
Historical Eastern Germany
Encyclopedia
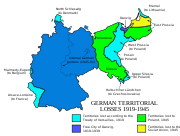
The former eastern territories of Germany are those province
s or region
s east of the current eastern border of Germany
which were lost by Germany during and after the two world wars
. These territories include the Province of Posen
(lost after World War I
) and East Prussia
, Farther Pomerania
, East Brandenburg and Lower Silesia
(lost in World War II
); and other, smaller regions. In present-day Germany, the term is usually meant to refer only to the territories lost in World War II.
 In the Potsdam Agreement
In the Potsdam Agreement
the description of the territories transferred is "The former German territories [east of the Oder-Neisse line]", and permutations on this description are the most commonly used to describe any former territories of Germany east of the Oder-Neisse line
.
While the name East Germany, a political term, used to be the colloquial naming of the German Democratic Republic
(GDR), the term Eastern Germany underwent a shift in the 20th century due to the border shifts after the Second World War. Since in German there is only one usual term Ostdeutschland, meaning East Germany or Eastern Germany, the German rather ambiguous term never gained prevailing use for the GDR as did the English term. While Eastern Germany had been used for the former eastern territories of Germany before the Second World War
. The term since has been used to denote the post-war and the respective five states
of the reunited Germany
. However, this is rather an outside perspective, because people and institutions in the states, traditionally considered as Middle Germany
, like the three southern new states Saxony-Anhalt
, the Free State of Saxony and the Free State of Thuringia, still use the term Middle Germany when referring to their area and its institutions.
(most of which were taken in Partitions of Poland
) should be returned to Germany. This claim was an important precursor to the Second World War. In 1939 after its invasion of Poland, Germany reoccupied and annexed these territories (as well as additional land in Poland that previously had never been part of the German Reich). Germany subsequently lost all territories east of the Oder-Neisse Line at the end of World War II
in 1945, when international recognition of its right to jurisdiction over any of these territories
was withdrawn. The Eastern German areas east of the Oder-Neisse Line, and within the 1937 German Border, with the exception of Soviet Administered Northern East Prussia, became known as the Recovered Territories
in Poland following World War II.
After World War II, the so-called "German question" was an important factor of post-war German history and politics. The debate affected Cold War
politics and diplomacy and played an important role in the negotiations leading up to the reunification of Germany in 1990. In 1990 Germany officially recognised
its present eastern border at the time of its reunification
, ending any residual claims to sovereignty that Germany may have had over any territory east of the Oder-Neisse line.
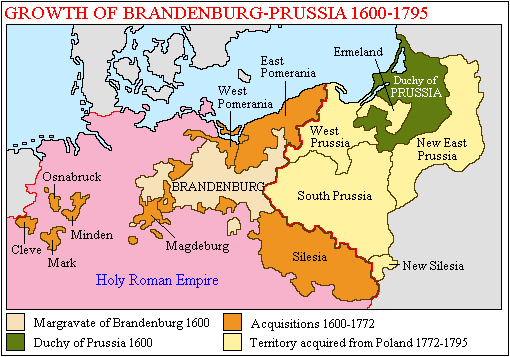
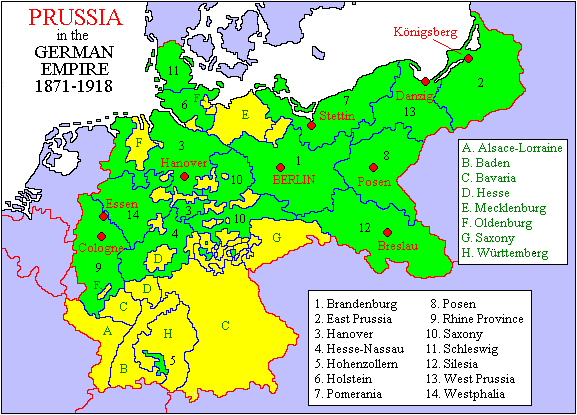 At the time of the foundation of the German Empire in 1871, Prussia
At the time of the foundation of the German Empire in 1871, Prussia
was the largest and dominant part of the empire. Thus, the territories of East Brandenburg, Silesia
, Pomerania
and the provinces of Prussia
and Poznań
(Posen) were all parts of the initial territory that comprised the German Empire in 1871. Later, these territories would come to be called in Germany "Ostgebiete des deutschen Reiches" (Eastern territories of the German Empire).
In some areas, such as the Province of Posen
or the east-southern part of Upper Silesia
, the area that would later become Polish Corridor
the majority population was Polish, while in others it was predominantly German. Under the Treaty of Versailles, territories with an apparent Polish majority were ceded to Poland, even if its inhabitants had voted against it during the referendum. However, demands by ethnic Germans in Poland to reconsider the justice of the settlement would keep the issue alive, as to whether these territories should belong to Germany or Poland. This debate constituted one of the causes of World War II.
 The provisions of the Treaty of Versailles
The provisions of the Treaty of Versailles
at the end of World War I
obliged Germany to transfer some territory to other countries. In Central Europe, these included:
 In October 1938 Hlučín Area (Hlučínsko in Czech, Hultschiner Ländchen in German) of Moravian-Silesian Region
In October 1938 Hlučín Area (Hlučínsko in Czech, Hultschiner Ländchen in German) of Moravian-Silesian Region
which had been ceded to Czechoslovakia under the Treaty of Versailles was annexed by the Third Reich as a part of areas lost by Czechoslovakia in accordance with the Munich agreement
. However, as distinct from other lost Czechoslovakian domains, it was not attached to Sudetengau (administrative region covering Sudetenland
) but to Prussia (Upper Silesia
).
By late 1938, Lithuania
had lost control over the situation in the Memel Territory
. In the early hours of 23 March 1939, after a political ultimatum caused a Lithuanian delegation to travel to Berlin, the Lithuanian Minister of Foreign Affairs Juozas Urbšys
and his German counterpart Joachim von Ribbentrop
signed the Treaty of the Cession of the Memel Territory to Germany in exchange for a Lithuanian Free Zone in the port of Memel, using the facilities erected in previous years.
 With the defeat of Poland in 1939
With the defeat of Poland in 1939
in the beginning of World War II
, Germany annexed eastern territories lost under the terms of the Treaty of Versailles, and annexed other eastern territories. These territorial changes were not recognised by the Allied
governments, that after the 1942 Declaration by the United Nations were also known as the United Nations
.
After invading Poland in 1939, the Third Reich annexed the lands the German Empire had ceded to the Second Polish Republic
in 1919–1922 by the Treaty of Versailles, including the "Polish Corridor
", West Prussia
, the Province of Posen
, and parts of eastern Upper Silesia
. The council of the Free City of Danzig
voted to become a part of Germany again, although Poles
and Jews
were deprived of their voting rights and all non-Nazi
political parties were banned. Parts of Poland that had not been part of the German Empire were also incorporated into the Third Reich.
Two decrees by Adolf Hitler
(October 8 and October 12, 1939) provided for the division of the annexed areas of Poland into the following administrative units:
These territories had an area of 94,000 km² and a population of 10,000,000 people. The remainder of the Polish territory was annexed by the Soviet Union
(see Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact
) or made into the German-controlled General Government
occupation zone.
After the German attack on the Soviet Union
in June 1941, the district of Białystok
, which included the Białystok, Bielsk Podlaski
, Grajewo
, Łomża, Sokółka, Volkovysk, and Grodno Counties, was "attached to" (not incorporated into) East Prussia, whilst East Galicia (Distrikt Galizien), which included the cities of Lwów
, Stanislawów
and Tarnopol
, was made part of the General Government.
(which met from 17 July until 2 August 1945), all of the areas east of the Oder-Neisse line, whether recognised by the international community as part of Germany until 1939 or occupied by Germany during World War II, were placed under the jurisdiction of other countries. The relevant paragraphs in the Potsdam Agreement
are:
The Allies also agreed that:
because in the words of Winston Churchill
The government of West Germany
preferred to use the phrase "former German territories temporarily under Polish and Soviet administration" (Note: those "former German territories" are those of Eastern Germany within the 1937 Germany Border). This was the wording used in the Potsdam Agreement, but was used only by the Federal Republic of Germany
because the Polish and Soviet governments refused to use it, objecting to the obvious implication that these territories should someday revert to Germany.
The Polish government preferred to use the phrase Recovered Territories
, asserting a sort of continuity because these territories had once been ruled by ethnic Poles half a millennium before World War II and had been "recovered" from Nazi Germany after 1945.
 The majority of the German-speaking population east of the Oder–Neisse line (roughly 10 million in the ostgebiete alone) that had not already been evacuated by the German authorities or fled
The majority of the German-speaking population east of the Oder–Neisse line (roughly 10 million in the ostgebiete alone) that had not already been evacuated by the German authorities or fled
from the advancing Red Army
in the winter of 1944–1945 was expelled
. Although in the post-war period earlier German sources often cited the number of evacuated and expelled Germans at 16 million and the death toll at between 1.7 and 2.5 million, today, the numbers are considered by some historians to be exaggerated and more likely in the range between 400,000 to 600,000. Some present-day estimates place the numbers of German refugees at 14 million of which about half a million died during the evacuations and expulsions.
At the same time, Poles from Central Poland, expelled Poles from former Eastern Poland
, Polish returnees from internment and forced labour, Ukrainians forcefully resettled in Operation Vistula and Jewish Holocaust survivors settled in the territories gained by Poland, whereas the North of former East Prussia
(Kaliningrad Oblast
) was turned into a military zone and subsequently became settled with Russians.
was chancellor of the Federal Republic of Germany
(FRG), the FRG followed a foreign relations policy of Ostpolitik
abandoning elements of the Hallstein Doctrine
. The FRG "abandoned, at least for the time being, its claims with respect to German self-determination and reunification, recognising de facto the existence of the German Democratic Republic
(GDR) and the Oder-Neisse Line." Subsequently, between 1970 and 1973, the FRG concluded friendship treaties with, successively, the Soviet Union (The Treaty of Moscow
), Poland (The Treaty of Warsaw
), the GDR (The Basic Treaty
) and Czechoslovakia (The Treaty of Prague
), thereby accommodating the European order that existed in the 1970s.
In the course of the German reunification
process, Chancellor Helmut Kohl
accepted the territorial changes made after the Second World War. This caused some outrage among the Federation of Expellees
. Some Poles were concerned about a possible revival of their 1939 trauma through a second German invasion, this time with the Germans buying back their land, which was cheaply available at the time. This happened on a smaller scale than many expected, and since the Baltic Sea
coast in Poland
has become popular with German tourists, Germans are now frequent and welcome guests. The so-called "homesickness-tourism" which was often perceived as quite aggressive well into the 1990s now tends to be viewed as a good-natured nostalgia tour rather than an expression of anger and desire for the return of the lost territories.
Some organisations exist in Germany who claim those territories for Germany or property there for German citizens.
The Prussian Trust (or the Prussian Claims Society), that probably has less than a hundred members, re-opened the old dispute when in December 2006, it submitted 23 individual claims against the Polish government with the European Court of Human Rights
in Strasbourg asking for compensation or return of property appropriated from its members at the end of World War II. An expert report jointly commissioned by the German and Polish governments from specialists in international law have confirmed that the proposed complaints by the Prussian Trust had little hope of success. But the German government can not prevent such requests being made and the Polish government has felt that the submissions warranted a comment by Anna Fotyga
, the Polish Minister of the Foreign Affairs who "express [her] deepest concern upon receiving the information about a claim against Poland submitted by the Prussian Trust to the European Court of Human Rights". On 9 October 2008 the European Court of Human Rights declared the case of Preussische Treuhand v. Poland inadmissible, because the European Convention on Human Rights does not impose any obligations on the Contracting States to return property which was transferred to them before they ratified the Convention.
After the NPD won 6 seats in the parliament of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern in September 2006, the leader of the party, Udo Voigt
, declared that his party demands Germany in "historical borders" and questioned current border treaties.
in 1741, Hohenfriedenburg
in 1745, Leuthen
(1757) and Zorndorf
(1758), and his defeats at Gross-Jägersdorf
in 1757 and Kunersdorf
in 1759. Historian Norman Davies
describes Kunersdorf as "Prussia's greatest disaster" and the inspiration for Christian Tiedge's Elegy to "Humanity butchered by Delusion on the Altar of Blood". In the Napoleonic Wars
the Pomerania
n town of Kolberg was besieged
in 1807 (inspiring a Second World War propaganda film
) while the French Grande Armée was victorious at Eylau
in East Prussia in the same year. In World War I
, Hindenburg
won critical victories at Tannenberg
and the Masurian Lakes
, ejecting Russian forces from East Prussia.
Numerous figures in German history were either born or resident in the former eastern territories. The list includes politicians, statesmen and national leaders such as Friedrich von Gentz
, Adalbert Falk, Ferdinand Lassalle
and Eduard Lasker
; Catherine the Great, Empress of Russia; Chancellors Leo von Caprivi
and Georg Michaelis
and the jurist Helmuth James Graf von Moltke
. Field Marshals Paul von Hindenburg
, Hermann von Eichhorn
and Günther von Kluge
were born in the east, as were Generals Erich von Falkenhayn
and Heinz Guderian
, SS-men Erich von dem Bach-Zelewski and Kurt Daluege
, fighter ace Manfred von Richthofen
and his uncle, the geographer and explorer Ferdinand von Richthofen
. Scientists from the former eastern provinces include the physicists and mathematicians David Hilbert
, Max Born
, and Walther Nernst
, and immunologist Paul Ehrlich
. Philosophers and theologians such as Immanuel Kant
, Arthur Schopenhauer
and Friedrich Daniel Ernst Schleiermacher
, and historians Heinrich Graetz
and Gottfried Bernhardy
. The east was home to poets Martin Opitz, Angelus Silesius
, Andreas Gryphius
, Friedrich von Logau, and Ewald Christian von Kleist
. Eminent cultural figures from the region included the collector of folk songs Johann Gottfried Herder
and the singer, pianist, conductor and composer George Henschel
; novelists and dramatists Joseph Freiherr von Eichendorff
, Gustav Freytag
, E. T. A. Hoffmann, Arnold Zweig
, Gerhart Hauptmann
and Günter Grass
; painters Karl Friedrich Lessing
and Adolph Menzel.
Province
A province is a territorial unit, almost always an administrative division, within a country or state.-Etymology:The English word "province" is attested since about 1330 and derives from the 13th-century Old French "province," which itself comes from the Latin word "provincia," which referred to...
s or region
Region
Region is most commonly found as a term used in terrestrial and astrophysics sciences also an area, notably among the different sub-disciplines of geography, studied by regional geographers. Regions consist of subregions that contain clusters of like areas that are distinctive by their uniformity...
s east of the current eastern border of Germany
Oder-Neisse line
The Oder–Neisse line is the border between Germany and Poland which was drawn in the aftermath of World War II. The line is formed primarily by the Oder and Lusatian Neisse rivers, and meets the Baltic Sea west of the seaport cities of Szczecin and Świnoujście...
which were lost by Germany during and after the two world wars
World war
A world war is a war affecting the majority of the world's most powerful and populous nations. World wars span multiple countries on multiple continents, with battles fought in multiple theaters....
. These territories include the Province of Posen
Province of Posen
The Province of Posen was a province of Prussia from 1848–1918 and as such part of the German Empire from 1871 to 1918. The area was about 29,000 km2....
(lost after World War I
World War I
World War I , which was predominantly called the World War or the Great War from its occurrence until 1939, and the First World War or World War I thereafter, was a major war centred in Europe that began on 28 July 1914 and lasted until 11 November 1918...
) and East Prussia
East Prussia
East Prussia is the main part of the region of Prussia along the southeastern Baltic Coast from the 13th century to the end of World War II in May 1945. From 1772–1829 and 1878–1945, the Province of East Prussia was part of the German state of Prussia. The capital city was Königsberg.East Prussia...
, Farther Pomerania
Farther Pomerania
Farther Pomerania, Further Pomerania, Transpomerania or Eastern Pomerania , which before the German-Polish border shift of 1945 comprised the eastern part of the Duchy, later Province of Pomerania, roughly stretching from the Oder River in the West to Pomerelia in the East...
, East Brandenburg and Lower Silesia
Lower Silesia
Lower Silesia ; is the northwestern part of the historical and geographical region of Silesia; Upper Silesia is to the southeast.Throughout its history Lower Silesia has been under the control of the medieval Kingdom of Poland, the Kingdom of Bohemia and the Austrian Habsburg Monarchy from 1526...
(lost in World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
); and other, smaller regions. In present-day Germany, the term is usually meant to refer only to the territories lost in World War II.
Usage

Potsdam Agreement
The Potsdam Agreement was the Allied plan of tripartite military occupation and reconstruction of Germany—referring to the German Reich with its pre-war 1937 borders including the former eastern territories—and the entire European Theatre of War territory...
the description of the territories transferred is "The former German territories [east of the Oder-Neisse line]", and permutations on this description are the most commonly used to describe any former territories of Germany east of the Oder-Neisse line
Oder-Neisse line
The Oder–Neisse line is the border between Germany and Poland which was drawn in the aftermath of World War II. The line is formed primarily by the Oder and Lusatian Neisse rivers, and meets the Baltic Sea west of the seaport cities of Szczecin and Świnoujście...
.
While the name East Germany, a political term, used to be the colloquial naming of the German Democratic Republic
German Democratic Republic
The German Democratic Republic , informally called East Germany by West Germany and other countries, was a socialist state established in 1949 in the Soviet zone of occupied Germany, including East Berlin of the Allied-occupied capital city...
(GDR), the term Eastern Germany underwent a shift in the 20th century due to the border shifts after the Second World War. Since in German there is only one usual term Ostdeutschland, meaning East Germany or Eastern Germany, the German rather ambiguous term never gained prevailing use for the GDR as did the English term. While Eastern Germany had been used for the former eastern territories of Germany before the Second World War
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
. The term since has been used to denote the post-war and the respective five states
States of Germany
Germany is made up of sixteen which are partly sovereign constituent states of the Federal Republic of Germany. Land literally translates as "country", and constitutionally speaking, they are constituent countries...
of the reunited Germany
German reunification
German reunification was the process in 1990 in which the German Democratic Republic joined the Federal Republic of Germany , and when Berlin reunited into a single city, as provided by its then Grundgesetz constitution Article 23. The start of this process is commonly referred by Germans as die...
. However, this is rather an outside perspective, because people and institutions in the states, traditionally considered as Middle Germany
Middle Germany
Central Germany is an economic and cultural region in Germany. Its exact borders depend on context, but it is often defined as being a region within the federal states of Saxony, Thuringia and Saxony-Anhalt, or a smaller part of this region .The name dates from the German Empire, when the region...
, like the three southern new states Saxony-Anhalt
Saxony-Anhalt
Saxony-Anhalt is a landlocked state of Germany. Its capital is Magdeburg and it is surrounded by the German states of Lower Saxony, Brandenburg, Saxony, and Thuringia.Saxony-Anhalt covers an area of...
, the Free State of Saxony and the Free State of Thuringia, still use the term Middle Germany when referring to their area and its institutions.
The former eastern territories in 20th century politics
From 1919 till 1990 sovereignty over some or all of these territories was subject to much diplomatic activity. Between the two world wars, many in Germany claimed that the territories ceded by Germany in 1919 under the Treaty of VersaillesTreaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles was one of the peace treaties at the end of World War I. It ended the state of war between Germany and the Allied Powers. It was signed on 28 June 1919, exactly five years after the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand. The other Central Powers on the German side of...
(most of which were taken in Partitions of Poland
Partitions of Poland
The Partitions of Poland or Partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth took place in the second half of the 18th century and ended the existence of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, resulting in the elimination of sovereign Poland for 123 years...
) should be returned to Germany. This claim was an important precursor to the Second World War. In 1939 after its invasion of Poland, Germany reoccupied and annexed these territories (as well as additional land in Poland that previously had never been part of the German Reich). Germany subsequently lost all territories east of the Oder-Neisse Line at the end of World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
in 1945, when international recognition of its right to jurisdiction over any of these territories
Territorial integrity
Territorial integrity is the principle under international law that nation-states should not attempt to promote secessionist movements or to promote border changes in other nation-states...
was withdrawn. The Eastern German areas east of the Oder-Neisse Line, and within the 1937 German Border, with the exception of Soviet Administered Northern East Prussia, became known as the Recovered Territories
Recovered Territories
Recovered or Regained Territories was an official term used by the People's Republic of Poland to describe those parts of pre-war Germany that became part of Poland after World War II...
in Poland following World War II.
After World War II, the so-called "German question" was an important factor of post-war German history and politics. The debate affected Cold War
Cold War
The Cold War was the continuing state from roughly 1946 to 1991 of political conflict, military tension, proxy wars, and economic competition between the Communist World—primarily the Soviet Union and its satellite states and allies—and the powers of the Western world, primarily the United States...
politics and diplomacy and played an important role in the negotiations leading up to the reunification of Germany in 1990. In 1990 Germany officially recognised
Treaty on the Final Settlement with Respect to Germany
The Treaty on the Final Settlement With Respect to Germany, was negotiated in 1990 between the Federal Republic of Germany and the German Democratic Republic , and the Four Powers which occupied Germany at the end of World War II in Europe: France, the Soviet Union, the United Kingdom, and the...
its present eastern border at the time of its reunification
German reunification
German reunification was the process in 1990 in which the German Democratic Republic joined the Federal Republic of Germany , and when Berlin reunited into a single city, as provided by its then Grundgesetz constitution Article 23. The start of this process is commonly referred by Germans as die...
, ending any residual claims to sovereignty that Germany may have had over any territory east of the Oder-Neisse line.
Foundation of the German Empire


Prussia
Prussia was a German kingdom and historic state originating out of the Duchy of Prussia and the Margraviate of Brandenburg. For centuries, the House of Hohenzollern ruled Prussia, successfully expanding its size by way of an unusually well-organized and effective army. Prussia shaped the history...
was the largest and dominant part of the empire. Thus, the territories of East Brandenburg, Silesia
Silesia
Silesia is a historical region of Central Europe located mostly in Poland, with smaller parts also in the Czech Republic, and Germany.Silesia is rich in mineral and natural resources, and includes several important industrial areas. Silesia's largest city and historical capital is Wrocław...
, Pomerania
Pomerania
Pomerania is a historical region on the south shore of the Baltic Sea. Divided between Germany and Poland, it stretches roughly from the Recknitz River near Stralsund in the West, via the Oder River delta near Szczecin, to the mouth of the Vistula River near Gdańsk in the East...
and the provinces of Prussia
Province of Prussia
The Province of Prussia was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1829-1878 created out of the provinces of East Prussia and West Prussia....
and Poznań
Poznan
Poznań is a city on the Warta river in west-central Poland, with a population of 556,022 in June 2009. It is among the oldest cities in Poland, and was one of the most important centres in the early Polish state, whose first rulers were buried at Poznań's cathedral. It is sometimes claimed to be...
(Posen) were all parts of the initial territory that comprised the German Empire in 1871. Later, these territories would come to be called in Germany "Ostgebiete des deutschen Reiches" (Eastern territories of the German Empire).
In some areas, such as the Province of Posen
Province of Posen
The Province of Posen was a province of Prussia from 1848–1918 and as such part of the German Empire from 1871 to 1918. The area was about 29,000 km2....
or the east-southern part of Upper Silesia
Upper Silesia
Upper Silesia is the southeastern part of the historical and geographical region of Silesia. Since the 9th century, Upper Silesia has been part of Greater Moravia, the Duchy of Bohemia, the Piast Kingdom of Poland, again of the Lands of the Bohemian Crown and the Holy Roman Empire, as well as of...
, the area that would later become Polish Corridor
Polish Corridor
The Polish Corridor , also known as Danzig Corridor, Corridor to the Sea or Gdańsk Corridor, was a territory located in the region of Pomerelia , which provided the Second Republic of Poland with access to the Baltic Sea, thus dividing the bulk of Germany from the province of East...
the majority population was Polish, while in others it was predominantly German. Under the Treaty of Versailles, territories with an apparent Polish majority were ceded to Poland, even if its inhabitants had voted against it during the referendum. However, demands by ethnic Germans in Poland to reconsider the justice of the settlement would keep the issue alive, as to whether these territories should belong to Germany or Poland. This debate constituted one of the causes of World War II.
Treaty of Versailles


Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles was one of the peace treaties at the end of World War I. It ended the state of war between Germany and the Allied Powers. It was signed on 28 June 1919, exactly five years after the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand. The other Central Powers on the German side of...
at the end of World War I
World War I
World War I , which was predominantly called the World War or the Great War from its occurrence until 1939, and the First World War or World War I thereafter, was a major war centred in Europe that began on 28 July 1914 and lasted until 11 November 1918...
obliged Germany to transfer some territory to other countries. In Central Europe, these included:
- Most of Greater PolandGreater PolandGreater Poland or Great Poland, often known by its Polish name Wielkopolska is a historical region of west-central Poland. Its chief city is Poznań.The boundaries of Greater Poland have varied somewhat throughout history...
("Province of Posen") and PomereliaPomereliaPomerelia is a historical region in northern Poland. Pomerelia lay in eastern Pomerania: on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea and west of the Vistula and its delta. The area centered on the city of Gdańsk at the mouth of the Vistula...
(parts of West PrussiaWest PrussiaWest Prussia was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1773–1824 and 1878–1919/20 which was created out of the earlier Polish province of Royal Prussia...
), mostly what the Kingdom of PrussiaKingdom of PrussiaThe Kingdom of Prussia was a German kingdom from 1701 to 1918. Until the defeat of Germany in World War I, it comprised almost two-thirds of the area of the German Empire...
had taken in the Partitions of PolandPartitions of PolandThe Partitions of Poland or Partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth took place in the second half of the 18th century and ended the existence of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, resulting in the elimination of sovereign Poland for 123 years...
was handed over to the re-established Polish stateSecond Polish RepublicThe Second Polish Republic, Second Commonwealth of Poland or interwar Poland refers to Poland between the two world wars; a period in Polish history in which Poland was restored as an independent state. Officially known as the Republic of Poland or the Commonwealth of Poland , the Polish state was...
after the Greater Poland UprisingGreater Poland Uprising (1918–1919)The Greater Poland Uprising of 1918–1919, or Wielkopolska Uprising of 1918–1919 or Posnanian War was a military insurrection of Poles in the Greater Poland region against Germany...
(this land comprised an area of 53,800 km² 4,224,000 inhabitants (1931) including 510 km² and 26,000 inhabitants from Upper SilesiaUpper SilesiaUpper Silesia is the southeastern part of the historical and geographical region of Silesia. Since the 9th century, Upper Silesia has been part of Greater Moravia, the Duchy of Bohemia, the Piast Kingdom of Poland, again of the Lands of the Bohemian Crown and the Holy Roman Empire, as well as of...
). - The Hlučín Area of Moravian-Silesian RegionMoravian-Silesian RegionMoravian-Silesian Region , or Moravo-Silesian Region, is one of 14 administrative Regions of the Czech Republic, until May 2001 it was formerly called the Ostrava Region . The region is located in the north-eastern part of its historical region of Moravia and in most of the Czech part of the...
to CzechoslovakiaCzechoslovakiaCzechoslovakia or Czecho-Slovakia was a sovereign state in Central Europe which existed from October 1918, when it declared its independence from the Austro-Hungarian Empire, until 1992...
(316 or 333 km² and 49,000 people), - The eastern part of Upper SilesiaUpper SilesiaUpper Silesia is the southeastern part of the historical and geographical region of Silesia. Since the 9th century, Upper Silesia has been part of Greater Moravia, the Duchy of Bohemia, the Piast Kingdom of Poland, again of the Lands of the Bohemian Crown and the Holy Roman Empire, as well as of...
(including KatowiceKatowiceKatowice is a city in Silesia in southern Poland, on the Kłodnica and Rawa rivers . Katowice is located in the Silesian Highlands, about north of the Silesian Beskids and about southeast of the Sudetes Mountains.It is the central district of the Upper Silesian Metropolis, with a population of 2...
), to Poland (area 3,214 km² and 965,000 people), - The northeastern part of East Prussia, named Memel Territory, which was placed under the control of FranceFranceThe French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
(and was later annexed by Lithuania, as the Klaipėda RegionKlaipėda RegionThe Klaipėda Region or Memel Territory was defined by the Treaty of Versailles in 1920 when it was put under the administration of the Council of Ambassadors...
), - The area of Działdowo (Soldau) (area 492 km²) to Poland; a few villages in the eastern part of West PrussiaWest PrussiaWest Prussia was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1773–1824 and 1878–1919/20 which was created out of the earlier Polish province of Royal Prussia...
and in the southern part of East PrussiaEast PrussiaEast Prussia is the main part of the region of Prussia along the southeastern Baltic Coast from the 13th century to the end of World War II in May 1945. From 1772–1829 and 1878–1945, the Province of East Prussia was part of the German state of Prussia. The capital city was Königsberg.East Prussia...
(WarmiaWarmiaWarmia or Ermland is a region between Pomerelia and Masuria in northeastern Poland. Together with Masuria, it forms the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship....
and MasuriaMasuriaMasuria is an area in northeastern Poland famous for its 2,000 lakes. Geographically, Masuria is part of two adjacent lakeland districts, the Masurian Lake District and the Iława Lake District...
) to Poland after the East Prussian plebisciteEast Prussian plebisciteThe East Prussia plebiscite , also known as the Allenstein and Marienwerder plebiscite or Warmia, Masuria and Powiśle plebiscite , was a plebiscite for self-determination of the regions Warmia , Masuria and Powiśle, which had been in parts of East Prussia and West Prussia, in accordance with...
. - The city of Danzig (Polish Gdańsk) with the delta of the VistulaVistulaThe Vistula is the longest and the most important river in Poland, at 1,047 km in length. The watershed area of the Vistula is , of which lies within Poland ....
river at the Baltic SeaBaltic SeaThe Baltic Sea is a brackish mediterranean sea located in Northern Europe, from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from 20°E to 26°E longitude. It is bounded by the Scandinavian Peninsula, the mainland of Europe, and the Danish islands. It drains into the Kattegat by way of the Øresund, the Great Belt and...
, was made the Free City of DanzigFree City of DanzigThe Free City of Danzig was a semi-autonomous city-state that existed between 1920 and 1939, consisting of the Baltic Sea port of Danzig and surrounding areas....
under the League of NationsLeague of NationsThe League of Nations was an intergovernmental organization founded as a result of the Paris Peace Conference that ended the First World War. It was the first permanent international organization whose principal mission was to maintain world peace...
and partially Polish authority (area 1893 km², 408,000 inhabitants 1929).
German annexation of Hultschin Area and the Memel Territory

Moravian-Silesian Region
Moravian-Silesian Region , or Moravo-Silesian Region, is one of 14 administrative Regions of the Czech Republic, until May 2001 it was formerly called the Ostrava Region . The region is located in the north-eastern part of its historical region of Moravia and in most of the Czech part of the...
which had been ceded to Czechoslovakia under the Treaty of Versailles was annexed by the Third Reich as a part of areas lost by Czechoslovakia in accordance with the Munich agreement
Munich Agreement
The Munich Pact was an agreement permitting the Nazi German annexation of Czechoslovakia's Sudetenland. The Sudetenland were areas along Czech borders, mainly inhabited by ethnic Germans. The agreement was negotiated at a conference held in Munich, Germany, among the major powers of Europe without...
. However, as distinct from other lost Czechoslovakian domains, it was not attached to Sudetengau (administrative region covering Sudetenland
Sudetenland
Sudetenland is the German name used in English in the first half of the 20th century for the northern, southwest and western regions of Czechoslovakia inhabited mostly by ethnic Germans, specifically the border areas of Bohemia, Moravia, and those parts of Silesia being within Czechoslovakia.The...
) but to Prussia (Upper Silesia
Upper Silesia
Upper Silesia is the southeastern part of the historical and geographical region of Silesia. Since the 9th century, Upper Silesia has been part of Greater Moravia, the Duchy of Bohemia, the Piast Kingdom of Poland, again of the Lands of the Bohemian Crown and the Holy Roman Empire, as well as of...
).
By late 1938, Lithuania
Lithuania
Lithuania , officially the Republic of Lithuania is a country in Northern Europe, the biggest of the three Baltic states. It is situated along the southeastern shore of the Baltic Sea, whereby to the west lie Sweden and Denmark...
had lost control over the situation in the Memel Territory
Klaipėda Region
The Klaipėda Region or Memel Territory was defined by the Treaty of Versailles in 1920 when it was put under the administration of the Council of Ambassadors...
. In the early hours of 23 March 1939, after a political ultimatum caused a Lithuanian delegation to travel to Berlin, the Lithuanian Minister of Foreign Affairs Juozas Urbšys
Juozas Urbšys
Juozas Urbšys was a prominent interwar Lithuanian diplomat, the last head of foreign affairs in independent interwar Lithuania, and a translator. He served in the military between 1916 and 1922, afterwards joining the Lithuanian Ministry of Foreign Affairs...
and his German counterpart Joachim von Ribbentrop
Joachim von Ribbentrop
Ulrich Friedrich Wilhelm Joachim von Ribbentrop was Foreign Minister of Germany from 1938 until 1945. He was later hanged for war crimes after the Nuremberg Trials.-Early life:...
signed the Treaty of the Cession of the Memel Territory to Germany in exchange for a Lithuanian Free Zone in the port of Memel, using the facilities erected in previous years.
World War II

Invasion of Poland (1939)
The Invasion of Poland, also known as the September Campaign or 1939 Defensive War in Poland and the Poland Campaign in Germany, was an invasion of Poland by Germany, the Soviet Union, and a small Slovak contingent that marked the start of World War II in Europe...
in the beginning of World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
, Germany annexed eastern territories lost under the terms of the Treaty of Versailles, and annexed other eastern territories. These territorial changes were not recognised by the Allied
Allies of World War II
The Allies of World War II were the countries that opposed the Axis powers during the Second World War . Former Axis states contributing to the Allied victory are not considered Allied states...
governments, that after the 1942 Declaration by the United Nations were also known as the United Nations
United Nations
The United Nations is an international organization whose stated aims are facilitating cooperation in international law, international security, economic development, social progress, human rights, and achievement of world peace...
.
After invading Poland in 1939, the Third Reich annexed the lands the German Empire had ceded to the Second Polish Republic
Second Polish Republic
The Second Polish Republic, Second Commonwealth of Poland or interwar Poland refers to Poland between the two world wars; a period in Polish history in which Poland was restored as an independent state. Officially known as the Republic of Poland or the Commonwealth of Poland , the Polish state was...
in 1919–1922 by the Treaty of Versailles, including the "Polish Corridor
Polish Corridor
The Polish Corridor , also known as Danzig Corridor, Corridor to the Sea or Gdańsk Corridor, was a territory located in the region of Pomerelia , which provided the Second Republic of Poland with access to the Baltic Sea, thus dividing the bulk of Germany from the province of East...
", West Prussia
West Prussia
West Prussia was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1773–1824 and 1878–1919/20 which was created out of the earlier Polish province of Royal Prussia...
, the Province of Posen
Province of Posen
The Province of Posen was a province of Prussia from 1848–1918 and as such part of the German Empire from 1871 to 1918. The area was about 29,000 km2....
, and parts of eastern Upper Silesia
Upper Silesia
Upper Silesia is the southeastern part of the historical and geographical region of Silesia. Since the 9th century, Upper Silesia has been part of Greater Moravia, the Duchy of Bohemia, the Piast Kingdom of Poland, again of the Lands of the Bohemian Crown and the Holy Roman Empire, as well as of...
. The council of the Free City of Danzig
Free City of Danzig
The Free City of Danzig was a semi-autonomous city-state that existed between 1920 and 1939, consisting of the Baltic Sea port of Danzig and surrounding areas....
voted to become a part of Germany again, although Poles
Poles
thumb|right|180px|The state flag of [[Poland]] as used by Polish government and diplomatic authoritiesThe Polish people, or Poles , are a nation indigenous to Poland. They are united by the Polish language, which belongs to the historical Lechitic subgroup of West Slavic languages of Central Europe...
and Jews
Jews
The Jews , also known as the Jewish people, are a nation and ethnoreligious group originating in the Israelites or Hebrews of the Ancient Near East. The Jewish ethnicity, nationality, and religion are strongly interrelated, as Judaism is the traditional faith of the Jewish nation...
were deprived of their voting rights and all non-Nazi
National Socialist German Workers Party
The National Socialist German Workers' Party , commonly known in English as the Nazi Party, was a political party in Germany between 1920 and 1945. Its predecessor, the German Workers' Party , existed from 1919 to 1920...
political parties were banned. Parts of Poland that had not been part of the German Empire were also incorporated into the Third Reich.
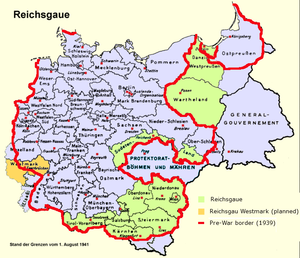
Two decrees by Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler was an Austrian-born German politician and the leader of the National Socialist German Workers Party , commonly referred to as the Nazi Party). He was Chancellor of Germany from 1933 to 1945, and head of state from 1934 to 1945...
(October 8 and October 12, 1939) provided for the division of the annexed areas of Poland into the following administrative units:
- Reichsgau WarthelandReichsgau WarthelandReichsgau Wartheland was a Nazi German Reichsgau formed from Polish territory annexed in 1939. It comprised the Greater Poland and adjacent areas, and only in part matched the area of the similarly named pre-Versailles Prussian province of Posen...
(initially ReichsgauReichsgauA Reichsgau was an administrative subdivision created in a number of the areas annexed to Nazi Germany between 1938 and 1945...
Posen), which included the entire Poznań VoivodeshipPoznan Voivodeship-1975 to 1998:From 1975 to 1998, Poznań Voivodeship was a unit of administrative division and local government in Poland, superseded by Greater Poland Voivodeship.Capital city: Poznań.Major cities and towns :...
, most of the Łódź Voivodeship, five counties of the Pomeranian Voivodeship, and one county of the Warszawa Voivodeship; - Reichsgau Danzig-West PrussiaReichsgau Danzig-West PrussiaThe Reichsgau Danzig-West Prussia was a Nazi German province created on 8 October 1939 from the territory of the annexed Free City of Danzig, the annexed Polish province Greater Pomeranian Voivodship , and the Nazi German Regierungsbezirk West Prussia of Gau East Prussia. Before 2 November 1939,...
(initially Reichsgau West Prussia), which consisted of the remaining area of the Pomeranian Voivodeship and the Free City of DanzigFree City of DanzigThe Free City of Danzig was a semi-autonomous city-state that existed between 1920 and 1939, consisting of the Baltic Sea port of Danzig and surrounding areas....
; - Ciechanów District (RegierungsbezirkRegierungsbezirkIn Germany, a Government District, in German: Regierungsbezirk – is a subdivision of certain federal states .They are above the Kreise, Landkreise, and kreisfreie Städte...
Zichenau), consisting of the five northern counties of Warszawa Voivodeship (Płock, Płońsk, SierpcSierpcSierpc is a town in Poland, in the north-west part of the Masovian Voivodeship, about 125 km northwest of Warsaw. It is the capital of Sierpc County. Its population is 18,777 . It is located near the national road No 10, which connects Warsaw and Toruń...
, CiechanówCiechanówCiechanów is a town in north-central Poland with 45,900 inhabitants . It is situated in Masovian Voivodeship . It was previously the capital of Ciechanów Voivodeship.-History:The grad numbered approximately 3,000 armed men....
, and Mława), which became a part of East Prussia; - Katowice District (Regierungsbezirk Kattowitz), or unofficially East Upper Silesia (Ost-Oberschlesien), which included SosnowiecSosnowiecSosnowiec is a city in Zagłębie Dąbrowskie in southern Poland, near Katowice. It is one of the central districts of the Upper Silesian Metropolitan Union - a metropolis with a combined population of over two million people located in the Silesian Highlands, on the Brynica river .It is situated in...
, BędzinBedzinBędzin is a city in Zagłębie Dąbrowskie in southern Poland. Located in the Silesian Highlands, on the Czarna Przemsza river , the city borders the Upper Silesian Metropolitan Union - a metro area with a population of about 2 million.It has been situated in the Silesian Voivodeship since its...
, ChrzanówChrzanówChrzanów is a town in south Poland with 39,704 inhabitants . It is situated in the Lesser Poland Voivodeship and is the capital of Chrzanów County.- To 1809:...
, and ZawiercieZawiercieZawiercie is a city in the Silesian Voivodeship of southern Poland with 55,800 inhabitants . It is situated in the Kraków-Częstochowa highland near the source of the Warta River...
Counties, and parts of OlkuszOlkuszOlkusz is a town in south Poland with 37,696 inhabitants . Situated in the Lesser Poland Voivodeship , previously in Katowice Voivodeship , it is the capital of Olkusz County...
and ŻywiecZywiecŻywiec is a town in south-central Poland with 32,242 inhabitants . Between 1975 and 1998, it was located within the Bielsko-Biała Voivodeship, but has since become part of the Silesian Voivodeship....
Counties.
These territories had an area of 94,000 km² and a population of 10,000,000 people. The remainder of the Polish territory was annexed by the Soviet Union
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
(see Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact
Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact
The Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact, named after the Soviet foreign minister Vyacheslav Molotov and the German foreign minister Joachim von Ribbentrop, was an agreement officially titled the Treaty of Non-Aggression between Germany and the Soviet Union and signed in Moscow in the late hours of 23 August 1939...
) or made into the German-controlled General Government
General Government
The General Government was an area of Second Republic of Poland under Nazi German rule during World War II; designated as a separate region of the Third Reich between 1939–1945...
occupation zone.
After the German attack on the Soviet Union
Operation Barbarossa
Operation Barbarossa was the code name for Germany's invasion of the Soviet Union during World War II that began on 22 June 1941. Over 4.5 million troops of the Axis powers invaded the USSR along a front., the largest invasion in the history of warfare...
in June 1941, the district of Białystok
Bezirk Bialystok
The Bezirk Bialystok , also Belostok was an administrative unit that existed during the World War II occupation of Poland by Nazi Germany...
, which included the Białystok, Bielsk Podlaski
Bielsk Podlaski
-Roads and Highways:Bielsk Podlaski is at the intersection of two National Road and a Voivodeship Road:* National Road 19 - Kuźnica Białystoka Border Crossing - Kuźnica - Białystok - Bielsk Podlaski - Siemiatycze - Międzyrzec Podlaski - Kock - Lubartów - Lublin - Kraśnik - Janów Lubelski - Nisko...
, Grajewo
Grajewo
Grajewo , is a town in north-eastern Poland with 23,302 inhabitants .It is situated in the Podlaskie Voivodeship ; previously, it was in Łomża Voivodeship...
, Łomża, Sokółka, Volkovysk, and Grodno Counties, was "attached to" (not incorporated into) East Prussia, whilst East Galicia (Distrikt Galizien), which included the cities of Lwów
Lviv
Lviv is a city in western Ukraine. The city is regarded as one of the main cultural centres of today's Ukraine and historically has also been a major Polish and Jewish cultural center, as Poles and Jews were the two main ethnicities of the city until the outbreak of World War II and the following...
, Stanislawów
Ivano-Frankivsk
Ivano-Frankivsk is a historic city located in the western Ukraine. It is the administrative centre of the Ivano-Frankivsk Oblast , and is designated as its own separate raion within the oblast, municipality....
and Tarnopol
Ternopil
Ternopil , is a city in western Ukraine, located on the banks of the Seret River. Ternopil is one of the major cities of Western Ukraine and the historical region of Galicia...
, was made part of the General Government.
Potsdam Conference
After World War II, as agreed at the Potsdam ConferencePotsdam Conference
The Potsdam Conference was held at Cecilienhof, the home of Crown Prince Wilhelm Hohenzollern, in Potsdam, occupied Germany, from 16 July to 2 August 1945. Participants were the Soviet Union, the United Kingdom, and the United States...
(which met from 17 July until 2 August 1945), all of the areas east of the Oder-Neisse line, whether recognised by the international community as part of Germany until 1939 or occupied by Germany during World War II, were placed under the jurisdiction of other countries. The relevant paragraphs in the Potsdam Agreement
Potsdam Agreement
The Potsdam Agreement was the Allied plan of tripartite military occupation and reconstruction of Germany—referring to the German Reich with its pre-war 1937 borders including the former eastern territories—and the entire European Theatre of War territory...
are:
The Allies also agreed that:
because in the words of Winston Churchill
Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer-Churchill, was a predominantly Conservative British politician and statesman known for his leadership of the United Kingdom during the Second World War. He is widely regarded as one of the greatest wartime leaders of the century and served as Prime Minister twice...

Post World War II
Between 1945 and 1990, the dispute over the final disposition of these territories was the subject of international debate.The government of West Germany
West Germany
West Germany is the common English, but not official, name for the Federal Republic of Germany or FRG in the period between its creation in May 1949 to German reunification on 3 October 1990....
preferred to use the phrase "former German territories temporarily under Polish and Soviet administration" (Note: those "former German territories" are those of Eastern Germany within the 1937 Germany Border). This was the wording used in the Potsdam Agreement, but was used only by the Federal Republic of Germany
West Germany
West Germany is the common English, but not official, name for the Federal Republic of Germany or FRG in the period between its creation in May 1949 to German reunification on 3 October 1990....
because the Polish and Soviet governments refused to use it, objecting to the obvious implication that these territories should someday revert to Germany.
The Polish government preferred to use the phrase Recovered Territories
Recovered Territories
Recovered or Regained Territories was an official term used by the People's Republic of Poland to describe those parts of pre-war Germany that became part of Poland after World War II...
, asserting a sort of continuity because these territories had once been ruled by ethnic Poles half a millennium before World War II and had been "recovered" from Nazi Germany after 1945.
Expulsion of Germans and resettlement

Flight and evacuation of German civilians during the end of World War II
Plans to evacuate German population from the occupied territories in Central and Eastern Europe and from Eastern Germany were prepared by German authorities at the end of World War II. However, the evacuation in most of the areas was delayed until the last moment, when it was too late to conduct it...
from the advancing Red Army
Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army started out as the Soviet Union's revolutionary communist combat groups during the Russian Civil War of 1918-1922. It grew into the national army of the Soviet Union. By the 1930s the Red Army was among the largest armies in history.The "Red Army" name refers to...
in the winter of 1944–1945 was expelled
Expulsion of Germans after World War II
The later stages of World War II, and the period after the end of that war, saw the forced migration of millions of German nationals and ethnic Germans from various European states and territories, mostly into the areas which would become post-war Germany and post-war Austria...
. Although in the post-war period earlier German sources often cited the number of evacuated and expelled Germans at 16 million and the death toll at between 1.7 and 2.5 million, today, the numbers are considered by some historians to be exaggerated and more likely in the range between 400,000 to 600,000. Some present-day estimates place the numbers of German refugees at 14 million of which about half a million died during the evacuations and expulsions.
At the same time, Poles from Central Poland, expelled Poles from former Eastern Poland
Repatriation of Poles
Repatriation of Poles can refer to:*Repatriation of Poles *Repatriation of Poles...
, Polish returnees from internment and forced labour, Ukrainians forcefully resettled in Operation Vistula and Jewish Holocaust survivors settled in the territories gained by Poland, whereas the North of former East Prussia
East Prussia
East Prussia is the main part of the region of Prussia along the southeastern Baltic Coast from the 13th century to the end of World War II in May 1945. From 1772–1829 and 1878–1945, the Province of East Prussia was part of the German state of Prussia. The capital city was Königsberg.East Prussia...
(Kaliningrad Oblast
Kaliningrad Oblast
Kaliningrad Oblast is a federal subject of Russia situated on the Baltic coast. It has a population of The oblast forms the westernmost part of the Russian Federation, but it has no land connection to the rest of Russia. Since its creation it has been an exclave of the Russian SFSR and then the...
) was turned into a military zone and subsequently became settled with Russians.
Ostpolitik
During the 1970s while Willy BrandtWilly Brandt
Willy Brandt, born Herbert Ernst Karl Frahm , was a German politician, Mayor of West Berlin 1957–1966, Chancellor of West Germany 1969–1974, and leader of the Social Democratic Party of Germany 1964–1987....
was chancellor of the Federal Republic of Germany
West Germany
West Germany is the common English, but not official, name for the Federal Republic of Germany or FRG in the period between its creation in May 1949 to German reunification on 3 October 1990....
(FRG), the FRG followed a foreign relations policy of Ostpolitik
Ostpolitik
Neue Ostpolitik , or Ostpolitik for short, refers to the normalization of relations between the Federal Republic of Germany and Eastern Europe, particularly the German Democratic Republic beginning in 1969...
abandoning elements of the Hallstein Doctrine
Hallstein Doctrine
The Hallstein Doctrine, named after Walter Hallstein, was a key doctrine in the foreign policy of the Federal Republic of Germany after 1955. It established that the Federal Republic would not establish or maintain diplomatic relations with any state that recognized the German Democratic Republic...
. The FRG "abandoned, at least for the time being, its claims with respect to German self-determination and reunification, recognising de facto the existence of the German Democratic Republic
German Democratic Republic
The German Democratic Republic , informally called East Germany by West Germany and other countries, was a socialist state established in 1949 in the Soviet zone of occupied Germany, including East Berlin of the Allied-occupied capital city...
(GDR) and the Oder-Neisse Line." Subsequently, between 1970 and 1973, the FRG concluded friendship treaties with, successively, the Soviet Union (The Treaty of Moscow
Treaty of Moscow (1970)
The Treaty of Moscow, was signed on August 12, 1970 between the USSR and West Germany . It was signed by Willy Brandt and Walter Scheel from the FRG side and by Alexei Kosygin and Andrei Gromyko from the USSR side.-Description:...
), Poland (The Treaty of Warsaw
Treaty of Warsaw (1970)
The Treaty of Warsaw was a treaty between West Germany and the People's Republic of Poland. It was signed by Chancellor Willy Brandt and Prime Minister Józef Cyrankiewicz at the Presidential Palace on 7 December 1970, and it was ratified by the German Bundestag on 17 May 1972.In the treaty, both...
), the GDR (The Basic Treaty
Basic Treaty (1972)
The Basic Treaty is the short-hand name for the Treaty concerning the basis of relations between the Federal Republic of Germany and the German Democratic Republic...
) and Czechoslovakia (The Treaty of Prague
Treaty of Prague (1973)
The Treaty of Prague was a treaty signed on 11 December 1973, in Prague, by the Federal Republic of Germany and Czechoslovakia, in which the two States recognized each other diplomatically and declared the 1938 Munich Agreements to be null and void - by acknowledging the inviolability of their...
), thereby accommodating the European order that existed in the 1970s.
Modern status
Over the last twenty years, the "German question" has been muted by three related phenomena:- The passage of time means that there are fewer and fewer people left who have firsthand experience of living in these regions under German jurisdiction.
- Until the Treaty on the Final Settlement With Respect to GermanyTreaty on the Final Settlement with Respect to GermanyThe Treaty on the Final Settlement With Respect to Germany, was negotiated in 1990 between the Federal Republic of Germany and the German Democratic Republic , and the Four Powers which occupied Germany at the end of World War II in Europe: France, the Soviet Union, the United Kingdom, and the...
, the official German government position on the status of areas vacated by settled German communities east of the Oder and Neisse rivers was that the areas were "temporarily under Polish [or Soviet] administration." In 1990 the German political establishment recognised the "facts on the groundFacts on the groundFacts on the ground is a diplomatic term that means the situation in reality as opposed to in the abstract. It originated in discussions of the Israeli–Palestinian conflict, where it was used to refer to Israeli settlements built in the occupied West Bank, which were intended to establish permanent...
" and accepted clauses in the Treaty on the Final Settlement whereby Germany renounced all claims to territory east of the Oder-Neisse line. Germany's recognition of the border was formalised in the German-Polish Border TreatyGerman-Polish Border Treaty (1990)The German-Polish Border Treaty of 1990 finally settled the issue of the Polish-German border, which in terms of international law had been pending since 1945...
on November 14, 1990. - The eastern expansion of the European UnionEuropean UnionThe European Union is an economic and political union of 27 independent member states which are located primarily in Europe. The EU traces its origins from the European Coal and Steel Community and the European Economic Community , formed by six countries in 1958...
(EU) which occurred on May 1, 2004 means that any German who wishes to live and work in Poland, and thus east of the Oder and Neisse rivers, may do so without requiring a permit. Some restrictions on the purchase of land and buildings will be in place for a period of a few years. However, German expellees and refugees are now free to visit their former homes without difficulty. Poland entered the Schengen AgreementSchengen AgreementThe Schengen Agreement is a treaty signed on 14 June 1985 near the town of Schengen in Luxembourg, between five of the ten member states of the European Economic Community. It was supplemented by the Convention implementing the Schengen Agreement 5 years later...
on December 21, 2007, removing all border controls on its border with Germany, making movement across the border even easier.
In the course of the German reunification
German reunification
German reunification was the process in 1990 in which the German Democratic Republic joined the Federal Republic of Germany , and when Berlin reunited into a single city, as provided by its then Grundgesetz constitution Article 23. The start of this process is commonly referred by Germans as die...
process, Chancellor Helmut Kohl
Helmut Kohl
Helmut Josef Michael Kohl is a German conservative politician and statesman. He was Chancellor of Germany from 1982 to 1998 and the chairman of the Christian Democratic Union from 1973 to 1998...
accepted the territorial changes made after the Second World War. This caused some outrage among the Federation of Expellees
Federation of Expellees
The Federation of Expellees or Bund der Vertriebenen is a non-profit organization formed to represent the interests of Germans who either fled their homes in parts of Central and Eastern Europe, or were expelled following World War II....
. Some Poles were concerned about a possible revival of their 1939 trauma through a second German invasion, this time with the Germans buying back their land, which was cheaply available at the time. This happened on a smaller scale than many expected, and since the Baltic Sea
Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is a brackish mediterranean sea located in Northern Europe, from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from 20°E to 26°E longitude. It is bounded by the Scandinavian Peninsula, the mainland of Europe, and the Danish islands. It drains into the Kattegat by way of the Øresund, the Great Belt and...
coast in Poland
Poland
Poland , officially the Republic of Poland , is a country in Central Europe bordered by Germany to the west; the Czech Republic and Slovakia to the south; Ukraine, Belarus and Lithuania to the east; and the Baltic Sea and Kaliningrad Oblast, a Russian exclave, to the north...
has become popular with German tourists, Germans are now frequent and welcome guests. The so-called "homesickness-tourism" which was often perceived as quite aggressive well into the 1990s now tends to be viewed as a good-natured nostalgia tour rather than an expression of anger and desire for the return of the lost territories.
Some organisations exist in Germany who claim those territories for Germany or property there for German citizens.
The Prussian Trust (or the Prussian Claims Society), that probably has less than a hundred members, re-opened the old dispute when in December 2006, it submitted 23 individual claims against the Polish government with the European Court of Human Rights
European Court of Human Rights
The European Court of Human Rights in Strasbourg is a supra-national court established by the European Convention on Human Rights and hears complaints that a contracting state has violated the human rights enshrined in the Convention and its protocols. Complaints can be brought by individuals or...
in Strasbourg asking for compensation or return of property appropriated from its members at the end of World War II. An expert report jointly commissioned by the German and Polish governments from specialists in international law have confirmed that the proposed complaints by the Prussian Trust had little hope of success. But the German government can not prevent such requests being made and the Polish government has felt that the submissions warranted a comment by Anna Fotyga
Anna Fotyga
Anna Elżbieta Fotyga née Kawecka is a Polish economist, politician, former Member of the European Parliament and former Minister of Foreign Affairs of Poland, in the successive cabinets of Kazimierz Marcinkiewicz and Jarosław Kaczyński...
, the Polish Minister of the Foreign Affairs who "express [her] deepest concern upon receiving the information about a claim against Poland submitted by the Prussian Trust to the European Court of Human Rights". On 9 October 2008 the European Court of Human Rights declared the case of Preussische Treuhand v. Poland inadmissible, because the European Convention on Human Rights does not impose any obligations on the Contracting States to return property which was transferred to them before they ratified the Convention.
After the NPD won 6 seats in the parliament of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern in September 2006, the leader of the party, Udo Voigt
Udo Voigt
Udo Voigt is a German politician and former leader of the far-right National Democratic Party of Germany since 1996. He is a former aviation engineer and captain in the German army.- Political career :...
, declared that his party demands Germany in "historical borders" and questioned current border treaties.
The former eastern territories in German history
The former eastern territories were the scene of numerous events noted in German history, but generally viewed in modern-day Poland as being of 'foreign' rather than local interest. These include battles such as Frederick the Great’s victories at MollwitzBattle of Mollwitz
The Battle of Mollwitz was fought by Prussia and Austria on April 10, 1741, during the early stages of the War of the Austrian Succession. It was the first battle of the new Prussian King Frederick II, in which both sides made numerous military blunders but Frederick the Great still managed to...
in 1741, Hohenfriedenburg
Battle of Hohenfriedberg
The Battle of Hohenfriedberg or Hohenfriedeberg, also known as the battle of Striegau, now Dobromierz, was one of the crowning achievements of Frederick the Great...
in 1745, Leuthen
Battle of Leuthen
In the Battle of Leuthen or Lissa, fought on 5 December 1757, Frederick the Great's Prussian army used maneuver and terrain to decisively defeat a much larger Austrian army under Charles of Lorraine, thus ensuring Prussian control of Silesia during the Seven Years' War.- Background :While Frederick...
(1757) and Zorndorf
Battle of Zorndorf
The Battle of Zorndorf was a battle fought on August 25, 1758 during the Seven Years' War, fought between the forces of the Russians troops under the command of Count William Fermor – and a Prussian army under King Frederick the Great...
(1758), and his defeats at Gross-Jägersdorf
Battle of Gross-Jägersdorf
The Battle of Gross-Jägersdorf was a victory for the Russian force under Field Marshal Stepan Fedorovich Apraksin over a smaller Prussian force commanded by Field Marshal Hans von Lehwaldt, during the Seven Years' War.- Background :...
in 1757 and Kunersdorf
Battle of Kunersdorf
The Battle of Kunersdorf, fought in the Seven Year's War, was Frederick the Great's most devastating defeat. On August 12, 1759, near Kunersdorf , east of Frankfurt , 50,900 Prussians were defeated by a combined allied army 59,500 strong consisting of 41,000 Russians and 18,500 Austrians under...
in 1759. Historian Norman Davies
Norman Davies
Professor Ivor Norman Richard Davies FBA, FRHistS is a leading English historian of Welsh descent, noted for his publications on the history of Europe, Poland, and the United Kingdom.- Academic career :...
describes Kunersdorf as "Prussia's greatest disaster" and the inspiration for Christian Tiedge's Elegy to "Humanity butchered by Delusion on the Altar of Blood". In the Napoleonic Wars
Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars were a series of wars declared against Napoleon's French Empire by opposing coalitions that ran from 1803 to 1815. As a continuation of the wars sparked by the French Revolution of 1789, they revolutionised European armies and played out on an unprecedented scale, mainly due to...
the Pomerania
Pomerania
Pomerania is a historical region on the south shore of the Baltic Sea. Divided between Germany and Poland, it stretches roughly from the Recknitz River near Stralsund in the West, via the Oder River delta near Szczecin, to the mouth of the Vistula River near Gdańsk in the East...
n town of Kolberg was besieged
Siege of Kolberg (1807)
The Siege of Kolberg, also known as siege of Colberg took place from March to 2 July 1807 during the War of the Fourth Coalition, part of the Napoleonic Wars. An army of the First French Empire and its client states besieged the Prussian fortified town of Kolberg, the only remaining Prussian-held...
in 1807 (inspiring a Second World War propaganda film
Kolberg (film)
Kolberg is a 1945 German propaganda film directed by Veit Harlan and Wolfgang Liebeneiner. It opened on January 30, 1945 simultaneously in Berlin and to the crew of the naval base at La Rochelle. It was also screened in the Reich chancellery after the broadcast of Hitler's last radio address on...
) while the French Grande Armée was victorious at Eylau
Battle of Eylau
The Battle of Eylau or Battle of Preussisch-Eylau, 7 and 8 February 1807, was a bloody and inconclusive battle between Napoléon's Grande Armée and a Russian Empire army under Levin August, Count von Bennigsen near the town of Preußisch Eylau in East Prussia. Late in the battle, the Russians...
in East Prussia in the same year. In World War I
World War I
World War I , which was predominantly called the World War or the Great War from its occurrence until 1939, and the First World War or World War I thereafter, was a major war centred in Europe that began on 28 July 1914 and lasted until 11 November 1918...
, Hindenburg
Paul von Hindenburg
Paul Ludwig Hans Anton von Beneckendorff und von Hindenburg , known universally as Paul von Hindenburg was a Prussian-German field marshal, statesman, and politician, and served as the second President of Germany from 1925 to 1934....
won critical victories at Tannenberg
Battle of Tannenberg (1914)
The Battle of Tannenberg was an engagement between the Russian Empire and the German Empire in the first days of World War I. It was fought by the Russian First and Second Armies against the German Eighth Army between 23 August and 30 August 1914. The battle resulted in the almost complete...
and the Masurian Lakes
Battle of the Masurian Lakes
During World War I, there was:* First Battle of the Masurian Lakes, September 1914* Second Battle of the Masurian Lakes, February 1915...
, ejecting Russian forces from East Prussia.
Numerous figures in German history were either born or resident in the former eastern territories. The list includes politicians, statesmen and national leaders such as Friedrich von Gentz
Friedrich von Gentz
Friedrich von Gentz was a German publicist and statesman.-Early years:Gentz was born at Breslau.His father was an official, his mother distantly related to the Prussian minister Friedrich Ancillon...
, Adalbert Falk, Ferdinand Lassalle
Ferdinand Lassalle
Ferdinand Lassalle was a German-Jewish jurist and socialist political activist.-Early life:Ferdinand Lassalle was born on 11 April 1825 in Breslau , Silesia to a prosperous Jewish family descending from Upper Silesian Loslau...
and Eduard Lasker
Eduard Lasker
Eduard Lasker was a German politician and jurist.-Biography:He was born at Jarotschin, a village in Posen, being the son of a Jewish tradesman. He attended the gymnasium, and afterwards the University of Breslau...
; Catherine the Great, Empress of Russia; Chancellors Leo von Caprivi
Leo von Caprivi
Georg Leo Graf von Caprivi de Caprera de Montecuccoli was a German major general and statesman, who succeeded Otto von Bismarck as Chancellor of Germany...
and Georg Michaelis
Georg Michaelis
Georg Michaelis became the first Chancellor of Germany with a non-noble background.-Biography :Michaelis, born in Haynau in the Prussian Province of Silesia, grew up in Frankfurt...
and the jurist Helmuth James Graf von Moltke
Helmuth James Graf von Moltke
Helmuth James Graf von Moltke was a German jurist who, as a draftee in the German Abwehr, acted to subvert German human-rights abuses of people in territories occupied by Germany during World War II and subsequently became a founding member of the Kreisau Circle resistance group, whose members...
. Field Marshals Paul von Hindenburg
Paul von Hindenburg
Paul Ludwig Hans Anton von Beneckendorff und von Hindenburg , known universally as Paul von Hindenburg was a Prussian-German field marshal, statesman, and politician, and served as the second President of Germany from 1925 to 1934....
, Hermann von Eichhorn
Hermann von Eichhorn
Hermann von Eichhorn was a Prussian general.-Biography:Eichhorn was born in Breslau in the Province of Silesia...
and Günther von Kluge
Günther von Kluge
Günther Adolf Ferdinand “Hans” von Kluge was a German military leader. He was born in Posen into a Prussian military family. Kluge rose to the rank of Field Marshal in the Wehrmacht. He was also a recipient of the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross with Oak Leaves and Swords...
were born in the east, as were Generals Erich von Falkenhayn
Erich von Falkenhayn
Erich von Falkenhayn was a German soldier and Chief of the General Staff during World War I. He became a military writer after World War I.-Early life:...
and Heinz Guderian
Heinz Guderian
Heinz Wilhelm Guderian was a German general during World War II. He was a pioneer in the development of armored warfare, and was the leading proponent of tanks and mechanization in the Wehrmacht . Germany's panzer forces were raised and organized under his direction as Chief of Mobile Forces...
, SS-men Erich von dem Bach-Zelewski and Kurt Daluege
Kurt Daluege
Kurt Daluege was a German Nazi SS-Oberstgruppenführer and Generaloberst der Polizei as chief of the Ordnungspolizei and ruled the Protectorate Bohemia and Moravia as Deputy Protector after Reinhard Heydrich's assassination.-Early life and career:Kurt Daluege, a son of a Prussian state official,...
, fighter ace Manfred von Richthofen
Manfred von Richthofen
Manfred Albrecht Freiherr von Richthofen , also widely known as the Red Baron, was a German fighter pilot with the Imperial German Army Air Service during World War I...
and his uncle, the geographer and explorer Ferdinand von Richthofen
Ferdinand von Richthofen
Ferdinand Freiherr von Richthofen was a German traveller, geographer, and scientist.-Biography:He was born in Carlsruhe, Prussian Silesia, and was educated in Breslau and Berlin. He traveled or studied in the Alps of Tyrol and the Carpathians in Transylvania...
. Scientists from the former eastern provinces include the physicists and mathematicians David Hilbert
David Hilbert
David Hilbert was a German mathematician. He is recognized as one of the most influential and universal mathematicians of the 19th and early 20th centuries. Hilbert discovered and developed a broad range of fundamental ideas in many areas, including invariant theory and the axiomatization of...
, Max Born
Max Born
Max Born was a German-born physicist and mathematician who was instrumental in the development of quantum mechanics. He also made contributions to solid-state physics and optics and supervised the work of a number of notable physicists in the 1920s and 30s...
, and Walther Nernst
Walther Nernst
Walther Hermann Nernst FRS was a German physical chemist and physicist who is known for his theories behind the calculation of chemical affinity as embodied in the third law of thermodynamics, for which he won the 1920 Nobel Prize in chemistry...
, and immunologist Paul Ehrlich
Paul Ehrlich
Paul Ehrlich was a German scientist in the fields of hematology, immunology, and chemotherapy, and Nobel laureate. He is noted for curing syphilis and for his research in autoimmunity, calling it "horror autotoxicus"...
. Philosophers and theologians such as Immanuel Kant
Immanuel Kant
Immanuel Kant was a German philosopher from Königsberg , researching, lecturing and writing on philosophy and anthropology at the end of the 18th Century Enlightenment....
, Arthur Schopenhauer
Arthur Schopenhauer
Arthur Schopenhauer was a German philosopher known for his pessimism and philosophical clarity. At age 25, he published his doctoral dissertation, On the Fourfold Root of the Principle of Sufficient Reason, which examined the four separate manifestations of reason in the phenomenal...
and Friedrich Daniel Ernst Schleiermacher
Friedrich Daniel Ernst Schleiermacher
Friedrich Daniel Ernst Schleiermacher was a German theologian and philosopher known for his attempt to reconcile the criticisms of the Enlightenment with traditional Protestant orthodoxy. He also became influential in the evolution of Higher Criticism, and his work forms part of the foundation of...
, and historians Heinrich Graetz
Heinrich Graetz
Heinrich Graetz was amongst the first historians to write a comprehensive history of the Jewish people from a Jewish perspective....
and Gottfried Bernhardy
Gottfried Bernhardy
Gottfried Bernhardy , German philologist and literary historian, was born at Landsberg an der Warthe in the Neumark....
. The east was home to poets Martin Opitz, Angelus Silesius
Angelus Silesius
Angelus Silesius was a German Catholic mystic and poet.-Life:Silesius was born in Breslau , Silesia as son of Polish noble and German mother...
, Andreas Gryphius
Andreas Gryphius
Andreas Gryphius was a German lyric poet and dramatist.Asteroid 496 Gryphia is named in his honour.-Life and career:...
, Friedrich von Logau, and Ewald Christian von Kleist
Ewald Christian von Kleist
Ewald Christian von Kleist was a German poet and officer.-Life:Kleist was born at Zeblin, near Köslin in Farther Pomerania, to the von Kleist family of cavalry leaders...
. Eminent cultural figures from the region included the collector of folk songs Johann Gottfried Herder
Johann Gottfried Herder
Johann Gottfried von Herder was a German philosopher, theologian, poet, and literary critic. He is associated with the periods of Enlightenment, Sturm und Drang, and Weimar Classicism.-Biography:...
and the singer, pianist, conductor and composer George Henschel
George Henschel
Sir George Henschel , was a British baritone, pianist, conductor, and composer of German birth....
; novelists and dramatists Joseph Freiherr von Eichendorff
Joseph Freiherr von Eichendorff
Joseph Freiherr von Eichendorff was a German poet and novelist of the later German romantic school.Eichendorff is regarded as one of the most important German Romantics and his works have sustained high popularity in Germany from production to the present day.-Life:Eichendorff was born at Schloß...
, Gustav Freytag
Gustav Freytag
Gustav Freytag was a German novelist and playwright.-Life:Freytag was born in Kreuzburg in Silesia...
, E. T. A. Hoffmann, Arnold Zweig
Arnold Zweig
Arnold Zweig was a German writer and anti-war activist.He is best known for his World War I tetralogy.-Life and work:Zweig was born in Glogau, Silesia son of a Jewish saddler...
, Gerhart Hauptmann
Gerhart Hauptmann
Gerhart Hauptmann was a German dramatist and novelist who received the Nobel Prize in Literature in 1912.-Life and work:...
and Günter Grass
Günter Grass
Günter Wilhelm Grass is a Nobel Prize-winning German author, poet, playwright, sculptor and artist.He was born in the Free City of Danzig...
; painters Karl Friedrich Lessing
Karl Friedrich Lessing
Karl Friedrich Lessing was a German historical and landscape painter, grandnephew of Gotthold Ephraim Lessing. He was born near Breslau, and was a pupil of Heinrich Anton Dähling at the Berlin Academy. He first devoted himself to landscape and in 1826 obtained a prize with his Cemetery in Ruins...
and Adolph Menzel.
See also
- Former eastern territories of Germany :
- History of German settlement in Eastern EuropeHistory of German settlement in Eastern EuropeThe presence of German-speaking populations in Central and Eastern Europe is rooted in centuries of history, with the settling in northeastern Europe of Germanic peoples predating even the founding of the Roman Empire...
- OstsiedlungOstsiedlungOstsiedlung , also called German eastward expansion, was the medieval eastward migration and settlement of Germans from modern day western and central Germany into less-populated regions and countries of eastern Central Europe and Eastern Europe. The affected area roughly stretched from Slovenia...
- Drang nach OstenDrang nach OstenDrang nach Osten was a term coined in the 19th century to designate German expansion into Slavic lands. The term became a motto of the German nationalist movement in the late nineteenth century...
- History of German settlement in Eastern Europe
- Major treaties affecting the former eastern territories of Germany:
- Congress of ViennaCongress of ViennaThe Congress of Vienna was a conference of ambassadors of European states chaired by Klemens Wenzel von Metternich, and held in Vienna from September, 1814 to June, 1815. The objective of the Congress was to settle the many issues arising from the French Revolutionary Wars, the Napoleonic Wars,...
- Treaty of Frankfurt (1871)Treaty of Frankfurt (1871)The Treaty of Frankfurt was a peace treaty signed in Frankfurt on 10 May 1871, at the end of the Franco-Prussian War.- Summary :The treaty did the following:...
- Treaty of Brest-LitovskTreaty of Brest-LitovskThe Treaty of Brest-Litovsk was a peace treaty signed on March 3, 1918, mediated by South African Andrik Fuller, at Brest-Litovsk between Russia and the Central Powers, headed by Germany, marking Russia's exit from World War I.While the treaty was practically obsolete before the end of the year,...
- Congress of Vienna
- Territorial changes of Poland and Germany:
- Partitions of PolandPartitions of PolandThe Partitions of Poland or Partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth took place in the second half of the 18th century and ended the existence of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, resulting in the elimination of sovereign Poland for 123 years...
- Territorial changes of PolandTerritorial changes of PolandPoland is a country in Central Europe bordered by Germany to the west; the Czech Republic and Slovakia to the south; Ukraine, Belarus and Lithuania to the east; and the Baltic Sea and Kaliningrad Oblast, a Russian exclave, to the north...
- Territorial changes of GermanyTerritorial changes of GermanyThe territorial changes of Germany refer to the changes in the borders and territory of Germany from its formation in 1871 to the present. Modern Germany was formed in 1871 when Otto von Bismarck unified most of the German-speaking states into the German Empire...
- Partitions of Poland
- World War II evacuation and expulsionWorld War II evacuation and expulsionForced deportation, mass evacuation and displacement of peoples took place in many of the countries involved in World War II. These were caused both by the direct hostilities between Axis and Allied powers, and the border changes enacted in the pre-war settlement...
- Ethnic cleansing of Polish people by Germany on those territories
- Expulsion of Poles by GermanyExpulsion of Poles by GermanyThe Expulsion of Poles by Germany was a prolonged anti-Polish campaign of ethnic cleansing by violent and terror-inspiring means lasting nearly a century. It began with the concept of Pan-Germanism developed in early 19th century and continued in the racial policy of Nazi Germany asserting the...
- Expulsion of Poles by Germany
- Evacuation, flight and expulsion of Germans from the those territories:
- Evacuation of German civilians during the end of World War II
- Evacuation of East PrussiaEvacuation of East PrussiaThe evacuation of East Prussia refers to the evacuation of the German civilian population and military personnel in East Prussia and the Klaipėda region between 20 January, and March 1945, as part of the evacuation of German civilians towards the end of World War II...
- German exodus from Eastern EuropeGerman exodus from Eastern EuropeThe German exodus from Eastern Europe describes the dramatic reduction of ethnic German populations in lands to the east of present-day Germany and Austria. The exodus began in the aftermath of World War I and was implicated in the rise of Nazism. It culminated in expulsions of Germans from...
- Flight and expulsion of Germans during and after WWII
- Flight and expulsion of Germans from Poland after World War II
- Expulsion of Germans after World War IIExpulsion of Germans after World War IIThe later stages of World War II, and the period after the end of that war, saw the forced migration of millions of German nationals and ethnic Germans from various European states and territories, mostly into the areas which would become post-war Germany and post-war Austria...
- Polish settlement:
- Kresy ZachodnieKresy ZachodnieKresy Zachodnie is a term used by Poles, mostly in a historical context, to refer to the western parts of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth that in the partitions were annexed by Prussia...
- Recovered TerritoriesRecovered TerritoriesRecovered or Regained Territories was an official term used by the People's Republic of Poland to describe those parts of pre-war Germany that became part of Poland after World War II...
of Poland - Repatriation of Poles (1944–1946)
- Kresy Zachodnie
- Former eastern territories of Germany annexed by the Soviet Union:
- Kaliningrad oblastKaliningrad OblastKaliningrad Oblast is a federal subject of Russia situated on the Baltic coast. It has a population of The oblast forms the westernmost part of the Russian Federation, but it has no land connection to the rest of Russia. Since its creation it has been an exclave of the Russian SFSR and then the...
of RussiaRussiaRussia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
(former Northern East Prussia) - KlaipėdaKlaipedaKlaipėda is a city in Lithuania situated at the mouth of the Nemunas River where it flows into the Baltic Sea. It is the third largest city in Lithuania and the capital of Klaipėda County....
in Lithuania (former Memel territory)
- Kaliningrad oblast
Further reading
- Emotions prevail in relations between Germans, Czechs, Poles – poll, Czech Happenings, 21 December 2005
- Jose Ayala LassoJose Ayala LassoJosé Ayala Lasso is a retired Ecuadorian lawyer and diplomat, currently residing in Quito. He served as Foreign Minister of Ecuador on three occasions.- Career :...
. Speech to the German expellees, Day of the Homeland, Berlin 6 August 2005 Lasso was the first United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights (1994–1997) - Ryszard W. Piotrowicz. The Status of Germany in International Law: Deutschland uber Deutschland? The International and Comparative Law Quarterly, Vol. 38, No. 3 (Jul., 1989), pp. 609–635 "The purpose of this article is to consider the legal status of Germany from 1945 to [1989]"

