,000 students. It was founded in 1833 from the existing colleges of theology, law, medicine and a new faculty of philosophy....
recently developed and implemented a new curriculum for teaching pathology which includes an extensive clinical component. Veterinary schools in Israel
Israel
The State of Israel is a parliamentary republic located in the Middle East, along the eastern shore of the Mediterranean Sea...
, Spain
Spain
Spain , officially the Kingdom of Spain languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Spain's official name is as follows:;;;;;;), is a country and member state of the European Union located in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula...
, the Czech Republic
Czech Republic
The Czech Republic is a landlocked country in Central Europe. The country is bordered by Poland to the northeast, Slovakia to the east, Austria to the south, and Germany to the west and northwest....
, and Slovakia
Slovakia
The Slovak Republic is a landlocked state in Central Europe. It has a population of over five million and an area of about . Slovakia is bordered by the Czech Republic and Austria to the west, Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east and Hungary to the south...
also focus heavily on clinical training.
The level of participation in clinical training can be quite limited in some schools and countries, however. In Japan, students are not permitted to engage in clinical education until they have studied for six years. For example, in Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka is a country off the southern coast of the Indian subcontinent. Known until 1972 as Ceylon , Sri Lanka is an island surrounded by the Indian Ocean, the Gulf of Mannar and the Palk Strait, and lies in the vicinity of India and the...
, until recently the public owned relatively few companion animals
Pet
A pet is a household animal kept for companionship and a person's enjoyment, as opposed to wild animals or to livestock, laboratory animals, working animals or sport animals, which are kept for economic or productive reasons. The most popular pets are noted for their loyal or playful...
, and veterinary medical education focused on herd health—with the result that veterinary schools focused little attention on clinical skills. As recently as 2004, this had not changed. In Ethiopia, few schools have clinical training facilities, and the government has placed a priority on opening more schools rather than improving the existing colleges. Even in the United States, there is some concern that clinical training may suffer because many veterinary teaching hospitals are in deep financial trouble.

Unlike human medicine, almost no veterinary medical education regimes require students to enroll in an internship and/or residency upon graduation. However, internships and residencies are often required for veterinarians seeking board certification
Board certification
Board certification is the process by which a physician , dentist , or podiatrist in the United States demonstrates through either written, practical, and/or simulator based testing, a mastery of the basic knowledge and skills that define an area of medical specialization...
in Canada, Europe and the US.
Lecture
Lecture
thumb|A lecture on [[linear algebra]] at the [[Helsinki University of Technology]]A lecture is an oral presentation intended to present information or teach people about a particular subject, for example by a university or college teacher. Lectures are used to convey critical information, history,...
and rote learning
Rote learning
Rote learning is a learning technique which focuses on memorization. The major practice involved in rote learning is learning by repetition by which students commit information to memory in a highly structured way. The idea is that one will be able to quickly recall the meaning of the material the...
are two of the most common teaching methods used in veterinary medical education. To a lesser degree, outcome-based education
Outcome-based education
Outcome-based education is a recurring education reform model. It is a student-centered learning philosophy that focuses on empirically measuring student performance, which are called outcomes. OBE contrasts with traditional education, which primarily focuses on the resources that are available...
and discovery learning
Discovery learning
Discovery Learning is a method of inquiry-based instruction and is considered a constructivist based approach to education. It is supported by the work of learning theorists and psychologists Jean Piaget, Jerome Bruner, and Seymour Papert...
are also common pedagogical approaches. Inquiry-based learning
Inquiry-based learning
Inquiry-based learning or inquiry-based science describes a range of philosophical, curricular and pedagogical approaches to teaching....
is also sometimes used. In the last two decades, problem-based learning
Problem-based learning
Problem-based learning is a student-centered pedagogy in which students learn about a subject in the context of complex, multifaceted, and realistic problems...
has been adopted in most veterinary schools in developed countries, especially those in Australia, Canada, New Zealand, the United States, and Western Europe
Western Europe
Western Europe is a loose term for the collection of countries in the western most region of the European continents, though this definition is context-dependent and carries cultural and political connotations. One definition describes Western Europe as a geographic entity—the region lying in the...
.
See also
- History of Veterinary Medicine in PennsylvaniaHistory of Veterinary Medicine in Pennsylvania- The Need for Veterinary Medicine :By 1710 pioneers had settled land as far as sixty miles from Philadelphia. As early as 1757, Carlisle has become a supply center for the forts of the frontier...
- List of schools of veterinary medicine
- Veterinary Medical College Application ServiceVeterinary Medical College Application ServiceThe Veterinary Medical College Application Service is a centralized application service for students applying to veterinary school...
- First professional degreeFirst professional degreeA professional degree prepares the holder for a particular profession by emphasizing competency skills along with theory and analysis. These professions are typically licensed or otherwise regulated by a governmental or government-approved body...
- VeterinarianVeterinarianA veterinary physician, colloquially called a vet, shortened from veterinarian or veterinary surgeon , is a professional who treats disease, disorder and injury in animals....
- Veterinary medicineVeterinary medicineVeterinary Medicine is the branch of science that deals with the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of disease, disorder and injury in non-human animals...

