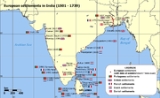
Colonial India
Encyclopedia
Colonial India refers to areas of the Indian Subcontinent
under the control of European colonial
powers, through trade and conquest. The first European power to arrive in India was the army of Alexander the Great in 327–326 BC. The satrap
s he established in the north west of the subcontinent quickly crumbled after he left. Later, trade was carried between Indian states and the Roman Empire
by Roman sailors who reached India by ship through the Red
and Arabian Sea
s. The spice trade
between India and Europe was one of the main drivers of the world economy
and was the main catalyst for the Age of Discovery
.
The search for the wealth and prosperity of India led to the accidental discovery of the Americas
by Christopher Columbus
in 1492. However, it was also near the end of the 15th century that Portuguese
sailor Vasco da Gama
became the first European to re-establish direct trade links with India since Roman times, by being the first to arrive by circumnavigating Africa
. Having arrived in Calicut
, which by then was one of the major trading ports of the eastern world, he obtained permission to trade in the city from Saamoothiri Rajah
.
Trading rivalries brought other Europe
an powers to India. The Dutch
, English
, French
and Danes
established trading posts in India in the early 17th century. As the Mughal Empire
disintegrated in the early 18th century and then the Maratha Empire
became weakened after the third battle of Panipat
, the relatively weak and unstable Indian states which emerged were increasingly open to manipulation by the Europeans through dependent "friendly" Indian rulers.
In the later 18th century the British
and French entered into intense struggles for dominance through proxy Indian rulers and also by direct military intervention. The defeat of the redoubtable Indian ruler Tipu Sultan
in 1799 marginalized French influence. This was followed by a rapid expansion of British power through the greater part of the subcontinent in the early 19th century. By the middle of the century, the British had already gained direct or indirect control over almost all of India. British India contained the most populous and valuable provinces of the British Empire
and thus became known as "the jewel in the British crown".
 Long after the decline of the Roman Empire
Long after the decline of the Roman Empire
's sea-borne trade with India, the Portuguese were the next Europeans to arrive for the purpose of trade, first arriving in May 1498. The closing of the traditional trade routes in western Asia by the Ottomans and rivalry with the Italian
states sent Portugal in search of an alternate sea route to India. The first successful voyage to India was by Vasco da Gama
in 1498, when he arrived in Calicut
, now in Kerala
. Having arrived in Calicut he obtained from Saamoothiri Rajah
permission to trade in the city. The navigator was received with traditional hospitality, but an interview with the Saamoothiri (Zamorin) failed to produce any definitive results. Vasco da Gama requested permission to leave a factor behind in charge of the merchandise he could not sell; his request was refused, and the king insisted da Gama should pay customs duty, like any other trader, which strained relations between the two.
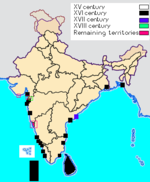
The colonial era in India began in 1502, when the Portuguese Empire
established the first European trading centre at Kollam
, Kerala
. In 1505 the King of Portugal appointed Dom Francisco de Almeida
as the first Portuguese viceroy in India, followed in 1509 by Dom Afonso de Albuquerque
. In 1510 Albuquerque established an important trading presence in Goa
by conquering the city, which had been dominated by Muslims. He inaugurated the policy of marrying Portuguese soldiers and sailors with local Indian girls, the consequence of which was a great miscegenation
in Goa and other Portuguese territories in Asia. Another feature of the Portuguese presence in India was their will to evangelize and promote Catholicism. In this, the Jesuits played a fundamental role, and to this day the Jesuit missionary Saint Francis Xavier is revered among the Catholics of India.
The Portuguese established a chain of outposts along India's west coast and on the island of Ceylon in the early 16th century. They built the St. Angelo Fort at Kannur
to guard their possessions in North Malabar
. Goa was their prized possession and the seat of Portugal's viceroy. Portugal's northern province included settlements at Daman, Diu, Chaul
, Baçaim
, Salsette, and Mumbai
. The rest of the northern province, with the exception of Daman and Diu, was lost to the Maratha Empire
in the early 18th century.
In 1661 Portugal was at war against Spain and needed support from England
, which led to the signing of the agreement for a marriage between Princess Catherine of Portugal
and Charles II of England
, with a dowry that included the city of Bombay. This was the beginning of the English presence
in India.
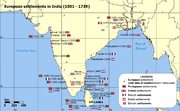 The Dutch East India Company
The Dutch East India Company
established trading posts on different parts along the Indian coast. For some while, they controlled the Malabar
southwest coast (Cranganore/Cranganor/Kodungallor, Cochin de Cima/Pallipuram, Cochin, Cochin de Baixo/Santa Cruz
, Quilon
(Coylan), Cannanore
, Kundapura
, Kayankulam, Ponnani) and the Coromandel
southeastern coast (Golkonda, Bimilipatnam, Jaggernaikpoeram/Kakinada
, Palikol, Pulicat
, Porto Novo/Parangippettai, Negapatnam) and Surat (1616–1795). They conquered Ceylon from the Portuguese. The Dutch also established trading stations in Travancore
and coastal Tamil Nadu
as well as at Rajshahi
in present-day Bangladesh
, Pipely, Hugli-Chinsura, and Murshidabad
in present-day West Bengal
, Balasore
(Baleshwar or Bellasoor) in Orissa
, and Ava
, Arakan
, and Syriam in present-day Myanmar
(Burma). Ceylon was lost at the Congress of Vienna
in the aftermath of the Napoleonic Wars
, where the Dutch having fallen subject to France, saw their colonies raided by Britain. The Dutch later became less involved in India, as they had the Dutch East Indies
(now Indonesia
) as their prized possession.
and the United Netherlands
began to challenge Portugal's monopoly of trade with Asia, forming private joint-stock companies
to finance the voyages—the English
, later British, and the Dutch
East India Companies, which were chartered in 1600 and 1602 respectively. The primary aim of these companies was to tap into the lucrative spice trade
, and they focused their efforts on the areas of production, the Indonesia
n archipelago
and especially the "Spice Islands
", and on India as an important market for the trade. The close proximity of London
and Amsterdam
across the North Sea
, and the intense rivalry between England and the Netherlands, inevitably led to conflict between the two companies, with the Dutch gaining the upper hand in the Moluccas
(previously a Portuguese stronghold) after the withdrawal of the English in 1622, but with the English enjoying more success in India, at Surat
, after the establishment of a factory
in 1613.
 The Netherlands' more advanced financial system and the three Anglo-Dutch Wars
The Netherlands' more advanced financial system and the three Anglo-Dutch Wars
of the 17th century left the Dutch as the dominant naval and trading power in Asia. Hostilities ceased after the Glorious Revolution
of 1688, when the Dutch William of Orange
ascended the English throne, bringing peace between the Netherlands and England. A deal between the two nations left the more valuable spice trade of the Indonesian archipelago to the Netherlands and the textiles industry of India to England, but textiles overtook spices in terms of profitability, so that by 1720, in terms of sales, the English company had overtaken the Dutch. The English East India Company shifted its focus from Surat—a hub of the spice trade network—to Fort St. George.
, the commander in chief of the army of the Nawab of Bengal
, along with Jagat Seth
, Maharaja Krishna Nath, Umi Chand and some others, secretly connived with the British
asking logistic support to overthrow the Nawab in return for trade grants. The British forces, whose sole duty until then was guarding their British East India Company
property, were numerically inferior to the Bengali
armed forces. At the Battle of Plassey
on 23 June 1757, fought between the British under the command of Robert Clive and the Nawab, Mir Jafar's forces betrayed the Nawab and helped defeat him. Jafar was installed on the throne as a British subservient ruler. The battle transformed British perspective as they realized their strength and potential to conquer smaller Indian kingdoms and marked the beginning of the imperial or colonial era.
 British policy in Asia during the 19th century was chiefly concerned with expanding and protecting its hold on India, viewed as its most important colony and the key to the rest of Asia. The East India Company
British policy in Asia during the 19th century was chiefly concerned with expanding and protecting its hold on India, viewed as its most important colony and the key to the rest of Asia. The East India Company
drove the expansion of the British Empire
in Asia. The company's army had first joined forces with the Royal Navy
during the Seven Years' War
, and the two continued to cooperate in arenas outside India: the eviction of Napoleon from Egypt
(1799), the capture of Java
from the Netherlands (1811), the acquisition of Singapore
(1819) and Malacca
(1824), and the defeat of Burma (1826).
From its base in India, the company had also been engaged in an increasingly profitable opium
export trade to China since the 1730s. This trade, unlawful in China since it was outlawed by the Qing dynasty
in 1729, helped reverse the trade imbalances resulting from the British imports of tea
, which saw large outflows of silver from Britain to China. In 1839, the confiscation by the Chinese authorities at Canton
of 20,000 chests of opium led Britain to attack China in the First Opium War
, and the seizure by Britain of the island of Hong Kong
, at that time a minor settlement.
The British had direct or indirect control over all of present-day India before the middle of the 19th century. In 1857, a local rebellion by an army of sepoy
s escalated into the Rebellion of 1857, which took six months to suppress with heavy loss of life on both sides. This resistance, although short-lived, was triggered by British attempts to Westernise India. As a result, the East India Company lost its powers of government and British India formally came under direct British rule
, with an appointed governor-general
administering India. The East India Company was dissolved the following year in 1858. A few years later, Queen Victoria took the title of Empress of India..
India suffered a series of serious crop failures in the late 19th century, leading to widespread famines
in which at least 10 million people died. The East India Company had failed to implement any coordinated policy to deal with the famines during its period of rule. This changed during the Raj
, in which commissions were set up after each famine to investigate the causes and implement new policies, which took until the early 1900s to have an effect.
The slow but momentous reform movement developed gradually into the Indian Independence Movement
. During the years of World War I
, the hitherto bourgeois "home-rule" movement was transformed into a popular mass movement by Mahatma Gandhi
, a pacifist. Apart from Gandhi, other revolutionaries such as Shaheed Bhagat Singh, Chandrashekar Azad and Subhash Chandra Bose
, were not against use of violence to oppose the British rule. The independence movement attained its objective with the independence of Pakistan and India on 14 August and 15 August 1947 respectively.
also established trading bases in India. Their first establishment was in Pondicherry on the Coromandel Coast
in southeastern India in 1674. Subsequent French settlements were Chandernagore in Bengal, northeastern India in 1688, Yanam in Andhra Pradesh
in 1723, Mahe in 1725, and Karaikal
in 1739. The French were constantly in conflict with the Dutch and later on mainly with the British in India. At the height of French power in the mid-18th century, the French occupied large areas of southern India and the area lying in today's northern Andhra Pradesh
and Orissa
. Between 1744 and 1761, the British and the French repeatedly attacked and conquered each other's forts and towns in southeastern India and in Bengal in the northeast. After some initial French successes, the British decisively defeated the French in Bengal in the Battle of Plassey
in 1757 and in the southeast in 1761 in the Battle of Wandiwash
, after which the British East India Company was the supreme military and political power in southern India as well as in Bengal. In the following decades it gradually increased the size of the territories under its control. The enclaves of Pondicherry, Karaikal, Yanam, Mahé and Chandernagore were returned to France in 1816 and were integrated with the Republic of India after its independence in 1947.
was a minor colonial power to set foot in India. It established trading outposts in Tranquebar
, Tamil Nadu
(1620), Serampore
, West Bengal (1755) and the Nicobar Islands
(1750s). At one time, the main Danish and Swedish East Asia companies together imported more tea
to Europe than the British did. Their outposts lost economic and strategic importance, and Tranquebar, the last Danish outpost, was sold to the British in 1845.
were briefly given territorial rights to India by Pope Alexander VI
on 25 September 1493 by the bull
Dudum siquidem before these rights were removed by the Treaty of Tordesillas
less than one year later. The Japanese briefly occupied the Andaman and Nicobar Islands during World War II
.
Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent, also Indian Subcontinent, Indo-Pak Subcontinent or South Asian Subcontinent is a region of the Asian continent on the Indian tectonic plate from the Hindu Kush or Hindu Koh, Himalayas and including the Kuen Lun and Karakoram ranges, forming a land mass which extends...
under the control of European colonial
Colonialism
Colonialism is the establishment, maintenance, acquisition and expansion of colonies in one territory by people from another territory. It is a process whereby the metropole claims sovereignty over the colony and the social structure, government, and economics of the colony are changed by...
powers, through trade and conquest. The first European power to arrive in India was the army of Alexander the Great in 327–326 BC. The satrap
Satrap
Satrap was the name given to the governors of the provinces of the ancient Median and Achaemenid Empires and in several of their successors, such as the Sassanid Empire and the Hellenistic empires....
s he established in the north west of the subcontinent quickly crumbled after he left. Later, trade was carried between Indian states and the Roman Empire
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of the ancient Roman civilization, characterised by an autocratic form of government and large territorial holdings in Europe and around the Mediterranean....
by Roman sailors who reached India by ship through the Red
Red Sea
The Red Sea is a seawater inlet of the Indian Ocean, lying between Africa and Asia. The connection to the ocean is in the south through the Bab el Mandeb strait and the Gulf of Aden. In the north, there is the Sinai Peninsula, the Gulf of Aqaba, and the Gulf of Suez...
and Arabian Sea
Arabian Sea
The Arabian Sea is a region of the Indian Ocean bounded on the east by India, on the north by Pakistan and Iran, on the west by the Arabian Peninsula, on the south, approximately, by a line between Cape Guardafui in northeastern Somalia and Kanyakumari in India...
s. The spice trade
Spice trade
Civilizations of Asia were involved in spice trade from the ancient times, and the Greco-Roman world soon followed by trading along the Incense route and the Roman-India routes...
between India and Europe was one of the main drivers of the world economy
World economy
The world economy, or global economy, generally refers to the economy, which is based on economies of all of the world's countries, national economies. Also global economy can be seen as the economy of global society and national economies – as economies of local societies, making the global one....
and was the main catalyst for the Age of Discovery
Age of Discovery
The Age of Discovery, also known as the Age of Exploration and the Great Navigations , was a period in history starting in the early 15th century and continuing into the early 17th century during which Europeans engaged in intensive exploration of the world, establishing direct contacts with...
.
The search for the wealth and prosperity of India led to the accidental discovery of the Americas
Americas
The Americas, or America , are lands in the Western hemisphere, also known as the New World. In English, the plural form the Americas is often used to refer to the landmasses of North America and South America with their associated islands and regions, while the singular form America is primarily...
by Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus was an explorer, colonizer, and navigator, born in the Republic of Genoa, in northwestern Italy. Under the auspices of the Catholic Monarchs of Spain, he completed four voyages across the Atlantic Ocean that led to general European awareness of the American continents in the...
in 1492. However, it was also near the end of the 15th century that Portuguese
Portugal
Portugal , officially the Portuguese Republic is a country situated in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula. Portugal is the westernmost country of Europe, and is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the West and South and by Spain to the North and East. The Atlantic archipelagos of the...
sailor Vasco da Gama
Vasco da Gama
Vasco da Gama, 1st Count of Vidigueira was a Portuguese explorer, one of the most successful in the Age of Discovery and the commander of the first ships to sail directly from Europe to India...
became the first European to re-establish direct trade links with India since Roman times, by being the first to arrive by circumnavigating Africa
Africa
Africa is the world's second largest and second most populous continent, after Asia. At about 30.2 million km² including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of the Earth's total surface area and 20.4% of the total land area...
. Having arrived in Calicut
History of Kozhikode
Kozhikode , also known as Calicut, is a city in the southern Indian state of Kerala. It is the third largest city in Kerala and the headquarters of Kozhikode district....
, which by then was one of the major trading ports of the eastern world, he obtained permission to trade in the city from Saamoothiri Rajah
Saamoothiri
Zamorin is the title used by the Hindu Eradi Samanthan kshatriya rulers of the erstwhile late medieval feudal kingdom of Kozhikode located in the present day state of Kerala, India....
.
Trading rivalries brought other Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
an powers to India. The Dutch
Dutch Republic
The Dutch Republic — officially known as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands , the Republic of the United Netherlands, or the Republic of the Seven United Provinces — was a republic in Europe existing from 1581 to 1795, preceding the Batavian Republic and ultimately...
, English
English colonial empire
The English colonial empire consisted of a variety of overseas territories colonized, conquered, or otherwise acquired by the former Kingdom of England between the late 16th and early 18th centuries....
, French
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
and Danes
Danes
Danish people or Danes are the nation and ethnic group that is native to Denmark, and who speak Danish.The first mention of Danes within the Danish territory is on the Jelling Rune Stone which mentions how Harald Bluetooth converted the Danes to Christianity in the 10th century...
established trading posts in India in the early 17th century. As the Mughal Empire
Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire , or Mogul Empire in traditional English usage, was an imperial power from the Indian Subcontinent. The Mughal emperors were descendants of the Timurids...
disintegrated in the early 18th century and then the Maratha Empire
Maratha Empire
The Maratha Empire or the Maratha Confederacy was an Indian imperial power that existed from 1674 to 1818. At its peak, the empire covered much of South Asia, encompassing a territory of over 2.8 million km²....
became weakened after the third battle of Panipat
Third battle of Panipat
The Third Battle of Panipat took place on 14 January 1761, at Panipat , about 60 miles north of Delhi between a northern expeditionary force of the Maratha Confederacy and a coalition of the King of Afghanistan, Ahmad Shah Abdali with 2 Indian Muslim allies—the Rohilla Afghans of the Doab, and the...
, the relatively weak and unstable Indian states which emerged were increasingly open to manipulation by the Europeans through dependent "friendly" Indian rulers.
In the later 18th century the British
Kingdom of Great Britain
The former Kingdom of Great Britain, sometimes described as the 'United Kingdom of Great Britain', That the Two Kingdoms of Scotland and England, shall upon the 1st May next ensuing the date hereof, and forever after, be United into One Kingdom by the Name of GREAT BRITAIN. was a sovereign...
and French entered into intense struggles for dominance through proxy Indian rulers and also by direct military intervention. The defeat of the redoubtable Indian ruler Tipu Sultan
Tipu Sultan
Tipu Sultan , also known as the Tiger of Mysore, was the de facto ruler of the Kingdom of Mysore. He was the son of Hyder Ali, at that time an officer in the Mysorean army, and his second wife, Fatima or Fakhr-un-Nissa...
in 1799 marginalized French influence. This was followed by a rapid expansion of British power through the greater part of the subcontinent in the early 19th century. By the middle of the century, the British had already gained direct or indirect control over almost all of India. British India contained the most populous and valuable provinces of the British Empire
British Empire
The British Empire comprised the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom. It originated with the overseas colonies and trading posts established by England in the late 16th and early 17th centuries. At its height, it was the...
and thus became known as "the jewel in the British crown".
European contact


Roman Empire
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of the ancient Roman civilization, characterised by an autocratic form of government and large territorial holdings in Europe and around the Mediterranean....
's sea-borne trade with India, the Portuguese were the next Europeans to arrive for the purpose of trade, first arriving in May 1498. The closing of the traditional trade routes in western Asia by the Ottomans and rivalry with the Italian
Italy
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
states sent Portugal in search of an alternate sea route to India. The first successful voyage to India was by Vasco da Gama
Vasco da Gama
Vasco da Gama, 1st Count of Vidigueira was a Portuguese explorer, one of the most successful in the Age of Discovery and the commander of the first ships to sail directly from Europe to India...
in 1498, when he arrived in Calicut
Kozhikode
Kozhikode During Classical antiquity and the Middle Ages, Kozhikkode was dubbed the "City of Spices" for its role as the major trading point of eastern spices. Kozhikode was once the capital of an independent kingdom of the same name and later of the erstwhile Malabar District...
, now in Kerala
Kerala
or Keralam is an Indian state located on the Malabar coast of south-west India. It was created on 1 November 1956 by the States Reorganisation Act by combining various Malayalam speaking regions....
. Having arrived in Calicut he obtained from Saamoothiri Rajah
Saamoothiri
Zamorin is the title used by the Hindu Eradi Samanthan kshatriya rulers of the erstwhile late medieval feudal kingdom of Kozhikode located in the present day state of Kerala, India....
permission to trade in the city. The navigator was received with traditional hospitality, but an interview with the Saamoothiri (Zamorin) failed to produce any definitive results. Vasco da Gama requested permission to leave a factor behind in charge of the merchandise he could not sell; his request was refused, and the king insisted da Gama should pay customs duty, like any other trader, which strained relations between the two.
The colonial era in India began in 1502, when the Portuguese Empire
Portuguese Empire
The Portuguese Empire , also known as the Portuguese Overseas Empire or the Portuguese Colonial Empire , was the first global empire in history...
established the first European trading centre at Kollam
Kollam
Kollam , often anglicized as ', is a city in the Indian state of Kerala. The city lies on the banks of Ashtamudi Lake on the Arabian sea coast and is situated about north of the state capital, Thiruvananthapuram...
, Kerala
Kerala
or Keralam is an Indian state located on the Malabar coast of south-west India. It was created on 1 November 1956 by the States Reorganisation Act by combining various Malayalam speaking regions....
. In 1505 the King of Portugal appointed Dom Francisco de Almeida
Francisco de Almeida
Dom Francisco de Almeida , also known as "the Great Dom Francisco" , was a Portuguese nobleman, soldier and explorer. He distinguished himself as a counsellor to King John II of Portugal and later in the wars against the Moors and in the conquest of Granada in 1492...
as the first Portuguese viceroy in India, followed in 1509 by Dom Afonso de Albuquerque
Afonso de Albuquerque
Afonso de Albuquerque[p][n] was a Portuguese fidalgo, or nobleman, an admiral whose military and administrative activities as second governor of Portuguese India conquered and established the Portuguese colonial empire in the Indian Ocean...
. In 1510 Albuquerque established an important trading presence in Goa
Goa
Goa , a former Portuguese colony, is India's smallest state by area and the fourth smallest by population. Located in South West India in the region known as the Konkan, it is bounded by the state of Maharashtra to the north, and by Karnataka to the east and south, while the Arabian Sea forms its...
by conquering the city, which had been dominated by Muslims. He inaugurated the policy of marrying Portuguese soldiers and sailors with local Indian girls, the consequence of which was a great miscegenation
Miscegenation
Miscegenation is the mixing of different racial groups through marriage, cohabitation, sexual relations, and procreation....
in Goa and other Portuguese territories in Asia. Another feature of the Portuguese presence in India was their will to evangelize and promote Catholicism. In this, the Jesuits played a fundamental role, and to this day the Jesuit missionary Saint Francis Xavier is revered among the Catholics of India.
The Portuguese established a chain of outposts along India's west coast and on the island of Ceylon in the early 16th century. They built the St. Angelo Fort at Kannur
Kannur
Kannur , also known as Cannanore, is a city in Kannur district in the Indian state of Kerala. It is the administrative headquarters of the District of Kannur and 518km north of state capital Trivandrum. During British rule in India, Kannur was known by its old name Cannanore, which is still in...
to guard their possessions in North Malabar
North Malabar
North Malabar , is a historic as well as geographic distinction in India used to refer the area covering; present Kasaragod and Kannur Districts, Mananthavady taluk of Wayanad District and Koyilandy & Vatakara taluks of Kozhikode District in modern Kerala and the entire Mahé sub-Division of...
. Goa was their prized possession and the seat of Portugal's viceroy. Portugal's northern province included settlements at Daman, Diu, Chaul
Chaul
Chaul is a former city of Portuguese India, now in ruins. It is located 60 km south of Mumbai, in Raigad District of Maharashtra state in western India....
, Baçaim
Vasai-Virar
Vasai-Virar is a city in Maharashtra state in western India. As per 2011 census this is the 5th largest city in Maharashtra . It is located in Thane District, 50 km north of Mumbai. The city is located on the north bank of Vasai Creek, part of the estuary of the Ulhas River...
, Salsette, and Mumbai
Mumbai
Mumbai , formerly known as Bombay in English, is the capital of the Indian state of Maharashtra. It is the most populous city in India, and the fourth most populous city in the world, with a total metropolitan area population of approximately 20.5 million...
. The rest of the northern province, with the exception of Daman and Diu, was lost to the Maratha Empire
Maratha Empire
The Maratha Empire or the Maratha Confederacy was an Indian imperial power that existed from 1674 to 1818. At its peak, the empire covered much of South Asia, encompassing a territory of over 2.8 million km²....
in the early 18th century.
In 1661 Portugal was at war against Spain and needed support from England
Kingdom of England
The Kingdom of England was, from 927 to 1707, a sovereign state to the northwest of continental Europe. At its height, the Kingdom of England spanned the southern two-thirds of the island of Great Britain and several smaller outlying islands; what today comprises the legal jurisdiction of England...
, which led to the signing of the agreement for a marriage between Princess Catherine of Portugal
Catherine of Braganza
Catherine of Braganza was a Portuguese infanta and queen consort of England, Scotland and Ireland as the wife of King Charles II.She married the king in 1662...
and Charles II of England
Charles II of England
Charles II was monarch of the three kingdoms of England, Scotland, and Ireland.Charles II's father, King Charles I, was executed at Whitehall on 30 January 1649, at the climax of the English Civil War...
, with a dowry that included the city of Bombay. This was the beginning of the English presence
English colonial empire
The English colonial empire consisted of a variety of overseas territories colonized, conquered, or otherwise acquired by the former Kingdom of England between the late 16th and early 18th centuries....
in India.
Dutch

Dutch East India Company
The Dutch East India Company was a chartered company established in 1602, when the States-General of the Netherlands granted it a 21-year monopoly to carry out colonial activities in Asia...
established trading posts on different parts along the Indian coast. For some while, they controlled the Malabar
Dutch Malabar
Malabar, also known by the name of its main settlement Cochin, was a commandment of the Dutch East India Company on the Malabar Coast between 1661 and 1795, and is part of what is today collectively referred to as Dutch India...
southwest coast (Cranganore/Cranganor/Kodungallor, Cochin de Cima/Pallipuram, Cochin, Cochin de Baixo/Santa Cruz
Santa Cruz, Goa
Santa Cruz or Calaphur is a village-suburb of the Goan state capital of Panaji .-Basics:Santa Cruz is the largest village in Goa with a population of 21,000 people all from different religions and also from different parts of India...
, Quilon
Quilon
Quilon may refer to,* Venad, a former state on Malabar Coast, India* Kollam , Kerala state, India* Kollam district, Kerala state...
(Coylan), Cannanore
Kannur
Kannur , also known as Cannanore, is a city in Kannur district in the Indian state of Kerala. It is the administrative headquarters of the District of Kannur and 518km north of state capital Trivandrum. During British rule in India, Kannur was known by its old name Cannanore, which is still in...
, Kundapura
Kundapura
-Languages and culture :The town mainly consists of Kannadigas who speak Kundagannada, Konkanis and Tuluvas. The Goud Saraswat Brahmins who fled Goa during the Portuguese arrival in the 16th century arrived by Boat in Basrur and some settled in Kundapura and surrounding villages. These people and...
, Kayankulam, Ponnani) and the Coromandel
Coromandel Coast
The Coromandel Coast is the name given to the southeastern coast of the Indian Subcontinent between Cape Comorin and False Divi Point...
southeastern coast (Golkonda, Bimilipatnam, Jaggernaikpoeram/Kakinada
Kakinada
Kakinada is a city and a municipal corporation in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is located east of the state capital, Hyderabad. It is also the headquarters of East Godavari district. It is nicknamed "Fertilizer City" , "Pensioner's Paradise" and "Second Madras"...
, Palikol, Pulicat
Pulicat
Pulicat is a historic seashore town in Thiruvallur District, of Tamil Nadu state, South India. It is about 60 km north of Chennai and 3 km from Elavur, on the barrier island of Sriharikota, which separates Pulicat Lake from the Bay of Bengal. Pulicat lake is a shallow salt water lagoon...
, Porto Novo/Parangippettai, Negapatnam) and Surat (1616–1795). They conquered Ceylon from the Portuguese. The Dutch also established trading stations in Travancore
Travancore
Kingdom of Travancore was a former Hindu feudal kingdom and Indian Princely State with its capital at Padmanabhapuram or Trivandrum ruled by the Travancore Royal Family. The Kingdom of Travancore comprised most of modern day southern Kerala, Kanyakumari district, and the southernmost parts of...
and coastal Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu is one of the 28 states of India. Its capital and largest city is Chennai. Tamil Nadu lies in the southernmost part of the Indian Peninsula and is bordered by the union territory of Pondicherry, and the states of Kerala, Karnataka, and Andhra Pradesh...
as well as at Rajshahi
Rajshahi
The city of Rajshahi is the divisional headquarters of Rajshahi division as well as the administrative district that bears its name and is one of the six metropolitan cities of Bangladesh. Often referred to as Silk City and Education City, Rajshahi is located in the north-west of the country and...
in present-day Bangladesh
Bangladesh
Bangladesh , officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh is a sovereign state located in South Asia. It is bordered by India on all sides except for a small border with Burma to the far southeast and by the Bay of Bengal to the south...
, Pipely, Hugli-Chinsura, and Murshidabad
Murshidabad
Murshidabad is a city in Murshidabad district of West Bengal state in India. The city of Murshidabad is located on the southern bank of the Bhagirathi, a distributary of the Ganges River. It was the capital of undivided Bengal during the Mughal rule. Nawabs of Bengal used to rule Bengal from this...
in present-day West Bengal
West Bengal
West Bengal is a state in the eastern region of India and is the nation's fourth-most populous. It is also the seventh-most populous sub-national entity in the world, with over 91 million inhabitants. A major agricultural producer, West Bengal is the sixth-largest contributor to India's GDP...
, Balasore
Balasore
Balasore is a strategically located city in the state of Orissa, about north of the state capital Bhubaneswar, in eastern India. It is the administrative headquarters of Balasore district. It is best known for Chandipur beach. It is also the site of the Indian Ballistic Missile Defense...
(Baleshwar or Bellasoor) in Orissa
Orissa
Orissa , officially Odisha since Nov 2011, is a state of India, located on the east coast of India, by the Bay of Bengal. It is the modern name of the ancient nation of Kalinga, which was invaded by the Maurya Emperor Ashoka in 261 BC. The modern state of Orissa was established on 1 April...
, and Ava
Ava
Innwa is a city in the Mandalay Division of Burma , situated just to the south of Amarapura on the Ayeyarwady River. Its formal title is Ratanapura , which means City of Gems in Pali. The name Innwa means mouth of the lake, which comes from in , meaning lake, and wa , which means mouth...
, Arakan
Rakhine State
Rakhine State is a Burmese state. Situated on the western coast, it is bordered by Chin State in the north, Magway Region, Bago Region and Ayeyarwady Region in the east, the Bay of Bengal to the west, and the Chittagong Division of Bangladesh to the northwest. It is located approximately between...
, and Syriam in present-day Myanmar
Myanmar
Burma , officially the Republic of the Union of Myanmar , is a country in Southeast Asia. Burma is bordered by China on the northeast, Laos on the east, Thailand on the southeast, Bangladesh on the west, India on the northwest, the Bay of Bengal to the southwest, and the Andaman Sea on the south....
(Burma). Ceylon was lost at the Congress of Vienna
Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna was a conference of ambassadors of European states chaired by Klemens Wenzel von Metternich, and held in Vienna from September, 1814 to June, 1815. The objective of the Congress was to settle the many issues arising from the French Revolutionary Wars, the Napoleonic Wars,...
in the aftermath of the Napoleonic Wars
Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars were a series of wars declared against Napoleon's French Empire by opposing coalitions that ran from 1803 to 1815. As a continuation of the wars sparked by the French Revolution of 1789, they revolutionised European armies and played out on an unprecedented scale, mainly due to...
, where the Dutch having fallen subject to France, saw their colonies raided by Britain. The Dutch later became less involved in India, as they had the Dutch East Indies
Dutch East Indies
The Dutch East Indies was a Dutch colony that became modern Indonesia following World War II. It was formed from the nationalised colonies of the Dutch East India Company, which came under the administration of the Netherlands government in 1800....
(now Indonesia
Indonesia
Indonesia , officially the Republic of Indonesia , is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania. Indonesia is an archipelago comprising approximately 13,000 islands. It has 33 provinces with over 238 million people, and is the world's fourth most populous country. Indonesia is a republic, with an...
) as their prized possession.
Rivalry with the Netherlands
At the end of the 16th century, EnglandKingdom of England
The Kingdom of England was, from 927 to 1707, a sovereign state to the northwest of continental Europe. At its height, the Kingdom of England spanned the southern two-thirds of the island of Great Britain and several smaller outlying islands; what today comprises the legal jurisdiction of England...
and the United Netherlands
Dutch Republic
The Dutch Republic — officially known as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands , the Republic of the United Netherlands, or the Republic of the Seven United Provinces — was a republic in Europe existing from 1581 to 1795, preceding the Batavian Republic and ultimately...
began to challenge Portugal's monopoly of trade with Asia, forming private joint-stock companies
Joint stock company
A joint-stock company is a type of corporation or partnership involving two or more individuals that own shares of stock in the company...
to finance the voyages—the English
East India Company
The East India Company was an early English joint-stock company that was formed initially for pursuing trade with the East Indies, but that ended up trading mainly with the Indian subcontinent and China...
, later British, and the Dutch
Dutch East India Company
The Dutch East India Company was a chartered company established in 1602, when the States-General of the Netherlands granted it a 21-year monopoly to carry out colonial activities in Asia...
East India Companies, which were chartered in 1600 and 1602 respectively. The primary aim of these companies was to tap into the lucrative spice trade
Spice trade
Civilizations of Asia were involved in spice trade from the ancient times, and the Greco-Roman world soon followed by trading along the Incense route and the Roman-India routes...
, and they focused their efforts on the areas of production, the Indonesia
Indonesia
Indonesia , officially the Republic of Indonesia , is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania. Indonesia is an archipelago comprising approximately 13,000 islands. It has 33 provinces with over 238 million people, and is the world's fourth most populous country. Indonesia is a republic, with an...
n archipelago
Archipelago
An archipelago , sometimes called an island group, is a chain or cluster of islands. The word archipelago is derived from the Greek ἄρχι- – arkhi- and πέλαγος – pélagos through the Italian arcipelago...
and especially the "Spice Islands
Maluku Islands
The Maluku Islands are an archipelago that is part of Indonesia, and part of the larger Maritime Southeast Asia region. Tectonically they are located on the Halmahera Plate within the Molucca Sea Collision Zone...
", and on India as an important market for the trade. The close proximity of London
London
London is the capital city of :England and the :United Kingdom, the largest metropolitan area in the United Kingdom, and the largest urban zone in the European Union by most measures. Located on the River Thames, London has been a major settlement for two millennia, its history going back to its...
and Amsterdam
Amsterdam
Amsterdam is the largest city and the capital of the Netherlands. The current position of Amsterdam as capital city of the Kingdom of the Netherlands is governed by the constitution of August 24, 1815 and its successors. Amsterdam has a population of 783,364 within city limits, an urban population...
across the North Sea
North Sea
In the southwest, beyond the Straits of Dover, the North Sea becomes the English Channel connecting to the Atlantic Ocean. In the east, it connects to the Baltic Sea via the Skagerrak and Kattegat, narrow straits that separate Denmark from Norway and Sweden respectively...
, and the intense rivalry between England and the Netherlands, inevitably led to conflict between the two companies, with the Dutch gaining the upper hand in the Moluccas
Maluku Islands
The Maluku Islands are an archipelago that is part of Indonesia, and part of the larger Maritime Southeast Asia region. Tectonically they are located on the Halmahera Plate within the Molucca Sea Collision Zone...
(previously a Portuguese stronghold) after the withdrawal of the English in 1622, but with the English enjoying more success in India, at Surat
Surat
Surat , also known as Suryapur, is the commercial capital city of the Indian state of Gujarat. Surat is India's Eighth most populous city and Ninth-most populous urban agglomeration. It is also administrative capital of Surat district and one of the fastest growing cities in India. The city proper...
, after the establishment of a factory
Factory (trading post)
Factory was the English term for the trading posts system originally established by Europeans in foreign territories, first within different states of medieval Europe, and later in their colonial possessions...
in 1613.

Anglo-Dutch Wars
The Anglo–Dutch Wars were a series of wars fought between the English and the Dutch in the 17th and 18th centuries for control over the seas and trade routes. The first war took place during the English Interregnum, and was fought between the Commonwealth of England and the Dutch Republic...
of the 17th century left the Dutch as the dominant naval and trading power in Asia. Hostilities ceased after the Glorious Revolution
Glorious Revolution
The Glorious Revolution, also called the Revolution of 1688, is the overthrow of King James II of England by a union of English Parliamentarians with the Dutch stadtholder William III of Orange-Nassau...
of 1688, when the Dutch William of Orange
William III of England
William III & II was a sovereign Prince of Orange of the House of Orange-Nassau by birth. From 1672 he governed as Stadtholder William III of Orange over Holland, Zeeland, Utrecht, Guelders, and Overijssel of the Dutch Republic. From 1689 he reigned as William III over England and Ireland...
ascended the English throne, bringing peace between the Netherlands and England. A deal between the two nations left the more valuable spice trade of the Indonesian archipelago to the Netherlands and the textiles industry of India to England, but textiles overtook spices in terms of profitability, so that by 1720, in terms of sales, the English company had overtaken the Dutch. The English East India Company shifted its focus from Surat—a hub of the spice trade network—to Fort St. George.
East India Company
In 1757 Mir JafarMir Jafar
-Notes:# "Riyazu-s-salatin", Ghulam Husain Salim - a reference to the appointment of Mohanlal can be found # "Seir Muaqherin", Ghulam Husain Tabatabai - a reference to the conspiracy can be found...
, the commander in chief of the army of the Nawab of Bengal
Nawab of Bengal
The Nawabs of Bengal were the hereditary nazims or subadars of the subah of Bengal during the Mughal rule and the de-facto rulers of the province.-History:...
, along with Jagat Seth
Jagat Seth
Jagat Seth was a rich businessman from Murshidabad during the rule of Nawab Siraj-ud-Daula. He came from a rich Jain Marwari business family in Murshidabad. His spiritual guru was Jain Acharya Sri BhratruChandra Suri. Jagat Seths were among the most powerful bankers of India during the first half...
, Maharaja Krishna Nath, Umi Chand and some others, secretly connived with the British
Kingdom of Great Britain
The former Kingdom of Great Britain, sometimes described as the 'United Kingdom of Great Britain', That the Two Kingdoms of Scotland and England, shall upon the 1st May next ensuing the date hereof, and forever after, be United into One Kingdom by the Name of GREAT BRITAIN. was a sovereign...
asking logistic support to overthrow the Nawab in return for trade grants. The British forces, whose sole duty until then was guarding their British East India Company
British East India Company
The East India Company was an early English joint-stock company that was formed initially for pursuing trade with the East Indies, but that ended up trading mainly with the Indian subcontinent and China...
property, were numerically inferior to the Bengali
Bengali people
The Bengali people are an ethnic community native to the historic region of Bengal in South Asia. They speak Bengali , which is an Indo-Aryan language of the eastern Indian subcontinent, evolved from the Magadhi Prakrit and Sanskrit languages. In their native language, they are referred to as বাঙালী...
armed forces. At the Battle of Plassey
Battle of Plassey
The Battle of Plassey , 23 June 1757, was a decisive British East India Company victory over the Nawab of Bengal and his French allies, establishing Company rule in South Asia which expanded over much of the Indies for the next hundred years...
on 23 June 1757, fought between the British under the command of Robert Clive and the Nawab, Mir Jafar's forces betrayed the Nawab and helped defeat him. Jafar was installed on the throne as a British subservient ruler. The battle transformed British perspective as they realized their strength and potential to conquer smaller Indian kingdoms and marked the beginning of the imperial or colonial era.

East India Company
The East India Company was an early English joint-stock company that was formed initially for pursuing trade with the East Indies, but that ended up trading mainly with the Indian subcontinent and China...
drove the expansion of the British Empire
British Empire
The British Empire comprised the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom. It originated with the overseas colonies and trading posts established by England in the late 16th and early 17th centuries. At its height, it was the...
in Asia. The company's army had first joined forces with the Royal Navy
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy is the naval warfare service branch of the British Armed Forces. Founded in the 16th century, it is the oldest service branch and is known as the Senior Service...
during the Seven Years' War
Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War was a global military war between 1756 and 1763, involving most of the great powers of the time and affecting Europe, North America, Central America, the West African coast, India, and the Philippines...
, and the two continued to cooperate in arenas outside India: the eviction of Napoleon from Egypt
Egypt
Egypt , officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, Arabic: , is a country mainly in North Africa, with the Sinai Peninsula forming a land bridge in Southwest Asia. Egypt is thus a transcontinental country, and a major power in Africa, the Mediterranean Basin, the Middle East and the Muslim world...
(1799), the capture of Java
Java
Java is an island of Indonesia. With a population of 135 million , it is the world's most populous island, and one of the most densely populated regions in the world. It is home to 60% of Indonesia's population. The Indonesian capital city, Jakarta, is in west Java...
from the Netherlands (1811), the acquisition of Singapore
Singapore
Singapore , officially the Republic of Singapore, is a Southeast Asian city-state off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, north of the equator. An island country made up of 63 islands, it is separated from Malaysia by the Straits of Johor to its north and from Indonesia's Riau Islands by the...
(1819) and Malacca
Malacca
Malacca , dubbed The Historic State or Negeri Bersejarah among locals) is the third smallest Malaysian state, after Perlis and Penang. It is located in the southern region of the Malay Peninsula, on the Straits of Malacca. It borders Negeri Sembilan to the north and the state of Johor to the south...
(1824), and the defeat of Burma (1826).
From its base in India, the company had also been engaged in an increasingly profitable opium
Opium
Opium is the dried latex obtained from the opium poppy . Opium contains up to 12% morphine, an alkaloid, which is frequently processed chemically to produce heroin for the illegal drug trade. The latex also includes codeine and non-narcotic alkaloids such as papaverine, thebaine and noscapine...
export trade to China since the 1730s. This trade, unlawful in China since it was outlawed by the Qing dynasty
Qing Dynasty
The Qing Dynasty was the last dynasty of China, ruling from 1644 to 1912 with a brief, abortive restoration in 1917. It was preceded by the Ming Dynasty and followed by the Republic of China....
in 1729, helped reverse the trade imbalances resulting from the British imports of tea
Tea
Tea is an aromatic beverage prepared by adding cured leaves of the Camellia sinensis plant to hot water. The term also refers to the plant itself. After water, tea is the most widely consumed beverage in the world...
, which saw large outflows of silver from Britain to China. In 1839, the confiscation by the Chinese authorities at Canton
Guangzhou
Guangzhou , known historically as Canton or Kwangchow, is the capital and largest city of the Guangdong province in the People's Republic of China. Located in southern China on the Pearl River, about north-northwest of Hong Kong, Guangzhou is a key national transportation hub and trading port...
of 20,000 chests of opium led Britain to attack China in the First Opium War
First Opium War
The First Anglo-Chinese War , known popularly as the First Opium War or simply the Opium War, was fought between the United Kingdom and the Qing Dynasty of China over their conflicting viewpoints on diplomatic relations, trade, and the administration of justice...
, and the seizure by Britain of the island of Hong Kong
Hong Kong
Hong Kong is one of two Special Administrative Regions of the People's Republic of China , the other being Macau. A city-state situated on China's south coast and enclosed by the Pearl River Delta and South China Sea, it is renowned for its expansive skyline and deep natural harbour...
, at that time a minor settlement.
The British had direct or indirect control over all of present-day India before the middle of the 19th century. In 1857, a local rebellion by an army of sepoy
Sepoy
A sepoy was formerly the designation given to an Indian soldier in the service of a European power. In the modern Indian Army, Pakistan Army and Bangladesh Army it remains in use for the rank of private soldier.-Etymology and Historical usage:...
s escalated into the Rebellion of 1857, which took six months to suppress with heavy loss of life on both sides. This resistance, although short-lived, was triggered by British attempts to Westernise India. As a result, the East India Company lost its powers of government and British India formally came under direct British rule
British Raj
British Raj was the British rule in the Indian subcontinent between 1858 and 1947; The term can also refer to the period of dominion...
, with an appointed governor-general
Governor-General of India
The Governor-General of India was the head of the British administration in India, and later, after Indian independence, the representative of the monarch and de facto head of state. The office was created in 1773, with the title of Governor-General of the Presidency of Fort William...
administering India. The East India Company was dissolved the following year in 1858. A few years later, Queen Victoria took the title of Empress of India..
India suffered a series of serious crop failures in the late 19th century, leading to widespread famines
Famine in India
Famine has been a recurrent feature of life in the Indian sub-continental countries of India, Pakistan and Bangladesh, and reached its numerically deadliest peak in the late eighteenth and nineteenth centuries. Historical and legendary evidence names some 90 famines in 2,500 years of history. There...
in which at least 10 million people died. The East India Company had failed to implement any coordinated policy to deal with the famines during its period of rule. This changed during the Raj
British Raj
British Raj was the British rule in the Indian subcontinent between 1858 and 1947; The term can also refer to the period of dominion...
, in which commissions were set up after each famine to investigate the causes and implement new policies, which took until the early 1900s to have an effect.
The slow but momentous reform movement developed gradually into the Indian Independence Movement
Indian independence movement
The term Indian independence movement encompasses a wide area of political organisations, philosophies, and movements which had the common aim of ending first British East India Company rule, and then British imperial authority, in parts of South Asia...
. During the years of World War I
World War I
World War I , which was predominantly called the World War or the Great War from its occurrence until 1939, and the First World War or World War I thereafter, was a major war centred in Europe that began on 28 July 1914 and lasted until 11 November 1918...
, the hitherto bourgeois "home-rule" movement was transformed into a popular mass movement by Mahatma Gandhi
Mahatma Gandhi
Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi , pronounced . 2 October 1869 – 30 January 1948) was the pre-eminent political and ideological leader of India during the Indian independence movement...
, a pacifist. Apart from Gandhi, other revolutionaries such as Shaheed Bhagat Singh, Chandrashekar Azad and Subhash Chandra Bose
Subhash Chandra Bose
Subhas Chandra Bose known by name Netaji was an Indian revolutionary who led an Indian national political and military force against Britain and the Western powers during World War II. Bose was one of the most prominent leaders in the Indian independence movement and is a legendary figure in...
, were not against use of violence to oppose the British rule. The independence movement attained its objective with the independence of Pakistan and India on 14 August and 15 August 1947 respectively.
French
Following the Portuguese, English, and Dutch, the FrenchFrance
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
also established trading bases in India. Their first establishment was in Pondicherry on the Coromandel Coast
Coromandel Coast
The Coromandel Coast is the name given to the southeastern coast of the Indian Subcontinent between Cape Comorin and False Divi Point...
in southeastern India in 1674. Subsequent French settlements were Chandernagore in Bengal, northeastern India in 1688, Yanam in Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh , is one of the 28 states of India, situated on the southeastern coast of India. It is India's fourth largest state by area and fifth largest by population. Its capital and largest city by population is Hyderabad.The total GDP of Andhra Pradesh is $100 billion and is ranked third...
in 1723, Mahe in 1725, and Karaikal
Karaikal
Karaikal is a major port city of east coast of India and a municipality in Karaikal district in the Union Territory of Pondicherry, India. Several explanations are offered for the word 'Karaikal'. The imperial Gazetteer gives it the meaning 'fish pass'. According to Julien vinson the town is said...
in 1739. The French were constantly in conflict with the Dutch and later on mainly with the British in India. At the height of French power in the mid-18th century, the French occupied large areas of southern India and the area lying in today's northern Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh , is one of the 28 states of India, situated on the southeastern coast of India. It is India's fourth largest state by area and fifth largest by population. Its capital and largest city by population is Hyderabad.The total GDP of Andhra Pradesh is $100 billion and is ranked third...
and Orissa
Orissa
Orissa , officially Odisha since Nov 2011, is a state of India, located on the east coast of India, by the Bay of Bengal. It is the modern name of the ancient nation of Kalinga, which was invaded by the Maurya Emperor Ashoka in 261 BC. The modern state of Orissa was established on 1 April...
. Between 1744 and 1761, the British and the French repeatedly attacked and conquered each other's forts and towns in southeastern India and in Bengal in the northeast. After some initial French successes, the British decisively defeated the French in Bengal in the Battle of Plassey
Battle of Plassey
The Battle of Plassey , 23 June 1757, was a decisive British East India Company victory over the Nawab of Bengal and his French allies, establishing Company rule in South Asia which expanded over much of the Indies for the next hundred years...
in 1757 and in the southeast in 1761 in the Battle of Wandiwash
Battle of Wandiwash
The Battle of Wandiwash was a decisive battle in India during the Seven Years' War. The Count de Lally's army, burdened by a lack of naval support and funds, attempted to regain the fort at Vandavasi near Pondicherry. He was attacked by Sir Eyre Coote's forces and decisively defeated...
, after which the British East India Company was the supreme military and political power in southern India as well as in Bengal. In the following decades it gradually increased the size of the territories under its control. The enclaves of Pondicherry, Karaikal, Yanam, Mahé and Chandernagore were returned to France in 1816 and were integrated with the Republic of India after its independence in 1947.
Danish
DenmarkDenmark
Denmark is a Scandinavian country in Northern Europe. The countries of Denmark and Greenland, as well as the Faroe Islands, constitute the Kingdom of Denmark . It is the southernmost of the Nordic countries, southwest of Sweden and south of Norway, and bordered to the south by Germany. Denmark...
was a minor colonial power to set foot in India. It established trading outposts in Tranquebar
Tranquebar
Tharangambadi is a panchayat town in Nagapattinam district in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu, 15 km north of Karaikal, near the mouth of a distributary of the Kaveri River. Its name means "place of the singing waves"...
, Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu is one of the 28 states of India. Its capital and largest city is Chennai. Tamil Nadu lies in the southernmost part of the Indian Peninsula and is bordered by the union territory of Pondicherry, and the states of Kerala, Karnataka, and Andhra Pradesh...
(1620), Serampore
Serampore
Serampore is a city and a municipality in Hooghly district in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is a part of the area covered by Kolkata Metropolitan Development Authority. It is a pre-colonial town on the right bank of the Hoogli River...
, West Bengal (1755) and the Nicobar Islands
Nicobar Islands
The Nicobar Islands are an archipelagic island chain in the eastern Indian Ocean...
(1750s). At one time, the main Danish and Swedish East Asia companies together imported more tea
Tea
Tea is an aromatic beverage prepared by adding cured leaves of the Camellia sinensis plant to hot water. The term also refers to the plant itself. After water, tea is the most widely consumed beverage in the world...
to Europe than the British did. Their outposts lost economic and strategic importance, and Tranquebar, the last Danish outpost, was sold to the British in 1845.
Other external powers
The SpanishSpanish Empire
The Spanish Empire comprised territories and colonies administered directly by Spain in Europe, in America, Africa, Asia and Oceania. It originated during the Age of Exploration and was therefore one of the first global empires. At the time of Habsburgs, Spain reached the peak of its world power....
were briefly given territorial rights to India by Pope Alexander VI
Pope Alexander VI
Pope Alexander VI , born Roderic Llançol i Borja was Pope from 1492 until his death on 18 August 1503. He is one of the most controversial of the Renaissance popes, and his Italianized surname—Borgia—became a byword for the debased standards of the Papacy of that era, most notoriously the Banquet...
on 25 September 1493 by the bull
Papal bull
A Papal bull is a particular type of letters patent or charter issued by a Pope of the Catholic Church. It is named after the bulla that was appended to the end in order to authenticate it....
Dudum siquidem before these rights were removed by the Treaty of Tordesillas
Treaty of Tordesillas
The Treaty of Tordesillas , signed at Tordesillas , , divided the newly discovered lands outside Europe between Spain and Portugal along a meridian 370 leagueswest of the Cape Verde islands...
less than one year later. The Japanese briefly occupied the Andaman and Nicobar Islands during World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
.
Wars
The wars that took place involving the British East India Company or British India during the Colonial era:- Anglo-Mysore WarsAnglo-Mysore WarsThe Anglo-Mysore Wars were a series of wars fought in India over the last three decades of the 18th century between the Kingdom of Mysore and the British East India Company, represented chiefly by the Madras Presidency...
- First Anglo-Maratha WarFirst Anglo-Maratha WarThe First Anglo-Maratha War was the first of three Anglo-Maratha wars fought between the British East India Company and Maratha Empire in India. The war began with the Treaty of Surat and ended with the Treaty of Salbai.-Background:...
- Second Anglo-Maratha WarSecond Anglo-Maratha WarThe Second Anglo-Maratha War was the second conflict between the British East India Company and the Maratha Empire in India.-Background:...
- Third Anglo-Maratha WarThird Anglo-Maratha WarThe Third Anglo-Maratha War was the final and decisive conflict between the British East India Company and the Maratha Empire in India. The war left the Company in control of most of India. It began with an invasion of Maratha territory by 110,400 British East India Company troops, the largest...
- First Anglo-Sikh WarFirst Anglo-Sikh WarThe First Anglo-Sikh War was fought between the Sikh Empire and the British East India Company between 1845 and 1846. It resulted in partial subjugation of the Sikh kingdom.-Background and causes of the war:...
- Second Anglo-Sikh WarSecond Anglo-Sikh WarThe Second Anglo-Sikh War took place in 1848 and 1849, between the Sikh Empire and the British East India Company. It resulted in the subjugation of the Sikh Empire, and the annexation of the Punjab and what subsequently became the North-West Frontier Province by the East India Company.-Background...
- Gurkha WarGurkha WarThe Gurkha War , sometimes called the Gorkha War or the Anglo–Nepalese War, was fought between the Kingdom of Nepal and the British East India Company as a result of border tensions and ambitious expansionism...
- Burmese WarBurmese WarThere have been three Burmese Wars or Anglo-Burmese Wars:* First Anglo-Burmese War * Second Anglo-Burmese War * Third Anglo-Burmese War -War with Britain and the fall of Burma:...
s - First Opium WarFirst Opium WarThe First Anglo-Chinese War , known popularly as the First Opium War or simply the Opium War, was fought between the United Kingdom and the Qing Dynasty of China over their conflicting viewpoints on diplomatic relations, trade, and the administration of justice...
- Second Opium WarSecond Opium WarThe Second Opium War, the Second Anglo-Chinese War, the Second China War, the Arrow War, or the Anglo-French expedition to China, was a war pitting the British Empire and the Second French Empire against the Qing Dynasty of China, lasting from 1856 to 1860...
- First Anglo-Afghan WarFirst Anglo-Afghan WarThe First Anglo-Afghan War was fought between British India and Afghanistan from 1839 to 1842. It was one of the first major conflicts during the Great Game, the 19th century competition for power and influence in Central Asia between the United Kingdom and Russia, and also marked one of the worst...
- Second Anglo-Afghan WarSecond Anglo-Afghan WarThe Second Anglo-Afghan War was fought between the United Kingdom and Afghanistan from 1878 to 1880, when the nation was ruled by Sher Ali Khan of the Barakzai dynasty, the son of former Emir Dost Mohammad Khan. This was the second time British India invaded Afghanistan. The war ended in a manner...
- Third Anglo-Afghan WarThird Anglo-Afghan WarThe Third Anglo-Afghan War began on 6 May 1919 and ended with an armistice on 8 August 1919. It was a minor tactical victory for the British. For the British, the Durand Line was reaffirmed as the political boundary between the Emirate of Afghanistan and British India and the Afghans agreed not to...
- World War IWorld War IWorld War I , which was predominantly called the World War or the Great War from its occurrence until 1939, and the First World War or World War I thereafter, was a major war centred in Europe that began on 28 July 1914 and lasted until 11 November 1918...
, see List of Indian divisions in World War I, Bombardment of MadrasBombardment of MadrasThe Bombardment of Madras was an engagement of World War I, at Madras in British India, now the modern day Chennai. The bombardment was initiated by the German light cruiser Emden at the start of the war in 1914.... - World War IIWorld War IIWorld War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
See also
- Maratha EmpireMaratha EmpireThe Maratha Empire or the Maratha Confederacy was an Indian imperial power that existed from 1674 to 1818. At its peak, the empire covered much of South Asia, encompassing a territory of over 2.8 million km²....
- Sikh Empire
- MacaulayismMacaulayismMacaulayism is the conscious policy of liquidating indigenous culture through the planned substitution of the alien culture of a colonizing power via the education system...
- List of Indian Princely States
- Hyderabad StateHyderabad State-After Indian independence :When India gained independence in 1947 and Pakistan came into existence in 1947, the British left the local rulers of the princely states the choice of whether to join one of the new dominions or to remain independent...
- Rajput StatesRajputanaRājputāna was the pre-1949 name of the present-day Indian state of Rājasthān, the largest state of the Republic of India in terms of area. George Thomas was the first in 1800 A.D., to term this region as Rajputana...
- Kingdom of Calicut
- Kingdom of MysoreKingdom of MysoreThe Kingdom of Mysore was a kingdom of southern India, traditionally believed to have been founded in 1399 in the vicinity of the modern city of Mysore. The kingdom, which was ruled by the Wodeyar family, initially served as a vassal state of the Vijayanagara Empire...
- Kingdom of Travancore
Further reading
- Andrada (undated). The Life of Dom John de Castro: The Fourth Vice Roy of India. Jacinto Freire de Andrada. Translated into English by Peter Wyche. (1664). Henry Herrington, New Exchange, London. Facsimilie edition (1994) AES Reprint, New Delhi. ISBN 81-206-0900-X.

