
Convex uniform honeycombs in hyperbolic space
Encyclopedia

Geometry
Geometry arose as the field of knowledge dealing with spatial relationships. Geometry was one of the two fields of pre-modern mathematics, the other being the study of numbers ....
, a convex uniform honeycomb
Convex uniform honeycomb
In geometry, a convex uniform honeycomb is a uniform tessellation which fills three-dimensional Euclidean space with non-overlapping convex uniform polyhedral cells.Twenty-eight such honeycombs exist:* the familiar cubic honeycomb and 7 truncations thereof;...
is a tessellation
Tessellation
A tessellation or tiling of the plane is a pattern of plane figures that fills the plane with no overlaps and no gaps. One may also speak of tessellations of parts of the plane or of other surfaces. Generalizations to higher dimensions are also possible. Tessellations frequently appeared in the art...
of convex uniform polyhedron
Uniform polyhedron
A uniform polyhedron is a polyhedron which has regular polygons as faces and is vertex-transitive...
cells
Cell (geometry)
In geometry, a cell is a three-dimensional element that is part of a higher-dimensional object.- In polytopes :A cell is a three-dimensional polyhedron element that is part of the boundary of a higher-dimensional polytope, such as a polychoron or honeycomb For example, a cubic honeycomb is made...
. In 3-dimensional hyperbolic space
Hyperbolic space
In mathematics, hyperbolic space is a type of non-Euclidean geometry. Whereas spherical geometry has a constant positive curvature, hyperbolic geometry has a negative curvature: every point in hyperbolic space is a saddle point...
there are nine Coxeter group
Coxeter group
In mathematics, a Coxeter group, named after H.S.M. Coxeter, is an abstract group that admits a formal description in terms of mirror symmetries. Indeed, the finite Coxeter groups are precisely the finite Euclidean reflection groups; the symmetry groups of regular polyhedra are an example...
families of compact convex uniform honeycomb
Convex uniform honeycomb
In geometry, a convex uniform honeycomb is a uniform tessellation which fills three-dimensional Euclidean space with non-overlapping convex uniform polyhedral cells.Twenty-eight such honeycombs exist:* the familiar cubic honeycomb and 7 truncations thereof;...
s, generated as Wythoff construction
Wythoff construction
In geometry, a Wythoff construction, named after mathematician Willem Abraham Wythoff, is a method for constructing a uniform polyhedron or plane tiling. It is often referred to as Wythoff's kaleidoscopic construction.- Construction process :...
s, and represented by ring permutations of the Coxeter–Dynkin diagrams for each family.
Nine Coxeter group families
By Coxeter groupCoxeter group
In mathematics, a Coxeter group, named after H.S.M. Coxeter, is an abstract group that admits a formal description in terms of mirror symmetries. Indeed, the finite Coxeter groups are precisely the finite Euclidean reflection groups; the symmetry groups of regular polyhedra are an example...
and Coxeter–Dynkin diagrams, the nine are:
| # | Witt symbol |
Coxeter symbol |
Coxeter graph |
Honeycombs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 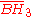 |
[4,3,5] | 15 forms | |
| 2 | 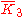 |
[5,3,5] | 9 forms | |
| 2 | 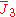 |
[3,5,3] | 9 forms | |
| 4 | 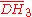 |
[5,31,1] | 11 forms (7 overlap with [5,3,4] family, 4 are unique) | |
| 5 | 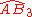 |
[(3,3,3,4)] | 9 forms | |
| 6 | 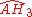 |
[(3,3,3,5)] | 9 forms | |
| 7 |  |
[(3,4,3,4)] | 6 forms | |
| 8 | 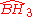 |
[(3,4,3,5)] | 9 forms | |
| 9 | 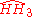 |
[(3,5,3,5)] | 6 forms |
These 9 families generate a total of 76 unique uniform honeycombs.
The full list of hyperbolic uniform honeycombs has not been proven and an unknown number of non-Wythoffian forms exist. One known example is cited with the {3,5,3} family below.
Noncompact honeycombs
There are also 23 noncompact Coxeter groupCoxeter group
In mathematics, a Coxeter group, named after H.S.M. Coxeter, is an abstract group that admits a formal description in terms of mirror symmetries. Indeed, the finite Coxeter groups are precisely the finite Euclidean reflection groups; the symmetry groups of regular polyhedra are an example...
s of rank 4. These families can produce uniform honeycombs with infinite or unbounded facets or vertex figure
Vertex figure
In geometry a vertex figure is, broadly speaking, the figure exposed when a corner of a polyhedron or polytope is sliced off.-Definitions - theme and variations:...
, including ideal vertices at infinity. These forms are not listed in this article.
| Type | Coxeter groups | Group count | Honeycomb count |
|---|---|---|---|
| linear graphs | , , , , , , | 7 | 15+9+15+15+9+15+9=87 |
| bifurcating graphs | , , | 3 | 11+11+7=29 |
| cyclic graphs | , , , , , , | 7 | |
| mixed graphs | , , , , , | 6 |
[3,5,3] family
There are 9 forms, generated by ring permutations of the Coxeter groupCoxeter group
In mathematics, a Coxeter group, named after H.S.M. Coxeter, is an abstract group that admits a formal description in terms of mirror symmetries. Indeed, the finite Coxeter groups are precisely the finite Euclidean reflection groups; the symmetry groups of regular polyhedra are an example...
: [3,5,3] or
One related non-wythoffian
Wythoff construction
In geometry, a Wythoff construction, named after mathematician Willem Abraham Wythoff, is a method for constructing a uniform polyhedron or plane tiling. It is often referred to as Wythoff's kaleidoscopic construction.- Construction process :...
form is constructed from the {3,5,3} vertex figure with 4 (tetrahedrally arranged) vertices removed, creating pentagonal antiprisms and dodecahedra filling in the gaps.
| # | Honeycomb name Coxeter–Dynkin and Schläfli symbols |
Cell counts/vertex and positions in honeycomb |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vertex figure Vertex figure In geometry a vertex figure is, broadly speaking, the figure exposed when a corner of a polyhedron or polytope is sliced off.-Definitions - theme and variations:... |
picture | ||||||
| 1 | icosahedral (Regular) t0{3,5,3} |
(20) (3.3.3.3.3) Icosahedron In geometry, an icosahedron is a regular polyhedron with 20 identical equilateral triangular faces, 30 edges and 12 vertices. It is one of the five Platonic solids.... |
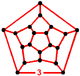 |
 |
|||
| 2 | rectified icosahedral t1{3,5,3} |
(2) (5.5.5) |
(3)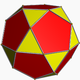 (3.5.3.5) Icosidodecahedron In geometry, an icosidodecahedron is a polyhedron with twenty triangular faces and twelve pentagonal faces. An icosidodecahedron has 30 identical vertices, with two triangles and two pentagons meeting at each, and 60 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a pentagon... |
 |
|||
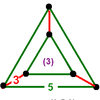
| 3 | truncated icosahedral t0,1{3,5,3} |
(1) (5.5.5) |
(3) (4.6.6) Truncated icosahedron In geometry, the truncated icosahedron is an Archimedean solid, one of thirteen convex isogonal nonprismatic solids whose faces are two or more types of regular polygons.It has 12 regular pentagonal faces, 20 regular hexagonal faces, 60 vertices and 90 edges.... |
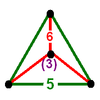 |
|||
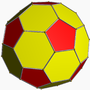
| 4 | cantellated icosahedral t0,2{3,5,3} |
(1) (3.5.3.5) Icosidodecahedron In geometry, an icosidodecahedron is a polyhedron with twenty triangular faces and twelve pentagonal faces. An icosidodecahedron has 30 identical vertices, with two triangles and two pentagons meeting at each, and 60 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a pentagon... |
(2)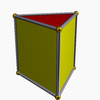 (4.4.3) Triangular prism In geometry, a triangular prism is a three-sided prism; it is a polyhedron made of a triangular base, a translated copy, and 3 faces joining corresponding sides.... |
(2) (3.5.4.5) |
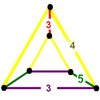 |
||
| 5 | Runcinated icosahedral t0,3{3,5,3} |
(1) (3.3.3.3.3) Icosahedron In geometry, an icosahedron is a regular polyhedron with 20 identical equilateral triangular faces, 30 edges and 12 vertices. It is one of the five Platonic solids.... |
(5) (4.4.3) Triangular prism In geometry, a triangular prism is a three-sided prism; it is a polyhedron made of a triangular base, a translated copy, and 3 faces joining corresponding sides.... |
(5) (4.4.3) Triangular prism In geometry, a triangular prism is a three-sided prism; it is a polyhedron made of a triangular base, a translated copy, and 3 faces joining corresponding sides.... |
(1) (3.3.3.3.3) Icosahedron In geometry, an icosahedron is a regular polyhedron with 20 identical equilateral triangular faces, 30 edges and 12 vertices. It is one of the five Platonic solids.... |
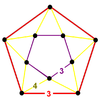 |
|
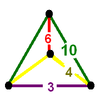
| 6 | bitruncated icosahedral t1,2{3,5,3} |
(2)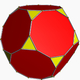 (3.10.10) Truncated dodecahedron In geometry, the truncated dodecahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 12 regular decagonal faces, 20 regular triangular faces, 60 vertices and 90 edges.- Geometric relations :... |
(2) (3.10.10) Truncated dodecahedron In geometry, the truncated dodecahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 12 regular decagonal faces, 20 regular triangular faces, 60 vertices and 90 edges.- Geometric relations :... |
 |
|||
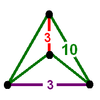
| 7 | cantitruncated icosahedral t0,1,2{3,5,3} |
(1) (3.10.10) Truncated dodecahedron In geometry, the truncated dodecahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 12 regular decagonal faces, 20 regular triangular faces, 60 vertices and 90 edges.- Geometric relations :... |
(1) (4.4.3) Triangular prism In geometry, a triangular prism is a three-sided prism; it is a polyhedron made of a triangular base, a translated copy, and 3 faces joining corresponding sides.... |
(2) (4.6.10) |
 |
||
| 8 | runcitruncated icosahedral t0,1,3{3,5,3} |
(1) (3.5.4.5) |
(1) (4.4.3) Triangular prism In geometry, a triangular prism is a three-sided prism; it is a polyhedron made of a triangular base, a translated copy, and 3 faces joining corresponding sides.... |
(2) (4.4.6) Hexagonal prism In geometry, the hexagonal prism is a prism with hexagonal base. The shape has 8 faces, 18 edges, and 12 vertices.Since it has eight faces, it is an octahedron. However, the term octahedron is primarily used to refer to the regular octahedron, which has eight triangular faces... |
(1) (4.6.6) Truncated icosahedron In geometry, the truncated icosahedron is an Archimedean solid, one of thirteen convex isogonal nonprismatic solids whose faces are two or more types of regular polygons.It has 12 regular pentagonal faces, 20 regular hexagonal faces, 60 vertices and 90 edges.... |
 |
|
| 9 | omnitruncated icosahedral t0,1,2,3{3,5,3} |
(1) (4.6.10) |
(1) (4.4.6) Hexagonal prism In geometry, the hexagonal prism is a prism with hexagonal base. The shape has 8 faces, 18 edges, and 12 vertices.Since it has eight faces, it is an octahedron. However, the term octahedron is primarily used to refer to the regular octahedron, which has eight triangular faces... |
(1) (4.4.6) Hexagonal prism In geometry, the hexagonal prism is a prism with hexagonal base. The shape has 8 faces, 18 edges, and 12 vertices.Since it has eight faces, it is an octahedron. However, the term octahedron is primarily used to refer to the regular octahedron, which has eight triangular faces... |
(1) (4.6.10) |
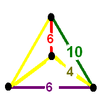 |
|
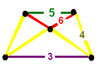
| [77] | partially truncated icosahedral pt{3,5,3} |
(4) (5.5.5) |
(12) (3.3.3.5) Pentagonal antiprism In geometry, the pentagonal antiprism is the third in an infinite set of antiprisms formed by an even-numbered sequence of triangle sides closed by two polygon caps. It consists of two pentagons joined to each other by a ring of 10 triangles for a total of 12 faces... |
 |
[5,3,4] family
There are 15 forms, generated by ring permutations of the Coxeter groupCoxeter group
In mathematics, a Coxeter group, named after H.S.M. Coxeter, is an abstract group that admits a formal description in terms of mirror symmetries. Indeed, the finite Coxeter groups are precisely the finite Euclidean reflection groups; the symmetry groups of regular polyhedra are an example...
: [5,3,4] or
| # | Name of honeycomb Coxeter–Dynkin diagram |
Cells by location and count per vertex | Vertex figure Vertex figure In geometry a vertex figure is, broadly speaking, the figure exposed when a corner of a polyhedron or polytope is sliced off.-Definitions - theme and variations:... |
Picture | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | order-4 dodecahedral (Regular) |
- | - | - | (8) (5.5.5) |
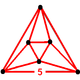 |
 |
| 11 | Rectified order-4 dodecahedral |
(2) (3.3.3.3) Octahedron In geometry, an octahedron is a polyhedron with eight faces. A regular octahedron is a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex.... |
- | - | (4) (3.5.3.5) Icosidodecahedron In geometry, an icosidodecahedron is a polyhedron with twenty triangular faces and twelve pentagonal faces. An icosidodecahedron has 30 identical vertices, with two triangles and two pentagons meeting at each, and 60 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a pentagon... |
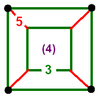 |
|
| 12 | Rectified order-5 cubic |
(5) (3.4.3.4) Cuboctahedron In geometry, a cuboctahedron is a polyhedron with eight triangular faces and six square faces. A cuboctahedron has 12 identical vertices, with two triangles and two squares meeting at each, and 24 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a square. As such it is a quasiregular polyhedron,... |
- | - | (2) (3.3.3.3.3) Icosahedron In geometry, an icosahedron is a regular polyhedron with 20 identical equilateral triangular faces, 30 edges and 12 vertices. It is one of the five Platonic solids.... |
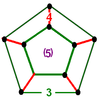 |
|
| 13 | order-5 cubic (Regular) |
(20) (4.4.4) Cube In geometry, a cube is a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets or sides, with three meeting at each vertex. The cube can also be called a regular hexahedron and is one of the five Platonic solids. It is a special kind of square prism, of rectangular parallelepiped and... |
- | - | - | 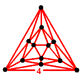 |
 |
| 14 | Truncated order-4 dodecahedral |
(1) (3.3.3.3) Octahedron In geometry, an octahedron is a polyhedron with eight faces. A regular octahedron is a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex.... |
- | - | (4) (3.10.10) Truncated dodecahedron In geometry, the truncated dodecahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 12 regular decagonal faces, 20 regular triangular faces, 60 vertices and 90 edges.- Geometric relations :... |
 |
|
| 15 | Bitruncated order-5 cubic |
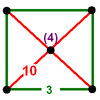
(2) (4.6.6) Truncated octahedron In geometry, the truncated octahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 14 faces , 36 edges, and 24 vertices. Since each of its faces has point symmetry the truncated octahedron is a zonohedron.... |
- | - | (2) (5.6.6) Truncated icosahedron In geometry, the truncated icosahedron is an Archimedean solid, one of thirteen convex isogonal nonprismatic solids whose faces are two or more types of regular polygons.It has 12 regular pentagonal faces, 20 regular hexagonal faces, 60 vertices and 90 edges.... |
 |
|
| 16 | Truncated order-5 cubic |
(5) (3.8.8) Truncated cube In geometry, the truncated cube, or truncated hexahedron, is an Archimedean solid. It has 14 regular faces , 36 edges, and 24 vertices.... |
- | - | (1) (3.3.3.3.3) Icosahedron In geometry, an icosahedron is a regular polyhedron with 20 identical equilateral triangular faces, 30 edges and 12 vertices. It is one of the five Platonic solids.... |
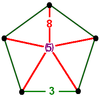 |
|
| 17 | Cantellated order-4 dodecahedral |
(1) (3.4.3.4) Cuboctahedron In geometry, a cuboctahedron is a polyhedron with eight triangular faces and six square faces. A cuboctahedron has 12 identical vertices, with two triangles and two squares meeting at each, and 24 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a square. As such it is a quasiregular polyhedron,... |
(2)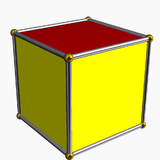 (4.4.4) Cube In geometry, a cube is a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets or sides, with three meeting at each vertex. The cube can also be called a regular hexahedron and is one of the five Platonic solids. It is a special kind of square prism, of rectangular parallelepiped and... |
- | (2) (3.4.5.4) Rhombicosidodecahedron In geometry, the rhombicosidodecahedron, or small rhombicosidodecahedron, is an Archimedean solid, one of thirteen convex isogonal nonprismatic solids constructed of two or more types of regular polygon faces.... |
 |
|
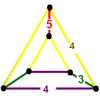
| 18 | Cantellated order-5 cubic |
(2) (3.4.4.4) Rhombicuboctahedron In geometry, the rhombicuboctahedron, or small rhombicuboctahedron, is an Archimedean solid with eight triangular and eighteen square faces. There are 24 identical vertices, with one triangle and three squares meeting at each. Note that six of the squares only share vertices with the triangles... |
- | (2) (4.4.5) Pentagonal prism In geometry, the pentagonal prism is a prism with a pentagonal base. It is a type of heptahedron with 7 faces, 15 edges, and 10 vertices.- As a semiregular polyhedron :... |
(1) (3.5.3.5) Icosidodecahedron In geometry, an icosidodecahedron is a polyhedron with twenty triangular faces and twelve pentagonal faces. An icosidodecahedron has 30 identical vertices, with two triangles and two pentagons meeting at each, and 60 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a pentagon... |
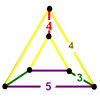 |
|
| 19 | Runcinated order-5 cubic |
(1) (4.4.4) Cube In geometry, a cube is a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets or sides, with three meeting at each vertex. The cube can also be called a regular hexahedron and is one of the five Platonic solids. It is a special kind of square prism, of rectangular parallelepiped and... |
(3) (4.4.4) Cube In geometry, a cube is a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets or sides, with three meeting at each vertex. The cube can also be called a regular hexahedron and is one of the five Platonic solids. It is a special kind of square prism, of rectangular parallelepiped and... |
(3) (4.4.5) Pentagonal prism In geometry, the pentagonal prism is a prism with a pentagonal base. It is a type of heptahedron with 7 faces, 15 edges, and 10 vertices.- As a semiregular polyhedron :... |
(1) (5.5.5) |
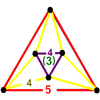 |
|
| 20 | Cantitruncated order-4 dodecahedral |
(1) (4.6.6) Truncated octahedron In geometry, the truncated octahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 14 faces , 36 edges, and 24 vertices. Since each of its faces has point symmetry the truncated octahedron is a zonohedron.... |
(1) (4.4.4) Cube In geometry, a cube is a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets or sides, with three meeting at each vertex. The cube can also be called a regular hexahedron and is one of the five Platonic solids. It is a special kind of square prism, of rectangular parallelepiped and... |
- | (2) (4.6.10) |
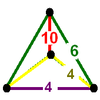 |
|
| 21 | Cantitruncated order-5 cubic |
(2) (4.6.8) |
- | (1) (4.4.5) Pentagonal prism In geometry, the pentagonal prism is a prism with a pentagonal base. It is a type of heptahedron with 7 faces, 15 edges, and 10 vertices.- As a semiregular polyhedron :... |
(1) (5.6.6) Truncated icosahedron In geometry, the truncated icosahedron is an Archimedean solid, one of thirteen convex isogonal nonprismatic solids whose faces are two or more types of regular polygons.It has 12 regular pentagonal faces, 20 regular hexagonal faces, 60 vertices and 90 edges.... |
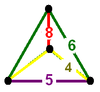 |
|
| 22 | Runcitruncated order-4 dodecahedral |
(1) (3.4.4.4) Rhombicuboctahedron In geometry, the rhombicuboctahedron, or small rhombicuboctahedron, is an Archimedean solid with eight triangular and eighteen square faces. There are 24 identical vertices, with one triangle and three squares meeting at each. Note that six of the squares only share vertices with the triangles... |
(1) (4.4.4) Cube In geometry, a cube is a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets or sides, with three meeting at each vertex. The cube can also be called a regular hexahedron and is one of the five Platonic solids. It is a special kind of square prism, of rectangular parallelepiped and... |
(2) (4.4.10) Decagonal prism In geometry, the decagonal prism is the eighth in an infinite set of prisms, formed by ten square side faces and two regular decagon caps. With twelve faces, it is one of many nonregular dodecahedra.If faces are all regular, it is a semiregular polyhedron.... |
(1) (3.10.10) Truncated dodecahedron In geometry, the truncated dodecahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 12 regular decagonal faces, 20 regular triangular faces, 60 vertices and 90 edges.- Geometric relations :... |
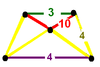 |
|
| 23 | Runcitruncated order-5 cubic |
(1) (3.8.8) Truncated cube In geometry, the truncated cube, or truncated hexahedron, is an Archimedean solid. It has 14 regular faces , 36 edges, and 24 vertices.... |
(2) (4.4.8) Octagonal prism In geometry, the octagonal prism is the sixth in an infinite set of prisms, formed by square sides and two regular octagon caps.If faces are all regular, it is a semiregular polyhedron.- Use :... |
(1) (4.4.5) Pentagonal prism In geometry, the pentagonal prism is a prism with a pentagonal base. It is a type of heptahedron with 7 faces, 15 edges, and 10 vertices.- As a semiregular polyhedron :... |
(1) (3.4.5.4) Rhombicosidodecahedron In geometry, the rhombicosidodecahedron, or small rhombicosidodecahedron, is an Archimedean solid, one of thirteen convex isogonal nonprismatic solids constructed of two or more types of regular polygon faces.... |
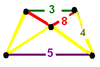 |
|
| 24 | Omnitruncated order-5 cubic |
(1) (4.6.8) |
(1) (4.4.8) Octagonal prism In geometry, the octagonal prism is the sixth in an infinite set of prisms, formed by square sides and two regular octagon caps.If faces are all regular, it is a semiregular polyhedron.- Use :... |
(1) (4.4.10) Decagonal prism In geometry, the decagonal prism is the eighth in an infinite set of prisms, formed by ten square side faces and two regular decagon caps. With twelve faces, it is one of many nonregular dodecahedra.If faces are all regular, it is a semiregular polyhedron.... |
(1) (4.6.10) |
||
| [34] | alternated order-5 cubic |
(20) (3.3.3) Tetrahedron In geometry, a tetrahedron is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, three of which meet at each vertex. A regular tetrahedron is one in which the four triangles are regular, or "equilateral", and is one of the Platonic solids... |
(12) (3.3.3.3) Octahedron In geometry, an octahedron is a polyhedron with eight faces. A regular octahedron is a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex.... |
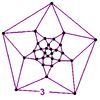 |
[5,3,5] family
There are 9 forms, generated by ring permutations of the Coxeter groupCoxeter group
In mathematics, a Coxeter group, named after H.S.M. Coxeter, is an abstract group that admits a formal description in terms of mirror symmetries. Indeed, the finite Coxeter groups are precisely the finite Euclidean reflection groups; the symmetry groups of regular polyhedra are an example...
: [5,3,5] or
| # | Name of honeycomb Coxeter–Dynkin diagram |
Cells by location and count per vertex | Vertex figure Vertex figure In geometry a vertex figure is, broadly speaking, the figure exposed when a corner of a polyhedron or polytope is sliced off.-Definitions - theme and variations:... |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 | Order-5 dodecahedral t0{5,3,5} |
(20) (5.5.5) |
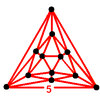 |
|||
| 26 | rectified order-5 dodecahedral t1{5,3,5} |
(2) (3.3.3.3.3) Icosahedron In geometry, an icosahedron is a regular polyhedron with 20 identical equilateral triangular faces, 30 edges and 12 vertices. It is one of the five Platonic solids.... |
(5) (3.5.3.5) Icosidodecahedron In geometry, an icosidodecahedron is a polyhedron with twenty triangular faces and twelve pentagonal faces. An icosidodecahedron has 30 identical vertices, with two triangles and two pentagons meeting at each, and 60 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a pentagon... |
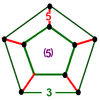 |
||
| 27 | truncated order-5 dodecahedral t0,1{5,3,5} |
(1) (3.3.3.3.3) Icosahedron In geometry, an icosahedron is a regular polyhedron with 20 identical equilateral triangular faces, 30 edges and 12 vertices. It is one of the five Platonic solids.... |
(5) (3.10.10) Truncated dodecahedron In geometry, the truncated dodecahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 12 regular decagonal faces, 20 regular triangular faces, 60 vertices and 90 edges.- Geometric relations :... |
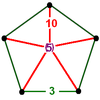 |
||
| 28 | cantellated order-5 dodecahedral t0,2{5,3,5} |
(1) (3.5.3.5) Icosidodecahedron In geometry, an icosidodecahedron is a polyhedron with twenty triangular faces and twelve pentagonal faces. An icosidodecahedron has 30 identical vertices, with two triangles and two pentagons meeting at each, and 60 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a pentagon... |
(2) (4.4.5) Pentagonal prism In geometry, the pentagonal prism is a prism with a pentagonal base. It is a type of heptahedron with 7 faces, 15 edges, and 10 vertices.- As a semiregular polyhedron :... |
(2) (3.5.4.5) |
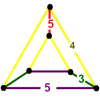 |
|
| 29 | Runcinated order-5 dodecahedral t0,3{5,3,5} |
(1) (5.5.5) |
(3) (4.4.5) Pentagonal prism In geometry, the pentagonal prism is a prism with a pentagonal base. It is a type of heptahedron with 7 faces, 15 edges, and 10 vertices.- As a semiregular polyhedron :... |
(3) (4.4.5) Pentagonal prism In geometry, the pentagonal prism is a prism with a pentagonal base. It is a type of heptahedron with 7 faces, 15 edges, and 10 vertices.- As a semiregular polyhedron :... |
(1) (5.5.5) |
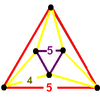 |
| 30 | bitruncated order-5 dodecahedral t1,2{5,3,5} |
(2) (4.6.6) Truncated icosahedron In geometry, the truncated icosahedron is an Archimedean solid, one of thirteen convex isogonal nonprismatic solids whose faces are two or more types of regular polygons.It has 12 regular pentagonal faces, 20 regular hexagonal faces, 60 vertices and 90 edges.... |
(2) (4.6.6) Truncated icosahedron In geometry, the truncated icosahedron is an Archimedean solid, one of thirteen convex isogonal nonprismatic solids whose faces are two or more types of regular polygons.It has 12 regular pentagonal faces, 20 regular hexagonal faces, 60 vertices and 90 edges.... |
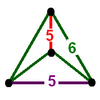 |
||
| 31 | cantitruncated order-5 dodecahedral t0,1,2{5,3,5} |
(1) (4.6.6) Truncated icosahedron In geometry, the truncated icosahedron is an Archimedean solid, one of thirteen convex isogonal nonprismatic solids whose faces are two or more types of regular polygons.It has 12 regular pentagonal faces, 20 regular hexagonal faces, 60 vertices and 90 edges.... |
(1) (4.4.5) Pentagonal prism In geometry, the pentagonal prism is a prism with a pentagonal base. It is a type of heptahedron with 7 faces, 15 edges, and 10 vertices.- As a semiregular polyhedron :... |
(2) (4.6.10) |
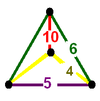 |
|
| 32 | runcitruncated order-5 dodecahedral t0,1,3{5,3,5} |
(1) (3.5.4.5) |
(1) (4.4.5) Pentagonal prism In geometry, the pentagonal prism is a prism with a pentagonal base. It is a type of heptahedron with 7 faces, 15 edges, and 10 vertices.- As a semiregular polyhedron :... |
(2) (4.4.10) Decagonal prism In geometry, the decagonal prism is the eighth in an infinite set of prisms, formed by ten square side faces and two regular decagon caps. With twelve faces, it is one of many nonregular dodecahedra.If faces are all regular, it is a semiregular polyhedron.... |
(1) (3.10.10) Truncated dodecahedron In geometry, the truncated dodecahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 12 regular decagonal faces, 20 regular triangular faces, 60 vertices and 90 edges.- Geometric relations :... |
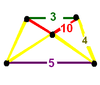 |
| 33 | omnitruncated order-5 dodecahedral t0,1,2,3{5,3,5} |
(1) (4.6.10) |
(1) (4.4.10) Decagonal prism In geometry, the decagonal prism is the eighth in an infinite set of prisms, formed by ten square side faces and two regular decagon caps. With twelve faces, it is one of many nonregular dodecahedra.If faces are all regular, it is a semiregular polyhedron.... |
(1) (4.4.10) Decagonal prism In geometry, the decagonal prism is the eighth in an infinite set of prisms, formed by ten square side faces and two regular decagon caps. With twelve faces, it is one of many nonregular dodecahedra.If faces are all regular, it is a semiregular polyhedron.... |
(1) (4.6.10) |
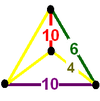 |
[5,31,1] family
There are 11 forms (4 of which are not seen above), generated by ring permutations of the Coxeter groupCoxeter group
In mathematics, a Coxeter group, named after H.S.M. Coxeter, is an abstract group that admits a formal description in terms of mirror symmetries. Indeed, the finite Coxeter groups are precisely the finite Euclidean reflection groups; the symmetry groups of regular polyhedra are an example...
: [5,31,1] or
| # | Honeycomb name Coxeter–Dynkin diagram |
Cells by location (and count around each vertex) |
vertex figure Vertex figure In geometry a vertex figure is, broadly speaking, the figure exposed when a corner of a polyhedron or polytope is sliced off.-Definitions - theme and variations:... |
Picture | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 34 | alternated order-5 cubic |
(12) (3.3.3.3) Octahedron In geometry, an octahedron is a polyhedron with eight faces. A regular octahedron is a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex.... |
(20) (3.3.3) Tetrahedron In geometry, a tetrahedron is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, three of which meet at each vertex. A regular tetrahedron is one in which the four triangles are regular, or "equilateral", and is one of the Platonic solids... |
 |
|||
| 35 | truncated alternated order-5 cubic |
(1) (3.5.3.5) Icosidodecahedron In geometry, an icosidodecahedron is a polyhedron with twenty triangular faces and twelve pentagonal faces. An icosidodecahedron has 30 identical vertices, with two triangles and two pentagons meeting at each, and 60 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a pentagon... |
(2) (5.6.6) Truncated icosahedron In geometry, the truncated icosahedron is an Archimedean solid, one of thirteen convex isogonal nonprismatic solids whose faces are two or more types of regular polygons.It has 12 regular pentagonal faces, 20 regular hexagonal faces, 60 vertices and 90 edges.... |
(2)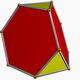 (3.6.6) Truncated tetrahedron In geometry, the truncated tetrahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 4 regular hexagonal faces, 4 regular triangular faces, 12 vertices and 18 edges.- Area and volume :... |
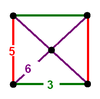 |
||
| [11] | rectified order-4 dodecahedral (rectified alternated order-5 cubic) |
(2) (3.5.3.5) Icosidodecahedron In geometry, an icosidodecahedron is a polyhedron with twenty triangular faces and twelve pentagonal faces. An icosidodecahedron has 30 identical vertices, with two triangles and two pentagons meeting at each, and 60 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a pentagon... |
(2) (3.5.3.5) Icosidodecahedron In geometry, an icosidodecahedron is a polyhedron with twenty triangular faces and twelve pentagonal faces. An icosidodecahedron has 30 identical vertices, with two triangles and two pentagons meeting at each, and 60 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a pentagon... |
(2) (3.3.3.3) Octahedron In geometry, an octahedron is a polyhedron with eight faces. A regular octahedron is a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex.... |
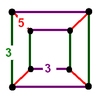 |
||
| [12] | rectified order-5 cubic (cantellated alternated order-5 cubic) |
(1) (3.3.3.3.3) Icosahedron In geometry, an icosahedron is a regular polyhedron with 20 identical equilateral triangular faces, 30 edges and 12 vertices. It is one of the five Platonic solids.... |
(1) (3.3.3.3.3) Icosahedron In geometry, an icosahedron is a regular polyhedron with 20 identical equilateral triangular faces, 30 edges and 12 vertices. It is one of the five Platonic solids.... |
(5) (3.4.3.4) Cuboctahedron In geometry, a cuboctahedron is a polyhedron with eight triangular faces and six square faces. A cuboctahedron has 12 identical vertices, with two triangles and two squares meeting at each, and 24 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a square. As such it is a quasiregular polyhedron,... |
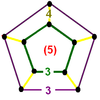 |
||
| [15] | bitruncated order-5 cubic (cantitruncated alternated order-5 cubic) |
(1) (5.6.6) Truncated icosahedron In geometry, the truncated icosahedron is an Archimedean solid, one of thirteen convex isogonal nonprismatic solids whose faces are two or more types of regular polygons.It has 12 regular pentagonal faces, 20 regular hexagonal faces, 60 vertices and 90 edges.... |
(1) (5.6.6) Truncated icosahedron In geometry, the truncated icosahedron is an Archimedean solid, one of thirteen convex isogonal nonprismatic solids whose faces are two or more types of regular polygons.It has 12 regular pentagonal faces, 20 regular hexagonal faces, 60 vertices and 90 edges.... |
(2) (4.6.6) Truncated octahedron In geometry, the truncated octahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 14 faces , 36 edges, and 24 vertices. Since each of its faces has point symmetry the truncated octahedron is a zonohedron.... |
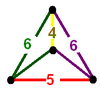 |
||
| [14] | truncated order-4 dodecahedral (bicantellated alternated order-5 cubic) |
(2) (3.10.10) Truncated dodecahedron In geometry, the truncated dodecahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 12 regular decagonal faces, 20 regular triangular faces, 60 vertices and 90 edges.- Geometric relations :... |
(2) (3.10.10) Truncated dodecahedron In geometry, the truncated dodecahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 12 regular decagonal faces, 20 regular triangular faces, 60 vertices and 90 edges.- Geometric relations :... |
(1) (3.3.3.3) Octahedron In geometry, an octahedron is a polyhedron with eight faces. A regular octahedron is a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex.... |
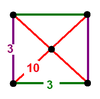 |
||
| [10] | Order-4 dodecahedral (trirectified alternated order-5 cubic) |
(4) (5.5.5) |
(4) (5.5.5) |
 |
 |
||
| 36 | runcinated alternated order-5 cubic |
(1) (3.3.3) |
(3) (3.4.4.4) Rhombicosidodecahedron In geometry, the rhombicosidodecahedron, or small rhombicosidodecahedron, is an Archimedean solid, one of thirteen convex isogonal nonprismatic solids constructed of two or more types of regular polygon faces.... |
(1) (3.3.3) Tetrahedron In geometry, a tetrahedron is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, three of which meet at each vertex. A regular tetrahedron is one in which the four triangles are regular, or "equilateral", and is one of the Platonic solids... |
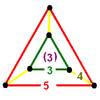 |
||
| [17] | cantellated order-4 dodecahedral (runcicantellated alternated order-5 cubic) |
(1) (3.4.5.4) |
(2) (4.4.4) Cube In geometry, a cube is a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets or sides, with three meeting at each vertex. The cube can also be called a regular hexahedron and is one of the five Platonic solids. It is a special kind of square prism, of rectangular parallelepiped and... |
(1) (3.4.5.4) |
(1) (3.4.3.4) Cuboctahedron In geometry, a cuboctahedron is a polyhedron with eight triangular faces and six square faces. A cuboctahedron has 12 identical vertices, with two triangles and two squares meeting at each, and 24 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a square. As such it is a quasiregular polyhedron,... |
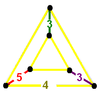 |
|
| 37 | runcitruncated alternated order-5 cubic |
(1) (3.10.10) Truncated dodecahedron In geometry, the truncated dodecahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 12 regular decagonal faces, 20 regular triangular faces, 60 vertices and 90 edges.- Geometric relations :... |
(2) (4.6.10) Truncated icosidodecahedron In geometry, the truncated icosidodecahedron is an Archimedean solid, one of thirteen convex isogonal nonprismatic solids constructed by two or more types of regular polygon faces.... |
(1) (3.6.6) Truncated tetrahedron In geometry, the truncated tetrahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 4 regular hexagonal faces, 4 regular triangular faces, 12 vertices and 18 edges.- Area and volume :... |
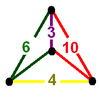 |
||
| [20] | cantitruncated order-4 dodecahedral (omnitruncated alternated order-5 cubic) |
(1) (4.6.10) |
(1) (4.4.4) Cube In geometry, a cube is a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets or sides, with three meeting at each vertex. The cube can also be called a regular hexahedron and is one of the five Platonic solids. It is a special kind of square prism, of rectangular parallelepiped and... |
(1) (4.6.10) |
(1) (4.6.6) Truncated octahedron In geometry, the truncated octahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 14 faces , 36 edges, and 24 vertices. Since each of its faces has point symmetry the truncated octahedron is a zonohedron.... |
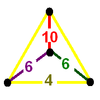 |
[(4,3,3,3)] family
There are 9 forms, generated by ring permutations of the Coxeter groupCoxeter group
In mathematics, a Coxeter group, named after H.S.M. Coxeter, is an abstract group that admits a formal description in terms of mirror symmetries. Indeed, the finite Coxeter groups are precisely the finite Euclidean reflection groups; the symmetry groups of regular polyhedra are an example...
:
| # | Honeycomb name Coxeter–Dynkin diagram |
Cells by location (and count around each vertex) |
vertex figure Vertex figure In geometry a vertex figure is, broadly speaking, the figure exposed when a corner of a polyhedron or polytope is sliced off.-Definitions - theme and variations:... |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 38 | (4) (3.3.3) Tetrahedron In geometry, a tetrahedron is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, three of which meet at each vertex. A regular tetrahedron is one in which the four triangles are regular, or "equilateral", and is one of the Platonic solids... |
- | (4) (4.4.4) Cube In geometry, a cube is a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets or sides, with three meeting at each vertex. The cube can also be called a regular hexahedron and is one of the five Platonic solids. It is a special kind of square prism, of rectangular parallelepiped and... |
(6) (3.4.3.4) Cuboctahedron In geometry, a cuboctahedron is a polyhedron with eight triangular faces and six square faces. A cuboctahedron has 12 identical vertices, with two triangles and two squares meeting at each, and 24 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a square. As such it is a quasiregular polyhedron,... |
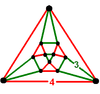 |
|
| 39 | (12) (3.3.3.3) Octahedron In geometry, an octahedron is a polyhedron with eight faces. A regular octahedron is a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex.... |
(8) (3.3.3) Tetrahedron In geometry, a tetrahedron is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, three of which meet at each vertex. A regular tetrahedron is one in which the four triangles are regular, or "equilateral", and is one of the Platonic solids... |
- | (8) (3.3.3.3) Octahedron In geometry, an octahedron is a polyhedron with eight faces. A regular octahedron is a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex.... |
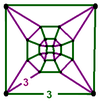 |
|
| 40 | (3) (3.6.6) Truncated tetrahedron In geometry, the truncated tetrahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 4 regular hexagonal faces, 4 regular triangular faces, 12 vertices and 18 edges.- Area and volume :... |
(1) (3.3.3) Tetrahedron In geometry, a tetrahedron is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, three of which meet at each vertex. A regular tetrahedron is one in which the four triangles are regular, or "equilateral", and is one of the Platonic solids... |
(1) (4.4.4) Cube In geometry, a cube is a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets or sides, with three meeting at each vertex. The cube can also be called a regular hexahedron and is one of the five Platonic solids. It is a special kind of square prism, of rectangular parallelepiped and... |
(3) (4.6.6) Truncated octahedron In geometry, the truncated octahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 14 faces , 36 edges, and 24 vertices. Since each of its faces has point symmetry the truncated octahedron is a zonohedron.... |
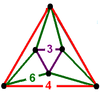 |
|
| 41 | (1) (3.3.3) Tetrahedron In geometry, a tetrahedron is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, three of which meet at each vertex. A regular tetrahedron is one in which the four triangles are regular, or "equilateral", and is one of the Platonic solids... |
(1) (3.3.3) Tetrahedron In geometry, a tetrahedron is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, three of which meet at each vertex. A regular tetrahedron is one in which the four triangles are regular, or "equilateral", and is one of the Platonic solids... |
(3) (3.8.8) Truncated cube In geometry, the truncated cube, or truncated hexahedron, is an Archimedean solid. It has 14 regular faces , 36 edges, and 24 vertices.... |
(3) (3.8.8) Truncated cube In geometry, the truncated cube, or truncated hexahedron, is an Archimedean solid. It has 14 regular faces , 36 edges, and 24 vertices.... |
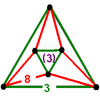 |
|
| 42 | (4) (3.6.6) Truncated tetrahedron In geometry, the truncated tetrahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 4 regular hexagonal faces, 4 regular triangular faces, 12 vertices and 18 edges.- Area and volume :... |
(4) (3.6.6) Truncated tetrahedron In geometry, the truncated tetrahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 4 regular hexagonal faces, 4 regular triangular faces, 12 vertices and 18 edges.- Area and volume :... |
(1) (3.3.3.3) Octahedron In geometry, an octahedron is a polyhedron with eight faces. A regular octahedron is a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex.... |
(1) (3.3.3.3) Octahedron In geometry, an octahedron is a polyhedron with eight faces. A regular octahedron is a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex.... |
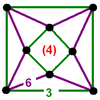 |
|
| 43 | (1) (3.3.3.3) Octahedron In geometry, an octahedron is a polyhedron with eight faces. A regular octahedron is a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex.... |
(2) (3.4.3.4) Cuboctahedron In geometry, a cuboctahedron is a polyhedron with eight triangular faces and six square faces. A cuboctahedron has 12 identical vertices, with two triangles and two squares meeting at each, and 24 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a square. As such it is a quasiregular polyhedron,... |
(1) (3.4.3.4) Cuboctahedron In geometry, a cuboctahedron is a polyhedron with eight triangular faces and six square faces. A cuboctahedron has 12 identical vertices, with two triangles and two squares meeting at each, and 24 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a square. As such it is a quasiregular polyhedron,... |
(2) (3.4.4.4) |
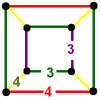 |
|
| 44 | (1) (3.6.6) Truncated tetrahedron In geometry, the truncated tetrahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 4 regular hexagonal faces, 4 regular triangular faces, 12 vertices and 18 edges.- Area and volume :... |
(1) (3.4.3.4) Cuboctahedron In geometry, a cuboctahedron is a polyhedron with eight triangular faces and six square faces. A cuboctahedron has 12 identical vertices, with two triangles and two squares meeting at each, and 24 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a square. As such it is a quasiregular polyhedron,... |
(1) (3.8.8) Truncated cube In geometry, the truncated cube, or truncated hexahedron, is an Archimedean solid. It has 14 regular faces , 36 edges, and 24 vertices.... |
(2) (4.6.8) |
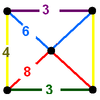 |
|
| 45 | (2) (4.6.6) Truncated octahedron In geometry, the truncated octahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 14 faces , 36 edges, and 24 vertices. Since each of its faces has point symmetry the truncated octahedron is a zonohedron.... |
(1) (3.6.6) Truncated tetrahedron In geometry, the truncated tetrahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 4 regular hexagonal faces, 4 regular triangular faces, 12 vertices and 18 edges.- Area and volume :... |
(1) (3.4.4.4) |
(1) (4.6.6) Truncated octahedron In geometry, the truncated octahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 14 faces , 36 edges, and 24 vertices. Since each of its faces has point symmetry the truncated octahedron is a zonohedron.... |
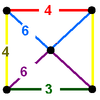 |
|
| 46 | (1) (4.6.6) Truncated octahedron In geometry, the truncated octahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 14 faces , 36 edges, and 24 vertices. Since each of its faces has point symmetry the truncated octahedron is a zonohedron.... |
(1) (4.6.6) Truncated octahedron In geometry, the truncated octahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 14 faces , 36 edges, and 24 vertices. Since each of its faces has point symmetry the truncated octahedron is a zonohedron.... |
(1) (4.6.8) |
(1) (4.6.8) |
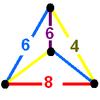 |
[(5,3,3,3)] family
There are 9 forms, generated by ring permutations of the Coxeter groupCoxeter group
In mathematics, a Coxeter group, named after H.S.M. Coxeter, is an abstract group that admits a formal description in terms of mirror symmetries. Indeed, the finite Coxeter groups are precisely the finite Euclidean reflection groups; the symmetry groups of regular polyhedra are an example...
:
| # | Honeycomb name Coxeter–Dynkin diagram |
Cells by location (and count around each vertex) |
vertex figure Vertex figure In geometry a vertex figure is, broadly speaking, the figure exposed when a corner of a polyhedron or polytope is sliced off.-Definitions - theme and variations:... |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 47 | (4) (3.3.3) Tetrahedron In geometry, a tetrahedron is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, three of which meet at each vertex. A regular tetrahedron is one in which the four triangles are regular, or "equilateral", and is one of the Platonic solids... |
- | (4) (5.5.5) |
(6) (3.5.3.5) Icosidodecahedron In geometry, an icosidodecahedron is a polyhedron with twenty triangular faces and twelve pentagonal faces. An icosidodecahedron has 30 identical vertices, with two triangles and two pentagons meeting at each, and 60 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a pentagon... |
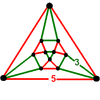 |
|
| 48 | (30) (3.3.3.3) Octahedron In geometry, an octahedron is a polyhedron with eight faces. A regular octahedron is a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex.... |
(20) (3.3.3) Tetrahedron In geometry, a tetrahedron is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, three of which meet at each vertex. A regular tetrahedron is one in which the four triangles are regular, or "equilateral", and is one of the Platonic solids... |
- | (12) (3.3.3.3.3) Icosahedron In geometry, an icosahedron is a regular polyhedron with 20 identical equilateral triangular faces, 30 edges and 12 vertices. It is one of the five Platonic solids.... |
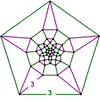 |
|
| 49 | (3) (3.6.6) Truncated tetrahedron In geometry, the truncated tetrahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 4 regular hexagonal faces, 4 regular triangular faces, 12 vertices and 18 edges.- Area and volume :... |
(1) (3.3.3) Tetrahedron In geometry, a tetrahedron is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, three of which meet at each vertex. A regular tetrahedron is one in which the four triangles are regular, or "equilateral", and is one of the Platonic solids... |
(1) (5.5.5) |
(3) (5.6.6) Truncated icosahedron In geometry, the truncated icosahedron is an Archimedean solid, one of thirteen convex isogonal nonprismatic solids whose faces are two or more types of regular polygons.It has 12 regular pentagonal faces, 20 regular hexagonal faces, 60 vertices and 90 edges.... |
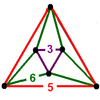 |
|
| 50 | (1) (3.3.3) Tetrahedron In geometry, a tetrahedron is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, three of which meet at each vertex. A regular tetrahedron is one in which the four triangles are regular, or "equilateral", and is one of the Platonic solids... |
(1) (3.3.3) Tetrahedron In geometry, a tetrahedron is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, three of which meet at each vertex. A regular tetrahedron is one in which the four triangles are regular, or "equilateral", and is one of the Platonic solids... |
(3) (3.10.10) Truncated dodecahedron In geometry, the truncated dodecahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 12 regular decagonal faces, 20 regular triangular faces, 60 vertices and 90 edges.- Geometric relations :... |
(3) (3.10.10) Truncated dodecahedron In geometry, the truncated dodecahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 12 regular decagonal faces, 20 regular triangular faces, 60 vertices and 90 edges.- Geometric relations :... |
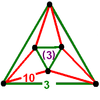 |
|
| 51 | (5) (3.6.6) Truncated tetrahedron In geometry, the truncated tetrahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 4 regular hexagonal faces, 4 regular triangular faces, 12 vertices and 18 edges.- Area and volume :... |
(5) (3.6.6) Truncated tetrahedron In geometry, the truncated tetrahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 4 regular hexagonal faces, 4 regular triangular faces, 12 vertices and 18 edges.- Area and volume :... |
(1) (3.3.3.3.3) Icosahedron In geometry, an icosahedron is a regular polyhedron with 20 identical equilateral triangular faces, 30 edges and 12 vertices. It is one of the five Platonic solids.... |
(1) (3.3.3.3.3) Icosahedron In geometry, an icosahedron is a regular polyhedron with 20 identical equilateral triangular faces, 30 edges and 12 vertices. It is one of the five Platonic solids.... |
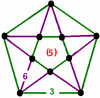 |
|
| 52 | (1) (3.3.3.3) Octahedron In geometry, an octahedron is a polyhedron with eight faces. A regular octahedron is a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex.... |
(2) (3.4.3.4) Cuboctahedron In geometry, a cuboctahedron is a polyhedron with eight triangular faces and six square faces. A cuboctahedron has 12 identical vertices, with two triangles and two squares meeting at each, and 24 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a square. As such it is a quasiregular polyhedron,... |
(1) (3.5.3.5) Icosidodecahedron In geometry, an icosidodecahedron is a polyhedron with twenty triangular faces and twelve pentagonal faces. An icosidodecahedron has 30 identical vertices, with two triangles and two pentagons meeting at each, and 60 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a pentagon... |
(2) (3.4.5.4) |
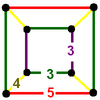 |
|
| 53 | (1) (3.6.6) Truncated tetrahedron In geometry, the truncated tetrahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 4 regular hexagonal faces, 4 regular triangular faces, 12 vertices and 18 edges.- Area and volume :... |
(1) (3.4.3.4) Cuboctahedron In geometry, a cuboctahedron is a polyhedron with eight triangular faces and six square faces. A cuboctahedron has 12 identical vertices, with two triangles and two squares meeting at each, and 24 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a square. As such it is a quasiregular polyhedron,... |
(1) (3.10.10) Truncated dodecahedron In geometry, the truncated dodecahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 12 regular decagonal faces, 20 regular triangular faces, 60 vertices and 90 edges.- Geometric relations :... |
(2) (4.6.10) Truncated icosidodecahedron In geometry, the truncated icosidodecahedron is an Archimedean solid, one of thirteen convex isogonal nonprismatic solids constructed by two or more types of regular polygon faces.... |
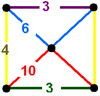 |
|
| 54 | (2) (4.6.6) Truncated octahedron In geometry, the truncated octahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 14 faces , 36 edges, and 24 vertices. Since each of its faces has point symmetry the truncated octahedron is a zonohedron.... |
(1) (3.6.6) Truncated tetrahedron In geometry, the truncated tetrahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 4 regular hexagonal faces, 4 regular triangular faces, 12 vertices and 18 edges.- Area and volume :... |
(1) (3.4.5.4) |
(1) (5.6.6) Truncated icosahedron In geometry, the truncated icosahedron is an Archimedean solid, one of thirteen convex isogonal nonprismatic solids whose faces are two or more types of regular polygons.It has 12 regular pentagonal faces, 20 regular hexagonal faces, 60 vertices and 90 edges.... |
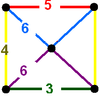 |
|
| 55 | (1) (4.6.6) Truncated octahedron In geometry, the truncated octahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 14 faces , 36 edges, and 24 vertices. Since each of its faces has point symmetry the truncated octahedron is a zonohedron.... |
(1) (4.6.6) Truncated octahedron In geometry, the truncated octahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 14 faces , 36 edges, and 24 vertices. Since each of its faces has point symmetry the truncated octahedron is a zonohedron.... |
(1) (4.6.10) Truncated icosidodecahedron In geometry, the truncated icosidodecahedron is an Archimedean solid, one of thirteen convex isogonal nonprismatic solids constructed by two or more types of regular polygon faces.... |
(1) (4.6.10) Truncated icosidodecahedron In geometry, the truncated icosidodecahedron is an Archimedean solid, one of thirteen convex isogonal nonprismatic solids constructed by two or more types of regular polygon faces.... |
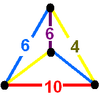 |
[(4,3,4,3)] family
There are 6 forms, generated by ring permutations of the Coxeter groupCoxeter group
In mathematics, a Coxeter group, named after H.S.M. Coxeter, is an abstract group that admits a formal description in terms of mirror symmetries. Indeed, the finite Coxeter groups are precisely the finite Euclidean reflection groups; the symmetry groups of regular polyhedra are an example...
:
| # | Honeycomb name Coxeter–Dynkin diagram |
Cells by location (and count around each vertex) |
vertex figure Vertex figure In geometry a vertex figure is, broadly speaking, the figure exposed when a corner of a polyhedron or polytope is sliced off.-Definitions - theme and variations:... |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 56 | (6) (3.3.3.3) Octahedron In geometry, an octahedron is a polyhedron with eight faces. A regular octahedron is a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex.... |
- | (8) (4.4.4) Cube In geometry, a cube is a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets or sides, with three meeting at each vertex. The cube can also be called a regular hexahedron and is one of the five Platonic solids. It is a special kind of square prism, of rectangular parallelepiped and... |
(12) (3.4.3.4) Cuboctahedron In geometry, a cuboctahedron is a polyhedron with eight triangular faces and six square faces. A cuboctahedron has 12 identical vertices, with two triangles and two squares meeting at each, and 24 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a square. As such it is a quasiregular polyhedron,... |
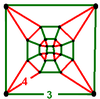 |
|
| 57 | (3) (4.6.6) Truncated octahedron In geometry, the truncated octahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 14 faces , 36 edges, and 24 vertices. Since each of its faces has point symmetry the truncated octahedron is a zonohedron.... |
(1) (4.4.4) Cube In geometry, a cube is a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets or sides, with three meeting at each vertex. The cube can also be called a regular hexahedron and is one of the five Platonic solids. It is a special kind of square prism, of rectangular parallelepiped and... |
(1) (4.4.4) Cube In geometry, a cube is a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets or sides, with three meeting at each vertex. The cube can also be called a regular hexahedron and is one of the five Platonic solids. It is a special kind of square prism, of rectangular parallelepiped and... |
(3) (4.6.6) Truncated octahedron In geometry, the truncated octahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 14 faces , 36 edges, and 24 vertices. Since each of its faces has point symmetry the truncated octahedron is a zonohedron.... |
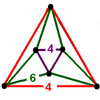 |
|
| 58 | (1) (3.3.3.3) Octahedron In geometry, an octahedron is a polyhedron with eight faces. A regular octahedron is a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex.... |
(1) (3.3.3.3) Octahedron In geometry, an octahedron is a polyhedron with eight faces. A regular octahedron is a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex.... |
(3) (3.8.8) Truncated cube In geometry, the truncated cube, or truncated hexahedron, is an Archimedean solid. It has 14 regular faces , 36 edges, and 24 vertices.... |
(3) (3.8.8) Truncated cube In geometry, the truncated cube, or truncated hexahedron, is an Archimedean solid. It has 14 regular faces , 36 edges, and 24 vertices.... |
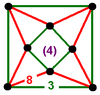 |
|
| 59 | (1) (3.4.3.4) Cuboctahedron In geometry, a cuboctahedron is a polyhedron with eight triangular faces and six square faces. A cuboctahedron has 12 identical vertices, with two triangles and two squares meeting at each, and 24 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a square. As such it is a quasiregular polyhedron,... |
(2) (3.4.4.4) |
(1) (3.4.3.4) Cuboctahedron In geometry, a cuboctahedron is a polyhedron with eight triangular faces and six square faces. A cuboctahedron has 12 identical vertices, with two triangles and two squares meeting at each, and 24 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a square. As such it is a quasiregular polyhedron,... |
(2) (3.4.4.4) |
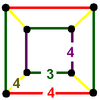 |
|
| 60 | (1) (4.6.6) Truncated octahedron In geometry, the truncated octahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 14 faces , 36 edges, and 24 vertices. Since each of its faces has point symmetry the truncated octahedron is a zonohedron.... |
(1) (3.4.4.4) |
(1) (3.8.8) Truncated cube In geometry, the truncated cube, or truncated hexahedron, is an Archimedean solid. It has 14 regular faces , 36 edges, and 24 vertices.... |
(2) (4.6.8) |
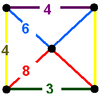 |
|
| 61 | (1) (4.6.8) |
(1) (4.6.8) |
(1) (4.6.8) |
(1) (4.6.8) |
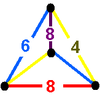 |
[(4,3,5,3)] family
There are 9 forms, generated by ring permutations of the Coxeter groupCoxeter group
In mathematics, a Coxeter group, named after H.S.M. Coxeter, is an abstract group that admits a formal description in terms of mirror symmetries. Indeed, the finite Coxeter groups are precisely the finite Euclidean reflection groups; the symmetry groups of regular polyhedra are an example...
:
| # | Honeycomb name Coxeter–Dynkin diagram |
Cells by location (and count around each vertex) |
vertex figure Vertex figure In geometry a vertex figure is, broadly speaking, the figure exposed when a corner of a polyhedron or polytope is sliced off.-Definitions - theme and variations:... |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 62 | (6) (3.3.3.3) Octahedron In geometry, an octahedron is a polyhedron with eight faces. A regular octahedron is a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex.... |
- | (8) (5.5.5) |
(1) (3.5.3.5) Icosidodecahedron In geometry, an icosidodecahedron is a polyhedron with twenty triangular faces and twelve pentagonal faces. An icosidodecahedron has 30 identical vertices, with two triangles and two pentagons meeting at each, and 60 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a pentagon... |
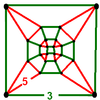 |
|
| 63 | (30) (3.4.3.4) Cuboctahedron In geometry, a cuboctahedron is a polyhedron with eight triangular faces and six square faces. A cuboctahedron has 12 identical vertices, with two triangles and two squares meeting at each, and 24 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a square. As such it is a quasiregular polyhedron,... |
(20) (4.4.4) Cube In geometry, a cube is a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets or sides, with three meeting at each vertex. The cube can also be called a regular hexahedron and is one of the five Platonic solids. It is a special kind of square prism, of rectangular parallelepiped and... |
- | (12) (3.3.3.3.3) Icosahedron In geometry, an icosahedron is a regular polyhedron with 20 identical equilateral triangular faces, 30 edges and 12 vertices. It is one of the five Platonic solids.... |
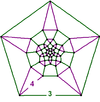 |
|
| 64 | (3) (4.6.6) Truncated octahedron In geometry, the truncated octahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 14 faces , 36 edges, and 24 vertices. Since each of its faces has point symmetry the truncated octahedron is a zonohedron.... |
(1) (4.4.4) Cube In geometry, a cube is a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets or sides, with three meeting at each vertex. The cube can also be called a regular hexahedron and is one of the five Platonic solids. It is a special kind of square prism, of rectangular parallelepiped and... |
(1) (5.5.5) |
(3) (5.6.6) Truncated icosahedron In geometry, the truncated icosahedron is an Archimedean solid, one of thirteen convex isogonal nonprismatic solids whose faces are two or more types of regular polygons.It has 12 regular pentagonal faces, 20 regular hexagonal faces, 60 vertices and 90 edges.... |
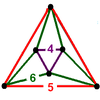 |
|
| 65 | (1) (3.3.3.3) Octahedron In geometry, an octahedron is a polyhedron with eight faces. A regular octahedron is a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex.... |
(1) (3.3.3.3) Octahedron In geometry, an octahedron is a polyhedron with eight faces. A regular octahedron is a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex.... |
(4) (3.10.10) Truncated dodecahedron In geometry, the truncated dodecahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 12 regular decagonal faces, 20 regular triangular faces, 60 vertices and 90 edges.- Geometric relations :... |
(4) (3.10.10) Truncated dodecahedron In geometry, the truncated dodecahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 12 regular decagonal faces, 20 regular triangular faces, 60 vertices and 90 edges.- Geometric relations :... |
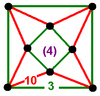 |
|
| 66 | (5) (3.8.8) Truncated cube In geometry, the truncated cube, or truncated hexahedron, is an Archimedean solid. It has 14 regular faces , 36 edges, and 24 vertices.... |
(5) (3.8.8) Truncated cube In geometry, the truncated cube, or truncated hexahedron, is an Archimedean solid. It has 14 regular faces , 36 edges, and 24 vertices.... |
(1) (3.3.3.3.3) Icosahedron In geometry, an icosahedron is a regular polyhedron with 20 identical equilateral triangular faces, 30 edges and 12 vertices. It is one of the five Platonic solids.... |
(1) (3.3.3.3.3) Icosahedron In geometry, an icosahedron is a regular polyhedron with 20 identical equilateral triangular faces, 30 edges and 12 vertices. It is one of the five Platonic solids.... |
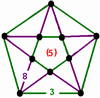 |
|
| 67 | (1) (3.4.3.4) Cuboctahedron In geometry, a cuboctahedron is a polyhedron with eight triangular faces and six square faces. A cuboctahedron has 12 identical vertices, with two triangles and two squares meeting at each, and 24 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a square. As such it is a quasiregular polyhedron,... |
(2) (3.4.4.4) Rhombicuboctahedron In geometry, the rhombicuboctahedron, or small rhombicuboctahedron, is an Archimedean solid with eight triangular and eighteen square faces. There are 24 identical vertices, with one triangle and three squares meeting at each. Note that six of the squares only share vertices with the triangles... |
(1) (3.5.3.5) Icosidodecahedron In geometry, an icosidodecahedron is a polyhedron with twenty triangular faces and twelve pentagonal faces. An icosidodecahedron has 30 identical vertices, with two triangles and two pentagons meeting at each, and 60 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a pentagon... |
(2) (3.4.5.4) Rhombicosidodecahedron In geometry, the rhombicosidodecahedron, or small rhombicosidodecahedron, is an Archimedean solid, one of thirteen convex isogonal nonprismatic solids constructed of two or more types of regular polygon faces.... |
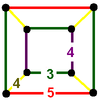 |
|
| 68 | (1) (4.6.6) Truncated octahedron In geometry, the truncated octahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 14 faces , 36 edges, and 24 vertices. Since each of its faces has point symmetry the truncated octahedron is a zonohedron.... |
(1) (3.4.4.4) Rhombicuboctahedron In geometry, the rhombicuboctahedron, or small rhombicuboctahedron, is an Archimedean solid with eight triangular and eighteen square faces. There are 24 identical vertices, with one triangle and three squares meeting at each. Note that six of the squares only share vertices with the triangles... |
(1) (3.10.10) Truncated dodecahedron In geometry, the truncated dodecahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 12 regular decagonal faces, 20 regular triangular faces, 60 vertices and 90 edges.- Geometric relations :... |
(2) (4.6.10) Truncated icosidodecahedron In geometry, the truncated icosidodecahedron is an Archimedean solid, one of thirteen convex isogonal nonprismatic solids constructed by two or more types of regular polygon faces.... |
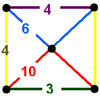 |
|
| 69 | (2) (4.6.8) Truncated cuboctahedron In geometry, the truncated cuboctahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 12 square faces, 8 regular hexagonal faces, 6 regular octagonal faces, 48 vertices and 72 edges... |
(1) (3.8.8) Truncated cube In geometry, the truncated cube, or truncated hexahedron, is an Archimedean solid. It has 14 regular faces , 36 edges, and 24 vertices.... |
(1) (3.4.5.4) Rhombicosidodecahedron In geometry, the rhombicosidodecahedron, or small rhombicosidodecahedron, is an Archimedean solid, one of thirteen convex isogonal nonprismatic solids constructed of two or more types of regular polygon faces.... |
(1) (5.6.6) Truncated icosahedron In geometry, the truncated icosahedron is an Archimedean solid, one of thirteen convex isogonal nonprismatic solids whose faces are two or more types of regular polygons.It has 12 regular pentagonal faces, 20 regular hexagonal faces, 60 vertices and 90 edges.... |
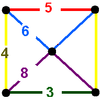 |
|
| 70 | (1) (4.6.8) Truncated cuboctahedron In geometry, the truncated cuboctahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 12 square faces, 8 regular hexagonal faces, 6 regular octagonal faces, 48 vertices and 72 edges... |
(1) (4.6.8) Truncated cuboctahedron In geometry, the truncated cuboctahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 12 square faces, 8 regular hexagonal faces, 6 regular octagonal faces, 48 vertices and 72 edges... |
(1) (4.6.10) Truncated icosidodecahedron In geometry, the truncated icosidodecahedron is an Archimedean solid, one of thirteen convex isogonal nonprismatic solids constructed by two or more types of regular polygon faces.... |
(1) (4.6.10) Truncated icosidodecahedron In geometry, the truncated icosidodecahedron is an Archimedean solid, one of thirteen convex isogonal nonprismatic solids constructed by two or more types of regular polygon faces.... |
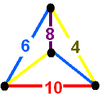 |
[(5,3,5,3)] family
There are 6 forms, generated by ring permutations of the Coxeter groupCoxeter group
In mathematics, a Coxeter group, named after H.S.M. Coxeter, is an abstract group that admits a formal description in terms of mirror symmetries. Indeed, the finite Coxeter groups are precisely the finite Euclidean reflection groups; the symmetry groups of regular polyhedra are an example...
:
| # | Honeycomb name Coxeter–Dynkin diagram |
Cells by location (and count around each vertex) |
vertex figure Vertex figure In geometry a vertex figure is, broadly speaking, the figure exposed when a corner of a polyhedron or polytope is sliced off.-Definitions - theme and variations:... |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 71 | (12) (3.3.3.3.3) Icosahedron In geometry, an icosahedron is a regular polyhedron with 20 identical equilateral triangular faces, 30 edges and 12 vertices. It is one of the five Platonic solids.... |
- | (20) (5.5.5) |
(30) (3.5.3.5) Icosidodecahedron In geometry, an icosidodecahedron is a polyhedron with twenty triangular faces and twelve pentagonal faces. An icosidodecahedron has 30 identical vertices, with two triangles and two pentagons meeting at each, and 60 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a pentagon... |
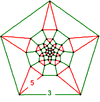 |
|
| 72 | (3) (5.6.6) Truncated icosahedron In geometry, the truncated icosahedron is an Archimedean solid, one of thirteen convex isogonal nonprismatic solids whose faces are two or more types of regular polygons.It has 12 regular pentagonal faces, 20 regular hexagonal faces, 60 vertices and 90 edges.... |
(1) (5.5.5) |
(1) (5.5.5) |
(3) (5.6.6) Truncated icosahedron In geometry, the truncated icosahedron is an Archimedean solid, one of thirteen convex isogonal nonprismatic solids whose faces are two or more types of regular polygons.It has 12 regular pentagonal faces, 20 regular hexagonal faces, 60 vertices and 90 edges.... |
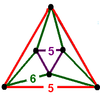 |
|
| 73 | (1) (3.3.3.3.3) Icosahedron In geometry, an icosahedron is a regular polyhedron with 20 identical equilateral triangular faces, 30 edges and 12 vertices. It is one of the five Platonic solids.... |
(1) (3.3.3.3.3) Icosahedron In geometry, an icosahedron is a regular polyhedron with 20 identical equilateral triangular faces, 30 edges and 12 vertices. It is one of the five Platonic solids.... |
(3) (3.10.10) Truncated dodecahedron In geometry, the truncated dodecahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 12 regular decagonal faces, 20 regular triangular faces, 60 vertices and 90 edges.- Geometric relations :... |
(3) (3.10.10) Truncated dodecahedron In geometry, the truncated dodecahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 12 regular decagonal faces, 20 regular triangular faces, 60 vertices and 90 edges.- Geometric relations :... |
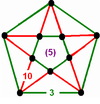 |
|
| 74 | (1) (3.5.3.5) Icosidodecahedron In geometry, an icosidodecahedron is a polyhedron with twenty triangular faces and twelve pentagonal faces. An icosidodecahedron has 30 identical vertices, with two triangles and two pentagons meeting at each, and 60 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a pentagon... |
(2) (3.4.5.4) |
(1) (3.5.3.5) Icosidodecahedron In geometry, an icosidodecahedron is a polyhedron with twenty triangular faces and twelve pentagonal faces. An icosidodecahedron has 30 identical vertices, with two triangles and two pentagons meeting at each, and 60 identical edges, each separating a triangle from a pentagon... |
(2) (3.4.5.4) |
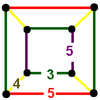 |
|
| 75 | (1) (5.6.6) Truncated icosahedron In geometry, the truncated icosahedron is an Archimedean solid, one of thirteen convex isogonal nonprismatic solids whose faces are two or more types of regular polygons.It has 12 regular pentagonal faces, 20 regular hexagonal faces, 60 vertices and 90 edges.... |
(1) (3.4.5.4) |
(1) (3.10.10) Truncated dodecahedron In geometry, the truncated dodecahedron is an Archimedean solid. It has 12 regular decagonal faces, 20 regular triangular faces, 60 vertices and 90 edges.- Geometric relations :... |
(2) (4.6.10) Truncated icosidodecahedron In geometry, the truncated icosidodecahedron is an Archimedean solid, one of thirteen convex isogonal nonprismatic solids constructed by two or more types of regular polygon faces.... |
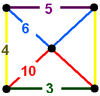 |
|
| 76 | (1) (4.6.10) Truncated icosidodecahedron In geometry, the truncated icosidodecahedron is an Archimedean solid, one of thirteen convex isogonal nonprismatic solids constructed by two or more types of regular polygon faces.... |
(1) (4.6.10) Truncated icosidodecahedron In geometry, the truncated icosidodecahedron is an Archimedean solid, one of thirteen convex isogonal nonprismatic solids constructed by two or more types of regular polygon faces.... |
(1) (4.6.10) Truncated icosidodecahedron In geometry, the truncated icosidodecahedron is an Archimedean solid, one of thirteen convex isogonal nonprismatic solids constructed by two or more types of regular polygon faces.... |
(1) (4.6.10) Truncated icosidodecahedron In geometry, the truncated icosidodecahedron is an Archimedean solid, one of thirteen convex isogonal nonprismatic solids constructed by two or more types of regular polygon faces.... |
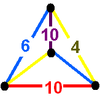 |
See also
- Uniform tilings in hyperbolic planeUniform tilings in hyperbolic planeThere are an infinite number of uniform tilings on the hyperbolic plane based on the where 1/p + 1/q + 1/r ...
- List of regular polytopes#Tessellations of hyperbolic 3-space

