
Sex differences in humans
Encyclopedia
A sex difference is a distinction of biological and/or physiological characteristics associated with either males or females of a species. These can be of several types, including direct and indirect. Direct being the direct result of differences prescribed by the Y-chromosome, and indirect being a characteristic influenced indirectly (e.g. hormonally) by the Y-chromosome. Sexual dimorphism
is a term for the phenotypic
difference between males and females of the same species.
Direct sex differences follow a binary distribution
. Through the process of meiosis
and fertilization (with rare exceptions), each individual is created with zero or one Y-chromosome. The complimentary result for the X-chromosome follows, either a double or a single X. Therefore, direct sex differences are usually binary in expression (although the deviations in complex biological processes produce a menagerie of exceptions). These include, most conspicuously, male (vs female) gonads.
Indirect sex differences are general differences in class, as quantified by empirical data and statistical
analysis. Most differing characteristics will conform to a bell-curve (i.e. normal) distribution which can be broadly described by the mean (peak distribution) and standard deviation (indicator of size of range). Often only the mean or mean difference between sexes is given. This may or may not preclude overlap in distributions. For example, males are taller than females on average, but an individual female may be taller than an individual male.
The most obvious differences between males and females include all the features related to reproductive role, notably the endocrine (hormonal) systems and their physiological and behavioural effects, including gonadal differentiation, internal and external genital and breast differentiation, and differentiation of muscle mass, height, and hair distribution.

The human genome
consists of two copies of each of 23 chromosomes (a total of 46). One set of 23 comes from the mother and one set comes from the father. Of these 23 pairs of chromosomes, 22 are autosomes, and one is a sex chromosome. There are two kinds of sex chromosomes–"X"
and "Y"
. In humans and in almost all other mammals, females carry two X chromosomes, designated XX, and males carry one X and one Y, designated XY.
A human egg contains only one set of chromosomes (23) and is said to be haploid. Sperm also have only one set of 23 chromosomes and are therefore haploid. When an egg and sperm fuse at fertilization, the two sets of chromosomes come together to form a unique "diploid" individual with 46 chromosomes.
The sex chromosome in a human egg is always an X chromosome, since a female only has X sex chromosomes. In sperm, about half the sperm have an X chromosome and half have a Y chromosome. If an egg fuses with a sperm with a Y chromosome, the resulting individual is usually male. If an egg fuses with a sperm with an X chromosome, the resulting individual is usually female. An egg's sex chromosome is always an X, so it is the sperm's sex chromosome that determines an individual's sex. There are rare exceptions to this rule in which, for example, XX individuals develop as males or XY individuals develop as females.
Sexual dimorphism (two forms) refers to the general phenomenon in which male and female forms of an organism display distinct morphological characteristics or features.
Sexual dimorphism in humans is the subject of much controversy, especially relating to mental ability and psychological gender. (For a discussion, see biology of gender
, sex and intelligence
, gender
, and transgender
.) Obvious differences between men and women include all the features related to reproductive role, notably the endocrine (hormonal) systems and their physical, psychological and behavioral effects. Although sex is a binary dichotomy, with "male" and "female" representing opposite and complementary sex categories for the purpose of reproduction, a small number of individuals have an anatomy that does not conform to either male or female standards, or contains features closely associated with both. Such individuals, described as intersexuals, are sometimes infertile but are often capable of reproducing.
Some biologists theorise that a species' degree of sexual dimorphism is inversely related to the degree of paternal investment in parenting
. Species with the highest sexual dimorphism, such as the pheasant, tend to be those species in which the care and raising of offspring is done only by the mother, with no involvement of the father (low degree of paternal investment). This would also explain the moderate degree of sexual dimorphism in humans, who have a moderate degree of paternal investment compared to most other mammals.
As a result, gross measures of body strength
suggest an average 40-50% difference in upper body strength between the sexes as a result of this difference, and a 20-30% difference in lower body strength. This is supported by another study that found females are about 52-66 percent as strong as males in the upper body (34-48% difference), and about 70-80 percent as strong in the lower body (20-30% difference). One study of muscle strength in the elbows and knees—in 45 and older males and females—found the strength of females to range from 42 to 63% of male strength.
and branching bronchi
, with about 56 percent greater lung volume
per body mass. They also have larger heart
s, 10 percent higher red blood cell
count, higher haemoglobin, hence greater oxygen-carrying capacity. They also have higher circulating clotting factors
(vitamin K
, prothrombin
and platelet
s). These differences lead to faster healing of wound
s and higher peripheral pain tolerance.
[]
) and oilier (more sebum) than female skin.
The skin of females is warmer on average than that of males.
than females. Males have relatively more of the type of hair called terminal hair
, especially on the face
, chest
, abdomen
and back. In contrast, females have more vellus hair. Vellus hairs are smaller and therefore less visible.
Baldness
is much more common in males than in females. The main cause for this is male pattern baldness or androgenic alopecia. Male pattern baldness is a condition where hair starts to get lost in a typical pattern of receding hairline and hair thinning on the crown, and is caused by hormones and genetic predisposition.
, males have darker hair than females and according to most studies they also have darker skin (male skin is also redder, but this is due to greater blood volume rather than melanin). Male eyes are also more likely to be one of the darker eye colors. Conversely, women are lighter-skinned than men in all human populations. The differences in color are mainly caused by higher levels of melanin
in the skin, hair and eyes in males. In one study, almost twice as many females as males had red or auburn hair. A higher proportion of females were also found to have blond
hair, whereas males were more likely to have black or dark brown hair. Another study found green eyes, which are a result of lower melanin levels, to be much more common in women than in men, at least by a factor of two. However, a more recent study found that while women indeed tend to have a lower frequency of black hair, men on the other hand had a higher frequency of red-blond hair, blue eyes and lighter skin. According to one theory the cause for this is a higher frequency of genetic recombination in women than in men, possibly due to sex-linked genes, and as a result women tend to show less phenotypical variation in any given population. Also, women tend to bleach or color their hair while men tend not to, which would make the proportion of blond or red-haired women seem higher than what it is naturally.
The human sexual dimorphism in color seems to be greater in populations that are medium in skin color than in very light or very dark colored populations.
s. Women have two ovaries that stores the eggs
, and uterus
which is connected to a vagina
. Men have testicles that produce sperm
. The testicles are placed in the scrotum
behind the penis
. The male penis and scrotum are external extremities, whereas the female sex organs are placed "inside" the body.
 Men's orgasm
Men's orgasm
is nearly essential ("nearly" as small groups of sperm can escape the penis before orgasm is reached) for reproduction, whereas female orgasm is not. The female orgasm was believed to have no obvious function other than to be pleasurable although some evidence suggests that it may have evolved as a discriminatory advantage in regards to mate selection.
(1646–1727) who reportedly fathered more than 800 children from a harem
of 500 women.
declines after age 30 and ends with the menopause
. Pregnancy in the 40s or later has been correlated with increased chance of Down's Syndrome in the children. Men are capable of fathering children into old age. Paternal age effects in the children include multiple sclerosis, autism, breast cancer and schizophrenia, as well as reduced intelligence. Adriana Iliescu
was reported as the world's oldest woman to give birth
, at age 66. Her record stood until Maria del Carmen Bousada de Lara gave birth to twin sons at Sant Pau Hospital in Barcelona, Spain on December 29, 2006, at the age of 67. In both cases IVF was used. The oldest known father was former Australian miner Les Colley, who fathered a child at age 93.
 The brains of many animals, including humans, are significantly
The brains of many animals, including humans, are significantly
different for male
s and female
s of the species
.
than females.
In 1861, Paul Broca
examined 432 human brains and found that the brains of males had an average weight of 1325 grams, while the brains of females had an average weight of 1144 grams. More recently, a 1992 study of 6,325 Army personnel found that men's brains had an average volume of 1442 cm³, while the women averaged 1332 cm³. These differences were shown to be smaller but to persist even when adjusted for body size measured as body height or body surface, such that women averaged 100 g less brain mass than men of equal size.
According to another estimate, on average, male brains have approximately 4 % more cells and weigh 100 grams more than female brains do. However, both sexes have a similar brain weight to body weight ratio. Female brains are more compact than male brain
s in that, though smaller, they are more densely packed with neuron
s, particularly in the region responsible for language. Men only think with one side of the brain while women use both sides for thinking this explains why encoding failure is worse among men.
In studies concerning intelligence
, it has been suggested that the ratio of brain weight to body weight (rather than actual brain weight) is more predictive of IQ levels. While men's brains are an average of 10-15% larger and heavier than women's brains, some researchers propose that the ratio of brain to body size does not differ between the sexes.
However, some argue that since brain-to-body-size ratios tend to decrease as body size increases, a sex difference in brain-weight ratios still exists between men and women of the same size.
s, though another study failed to find any statistically significant difference. At the same time, females have larger Wernicke's
and Broca's area
s, areas responsible for language processing. Studies using MRI scanning have shown that the auditory and language-related regions in the left hemisphere are proportionally expanded in females versus in males. Conversely, the primary visual, and visuo-spatial association areas of the parietal lobes are proportionally larger in males. Evidence of a sex difference in the relative size of the corpus callosum
was discussed during the 1980s and 90s. However, a 1997 meta-study concluded that there is no relative size difference, and that the larger corpus callosum in males is due to generally larger brains in males on average.
In total and on average, females have a higher percentage of grey matter
in comparison to males, and males a higher percentage of white matter
. However, some researchers maintain that as males have larger brains on average than females, when adjusted for total brain volume, the grey matter differences between sexes is small or nonexistent. Thus, the percentage of grey matter appears to be more related to brain size than it is to gender.
A proposed alternative way of measuring intelligence is by using grey matter or white matter
volume in the brain as an indicator. The former is used for information processing, whereas the latter makes up the connections between processing centers. In 2005, Haier et al. reported that, compared with men, women show more white matter and fewer grey matter areas as related to intelligence. However, he concluded that "men and women apparently achieve similar IQ results with different brain regions, suggesting that there is no singular underlying neuroanatomical structure to general intelligence and that different types of brain designs may manifest equivalent intellectual performance." Using brain mapping
, it was shown that men have more than six times the amount of gray matter related to general intelligence than women, and women have nearly ten times the amount of white matter related to intelligence than men. They also report that the brain areas correlated with IQ differ between the sexes. In short, men and women apparently achieve similar IQ results with different brain regions.
Other differences that have been established include greater length in males of myelinated axons in their white matter (176,000 km compared to 146,000 km); and 33% more synapses per mm3 of cerebral cortex. Another difference is that females generally have faster blood flow to their brains and lose less brain tissue as they age than males do. Additionally, depression and chronic anxiety are much more common in women than in men, and it has been speculated, by some, that this is due to differences in the brain's serotonin
system).
and hormone
s affect the formation of human brains before birth
, as well as the behavior of adult individuals. Several genes that code for differences between male and female brains have been identified. In the human brain
, a difference between sexes was observed in the transcription of the PCDH11X
/Y gene pair, a pair unique to Homo sapiens. It has been argued that the Y chromosome is primarily responsible for males being more susceptible to mental illnesses.
Hormones significantly affect human brain formation, as well as brain development at puberty. A 2004 review in Nature Reviews Neuroscience
observed that "because it is easier to manipulate hormone levels than the expression of sex chromosome genes, the effects of hormones have been studied much more extensively, and are much better understood, than the direct actions in the brain of sex chromosome genes." It concluded that while "the differentiating effects of gonadal secretions seem to be
dominant," the existing body of research "support the idea that sex differences in neural expression
of X and Y genes significantly contribute to sex differences in brain functions and disease."
s that regulate sex differentiation. Some conditions are X-linked recessive
, in that the gene is carried on the X chromosome. Genetic females (XX) will show symptoms of the disease only if both their X chromosomes are defective with a similar deficiency, whereas genetic males (XY) will show symptoms of the disease if their only X chromosome is defective. (A woman may carry such a disease on one X chromosome but not show symptoms if the other X chromosome works sufficiently.) For this reason, such conditions are far more common in males than in females. Examples of X-linked recessive conditions are color blindness
, hemophilia, and Duchenne muscular dystrophy
.
No vital genes reside only on the Y chromosome
, since roughly half of humans (females) do not have Y chromosomes. Still, there are diseases that are caused by a defective Y chromosome or of a defective number of them. One human disease linked to a defect on the Y chromosome is defective testicular development. Other conditions include Klinefelter's syndrome
and XX male syndrome
.
(WHO) has produced a number of reports on gender and health. The following trends are shown:
Infectious disease prevalence varies - this is largely due to cultural and exposure factors. In particular the WHO notes that:
Some other sex-related health differences include:
for the entire world population
is 101 males to 100 females. However, in developed countries, there are more females than males.
Sexual dimorphism
Sexual dimorphism is a phenotypic difference between males and females of the same species. Examples of such differences include differences in morphology, ornamentation, and behavior.-Examples:-Ornamentation / coloration:...
is a term for the phenotypic
Phenotype
A phenotype is an organism's observable characteristics or traits: such as its morphology, development, biochemical or physiological properties, behavior, and products of behavior...
difference between males and females of the same species.
Direct sex differences follow a binary distribution
Binary distribution
Binary distribution is when a country has 2 or more dominant cities .-Countries with binary distribution:*Brazil *China *India *Japan...
. Through the process of meiosis
Meiosis
Meiosis is a special type of cell division necessary for sexual reproduction. The cells produced by meiosis are gametes or spores. The animals' gametes are called sperm and egg cells....
and fertilization (with rare exceptions), each individual is created with zero or one Y-chromosome. The complimentary result for the X-chromosome follows, either a double or a single X. Therefore, direct sex differences are usually binary in expression (although the deviations in complex biological processes produce a menagerie of exceptions). These include, most conspicuously, male (vs female) gonads.
Indirect sex differences are general differences in class, as quantified by empirical data and statistical
Statistics
Statistics is the study of the collection, organization, analysis, and interpretation of data. It deals with all aspects of this, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments....
analysis. Most differing characteristics will conform to a bell-curve (i.e. normal) distribution which can be broadly described by the mean (peak distribution) and standard deviation (indicator of size of range). Often only the mean or mean difference between sexes is given. This may or may not preclude overlap in distributions. For example, males are taller than females on average, but an individual female may be taller than an individual male.
The most obvious differences between males and females include all the features related to reproductive role, notably the endocrine (hormonal) systems and their physiological and behavioural effects, including gonadal differentiation, internal and external genital and breast differentiation, and differentiation of muscle mass, height, and hair distribution.
Sex determination and differentiation

The human genome
Human genome
The human genome is the genome of Homo sapiens, which is stored on 23 chromosome pairs plus the small mitochondrial DNA. 22 of the 23 chromosomes are autosomal chromosome pairs, while the remaining pair is sex-determining...
consists of two copies of each of 23 chromosomes (a total of 46). One set of 23 comes from the mother and one set comes from the father. Of these 23 pairs of chromosomes, 22 are autosomes, and one is a sex chromosome. There are two kinds of sex chromosomes–"X"
X chromosome
The X chromosome is one of the two sex-determining chromosomes in many animal species, including mammals and is common in both males and females. It is a part of the XY sex-determination system and X0 sex-determination system...
and "Y"
Y chromosome
The Y chromosome is one of the two sex-determining chromosomes in most mammals, including humans. In mammals, it contains the gene SRY, which triggers testis development if present. The human Y chromosome is composed of about 60 million base pairs...
. In humans and in almost all other mammals, females carry two X chromosomes, designated XX, and males carry one X and one Y, designated XY.
A human egg contains only one set of chromosomes (23) and is said to be haploid. Sperm also have only one set of 23 chromosomes and are therefore haploid. When an egg and sperm fuse at fertilization, the two sets of chromosomes come together to form a unique "diploid" individual with 46 chromosomes.
The sex chromosome in a human egg is always an X chromosome, since a female only has X sex chromosomes. In sperm, about half the sperm have an X chromosome and half have a Y chromosome. If an egg fuses with a sperm with a Y chromosome, the resulting individual is usually male. If an egg fuses with a sperm with an X chromosome, the resulting individual is usually female. An egg's sex chromosome is always an X, so it is the sperm's sex chromosome that determines an individual's sex. There are rare exceptions to this rule in which, for example, XX individuals develop as males or XY individuals develop as females.
Sexual dimorphism
- For information about how males and females develop differences throughout the lifespan, see sexual differentiationSexual differentiationSexual differentiation is the process of development of the differences between males and females from an undifferentiated zygote...
.
Sexual dimorphism (two forms) refers to the general phenomenon in which male and female forms of an organism display distinct morphological characteristics or features.
Sexual dimorphism in humans is the subject of much controversy, especially relating to mental ability and psychological gender. (For a discussion, see biology of gender
Sexual dimorphism
Sexual dimorphism is a phenotypic difference between males and females of the same species. Examples of such differences include differences in morphology, ornamentation, and behavior.-Examples:-Ornamentation / coloration:...
, sex and intelligence
Sex and intelligence
Research on sex and psychology investigates cognitive and behavioral differences between men and women. This research employs experimental tests of cognition, which take a variety of forms. Tests focus on possible differences in areas such as IQ, spatial reasoning, and emotion.Most IQ tests are...
, gender
Gender
Gender is a range of characteristics used to distinguish between males and females, particularly in the cases of men and women and the masculine and feminine attributes assigned to them. Depending on the context, the discriminating characteristics vary from sex to social role to gender identity...
, and transgender
Transgender
Transgender is a general term applied to a variety of individuals, behaviors, and groups involving tendencies to vary from culturally conventional gender roles....
.) Obvious differences between men and women include all the features related to reproductive role, notably the endocrine (hormonal) systems and their physical, psychological and behavioral effects. Although sex is a binary dichotomy, with "male" and "female" representing opposite and complementary sex categories for the purpose of reproduction, a small number of individuals have an anatomy that does not conform to either male or female standards, or contains features closely associated with both. Such individuals, described as intersexuals, are sometimes infertile but are often capable of reproducing.
Some biologists theorise that a species' degree of sexual dimorphism is inversely related to the degree of paternal investment in parenting
Parenting
Parenting is the process of promoting and supporting the physical, emotional, social, and intellectual development of a child from infancy to adulthood...
. Species with the highest sexual dimorphism, such as the pheasant, tend to be those species in which the care and raising of offspring is done only by the mother, with no involvement of the father (low degree of paternal investment). This would also explain the moderate degree of sexual dimorphism in humans, who have a moderate degree of paternal investment compared to most other mammals.
Size, weight and body shape
- Externally, the most sexually dimorphic portions of the human body are the chest, the lower half of the face, and the area between the waist and the knees.
- Males weigh about 15 % more than females, on average. For those older than 20 years of age, males in the US have an average weight of 86.1 kg (190 lbs), whereas females have an average weight of 74 kg (163 lbs).
- On average, men are taller than women, by about 15 cm (6 inches). American males who are 20 years old or older have an average height of 175.8 cm (5 ft 9 in). The average height of corresponding females is 162 cm (5 ft 4in).
- On average, men have a larger waist in comparison to their hips (see waist-hip ratio) than women.
- Women have a larger hip section than men, an adaptation for giving birth to infants with large skulls.
Strength, power and muscle mass
On average, males are physically stronger than females. The difference is due to females, on average, having less total muscle mass than males, and also having lower muscle mass in comparison to total body mass. While individual muscle fibers have similar strength, males have more fibers due to their greater total muscle mass. The greater muscle mass of males is in turn due to a greater capacity for muscular hypertrophy as a result of men's higher levels of testosterone. Males remain stronger than females, when adjusting for differences in total body mass. This is due to the higher male muscle-mass to body-mass ratio.As a result, gross measures of body strength
Strength
- Physical ability :*Physical strength, as in people or animals*Superhuman strength, as in fictional characters*A common character attribute in role-playing gamesConflict between persons or groups:*Virtue and moral uprightness...
suggest an average 40-50% difference in upper body strength between the sexes as a result of this difference, and a 20-30% difference in lower body strength. This is supported by another study that found females are about 52-66 percent as strong as males in the upper body (34-48% difference), and about 70-80 percent as strong in the lower body (20-30% difference). One study of muscle strength in the elbows and knees—in 45 and older males and females—found the strength of females to range from 42 to 63% of male strength.
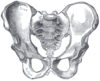 |
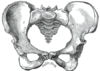 |
Comparison between a male (left) and a female pelvis (right). |
Skeleton
- Males, on average, have denser, stronger boneBoneBones are rigid organs that constitute part of the endoskeleton of vertebrates. They support, and protect the various organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells and store minerals. Bone tissue is a type of dense connective tissue...
s, tendonTendonA tendon is a tough band of fibrous connective tissue that usually connects muscle to bone and is capable of withstanding tension. Tendons are similar to ligaments and fasciae as they are all made of collagen except that ligaments join one bone to another bone, and fasciae connect muscles to other...
s, and ligamentLigamentIn anatomy, the term ligament is used to denote any of three types of structures. Most commonly, it refers to fibrous tissue that connects bones to other bones and is also known as articular ligament, articular larua, fibrous ligament, or true ligament.Ligament can also refer to:* Peritoneal...
s. - In men, the second digit (index finger) tends to be shorter than the fourth digit (ring finger), while in women the second digit tends to be longer than the fourth (see digit ratioDigit ratioThe digit ratio is the ratio of the lengths of different digits or fingers typically measured from the bottom crease where the finger joins the hand to the tip of the finger. It has been suggested by some scientists that the ratio of two digits in particular, the 2nd and 4th , is affected by...
). - Men have a more pronounced 'Adam's Apple' or thyroid cartilage (and deeper voices) due to larger vocal cords.
- On average, men have longer canine teeth than women.
- Male skullHuman skullThe human skull is a bony structure, skeleton, that is in the human head and which supports the structures of the face and forms a cavity for the brain.In humans, the adult skull is normally made up of 22 bones...
s and head bones have a different shape than female skulls. One difference is in the roundness of the eye cavities, another is the male's bony brow, and a third difference is the shape of the jawJawThe jaw is any opposable articulated structure at the entrance of the mouth, typically used for grasping and manipulating food. The term jaws is also broadly applied to the whole of the structures constituting the vault of the mouth and serving to open and close it and is part of the body plan of...
. - Male and female pelvises are shaped differently. The female pelvis features a wider pelvic cavityPelvic cavity-External links:* * *...
, which is necessary when giving birthChildbirthChildbirth is the culmination of a human pregnancy or gestation period with the birth of one or more newborn infants from a woman's uterus...
. The female pelvis has evolved to its maximum width for childbirth — an even wider pelvis would make women unable to walk. In contrast, human male pelves did not evolve to give birth and are therefore slightly more optimized for walking. The female pelvis is larger and broader than the male pelvis which is taller, narrower, and more compact. The female inlet is larger and oval in shape, while the male inlet is more heart-shaped.
- Contrary to popular belief, however, males and females do not differ in the number of ribs; both have twelve pairs.
Respiratory system
Males typically have larger tracheaeVertebrate trachea
In tetrapod anatomy the trachea, or windpipe, is a tube that connects the pharynx or larynx to the lungs, allowing the passage of air. It is lined with pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium cells with goblet cells that produce mucus...
and branching bronchi
Bronchus
A bronchus is a passage of airway in the respiratory tract that conducts air into the lungs. The bronchus branches into smaller tubes, which in turn become bronchioles....
, with about 56 percent greater lung volume
Lung volumes
Lung volumes and lung capacities refer to the volume of air associated with different phases of the respiratory cycle. Lung volumes are directly measured...
per body mass. They also have larger heart
Heart
The heart is a myogenic muscular organ found in all animals with a circulatory system , that is responsible for pumping blood throughout the blood vessels by repeated, rhythmic contractions...
s, 10 percent higher red blood cell
Red blood cell
Red blood cells are the most common type of blood cell and the vertebrate organism's principal means of delivering oxygen to the body tissues via the blood flow through the circulatory system...
count, higher haemoglobin, hence greater oxygen-carrying capacity. They also have higher circulating clotting factors
Coagulation
Coagulation is a complex process by which blood forms clots. It is an important part of hemostasis, the cessation of blood loss from a damaged vessel, wherein a damaged blood vessel wall is covered by a platelet and fibrin-containing clot to stop bleeding and begin repair of the damaged vessel...
(vitamin K
Vitamin K
Vitamin K is a group of structurally similar, fat soluble vitamins that are needed for the posttranslational modification of certain proteins required for blood coagulation and in metabolic pathways in bone and other tissue. They are 2-methyl-1,4-naphthoquinone derivatives...
, prothrombin
Thrombin
Thrombin is a "trypsin-like" serine protease protein that in humans is encoded by the F2 gene. Prothrombin is proteolytically cleaved to form thrombin in the first step of the coagulation cascade, which ultimately results in the stemming of blood loss...
and platelet
Platelet
Platelets, or thrombocytes , are small,irregularly shaped clear cell fragments , 2–3 µm in diameter, which are derived from fragmentation of precursor megakaryocytes. The average lifespan of a platelet is normally just 5 to 9 days...
s). These differences lead to faster healing of wound
Wound
A wound is a type of injury in which skin is torn, cut or punctured , or where blunt force trauma causes a contusion . In pathology, it specifically refers to a sharp injury which damages the dermis of the skin.-Open:...
s and higher peripheral pain tolerance.
[]
Skin and hair
Skin
Male skin is thicker (more collagenCollagen
Collagen is a group of naturally occurring proteins found in animals, especially in the flesh and connective tissues of mammals. It is the main component of connective tissue, and is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up about 25% to 35% of the whole-body protein content...
) and oilier (more sebum) than female skin.
The skin of females is warmer on average than that of males.
Hair
On average, males have more body hairAndrogenic hair
Androgenic hair, colloquially body hair, is the terminal hair that develops on the body during and after puberty. It is differentiated from the head hair and less visible vellus hair, which are much finer and lighter in color. The growth of androgenic hair is related to the level of androgens in...
than females. Males have relatively more of the type of hair called terminal hair
Terminal hair
Terminal hairs are thick, long, and dark, as compared with vellus hair. During puberty, the increase in androgenic hormone levels causes vellus hair to be replaced with terminal hair in certain parts of the human body...
, especially on the face
Facial hair
Facial hair is a secondary sex characteristic of human males. Men often start developing facial hair in the later years of puberty or adolescence, approximately between 17–20 years of age, and most do not finish developing a fully adult beard until their early 20s or even later...
, chest
Chest hair
The term chest hair is generally used to describe hair that grows on the chest of human males, in the region between the neck and the abdomen. Chest hair, which is a secondary sex characteristic, develops during and after puberty...
, abdomen
Abdominal hair
The term abdominal hair refers to the hair that grows on the abdomen of humans and non-human mammals, in the region between the pubic area and the thorax . The growth of abdominal hair follows the same pattern on nearly all mammals, vertically from the pubic area upwards and from the thorax...
and back. In contrast, females have more vellus hair. Vellus hairs are smaller and therefore less visible.
Baldness
Baldness
Baldness implies partial or complete lack of hair and can be understood as part of the wider topic of "hair thinning". The degree and pattern of baldness can vary greatly, but its most common cause is male and female pattern baldness, also known as androgenic alopecia, alopecia androgenetica or...
is much more common in males than in females. The main cause for this is male pattern baldness or androgenic alopecia. Male pattern baldness is a condition where hair starts to get lost in a typical pattern of receding hairline and hair thinning on the crown, and is caused by hormones and genetic predisposition.
Color
On average and after the end of pubertyPuberty
Puberty is the process of physical changes by which a child's body matures into an adult body capable of reproduction, as initiated by hormonal signals from the brain to the gonads; the ovaries in a girl, the testes in a boy...
, males have darker hair than females and according to most studies they also have darker skin (male skin is also redder, but this is due to greater blood volume rather than melanin). Male eyes are also more likely to be one of the darker eye colors. Conversely, women are lighter-skinned than men in all human populations. The differences in color are mainly caused by higher levels of melanin
Melanin
Melanin is a pigment that is ubiquitous in nature, being found in most organisms . In animals melanin pigments are derivatives of the amino acid tyrosine. The most common form of biological melanin is eumelanin, a brown-black polymer of dihydroxyindole carboxylic acids, and their reduced forms...
in the skin, hair and eyes in males. In one study, almost twice as many females as males had red or auburn hair. A higher proportion of females were also found to have blond
Blond
Blond or blonde or fair-hair is a hair color characterized by low levels of the dark pigment eumelanin. The resultant visible hue depends on various factors, but always has some sort of yellowish color...
hair, whereas males were more likely to have black or dark brown hair. Another study found green eyes, which are a result of lower melanin levels, to be much more common in women than in men, at least by a factor of two. However, a more recent study found that while women indeed tend to have a lower frequency of black hair, men on the other hand had a higher frequency of red-blond hair, blue eyes and lighter skin. According to one theory the cause for this is a higher frequency of genetic recombination in women than in men, possibly due to sex-linked genes, and as a result women tend to show less phenotypical variation in any given population. Also, women tend to bleach or color their hair while men tend not to, which would make the proportion of blond or red-haired women seem higher than what it is naturally.
The human sexual dimorphism in color seems to be greater in populations that are medium in skin color than in very light or very dark colored populations.
Sexual organs and reproductive systems
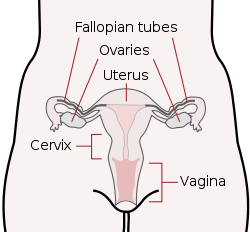
Men and women have different sex organSex organ
A sex organ, or primary sexual characteristic, as narrowly defined, is any of the anatomical parts of the body which are involved in sexual reproduction and constitute the reproductive system in a complex organism; flowers are the reproductive organs of flowering plants, cones are the reproductive...
s. Women have two ovaries that stores the eggs
Egg (biology)
An egg is an organic vessel in which an embryo first begins to develop. In most birds, reptiles, insects, molluscs, fish, and monotremes, an egg is the zygote, resulting from fertilization of the ovum, which is expelled from the body and permitted to develop outside the body until the developing...
, and uterus
Uterus
The uterus or womb is a major female hormone-responsive reproductive sex organ of most mammals including humans. One end, the cervix, opens into the vagina, while the other is connected to one or both fallopian tubes, depending on the species...
which is connected to a vagina
Vagina
The vagina is a fibromuscular tubular tract leading from the uterus to the exterior of the body in female placental mammals and marsupials, or to the cloaca in female birds, monotremes, and some reptiles. Female insects and other invertebrates also have a vagina, which is the terminal part of the...
. Men have testicles that produce sperm
Sperm
The term sperm is derived from the Greek word sperma and refers to the male reproductive cells. In the types of sexual reproduction known as anisogamy and oogamy, there is a marked difference in the size of the gametes with the smaller one being termed the "male" or sperm cell...
. The testicles are placed in the scrotum
Scrotum
In some male mammals the scrotum is a dual-chambered protuberance of skin and muscle containing the testicles and divided by a septum. It is an extension of the perineum, and is located between the penis and anus. In humans and some other mammals, the base of the scrotum becomes covered with curly...
behind the penis
Penis
The penis is a biological feature of male animals including both vertebrates and invertebrates...
. The male penis and scrotum are external extremities, whereas the female sex organs are placed "inside" the body.

Orgasm
Orgasm is the peak of the plateau phase of the sexual response cycle, characterized by an intense sensation of pleasure...
is nearly essential ("nearly" as small groups of sperm can escape the penis before orgasm is reached) for reproduction, whereas female orgasm is not. The female orgasm was believed to have no obvious function other than to be pleasurable although some evidence suggests that it may have evolved as a discriminatory advantage in regards to mate selection.
Reproductive capacity and cost
Men typically produce billions of sperm each month, many of which are capable of fertilization. Women typically produce one egg a month that can be fertilized into an embryo. Thus during a lifetime men are able to father a significantly greater number of children than women can give birth to. The most fertile woman, according to the Guinness Book of World Records, was the wife of Feodor Vassilyev of Russia (1707–1782) who had 67 surviving children. The most prolific father of all time is believed to be the last Sharifian Emperor of Morocco, Mulai IsmailIsmail Ibn Sharif
Moulay Ismaïl Ibn Sharif was the second ruler of the Moroccan Alaouite dynasty. Like others of the dynasty, Ismaïl claimed to be a descendant of Muhammad through his roots to Hassan ibn Ali...
(1646–1727) who reportedly fathered more than 800 children from a harem
Harem
Harem refers to the sphere of women in what is usually a polygynous household and their enclosed quarters which are forbidden to men...
of 500 women.
Fertility
Female fertilityFertility
Fertility is the natural capability of producing offsprings. As a measure, "fertility rate" is the number of children born per couple, person or population. Fertility differs from fecundity, which is defined as the potential for reproduction...
declines after age 30 and ends with the menopause
Menopause
Menopause is a term used to describe the permanent cessation of the primary functions of the human ovaries: the ripening and release of ova and the release of hormones that cause both the creation of the uterine lining and the subsequent shedding of the uterine lining...
. Pregnancy in the 40s or later has been correlated with increased chance of Down's Syndrome in the children. Men are capable of fathering children into old age. Paternal age effects in the children include multiple sclerosis, autism, breast cancer and schizophrenia, as well as reduced intelligence. Adriana Iliescu
Adriana Iliescu
Adriana Iliescu is a retired Romanian university lecturer and author of children's novels. She received international media attention in 2005, when she gave birth to daughter Eliza at age 66, making her the oldest birth mother in the world until this record was broken in 2006...
was reported as the world's oldest woman to give birth
Childbirth
Childbirth is the culmination of a human pregnancy or gestation period with the birth of one or more newborn infants from a woman's uterus...
, at age 66. Her record stood until Maria del Carmen Bousada de Lara gave birth to twin sons at Sant Pau Hospital in Barcelona, Spain on December 29, 2006, at the age of 67. In both cases IVF was used. The oldest known father was former Australian miner Les Colley, who fathered a child at age 93.
Brain

Statistical significance
In statistics, a result is called statistically significant if it is unlikely to have occurred by chance. The phrase test of significance was coined by Ronald Fisher....
different for male
Male
Male refers to the biological sex of an organism, or part of an organism, which produces small mobile gametes, called spermatozoa. Each spermatozoon can fuse with a larger female gamete or ovum, in the process of fertilization...
s and female
Female
Female is the sex of an organism, or a part of an organism, which produces non-mobile ova .- Defining characteristics :The ova are defined as the larger gametes in a heterogamous reproduction system, while the smaller, usually motile gamete, the spermatozoon, is produced by the male...
s of the species
Species
In biology, a species is one of the basic units of biological classification and a taxonomic rank. A species is often defined as a group of organisms capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring. While in many cases this definition is adequate, more precise or differing measures are...
.
Brain size
Human males, on average, have larger brainsHuman brain
The human brain has the same general structure as the brains of other mammals, but is over three times larger than the brain of a typical mammal with an equivalent body size. Estimates for the number of neurons in the human brain range from 80 to 120 billion...
than females.
In 1861, Paul Broca
Paul Broca
Pierre Paul Broca was a French physician, surgeon, anatomist, and anthropologist. He was born in Sainte-Foy-la-Grande, Gironde. He is best known for his research on Broca's area, a region of the frontal lobe that has been named after him. Broca’s Area is responsible for articulated language...
examined 432 human brains and found that the brains of males had an average weight of 1325 grams, while the brains of females had an average weight of 1144 grams. More recently, a 1992 study of 6,325 Army personnel found that men's brains had an average volume of 1442 cm³, while the women averaged 1332 cm³. These differences were shown to be smaller but to persist even when adjusted for body size measured as body height or body surface, such that women averaged 100 g less brain mass than men of equal size.
According to another estimate, on average, male brains have approximately 4 % more cells and weigh 100 grams more than female brains do. However, both sexes have a similar brain weight to body weight ratio. Female brains are more compact than male brain
Brain
The brain is the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals—only a few primitive invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, sea squirts and starfishes do not have one. It is located in the head, usually close to primary sensory apparatus such as vision, hearing,...
s in that, though smaller, they are more densely packed with neuron
Neuron
A neuron is an electrically excitable cell that processes and transmits information by electrical and chemical signaling. Chemical signaling occurs via synapses, specialized connections with other cells. Neurons connect to each other to form networks. Neurons are the core components of the nervous...
s, particularly in the region responsible for language. Men only think with one side of the brain while women use both sides for thinking this explains why encoding failure is worse among men.
In studies concerning intelligence
Intelligence
Intelligence has been defined in different ways, including the abilities for abstract thought, understanding, communication, reasoning, learning, planning, emotional intelligence and problem solving....
, it has been suggested that the ratio of brain weight to body weight (rather than actual brain weight) is more predictive of IQ levels. While men's brains are an average of 10-15% larger and heavier than women's brains, some researchers propose that the ratio of brain to body size does not differ between the sexes.
However, some argue that since brain-to-body-size ratios tend to decrease as body size increases, a sex difference in brain-weight ratios still exists between men and women of the same size.
Brain structure
There are also differences in the structure of and in specific areas of the brain. For instance, two studies found that men have larger parietal lobeParietal lobe
The parietal lobe is a part of the Brain positioned above the occipital lobe and behind the frontal lobe.The parietal lobe integrates sensory information from different modalities, particularly determining spatial sense and navigation. For example, it comprises somatosensory cortex and the...
s, though another study failed to find any statistically significant difference. At the same time, females have larger Wernicke's
Wernicke's area
Wernicke's area is one of the two parts of the cerebral cortex linked since the late nineteenth century to speech . It is involved in the understanding of written and spoken language...
and Broca's area
Broca's area
Broca's area is a region of the hominid brain with functions linked to speech production.The production of language has been linked to the Broca’s area since Pierre Paul Broca reported impairments in two patients. They had lost the ability to speak after injury to the posterior inferior frontal...
s, areas responsible for language processing. Studies using MRI scanning have shown that the auditory and language-related regions in the left hemisphere are proportionally expanded in females versus in males. Conversely, the primary visual, and visuo-spatial association areas of the parietal lobes are proportionally larger in males. Evidence of a sex difference in the relative size of the corpus callosum
Corpus callosum
The corpus callosum , also known as the colossal commissure, is a wide, flat bundle of neural fibers beneath the cortex in the eutherian brain at the longitudinal fissure. It connects the left and right cerebral hemispheres and facilitates interhemispheric communication...
was discussed during the 1980s and 90s. However, a 1997 meta-study concluded that there is no relative size difference, and that the larger corpus callosum in males is due to generally larger brains in males on average.
In total and on average, females have a higher percentage of grey matter
Grey matter
Grey matter is a major component of the central nervous system, consisting of neuronal cell bodies, neuropil , glial cells and capillaries. Grey matter contains neural cell bodies, in contrast to white matter, which does not and mostly contains myelinated axon tracts...
in comparison to males, and males a higher percentage of white matter
White matter
White matter is one of the two components of the central nervous system and consists mostly of myelinated axons. White matter tissue of the freshly cut brain appears pinkish white to the naked eye because myelin is composed largely of lipid tissue veined with capillaries. Its white color is due to...
. However, some researchers maintain that as males have larger brains on average than females, when adjusted for total brain volume, the grey matter differences between sexes is small or nonexistent. Thus, the percentage of grey matter appears to be more related to brain size than it is to gender.
A proposed alternative way of measuring intelligence is by using grey matter or white matter
White matter
White matter is one of the two components of the central nervous system and consists mostly of myelinated axons. White matter tissue of the freshly cut brain appears pinkish white to the naked eye because myelin is composed largely of lipid tissue veined with capillaries. Its white color is due to...
volume in the brain as an indicator. The former is used for information processing, whereas the latter makes up the connections between processing centers. In 2005, Haier et al. reported that, compared with men, women show more white matter and fewer grey matter areas as related to intelligence. However, he concluded that "men and women apparently achieve similar IQ results with different brain regions, suggesting that there is no singular underlying neuroanatomical structure to general intelligence and that different types of brain designs may manifest equivalent intellectual performance." Using brain mapping
Brain mapping
Brain mapping is a set of neuroscience techniques predicated on the mapping of quantities or properties onto spatial representations of the brain resulting in maps.- Overview :...
, it was shown that men have more than six times the amount of gray matter related to general intelligence than women, and women have nearly ten times the amount of white matter related to intelligence than men. They also report that the brain areas correlated with IQ differ between the sexes. In short, men and women apparently achieve similar IQ results with different brain regions.
Other differences that have been established include greater length in males of myelinated axons in their white matter (176,000 km compared to 146,000 km); and 33% more synapses per mm3 of cerebral cortex. Another difference is that females generally have faster blood flow to their brains and lose less brain tissue as they age than males do. Additionally, depression and chronic anxiety are much more common in women than in men, and it has been speculated, by some, that this is due to differences in the brain's serotonin
Serotonin
Serotonin or 5-hydroxytryptamine is a monoamine neurotransmitter. Biochemically derived from tryptophan, serotonin is primarily found in the gastrointestinal tract, platelets, and in the central nervous system of animals including humans...
system).
Genetic and hormonal causes
Both genesGênes
Gênes is the name of a département of the First French Empire in present Italy, named after the city of Genoa. It was formed in 1805, when Napoleon Bonaparte occupied the Republic of Genoa. Its capital was Genoa, and it was divided in the arrondissements of Genoa, Bobbio, Novi Ligure, Tortona and...
and hormone
Hormone
A hormone is a chemical released by a cell or a gland in one part of the body that sends out messages that affect cells in other parts of the organism. Only a small amount of hormone is required to alter cell metabolism. In essence, it is a chemical messenger that transports a signal from one...
s affect the formation of human brains before birth
Birth
Birth is the act or process of bearing or bringing forth offspring. The offspring is brought forth from the mother. The time of human birth is defined as the time at which the fetus comes out of the mother's womb into the world...
, as well as the behavior of adult individuals. Several genes that code for differences between male and female brains have been identified. In the human brain
Human brain
The human brain has the same general structure as the brains of other mammals, but is over three times larger than the brain of a typical mammal with an equivalent body size. Estimates for the number of neurons in the human brain range from 80 to 120 billion...
, a difference between sexes was observed in the transcription of the PCDH11X
PCDH11X
Protocadherin 11 X-linked, also known as PCDH11X, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the PCDH11X gene.- Function :This gene belongs to the protocadherin gene family, a subfamily of the cadherin superfamily...
/Y gene pair, a pair unique to Homo sapiens. It has been argued that the Y chromosome is primarily responsible for males being more susceptible to mental illnesses.
Hormones significantly affect human brain formation, as well as brain development at puberty. A 2004 review in Nature Reviews Neuroscience
Nature Reviews Neuroscience
Nature Reviews Neuroscience is a review journal covering neuroscience. Its 2008 impact factor is 25.94. The journal covers the following areas:*Biochemical signalling in neurons*Cellular and molecular neuroscience*Neural development...
observed that "because it is easier to manipulate hormone levels than the expression of sex chromosome genes, the effects of hormones have been studied much more extensively, and are much better understood, than the direct actions in the brain of sex chromosome genes." It concluded that while "the differentiating effects of gonadal secretions seem to be
dominant," the existing body of research "support the idea that sex differences in neural expression
of X and Y genes significantly contribute to sex differences in brain functions and disease."
Sensory systems
- Females have a more sensitive sense of smell than males, both in the differentiation of odors, and in the detection of slight or faint odors.
- There is also indication that females are better at discerning differences in colours, while males are more aware of, and capable of discerning movement.
- Females have more pain receptors in the skin. That may contribute to the lower pain tolerance of women.
Tissues and hormones
- Women generally have a higher body fat percentageBody fat percentageA person's body mass percentage is the total weight of the person's fat divided by the person's weight and consists of essential body fat and storage body fat. Essential body fat is necessary to maintain life and reproductive functions. The percentage of essential body fat for women is greater than...
than men. - Women usually have lower blood pressure than men, and women's hearts beat faster, even when they are asleep.
- Men generally have more muscle tissue mass, particularly in the upper body.
- Men and women have different levels of certain hormoneHormoneA hormone is a chemical released by a cell or a gland in one part of the body that sends out messages that affect cells in other parts of the organism. Only a small amount of hormone is required to alter cell metabolism. In essence, it is a chemical messenger that transports a signal from one...
s. Men have a higher concentration of androgenAndrogenAndrogen, also called androgenic hormone or testoid, is the generic term for any natural or synthetic compound, usually a steroid hormone, that stimulates or controls the development and maintenance of male characteristics in vertebrates by binding to androgen receptors...
s while women have a higher concentration of estrogenEstrogenEstrogens , oestrogens , or œstrogens, are a group of compounds named for their importance in the estrous cycle of humans and other animals. They are the primary female sex hormones. Natural estrogens are steroid hormones, while some synthetic ones are non-steroidal...
s. The main male-associated hormone is testosteroneTestosteroneTestosterone is a steroid hormone from the androgen group and is found in mammals, reptiles, birds, and other vertebrates. In mammals, testosterone is primarily secreted in the testes of males and the ovaries of females, although small amounts are also secreted by the adrenal glands...
. - Adult men have approximately 5.2 million red blood cells per cubic millimeter of blood, whereas women have approximately 4.6 million.
- Females typically have more white blood cellWhite blood cellWhite blood cells, or leukocytes , are cells of the immune system involved in defending the body against both infectious disease and foreign materials. Five different and diverse types of leukocytes exist, but they are all produced and derived from a multipotent cell in the bone marrow known as a...
s (stored and circulating), more granulocyteGranulocyteGranulocytes are a category of white blood cells characterized by the presence of granules in their cytoplasm. They are also called polymorphonuclear leukocytes because of the varying shapes of the nucleus, which is usually lobed into three segments...
s and B and T lymphocyteLymphocyteA lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell in the vertebrate immune system.Under the microscope, lymphocytes can be divided into large lymphocytes and small lymphocytes. Large granular lymphocytes include natural killer cells...
s. Additionally, they produce more antibodiesAntibodyAn antibody, also known as an immunoglobulin, is a large Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique part of the foreign target, termed an antigen...
at a faster rate than males. Hence they develop fewer infectiousInfectionAn infection is the colonization of a host organism by parasite species. Infecting parasites seek to use the host's resources to reproduce, often resulting in disease...
diseases and succumb for shorter periods.
Life span
Females live longer than males in most countries around the world. One possible explanation is the generally more risky behavior engaged in by males. More males than females die young because of war, criminal activity, and accidents. However, the gap between males and females is decreasing in many developed countries as more women take up unhealthy practices that were once considered masculine like smoking and drinking alcohol. In Russia, however, the sex-associated gap has been increasing as male life expectancy declines.Sex chromosome disorders
Certain diseases and conditions are clearly sex related in that they are caused by the same chromosomeChromosome
A chromosome is an organized structure of DNA and protein found in cells. It is a single piece of coiled DNA containing many genes, regulatory elements and other nucleotide sequences. Chromosomes also contain DNA-bound proteins, which serve to package the DNA and control its functions.Chromosomes...
s that regulate sex differentiation. Some conditions are X-linked recessive
X-linked recessive
X-linked recessive inheritance is a mode of inheritance in which a mutation in a gene on the X chromosome causes the phenotype to be expressed in males and in females who are homozygous for the gene mutation X-linked recessive inheritance is a mode of inheritance in which a mutation in a gene on...
, in that the gene is carried on the X chromosome. Genetic females (XX) will show symptoms of the disease only if both their X chromosomes are defective with a similar deficiency, whereas genetic males (XY) will show symptoms of the disease if their only X chromosome is defective. (A woman may carry such a disease on one X chromosome but not show symptoms if the other X chromosome works sufficiently.) For this reason, such conditions are far more common in males than in females. Examples of X-linked recessive conditions are color blindness
Color blindness
Color blindness or color vision deficiency is the inability or decreased ability to see color, or perceive color differences, under lighting conditions when color vision is not normally impaired...
, hemophilia, and Duchenne muscular dystrophy
Duchenne muscular dystrophy
Duchenne muscular dystrophy is a recessive X-linked form of muscular dystrophy, which results in muscle degeneration, difficulty walking, breathing, and death. The incidence is 1 in 3,000 boys. Females and males are affected, though females are rarely affected and are more often carriers...
.
No vital genes reside only on the Y chromosome
Y chromosome
The Y chromosome is one of the two sex-determining chromosomes in most mammals, including humans. In mammals, it contains the gene SRY, which triggers testis development if present. The human Y chromosome is composed of about 60 million base pairs...
, since roughly half of humans (females) do not have Y chromosomes. Still, there are diseases that are caused by a defective Y chromosome or of a defective number of them. One human disease linked to a defect on the Y chromosome is defective testicular development. Other conditions include Klinefelter's syndrome
Klinefelter's syndrome
Klinefelter syndrome, 46/47, XXY, or XXY syndrome is a condition in which human males have an extra X chromosome. While females have an XX chromosomal makeup, and males an XY, affected individuals have at least two X chromosomes and at least one Y chromosome...
and XX male syndrome
XX male syndrome
XX male syndrome is a rare sex chromosomal disorder. Usually it is caused by unequal crossing over between X and Y chromosomes during meiosis in the father, which results in the X chromosome containing the normally-male SRY gene...
.
Differences not linked to sex chromosomes
The World Health OrganizationWorld Health Organization
The World Health Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations that acts as a coordinating authority on international public health. Established on 7 April 1948, with headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland, the agency inherited the mandate and resources of its predecessor, the Health...
(WHO) has produced a number of reports on gender and health. The following trends are shown:
- Overall rates of mental illness are similar for men and women. There is no significant gender difference in rates of schizophreniaSchizophreniaSchizophrenia is a mental disorder characterized by a disintegration of thought processes and of emotional responsiveness. It most commonly manifests itself as auditory hallucinations, paranoid or bizarre delusions, or disorganized speech and thinking, and it is accompanied by significant social...
and bipolar depression. Women are more likely to suffer from unipolar depression, anxietyAnxietyAnxiety is a psychological and physiological state characterized by somatic, emotional, cognitive, and behavioral components. The root meaning of the word anxiety is 'to vex or trouble'; in either presence or absence of psychological stress, anxiety can create feelings of fear, worry, uneasiness,...
, eating disorders, and post-traumatic stress disorderPost-traumatic stress disorderPosttraumaticstress disorder is a severe anxiety disorder that can develop after exposure to any event that results in psychological trauma. This event may involve the threat of death to oneself or to someone else, or to one's own or someone else's physical, sexual, or psychological integrity,...
. Men are more likely to suffer from alcoholismAlcoholismAlcoholism is a broad term for problems with alcohol, and is generally used to mean compulsive and uncontrolled consumption of alcoholic beverages, usually to the detriment of the drinker's health, personal relationships, and social standing...
and antisocial personality disorderAntisocial personality disorderAntisocial personality disorder is described by the American Psychiatric Association's Diagnostic and Statistical Manual, fourth edition , as an Axis II personality disorder characterized by "...a pervasive pattern of disregard for, and violation of, the rights of others that begins in childhood...
, as well as developmental psychiatric disorders such as autism spectrum disorders and Tourette syndromeTourette syndromeTourette syndrome is an inherited neuropsychiatric disorder with onset in childhood, characterized by multiple physical tics and at least one vocal tic; these tics characteristically wax and wane...
. - Before menopauseMenopauseMenopause is a term used to describe the permanent cessation of the primary functions of the human ovaries: the ripening and release of ova and the release of hormones that cause both the creation of the uterine lining and the subsequent shedding of the uterine lining...
, women are less likely to suffer from cardiovascular diseaseCardiovascular diseaseHeart disease or cardiovascular disease are the class of diseases that involve the heart or blood vessels . While the term technically refers to any disease that affects the cardiovascular system , it is usually used to refer to those related to atherosclerosis...
. However, after age 60, the risk for both men and women is the same. - Overall, men are more likely to suffer from cancerCancerCancer , known medically as a malignant neoplasm, is a large group of different diseases, all involving unregulated cell growth. In cancer, cells divide and grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors, and invade nearby parts of the body. The cancer may also spread to more distant parts of the...
, with much of this driven by lung cancerLung cancerLung cancer is a disease characterized by uncontrolled cell growth in tissues of the lung. If left untreated, this growth can spread beyond the lung in a process called metastasis into nearby tissue and, eventually, into other parts of the body. Most cancers that start in lung, known as primary...
. In most countries, more men than women smokeTobacco smokingTobacco smoking is the practice where tobacco is burned and the resulting smoke is inhaled. The practice may have begun as early as 5000–3000 BCE. Tobacco was introduced to Eurasia in the late 16th century where it followed common trade routes...
, although this gap is narrowing especially among young women. - Women are twice as likely to be blindBlindnessBlindness is the condition of lacking visual perception due to physiological or neurological factors.Various scales have been developed to describe the extent of vision loss and define blindness...
as men. In developed countries, this may be linked to higher life expectancy and age-related conditions. In developing countries, women are less likely to get timely treatments for conditions that lead to blindness such as cataracts and trachomaTrachomaTrachoma is an infectious disease causing a characteristic roughening of the inner surface of the eyelids. Also called granular conjunctivitis and Egyptian ophthalmia, it is the leading cause of infectious blindness in the world...
. - Women are more likely to suffer from osteoarthritisOsteoarthritisOsteoarthritis also known as degenerative arthritis or degenerative joint disease, is a group of mechanical abnormalities involving degradation of joints, including articular cartilage and subchondral bone. Symptoms may include joint pain, tenderness, stiffness, locking, and sometimes an effusion...
and osteoporosisOsteoporosisOsteoporosis is a disease of bones that leads to an increased risk of fracture. In osteoporosis the bone mineral density is reduced, bone microarchitecture is deteriorating, and the amount and variety of proteins in bone is altered...
.
Infectious disease prevalence varies - this is largely due to cultural and exposure factors. In particular the WHO notes that:
- Worldwide, more men than women are infected with HIVHIVHuman immunodeficiency virus is a lentivirus that causes acquired immunodeficiency syndrome , a condition in humans in which progressive failure of the immune system allows life-threatening opportunistic infections and cancers to thrive...
. The exception is sub-Saharan AfricaSub-Saharan AfricaSub-Saharan Africa as a geographical term refers to the area of the African continent which lies south of the Sahara. A political definition of Sub-Saharan Africa, instead, covers all African countries which are fully or partially located south of the Sahara...
, where more women than men are infected. - Adult males are more likely to be diagnosed with tuberculosisTuberculosisTuberculosis, MTB, or TB is a common, and in many cases lethal, infectious disease caused by various strains of mycobacteria, usually Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Tuberculosis usually attacks the lungs but can also affect other parts of the body...
.
Some other sex-related health differences include:
- Anterior cruciate ligamentAnterior cruciate ligamentThe anterior cruciate ligament is a cruciate ligament which is one of the four major ligaments of the human knee. In the quadruped stifle , based on its anatomical position, it is referred to as the cranial cruciate ligament.The ACL originates from deep within the notch of the distal femur...
injuries, especially in basketball, occur more often in women than in men. - From conceptionHuman fertilizationHuman fertilization is the union of a humanoid egg and sperm, usually occurring in the ampulla of the uterine tube. The result of this union is the production of a zygote, or fertilized egg, initiating prenatal development...
to death, but particularly before adulthood, females are generally less vulnerable than males to developmental difficulties and chronic illnesses. This could be due to females having two x chromosomes instead of just one, or in the reduced exposure to testosteroneTestosteroneTestosterone is a steroid hormone from the androgen group and is found in mammals, reptiles, birds, and other vertebrates. In mammals, testosterone is primarily secreted in the testes of males and the ovaries of females, although small amounts are also secreted by the adrenal glands...
.
Sex ratio
The sex ratioSex ratio
Sex ratio is the ratio of males to females in a population. The primary sex ratio is the ratio at the time of conception, secondary sex ratio is the ratio at time of birth, and tertiary sex ratio is the ratio of mature organisms....
for the entire world population
World population
The world population is the total number of living humans on the planet Earth. As of today, it is estimated to be billion by the United States Census Bureau...
is 101 males to 100 females. However, in developed countries, there are more females than males.
See also
- Gender-based medicineGender-based medicineGender-based medicine or simply gender medicine is the field of medicine that studies the biological and physiological differences between the human sexes and how that affects differences in disease. Traditionally, medical research has mostly been conducted using the male body as the basis for...
- Genetics of gender
- Gender differences in coping
- Sexual dimorphismSexual dimorphismSexual dimorphism is a phenotypic difference between males and females of the same species. Examples of such differences include differences in morphology, ornamentation, and behavior.-Examples:-Ornamentation / coloration:...
- Sex differentiation
- Sex and intelligenceSex and intelligenceResearch on sex and psychology investigates cognitive and behavioral differences between men and women. This research employs experimental tests of cognition, which take a variety of forms. Tests focus on possible differences in areas such as IQ, spatial reasoning, and emotion.Most IQ tests are...
- VirilizationVirilizationIn biology and medicine, virilization refers to the biological development of sex differences, changes that make a male body different from a female body. Most of the changes of virilization are produced by androgens...
- List of homologues of the human reproductive system
- Man fluMan fluMan flu is a pejorative term that refers to the idea many men, when they have a cold, exaggerate and claim they have the flu — the implication being that women do not do so...

