Geography of Scotland
Encyclopedia
| cing="0"> |
 |
Continent
A continent is one of several very large landmasses on Earth. They are generally identified by convention rather than any strict criteria, with seven regions commonly regarded as continents—they are : Asia, Africa, North America, South America, Antarctica, Europe, and Australia.Plate tectonics is...
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
Subregion
A subregion is a conceptual unit which derives from a larger region or continent and is usually based on location. Cardinal directions, such as south or southern, are commonly used to define a subregion.- United Nations subregions :...
Great Britain
Great Britain or Britain is an island situated to the northwest of Continental Europe. It is the ninth largest island in the world, and the largest European island, as well as the largest of the British Isles...
Northern Europe
Northern Europe
Northern Europe is the northern part or region of Europe. Northern Europe typically refers to the seven countries in the northern part of the European subcontinent which includes Denmark, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Norway, Finland and Sweden...
Area
Area is a quantity that expresses the extent of a two-dimensional surface or shape in the plane. Area can be understood as the amount of material with a given thickness that would be necessary to fashion a model of the shape, or the amount of paint necessary to cover the surface with a single coat...
- Total
- Land (%)
- Water (%)
78772 km² (30,414 sq mi)
97%
3%
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
96 km (60 mi)
Ben Nevis
Ben Nevis is the highest mountain in the British Isles. It is located at the western end of the Grampian Mountains in the Lochaber area of the Scottish Highlands, close to the town of Fort William....
1344 m (4,409 ft)
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's oceanic divisions. With a total area of about , it covers approximately 20% of the Earth's surface and about 26% of its water surface area...
, 0 m
River Tay
The River Tay is the longest river in Scotland and the seventh-longest in the United Kingdom. The Tay originates in western Scotland on the slopes of Ben Lui , then flows easterly across the Highlands, through Loch Dochhart, Loch Lubhair and Loch Tay, then continues east through Strathtay , in...
193 km (120 mi)
Loch Lomond
Loch Lomond is a freshwater Scottish loch, lying on the Highland Boundary Fault. It is the largest lake in Great Britain by surface area. The lake contains many islands, including Inchmurrin, the largest fresh-water island in the British Isles, although the lake itself is smaller than many Irish...
71 km² (27.41 sq mi)
Climate
Climate encompasses the statistics of temperature, humidity, atmospheric pressure, wind, rainfall, atmospheric particle count and other meteorological elemental measurements in a given region over long periods...
:
Temperate
In geography, temperate or tepid latitudes of the globe lie between the tropics and the polar circles. The changes in these regions between summer and winter are generally relatively moderate, rather than extreme hot or cold...
Terrain
Terrain, or land relief, is the vertical and horizontal dimension of land surface. When relief is described underwater, the term bathymetry is used...
:
Mountain
Image:Himalaya_annotated.jpg|thumb|right|The Himalayan mountain range with Mount Everestrect 58 14 160 49 Chomo Lonzorect 200 28 335 52 Makalurect 378 24 566 45 Mount Everestrect 188 581 920 656 Tibetan Plateaurect 250 406 340 427 Rong River...
s, hill
Hill
A hill is a landform that extends above the surrounding terrain. Hills often have a distinct summit, although in areas with scarp/dip topography a hill may refer to a particular section of flat terrain without a massive summit A hill is a landform that extends above the surrounding terrain. Hills...
s, forest
Forest
A forest, also referred to as a wood or the woods, is an area with a high density of trees. As with cities, depending where you are in the world, what is considered a forest may vary significantly in size and have various classification according to how and what of the forest is composed...
, bog
Bog
A bog, quagmire or mire is a wetland that accumulates acidic peat, a deposit of dead plant material—often mosses or, in Arctic climates, lichens....
, urban
Urban area
An urban area is characterized by higher population density and vast human features in comparison to areas surrounding it. Urban areas may be cities, towns or conurbations, but the term is not commonly extended to rural settlements such as villages and hamlets.Urban areas are created and further...
Iron
Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust...
, zinc
Zinc
Zinc , or spelter , is a metallic chemical element; it has the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is the first element in group 12 of the periodic table. Zinc is, in some respects, chemically similar to magnesium, because its ion is of similar size and its only common oxidation state is +2...
, potash
Potash
Potash is the common name for various mined and manufactured salts that contain potassium in water-soluble form. In some rare cases, potash can be formed with traces of organic materials such as plant remains, and this was the major historical source for it before the industrial era...
, silica sand, coal
Coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock usually occurring in rock strata in layers or veins called coal beds or coal seams. The harder forms, such as anthracite coal, can be regarded as metamorphic rock because of later exposure to elevated temperature and pressure...
, fish
Fish
Fish are a paraphyletic group of organisms that consist of all gill-bearing aquatic vertebrate animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish, as well as various extinct related groups...
, timber
Timber
Timber may refer to:* Timber, a term common in the United Kingdom and Australia for wood materials * Timber, Oregon, an unincorporated community in the U.S...
, wildlife
Wildlife
Wildlife includes all non-domesticated plants, animals and other organisms. Domesticating wild plant and animal species for human benefit has occurred many times all over the planet, and has a major impact on the environment, both positive and negative....
, petroleum
Petroleum
Petroleum or crude oil is a naturally occurring, flammable liquid consisting of a complex mixture of hydrocarbons of various molecular weights and other liquid organic compounds, that are found in geologic formations beneath the Earth's surface. Petroleum is recovered mostly through oil drilling...
, natural gas
Natural gas
Natural gas is a naturally occurring gas mixture consisting primarily of methane, typically with 0–20% higher hydrocarbons . It is found associated with other hydrocarbon fuel, in coal beds, as methane clathrates, and is an important fuel source and a major feedstock for fertilizers.Most natural...
, hydropower
Hydropower
Hydropower, hydraulic power, hydrokinetic power or water power is power that is derived from the force or energy of falling water, which may be harnessed for useful purposes. Since ancient times, hydropower has been used for irrigation and the operation of various mechanical devices, such as...
Flood
A flood is an overflow of an expanse of water that submerges land. The EU Floods directive defines a flood as a temporary covering by water of land not normally covered by water...
s
Climate change
Climate change is a significant and lasting change in the statistical distribution of weather patterns over periods ranging from decades to millions of years. It may be a change in average weather conditions or the distribution of events around that average...
, renewable energy
Renewable energy
Renewable energy is energy which comes from natural resources such as sunlight, wind, rain, tides, and geothermal heat, which are renewable . About 16% of global final energy consumption comes from renewables, with 10% coming from traditional biomass, which is mainly used for heating, and 3.4% from...
, waste disposal and water pollution
Water pollution
Water pollution is the contamination of water bodies . Water pollution occurs when pollutants are discharged directly or indirectly into water bodies without adequate treatment to remove harmful compounds....
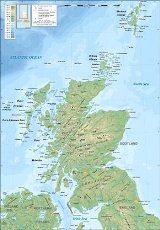
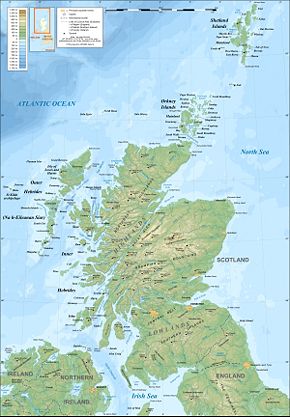
The geography of Scotland is highly varied, from rural lowlands to barren uplands, and from large cities to uninhabited islands. Located in north-west Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
, Scotland
Scotland
Scotland is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Occupying the northern third of the island of Great Britain, it shares a border with England to the south and is bounded by the North Sea to the east, the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, and the North Channel and Irish Sea to the...
comprises the northern one third of the island of Great Britain
Great Britain
Great Britain or Britain is an island situated to the northwest of Continental Europe. It is the ninth largest island in the world, and the largest European island, as well as the largest of the British Isles...
. Aside from the mainland, Scotland is surrounded by 790 islands encompassing the major archipelago
Archipelago
An archipelago , sometimes called an island group, is a chain or cluster of islands. The word archipelago is derived from the Greek ἄρχι- – arkhi- and πέλαγος – pélagos through the Italian arcipelago...
es of the Shetland Islands, Orkney Islands and the Outer Hebrides
Outer Hebrides
The Outer Hebrides also known as the Western Isles and the Long Island, is an island chain off the west coast of Scotland. The islands are geographically contiguous with Comhairle nan Eilean Siar, one of the 32 unitary council areas of Scotland...
.
Scotland's only land border is with England
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
, which runs for 96 kilometres (59.7 mi) in a northeasterly direction from the Solway Firth
Solway Firth
The Solway Firth is a firth that forms part of the border between England and Scotland, between Cumbria and Dumfries and Galloway. It stretches from St Bees Head, just south of Whitehaven in Cumbria, to the Mull of Galloway, on the western end of Dumfries and Galloway. The Isle of Man is also very...
in the west to the North Sea
North Sea
In the southwest, beyond the Straits of Dover, the North Sea becomes the English Channel connecting to the Atlantic Ocean. In the east, it connects to the Baltic Sea via the Skagerrak and Kattegat, narrow straits that separate Denmark from Norway and Sweden respectively...
on the east coast. Separated by the North Channel
North Channel (British Isles)
The North Channel is the strait which separates eastern Northern Ireland from southwestern Scotland...
, the island of Ireland
Ireland
Ireland is an island to the northwest of continental Europe. It is the third-largest island in Europe and the twentieth-largest island on Earth...
lies 30 kilometres (19 mi) from the southwest tip of the Scottish mainland. Norway
Norway
Norway , officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic unitary constitutional monarchy whose territory comprises the western portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula, Jan Mayen, and the Arctic archipelago of Svalbard and Bouvet Island. Norway has a total area of and a population of about 4.9 million...
is located 305 kilometres (190 mi) to the northeast of Scotland across the North Sea. The Atlantic Ocean
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's oceanic divisions. With a total area of about , it covers approximately 20% of the Earth's surface and about 26% of its water surface area...
, which fringes the coastline of western and northern Scotland and its islands, influences the temperate
Temperate
In geography, temperate or tepid latitudes of the globe lie between the tropics and the polar circles. The changes in these regions between summer and winter are generally relatively moderate, rather than extreme hot or cold...
, maritime climate of the country.
The topography of Scotland is distinguished by the Highland Boundary Fault
Highland Boundary Fault
The Highland Boundary Fault is a geological fault that traverses Scotland from Arran and Helensburgh on the west coast to Stonehaven in the east...
a geological rock fracture
Geologic fault
In geology, a fault is a planar fracture or discontinuity in a volume of rock, across which there has been significant displacement along the fractures as a result of earth movement. Large faults within the Earth's crust result from the action of tectonic forces...
which traverses the Scottish mainland from Helensburgh
Helensburgh
Helensburgh is a town in Argyll and Bute, Scotland. It lies on the north shore of the Firth of Clyde and the eastern shore of the entrance to the Gareloch....
to Stonehaven
Stonehaven
Stonehaven is a town in Aberdeenshire, Scotland. It lies on Scotland's northeast coast and had a population of 9,577 in 2001 census.Stonehaven, county town of Kincardineshire, grew around an Iron Age fishing village, now the "Auld Toon" , and expanded inland from the seaside...
. The faultline separates two distinctively different physiographic regions; namely the Highlands
Scottish Highlands
The Highlands is an historic region of Scotland. The area is sometimes referred to as the "Scottish Highlands". It was culturally distinguishable from the Lowlands from the later Middle Ages into the modern period, when Lowland Scots replaced Scottish Gaelic throughout most of the Lowlands...
to the north and west and the lowlands
Scottish Lowlands
The Scottish Lowlands is a name given to the Southern half of Scotland.The area is called a' Ghalldachd in Scottish Gaelic, and the Lawlands ....
to the south and east. The more rugged Highland region contains the majority of Scotland's mountainous terrain, including the highest peak, Ben Nevis
Ben Nevis
Ben Nevis is the highest mountain in the British Isles. It is located at the western end of the Grampian Mountains in the Lochaber area of the Scottish Highlands, close to the town of Fort William....
. Lowland areas, in the southern part of Scotland, are flatter and home to most of the population, especially the narrow waist of land between the Firth of Clyde
Firth of Clyde
The Firth of Clyde forms a large area of coastal water, sheltered from the Atlantic Ocean by the Kintyre peninsula which encloses the outer firth in Argyll and Ayrshire, Scotland. The Kilbrannan Sound is a large arm of the Firth of Clyde, separating the Kintyre Peninsula from the Isle of Arran.At...
and the Firth of Forth
Firth of Forth
The Firth of Forth is the estuary or firth of Scotland's River Forth, where it flows into the North Sea, between Fife to the north, and West Lothian, the City of Edinburgh and East Lothian to the south...
known as the Central Belt
Central Lowlands
The Central Lowlands or Midland Valley is a geologically defined area of relatively low-lying land in southern Scotland. It consists of a rift valley between the Highland Boundary Fault to the north and the Southern Uplands Fault to the south...
. Glasgow
Glasgow
Glasgow is the largest city in Scotland and third most populous in the United Kingdom. The city is situated on the River Clyde in the country's west central lowlands...
is the largest city in Scotland, although Edinburgh
Edinburgh
Edinburgh is the capital city of Scotland, the second largest city in Scotland, and the eighth most populous in the United Kingdom. The City of Edinburgh Council governs one of Scotland's 32 local government council areas. The council area includes urban Edinburgh and a rural area...
is the capital
Capital City
Capital City was a television show produced by Euston Films which focused on the lives of investment bankers in London living and working on the corporate trading floor for the fictional international bank Shane-Longman....
and political centre of the country.
An abundance of natural resources such as coal
Coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock usually occurring in rock strata in layers or veins called coal beds or coal seams. The harder forms, such as anthracite coal, can be regarded as metamorphic rock because of later exposure to elevated temperature and pressure...
, iron
Iron
Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust...
and zinc
Zinc
Zinc , or spelter , is a metallic chemical element; it has the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is the first element in group 12 of the periodic table. Zinc is, in some respects, chemically similar to magnesium, because its ion is of similar size and its only common oxidation state is +2...
contributed significantly to the industrial growth of Scotland during the 19th and early 20th centuries. Today, energy
Energy
In physics, energy is an indirectly observed quantity. It is often understood as the ability a physical system has to do work on other physical systems...
is a major component of Scotland's economy. Whilst Scotland is the largest producer of petroleum
North Sea oil
North Sea oil is a mixture of hydrocarbons, comprising liquid oil and natural gas, produced from oil reservoirs beneath the North Sea.In the oil industry, the term "North Sea" often includes areas such as the Norwegian Sea and the area known as "West of Shetland", "the Atlantic Frontier" or "the...
in the European Union
European Union
The European Union is an economic and political union of 27 independent member states which are located primarily in Europe. The EU traces its origins from the European Coal and Steel Community and the European Economic Community , formed by six countries in 1958...
, the production potential of renewable energy
Renewable energy in Scotland
The production of renewable energy in Scotland is an issue that has come to the fore in technical, economic, and political terms during the opening years of the 21st century. The natural resource base for renewables is extraordinary by European, and even global standards...
has emerged as an important economic and environmental issue in recent years.
Geology and geomorphology
The land area of Scotland is 78772 km² (30,414 sq mi), roughly 30% of the area of the United Kingdom (UK). The mainland of Scotland has 9911 km (6,158 mi) of coastline.The geomorphology
Geomorphology
Geomorphology is the scientific study of landforms and the processes that shape them...
of Scotland was formed by the action of tectonic plates, and subsequent erosion arising from glaciation. The major division of Scotland is the Highland Boundary Fault
Highland Boundary Fault
The Highland Boundary Fault is a geological fault that traverses Scotland from Arran and Helensburgh on the west coast to Stonehaven in the east...
, which separates the land into 'highland' to the north and west, and 'lowland' to the south and east. The Highlands of Scotland
Scottish Highlands
The Highlands is an historic region of Scotland. The area is sometimes referred to as the "Scottish Highlands". It was culturally distinguishable from the Lowlands from the later Middle Ages into the modern period, when Lowland Scots replaced Scottish Gaelic throughout most of the Lowlands...
are largely mountainous, and form the highest ground in the UK: they are bisected by the Great Glen
Great Glen
The Great Glen , also known as Glen Albyn or Glen More is a series of glens in Scotland running 100 kilometres from Inverness on the Moray Firth, to Fort William at the head of Loch Linnhe.The Great Glen follows a large geological fault known as the Great Glen Fault...
into the Grampian Mountains
Grampian Mountains (Scotland)
The Grampian Mountains or Grampians are one of the three major mountain ranges in Scotland, occupying a considerable portion of the Scottish Highlands in northeast Scotland.-Extent:...
to the southeast and the Northwest Highlands
Northwest Highlands
The Northwest Highlands are the northern third of Scotland that is separated from the Grampian Mountains by the Great Glen . The region comprises , Assynt, Caithness and Sutherland. The Caledonian Canal, which extends from Loch Linnhe in the west, via Loch Ness to the Moray Firth in the north...
. The Scottish Lowlands
Scottish Lowlands
The Scottish Lowlands is a name given to the Southern half of Scotland.The area is called a' Ghalldachd in Scottish Gaelic, and the Lawlands ....
can be further subdivided into the Southern Uplands
Southern Uplands
The Southern Uplands are the southernmost and least populous of mainland Scotland's three major geographic areas . The term is used both to describe the geographical region and to collectively denote the various ranges of hills within this region...
, an area of rolling farmland and high moorland
Moorland
Moorland or moor is a type of habitat, in the temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biome, found in upland areas, characterised by low-growing vegetation on acidic soils and heavy fog...
, and the lowland farmland of the Central Belt
Central Belt
The Central Belt of Scotland is a common term used to describe the area of highest population density within Scotland. Despite the name, it is not geographically central but is nevertheless situated at the 'waist' of Scotland on a conventional map and the term 'central' is used in many local...
and eastern Scotland.
Scotland has an incomparable variety of geology
Geology
Geology is the science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which it evolves. Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth, as it provides the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates...
for an area of its size. It is also the origin of many significant discoveries and important figures in the development of the science.
The oldest rocks of Scotland are the Lewisian gneisses
Lewisian complex
The Lewisian complex or Lewisian Gneiss is a suite of Precambrian metamorphic rocks that outcrop in the northwestern part of Scotland, forming part of the Hebridean Terrane. These rocks are of Archaean and Paleoproterozoic age, ranging from 3.0–1.7 Ga. They form the basement on which the...
, which were formed in the Precambrian
Precambrian
The Precambrian is the name which describes the large span of time in Earth's history before the current Phanerozoic Eon, and is a Supereon divided into several eons of the geologic time scale...
period, up to 3,000 Ma (Mega annum or million years ago). They are among the oldest rocks in the world. During the Precambrian, the Torridonian sandstones and the Moine
Moine Supergroup
The Moine Supergroup is a sequence of Neoproterozoic metamorphic rocks that form the dominant outcrop of the Scottish Highlands between the Moine Thrust Belt to the northwest and the Great Glen Fault to the southeast. The sequence is metasedimentary in nature and was metamorphosed and deformed in a...
were also laid down. Further sedimentary deposits were formed through the Cambrian
Cambrian
The Cambrian is the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, lasting from Mya ; it is succeeded by the Ordovician. Its subdivisions, and indeed its base, are somewhat in flux. The period was established by Adam Sedgwick, who named it after Cambria, the Latin name for Wales, where Britain's...
period, some of which metamorphosed
Metamorphic rock
Metamorphic rock is the transformation of an existing rock type, the protolith, in a process called metamorphism, which means "change in form". The protolith is subjected to heat and pressure causing profound physical and/or chemical change...
into the Dalradian
Dalradian
Dalradian in geology describes a series of metamorphic rocks, typically developed in the high ground which lies southeast of the Great Glen of Scotland...
series. The area which would become Scotland was at this time close to the south pole.
During the Silurian
Silurian
The Silurian is a geologic period and system that extends from the end of the Ordovician Period, about 443.7 ± 1.5 Mya , to the beginning of the Devonian Period, about 416.0 ± 2.8 Mya . As with other geologic periods, the rock beds that define the period's start and end are well identified, but the...
period (439-409 Ma), the area which became Scotland was part of the continent of Laurentia
Laurentia
Laurentia is a large area of continental craton, which forms the ancient geological core of the North American continent...
. Across the Iapetus
Iapetus Ocean
The Iapetus Ocean was an ocean that existed in the Neoproterozoic and Paleozoic eras of the geologic timescale . The Iapetus Ocean was situated in the southern hemisphere, between the paleocontinents of Laurentia, Baltica and Avalonia...
ocean to the south, was the continent of Baltica
Baltica
Baltica is a name applied by geologists to a late-Proterozoic, early-Palaeozoic continent that now includes the East European craton of northwestern Eurasia. Baltica was created as an entity not earlier than 1.8 billion years ago. Before this time, the three segments/continents that now comprise...
. The two continents gradually collided, joining Scotland to the area which would become England and Europe. This event is known as the Caledonian Orogeny
Caledonian orogeny
The Caledonian orogeny is a mountain building era recorded in the northern parts of the British Isles, the Scandinavian Mountains, Svalbard, eastern Greenland and parts of north-central Europe. The Caledonian orogeny encompasses events that occurred from the Ordovician to Early Devonian, roughly...
, and the Highland Boundary Fault
Highland Boundary Fault
The Highland Boundary Fault is a geological fault that traverses Scotland from Arran and Helensburgh on the west coast to Stonehaven in the east...
marks this stitching together of continents. Silurian rocks form the Southern Uplands
Southern Uplands
The Southern Uplands are the southernmost and least populous of mainland Scotland's three major geographic areas . The term is used both to describe the geographical region and to collectively denote the various ranges of hills within this region...
of Scotland, which was pushed up from the seabed during the collision. The highlands were also pushed up as a result of this collision, and may have been as high as the modern-day Alps
Alps
The Alps is one of the great mountain range systems of Europe, stretching from Austria and Slovenia in the east through Italy, Switzerland, Liechtenstein and Germany to France in the west....
at this time. The Old Red Sandstone
Old Red Sandstone
The Old Red Sandstone is a British rock formation of considerable importance to early paleontology. For convenience the short version of the term, 'ORS' is often used in literature on the subject.-Sedimentology:...
s were laid down in low-lying areas during this period. Volcanic activity
Volcano
2. Bedrock3. Conduit 4. Base5. Sill6. Dike7. Layers of ash emitted by the volcano8. Flank| 9. Layers of lava emitted by the volcano10. Throat11. Parasitic cone12. Lava flow13. Vent14. Crater15...
occurred across Scotland as a result of the collision of the tectonic plates, with volcanoes in southern Scotland, and magma chamber
Magma chamber
A magma chamber is a large underground pool of molten rock found beneath the surface of the Earth. The molten rock in such a chamber is under great pressure, and given enough time, that pressure can gradually fracture the rock around it creating outlets for the magma...
s in the north, which today form the granite
Granite
Granite is a common and widely occurring type of intrusive, felsic, igneous rock. Granite usually has a medium- to coarse-grained texture. Occasionally some individual crystals are larger than the groundmass, in which case the texture is known as porphyritic. A granitic rock with a porphyritic...
mountains such as the Cairngorms
Cairngorms
The Cairngorms are a mountain range in the eastern Highlands of Scotland closely associated with the mountain of the same name - Cairn Gorm.-Name:...
.
During the Carboniferous
Carboniferous
The Carboniferous is a geologic period and system that extends from the end of the Devonian Period, about 359.2 ± 2.5 Mya , to the beginning of the Permian Period, about 299.0 ± 0.8 Mya . The name is derived from the Latin word for coal, carbo. Carboniferous means "coal-bearing"...
period (363-290 Ma), Scotland lay close to the equator. Several changes in sea level occurred during this time. The coal
Coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock usually occurring in rock strata in layers or veins called coal beds or coal seams. The harder forms, such as anthracite coal, can be regarded as metamorphic rock because of later exposure to elevated temperature and pressure...
deposits of Lanarkshire
Lanarkshire
Lanarkshire or the County of Lanark ) is a Lieutenancy area, registration county and former local government county in the central Lowlands of Scotland...
, and further sedimentary deposits, date from this time. More volcanic activity formed Arthur's Seat
Arthur's Seat, Edinburgh
Arthur's Seat is the main peak of the group of hills which form most of Holyrood Park, described by Robert Louis Stevenson as "a hill for magnitude, a mountain in virtue of its bold design". It is situated in the centre of the city of Edinburgh, about a mile to the east of Edinburgh Castle...
in Edinburgh
Edinburgh
Edinburgh is the capital city of Scotland, the second largest city in Scotland, and the eighth most populous in the United Kingdom. The City of Edinburgh Council governs one of Scotland's 32 local government council areas. The council area includes urban Edinburgh and a rural area...
, among other hills. By the Triassic
Triassic
The Triassic is a geologic period and system that extends from about 250 to 200 Mya . As the first period of the Mesozoic Era, the Triassic follows the Permian and is followed by the Jurassic. Both the start and end of the Triassic are marked by major extinction events...
, Scotland was a desert, the origin of large sandstone
Sandstone
Sandstone is a sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized minerals or rock grains.Most sandstone is composed of quartz and/or feldspar because these are the most common minerals in the Earth's crust. Like sand, sandstone may be any colour, but the most common colours are tan, brown, yellow,...
outcrops of the southwest. Although large deposits of Cretaceous
Cretaceous
The Cretaceous , derived from the Latin "creta" , usually abbreviated K for its German translation Kreide , is a geologic period and system from circa to million years ago. In the geologic timescale, the Cretaceous follows the Jurassic period and is followed by the Paleogene period of the...
rocks would have been laid down over Scotland, these have not survived erosion, as have the chalk
Chalk
Chalk is a soft, white, porous sedimentary rock, a form of limestone composed of the mineral calcite. Calcite is calcium carbonate or CaCO3. It forms under reasonably deep marine conditions from the gradual accumulation of minute calcite plates shed from micro-organisms called coccolithophores....
s of England.
By the Tertiary
Tertiary
The Tertiary is a deprecated term for a geologic period 65 million to 2.6 million years ago. The Tertiary covered the time span between the superseded Secondary period and the Quaternary...
period, the tectonic plates were again moving, separating into modern-day North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
and Europe with the creation of the Atlantic Ocean
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's oceanic divisions. With a total area of about , it covers approximately 20% of the Earth's surface and about 26% of its water surface area...
. The split occurred to the west of Scotland, leaving a chain of former volcanic sites through the Hebrides
Hebrides
The Hebrides comprise a widespread and diverse archipelago off the west coast of Scotland. There are two main groups: the Inner and Outer Hebrides. These islands have a long history of occupation dating back to the Mesolithic and the culture of the residents has been affected by the successive...
, including Skye and St. Kilda
St Kilda, Scotland
St Kilda is an isolated archipelago west-northwest of North Uist in the North Atlantic Ocean. It contains the westernmost islands of the Outer Hebrides of Scotland. The largest island is Hirta, whose sea cliffs are the highest in the United Kingdom and three other islands , were also used for...
. This was the last period of rock formation in Scotland. Since then, several ice age
Ice age
An ice age or, more precisely, glacial age, is a generic geological period of long-term reduction in the temperature of the Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental ice sheets, polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers...
s have shaped the land through glacial erosion, creating u-shaped valleys and depositing boulder clay
Boulder clay
Boulder clay, in geology, is a deposit of clay, often full of boulders, which is formed in and beneath glaciers and ice-sheets wherever they are found, but is in a special sense the typical deposit of the Glacial Period in northern Europe and North America...
s. In the present day, Scotland continues to move slowly north.
Extreme points

- North: Easter Head, Dunnet HeadDunnet HeadDunnet Head is a peninsula in Caithness, on the north coast of Scotland, that includes the most northerly point of the mainland of Great Britain. The point, known as Easter Head, is at , about westnorthwest of John o' Groats and about from Duncansby Head...
, CaithnessCaithnessCaithness is a registration county, lieutenancy area and historic local government area of Scotland. The name was used also for the earldom of Caithness and the Caithness constituency of the Parliament of the United Kingdom . Boundaries are not identical in all contexts, but the Caithness area is... - East: Keith InchKeith InchNot to be confused with "Inchkeith", in the Firth of ForthKeith Inch is the easternmost point of mainland Scotland.It is located in Peterhead in Aberdeenshire, forming the north point of Peterhead Bay at ....
, PeterheadPeterheadPeterhead is a town in Aberdeenshire, Scotland. It is Aberdeenshire's biggest settlement , with a population of 17,947 at the 2001 Census and estimated to have fallen to 17,330 by 2006....
, Aberdeenshire - South: Mull of GallowayMull of GallowayThe Mull of Galloway is the southernmost point of Scotland. It is situated in Wigtownshire, Dumfries and Galloway.A lighthouse is positioned at the point . Built in 1830 by engineer Robert Stevenson, the white-painted round tower is high...
, Dumfries and GallowayDumfries and GallowayDumfries and Galloway is one of 32 unitary council areas of Scotland. It was one of the nine administrative 'regions' of mainland Scotland created in 1975 by the Local Government etc. Act 1973... - West: Corrachadh MòrCorrachadh MorCorrachadh Mòr ETRS89 is a small hillock on the Ardnamurchan peninsula in Lochaber, Highland, Scotland, notable for adjoining the most westerly point on the island of Great Britain. It is about further west than Land's End in Cornwall....
, ArdnamurchanArdnamurchanArdnamurchan is a peninsula in Lochaber, Highland, Scotland, noted for being very unspoilt and undisturbed. Its remoteness is accentuated by the main access route being a single track road for much of its length.-Geography:...
(headland), LochaberLochaberDistrict of Lochaber 1975 to 1996Highland council area shown as one of the council areas of ScotlandLochaber is one of the 16 ward management areas of the Highland Council of Scotland and one of eight former local government districts of the two-tier Highland region...
It is often yet incorrectly stated that John o' Groats
John o' Groats
John o' Groats is a village in the Highland council area of Scotland. Part of the county of Caithness, John o' Groats is popular with tourists because it is usually regarded as the most northerly settlement of mainland Great Britain, although this is not a claim made by the inhabitants...
is the most northerly point of mainland Scotland. The pre-Union phrase "John o' Groats to Maidenkirk
Maidenkirk
Maidenkirk is a small settlement in Galloway, ScotlandUntil Union with England, Scotland's equivalent of the phrase "Land's End to John o' Groats" was often "John o' Groats to Maidenkirk", as Maidenkirk was traditionally considered the southernmost part of that country...
" was the Scottish equivalent of the British Land's End to John o' Groats
Land's End to John o' Groats
Land's End to John o' Groats is the traversal of the whole length of the island of Great Britain between two extremities; in the southwest and northeast. The traditional distance by road is and takes most cyclists ten to fourteen days; the record for running the route is nine days. Off-road...
.
The extreme points of Scotland, including outlying islands, are:
- North: Out StackOut StackOut Stack or Ootsta in Shetland, Scotland, is the northernmost of the British Isles, lying immediately to the north of Muckle Flugga and north of the island of Unst. It is one of the North Isles of the Shetland Islands and lies within the Hermaness National Nature Reserve.Out Stack is little more...
, north of UnstUnstUnst is one of the North Isles of the Shetland Islands, Scotland. It is the northernmost of the inhabited British Isles and is the third largest island in Shetland after the Mainland and Yell. It has an area of .Unst is largely grassland, with coastal cliffs...
, Shetland IslandsShetland IslandsShetland is a subarctic archipelago of Scotland that lies north and east of mainland Great Britain. The islands lie some to the northeast of Orkney and southeast of the Faroe Islands and form part of the division between the Atlantic Ocean to the west and the North Sea to the east. The total... - East: Bound SkerryBound SkerryBound Skerry is part of the Out Skerries group in the Shetland Islands. As well as being the most easterly island of that group, it is also the easternmost point of Scotland....
, Out SkerriesOuter SkerriesThe Out Skerries are an archipelago in Shetland, Scotland, lying to the east of the main Shetland Island group. Locally, they are usually called Da Skerries or just Skerries.-Geography:...
, Shetland Islands - South: Mull of Galloway, Dumfries and Galloway
- West: Either RockallRockallRockall is an extremely small, uninhabited, remote rocky islet in the North Atlantic Ocean. It gives its name to one of the sea areas named in the shipping forecast provided by the British Meteorological Office....
(annexed in 1972 to the former Inverness-shireInverness-shireThe County of Inverness or Inverness-shire was a general purpose county of Scotland, with the burgh of Inverness as the county town, until 1975, when, under the Local Government Act 1973, the county area was divided between the two-tier Highland region and the unitary Western Isles. The Highland...
), the international status of which is disputed, or SoaySoay, St KildaSoay is an uninhabited islet in the St Kilda archipelago, Scotland. The island is part of the St Kilda World Heritage Site and home to a primitive breed of sheep...
, St. KildaSt Kilda, ScotlandSt Kilda is an isolated archipelago west-northwest of North Uist in the North Atlantic Ocean. It contains the westernmost islands of the Outer Hebrides of Scotland. The largest island is Hirta, whose sea cliffs are the highest in the United Kingdom and three other islands , were also used for...
, Western IslesOuter HebridesThe Outer Hebrides also known as the Western Isles and the Long Island, is an island chain off the west coast of Scotland. The islands are geographically contiguous with Comhairle nan Eilean Siar, one of the 32 unitary council areas of Scotland...
The geographical centre of Scotland
Centre of Scotland
There is some debate as to the location of the geographical centre of Scotland. This is due to different methods of calculating the centre, and whether surrounding islands are included....
lies a few miles from the village of Newtonmore
Newtonmore
Newtonmore is a village in the Highland council area of Scotland. It has a population of about 1000. The village is only a few miles from a location that is claimed to be the exact geographical centre of Scotland...
in Badenoch
Badenoch
Badenoch is a traditional district which today forms part of Badenoch and Strathspey, an area of Highland Council, in Scotland, bounded on the north by the Monadhliath Mountains, on the east by the Cairngorms and Braemar, on the south by Atholl and the Grampians, and on the west by Lochaber...
, far to the north of the modern population heartlands.
Land use
The total land area of Scotland is 7,710,000 hectares. Crops and fallow land account for 7 per cent of the land area, grasses and rough grazing 67%, other agricultural land 2per cent, forest and woodland 17 per cent, and urban development 8 per cent.Topography, mountains and hills

Northwest Highlands
The Northwest Highlands are the northern third of Scotland that is separated from the Grampian Mountains by the Great Glen . The region comprises , Assynt, Caithness and Sutherland. The Caledonian Canal, which extends from Loch Linnhe in the west, via Loch Ness to the Moray Firth in the north...
and Grampian ranges. The Cuillin
Cuillin
This article is about the Cuillin of Skye. See Rùm for the Cuillin of Rùm.The Cuillin are a range of rocky mountains located on the Isle of Skye in Scotland. The true Cuillin are also known as the Black Cuillin to distinguish them from the Red Hills across Glen Sligachan...
on the Isle of Skye, represents a major mountain range that is not located on the Scottish mainland. Located at the western end of the Grampian Mountains, at an altitude of 1344 m (4,409 ft), Ben Nevis
Ben Nevis
Ben Nevis is the highest mountain in the British Isles. It is located at the western end of the Grampian Mountains in the Lochaber area of the Scottish Highlands, close to the town of Fort William....
is the highest mountain in Scotland and Great Britain. Ben Macdui and Braeriach
Braeriach
Braeriach is the third highest mountain in Great Britain, surpassed only by Ben Nevis and Ben Macdui. It is the highest point in the western massif of the Cairngorms, separated from the central section by the pass of the Lairig Ghru. The summit has a crescent shape, with several corries...
are, respectively, the second and third tallest peaks in Scotland.
Mountains in Scotland are categorised by their height. Peaks over 3000 ft (914.4 m) are known as Munro
Munro
A Munro is a mountain in Scotland with a height over . They are named after Sir Hugh Munro, 4th Baronet , who produced the first list of such hills, known as Munros Tables, in 1891. A Munro top is a summit over 3,000 ft which is not regarded as a separate mountain...
s. There are 284 Munros in Scotland, all within the Highlands. Corbetts are peaks with an altitude of between 2500 and 3000 ft (762 and 914.4 m), with a relative height
Topographic prominence
In topography, prominence, also known as autonomous height, relative height, shoulder drop , or prime factor , categorizes the height of the mountain's or hill's summit by the elevation between it and the lowest contour line encircling it and no higher summit...
of at least 500 ft (152.4 m) . The classification of peaks in Scotland is kept under periodic review by the Scottish Mountaineering Club
Scottish Mountaineering Club
The Scottish Mountaineering Club is Scotland's second oldest mountaineering club. Founded in 1889, in Glasgow, the private club, with about 400 members, publishes guidebooks and runs a list of Munroists.-History:At the time of the club's founding there were a number of experienced Alpinists...
.
Topographically, mainland Scotland can be divided into three main areas which reflect the underlying geology. These are divided from one another by south-west to north east lines that roughly parallel the artificial line representing the English Border.
Southern Uplands
The southern 20% or so of the country makes up the Southern UplandsSouthern Uplands
The Southern Uplands are the southernmost and least populous of mainland Scotland's three major geographic areas . The term is used both to describe the geographical region and to collectively denote the various ranges of hills within this region...
, a pastoral upland area characterised by lines of hills divided by broad valleys. It is also home to some of the most remote and least populated areas in Scotland and to the country's highest village, Wanlockhead
Wanlockhead
Wanlockhead is a village in Dumfries and Galloway, Scotland nestling in the Lowther Hills one mile south of Leadhills at the head of the Mennock Pass, which forms part of the Southern Uplands...
, at 467 m or 1,532 ft.
The Pentland Hills
Pentland Hills
The Pentland Hills are a range of hills to the south-west of Edinburgh, Scotland. The range is around 20 miles in length, and runs south west from Edinburgh towards Biggar and the upper Clydesdale.Some of the peaks include:* Scald Law...
and the Lammermuir Hills
Lammermuir Hills
The Lammermuir Hills, usually simply called the Lammermuirs , in southern Scotland, form a natural boundary between Lothian and the Scottish Borders....
are several of the local ranges which make up the Southern Uplands. In addition to the main upland zones in southern Scotland there are many individual hills, not part of any range. Several of these elevations are volcanic in origin and are known by the Scots
Scots language
Scots is the Germanic language variety spoken in Lowland Scotland and parts of Ulster . It is sometimes called Lowland Scots to distinguish it from Scottish Gaelic, the Celtic language variety spoken in most of the western Highlands and in the Hebrides.Since there are no universally accepted...
word Law, meaning hill. North Berwick Law
North Berwick Law
North Berwick Law is a conical hill which rises incongruously from the surrounding landscape . It overlooks the East Lothian town of North Berwick and stands at 613 ft above sea level.Geologically, the law is a volcanic plug of hard phonolitic trachyte rock of Carboniferous age...
and Traprain Law
Traprain Law
Traprain Law is a hill about 221m in elevation, located east of Haddington in East Lothian, Scotland. It is the site of an oppidum or hill fort, which covered at its maximum extent about 16 ha and must have been a veritable town...
are two examples of these extinct volcanic outliers.
The Southern Uplands fault line running north-east from near Girvan
Girvan
Girvan is a burgh in Carrick, South Ayrshire, Scotland, with a population of about 8000 people. Originally a fishing port, it is now also a seaside resort with beaches and cliffs. Girvan dates back to 1668 when is became a municipal burgh incorporated by by charter...
in Ayrshire
Ayrshire
Ayrshire is a registration county, and former administrative county in south-west Scotland, United Kingdom, located on the shores of the Firth of Clyde. Its principal towns include Ayr, Kilmarnock and Irvine. The town of Troon on the coast has hosted the British Open Golf Championship twice in the...
, to the North Sea near Dunbar separates the Southern Uplands from the Central Lowlands.
Central Lowlands
The Central Lowlands can be thought of, very roughly, as the next 20% of the country as you progress north from the English Border and include the Forth-Clyde valley. The Central Lowlands were also the home of widespread industrialization from the late 18th century onwards. This was based on the large and widely scattered reserves of coal and iron ore found across most of the Central Lowlands, whose use was supported by the development of canals and then of railways. Deep-mined coal and large scale iron and steel works are no longer part of the picture in Scotland.The Sidlaw Hills
Sidlaw Hills
The Sidlaws are a range of hills of volcanic origin in the counties of Perthshire and Angus in Scotland that extend for 30 miles from Kinnoull Hill, near Perth, northeast to Forfar. Law is a Lowland Scots word of Old English origin meaning a hill which rises sharply from the surrounding land...
to the north of Dundee, the Ochils
Ochil Hills
The Ochil Hills is a range of hills in Scotland north of the Forth valley bordered by the towns of Stirling, Alloa, Kinross and Perth. The only major roads crossing the hills pass through Glen Devon/Glen Eagles and Glenfarg, the latter now largely replaced except for local traffic by the M90...
to the east of Stirling and the Campsie Fells
Campsie Fells
The Campsie Fells are a range of hills in central Scotland, stretching east to west, from Denny Muir to Dumgoyne, in Stirlingshire. . The highest point in the range is Earl's Seat which is 578 m high...
to the north of Glasgow constitute important upland ranges in the Central Lowlands.
Highlands
By far the largest zone, the Highlands comprises the north western 60% of Scotland. Technically this includes everywhere north and west of the Highland Boundary Fault, a fault line running from ArranIsle of Arran
Arran or the Isle of Arran is the largest island in the Firth of Clyde, Scotland, and with an area of is the seventh largest Scottish island. It is in the unitary council area of North Ayrshire and the 2001 census had a resident population of 5,058...
and Helensburgh
Helensburgh
Helensburgh is a town in Argyll and Bute, Scotland. It lies on the north shore of the Firth of Clyde and the eastern shore of the entrance to the Gareloch....
in the West to Stonehaven
Stonehaven
Stonehaven is a town in Aberdeenshire, Scotland. It lies on Scotland's northeast coast and had a population of 9,577 in 2001 census.Stonehaven, county town of Kincardineshire, grew around an Iron Age fishing village, now the "Auld Toon" , and expanded inland from the seaside...
in the east. Scotland's third largest city, Aberdeen
Aberdeen
Aberdeen is Scotland's third most populous city, one of Scotland's 32 local government council areas and the United Kingdom's 25th most populous city, with an official population estimate of ....
, lies just to the north of the Highland Boundary Fault, but like the fertile plains of eastern Aberdeenshire
Aberdeenshire
Aberdeenshire is one of the 32 unitary council areas in Scotland and a lieutenancy area.The present day Aberdeenshire council area does not include the City of Aberdeen, now a separate council area, from which its name derives. Together, the modern council area and the city formed historic...
it has more in common with the Central Lowlands than with the rest of the Highlands.
The Highlands are extensive mountainous areas rising to peaks of a maximum height of around 4400 ft or 1300m. Scotland's mountains are not high by international standards but their exposure to highly changeable and unpredictable weather patterns influenced by the meeting of Atlantic and Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
an air streams gives them a seriousness out of proportion to their height.
The area of the Highlands is split in two by the line of the Great Glen
Great Glen
The Great Glen , also known as Glen Albyn or Glen More is a series of glens in Scotland running 100 kilometres from Inverness on the Moray Firth, to Fort William at the head of Loch Linnhe.The Great Glen follows a large geological fault known as the Great Glen Fault...
, a rift valley
Rift valley
A rift valley is a linear-shaped lowland between highlands or mountain ranges created by the action of a geologic rift or fault. This action is manifest as crustal extension, a spreading apart of the surface which is subsequently further deepened by the forces of erosion...
running from Fort William
Fort William, Scotland
Fort William is the second largest settlement in the highlands of Scotland and the largest town: only the city of Inverness is larger.Fort William is a major tourist centre with Glen Coe just to the south, Aonach Mòr to the north and Glenfinnan to the west, on the Road to the Isles...
to Inverness
Inverness
Inverness is a city in the Scottish Highlands. It is the administrative centre for the Highland council area, and is regarded as the capital of the Highlands of Scotland...
. The land to the north west of the Great Glen is usually referred to as the North West Highlands, with that to its east forming the Grampians. The Grampians are characterised by large areas of upland plateau, while the North West Highlands have a much rougher, rockier look and feel, with the landmass deeply indented by numerous sea lochs.
Coastline

Fjord
Geologically, a fjord is a long, narrow inlet with steep sides or cliffs, created in a valley carved by glacial activity.-Formation:A fjord is formed when a glacier cuts a U-shaped valley by abrasion of the surrounding bedrock. Glacial melting is accompanied by rebound of Earth's crust as the ice...
like sea lochs. The east coast is more regular, with a series of large estuarine inlets, or firth
Firth
Firth is the word in the Lowland Scots language and in English used to denote various coastal waters in Scotland and England. In mainland Scotland it is used to describe a large sea bay, or even a strait. In the Northern Isles it more usually refers to a smaller inlet...
s, and long sandy beaches, for example at Aberdeen
Aberdeen
Aberdeen is Scotland's third most populous city, one of Scotland's 32 local government council areas and the United Kingdom's 25th most populous city, with an official population estimate of ....
. Much of the Scottish coastline consists of a machair formation
Machair (geography)
The machair refers to a fertile low-lying grassy plain found on some of the north-west coastlines of Ireland and Scotland, in particular the Outer Hebrides...
, a dune pasture land formed as sea levels subsided.
The east coast has several significant estuaries and other nature reserve
Nature reserve
A nature reserve is a protected area of importance for wildlife, flora, fauna or features of geological or other special interest, which is reserved and managed for conservation and to provide special opportunities for study or research...
s including the Ythan Estuary
Ythan Estuary
The Ythan Estuary is the tidal component of the Ythan River, emptying into the North Sea approximately north of Aberdeen, Scotland. The estuary’s tidal action extends a full inland and has characteristic widths of between and . Besides the tidal channel there are several types of interfaces to...
and Fowlsheugh
Fowlsheugh
Fowlsheugh is a coastal nature reserve in Kincardineshire, northeast Scotland, known for its seventy metre high cliff formations and habitat supporting prolific seabird nesting colonies. Designated as a Site of Special Scientific Interest by Scottish Natural Heritage, the property is owned by the...
, both of which have been designated as Important Bird Area
Important Bird Area
An Important Bird Area is an area recognized as being globally important habitat for the conservation of bird populations. Currently there are about 10,000 IBAs worldwide. The program was developed and sites are identified by BirdLife International...
s.
Firths of Scotland include the Solway Firth
Solway Firth
The Solway Firth is a firth that forms part of the border between England and Scotland, between Cumbria and Dumfries and Galloway. It stretches from St Bees Head, just south of Whitehaven in Cumbria, to the Mull of Galloway, on the western end of Dumfries and Galloway. The Isle of Man is also very...
, Firth of Clyde
Firth of Clyde
The Firth of Clyde forms a large area of coastal water, sheltered from the Atlantic Ocean by the Kintyre peninsula which encloses the outer firth in Argyll and Ayrshire, Scotland. The Kilbrannan Sound is a large arm of the Firth of Clyde, separating the Kintyre Peninsula from the Isle of Arran.At...
, and Firth of Lorne
Firth of Lorne
The Firth of Lorn is a body of water on Scotland's west coast, in Argyll and Bute. It lies between the Isle of Mull to the northwest and the Isles of Kerrera, Seil and Luing along with parts of the Scottish mainland southwest of Oban on the southeast side...
on the west coast, and the Cromarty Firth
Cromarty Firth
The Cromarty Firth of Cromarty') is an arm of the North Sea in Scotland. It is the middle of the three sea lochs at the head of the Moray Firth: to the north lies the Dornoch Firth, and to the south the Beauly Firth....
, Moray Firth
Moray Firth
The Moray Firth is a roughly triangular inlet of the North Sea, north and east of Inverness, which is in the Highland council area of north of Scotland...
, Firth of Tay
Firth of Tay
The Firth of Tay is a firth in Scotland between the council areas of Fife, Perth and Kinross, the City of Dundee and Angus, into which Scotland's largest river in terms of flow, the River Tay, empties....
, and Firth of Forth
Firth of Forth
The Firth of Forth is the estuary or firth of Scotland's River Forth, where it flows into the North Sea, between Fife to the north, and West Lothian, the City of Edinburgh and East Lothian to the south...
on the east coast. The Pentland Firth
Pentland Firth
The Pentland Firth , which is actually more of a strait than a firth, separates the Orkney Islands from Caithness in the north of Scotland.-Etymology:...
is not an inlet, but the strait
Strait
A strait or straits is a narrow, typically navigable channel of water that connects two larger, navigable bodies of water. It most commonly refers to a channel of water that lies between two land masses, but it may also refer to a navigable channel through a body of water that is otherwise not...
that separates the Orkney Isles from the mainland.
Major sea lochs include Loch Fyne
Loch Fyne
Loch Fyne is a sea loch on the west coast of Argyll and Bute, Scotland. It extends inland from the Sound of Bute, making it the longest of the sea lochs...
, Loch Long
Loch Long
Loch Long is a body of water in Argyll and Bute, Scotland. The sea loch extends from the Firth of Clyde at its southwestern end. It measures approximately 20 miles in length, with a width of between one and two miles...
, Loch Ryan
Loch Ryan
Loch Ryan is a Scottish sea loch that acts as an important natural harbour for shipping, providing calm waters for ferries operating between Scotland and Northern Ireland...
, Loch Linnhe
Loch Linnhe
Loch Linnhe is a sea loch on the west coast of Scotland....
, Loch Torridon
Loch Torridon
Loch Torridon is a sea loch on the west coast of Scotland in the Northwest Highlands. The loch was created by glacial processes and is in total around 15 miles long. It has two sections: Upper Loch Torridon to landward, east of Rubha na h-Airde Ghlaise, at which point it joins Loch Sheildaig;...
, Loch Ewe
Loch Ewe
Loch Ewe is a sea loch in the region of in the Northwest Highlands of Scotland. The shores are inhabited by a traditionally Gàidhlig speaking people living in or sustained by crofting villages, the most notable of which, situated on the north-eastern shore, is the Aultbea settlement...
, and on the Isle of Lewis
Lewis
Lewis is the northern part of Lewis and Harris, the largest island of the Western Isles or Outer Hebrides of Scotland. The total area of Lewis is ....
, Loch Seaforth
Loch Seaforth
Loch Seaforth is sea loch in the Outer Hebrides of Scotland. It forms the boundary between Lewis and Harris and formerly was the boundary between the traditional counties of Ross and Cromarty and Inverness-shire....
.
Islands

Northern Isles
The Northern Isles is a chain of islands off the north coast of mainland Scotland. The climate is cool and temperate and much influenced by the surrounding seas. There are two main island groups: Shetland and Orkney...
and western islands of Scotland can be found in three main groups: Shetland
Shetland Islands
Shetland is a subarctic archipelago of Scotland that lies north and east of mainland Great Britain. The islands lie some to the northeast of Orkney and southeast of the Faroe Islands and form part of the division between the Atlantic Ocean to the west and the North Sea to the east. The total...
, Orkney
Orkney Islands
Orkney also known as the Orkney Islands , is an archipelago in northern Scotland, situated north of the coast of Caithness...
and the Hebrides
Hebrides
The Hebrides comprise a widespread and diverse archipelago off the west coast of Scotland. There are two main groups: the Inner and Outer Hebrides. These islands have a long history of occupation dating back to the Mesolithic and the culture of the residents has been affected by the successive...
which can be divided into the Inner Hebrides
Inner Hebrides
The Inner Hebrides is an archipelago off the west coast of Scotland, to the south east of the Outer Hebrides. Together these two island chains form the Hebrides, which enjoy a mild oceanic climate. There are 36 inhabited islands and a further 43 uninhabited Inner Hebrides with an area greater than...
and the Outer Hebrides
Outer Hebrides
The Outer Hebrides also known as the Western Isles and the Long Island, is an island chain off the west coast of Scotland. The islands are geographically contiguous with Comhairle nan Eilean Siar, one of the 32 unitary council areas of Scotland...
. Shetland and Orkney, together with Fair Isle
Fair Isle
Fair Isle is an island in northern Scotland, lying around halfway between mainland Shetland and the Orkney islands. It is famous for its bird observatory and a traditional style of knitting.-Geography:...
and Stroma
Stroma, Scotland
Stroma is an island off the northern coast of the Scottish mainland. It is the more southerly of the two islands in the Pentland Firth between the Orkney Islands and Caithness. It is administratively part of Caithness , while its neighbour Swona, to the north, is part of the Orkney Islands...
are referred to as the Northern Isles
Northern Isles
The Northern Isles is a chain of islands off the north coast of mainland Scotland. The climate is cool and temperate and much influenced by the surrounding seas. There are two main island groups: Shetland and Orkney...
. With a total land area of 2225 square kilometre Lewis and Harris
Lewis and Harris
Lewis and Harris in the Outer Hebrides make up the largest island in Scotland. This is the largest single island of the British Isles after Great Britain and Ireland.-Geography:...
is the largest island surrounding Scotland.
Many of these offshore islands are swept by strong tides, and the Corryvreckan tide race
Gulf of Corryvreckan
The Gulf of Corryvreckan , also called the Strait of Corryvreckan, is a narrow strait between the islands of Jura and Scarba, in Argyll and Bute, off the west coast of Scotland.It is possible for tourists to visit the site by way of boats trips from local harbours.- Topography...
between Scarba
Scarba
Scarba is a small island, in Argyll and Bute, Scotland, just north of the much larger island of Jura. The island is owned by Richard Hill, 7th Baron Sandys and has not been permanently inhabited since the 1960s. It is now covered in heather and used for grazing animals...
and Jura
Jura, Scotland
Jura is an island in the Inner Hebrides of Scotland, situated adjacent and to the north-east of Islay. Part of the island is designated as a National Scenic Area. Until the twentieth century Jura was dominated - and most of it was eventually owned - by the Campbell clan of Inveraray Castle on Loch...
is one of the largest whirlpool
Whirlpool
A whirlpool is a swirling body of water usually produced by ocean tides. The vast majority of whirlpools are not very powerful. More powerful ones are more properly termed maelstroms. Vortex is the proper term for any whirlpool that has a downdraft...
s in the world. Other strong tides are to be found in the Pentland Firth
Pentland Firth
The Pentland Firth , which is actually more of a strait than a firth, separates the Orkney Islands from Caithness in the north of Scotland.-Etymology:...
between mainland Scotland and Orkney, and the Grey Dog between Scarba and Lunga
Lunga, Firth of Lorn
Lunga is one of the Slate Islands in the Firth of Lorn, Scotland. The "Grey Dog" tidal race, which runs in the sea channel to the south, reaches 8 knots in full flood. The name 'Lunga' is derived from the Old Norse for 'isle of the longships', but almost all other place names are Gaelic in origin...
. There are also numerous clusters of islands in the Firth of Forth
Firth of Forth
The Firth of Forth is the estuary or firth of Scotland's River Forth, where it flows into the North Sea, between Fife to the north, and West Lothian, the City of Edinburgh and East Lothian to the south...
and the Firth of Clyde
Firth of Clyde
The Firth of Clyde forms a large area of coastal water, sheltered from the Atlantic Ocean by the Kintyre peninsula which encloses the outer firth in Argyll and Ayrshire, Scotland. The Kilbrannan Sound is a large arm of the Firth of Clyde, separating the Kintyre Peninsula from the Isle of Arran.At...
and in freshwater lochs such as Loch Lomond and Loch Maree
Loch Maree
Loch Maree is a loch in Wester Ross in the Northwest Highlands of Scotland. At long and with a maximum width of , it is the fourth largest freshwater loch in Scotland; it is the largest north of Loch Ness. Its surface area is ....
. Outlying islands include St Kilda
St Kilda, Scotland
St Kilda is an isolated archipelago west-northwest of North Uist in the North Atlantic Ocean. It contains the westernmost islands of the Outer Hebrides of Scotland. The largest island is Hirta, whose sea cliffs are the highest in the United Kingdom and three other islands , were also used for...
and Rockall
Rockall
Rockall is an extremely small, uninhabited, remote rocky islet in the North Atlantic Ocean. It gives its name to one of the sea areas named in the shipping forecast provided by the British Meteorological Office....
the status of which is disputed.
Scotland's islands have a varied topography. Mull
Isle of Mull
The Isle of Mull or simply Mull is the second largest island of the Inner Hebrides, off the west coast of Scotland in the council area of Argyll and Bute....
, Skye and Arran
Isle of Arran
Arran or the Isle of Arran is the largest island in the Firth of Clyde, Scotland, and with an area of is the seventh largest Scottish island. It is in the unitary council area of North Ayrshire and the 2001 census had a resident population of 5,058...
are noted for their mountainous terrain, whilst Tiree
Tiree
-History:Tiree is known for the 1st century BC Dùn Mòr broch, for the prehistoric carved Ringing Stone and for the birds of the Ceann a' Mhara headland....
, Coll
Coll
Coll is a small island, west of Mull in the Inner Hebrides of Scotland. Coll is known for its sandy beaches, which rise to form large sand dunes, for its corncrakes, and for Breachacha Castle.-Geography and geology:...
and most of the Shetland group are flat or low lying. Striking topographical differences can be seen within island groups themselves; in Orkney, the Island of Hoy
Hoy
Hoy is an island in Orkney, Scotland. With an area of it is the second largest in the archipelago after the Mainland. It is connected by a causeway called The Ayre to South Walls...
is hillier and more rugged than surrounding islands and Harris is distinctive in being more mountainous than the islands of Lewis, North Uist
North Uist
North Uist is an island and community in the Outer Hebrides of Scotland.-Geography:North Uist is the tenth largest Scottish island and the thirteenth largest island surrounding Great Britain. It has an area of , slightly smaller than South Uist. North Uist is connected by causeways to Benbecula...
, South Uist
South Uist
South Uist is an island of the Outer Hebrides in Scotland. In the 2001 census it had a usually resident population of 1,818. There is a nature reserve and a number of sites of archaeological interest, including the only location in Great Britain where prehistoric mummies have been found. The...
and Barra
Barra
The island of Barra is a predominantly Gaelic-speaking island, and apart from the adjacent island of Vatersay, to which it is connected by a causeway, is the southernmost inhabited island of the Outer Hebrides in Scotland.-Geography:The 2001 census showed that the resident population was 1,078...
, in the Outer Hebrides.
Rivers

The ten major rivers of Scotland, in order of length, are:
- River TayRiver TayThe River Tay is the longest river in Scotland and the seventh-longest in the United Kingdom. The Tay originates in western Scotland on the slopes of Ben Lui , then flows easterly across the Highlands, through Loch Dochhart, Loch Lubhair and Loch Tay, then continues east through Strathtay , in...
193 km (120 mi) - River SpeyRiver SpeyThe River Spey is a river in the northeast of Scotland, the second longest and the fastest-flowing river in Scotland...
172 km (107 mi) - River ClydeRiver ClydeThe River Clyde is a major river in Scotland. It is the ninth longest river in the United Kingdom, and the third longest in Scotland. Flowing through the major city of Glasgow, it was an important river for shipbuilding and trade in the British Empire....
171 km (106 mi) - River TweedRiver TweedThe River Tweed, or Tweed Water, is long and flows primarily through the Borders region of Great Britain. It rises on Tweedsmuir at Tweed's Well near where the Clyde, draining northwest, and the Annan draining south also rise. "Annan, Tweed and Clyde rise oot the ae hillside" as the Border saying...
156 km (97 mi) - River DeeRiver Dee, AberdeenshireThe River Dee is a river in Aberdeenshire, Scotland. It rises in the Cairngorms and flows through Strathdee to reach the North Sea at Aberdeen...
137 km (85 mi) - River DonRiver Don, AberdeenshireThe River Don is a river in north-east Scotland. It rises in the Grampians and flows eastwards, through Aberdeenshire, to the North Sea at Aberdeen. The Don passes through Alford, Kemnay, Inverurie, Kintore, and Dyce...
132 km (82 mi) - River ForthRiver ForthThe River Forth , long, is the major river draining the eastern part of the central belt of Scotland.The Forth rises in Loch Ard in the Trossachs, a mountainous area some west of Stirling...
105 km (65 mi) - River FindhornRiver FindhornThe River Findhorn is one of the longest rivers in Scotland. Located in the north east, it flows into the Moray Firth on the north coast. It has one of the largest non-firth estuaries in Scotland....
101 km (63 mi) - River DeveronRiver DeveronThe River Deveron , known anciently as the Dovern, is a river in the north east of Scotland. The river has a length of 60 miles, and has a reputation for its salmon, sea trout and brown trout fishing...
98 km (61 mi) - River AnnanRiver AnnanThe River Annan is a river in southwest Scotland. It rises at the foot of Hart Fell, five miles north of Moffat. A second fork rises on Annanhead Hill and flows through the Devil's Beef Tub before joining at the Hart Fell fork north of Moffat.From there it flows past the town of Lockerbie, and...
79 km (49 mi)
The watershed between river systems flowing west to the Atlantic Ocean
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's oceanic divisions. With a total area of about , it covers approximately 20% of the Earth's surface and about 26% of its water surface area...
and east into the North Sea
North Sea
In the southwest, beyond the Straits of Dover, the North Sea becomes the English Channel connecting to the Atlantic Ocean. In the east, it connects to the Baltic Sea via the Skagerrak and Kattegat, narrow straits that separate Denmark from Norway and Sweden respectively...
is 1200 km (745.6 mi) long.
Lochs

Freshwater
Fresh water is naturally occurring water on the Earth's surface in ice sheets, ice caps, glaciers, bogs, ponds, lakes, rivers and streams, and underground as groundwater in aquifers and underground streams. Fresh water is generally characterized by having low concentrations of dissolved salts and...
bodies in Scotland are known as loch
Loch
Loch is the Irish and Scottish Gaelic word for a lake or a sea inlet. It has been anglicised as lough, although this is pronounced the same way as loch. Some lochs could also be called a firth, fjord, estuary, strait or bay...
s, with the exception of the Lake of Menteith
Lake of Menteith
The Lake of Menteith , is a loch in Scotland, located on the Carse of Stirling, the flood plain of the upper reaches of the rivers Forth and Teith, upstream of Stirling. Until the early 19th century, the more usual Scottish name of Loch of Menteith was used...
and one or two man-made "lakes". 90% of the standing fresh water volume of Great Britain lies within Scotland. Loch Lomond
Loch Lomond
Loch Lomond is a freshwater Scottish loch, lying on the Highland Boundary Fault. It is the largest lake in Great Britain by surface area. The lake contains many islands, including Inchmurrin, the largest fresh-water island in the British Isles, although the lake itself is smaller than many Irish...
is the largest freshwater body in Britain by area, although with a capacity of 7.45 km3 (1.78 m3) Loch Ness
Loch Ness
Loch Ness is a large, deep, freshwater loch in the Scottish Highlands extending for approximately southwest of Inverness. Its surface is above sea level. Loch Ness is best known for the alleged sightings of the cryptozoological Loch Ness Monster, also known affectionately as "Nessie"...
is the most voluminous. The water in Loch Ness is nearly double that of all the lakes of England and Wales combined.
- Loch LomondLoch LomondLoch Lomond is a freshwater Scottish loch, lying on the Highland Boundary Fault. It is the largest lake in Great Britain by surface area. The lake contains many islands, including Inchmurrin, the largest fresh-water island in the British Isles, although the lake itself is smaller than many Irish...
71.1 square kilometre - Loch NessLoch NessLoch Ness is a large, deep, freshwater loch in the Scottish Highlands extending for approximately southwest of Inverness. Its surface is above sea level. Loch Ness is best known for the alleged sightings of the cryptozoological Loch Ness Monster, also known affectionately as "Nessie"...
56.4 square kilometre - Loch AweLoch AweLoch Awe is a large body of water in Argyll and Bute, Scotland. It has also given its name to a village on its banks, variously known as Loch Awe, or Lochawe. There are islands within the loch such as Innis Chonnell and Inishail.- The loch :It is the third largest freshwater loch in Scotland with...
38.5 square kilometre - Loch MareeLoch MareeLoch Maree is a loch in Wester Ross in the Northwest Highlands of Scotland. At long and with a maximum width of , it is the fourth largest freshwater loch in Scotland; it is the largest north of Loch Ness. Its surface area is ....
28.6 square kilometre - Loch MorarLoch MorarLoch Morar is a freshwater loch in Morar, Lochaber, Highland, Scotland. It is the fifth-largest loch in Scotland, with a surface area of and the deepest freshwater body in the British Isles, with a maximum depth of ....
26.7 square kilometre) - Loch TayLoch TayLoch Tay is a freshwater loch in the central highlands of Scotland, in the district of Perthshire.It is a long narrow loch of around 14 miles long, and typically around 1 to 1½ miles wide, following the line of the valley from the south west to north east...
26.4 square kilometre - Loch ShinLoch ShinLoch Shin is a loch in the Scottish North West Highlands. To the south is the small town of Lairg. The loch is the largest in Sutherland, runs from the north-west to the south-east and is 17 miles long....
22.5 square kilometre) - Loch ShielLoch ShielLoch Shiel is a 19.3 km2 freshwater loch, 120 m deep, situated 20 km west of Fort William in Lochaber, Highland, Scotland...
19.6 square kilometre - Loch RannochLoch RannochLoch Rannoch is a large body of fresh water in Perth and Kinross, Scotland.The loch is over long in a west-east direction with an average width of about . The River Tummel begins at its eastern end. The Tay Forest Park lies along its southern shore...
19.1 square kilometre - Loch ErichtLoch ErichtLoch Ericht is a freshwater loch on the border between Perth and Kinross and the Highlands Council areas of Scotland. It is situated at a height of 351 metres above sea level and has a north-east to south-west orientation. The village of Dalwhinnie lies at the north east end of the loch...
18.7 square kilometre
Distances to other countries
Scotland's only land border is with England, and runs for 96 kilometres (60 mi) between the basin of the River TweedRiver Tweed
The River Tweed, or Tweed Water, is long and flows primarily through the Borders region of Great Britain. It rises on Tweedsmuir at Tweed's Well near where the Clyde, draining northwest, and the Annan draining south also rise. "Annan, Tweed and Clyde rise oot the ae hillside" as the Border saying...
on the east coast and the Solway Firth
Solway Firth
The Solway Firth is a firth that forms part of the border between England and Scotland, between Cumbria and Dumfries and Galloway. It stretches from St Bees Head, just south of Whitehaven in Cumbria, to the Mull of Galloway, on the western end of Dumfries and Galloway. The Isle of Man is also very...
in the west. The Atlantic Ocean
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's oceanic divisions. With a total area of about , it covers approximately 20% of the Earth's surface and about 26% of its water surface area...
borders the west coast and the North Sea
North Sea
In the southwest, beyond the Straits of Dover, the North Sea becomes the English Channel connecting to the Atlantic Ocean. In the east, it connects to the Baltic Sea via the Skagerrak and Kattegat, narrow straits that separate Denmark from Norway and Sweden respectively...
is to the east. The island of Ireland
Ireland
Ireland is an island to the northwest of continental Europe. It is the third-largest island in Europe and the twentieth-largest island on Earth...
lies only 30 kilometres (19 mi) from the southwestern peninsula of Kintyre
Kintyre
Kintyre is a peninsula in western Scotland, in the southwest of Argyll and Bute. The region stretches approximately 30 miles , from the Mull of Kintyre in the south, to East Loch Tarbert in the north...
; Norway
Norway
Norway , officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic unitary constitutional monarchy whose territory comprises the western portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula, Jan Mayen, and the Arctic archipelago of Svalbard and Bouvet Island. Norway has a total area of and a population of about 4.9 million...
is 305 kilometres (190 mi) to the east; the Faroes, 270 kilometres (168 mi) to the north; and Iceland
Iceland
Iceland , described as the Republic of Iceland, is a Nordic and European island country in the North Atlantic Ocean, on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. Iceland also refers to the main island of the country, which contains almost all the population and almost all the land area. The country has a population...
, 740 kilometres (460 mi) to the northwest.
Climate
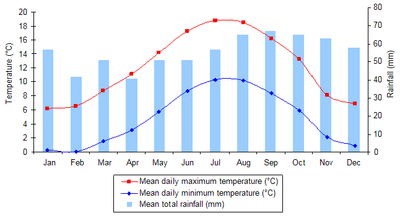
Temperate
In geography, temperate or tepid latitudes of the globe lie between the tropics and the polar circles. The changes in these regions between summer and winter are generally relatively moderate, rather than extreme hot or cold...
and very changeable, but rarely extreme. Scotland is warmed by the North Atlantic Drift
North Atlantic Current
The North Atlantic Current is a powerful warm ocean current that continues the Gulf Stream northeast. West of Ireland it splits in two; one branch, the Canary Current, goes south, while the other continues north along the coast of northwestern Europe...
and given the northerly location of the country, experiences much milder conditions than areas on similar latitudes, such as Labrador
Labrador
Labrador is the distinct, northerly region of the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador. It comprises the mainland portion of the province, separated from the island of Newfoundland by the Strait of Belle Isle...
in Canada
Canada
Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
—where icebergs are a common feature in winter.
Average temperatures are lower than in the rest of Great Britain, with the coldest ever UK temperature of -27.2 °C recorded at Braemar
Braemar
Braemar is a village in Aberdeenshire, Scotland, around west of Aberdeen in the Highlands. It is the closest significantly-sized settlement to the upper course of the River Dee sitting at an altitude of ....
in the Grampian Mountains
Grampian Mountains (Scotland)
The Grampian Mountains or Grampians are one of the three major mountain ranges in Scotland, occupying a considerable portion of the Scottish Highlands in northeast Scotland.-Extent:...
, on January 10, 1982 and also at Altnaharra
Altnaharra
-Notable persons:*Linda Norgrove, kidnapped by the Taliban in Afghanistan, and killed by a US grenade during a rescue effort.-External links:**...
, Highland
Highland (council area)
Highland is a council area in the Scottish Highlands and is the largest local government area in both Scotland and the United Kingdom as a whole. It shares borders with the council areas of Moray, Aberdeenshire, Perth and Kinross, and Argyll and Bute. Their councils, and those of Angus and...
, on December 30, 1995. Winter maximums average 5 to 5.7 °C (41 to 42.3 °F), with summer maximums averaging 14.9 to 16.9 °C (58.8 to 62.4 °F). Western coastal areas of Scotland
Scotland
Scotland is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Occupying the northern third of the island of Great Britain, it shares a border with England to the south and is bounded by the North Sea to the east, the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, and the North Channel and Irish Sea to the...
are warmer than the east and inland areas, due to the influence of the Atlantic currents, and the colder surface temperatures of the North Sea
North Sea
In the southwest, beyond the Straits of Dover, the North Sea becomes the English Channel connecting to the Atlantic Ocean. In the east, it connects to the Baltic Sea via the Skagerrak and Kattegat, narrow straits that separate Denmark from Norway and Sweden respectively...
. The highest temperature recorded was 32.9 °C (91.2 °F) at Greycrook
Greycrook
Greycrook is a village off the A68 and the A699, in the Scottish Borders, approximately 0.5km south-east of St Boswells, and close to Dryburgh, Dryburgh Abbey, Maxton, Newtown St Boswells, and the River Tweed....
in the Scottish Borders
Scottish Borders
The Scottish Borders is one of 32 local government council areas of Scotland. It is bordered by Dumfries and Galloway in the west, South Lanarkshire and West Lothian in the north west, City of Edinburgh, East Lothian, Midlothian to the north; and the non-metropolitan counties of Northumberland...
on August 9, 2003.
Rainfall totals vary widely across Scotland—the western highlands of Scotland are one of the wettest places in the UK with annual rainfall up to 4577 mm (180.2 in). Due to the mountainous topography of the western Highlands, this type of precipitation is orographic in nature, with the warm, wet air forced to rise on contact with the mountainous coast, where it consequently, cools and condenses
Condensation
Condensation is the change of the physical state of matter from gaseous phase into liquid phase, and is the reverse of vaporization. When the transition happens from the gaseous phase into the solid phase directly, the change is called deposition....
, forming clouds. In comparison, much of eastern Scotland receives less than 870 mm (34.3 in) annually; lying in the rain shadow
Rain shadow
A rain shadow is a dry area on the lee side of a mountainous area. The mountains block the passage of rain-producing weather systems, casting a "shadow" of dryness behind them. As shown by the diagram to the right, the warm moist air is "pulled" by the prevailing winds over a mountain...
of the western uplands. Snowfall is less common in the lowlands, but becomes more common with altitude. Parts of the Highlands have an average of 36 to 105 snow days per year, while some western coastal areas have between 0 and 6 days with snow a year.
The Hebridean island of Tiree
Tiree
-History:Tiree is known for the 1st century BC Dùn Mòr broch, for the prehistoric carved Ringing Stone and for the birds of the Ceann a' Mhara headland....
received a total of 329 hours of sunshine in May 1946 and again in May 1975, the highest number of sunshine hours ever recorded in one month in Scotland. On the longest day of the year
Solstice
A solstice is an astronomical event that happens twice each year when the Sun's apparent position in the sky, as viewed from Earth, reaches its northernmost or southernmost extremes...
there is no complete darkness over the northern isles of Scotland. Lerwick
Lerwick
Lerwick is the capital and main port of the Shetland Islands, Scotland, located more than 100 miles off the north coast of mainland Scotland on the east coast of the Shetland Mainland...
, in Shetland, has four hours more daylight at midsummer than London
London
London is the capital city of :England and the :United Kingdom, the largest metropolitan area in the United Kingdom, and the largest urban zone in the European Union by most measures. Located on the River Thames, London has been a major settlement for two millennia, its history going back to its...
, although this is reversed in midwinter. Annual average sunshine totals vary from as little as 711–1140 hours in the Highlands and the north-west up to 1471–1540 hours on the extreme eastern and south-western coasts.
In common with the rest of the British Isles, wind prevails from the south-west, bringing warm, wet and unstable air from the Atlantic. The windiest areas of Scotland are in the north and west, with parts of the Outer Hebrides, Orkney and Shetland experiencing over 30 days with gales per year. Vigorous Atlantic depressions
Low pressure area
A low-pressure area, or "low", is a region where the atmospheric pressure at sea level is below that of surrounding locations. Low-pressure systems form under areas of wind divergence which occur in upper levels of the troposphere. The formation process of a low-pressure area is known as...
, also known as European windstorm
European windstorm
A European windstorm is a severe cyclonic windstorm associated with areas of low atmospheric pressure that track across the North Atlantic towards northwestern Europe. They are most common in the winter months...
s, are a common feature of the autumn and winter in Scotland.
Human geography

General Register Office for Scotland
The General Register Office for Scotland was a non-ministerial directorate of the Scottish Government that administered the registration of births, deaths, marriages, divorces and adoptions in Scotland. It was also responsible for the statutes relating to the formalities of marriage and conduct...
, the total population of Scotland stood at 5,168,500 in June 2008, an increase of 2.1% since the census
United Kingdom Census 2001
A nationwide census, known as Census 2001, was conducted in the United Kingdom on Sunday, 29 April 2001. This was the 20th UK Census and recorded a resident population of 58,789,194....
of April 2001. Scotland's share of the United Kingdom population has been declining in recent years and stands at just over 8.5% due to differential rates of growth in the home nations
Home Nations
Home Nations is a collective term with one of two meanings depending on the context. Politically, it means the nations of the constituent countries of the United Kingdom...
. However an increasing birth rate
Birth rate
Crude birth rate is the nativity or childbirths per 1,000 people per year . Another word used interchangeably with "birth rate" is "natality". When the crude birth rate is subtracted from the crude death rate, it reveals the rate of natural increase...
and higher levels of inward migration to Scotland have reversed the decline and contributed to the recent population growth.
Compared with the rest of Europe, Scotland has a low population density
Population density
Population density is a measurement of population per unit area or unit volume. It is frequently applied to living organisms, and particularly to humans...
at 65 people per square kilometre. However Scotland is a highly urbanised
Urban area
An urban area is characterized by higher population density and vast human features in comparison to areas surrounding it. Urban areas may be cities, towns or conurbations, but the term is not commonly extended to rural settlements such as villages and hamlets.Urban areas are created and further...
country, with 82% of the population living in settlements of 3,000 people or more. As a result, the majority of the population live in the Central Lowlands
Central Belt
The Central Belt of Scotland is a common term used to describe the area of highest population density within Scotland. Despite the name, it is not geographically central but is nevertheless situated at the 'waist' of Scotland on a conventional map and the term 'central' is used in many local...
of Scotland, surrounding the chief cities of Glasgow
Glasgow
Glasgow is the largest city in Scotland and third most populous in the United Kingdom. The city is situated on the River Clyde in the country's west central lowlands...
and Edinburgh
Edinburgh
Edinburgh is the capital city of Scotland, the second largest city in Scotland, and the eighth most populous in the United Kingdom. The City of Edinburgh Council governs one of Scotland's 32 local government council areas. The council area includes urban Edinburgh and a rural area...
. Other concentrations of population include the northeast coast of Scotland - principally surrounding the city of Aberdeen
Aberdeen
Aberdeen is Scotland's third most populous city, one of Scotland's 32 local government council areas and the United Kingdom's 25th most populous city, with an official population estimate of ....
and its environs - and around Inverness
Inverness
Inverness is a city in the Scottish Highlands. It is the administrative centre for the Highland council area, and is regarded as the capital of the Highlands of Scotland...
. With a population density of 8 people per square kilometre, the Highlands
Scottish Highlands
The Highlands is an historic region of Scotland. The area is sometimes referred to as the "Scottish Highlands". It was culturally distinguishable from the Lowlands from the later Middle Ages into the modern period, when Lowland Scots replaced Scottish Gaelic throughout most of the Lowlands...
are the most sparsely populated part of the country. In these areas, the population is scattered in villages, small towns and isolated farmsteads or croft
Croft (land)
A croft is a fenced or enclosed area of land, usually small and arable with a crofter's dwelling thereon. A crofter is one who has tenure and use of the land, typically as a tenant farmer.- Etymology :...
s.
Nearly 100 of Scotland's islands are inhabited, the most populous being Lewis
Lewis
Lewis is the northern part of Lewis and Harris, the largest island of the Western Isles or Outer Hebrides of Scotland. The total area of Lewis is ....
with 16,782 people resident in 2001, primarily concentrated in Stornoway, the only burgh
Burgh
A burgh was an autonomous corporate entity in Scotland and Northern England, usually a town. This type of administrative division existed from the 12th century, when King David I created the first royal burghs. Burgh status was broadly analogous to borough status, found in the rest of the United...
of the Outer Hebrides
Outer Hebrides
The Outer Hebrides also known as the Western Isles and the Long Island, is an island chain off the west coast of Scotland. The islands are geographically contiguous with Comhairle nan Eilean Siar, one of the 32 unitary council areas of Scotland...
. Other island populations range down to very low levels on certain small isles. Between 1991 and 2001, the total number of people living on Scotland's islands fell by 3%. Conversely, islands such as Tiree
Tiree
-History:Tiree is known for the 1st century BC Dùn Mòr broch, for the prehistoric carved Ringing Stone and for the birds of the Ceann a' Mhara headland....
, Skye and Eigg
Eigg
Eigg is one of the Small Isles, in the Scottish Inner Hebrides. It lies to the south of the Skye and to the north of the Ardnamurchan peninsula. Eigg is long from north to south, and east to west. With an area of , it is the second largest of the Small Isles after Rùm.-Geography:The main...
experienced increases in their respective populations over the same decade.
There are six cities
City status in the United Kingdom
City status in the United Kingdom is granted by the British monarch to a select group of communities. The holding of city status gives a settlement no special rights other than that of calling itself a "city". Nonetheless, this appellation carries its own prestige and, consequently, competitions...
in Scotland; Glasgow, Edinburgh, Aberdeen
Aberdeen
Aberdeen is Scotland's third most populous city, one of Scotland's 32 local government council areas and the United Kingdom's 25th most populous city, with an official population estimate of ....
, Dundee
Dundee
Dundee is the fourth-largest city in Scotland and the 39th most populous settlement in the United Kingdom. It lies within the eastern central Lowlands on the north bank of the Firth of Tay, which feeds into the North Sea...
, Inverness
Inverness
Inverness is a city in the Scottish Highlands. It is the administrative centre for the Highland council area, and is regarded as the capital of the Highlands of Scotland...
and Stirling
Stirling
Stirling is a city and former ancient burgh in Scotland, and is at the heart of the wider Stirling council area. The city is clustered around a large fortress and medieval old-town beside the River Forth...
. The 2001 census identified Glasgow as being the largest city in Scotland, with a total population of 629,501, while the Scottish capital
Capital City
Capital City was a television show produced by Euston Films which focused on the lives of investment bankers in London living and working on the corporate trading floor for the fictional international bank Shane-Longman....
, Edinburgh had a population of 448,624, in the same year. Between 1991 and 2001, the populations of Edinburgh and Stirling grew by 2.9% and 6.5% respectively. Inverness experienced population growth of over 10% during the same period. At the same time, Glasgow, Dundee and Aberdeen all witnessed population decline. Aside from the cities, the greatest intra-census population growth was experienced in the local authorities of West Lothian
West Lothian
West Lothian is one of the 32 unitary council areas in Scotland, and a Lieutenancy area. It borders the City of Edinburgh, Falkirk, North Lanarkshire, the Scottish Borders and South Lanarkshire....
, East Lothian
East Lothian
East Lothian is one of the 32 council areas of Scotland, and a lieutenancy Area. It borders the City of Edinburgh, Scottish Borders and Midlothian. Its administrative centre is Haddington, although its largest town is Musselburgh....
, Aberdeenshire
Aberdeenshire
Aberdeenshire is one of the 32 unitary council areas in Scotland and a lieutenancy area.The present day Aberdeenshire council area does not include the City of Aberdeen, now a separate council area, from which its name derives. Together, the modern council area and the city formed historic...
and Perth and Kinross
Perth and Kinross
Perth and Kinross is one of 32 council areas in Scotland, and a Lieutenancy Area. It borders onto the Aberdeenshire, Angus, Dundee City, Fife, Clackmannanshire, Stirling, Argyll and Bute and Highland council areas. Perth is the administrative centre...
. The Western Isles saw a 9.8% decrease in population between 1991 and 2001.
Political geography
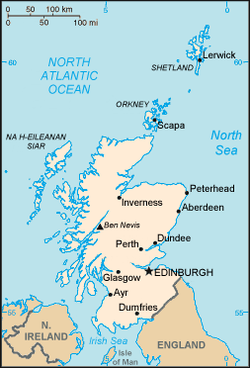
The territorial extent of Scotland is generally that established by the 1237 Treaty of York
Treaty of York
The Treaty of York was an agreement between Henry III of England and Alexander II of Scotland, signed at York on 25 September 1237. It detailed the future status of several feudal properties and addressed other issues between the two kings, and indirectly marked the end of Scotland's attempts to...
between Scotland and England
Kingdom of England
The Kingdom of England was, from 927 to 1707, a sovereign state to the northwest of continental Europe. At its height, the Kingdom of England spanned the southern two-thirds of the island of Great Britain and several smaller outlying islands; what today comprises the legal jurisdiction of England...
and the 1266 Treaty of Perth
Treaty of Perth
The Treaty of Perth, 1266, ended military conflict between Norway, under King Magnus VI of Norway, and Scotland, under King Alexander III, over the sovereignty of the Hebrides and the Isle of Man....
between Scotland and Norway
Norway
Norway , officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic unitary constitutional monarchy whose territory comprises the western portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula, Jan Mayen, and the Arctic archipelago of Svalbard and Bouvet Island. Norway has a total area of and a population of about 4.9 million...
. Exceptions include: the Isle of Man
Isle of Man
The Isle of Man , otherwise known simply as Mann , is a self-governing British Crown Dependency, located in the Irish Sea between the islands of Great Britain and Ireland, within the British Isles. The head of state is Queen Elizabeth II, who holds the title of Lord of Mann. The Lord of Mann is...
, which having been lost to England in the 14th century is now a crown dependency
Crown dependency
The Crown Dependencies are British possessions of the Crown, as opposed to overseas territories of the United Kingdom. They comprise the Channel Island Bailiwicks of Jersey and Guernsey in the English Channel, and the Isle of Man in the Irish Sea....
outside of the United Kingdom, the acquisition of Orkney and Shetland from Norway in 1472, and the permanent recovery of Berwick by England in 1482. Originally an independent country, Scotland joined with England to form the Kingdom of Great Britain
Kingdom of Great Britain
The former Kingdom of Great Britain, sometimes described as the 'United Kingdom of Great Britain', That the Two Kingdoms of Scotland and England, shall upon the 1st May next ensuing the date hereof, and forever after, be United into One Kingdom by the Name of GREAT BRITAIN. was a sovereign...
in 1707 with the Acts of Union.
As one of the constituent parts of the United Kingdom, Scotland is represented by Members of Parliament at the Parliament of the United Kingdom
Parliament of the United Kingdom
The Parliament of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland is the supreme legislative body in the United Kingdom, British Crown dependencies and British overseas territories, located in London...
at Westminster
Palace of Westminster
The Palace of Westminster, also known as the Houses of Parliament or Westminster Palace, is the meeting place of the two houses of the Parliament of the United Kingdom—the House of Lords and the House of Commons...
, London
London
London is the capital city of :England and the :United Kingdom, the largest metropolitan area in the United Kingdom, and the largest urban zone in the European Union by most measures. Located on the River Thames, London has been a major settlement for two millennia, its history going back to its...
. In 1997 a referendum
Referendum
A referendum is a direct vote in which an entire electorate is asked to either accept or reject a particular proposal. This may result in the adoption of a new constitution, a constitutional amendment, a law, the recall of an elected official or simply a specific government policy. It is a form of...
was held, and the people of Scotland voted for the establishment of a devolved
Devolution
Devolution is the statutory granting of powers from the central government of a sovereign state to government at a subnational level, such as a regional, local, or state level. Devolution can be mainly financial, e.g. giving areas a budget which was formerly administered by central government...
Scottish Parliament in Edinburgh. The new parliament has the power to govern the country on Scotland-specific matters and has a limited power to vary income tax
Income tax
An income tax is a tax levied on the income of individuals or businesses . Various income tax systems exist, with varying degrees of tax incidence. Income taxation can be progressive, proportional, or regressive. When the tax is levied on the income of companies, it is often called a corporate...
. The United Kingdom Parliament retains responsibility for Scotland's defence
Defense (military)
Defense has several uses in the sphere of military application.Personal defense implies measures taken by individual soldiers in protecting themselves whether by use of protective materials such as armor, or field construction of trenches or a bunker, or by using weapons that prevent the enemy...
, international relations
International relations
International relations is the study of relationships between countries, including the roles of states, inter-governmental organizations , international nongovernmental organizations , non-governmental organizations and multinational corporations...
and certain other areas.
Between 1889 and 1975 Scotland was divided into burgh
Burgh
A burgh was an autonomous corporate entity in Scotland and Northern England, usually a town. This type of administrative division existed from the 12th century, when King David I created the first royal burghs. Burgh status was broadly analogous to borough status, found in the rest of the United...
s and counties
Counties of Scotland
The counties of Scotland were the principal local government divisions of Scotland until 1975. Scotland's current lieutenancy areas and registration counties are largely based on them. They are often referred to as historic counties....
, which were replaced by regions and districts. Since 1996, for the purposes of local government
Local government of Scotland
Local government in Scotland is organised through 32 unitary authorities designated as Councils which consist of councillors elected every four years by registered voters in each of the council areas....
, Scotland has been divided into 32 council areas
Subdivisions of Scotland
For local government purposes, Scotland is divided into 32 areas designated as "council areas" which are all governed by unitary authorities designated as "councils"...
.
Rockall
Rockall
Rockall is an extremely small, uninhabited, remote rocky islet in the North Atlantic Ocean. It gives its name to one of the sea areas named in the shipping forecast provided by the British Meteorological Office....
, a small and uninhabitable rocky islet in the North Atlantic, was annexed by the UK in 1955 and later declared part of Scotland by the Island of Rockall Act 1972
Island of Rockall Act 1972
The Island of Rockall Act 1972 is a British Act of Parliament formally incorporating the island Rockall into the United Kingdom to protect it from Irish and Icelandic claims...
. However, the legality of this claim is disputed by the Republic of Ireland
Republic of Ireland
Ireland , described as the Republic of Ireland , is a sovereign state in Europe occupying approximately five-sixths of the island of the same name. Its capital is Dublin. Ireland, which had a population of 4.58 million in 2011, is a constitutional republic governed as a parliamentary democracy,...
, Denmark
Denmark
Denmark is a Scandinavian country in Northern Europe. The countries of Denmark and Greenland, as well as the Faroe Islands, constitute the Kingdom of Denmark . It is the southernmost of the Nordic countries, southwest of Sweden and south of Norway, and bordered to the south by Germany. Denmark...
and Iceland
Iceland
Iceland , described as the Republic of Iceland, is a Nordic and European island country in the North Atlantic Ocean, on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. Iceland also refers to the main island of the country, which contains almost all the population and almost all the land area. The country has a population...
and it is probably unenforceable in international law.
Economic Geography
The Gross domestic productGross domestic product
Gross domestic product refers to the market value of all final goods and services produced within a country in a given period. GDP per capita is often considered an indicator of a country's standard of living....
(GDP) of Scotland in 2006 is estimated to have been £124 billion, resulting a per capita GDP of approximately £24,000. Major industries include banking and financial services, steel
Steel
Steel is an alloy that consists mostly of iron and has a carbon content between 0.2% and 2.1% by weight, depending on the grade. Carbon is the most common alloying material for iron, but various other alloying elements are used, such as manganese, chromium, vanadium, and tungsten...
, transport equipment, oil
Petroleum
Petroleum or crude oil is a naturally occurring, flammable liquid consisting of a complex mixture of hydrocarbons of various molecular weights and other liquid organic compounds, that are found in geologic formations beneath the Earth's surface. Petroleum is recovered mostly through oil drilling...
and gas
Natural gas
Natural gas is a naturally occurring gas mixture consisting primarily of methane, typically with 0–20% higher hydrocarbons . It is found associated with other hydrocarbon fuel, in coal beds, as methane clathrates, and is an important fuel source and a major feedstock for fertilizers.Most natural...
, whisky
Whisky
Whisky or whiskey is a type of distilled alcoholic beverage made from fermented grain mash. Different grains are used for different varieties, including barley, malted barley, rye, malted rye, wheat, and corn...
, and tourism
Tourism
Tourism is travel for recreational, leisure or business purposes. The World Tourism Organization defines tourists as people "traveling to and staying in places outside their usual environment for not more than one consecutive year for leisure, business and other purposes".Tourism has become a...
.
See also
- Royal Scottish Geographical SocietyRoyal Scottish Geographical SocietyThe Royal Scottish Geographical Society is a learned society founded in 1884 and based in Perth. The Society has a membership of 2500 and aims to advance the science of geography worldwide by supporting education, research, expeditions, through its journal , its newsletter and other publications...
- Geography of the United KingdomGeography of the United KingdomThe United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, or UK, is a sovereign state located off the northwestern coast of continental Europe. With a total area of approximately , the UK occupies the major part of the British Isles archipelago and includes the island of Great Britain, the...
- Geography of EnglandGeography of EnglandEngland comprises most of the central and southern two-thirds of the island of Great Britain, in addition to a number of small islands of which the largest is the Isle of Wight. England is bordered to the north by Scotland and to the west by Wales...
- Geography of WalesGeography of WalesWales is a generally mountainous country on the western side of central southern Great Britain, between the Irish Sea to the north and the Bristol Channel to the south. It is part of the United Kingdom, and is bordered by England to its east and the Atlantic Ocean, St George's Channel and Irish...
- Geography of IrelandGeography of IrelandIreland is an island in northwest Europe in the north Atlantic Ocean whose main geographical features include low central plains surrounded by a ring of coastal mountains. The highest peak is Carrauntoohil , which is above sea level. The western coastline is rugged, with many islands, peninsulas,...

