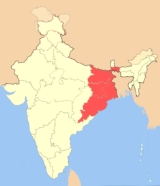
East India
Encyclopedia
West Bengal
West Bengal is a state in the eastern region of India and is the nation's fourth-most populous. It is also the seventh-most populous sub-national entity in the world, with over 91 million inhabitants. A major agricultural producer, West Bengal is the sixth-largest contributor to India's GDP...
, Bihar
Bihar
Bihar is a state in eastern India. It is the 12th largest state in terms of geographical size at and 3rd largest by population. Almost 58% of Biharis are below the age of 25, which is the highest proportion in India....
, Jharkhand
Jharkhand
Jharkhand is a state in eastern India. It was carved out of the southern part of Bihar on 15 November 2000. Jharkhand shares its border with the states of Bihar to the north, Uttar Pradesh and Chhattisgarh to the west, Orissa to the south, and West Bengal to the east...
, and Orissa
Orissa
Orissa , officially Odisha since Nov 2011, is a state of India, located on the east coast of India, by the Bay of Bengal. It is the modern name of the ancient nation of Kalinga, which was invaded by the Maurya Emperor Ashoka in 261 BC. The modern state of Orissa was established on 1 April...
. The states of Orissa and West Bengal share some cultural and linguistic characteristics with Bangladesh
Bangladesh
Bangladesh , officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh is a sovereign state located in South Asia. It is bordered by India on all sides except for a small border with Burma to the far southeast and by the Bay of Bengal to the south...
and with the state of Assam
Assam
Assam , also, rarely, Assam Valley and formerly the Assam Province , is a northeastern state of India and is one of the most culturally and geographically distinct regions of the country...
. Together with Bangladesh, West Bengal formed the ethno-linguistic region of Bengal
Bengal
Bengal is a historical and geographical region in the northeast region of the Indian Subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal. Today, it is mainly divided between the sovereign land of People's Republic of Bangladesh and the Indian state of West Bengal, although some regions of the previous...
before Partition
Partition of India
The Partition of India was the partition of British India on the basis of religious demographics that led to the creation of the sovereign states of the Dominion of Pakistan and the Union of India on 14 and 15...
in 1947. Historic region of Bengal which was ruled by Nawabs of Bengal comprises present Bihar,Jharkhand, West Bengal and Bangladesh from where British
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
started their conquest of India.
The bulk of the region lies on the east coast of India by the Bay of Bengal
Bay of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal , the largest bay in the world, forms the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean. It resembles a triangle in shape, and is bordered mostly by the Eastern Coast of India, southern coast of Bangladesh and Sri Lanka to the west and Burma and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands to the...
, and on the Indo-Gangetic plain
Indo-Gangetic plain
The northern Plains also known as the Indo - Gangetic Plain and The North Indian River Plain is a large and fertile plain encompassing most of northern and eastern India, the most populous parts of Pakistan, parts of southern Nepal and virtually all of Bangladesh...
. Jharkhand, on the Chhota Nagpur
Chota Nagpur Plateau
The Chota Nagpur Plateau is a plateau in eastern India, which covers much of Jharkhand state as well as adjacent parts of Orissa, West Bengal, Bihar and Chhattisgarh. The Indo-Gangetic plain lies to the north and east of the plateau, and the basin of the Mahanadi River lies to the south...
plateau, is a hilly and a heavily forested state rich in mineral wealth. The region is bounded by the Nepal
Nepal
Nepal , officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, is a landlocked sovereign state located in South Asia. It is located in the Himalayas and bordered to the north by the People's Republic of China, and to the south, east, and west by the Republic of India...
and Sikkim
Sikkim
Sikkim is a landlocked Indian state nestled in the Himalayan mountains...
Himalayas
Himalayas
The Himalaya Range or Himalaya Mountains Sanskrit: Devanagari: हिमालय, literally "abode of snow"), usually called the Himalayas or Himalaya for short, is a mountain range in Asia, separating the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau...
in the north, the states of Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh abbreviation U.P. , is a state located in the northern part of India. With a population of over 200 million people, it is India's most populous state, as well as the world's most populous sub-national entity...
and Chhattisgarh
Chhattisgarh
Chhattisgarh is a state in Central India, formed when the 16 Chhattisgarhi-speaking South-Eastern districts of Madhya Pradesh gained separate statehood on 1 November 2000....
on the west, the state of Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh , is one of the 28 states of India, situated on the southeastern coast of India. It is India's fourth largest state by area and fifth largest by population. Its capital and largest city by population is Hyderabad.The total GDP of Andhra Pradesh is $100 billion and is ranked third...
in the south and the Bay of Bengal
Bay of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal , the largest bay in the world, forms the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean. It resembles a triangle in shape, and is bordered mostly by the Eastern Coast of India, southern coast of Bangladesh and Sri Lanka to the west and Burma and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands to the...
on the east.
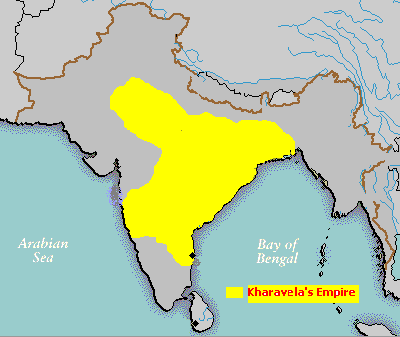
The region was the historical centre of the Nanda, Maurya, Kharavela
Kharavela
Khārabēḷa was the third and greatest emperor of the Mahāmēghabāhana Dynasty of Kaḷinga . The main source of information about Khārabeḷa is his famous seventeen line rock-cut Hātigumphā inscription in a cave in the Udayagiri hills near Bhubaneswar, Orissa.During the reign of Khārabēḷa, the Chedi...
, Sunga, Kalinga
Kalinga (India)
Kalinga was an early state in central-eastern India, which comprised most of the modern state of Orissa/Utkal , as well as the Andhra region of the bordering state of Andhra Pradesh. It was a rich and fertile land that extended from the river Damodar/Ganges to Godavari and from Bay of Bengal to...
, Gupta
Gupta Empire
The Gupta Empire was an ancient Indian empire which existed approximately from 320 to 550 CE and covered much of the Indian Subcontinent. Founded by Maharaja Sri-Gupta, the dynasty was the model of a classical civilization. The peace and prosperity created under leadership of Guptas enabled the...
and Pala
Pala Empire
The Pāla Empire was one of the major middle kingdoms of India existed from 750–1174 CE. It was ruled by a Buddhist dynasty from Bengal in the eastern region of the Indian subcontinent, all the rulers bearing names ending with the suffix Pala , which means protector. The Palas were often described...
empires that ruled much of the Indian sub-continent at their prime. In medieval India, it was incorporated into the Mughal
Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire , or Mogul Empire in traditional English usage, was an imperial power from the Indian Subcontinent. The Mughal emperors were descendants of the Timurids...
and then the British
British Raj
British Raj was the British rule in the Indian subcontinent between 1858 and 1947; The term can also refer to the period of dominion...
empire. After independence in 1947, the states joined the Indian Union and took their current form after the States Reorganization Act of 1956. Today, they continue to face problems of overpopulation, environmental degradation and pervasive corruption despite significant economic and social progress.
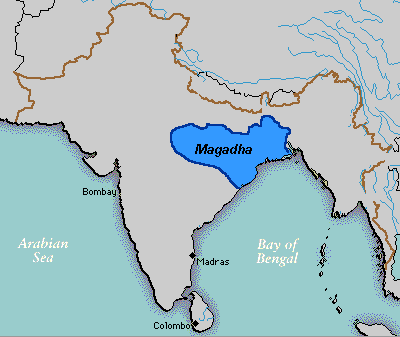
East India was at the heart of the ancient Sena
Sena
The word sena literally means army in Hindi and Bangla, and to praise in arabic language.In Benin, West Africa, the name SENA means "bringing Heaven to Earth".Sena could also refer to:-Places:...
, Magadha, Maurya and Kalinga
Kalinga (India)
Kalinga was an early state in central-eastern India, which comprised most of the modern state of Orissa/Utkal , as well as the Andhra region of the bordering state of Andhra Pradesh. It was a rich and fertile land that extended from the river Damodar/Ganges to Godavari and from Bay of Bengal to...
empires.
After the Kalinga War
Kalinga War
The Kalinga War was a war fought between the Mauryan Empire under Ashoka the Great and the state of Kalinga, a feudal republic located on the coast of the present-day Indian state of Orissa. The Kalinga war is one of the major battles in the History of India. Kalinga put up a stiff resistance,...
The Maurya king Ashoka
Ashoka
Ashok Maurya or Ashoka , popularly known as Ashoka the Great, was an Indian emperor of the Maurya Dynasty who ruled almost all of the Indian subcontinent from ca. 269 BC to 232 BC. One of India's greatest emperors, Ashoka reigned over most of present-day India after a number of military conquests...
send out emissaries to spread Buddhism across Asia. The famous university of Nalanda was in East India. Chinese travellers visited Buddhist and Hindu temples and libraries in the universities of Magadha Empire. The Emperor of Kalinga Mahameghavahana Aira Kharavela
Kharavela
Khārabēḷa was the third and greatest emperor of the Mahāmēghabāhana Dynasty of Kaḷinga . The main source of information about Khārabeḷa is his famous seventeen line rock-cut Hātigumphā inscription in a cave in the Udayagiri hills near Bhubaneswar, Orissa.During the reign of Khārabēḷa, the Chedi...
was one of the most powerful monarchs of ancient India.
The Jain thirkhankar Mahaveer was born here and founded Jainism
Jainism
Jainism is an Indian religion that prescribes a path of non-violence towards all living beings. Its philosophy and practice emphasize the necessity of self-effort to move the soul towards divine consciousness and liberation. Any soul that has conquered its own inner enemies and achieved the state...
.
Islamic invasions in the 13th century resulted in the collapse of Hindu kings and most Buddhists, especially in East Bengal, converted to Islam. East India including Bihar and West Bengal was part of the Mughal Empire in the 16th and 17th centuries.Orissa remained a powerful Hindu dynasty under the rule of Soma/Keshari Dynasty, Eastern Ganga Dynasty, Surya Dynasty till the end of 16th century. The mighty Nalanda University existed at Nalanda
Nalanda
Nālandā is the name of an ancient center of higher learning in Bihar, India.The site of Nalanda is located in the Indian state of Bihar, about 55 miles south east of Patna, and was a Buddhist center of learning from the fifth or sixth century CE to 1197 CE. It has been called "one of the...
which was destroyed by Bakhtiar Khilji during 12th century and also defeated Sena Dynasty
Sena dynasty
The Sena Empire was a Hindu dynasty that ruled from Bengal through the 11th and 12th centuries. At its peak the empire covered much of the north-eastern region in the Indian Subcontinent. They were called Brahma-Kshatriyas, as evidenced through their surname, which is derived from the Sanskrit,...
. Sher Shah Suri
Sher Shah Suri
Sher Shah Suri , birth name Farid Khan, also known as Sher Khan , was the founder of the short-lived Sur Empire in northern India, with its capital at Delhi, before its demise in the hands of the resurgent Mughal Empire...
, who became king of India after defeating Humayun
Humayun
Nasir ud-din Muhammad Humayun was the second Mughal Emperor who ruled present day Afghanistan, Pakistan, and parts of northern India from 1530–1540 and again from 1555–1556. Like his father, Babur, he lost his kingdom early, but with Persian aid, he eventually regained an even larger one...
, founded the city of Patna
Patna
Paṭnā , is the capital of the Indian state of Bihar and the second largest city in Eastern India . Patna is one of the oldest continuously inhabited places in the world...
on the ruins of ancient Patliputra
Patliputra
Pāṭaliputra , modern-day Patna, was a city in ancient India, originally built by Ajatashatru in 490 BC as a small fort near the River Ganges, and later the capital of the ancient Mahājanapadas kingdom of Magadha....
.
With the arrival of the Europeans in the 17th century, outposts were established in Orissa Coast and Bengal. The European traders established their trade centers in the famous ports of Balasore
Balasore
Balasore is a strategically located city in the state of Orissa, about north of the state capital Bhubaneswar, in eastern India. It is the administrative headquarters of Balasore district. It is best known for Chandipur beach. It is also the site of the Indian Ballistic Missile Defense...
,Pipili,Palur in the Orissa Coast during the rule of the last independent Hindu king Gajapati Prataprudra Dev.The Portuguese were in Chittagong, Dutch in Chinsura, French in Pondicherry and the English founded Calcutta. In 1756, the British East India Company
British East India Company
The East India Company was an early English joint-stock company that was formed initially for pursuing trade with the East Indies, but that ended up trading mainly with the Indian subcontinent and China...
defeated the local Indian Muslim rulers in Plassey and established British Rule in the subcontinent. Its capital Calcutta grew into one of the world's greatest ports. Tea from Calcutta was off-loaded by American separatists in the American War of Independence in the 1770s. In the 19th century, Calcutta's traders and merchants traded with the rest of the British Empire, continental Europe, the United States and China. Indentured Indian labourers from Bihar, sailed to new homes in Fiji
Fiji
Fiji , officially the Republic of Fiji , is an island nation in Melanesia in the South Pacific Ocean about northeast of New Zealand's North Island...
, Mauritius
Mauritius
Mauritius , officially the Republic of Mauritius is an island nation off the southeast coast of the African continent in the southwest Indian Ocean, about east of Madagascar...
, Guyana
Guyana
Guyana , officially the Co-operative Republic of Guyana, previously the colony of British Guiana, is a sovereign state on the northern coast of South America that is culturally part of the Anglophone Caribbean. Guyana was a former colony of the Dutch and of the British...
, Surinam and South Africa
South Africa
The Republic of South Africa is a country in southern Africa. Located at the southern tip of Africa, it is divided into nine provinces, with of coastline on the Atlantic and Indian oceans...
.
India's independence movement had strong roots in East India. The feudal land system, established through the Permanent Settlement of Bengal, was unpopular among the peasant cultivators and the numerous agricultural labourers found all over Bihar and Bengal (Khetmazdoors). The Indian War of Independence in 1857 started in Bengal. British war propaganda asserted there were atrocities by the mutinous soldiers in the Black Hole of Calcutta. Eventually the British prevailed and Calcutta remained capital of Britain's Asian dominions until 1911. The Indian National Congress
Indian National Congress
The Indian National Congress is one of the two major political parties in India, the other being the Bharatiya Janata Party. It is the largest and one of the oldest democratic political parties in the world. The party's modern liberal platform is largely considered center-left in the Indian...
was founded in Calcutta. During Mahatma Gandhi's freedom movement, the Bihari village of Champaran was an important supporter of non-violent resistance. Great poets of the stature of Rabindranath Tagore
Rabindranath Tagore
Rabindranath Tagore , sobriquet Gurudev, was a Bengali polymath who reshaped his region's literature and music. Author of Gitanjali and its "profoundly sensitive, fresh and beautiful verse", he became the first non-European Nobel laureate by earning the 1913 Prize in Literature...
championed the movement for self-rule.
The Partition also had its roots in undivided Eastern India. The Muslim League was founded in Dhaka
Dhaka
Dhaka is the capital of Bangladesh and the principal city of Dhaka Division. Dhaka is a megacity and one of the major cities of South Asia. Located on the banks of the Buriganga River, Dhaka, along with its metropolitan area, had a population of over 15 million in 2010, making it the largest city...
in 1906. In the 1937 provincial elections, it came to power in Bengal in alliance with the Krishak Praja Party
Krishak Praja Party
Krishak Praja Party , originally known as "Proja-Shamiti" , was a political party in British India. It struggled for the abolition of zamindari .In the late 1930s, A. K...
. in 1944, it gained an absolute majority in the Bengal Assembly, and Hussein Suhrawardy became the Chief Minister
Chief Minister
A Chief Minister is the elected head of government of a sub-national state, provinces of Sri Lanka, Pakistan, notably a state of India, a territory of Australia or a British Overseas Territory that has attained self-government...
. After widespread communal violence during the Direct Action Day
Direct Action Day
Direct Action Day , also known as the Great Calcutta Killings, was a day of widespread riot and manslaughter in the city of Calcutta in the Bengal province of British India...
protests in Calcutta, leading to further communal violence across British India, the creation of Pakistan became inevitable. In 1947, further communal violence displaced millions as independence and partition
Partition of India
The Partition of India was the partition of British India on the basis of religious demographics that led to the creation of the sovereign states of the Dominion of Pakistan and the Union of India on 14 and 15...
of British India occurred. Some Bihari and Bengali Muslims fled to the newly created East Pakistan
East Pakistan
East Pakistan was a provincial state of Pakistan established in 14 August 1947. The provincial state existed until its declaration of independence on 26 March 1971 as the independent nation of Bangladesh. Pakistan recognized the new nation on 16 December 1971. East Pakistan was created from Bengal...
. Most East Bengal Hindus fled to India.
The 1950s saw industrial progress in East India. These were cut short with the conflict in neighbouring East Pakistan
East Pakistan
East Pakistan was a provincial state of Pakistan established in 14 August 1947. The provincial state existed until its declaration of independence on 26 March 1971 as the independent nation of Bangladesh. Pakistan recognized the new nation on 16 December 1971. East Pakistan was created from Bengal...
and by the Communist movement at home. In 1971, in the course of Bangladesh's independence struggle, millions of refugees poured into East India. From the turn of the century West Bengal's economic recovery flew through its roofs and now racks second largest GDP contributor after Maharastra according to List of Indian states by GDP and is now the third fastest growing economy.
Bihar and Orissa struggled with economic issues but developed steadily. Jharkhand became a separate state on 15 November 2000. The economic boom since 2005 started to spread new malls, highways, airports and IT office complexes, but not evenly across the region.
Education
East India is home to some great universities and centres of excellence such as Indian Institute of Technology Bhubaneswar, International Institute of Information Technology, BhubaneswarInternational Institute of Information Technology, Bhubaneswar
International Institute of Information Technology Bhubaneswar is an information technology higher education institute located in Bhubaneswar, Orissa, India. It was established in 2006 by the Government of Orissa. It is affiliated with Biju Patnaik University of Technology .-History:IIIT...
, National Institute of Science Education and Research, Bhubaneswar
National Institute of Science Education and Research, Bhubaneswar
The National Institute of Science Education and Research is a research institution in Bhubaneswar, Orissa, India. The Prime Minister of India laid the foundation stone on August 28, 2006, establishing the institute along the lines of the IISc in Bangalore, and its five sister institutions, the...
, Institute of Mathematics and Applications, Bhubaneswar
Institute of Mathematics and Applications, Bhubaneswar
The Institute of Mathematics and Applications, Bhubaneswar is an academic institution that was established by the government of Orissa in 1999. Its dual purposes are to conduct advanced research in pure and applied mathematics, and to provide postgraduate education leading to Masters and Ph.D....
, National Law University, Orissa
National Law University, Orissa
National Law University, Orissa is the newest addition to the list of the National Law Universities in India. It is located at Cuttack, Orissa. The university offers courses for undergraduate and graduate legal education...
, Indian Institute of Mass Communication
Indian Institute of Mass Communication
The Indian Institute of Mass Communication is India's premier media school funded and promoted by the Government of India. IIMC is an autonomous society under the Ministry of Information and Broadcasting. The institution was established on August 17, 1965 with support from UNESCO.-The...
Orissa
Orissa
Orissa , officially Odisha since Nov 2011, is a state of India, located on the east coast of India, by the Bay of Bengal. It is the modern name of the ancient nation of Kalinga, which was invaded by the Maurya Emperor Ashoka in 261 BC. The modern state of Orissa was established on 1 April...
, Central Institute of Plastics Engineering and Technology (India)
Central Institute of Plastics Engineering and Technology (India)
CIPET or Central Institute of Plastics Engineering and Technology is an autonomous institute under the department of chemicals and petrochemicals, ministry of chemicals and fertilizers, Government of India.-The institute:...
Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar is the capital of the Indian state of Orissa, officially Odisha. The city has a long history of over 2000 years starting with Chedi dynasty who had Sisupalgarh near present-day Bhubaneswar as their capital...
, National Council of Educational Research and Training
National Council of Educational Research and Training
The National Council of Educational Research and Training is an apex resource organization set up by the Government of India, with headquarters at New Delhi, to assist and advise the Central and State Governments on academic matters related to school education.it was Established in the year of...
East Zone institute in Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar is the capital of the Indian state of Orissa, officially Odisha. The city has a long history of over 2000 years starting with Chedi dynasty who had Sisupalgarh near present-day Bhubaneswar as their capital...
, Central Rice Research Institute
Central Rice Research Institute
The Central Rice Research Institute is situated near Vidyadharpur village on the Cuttack-Paradip Road, Orissa, India...
Orissa
Orissa
Orissa , officially Odisha since Nov 2011, is a state of India, located on the east coast of India, by the Bay of Bengal. It is the modern name of the ancient nation of Kalinga, which was invaded by the Maurya Emperor Ashoka in 261 BC. The modern state of Orissa was established on 1 April...
, Indian Institute of Technology Patna
Indian Institute of Technology Patna
The Indian Institute of Technology, Patna is an autonomous institute for education and research in science, engineering and technology located in Patna, India. It is one of the 8 new IITs which have become functional between 2008 and 2009...
, Bengal Engineering and Science University (founded in 1856), Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur
Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur
The Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur is an autonomous engineering, technology and management oriented institute of higher education established by the government of India in 1951...
, Indian Institute of Science Education and Research, Kolkata
Indian Institute of Science Education and Research, Kolkata
Indian Institute of Science Education and Research, Kolkata is an autonomous institute of higher education for research and education in science established by the Ministry of Human Resource Development, Government of India in 2006.-Campus:IISER Kolkata's...
, Indian Institute of Management Calcutta
Indian Institute of Management Calcutta
The Indian Institute of Management Calcutta is an institute of management located in Kolkata , India giving diplomas in management...
, Indian Statistical Institute
Indian Statistical Institute
Indian Statistical Institute is a public research institute and university in Kolkata's northern outskirt of Baranagar, India founded by Prasanta Chandra Mahalanobis in 1931...
, Institute of Physics, Bhubaneswar
Institute of Physics, Bhubaneswar
Institute of Physics, Bhubaneswar is an autonomous research institution of the Department of Atomic Energy , Government of India. The Institute was established in 1972 by the Government of Orissa, under the founding director Dr. Trilochan Pradhan, when the Institute started theoretical research...
, Saha Institute of Nuclear Physics
Saha Institute of Nuclear Physics
The Saha Institute of Nuclear Physics is an institution of basic research and training in physical and biophysical sciences located in Bidhannagar, Kolkata, India. The institute is named after the famous Indian physicist Meghnad Saha.-History:...
, S.N. Bose National Centre for Basic Sciences
S.N. Bose National Centre for Basic Sciences
S.N. Bose National Centre for Basic Sciences is an autonomous research institute under Department of Science and Technology of Government of India, located in Salt Lake, Kolkata. Named after scientist Satyendra Nath Bose, this institution was established in 1986.Students of this institute can...
, Visva-Bharati University
Visva-Bharati University
Visva Bharati University is a Central University for research and teaching in India, located in the twin towns of Santiniketan and Sriniketan in the Indian state of West Bengal. It was founded by Rabindranath Tagore who called it Visva Bharati, which means the communion of the world with India...
, NITs
National Institutes of Technology
The National Institutes of Technology , are a group of higher education engineering institutes in India. Comprising thirty autonomous institutes, they are located in one each major state/territory of India. On their inception decades ago, all NITs were referred as Regional Engineering Colleges ...
in Rourkela
National Institute of Technology, Rourkela
National Institute of Technology – Rourkela , formerly known as the Regional Engineering College Rourkela , is a publicly funded institute of higher learning for engineering and technology located in the steel city of Rourkela, Orissa, India. It was established in the year 1961 by a joint...
, Durgapur
National Institute of Technology, Durgapur
The National Institute of Technology, Durgapur , formerly the Regional Engineering College , Durgapur, was established under an Act of the Parliament of India in 1960 as one of the eight RECs...
, Jamshedpur
National Institute of Technology, Jamshedpur
National Institute of Technology Jamshedpur , formerly Regional Institute of Technology, Jamshedpur, is a technology higher education institute located at Jamshedpur, Jharkhand, India...
& Patna
National Institute of Technology, Patna
The National Institute of Technology Patna , formerly Bihar School of Engineering and Bihar College of Engineering, is a National Institute of Technology located in Patna, Bihar, India. It was created by the Government of India on January 28, 2004.-History:NITP is the sixth oldest engineering...
, Xavier Labour Relations Institute (XLRI)
XLRI
The XLRI School of Business and Human Resources, Jamshedpur is a graduate business school in Jamshedpur, India. Established in 1949, XLRI is arguably the oldest business school in India and is regarded as consistently among the top 5 business schools of the country...
, Jamshedpur, Xaviers Institute of Management XIMB at Bhubaneswar,Xaviers Institute of Social Services[XISS]Ranchi, University of Calcutta
University of Calcutta
The University of Calcutta is a public university located in the city of Kolkata , India, founded on 24 January 1857...
, Presidency University, Kolkata, Jadavpur University
Jadavpur University
Jadavpur University , is a premier educational and research institution in India.It is located in Kolkata, West Bengal and comprises two campuses - the main campus at Jadavpur and the new campus at Salt Lake...
, Utkal University
Utkal University
Utkal University, Bhubaneswar is the oldest university in Orissa and the 17th oldest university in India. It is a teaching-cum-affiliating university that has produced some of the best brains in Orissa. There are at 26 post-graduate departments at the university campus for studies and research in...
, Sri Sri University
Sri Sri University
- Vision :VISION : TO IMPART HOLISTIC, VALUE-INTEGRATED EDUCATION THAT DEVELOPS VISIONARY THINKERS WITH THE SOCIAL-CONSCIOUSNESS TO LEAD SOCIETAL AND ECONOMIC CHANGE....
, Orissa, KIIT University , Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar is the capital of the Indian state of Orissa, officially Odisha. The city has a long history of over 2000 years starting with Chedi dynasty who had Sisupalgarh near present-day Bhubaneswar as their capital...
, Indian School of Mines University, Birla Institute Of Technology, Sindri; Birla Institute of Technology, Mesra
Birla Institute of Technology
Birla Institute of Technology, Mesra , is an autonomous engineering and technology oriented institute of higher education located in Ranchi, Jharkhand, India...
and Birla Agricultural University. One of the first great universities in recorded history, the Nalanda University,] of this ancient University including a consortium led by Singapore along with China, India and is located in the state of Bihar, while another recently discovered one, Puspagiri University
Puspagiri University
Puspagiri Mahavihara was a prominent Buddhist seat of learning that flourished until the 11th century in India. Today, its ruins lie atop the Langudi hills, low hills about 90 km from the Mahanadi delta, in the districts of Jajpur and Cuttack in Orissa...
in Orissa. There has been various plans for revival Japan. Vedanta University
Vedanta University
Vedanta University was a proposed, private, multi-disciplinary, co-educational university to be started by Anil Agarwal of Vedanta Resources corporation near Puri-Konark highway, Orissa, India.-The vision:...
, which plans to establish itself as one of the biggest academic institutions in the world, is being established in Puri, Orissa.
Urban areas
West Bengal's capital KolkataKolkata
Kolkata , formerly known as Calcutta, is the capital of the Indian state of West Bengal. Located on the east bank of the Hooghly River, it was the commercial capital of East India...
, the capital of British India until 1911, is the biggest metropolis and economically dominant city of the region and third largest in India and one of the fastest growing cities in the world. Kolkata is very fast transforming it self to become city equipped with every facilities for IT and ITES and also financial outsourcing hub and its satellites Saltlake City and Rajarhat
Rajarhat
Rajarhat Gopalpur , a neighbourhood of Calcutta, located in North 24 Parganas district of West Bengal, is a fast-growing planned new city. It is situated near the Netaji Subhash Chandra Bose International Airport. Many high-profile industrialists of national and international standing are...
are taken the burdens of India's IT and financial boom. However, the mid-sized cities of Bhubaneshwar, Cuttack
Cuttack
Cuttack is the former capital of the state of Orissa, India. It is the headquarters of Cuttack district and is located about 20 km to the north east of Bhubaneswar, the capital of Orissa. The name of the city is an anglicised form of Kataka that literally means The Fort, a reference to the...
, rourkela
Rourkela
Rourkela is located in the northwestern tip of the Indian state of Orissa at the heart of a rich mineral belt. It is situated about north of state capital Bhubaneswar.It is surrounded by a range of hills and encircled by rivers. One of the largest steel plants of the Steel Authority of India...
, Puri
Puri
Puri is district headquarter, a city situated about south of state capital Bhubaneswar, on the eastern coast of the Bay of Bengal in the Indian state of Orissa. It is also known as Jagannath Puri after the Jagannath Temple . It is a holy city of the Hindus as a part of the Char Dham pilgrimages...
in Orissa and Durgapur, Siliguri
Siliguri
Siliguri is a city in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is located in the Siliguri Corridor or Chicken's Neck - a very narrow strip of land linking mainland India to its north-eastern states. It is also the transit point for air, road and rail traffic to the neighbouring countries of Nepal,...
, Asansol
Asansol
Asansol is a coal mining and industrial metropolis and one of the busiest commercial centres in India. It is the second largest city and urban agglomeration in West Bengal after Kolkata and the 19th largest urban agglomeration in India. Asansol is located in the western part of the Burdwan...
in West Bengal are emerging urban areas . In Bihar, Patna
Patna
Paṭnā , is the capital of the Indian state of Bihar and the second largest city in Eastern India . Patna is one of the oldest continuously inhabited places in the world...
, Bhagalpur
Bhagalpur
Bhagdattpuram was one of the most influential towns in "Aryavarta" . It is supposed to have been concurrent to Patliputra or Patna. Bhagdattpuram finds its mention in the Vedas and Ramayana as well. It is supposed to be the kingdom of Daanvir Karna, the son of Kunti and the Sun God...
, Muzaffarpur
Muzaffarpur
Muzaffarpur Town is a town in Muzaffarpur district in the Indian state of Bihar. It serves as the headquarters of Muzaffarpur district and Tirhut division....
and Gaya
Gaya, India
Gaya is the second largest city of Bihar, India, and it is also the headquarters of Gaya District.Gaya is 100 kilometers south of Patna, the capital city of Bihar. Situated on the banks of Falgu River , it is a place sanctified by both the Hindu and the Buddhist religions...
are important urban areas.
Bhubaneswar is the capital of the Indian state
States and territories of India
India is a federal union of states comprising twenty-eight states and seven union territories. The states and territories are further subdivided into districts and so on.-List of states and territories:...
of Orissa
Orissa
Orissa , officially Odisha since Nov 2011, is a state of India, located on the east coast of India, by the Bay of Bengal. It is the modern name of the ancient nation of Kalinga, which was invaded by the Maurya Emperor Ashoka in 261 BC. The modern state of Orissa was established on 1 April...
. The city has a long history of over 2000 years starting with Chedi dynasty (around 2nd century BCE) who had Sisupalgarh near present-day Bhubaneswar as their capital. Historically Bhubaneswar has been known by different names such as Toshali, Kalinga Nagari, Nagar Kalinga, Ekamra Kanan, Ekamra Kshetra and Mandira Malini Nagari(city of temples) otherwise known as the temple city of India. The largest city of Orissa, Bhubaneswar today is a center of economic and religious importance in the region.
With the economic liberalisation policy adopted by the Government of India
Government of India
The Government of India, officially known as the Union Government, and also known as the Central Government, was established by the Constitution of India, and is the governing authority of the union of 28 states and seven union territories, collectively called the Republic of India...
in the 90s, Bhubaneswar received large investments in the fields of telecommunications, IT
Information technology
Information technology is the acquisition, processing, storage and dissemination of vocal, pictorial, textual and numerical information by a microelectronics-based combination of computing and telecommunications...
and higher education, particularly engineering. The city is home to around 60 engineering colleges (as of 2009) and the number is growing every year. The city is also home to many tutorials and coaching institutes who prepare students for various entrance exams.
Retail
Retail
Retail consists of the sale of physical goods or merchandise from a fixed location, such as a department store, boutique or kiosk, or by mail, in small or individual lots for direct consumption by the purchaser. Retailing may include subordinated services, such as delivery. Purchasers may be...
and Real Estate
Real estate
In general use, esp. North American, 'real estate' is taken to mean "Property consisting of land and the buildings on it, along with its natural resources such as crops, minerals, or water; immovable property of this nature; an interest vested in this; an item of real property; buildings or...
have also emerged as big players. Recent times have seen large scale retail chains such as Reliance, Vishal MegaMart, Big Bazaar, Pantaloon, Pal Heights, Indulge, New Leaf, Habib's, had opened outlets in Bhubaneswar. Large corporations like DLF Universal and Reliance Industries have entered the real estate market in the city. DLF Limited is developing an Infopark spread over an area of 54 acres (218,530.4 m²) in the city. Expanding its business portfolio, the Kolkata
Kolkata
Kolkata , formerly known as Calcutta, is the capital of the Indian state of West Bengal. Located on the east bank of the Hooghly River, it was the commercial capital of East India...
-based Saraf Group, promoters of Forum Mart shopping malls is constructing another Shopping mall named Forum Lifestyle mall a 550000 sq ft (51,096.7 m²) lifestyle mall in Bhubaneswar with 1,200 car parks. The rich minerals resources of Orissa have been the backbone of the economy dominated by Government.Steel Authority of India Limited (SAIL) and private organizations like Jindal, Vedanta and TATAS. Despite this rapid growth, an ample number of the populace live in slums. Migration from rural areas, especially from the northern districts of Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh , is one of the 28 states of India, situated on the southeastern coast of India. It is India's fourth largest state by area and fifth largest by population. Its capital and largest city by population is Hyderabad.The total GDP of Andhra Pradesh is $100 billion and is ranked third...
, has led to the growth of slums which are a major challenge to the city's growth. The slum dwellers work as auto rickshaw
Auto rickshaw
An auto rickshaw or three-wheeler is a usually three-wheeled cabin cycle for private use and as a vehicle for hire. It is a motorized version of the traditional pulled rickshaw or cycle rickshaw...
drivers or small vendors but this is not true for everyone. A lot of them are unemployed and are being drawn into crime.The main problem of the city is transport as the quality and length of roads have not increased with respect to the rise in number of vehicles. Purchasing power of people of this city is quite high but this city does not get enough highlightment and often neglected by big channels like Discovery, NatGeo,etc.

Infosys
Infosys Limited, formerly Infosys Technologies Limited is a global technology services company headquartered in Bangalore, India. It is the second largest IT exporter in India with 133,560 employees as of March 2011. It has offices in 33 countries and development centers in India, China,...
and Satyam Computer Services Ltd.
Satyam Computer Services Ltd.
Mahindra Satyam is a Brand identity of Satyam Computer Services Limited. Satyam Computer Services Limited was founded in 1987 by B Ramalinga Raju. Mahindra Satyam is a part of the Mahindra Group which is one of the top 10 industrial firms based in India...
have been present in Bhubaneswar since 1996-97. Its current head count stands at around 5000. The first part of the TCS
Tata Consultancy Services
Tata Consultancy Services Limited is a global IT services, business solutions and outsourcing company headquartered in Mumbai, India. It is the largest provider of information technology in Asia and second largest provider of business process outsourcing services in India...
centre is ready and has a capacity to accommodate nearly 1,200 professionals but the software major has only 250 employees at present. The Finland telecommunication company, Nethawk (http://www.nethawk.fi), has its India R&D center at Bhubaneswar. The Canadian giant, Gennum Corporation has its India development centre at Bhubaneswar. The famous auditors PricewaterhouseCoopers Pvt. Ltd. also have a center in Bhubaneswar. The private STP is located at Infocity in Chandaka, Bhubaneswar with a view to provide incubation and infrastructure facilities to new and young entrepreneurs in the MSME sector, The intelligent building of the JSS STP is spread in a sprawling 3 acres (12,140.6 m²) campus and houses state-of-art technology to fulfil the growing demands of highly competent IT professionals.
The Eastern India particularly Jharkhand is rich in mineral resources which resulted in Economic boom in Damodar Valley region and regions near Kolkata which resulted in development of cities such as Jamshedpur, Bokaro
Bokaro Steel City
Bokaro Steel City is one of the largest Industrial city situated in the State of Jharkhand, in India. Bokaro is the 48th cleanest city in India and second in Jharkhand after Jamshedpur and one of the best cities to live in India...
, Dhanbad
Dhanbad
Dhanbad features climate that is transitional between a humid subtropical climate and a tropical wet and dry climate. Summer starts from last week of March and ends in mid-June. Peak temperature in summer can reach 47oC. Dhanbad also receives heavy rainfall...
, Ranchi
Ranchi
-Climate:Ranchi has a humid subtropical climate. However, due to its position and the forests around the city, it is known for its pleasant climate. Its climate is the primary reason why Ranchi was once the summer capital of the undivided State of Bihar...
, and Patna.
Languages
BengaliBengali language
Bengali or Bangla is an eastern Indo-Aryan language. It is native to the region of eastern South Asia known as Bengal, which comprises present day Bangladesh, the Indian state of West Bengal, and parts of the Indian states of Tripura and Assam. It is written with the Bengali script...
is the dominant language of West Bengal as well as the whole of East India,spoken by well over 90 million people . Hindi along with Maithili
Maithili language
Maithili language is spoken in the eastern region of India and South-eastern region of Nepal. The native speakers of Maithili reside in Bihar, Jharkhand,parts of West Bengal and South-east Nepal...
, Magahi and Urdu
Urdu
Urdu is a register of the Hindustani language that is identified with Muslims in South Asia. It belongs to the Indo-European family. Urdu is the national language and lingua franca of Pakistan. It is also widely spoken in some regions of India, where it is one of the 22 scheduled languages and an...
is the dominant language of Bihar. Hindi and Urdu are the dominant language of Jharkhand, however 34% people of Jharkhand are tribals (2001 Census) and speak their own tribal languages and use Hindi
Hindi
Standard Hindi, or more precisely Modern Standard Hindi, also known as Manak Hindi , High Hindi, Nagari Hindi, and Literary Hindi, is a standardized and sanskritized register of the Hindustani language derived from the Khariboli dialect of Delhi...
as second language.
Oriya
Oriya language
Oriya , officially Odia from November, 2011, is an Indian language, belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European language family. It is mainly spoken in the Indian states of Orissa and West Bengal...
is the dominant language of the state of Orissa.
The Indo-Aryan languages
Indo-Aryan languages
The Indo-Aryan languages constitutes a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages, itself a branch of the Indo-European language family...
spoken in this region descend from the Magadhi Prakrit
Magadhi Prakrit
Magadhi Prakrit is of one of the three Dramatic Prakrits, the written languages of Ancient India following the decline of Pali and Sanskrit. Magadhi Prakrit was spoken in the eastern Indian subcontinent, in a region spanning what is now eastern India, Bangladesh, and Nepal. It is believed to be the...
, which was spoken in the ancient kingdom of Magadha. Bengali, Oriya
Oriya language
Oriya , officially Odia from November, 2011, is an Indian language, belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European language family. It is mainly spoken in the Indian states of Orissa and West Bengal...
and Assamese
Assamese language
Assamese is the easternmost Indo-Aryan language. It is used mainly in the state of Assam in North-East India. It is also the official language of Assam. It is also spoken in parts of Arunachal Pradesh and other northeast Indian states. Nagamese, an Assamese-based Creole language is widely used in...
emerged as distinct languages from Magadhi Prakrit and [Maithili] around 9/10th century A.D.
Many of the minority adivasi
Adivasi
Adivasi is an umbrella term for a heterogeneous set of ethnic and tribal groups claimed to be the aboriginal population of India. They comprise a substantial indigenous minority of the population of India...
s (indigenous tribal people) of East India belong to the Munda
Munda languages
-Anderson :Gregory Anderson's 1999 proposal is as follows. Individual languages are highlighted in italics.*North Munda **Korku**Kherwarian***Santhali***Mundari*South Munda **Kharia–Juang***Juang***Kharia...
branch of the Austro-Asiatic language family
Austro-Asiatic languages
The Austro-Asiatic languages, in recent classifications synonymous with Mon–Khmer, are a large language family of Southeast Asia, also scattered throughout India and Bangladesh. The name Austro-Asiatic comes from the Latin words for "south" and "Asia", hence "South Asia"...
. Major representatives of this group include the Munda
Munda people
The Munda are tribal people of the Chota Nagpur Plateau region.They are found across Jharkhand, Bihar, West Bengal, Chhattisgarh, Orissa and Assam states of India, and into parts of Bangladesh...
, Santal
Santals
The Santhal , are the largest tribal community in India, who live mainly in the states of Jharkhand, West Bengal, Bihar, Orissa, and Assam. There is also a significant Santal minority in neighboring Bangladesh, and a small population in Nepal....
, Oraon
Oraon
The Oraon उरांव or Kurukh कुड़ुख tribe , also spelled Uraon, Oran, or Oram, are tribal aborigines inhabiting various states across central and eastern India as well as Bangladesh...
and Ho
Ho people
The Ho people are a tribe of people belonging to the Indian state of Jharkhand.They are the fourth most numerous scheduled tribe Jharkhand after Santals, Oraons, and Mundas, and constitute around 10.5 percent of the total population in the state, numbering 7,087,068 in the 2001 census...
peoples. Santals
Santals
The Santhal , are the largest tribal community in India, who live mainly in the states of Jharkhand, West Bengal, Bihar, Orissa, and Assam. There is also a significant Santal minority in neighboring Bangladesh, and a small population in Nepal....
are the largest tribal group from the region.
Climate
The region lies in the humid-subtropical zone, and experiences hot summers from March to June, the monsoon from July to October and mild winters from November to February. The interior states have a drier climate and slightly more extreme climate, especially during the winters and summers, but the whole region receives heavy, sustained rainfall during the monsoon months.Snowfall occurs in the extreme northern regions of West Bengal and Daringbadi in Orissa.History
Orissa which is now known Orissa has a history spanning a period of over 5,000 years. Before Kalinga it was named as Udra or "Odra Desa". The Ancient Odra desa or Ordesa was limited to the valley of Mahanadi and to the lower course of Subarnarekha River. It comprised the whole of the present districts of Cuttack and Sambalpur and a portion of Midnapur. Bounded on the west by Gondwana, on the north by the wild hill states of Jaspur and Singhbhum, on the east by the sea and on the South by Ganjam, Orissa has a legendary history. The name Oriya originated from Odra or Udra tribes that inhabited the central coastal belt (Khordha DistrictKhordha district
Khordha is an administrative division of the state of Orissa, India. It was formed on April 1, 1993 by the division of former Puri District into Puri, Khurda and Nayagarh districts. In the year 2000 the district name was changed to Khordha. The district headquarters is Khordha Town, formerly...
and Nayagarh District
Nayagarh District
Nayagarh district is one of the 30 districts of Orissa State in eastern India. It was created in 1995 when the erstwhile Puri District was split into three distinct districts. It is home to the Baisipali Wildlife Sanctuary.-Maoist attacks:...
) of modern Orissa. Orissa has also been the home of the Kalinga
Kalinga (India)
Kalinga was an early state in central-eastern India, which comprised most of the modern state of Orissa/Utkal , as well as the Andhra region of the bordering state of Andhra Pradesh. It was a rich and fertile land that extended from the river Damodar/Ganges to Godavari and from Bay of Bengal to...
, Utkal, Mahakantara/Kantara and Kosal that played a particularly prominent role in the region's history, and one of the earliest references to the ancient Kalingas appears in the writings of Vedic chroniclers. In the 6th century BC, Vedic
Vedic period
The Vedic period was a period in history during which the Vedas, the oldest scriptures of Hinduism, were composed. The time span of the period is uncertain. Philological and linguistic evidence indicates that the Rigveda, the oldest of the Vedas, was composed roughly between 1700–1100 BCE, also...
Sutrakara Baudhayana mentions Kalinga as being beyond the Vedic fold, indicating that Brahminical influences had not yet touched the land. Unlike some other parts of India, tribal customs and traditions played a significant role in shaping political structures and cultural practices right up to the 15th century, when Brahminical influences triumphed over competing traditions and caste differentiation began to inhibit social mobility and erode what had survived of the ancient republican tradition.

Kalinga War
The Kalinga War was a war fought between the Mauryan Empire under Ashoka the Great and the state of Kalinga, a feudal republic located on the coast of the present-day Indian state of Orissa. The Kalinga war is one of the major battles in the History of India. Kalinga put up a stiff resistance,...
that led emperor Ashoka
Ashoka
Ashok Maurya or Ashoka , popularly known as Ashoka the Great, was an Indian emperor of the Maurya Dynasty who ruled almost all of the Indian subcontinent from ca. 269 BC to 232 BC. One of India's greatest emperors, Ashoka reigned over most of present-day India after a number of military conquests...
to embrace non-violence and the teachings of Buddha
Gautama Buddha
Siddhārtha Gautama was a spiritual teacher from the Indian subcontinent, on whose teachings Buddhism was founded. In most Buddhist traditions, he is regarded as the Supreme Buddha Siddhārtha Gautama (Sanskrit: सिद्धार्थ गौतम; Pali: Siddhattha Gotama) was a spiritual teacher from the Indian...
was fought here in 261 BC. Ashoka's military campaign against Kalinga
Kalinga
Kalinga is a landlocked province of the Philippines in the Cordillera Administrative Region in Luzon. Its capital is Tabuk and borders Mountain Province to the south, Abra to the west, Isabela to the east, Cagayan to the northeast, and Apayao to the north...
was one of the bloodiest in Mauryan history on account of the fearless and heroic resistance offered by the Kalingas to the mighty armies of the expanding Mauryan empire. Perhaps on account of their unexpected bravery, emperor Ashoka
Ashoka
Ashok Maurya or Ashoka , popularly known as Ashoka the Great, was an Indian emperor of the Maurya Dynasty who ruled almost all of the Indian subcontinent from ca. 269 BC to 232 BC. One of India's greatest emperors, Ashoka reigned over most of present-day India after a number of military conquests...
was compelled to issue two edicts specifically calling for a just and benign administration in Kalinga. Later on, Ashoka was instrumental in spreading Buddhist philosophy
Buddhist philosophy
Buddhist philosophy deals extensively with problems in metaphysics, phenomenology, ethics, and epistemology.Some scholars assert that early Buddhist philosophy did not engage in ontological or metaphysical speculation, but was based instead on empirical evidence gained by the sense organs...
all over Asia
Asia
Asia is the world's largest and most populous continent, located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres. It covers 8.7% of the Earth's total surface area and with approximately 3.879 billion people, it hosts 60% of the world's current human population...
. However, Ativ Land (Southwestern Orissa) was unconquered by Ashoka.
East India has some good archaeological sites. Buddhist relics of Orissa is good archaeological example. It is found during the excavation at Lalitgiri in Orissa.Tel river civilization put light towards a great civilization existing in Kalahandi, Balangir, Koraput (KBK) region in the past that is recently getting explored. The discovered archaeological wealth of Tel Valley suggest a well civilized, urbanized, cultured people inhabited on this land mass around 2000 years ago and Asurgarh was its capital. Kalahandi along with Koraput and Bastar was part of Kantara referred in Ramayana
Ramayana
The Ramayana is an ancient Sanskrit epic. It is ascribed to the Hindu sage Valmiki and forms an important part of the Hindu canon , considered to be itihāsa. The Ramayana is one of the two great epics of India and Nepal, the other being the Mahabharata...
and Mahabharata
Mahabharata
The Mahabharata is one of the two major Sanskrit epics of ancient India and Nepal, the other being the Ramayana. The epic is part of itihasa....
. In 4th century B.C. this region was known as Indravana from where precious gem-stones and diamond were collected for the imperial Maurya treasury. During the period of Maurya emperor Ashoka, Kalahandi along with Koraput and Bastar region was called Atavi Land. This land was unconquered as per Ashokan record. In the beginning of Chrisitan era probably it was known as Mahavana. In 4th Century A.D. Vyaghraraja was ruling over Mahakantara comprising Kalahandi, undivided Koraput and Bastar region. Asurgarh was capital of Mahakantara.



Jainism
Jainism is an Indian religion that prescribes a path of non-violence towards all living beings. Its philosophy and practice emphasize the necessity of self-effort to move the soul towards divine consciousness and liberation. Any soul that has conquered its own inner enemies and achieved the state...
emperor, Kharavela
Kharavela
Khārabēḷa was the third and greatest emperor of the Mahāmēghabāhana Dynasty of Kaḷinga . The main source of information about Khārabeḷa is his famous seventeen line rock-cut Hātigumphā inscription in a cave in the Udayagiri hills near Bhubaneswar, Orissa.During the reign of Khārabēḷa, the Chedi...
. He ruled all the way down south to include parts of the Tamil country
Ancient Tamil country
The Sangam period is the classical period in the history of Tamil Nadu, Kerala and other parts of South India, spanning about the 3rd century BCE to the 3rd century CE...
. He built the superb monastic caves at Udayagiri and Khandagiri Caves
Udayagiri and Khandagiri Caves
Udayagiri and Khandagiri Caves are partly natural and partly artificial caves of archaeological, historical and religious importance near the city of Bhubaneswar in Orissa, India. The caves are situated on two hills Udayagiri and Khandagiri, mentioned as Kumari Parvat in Hathigumpha inscription...
. Subsequently, the region was ruled under various monarchs, such as Samudragupta
Samudragupta
Samudragupta , ruler of the Gupta Empire , and successor to Chandragupta I, is considered to be one of the greatest military geniuses in Indian history according to Historian V. A. Smith. His name is taken to be a title acquired by his conquests...
and Shashanka
Shashanka
Shashanka is often attributed with creating the first separate political entity in a unified Bengal called Gauda and as such is a major figure in Bengali history. He reigned in 7th century AD, and some historians place his rule approximately between 590 AD and 625 AD. He is the contemporary of...
. It also was a part of Harsha
Harsha
Harsha or Harsha Vardhana or Harshvardhan was an Indian emperor who ruled northern India from 606 to 647 AD. He was the son of Prabhakara Vardhana and younger brother of Rajya Vardhana, a king of Thanesar, Haryana...
's empire. In 795 AD, the king Yayati Kesari I of Kesari or Soma dynasty of Kosala united Kosala and Utkala into a single empire. He is also supposed to have built the first Jagannath Temple
Jagannath Temple
-India:*Jagannath Temple, Puri, Orissa, India*Jagannath Temple, Koraput, Orissa, India*Jagannath Temple, Baripada, Mayurbhanj, Orissa, India*Jagannath Temple, Nayagarh, Orissa, India*Jagannath Temple, Ranchi, Jharkhand, India*Jagannath Temple, Delhi, India...
at Puri
Puri
Puri is district headquarter, a city situated about south of state capital Bhubaneswar, on the eastern coast of the Bay of Bengal in the Indian state of Orissa. It is also known as Jagannath Puri after the Jagannath Temple . It is a holy city of the Hindus as a part of the Char Dham pilgrimages...
, although the current structure of the temple is entirely different and was built by Kings Choda Gangadeva and Ananga Bhimadeva of the Eastern Ganga Dynasty
Eastern Ganga dynasty
The Eastern Ganga dynasty reigned from Kalinga and their rule consisted of the whole of the modern day Indian state of Orissa as well as parts of West Bengal, Andhra Pradesh and Chhattisgarh from the 11th century to the early 15th century. Their capital was known by the name Kalinganagar, which is...
in the 12th century. The famous Lingaraja temple in Bhubaneshwar was started by Keshari dynasty king Yayati Keshari III and completed by his son Lalatendu Keshari in the 10th century. King Narasimha Dev
Narasimhadeva I
Narasimha Deva I was generally thought to be one of the greatest rulers of the Eastern Ganga Dynasty. He ruled the dynasty from 1238–1264. Today he is most remembered as the builder of the Konark Sun Temple, a World Heritage Site at Konark, Orissa....
is reputed to have built the magnificent Konark Sun Temple
Konark Sun Temple
Konark Sun Temple is a 13th-century Sun Temple , at Konark, in Orissa. It was constructed from oxidized and weathered ferruginous sandstone by King Narasimhadeva I of the Eastern Ganga Dynasty. The temple is an example of Orissan architecture of Ganga dynasty...
. Although now largely in ruins, the temple may have once rivaled the Taj Mahal
Taj Mahal
The Taj Mahal is a white Marble mausoleum located in Agra, India. It was built by Mughal emperor Shah Jahan in memory of his third wife, Mumtaz Mahal...
in splendour.
The Mughals conquered Coastal Orissa in 1576. The last Hindu Emperor of Orissa, Gajapati
Gajapati Kingdom
The Gajapatis were a medieval Hindu dynasty that ruled over Kalinga , large parts of Andhra Pradesh and West Bengal, and the eastern and central parts of Madhya Pradesh and the southern parts of Bihar from 1434-1541. Gajapati dynasty was established by Kapilendra Deva in 1434...
Mukunda Deva, was defeated and was killed in the battle of Gohiratikiri. The coastal plain of Orissa from Medinipur to Rajahmundry
Rajahmundry
Rajahmundry is a city and municipal corporation of the Andhra Pradesh state in India. It is located east of the state capital, Hyderabad, on the banks of the River Godavari. Known as the Cultural Capital, Rajahmundry is noted for its intense Veda culture and intellect...
came under Mughal rule, which was broadly divided into six parts as Jaleswar
Jaleswar
Jaleswar is a small town that falls under the state of Orissa. It belongs to Balasore district of state Orissa and is adjacent to border of West Bengal. 'Jaleswar' town is a notified area committee...
Sarkar, Bhadrak
Bhadrak
Bhadrak is a city and a municipality in Bhadrak district in the state of Orissa, India.-Demographics: India census, Bhadrak had a population of 1,33,4000. Males constitute 52% of the population and females 48%. Bhadrak has an average literacy rate of 73.86, higher than the national average of...
Sarkar, Cuttack
Cuttack
Cuttack is the former capital of the state of Orissa, India. It is the headquarters of Cuttack district and is located about 20 km to the north east of Bhubaneswar, the capital of Orissa. The name of the city is an anglicised form of Kataka that literally means The Fort, a reference to the...
Sarkar, Chicacole
Chicacole
Chicacole, was the former name for the city of Srikakulam that was applied by British colonial rulers. It is said that the word Chicacole came from two Persian words - Chica and Khol. Chica means "a small cloth bag which can be closed by pulling a thread around its neck" and Khol means 'open'...
(Srikakulam
Srikakulam
Srikakulam is a town, municipality and headquarters of Srikakulam district in the north-eastern Andhra Pradesh, India. It is part of Srikakulam Assembly constituency and Srikakulam Parliament Constituency. Srikakulam was formerly called as Gulshanabad during Muslim rule and was headquarter of...
) Sarkar, Kalinga Dandapat and Rajamundry Sarkar or Godavari Province. Orissa's Central, Northern, Western and Southern hilly areas were ruled independently by Hindu kings. The Nizam of Hyderabad occupied the area between Rajahmundry
Rajahmundry
Rajahmundry is a city and municipal corporation of the Andhra Pradesh state in India. It is located east of the state capital, Hyderabad, on the banks of the River Godavari. Known as the Cultural Capital, Rajahmundry is noted for its intense Veda culture and intellect...
to Srikakulam
Srikakulam
Srikakulam is a town, municipality and headquarters of Srikakulam district in the north-eastern Andhra Pradesh, India. It is part of Srikakulam Assembly constituency and Srikakulam Parliament Constituency. Srikakulam was formerly called as Gulshanabad during Muslim rule and was headquarter of...
in 16th century. Medinipur was attached to Bengal
Bengal
Bengal is a historical and geographical region in the northeast region of the Indian Subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal. Today, it is mainly divided between the sovereign land of People's Republic of Bangladesh and the Indian state of West Bengal, although some regions of the previous...
province in 18th century. The remaining parts of Coastal Orissa, were subsequently ceded to the Maratha Empire
Maratha Empire
The Maratha Empire or the Maratha Confederacy was an Indian imperial power that existed from 1674 to 1818. At its peak, the empire covered much of South Asia, encompassing a territory of over 2.8 million km²....
in 1751.
The British occupied the Northern Circars comprising the southern coast of Orissa as a result of the Carnatic Wars in the early 1760s and incorporated them into the Madras Presidency
Madras Presidency
The Madras Presidency , officially the Presidency of Fort St. George and also known as Madras Province, was an administrative subdivision of British India...
gradually. In 1803, the British under the British East India Company
British East India Company
The East India Company was an early English joint-stock company that was formed initially for pursuing trade with the East Indies, but that ended up trading mainly with the Indian subcontinent and China...
annexed the Maratha province of Orissa after the Second Anglo-Maratha War
Second Anglo-Maratha War
The Second Anglo-Maratha War was the second conflict between the British East India Company and the Maratha Empire in India.-Background:...
. The northern and western districts of Orissa were incorporated into Bengal Presidency
Bengal Presidency
The Bengal Presidency originally comprising east and west Bengal, was a colonial region of the British Empire in South-Asia and beyond it. It comprised areas which are now within Bangladesh, and the present day Indian States of West Bengal, Assam, Bihar, Meghalaya, Orissa and Tripura.Penang and...
. Following famine and floods in 1866, large scale irrigation
Irrigation
Irrigation may be defined as the science of artificial application of water to the land or soil. It is used to assist in the growing of agricultural crops, maintenance of landscapes, and revegetation of disturbed soils in dry areas and during periods of inadequate rainfall...
projects were undertaken in the last half of the 19th century. The coastal section was separated from Bengal and made into the Province of Bihar and Orissa in 1912, in response to local agitation for a separate state for the Oriya
Oriya language
Oriya , officially Odia from November, 2011, is an Indian language, belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European language family. It is mainly spoken in the Indian states of Orissa and West Bengal...
-speaking people. In 1936, Bihar
Bihar
Bihar is a state in eastern India. It is the 12th largest state in terms of geographical size at and 3rd largest by population. Almost 58% of Biharis are below the age of 25, which is the highest proportion in India....
and Orissa were split into separate provinces. Thus after a long period of struggle the Oriya people got re-united after centuries of political separation. On 1 April 1936, the new province of Orissa came into existence on linguistic basis during the British rule in India with Sir Jhon Austin Hubbak as the first Governor. A long cherished dream of Oriya people and their leaders like Madhusudan Das, Maharaja Krushna Chnadra Gajapati, Pandit Nilakantha Das, Bhubanananda Das and many other came true. The district of Ganjam
Ganjam
Ganjam is a town and a notified area committee in Ganjam district in the state of Orissa, India.-Geography:Ganjam is located at . It has an average elevation of 3 metres .-Demographics:...
was transferred from Madras Presidency to the new province of Orissa on 1 April 1936. From that time onwards people of Orissa celebrate the day 1 April as Utkal Divas or Orissa Day.
Following Indian independence, the area of Orissa was almost doubled and the population was increased by a third by the addition of 24 former princely states. In 1950, Orissa became a constituent state in the Union of India.
The first recorded independent king of Bengal was Shashanka
Shashanka
Shashanka is often attributed with creating the first separate political entity in a unified Bengal called Gauda and as such is a major figure in Bengali history. He reigned in 7th century AD, and some historians place his rule approximately between 590 AD and 625 AD. He is the contemporary of...
, reigning around early 7th century. After a period of anarchy, the native Buddhist
Buddhism
Buddhism is a religion and philosophy encompassing a variety of traditions, beliefs and practices, largely based on teachings attributed to Siddhartha Gautama, commonly known as the Buddha . The Buddha lived and taught in the northeastern Indian subcontinent some time between the 6th and 4th...
-Hindu Pala Empire
Pala Empire
The Pāla Empire was one of the major middle kingdoms of India existed from 750–1174 CE. It was ruled by a Buddhist dynasty from Bengal in the eastern region of the Indian subcontinent, all the rulers bearing names ending with the suffix Pala , which means protector. The Palas were often described...
ruled the region for four hundred years, and expanded across much of the Indian subcontinent
Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent, also Indian Subcontinent, Indo-Pak Subcontinent or South Asian Subcontinent is a region of the Asian continent on the Indian tectonic plate from the Hindu Kush or Hindu Koh, Himalayas and including the Kuen Lun and Karakoram ranges, forming a land mass which extends...
into Afghanistan
Afghanistan
Afghanistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located in the centre of Asia, forming South Asia, Central Asia and the Middle East. With a population of about 29 million, it has an area of , making it the 42nd most populous and 41st largest nation in the world...
during the reigns of Dharmapala
Dharmapala of Bengal
Dharama Pala was the second ruler of the Pala Empire of Bengal region in the Indian Subcontinent. He was the son and succeessor of Gopala , the founder of the Pala Dynasty. He greatly expanded the boundaries of the Pala Empire founded by his father and made the Palas the most dominant power in...
and Devapala
Devapala
Deva Pala , was a powerful emperor from the Pala Empire of Bengal region in the Indian Subcontinent. He was the third king in the line and had succeeded his father, emperor Dharamapala...
. The Pala dynasty was followed by a shorter reign of the Hindu
Hindu
Hindu refers to an identity associated with the philosophical, religious and cultural systems that are indigenous to the Indian subcontinent. As used in the Constitution of India, the word "Hindu" is also attributed to all persons professing any Indian religion...
Saiva Sena dynasty
Sena dynasty
The Sena Empire was a Hindu dynasty that ruled from Bengal through the 11th and 12th centuries. At its peak the empire covered much of the north-eastern region in the Indian Subcontinent. They were called Brahma-Kshatriyas, as evidenced through their surname, which is derived from the Sanskrit,...
. Islam
Islam
Islam . The most common are and . : Arabic pronunciation varies regionally. The first vowel ranges from ~~. The second vowel ranges from ~~~...
was introduced to Bengal by Arab Muslim traders. A large number of people became Muslims in the twelfth century through Sufi
Sufism
Sufism or ' is defined by its adherents as the inner, mystical dimension of Islam. A practitioner of this tradition is generally known as a '...
missionaries. Subsequent Muslim conquests
Muslim conquests
Muslim conquests also referred to as the Islamic conquests or Arab conquests, began with the Islamic prophet Muhammad. He established a new unified polity in the Arabian Peninsula which under the subsequent Rashidun and Umayyad Caliphates saw a century of rapid expansion of Muslim power.They...
helped spread Islam throughout the region. Bakhtiar Khilji, a Turkic
Turkic peoples
The Turkic peoples are peoples residing in northern, central and western Asia, southern Siberia and northwestern China and parts of eastern Europe. They speak languages belonging to the Turkic language family. They share, to varying degrees, certain cultural traits and historical backgrounds...
general of the Slave dynasty
Slave dynasty
The Slave Dynasty or Mamluk Dynasty or Ghulam Dynasty , was directed into India by Qutb-ud-din Aybak, a Turkic general of Central Asian birth. It was the first of five unrelated dynasties to rule India's Delhi Sultanate from 1206 to 1290...
of Delhi Sultanate
Delhi Sultanate
The Delhi Sultanate is a term used to cover five short-lived, Delhi based kingdoms or sultanates, of Turkic origin in medieval India. The sultanates ruled from Delhi between 1206 and 1526, when the last was replaced by the Mughal dynasty...
, defeated Lakshman Sen
Lakshman Sen
Lakshman Sen was the fourth king of the Sen dynasty of Bengal, who ruled for about 28 years. Lakshman Sen succeeded his father Ballal Sen...
of the Sena dynasty and conquered large parts of Bengal. Consequently, the region was ruled by dynasties of sultan
Sultan
Sultan is a title with several historical meanings. Originally, it was an Arabic language abstract noun meaning "strength", "authority", "rulership", and "dictatorship", derived from the masdar سلطة , meaning "authority" or "power". Later, it came to be used as the title of certain rulers who...
s and feudal lords under the Delhi Sultanate for the next few hundred years. In the sixteenth century, Mughal general Islam Khan
Islam Khan
Islam Khan may refer to:*Islam Khan I - also known as Islam Khan Chisti *Islam Khan II - also known as Islam Khan Mashhadi *Islam Khan III - also known as Islam Khan Badakhshi...
conquered Bengal. Susequently, Afghan ruler Sher Shah Suri
Sher Shah Suri
Sher Shah Suri , birth name Farid Khan, also known as Sher Khan , was the founder of the short-lived Sur Empire in northern India, with its capital at Delhi, before its demise in the hands of the resurgent Mughal Empire...
and Hindu emperor Hemu
Hemu
Samrat Hem Chandra Vikramaditya, Hemu Vikramaditya or simply Hemu was a Hindu Emperor of India during the sixteenth century, in medieval times...
had ruled for shorter periods. However, administration by governors appointed by the court of the Mughal Empire
Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire , or Mogul Empire in traditional English usage, was an imperial power from the Indian Subcontinent. The Mughal emperors were descendants of the Timurids...
gave way to semi-independence of the area under the Nawab
Nawab
A Nawab or Nawaab is an honorific title given to Muslim rulers of princely states in South Asia. It is the Muslim equivalent of the term "maharaja" that was granted to Hindu rulers....
s of Murshidabad
Murshidabad
Murshidabad is a city in Murshidabad district of West Bengal state in India. The city of Murshidabad is located on the southern bank of the Bhagirathi, a distributary of the Ganges River. It was the capital of undivided Bengal during the Mughal rule. Nawabs of Bengal used to rule Bengal from this...
, who nominally respected the sovereignty of the Mughals in Delhi
Delhi
Delhi , officially National Capital Territory of Delhi , is the largest metropolis by area and the second-largest by population in India, next to Mumbai. It is the eighth largest metropolis in the world by population with 16,753,265 inhabitants in the Territory at the 2011 Census...
. The most notable among them is Murshid Quli Khan
Murshid Quli Khan
Murshid Quli Khan was the first Nawab of Bengal. In fact circumstances resulted in his being the first independent ruler of Bengal post the death of Emperor Aurangzeb...
, who was succeeded by Alivardi Khan
Alivardi Khan
Ali Vardi Khan was the Nawab of Bengal, Bihar and Orissa during 1740 - 1756. He toppled the Nasiri Dynasty of Bengal and took power as Nawab.-Early life:...
.

Patliputra
Pāṭaliputra , modern-day Patna, was a city in ancient India, originally built by Ajatashatru in 490 BC as a small fort near the River Ganges, and later the capital of the ancient Mahājanapadas kingdom of Magadha....
(modern Patna
Patna
Paṭnā , is the capital of the Indian state of Bihar and the second largest city in Eastern India . Patna is one of the oldest continuously inhabited places in the world...
). The Mauryan Emperor, Ashoka
Ashoka
Ashok Maurya or Ashoka , popularly known as Ashoka the Great, was an Indian emperor of the Maurya Dynasty who ruled almost all of the Indian subcontinent from ca. 269 BC to 232 BC. One of India's greatest emperors, Ashoka reigned over most of present-day India after a number of military conquests...
, who was born in Patliputra (Patna) is believed to be one of the greatest rulers in the history of India and the world.
According to indologist A.L. Basham
Arthur Llewellyn Basham
Professor Arthur Llewellyn Basham was a noted historian and indologist and author of a number of books. It is perhaps not a mere coincidence that two of the most renowned living historians of early India, Professors R.S...
, the author of the book The Wonder that was India
The Wonder That was India
The Wonder That was India : a survey of the culture of the Indian sub-continent before the coming of the Muslims, is a book on Indian history written by A.L. Basham and published in 1954. The second edition of the first volume by Basham was published in 1963 and reprinted several times.There is...
,
Bihar remained an important place of power, culture and education during the next one thousand years. The Gupta Empire, which again originated from Magadha in 240 CE, is referred to as the Golden Age of India in science, mathematics, astronomy, religion and Indian philosophy
Indian philosophy
India has a rich and diverse philosophical tradition dating back to ancient times. According to Radhakrishnan, the earlier Upanisads constitute "...the earliest philosophical compositions of the world."...
. The peace and prosperity created under leadership of Gupta
Gupta
Gupta is a common surname of Indian origin.According to some academicians, the name Gupta is derived from Sanskrit goptri, meaning military governor. A more direct translation of the Sanskrit word gupta is 'secret' or 'hidden'. According to prominent historian R. C...
s enabled the pursuit of scientific and artistic endeavors. Historians place the Gupta dynasty alongside with the Han Dynasty
Han Dynasty
The Han Dynasty was the second imperial dynasty of China, preceded by the Qin Dynasty and succeeded by the Three Kingdoms . It was founded by the rebel leader Liu Bang, known posthumously as Emperor Gaozu of Han. It was briefly interrupted by the Xin Dynasty of the former regent Wang Mang...
, Tang Dynasty
Tang Dynasty
The Tang Dynasty was an imperial dynasty of China preceded by the Sui Dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms Period. It was founded by the Li family, who seized power during the decline and collapse of the Sui Empire...
and Roman Empire
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of the ancient Roman civilization, characterised by an autocratic form of government and large territorial holdings in Europe and around the Mediterranean....
as a model of a classical civilization. The capital of Gupta empire
Gupta Empire
The Gupta Empire was an ancient Indian empire which existed approximately from 320 to 550 CE and covered much of the Indian Subcontinent. Founded by Maharaja Sri-Gupta, the dynasty was the model of a classical civilization. The peace and prosperity created under leadership of Guptas enabled the...
was Pataliputra, present day Patna
Patna
Paṭnā , is the capital of the Indian state of Bihar and the second largest city in Eastern India . Patna is one of the oldest continuously inhabited places in the world...
. The Vikramshila
Vikramshila
University was one of the two most important centers of Buddhist learning in India during the Pala dynasty, along with University. was established by King Dharmapala in response to a supposed decline in the quality of scholarship at Nālandā...
and Nalanda
Nalanda
Nālandā is the name of an ancient center of higher learning in Bihar, India.The site of Nalanda is located in the Indian state of Bihar, about 55 miles south east of Patna, and was a Buddhist center of learning from the fifth or sixth century CE to 1197 CE. It has been called "one of the...
universities were among the oldest and best centres of education in ancient India. Some writers believe the period between the 400 CE and 1000 CE saw gains by Hinduism
Hinduism
Hinduism is the predominant and indigenous religious tradition of the Indian Subcontinent. Hinduism is known to its followers as , amongst many other expressions...
at the expense of Buddhism. The Hindu kings gave much grants to the Buddhist monks for building Brahmavihara
Brahmavihara
The brahmavihāras are a series of four Buddhist virtues and the meditation practices made to cultivate them. They are also known as the four immeasurables...
s. A National Geographic edition reads, "The essential tenets of Buddhism and Hinduism arose from similar ideas best described in the Upanishads, a set of Hindu treatises set down in India largely between the eighth and fourth centuries B.C."
Religion and culture
The majority of the population of East India is HinduHindu
Hindu refers to an identity associated with the philosophical, religious and cultural systems that are indigenous to the Indian subcontinent. As used in the Constitution of India, the word "Hindu" is also attributed to all persons professing any Indian religion...
with Muslim
Muslim
A Muslim, also spelled Moslem, is an adherent of Islam, a monotheistic, Abrahamic religion based on the Quran, which Muslims consider the verbatim word of God as revealed to prophet Muhammad. "Muslim" is the Arabic term for "submitter" .Muslims believe that God is one and incomparable...
, Christian
Christian
A Christian is a person who adheres to Christianity, an Abrahamic, monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth as recorded in the Canonical gospels and the letters of the New Testament...
, Buddhist and Sikh
Sikh
A Sikh is a follower of Sikhism. It primarily originated in the 15th century in the Punjab region of South Asia. The term "Sikh" has its origin in Sanskrit term शिष्य , meaning "disciple, student" or शिक्ष , meaning "instruction"...
minorities. The Muslims constitute a very large minority in this region , with 25% of the population in Bengal and 17% in Bihar.They can be found in each and every District of West Bengal and Bihar.Hindus formed 94% of total population of Orissa.Christians are the largest minority in Orissa.
Durga
Durga
For the 1985 Hindi Film of Rajesh Khanna see DurgaaIn Hinduism, Durga ; ; meaning "the inaccessible" or "the invincible"; , durga) or Maa Durga "one who can redeem in situations of utmost distress" is a form of Devi, the supremely radiant goddess, depicted as having eighteen arms, riding a lion...
, Jagannath
Jagannath
Jagannath is a transcendental non-anthropotheistic Hindu god worshiped primarily by the people of Indian state of Orissa, and, to a great extent, West Bengal...
and Shiva
Shiva
Shiva is a major Hindu deity, and is the destroyer god or transformer among the Trimurti, the Hindu Trinity of the primary aspects of the divine. God Shiva is a yogi who has notice of everything that happens in the world and is the main aspect of life. Yet one with great power lives a life of a...
are particularly popular Hindu
Hindu
Hindu refers to an identity associated with the philosophical, religious and cultural systems that are indigenous to the Indian subcontinent. As used in the Constitution of India, the word "Hindu" is also attributed to all persons professing any Indian religion...
deities in this region.
Durga
Durga
For the 1985 Hindi Film of Rajesh Khanna see DurgaaIn Hinduism, Durga ; ; meaning "the inaccessible" or "the invincible"; , durga) or Maa Durga "one who can redeem in situations of utmost distress" is a form of Devi, the supremely radiant goddess, depicted as having eighteen arms, riding a lion...
&Kali
Kali
' , also known as ' , is the Hindu goddess associated with power, shakti. The name Kali comes from kāla, which means black, time, death, lord of death, Shiva. Kali means "the black one". Since Shiva is called Kāla - the eternal time, Kālī, his consort, also means "Time" or "Death" . Hence, Kāli is...
are patron deities of Bengal and Mithila whereas Jagannath
Jagannath
Jagannath is a transcendental non-anthropotheistic Hindu god worshiped primarily by the people of Indian state of Orissa, and, to a great extent, West Bengal...
or Vishnu
Vishnu
Vishnu is the Supreme god in the Vaishnavite tradition of Hinduism. Smarta followers of Adi Shankara, among others, venerate Vishnu as one of the five primary forms of God....
is patron god
God
God is the English name given to a singular being in theistic and deistic religions who is either the sole deity in monotheism, or a single deity in polytheism....
among Oriya people
Oriya people
The Oriya, known classically by various names , are an ethnic group of eastern India and of eastern Indo-Aryan stock...
. Shiva
Shiva
Shiva is a major Hindu deity, and is the destroyer god or transformer among the Trimurti, the Hindu Trinity of the primary aspects of the divine. God Shiva is a yogi who has notice of everything that happens in the world and is the main aspect of life. Yet one with great power lives a life of a...
is popular in all areas of eastern states.
Among tribals of the region Hinduism
Hinduism
Hinduism is the predominant and indigenous religious tradition of the Indian Subcontinent. Hinduism is known to its followers as , amongst many other expressions...
is the dominant religion. Some tribals also follow their indigenous religions (Sarana).
There are several places of pilgrimage for Hinduism
Hinduism
Hinduism is the predominant and indigenous religious tradition of the Indian Subcontinent. Hinduism is known to its followers as , amongst many other expressions...
. Puri
Puri
Puri is district headquarter, a city situated about south of state capital Bhubaneswar, on the eastern coast of the Bay of Bengal in the Indian state of Orissa. It is also known as Jagannath Puri after the Jagannath Temple . It is a holy city of the Hindus as a part of the Char Dham pilgrimages...
in Orissa is one the four holy City/Dham of Hindu religion and particularly known for Rath Yatra
Rath Yatra
Ratha Yatra is a huge Hindu festival associated with Lord Jagannath held at Puri in the state of Orissa, India during the months of June or July. Most of the city's society is based around the worship of Jagannath with the ancient temple being the fulcrum of the area...
festival. Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar is the capital of the Indian state of Orissa, officially Odisha. The city has a long history of over 2000 years starting with Chedi dynasty who had Sisupalgarh near present-day Bhubaneswar as their capital...
is considered to be the "City of Temples".Konark
Konark
Konark is a small town in Puri district in the state of Orissa, India, on the Bay of Bengal, sixty-five kilometers from Bhubaneswar. It is the site of the 13th-century Sun Temple , built in black granite by King Narasimhadeva-I of the Eastern Ganga Dynasty. The temple is a World Heritage Site...
houses an old sun temple.
Bihar Sharif
Bihar Sharif
Bihar Sri is the district headquarters of Nalanda district in the state of Bihar in eastern India.-History:The ancient Odantpuri University was located here, an important centre for the learning of Buddhism. Odatpuri is center of Buddhist culture...
is an important pilgrimage centre for Muslims all over Bihar.
Dakshineswar Kali Temple
Dakshineswar Kali Temple
The Dakshineswar Kali Temple is a Hindu temple located in Dakshineswar near Kolkata. Situated on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River, the presiding deity of the temple is Bhavatarini, an aspect of Kali, meaning, 'She who liberates Her devotees from the ocean of existence i.e Saṃsāra'...
is a famous Kali
Kali
' , also known as ' , is the Hindu goddess associated with power, shakti. The name Kali comes from kāla, which means black, time, death, lord of death, Shiva. Kali means "the black one". Since Shiva is called Kāla - the eternal time, Kālī, his consort, also means "Time" or "Death" . Hence, Kāli is...
temple in West Bengal.
In Bihar, Gaya
Gaya, India
Gaya is the second largest city of Bihar, India, and it is also the headquarters of Gaya District.Gaya is 100 kilometers south of Patna, the capital city of Bihar. Situated on the banks of Falgu River , it is a place sanctified by both the Hindu and the Buddhist religions...
is known for temple for salvation of ancestors. Other places are Sultanganj in Bhagalpur
Bhagalpur
Bhagdattpuram was one of the most influential towns in "Aryavarta" . It is supposed to have been concurrent to Patliputra or Patna. Bhagdattpuram finds its mention in the Vedas and Ramayana as well. It is supposed to be the kingdom of Daanvir Karna, the son of Kunti and the Sun God...
and Vaidyanath Jyotirlinga
Vaidyanath Jyotirlinga
Vaidyanath Jyotirlinga temple, also known as Baba dham and Baidyanath dham is one of the twelve Jyotirlingas, the most sacred abodes of Shiva. The location of Vaidyanath Jyotirlinga is disputed. The claimed locations are:...
in Deoghar
Deoghar
Deoghar is the headquarters city of Deoghar District in the Santhal Parganas division of the state of Jharkhand, India. It is an important Hindu pilgrimage centre, having in Baidyanath Temple one of the twelve Shiva Jyothirlingams in India and also one of the 51 Shakti Peethas in India.-Origin of...
, Jharkhand. Bodh Gaya is the city sacred to Buddhism
Buddhism
Buddhism is a religion and philosophy encompassing a variety of traditions, beliefs and practices, largely based on teachings attributed to Siddhartha Gautama, commonly known as the Buddha . The Buddha lived and taught in the northeastern Indian subcontinent some time between the 6th and 4th...
. There are also other cities sacred to Jains
Jainism
Jainism is an Indian religion that prescribes a path of non-violence towards all living beings. Its philosophy and practice emphasize the necessity of self-effort to move the soul towards divine consciousness and liberation. Any soul that has conquered its own inner enemies and achieved the state...
in Bihar
Bihar
Bihar is a state in eastern India. It is the 12th largest state in terms of geographical size at and 3rd largest by population. Almost 58% of Biharis are below the age of 25, which is the highest proportion in India....
and Jharkhand.
Dance

Odissi
Odissi, also spelled Orissi , is one of the eight classical dance forms of India. It originates from the state of Orissa, in eastern India. It is the oldest surviving dance form of India on the basis of archaeological evidences. The classic treatise of Indian dance, Natya Shastra, refers to it as...
is the only classical dance in eastern India. It originates from the state of Orissa
Orissa
Orissa , officially Odisha since Nov 2011, is a state of India, located on the east coast of India, by the Bay of Bengal. It is the modern name of the ancient nation of Kalinga, which was invaded by the Maurya Emperor Ashoka in 261 BC. The modern state of Orissa was established on 1 April...
, in eastern India. It is the oldest surviving dance form of India on the basis of archaeological evidences. Odissi has a long, unbroken tradition of 2,000 years and finds mention in the Natyashastra
Natya Shastra
The Natya Shastra is an ancient Indian treatise on the performing arts, encompassing theatre, dance and music. It was written during the period between 200 BC and 200 AD in classical India and is traditionally attributed to the Sage Bharata.The Natya Shastra is incredibly wide in its scope...
of Bharatamuni
Bharata Muni
Bharata was an ancient Indian musicologist who authored the Natya Shastra, a theoretical treatise on ancient Indian dramaturgy and histrionics, dated to between roughly 400 BC and 200 BC. Indian dance and music find their root in the Natyashastra...
, possibly written circa 200 BC.
Mahari Dance is one of the important dance forms of Orissa and originated in the temples of Orissa. History of Orissa provides evidence of the 'Devadasi' cult in Orissa. Devadasis were dancing girls who were dedicated to the temples of Orissa. The Devadasis in Orissa were known as 'Maharis' and the dance performed by them came to be known as Mahari Dance.
Gotipua dance is another form of dance in Orissa. In Oriya colloquial language Gotipua means single boy. The dance performance done by a single boy is known as Gotipua dance.
There are many folk dance in east India. The well Known folk dance from east India are Ghumura Dance
Ghumura Dance
Ghumura Folk Dance[ , Kalahandia : ଘୁମ୍ରା ନାଚ୍ ] has earned both national and international name and fame in past three decades, after winning heart of Oriya people throughout Orissa. Its popular music is considered as one of those ancient folk musics, which after struggling a lot with the current...
, Sambalpuri, Chhau dance
Chhau dance
thumb|A video of Chau dance in PuruliaChhau dance is a genre of Indian tribal martial dance which is popular in the Indian states of Orissa, Jharkhand and West Bengal...
.
Chhau dance (or Chau dance) is form of tribal martial dance attributed to origins in Mayurbhanj princly state of Orissa
Orissa
Orissa , officially Odisha since Nov 2011, is a state of India, located on the east coast of India, by the Bay of Bengal. It is the modern name of the ancient nation of Kalinga, which was invaded by the Maurya Emperor Ashoka in 261 BC. The modern state of Orissa was established on 1 April...
.and seen in the India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
n states of West Bengal
West Bengal
West Bengal is a state in the eastern region of India and is the nation's fourth-most populous. It is also the seventh-most populous sub-national entity in the world, with over 91 million inhabitants. A major agricultural producer, West Bengal is the sixth-largest contributor to India's GDP...
, Jharkhand
Jharkhand
Jharkhand is a state in eastern India. It was carved out of the southern part of Bihar on 15 November 2000. Jharkhand shares its border with the states of Bihar to the north, Uttar Pradesh and Chhattisgarh to the west, Orissa to the south, and West Bengal to the east...
and Orissa
Orissa
Orissa , officially Odisha since Nov 2011, is a state of India, located on the east coast of India, by the Bay of Bengal. It is the modern name of the ancient nation of Kalinga, which was invaded by the Maurya Emperor Ashoka in 261 BC. The modern state of Orissa was established on 1 April...
. There are three subtypes of the dance, based on the original places where the subtypes were developed. Seraikella Chau was developed in Seraikella, the administrative head of the Seraikela Kharsawan
Seraikela Kharsawan
Seraikela-Kharsawan district ; formerly the princely state of Seraikella/Saraikella is one of the twenty-four districts of Jharkhand state in eastern India. Seraikela town is the district headquarters of Saraikela Kharsawan district. The district is well-known for Seraikela Chhau, one of the three...
district of Jharkhand
Jharkhand
Jharkhand is a state in eastern India. It was carved out of the southern part of Bihar on 15 November 2000. Jharkhand shares its border with the states of Bihar to the north, Uttar Pradesh and Chhattisgarh to the west, Orissa to the south, and West Bengal to the east...
, Purulia Chau in Purulia district
Purulia District
Purulia district is one of the nineteen districts of West Bengal state in eastern India. The town of Purulia is the administrative headquarters of the district.-History:...
of West Bengal and Mayurbhanj Chau in Mayurbhanj district
Mayurbhanj District
Mayurbhanj district is one of the 30 districts in Orissa state in eastern India. It is the largest district of Orissa by area. Baripada city is the district headquarters. As of 2011 it is the third most populous district of Orissa , after Ganjam and Cuttack.-History:Mayurbhanj District was formed...
of Orissa
Orissa
Orissa , officially Odisha since Nov 2011, is a state of India, located on the east coast of India, by the Bay of Bengal. It is the modern name of the ancient nation of Kalinga, which was invaded by the Maurya Emperor Ashoka in 261 BC. The modern state of Orissa was established on 1 April...
.
Ghumura Dance
Ghumura Dance
Ghumura Folk Dance[ , Kalahandia : ଘୁମ୍ରା ନାଚ୍ ] has earned both national and international name and fame in past three decades, after winning heart of Oriya people throughout Orissa. Its popular music is considered as one of those ancient folk musics, which after struggling a lot with the current...
Archaeological evidence proves that there are some cave painting from per-historic period discovered from Gudahandi of Kalahandi
Kalahandi
Kalahandi, , is a district of Orissa in India. The region had a glorious past and great civilization in ancient time. Archaeological evidence of stone age and Iron Age human settlement has been recovered from the region. Asurgarh offered an advanced, well civilized, cultured and urban human...
and Yogi Matha of Nuapada district
Nuapada District
Nuapada is a district of Orissa, India.-History:The District of Nuapada was a part of Kalahandi District till early March 1993, but for the administrative convenience, Kalahandi District was divided into two parts i.e. Kalahandi and Nuapada vide State Government Notification No. DRC-44/93/14218/R....
that looks like Ghumura, Damru and other attractive things. These rock art sites belongs to more than 8000 B.C. and from such painiting the antiquity of musical instrument Ghumura and Damru can be imagined. It is also proved that during mythological age, Kalahandi had prosperous and developed civilization. The origin of Ghumura goes back to ancient times. There is a beautiful waterfall in the river valley of Indravati which was initially recognized by Chindak Nagas of Chakrakot. Many believe that Ghumura dance originated from this river valley and gradually spread into the areas between Indravati and Mahanadi, indicating this dance form belongs to 10th century A.D.
The western Orissa has also great verity of dance forms unique to Orissa culture.The children's verses are known as "Chhiollai", "Humobauli" and "Dauligit", the adolescent poems are "Sajani", "Chhata", "Daika", "Bhekani" : the eternal youth composes "Rasarkeli", "Jaiphul", "Maila Jada", "Bayamana", "Gunchikuta" and "Dalkhai", The work-man's poetry comprises "Karma" and "Jhumer" pertaining to Lord Vishwakarma and the "Karamashani" goddess. The professional entertainers perform Dand, Danggada, Mudgada, Ghumra, Sadhana, sabar – Sabaren, Disdigo, Nachina – Bajnia, Samparda and Sanchar. They are for all occasions, for all time with varieties of rhythm and rhyme.
Bengali dance forms draw from folk traditions, especially those of the tribal groups, as well as the broader Indian dance traditions.
Dance forms of Bihar are another expression of rich traditions and ethnic identity. There are several folk dance forms that can keep one enthralled, such as dhobi nach, jhumarnach, manjhi, gondnach, jitiyanach, more morni, dom-domin, bhuiababa, rah baba, kathghorwa nach, jat jatin, launda nach, bamar nach, jharni, jhijhia, natua nach, bidapad nach, sohrai nach, and gond nach.
Music
Odissi musicOdissi music
Odissi music is a classical music in India originated from the eastern state of Orissa. Indian Classical music has five significant branches: Avanti, Panchali, Odramagadhi, Hindustani and carnatic. Of these, Odramagadhi exists in the form of Odissi music. Generally, Odissi dance is one of the...
is a classical music in India originated from the eastern state of Orissa
Orissa
Orissa , officially Odisha since Nov 2011, is a state of India, located on the east coast of India, by the Bay of Bengal. It is the modern name of the ancient nation of Kalinga, which was invaded by the Maurya Emperor Ashoka in 261 BC. The modern state of Orissa was established on 1 April...
. Indian Classical music has five significant branches: Avanti, Panchali, Udramagadhi, Hindustani and carnatic. Of these, Udramagadhi exists in the form of Odissi music. Generally, Odissi dance is one of the classical dances of India performed with Odissi music. Odissi music got shaped during the time of famous Oriya poet, Jayadeva
Jayadeva
Jayadeva was a Sanskrit poet circa 1200 AD. He is most known for his composition, the epic poem Gita Govinda, which depicts the divine love of Krishna-an avatar of Vishnu and his consort, Radha, and it is mentioned that Radha is greater than Hari, and is considered an important text in the...
, who composed lyrics meant to be sung. By the 11th century AD folk music
Folk music
Folk music is an English term encompassing both traditional folk music and contemporary folk music. The term originated in the 19th century. Traditional folk music has been defined in several ways: as music transmitted by mouth, as music of the lower classes, and as music with unknown composers....
of Orissa existing in the form of Triswari, Chatuhswari, and Panchaswari was modified into the classical style. However, Odissi songs were written even before the Oriya language developed. Odissi music has a rich legacy dating back to the 2nd century BCE, when king Kharvela, the ruler of Orissa (Kalinga
Kalinga
Kalinga is a landlocked province of the Philippines in the Cordillera Administrative Region in Luzon. Its capital is Tabuk and borders Mountain Province to the south, Abra to the west, Isabela to the east, Cagayan to the northeast, and Apayao to the north...
) patronized this music and dance.
Like Hindustani and Carnatic systems, Odissi music is a separate system of Indian classical music and is having all the essential as well as potential ingredients of Indian Classical form. But it has not come to limelight due to apathy from the time of British rule in Orissa, want of its proper study, revival, propagation, etc. Despite the fact, the traditional music form could be saved and maintained in its pristine form. Thanks to the musicians particularly of Jaga Akhadas of Puri district, who could develop and maintain the music. The music movement of Orissa, however, took a different turn after independence.
Like other aspects of her culture, music of the sacred land (Orissa) is charming, colourful, variegated encompassing various types. The existing musical tradition of Orissa, the cumulative experience of the last two thousand five hundred years if not more, can broadly be grouped under five categories such as : (1) Tribal Music, (2) Folk Music, (3) Light Music, (4) Light-Classical Music, (5) Classical Music, which need a short elucidations for better understanding the subject in all India context.
The tribal music as the title signifies is confined to the tribals living mainly in the hilly and jungle regions and sparsely in the coastal belt of Orissa. It is interesting to note that Orissa has the third largest concentration of tribes constituting about one fourth of the total population. They are distributed over 62 tribal communities.
Orissa is the treasure house of Folk Songs which are sung on different festivals and specific occasions in their own enjoyment. Folk music in general is the expression of the ethos and mores of the folk communities. Of the bewildering variety of folk music of Orissa, mention may be made of Geeta, Balipuja Geeta, Kela Keluni Geeta, Dalkhai Geeta, Kendra Geeta, Jaiphula Geeta, Ghumura Geeta, Ghoda Nacha and Danda Nacha Geeta, Gopal Ugala and Osa-Parva-Geeta etc.
Bhajan, Janan, Oriya songs based on ragas, Rangila Chaupadi etc. are grouped under Light classical music, which forms an important segment of Orissan music. Sri Geetagovinda, Anirjukta Pravadha, Divya Manusi Prabandha, Chautisa, Chhanda, Chaupadi (now known as Odissi), Champu, Malasri, Sariman, Vyanjani, Chaturang, Tribhang, Kuduka Geeta, Laxana and Swaramalika are the various sub-forms, which individually or collectively constitute the traditional Odissi music. These sub-forms of the traditional Odissi music, can be categorised under the classical music of Orissa.
Panchali is a form of narrative folk songs of the India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
n state of West Bengal
West Bengal
West Bengal is a state in the eastern region of India and is the nation's fourth-most populous. It is also the seventh-most populous sub-national entity in the world, with over 91 million inhabitants. A major agricultural producer, West Bengal is the sixth-largest contributor to India's GDP...
.The word Panchali probably originates from panchal or panchalika, meaning puppet. According to another school of that, Panchali originates from the word panch, which means five in Bengali language
Bengali language
Bengali or Bangla is an eastern Indo-Aryan language. It is native to the region of eastern South Asia known as Bengal, which comprises present day Bangladesh, the Indian state of West Bengal, and parts of the Indian states of Tripura and Assam. It is written with the Bengali script...
, referring to the five elements of this genre: song, music, extempore versifying, poetic contests, and dance.
Bihar is among the few Indian states which has a rich subaltern culture. The region's folk songs are associated with the various events in the life of an ordinary person. There are songs like sohar
Sohar
Sohar is the most developed city in Sultanate of Oman outside the capital Muscat. It is about 200 kilometers north of Muscat. Sohar was an ancient capital of Oman and many believe it to be the birthplace of Sinbad the Sailor...
- performed during childbirth
Childbirth
Childbirth is the culmination of a human pregnancy or gestation period with the birth of one or more newborn infants from a woman's uterus...
, sumangali
Sumangali
Sumangali is a 1940 Telugu film directed by B. N. Reddi. The main concept of the film Widow remarriage is inspired by Kandukuri Veeresalingam. The protagonist role was played by Chittor V. Nagaiah and A. S. Giri.-The plot:...
- associated with wedding
Wedding song
Wedding song may refer to* "The Wedding Song ", a song by Paul Stookey, of Peter, Paul, and Mary fame.* "Wedding Song", a song by The Psychedelic Furs.* Wedding Song, a novel by Naguib Mahfouz....
, ropnigeet - performed during the season of sowing paddy, katnigeet - performed during the paddy harvesting season, purbi, chaita, hori, bidesia, ghato, birha, kajari, irni/ birni, pachra, jhumar, jatsari, aalah, nirgun, and samdaun. There is also the tradition of war songs called Beer Kunwar.
The influence of Bihari music in seen in regions such as Mauritius
Mauritius
Mauritius , officially the Republic of Mauritius is an island nation off the southeast coast of the African continent in the southwest Indian Ocean, about east of Madagascar...
, South Africa and the Caribbean
Caribbean
The Caribbean is a crescent-shaped group of islands more than 2,000 miles long separating the Gulf of Mexico and the Caribbean Sea, to the west and south, from the Atlantic Ocean, to the east and north...
, where a large of Bihari indentured labourers were taken as coolies during the nineteenth century.
There is a great tradition of folk songs started by Bhikhari Thakur
Bhikhari Thakur
Bhikari Thakur was an Indian author popularly known as the "Shakespeare of Bhojpuri". Thakur was born in a barber-family on 18 December 1887 at Kutubpur Village in Saran District. Name of his father and mother was Dal Singar Thakur and Shivkali Devi respectively. He had a younger brother named...
, the redoubtable artist from the Bhojpur region.
Other wandering folk singers include the Kathak
Kathak
Kathak is one of the eight forms of Indian classical dances, originated from Uttar Pradesh, India. This dance form traces its origins to the nomadic bards of ancient northern India, known as Kathaks, or storytellers...
s, who travelled in groups and performed accompanied by dholak
Dholak
The Dholak is a North Indian, Pakistani and Nepalese double-headed hand-drum Madal. The name dholki may also refer to a slightly different instrument that uses high-pitch tabla style syahi masala on its treble skin. This instrument is also known as Naal or Dholki....
, sarangi
Sarangi
The Sārangī is a bowed, short-necked string instrument of India which is originated from Rajasthani folk instruments. It plays an important role in India's Hindustani classical music tradition...
, tamburu and majira. Other musician classes included Roshan Chouki, Bhajaniya, Kirtaniya, Pamaria
Pamaria
- Origin :The Pamaria are said to be Muslim converts from the Parmar Rajput community. This conversion is said to have taken place during the rule of the Mugal Emperor Akbar. The Pamaria are then said to have left Rajasthan, their own original home, and moved to Bihar. When in Bihar, the community...
and Bhakliya.
See also
- North IndiaNorth IndiaNorth India, known natively as Uttar Bhārat or Shumālī Hindustān , is a loosely defined region in the northern part of India. The exact meaning of the term varies by usage...
- North-East IndiaNorth-East IndiaNortheast India refers to the easternmost region of India consisting of the contiguous Seven Sister States, Sikkim, and parts of North Bengal...
- West IndiaWest IndiaWest India or the Western region of India consists of the states of Goa, Gujarat and Maharashtra, along with the Union Territories of Daman and Diu and Dadra and Nagar Haveli. It is highly industrialized, with a large urban population. Most of Western India was part of the Maratha Empire before...
- Central India
- South IndiaSouth IndiaSouth India is the area encompassing India's states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala and Tamil Nadu as well as the union territories of Lakshadweep and Pondicherry, occupying 19.31% of India's area...

