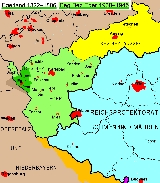
Egerland
Encyclopedia
The Egerland is a historical region in the far north west of Bohemia
in the Czech Republic
at the border with Germany
. It is named after the German name Eger for the city of Cheb
and the main river Ohře
. Recently the northern parts around the town of Aš
are also called Böhmisches Vogtland (Fojtsko) related to the adjacent German Vogtland
region in Saxony
, Thuringia
and Bavaria
, today constituent parts of the Egrensis Euroregion
initiative.
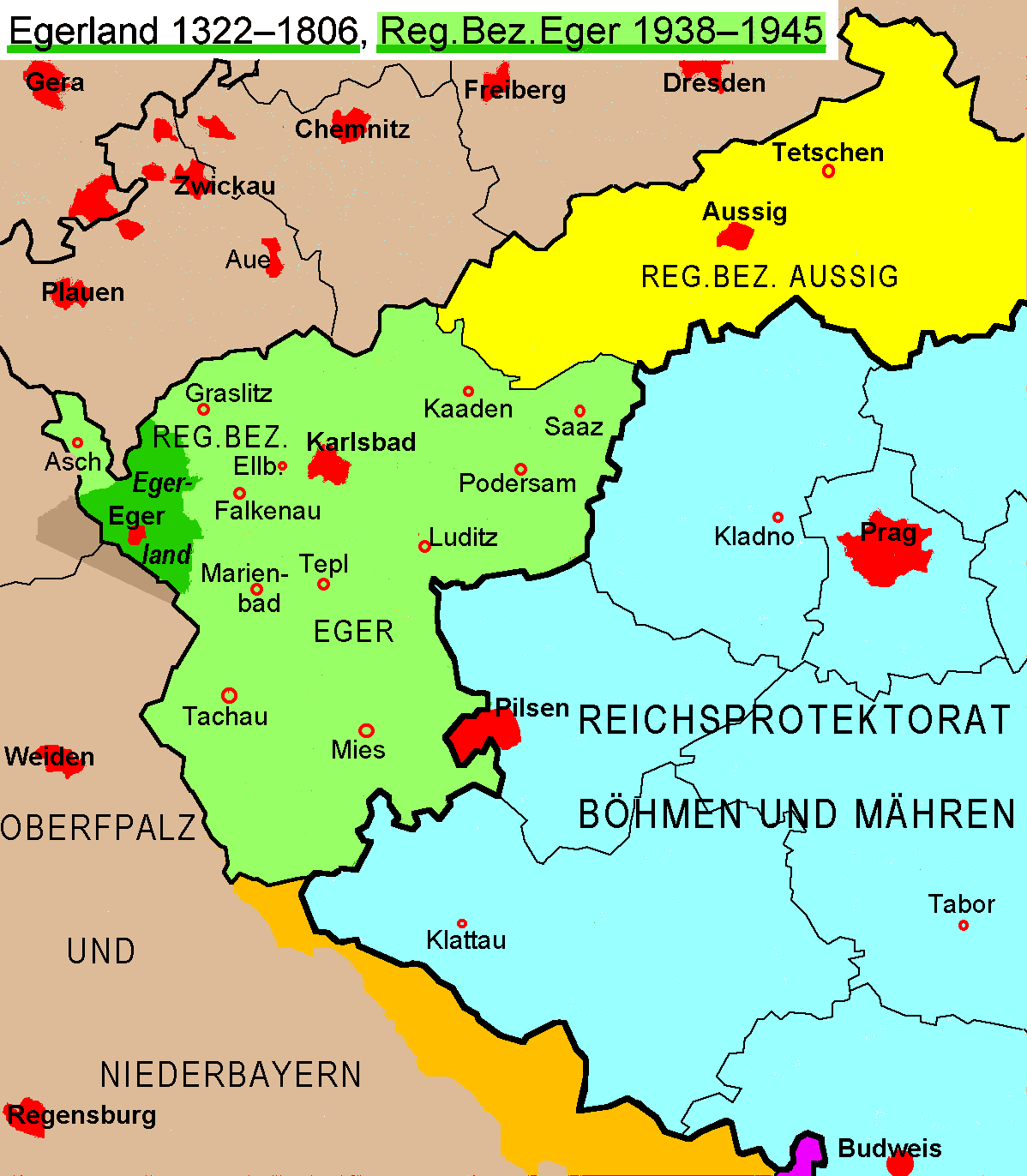
of the Karlovy Vary Region, originally with the exception of Aš, but including the headwaters of the Ohře river and the area of Marktredwitz
in today's Upper Franconia
.
In contrast, after the beginning of the German occupation of Czechoslovakia
in 1938, Cheb and the historic Egerland were incorporated as part of the "Sudetenland
" into an extended area of 7466 km² (2,882.6 sq mi). Though the seat of the administration was established at Karlovy Vary
(Carlsbad) the entity was officially named Regierungsbezirk
Eger in order to deduce territorial claims. It included large Bohemian territories up to the outskirts of Plzeň, comprising cities like Falknov
(today Sokolov), Kraslice
, Chodov
, Mariánské Lázně
(Marienbad), Tachov
and Domažlice
, which never belonged to historical region.
was first mentioned in 1061 records of trade routes laid out in the course of the German Ostsiedlung
migration. In 1135 the regio Egere is recorded as a part of the Bavarian March of the Nordgau
under the rule of Count Diepold III of Vohburg
. After his death in 1146, the Egerland was inherited by the later Emperor Frederick I Barbarossa
of Hohenstaufen by marriage with Diepold's daughter Adelheid
. The Staufer finally severed the Provincia Egrensis from Bavaria and built it up as an exemplary model of a Reichsgut territory under immediate rule of the Holy Roman Emperor
. Along this development Cheb became the site of a Kaiserpfalz
residence (Chebský hrad), the only one in the present-day Czech Republic.

since 1277, and the reichsunmittelbar Egerland were given as a lien to King John of Bohemia in 1322 by Emperor Louis IV of Wittelsbach
. In return for John's support against Louis' rival Frederick of Habsburg at the Battle of Mühldorf
, he received Eger as a Reichspfandschaft (Imperial lien) with the "guarantee of complete independence from the Kingdom of Bohemia
". This reservation however became meaningless as Louis never redeemed the pawn, and with the accession of Emperor Charles IV of Luxembourg
in 1346, the crowns of the Holy Roman Empire
and Bohemia were united in one hand. Charles' successors from the House of Luxembourg
and (from 1526) Habsburg continuously eliminated the autonomy of the Egerland against the resistance of the Cheb citizens and the local nobility. While the present-day Franconian parts up to the Fichtelgebirge
were acquired by the Principality of Bayreuth
under Hohenzollern
rule, the remaining territory was administrated within the Bohemian kraj
of Loket
from 1751.
The incorporation of the Bohemian kingdom into the Habsburg Monarchy
had created ongoing conflicts at first along the fault-lines between the Catholic
dynasty and the Protestant
nobility culminating in the Thirty Years' War
. Cheb and the Egerland insisting on their independence tried to maintain a neutral position, they nevertheless were seized as a stronghold by Albrecht von Wallenstein
, who was murdered at Cheb on 25 February 1634. In the following decades the absolute
Habsburg rulers aimed at a centralized government
. Emperor Joseph II of Habsburg
on the one hand issued an Edict of Religious Tolerance
in 1781, but also denied the Bohemian autonomy by renouncing the ceremony of the coronation as Bohemian king. With the determination of German
as official language in all Habsburg lands (instead of Latin), he laid the foundations for future ethnic conflicts. In the course of the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire in 1806 and the onset of the Austrian Empire
, the eastern part of Egerland finally became an ordinary district of the Austrian province of Bohemia.
The suppression during the Age of Metternich led to a second-class status of the Czech people
in the Austrian crown land of Bohemia, despite them being much more numerous than the German speaking population. From about 1830 on Czech scholars like František Palacký
encouraged the Austroslavism
movement demanding autonomy for the Bohemian crown lands and admission of the Czech language
. In the aftermath of the 1848 Spring of Nations
, the Czechs, as well as some other Slavic nations, began Pan-Slavic movements aiming at complete independence, fiercely opposed by Pan-German
organisations like the German Worker's Party
based in Cheb. The rise of ethnic nationalism
turned out to be fatal, as, while the central parts of Bohemia were only inhabited by a smaller German-speaking elite, in border regions like the Egerland people who had adopted the German language were more numerous.
including the Egerland and further peripheral regions of German Bohemia
, that were to become part of Czechoslovakia
. They demanded the unification with Germany
, referring to the self-determination
doctrine proclaimed by U.S. president Woodrow Wilson
that had been the basis for the dissolution of the Austro-Hungarian Empire. Nevertheless the Czech majority insisted to "restore their countries in their historical borders", as a revision of the former Germanization. Both parties acted unilaterally, the Czechs prevailed establishing the Czechoslovakian Republic comprising all parts of Bohemia including the Egerland, while the German minority drew a completely new border between predominantly Czech- and predominantly German-speaking parts of the country.
With the 1933 Nazi seizure of power
in Germany, the separatists of the Sudeten German Party under Konrad Henlein
became more and more dominant, calling themselves Sudeten Germans. After Hitler
had pushed the situation towards an armed conflict, the prime ministers of Britain
and France
in the 1938 Munich Agreement
backed the annexation of the Sudetenland with the Egerland by Nazi Germany
, resulting in flight and expulsion of Czech people. At that time, the term "Egerland" came in use for the western district of the Sudetenland, itself a Reichsgau
from 1939 on.
Following the German defeat in World War II, the region was rejoined to Czechoslovakia in 1945 and most of the ethnic Germans were expelled
to Germany on the basis of the Beneš decrees
, nearly 90,000 from Egerland proper and almost 800,000 from the short-lived Regierunsgbezirk Eger.
Bohemia
Bohemia is a historical region in central Europe, occupying the western two-thirds of the traditional Czech Lands. It is located in the contemporary Czech Republic with its capital in Prague...
in the Czech Republic
Czech Republic
The Czech Republic is a landlocked country in Central Europe. The country is bordered by Poland to the northeast, Slovakia to the east, Austria to the south, and Germany to the west and northwest....
at the border with Germany
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
. It is named after the German name Eger for the city of Cheb
Cheb
Cheb is a city in the Karlovy Vary Region of the Czech Republic, with about 33,000 inhabitants. It is situated on the river Ohře , at the foot of one of the spurs of the Smrčiny and near the border with Germany...
and the main river Ohře
Ohre
The Ohře is a 316 km long river in Germany and the Czech Republic , left tributary of the Elbe. The basin area of the river has a size of 6,255 km², of which 5,614 km² are in the Czech Republic and 641 km² in Germany...
. Recently the northern parts around the town of Aš
Aš
Aš is a town in the Karlovy Vary Region of the Czech Republic.-History:Previously uninhabited hills and swamps, the town of Asch was founded in the early 11th century by German colonists. Slavic settlements in the area are not known. The dialect spoken in the town was that of the Upper Palatinate,...
are also called Böhmisches Vogtland (Fojtsko) related to the adjacent German Vogtland
Vogtland
The term Vogtland refers to a region reaching across the German free states of Bavaria, Saxony and Thuringia and into the Czech Republic . The name of the region contains a reference to the former leadership by the Vögte of Weida, Gera and Plauen, which translates approximately to advocates or lord...
region in Saxony
Saxony
The Free State of Saxony is a landlocked state of Germany, contingent with Brandenburg, Saxony Anhalt, Thuringia, Bavaria, the Czech Republic and Poland. It is the tenth-largest German state in area, with of Germany's sixteen states....
, Thuringia
Thuringia
The Free State of Thuringia is a state of Germany, located in the central part of the country.It has an area of and 2.29 million inhabitants, making it the sixth smallest by area and the fifth smallest by population of Germany's sixteen states....
and Bavaria
Bavaria
Bavaria, formally the Free State of Bavaria is a state of Germany, located in the southeast of Germany. With an area of , it is the largest state by area, forming almost 20% of the total land area of Germany...
, today constituent parts of the Egrensis Euroregion
Euroregion
In European politics, the term Euroregion usually refers to a transnational co-operation structure between two contiguous territories located in different European countries. Euroregions represent a specific type of cross-border region.-Scope:...
initiative.

Geography
The Egerland forms the northwestern edge of the Czech Republic. Originally, it was a small region of less than 1000 km² (386.1 sq mi) around the historic city of Cheb, roughly corresponding with the present-day Cheb DistrictCheb District
Cheb District is a district within Karlovy Vary Region of the Czech Republic. Its capital is the city of Cheb.-Complete list of towns and villages:Aš -Cheb -Dolní Žandov -Drmoul -...
of the Karlovy Vary Region, originally with the exception of Aš, but including the headwaters of the Ohře river and the area of Marktredwitz
Marktredwitz
Marktredwitz is a municipality in the district of Wunsiedel, in Bavaria, Germany. It is situated 22 km west of Cheb, 50 km east of Bayreuth and 50 km south of Hof/Saale.The town celebrated the Horticultural Show 2006 in cooperation with Cheb....
in today's Upper Franconia
Upper Franconia
Upper Franconia is a Regierungsbezirk of the state of Bavaria, southern Germany. It forms part of the historically significant region of Franconia , all now part of the German Federal State of Bayern .With more than 200 independent breweries which brew...
.
In contrast, after the beginning of the German occupation of Czechoslovakia
German occupation of Czechoslovakia
German occupation of Czechoslovakia began with the Nazi annexation of Czechoslovakia's northern and western border regions, known collectively as the Sudetenland, under terms outlined by the Munich Agreement. Nazi leader Adolf Hitler's pretext for this effort was the alleged privations suffered by...
in 1938, Cheb and the historic Egerland were incorporated as part of the "Sudetenland
Sudetenland
Sudetenland is the German name used in English in the first half of the 20th century for the northern, southwest and western regions of Czechoslovakia inhabited mostly by ethnic Germans, specifically the border areas of Bohemia, Moravia, and those parts of Silesia being within Czechoslovakia.The...
" into an extended area of 7466 km² (2,882.6 sq mi). Though the seat of the administration was established at Karlovy Vary
Karlovy Vary
Karlovy Vary is a spa city situated in western Bohemia, Czech Republic, on the confluence of the rivers Ohře and Teplá, approximately west of Prague . It is named after King of Bohemia and Holy Roman Emperor Charles IV, who founded the city in 1370...
(Carlsbad) the entity was officially named Regierungsbezirk
Regierungsbezirk
In Germany, a Government District, in German: Regierungsbezirk – is a subdivision of certain federal states .They are above the Kreise, Landkreise, and kreisfreie Städte...
Eger in order to deduce territorial claims. It included large Bohemian territories up to the outskirts of Plzeň, comprising cities like Falknov
Sokolov (Sokolov District)
Sokolov , Falknov nad Ohří until 1948 is a town in the Karlovy Vary Region of the Czech Republic, located to the north-east of Cheb. It has about 28,000 inhabitants....
(today Sokolov), Kraslice
Kraslice
Kraslice is a town in the Karlovy Vary Region of the Czech Republic.-Geography:The town is situated on the southern slopes of the eastern reaches of the Ore Mountains, some 5 km from the neighbouring German town of Klingenthal....
, Chodov
Chodov (Sokolov District)
Chodov is a town in Sokolov District of the Czech Republic, on the border with the Karlovy Vary District . , it has around 14,500 inhabitants.- History :...
, Mariánské Lázně
Mariánské Lázne
Mariánské Lázně is a spa town in the Karlovy Vary Region of the Czech Republic. The town, surrounded by green mountains, is a mosaic of parks and noble houses...
(Marienbad), Tachov
Tachov
Tachov is a town in the Pilsen Region of the Czech Republic. It lies on the Mže River, some to the west from the region capital of Pilsen....
and Domažlice
Domažlice
Domažlice is a town in the Plzeň Region of the Czech Republic.Domažlice is also a Municipality with Extended Competence and a Municipality with Commissioned Local Authority within the same borders.-History:...
, which never belonged to historical region.
History
The settlement of Eger in the Bavaria SlavicaGermania Slavica
Germania Slavica is a historiographic term used since the 1950s to denote the medieval contact zone between Germans and Slavs in East Central Europe...
was first mentioned in 1061 records of trade routes laid out in the course of the German Ostsiedlung
Ostsiedlung
Ostsiedlung , also called German eastward expansion, was the medieval eastward migration and settlement of Germans from modern day western and central Germany into less-populated regions and countries of eastern Central Europe and Eastern Europe. The affected area roughly stretched from Slovenia...
migration. In 1135 the regio Egere is recorded as a part of the Bavarian March of the Nordgau
March of the Nordgau
The March of the Nordgau or the Bavarian Nordgau was a margraviate in the north of the duchy of Bavaria in the High Middle Ages. It covered the region roughly covered by the modern Upper Palatinate along the river Main. The chief cities of the Nordgau were the Frankish cities Nuremberg and...
under the rule of Count Diepold III of Vohburg
Diepold III, Margrave of Vohburg
Diepold III, Margrave of Vohburg , also known as Diepold von Vohburg and Diepold III von Giengen, was a Bavarian noble in the 12th century...
. After his death in 1146, the Egerland was inherited by the later Emperor Frederick I Barbarossa
Frederick I, Holy Roman Emperor
Frederick I Barbarossa was a German Holy Roman Emperor. He was elected King of Germany at Frankfurt on 4 March 1152 and crowned in Aachen on 9 March, crowned King of Italy in Pavia in 1155, and finally crowned Roman Emperor by Pope Adrian IV, on 18 June 1155, and two years later in 1157 the term...
of Hohenstaufen by marriage with Diepold's daughter Adelheid
Adelheid of Vohburg
Adelheid of Vohburg was the first Queen consort of Frederick I, Holy Roman Emperor.-Family:Adelheid was a daughter of Diepold III, Margrave of Vohburg and either his first wife, Adelajda of Poland, or his second wife Kunigunde of Beichlingen.Her paternal grandparents were Diepold II, Count of...
. The Staufer finally severed the Provincia Egrensis from Bavaria and built it up as an exemplary model of a Reichsgut territory under immediate rule of the Holy Roman Emperor
Holy Roman Emperor
The Holy Roman Emperor is a term used by historians to denote a medieval ruler who, as German King, had also received the title of "Emperor of the Romans" from the Pope...
. Along this development Cheb became the site of a Kaiserpfalz
Kaiserpfalz
The term Kaiserpfalz or Königspfalz refers to a number of castles across the Holy Roman Empire which served as temporary, secondary seats of power for the Holy Roman Emperor in the Early and High Middle Ages...
residence (Chebský hrad), the only one in the present-day Czech Republic.

Kingdom of Bohemia
Cheb, a free imperial cityFree Imperial City
In the Holy Roman Empire, a free imperial city was a city formally ruled by the emperor only — as opposed to the majority of cities in the Empire, which were governed by one of the many princes of the Empire, such as dukes or prince-bishops...
since 1277, and the reichsunmittelbar Egerland were given as a lien to King John of Bohemia in 1322 by Emperor Louis IV of Wittelsbach
Louis IV, Holy Roman Emperor
Louis IV , called the Bavarian, of the house of Wittelsbach, was the King of Germany from 1314, the King of Italy from 1327 and the Holy Roman Emperor from 1328....
. In return for John's support against Louis' rival Frederick of Habsburg at the Battle of Mühldorf
Battle of Mühldorf
The Battle of Mühldorf was fought near Mühldorf am Inn on September 28, 1322 between the Duchy of Bavaria and Austria...
, he received Eger as a Reichspfandschaft (Imperial lien) with the "guarantee of complete independence from the Kingdom of Bohemia
Kingdom of Bohemia
The Kingdom of Bohemia was a country located in the region of Bohemia in Central Europe, most of whose territory is currently located in the modern-day Czech Republic. The King was Elector of Holy Roman Empire until its dissolution in 1806, whereupon it became part of the Austrian Empire, and...
". This reservation however became meaningless as Louis never redeemed the pawn, and with the accession of Emperor Charles IV of Luxembourg
Charles IV, Holy Roman Emperor
Charles IV , born Wenceslaus , was the second king of Bohemia from the House of Luxembourg, and the first king of Bohemia to also become Holy Roman Emperor....
in 1346, the crowns of the Holy Roman Empire
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a realm that existed from 962 to 1806 in Central Europe.It was ruled by the Holy Roman Emperor. Its character changed during the Middle Ages and the Early Modern period, when the power of the emperor gradually weakened in favour of the princes...
and Bohemia were united in one hand. Charles' successors from the House of Luxembourg
House of Luxembourg
The House of Luxembourg was a late medieval German dynasty, which between 1308 and 1437 ruled the Holy Roman Empire, twice interrupted by the rivaling House of Wittelsbach.-History:...
and (from 1526) Habsburg continuously eliminated the autonomy of the Egerland against the resistance of the Cheb citizens and the local nobility. While the present-day Franconian parts up to the Fichtelgebirge
Fichtelgebirge
The Fichtelgebirge is a mountain range in northeastern Bavaria, Germany. It extends from the valley of the Red Main River to the Czech border, a few foothills spilling over into the Czech Republic. It continues in a northeastern direction as the Ore Mountains, and in a southeastern direction as...
were acquired by the Principality of Bayreuth
Principality of Bayreuth
The Principality of Bayreuth or Brandenburg-Bayreuth was a reichsfrei principality in the Holy Roman Empire centered on the Bavarian city of Bayreuth. Until 1604 its capital city was Kulmbach; then the margraves used their palaces in Bayreuth as their residence...
under Hohenzollern
House of Hohenzollern
The House of Hohenzollern is a noble family and royal dynasty of electors, kings and emperors of Prussia, Germany and Romania. It originated in the area around the town of Hechingen in Swabia during the 11th century. They took their name from their ancestral home, the Burg Hohenzollern castle near...
rule, the remaining territory was administrated within the Bohemian kraj
Kraj
A kraj is the highest-level administrative unit in the Czech Republic and Slovak Republic. For lack of other English expressions, the Slavic term is often translated as "province", "region", or "territory", although it actually approximately means " country", or " countryside"...
of Loket
Loket
Loket is a town of some 3 000 inhabitants in the Sokolov District in the Karlovy Vary region of the Czech Republic.Loket means "elbow" in English. The town is named this due to the town centre being surrounded on three sides by the Ohře River, and the shape the river takes is similar to that of an...
from 1751.
The incorporation of the Bohemian kingdom into the Habsburg Monarchy
Habsburg Monarchy
The Habsburg Monarchy covered the territories ruled by the junior Austrian branch of the House of Habsburg , and then by the successor House of Habsburg-Lorraine , between 1526 and 1867/1918. The Imperial capital was Vienna, except from 1583 to 1611, when it was moved to Prague...
had created ongoing conflicts at first along the fault-lines between the Catholic
Catholicism
Catholicism is a broad term for the body of the Catholic faith, its theologies and doctrines, its liturgical, ethical, spiritual, and behavioral characteristics, as well as a religious people as a whole....
dynasty and the Protestant
Protestantism
Protestantism is one of the three major groupings within Christianity. It is a movement that began in Germany in the early 16th century as a reaction against medieval Roman Catholic doctrines and practices, especially in regards to salvation, justification, and ecclesiology.The doctrines of the...
nobility culminating in the Thirty Years' War
Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War was fought primarily in what is now Germany, and at various points involved most countries in Europe. It was one of the most destructive conflicts in European history....
. Cheb and the Egerland insisting on their independence tried to maintain a neutral position, they nevertheless were seized as a stronghold by Albrecht von Wallenstein
Albrecht von Wallenstein
Albrecht Wenzel Eusebius von Wallenstein , actually von Waldstein, was a Bohemian soldier and politician, who offered his services, and an army of 30,000 to 100,000 men during the Danish period of the Thirty Years' War , to the Holy Roman Emperor Ferdinand II...
, who was murdered at Cheb on 25 February 1634. In the following decades the absolute
Absolute monarchy
Absolute monarchy is a monarchical form of government in which the monarch exercises ultimate governing authority as head of state and head of government, his or her power not being limited by a constitution or by the law. An absolute monarch thus wields unrestricted political power over the...
Habsburg rulers aimed at a centralized government
Centralized government
A centralized or centralised government is one in which power or legal authority is exerted or coordinated by a de facto political executive to which federal states, local authorities, and smaller units are considered subject...
. Emperor Joseph II of Habsburg
Joseph II, Holy Roman Emperor
Joseph II was Holy Roman Emperor from 1765 to 1790 and ruler of the Habsburg lands from 1780 to 1790. He was the eldest son of Empress Maria Theresa and her husband, Francis I...
on the one hand issued an Edict of Religious Tolerance
1782 Edict of Tolerance
The 1782 Edict of Tolerance was a religious reform of Joseph II during the time he was emperor of the Habsburg Monarchy as part of his policy of Josephinism, a series of drastic reforms to remodel Austria in the form of the ideal Enlightened state. Joseph II's enlightened despotism included the...
in 1781, but also denied the Bohemian autonomy by renouncing the ceremony of the coronation as Bohemian king. With the determination of German
German language
German is a West Germanic language, related to and classified alongside English and Dutch. With an estimated 90 – 98 million native speakers, German is one of the world's major languages and is the most widely-spoken first language in the European Union....
as official language in all Habsburg lands (instead of Latin), he laid the foundations for future ethnic conflicts. In the course of the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire in 1806 and the onset of the Austrian Empire
Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire was a modern era successor empire, which was centered on what is today's Austria and which officially lasted from 1804 to 1867. It was followed by the Empire of Austria-Hungary, whose proclamation was a diplomatic move that elevated Hungary's status within the Austrian Empire...
, the eastern part of Egerland finally became an ordinary district of the Austrian province of Bohemia.
The suppression during the Age of Metternich led to a second-class status of the Czech people
Czech people
Czechs, or Czech people are a western Slavic people of Central Europe, living predominantly in the Czech Republic. Small populations of Czechs also live in Slovakia, Austria, the United States, the United Kingdom, Chile, Argentina, Canada, Germany, Russia and other countries...
in the Austrian crown land of Bohemia, despite them being much more numerous than the German speaking population. From about 1830 on Czech scholars like František Palacký
František Palacký
František Palacký was a Czech historian and politician.-Biography:...
encouraged the Austroslavism
Austroslavism
Austroslavism was a political concept and program aimed to solve problems of Slavic peoples in the Austrian Empire.It was most influential among Czech liberals around the middle of the 19th century...
movement demanding autonomy for the Bohemian crown lands and admission of the Czech language
Czech language
Czech is a West Slavic language with about 12 million native speakers; it is the majority language in the Czech Republic and spoken by Czechs worldwide. The language was known as Bohemian in English until the late 19th century...
. In the aftermath of the 1848 Spring of Nations
Revolutions of 1848
The European Revolutions of 1848, known in some countries as the Spring of Nations, Springtime of the Peoples or the Year of Revolution, were a series of political upheavals throughout Europe in 1848. It was the first Europe-wide collapse of traditional authority, but within a year reactionary...
, the Czechs, as well as some other Slavic nations, began Pan-Slavic movements aiming at complete independence, fiercely opposed by Pan-German
Pan-Germanism
Pan-Germanism is a pan-nationalist political idea. Pan-Germanists originally sought to unify the German-speaking populations of Europe in a single nation-state known as Großdeutschland , where "German-speaking" was taken to include the Low German, Frisian and Dutch-speaking populations of the Low...
organisations like the German Worker's Party
German Workers' Party (Austria-Hungary)
----The German Workers' Party in Austria-Hungary is the predecessor of the Austrian and Czechoslovak Deutsche Nationalsozialistische Arbeiterpartei , founded on 14 November 1903, in Aussig , Bohemia...
based in Cheb. The rise of ethnic nationalism
Ethnic nationalism
Ethnic nationalism is a form of nationalism wherein the "nation" is defined in terms of ethnicity. Whatever specific ethnicity is involved, ethnic nationalism always includes some element of descent from previous generations and the implied claim of ethnic essentialism, i.e...
turned out to be fatal, as, while the central parts of Bohemia were only inhabited by a smaller German-speaking elite, in border regions like the Egerland people who had adopted the German language were more numerous.
Czechoslovakia
At the end of World War I, the German-speaking population of former Austria–Hungary proclaimed the Republic of German AustriaGerman Austria
Republic of German Austria was created following World War I as the initial rump state for areas with a predominantly German-speaking population within what had been the Austro-Hungarian Empire, without the Kingdom of Hungary, which in 1918 had become the Hungarian Democratic Republic.German...
including the Egerland and further peripheral regions of German Bohemia
German Bohemia
German Bohemia was a region in Czech Republic established, for a short period of time, after World War I. It included parts of northern and western Bohemia once largely populated by ethnic Germans...
, that were to become part of Czechoslovakia
Czechoslovakia
Czechoslovakia or Czecho-Slovakia was a sovereign state in Central Europe which existed from October 1918, when it declared its independence from the Austro-Hungarian Empire, until 1992...
. They demanded the unification with Germany
Weimar Republic
The Weimar Republic is the name given by historians to the parliamentary republic established in 1919 in Germany to replace the imperial form of government...
, referring to the self-determination
Self-determination
Self-determination is the principle in international law that nations have the right to freely choose their sovereignty and international political status with no external compulsion or external interference...
doctrine proclaimed by U.S. president Woodrow Wilson
Woodrow Wilson
Thomas Woodrow Wilson was the 28th President of the United States, from 1913 to 1921. A leader of the Progressive Movement, he served as President of Princeton University from 1902 to 1910, and then as the Governor of New Jersey from 1911 to 1913...
that had been the basis for the dissolution of the Austro-Hungarian Empire. Nevertheless the Czech majority insisted to "restore their countries in their historical borders", as a revision of the former Germanization. Both parties acted unilaterally, the Czechs prevailed establishing the Czechoslovakian Republic comprising all parts of Bohemia including the Egerland, while the German minority drew a completely new border between predominantly Czech- and predominantly German-speaking parts of the country.
With the 1933 Nazi seizure of power
Machtergreifung
Machtergreifung is a German word meaning "seizure of power". It is normally used specifically to refer to the Nazi takeover of power in the democratic Weimar Republic on 30 January 1933, the day Hitler was sworn in as Chancellor of Germany, turning it into the Nazi German dictatorship.-Term:The...
in Germany, the separatists of the Sudeten German Party under Konrad Henlein
Konrad Henlein
Konrad Ernst Eduard Henlein was a leading pro-Nazi ethnic German politician in Czechoslovakia and leader of Sudeten German separatists...
became more and more dominant, calling themselves Sudeten Germans. After Hitler
Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler was an Austrian-born German politician and the leader of the National Socialist German Workers Party , commonly referred to as the Nazi Party). He was Chancellor of Germany from 1933 to 1945, and head of state from 1934 to 1945...
had pushed the situation towards an armed conflict, the prime ministers of Britain
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
and France
French Third Republic
The French Third Republic was the republican government of France from 1870, when the Second French Empire collapsed due to the French defeat in the Franco-Prussian War, to 1940, when France was overrun by Nazi Germany during World War II, resulting in the German and Italian occupations of France...
in the 1938 Munich Agreement
Munich Agreement
The Munich Pact was an agreement permitting the Nazi German annexation of Czechoslovakia's Sudetenland. The Sudetenland were areas along Czech borders, mainly inhabited by ethnic Germans. The agreement was negotiated at a conference held in Munich, Germany, among the major powers of Europe without...
backed the annexation of the Sudetenland with the Egerland by Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany , also known as the Third Reich , but officially called German Reich from 1933 to 1943 and Greater German Reich from 26 June 1943 onward, is the name commonly used to refer to the state of Germany from 1933 to 1945, when it was a totalitarian dictatorship ruled by...
, resulting in flight and expulsion of Czech people. At that time, the term "Egerland" came in use for the western district of the Sudetenland, itself a Reichsgau
Reichsgau
A Reichsgau was an administrative subdivision created in a number of the areas annexed to Nazi Germany between 1938 and 1945...
from 1939 on.
Following the German defeat in World War II, the region was rejoined to Czechoslovakia in 1945 and most of the ethnic Germans were expelled
Expulsion of Germans from Czechoslovakia
The expulsion of Germans from Czechoslovakia after World War II was part of a series of evacuations and expulsions of Germans from Central and Eastern Europe during and after World War II....
to Germany on the basis of the Beneš decrees
Beneš decrees
Decrees of the President of the Republic , more commonly known as the Beneš decrees, were a series of laws that were drafted by the Czechoslovak Government-in-Exile in the absence of the Czechoslovak parliament during the German occupation of Czechoslovakia in World War II and issued by President...
, nearly 90,000 from Egerland proper and almost 800,000 from the short-lived Regierunsgbezirk Eger.
External links
Euregio Egrensis cooperation- Überblick über die Geschichte der Stadt Eger und des Egerlandes (Survey of the history of the City of Cheb and the Egerland – in German)
Literature
- Bernd Rill: 2006. Böhmen und Mähren - Geschichte im Herzen Mitteleuropas. ISBN 3-938047-17-8 (in German)
- W. Koschmal, M. Nekula, J. Rogall: Deutsche und Tschechen – Geschichte, Kultur, Politik, Beck'sche Reihe 2001, ISBN 3-406-45954-4, in German)

