
Old Frankish
Encyclopedia
- Not to be confused with Old FrenchOld FrenchOld French was the Romance dialect continuum spoken in territories that span roughly the northern half of modern France and parts of modern Belgium and Switzerland from the 9th century to the 14th century...
.
Old Frankish is an extinct West Germanic language, once spoken by the Franks
Franks
The Franks were a confederation of Germanic tribes first attested in the third century AD as living north and east of the Lower Rhine River. From the third to fifth centuries some Franks raided Roman territory while other Franks joined the Roman troops in Gaul. Only the Salian Franks formed a...
. It is the parent language of the Franconian languages, of which Dutch
Dutch language
Dutch is a West Germanic language and the native language of the majority of the population of the Netherlands, Belgium, and Suriname, the three member states of the Dutch Language Union. Most speakers live in the European Union, where it is a first language for about 23 million and a second...
and Afrikaans
Afrikaans
Afrikaans is a West Germanic language, spoken natively in South Africa and Namibia. It is a daughter language of Dutch, originating in its 17th century dialects, collectively referred to as Cape Dutch .Afrikaans is a daughter language of Dutch; see , , , , , .Afrikaans was historically called Cape...
are the most known descendants. Frankish was spoken in areas covering modern Low Countries
Low Countries
The Low Countries are the historical lands around the low-lying delta of the Rhine, Scheldt, and Meuse rivers, including the modern countries of Belgium, the Netherlands, Luxembourg and parts of northern France and western Germany....
and adjacent parts of France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
and Germany
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
between the 4th and 8th century AD.
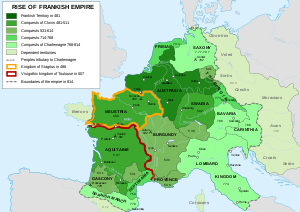
The Franks descended from Germanic tribes that settled parts of the Netherlands
Netherlands
The Netherlands is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, located mainly in North-West Europe and with several islands in the Caribbean. Mainland Netherlands borders the North Sea to the north and west, Belgium to the south, and Germany to the east, and shares maritime borders...
and western Germany during the early Iron Age
Iron Age
The Iron Age is the archaeological period generally occurring after the Bronze Age, marked by the prevalent use of iron. The early period of the age is characterized by the widespread use of iron or steel. The adoption of such material coincided with other changes in society, including differing...
. From the 4th century they are attested as moving from the Roman Empire
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of the ancient Roman civilization, characterised by an autocratic form of government and large territorial holdings in Europe and around the Mediterranean....
into what is now the southern Netherlands
Netherlands
The Netherlands is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, located mainly in North-West Europe and with several islands in the Caribbean. Mainland Netherlands borders the North Sea to the north and west, Belgium to the south, and Germany to the east, and shares maritime borders...
and northern Belgium
Belgium
Belgium , officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a federal state in Western Europe. It is a founding member of the European Union and hosts the EU's headquarters, and those of several other major international organisations such as NATO.Belgium is also a member of, or affiliated to, many...
. In the 5th and 6th century they expanded their realm
Realm
A realm is a dominion of a monarch or other sovereign ruler.The Old French word reaume, modern French royaume, was the word first adopted in English; the fixed modern spelling does not appear until the beginning of the 17th century...
and conquered Roman Gaul
Gaul
Gaul was a region of Western Europe during the Iron Age and Roman era, encompassing present day France, Luxembourg and Belgium, most of Switzerland, the western part of Northern Italy, as well as the parts of the Netherlands and Germany on the left bank of the Rhine. The Gauls were the speakers of...
completely as well as client states such as Bavaria
Bavaria
Bavaria, formally the Free State of Bavaria is a state of Germany, located in the southeast of Germany. With an area of , it is the largest state by area, forming almost 20% of the total land area of Germany...
and Thuringia
Thuringia
The Free State of Thuringia is a state of Germany, located in the central part of the country.It has an area of and 2.29 million inhabitants, making it the sixth smallest by area and the fifth smallest by population of Germany's sixteen states....
. During that period, it had a major influence on the lexicon
Lexicon
In linguistics, the lexicon of a language is its vocabulary, including its words and expressions. A lexicon is also a synonym of the word thesaurus. More formally, it is a language's inventory of lexemes. Coined in English 1603, the word "lexicon" derives from the Greek "λεξικόν" , neut...
, pronounciation and grammar
Grammar
In linguistics, grammar is the set of structural rules that govern the composition of clauses, phrases, and words in any given natural language. The term refers also to the study of such rules, and this field includes morphology, syntax, and phonology, often complemented by phonetics, semantics,...
of the Romance language spoken in former Roman Gaul.
Between the 5th and 8th century, Old Frankish evolved into Old Dutch
Old Dutch
In linguistics, Old Dutch denotes the forms of West Franconian spoken and written in the Netherlands and present-day northern Belgium during the Early Middle Ages. It is regarded as the primary stage in the development of a separate Dutch language...
(Old Low Franconian), a language that remained spoken in the area that was originally held by Franks of the 4th century (e.g., what is now the southern Netherlands and northern Belgium), while in Picardy
Picardy
This article is about the historical French province. For other uses, see Picardy .Picardy is a historical province of France, in the north of France...
and Île-de-France
Île-de-France (province)
The province of Île-de-France or Isle de France is an historical province of France, and the one at the centre of power during most of French history...
it was eclipsed by Old French
Old French
Old French was the Romance dialect continuum spoken in territories that span roughly the northern half of modern France and parts of modern Belgium and Switzerland from the 9th century to the 14th century...
as the dominant language.
Knowledge of Old Frankish is almost entirely reconstructed from Old Dutch and from etyma and loanwords from Old French. However, a notable exception is the Bergakker inscription
Bergakker inscription
The Bergakker inscription was found in 1996 near the town of Bergakker, near Tiel.It is a 5th-century Elder Futhark inscription on a metal mount for a sword scabbard....
found in 1996, which may be a direct attestation of Old Frankish.
Predecessor of Old Dutch
The language from which Old DutchOld Dutch
In linguistics, Old Dutch denotes the forms of West Franconian spoken and written in the Netherlands and present-day northern Belgium during the Early Middle Ages. It is regarded as the primary stage in the development of a separate Dutch language...
arose is not known with certainty, but it is thought to be Old Frankish, specifically Old West Low Franconian, the language spoken by the Salian Franks
Salian Franks
The Salian Franks or Salii were a subgroup of the early Franks who originally had been living north of the limes in the area above the Rhine. The Merovingian kings responsible for the conquest of Gaul were Salians. From the 3rd century on, the Salian Franks appear in the historical records as...
. Even though the Franks are traditionally categorized as Weser-Rhine Germanic, Dutch has a number of Ingvaeonic
Ingvaeonic
Ingvaeonic , also known as North Sea Germanic, is a postulated grouping of the West Germanic languages that comprises Old Frisian, Old English and Old Saxon....
characteristics and is classified by modern linguists as an Ingvaeonic
Ingvaeonic
Ingvaeonic , also known as North Sea Germanic, is a postulated grouping of the West Germanic languages that comprises Old Frisian, Old English and Old Saxon....
language. Dutch also has a number of Old Saxon
Old Saxon
Old Saxon, also known as Old Low German, is the earliest recorded form of Low German, documented from the 8th century until the 12th century, when it evolved into Middle Low German. It was spoken on the north-west coast of Germany and in the Netherlands by Saxon peoples...
characteristics. There was a close relationship between Old Frankish, Old Saxon
Old Saxon
Old Saxon, also known as Old Low German, is the earliest recorded form of Low German, documented from the 8th century until the 12th century, when it evolved into Middle Low German. It was spoken on the north-west coast of Germany and in the Netherlands by Saxon peoples...
, Old English and Old Frisian
Old Frisian
Old Frisian is a West Germanic language spoken between the 8th and 16th centuries in the area between the Rhine and Weser on the European North Sea coast. The Frisian settlers on the coast of South Jutland also spoke Old Frisian but no medieval texts of this area are known...
. Because Old Frankish texts are almost non-existent and Old Dutch
Old Dutch
In linguistics, Old Dutch denotes the forms of West Franconian spoken and written in the Netherlands and present-day northern Belgium during the Early Middle Ages. It is regarded as the primary stage in the development of a separate Dutch language...
texts scarce and fragmentary, it is difficult to determine when the transition from Old Frankish to Old Dutch
Old Dutch
In linguistics, Old Dutch denotes the forms of West Franconian spoken and written in the Netherlands and present-day northern Belgium during the Early Middle Ages. It is regarded as the primary stage in the development of a separate Dutch language...
occurred, but it is thought to have happened by the end of the ninth century A.D. and perhaps occurred before then. Old Dutch
Old Dutch
In linguistics, Old Dutch denotes the forms of West Franconian spoken and written in the Netherlands and present-day northern Belgium during the Early Middle Ages. It is regarded as the primary stage in the development of a separate Dutch language...
made the transition to Middle Dutch
Middle Dutch
Middle Dutch is a collective name for a number of closely related West Germanic dialects which were spoken and written between 1150 and 1500...
around 1150.
Influence of Old Frankish on French and other languages
Latin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
word which would have been used. It is estimated that French took between 700 and 1000 stem words from Old Frankish. Many of these words were concerned with agriculture (e.g., "garden"), war (e.g., "war") or social organization (e.g., "baron"). Old Frankish has introduced the modern French word for the nation, France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
(Francia), meaning "land of the Franks". The influence of Frankish on French is comparable but greater than the respective influence of Lombardic
Lombardic language
Lombardic or Langobardic is the extinct language of the Lombards , the Germanic speaking people who settled in Italy in the 6th century. The language declined rapidly already in the 7th century as the invaders quickly adopted the Latin vernacular spoken by the local Roman population. E.g...
and Visigothic
Gothic language
Gothic is an extinct Germanic language that was spoken by the Goths. It is known primarily from the Codex Argenteus, a 6th-century copy of a 4th-century Bible translation, and is the only East Germanic language with a sizable Text corpus...
(both Germanic languages
Germanic languages
The Germanic languages constitute a sub-branch of the Indo-European language family. The common ancestor of all of the languages in this branch is called Proto-Germanic , which was spoken in approximately the mid-1st millennium BC in Iron Age northern Europe...
) on Italian
Italian language
Italian is a Romance language spoken mainly in Europe: Italy, Switzerland, San Marino, Vatican City, by minorities in Malta, Monaco, Croatia, Slovenia, France, Libya, Eritrea, and Somalia, and by immigrant communities in the Americas and Australia...
and the Romance languages of Iberia (Spanish
Spanish language
Spanish , also known as Castilian , is a Romance language in the Ibero-Romance group that evolved from several languages and dialects in central-northern Iberia around the 9th century and gradually spread with the expansion of the Kingdom of Castile into central and southern Iberia during the...
, Portuguese
Portuguese language
Portuguese is a Romance language that arose in the medieval Kingdom of Galicia, nowadays Galicia and Northern Portugal. The southern part of the Kingdom of Galicia became independent as the County of Portugal in 1095...
and Catalan
Catalan language
Catalan is a Romance language, the national and only official language of Andorra and a co-official language in the Spanish autonomous communities of Catalonia, the Balearic Islands and Valencian Community, where it is known as Valencian , as well as in the city of Alghero, on the Italian island...
). Not all of these loanwords have been retained in modern French. French has also passed on words of Frankish origin to other Romance languages.
Frankish also had an influence on late Latin
Latin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
itself. Latin words with Frankish roots include sacire, meaning "seize" (from Frankish sekjan, related to English "seek"). Frankish speech habits are also responsible for the substitution of Latin cum ("with") with aboc (a Frankish corruption of apud hoc "near this") in Old French (Modern French avec), and for the use of Old French homme as a pronoun (Modern French on). English also has many words with Frankish roots, usually through Old French e.g. random (via Old French randon, from rant "a running"), standard (via Old French estandart, from *standhard "stand firm), scabbard (via Anglo-French *escauberc, from *skar-berg), grape, stale, march
Marches
A march or mark refers to a border region similar to a frontier, such as the Welsh Marches, the borderland between England and Wales. During the Frankish Carolingian Dynasty, the word spread throughout Europe....
(via Old French marche, from *marka) among others. It has also left many etyma in the different Northern Langues d'oïl
Langues d'oïl
The langues d'oïl or langues d'oui , in English the Oïl or Oui languages, are a dialect continuum that includes standard French and its closest autochthonous relatives spoken today in the northern half of France, southern Belgium, and the Channel Islands...
s such as Picard
Picard
Picard may refer to:* a native of, or anything originating in, Picardy* the Picard language, a Langue d'oïl and one of the languages of France* A member of the Picards, a religious sect in the fifteenth century...
, Champenois
Champenois
Champenois is a language spoken by a minority of people in Champagne in France and in Wallonia in Belgium. It is one of the langues d'oïl. It is classified as a regional language of France, and has the recognized status of a regional language of Wallonia....
, Bas Lorrain and Walloon
Walloon language
Walloon is a Romance language which was spoken as a primary language in large portions of the Walloon Region of Belgium and some villages of Northern France until the middle of the 20th century. It belongs to the langue d'oïl language family, whose most prominent member is the French language...
, more than in Common French, and not always the same ones.
See below a non-exhaustive list of French words of Frankish origin. An asterisk prefixing a term indicates a reconstructed form
Linguistic reconstruction
Linguistic reconstruction is the practice of establishing the features of the unattested ancestor of one or more given languages. There are two kinds of reconstruction. Internal reconstruction uses irregularities in a single language to make inferences about an earlier stage of that language...
of the Frankish word. Most Frankish words with the phoneme w, changed it to gu when entering Old French and other Romance languages
Romance languages
The Romance languages are a branch of the Indo-European language family, more precisely of the Italic languages subfamily, comprising all the languages that descend from Vulgar Latin, the language of ancient Rome...
; however, the northern langue d'oïl dialects such as Picard, Northern Norman, Walloon, Burgundian, Champenois and Bas-Lorrain retained the [w] or turned it into [v]. Perhaps the best known example is the Frankish *werra ("war"), which entered modern French as guerre and guerra in Italian
Italian language
Italian is a Romance language spoken mainly in Europe: Italy, Switzerland, San Marino, Vatican City, by minorities in Malta, Monaco, Croatia, Slovenia, France, Libya, Eritrea, and Somalia, and by immigrant communities in the Americas and Australia...
, Occitan, Catalan
Catalan language
Catalan is a Romance language, the national and only official language of Andorra and a co-official language in the Spanish autonomous communities of Catalonia, the Balearic Islands and Valencian Community, where it is known as Valencian , as well as in the city of Alghero, on the Italian island...
, Spanish
Spanish language
Spanish , also known as Castilian , is a Romance language in the Ibero-Romance group that evolved from several languages and dialects in central-northern Iberia around the 9th century and gradually spread with the expansion of the Kingdom of Castile into central and southern Iberia during the...
and Portuguese
Portuguese language
Portuguese is a Romance language that arose in the medieval Kingdom of Galicia, nowadays Galicia and Northern Portugal. The southern part of the Kingdom of Galicia became independent as the County of Portugal in 1095...
. Other examples include "gant" ("gauntlet", from *want) and "garder" ("to guard", from *wardōn). Frankish words starting with the phoneme s changed to es when entering Old French (e.g., Frankish skirm and Old French escrime).
| Current French word | Old Frankish | Dutch or other Germanic cognates | Latin/Romance |
|---|---|---|---|
| affranchir "to free" | *frank "freeborn; unsubjugated, answering to no one", nasalized variant of *frāki "rash, untamed, impudent" | MDu vrec "insolent", Du frank "unforced, sincere, frank", vrank "carefree, brazen", Du Frankrijk "France", Du vrek "miser", OHG franko "free man" | L līberāre |
| alène "awl" (Sp Spanish language Spanish , also known as Castilian , is a Romance language in the Ibero-Romance group that evolved from several languages and dialects in central-northern Iberia around the 9th century and gradually spread with the expansion of the Kingdom of Castile into central and southern Iberia during the... alesna, It Italian language Italian is a Romance language spoken mainly in Europe: Italy, Switzerland, San Marino, Vatican City, by minorities in Malta, Monaco, Croatia, Slovenia, France, Libya, Eritrea, and Somalia, and by immigrant communities in the Americas and Australia... lesina) |
*alisna | MDu Middle Dutch Middle Dutch is a collective name for a number of closely related West Germanic dialects which were spoken and written between 1150 and 1500... elsene, else, Du Dutch language Dutch is a West Germanic language and the native language of the majority of the population of the Netherlands, Belgium, and Suriname, the three member states of the Dutch Language Union. Most speakers live in the European Union, where it is a first language for about 23 million and a second... els |
L sūbula |
| alise "whitebeam berry" (OFr Old French Old French was the Romance dialect continuum spoken in territories that span roughly the northern half of modern France and parts of modern Belgium and Switzerland from the 9th century to the 14th century... alis, alie "whitebeam") |
*alísō "alder" | MDu elze, Du els "alder" (vs. G German language German is a West Germanic language, related to and classified alongside English and Dutch. With an estimated 90 – 98 million native speakers, German is one of the world's major languages and is the most widely-spoken first language in the European Union.... Erle "alder"); Du elsbes "whitebeam", G Else "id." |
non-native to the Mediterranean |
| baron | *baro "freeman" | MDu baren "to attribute", Du bar "gravely", OHG baro "freeman", OE beorn "noble" | Germanic cultural import |
| bâtard "bastard" (FrProv Franco-Provençal language Franco-Provençal , Arpitan, or Romand is a Romance language with several distinct dialects that form a linguistic sub-group separate from Langue d'Oïl and Langue d'Oc. The name Franco-Provençal was given to the language by G.I... bâsco) |
*bāst "marriage" | MDu bast "lust, heat, reproductive season", WFris West Frisian language West Frisian is a language spoken mostly in the province of Friesland in the north of the Netherlands. West Frisian is the name by which this language is usually known outside the Netherlands, to distinguish it from the closely related Frisian languages of Saterland Frisian and North Frisian,... boaste, boask "marriage" |
L nothus |
| bâtir "to build" (OFr bastir "to baste, tie together") bâtiment "building" bastille "fortress" bastion "fortress" |
*bastian "to bind with bast string" | MDu besten "to sow up, to connect", OHG bestan "to mend, patch"; MDu best "liaison" (Du gemenebest "commonwealth") | L construere (It costruire) |
| bière "beer" | *bera | Du bier | L cervisia |
| bleu "blue" (OFr blou, bleve) | *blao | MDu blā, blau, blaeuw, Du blauw | L caeruleus "light blue", lividus "dark blue" |
| bois "wood, forest" | *busk "bush, underbrush" | MDu bosch, busch, Du bos "bush" | L silva "forest" (OFr selve), L lignum "wood" (OFr lein) |
| broder "to embroider" (OFr brosder, broisder) | *brosdōn, blend of *borst "bristle" and *brordōn "to embroider" | G Borste "boar bristle", Du borstel "bristle"; OS brordōn "to embroider, decorate", brord "needle" | L pingere "to paint; embroider" (Fr peindre "to paint") |
| broyer "to grind, crush" (OFr brier) | *brekan "to break" | Du breken "to break" | LL Late Latin Late Latin is the scholarly name for the written Latin of Late Antiquity. The English dictionary definition of Late Latin dates this period from the 3rd to the 6th centuries AD extending in Spain to the 7th. This somewhat ambiguously defined period fits between Classical Latin and Medieval Latin... tritāre (Occ trissar "to grind", but Fr trier "to sort"), LL pistāre (It pestare "to pound, crush", OFr pester), L machīnare (Dalm Dalmatian language Dalmatian was a Romance language spoken in the Dalmatia region of Croatia, and as far south as Kotor in Montenegro. The name refers to a pre-Roman tribe of the Illyrian linguistic group, Dalmatae... maknur "to grind", Rom Romanian language Romanian Romanian Romanian (or Daco-Romanian; obsolete spellings Rumanian, Roumanian; self-designation: română, limba română ("the Romanian language") or românește (lit. "in Romanian") is a Romance language spoken by around 24 to 28 million people, primarily in Romania and Moldova... măcina, It macinare) |
| choquer "to shock" | *skukjan | Du schokken "to shock, to shake" | |
| choisir "to choose" | *kiosan | MDu kiesen, Du kiezen | L eligēre (Fr élire "to elect"), VL Vulgar Latin Vulgar Latin is any of the nonstandard forms of Latin from which the Romance languages developed. Because of its nonstandard nature, it had no official orthography. All written works used Classical Latin, with very few exceptions... exeligēre (cf. It scegliere), excolligere (Cat Catalan language Catalan is a Romance language, the national and only official language of Andorra and a co-official language in the Spanish autonomous communities of Catalonia, the Balearic Islands and Valencian Community, where it is known as Valencian , as well as in the city of Alghero, on the Italian island... escollir, Sp escoger, Pg Portuguese language Portuguese is a Romance language that arose in the medieval Kingdom of Galicia, nowadays Galicia and Northern Portugal. The southern part of the Kingdom of Galicia became independent as the County of Portugal in 1095... escolher) |
| chouette "barn owl" (OFr çuete, dim. of choë, choue "jackdaw") | *kōwa, kāwa "chough, jackdaw" | MDu couwe "rook", Du kauw, kaauw "chough" | not distinguished in Latin: L būbō "owl", ōtus "eared owl", ulula "screech owl", ulucus "id" (cf. Sp loco "crazy"), noctua "night owl" |
| cresson "watercress" | *kresso | MDu kersse, korsse, Du kers, dial. kors | L nasturtium, LL berula (but Fr berle "water parsnip") |
| danser "to dance" (OFr dancier) | *dansōn | OHG dansōn "to drag along, trail"; further to MDu densen, deinsen "to shrink back", Du deinzen "to stir; move away, back up", OHG dinsan "to pull, stretch" | LL ballare (OFr baller, It ballare, Pg bailar) |
| déchirer "to rip, tear" (OFr escirer) | *skerian "to cut, shear" | MDu scēren, Du scheren "to shave, shear" | VL extracticāre (Prov estraçar, It stracciare), VL exquartiare "to rip into fours" (It squarciare, but Fr écarter "to move apart, distance"), exquintiare "to rip into five" (Cat/Occ esquinçar) |
| dérober "to steal, reave" (OFr rober, Sp robar) | *rōbon "to steal" | MDu rōven, Du roven "to rob" | VL furicare "to steal" (It frugare) |
| écang "swingle-dag" | *swank "bat, rod" | MDu swanc "wand, rod", Du (dial. Holland) zwang "rod" | L pistillum (Fr dial. pesselle "swingle-dag") |
| écran "screen" (OFr escran) | *skrank | MDu schrank "chassis"; G Schrank "cupboard", Schranke "fence" | L obex |
| écrevisse "crayfish" (OFr crevice) | *krebit | Du kreeft "crayfish, lobster" | L cammārus "crayfish" (cf. Occ chambre, It gambero, Pg camarão) |
| éperon "spur" (OFr esporon) | *sporo | MDu spōre, Du spoor | L calcar |
| espier "to spy" espion "male spy", espionne "female spy", espionnage "espionnage" |
*spehōn "to spy" | Du spieden, bespieden "to spy" | |
| escrime "fencing" | *skirm "to protect" | Du schermen "to fence", scherm "(protective) screen" | |
| étrier "stirrup" (OFr estrieu, estrief) | *stīgarēp, from stīgan "to go up, to mount" and rēp "band" | MDu steegereep, Du stijgreep, stijgen "to rise", steigeren | LL stapia (later ML stapēs), ML saltatorium (cf. MFr saultoir) |
| flèche "arrow" | *fliukka | MDu vliecke, OS fliuca (MLG Middle Low German Middle Low German is a language that is the descendant of Old Saxon and is the ancestor of modern Low German. It served as the international lingua franca of the Hanseatic League... fliecke "long arrow") |
L sagitta (OFr saete, Pg seta) |
| frais "fresh" (OFr freis, fresche) | *friska "fresh" | Du vers "fresh", fris "cold" | |
| franc "free, exempt; straightforward, without hassle" (LL francus "freeborn, freedman") France "France" (OFr Francia) franchement "frankly" |
*frank "freeborn; unsubjugated, answering to no one", nasalized variant of *frāki "rash, untamed, impudent" | MDu vrec "insolent", Du frank "unforced, sincere, frank", vrank "carefree, brazen", Du Frankrijk "France", Du vrek "miser", OHG franko "free man" | L ingenuus "freeborn" L Gallia |
| frapper "to hit, strike" (OFr fraper) | *hrapan "to jerk, snatch" | Du rapen "gather up, collect", G raffen "to grab" | L ferire (OFr ferir) |
| frelon "hornet" (OFr furlone, ML fursleone) | *hurslo | MDu horsel, Du horzel | L crābrō (cf. It calabrone) |
| freux "rook" (OFr frox, fru) | *hrōk | MDu roec, Du roek | not distinguished in Latin |
| galloper "to gallop" | *wala hlaupan "to run well" | Du wel "good, well" + lopen "to run" | |
| garder "to guard" | *wardōn | MDu waerden "to defend", OS wardōn | L cavere, servare |
| gant "gauntlet" | *want | Du want "gauntlet" | |
| givre "frost (substance)" | *gibara "drool, slobber" | EFris gever, LG Geiber, G Geifer "drool, slobber" | L gelū (cf. Fr gel "frost (event); freezing") |
| glisser "to slip" (OFr glier) | *glīdan "to glide" | MDu glīden, Du glijden "to glide"; Du glis "skid"; G gleiten, Gleis "track" | ML planare |
| grappe "bunch (of grapes)" (OFr crape, grape "hook, grape stalk") | *krāppa "hook" | MDu crappe "hook", Du (dial. Holland) krap "krank", G Krapfe "hook", (dial. Franconian West Central German West Central German belongs to the Central, High German dialect family in the German language. Its dialects are thoroughly Franconian including the following sub-families:* Central Franconian... ) Krape "torture clamp, vice" |
L racemus (Prov rasim "bunch", Cat raïm, Sp racimo, but Fr raisin "grape") |
| gris "grey" | *grîs "grey" | Du grijs "grey" | cinereus "ash-coloured, grey" |
| guérir "to heal, cure" (OFr garir "to defend") guérison "healing" (OFr garison "healing") |
*warjan "to protect, defend" | MDu weeren, Du weren "to protect, defend", Du bewaren "to keep, preserve" | L sānāre (Sard sanare, Sp/Pg sanar, OFr saner), medicāre (Dalm medcuar "to heal") |
| guerre "war" | *werra "war" | Du war "chaos", verwarren "to confuse" | L bellum |
| guigne "heart cherry" (OFr guisne) | *wīksina | G Weichsel "sour cherry", (dial. Rhine Franconian Rhine Franconian Rhine Franconian , or Rhenish Franconian, is a dialect family of West Central German. It comprises the German dialects spoken across the western regions of the states of Saarland, Rhineland-Palatinate, and Hesse in Germany... ) Waingsl, (dial. East Franconian East Franconian German East Franconian is a dialect which is spoken in northern Bavaria and other areas in Germany around Nuremberg, Bamberg, Coburg, Würzburg, Hof, Bayreuth, Bad Mergentheim, Crailsheim and Suhl... ) Wassen, Wachsen |
non-native to the Mediterranean |
| haïr "to hate" (OFr haïr "to hate") haine "hatred" (OFr haïne "hatred") |
*hatjan | Du haten "to hate", haat "hatred" | L odium |
| hanneton "cockchafer" | *hāno "rooster" + -eto (diminutive suffix) with sense of "beetle, weevil" | Du haan "rooster", leliehaantje "lily beetle", bladhaantje "leaf beetle", G Hahn "rooster", (dial. Rhine Franconian) Hahn "sloe bug, shield bug", Lilienhähnchen "lily beetle" | LL bruchus "chafer" (cf. Fr dial. brgue, beùrgne, brégue), cossus (cf. SwRom coss, OFr cosson "weevil") |
| haubert "hauberk Hauberk A hauberk is a shirt of chainmail. The term is usually used to describe a shirt reaching at least to mid-thigh and including sleeves. Haubergeon generally refers to a shorter variant with partial sleeves, but the terms are often used interchangeably.- History :The word hauberk is derived from the... " |
*halsberg "neck-cover" | Du hals "neck" + berg "cover" (cf Du herberg "hostel") | |
| héron "heron" | *heigero, variant of *hraigro | MDu heiger "heron", Du reiger "heron" | L ardea |
| houx "holly" | *hulis | MDu huls, Du hulst | L aquifolium (Sp acebo), later VL acrifolium (Occ grefuèlh, agreu, Cat grèvol, It agrifoglio) |
| jardin "garden" (VL hortus gardinus "enclosed garden", Ofr jardin, jart) | *gardo "garden" | Du gaard "garden", boomgaard "orchard"; OS gardo "garden" | L hortus |
| lécher "to lick" (OFr lechier "to live in debauchery") | *leccōn "to lick" | MDu lecken, Du likken "to lick" | L lingere (Sard línghere), lambere (Sp lamer, Pg lamber) |
| maçon "bricklayer" (OFr masson, machun) | *mattio "mason" | Du metsen "to mason", metselaar "masoner"; OHG mezzo "stonemason", meizan "to beat, cut", G Metz, Steinmetz "mason" | VL murator (Occ murador, Sard muradore, It muratóre) |
| maint "many" (OFr maint, meint "many") | *menigþa "many" | Du menig "many", menigte "group of people" | |
| marais "marsh, swamp" | *marisk "marsh" | MDu marasch, meresch, maersc, Du meers "grassland", (dial. Holland) mars | L paludem (Occ palun, It palude) |
| maréchal "marshal" maréchausse "military police" |
*marh-skalk "horse-servant" | ODu marscalk "horse-servant" (marchi "mare" + skalk "servant"); MDu marscalc "horse-servant, royal servant" (mare "mare" + skalk "serf"); Du maarschalk "marshal" (merrie "mare" + schalk "comic", schalks "teasingly") | |
| osier "osier (basket willow); withy" (OFr osière, ML auseria) | *halster | MDu halster, LG dial. Halster, Hilster "bay willow" | L vīmen "withy" (It vimine "withy", Sp mimbre, vimbre "osier", Pg vimeiro, Cat vímet "withy"), vinculum (It vinco "osier", dial. vinchio, Friul venc) |
| patte "paw" | *pata "foot sole" | Du pets "strike"; LG Pad "sole of the foot"; further to G Patsche "instrument for striking the hand", Patschfuss "web foot", patschen "to dabble", (dial. Bavarian Austro-Bavarian Bavarian , also Austro-Bavarian, is a major group of Upper German varieties spoken in the south east of the German language area.-History and origin:... ) patzen "to blot, pat, stain" |
LL branca "paw" (Sard brànca, It brince, Rom brîncă, Prov branca, Romansh franka, but Fr branche "treelimb") |
| poche "pocket Pocket A pocket is a bag- or envelope-like receptacle either fastened to or inserted in an article of clothing to hold small items. Pockets may also be attached to luggage, backpacks, and similar items... " |
*poka "pouch Pouch Pouch may refer to:* A small bag such as a pocket, teabag, money pouch, sporran, etc* Cadaver pouch, body bag * Diplomatic pouch* Electric heating pouch, medical apparatus, electric heating device for curative treatment... " |
MDu poke, G dial. Pfoch "pouch, change purse" | L bulga "leather bag" (Fr bouge "bulge"), LL bursa "coin purse Coin purse A coin purse is a small money bag or pouch, similar to a wallet, but typically used by women and include a compartment for coins. In some countries, it is known simply as a purse... " (Fr bourse "money pouch, purse", It bórsa, Sp/Pg bolsa) |
| riche "rich Rich Rich may refer to wealth. Rich may also refer to:- Organizations :* B.C. Rich, guitar manufacturer* Rich Products, international food products corporation* Rich's, U.S. department store retail chain in the southern U.S.... " |
*riki "rich" | MDu rike, Du rijk | L ŏpĭpărus |
| sale "dirty Dirty Dirty is the seventh album by the American alternative rock group Sonic Youth, originally released on July 21, 1992 by DGC Records. It was deemed best album of 1992 by Entertainment Weekly.-Recording:... " |
*salo "pale Pale -Color:*Pale, an adjective meaning of a light shade or hue; approaching white*Paleness , a relative lightness of color*Pale, a variance of human skin color, especially:**Pallor, a symptom of low oxygen content in blood or avoidance of sunlight... , sallow" |
MDu salu, saluwe "discolored, dirty", Du zaluw | L succidus (cf. It sucido, Sp sucio, Pg sujo, Ladin Ladin Ladin is a language consisting of a group of dialects spoken in the Dolomite Mountains in Northern Italy in the border regions of the provinces Trentino, South Tyrol and Belluno... scich, Friul Friulian language Friulan , is a Romance language belonging to the Rhaeto-Romance family, spoken in the Friuli region of northeastern Italy. Friulan has around 800,000 speakers, the vast majority of whom also speak Italian... soç) |
| salle "room" | *sala "hall, room" | Du zaal | |
| saule "willow Willow Willows, sallows, and osiers form the genus Salix, around 400 species of deciduous trees and shrubs, found primarily on moist soils in cold and temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere... " |
*salha "sallow, pussy willow Pussy Willow Pussy willow is a name given to many of the smaller species of the genus Salix when their furry catkins are young in early spring... " |
OHG salaha, G Salweide "pussy willow", OE sealh | L salix "willow" (OFr sauz, sausse) |
| saisir "to seize Seize Seize may refer to:*Seisin, legal possession*Seizing, a class of knots used to semi-permanently bind together two ropes*Seize , a British electronic band*The jamming of machine parts against each other, usually due to insufficient lubrication... , snatch Snatch Snatch may refer to:* Snatch , a 2000 British gangster movie by director Guy Ritchie* Snatch theft, grab-and-run theft from a motorcycle, in Malaysia* Snatch, an album by Howie B* Snatch , or Anagrams, word game... ; bring suit, vest a court" (ML sacīre "to lay claim to, appropriate") |
*sakan "to take legal action" | Du zeiken "to nag, to quarrel", zaak "court case", OS sakan "to accuse", OHG sahhan "to strive, quarrel Quarrel A quarrel or bolt is the term for the ammunition used in a crossbow. The name "quarrel" is derived from the French carré, "square", referring to the fact that they typically have square heads. Although their length varies, they are typically shorter than traditional arrows.Bolts and arrows have... , rebuke", OE sacan "to quarrel, claim by law, accuse"; |
VL aderigere (OFr aerdre "to seize") |
| standard "standard" (OFr estandart "standard") | *standhard "stand hard, stand firm" | Du staan (to stand) + hard "hard" | |
| tamis "sieve Sieve A sieve, or sifter, separates wanted elements from unwanted material using a woven screen such as a mesh or net. However, in cooking, especially with flour, a sifter is used to aerate the substance, among other things. A strainer is a type of sieve typically used to separate a solid from a liquid... " (It tamigio) |
*tamisa | MDu temse, teemse, obs. Du teems "sifter" | L crībrum (Fr crible "riddle Riddle A riddle is a statement or question or phrase having a double or veiled meaning, put forth as a puzzle to be solved. Riddles are of two types: enigmas, which are problems generally expressed in metaphorical or allegorical language that require ingenuity and careful thinking for their solution, and... , sift") |
| tomber "to fall" (OFr tumer "to somersault Somersault A somersault is an acrobatic exercise in which a person does a full 360° flip, moving the feet over the head. A somersault can be performed either forwards, backwards, or sideways and can be executed in the air or on the ground... ") |
*tūmōn "to tumble" | Du tuimelen "to tumble", OS/OHG tūmōn "to tumble", | L cædere (obsolete Fr cheoir) |
| trêve "truce" | *treuwa "loyalty, agreement" | Du trouw "faithfulness, loyalty" | L pausa (Fr pause) |
| troène "privet" (dialectal truèle, ML Medieval Latin Medieval Latin was the form of Latin used in the Middle Ages, primarily as a medium of scholarly exchange and as the liturgical language of the medieval Roman Catholic Church, but also as a language of science, literature, law, and administration. Despite the clerical origin of many of its authors,... trūlla) |
*trugil "hard wood; small trough" | OHG trugilboum, harttrugil "dogwood Dogwood The genus Cornus is a group of about 30-60 species of woody plants in the family Cornaceae, commonly known as dogwoods. Most dogwoods are deciduous trees or shrubs, but a few species are nearly herbaceous perennial subshrubs, and a few of the woody species are evergreen... ; privet", G Hartriegel "dogwood", dialectally "privet", (dial. Eastern) Trögel, archaic (dial. Swabian) Trügel "small trough, trunk Trunk Trunk may refer to:In biology:*Trunk, an elephant's proboscis or nose*Trunk, torso*Trunk , a tree's central superstructureIn containers:*Trunk , a large storage compartment*Trunk... , basin Basin Basin may refer to:* Basin , a poem about Charlemagne's childhood* basin , the area of a drydock which can be flooded and drained* basin of attraction , an area of a nonlinear system with an attractor... " |
L ligustrum |
| tuyau "pipe Pipe Pipe may refer to:* Pipe , a hollow cylinder following certain dimension rules* Smoking pipe* Pipe or butt, a cask measurement* Pipe , a type of metal casting defect... , hose Hose A hose is a hollow tube designed to carry fluids from one location to another. Hoses are also sometimes called pipes , or more generally tubing... " (OFr tuiel, tuel) |
*þūta | MDu tūte "nipple Nipple In its most general form, a nipple is a structure from which a fluid emanates. More specifically, it is the projection on the breasts or udder of a mammal by which breast milk is delivered to a mother's young. In this sense, it is often called a teat, especially when referring to non-humans, and... ; pipe", Du tuit "spout, nozzle Nozzle A nozzle is a device designed to control the direction or characteristics of a fluid flow as it exits an enclosed chamber or pipe via an orifice.... " |
L canna "reed Reed - Musical instruments :* Single-reed instrument, a woodwind instrument that uses only one reed to produce sound* Double reed instrument, a woodwind instrument that uses two reeds to produce sound... ; pipe" (It/SwRom/FrProv cana "pipe") |
See also
- Low Franconian languagesLow Franconian languagesLow Franconian, Low Frankish, or Istvaeonic, is a group of several West Germanic languages spoken in the Netherlands, northern Belgium , in the northern department of France, in western Germany , as well as in Suriname, South Africa and Namibia that originally descended from Old Frankish.- The...
- Franconian languagesFranconian languagesFranconian refers to a West Germanic dialect continuum spoken in the Rhineland, including Dutch at one end and all the transitional dialects between Dutch and standard German which do not fully participate in the High German consonant shift or German diphthongization of long vowels...
- List of French words of Germanic origin
- List of Portuguese words of Frankish origin
- List of Spanish words of Frankish origin
- Old High GermanOld High GermanThe term Old High German refers to the earliest stage of the German language and it conventionally covers the period from around 500 to 1050. Coherent written texts do not appear until the second half of the 8th century, and some treat the period before 750 as 'prehistoric' and date the start of...
- History of FrenchHistory of FrenchFrench is a Romance language that evolved out of the Gallo-Romance dialects spoken in northern France....
External links
- Gotische Runeninschriften (photo of Bergakker scabbard)

