
Methylmercury
Encyclopedia
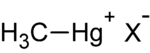
Structure
"Methylmercury" is a shorthand for "monomethylmercury", and is more correctly "monomethylmercuric cation". It is composed of a methyl groupFunctional group
In organic chemistry, functional groups are specific groups of atoms within molecules that are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those molecules. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reaction regardless of the size of the molecule it is a part of...
(3-) bonded
Chemical bond
A chemical bond is an attraction between atoms that allows the formation of chemical substances that contain two or more atoms. The bond is caused by the electromagnetic force attraction between opposite charges, either between electrons and nuclei, or as the result of a dipole attraction...
to a mercury
Mercury (element)
Mercury is a chemical element with the symbol Hg and atomic number 80. It is also known as quicksilver or hydrargyrum...
atom
Atom
The atom is a basic unit of matter that consists of a dense central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The atomic nucleus contains a mix of positively charged protons and electrically neutral neutrons...
; its chemical formula
Chemical formula
A chemical formula or molecular formula is a way of expressing information about the atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound....
is + (sometimes written as MeHg+). As a positively charged ion it readily combines with anions such as chloride
Chloride
The chloride ion is formed when the element chlorine, a halogen, picks up one electron to form an anion Cl−. The salts of hydrochloric acid HCl contain chloride ions and can also be called chlorides. The chloride ion, and its salts such as sodium chloride, are very soluble in water...
(−), hydroxide
Hydroxide
Hydroxide is a diatomic anion with chemical formula OH−. It consists of an oxygen and a hydrogen atom held together by a covalent bond, and carrying a negative electric charge. It is an important but usually minor constituent of water. It functions as a base, as a ligand, a nucleophile, and a...
(-) and nitrate
Nitrate
The nitrate ion is a polyatomic ion with the molecular formula NO and a molecular mass of 62.0049 g/mol. It is the conjugate base of nitric acid, consisting of one central nitrogen atom surrounded by three identically-bonded oxygen atoms in a trigonal planar arrangement. The nitrate ion carries a...
(3−). It also has very high affinity for sulfur
Sulfur
Sulfur or sulphur is the chemical element with atomic number 16. In the periodic table it is represented by the symbol S. It is an abundant, multivalent non-metal. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow...
-containing anions, particularly the thiol
Thiol
In organic chemistry, a thiol is an organosulfur compound that contains a carbon-bonded sulfhydryl group...
(-) groups on the amino acid
Amino acid
Amino acids are molecules containing an amine group, a carboxylic acid group and a side-chain that varies between different amino acids. The key elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen...
cysteine
Cysteine
Cysteine is an α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCHCH2SH. It is a non-essential amino acid, which means that it is biosynthesized in humans. Its codons are UGU and UGC. The side chain on cysteine is thiol, which is polar and thus cysteine is usually classified as a hydrophilic amino acid...
and hence in protein
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
s containing cysteine, forming a covalent bond
Covalent bond
A covalent bond is a form of chemical bonding that is characterized by the sharing of pairs of electrons between atoms. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atoms when they share electrons is known as covalent bonding....
. More than one cysteine moiety may coordinate with methylmercury, and methylmercury may migrate to other metal-binding sites in proteins.
Environmental sources
In the past, methylmercury was produced directly and indirectly as part of several industrial processes such as the manufacture of acetaldehydeAcetaldehyde
Acetaldehyde is an organic chemical compound with the formula CH3CHO or MeCHO. It is one of the most important aldehydes, occurring widely in nature and being produced on a large scale industrially. Acetaldehyde occurs naturally in coffee, bread, and ripe fruit, and is produced by plants as part...
. Currently there are few anthropogenic
Anthropogenic
Human impact on the environment or anthropogenic impact on the environment includes impacts on biophysical environments, biodiversity and other resources. The term anthropogenic designates an effect or object resulting from human activity. The term was first used in the technical sense by Russian...
sources of methylmercury pollution
Pollution
Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into a natural environment that causes instability, disorder, harm or discomfort to the ecosystem i.e. physical systems or living organisms. Pollution can take the form of chemical substances or energy, such as noise, heat or light...
other than as an indirect consequence of the burning
Combustion
Combustion or burning is the sequence of exothermic chemical reactions between a fuel and an oxidant accompanied by the production of heat and conversion of chemical species. The release of heat can result in the production of light in the form of either glowing or a flame...
of wastes containing inorganic mercury and from the burning of fossil fuel
Fossil fuel
Fossil fuels are fuels formed by natural processes such as anaerobic decomposition of buried dead organisms. The age of the organisms and their resulting fossil fuels is typically millions of years, and sometimes exceeds 650 million years...
s, particularly coal
Coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock usually occurring in rock strata in layers or veins called coal beds or coal seams. The harder forms, such as anthracite coal, can be regarded as metamorphic rock because of later exposure to elevated temperature and pressure...
. Although inorganic mercury is only a trace constituent of such fuels, their large scale combustion in utility and commercial/industrial boilers in the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
alone results in release of some 80.2 tons (73 tonne
Tonne
The tonne, known as the metric ton in the US , often put pleonastically as "metric tonne" to avoid confusion with ton, is a metric system unit of mass equal to 1000 kilograms. The tonne is not an International System of Units unit, but is accepted for use with the SI...
s) of elemental mercury to the atmosphere
Earth's atmosphere
The atmosphere of Earth is a layer of gases surrounding the planet Earth that is retained by Earth's gravity. The atmosphere protects life on Earth by absorbing ultraviolet solar radiation, warming the surface through heat retention , and reducing temperature extremes between day and night...
each year, out of total anthropogenic mercury emissions in the United States of 158 tons (144 tonnes)/year. Natural sources of mercury to the atmosphere include volcano
Volcano
2. Bedrock3. Conduit 4. Base5. Sill6. Dike7. Layers of ash emitted by the volcano8. Flank| 9. Layers of lava emitted by the volcano10. Throat11. Parasitic cone12. Lava flow13. Vent14. Crater15...
es, forest fires
Wildfire
A wildfire is any uncontrolled fire in combustible vegetation that occurs in the countryside or a wilderness area. Other names such as brush fire, bushfire, forest fire, desert fire, grass fire, hill fire, squirrel fire, vegetation fire, veldfire, and wilkjjofire may be used to describe the same...
and weathering
Weathering
Weathering is the breaking down of rocks, soils and minerals as well as artificial materials through contact with the Earth's atmosphere, biota and waters...
of mercury-bearing
Cinnabar
Cinnabar or cinnabarite , is the common ore of mercury.-Word origin:The name comes from κινναβαρι , a Greek word most likely applied by Theophrastus to several distinct substances...
rocks
Rock (geology)
In geology, rock or stone is a naturally occurring solid aggregate of minerals and/or mineraloids.The Earth's outer solid layer, the lithosphere, is made of rock. In general rocks are of three types, namely, igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic...
.
Methylmercury is formed from inorganic mercury by the action of anaerobic organism
Anaerobic organism
An anaerobic organism or anaerobe is any organism that does not require oxygen for growth. It could possibly react negatively and may even die if oxygen is present...
s that live in aquatic systems including lake
Lake
A lake is a body of relatively still fresh or salt water of considerable size, localized in a basin, that is surrounded by land. Lakes are inland and not part of the ocean and therefore are distinct from lagoons, and are larger and deeper than ponds. Lakes can be contrasted with rivers or streams,...
s, river
River
A river is a natural watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, a lake, a sea, or another river. In a few cases, a river simply flows into the ground or dries up completely before reaching another body of water. Small rivers may also be called by several other names, including...
s, wetland
Wetland
A wetland is an area of land whose soil is saturated with water either permanently or seasonally. Wetlands are categorised by their characteristic vegetation, which is adapted to these unique soil conditions....
s, sediment
Sediment
Sediment is naturally occurring material that is broken down by processes of weathering and erosion, and is subsequently transported by the action of fluids such as wind, water, or ice, and/or by the force of gravity acting on the particle itself....
s, soil
Soil
Soil is a natural body consisting of layers of mineral constituents of variable thicknesses, which differ from the parent materials in their morphological, physical, chemical, and mineralogical characteristics...
s and the open ocean
Ocean
An ocean is a major body of saline water, and a principal component of the hydrosphere. Approximately 71% of the Earth's surface is covered by ocean, a continuous body of water that is customarily divided into several principal oceans and smaller seas.More than half of this area is over 3,000...
. This methylation process converts inorganic mercury to methylmercury in the natural environment. Acute methylmercury poisoning occurred at Grassy Narrows in Ontario, Canada (see Ontario Minamata disease
Ontario Minamata disease
Ontario Minamata disease is a neurological syndrome caused by severe mercury poisoning. It occurred in the Canadian province of Ontario in 1970 and severely affected two First Nation communities located in Northwestern Ontario following consumption of local fish that were contaminated with mercury...
) as a result of mercury released from the mercury-cell Chloralkali process
Chloralkali process
The chloralkali process is an industrial process for the electrolysis of sodium chloride solution . Depending on the method several products beside hydrogen can be produced. If the products are separated, chlorine and sodium hydroxide are the products; by mixing, sodium hypochlorite or sodium...
, which uses liquid mercury as an electrode in a process that entails electrolytic decomposition of brine, followed by mercury methylation in the aquatic environment.
An acute methylmercury poisoning tragedy occurred in Minamata, Japan following release of methylmercury into Minamata Bay and its tributaries (see Minamata disease
Minamata disease
', sometimes referred to as , is a neurological syndrome caused by severe mercury poisoning. Symptoms include ataxia, numbness in the hands and feet, general muscle weakness, narrowing of the field of vision and damage to hearing and speech. In extreme cases, insanity, paralysis, coma, and death...
). In the Ontario case, inorganic mercury discharged into the environment was methylated in the environment; whereas in Minimata, Japan, there was direct industrial discharge of methylmercury.
Dietary sources
Because methylmercury is formed in aquatic systems and because it is not readily eliminated from organisms it is biomagnifiedBiomagnification
Biomagnification, also known as bioamplification or biological magnification, is the increase in concentration of a substance that occurs in a food chain as a consequence of:* Persistence...
in aquatic food chain
Food chain
A food web depicts feeding connections in an ecological community. Ecologists can broadly lump all life forms into one of two categories called trophic levels: 1) the autotrophs, and 2) the heterotrophs...
s from bacteria
Bacteria
Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals...
, to plankton
Plankton
Plankton are any drifting organisms that inhabit the pelagic zone of oceans, seas, or bodies of fresh water. That is, plankton are defined by their ecological niche rather than phylogenetic or taxonomic classification...
, through macroinvertebrates, to herbivorous
Herbivore
Herbivores are organisms that are anatomically and physiologically adapted to eat plant-based foods. Herbivory is a form of consumption in which an organism principally eats autotrophs such as plants, algae and photosynthesizing bacteria. More generally, organisms that feed on autotrophs in...
fish
Fish
Fish are a paraphyletic group of organisms that consist of all gill-bearing aquatic vertebrate animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish, as well as various extinct related groups...
and to piscivorous (fish-eating) fish. At each step in the food chain, the concentration
Concentration
In chemistry, concentration is defined as the abundance of a constituent divided by the total volume of a mixture. Four types can be distinguished: mass concentration, molar concentration, number concentration, and volume concentration...
of methylmercury in the organism increases. The concentration of methylmercury in the top level aquatic predators can reach a level a million times higher than the level in the water. This is because methylmercury has a half-life of about 72 days in aquatic organisms resulting in its bioaccumulation
Bioaccumulation
Bioaccumulation refers to the accumulation of substances, such as pesticides, or other organic chemicals in an organism. Bioaccumulation occurs when an organism absorbs a toxic substance at a rate greater than that at which the substance is lost...
within these food chains. Organisms, including humans, fish-eating birds, and fish-eating mammals such as otter
Otter
The Otters are twelve species of semi-aquatic mammals which feed on fish and shellfish, and also other invertebrates, amphibians, birds and small mammals....
s and whale
Whale
Whale is the common name for various marine mammals of the order Cetacea. The term whale sometimes refers to all cetaceans, but more often it excludes dolphins and porpoises, which belong to suborder Odontoceti . This suborder also includes the sperm whale, killer whale, pilot whale, and beluga...
s that consume fish from the top of the aquatic food chain receive the methylmercury that has accumulated through this process. Fish and other aquatic species
Species
In biology, a species is one of the basic units of biological classification and a taxonomic rank. A species is often defined as a group of organisms capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring. While in many cases this definition is adequate, more precise or differing measures are...
are the only significant source of human methylmercury exposure.
The concentration of mercury in any given fish depends on the species of fish, the age and size of the fish and the type of water body in which it is found. In general, fish-eating fish such as shark
Shark
Sharks are a type of fish with a full cartilaginous skeleton and a highly streamlined body. The earliest known sharks date from more than 420 million years ago....
, swordfish
Swordfish
Swordfish , also known as broadbill in some countries, are large, highly migratory, predatory fish characterized by a long, flat bill. They are a popular sport fish of the billfish category, though elusive. Swordfish are elongated, round-bodied, and lose all teeth and scales by adulthood...
, marlin
Marlin
Marlin, family Istiophoridae, are fish with an elongated body, a spear-like snout or bill, and a long rigid dorsal fin, which extends forward to form a crest. Its common name is thought to derive from its resemblance to a sailor's marlinspike...
, larger species of tuna
Tuna
Tuna is a salt water fish from the family Scombridae, mostly in the genus Thunnus. Tuna are fast swimmers, and some species are capable of speeds of . Unlike most fish, which have white flesh, the muscle tissue of tuna ranges from pink to dark red. The red coloration derives from myoglobin, an...
, walleye
Walleye
Walleye is a freshwater perciform fish native to most of Canada and to the northern United States. It is a North American close relative of the European pikeperch...
, largemouth bass
Largemouth bass
The largemouth bass is a species of black bass in the sunfish family native to North America . It is also known as widemouth bass, bigmouth, black bass, bucketmouth, Potter's fish, Florida bass, Florida largemouth, green bass, green trout, linesides, Oswego bass, southern largemouth...
, and northern pike
Northern Pike
The northern pike , is a species of carnivorous fish of the genus Esox...
have higher levels of methylmercury than herbivorous fish or smaller fish such as tilapia
Tilapia
Tilapia , is the common name for nearly a hundred species of cichlid fish from the tilapiine cichlid tribe. Tilapia inhabit a variety of fresh water habitats, including shallow streams, ponds, rivers and lakes. Historically, they have been of major importance in artisan fishing in Africa and the...
, and herring
Herring
Herring is an oily fish of the genus Clupea, found in the shallow, temperate waters of the North Pacific and the North Atlantic oceans, including the Baltic Sea. Three species of Clupea are recognized. The main taxa, the Atlantic herring and the Pacific herring may each be divided into subspecies...
. Within a given species of fish, older and larger fish have higher levels of methylmercury than smaller fish. Fish that develop in water bodies that are more acid
Acid
An acid is a substance which reacts with a base. Commonly, acids can be identified as tasting sour, reacting with metals such as calcium, and bases like sodium carbonate. Aqueous acids have a pH of less than 7, where an acid of lower pH is typically stronger, and turn blue litmus paper red...
ic also tend to have higher levels of methylmercury.
Human health effects
IngestedIngestion
Ingestion is the consumption of a substance by an organism. In animals, it normally is accomplished by taking in the substance through the mouth into the gastrointestinal tract, such as through eating or drinking...
methylmercury is readily and completely absorbed by the gastrointestinal tract
Gastrointestinal tract
The human gastrointestinal tract refers to the stomach and intestine, and sometimes to all the structures from the mouth to the anus. ....
. It is mostly found complexed with free cysteine and with proteins and peptide
Peptide
Peptides are short polymers of amino acid monomers linked by peptide bonds. They are distinguished from proteins on the basis of size, typically containing less than 50 monomer units. The shortest peptides are dipeptides, consisting of two amino acids joined by a single peptide bond...
s containing that amino acid. The methylmercuric-cysteinyl complex is recognized by amino acid transporting proteins in the body as methionine
Methionine
Methionine is an α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCHCH2CH2SCH3. This essential amino acid is classified as nonpolar. This amino-acid is coded by the codon AUG, also known as the initiation codon, since it indicates mRNA's coding region where translation into protein...
, another essential amino acid
Essential amino acid
An essential amino acid or indispensable amino acid is an amino acid that cannot be synthesized de novo by the organism , and therefore must be supplied in the diet.-Essentiality vs. conditional essentiality in humans:...
. Because of this mimicry, it is transported freely throughout the body including across the blood-brain barrier
Blood-brain barrier
The blood–brain barrier is a separation of circulating blood and the brain extracellular fluid in the central nervous system . It occurs along all capillaries and consists of tight junctions around the capillaries that do not exist in normal circulation. Endothelial cells restrict the diffusion...
and across the placenta
Placenta
The placenta is an organ that connects the developing fetus to the uterine wall to allow nutrient uptake, waste elimination, and gas exchange via the mother's blood supply. "True" placentas are a defining characteristic of eutherian or "placental" mammals, but are also found in some snakes and...
, where it is absorbed by the developing fetus
Fetus
A fetus is a developing mammal or other viviparous vertebrate after the embryonic stage and before birth.In humans, the fetal stage of prenatal development starts at the beginning of the 11th week in gestational age, which is the 9th week after fertilization.-Etymology and spelling variations:The...
. Also for this reason as well as its strong binding to proteins, methylmercury is not readily eliminated. Methylmercury has a half-life
Half-life
Half-life, abbreviated t½, is the period of time it takes for the amount of a substance undergoing decay to decrease by half. The name was originally used to describe a characteristic of unstable atoms , but it may apply to any quantity which follows a set-rate decay.The original term, dating to...
in human blood
Blood
Blood is a specialized bodily fluid in animals that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells....
of about 50 days.
Several studies indicate that methylmercury is linked to subtle developmental deficits in children exposed in-utero such as loss of IQ points, and decreased performance in tests of language skills, memory function and attention deficits. Methylmercury exposure in adults has also been linked to increased risk of cardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease
Heart disease or cardiovascular disease are the class of diseases that involve the heart or blood vessels . While the term technically refers to any disease that affects the cardiovascular system , it is usually used to refer to those related to atherosclerosis...
including heart attack
Myocardial infarction
Myocardial infarction or acute myocardial infarction , commonly known as a heart attack, results from the interruption of blood supply to a part of the heart, causing heart cells to die...
. Some evidence also suggests that methylmercury can cause autoimmune effects in sensitive individuals. However, to date, methylmercury has not been linked to any specific neurologic or autoimmune disease. Although there is no doubt that methylmercury is toxic in several respects, including through exposure of the developing fetus, there is still some controversy as to the levels of methylmercury in the diet that can result in adverse effects.
There have been several episodes in which large numbers of people were severely poisoned by food contaminated with high levels of methylmercury, notably the dumping of industrial waste
Industrial waste
Industrial waste is a type of waste produced by industrial activity, such as that of factories, mills and mines. It has existed since the outset of the industrial revolution....
that resulted in the pollution and subsequent mass poisoning
Minamata disease
', sometimes referred to as , is a neurological syndrome caused by severe mercury poisoning. Symptoms include ataxia, numbness in the hands and feet, general muscle weakness, narrowing of the field of vision and damage to hearing and speech. In extreme cases, insanity, paralysis, coma, and death...
in Minamata and Niigata
Niigata, Niigata
is the capital and the most populous city of Niigata Prefecture, Japan. It lies on the northwest coast of Honshu, the largest island of Japan, and faces the Sea of Japan and Sado Island....
, Japan
Japan
Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south...
and the situation in Iraq
Iraq
Iraq ; officially the Republic of Iraq is a country in Western Asia spanning most of the northwestern end of the Zagros mountain range, the eastern part of the Syrian Desert and the northern part of the Arabian Desert....
in the 1960s and 1970s in which wheat treated with methylmercury as a preservative and intended as seed grain was fed to animals and directly consumed by people (see Basra poison grain disaster
Basra poison grain disaster
The 1971 Iraq poison grain disaster was a mass methylmercury poisoning incident that began in late 1971. Grain treated with a methylmercury fungicide and never intended for human consumption was imported into Iraq as seed grain from Mexico and the United States...
). These episodes resulted in neurologic
Neurology
Neurology is a medical specialty dealing with disorders of the nervous system. Specifically, it deals with the diagnosis and treatment of all categories of disease involving the central, peripheral, and autonomic nervous systems, including their coverings, blood vessels, and all effector tissue,...
symptom
Symptom
A symptom is a departure from normal function or feeling which is noticed by a patient, indicating the presence of disease or abnormality...
s including paresthesia
Paresthesia
Paresthesia , spelled "paraesthesia" in British English, is a sensation of tingling, burning, pricking, or numbness of a person's skin with no apparent long-term physical effect. It is more generally known as the feeling of "pins and needles" or of a limb "falling asleep"...
s, loss of physical coordination, difficulty in speech
Dysarthria
Dysarthria is a motor speech disorder resulting from neurological injury of the motor component of the motor-speech system and is characterized by poor articulation of phonemes...
, narrowing of the visual field, hearing impairment
Hearing impairment
-Definition:Deafness is the inability for the ear to interpret certain or all frequencies of sound.-Environmental Situations:Deafness can be caused by environmental situations such as noise, trauma, or other ear defections...
, blindness
Blindness
Blindness is the condition of lacking visual perception due to physiological or neurological factors.Various scales have been developed to describe the extent of vision loss and define blindness...
, and death. Children who had been exposed in-utero through their mothers' ingestion were also affected with a range of symptoms including motor difficulties, sensory problems and mental retardation
Mental retardation
Mental retardation is a generalized disorder appearing before adulthood, characterized by significantly impaired cognitive functioning and deficits in two or more adaptive behaviors...
.
At present, exposures of this magnitude are rarely seen and are confined to isolated incidents. Accordingly, concern over methylmercury pollution is currently focused on more subtle effects that may be linked to levels of exposure presently seen in populations with high to moderate levels of dietary fish consumption. These effects are not necessarily identifiable on an individual level or may not be uniquely recognizable as due to methylmercury. However, such effects may be detected by comparing populations with different levels of exposure. There are isolated reports of various clinical health effects in individuals who consume large amounts of fish; however, the specific health effects and exposure patterns have not been verified with larger, controlled studies.
Many governmental agencies, the most notable ones being the United States Environmental Protection Agency
United States Environmental Protection Agency
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency is an agency of the federal government of the United States charged with protecting human health and the environment, by writing and enforcing regulations based on laws passed by Congress...
(EPA), the United States Food and Drug Administration
Food and Drug Administration
The Food and Drug Administration is an agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, one of the United States federal executive departments...
(FDA), Health Canada
Health Canada
Health Canada is the department of the government of Canada with responsibility for national public health.The current Minister of Health is Leona Aglukkaq, a Conservative Member of Parliament appointed to the position by Prime Minister Stephen Harper.-Branches, regions and agencies:Health Canada...
, and the European Union Health and Consumer Protection Directorate-General, as well as the World Health Organization
World Health Organization
The World Health Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations that acts as a coordinating authority on international public health. Established on 7 April 1948, with headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland, the agency inherited the mandate and resources of its predecessor, the Health...
(WHO) and the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization
Food and Agriculture Organization
The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations is a specialised agency of the United Nations that leads international efforts to defeat hunger. Serving both developed and developing countries, FAO acts as a neutral forum where all nations meet as equals to negotiate agreements and...
(FAO), have issued guidance for fish consumers that is designed to limit methylmercury exposure from fish consumption. At present, most of this guidance is based on protection of the developing fetus; future guidance, however, may also address cardiovascular risk. In general, fish consumption advice attempts to convey the message that fish is a good source of nutrition and has significant health benefits, but that consumers, in particular pregnant women, women of child-bearing age, nursing mothers, and young children, should avoid fish with high levels of methylmercury, limit their intake of fish with moderate levels of methylmercury, and consume fish with low levels of methylmercury no more than twice a week.
Effects of methylmercury on fish and wildlife
In recent years, there has been increasing recognition that methylmercury affects fish and wildlife health, both in acutely polluted ecosystems and ecosystems with modest methylmercury levels. Two reviews document numerous studies of diminished reproductive success of both fish, fish-eating birds, and mammals due to methylmercury contamination in aquatic ecosystems.A study by U.S. researcher Peter Frederick suggests methylmercury may increase male homosexuality in birds: Except a control group, all of 160 captured young ibises were given small amounts of methylmercury with their food. The reproductive behaviour of these coastal wading birds changed in such a way, that the more methylmercury was ingested the more male birds choose to build nests with other males, and snub females.
In public policy
Methylmercury contamination in fish, along with fish consumption advisories, have the potential to disrupt people's eating habits, fishing traditions, and livelihoods of people involved in the capture, distribution, and preparation of fish as a foodstuff for humans. Furthermore, proposed limits on mercury emissions have the potential to add costly pollution controls on coal-fired utility boilers. Therefore, the methylmercury issue has attracted the attention of many levels of government (see selected external links), environmental groups, consumer advocates, science groups, food-industry-funded groups that question the science, and significant interest from electric utilities.See also
- DimethylmercuryDimethylmercuryDimethylmercury is an organomercury compound. This colorless liquid is one of the strongest known neurotoxins. It is described as having a slightly sweet smell, although inhaling enough vapor to detect its odor would be hazardous....
(neurotoxin), mercury with a second methyl groupMethyl groupMethyl group is a functional group derived from methane, containing one carbon atom bonded to three hydrogen atoms —CH3. The group is often abbreviated Me. Such hydrocarbon groups occur in many organic compounds. The methyl group can be found in three forms: anion, cation and radical. The anion... - EthylmercuryEthylmercuryEthylmercury is a cation composed of an ethyl group bound to a mercury centre; its chemical formula is C2H5Hg+...
, a related compound - Mercury poisoningMercury poisoningMercury poisoning is a disease caused by exposure to mercury or its compounds. Mercury is a heavy metal occurring in several forms, all of which can produce toxic effects in high enough doses...
- Minamata diseaseMinamata disease', sometimes referred to as , is a neurological syndrome caused by severe mercury poisoning. Symptoms include ataxia, numbness in the hands and feet, general muscle weakness, narrowing of the field of vision and damage to hearing and speech. In extreme cases, insanity, paralysis, coma, and death...
External links
- ATSDR - ToxFAQs: Mercury
- ATSDR - Public Health Statement: Mercury
- ATSDR - ALERT! Patterns of Metallic Mercury Exposure, 6/26/97
- ATSDR - MMG: Mercury
- ATSDR - Toxicological Profile: Mercury
- National Pollutant Inventory - Mercury and compounds Fact Sheet
- Methylmercury-in-fish exposure calculator provided by GotMercury.Org, which uses FDA mercury data with the EPA's calculated safe exposure levels.
- Methylmercury Contamination in Fish and Shellfish
- nytimes.com, Tuna Fish Stories: The Candidates Spin the Sushi
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency's mercury site
- U.S. Geological Survey's mercury site
- Environment Canada's mercury site
- Health Canada's mercury site
- International Conference on Mercury as a Global Pollutant 2006-Madison, WI USA 2009-Guizhou, China 2011-Halifax, NS Canada

