
Lima
Encyclopedia
Lima is the capital and the largest city of Peru
. It is located in the valleys of the Chillón
, Rímac
and Lurín
rivers, in the central part of the country, on a desert coast overlooking the Pacific Ocean. Together with the seaport of Callao
, it forms a contiguous urban area known as the Lima Metropolitan Area
. With a population fast approaching 9 million, Lima is the fifth largest city in Latin America, behind Mexico City
, São Paulo
, Buenos Aires
and Rio de Janeiro
. Lima is home to one of the largest financial hubs in Latin America. It has been defined as a beta world city by GaWC international ranking.
Lima was founded by Spanish
conquistador
Francisco Pizarro
on January 18, 1535, as la Ciudad de los Reyes, or "the City of Kings
". It became the capital and most important city in the Spanish Viceroyalty of Peru
. Following the Peruvian War of Independence, it became the capital of the Republic of Peru. Today, around one-third of the Peruvian population lives in the metropolitan area
.
Lima is home to one of the oldest higher learning institutions in the New World. The National University of San Marcos
, founded on May 12, 1551 during Spanish colonial regime
, is the oldest continuously functioning university in the Americas
.
Modern scholars speculate that the word "Lima" originated as the Spanish pronunciation of the native name Limaq. Linguistic evidence seems to support this theory as spoken Spanish consistently rejects stop consonant
s in word-final position. The city was founded in 1535 under the name City of the Kings
because its foundation was decided on January 6, date of the feast of the Epiphany
. Nevertheless, this name quickly fell into disuse and Lima became the city's name of choice; on the oldest Spanish maps of Peru, both Lima and Ciudad de los Reyes can be seen together as names for the city.
It is worth noting that the river that feeds Lima is called Rímac, and many people erroneously assume that this is because its original Inca name is "Talking River" (the Incas spoke a highland variety of Quechua where the word for "talker" was pronounced ˈrimɑq). However, the original inhabitants of the valley were not the Incas, and this name is actually an innovation arising from an effort by the Cuzco
nobility in colonial times to standardize the toponym so that it would conform to the phonology of Cuzco Quechua
. Later, as the original inhabitants of the valley died out and the local Quechua became extinct, the Cuzco pronunciation prevailed. In modern times, Spanish-speaking locals do not see the connection between the name of their city and the name of the river that runs through it. They often assume that the valley is named after the river; however, Spanish documents from the colonial period show the opposite to be true.
 In the pre-Columbian
In the pre-Columbian
era, the location of what is now the city of Lima was inhabited by several Amerindian
groups under the Ychsma polity, which was incorporated into the Inca Empire
in the 15th century. In 1532, a group of Spanish conquistador
s led by Francisco Pizarro
defeated the Inca ruler Atahualpa
and took over his Empire. As the Spanish Crown
had named Pizarro governor of the lands he conquered, he chose the Rímac valley to found his capital on January 18, 1535 as Ciudad de los Reyes (City of the Kings). In August 1536, rebel Inca troops led by Manco Inca
besieged the city but were defeated by the Spaniards and their native allies.
Lima gained prestige after being designated capital of the Viceroyalty of Peru
and site of a Real Audiencia in 1543. During the next century it flourished as the centre of an extensive trade network which integrated the Viceroyalty with the rest of the Americas, Europe and the Far East. However, the city was not free from dangers; the presence of pirates and privateers in the Pacific Ocean lead to the building of the Lima City Walls
between 1684 and 1687. Also in this last year a powerful earthquake
destroyed most of the city buildings; the earthquake marked a turning point in the history of Lima as it coincided with a recession in trade and growing economic competition with other cities such as Buenos Aires
.
 In 1746, a powerful earthquake
In 1746, a powerful earthquake
severely damaged Lima and destroyed Callao, forcing a massive rebuilding effort under Viceroy José Antonio Manso de Velasco
. In the later half of the 18th century, Enlightenment
ideas on public health and social control shaped the development of the city. During this period, Lima was adversely affected by the Bourbon Reforms
as it lost its monopoly on overseas trade and its control over the important mining region of Upper Peru
. The city's economic decline made its elite dependent on royal and ecclesiastical appointment and thus, reluctant to advocate independence.
A combined expedition of Argentine and Chilean patriots under General José de San Martín
managed to land south of Lima in 1820 but did not attack the city. Faced with a naval blockade and the action of guerrillas on land, Viceroy José de la Serna was forced to evacuate its capital on July 1821 to save the Royalist army. Fearing a popular uprising and lacking any means to impose order, the city council invited San Martín to enter Lima and signed a Declaration of Independence at his request. However, the war was not over; in the next two years the city changed hands several times and suffered exactions from both sides.
 After independence, Lima became the capital of the Republic of Peru but economic stagnation and political turmoil brought urban development to a halt. This hiatus ended in the 1850s, when increased public and private revenues from guano
After independence, Lima became the capital of the Republic of Peru but economic stagnation and political turmoil brought urban development to a halt. This hiatus ended in the 1850s, when increased public and private revenues from guano
exports led to a rapid development of the city. The export-led expansion also widened the gap between rich and poor, fostering social unrest. During the 1879–1883 War of the Pacific
, Chilean troops occupied Lima, looting public museums, libraries and educational institutions. At the same time, angry mobs attacked wealthy citizens and the Asian population; sacking their properties and businesses. After the war, the city underwent a process of renewal and expansion from the 1890s up to the 1920s. During this period, the urban layout was modified by the construction of big avenues that crisscrossed the city and connected it with neighboring towns.
In 1940, an earthquake destroyed most of the city, which at that time was mostly built of adobe
and quincha
. In the 1940s, Lima started a period of rapid growth spurred by migration from the Andean regions of Peru, as rural people sought better opportunities for work and education. The population, estimated at 0.6 million in 1940, reached 1.9M by 1960 and 4.8M by 1980. At the start of this period, the urban area was confined to a triangular area bounded by the city's historic centre
, Callao
and Chorrillos; in the following decades settlements spread to the north, beyond the Rímac River, to the east, along the Central Highway, and to the south. The new migrants, at first confined to slum
s in downtown Lima, led this expansion through large-scale land invasions, which evolved into shanty towns, known as pueblos jóvenes
.
 The urban area of Lima covers about 800 km² (308.9 sq mi). It is located on mostly flat terrain in the Peruvian coastal plain
The urban area of Lima covers about 800 km² (308.9 sq mi). It is located on mostly flat terrain in the Peruvian coastal plain
, within the valleys of the Chillón
, Rímac
and Lurín
rivers. The city slopes gently from the shores of the Pacific Ocean into valleys and mountain slopes located as high as 500 metres (1,640.4 ft) above mean sea level. Within the city there are isolated hills which are not connected to the surrounding hill chains, such as El Agustino, San Cosme, El Pino, La Milla, Muleria and Pro hills. The San Cristobal hill in the Rimac district, which lies directly north of the downtown area, is the local extreme of an Andean hill outgrowth.
Metropolitan Lima has an area of 2672.28 km² (1,031.8 sq mi), of which 825.88 km² (318.9 sq mi) (31%) comprise the actual city and 1846.4 km² (712.9 sq mi) (69%) the city outskirts. The urban area extends around 60 km (37.3 mi) from north to south and around 30 km (18.6 mi) from west to east. The city center is located 15 km (9.3 mi) inland at the shore of the Rimac river, a vital resource for the city, since it carries what will become drinking water for its inhabitants and fuels the hydroelectric dams that provide electricity to the area. While no official administrative definition for the city exists, it is usually considered to be composed of the central 30 out of the 43 districts of Lima Province
, corresponding to an urban area centered around the historic Cercado de Lima
district. The city is the core of the Lima Metropolitan Area
, one of the ten largest metropolitan areas in the Americas. Lima is the second largest city in the world located in a desert, after Cairo
, Egypt
.
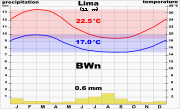 Lima's climate is mild and comfortable, despite being located in the subtropics
Lima's climate is mild and comfortable, despite being located in the subtropics
and in a desert
. Although classified as subtropical, Lima's proximity to the cool waters of the Pacific Ocean leads to temperatures much cooler than those expected for a subtropical desert, and can be classified as a cool desert climate
. It is neither cold nor very hot. Temperatures rarely fall below 12 °C (53.6 °F) or rise above 29 °C (84.2 °F) throughout the entire year. Two distinct seasons can be identified: summer, from December through April; and winter from June through October. May and November are generally transition months, with the warm-to-cool weather transition being more dramatic.
Summers are warm, humid and sunny. Daily temperatures oscillate between lows of 18 °C (64.4 °F) to 22 °C (71.6 °F), and highs of 24 °C (75.2 °F) to 29 °C (84.2 °F). Skies are generally cloud free, especially during daytime. Occasional coastal fogs during some mornings and high clouds during some afternoons and evenings can be present. Lima summer sunsets are well known for being colorful. As such, they have been labeled by the locals as "cielo de brujas" (Spanish for "sky of witches"), since the sky commonly turns into shades of orange, pink and red around 7 pm. Winter weather is dramatically different. Gray skies, breezy conditions, high humidity and cool temperatures prevail. Long (1-week or more) stretches of dark overcast skies are not uncommon. Persistent morning drizzle occurs occasionally from June through September, coating the streets with a thin layer of water that generally dries up by early afternoon. Winter temperatures in Lima do not vary much between day and night. They range from lows of 12 °C (53.6 °F) to 16 °C (60.8 °F) and highs of 16 °C (60.8 °F) to 19 °C (66.2 °F), rarely exceeding 20 °C (68 °F) except in the easternmost districts.
Relative humidity
is always very high, particularly in the mornings. High humidity produces brief morning fog during the early summer and a usually persistent low cloud deck during the winter (generally developing in May and persisting all the way into late November or even early December). Predominant onshore flow makes the Lima area one of the cloudiest among the entire Peruvian coast. Lima has only 1284 hours of sunshine a year, 28.6 hours in July and 179.1 hours in January, exceptionally low values for the latitude. Winter cloudiness prompts locals to seek for sunshine in Andean valleys located at elevations generally above 500 meters above sea level
.
Although relative humidity levels are high, rainfall is very low due to strong atmospheric stability. The severely low rainfall impacts on water supply in the city, which originates from wells and from rivers that flow from the Andes
. Inland districts receive anywhere between 1 to 6 cm (2.4 in) of rainfall per year, which accumulates mainly during the winter months. Coastal districts receive only 1 to 3 cm (1.2 in). As previously mentioned, winter precipitation occurs in the form of persistent morning drizzle events. These are locally called 'garúa', 'llovizna' or 'camanchacas
'. Summer rain, on the other hand, is infrequent, and occurs in the form of isolated light and brief showers. These generally occur during afternoons and evenings when leftovers from Andean storms arrive from the east. The lack of heavy rainfall arises from high atmospheric stability caused, in term, by the combination of cool waters from semi-permanent coastal upwelling and the presence of the cold Humboldt Current
; and warm air aloft associated with the South Pacific anticyclone.
The climate of Lima (as that of most of the Peruvian coast) gets severely disrupted during El Niño
events. Water temperatures along the coast, which usually average around 17 –, get much warmer (as in 1998 when the water temperature reached 26 °C (78.8 °F)). Air temperatures rise accordingly. Such was the case when Lima hit its all-time record high of 34 °C (93.2 °F). Cooler climate develops during La Niña years. The all-time record low in the metropolitan area is 8 °C (46.4 °F), measured during the winter of 1988.
and a population density of 3008.8 PD/km2 as of 2007, Lima ranks as the 27th most populous 'agglomeration' in the world. Its population features a very complex mix of racial and ethnic groups. Mestizo
s of mixed Amerindian
and European
(mostly Spanish and Italians) ancestry are the largest ethnic group. European Peruvians are the second largest group. Many are of Spanish
, Italian
or German
descent; many others are of French
, British
, or Croatian descent. The minorities in Lima include Amerindians (mostly Aymara and Quechua
), Afro-Peruvian
s, whose African ancestors were initially brought to the region as slaves, are yet another part of the city's ethnic diversity. There are also numerous Jews of European descent and Middle Easterners. Asians
make up a large number of the metropolitan population, especially of Chinese (Cantonese) and Japanese
descent, whose ancestors came mostly in the 19th and early 20th centuries. Lima has, by far, the largest ethnic Chinese community in Latin America.
The first settlement in what would become Lima was made up of only 117 housing blocks. In 1562, another district was built at the other side of the Rimac River and in 1610, the first stone bridge was built. Lima then had a population of around 26,000; blacks made up around 40% of the population, and whites made up around 38% of the population. By 1748, the white population totaled 16,000–18,000. In 1861, the number of inhabitants surpassed 100,000, and by 1927, this amount was doubled.
During the early twentieth century, thousands of immigrants came to the city, including a significant number of French, Italians and Germans, many of whom have assimilated to the Peruvian society. They organized in social clubs, and they built their own schools; for example, The American-Peruvian school which is located in Miraflores; the French Alliance (Alianza Francesa de Lima), the notable Lycée Franco-Péruvien and the hospital Maison de Sante;; the British-Peruvian school in Monterrico and also several German-Peruvian schools.
They influenced Peruvian cuisine, the Italians in particular exerting a strong influence in the Miraflores and San Isidro areas with their restaurants, called trattorias.
A great number of Chinese immigrants, and a lesser amount of Japanese, came to Lima and established themselves in the Barrios Altos neighborhood near downtown Lima. Lima residents refer to their Chinatown as Calle Capon, and the city's ubiquitous Chifa restaurants a small, sit-down, usually Chinese-run restaurant serving the Peruvian spin on Chinese cuisine can be found by the dozen in this Chinese enclave.
The Metropolitan area, with around 7000 factories, spearheads the industrial development of the country, thanks to the quantity and quality of the available workforce
, cheap infrastructure and the mostly developed routes and highways in the city. The most relevant industrial sectors are textiles, clothing and food. Chemicals, fish, leather and oil derivatives are also manufactured and/or processed in Lima. The financial district is located in the district of San Isidro, while much of the industrial activity takes place in the area stretching west of downtown Lima to the airport in Callao
. Lima has the largest exportation industry in South America, and it is a regional hub for the operational cargo industry.
Industrialization began to take hold in Lima in 1930s and by 1950s, through import substitution policies, by 1950 manufacturing made up 14% of the GNP
. In the late 1950s, up to 70% of consumer goods were manufactured in factories located in Lima.
The Callao seaport is one of the main fishing and commerce ports in South America, with 75% of the country's imports and 25% of its exports using it as their entry/departure point. The main export goods leaving the country through Callao are oil, steel, silver, zinc, cotton, sugar and coffee.
Lima generates 53% of the GDP of Peru
. In 2010, GDP per capita in Lima reached $20,000.
Most of the foreign companies operating in the country have settled in Lima, which has led to the previously mentioned concentration of economic and financial activity on the city.
There has been a noticeable increase in light industries, services and high technologies. In 2007, the Peruvian economy grew 9%, the largest growth rate in all of South America which was spearheaded by economic policies originating in Lima. The Lima Stock Exchange grew 185.24% in 2006 and in 2007 grew 168.3%, making it one of the fastest growing stock exchanges in the world. In 2006, the Lima Stock Exchange was the most profitable in the world. The unemployment rate in the metropolitan area is 7.2%.
The Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation Summit
and the Latin America, the Caribbean and the European Union Summit
were hosted by the city of Lima.
Lima is headquarters to many major banks such as Banco de Crédito del Perú
, Interbank
, Bank of the Nation
, Banco Continental, MiBanco, Banco Interamericano de Finanzas, Banco Finaciero, Banco de Comercio, and Credi Scotia. It is also a regional headquarters to Standard Chartered. Major insurance coorperations based in Lima include Rimac Seguros, Mapfre Peru, Interseguro, Pacifico, Protecta, and La Positiva.
. As such, it is home to the three branches of the Government of Peru
. The executive branch is headquartered in the Government Palace
, located in the Plaza Mayor
. The legislative branch
is headquartered in the Legislative Palace
and is home to the Congress of Peru
. The Judicial branch
is headquartered in the Palace of Justice
and is home to the Supreme Court of Peru
. Likewise, all the ministries are located in the city of Lima. In international government, the city of Lima is home to the headquarters of the Andean Community of Nations
and the South American Community of Nations
, along with other regional and international organizations.
The Palace of Justice
in Lima is seat of the Supreme Court of Justice
the highest judicial court in Peru with jurisdiction over the entire territory of Peru. Lima is also seat of two of the 28 second highest or Superior Courts of Justice
. The first and oldest Superior Court in Lima is the Superior Court of Justice of Lima belonging to the Judicial District of Lima
. Due to the judicial organization of Peru
, the highest concentration of courts is located in Lima despite the fact that its judicial district only has jurisdiction over 35 of the 43 districts of Lima. The Superior Court of the Cono Norte is the second Superior Court located in Lima and is part of the Judicial District of North Lima
. This judicial district has jurisdiction over the remaining eight districts all located in northern Lima.
, acts as and has functions similar to a regional government
, as it does not belong to any of the 25 regions of Peru
.
.jpg) Lima's architecture is characterized by a mix in styles as reflected from shifts between trends throughout various time periods of the city's history. Examples of early colonial architecture include such structures as the Monastery of San Francisco, the Cathedral of Lima and the Torre Tagle Palace
Lima's architecture is characterized by a mix in styles as reflected from shifts between trends throughout various time periods of the city's history. Examples of early colonial architecture include such structures as the Monastery of San Francisco, the Cathedral of Lima and the Torre Tagle Palace
. These constructions are generally influenced by the Spanish baroque
, Spanish Neoclassicism
, and Spanish Colonial styles. After independence, a gradual shift towards the neoclassical
and Art Nouveau
styles took place. Many of these constructions were greatly influenced by French architectural
styles. Many government buildings as well as major cultural institutions were contracted in this architectural time period. During 1960s, constructions utilizing the brutalist
style began appearing in Lima due to the military government of Juan Velasco. Examples of this architecture include the Museum of the Nation
and the Ministry of Defense. The 21st century has seen the appearance of glass skyscrapers
, particularly around the city's financial district. Also there are several new architectural and real estate projects.
The largest parks of Lima are located near the downtown area such as the Park of the Reserve
, Park of the Exposition
, Campo de Marte
, and the University Park. The Park of the Reserve
is home to the largest fountain complex in the world known as the Magical Circuit of Water. A number of large parks lie outside the city center, including Reducto Park, Pantanos de Villa, El Golf (San Isidro), Parque de las Leyendas (Lima Zoo), El Malecon de Miraflores, and the Golf Los Incas. The street grid of the city of Lima, is laid out with a system of plazas of which serve a purpose similar to roundabouts or junctions. In addition to this practical purpose, plazas serve as one of Lima's principal green spaces and contain a variety of different types of architecture ranging from monuments to statues, and water fountains.
, African
and Asian
culture, Lima is a melting pot of cultures due to colonization, immigration
, and indigenous influences. The Historic Center of Lima was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1988. Like many other world capitals, Lima is home to prestigious museums, many of which are world renowned.
Limean cuisine is known to be among the best in the world, and the city is known as the Gastronomical Capital of the Americas. Lima's gastronomy is a mix of Spanish
, Andean
, and Asian
culinary traditions.
Lima's beaches, located along the northern and southern ends of the city, are heavily visited during the summer months. Numerous restaurants, clubs and hotels have been opened in these places to serve the many beachgoers. Lima has a vibrant and active theater scene, as there are many theaters presenting not only classic theater, but also cultural presentations, modern theater, experimental theater, dramas, dance performances, and theater for children. Lima is home to many important theaters, such as the Municipal Theater
, Segura Theater, Japanese-Peruvian Theater, Marsano Theater, British theater, Theater of the PUCP Cultural Center, and the Yuyachkani Theater.
. Throughout the colonial era, most of the Spanish colonial nobility based in Lima were originally from Castile. Limean Spanish is also characterized by the lack of voseo
, a trait present in the dialects of many other Latin American countries. This is because voseo was primarily used by the lower socioeconomic classes of Spain, a social group that did not begin to appear in Lima until the late colonial era.
Limean Spanish is distinguished by its relative clarity in comparison to other Latin American accents. Limean Spanish has been influenced by a number of immigrant groups including Italians, Andalusians
, Chinese and Japanese. It also has been influenced by anglicism
s as a result of globalization
, as well as by Andean Spanish, due to the recent migration from the Andean highlands to Lima.
, The Sala Museo Oro del Perú Larcomar, the Museum of Italian Art, and the Museum of Gold, and the Larco Museum
. These museums mostly focus on art, pre-Columbian cultures
, natural history, science and religion. There's a particularity with the Museum of Italian Art
, which is the only museum that shows European art in Peru.
The Historic Center of Lima, made up of the districts of Lima
and Rimac
, was declared a World Heritage Site
by UNESCO
in 1988 due to its importance during the colonial era leaving a testimony to architectural achievement. Some examples of this historical colonial architecture include the Monastery of San Francisco, the Plaza Mayor
, the Cathedral, Covenant of Santo Domingo, the Palace of Torre Tagle
, and much more.
A tour of the city's churches is a popular circuit among tourists. A short jaunt through the central district goes through many churches dating from as early as the 16th and 17th centuries, the most noteworthy of which are the Cathedral of Lima and the Monastery of San Francisco, said to be connected by their subterrestrial catacombs
. Both of these churches contain paintings from various schools of art, Sevilian tile, and finely sculpted wood furnishings.
Also notable is the Sanctuary of Las Nazarenas
, the point of origin for the Lord of Miracles
, whose festivities in the month of October constitute the most important religious event in Lima, and a major one of Peru. Some sections of the Lima City Walls
still remain and are frequented by tourists. These examples of medieval Spanish fortifications were built to defend the city from attacks by pirates and privateers.
Beaches are visited during the summer months, which are located along the Pan-American Highway
, to the south of the city in districts such as Lurin
, Punta Hermosa, Santa María del Mar (Peru), San Bartolo
and Asia
. Many restaurants, nightclubs, lounges, bars, clubs, and hotels have developed in said places to cater to beachgoers.
The suburban districts of Cieneguilla
, Pachacamac
, and the city of Chosica
, are important tourist attractions among locals. Because they are located at a higher elevation than Lima, they receive more sunshine in winter months, something that the city of Lima frequently lacks under seasonal fog.
, Chifa
s, Cebicherias
, and Pollerias
. Peruvian cuisine
, widely represented in Lima, holds various Guinness World Records
, for its diversity and quality.
and basketball
, many of which are located within private clubs. A popular sport among Limeans is fronton, a racquet sport
similar to squash invented in Lima. The city is home to seven international-class golf
links. Equestrian
is popular in Lima with many private clubs as well as the Hipódromo de Monterrico
horse racing track. The most popular sport in Lima by far is football with many professional club teams being located in the city.
The Historic Plaza de Acho, located in the Rimac district a few minutes from the Plaza de Armas, holds bullfights yearly. The season typically runs from late October to December.
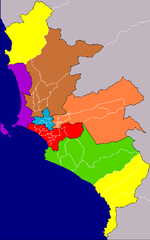 Lima is made up of thirty densely-populated districts, each headed by a local mayor and the Mayor of Lima, whose authority extends to these and the thirteen outer districts of the Lima province.
Lima is made up of thirty densely-populated districts, each headed by a local mayor and the Mayor of Lima, whose authority extends to these and the thirteen outer districts of the Lima province.
The city's historic centre
is located in the Cercado de Lima
district, locally known as simply Lima, or as "El Centro" ("Downtown
"), and it is home to most of the vestiges of Lima's colonial
past, the Presidential Palace , the Metropolitan Municipality of Lima , and dozens of hotels, some operating and some defunct, that used to cater to the national and international elite.
The upscale San Isidro district is the city's financial center. It is home to many prominent figures such as politicians and celebrities. It is also where the main banks of Peru and branch offices of world banks are headquartered. San Isidro has many parks, including Parque El Olivar, which has olive trees that were brought from Spain during the seventeenth century.
Another upscale district is Miraflores
, which has many luxury hotels, shops and restaurants. Miraflores
has more parks and green areas in the south of Lima than most other districts. Larcomar, a popular shopping mall and entertainment center built on cliffs overlooking the Pacific Ocean, featuring bars, dance clubs, movie theaters, cafes, shops, boutiques and galleries, is also located in this district. Nightlife, shopping and entertainment also center around Parque Kennedy, a park in the heart of Miraflores that is always bustling with people and live performances.
La Molina, San Borja and Santiago de Surco
, home to the American Embassy and the exclusive Club Polo Lima, are the other three wealthy districts of Lima.
The most densely-populated districts of Lima lie in the northern and southern ends of the city (Spanish: Cono Norte
and Cono Sur
, respectively), and they are mostly composed of Andean immigrants who arrived during the mid and late 20th century looking for better living standards and economic opportunities, or as refugees of the country's internal conflict with the Shining Path
during the late 80s and early '90s. In the case of Cono Norte (now called Lima Norte
), certain shopping malls like Megaplaza and Royal Plaza have been recently built in the Independencia
district, right on the border with the Los Olivos district, the latter being the most residential neighborhood in the Northern part of Lima. Most of the inhabitants of this area belong to the middle class
or lower middle class
.
Barranco, which borders Miraflores
by the Pacific Ocean, is known as the city's bohemian district, home or once home of many Peruvian writers and intellectuals like Mario Vargas Llosa, Chabuca Granda and Alfredo Bryce Echenique. This district has many acclaimed restaurants, music venues called "peñas" featuring the traditional folk music of coastal Peru (in Spanish, "música criolla"), and beautiful Victorian-style chalets. It along with Miraflores serves as the home to the foreign nightlife scene.
, founded on May 12, 1551 during Spanish colonial regime
, is the oldest continuously functioning university in the Americas
.
Universidad Nacional de Ingeniería (UNI) was founded in 1876 by Polish engineer Eduardo de Habich and is the most important engineering school in the country. Other public universities also play key roles in teaching and research, such as the Universidad Nacional Federico Villarreal
(the second largest in the country), the Universidad Nacional Agraria La Molina where ex-president Alberto Fujimori
once taught, and the National University of Callao.
The Pontificia Universidad Católica del Perú, established in 1917, is the oldest private university. Other private institutions that are located in the city are Universidad del Pacifico, Universidad de Lima, Universidad San Martín de Porres
, Universidad Peruana Cayetano Heredia, Universidad Cientifica del Sur
, Universidad San Ignacio de Loyola
, Universidad Peruana de Ciencias Aplicadas and Universidad Ricardo Palma.
, located in Callao
(LIM). It is the largest airport of the country with the largest amount of domestic and international air traffic. It also serves as a major hub in the Latin American air network. Lima's Jorge Chavez International Airport is the fourth largest air hub in South America. The airport, however it is the base for the largest cargo hub in the continent. Additionally, Lima possesses five other airports: the Las Palmas Air Force Base, Collique Airport, and runways in Santa María del Mar, San Bartolo
and Chilca
.
. Because of its location on the country's central coast, Lima is also an important junction in Peru's highway system. Three of the major highways originate in Lima.
The city of Lima has one big bus terminus station located next to the mall Plaza norte in the north of the city. This bus station is the point of departure and arrival of a lot of buses with national and international destinations.
There are other bus stations for each company around the city. In addition, there are informals bus stations located in the south, center and north of the city; these bus stations are cheap and confusing, but manageable if you know your destination and have a basic comprehension of Spanish.
allows Callao to act as the metropolitan area's foremost port. Callao concentrates nearly all of the maritime transport of the metropolitan area. There is, however, a small port in Lurín
whose transit mostly is accounted for by oil tankers due to a refinery being located nearby. Nonetheless, maritime transport inside Lima's city limits is relatively insignificant compared to that of Callao, the nation's leading port and one of Latin America's largest.
which runs from Lima through the departments of Junin
, Huancavelica
, Pasco
, and Huanuco
. Major cities along this line include Huancayo
, La Oroya
, Huancavelica
, and Cerro de Pasco
. Another inactive line runs from Lima northwards to the city of Huacho
.
The urban transport system is composed of over 652 transit routes which are served by buses, microbuses, and combis. The system is unorganized and is characterized by the lack of formality. The service is run by 464 private companies which are poorly regulated by the local government. Fares average at around one sol
or $0.30 USD. The city of Lima has also more than 100 km of cycle paths.
Taxis in the city are mostly informal; they are relatively cheap but could be dangerous (mostly because of the way the "taxistas" drive). There are no meters so drivers are told the desired destination and the fare is agreed upon before the passenger enters the taxi. Taxis vary in sizes from small four door compacts to large vans. They are virtually everywhere, with different colours, accounting for a large part of the car stock. In many cases they are just a private car with a taxi sticker on the windshield. Additionally, there are several companies that provide taxi service on-call.
Automobile
s, known as colectivos, render express service on some major roads of the Lima Metropolitan Area
. The colectivos signal their specific destination with a sign on the their windshield. Their routes are not generally publicitized but are understood by frequent users. The cost is generally higher than public transport however they cover greater distances at greater speeds due to the lack of stops. This service is informal and is not allowed in the city. Some people in the periphery of the city use the so called "mototaxi" for short distances
The Metropolitan Transportation System or El Metropolitano
is a public transportation system which integrate the Independent Corridor of Mass-Transit Buses known by its Spanish initials as (COSAC 1). This system links the principal points of the Lima Metropolitan Area
and the first phase of this project has thirty three km line from the north of the city to Chorrillos in the south of the city. It began commercial operations on July 28th, 2010. This system is similar to the TransMilenio
of Bogotá
, Colombia
.
The Lima Metro
, an above ground mass transit system, which 3rd phase of the Line One is already opened to public. There are six more lines in planning phase. Line 1's extension to the city's center
was opened in July 2011, linking Villa el Salvador
with downtown Lima
in a matter of only thirty minutes, a trip which currently lasts one hour and forty minutes with other public transport system.
The Lima Metro has sixteen passenger stations, located at an average distance of 1.2 km (0.7 mi). It starts its path in the Industrial Park of Villa El Salvador, south of the city, continuing on to Av. Pachacútec in Villa María del Triunfo and then to Av. Los Héroes in San Juan de Miraflores. Afterwards, it continues through Av. Tomás Marsano in Surco to reach Ov. Los Cabitos and then on to Av. Aviación to finish in Av. Grau in the city center.
Construction to extend Line 1 until its final destination, through Av. Próceres de la Independencia in San Juan de Lurigancho, is scheduled to begin shortly.
Lima is twinned with:
Peru
Peru , officially the Republic of Peru , is a country in western South America. It is bordered on the north by Ecuador and Colombia, on the east by Brazil, on the southeast by Bolivia, on the south by Chile, and on the west by the Pacific Ocean....
. It is located in the valleys of the Chillón
Chillón River
The Chillón River is a river located in western Peru. Its waters are produced by the melting of ice in the glaciers of the Andes, and its mouth is located in the Pacific Ocean coast of the Callao Region. Its volume gets higher during the summer months . The river's valley is very fertile...
, Rímac
Rímac River
The Rímac River is located in western Peru and is the most important source of potable water for the Lima and Callao Metropolitan Area.The river is part of the Pacific watershed and has a length of 160 km...
and Lurín
Lurín River
The the lurin river is a is a long watercourse located in the Lima Region of Peru. It originates in the glaciers and lagoons of the western Andes and is known as the Chalilla River until joining the Taquía creek where it receives its common name. Its main tributaries are the Taquía, Llacomayqui,...
rivers, in the central part of the country, on a desert coast overlooking the Pacific Ocean. Together with the seaport of Callao
Callao
Callao is the largest and most important port in Peru. The city is coterminous with the Constitutional Province of Callao, the only province of the Callao Region. Callao is located west of Lima, the country's capital, and is part of the Lima Metropolitan Area, a large metropolis that holds almost...
, it forms a contiguous urban area known as the Lima Metropolitan Area
Lima Metropolitan Area
The Lima Metropolitan Area , is an area formed by the conurbation of the Peruvian cities of Lima and Callao. It is the largest metropolitan area in Peru, the eighth largest in the Americas, and among the thirty largest in the world. The conurbation process started to be evident in the 1980s. The...
. With a population fast approaching 9 million, Lima is the fifth largest city in Latin America, behind Mexico City
Mexico City
Mexico City is the Federal District , capital of Mexico and seat of the federal powers of the Mexican Union. It is a federal entity within Mexico which is not part of any one of the 31 Mexican states but belongs to the federation as a whole...
, São Paulo
São Paulo
São Paulo is the largest city in Brazil, the largest city in the southern hemisphere and South America, and the world's seventh largest city by population. The metropolis is anchor to the São Paulo metropolitan area, ranked as the second-most populous metropolitan area in the Americas and among...
, Buenos Aires
Buenos Aires
Buenos Aires is the capital and largest city of Argentina, and the second-largest metropolitan area in South America, after São Paulo. It is located on the western shore of the estuary of the Río de la Plata, on the southeastern coast of the South American continent...
and Rio de Janeiro
Rio de Janeiro
Rio de Janeiro , commonly referred to simply as Rio, is the capital city of the State of Rio de Janeiro, the second largest city of Brazil, and the third largest metropolitan area and agglomeration in South America, boasting approximately 6.3 million people within the city proper, making it the 6th...
. Lima is home to one of the largest financial hubs in Latin America. It has been defined as a beta world city by GaWC international ranking.
Lima was founded by Spanish
Spanish people
The Spanish are citizens of the Kingdom of Spain. Within Spain, there are also a number of vigorous nationalisms and regionalisms, reflecting the country's complex history....
conquistador
Conquistador
Conquistadors were Spanish soldiers, explorers, and adventurers who brought much of the Americas under the control of Spain in the 15th to 16th centuries, following Europe's discovery of the New World by Christopher Columbus in 1492...
Francisco Pizarro
Francisco Pizarro
Francisco Pizarro González, Marquess was a Spanish conquistador, conqueror of the Incan Empire, and founder of Lima, the modern-day capital of the Republic of Peru.-Early life:...
on January 18, 1535, as la Ciudad de los Reyes, or "the City of Kings
Biblical Magi
The Magi Greek: μάγοι, magoi), also referred to as the Wise Men, Kings, Astrologers, or Kings from the East, were a group of distinguished foreigners who were said to have visited Jesus after his birth, bearing gifts of gold, frankincense and myrrh...
". It became the capital and most important city in the Spanish Viceroyalty of Peru
Viceroyalty of Peru
Created in 1542, the Viceroyalty of Peru was a Spanish colonial administrative district that originally contained most of Spanish-ruled South America, governed from the capital of Lima...
. Following the Peruvian War of Independence, it became the capital of the Republic of Peru. Today, around one-third of the Peruvian population lives in the metropolitan area
Lima Metropolitan Area
The Lima Metropolitan Area , is an area formed by the conurbation of the Peruvian cities of Lima and Callao. It is the largest metropolitan area in Peru, the eighth largest in the Americas, and among the thirty largest in the world. The conurbation process started to be evident in the 1980s. The...
.
Lima is home to one of the oldest higher learning institutions in the New World. The National University of San Marcos
National University of San Marcos
The National University of San Marcos is the most important and respected higher-education institution in Peru. Its main campus, the University City, is located in Lima...
, founded on May 12, 1551 during Spanish colonial regime
Viceroyalty of Peru
Created in 1542, the Viceroyalty of Peru was a Spanish colonial administrative district that originally contained most of Spanish-ruled South America, governed from the capital of Lima...
, is the oldest continuously functioning university in the Americas
Americas
The Americas, or America , are lands in the Western hemisphere, also known as the New World. In English, the plural form the Americas is often used to refer to the landmasses of North America and South America with their associated islands and regions, while the singular form America is primarily...
.
Etymology
According to early Spanish chronicles the Lima area was once called Itchyma, after its original inhabitants. However, even before the Inca occupation of the area in the 15th century, a famous oracle in the Rímac valley had come to be known by visitors as limaq (limaq, pronounced ˈlimɑq, which means "talker" in coastal Quechua). This oracle was eventually destroyed by the Spanish and replaced with a church, but the name persisted in the local language, thus the chronicles show "Límac" replacing "Ychma" as the common name for the area.Modern scholars speculate that the word "Lima" originated as the Spanish pronunciation of the native name Limaq. Linguistic evidence seems to support this theory as spoken Spanish consistently rejects stop consonant
Stop consonant
In phonetics, a plosive, also known as an occlusive or an oral stop, is a stop consonant in which the vocal tract is blocked so that all airflow ceases. The occlusion may be done with the tongue , lips , and &...
s in word-final position. The city was founded in 1535 under the name City of the Kings
Biblical Magi
The Magi Greek: μάγοι, magoi), also referred to as the Wise Men, Kings, Astrologers, or Kings from the East, were a group of distinguished foreigners who were said to have visited Jesus after his birth, bearing gifts of gold, frankincense and myrrh...
because its foundation was decided on January 6, date of the feast of the Epiphany
Epiphany (Christian)
Epiphany, or Theophany, meaning "vision of God",...
. Nevertheless, this name quickly fell into disuse and Lima became the city's name of choice; on the oldest Spanish maps of Peru, both Lima and Ciudad de los Reyes can be seen together as names for the city.
It is worth noting that the river that feeds Lima is called Rímac, and many people erroneously assume that this is because its original Inca name is "Talking River" (the Incas spoke a highland variety of Quechua where the word for "talker" was pronounced ˈrimɑq). However, the original inhabitants of the valley were not the Incas, and this name is actually an innovation arising from an effort by the Cuzco
Cusco
Cusco , often spelled Cuzco , is a city in southeastern Peru, near the Urubamba Valley of the Andes mountain range. It is the capital of the Cusco Region as well as the Cuzco Province. In 2007, the city had a population of 358,935 which was triple the figure of 20 years ago...
nobility in colonial times to standardize the toponym so that it would conform to the phonology of Cuzco Quechua
Cusco Quechua
Cusco Quechua is a dialect of the Southern Quechua language, more specifically Qusqu-Qullaw Quechua, spoken in city and the department of Cusco....
. Later, as the original inhabitants of the valley died out and the local Quechua became extinct, the Cuzco pronunciation prevailed. In modern times, Spanish-speaking locals do not see the connection between the name of their city and the name of the river that runs through it. They often assume that the valley is named after the river; however, Spanish documents from the colonial period show the opposite to be true.
History

Pre-Columbian
The pre-Columbian era incorporates all period subdivisions in the history and prehistory of the Americas before the appearance of significant European influences on the American continents, spanning the time of the original settlement in the Upper Paleolithic period to European colonization during...
era, the location of what is now the city of Lima was inhabited by several Amerindian
Indigenous peoples of the Americas
The indigenous peoples of the Americas are the pre-Columbian inhabitants of North and South America, their descendants and other ethnic groups who are identified with those peoples. Indigenous peoples are known in Canada as Aboriginal peoples, and in the United States as Native Americans...
groups under the Ychsma polity, which was incorporated into the Inca Empire
Inca Empire
The Inca Empire, or Inka Empire , was the largest empire in pre-Columbian America. The administrative, political and military center of the empire was located in Cusco in modern-day Peru. The Inca civilization arose from the highlands of Peru sometime in the early 13th century...
in the 15th century. In 1532, a group of Spanish conquistador
Conquistador
Conquistadors were Spanish soldiers, explorers, and adventurers who brought much of the Americas under the control of Spain in the 15th to 16th centuries, following Europe's discovery of the New World by Christopher Columbus in 1492...
s led by Francisco Pizarro
Francisco Pizarro
Francisco Pizarro González, Marquess was a Spanish conquistador, conqueror of the Incan Empire, and founder of Lima, the modern-day capital of the Republic of Peru.-Early life:...
defeated the Inca ruler Atahualpa
Spanish conquest of the Inca Empire
The Spanish conquest of the Inca Empire was one of the most important campaigns in the Spanish colonization of the Americas. This historic process of military conquest was made by Spanish conquistadores and their native allies....
and took over his Empire. As the Spanish Crown
Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire comprised territories and colonies administered directly by Spain in Europe, in America, Africa, Asia and Oceania. It originated during the Age of Exploration and was therefore one of the first global empires. At the time of Habsburgs, Spain reached the peak of its world power....
had named Pizarro governor of the lands he conquered, he chose the Rímac valley to found his capital on January 18, 1535 as Ciudad de los Reyes (City of the Kings). In August 1536, rebel Inca troops led by Manco Inca
Manco Inca Yupanqui
Manco Inca Yupanqui was one of the Incas of Vilcabamba. He was also known as "Manco II" and "Manco Cápac II" . Born in 1516, he was one of the sons of Huayna Cápac and came from a lower class of the nobility.Túpac Huallpa, a puppet ruler crowned by conquistador Francisco Pizarro, died in 1533...
besieged the city but were defeated by the Spaniards and their native allies.
Lima gained prestige after being designated capital of the Viceroyalty of Peru
Viceroyalty of Peru
Created in 1542, the Viceroyalty of Peru was a Spanish colonial administrative district that originally contained most of Spanish-ruled South America, governed from the capital of Lima...
and site of a Real Audiencia in 1543. During the next century it flourished as the centre of an extensive trade network which integrated the Viceroyalty with the rest of the Americas, Europe and the Far East. However, the city was not free from dangers; the presence of pirates and privateers in the Pacific Ocean lead to the building of the Lima City Walls
Lima City Walls
The Lima city walls were built by Viceroy Melchor de Navarra y Rocafull between 1684 and 1687 to protect Lima against attacks from pirates and privateers. They included 34 bulwarks and five gates; their total cost was estimated at 400,000 Spanish dollars...
between 1684 and 1687. Also in this last year a powerful earthquake
1687 Peru earthquake
The 1687 Peru earthquake occurred at 11:30 UTC on October 20. It had an estimated magnitude of 8.4–8.7 and caused severe damage to Lima, Callao and Ica. It triggered a tsunami and overall about 5,000 people died.-Tectonic setting:...
destroyed most of the city buildings; the earthquake marked a turning point in the history of Lima as it coincided with a recession in trade and growing economic competition with other cities such as Buenos Aires
Buenos Aires
Buenos Aires is the capital and largest city of Argentina, and the second-largest metropolitan area in South America, after São Paulo. It is located on the western shore of the estuary of the Río de la Plata, on the southeastern coast of the South American continent...
.

1746 Lima-Callao earthquake
The 1746 Lima-Callao earthquake occurred at 22:30 local time on 28 October . The epicenter was located about 90 km north-northwest from Lima. It caused almost complete destruction of the capital Lima and the subsequent tsunami devastated the port city of Callao...
severely damaged Lima and destroyed Callao, forcing a massive rebuilding effort under Viceroy José Antonio Manso de Velasco
José Antonio Manso de Velasco
José Antonio Manso de Velasco y Sánchez de Samaniego, 1st Count of Superunda was a Spanish soldier and politician who served as governor of Chile and viceroy of Peru.-As Governor of Chile:...
. In the later half of the 18th century, Enlightenment
Age of Enlightenment
The Age of Enlightenment was an elite cultural movement of intellectuals in 18th century Europe that sought to mobilize the power of reason in order to reform society and advance knowledge. It promoted intellectual interchange and opposed intolerance and abuses in church and state...
ideas on public health and social control shaped the development of the city. During this period, Lima was adversely affected by the Bourbon Reforms
Bourbon Reforms
The Bourbon Reforms were a set of economic and political legislation introduced by the Spanish Crown under various kings of the House of Bourbon throughout the 18th century. The reforms were intended to stimulate manufacturing and technology in order to modernize Spain...
as it lost its monopoly on overseas trade and its control over the important mining region of Upper Peru
Upper Peru
Upper Peru was the region in the Viceroyalty of Peru, and after 1776, the Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata, comprising the governorships of Potosí, La Paz, Cochabamba, Los Chiquitos, Moxos and Charcas...
. The city's economic decline made its elite dependent on royal and ecclesiastical appointment and thus, reluctant to advocate independence.
A combined expedition of Argentine and Chilean patriots under General José de San Martín
José de San Martín
José Francisco de San Martín, known simply as Don José de San Martín , was an Argentine general and the prime leader of the southern part of South America's successful struggle for independence from Spain.Born in Yapeyú, Corrientes , he left his mother country at the...
managed to land south of Lima in 1820 but did not attack the city. Faced with a naval blockade and the action of guerrillas on land, Viceroy José de la Serna was forced to evacuate its capital on July 1821 to save the Royalist army. Fearing a popular uprising and lacking any means to impose order, the city council invited San Martín to enter Lima and signed a Declaration of Independence at his request. However, the war was not over; in the next two years the city changed hands several times and suffered exactions from both sides.

Guano
Guano is the excrement of seabirds, cave dwelling bats, and seals. Guano manure is an effective fertilizer due to its high levels of phosphorus and nitrogen and also its lack of odor. It was an important source of nitrates for gunpowder...
exports led to a rapid development of the city. The export-led expansion also widened the gap between rich and poor, fostering social unrest. During the 1879–1883 War of the Pacific
War of the Pacific
The War of the Pacific took place in western South America from 1879 through 1883. Chile fought against Bolivia and Peru. Despite cooperation among the three nations in the war against Spain, disputes soon arose over the mineral-rich Peruvian provinces of Tarapaca, Tacna, and Arica, and the...
, Chilean troops occupied Lima, looting public museums, libraries and educational institutions. At the same time, angry mobs attacked wealthy citizens and the Asian population; sacking their properties and businesses. After the war, the city underwent a process of renewal and expansion from the 1890s up to the 1920s. During this period, the urban layout was modified by the construction of big avenues that crisscrossed the city and connected it with neighboring towns.
In 1940, an earthquake destroyed most of the city, which at that time was mostly built of adobe
Adobe
Adobe is a natural building material made from sand, clay, water, and some kind of fibrous or organic material , which the builders shape into bricks using frames and dry in the sun. Adobe buildings are similar to cob and mudbrick buildings. Adobe structures are extremely durable, and account for...
and quincha
Quincha
Quincha is a traditional construction system that uses, fundamentally, wood and cane or giant reed forming an earthquake-proof framework that is covered in mud and plaster....
. In the 1940s, Lima started a period of rapid growth spurred by migration from the Andean regions of Peru, as rural people sought better opportunities for work and education. The population, estimated at 0.6 million in 1940, reached 1.9M by 1960 and 4.8M by 1980. At the start of this period, the urban area was confined to a triangular area bounded by the city's historic centre
Historic Centre of Lima
Located principally in the city centre or Cercado de Lima and Rímac areas, the Historic Centre of Lima is among the most important tourist destinations in Peru.-Foundation:...
, Callao
Callao
Callao is the largest and most important port in Peru. The city is coterminous with the Constitutional Province of Callao, the only province of the Callao Region. Callao is located west of Lima, the country's capital, and is part of the Lima Metropolitan Area, a large metropolis that holds almost...
and Chorrillos; in the following decades settlements spread to the north, beyond the Rímac River, to the east, along the Central Highway, and to the south. The new migrants, at first confined to slum
Slum
A slum, as defined by United Nations agency UN-HABITAT, is a run-down area of a city characterized by substandard housing and squalor and lacking in tenure security. According to the United Nations, the percentage of urban dwellers living in slums decreased from 47 percent to 37 percent in the...
s in downtown Lima, led this expansion through large-scale land invasions, which evolved into shanty towns, known as pueblos jóvenes
Pueblos jóvenes
Pueblos jóvenes is the nickname given to the vast shanty towns that surround Lima and other cities of Peru. Many of these towns have developed into significant districts in Lima such as Villa El Salvador and Comas.- Population :...
.
Geography

Sechura Desert
The Sechura Desert is located south of the Piura Region of Peru along the Pacific Ocean coast and inland to the foothills of the Andes Mountains...
, within the valleys of the Chillón
Chillón River
The Chillón River is a river located in western Peru. Its waters are produced by the melting of ice in the glaciers of the Andes, and its mouth is located in the Pacific Ocean coast of the Callao Region. Its volume gets higher during the summer months . The river's valley is very fertile...
, Rímac
Rímac River
The Rímac River is located in western Peru and is the most important source of potable water for the Lima and Callao Metropolitan Area.The river is part of the Pacific watershed and has a length of 160 km...
and Lurín
Lurín River
The the lurin river is a is a long watercourse located in the Lima Region of Peru. It originates in the glaciers and lagoons of the western Andes and is known as the Chalilla River until joining the Taquía creek where it receives its common name. Its main tributaries are the Taquía, Llacomayqui,...
rivers. The city slopes gently from the shores of the Pacific Ocean into valleys and mountain slopes located as high as 500 metres (1,640.4 ft) above mean sea level. Within the city there are isolated hills which are not connected to the surrounding hill chains, such as El Agustino, San Cosme, El Pino, La Milla, Muleria and Pro hills. The San Cristobal hill in the Rimac district, which lies directly north of the downtown area, is the local extreme of an Andean hill outgrowth.
Metropolitan Lima has an area of 2672.28 km² (1,031.8 sq mi), of which 825.88 km² (318.9 sq mi) (31%) comprise the actual city and 1846.4 km² (712.9 sq mi) (69%) the city outskirts. The urban area extends around 60 km (37.3 mi) from north to south and around 30 km (18.6 mi) from west to east. The city center is located 15 km (9.3 mi) inland at the shore of the Rimac river, a vital resource for the city, since it carries what will become drinking water for its inhabitants and fuels the hydroelectric dams that provide electricity to the area. While no official administrative definition for the city exists, it is usually considered to be composed of the central 30 out of the 43 districts of Lima Province
Lima Province
Lima Province is located in the central coast of Peru and is the only province in the country not belonging to any of the twenty-five regions. Its capital is Lima, which is also the nation's capital....
, corresponding to an urban area centered around the historic Cercado de Lima
Lima District
Lima is a district of the Lima Province in Peru. It is not where the inner city zone of Lima, the country's capital city, is located, San Isidro District being such area in Lima....
district. The city is the core of the Lima Metropolitan Area
Lima Metropolitan Area
The Lima Metropolitan Area , is an area formed by the conurbation of the Peruvian cities of Lima and Callao. It is the largest metropolitan area in Peru, the eighth largest in the Americas, and among the thirty largest in the world. The conurbation process started to be evident in the 1980s. The...
, one of the ten largest metropolitan areas in the Americas. Lima is the second largest city in the world located in a desert, after Cairo
Cairo
Cairo , is the capital of Egypt and the largest city in the Arab world and Africa, and the 16th largest metropolitan area in the world. Nicknamed "The City of a Thousand Minarets" for its preponderance of Islamic architecture, Cairo has long been a centre of the region's political and cultural life...
, Egypt
Egypt
Egypt , officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, Arabic: , is a country mainly in North Africa, with the Sinai Peninsula forming a land bridge in Southwest Asia. Egypt is thus a transcontinental country, and a major power in Africa, the Mediterranean Basin, the Middle East and the Muslim world...
.
Climate

Subtropics
The subtropics are the geographical and climatical zone of the Earth immediately north and south of the tropical zone, which is bounded by the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn, at latitudes 23.5°N and 23.5°S...
and in a desert
Desert
A desert is a landscape or region that receives an extremely low amount of precipitation, less than enough to support growth of most plants. Most deserts have an average annual precipitation of less than...
. Although classified as subtropical, Lima's proximity to the cool waters of the Pacific Ocean leads to temperatures much cooler than those expected for a subtropical desert, and can be classified as a cool desert climate
Desert climate
A desert climate , also known as an arid climate, is a climate that does not meet the criteria to be classified as a polar climate, and in which precipitation is too low to sustain any vegetation at all, or at most a very scanty scrub.An area that features this climate usually experiences less than...
. It is neither cold nor very hot. Temperatures rarely fall below 12 °C (53.6 °F) or rise above 29 °C (84.2 °F) throughout the entire year. Two distinct seasons can be identified: summer, from December through April; and winter from June through October. May and November are generally transition months, with the warm-to-cool weather transition being more dramatic.
Summers are warm, humid and sunny. Daily temperatures oscillate between lows of 18 °C (64.4 °F) to 22 °C (71.6 °F), and highs of 24 °C (75.2 °F) to 29 °C (84.2 °F). Skies are generally cloud free, especially during daytime. Occasional coastal fogs during some mornings and high clouds during some afternoons and evenings can be present. Lima summer sunsets are well known for being colorful. As such, they have been labeled by the locals as "cielo de brujas" (Spanish for "sky of witches"), since the sky commonly turns into shades of orange, pink and red around 7 pm. Winter weather is dramatically different. Gray skies, breezy conditions, high humidity and cool temperatures prevail. Long (1-week or more) stretches of dark overcast skies are not uncommon. Persistent morning drizzle occurs occasionally from June through September, coating the streets with a thin layer of water that generally dries up by early afternoon. Winter temperatures in Lima do not vary much between day and night. They range from lows of 12 °C (53.6 °F) to 16 °C (60.8 °F) and highs of 16 °C (60.8 °F) to 19 °C (66.2 °F), rarely exceeding 20 °C (68 °F) except in the easternmost districts.
Relative humidity
Relative humidity
Relative humidity is a term used to describe the amount of water vapor in a mixture of air and water vapor. It is defined as the partial pressure of water vapor in the air-water mixture, given as a percentage of the saturated vapor pressure under those conditions...
is always very high, particularly in the mornings. High humidity produces brief morning fog during the early summer and a usually persistent low cloud deck during the winter (generally developing in May and persisting all the way into late November or even early December). Predominant onshore flow makes the Lima area one of the cloudiest among the entire Peruvian coast. Lima has only 1284 hours of sunshine a year, 28.6 hours in July and 179.1 hours in January, exceptionally low values for the latitude. Winter cloudiness prompts locals to seek for sunshine in Andean valleys located at elevations generally above 500 meters above sea level
Above mean sea level
The term above mean sea level refers to the elevation or altitude of any object, relative to the average sea level datum. AMSL is used extensively in radio by engineers to determine the coverage area a station will be able to reach...
.
Although relative humidity levels are high, rainfall is very low due to strong atmospheric stability. The severely low rainfall impacts on water supply in the city, which originates from wells and from rivers that flow from the Andes
Andes
The Andes is the world's longest continental mountain range. It is a continual range of highlands along the western coast of South America. This range is about long, about to wide , and of an average height of about .Along its length, the Andes is split into several ranges, which are separated...
. Inland districts receive anywhere between 1 to 6 cm (2.4 in) of rainfall per year, which accumulates mainly during the winter months. Coastal districts receive only 1 to 3 cm (1.2 in). As previously mentioned, winter precipitation occurs in the form of persistent morning drizzle events. These are locally called 'garúa', 'llovizna' or 'camanchacas
Camanchacas
Camanchacas are cloud banks that forms in the coast of Atacama Desert and moves inland. On the side of the mountains where this cloud bank forms, it is a dense fog that does not drop any rain. Scientists have devised a fog collection system of polypropylene netting to capture the water droplets in...
'. Summer rain, on the other hand, is infrequent, and occurs in the form of isolated light and brief showers. These generally occur during afternoons and evenings when leftovers from Andean storms arrive from the east. The lack of heavy rainfall arises from high atmospheric stability caused, in term, by the combination of cool waters from semi-permanent coastal upwelling and the presence of the cold Humboldt Current
Humboldt Current
The Humboldt Current , also known as the Peru Current, is a cold, low-salinity ocean current that flows north-westward along the west coast of South America from the southern tip of Chile to northern Peru. It is an eastern boundary current flowing in the direction of the equator, and can extend...
; and warm air aloft associated with the South Pacific anticyclone.
The climate of Lima (as that of most of the Peruvian coast) gets severely disrupted during El Niño
El Niño-Southern Oscillation
El Niño/La Niña-Southern Oscillation, or ENSO, is a quasiperiodic climate pattern that occurs across the tropical Pacific Ocean roughly every five years...
events. Water temperatures along the coast, which usually average around 17 –, get much warmer (as in 1998 when the water temperature reached 26 °C (78.8 °F)). Air temperatures rise accordingly. Such was the case when Lima hit its all-time record high of 34 °C (93.2 °F). Cooler climate develops during La Niña years. The all-time record low in the metropolitan area is 8 °C (46.4 °F), measured during the winter of 1988.
Demographics
With a municipal population of 7,605,743, and 8,472,935 for the metropolitan areaLima Metropolitan Area
The Lima Metropolitan Area , is an area formed by the conurbation of the Peruvian cities of Lima and Callao. It is the largest metropolitan area in Peru, the eighth largest in the Americas, and among the thirty largest in the world. The conurbation process started to be evident in the 1980s. The...
and a population density of 3008.8 PD/km2 as of 2007, Lima ranks as the 27th most populous 'agglomeration' in the world. Its population features a very complex mix of racial and ethnic groups. Mestizo
Mestizo
Mestizo is a term traditionally used in Latin America, Philippines and Spain for people of mixed European and Native American heritage or descent...
s of mixed Amerindian
Indigenous peoples of the Americas
The indigenous peoples of the Americas are the pre-Columbian inhabitants of North and South America, their descendants and other ethnic groups who are identified with those peoples. Indigenous peoples are known in Canada as Aboriginal peoples, and in the United States as Native Americans...
and European
White Latin American
White Latin Americans are the people of Latin America who are white in the racial classification systems used in individual Latin American countries. Persons who are classified as White in one Latin American country may be classified differently in another country...
(mostly Spanish and Italians) ancestry are the largest ethnic group. European Peruvians are the second largest group. Many are of Spanish
Spanish Peruvian
A Spanish Peruvian is a Peruvian citizen of Spanish descent. Among European Peruvians, the Spanish are the largest group of immigrants to settle in the country.-History:...
, Italian
Italian Peruvian
An Italian Peruvian is a Peruvian citizen of Italian descent. The phrase may refer to someone born in Peru of Italian descent or to someone who has immigrated to Peru from Italy...
or German
German Peruvian
A German Peruvian is a Peruvian citizen of German descent. In generally, the term is also applied to descents of other German speaking immigrants, such as Austrians or Swiss...
descent; many others are of French
French Peruvian
A French-Peruvian may be a Peruvian of French descent; a French of Peruvian descent or a person of both French and Peruvian descent. The French were the fourth largest group of immigrants to settle in the country after the Spanish, Italians, and the Germans...
, British
British Peruvian
A British Peruvian is a Peruvian person of British descent. The phrase may refer to someone born in Peru of British descent. Among European Peruvians, the British were the fifth largest group of immigrants to settle in the country after the Spanish, Italians, Germans, the Swiss or/and the French...
, or Croatian descent. The minorities in Lima include Amerindians (mostly Aymara and Quechua
Quechuas
Quechuas is the collective term for several indigenous ethnic groups in South America who speak a Quechua language , belonging to several ethnic groups in South America, especially in Peru, Ecuador, Bolivia, Chile, Colombia and Argentina.The Quechuas of Ecuador call themselves as well as their...
), Afro-Peruvian
Afro-Peruvian
Afro Peruvians are citizens of Peru mostly descended from African slaves who were brought to the Western hemisphere with the arrival of the conquistadors towards the end of the slave trade.-Early history:...
s, whose African ancestors were initially brought to the region as slaves, are yet another part of the city's ethnic diversity. There are also numerous Jews of European descent and Middle Easterners. Asians
Asian Peruvian
Asian Peruvians, primarily Chinese and Japanese, constitute some 3-5% of the total population, which in proportion to the overall population is one of the largest of any Latin American nation. Peru has the second largest population of Japanese people in Latin America after Brazil and the largest...
make up a large number of the metropolitan population, especially of Chinese (Cantonese) and Japanese
Japanese Peruvian
Japanese Peruvians are people of Japanese ancestry who were born in or immigrated to Peru. The immigrants from Japan are called the Issei generation. Second and third generation Peruvians are referred to as nisei and sansei in Japanese...
descent, whose ancestors came mostly in the 19th and early 20th centuries. Lima has, by far, the largest ethnic Chinese community in Latin America.
The first settlement in what would become Lima was made up of only 117 housing blocks. In 1562, another district was built at the other side of the Rimac River and in 1610, the first stone bridge was built. Lima then had a population of around 26,000; blacks made up around 40% of the population, and whites made up around 38% of the population. By 1748, the white population totaled 16,000–18,000. In 1861, the number of inhabitants surpassed 100,000, and by 1927, this amount was doubled.
During the early twentieth century, thousands of immigrants came to the city, including a significant number of French, Italians and Germans, many of whom have assimilated to the Peruvian society. They organized in social clubs, and they built their own schools; for example, The American-Peruvian school which is located in Miraflores; the French Alliance (Alianza Francesa de Lima), the notable Lycée Franco-Péruvien and the hospital Maison de Sante;; the British-Peruvian school in Monterrico and also several German-Peruvian schools.
They influenced Peruvian cuisine, the Italians in particular exerting a strong influence in the Miraflores and San Isidro areas with their restaurants, called trattorias.
A great number of Chinese immigrants, and a lesser amount of Japanese, came to Lima and established themselves in the Barrios Altos neighborhood near downtown Lima. Lima residents refer to their Chinatown as Calle Capon, and the city's ubiquitous Chifa restaurants a small, sit-down, usually Chinese-run restaurant serving the Peruvian spin on Chinese cuisine can be found by the dozen in this Chinese enclave.
Economy
Lima is the industrial and financial center of Peru, and one of the most important financial centers in Latin America. Today it is home to many national companies. It accounts for more than two thirds of Peru's industrial production and most of its tertiary sector.The Metropolitan area, with around 7000 factories, spearheads the industrial development of the country, thanks to the quantity and quality of the available workforce
Workforce
The workforce is the labour pool in employment. It is generally used to describe those working for a single company or industry, but can also apply to a geographic region like a city, country, state, etc. The term generally excludes the employers or management, and implies those involved in...
, cheap infrastructure and the mostly developed routes and highways in the city. The most relevant industrial sectors are textiles, clothing and food. Chemicals, fish, leather and oil derivatives are also manufactured and/or processed in Lima. The financial district is located in the district of San Isidro, while much of the industrial activity takes place in the area stretching west of downtown Lima to the airport in Callao
Callao
Callao is the largest and most important port in Peru. The city is coterminous with the Constitutional Province of Callao, the only province of the Callao Region. Callao is located west of Lima, the country's capital, and is part of the Lima Metropolitan Area, a large metropolis that holds almost...
. Lima has the largest exportation industry in South America, and it is a regional hub for the operational cargo industry.
Industrialization began to take hold in Lima in 1930s and by 1950s, through import substitution policies, by 1950 manufacturing made up 14% of the GNP
GNP
Gross National Product is the market value of all products and services produced in one year by labor and property supplied by the residents of a country...
. In the late 1950s, up to 70% of consumer goods were manufactured in factories located in Lima.
The Callao seaport is one of the main fishing and commerce ports in South America, with 75% of the country's imports and 25% of its exports using it as their entry/departure point. The main export goods leaving the country through Callao are oil, steel, silver, zinc, cotton, sugar and coffee.
Lima generates 53% of the GDP of Peru
Peru
Peru , officially the Republic of Peru , is a country in western South America. It is bordered on the north by Ecuador and Colombia, on the east by Brazil, on the southeast by Bolivia, on the south by Chile, and on the west by the Pacific Ocean....
. In 2010, GDP per capita in Lima reached $20,000.
Most of the foreign companies operating in the country have settled in Lima, which has led to the previously mentioned concentration of economic and financial activity on the city.
There has been a noticeable increase in light industries, services and high technologies. In 2007, the Peruvian economy grew 9%, the largest growth rate in all of South America which was spearheaded by economic policies originating in Lima. The Lima Stock Exchange grew 185.24% in 2006 and in 2007 grew 168.3%, making it one of the fastest growing stock exchanges in the world. In 2006, the Lima Stock Exchange was the most profitable in the world. The unemployment rate in the metropolitan area is 7.2%.
The Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation Summit
APEC Peru 2008
The APEC Peru 2008 summit was the twentieth annual gather of APEC leaders. The meet was primarily a series of political-economic meetings, which were held in Peru between the 21 members of the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation , although business leaders of the region also met before the summit...
and the Latin America, the Caribbean and the European Union Summit
Latin America, the Caribbean and the European Union Summit
The Latin America, the Caribbean and the European Union Summit is a biennial meeting of heads of state and government of Latin America, the Caribbean and the European Union...
were hosted by the city of Lima.
Lima is headquarters to many major banks such as Banco de Crédito del Perú
Banco de Crédito del Perú
Banco de Crédito del Perú is a Peruvian bank, and the largest in the country. It is traded in the New York Stock Exchange and the Lima Stock Exchange . It is controlled by the Romero family...
, Interbank
Interbank
Interbank is a Peruvian provider of financial services.-History:In 1897, Elias Mujica opened an agency at Jiron de la Union in Lima's historical center under the name of Banco Internacional...
, Bank of the Nation
National bank
In banking, the term national bank carries several meanings:* especially in developing countries, a bank owned by the state* an ordinary private bank which operates nationally...
, Banco Continental, MiBanco, Banco Interamericano de Finanzas, Banco Finaciero, Banco de Comercio, and Credi Scotia. It is also a regional headquarters to Standard Chartered. Major insurance coorperations based in Lima include Rimac Seguros, Mapfre Peru, Interseguro, Pacifico, Protecta, and La Positiva.
National government
Lima is the capital city of the Republic of Peru and the department of LimaLima Region
Lima Region, also known as Lima Provincias, is one of twenty-five regions of Peru. Located in the central coast of the country, its regional seat is Huacho....
. As such, it is home to the three branches of the Government of Peru
Government of Peru
Peru is a presidential representative democratic republic with a multi-party system. Under the current constitution, the President is the head of state and government; he or she is elected for five years and cannot seek immediate re-election, he or she must stand down for at least one full...
. The executive branch is headquartered in the Government Palace
Government Palace (Peru)
The Government Palace of Peru, also known as House of Pizarro, renoved in 1937, was the house of the Peruvian government headquarters and was built over a huge Indian burying ground Waka that had a shrine of Indian chief Taulichusco. It has been through many alterations...
, located in the Plaza Mayor
Plaza Mayor of Lima
The Plaza Mayor or Plaza de Armas of Lima, is the birthplace of the city of Lima, as well as the core of the city. Located in the Historic Centre of Lima, it is surrounded by the Government Palace, Cathedral of Lima, Archbishop's Palace of Lima, the Municipal Palace, and the Palace of the Union.-...
. The legislative branch
Congress of Peru
The Congress of the Republic of Peru or the National Congress of Peru is the unicameral body that assumes legislative power in Peru.Congress consists of 130 members of congress , who are elected for five year periods in office on a proportional representation basis...
is headquartered in the Legislative Palace
Legislative Palace (Peru)
The Legislative Palace of Peru is the seat of the Congress of Peru, located on the second block of Jiron Ayacucho, on the Plaza Bolivar, in Lima, the capital of Peru...
and is home to the Congress of Peru
Congress of Peru
The Congress of the Republic of Peru or the National Congress of Peru is the unicameral body that assumes legislative power in Peru.Congress consists of 130 members of congress , who are elected for five year periods in office on a proportional representation basis...
. The Judicial branch
Judicial System of Peru
The Judicial System of Peru, usually known as the Judicial Power in Peru, is an organism of the government of the Republic of Peru composed of a hierarchic organization of institutions, that exercise equal justice to all people....
is headquartered in the Palace of Justice
Palace of Justice (Peru)
The Palace of Justice is the seat of the Supreme Court of Peru. It is located in the Lima District of the city of Lima, capital of Peru. Construction started during the second government of Augusto B. Leguía and finished under the presidency of Óscar R. Benavides, who inaugurated the building in...
and is home to the Supreme Court of Peru
Supreme Court of Peru
The Supreme Court of Justice is the highest judicial court in Peru. Its jurisdiction extends over the entire territory of the nation. It is headquartered in the Palace of Justice in Lima.The supreme court is composed of three Supreme Sectors:...
. Likewise, all the ministries are located in the city of Lima. In international government, the city of Lima is home to the headquarters of the Andean Community of Nations
Andean Community of Nations
The Andean Community is a customs union comprising the South American countries of Bolivia, Colombia, Ecuador and Peru. The trade bloc was called the Andean Pact until 1996 and came into existence with the signing of the Cartagena Agreement in 1969...
and the South American Community of Nations
South American Community of Nations
The Union of South American Nations is an intergovernmental union integrating two existing customs unions: Mercosur and the Andean Community of Nations , as part of a continuing process of South American integration. It is modeled on the European Union....
, along with other regional and international organizations.
The Palace of Justice
Palace of Justice (Peru)
The Palace of Justice is the seat of the Supreme Court of Peru. It is located in the Lima District of the city of Lima, capital of Peru. Construction started during the second government of Augusto B. Leguía and finished under the presidency of Óscar R. Benavides, who inaugurated the building in...
in Lima is seat of the Supreme Court of Justice
Supreme Court of Peru
The Supreme Court of Justice is the highest judicial court in Peru. Its jurisdiction extends over the entire territory of the nation. It is headquartered in the Palace of Justice in Lima.The supreme court is composed of three Supreme Sectors:...
the highest judicial court in Peru with jurisdiction over the entire territory of Peru. Lima is also seat of two of the 28 second highest or Superior Courts of Justice
Superior Courts of Justice of Peru
The Superior Courts of Justice or Superior Sectors of Peru are the second highest courts of the Judicial System of Peru. It is only second to the Supreme Court.There is one court for each Judicial District which more or less correspond with each of the 25 Regions of Peru...
. The first and oldest Superior Court in Lima is the Superior Court of Justice of Lima belonging to the Judicial District of Lima
Judicial District of Lima
The Judicial District of Lima is one of the 28 Judicial Districts of the Judicial System of Peru.Its main seat is in the city of Lima and its jurisdiction extends to 35 of the 43 Districts of Lima...
. Due to the judicial organization of Peru
Judicial System of Peru
The Judicial System of Peru, usually known as the Judicial Power in Peru, is an organism of the government of the Republic of Peru composed of a hierarchic organization of institutions, that exercise equal justice to all people....
, the highest concentration of courts is located in Lima despite the fact that its judicial district only has jurisdiction over 35 of the 43 districts of Lima. The Superior Court of the Cono Norte is the second Superior Court located in Lima and is part of the Judicial District of North Lima
Judicial District of Cono Norte
The Judicial District of Cono Norte is one of the 28 Judicial Districts of the Judicial System of Peru.Its main seat is in the district of Independencia in Lima and its jurisdiction extends over the Limean districts of Independencia, San Martín de Porres, Comas, Los Olivos, Puente Piedra, Ancon,...
. This judicial district has jurisdiction over the remaining eight districts all located in northern Lima.
Local government
The city is roughly equivalent to the Province of Lima, which is subdivided into 43 districts. The Metropolitan Municipality of Lima is utmost authority of the entire city while each district has its own local government. Unlike the rest of the country, the Metropolitan Municipality, although a provincial municipalityMunicipalities of Peru
Municipalities, in Peru, are the government organizations that govern the provinces and districts of that country.-Classification:According to the Base law of Municipalities, these entities are classified in to Provincial Municipalities and District Municipalities. The provincial municipalities...
, acts as and has functions similar to a regional government
Regional Governments of Peru
Regional Governments, in the Government of Peru, is a government organization which organizes, conducts, and manages, each one of the twenty-five regions of Peru. It has political, economic, and administrative autonomy in the subjects of its matter....
, as it does not belong to any of the 25 regions of Peru
Regions of Peru
The regions of Peru are the first-level administrative subdivisions of Peru. Since its 1821 independence, Peru had been divided into departments but faced the problem of an increasing centralization of political and economic power in its capital, Lima...
.
Cityscape
.jpg)
Torre Tagle Palace
The Torre Tagle Palace is a Spanish Baroque palace located at Jr. Ucayali 363, in downtown Lima, Peru, a couple blocks east of the Plaza de Armas...
. These constructions are generally influenced by the Spanish baroque
Spanish Baroque
Spanish Baroque is a strand of Baroque architecture that evolved in Spain and its provinces and former colonies, notably Spanish America and Belgium....
, Spanish Neoclassicism
Neoclassicism
Neoclassicism is the name given to Western movements in the decorative and visual arts, literature, theatre, music, and architecture that draw inspiration from the "classical" art and culture of Ancient Greece or Ancient Rome...
, and Spanish Colonial styles. After independence, a gradual shift towards the neoclassical
Neoclassical architecture
Neoclassical architecture was an architectural style produced by the neoclassical movement that began in the mid-18th century, manifested both in its details as a reaction against the Rococo style of naturalistic ornament, and in its architectural formulas as an outgrowth of some classicizing...
and Art Nouveau
Art Nouveau
Art Nouveau is an international philosophy and style of art, architecture and applied art—especially the decorative arts—that were most popular during 1890–1910. The name "Art Nouveau" is French for "new art"...
styles took place. Many of these constructions were greatly influenced by French architectural
French architecture
The history of French architecture runs in parallel with its neighbouring countries in Europe, with France being home to both some of the earliest pioneers in many architectural styles, and also containing some of the finest architectural creations of the continent.-Roman:The architecture of...
styles. Many government buildings as well as major cultural institutions were contracted in this architectural time period. During 1960s, constructions utilizing the brutalist
Brutalist architecture
Brutalist architecture is a style of architecture which flourished from the 1950s to the mid 1970s, spawned from the modernist architectural movement.-The term "brutalism":...
style began appearing in Lima due to the military government of Juan Velasco. Examples of this architecture include the Museum of the Nation
Museum of the Nation
The Museum of the Nation ' is one of two major museums of Peruvian history in Lima, Peru. It is much larger than the other main museum in Lima, the Peruvian National Museum of Archaeology, Anthropology, and History....
and the Ministry of Defense. The 21st century has seen the appearance of glass skyscrapers
Skyscraper
A skyscraper is a tall, continuously habitable building of many stories, often designed for office and commercial use. There is no official definition or height above which a building may be classified as a skyscraper...
, particularly around the city's financial district. Also there are several new architectural and real estate projects.
The largest parks of Lima are located near the downtown area such as the Park of the Reserve
Park of the Reserve
The Park of the Reserve or the Parque de la Reserva in Spanish is a park located in downtown Lima, in Peru. Built in an irregular shape, it is located between two of the city's principal streets, the Paseo de la Republica expressway and Arequipa Avenue....
, Park of the Exposition
Exposition Park
Exposition Park is the name of more than one place:*Exposition Park - a neighborhood in south Dallas, Texas*Exposition Park - A former baseball park in Kansas City...
, Campo de Marte
El Campo de Marte
The Campo de Marte is one of the largest parks in the metropolitan area of Lima, capital city of Peru. Similar in size to Parque de la Exposición and Parque de la Reserva.- Location :...
, and the University Park. The Park of the Reserve
Park of the Reserve
The Park of the Reserve or the Parque de la Reserva in Spanish is a park located in downtown Lima, in Peru. Built in an irregular shape, it is located between two of the city's principal streets, the Paseo de la Republica expressway and Arequipa Avenue....
is home to the largest fountain complex in the world known as the Magical Circuit of Water. A number of large parks lie outside the city center, including Reducto Park, Pantanos de Villa, El Golf (San Isidro), Parque de las Leyendas (Lima Zoo), El Malecon de Miraflores, and the Golf Los Incas. The street grid of the city of Lima, is laid out with a system of plazas of which serve a purpose similar to roundabouts or junctions. In addition to this practical purpose, plazas serve as one of Lima's principal green spaces and contain a variety of different types of architecture ranging from monuments to statues, and water fountains.
Society and culture
Strongly influenced by European, AndeanAndes
The Andes is the world's longest continental mountain range. It is a continual range of highlands along the western coast of South America. This range is about long, about to wide , and of an average height of about .Along its length, the Andes is split into several ranges, which are separated...
, African
Culture of Africa
The culture of Africa encompasses and includes all cultures within the continent of Africa. There is a political or racial split between North Africa, and Sub-Saharan Africa, which is in turn divided into a great number of ethnic cultures...
and Asian
Culture of Asia
The culture of Asia is human civilization in Asia. It features different kinds of cultural heritage of many nationalities, societies, and ethnic groups in the region, traditionally called a continent from a Western-centric perspective, of Asia...
culture, Lima is a melting pot of cultures due to colonization, immigration
Immigration
Immigration is the act of foreigners passing or coming into a country for the purpose of permanent residence...
, and indigenous influences. The Historic Center of Lima was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1988. Like many other world capitals, Lima is home to prestigious museums, many of which are world renowned.
Limean cuisine is known to be among the best in the world, and the city is known as the Gastronomical Capital of the Americas. Lima's gastronomy is a mix of Spanish
Spanish cuisine
Spanish cuisine consists of a variety of dishes, which stem from differences in geography, culture and climate. It is heavily influenced by seafood available from the waters that surround the country, and reflects the country's deep maritime roots...
, Andean
Andes
The Andes is the world's longest continental mountain range. It is a continual range of highlands along the western coast of South America. This range is about long, about to wide , and of an average height of about .Along its length, the Andes is split into several ranges, which are separated...
, and Asian
Asian cuisine
Asian cuisine styles can be broken down into several tiny regional styles that have roots in the peoples and cultures of those regions. The major types can be roughly defined as East Asian with its origins in Imperial China and now encompassing modern Japan and the Korean peninsula; Southeast Asian...
culinary traditions.
Lima's beaches, located along the northern and southern ends of the city, are heavily visited during the summer months. Numerous restaurants, clubs and hotels have been opened in these places to serve the many beachgoers. Lima has a vibrant and active theater scene, as there are many theaters presenting not only classic theater, but also cultural presentations, modern theater, experimental theater, dramas, dance performances, and theater for children. Lima is home to many important theaters, such as the Municipal Theater
Teatro Municipal (Lima)
The Teatro Municipal de Lima is a stunning theatre and concert hall in Lima, Peru. It is home to the National Symphony Orchestra of Peru. The building was inaugurated in 1920 under the name of "Teatro Forero". It was later bought by the "Municipalidad Metropolitana de Lima" in 1929 and renamed...
, Segura Theater, Japanese-Peruvian Theater, Marsano Theater, British theater, Theater of the PUCP Cultural Center, and the Yuyachkani Theater.
Language
Known as Peruvian Coastal Spanish, Lima's Spanish is characterized by the lack of strong innotations as found in many other regions of the Spanish-speaking world. It is heavily influenced by the historical Spanish spoken in CastileCastile (historical region)
A former kingdom, Castile gradually merged with its neighbours to become the Crown of Castile and later the Kingdom of Spain when united with the Crown of Aragon and the Kingdom of Navarre...
. Throughout the colonial era, most of the Spanish colonial nobility based in Lima were originally from Castile. Limean Spanish is also characterized by the lack of voseo
Voseo
Voseo is the use of the second person singular pronoun vos in many dialects of Spanish. In dialects that have it, it is used either instead of tú, or alongside it....
, a trait present in the dialects of many other Latin American countries. This is because voseo was primarily used by the lower socioeconomic classes of Spain, a social group that did not begin to appear in Lima until the late colonial era.
Limean Spanish is distinguished by its relative clarity in comparison to other Latin American accents. Limean Spanish has been influenced by a number of immigrant groups including Italians, Andalusians
Andalusian people
The Andalusians are the people of the southern region in Spain approximated by what is now called Andalusia. They are generally not considered an ethnically distinct people because they lack two of the most important markers of distinctiveness: their own language and an awareness of a presumed...
, Chinese and Japanese. It also has been influenced by anglicism
Anglicism
An Anglicism, as most often defined, is a word borrowed from English into another language. "Anglicism" also describes English syntax, grammar, meaning, and structure used in another language with varying degrees of corruption.-Anglicisms in Chinese:...
s as a result of globalization
Globalization
Globalization refers to the increasingly global relationships of culture, people and economic activity. Most often, it refers to economics: the global distribution of the production of goods and services, through reduction of barriers to international trade such as tariffs, export fees, and import...
, as well as by Andean Spanish, due to the recent migration from the Andean highlands to Lima.
Museums
Lima is home to the highest concentration of museums of the country, the most notable of which are the Museo Nacional de Arqueología Antropología e Historia del Perú, Museum of Art of Lima, the Museum of Natural History, the Museum of the NationMuseum of the Nation
The Museum of the Nation ' is one of two major museums of Peruvian history in Lima, Peru. It is much larger than the other main museum in Lima, the Peruvian National Museum of Archaeology, Anthropology, and History....
, The Sala Museo Oro del Perú Larcomar, the Museum of Italian Art, and the Museum of Gold, and the Larco Museum
Larco Museum
The Larco Museum is a privately owned museum of pre-Columbian art, located in the Pueblo Libre District of Lima, Peru. The museum is housed in an 18th century vice-royal mansion built over a 7th century pre-Columbian pyramid. It showcases chronological galleries that provide a thorough overview of...
. These museums mostly focus on art, pre-Columbian cultures
Pre-Columbian
The pre-Columbian era incorporates all period subdivisions in the history and prehistory of the Americas before the appearance of significant European influences on the American continents, spanning the time of the original settlement in the Upper Paleolithic period to European colonization during...
, natural history, science and religion. There's a particularity with the Museum of Italian Art
Museum of Italian Art
The Museum of Italian Art is a public museum in Lima, Peru, under the administration of the National Culture Institute. It's the only European arts museum in Peru.-History:...
, which is the only museum that shows European art in Peru.
Tourism
As the major point of entry to the country, Lima has developed an important tourism industry, characterized by its historic center, archeological sites, nightlife, museums, art galleries, festivals, and popular traditions. Lima is home to an ample range of restaurants and bars where local as well as international cuisine is served.The Historic Center of Lima, made up of the districts of Lima
Lima District
Lima is a district of the Lima Province in Peru. It is not where the inner city zone of Lima, the country's capital city, is located, San Isidro District being such area in Lima....
and Rimac
Rímac District
Rímac is a district in the Lima Province, Peru. It lies directly to the north of downtown Lima, to which it is connected by six bridges over the Rímac River. The district also borders the Independencia, San Martín de Porres, and San Juan de Lurigancho districts...
, was declared a World Heritage Site
World Heritage Site
A UNESCO World Heritage Site is a place that is listed by the UNESCO as of special cultural or physical significance...
by UNESCO
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations...
in 1988 due to its importance during the colonial era leaving a testimony to architectural achievement. Some examples of this historical colonial architecture include the Monastery of San Francisco, the Plaza Mayor
Plaza Mayor of Lima
The Plaza Mayor or Plaza de Armas of Lima, is the birthplace of the city of Lima, as well as the core of the city. Located in the Historic Centre of Lima, it is surrounded by the Government Palace, Cathedral of Lima, Archbishop's Palace of Lima, the Municipal Palace, and the Palace of the Union.-...
, the Cathedral, Covenant of Santo Domingo, the Palace of Torre Tagle
Torre Tagle Palace
The Torre Tagle Palace is a Spanish Baroque palace located at Jr. Ucayali 363, in downtown Lima, Peru, a couple blocks east of the Plaza de Armas...
, and much more.
A tour of the city's churches is a popular circuit among tourists. A short jaunt through the central district goes through many churches dating from as early as the 16th and 17th centuries, the most noteworthy of which are the Cathedral of Lima and the Monastery of San Francisco, said to be connected by their subterrestrial catacombs
Catacombs
Catacombs, human-made subterranean passageways for religious practice. Any chamber used as a burial place can be described as a catacomb, although the word is most commonly associated with the Roman empire...
. Both of these churches contain paintings from various schools of art, Sevilian tile, and finely sculpted wood furnishings.
Also notable is the Sanctuary of Las Nazarenas
Sanctuary of Las Nazarenas
The Sanctuary of Las Nazarenas is a church in Lima and is the site of the Peruvian catholic procession of the Lord of Miracles, Señor de los Milagros, who is also the patron of the city...
, the point of origin for the Lord of Miracles
Lord of Miracles
Lord of Miracles is a mural painted of Jesus Christ that is venerated in Lima, Peru. It is the main Catholic festivity in Peru and one of the biggest processions around the world....
, whose festivities in the month of October constitute the most important religious event in Lima, and a major one of Peru. Some sections of the Lima City Walls
Lima City Walls
The Lima city walls were built by Viceroy Melchor de Navarra y Rocafull between 1684 and 1687 to protect Lima against attacks from pirates and privateers. They included 34 bulwarks and five gates; their total cost was estimated at 400,000 Spanish dollars...
still remain and are frequented by tourists. These examples of medieval Spanish fortifications were built to defend the city from attacks by pirates and privateers.
Beaches are visited during the summer months, which are located along the Pan-American Highway
Pan-American Highway
The Pan-American Highway is a network of roads measuring about in total length. Except for an rainforest break, called the Darién Gap, the road links the mainland nations of the Americas in a connected highway system. According to Guinness World Records, the Pan-American Highway is the world's...
, to the south of the city in districts such as Lurin
Lurín District
The Peruvian district of Lurín is one of the 43 that make up the Lima Province.-Boundaries:It borders on the north with the districts of Pachacamac, Villa María del Triunfo, and Villa el Salvador, to the east also with the Pachacamac District, to the south with Punta Hermosa, and to the west with...
, Punta Hermosa, Santa María del Mar (Peru), San Bartolo
San Bartolo District
San Bartolo is a district in southern Lima Province in Peru. It is bordered by the Pacific Ocean on the west, the district of Punta Negra on the north, the Huarochirí Province on the east, and the Santa María del Mar District on the south....
and Asia
Asia District, Peru
The Asia District is one of 16 that make up the Peru province of Cañete. Founded by Beinto Chumpitaz Chavez on July 24, 1964, it was originally part of the Coayllo District...
. Many restaurants, nightclubs, lounges, bars, clubs, and hotels have developed in said places to cater to beachgoers.
The suburban districts of Cieneguilla
Cieneguilla
The Peruvian district of Cieneguilla is one of the 43 districts that make up the Lima Province. It is located in the easternmost area of the province and is one of the few districts left that are not already completely urbanized.- Boundaries :...
, Pachacamac
Pachacamac District
The Pachacamac District is one of 43 districts of the Lima Province in Peru. The capital of the district is the village of Pachacamac. Its main asset is the archaeological Inca site Pachacamac.-History:...
, and the city of Chosica
Lurigancho
Lurigancho-Chosica is a district of the Lima Province in Peru, located in the valley of the Rímac River which it shares with neighboring Chaclacayo and Ate districts. It was created on January 2, 1857. Its capital is the town of Chosica. The district has a total land area of 236.47 km²...
, are important tourist attractions among locals. Because they are located at a higher elevation than Lima, they receive more sunshine in winter months, something that the city of Lima frequently lacks under seasonal fog.
Food
Lima is known as the Gastronomical Capital of the Americas. A center of immigration and the center of the Spanish Viceroyalty, Lima has incorporated unique dishes brought from the arrival of the Spanish conquistadors and many waves of immigrants: African, European, Chinese, and Japanese. Besides international immigration—a large portion of which happened in Lima—there has been, since the second half of the 20th century, a strong internal flow from rural areas to cities, in particular to Lima. This has strongly influenced Lima's cuisine with the incorporation of the immigrant's ingredients and techniques (for example, the Chinese extensive use of rice or the Japanese approach to preparing raw fish). The genres of restaurants in Lima include Creole foodCreole peoples
The term Creole and its cognates in other languages — such as crioulo, criollo, créole, kriolu, criol, kreyol, kreol, kriulo, kriol, krio, etc. — have been applied to people in different countries and epochs, with rather different meanings...
, Chifa
Chifa
Chifa is a term used in Peru to refer to a style of Chinese cooking in which ingredients which are available in Peru have been substituted for those originally used in China. Chinese immigrants came to Peru mainly from the southern province of Guangdong and particularly its capital city Guangzhou...
s, Cebicherias
Ceviche
Ceviche is a seafood dish popular in the coastal regions of the Americas, especially Central and South America. The dish is typically made from fresh raw fish marinated in citrus juices such as lemon or lime and spiced with chilli peppers. Additional seasonings such as onion, salt,...
, and Pollerias
Pollo a la Brasa
Pollo a la Brasa, also known as Peruvian chicken in the United States and Charcoal Chicken in Australia, is a common dish of Peruvian cuisine and one of the most consumed in Peru, along with ceviche, and Chifa. The dish originated in the city of Lima in the 1950s.The origins of the recipe are...
. Peruvian cuisine
Peruvian cuisine
Peruvian cuisine reflects local cooking practices and ingredients—and, through immigration, influences from Spain, China, Italy, West Africa, and Japan. Due to a lack of ingredients from their home countries, immigrants to Peru modified their traditional cuisines by using ingredients...
, widely represented in Lima, holds various Guinness World Records
Guinness World Records
Guinness World Records, known until 2000 as The Guinness Book of Records , is a reference book published annually, containing a collection of world records, both human achievements and the extremes of the natural world...
, for its diversity and quality.
Sports
The city of Lima has varied sports venues for football, volleyballVolleyball
Volleyball is a team sport in which two teams of six players are separated by a net. Each team tries to score points by grounding a ball on the other team's court under organized rules.The complete rules are extensive...
and basketball
Basketball
Basketball is a team sport in which two teams of five players try to score points by throwing or "shooting" a ball through the top of a basketball hoop while following a set of rules...
, many of which are located within private clubs. A popular sport among Limeans is fronton, a racquet sport
Racquet sport
Racquet sports are those where players use racquets to hit a ball or other object.-List of racquet sports:* Badminton* Ball badminton* Basque pelota** Frontenis** Jai alai* Beach tennis** Matkot* Bilbocatch* Frescoball* Lacrosse...
similar to squash invented in Lima. The city is home to seven international-class golf
Golf
Golf is a precision club and ball sport, in which competing players use many types of clubs to hit balls into a series of holes on a golf course using the fewest number of strokes....
links. Equestrian
Equestrianism
Equestrianism more often known as riding, horseback riding or horse riding refers to the skill of riding, driving, or vaulting with horses...
is popular in Lima with many private clubs as well as the Hipódromo de Monterrico
Hipódromo de Monterrico
The Hipódromo de Monterrico is a Thoroughbred horse racing facility opened in 1960 in Lima, Peru. Operated by the Jockey Club del Peru, it has a one and one-eight mile dirt racetrack with a one mile inside track for turf racing....
horse racing track. The most popular sport in Lima by far is football with many professional club teams being located in the city.
The Historic Plaza de Acho, located in the Rimac district a few minutes from the Plaza de Armas, holds bullfights yearly. The season typically runs from late October to December.
| Club | Sport | League | Venue |
|---|---|---|---|
| Peruvian Institute of Sport | Various | Various | Estadio Nacional (Lima) Estadio Nacional (Lima) The Estadio Nacional of Peru is a multi-purpose stadium located in Lima, Peru. Its current capacity is 50,000 as stated by the Peruvian Football Federation. The stadium was inaugurated on 27 October 1952 for the 1953 South American Championship—replacing the Stadium Nacional—and is Peru's principal... |
| Universitario de Deportes Universitario de Deportes Club Universitario de Deportes, also known as Universitario, or more popularly as [La] "U", is a Peruvian football club located in Lima. It is the most successful football club in Peru. The club was founded in 1924 under the name Federación Universitaria by students of the National University of... |
Football | Primera División Peruana Primera División Peruana The Peruvian Primera División is the top professional division of Peruvian football. It is known today as Torneo Descentralizado de Fútbol Profesional Peruano... |
Monumental "U" Stadium |
| Alianza Lima Alianza Lima Club Alianza Lima is a Peruvian First Division football club who plays at the Estadio Alejandro Villanueva in the La Victoria District of Lima, Peru. They are one of the most famous and well supported clubs in the country and the oldest team in the Peruvian First Division.Alianza enjoyed success... |
Football | Primera División Peruana Primera División Peruana The Peruvian Primera División is the top professional division of Peruvian football. It is known today as Torneo Descentralizado de Fútbol Profesional Peruano... |
Alejandro Villanueva Stadium Estadio Alejandro Villanueva Estadio Alejandro Villanueva is a stadium located in the neighborhood of Matute in La Victoria District in Lima, Peru. The stadium is the home field of the football club Alianza Lima. The stadium has a capacity of 40,000 people.-History:... |
| Sporting Cristal Sporting Cristal Club Sporting Cristal is a Peruvian football team. Based in the Rímac District, in the department of Lima, it plays in the professional league known as the Peruvian First Division. Founded on November 16, 1926 in the Rimac District given its approval to the merger and Snuff Sporting merging with... |
Football | Primera División Peruana Primera División Peruana The Peruvian Primera División is the top professional division of Peruvian football. It is known today as Torneo Descentralizado de Fútbol Profesional Peruano... |
San Martín de Porres Stadium Estadio San Martin de Porres Estadio San Martín de Porres is a multi-purpose stadium in Lima, Peru. It is currently used by the football club Sporting Cristal and Club Deportivo San Martín... |
| Universidad San Martín de Porres Universidad San Martín de Porres Club Deportivo Universidad San Martín de Porres is a Peruvian football club, who plays in the city of Lima. The club was founded in 2004 as a joint stock company, the first in Peru. They then bought Club Sport Coopsol's place in the First Division who was promoted to the Peruvian First Division... |
Football | Primera Division Peruana Primera División Peruana The Peruvian Primera División is the top professional division of Peruvian football. It is known today as Torneo Descentralizado de Fútbol Profesional Peruano... |
San Martín de Porres Stadium Estadio San Martin de Porres Estadio San Martín de Porres is a multi-purpose stadium in Lima, Peru. It is currently used by the football club Sporting Cristal and Club Deportivo San Martín... |
| Club de Regatas Lima Club de Regatas Lima Regatas Lima is a sport club in Peru and one of the oldest in South America.The club is the biggest of San Isidro city, and one of the biggest in Lima Province.... |
Various | Various | Regatas Headquarters Chorrillos |
| Real Club Lima | Basketball Basketball Basketball is a team sport in which two teams of five players try to score points by throwing or "shooting" a ball through the top of a basketball hoop while following a set of rules... , Volleyball Volleyball Volleyball is a team sport in which two teams of six players are separated by a net. Each team tries to score points by grounding a ball on the other team's court under organized rules.The complete rules are extensive... |
Various | San Isidro |
Subdivisions

The city's historic centre
Historic Centre of Lima
Located principally in the city centre or Cercado de Lima and Rímac areas, the Historic Centre of Lima is among the most important tourist destinations in Peru.-Foundation:...
is located in the Cercado de Lima
Lima District
Lima is a district of the Lima Province in Peru. It is not where the inner city zone of Lima, the country's capital city, is located, San Isidro District being such area in Lima....
district, locally known as simply Lima, or as "El Centro" ("Downtown
Downtown
Downtown is a term primarily used in North America by English speakers to refer to a city's core or central business district ....
"), and it is home to most of the vestiges of Lima's colonial
Colonialism
Colonialism is the establishment, maintenance, acquisition and expansion of colonies in one territory by people from another territory. It is a process whereby the metropole claims sovereignty over the colony and the social structure, government, and economics of the colony are changed by...
past, the Presidential Palace , the Metropolitan Municipality of Lima , and dozens of hotels, some operating and some defunct, that used to cater to the national and international elite.
The upscale San Isidro district is the city's financial center. It is home to many prominent figures such as politicians and celebrities. It is also where the main banks of Peru and branch offices of world banks are headquartered. San Isidro has many parks, including Parque El Olivar, which has olive trees that were brought from Spain during the seventeenth century.
Another upscale district is Miraflores
Miraflores District
Miraflores is a district of the Lima Province in Peru. Known for its shopping areas, gardens, flower-filled parks and beaches, it is one of the upscale districts that make up the city of Lima....
, which has many luxury hotels, shops and restaurants. Miraflores
Miraflores District
Miraflores is a district of the Lima Province in Peru. Known for its shopping areas, gardens, flower-filled parks and beaches, it is one of the upscale districts that make up the city of Lima....
has more parks and green areas in the south of Lima than most other districts. Larcomar, a popular shopping mall and entertainment center built on cliffs overlooking the Pacific Ocean, featuring bars, dance clubs, movie theaters, cafes, shops, boutiques and galleries, is also located in this district. Nightlife, shopping and entertainment also center around Parque Kennedy, a park in the heart of Miraflores that is always bustling with people and live performances.
La Molina, San Borja and Santiago de Surco
Santiago de Surco
Santiago de Surco, commonly known simply as Surco, is a district of Lima, Peru. It is bordered on the north by the districts of La Molina, Ate and San Borja; on the south by Chorrillos; on the east by La Molina, Villa María del Triunfo and San Juan de Miraflores; and on the west by San Borja,...
, home to the American Embassy and the exclusive Club Polo Lima, are the other three wealthy districts of Lima.
The most densely-populated districts of Lima lie in the northern and southern ends of the city (Spanish: Cono Norte
Cono Norte
The Cono Norte is one of the six areas that make up the Lima Metropolitan Area. It is located in the northern part of the metropolis, hence its name. The socioeconomic levels of its residents are varied. Ancón and Santa Rosa are popular beach resorts for wealthier residents of Lima...
and Cono Sur
Southern Cone
Southern Cone is a geographic region composed of the southernmost areas of South America, south of the Tropic of Capricorn. Although geographically this includes part of Southern and Southeast of Brazil, in terms of political geography the Southern cone has traditionally comprised Argentina,...
, respectively), and they are mostly composed of Andean immigrants who arrived during the mid and late 20th century looking for better living standards and economic opportunities, or as refugees of the country's internal conflict with the Shining Path
Shining Path
Shining Path is a Maoist guerrilla terrorist organization in Peru. The group never refers to itself as "Shining Path", and as several other Peruvian groups, prefers to be called the "Communist Party of Peru" or "PCP-SL" in short...
during the late 80s and early '90s. In the case of Cono Norte (now called Lima Norte
Cono Norte
The Cono Norte is one of the six areas that make up the Lima Metropolitan Area. It is located in the northern part of the metropolis, hence its name. The socioeconomic levels of its residents are varied. Ancón and Santa Rosa are popular beach resorts for wealthier residents of Lima...
), certain shopping malls like Megaplaza and Royal Plaza have been recently built in the Independencia
Independencia District, Lima
Independencia is a district of the Lima Province in Peru. It is part of city of Lima.Officially established as a district on March 16, 1964, the current mayor of Independencia is Lovell Yomond Vargas. The district's postal code is 28....
district, right on the border with the Los Olivos district, the latter being the most residential neighborhood in the Northern part of Lima. Most of the inhabitants of this area belong to the middle class
Middle class
The middle class is any class of people in the middle of a societal hierarchy. In Weberian socio-economic terms, the middle class is the broad group of people in contemporary society who fall socio-economically between the working class and upper class....
or lower middle class
Lower middle class
In developed nations across the world, the lower middle class is a sub-division of the greater middle class. Universally the term refers to the group of middle class households or individuals who have not attained the status of the upper middle class associated with the higher realms of the middle...
.
Barranco, which borders Miraflores
Miraflores District
Miraflores is a district of the Lima Province in Peru. Known for its shopping areas, gardens, flower-filled parks and beaches, it is one of the upscale districts that make up the city of Lima....
by the Pacific Ocean, is known as the city's bohemian district, home or once home of many Peruvian writers and intellectuals like Mario Vargas Llosa, Chabuca Granda and Alfredo Bryce Echenique. This district has many acclaimed restaurants, music venues called "peñas" featuring the traditional folk music of coastal Peru (in Spanish, "música criolla"), and beautiful Victorian-style chalets. It along with Miraflores serves as the home to the foreign nightlife scene.
Education
Lima is home to the oldest higher learning institution in the New World, San Marcos University founded in 1551. Home to a range of universities, institutions, and schools, Lima has the highest concentration of institutions of higher learning in the continent and is home to schools with worldwide recognition. Peru itself is one of the most educated countries in South America. The National University of San MarcosNational University of San Marcos
The National University of San Marcos is the most important and respected higher-education institution in Peru. Its main campus, the University City, is located in Lima...
, founded on May 12, 1551 during Spanish colonial regime
Viceroyalty of Peru
Created in 1542, the Viceroyalty of Peru was a Spanish colonial administrative district that originally contained most of Spanish-ruled South America, governed from the capital of Lima...
, is the oldest continuously functioning university in the Americas
Americas
The Americas, or America , are lands in the Western hemisphere, also known as the New World. In English, the plural form the Americas is often used to refer to the landmasses of North America and South America with their associated islands and regions, while the singular form America is primarily...
.
Universidad Nacional de Ingeniería (UNI) was founded in 1876 by Polish engineer Eduardo de Habich and is the most important engineering school in the country. Other public universities also play key roles in teaching and research, such as the Universidad Nacional Federico Villarreal
Universidad Nacional Federico Villarreal
Universidad Nacional Federico Villarreal ' is a public university located in Lima, Peru. It was created by Order Nº 14692 on October 30, 1963 .-External links:*...
(the second largest in the country), the Universidad Nacional Agraria La Molina where ex-president Alberto Fujimori
Alberto Fujimori
Alberto Fujimori Fujimori served as President of Peru from 28 July 1990 to 17 November 2000. A controversial figure, Fujimori has been credited with the creation of Fujimorism, uprooting terrorism in Peru and restoring its macroeconomic stability, though his methods have drawn charges of...
once taught, and the National University of Callao.
The Pontificia Universidad Católica del Perú, established in 1917, is the oldest private university. Other private institutions that are located in the city are Universidad del Pacifico, Universidad de Lima, Universidad San Martín de Porres
Universidad San Martín de Porres
Club Deportivo Universidad San Martín de Porres is a Peruvian football club, who plays in the city of Lima. The club was founded in 2004 as a joint stock company, the first in Peru. They then bought Club Sport Coopsol's place in the First Division who was promoted to the Peruvian First Division...
, Universidad Peruana Cayetano Heredia, Universidad Cientifica del Sur
Universidad Científica del Sur
The Universidad Científica del Sur, or UCSUR, is a higher education and research institution located in Lima, Peru. It has a four-hectare campus close to the Pantanos de Villa Reserved Zone, in Villa El Salvador.-History:...
, Universidad San Ignacio de Loyola
Universidad San Ignacio de Loyola
The St. Ignacio de Loyola University is a private university located in Lima, Perú, it was founded by businessman and politician Raúl Diez Canseco in 1993....
, Universidad Peruana de Ciencias Aplicadas and Universidad Ricardo Palma.
Air transport
Lima is served by the Jorge Chávez International AirportJorge Chávez International Airport
Jorge Chávez International Airport , known as Aeropuerto Internacional Jorge Chávez in Spanish, is Peru's main international and domestic airport. It is located in Callao, 11 kilometers from the Historic Centre of Lima and 17 km from Miraflores. Callao is the port city now fully...
, located in Callao
Callao
Callao is the largest and most important port in Peru. The city is coterminous with the Constitutional Province of Callao, the only province of the Callao Region. Callao is located west of Lima, the country's capital, and is part of the Lima Metropolitan Area, a large metropolis that holds almost...
(LIM). It is the largest airport of the country with the largest amount of domestic and international air traffic. It also serves as a major hub in the Latin American air network. Lima's Jorge Chavez International Airport is the fourth largest air hub in South America. The airport, however it is the base for the largest cargo hub in the continent. Additionally, Lima possesses five other airports: the Las Palmas Air Force Base, Collique Airport, and runways in Santa María del Mar, San Bartolo
San Bartolo District
San Bartolo is a district in southern Lima Province in Peru. It is bordered by the Pacific Ocean on the west, the district of Punta Negra on the north, the Huarochirí Province on the east, and the Santa María del Mar District on the south....
and Chilca
Chilca
Chilca was a rocket launch site in Peru at , near to Lima. Chilca was in service from 1974 and 1983 and was mainly used for launching Arcas and Nike rockets....
.
Land transportation
Lima is a major stop on the Pan-American HighwayPan-American Highway
The Pan-American Highway is a network of roads measuring about in total length. Except for an rainforest break, called the Darién Gap, the road links the mainland nations of the Americas in a connected highway system. According to Guinness World Records, the Pan-American Highway is the world's...
. Because of its location on the country's central coast, Lima is also an important junction in Peru's highway system. Three of the major highways originate in Lima.
- The Northern Panamerican HighwayPeru Highway 1Peru Highway 1, most widely known as Carretera Panamericana, is the most important highway in Peru.This road is the Peruvian portion of the Pan-American Highway...
, this highway extends more than 1330 kilometres (826.4 mi) to the border with Ecuador connecting the northern districts of Lima with many major cities along the northern Peruvian coast. - The Central Highway , this highway connects the eastern districts of Lima with many cities in central Peru. The highway extends 860 kilometres (534.4 mi) with its terminus at the city of PucallpaPucallpaPucallpa is a city in eastern Peru located on the banks of the Ucayali River, a major tributary of the Amazon River. It is the capital of the Ucayali region, the Coronel Portillo Province and the Calleria District....
near Brazil. - The Southern Panamerican HighwayPeru Highway 1Peru Highway 1, most widely known as Carretera Panamericana, is the most important highway in Peru.This road is the Peruvian portion of the Pan-American Highway...
, this highway connects the southern districts of Lima to cities on the southern coast. The highway extends 1450 kilometres (901 mi) to the border with Chile.
The city of Lima has one big bus terminus station located next to the mall Plaza norte in the north of the city. This bus station is the point of departure and arrival of a lot of buses with national and international destinations.
There are other bus stations for each company around the city. In addition, there are informals bus stations located in the south, center and north of the city; these bus stations are cheap and confusing, but manageable if you know your destination and have a basic comprehension of Spanish.
Maritime transport
The proximity of Lima to the port of CallaoCallao
Callao is the largest and most important port in Peru. The city is coterminous with the Constitutional Province of Callao, the only province of the Callao Region. Callao is located west of Lima, the country's capital, and is part of the Lima Metropolitan Area, a large metropolis that holds almost...
allows Callao to act as the metropolitan area's foremost port. Callao concentrates nearly all of the maritime transport of the metropolitan area. There is, however, a small port in Lurín
Lurín District
The Peruvian district of Lurín is one of the 43 that make up the Lima Province.-Boundaries:It borders on the north with the districts of Pachacamac, Villa María del Triunfo, and Villa el Salvador, to the east also with the Pachacamac District, to the south with Punta Hermosa, and to the west with...
whose transit mostly is accounted for by oil tankers due to a refinery being located nearby. Nonetheless, maritime transport inside Lima's city limits is relatively insignificant compared to that of Callao, the nation's leading port and one of Latin America's largest.
Rail transport
Lima is connected to the Central Andean region by the Ferrocarril Central AndinoFerrocarril Central Andino
Ferrocarril Central Andino is the consortium which operates the Ferrovías Central railway in Peru linking the Pacific port of Callao and the capital Lima with Huancayo and Cerro de Pasco...
which runs from Lima through the departments of Junin
Junín Region
Junín is a region in the central highlands and westernmost Amazonia of Peru. Its capital is Huancayo.-Geography:The region has a very heterogeneous topography. The western cordillera located near the border with the Lima Region, has snowy and ice covered peaks. On the east, there are high glacier...
, Huancavelica
Huancavelica Region
Huancavelica is a region in Peru. Area: 22,131.47 km². Population: 447,054 . The capital is the city of Huancavelica.It is bordered by Lima Region and Ica in the west, Junín in the north, and Ayacucho in the east....
, Pasco
Pasco Region
Pasco is a region in central Peru. Its capital is Cerro de Pasco.-Political division:The region is divided into 3 provinces , which are composed of 28 districts .-Provinces:...
, and Huanuco
Huánuco Region
Huánuco is a region in central Peru. It is bordered by the La Libertad, San Martín, Loreto and Ucayali regions on the north; the Ucayali Region on the east; the Pasco Region on the south; and the Lima and Ancash regions on the west. Its capital is the city of Huánuco.Huánuco has a rough topography...
. Major cities along this line include Huancayo
Huancayo
Huancayo with a rock') is the capital of the Junín Region, in the central highlands of Peru. It is located in Junín Province, of which it is also capital. Situated near the Mantaro Valley at an altitude of 3,271 meters, it has a population of 377,000 and is the fifth most populous city of the...
, La Oroya
La Oroya
La Oroya is a city of about 33,000 people on the River Mantaro in central Peru. It is situated on the Altiplano some 176 km east-north-east of the national capital, Lima, and is capital of the Yauli Province...
, Huancavelica
Huancavelica
Huancavelica is a city in Peru. It is the capital of the Huancavelica region and has a population of approximately 40,000. Indigenous peoples represent a major percentage of the population. It has an approximate altitude of 3,600 meters; the climate is cold and dry between the months of February...
, and Cerro de Pasco
Cerro de Pasco
Cerro de Pasco is a city in central Peru. It is the capital of the Pasco region, and an important mining center. It is connected by road and by rail to the city of Lima.- Overview :...
. Another inactive line runs from Lima northwards to the city of Huacho
Huacho
Huacho is a city in Peru, capital of the Huaura Province and capital of the Lima Region. It is located 223 feet above sea level and 148 km north of the city of Lima...
.
Public transport
Eighty percent of the city's history having occurred during the pre-automobile era, Lima's road network is based mostly on large divided avenues rather than freeways. In recent times however, Lima has developed a freeway network now made up of nine freeways which are, the Via Expresa Paseo de la Republica, Via Expresa Javier Prado, Via Expresa Grau, Panamericana Norte, Panamericana Sur, Carretera Central, Via Expresa Callao, Autopista Chillon Trapiche, and the Autopista Ramiro Priale.The urban transport system is composed of over 652 transit routes which are served by buses, microbuses, and combis. The system is unorganized and is characterized by the lack of formality. The service is run by 464 private companies which are poorly regulated by the local government. Fares average at around one sol
Peruvian nuevo sol
The nuevo sol plural: nuevos soles; currency sign: S/.) is the currency of Peru. It is subdivided into 100 cents, called céntimos in Spanish. The ISO 4217 currency code is PEN. It is most commonly referred to just as sol...
or $0.30 USD. The city of Lima has also more than 100 km of cycle paths.
Taxis in the city are mostly informal; they are relatively cheap but could be dangerous (mostly because of the way the "taxistas" drive). There are no meters so drivers are told the desired destination and the fare is agreed upon before the passenger enters the taxi. Taxis vary in sizes from small four door compacts to large vans. They are virtually everywhere, with different colours, accounting for a large part of the car stock. In many cases they are just a private car with a taxi sticker on the windshield. Additionally, there are several companies that provide taxi service on-call.
Automobile
Automobile
An automobile, autocar, motor car or car is a wheeled motor vehicle used for transporting passengers, which also carries its own engine or motor...
s, known as colectivos, render express service on some major roads of the Lima Metropolitan Area
Lima Metropolitan Area
The Lima Metropolitan Area , is an area formed by the conurbation of the Peruvian cities of Lima and Callao. It is the largest metropolitan area in Peru, the eighth largest in the Americas, and among the thirty largest in the world. The conurbation process started to be evident in the 1980s. The...
. The colectivos signal their specific destination with a sign on the their windshield. Their routes are not generally publicitized but are understood by frequent users. The cost is generally higher than public transport however they cover greater distances at greater speeds due to the lack of stops. This service is informal and is not allowed in the city. Some people in the periphery of the city use the so called "mototaxi" for short distances
The Metropolitan Transportation System or El Metropolitano
El Metropolitano
El Metropolitano is a new Bus Rapid Transit system serving the city of Lima, Peru. Its construction began in the year 2006 during Luis Castañeda Lossio's period as Mayor of Lima.-Services:...
is a public transportation system which integrate the Independent Corridor of Mass-Transit Buses known by its Spanish initials as (COSAC 1). This system links the principal points of the Lima Metropolitan Area
Lima Metropolitan Area
The Lima Metropolitan Area , is an area formed by the conurbation of the Peruvian cities of Lima and Callao. It is the largest metropolitan area in Peru, the eighth largest in the Americas, and among the thirty largest in the world. The conurbation process started to be evident in the 1980s. The...
and the first phase of this project has thirty three km line from the north of the city to Chorrillos in the south of the city. It began commercial operations on July 28th, 2010. This system is similar to the TransMilenio
TransMilenio
TransMilenio is a bus rapid transit system that serves Bogotá, the capital of Colombia. The system opened to the public in December 2000, covering Av. Caracas and Calle 80...
of Bogotá
Bogotá
Bogotá, Distrito Capital , from 1991 to 2000 called Santa Fé de Bogotá, is the capital, and largest city, of Colombia. It is also designated by the national constitution as the capital of the department of Cundinamarca, even though the city of Bogotá now comprises an independent Capital district...
, Colombia
Colombia
Colombia, officially the Republic of Colombia , is a unitary constitutional republic comprising thirty-two departments. The country is located in northwestern South America, bordered to the east by Venezuela and Brazil; to the south by Ecuador and Peru; to the north by the Caribbean Sea; to the...
.
The Lima Metro
Lima Metro
The Lima Metro, regarded by peruvians as Tren Eléctrico is a metropolitan railway currently linking the south of Lima, with the centre of the capital of Peru...
, an above ground mass transit system, which 3rd phase of the Line One is already opened to public. There are six more lines in planning phase. Line 1's extension to the city's center
Lima District
Lima is a district of the Lima Province in Peru. It is not where the inner city zone of Lima, the country's capital city, is located, San Isidro District being such area in Lima....
was opened in July 2011, linking Villa el Salvador
Villa El Salvador
Villa El Salvador is an urban, largely residential district on the outskirts of Lima, Peru. It borders the district of Chorrillos on the east; the Pacific Ocean on the southwest; Lurín on the southeast; Villa María del Triunfo on the east and San Juan de Miraflores on the north.- History :It began...
with downtown Lima
Lima District
Lima is a district of the Lima Province in Peru. It is not where the inner city zone of Lima, the country's capital city, is located, San Isidro District being such area in Lima....
in a matter of only thirty minutes, a trip which currently lasts one hour and forty minutes with other public transport system.
The Lima Metro has sixteen passenger stations, located at an average distance of 1.2 km (0.7 mi). It starts its path in the Industrial Park of Villa El Salvador, south of the city, continuing on to Av. Pachacútec in Villa María del Triunfo and then to Av. Los Héroes in San Juan de Miraflores. Afterwards, it continues through Av. Tomás Marsano in Surco to reach Ov. Los Cabitos and then on to Av. Aviación to finish in Av. Grau in the city center.
Construction to extend Line 1 until its final destination, through Av. Próceres de la Independencia in San Juan de Lurigancho, is scheduled to begin shortly.
International relations
Twin towns — Sister citiesLima is twinned with:
| Arequipa Arequipa Arequipa is the capital city of the Arequipa Region in southern Peru. With a population of 836,859 it is the second most populous city of the country... , Peru Cusco Cusco Cusco , often spelled Cuzco , is a city in southeastern Peru, near the Urubamba Valley of the Andes mountain range. It is the capital of the Cusco Region as well as the Cuzco Province. In 2007, the city had a population of 358,935 which was triple the figure of 20 years ago... , Peru Piura Piura Piura is a city in northwestern Peru. It is the capital of the Piura Region and the Piura Province. The population is 377,496.It was here that Spanish Conqueror Francisco Pizarro founded the third Spanish city in South America and first in Peru, San Miguel de Piura, in July 1532... , Peru Los Angeles Los Angeles, California Los Angeles , with a population at the 2010 United States Census of 3,792,621, is the most populous city in California, USA and the second most populous in the United States, after New York City. It has an area of , and is located in Southern California... , United States Austin Austin, Texas Austin is the capital city of the U.S. state of :Texas and the seat of Travis County. Located in Central Texas on the eastern edge of the American Southwest, it is the fourth-largest city in Texas and the 14th most populous city in the United States. It was the third-fastest-growing large city in... , United States, since 1981 Cleveland, United States Miami, United States Stamford Stamford, Connecticut Stamford is a city in Fairfield County, Connecticut, United States. According to the 2010 census, the population of the city is 122,643, making it the fourth largest city in the state and the eighth largest city in New England... , United States |
Bordeaux Bordeaux Bordeaux is a port city on the Garonne River in the Gironde department in southwestern France.The Bordeaux-Arcachon-Libourne metropolitan area, has a population of 1,010,000 and constitutes the sixth-largest urban area in France. It is the capital of the Aquitaine region, as well as the prefecture... , France. since 1957 Beijing Beijing Beijing , also known as Peking , is the capital of the People's Republic of China and one of the most populous cities in the world, with a population of 19,612,368 as of 2010. The city is the country's political, cultural, and educational center, and home to the headquarters for most of China's... , China, since November 1983 Manila Manila Manila is the capital of the Philippines. It is one of the sixteen cities forming Metro Manila.Manila is located on the eastern shores of Manila Bay and is bordered by Navotas and Caloocan to the north, Quezon City to the northeast, San Juan and Mandaluyong to the east, Makati on the southeast,... , Philippines Philippines The Philippines , officially known as the Republic of the Philippines , is a country in Southeast Asia in the western Pacific Ocean. To its north across the Luzon Strait lies Taiwan. West across the South China Sea sits Vietnam... Madrid Madrid Madrid is the capital and largest city of Spain. The population of the city is roughly 3.3 million and the entire population of the Madrid metropolitan area is calculated to be 6.271 million. It is the third largest city in the European Union, after London and Berlin, and its metropolitan... , Spain Mexico City Mexico City Mexico City is the Federal District , capital of Mexico and seat of the federal powers of the Mexican Union. It is a federal entity within Mexico which is not part of any one of the 31 Mexican states but belongs to the federation as a whole... , Mexico São Paulo São Paulo São Paulo is the largest city in Brazil, the largest city in the southern hemisphere and South America, and the world's seventh largest city by population. The metropolis is anchor to the São Paulo metropolitan area, ranked as the second-most populous metropolitan area in the Americas and among... , Brazil Tegucigalpa Tegucigalpa Tegucigalpa , and commonly referred as Tegus , is the capital of Honduras and seat of government of the Republic, along with its twin sister Comayagüela. Founded on September 29, 1578 by the Spanish, it became the country's capital on October 30, 1880 under President Marco Aurelio Soto... , Honduras Akhisar Akhisar Akhisar is a county district and its town center in Manisa Province in the Aegean region of Western Turkey... , Turkey |
Karaçoban Karaçoban Karaçoban is a town and district of Erzurum Province in the Eastern Anatolia region of Turkey. The mayor is Sedat Gümüş . The population 8,837 .... , Turkey Buenos Aires Buenos Aires Buenos Aires is the capital and largest city of Argentina, and the second-largest metropolitan area in South America, after São Paulo. It is located on the western shore of the estuary of the Río de la Plata, on the southeastern coast of the South American continent... , Argentina Guadalajara Guadalajara, Jalisco Guadalajara is the capital of the Mexican state of Jalisco, and the seat of the municipality of Guadalajara. The city is located in the central region of Jalisco in the western-pacific area of Mexico. With a population of 1,564,514 it is Mexico's second most populous municipality... , Mexico Toronto Toronto Toronto is the provincial capital of Ontario and the largest city in Canada. It is located in Southern Ontario on the northwestern shore of Lake Ontario. A relatively modern city, Toronto's history dates back to the late-18th century, when its land was first purchased by the British monarchy from... , Canada Bogotá Bogotá Bogotá, Distrito Capital , from 1991 to 2000 called Santa Fé de Bogotá, is the capital, and largest city, of Colombia. It is also designated by the national constitution as the capital of the department of Cundinamarca, even though the city of Bogotá now comprises an independent Capital district... , Colombia Cairo Cairo Cairo , is the capital of Egypt and the largest city in the Arab world and Africa, and the 16th largest metropolitan area in the world. Nicknamed "The City of a Thousand Minarets" for its preponderance of Islamic architecture, Cairo has long been a centre of the region's political and cultural life... , Egypt Cardiff Cardiff Cardiff is the capital, largest city and most populous county of Wales and the 10th largest city in the United Kingdom. The city is Wales' chief commercial centre, the base for most national cultural and sporting institutions, the Welsh national media, and the seat of the National Assembly for... , United Kingdom Pescara Pescara Pescara is the capital city of the Province of Pescara, in the Abruzzo region of Italy. As of January 1, 2007 it was the most populated city within Abruzzo at 123,059 residents, 400,000 with the surrounding metropolitan area... , Italy Kiev Kiev Kiev or Kyiv is the capital and the largest city of Ukraine, located in the north central part of the country on the Dnieper River. The population as of the 2001 census was 2,611,300. However, higher numbers have been cited in the press.... , Ukraine Brasília Brasília Brasília is the capital city of Brazil. The name is commonly spelled Brasilia in English. The city and its District are located in the Central-West region of the country, along a plateau known as Planalto Central. It has a population of about 2,557,000 as of the 2008 IBGE estimate, making it the... , Brazil |
See also
- Lima Metropolitan AreaLima Metropolitan AreaThe Lima Metropolitan Area , is an area formed by the conurbation of the Peruvian cities of Lima and Callao. It is the largest metropolitan area in Peru, the eighth largest in the Americas, and among the thirty largest in the world. The conurbation process started to be evident in the 1980s. The...
- List of people from Lima
- List of districts and neighborhoods of Lima
- List of sites of interest in the Lima Metropolitan area
- Largest cities in the AmericasLargest Cities in the AmericasThis is a list of the 50 largest cities in the Americas by population. Official definitions of cities are defined according to the concept of city proper, which is the territory within the city limits. The list ranks the world's urban municipal units according to population...

