Indo-Pakistani relations
Encyclopedia
Relations between India and Pakistan have been strained by a number of historical and political issues, and are defined by the violent partition of British India
in 1947, the Kashmir dispute and the numerous military conflicts
fought between the two nations. Consequently, even though the two South Asia
n nations share historic, cultural, geographic, and economic links, their relationship has been plagued by hostility and suspicion.
After the dissolution of the British Raj
in 1947, two new sovereign nations were formed—the Union of India and the Dominion of Pakistan
. The subsequent partition of the former British India displaced up to 12.5 million people, with estimates of loss of life varying from several hundred thousand to a million. India
emerged as a secular nation with a Hindu majority
population and a large Muslim minority
while Pakistan
was established as an Islamic republic
with an overwhelming Muslim majority
population.
Soon after their independence, India and Pakistan established diplomatic relations but the violent partition and numerous territorial disputes would overshadow their relationship. Since their independence, the two countries have fought three major wars, one undeclared war
and have been involved in numerous armed skirmishes and military standoffs. The Kashmir dispute is the main center-point of all of these conflicts with the exception of the Indo-Pakistan War of 1971, which resulted in the secession of East Pakistan
(now Bangladesh
).
There have been numerous attempts to improve the relationship—notably, the Shimla summit, the Agra summit
and the Lahore summit. Since the early 1980s, relations between the two nations soured particularly after the Siachen conflict
, the intensification of Kashmir insurgency in 1989, Indian
and Pakistani
nuclear tests in 1998 and the 1999 Kargil war
. Certain confidence-building measures—such as the 2003 ceasefire agreement and the Delhi–Lahore Bus service—were successful in deescalating tensions. However, these efforts have been impeded by periodic terrorist attacks. The 2001 Indian Parliament attack
almost brought the two nations on the brink of a nuclear war. The 2007 Samjhauta Express bombings
, which killed 68 civilians (most of whom were Pakistani), was also a crucial point in relations. Additionally, the 2008 Mumbai attacks
carried out by Pakistani militants resulted in a severe blow to the ongoing India-Pakistan peace talks.
 About half a million Muslims and Hindus were killed in communal riots following the partition of British India. Millions of Muslims living in India and Hindus and Sikhs living in Pakistan emigrated in one of the most colossal transfers of population in the modern era. Both countries accused each other of not providing adequate security to the minorities emigrating through their territory. This served to increase tensions between the newly-born countries.
About half a million Muslims and Hindus were killed in communal riots following the partition of British India. Millions of Muslims living in India and Hindus and Sikhs living in Pakistan emigrated in one of the most colossal transfers of population in the modern era. Both countries accused each other of not providing adequate security to the minorities emigrating through their territory. This served to increase tensions between the newly-born countries.
According to the British plan for the partition of British India, all the 680 princely states were allowed to decide which of the two countries to join. With the exception of a few, most of the Muslim-majority princely-states acceded to Pakistan while most of the Hindu-majority princely states joined India. However, the decisions of some of the princely-states would shape the Pakistan-India relationship considerably in the years to come.
 Junagadh
Junagadh
was a state on the southwestern end of Gujarat, with the principalities of Manavadar, Mangrol and Babriawad. The Arabian Sea
stood between it and Pakistan. The state had an overwhelming Hindu population which constituted more than 80% of its citizens, while the ruler of the state was a Muslim. On August 15, 1947, the ruler of the state, Nawab of Junagadh Mahabat Khan, acceded to Pakistan. Pakistan confirmed the acceptance of the accession in September 1947. India did not accept the accession as legitimate.
The Indian point of view was that since Junagadh was a state with a predominantly Hindu population it should be a part of India. Additionally, since the state was encircled by Indian territory it should have been a part of India. Indian politicians also stated that by giving Pakistan a predominantly Hindu region to govern, the basis of the two nation theory was contradicted.
The Pakistani point of view was that since Junagadh had a ruler and governing body who chose to accede to Pakistan, they should be allowed to do so. Junagadh, having a coastline, could have maintained maritime links with Pakistan. Additionally, Pakistani politicians stated that the two nation theory did not necessarily mean a clear division of land and absolute transfer of populations as the sheer magnitude of such a proceeding would wreak havoc upon millions.
Neither of the ten states were able to resolve this issue amicably and it only added fuel to an already charged environment.
Sardar Patel, India's then Home Minister, felt that if Junagadh was permitted to go to Pakistan, it would create communal unrest across Gujarat. The government of India gave Pakistan time to void the accession and hold a plebiscite in Junagadh to pre empt any violence in Gujarat. Samaldas Gandhi
formed a government-in-exile, the Arzi Hukumat (in Urdu
: Arzi: Transitional, Hukumat: Government) of the people of Junagadh. Patel ordered the annexation of Junagadh's three principalities.
was a princely state, ruled by a Hindu
king, Maharaja Hari Singh
. The Maharaja
of Kashmir was equally hesitant to join either India–, because he knew his Muslim subjects would not like to join a Hindu-based and Hindu-majority nation–, or Pakistan– which as a Hindu he was personally averse to. Pakistan coveted the Himalayan kingdom, while Indian leader Mahatma Gandhi
and Indian PM
Jawaharlal Nehru
hoped that the kingdom would join India. Hari Singh signed a Standstill Agreement (preserving status quo) with Pakistan, but did not make his decision by August 15, 1947.
Rumours spread in Pakistan that Hari Singh was trying to accede Kashmir to India. Alarmed by this threat, a team of Pakistani forces were dispatched into Kashmir, fearing an Indian invasion of the region. Backed by Pakistani paramilitary forces, Pashtuns
invaded Kashmir in September 1947. Kashmir's security forces were too weak and ill-equipped to fight against Pakistan. Troubled by the deteriorating political pressure that was being applied to Hari Singh and his governance, the Maharaja asked for India's help. However, the Constitution of India
barred the Indian Armed Forces
' intervention since Kashmir did not come under India's jurisdiction. Desperate to get India's help and get Kashmir back in his own control, the Maharaja acceded Kashmir to India (which was against the will of the majority of Kashmiris), and signed the Instrument of Accession
. By this time the raiders were close to the capital, Srinagar
. On October 27, 1947, the Indian Air Force
airdropped Indian troops into Srinagar and made an intervention. The Indian troops managed to seize parts of Kashmir which included Jammu
, Srinagar
and the Kashmir valley itself, but the strong and intense fighting, flagged with the onset of winter, made much of the state impassable. After weeks of intense fighting between Pakistan and India, Pakistani leaders and the Indian Prime Minister Nehru declared a ceasefire and sought U.N. arbitration with the promise of a plebiscite. Sardar Patel had argued against both, describing Kashmir as a bilateral dispute and its accession as justified by international law
. In 1957, north-western Kashmir was fully integrated into Pakistan, becoming Azad Kashmir
(Pakistan-administered Kashmir), while the other portion was acceded to Indian control, and the state of Jammu and Kashmir
(Indian-administered Kashmir) was created. In 1962, China
occupied Aksai Chin
, the northeastern region bordering Ladakh
. In 1984, India launched Operation Meghdoot
and captured more than 80% of the Siachen Glacier
.
Pakistan maintains Kashmiris' rights to self-determination through a plebiscite in accordance with an earlier Indian statement and a UN resolution. Pakistan also points to India's failure of not understanding its own political logic and applying it to Kashmir, by taking their opinion on the case of the accession of Junagadh as an example (that the Hindu majority state should have gone to India even though it had a Muslim ruler), that Kashmir should also rightfully and legally have become a part of Pakistan since majoirity of the people were Muslim, even though they had a Hindu ruler. Pakistan also states that at the very least, the promised plebiscite should be allowed to decide the fate of the Kashmiri people.
India on the other hand asserts that the Maharaja's decision, which was the norm for every other princely state at the time of independence, and subsequent elections, for over 40 years, on Kashmir has made it an integral part of India. This opinion has often become controversial, as Pakistan asserts that the decision of the ruler of Junagadh also adhered to Pakistan. Due to all such political differences, this dispute has also been the subject of wars between the two countries in 1947 and 1965, and a limited conflict in 1999. The state/province remains divided between the two countries by the Line of Control
(LoC), which demarcates the ceasefire line agreed upon in the 1947 conflict.
and Kori Creek
. Pakistan is also currently having dialogue with India regarding the Baglihar Dam
being built over the River Chenab in Jammu and Kashmir
.
governs the rivers that flow from India into Pakistan. Water is cited as one possible cause for a conflict between the two nations, but to date issues such as the Nimoo Bazgo Project
have been resolved through diplomacy.
and other states from East Pakistan
(now Bangladesh), owing to communal violence, intimidation and repression from authorities. The plight of the refugees outraged Hindus and Indian nationalists, and the refugee population drained the resources of Indian states, which were unable to absorb them. While not ruling out war, Prime Minister Nehru and Sardar Patel invited Liaquat Ali Khan
for talks in Delhi. Although many Indians termed this appeasement, Nehru signed a pact with Liaquat Ali Khan that pledged both nations to the protection of minorities and creation of minority commissions. Although opposed to the principle, Patel decided to back this Pact for the sake of peace, and played a critical role in garnering support from West Bengal and across India, and enforcing the provisions of the Pact. Khan and Nehru also signed a trade agreement, and committed to resolving bilateral disputes through peaceful means. Steadily, hundreds of thousands of Hindus returned to East Pakistan, but the thaw in relations did not last long, primarily owing to the Kashmir dispute.
and East Pakistan
. East Pakistan was occupied mostly by Bengali people
. In December 1971, following a political crisis in East Pakistan, the situation soon spiralled out of control in East Pakistan and India intervened in favour of the rebelling Bengali populace. The conflict, a brief but bloody war, resulted in an independence of East Pakistan. In the war, the Pakistani army swiftly fell to India, forcing the independence of East Pakistan, which separated and became Bangladesh
. The Pakistani military, being a thousand miles from its base and surrounded by enemies, was forced to give in.
and Pakistani President Zulfikar Ali Bhutto
met in the Indian hill station of Simla
. They signed the Simla Agreement, by which India would return all Pakistani personnel (over 90,000) and captured territory in the west, and the two countries would "settle their differences by peaceful means through bilateral negotiations." Diplomatic and trade relations were also re-established in 1976.
intervened
to protect the fragile communist government, and to prevent the collapse of Afghanistan Soviet Socialist Republic (Afghanistan SSR) into the hands of hard-line Islamist forces. With the deployment of Soviet Union's 40th Army
, new strains appeared in Indo-Pakistani relations, and proxy war between India and Pakistan began to take place first time in Afghanistan. Pakistan, with the backing of the United States
, actively supported the Afghan resistance against the Soviet Union
, which was a close ally of India, which brought opposing political opinions. India, on other hand, supported the communist government and vital support to communist government was provided by India.
After the Taliban regime in Afghanistan, after defeating the Northern Alliance
in much part of Afghanistan in recent civil war. Taliban regime was strongly supported by Pakistan – one of the few countries to do so – before the September 11 attacks. India firmly opposed the Taliban and criticized Pakistan for supporting it. India established its links with Northern Alliance
as India officially recognized their government, with the United Nations
. India's relations with Afghanistan, Pakistan's neighbor, and its increasing presence there has been a factor that has irked Pakistan and consequently compromised its own relations with Afghanistan.
. In an effort to curtail tensions, the two countries formed a joint commission to examine disputes. In December 1988, Prime Ministers Benazir Bhutto
and Rajiv Gandhi
concluded a pact not to attack each other's nuclear facilities. Agreements on cultural exchanges and civil aviation were also initiated.
In 1997, high-level Indo-Pakistan talks resumed after a three-year pause. The Prime Ministers of Pakistan and India met twice and the foreign secretaries conducted three rounds of talks. In June 1997, the foreign secretaries identified eight "outstanding issues" around which continuing talks would be focused. The dispute over the status of Kashmir, (referred by India as Jammu and Kashmir), an issue since Independence, remains the major stumbling block in their dialogue. India maintains that the entire former princely state is an integral part of the Indian union, while Pakistan insists that UN resolutions calling for self-determination of the people of the state/province must be taken into account. It however refuses to abide by the previous part of the resolution, which calls for it to vacate all territories occupied.
In September 1997, the talks broke down over the structure of how to deal with the issues of Kashmir, and peace and security. Pakistan advocated that the issues be treated by separate working group
s. India responded that the two issues be taken up along with six others on a simultaneous basis. In May 1998 India, and then Pakistan, conducted nuclear tests. (See Smiling Buddha
and Operation Shakti
(India), and Chagai-I
and Chagai-II) (Pakistan).)
After Manmohan Singh become prime minister of India the Punjab provincial Government declared it would develop Gah
, his place of birth, as a model village in his honour and name a school after him. There is also a village in India named Pakistan
, despite occasional pressure over the years to change its name the villagers have resisted.
to Ahmedabad
. That carried 200 tents and more than 2,000 Blankets. Furthermore the President called Indian PM to express his 'sympathy' over the loss from the earthquake.
including food, blankets and medicine. Large Indian companies such as Infosys
have offered aid up to $226,000. On October 12, an Ilyushin-76
cargo plane ferried across seven truckloads (about 82 ton
s) of army medicines, 15,000 blankets and 50 tents and returned to New Delhi. A senior airforce official also stated that they had been asked by the Indian government to be ready to fly out another similar consignment. On October 14, India dispatched the second consignment of relief material to Pakistan, by train through the Wagah Border. The consignment included 5,000 blankets, 370 tents, 5 tons of plastic sheets and 12 tons of medicine. A third consignment of medicine and relief material was also sent shortly afterwards by train. India also pledged $25 million as aid to Pakistan.
India
opened the first of three points at Chakan Da Bagh, in Poonch
, on the Line of Control (LoC) between India and Pakistan for the 2005 Kashmir earthquake
relief work. (Rediff) Such generous gestures signalled a new age in confidence, friendliness and cooperation between both India and Pakistan.
was a terrorist attack targeted on the Samjhauta Express
train on the 18th of February. The Samjhauta Express is an international train that runs from New Delhi, India to Lahore, Pakistan, and is one of two trains to cross the India-Pakistan border. At least 68 people were killed, mostly Pakistani civilians but also some Indian security personnel and civilians. Prasad Shrikant Purohit
, an Indian Army officer, was later identified and investigated as a key suspect responsible for the bombing. The attack was a turning point in Indo-Pakistani relations, and one of the many terrorist incidents that have plagued relations between the two.
by ten terrorists killed over 173 and wounded 308. The sole surviving gunman Ajmal Kasab
who was arrested during the attacks was found to be a Pakistani national. This fact was acknowledged by Pakistani authorities. In May 2010, an Indian court convicted him on four counts of murder
, waging war against India, conspiracy
and terrorism
offences, and sentenced him to death.
India blamed the Lashkar-e-Taiba
, a Pakistan-based militant group, for planning and executing the attacks. Islamabad resisted the claims and demanded evidence. India provided evidence in the form of interrogations, weapons, candy wrappers, Pakistani Brand Milk Packets, and telephone sets. Indian officials demanded Pakistan extradite suspects for trial. They also said that, given the sophistication of the attacks, the perpetrators "must have had the support of some official agencies in Pakistan".
apart from on the Indian Parliament in December 2001. The dead bodies of the terrorists and the data recovered from them revealed that Pakistan was solely responsible for the activity.
confrontation in 2001–02. However, international peace efforts ensured the cooling of tensions between the two nuclear-capable nations.
Apart from this, the most notable was the hijacking
of Indian Airlines Flight IC 814
en route New Delhi from Kathmandu, Nepal
. The plane was hijacked on December 24, 1999 approximately one hour after take off and was taken to Amritsar
airport and then to Lahore
in Pakistan. After refueling the plane took off for Dubai
and then finally landed in Kandahar
, Afghanistan
. Under intense media pressure, New Delhi complied with the hijackers' demand and freed Maulana Masood Azhar
from its captivity in return for the freedom of the Indian passengers on the flight. The decision, however, cost New Delhi dearly. Maulana, who is believed to be hiding in Karachi
, later became the leader of Jaish-e-Mohammed
, an organisation which has carried out several terrorist acts against Indian Security Forces in Kashmir.
On December 22, 2000, a group of terrorists belonging to the Lashkar-e-Toiba
stormed the famous Red Fort in New Delhi
. The Fort houses an Indian military
unit and a high-security interrogation cell used both by the Central Bureau of Investigation
and the Indian Army
. The terrorists successfully breached the security cover around the Red Fort and opened fire at the Indian military personnel on duty killing two of them on spot. The attack was significant because it was carried out just two days after the declaration of the cease-fire between India
and Pakistan
.
In 2002, India claimed again that terrorists from Jammy and Kashmir were infiltrating into India, a claim denied by Pakistan President Pervez Musharraf
, who claimed that such infiltration had stopped--India's spokesperson for the External Affairs Ministry did away with Pakistan's claim, calling it "terminological inexactitude." Only two months later, two Kashmiri terrorists belonging to Jaish-e-Mohammed
raided the Swami Narayan temple complex in Ahmedabad
, Gujarat killing 30 people, including 18 women and five children. The attack was carried out on September 25, 2002, just few days after state elections were held in Jammu and Kashmir
. Two identical letters found on both the terrorists claimed that the attack was done in retaliation for the deaths of thousands of Muslims during the Gujarat riots
.
Two car bombs exploded in south Mumbai
on August 25, 2003; one near the Gateway of India
and the other at the famous Zaveri Bazaar, killing at least 48 and injuring 150 people. Though no terrorist group claimed responsibility for the attacks, Mumbai Police and RAW
suspected Lashkar-e-Toiba
's hand in the twin blasts.
In an unsuccessful attempt, six terrorists belonging to Lashkar-e-Toiba
, stormed the Ayodhya Ram Janmbhomi complex on July 5, 2005. Before the terrorists could reach the main disputed site, they were shot down by Indian security forces. One Hindu worshipper and two police
men were injured during the incident.
2008 Mumbai attacks
The resumed relation between India and Pakistan again got strained following the 2008 Mumbai attacks
by 10 Pakistani insurgents, killing approximatively 168 people (including 28 foreign nationals and leaving injured 308).
, stated two main reasons for the improving human rights condition in the region: First, sincere efforts were made by the new Jammu and Kashmir
state government headed by Mufti Muhammad Sayeed to investigate cases of human rights abuses in the state and to punish those guilty including Indian soldiers
. More than 15 Indian army soldiers were convicted by the Indian government
in 2004 for carrying out human rights abuses in the state. Second, the decrease in cross-border infiltration into India
by armed insurgents.
and Islamabad
which consequently lead to a ceasefire
between the two countries in 2003 and the fencing of the LOC
being carried out by the Indian Army
. Moreover, coming under intense international pressure, Islamabad was compelled to take actions against the militants' training camps on its territory. In 2004, the two countries also agreed upon decreasing the number of troops present in the region.
Under pressure, Kashmiri militant organisations have made an offer for talks and negotiations with New Delhi, which India
has welcomed.
India's Border Security Force
blamed the Pakistan
i military for providing cover-fire for the terrorists whenever they infiltrated into Indian territory from Pakistan.
Pakistan in turn has also blamed India for providing support to terrorist organizations operating in Pakistan such as the BLA
.
In 2005, Pakistan's information minister, Sheikh Rashid, was alleged to have run a terrorist training camp in 1990 in N.W. Frontier, Pakistan. The Pakistani government dismissed the charges against its minister as an attempt to hamper the ongoing peace process between the two neighbours.
Both India and Pakistan have launched several mutual confidence-building measures
(CBMs) to ease tensions between the two. These include more high-level talks, easing visa
restrictions, and restarting of cricket
matches between the two. The new bus
service between Srinagar
and Muzaffarabad
has also helped bring the two sides closer. Pakistan and India have also decided to co-operate on economic fronts.
A major clash between Indian Security Forces
and militants occurred when a group of insurgents tried to infiltrate into the Indian-administered Kashmir
from Pakistan in July 2005. The same month also saw a Kashmiri militant attack on Ayodhya and Srinagar
. However, these developments had little impact on the peace process.
Some improvements in the relations are seen with the re-opening of a series of transportation networks near the India–Pakistan border, with the most important being bus routes and railway lines.
An Indian man held in Pakistani prisons since 1975 as an accused spy walked across the border to freedom March 3, 2008, an unconditional release that Pakistan said was done to improve relations between the two countries.
In 2006, a "Friends Without Borders" scheme began with the help of two British tourists. The idea was that Indian and Pakistani children would make pen pals and write friendly letters to each other. The idea was so successful in both countries that the organisation found it "impossible to keep up". The World's Largest Love Letter was recently sent from India to Pakistan.
In April 2010 a high profile Pakistani cricketer, Shoaib Malik
married the Indian tennis star Sania Mirza
. The wedding received much media attention and was said to transfix both India and Pakistan.
On 10 Feb, 2011, India agreed to resume talks with Pakistan which were suspended after 26/11 Mumbai Attacks. India had put on hold all the diplomatic relations saying it will only continue if Pakistan will act against the accused of Mumbai attacks.
movement, have gone through a lot of change in their ideology. Most of the insurgents portray their struggle as a religious one.
Indian analysts allege that by supporting these insurgents, Pakistan is trying to wage a proxy war
against India while Pakistan claims that it regards most of these insurgent
groups as "freedom fighters" rather than terrorists
Internationally known to be the most deadly theatre of conflict, nearly 10 million people, including Muslims, Hindus, and Buddhists, have been fighting a daily battle for survival. The cross-border firing between India
and Pakistan
, and the terrorist attacks combined have taken its toll on the Kashmiris, who have suffered poor living standards and an erosion of human rights.
and their signing of three agreements.
These efforts have since been stalled by the intrusion of Pakistani forces into Indian-held territory near Kargil
in Jammu and Kashmir in May 1999. This resulted in intense fighting between Indian and Pakistani forces, known as the Kargil conflict. Backed by the Indian Air Force, the Indian Army regained some of Kargil. Pakistan later withdrew from the remaining portion, under international pressure. A subsequent military coup in Pakistan that overturned the democratically elected Nawaz Sharif
government in October of the same year also proved a setback to relations.
In 2001, a summit was called in Agra
; Pakistani President
Pervez Musharraf
turned up to meet Indian Prime Minister
Atal Behari Vajpayee. The talks fell through.
On June 20, 2004, with a new government in place in India, both countries agreed to extend a nuclear testing
ban and to set up a hotline
between their foreign secretaries aimed at preventing misunderstandings that might lead to a nuclear war
. http://edition.cnn.com/2004/WORLD/asiapcf/06/20/india.pakistan
As of early 2005, both countries are committed to a process of dialogue to solve all outstanding issues. Baglihar Dam
issue was a new issue raised by Pakistan in 2005.
, of having a presence in Pakistan. On May 11, 2011, India released a list of 50 "Most Wanted Fugitives" hiding in Pakistan. This was to tactically pressurize Pakistan after the killing
of Osama bin Laden
in his compound in Abbottabad
.
After two errors in the list received publicity, the Central Bureau of Investigation
removed it from their website pending a review.After this incident the Pakistani interior ministry rejected the list of 50 Most Wanted men forwarded by India to Islamabad, saying it should first probe if those named in the list were even living in the country.
. Likewise, Indian music and films are very popular in Pakistan. Being located in the northernmost region of the Indian subcontinent
, much of Pakistan's culture is similar to that of North India
.
The Punjab region
was split into Punjab, Pakistan and Punjab, India following the independence and partition of the two countries in 1947. The Punjabi people
are today the largest ethnic group in Pakistan and also an important ethnic group of northern India. The founder of the Sikhism
religion was born in the modern-day Pakistani Punjab province, in the city of Nankana Sahib
. Each year, millions of Indian Sikh pilgrims cross over to visit holy Sikh sites in Nankana Sahib.
The Sindhi people
are the native ethnic group of the Pakistani province of Sindh
. Many Hindu Sindhis migrated to India in 1947, making the country home to a sizable Sindhi community. In addition, the millions of Muslims who migrated from India to the newly-created Pakistan during independence came to be known as as the Muhajir people
; they are settled predominantly in Karachi and still maintain family links in India.
Relations between Pakistan and India have also resumed through platforms such as media and communications. Aman ki Asha
is a joint venture and campaign between The Times of India
and the Jang Group calling for mutual peace and development of diplomatic and cultural relations.
and Gujarat from the Pakistani provinces of Punjab and Sindh. The Wagah
border is the only road crossing between India and Pakistan and lies on the famous Grand Trunk Road
, connecting Lahore
, Pakistan with Amritsar
, India. Each evening, the Wagah border ceremony
takes place at the Wagah border in which the flags are lowered and guards on both sides make a pompous military display and exchange handshakes.
, the national language in Pakistan, can usually understand a speaker of Hindi
, which is the primary official language of the Republic of India.
Apart from Hindi and Urdu, India and Pakistan also share a distribution of the Punjabi language
, Kashmiri language
and Sindhi language
.
In tennis
, Rohan Bopanna
of India and Aisam-ul-Haq Qureshi
of Pakistan have formed a successful duo and have been dubbed as the "Indo-Pak Express."
" and a "Little Pakistan
" to co-exist in South Asian ethnic enclaves in overseas countries. There are various cities such as Birmingham
, Blackburn and Manchester
where British Indian
s and British Pakistanis live alongside each other in peace and harmony. Both Indians and Pakistanis living in the UK fit under the category of British Asian
. The UK is also home to the Pakistan & India friendship forum.
In the United States, Indians and Pakistanis are classified under the South Asian American category and share many cultural traits.
The British MEP Saj Karim is of Pakistani origin. He is a member of the European Parliament Friends of India Group, Karim was also responsible for opening up Europe to free trade with India. He has given his full support to the Indian government for a death sentence to be given to Ajmal Kasab
, who was involved in the 2008 Mumbai attacks
.
Partition of India
The Partition of India was the partition of British India on the basis of religious demographics that led to the creation of the sovereign states of the Dominion of Pakistan and the Union of India on 14 and 15...
in 1947, the Kashmir dispute and the numerous military conflicts
Indo-Pakistani Wars
Since the partition of British India in 1947 and creation of India and Pakistan, the two South Asian countries have been involved in four wars, including one undeclared war, as well as many border skirmishes and military stand-offs...
fought between the two nations. Consequently, even though the two South Asia
South Asia
South Asia, also known as Southern Asia, is the southern region of the Asian continent, which comprises the sub-Himalayan countries and, for some authorities , also includes the adjoining countries to the west and the east...
n nations share historic, cultural, geographic, and economic links, their relationship has been plagued by hostility and suspicion.
After the dissolution of the British Raj
British Raj
British Raj was the British rule in the Indian subcontinent between 1858 and 1947; The term can also refer to the period of dominion...
in 1947, two new sovereign nations were formed—the Union of India and the Dominion of Pakistan
Dominion of Pakistan
The Dominion of Pakistan was an independent federal Commonwealth realm in South Asia that was established in 1947 on the partition of British India into two sovereign dominions . The Dominion of Pakistan, which included modern-day Pakistan and Bangladesh, was intended to be a homeland for the...
. The subsequent partition of the former British India displaced up to 12.5 million people, with estimates of loss of life varying from several hundred thousand to a million. India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
emerged as a secular nation with a Hindu majority
Hinduism in India
Hinduism is a religious tradition of India, with 80.5% of the population identifying themselves as Hindus. The vast majority of Hindus in India belong to Vaishnavite and Shaivite denominations.The Vedic culture originated in India between 2000 and 1500 BC...
population and a large Muslim minority
Islam in India
Islam is the second-most practiced religion in the Republic of India after Hinduism, with more than 13.4% of the country's population ....
while Pakistan
Pakistan
Pakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan...
was established as an Islamic republic
Islamic republic
Islamic republic is the name given to several states in the Muslim world including the Islamic Republics of Pakistan, Iran, Afghanistan, and Mauritania. Pakistan adopted the title under the constitution of 1956. Mauritania adopted it on 28 November 1958. Iran adopted it after the 1979 Iranian...
with an overwhelming Muslim majority
Islam in Pakistan
Islam is the official religion of the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, which has a population of about 174,578,558. The overwhelming majority of the Pakistani people are Muslims while the remaining 3-5% are Christian, Hindu, and others. Pakistan has the second largest Muslim population in the world...
population.
Soon after their independence, India and Pakistan established diplomatic relations but the violent partition and numerous territorial disputes would overshadow their relationship. Since their independence, the two countries have fought three major wars, one undeclared war
Kargil War
The Kargil War ,, also known as the Kargil conflict, was an armed conflict between India and Pakistan that took place between May and July 1999 in the Kargil district of Kashmir and elsewhere along the Line of Control...
and have been involved in numerous armed skirmishes and military standoffs. The Kashmir dispute is the main center-point of all of these conflicts with the exception of the Indo-Pakistan War of 1971, which resulted in the secession of East Pakistan
East Pakistan
East Pakistan was a provincial state of Pakistan established in 14 August 1947. The provincial state existed until its declaration of independence on 26 March 1971 as the independent nation of Bangladesh. Pakistan recognized the new nation on 16 December 1971. East Pakistan was created from Bengal...
(now Bangladesh
Bangladesh
Bangladesh , officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh is a sovereign state located in South Asia. It is bordered by India on all sides except for a small border with Burma to the far southeast and by the Bay of Bengal to the south...
).
There have been numerous attempts to improve the relationship—notably, the Shimla summit, the Agra summit
Agra summit
The Agra summit was a two-day summit held on July 15th and 16th, 2001 between Pakistani President Pervez Musharraf and Indian Prime Minister Atal Behari Vajpayee. It was organized with the aim to resolve long-standing issues between India and Pakistan....
and the Lahore summit. Since the early 1980s, relations between the two nations soured particularly after the Siachen conflict
Siachen conflict
The Siachen Conflict, sometimes referred to as the Siachen War, is a military conflict between India and Pakistan over the disputed Siachen Glacier region in Kashmir. The conflict began in 1984 with India's successful Operation Meghdoot during which it wrested control of the Siachen Glacier from...
, the intensification of Kashmir insurgency in 1989, Indian
Pokhran-II
Pokharan-II refers to test explosions of five nuclear devices, three on 11 May and two on 13 May 1998, conducted by India at the Pokhran test range. These nuclear tests resulted in a variety of sanctions against India by a number of major states....
and Pakistani
Chagai-I
The Chagai-I was a codename referring to the five underground nuclear tests conducted by Pakistan at 15:15hrs in 28th May of 1998. It was named Chagai-I, as the tests were conducted in the Chagai District...
nuclear tests in 1998 and the 1999 Kargil war
Kargil War
The Kargil War ,, also known as the Kargil conflict, was an armed conflict between India and Pakistan that took place between May and July 1999 in the Kargil district of Kashmir and elsewhere along the Line of Control...
. Certain confidence-building measures—such as the 2003 ceasefire agreement and the Delhi–Lahore Bus service—were successful in deescalating tensions. However, these efforts have been impeded by periodic terrorist attacks. The 2001 Indian Parliament attack
2001 Indian Parliament attack
The 2001 Indian Parliament attack was a high-profile attack by Lashkar-e-Toiba and Jaish-e-Mohammed terrorists against the building housing the Parliament of India in New Delhi...
almost brought the two nations on the brink of a nuclear war. The 2007 Samjhauta Express bombings
2007 Samjhauta Express bombings
The 2007 Samjhauta Express bombings were a terrorist attack that occurred around midnight on 18 February 2007 on the Samjhauta Express, a twice-weekly train service connecting Delhi, India, and Lahore, Pakistan. Bombs were set off in two carriages, both filled with passengers, just after the train...
, which killed 68 civilians (most of whom were Pakistani), was also a crucial point in relations. Additionally, the 2008 Mumbai attacks
2008 Mumbai attacks
The 2008 Mumbai attacks were more than 10 coordinated shooting and bombing attacks across Mumbai, India's largest city, by Islamist attackers who came from Pakistan...
carried out by Pakistani militants resulted in a severe blow to the ongoing India-Pakistan peace talks.
Country comparison
 India India |
 Pakistan Pakistan |
|
|---|---|---|
| Population | 1,210,193,422 | 170,600,000 |
| Area | 3,287,240 km² (1,269,210 sq mi) | 796,095 km² (307,374 sq mi) |
| Population Density | 382/km² (922/sq mi) | 214.3/km² (555/sq mi) |
| Capital | New Delhi New Delhi New Delhi is the capital city of India. It serves as the centre of the Government of India and the Government of the National Capital Territory of Delhi. New Delhi is situated within the metropolis of Delhi. It is one of the nine districts of Delhi Union Territory. The total area of the city is... |
Islamabad Islamabad Islamabad is the capital of Pakistan and the tenth largest city in the country. Located within the Islamabad Capital Territory , the population of the city has grown from 100,000 in 1951 to 1.7 million in 2011... |
| Largest City | Mumbai Mumbai Mumbai , formerly known as Bombay in English, is the capital of the Indian state of Maharashtra. It is the most populous city in India, and the fourth most populous city in the world, with a total metropolitan area population of approximately 20.5 million... |
Karachi Karachi Karachi is the largest city, main seaport and the main financial centre of Pakistan, as well as the capital of the province of Sindh. The city has an estimated population of 13 to 15 million, while the total metropolitan area has a population of over 18 million... |
| Government | Federal Federalism Federalism is a political concept in which a group of members are bound together by covenant with a governing representative head. The term "federalism" is also used to describe a system of the government in which sovereignty is constitutionally divided between a central governing authority and... republic Republic A republic is a form of government in which the people, or some significant portion of them, have supreme control over the government and where offices of state are elected or chosen by elected people. In modern times, a common simplified definition of a republic is a government where the head of... , Parliamentary democracy |
Islamic Parliamentary Republic Islamic republic Islamic republic is the name given to several states in the Muslim world including the Islamic Republics of Pakistan, Iran, Afghanistan, and Mauritania. Pakistan adopted the title under the constitution of 1956. Mauritania adopted it on 28 November 1958. Iran adopted it after the 1979 Iranian... |
| Official languages | Hindi, English English language English is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria... and 20 other official languages |
Urdu Urdu Urdu is a register of the Hindustani language that is identified with Muslims in South Asia. It belongs to the Indo-European family. Urdu is the national language and lingua franca of Pakistan. It is also widely spoken in some regions of India, where it is one of the 22 scheduled languages and an... , English English language English is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria... |
| Main Religions | 80.5% Hinduism Hinduism Hinduism is the predominant and indigenous religious tradition of the Indian Subcontinent. Hinduism is known to its followers as , amongst many other expressions... , 13.4% Islam Islam Islam . The most common are and . : Arabic pronunciation varies regionally. The first vowel ranges from ~~. The second vowel ranges from ~~~... , 2.3% Christianity Christianity Christianity is a monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus as presented in canonical gospels and other New Testament writings... , 1.9% Sikhism Sikhism Sikhism is a monotheistic religion founded during the 15th century in the Punjab region, by Guru Nanak Dev and continued to progress with ten successive Sikh Gurus . It is the fifth-largest organized religion in the world and one of the fastest-growing... , 0.8% Buddhism Buddhism Buddhism is a religion and philosophy encompassing a variety of traditions, beliefs and practices, largely based on teachings attributed to Siddhartha Gautama, commonly known as the Buddha . The Buddha lived and taught in the northeastern Indian subcontinent some time between the 6th and 4th... , 0.4% Jainism Jainism Jainism is an Indian religion that prescribes a path of non-violence towards all living beings. Its philosophy and practice emphasize the necessity of self-effort to move the soul towards divine consciousness and liberation. Any soul that has conquered its own inner enemies and achieved the state... |
95-98% Islam Islam Islam . The most common are and . : Arabic pronunciation varies regionally. The first vowel ranges from ~~. The second vowel ranges from ~~~... (80-95% Sunni Sunni Islam Sunni Islam is the largest branch of Islam. Sunni Muslims are referred to in Arabic as ʾAhl ūs-Sunnah wa āl-Ǧamāʿah or ʾAhl ūs-Sunnah for short; in English, they are known as Sunni Muslims, Sunnis or Sunnites.... , 5-20% Shi'a Shi'a Islam Shia Islam is the second largest denomination of Islam. The followers of Shia Islam are called Shi'ites or Shias. "Shia" is the short form of the historic phrase Shīʻatu ʻAlī , meaning "followers of Ali", "faction of Ali", or "party of Ali".Like other schools of thought in Islam, Shia Islam is... ), 1.6% Christianity Christianity Christianity is a monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus as presented in canonical gospels and other New Testament writings... , 1.6% Hinduism Hinduism Hinduism is the predominant and indigenous religious tradition of the Indian Subcontinent. Hinduism is known to its followers as , amongst many other expressions... , others |
| GDP (nominal) | $1.537 trillion ($1,265 per capita Per capita Per capita is a Latin prepositional phrase: per and capita . The phrase thus means "by heads" or "for each head", i.e. per individual or per person... ) |
$174.866 billion ($1,049 per capita Per capita Per capita is a Latin prepositional phrase: per and capita . The phrase thus means "by heads" or "for each head", i.e. per individual or per person... ) |
| GDP (PPP) | $4.06 trillion ($3,339 per capita Per capita Per capita is a Latin prepositional phrase: per and capita . The phrase thus means "by heads" or "for each head", i.e. per individual or per person... ) |
$464 billion ($2400 per capita Per capita Per capita is a Latin prepositional phrase: per and capita . The phrase thus means "by heads" or "for each head", i.e. per individual or per person... ) |
| Military expenditures | $36.03 billion (1.83% of GDP) | $5.1 billion (2.8% of GDP) |
Seeds of conflict during independence

According to the British plan for the partition of British India, all the 680 princely states were allowed to decide which of the two countries to join. With the exception of a few, most of the Muslim-majority princely-states acceded to Pakistan while most of the Hindu-majority princely states joined India. However, the decisions of some of the princely-states would shape the Pakistan-India relationship considerably in the years to come.
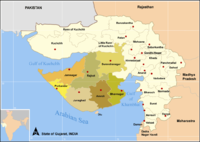
Junagadh dispute

Junagadh
Junagadh is the headquarters of Junagadh district in the Indian state of Gujarat. The city is the 7th largest in Gujarat. The city is located at the foot of the Girnar hills, 355 km south west of state capital Gandhinagar and Ahmedabad. The city is in western India. Literally translated,...
was a state on the southwestern end of Gujarat, with the principalities of Manavadar, Mangrol and Babriawad. The Arabian Sea
Arabian Sea
The Arabian Sea is a region of the Indian Ocean bounded on the east by India, on the north by Pakistan and Iran, on the west by the Arabian Peninsula, on the south, approximately, by a line between Cape Guardafui in northeastern Somalia and Kanyakumari in India...
stood between it and Pakistan. The state had an overwhelming Hindu population which constituted more than 80% of its citizens, while the ruler of the state was a Muslim. On August 15, 1947, the ruler of the state, Nawab of Junagadh Mahabat Khan, acceded to Pakistan. Pakistan confirmed the acceptance of the accession in September 1947. India did not accept the accession as legitimate.
The Indian point of view was that since Junagadh was a state with a predominantly Hindu population it should be a part of India. Additionally, since the state was encircled by Indian territory it should have been a part of India. Indian politicians also stated that by giving Pakistan a predominantly Hindu region to govern, the basis of the two nation theory was contradicted.
The Pakistani point of view was that since Junagadh had a ruler and governing body who chose to accede to Pakistan, they should be allowed to do so. Junagadh, having a coastline, could have maintained maritime links with Pakistan. Additionally, Pakistani politicians stated that the two nation theory did not necessarily mean a clear division of land and absolute transfer of populations as the sheer magnitude of such a proceeding would wreak havoc upon millions.
Neither of the ten states were able to resolve this issue amicably and it only added fuel to an already charged environment.
Sardar Patel, India's then Home Minister, felt that if Junagadh was permitted to go to Pakistan, it would create communal unrest across Gujarat. The government of India gave Pakistan time to void the accession and hold a plebiscite in Junagadh to pre empt any violence in Gujarat. Samaldas Gandhi
Samaldas Gandhi
Samaldas Gandhi was an Indian freedom fighter who headed the Aarzi Hukumat or Temporary Government of the erstwhile princely state of Junagadh.-Early life:...
formed a government-in-exile, the Arzi Hukumat (in Urdu
Urdu
Urdu is a register of the Hindustani language that is identified with Muslims in South Asia. It belongs to the Indo-European family. Urdu is the national language and lingua franca of Pakistan. It is also widely spoken in some regions of India, where it is one of the 22 scheduled languages and an...
: Arzi: Transitional, Hukumat: Government) of the people of Junagadh. Patel ordered the annexation of Junagadh's three principalities.
Kashmir dispute
KashmirKashmir
Kashmir is the northwestern region of the Indian subcontinent. Until the mid-19th century, the term Kashmir geographically denoted only the valley between the Great Himalayas and the Pir Panjal mountain range...
was a princely state, ruled by a Hindu
Hindu
Hindu refers to an identity associated with the philosophical, religious and cultural systems that are indigenous to the Indian subcontinent. As used in the Constitution of India, the word "Hindu" is also attributed to all persons professing any Indian religion...
king, Maharaja Hari Singh
Hari Singh
Maharaja Hari Singh was the last ruling Maharaja of the princely state of Jammu and Kashmir in India.He was married four times...
. The Maharaja
Maharaja
Mahārāja is a Sanskrit title for a "great king" or "high king". The female equivalent title Maharani denotes either the wife of a Maharaja or, in states where that was customary, a woman ruling in her own right. The widow of a Maharaja is known as a Rajamata...
of Kashmir was equally hesitant to join either India–, because he knew his Muslim subjects would not like to join a Hindu-based and Hindu-majority nation–, or Pakistan– which as a Hindu he was personally averse to. Pakistan coveted the Himalayan kingdom, while Indian leader Mahatma Gandhi
Mahatma Gandhi
Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi , pronounced . 2 October 1869 – 30 January 1948) was the pre-eminent political and ideological leader of India during the Indian independence movement...
and Indian PM
Prime Minister of India
The Prime Minister of India , as addressed to in the Constitution of India — Prime Minister for the Union, is the chief of government, head of the Council of Ministers and the leader of the majority party in parliament...
Jawaharlal Nehru
Jawaharlal Nehru
Jawaharlal Nehru , often referred to with the epithet of Panditji, was an Indian statesman who became the first Prime Minister of independent India and became noted for his “neutralist” policies in foreign affairs. He was also one of the principal leaders of India’s independence movement in the...
hoped that the kingdom would join India. Hari Singh signed a Standstill Agreement (preserving status quo) with Pakistan, but did not make his decision by August 15, 1947.
Rumours spread in Pakistan that Hari Singh was trying to accede Kashmir to India. Alarmed by this threat, a team of Pakistani forces were dispatched into Kashmir, fearing an Indian invasion of the region. Backed by Pakistani paramilitary forces, Pashtuns
Pashtun people
Pashtuns or Pathans , also known as ethnic Afghans , are an Eastern Iranic ethnic group with populations primarily between the Hindu Kush mountains in Afghanistan and the Indus River in Pakistan...
invaded Kashmir in September 1947. Kashmir's security forces were too weak and ill-equipped to fight against Pakistan. Troubled by the deteriorating political pressure that was being applied to Hari Singh and his governance, the Maharaja asked for India's help. However, the Constitution of India
Constitution of India
The Constitution of India is the supreme law of India. It lays down the framework defining fundamental political principles, establishes the structure, procedures, powers, and duties of government institutions, and sets out fundamental rights, directive principles, and the duties of citizens...
barred the Indian Armed Forces
Indian Armed Forces
The Indian Armed Forces are the military forces of the Republic of India. They consist of the Army, Navy and Air Force, supported by three paramilitary forces and various inter-service institutions such as the Strategic Forces Command.The President of India is...
' intervention since Kashmir did not come under India's jurisdiction. Desperate to get India's help and get Kashmir back in his own control, the Maharaja acceded Kashmir to India (which was against the will of the majority of Kashmiris), and signed the Instrument of Accession
Instrument of Accession
The Instrument of Accession was a legal document created in 1947 to enable each of the rulers of the princely states under British suzerainty to join one of the new dominions of India or Pakistan created by the Partition of British India.-Background:...
. By this time the raiders were close to the capital, Srinagar
Srinagar
Srinagar is the summer seasonal capital of Jammu and Kashmir. It is situated in Kashmir Valley and lies on the banks of the Jhelum River, a tributary of the Indus. It is one of the largest cities in India not to have a Hindu majority. The city is famous for its gardens, lakes and houseboats...
. On October 27, 1947, the Indian Air Force
Indian Air Force
The Indian Air Force is the air arm of the Indian armed forces. Its primary responsibility is to secure Indian airspace and to conduct aerial warfare during a conflict...
airdropped Indian troops into Srinagar and made an intervention. The Indian troops managed to seize parts of Kashmir which included Jammu
Jammu
Jammu , also known as Duggar, is one of the three administrative divisions within Jammu and Kashmir, the northernmost state in India.Jammu city is the largest city in Jammu and the winter capital of Jammu and Kashmir...
, Srinagar
Srinagar
Srinagar is the summer seasonal capital of Jammu and Kashmir. It is situated in Kashmir Valley and lies on the banks of the Jhelum River, a tributary of the Indus. It is one of the largest cities in India not to have a Hindu majority. The city is famous for its gardens, lakes and houseboats...
and the Kashmir valley itself, but the strong and intense fighting, flagged with the onset of winter, made much of the state impassable. After weeks of intense fighting between Pakistan and India, Pakistani leaders and the Indian Prime Minister Nehru declared a ceasefire and sought U.N. arbitration with the promise of a plebiscite. Sardar Patel had argued against both, describing Kashmir as a bilateral dispute and its accession as justified by international law
International law
Public international law concerns the structure and conduct of sovereign states; analogous entities, such as the Holy See; and intergovernmental organizations. To a lesser degree, international law also may affect multinational corporations and individuals, an impact increasingly evolving beyond...
. In 1957, north-western Kashmir was fully integrated into Pakistan, becoming Azad Kashmir
Azad Kashmir
Azad Jammu and Kashmir or Azad Kashmir for short, is the southernmost political entity within the Pakistani-administered part of the former princely state of Jammu and Kashmir...
(Pakistan-administered Kashmir), while the other portion was acceded to Indian control, and the state of Jammu and Kashmir
Jammu and Kashmir
Jammu and Kashmir is the northernmost state of India. It is situated mostly in the Himalayan mountains. Jammu and Kashmir shares a border with the states of Himachal Pradesh and Punjab to the south and internationally with the People's Republic of China to the north and east and the...
(Indian-administered Kashmir) was created. In 1962, China
China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
occupied Aksai Chin
Aksai Chin
Aksai Chin is one of the two main disputed border areas between China and India, and the other is South Tibet, which comprises most of India's Arunachal Pradesh. It is administered by China as part of Hotan County in the Hotan Prefecture of Xinjiang Autonomous Region, but is also claimed by India...
, the northeastern region bordering Ladakh
Ladakh
Ladakh is a region of Jammu and Kashmir, the northernmost state of the Republic of India. It lies between the Kunlun mountain range in the north and the main Great Himalayas to the south, inhabited by people of Indo-Aryan and Tibetan descent...
. In 1984, India launched Operation Meghdoot
Operation Meghdoot
Operation Meghdoot was the name given to the attack launched by the Indian Military to capture the Siachen Glacier in the disputed Kashmir region, precipitating the Siachen Conflict. Launched on 13 April 1984, this military operation was unique as the first assault launched in the world's highest...
and captured more than 80% of the Siachen Glacier
Siachen Glacier
The Siachen Glacier is located in the eastern Karakoram range in the Himalaya Mountains at about , just east of the Line of Control between India-Pakistan. India controls all of the Siachen Glacier itself, including all tributary glaciers. At long, it is the longest glacier in the Karakoram and...
.
Pakistan maintains Kashmiris' rights to self-determination through a plebiscite in accordance with an earlier Indian statement and a UN resolution. Pakistan also points to India's failure of not understanding its own political logic and applying it to Kashmir, by taking their opinion on the case of the accession of Junagadh as an example (that the Hindu majority state should have gone to India even though it had a Muslim ruler), that Kashmir should also rightfully and legally have become a part of Pakistan since majoirity of the people were Muslim, even though they had a Hindu ruler. Pakistan also states that at the very least, the promised plebiscite should be allowed to decide the fate of the Kashmiri people.
India on the other hand asserts that the Maharaja's decision, which was the norm for every other princely state at the time of independence, and subsequent elections, for over 40 years, on Kashmir has made it an integral part of India. This opinion has often become controversial, as Pakistan asserts that the decision of the ruler of Junagadh also adhered to Pakistan. Due to all such political differences, this dispute has also been the subject of wars between the two countries in 1947 and 1965, and a limited conflict in 1999. The state/province remains divided between the two countries by the Line of Control
Line of Control
The term Line of Control refers to the military control line between the Indian- and Pakistani-controlled parts of the former princely state of Jammu and Kashmir—a line which, to this day, does not constitute a legally recognized international boundary but is the de facto border...
(LoC), which demarcates the ceasefire line agreed upon in the 1947 conflict.
Wars and conflicts
India and Pakistan have fought in numerous armed conflicts since their independence. There are three major wars that have taken place between the two states, namely in 1947, 1965 and the Bangladesh Liberation War in 1971. In addition to this was the unofficial Kargil War and some border skirmishes.Other territorial disputes
Pakistan is locked in other territorial disputes with India such as the Siachen GlacierSiachen Glacier
The Siachen Glacier is located in the eastern Karakoram range in the Himalaya Mountains at about , just east of the Line of Control between India-Pakistan. India controls all of the Siachen Glacier itself, including all tributary glaciers. At long, it is the longest glacier in the Karakoram and...
and Kori Creek
Kori Creek
The Kori Creek is a creek in the Rann of Kachchh region of the Indian state of Gujarat and the Pakistani province of Sindh. It lies in the Kutch marshland.-Disputes:...
. Pakistan is also currently having dialogue with India regarding the Baglihar Dam
Baglihar Dam
Baglihar Dam , also known as Baglihar Hydroelectric Power Project, is a run-of-the-river power project on the Chenab River in the southern Doda district of the Indian state of Jammu and Kashmir. This project was conceived in 1992, approved in 1996 and construction began in 1999. The project is...
being built over the River Chenab in Jammu and Kashmir
Jammu and Kashmir
Jammu and Kashmir is the northernmost state of India. It is situated mostly in the Himalayan mountains. Jammu and Kashmir shares a border with the states of Himachal Pradesh and Punjab to the south and internationally with the People's Republic of China to the north and east and the...
.
Water rights
The Indus Waters TreatyIndus Waters Treaty
The Indus Waters Treaty is a water-sharing treaty between the Republic of India and Islamic Republic Of Pakistan, brokered by the World Bank . The treaty was signed in Karachi on September 19, 1960 by Indian Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru and President of Pakistan Mohammad Ayub Khan...
governs the rivers that flow from India into Pakistan. Water is cited as one possible cause for a conflict between the two nations, but to date issues such as the Nimoo Bazgo Project
Nimoo Bazgo Project
The Nimoo Bazgo power project is a run-of-the-river power project on the Indus River situated at village Alchi, 70 kilometers from Leh in the Indian state of Jammu and Kashmir. The project was conceived on July 1, 2001 and approved on June 8, 2005, and construction began on June 9, 2005...
have been resolved through diplomacy.
Bengal refugee crisis
In 1949, India recorded close to 1 million Hindu refugees, who flooded into West BengalWest Bengal
West Bengal is a state in the eastern region of India and is the nation's fourth-most populous. It is also the seventh-most populous sub-national entity in the world, with over 91 million inhabitants. A major agricultural producer, West Bengal is the sixth-largest contributor to India's GDP...
and other states from East Pakistan
East Pakistan
East Pakistan was a provincial state of Pakistan established in 14 August 1947. The provincial state existed until its declaration of independence on 26 March 1971 as the independent nation of Bangladesh. Pakistan recognized the new nation on 16 December 1971. East Pakistan was created from Bengal...
(now Bangladesh), owing to communal violence, intimidation and repression from authorities. The plight of the refugees outraged Hindus and Indian nationalists, and the refugee population drained the resources of Indian states, which were unable to absorb them. While not ruling out war, Prime Minister Nehru and Sardar Patel invited Liaquat Ali Khan
Liaquat Ali Khan
For other people with the same or similar name, see Liaqat Ali Nawabzada Liaquat Ali Khan was a Pakistani statesman who became the first Prime Minister of Pakistan, Defence minister and Commonwealth, Kashmir Affairs...
for talks in Delhi. Although many Indians termed this appeasement, Nehru signed a pact with Liaquat Ali Khan that pledged both nations to the protection of minorities and creation of minority commissions. Although opposed to the principle, Patel decided to back this Pact for the sake of peace, and played a critical role in garnering support from West Bengal and across India, and enforcing the provisions of the Pact. Khan and Nehru also signed a trade agreement, and committed to resolving bilateral disputes through peaceful means. Steadily, hundreds of thousands of Hindus returned to East Pakistan, but the thaw in relations did not last long, primarily owing to the Kashmir dispute.
1971 Bangladesh Liberation War
Pakistan, since independence, was geo-politically divided into two major regions, West PakistanWest Pakistan
West Pakistan , common name West-Pakistan , in the period between its establishment on 22 November 1955 to disintegration on December 16, 1971. This period, during which, Pakistan was divided, ended when East-Pakistan was disintegrated and succeeded to become which is now what is known as Bangladesh...
and East Pakistan
East Pakistan
East Pakistan was a provincial state of Pakistan established in 14 August 1947. The provincial state existed until its declaration of independence on 26 March 1971 as the independent nation of Bangladesh. Pakistan recognized the new nation on 16 December 1971. East Pakistan was created from Bengal...
. East Pakistan was occupied mostly by Bengali people
Bengali people
The Bengali people are an ethnic community native to the historic region of Bengal in South Asia. They speak Bengali , which is an Indo-Aryan language of the eastern Indian subcontinent, evolved from the Magadhi Prakrit and Sanskrit languages. In their native language, they are referred to as বাঙালী...
. In December 1971, following a political crisis in East Pakistan, the situation soon spiralled out of control in East Pakistan and India intervened in favour of the rebelling Bengali populace. The conflict, a brief but bloody war, resulted in an independence of East Pakistan. In the war, the Pakistani army swiftly fell to India, forcing the independence of East Pakistan, which separated and became Bangladesh
Bangladesh
Bangladesh , officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh is a sovereign state located in South Asia. It is bordered by India on all sides except for a small border with Burma to the far southeast and by the Bay of Bengal to the south...
. The Pakistani military, being a thousand miles from its base and surrounded by enemies, was forced to give in.
Simla Agreement
Since the 1971 war, Pakistan and India have made only slow progress towards the normalisation of relations. In July 1972, Indian Prime Minister Indira GandhiIndira Gandhi
Indira Priyadarshini Gandhara was an Indian politician who served as the third Prime Minister of India for three consecutive terms and a fourth term . She was assassinated by Sikh extremists...
and Pakistani President Zulfikar Ali Bhutto
Zulfikar Ali Bhutto
Zulfikar Ali Bhutto was 9th Prime Minister of Pakistan from 1973 to 1977, and prior to that, 4th President of Pakistan from 1971 to 1973. Bhutto was the founder of the Pakistan Peoples Party — the largest and most influential political party in Pakistan— and served as its chairman until his...
met in the Indian hill station of Simla
Shimla
Shimla , formerly known as Simla, is the capital city of Himachal Pradesh. In 1864, Shimla was declared the summer capital of the British Raj in India. A popular tourist destination, Shimla is often referred to as the "Queen of Hills," a term coined by the British...
. They signed the Simla Agreement, by which India would return all Pakistani personnel (over 90,000) and captured territory in the west, and the two countries would "settle their differences by peaceful means through bilateral negotiations." Diplomatic and trade relations were also re-established in 1976.
Afghanistan
Both Pakistan and India considered their relations with Afghanistan as most important relations with any other country. Since the renewal of the Afghanistan war, both countries have fought proxy wars against each other, and both countries are reportedly making an extensive efforts to gain influence on Afghan Government for their own regional interests. In 1979, Soviet UnionSoviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
intervened
Soviet war in Afghanistan
The Soviet war in Afghanistan was a nine-year conflict involving the Soviet Union, supporting the Marxist-Leninist government of the Democratic Republic of Afghanistan against the Afghan Mujahideen and foreign "Arab–Afghan" volunteers...
to protect the fragile communist government, and to prevent the collapse of Afghanistan Soviet Socialist Republic (Afghanistan SSR) into the hands of hard-line Islamist forces. With the deployment of Soviet Union's 40th Army
40th Army (Soviet Union)
The 40th Army of the Soviet Union's Red Army was an army-level command active from 1941 to 1945 and then again from 1979 to circa 1990.It was first formed, after Operation Barbarossa, the German invasion of the Soviet Union, had commenced, from elements of the 26th and 37th Armies under the command...
, new strains appeared in Indo-Pakistani relations, and proxy war between India and Pakistan began to take place first time in Afghanistan. Pakistan, with the backing of the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
, actively supported the Afghan resistance against the Soviet Union
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
, which was a close ally of India, which brought opposing political opinions. India, on other hand, supported the communist government and vital support to communist government was provided by India.
After the Taliban regime in Afghanistan, after defeating the Northern Alliance
Northern Alliance
The Afghan Northern Alliance is a military-political umbrella organization created by the Islamic State of Afghanistan in 1996.Northern Alliance may also refer to:*Northern Alliance , a Canadian white supremacist group...
in much part of Afghanistan in recent civil war. Taliban regime was strongly supported by Pakistan – one of the few countries to do so – before the September 11 attacks. India firmly opposed the Taliban and criticized Pakistan for supporting it. India established its links with Northern Alliance
Northern Alliance
The Afghan Northern Alliance is a military-political umbrella organization created by the Islamic State of Afghanistan in 1996.Northern Alliance may also refer to:*Northern Alliance , a Canadian white supremacist group...
as India officially recognized their government, with the United Nations
United Nations
The United Nations is an international organization whose stated aims are facilitating cooperation in international law, international security, economic development, social progress, human rights, and achievement of world peace...
. India's relations with Afghanistan, Pakistan's neighbor, and its increasing presence there has been a factor that has irked Pakistan and consequently compromised its own relations with Afghanistan.
Nuclear programmes and agreements, talks, and confidence building measures
In the following eight years, India voiced increasing concern over Pakistani arms purchases, U.S. military aid to Pakistan, and a clandestine nuclear weapons programmePakistan and weapons of mass destruction
Pakistan began focusing on nuclear weapons development in January 1972 under the leadership of Prime Minister Zulfiqar Ali Bhutto, who delegated the program to the Chairman of PAEC Munir Ahmad Khan...
. In an effort to curtail tensions, the two countries formed a joint commission to examine disputes. In December 1988, Prime Ministers Benazir Bhutto
Benazir Bhutto
Benazir Bhutto was a democratic socialist who served as the 11th Prime Minister of Pakistan in two non-consecutive terms from 1988 until 1990 and 1993 until 1996....
and Rajiv Gandhi
Rajiv Gandhi
Rajiv Ratna Gandhi was the sixth Prime Minister of India . He took office after his mother's assassination on 31 October 1984; he himself was assassinated on 21 May 1991. He became the youngest Prime Minister of India when he took office at the age of 40.Rajiv Gandhi was the elder son of Indira...
concluded a pact not to attack each other's nuclear facilities. Agreements on cultural exchanges and civil aviation were also initiated.
In 1997, high-level Indo-Pakistan talks resumed after a three-year pause. The Prime Ministers of Pakistan and India met twice and the foreign secretaries conducted three rounds of talks. In June 1997, the foreign secretaries identified eight "outstanding issues" around which continuing talks would be focused. The dispute over the status of Kashmir, (referred by India as Jammu and Kashmir), an issue since Independence, remains the major stumbling block in their dialogue. India maintains that the entire former princely state is an integral part of the Indian union, while Pakistan insists that UN resolutions calling for self-determination of the people of the state/province must be taken into account. It however refuses to abide by the previous part of the resolution, which calls for it to vacate all territories occupied.
In September 1997, the talks broke down over the structure of how to deal with the issues of Kashmir, and peace and security. Pakistan advocated that the issues be treated by separate working group
Working group
A working group is an interdisciplinary collaboration of researchers working on new research activities that would be difficult to develop under traditional funding mechanisms . The lifespan of the WG can last anywhere between a few months and several years...
s. India responded that the two issues be taken up along with six others on a simultaneous basis. In May 1998 India, and then Pakistan, conducted nuclear tests. (See Smiling Buddha
Smiling Buddha
The Smiling Buddha, formally designated as Pokhran-I, was the codename given to Republic of India's first nuclear test explosion that took place at the long-constructed Indian Army base, Pokhran Test Range at Pokhran municipality, Rajasthan state on 18 May 1974 at 8:05 a.m....
and Operation Shakti
Pokhran-II
Pokharan-II refers to test explosions of five nuclear devices, three on 11 May and two on 13 May 1998, conducted by India at the Pokhran test range. These nuclear tests resulted in a variety of sanctions against India by a number of major states....
(India), and Chagai-I
Chagai-I
The Chagai-I was a codename referring to the five underground nuclear tests conducted by Pakistan at 15:15hrs in 28th May of 1998. It was named Chagai-I, as the tests were conducted in the Chagai District...
and Chagai-II) (Pakistan).)
After Manmohan Singh become prime minister of India the Punjab provincial Government declared it would develop Gah
Gah
Gah is a village of Chakwal District in the Punjab province of Pakistan. It is located in the Union council of Begal at 33°3'45N 72°39'8E, the Naib Nazim or vice president of Begal is from Gah. Gah is notable for being the birth place of current Indian Prime minister Manmohan Singh...
, his place of birth, as a model village in his honour and name a school after him. There is also a village in India named Pakistan
Pakistan, India
Pakistan is a village situated in the Purnia district of Bihar, India. The village was named "Pakistan" in the memory of the Muslim residents who migrated in 1947 to what was then called East Pakistan...
, despite occasional pressure over the years to change its name the villagers have resisted.
2001 Gujarat Earthquake in India
Pakistani President Pervez Mushrraf sent a plane load of relief supplies to India from IslamabadIslamabad
Islamabad is the capital of Pakistan and the tenth largest city in the country. Located within the Islamabad Capital Territory , the population of the city has grown from 100,000 in 1951 to 1.7 million in 2011...
to Ahmedabad
Ahmedabad
Ahmedabad also known as Karnavati is the largest city in Gujarat, India. It is the former capital of Gujarat and is also the judicial capital of Gujarat as the Gujarat High Court has its seat in Ahmedabad...
. That carried 200 tents and more than 2,000 Blankets. Furthermore the President called Indian PM to express his 'sympathy' over the loss from the earthquake.
2005 Earthquake in Pakistan
India offered generous aid to Pakistan in response to the 2005 Earthquake. Indian and Pakistani High Commissioners consulted with one another regarding cooperation in relief work. India sent 25 tonnes of relief material to PakistanPakistan
Pakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan...
including food, blankets and medicine. Large Indian companies such as Infosys
Infosys
Infosys Limited, formerly Infosys Technologies Limited is a global technology services company headquartered in Bangalore, India. It is the second largest IT exporter in India with 133,560 employees as of March 2011. It has offices in 33 countries and development centers in India, China,...
have offered aid up to $226,000. On October 12, an Ilyushin-76
Ilyushin Il-76
The Ilyushin Il-76 is a multi-purpose four-engined strategic airlifter designed by Ilyushin design bureau. It was first planned as a commercial freighter in 1967. Intended as a replacement for the Antonov An-12, the Il-76 was designed for delivering heavy machinery to remote, poorly-serviced areas...
cargo plane ferried across seven truckloads (about 82 ton
Ton
The ton is a unit of measure. It has a long history and has acquired a number of meanings and uses over the years. It is used principally as a unit of weight, and as a unit of volume. It can also be used as a measure of energy, for truck classification, or as a colloquial term.It is derived from...
s) of army medicines, 15,000 blankets and 50 tents and returned to New Delhi. A senior airforce official also stated that they had been asked by the Indian government to be ready to fly out another similar consignment. On October 14, India dispatched the second consignment of relief material to Pakistan, by train through the Wagah Border. The consignment included 5,000 blankets, 370 tents, 5 tons of plastic sheets and 12 tons of medicine. A third consignment of medicine and relief material was also sent shortly afterwards by train. India also pledged $25 million as aid to Pakistan.
India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
opened the first of three points at Chakan Da Bagh, in Poonch
Poonch
Poonch is a town and a municipal committee in Poonch District in the Indian state of Jammu and Kashmir. Based on the Mahābhārata evidence, and the evidence from 7th Chinese traveler Xuanzang, the districts of Poonch along with Rajauri and Abhisara had been under the sway of the Republican Kambojas...
, on the Line of Control (LoC) between India and Pakistan for the 2005 Kashmir earthquake
2005 Kashmir earthquake
The 2005 Kashmir earthquake was a major earthquake centered in Pakistan-administered Kashmir known as Azad Kashmir, near the city of Muzaffarabad, affecting Gilgit-Baltistan and Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province of Pakistan. It occurred at 08:52:37 Pakistan Standard Time on 8 October 2005...
relief work. (Rediff) Such generous gestures signalled a new age in confidence, friendliness and cooperation between both India and Pakistan.
2007 Samjhauta Express bombings
The 2007 Samjhauta Express bombings2007 Samjhauta Express bombings
The 2007 Samjhauta Express bombings were a terrorist attack that occurred around midnight on 18 February 2007 on the Samjhauta Express, a twice-weekly train service connecting Delhi, India, and Lahore, Pakistan. Bombs were set off in two carriages, both filled with passengers, just after the train...
was a terrorist attack targeted on the Samjhauta Express
Samjhauta Express
The Samjhauta Express commonly called the Friendship Express, is a twice-weekly train Tuesdays and Fridays that runs between Delhi and Attari in India and Lahore in Pakistan. The word samjhauta means "Understanding","accord" and "compromise" in both Hindi and Urdu.Until the reopening of the Thar...
train on the 18th of February. The Samjhauta Express is an international train that runs from New Delhi, India to Lahore, Pakistan, and is one of two trains to cross the India-Pakistan border. At least 68 people were killed, mostly Pakistani civilians but also some Indian security personnel and civilians. Prasad Shrikant Purohit
Prasad Shrikant Purohit
Lt. Col. Shrikant Prasad Purohit is an Indian Army officer who is accused of charges of terrorism, as the alleged chief architect of the 2007 Samjhauta Express bombings. The attack took place on the Samjhauta Express, a train that connects Lahore, Pakistan with Delhi, the capital of India...
, an Indian Army officer, was later identified and investigated as a key suspect responsible for the bombing. The attack was a turning point in Indo-Pakistani relations, and one of the many terrorist incidents that have plagued relations between the two.
2008 Mumbai attacks
The 2008 Mumbai attacks2008 Mumbai attacks
The 2008 Mumbai attacks were more than 10 coordinated shooting and bombing attacks across Mumbai, India's largest city, by Islamist attackers who came from Pakistan...
by ten terrorists killed over 173 and wounded 308. The sole surviving gunman Ajmal Kasab
Ajmal Kasab
Mohammed Ajmal Amir Kasab is a Pakistani Islamic terrorist who was involved in the 2008 Mumbai attacks in India. Kasab is the only attacker captured alive by police and is currently in Indian custody. The Government of Pakistan initially denied that Kasab was from Pakistan, but in January 2009,...
who was arrested during the attacks was found to be a Pakistani national. This fact was acknowledged by Pakistani authorities. In May 2010, an Indian court convicted him on four counts of murder
Murder
Murder is the unlawful killing, with malice aforethought, of another human being, and generally this state of mind distinguishes murder from other forms of unlawful homicide...
, waging war against India, conspiracy
Conspiracy (crime)
In the criminal law, a conspiracy is an agreement between two or more persons to break the law at some time in the future, and, in some cases, with at least one overt act in furtherance of that agreement...
and terrorism
Terrorism
Terrorism is the systematic use of terror, especially as a means of coercion. In the international community, however, terrorism has no universally agreed, legally binding, criminal law definition...
offences, and sentenced him to death.
India blamed the Lashkar-e-Taiba
Lashkar-e-Taiba
Lashkar-e-Taiba – also transliterated as Lashkar-i-Tayyaba, Lashkar-e-Tayyaba, Lashkar-e-Tayyiba, Lashkar-i-Taiba, Lashkar Taiba or LeT – is one of the largest and most active militant Islamist terrorist organizations in South Asia, operating mainly from Pakistan.It was founded by Hafiz Muhammad...
, a Pakistan-based militant group, for planning and executing the attacks. Islamabad resisted the claims and demanded evidence. India provided evidence in the form of interrogations, weapons, candy wrappers, Pakistani Brand Milk Packets, and telephone sets. Indian officials demanded Pakistan extradite suspects for trial. They also said that, given the sophistication of the attacks, the perpetrators "must have had the support of some official agencies in Pakistan".
Conflict in Jammu and Kashmir
Insurgent attacks on Jammu and Kashmir State Assembly: A car bomb exploded near the Jammu and Kashmir State Assembly on October 1, 2001, killing 27 people on an attack that was blamed on Kashmiri separatists. It was one of the most prominent attacks against IndiaIndia
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
apart from on the Indian Parliament in December 2001. The dead bodies of the terrorists and the data recovered from them revealed that Pakistan was solely responsible for the activity.
- 1997 Sangrampora massacre1997 Sangrampora massacre1997 Sangrampora massacre was the killing of seven Kashmiri Pandit Hindu villagers in Sangrampora village of Budgam district of Jammu and Kashmir on 21 March 1997 by alleged Islamic militants.-Background:...
: On March 21, 1997, 7 Kashmiri Pandits were killed in Sangrampora village in the Budgam district. - Wandhama MassacreWandhama massacreThe 1998 Wandhama massacre refers to the murder of 23 Kashmiri Pandit Hindus in the town of Wandhama in the Muslim-majority Indian state of Jammu and Kashmir on 25 January 1998. The victims included four children, nine women and 10 men...
: In January 1998, 24 Kashmiri PanditKashmiri PanditThe Kashmiri Pandits are a Hindu Brahmin community originating from Kashmir, a mountainous region in South Asia.-Background:The Hindu caste system of the region was influenced by the influx of Buddhism from the time of Asoka, around the third century BCE, and a consequence of this was that the...
s living in the city WandhamaWandhama massacreThe 1998 Wandhama massacre refers to the murder of 23 Kashmiri Pandit Hindus in the town of Wandhama in the Muslim-majority Indian state of Jammu and Kashmir on 25 January 1998. The victims included four children, nine women and 10 men...
were killed by Islamic terrorists. - Qasim Nagar Attack: On July 13, 2003, armed men believed to be a part of the Lashkar-e-ToibaLashkar-e-ToibaLashkar-e-Taiba – also transliterated as Lashkar-i-Tayyaba, Lashkar-e-Tayyaba, Lashkar-e-Tayyiba, Lashkar-i-Taiba, Lashkar Taiba or LeT – is one of the largest and most active militant Islamist terrorist organizations in South Asia, operating mainly from Pakistan.It was founded by Hafiz Muhammad...
threw hand grenades at the Qasim Nagar market in SrinagarSrinagarSrinagar is the summer seasonal capital of Jammu and Kashmir. It is situated in Kashmir Valley and lies on the banks of the Jhelum River, a tributary of the Indus. It is one of the largest cities in India not to have a Hindu majority. The city is famous for its gardens, lakes and houseboats...
and then fired on civilians standing nearby killing twenty-seven and injuring many more. - Assassination of Abdul Ghani Lone: Abdul Ghani LoneAbdul Ghani LoneAbdul Ghani Lone was an Indian lawyer and politician who for most of his professional career worked as a Kashmiri separatist....
, a prominent All Party Hurriyat Conference leader, was assassinated by an unidentified gunmen during a memorial rally in SrinagarSrinagarSrinagar is the summer seasonal capital of Jammu and Kashmir. It is situated in Kashmir Valley and lies on the banks of the Jhelum River, a tributary of the Indus. It is one of the largest cities in India not to have a Hindu majority. The city is famous for its gardens, lakes and houseboats...
. The assassination resulted in wide-scale demonstrations against the Indian occupied-forces for failing to provide enough security cover for Mr. Lone. - July 20, 2005 SrinagarSrinagarSrinagar is the summer seasonal capital of Jammu and Kashmir. It is situated in Kashmir Valley and lies on the banks of the Jhelum River, a tributary of the Indus. It is one of the largest cities in India not to have a Hindu majority. The city is famous for its gardens, lakes and houseboats...
Bombing: A car bomb exploded near an armoured Indian ArmyIndian ArmyThe Indian Army is the land based branch and the largest component of the Indian Armed Forces. With about 1,100,000 soldiers in active service and about 1,150,000 reserve troops, the Indian Army is the world's largest standing volunteer army...
vehicle in the famous Church Lane area in SrinagarSrinagarSrinagar is the summer seasonal capital of Jammu and Kashmir. It is situated in Kashmir Valley and lies on the banks of the Jhelum River, a tributary of the Indus. It is one of the largest cities in India not to have a Hindu majority. The city is famous for its gardens, lakes and houseboats...
killing four Indian ArmyIndian ArmyThe Indian Army is the land based branch and the largest component of the Indian Armed Forces. With about 1,100,000 soldiers in active service and about 1,150,000 reserve troops, the Indian Army is the world's largest standing volunteer army...
personnel, one civilian and the suicide bomber. Terrorist group Hizbul MujahideenHizbul MujahideenHizbul Mujahideen , founded by Ahsan Dar in 1989, is a Kashmiri militant group active in the Indian state of Jammu and Kashmir since 1989. Their headquarters are located in Muzaffarabad, the capital of Pakistan-administered Kashmir. It is believed the group al-Badr, derived from Hizbul Mujahideen...
, claimed responsibility for the attack. - Budshah Chowk attack: A terrorist attack on July 29, 2005 at Srinigar's city centre, Budshah Chowk, killed two and left more than 17 people injured. Most of those injured were media journalists.
- Murder of Ghulam Nabi Lone: On October 18, 2005 suspected Army man killed Jammu and Kashmir's then education minister Ghulam Nabi Lone. No Terrorist group claimed responsibility for the attack.
Insurgent activities elsewhere
The attack on the Indian Parliament was by far the most dramatic attack carried out by Pakistani terrorists. India blamed Pakistan for carrying out the attacks, an allegation which Pakistan strongly denied and one that brought both nations to the brink of a nuclearNuclear warfare
Nuclear warfare, or atomic warfare, is a military conflict or political strategy in which nuclear weaponry is detonated on an opponent. Compared to conventional warfare, nuclear warfare can be vastly more destructive in range and extent of damage...
confrontation in 2001–02. However, international peace efforts ensured the cooling of tensions between the two nuclear-capable nations.
Apart from this, the most notable was the hijacking
Aircraft hijacking
Aircraft hijacking is the unlawful seizure of an aircraft by an individual or a group. In most cases, the pilot is forced to fly according to the orders of the hijackers. Occasionally, however, the hijackers have flown the aircraft themselves, such as the September 11 attacks of 2001...
of Indian Airlines Flight IC 814
Indian Airlines Flight 814
Indian Airlines Flight 814 commonly known as IC 814 was an Indian Airlines Airbus A300 en route from Tribhuvan International Airport in Kathmandu, Nepal to Indira Gandhi International Airport in Delhi, India on Friday, December 24, 1999, when it was hijacked...
en route New Delhi from Kathmandu, Nepal
Nepal
Nepal , officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, is a landlocked sovereign state located in South Asia. It is located in the Himalayas and bordered to the north by the People's Republic of China, and to the south, east, and west by the Republic of India...
. The plane was hijacked on December 24, 1999 approximately one hour after take off and was taken to Amritsar
Amritsar
Amritsar is a city in the northern part of India and is the administrative headquarters of Amritsar district in the state of Punjab, India. The 2001 Indian census reported the population of the city to be over 1,500,000, with that of the entire district numbering 3,695,077...
airport and then to Lahore
Lahore
Lahore is the capital of the Pakistani province of Punjab and the second largest city in the country. With a rich and fabulous history dating back to over a thousand years ago, Lahore is no doubt Pakistan's cultural capital. One of the most densely populated cities in the world, Lahore remains a...
in Pakistan. After refueling the plane took off for Dubai
Dubai
Dubai is a city and emirate in the United Arab Emirates . The emirate is located south of the Persian Gulf on the Arabian Peninsula and has the largest population with the second-largest land territory by area of all the emirates, after Abu Dhabi...
and then finally landed in Kandahar
Kandahar
Kandahar is the second largest city in Afghanistan, with a population of about 512,200 as of 2011. It is the capital of Kandahar Province, located in the south of the country at about 1,005 m above sea level...
, Afghanistan
Afghanistan
Afghanistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located in the centre of Asia, forming South Asia, Central Asia and the Middle East. With a population of about 29 million, it has an area of , making it the 42nd most populous and 41st largest nation in the world...
. Under intense media pressure, New Delhi complied with the hijackers' demand and freed Maulana Masood Azhar
Maulana Masood Azhar
Maulana Masood Azhar is a Pakistani mujaheddin leader and the founder of the militant group Jaish-e-Mohammed, based mainly in the Pakistan-administered portion of the state of Kashmir....
from its captivity in return for the freedom of the Indian passengers on the flight. The decision, however, cost New Delhi dearly. Maulana, who is believed to be hiding in Karachi
Karachi
Karachi is the largest city, main seaport and the main financial centre of Pakistan, as well as the capital of the province of Sindh. The city has an estimated population of 13 to 15 million, while the total metropolitan area has a population of over 18 million...
, later became the leader of Jaish-e-Mohammed
Jaish-e-Mohammed
Jaish-e-Mohammed is a Pakistani-based, militant Islamic group established by Maulana Masood Azhar in March 2000...
, an organisation which has carried out several terrorist acts against Indian Security Forces in Kashmir.
On December 22, 2000, a group of terrorists belonging to the Lashkar-e-Toiba
Lashkar-e-Toiba
Lashkar-e-Taiba – also transliterated as Lashkar-i-Tayyaba, Lashkar-e-Tayyaba, Lashkar-e-Tayyiba, Lashkar-i-Taiba, Lashkar Taiba or LeT – is one of the largest and most active militant Islamist terrorist organizations in South Asia, operating mainly from Pakistan.It was founded by Hafiz Muhammad...
stormed the famous Red Fort in New Delhi
New Delhi
New Delhi is the capital city of India. It serves as the centre of the Government of India and the Government of the National Capital Territory of Delhi. New Delhi is situated within the metropolis of Delhi. It is one of the nine districts of Delhi Union Territory. The total area of the city is...
. The Fort houses an Indian military
Indian Army
The Indian Army is the land based branch and the largest component of the Indian Armed Forces. With about 1,100,000 soldiers in active service and about 1,150,000 reserve troops, the Indian Army is the world's largest standing volunteer army...
unit and a high-security interrogation cell used both by the Central Bureau of Investigation
Central Bureau of Investigation
The Central Bureau of Investigation is a government agency of India that serves as a criminal investigation body, national security agency and intelligence agency. It was established on 1 April 1963 and evolved from the Special Police Establishment founded in 1941...
and the Indian Army
Indian Army
The Indian Army is the land based branch and the largest component of the Indian Armed Forces. With about 1,100,000 soldiers in active service and about 1,150,000 reserve troops, the Indian Army is the world's largest standing volunteer army...
. The terrorists successfully breached the security cover around the Red Fort and opened fire at the Indian military personnel on duty killing two of them on spot. The attack was significant because it was carried out just two days after the declaration of the cease-fire between India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
and Pakistan
Pakistan
Pakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan...
.
In 2002, India claimed again that terrorists from Jammy and Kashmir were infiltrating into India, a claim denied by Pakistan President Pervez Musharraf
Pervez Musharraf
Pervez Musharraf , is a retired four-star general who served as the 13th Chief of Army Staff and tenth President of Pakistan as well as tenth Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff Committee. Musharraf headed and led an administrative military government from October 1999 till August 2007. He ruled...
, who claimed that such infiltration had stopped--India's spokesperson for the External Affairs Ministry did away with Pakistan's claim, calling it "terminological inexactitude." Only two months later, two Kashmiri terrorists belonging to Jaish-e-Mohammed
Jaish-e-Mohammed
Jaish-e-Mohammed is a Pakistani-based, militant Islamic group established by Maulana Masood Azhar in March 2000...
raided the Swami Narayan temple complex in Ahmedabad
Ahmedabad
Ahmedabad also known as Karnavati is the largest city in Gujarat, India. It is the former capital of Gujarat and is also the judicial capital of Gujarat as the Gujarat High Court has its seat in Ahmedabad...
, Gujarat killing 30 people, including 18 women and five children. The attack was carried out on September 25, 2002, just few days after state elections were held in Jammu and Kashmir
Jammu and Kashmir
Jammu and Kashmir is the northernmost state of India. It is situated mostly in the Himalayan mountains. Jammu and Kashmir shares a border with the states of Himachal Pradesh and Punjab to the south and internationally with the People's Republic of China to the north and east and the...
. Two identical letters found on both the terrorists claimed that the attack was done in retaliation for the deaths of thousands of Muslims during the Gujarat riots
2002 Gujarat violence
The 2002 Gujarat violence describes the Godhra train burning and resulting communal riots between Hindus and Muslims. On 27 February 2002 at Godhra City in the state of Gujarat, the Sabarmati Express train was attacked by a large Muslim mob in a conspiracy. But some authentic sources deny the claim...
.
Two car bombs exploded in south Mumbai
Mumbai
Mumbai , formerly known as Bombay in English, is the capital of the Indian state of Maharashtra. It is the most populous city in India, and the fourth most populous city in the world, with a total metropolitan area population of approximately 20.5 million...
on August 25, 2003; one near the Gateway of India
Gateway of India
Its design is a combination of both Hindu and Muslim architectural styles, the arch is in Muslim style while the decorations are in Hindu style. The Gateway is built from yellow basalt and reinforced concrete. The stone was locally obtained, and the perforated screens were brought from Gwalior.The...
and the other at the famous Zaveri Bazaar, killing at least 48 and injuring 150 people. Though no terrorist group claimed responsibility for the attacks, Mumbai Police and RAW
Research and Analysis Wing
The Research and Analysis Wing is India's external intelligence agency. It was formed in September 1968 after the poor performance of the Intelligence Bureau in the Sino-Indian war of 1962 and the India-Pakistani war of 1965 convinced the then government of India that a specialized, independent...
suspected Lashkar-e-Toiba
Lashkar-e-Toiba
Lashkar-e-Taiba – also transliterated as Lashkar-i-Tayyaba, Lashkar-e-Tayyaba, Lashkar-e-Tayyiba, Lashkar-i-Taiba, Lashkar Taiba or LeT – is one of the largest and most active militant Islamist terrorist organizations in South Asia, operating mainly from Pakistan.It was founded by Hafiz Muhammad...
's hand in the twin blasts.
In an unsuccessful attempt, six terrorists belonging to Lashkar-e-Toiba
Lashkar-e-Toiba
Lashkar-e-Taiba – also transliterated as Lashkar-i-Tayyaba, Lashkar-e-Tayyaba, Lashkar-e-Tayyiba, Lashkar-i-Taiba, Lashkar Taiba or LeT – is one of the largest and most active militant Islamist terrorist organizations in South Asia, operating mainly from Pakistan.It was founded by Hafiz Muhammad...
, stormed the Ayodhya Ram Janmbhomi complex on July 5, 2005. Before the terrorists could reach the main disputed site, they were shot down by Indian security forces. One Hindu worshipper and two police
Police
The police is a personification of the state designated to put in practice the enforced law, protect property and reduce civil disorder in civilian matters. Their powers include the legitimized use of force...
men were injured during the incident.
2008 Mumbai attacks2008 Mumbai attacksThe 2008 Mumbai attacks were more than 10 coordinated shooting and bombing attacks across Mumbai, India's largest city, by Islamist attackers who came from Pakistan...
The resumed relation between India and Pakistan again got strained following the 2008 Mumbai attacks2008 Mumbai attacks
The 2008 Mumbai attacks were more than 10 coordinated shooting and bombing attacks across Mumbai, India's largest city, by Islamist attackers who came from Pakistan...
by 10 Pakistani insurgents, killing approximatively 168 people (including 28 foreign nationals and leaving injured 308).
Alleged Human rights violations by India
Pakistan has accused India of gross human rights violations in Indian-administered Kashmir. A report by the Human Rights WatchHuman Rights Watch
Human Rights Watch is an international non-governmental organization that conducts research and advocacy on human rights. Its headquarters are in New York City and it has offices in Berlin, Beirut, Brussels, Chicago, Geneva, Johannesburg, London, Los Angeles, Moscow, Paris, San Francisco, Tokyo,...
, stated two main reasons for the improving human rights condition in the region: First, sincere efforts were made by the new Jammu and Kashmir
Jammu and Kashmir
Jammu and Kashmir is the northernmost state of India. It is situated mostly in the Himalayan mountains. Jammu and Kashmir shares a border with the states of Himachal Pradesh and Punjab to the south and internationally with the People's Republic of China to the north and east and the...
state government headed by Mufti Muhammad Sayeed to investigate cases of human rights abuses in the state and to punish those guilty including Indian soldiers
Indian Army
The Indian Army is the land based branch and the largest component of the Indian Armed Forces. With about 1,100,000 soldiers in active service and about 1,150,000 reserve troops, the Indian Army is the world's largest standing volunteer army...
. More than 15 Indian army soldiers were convicted by the Indian government
Government of India
The Government of India, officially known as the Union Government, and also known as the Central Government, was established by the Constitution of India, and is the governing authority of the union of 28 states and seven union territories, collectively called the Republic of India...
in 2004 for carrying out human rights abuses in the state. Second, the decrease in cross-border infiltration into India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
by armed insurgents.
Developments since 2004
Violent activities in the region declined in 2004. There are two main reasons for this: warming of relations between New DelhiNew Delhi
New Delhi is the capital city of India. It serves as the centre of the Government of India and the Government of the National Capital Territory of Delhi. New Delhi is situated within the metropolis of Delhi. It is one of the nine districts of Delhi Union Territory. The total area of the city is...
and Islamabad
Islamabad
Islamabad is the capital of Pakistan and the tenth largest city in the country. Located within the Islamabad Capital Territory , the population of the city has grown from 100,000 in 1951 to 1.7 million in 2011...
which consequently lead to a ceasefire
Ceasefire
A ceasefire is a temporary stoppage of a war in which each side agrees with the other to suspend aggressive actions. Ceasefires may be declared as part of a formal treaty, but they have also been called as part of an informal understanding between opposing forces...
between the two countries in 2003 and the fencing of the LOC
LOC
LOC, Loc, or LoC may refer to:* Look out circular, a message used by interpol in India to stop wanted people from leaving country* Life Orientation Course - Aviation :* Localizer, a component of an Instrument Landing System...
being carried out by the Indian Army
Indian Army
The Indian Army is the land based branch and the largest component of the Indian Armed Forces. With about 1,100,000 soldiers in active service and about 1,150,000 reserve troops, the Indian Army is the world's largest standing volunteer army...
. Moreover, coming under intense international pressure, Islamabad was compelled to take actions against the militants' training camps on its territory. In 2004, the two countries also agreed upon decreasing the number of troops present in the region.
Under pressure, Kashmiri militant organisations have made an offer for talks and negotiations with New Delhi, which India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
has welcomed.
India's Border Security Force
Border Security Force
The Border Security Force is a border patrol agency of the Government of India. Established on December 1, 1965, it is one of the Central Armed Police Forces. Its primary role is to guard India's international borders during peacetime and also prevent transnational crime...
blamed the Pakistan
Pakistan
Pakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan...
i military for providing cover-fire for the terrorists whenever they infiltrated into Indian territory from Pakistan.
Pakistan in turn has also blamed India for providing support to terrorist organizations operating in Pakistan such as the BLA
Balochistan Liberation Army
The Balochistan Liberation Army is a terrorist group based in Balochistan, a mountainous region within southern Iran and Pakistan. The organization is a participant in the Balochistan conflict and strives to establish an independent state of Balochistan, free of Pakistani and Iranian rule...
.
In 2005, Pakistan's information minister, Sheikh Rashid, was alleged to have run a terrorist training camp in 1990 in N.W. Frontier, Pakistan. The Pakistani government dismissed the charges against its minister as an attempt to hamper the ongoing peace process between the two neighbours.
Both India and Pakistan have launched several mutual confidence-building measures
Confidence and Security-Building Measures
Confidence building measures or confidence and security building measures are actions taken to reduce fear of attack by both parties in a situation of tension with or without physical conflict...
(CBMs) to ease tensions between the two. These include more high-level talks, easing visa
Visa (document)
A visa is a document showing that a person is authorized to enter the territory for which it was issued, subject to permission of an immigration official at the time of actual entry. The authorization may be a document, but more commonly it is a stamp endorsed in the applicant's passport...
restrictions, and restarting of cricket
Cricket
Cricket is a bat-and-ball game played between two teams of 11 players on an oval-shaped field, at the centre of which is a rectangular 22-yard long pitch. One team bats, trying to score as many runs as possible while the other team bowls and fields, trying to dismiss the batsmen and thus limit the...
matches between the two. The new bus
Bus
A bus is a road vehicle designed to carry passengers. Buses can have a capacity as high as 300 passengers. The most common type of bus is the single-decker bus, with larger loads carried by double-decker buses and articulated buses, and smaller loads carried by midibuses and minibuses; coaches are...
service between Srinagar
Srinagar
Srinagar is the summer seasonal capital of Jammu and Kashmir. It is situated in Kashmir Valley and lies on the banks of the Jhelum River, a tributary of the Indus. It is one of the largest cities in India not to have a Hindu majority. The city is famous for its gardens, lakes and houseboats...
and Muzaffarabad
Muzaffarabad
Muzaffarabad is the capital of Pakistan Occupied Kashmir, Pakistan. It is located in Muzaffarabad District on the banks of the Jhelum and Neelum rivers...
has also helped bring the two sides closer. Pakistan and India have also decided to co-operate on economic fronts.
A major clash between Indian Security Forces
Indian Army
The Indian Army is the land based branch and the largest component of the Indian Armed Forces. With about 1,100,000 soldiers in active service and about 1,150,000 reserve troops, the Indian Army is the world's largest standing volunteer army...
and militants occurred when a group of insurgents tried to infiltrate into the Indian-administered Kashmir
Jammu and Kashmir
Jammu and Kashmir is the northernmost state of India. It is situated mostly in the Himalayan mountains. Jammu and Kashmir shares a border with the states of Himachal Pradesh and Punjab to the south and internationally with the People's Republic of China to the north and east and the...
from Pakistan in July 2005. The same month also saw a Kashmiri militant attack on Ayodhya and Srinagar
Srinagar
Srinagar is the summer seasonal capital of Jammu and Kashmir. It is situated in Kashmir Valley and lies on the banks of the Jhelum River, a tributary of the Indus. It is one of the largest cities in India not to have a Hindu majority. The city is famous for its gardens, lakes and houseboats...
. However, these developments had little impact on the peace process.
Some improvements in the relations are seen with the re-opening of a series of transportation networks near the India–Pakistan border, with the most important being bus routes and railway lines.
An Indian man held in Pakistani prisons since 1975 as an accused spy walked across the border to freedom March 3, 2008, an unconditional release that Pakistan said was done to improve relations between the two countries.
In 2006, a "Friends Without Borders" scheme began with the help of two British tourists. The idea was that Indian and Pakistani children would make pen pals and write friendly letters to each other. The idea was so successful in both countries that the organisation found it "impossible to keep up". The World's Largest Love Letter was recently sent from India to Pakistan.
In April 2010 a high profile Pakistani cricketer, Shoaib Malik
Shoaib Malik
Shoaib Malik is a Pakistani cricket player and former captain. He made his One-Day International debut in 1999 against the West Indies and his Test debut in 2001 against Bangladesh. He has taken over 100 ODI wickets, and has a batting average in the mid 30s in both Test and ODI cricket...
married the Indian tennis star Sania Mirza
Sania Mirza
Sania Mirza is a professional Indian tennis player. She began her tennis career in 2003 and is well known for her powerful forehand ground strokes. She is the first ever Indian to break into the top 30 WTA rankings...
. The wedding received much media attention and was said to transfix both India and Pakistan.
On 10 Feb, 2011, India agreed to resume talks with Pakistan which were suspended after 26/11 Mumbai Attacks. India had put on hold all the diplomatic relations saying it will only continue if Pakistan will act against the accused of Mumbai attacks.
Possible solutions to the Kashmir issue
Many consider that the best way to end present violence in Kashmir is negotiations between various Kashmiri-separatists groups, Pakistan and India. Here are a few possible solutions http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/shared/spl/hi/south_asia/03/kashmir_future/html/default.stm to the Kashmir dispute –| The status quo | Currently a boundary – the Line of Control (LOC LOC LOC, Loc, or LoC may refer to:* Look out circular, a message used by interpol in India to stop wanted people from leaving country* Life Orientation Course - Aviation :* Localizer, a component of an Instrument Landing System... )- divides the region in two, with one part administered by India India India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world... and one by Pakistan Pakistan Pakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan... . India would like to formalize this status quo and make it the accepted international boundary. Factors Opposing – Pakistan Pakistan Pakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan... rejects the plan partially as it will get lesser control over the region and wants greater. Kashmiri political parties too would oppose the plan as it violates the UN resolution for a referendum |
| Kashmir becomes a part of India India India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world... |
Though New Delhi New Delhi New Delhi is the capital city of India. It serves as the centre of the Government of India and the Government of the National Capital Territory of Delhi. New Delhi is situated within the metropolis of Delhi. It is one of the nine districts of Delhi Union Territory. The total area of the city is... and much of the Hindu population of Jammu and Buddhists in Ladakh would have no objections to such a plan. Factors Opposing– The Muslim majority population of Pakistan-administered Azad Kashmir Azad Kashmir Azad Jammu and Kashmir or Azad Kashmir for short, is the southernmost political entity within the Pakistani-administered part of the former princely state of Jammu and Kashmir... , might object the outcome as would a majority of those in Kashmir valley in India |
| The status quo for something else | Pakistan accepts the status quo in return for India giving away disputed Sir Creek Sir Creek The Sir Creek is a 96 km strip of water disputed between India and Pakistan in the Rann of Kutch marshlands. The creek, which opens up into the Arabian Sea, divides the Kutch region of the Indian state of Gujarat with the Sindh province of Pakistan. It is located at approximately .Originally... |
| Kashmir becomes a part of Pakistan Pakistan Pakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan... |
Kashmir joining Pakistan Pakistan Pakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan... . Factors Opposing– The communities of Hindus of Jammu Jammu Jammu , also known as Duggar, is one of the three administrative divisions within Jammu and Kashmir, the northernmost state in India.Jammu city is the largest city in Jammu and the winter capital of Jammu and Kashmir... and the Buddhists of Ladakh Ladakh Ladakh is a region of Jammu and Kashmir, the northernmost state of the Republic of India. It lies between the Kunlun mountain range in the north and the main Great Himalayas to the south, inhabited by people of Indo-Aryan and Tibetan descent... would object the outcome. Hindu Kashmiri Pandit Kashmiri Pandit The Kashmiri Pandits are a Hindu Brahmin community originating from Kashmir, a mountainous region in South Asia.-Background:The Hindu caste system of the region was influenced by the influx of Buddhism from the time of Asoka, around the third century BCE, and a consequence of this was that the... s, who were forced out of Kashmir by militants are also a major topic to consider. |
| Kashmir becomes an independent sovereign republic | As an independent state, the region would most likely be economically viable with tourism probably being the largest source of income, however being a landlocked country, it would be heavily dependent on India and Pakistan. Factors Opposing – The outcome is unlikely because it requires both India India India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world... and Pakistan Pakistan Pakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan... (and potentially China People's Republic of China China , officially the People's Republic of China , is the most populous country in the world, with over 1.3 billion citizens. Located in East Asia, the country covers approximately 9.6 million square kilometres... ) to give up territory. |
| A smaller independent Kashmir | A smaller independent Kashmir formed out of the current strip of Kashmir Kashmir Kashmir is the northwestern region of the Indian subcontinent. Until the mid-19th century, the term Kashmir geographically denoted only the valley between the Great Himalayas and the Pir Panjal mountain range... (administered by Pakistan) and the Kashmir valley (controlled by India). This would leave the Northern areas with Pakistan while India retains Jammu and Ladakh. However this region should maintain good relations with both India and Pakistan as it is landlocked and is covered with snow in winter. This region can also have its defence and foreign relations jointly handled by India and Pakistan. Factors Opposing – The outcome is unlikely because it requires both India India India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world... and Pakistan Pakistan Pakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan... to give up territory. |
Re-evaluation
The insurgents who initially started their movement as a pro-Kashmiri independenceIndependence
Independence is a condition of a nation, country, or state in which its residents and population, or some portion thereof, exercise self-government, and usually sovereignty, over its territory....
movement, have gone through a lot of change in their ideology. Most of the insurgents portray their struggle as a religious one.
Indian analysts allege that by supporting these insurgents, Pakistan is trying to wage a proxy war
Proxy war
A proxy war or proxy warfare is a war that results when opposing powers use third parties as substitutes for fighting each other directly. While powers have sometimes used governments as proxies, violent non-state actors, mercenaries, or other third parties are more often employed...
against India while Pakistan claims that it regards most of these insurgent
Insurgency
An insurgency is an armed rebellion against a constituted authority when those taking part in the rebellion are not recognized as belligerents...
groups as "freedom fighters" rather than terrorists
Internationally known to be the most deadly theatre of conflict, nearly 10 million people, including Muslims, Hindus, and Buddhists, have been fighting a daily battle for survival. The cross-border firing between India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
and Pakistan
Pakistan
Pakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan...
, and the terrorist attacks combined have taken its toll on the Kashmiris, who have suffered poor living standards and an erosion of human rights.
Kargil crisis
Attempts to restart dialogue between the two nations were given a major boost by the February 1999 meeting of both Prime Ministers in LahoreLahore
Lahore is the capital of the Pakistani province of Punjab and the second largest city in the country. With a rich and fabulous history dating back to over a thousand years ago, Lahore is no doubt Pakistan's cultural capital. One of the most densely populated cities in the world, Lahore remains a...
and their signing of three agreements.
These efforts have since been stalled by the intrusion of Pakistani forces into Indian-held territory near Kargil
Kargil District
Kargil is a district of Ladakh, Kashmir, India. Kargil lies near the Line of Control facing Pakistan-occupied Kashmir's Baltistan to the west, and Kashmir valley to the south. Zanskar is part of Kargil district along with Suru, Wakha and Dras valleys...
in Jammu and Kashmir in May 1999. This resulted in intense fighting between Indian and Pakistani forces, known as the Kargil conflict. Backed by the Indian Air Force, the Indian Army regained some of Kargil. Pakistan later withdrew from the remaining portion, under international pressure. A subsequent military coup in Pakistan that overturned the democratically elected Nawaz Sharif
Nawaz Sharif
Mian Mohammad Nawaz Sharif is a Pakistani conservative politician and steel magnate who served as 12th Prime Minister of Pakistan in two non-consecutive terms from November 1990 to July 1993, and from February 1997 to October 12, 1999...
government in October of the same year also proved a setback to relations.
In 2001, a summit was called in Agra
Agra
Agra a.k.a. Akbarabad is a city on the banks of the river Yamuna in the northern state of Uttar Pradesh, India, west of state capital, Lucknow and south from national capital New Delhi. With a population of 1,686,976 , it is one of the most populous cities in Uttar Pradesh and the 19th most...
; Pakistani President
President of Pakistan
The President of Pakistan is the head of state, as well as figurehead, of the Islamic Republic of Pakistan. Recently passed an XVIII Amendment , Pakistan has a parliamentary democratic system of government. According to the Constitution, the President is chosen by the Electoral College to serve a...
Pervez Musharraf
Pervez Musharraf
Pervez Musharraf , is a retired four-star general who served as the 13th Chief of Army Staff and tenth President of Pakistan as well as tenth Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff Committee. Musharraf headed and led an administrative military government from October 1999 till August 2007. He ruled...
turned up to meet Indian Prime Minister
Prime Minister of India
The Prime Minister of India , as addressed to in the Constitution of India — Prime Minister for the Union, is the chief of government, head of the Council of Ministers and the leader of the majority party in parliament...
Atal Behari Vajpayee. The talks fell through.
On June 20, 2004, with a new government in place in India, both countries agreed to extend a nuclear testing
Nuclear testing
Nuclear weapons tests are experiments carried out to determine the effectiveness, yield and explosive capability of nuclear weapons. Throughout the twentieth century, most nations that have developed nuclear weapons have tested them...
ban and to set up a hotline
Hotline
In telecommunication, a hotline is a point-to-point communications link in which a call is automatically directed to the preselected destination without any additional action by the user when the end instrument goes off-hook...
between their foreign secretaries aimed at preventing misunderstandings that might lead to a nuclear war
Nuclear warfare
Nuclear warfare, or atomic warfare, is a military conflict or political strategy in which nuclear weaponry is detonated on an opponent. Compared to conventional warfare, nuclear warfare can be vastly more destructive in range and extent of damage...
. http://edition.cnn.com/2004/WORLD/asiapcf/06/20/india.pakistan
As of early 2005, both countries are committed to a process of dialogue to solve all outstanding issues. Baglihar Dam
Baglihar Dam
Baglihar Dam , also known as Baglihar Hydroelectric Power Project, is a run-of-the-river power project on the Chenab River in the southern Doda district of the Indian state of Jammu and Kashmir. This project was conceived in 1992, approved in 1996 and construction began in 1999. The project is...
issue was a new issue raised by Pakistan in 2005.
Fugitives
India has accused some of the most wanted Indian fugitives, such as Dawood IbrahimDawood Ibrahim
Dawood Ibrahim , also known as Dawood Ebrahim, and Sheikh Dawood Hassan, is the head of the organized crime syndicate [[D-Company]] in Mumbai. He is currently on the wanted list of Interpol for organised crime and counterfeiting. He was No. 4 on the Forbes' World's Top 10 most dreaded criminals...
, of having a presence in Pakistan. On May 11, 2011, India released a list of 50 "Most Wanted Fugitives" hiding in Pakistan. This was to tactically pressurize Pakistan after the killing
Death of Osama bin Laden
Osama bin Laden, then head of the Islamist militant group al-Qaeda, was killed in Pakistan on May 2, 2011, shortly after 1 a.m. local time by a United States special forces military unit....
of Osama bin Laden
Osama bin Laden
Osama bin Mohammed bin Awad bin Laden was the founder of the militant Islamist organization Al-Qaeda, the jihadist organization responsible for the September 11 attacks on the United States and numerous other mass-casualty attacks against civilian and military targets...
in his compound in Abbottabad
Osama bin Laden's compound in Abbottabad
Osama bin Laden's compound, known locally as the Waziristan Haveli , is the safe house in which Osama bin Laden was hiding when he was killed. The structure is located at the end of a dirt road in Abbottabad, Pakistan. About 35 Miles north of the capital, Islamibad, and just 0.8 miles southwest of...
.
After two errors in the list received publicity, the Central Bureau of Investigation
Central Bureau of Investigation
The Central Bureau of Investigation is a government agency of India that serves as a criminal investigation body, national security agency and intelligence agency. It was established on 1 April 1963 and evolved from the Special Police Establishment founded in 1941...
removed it from their website pending a review.After this incident the Pakistani interior ministry rejected the list of 50 Most Wanted men forwarded by India to Islamabad, saying it should first probe if those named in the list were even living in the country.
Cultural links
India and Pakistan have shared cultures, cuisines and languages which underpin the historical ties between the two. Pakistani singers, musicians, comedians and entertainers have enjoyed widespread popularity in India, with many achieving overnight fame in the Indian filming industry BollywoodBollywood
Bollywood is the informal term popularly used for the Hindi-language film industry based in Mumbai , Maharashtra, India. The term is often incorrectly used to refer to the whole of Indian cinema; it is only a part of the total Indian film industry, which includes other production centers producing...
. Likewise, Indian music and films are very popular in Pakistan. Being located in the northernmost region of the Indian subcontinent
Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent, also Indian Subcontinent, Indo-Pak Subcontinent or South Asian Subcontinent is a region of the Asian continent on the Indian tectonic plate from the Hindu Kush or Hindu Koh, Himalayas and including the Kuen Lun and Karakoram ranges, forming a land mass which extends...
, much of Pakistan's culture is similar to that of North India
North India
North India, known natively as Uttar Bhārat or Shumālī Hindustān , is a loosely defined region in the northern part of India. The exact meaning of the term varies by usage...
.
The Punjab region
Punjab region
The Punjab , also spelled Panjab |water]]s"), is a geographical region straddling the border between Pakistan and India which includes Punjab province in Pakistan and the states of the Punjab, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Chandigarh and some northern parts of the National Capital Territory of Delhi...
was split into Punjab, Pakistan and Punjab, India following the independence and partition of the two countries in 1947. The Punjabi people
Punjabi people
The Punjabi people , ਪੰਜਾਬੀ ), also Panjabi people, are an Indo-Aryan group from South Asia. They are the second largest of the many ethnic groups in South Asia. They originate in the Punjab region, which has been been the location of some of the oldest civilizations in the world including, the...
are today the largest ethnic group in Pakistan and also an important ethnic group of northern India. The founder of the Sikhism
Sikhism
Sikhism is a monotheistic religion founded during the 15th century in the Punjab region, by Guru Nanak Dev and continued to progress with ten successive Sikh Gurus . It is the fifth-largest organized religion in the world and one of the fastest-growing...
religion was born in the modern-day Pakistani Punjab province, in the city of Nankana Sahib
Nankana Sahib
Nankana Sahib , earlier known as Rai-Bhoi-Di-Talwandi, is a city in the Pakistani province of Punjab. It is named after the first Guru of the Sikhs, Guru Nanak Dev, the central figure in Sikhism who was born here, so it is a city of high historic and religious value and is a popular pilgrimage site...
. Each year, millions of Indian Sikh pilgrims cross over to visit holy Sikh sites in Nankana Sahib.
The Sindhi people
Sindhi people
Sindhis are a Sindhi speaking socio-ethnic group of people originating from Sindh, a province Formerly of British India, now in Pakistan. Today Sindhis that live in Pakistan belong to various religious denominations including Islam, Zoroastrianism, Hinduism, Sikhism and Christianity...
are the native ethnic group of the Pakistani province of Sindh
Sindh
Sindh historically referred to as Ba'ab-ul-Islam , is one of the four provinces of Pakistan and historically is home to the Sindhi people. It is also locally known as the "Mehran". Though Muslims form the largest religious group in Sindh, a good number of Christians, Zoroastrians and Hindus can...
. Many Hindu Sindhis migrated to India in 1947, making the country home to a sizable Sindhi community. In addition, the millions of Muslims who migrated from India to the newly-created Pakistan during independence came to be known as as the Muhajir people
Muhajir people
Muhajir [literally – migrants] is a term commonly used especially by Pakistanis to describe the Muslim immigrants who chose to settle in Pakistan and shifted their domicile after partition of British India into Pakistan and India. Some had participated in the movement for creation of Pakistan in...
; they are settled predominantly in Karachi and still maintain family links in India.
Relations between Pakistan and India have also resumed through platforms such as media and communications. Aman ki Asha
Aman ki Asha
Aman ki Asha is a campaign jointly started by the two leading media houses The Jang Group in Pakistan and The Times of India in India. The campaign aims for mutual peace and development of the diplomatic and cultural relations between the two nations in South Asia. It started on the 1st of January...
is a joint venture and campaign between The Times of India
The Times of India
The Times of India is an Indian English-language daily newspaper. TOI has the largest circulation among all English-language newspaper in the world, across all formats . It is owned and managed by Bennett, Coleman & Co. Ltd...
and the Jang Group calling for mutual peace and development of diplomatic and cultural relations.
Geographic links
The Indo-Pakistani border is the official international boundary that demarcates the Indian states of Punjab, RajasthanRajasthan
Rājasthān the land of Rajasthanis, , is the largest state of the Republic of India by area. It is located in the northwest of India. It encompasses most of the area of the large, inhospitable Great Indian Desert , which has an edge paralleling the Sutlej-Indus river valley along its border with...
and Gujarat from the Pakistani provinces of Punjab and Sindh. The Wagah
Wagah
Wagah is the only road border crossing between Pakistan and India , and lies on the Grand Trunk Road between the cities of Lahore, Pakistan and Amritsar, India. Wagah itself is a village through which the controversial Radcliffe Line was drawn. The village was divided by independence in 1947...
border is the only road crossing between India and Pakistan and lies on the famous Grand Trunk Road
Grand Trunk Road
The Grand Trunk Road also formerly known as Uttarapatha, Shah Rah-e-Azam or Sadak-e-Azam or Badshahi Sadak is one of South Asia's oldest and longest major roads...
, connecting Lahore
Lahore
Lahore is the capital of the Pakistani province of Punjab and the second largest city in the country. With a rich and fabulous history dating back to over a thousand years ago, Lahore is no doubt Pakistan's cultural capital. One of the most densely populated cities in the world, Lahore remains a...
, Pakistan with Amritsar
Amritsar
Amritsar is a city in the northern part of India and is the administrative headquarters of Amritsar district in the state of Punjab, India. The 2001 Indian census reported the population of the city to be over 1,500,000, with that of the entire district numbering 3,695,077...
, India. Each evening, the Wagah border ceremony
Wagah border ceremony
The Wagah border closing 'lowering of the flags' ceremony was a daily military practice that the security forces of India and Pakistan have followed since 1959...
takes place at the Wagah border in which the flags are lowered and guards on both sides make a pompous military display and exchange handshakes.
Linguistic ties
Hindi and Urdu are an Indo-Aryan language and the linga franca, as well as national language, of North India and Pakistan respectively. Standard Urdu is mutually intelligible with Standard Hindi. Both languages share the same Indic base and are so similar in phonology and grammar that they appear to be one language. Most linguists consider them to be two standardized forms of a same language; thus, a speaker of UrduUrdu
Urdu is a register of the Hindustani language that is identified with Muslims in South Asia. It belongs to the Indo-European family. Urdu is the national language and lingua franca of Pakistan. It is also widely spoken in some regions of India, where it is one of the 22 scheduled languages and an...
, the national language in Pakistan, can usually understand a speaker of Hindi
Hindi
Standard Hindi, or more precisely Modern Standard Hindi, also known as Manak Hindi , High Hindi, Nagari Hindi, and Literary Hindi, is a standardized and sanskritized register of the Hindustani language derived from the Khariboli dialect of Delhi...
, which is the primary official language of the Republic of India.
Apart from Hindi and Urdu, India and Pakistan also share a distribution of the Punjabi language
Punjabi language
Punjabi is an Indo-Aryan language spoken by inhabitants of the historical Punjab region . For Sikhs, the Punjabi language stands as the official language in which all ceremonies take place. In Pakistan, Punjabi is the most widely spoken language...
, Kashmiri language
Kashmiri language
Kashmiri is a language from the Dardic sub-group and it is spoken primarily in the Kashmir Valley, in Jammu and Kashmir. There are approximately 5,554,496 speakers in Jammu and Kashmir, according to the Census of 2001. Most of the 105,000 speakers or so in Pakistan are émigrés from the Kashmir...
and Sindhi language
Sindhi language
Sindhi is the language of the Sindh region of Pakistan that is spoken by the Sindhi people. In India, it is among 22 constitutionally recognized languages, where Sindhis are a sizeable minority. It is spoken by 53,410,910 people in Pakistan, according to the national government's Statistics Division...
.
Sporting ties
Cricket and hockey matches between the two (as well as other sports to a lesser degree such as those of the SAARC games) have often been political in nature. During the Soviet invasion of Afghanistan General Zia-ul Haq traveled to India for a bout of "cricket diplomacy" to keep India from supporting the Soviets by opening another front. Pervez Musharaff also tried to do the same more than a decade later but to no avail.In tennis
Tennis
Tennis is a sport usually played between two players or between two teams of two players each . Each player uses a racket that is strung to strike a hollow rubber ball covered with felt over a net into the opponent's court. Tennis is an Olympic sport and is played at all levels of society at all...
, Rohan Bopanna
Rohan Bopanna
Rohan Bopanna is an Indian professional tennis player. His singles career high ranking was 213th in 2007. Recently, most of his appearances in professional tournaments has been in doubles matches. He is a member of the Indian Davis Cup team since 2002...
of India and Aisam-ul-Haq Qureshi
Aisam-ul-Haq Qureshi
Aisam-ul-Haq Qureshi is a professional tennis player from Pakistan. He is currently Pakistan's top player. A top 10 doubles player, his highest Singles Race ranking is 103rd and is the former Asian No. 3...
of Pakistan have formed a successful duo and have been dubbed as the "Indo-Pak Express."
Diasporic relations
Indians and Pakistanis living in Britain are said to have friendly relations with one another. It is quite common for a "Little IndiaLittle India (location)
Little India is an ethnic enclave containing a large population of Indian people within a society where the majority of people are either not South Asians or where the majority in the enclave are indigenous to states in the country of India within a South Asian Society not identifying as Indian...
" and a "Little Pakistan
Little Pakistan
"Little Pakistan" is a general name for an ethnic enclave populated primarily by Pakistanis or people of Pakistani ancestry , usually in an urban neighborhood.-List of Little Pakistans:-Norway:...
" to co-exist in South Asian ethnic enclaves in overseas countries. There are various cities such as Birmingham
Birmingham
Birmingham is a city and metropolitan borough in the West Midlands of England. It is the most populous British city outside the capital London, with a population of 1,036,900 , and lies at the heart of the West Midlands conurbation, the second most populous urban area in the United Kingdom with a...
, Blackburn and Manchester
Manchester
Manchester is a city and metropolitan borough in Greater Manchester, England. According to the Office for National Statistics, the 2010 mid-year population estimate for Manchester was 498,800. Manchester lies within one of the UK's largest metropolitan areas, the metropolitan county of Greater...
where British Indian
British Indian
The term British Indian refers to citizens of the United Kingdom whose ancestral roots lie in India. This includes people born in the UK who are of Indian descent, and Indian-born people who have migrated to the UK...
s and British Pakistanis live alongside each other in peace and harmony. Both Indians and Pakistanis living in the UK fit under the category of British Asian
British Asian
British Asian is a term used to describe British citizens who descended from mainly South Asia, also known as South Asians in the United Kingdom...
. The UK is also home to the Pakistan & India friendship forum.
In the United States, Indians and Pakistanis are classified under the South Asian American category and share many cultural traits.
The British MEP Saj Karim is of Pakistani origin. He is a member of the European Parliament Friends of India Group, Karim was also responsible for opening up Europe to free trade with India. He has given his full support to the Indian government for a death sentence to be given to Ajmal Kasab
Ajmal Kasab
Mohammed Ajmal Amir Kasab is a Pakistani Islamic terrorist who was involved in the 2008 Mumbai attacks in India. Kasab is the only attacker captured alive by police and is currently in Indian custody. The Government of Pakistan initially denied that Kasab was from Pakistan, but in January 2009,...
, who was involved in the 2008 Mumbai attacks
2008 Mumbai attacks
The 2008 Mumbai attacks were more than 10 coordinated shooting and bombing attacks across Mumbai, India's largest city, by Islamist attackers who came from Pakistan...
.
See also
- Foreign relations of IndiaForeign relations of IndiaIndia has formal diplomatic relations with most nations, as the world's second most populous country and the world's most-populous democracy and recently has one of the fastest economic growth rates in the world...
- Foreign relations of PakistanForeign relations of PakistanPakistan is the second largest Muslim country in terms of population , and its status as a declared nuclear power, being the only Islamic nation to have that status, plays a part in its international role....
- History of the Kashmir conflict
- Indo-Pakistani WarsIndo-Pakistani WarsSince the partition of British India in 1947 and creation of India and Pakistan, the two South Asian countries have been involved in four wars, including one undeclared war, as well as many border skirmishes and military stand-offs...
- History of IndiaHistory of IndiaThe history of India begins with evidence of human activity of Homo sapiens as long as 75,000 years ago, or with earlier hominids including Homo erectus from about 500,000 years ago. The Indus Valley Civilization, which spread and flourished in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent from...
- History of PakistanHistory of PakistanThe 1st known inhabitants of the modern-day Pakistan region are believed to have been the Soanian , who settled in the Soan Valley and Riwat almost 2 million years ago. Over the next several thousand years, the region would develop into various civilizations like Mehrgarh and the Indus Valley...
- Human rights in IndiaHuman rights in IndiaThe situation of human rights in India is a complex one, as a result of the country's large size and tremendous diversity, its status as a developing country and a sovereign, secular, democratic republic, and its history as a former colonial territory. The Constitution of India provides for...
- Human rights in PakistanHuman rights in PakistanPakistan’s human rights record has dramatically improved since the reforms that took place after the tenure of President Zia-ul-Haq in 1988. The situation of human rights in Pakistan is a complex one, as a result of the country's diversity, large population, its status as a developing country and a...
- Allegations of state terrorism committed by Pakistan
- India's 50 Most Wanted Fugitives in Pakistan

