List of Romance languages
Encyclopedia
According to the Summer Institute for Linguistics
's guide to world languages, the Ethnologue
, the Romance languages
include 47 language
s and dialect
s spoken in Europe. This language group is a part of the Italic languages
family, with Latin
being the only extant Italic non-Romanic language.
The classification described below is largely based on the analysis provided by the Ethnologue. The ISO-639-2
code roa is applied by the ISO for any Romance variety that does not have its own code. The Ethnologue classification is regarded to be at one extreme of points of view held by linguists, who are roughly divided into 'splitters' (like the Ethnologue) and 'lumpers'. The Ethnologue classification produces a very detailed classification, more reflectant of regional difference than many other linguists
would accept, but valuable as a description of varieties.
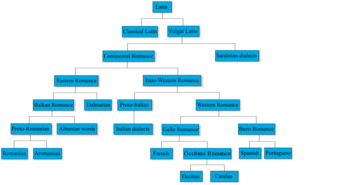
Top level groups are listed roughly East to West.
This article lists also the main groups of Romance-based Creole languages.
s, dialects, and varieties.
, and Iberian Romance
. But there is no consensus on how these four groups relate. The Ethnologue groups the first two under Gallo-Romance
(and generally lists Gallo-Italic first and Gallo-Rhaetian second), and considers Occitano Romance a subgroup of Iberian Romance. Sometimes, however, Occitano Romance is regarded as a group of its own. Yet another method is to lump Northern Italian and Occitano Romance as subgroups of a group of their own.
For simplicity of presentation, the four groups are listed separately below. However, note that all points of view among linguists reject a classifcation into four groups.
and Occitan languages. One way is to list them as a distinct group of its own. A second way is to lump them into the Ibero-Romance group, under the claim that they serve as transitional languages between Ibero-Romance and Gallo-Romance. A third way is to lump it with the Gallo-Italic subclad of the Gallo-Romance.
- Asturian, Leonese, Mirandese, Spanish, Galician, Portuguese and their dialects.
Romance languages has given rise to numerous creole language
s and pidgin
s. Some of the lesser-used languages have also had influences on varieties spoken far from their traditional regions. The following is a partial list of creole languages and pidgins, grouped by their main source language.
While not being pidgins nor creoles, English (see Middle English creole hypothesis
), Basque
and Albanian
have a substantial Romance influence in their vocabularies.
For mixed languages based on Romance languages, see the main article on Mixed language
s.
The Ethnologue classification does not include numerous other dialects and varieties of the Romance languages, such as:
SIL International
SIL International is a U.S.-based, worldwide, Christian non-profit organization, whose main purpose is to study, develop and document languages, especially those that are lesser-known, in order to expand linguistic knowledge, promote literacy, translate the Christian Bible into local languages,...
's guide to world languages, the Ethnologue
Ethnologue
Ethnologue: Languages of the World is a web and print publication of SIL International , a Christian linguistic service organization, which studies lesser-known languages, to provide the speakers with Bibles in their native language and support their efforts in language development.The Ethnologue...
, the Romance languages
Romance languages
The Romance languages are a branch of the Indo-European language family, more precisely of the Italic languages subfamily, comprising all the languages that descend from Vulgar Latin, the language of ancient Rome...
include 47 language
Language
Language may refer either to the specifically human capacity for acquiring and using complex systems of communication, or to a specific instance of such a system of complex communication...
s and dialect
Dialect
The term dialect is used in two distinct ways, even by linguists. One usage refers to a variety of a language that is a characteristic of a particular group of the language's speakers. The term is applied most often to regional speech patterns, but a dialect may also be defined by other factors,...
s spoken in Europe. This language group is a part of the Italic languages
Italic languages
The Italic subfamily is a member of the Indo-European language family. It includes the Romance languages derived from Latin , and a number of extinct languages of the Italian Peninsula, including Umbrian, Oscan, Faliscan, and Latin.In the past various definitions of "Italic" have prevailed...
family, with Latin
Latin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
being the only extant Italic non-Romanic language.
The classification described below is largely based on the analysis provided by the Ethnologue. The ISO-639-2
ISO 639
ISO 639 is a set of standards by the International Organization for Standardization that is concerned with representation of names for language and language groups....
code roa is applied by the ISO for any Romance variety that does not have its own code. The Ethnologue classification is regarded to be at one extreme of points of view held by linguists, who are roughly divided into 'splitters' (like the Ethnologue) and 'lumpers'. The Ethnologue classification produces a very detailed classification, more reflectant of regional difference than many other linguists
Linguistics
Linguistics is the scientific study of human language. Linguistics can be broadly broken into three categories or subfields of study: language form, language meaning, and language in context....
would accept, but valuable as a description of varieties.
Top level groups are listed roughly East to West.
This article lists also the main groups of Romance-based Creole languages.

Sardinian / Southern Romance
- SardinianSardinian languageSardinian is a Romance language spoken and written on most of the island of Sardinia . It is considered the most conservative of the Romance languages in terms of phonology and is noted for its Paleosardinian substratum....
: 1,300,000 speakers in SardiniaSardiniaSardinia is the second-largest island in the Mediterranean Sea . It is an autonomous region of Italy, and the nearest land masses are the French island of Corsica, the Italian Peninsula, Sicily, Tunisia and the Spanish Balearic Islands.The name Sardinia is from the pre-Roman noun *sard[],...
. Four varieties recognized; all are included in ISO 639-1 code, sc; ISO 639-2 code, srd)- Sardinian, SassareseSassareseSassarese is an Italo-Dalmatian language and transitional between Corsican and Sardinian. It is regarded as a Corsican–Sardinian language because of Sassari's historic ties with Tuscany and Corsica...
(SIL code, SDC) - Sardinian, GallureseGallureseGallurese is a Italo-Dalmatian Romance language spoken in the northeastern part of Sardinia. It is often considered as a variety of Corsican, or a transitional language between Corsican and Sardinian....
(SIL Code, SDN) also classified as CorsicanCorsican languageCorsican is a Italo-Dalmatian Romance language spoken and written on the islands of Corsica and northern Sardinia . Corsican is the traditional native language of the Corsican people, and was long the vernacular language alongside the Italian, official language in Corsica until 1859, which was...
. - Sardinian, LogudoreseSardo logudoreseLogudorese Sardinian is a standardised variety of Sardinian, often considered the most conservative of all Romance languages. Its ISO 639-3 code is src....
(SIL Code, SRD) - Sardinian, CampidaneseSardo campidaneseCampidanese Sardinian is a standardised variety of Sardinian primarily spoken in the Province of Cagliari. Traditionally, the name Campidano refers to the fertile area located around the towns of Guspini and Villacidro. Campidanese and its variants of the dialect can be found across the entire...
(SIL Code, SRO)
- Sardinian, Sassarese
- CorsicanCorsican languageCorsican is a Italo-Dalmatian Romance language spoken and written on the islands of Corsica and northern Sardinia . Corsican is the traditional native language of the Corsican people, and was long the vernacular language alongside the Italian, official language in Corsica until 1859, which was...
(SIL Code, COI; ISO 639-1 code, co; ISO 639-2 code, cos) is sometimes listed under Southern Romance languages, and other times under Italian-Dalmatian languages
Eastern Romance
- RomanianRomanian languageRomanian Romanian Romanian (or Daco-Romanian; obsolete spellings Rumanian, Roumanian; self-designation: română, limba română ("the Romanian language") or românește (lit. "in Romanian") is a Romance language spoken by around 24 to 28 million people, primarily in Romania and Moldova...
(SIL Code, RUM; ISO 639-1 code, ro; ISO 639-2(B) code, rum; ISO 639-2(T) code, ron), 28 million speakers RomaniaRomaniaRomania is a country located at the crossroads of Central and Southeastern Europe, on the Lower Danube, within and outside the Carpathian arch, bordering on the Black Sea...
, MoldovaMoldovaMoldova , officially the Republic of Moldova is a landlocked state in Eastern Europe, located between Romania to the West and Ukraine to the North, East and South. It declared itself an independent state with the same boundaries as the preceding Moldavian Soviet Socialist Republic in 1991, as part...
, UkraineUkraineUkraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It has an area of 603,628 km², making it the second largest contiguous country on the European continent, after Russia...
, SerbiaSerbiaSerbia , officially the Republic of Serbia , is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central and Southeast Europe, covering the southern part of the Carpathian basin and the central part of the Balkans... - AromanianAromanian languageAromanian , also known as Macedo-Romanian, Arumanian or Vlach is an Eastern Romance language spoken in Southeastern Europe...
(SIL Code, RUP; ISO 639-2 code, rup): 300,000 in Greece, 100,000 in AlbaniaAlbaniaAlbania , officially known as the Republic of Albania , is a country in Southeastern Europe, in the Balkans region. It is bordered by Montenegro to the northwest, Kosovo to the northeast, the Republic of Macedonia to the east and Greece to the south and southeast. It has a coast on the Adriatic Sea...
, 15,000 in the Republic of MacedoniaRepublic of MacedoniaMacedonia , officially the Republic of Macedonia , is a country located in the central Balkan peninsula in Southeast Europe. It is one of the successor states of the former Yugoslavia, from which it declared independence in 1991...
, and 10,000 in BulgariaBulgariaBulgaria , officially the Republic of Bulgaria , is a parliamentary democracy within a unitary constitutional republic in Southeast Europe. The country borders Romania to the north, Serbia and Macedonia to the west, Greece and Turkey to the south, as well as the Black Sea to the east...
. - Megleno-Romanian (SIL Code, RUQ; ISO 639-2 code, roa), also known as Moglenitic or Meglenitic: 5,000 in Greece and the Republic of MacedoniaRepublic of MacedoniaMacedonia , officially the Republic of Macedonia , is a country located in the central Balkan peninsula in Southeast Europe. It is one of the successor states of the former Yugoslavia, from which it declared independence in 1991...
- Istro-RomanianIstro-Romanian languageIstro-Romanian is an Eastern Romance language that is still spoken today in a few villages and hamlets in the peninsula of Istria, on the northern part of the Adriatic Sea, in what is now Croatia as well as in other countries around the world where the Istro-Romanian people settled after the two...
(SIL Code, RUO; ISO 639-2 code, roa): 170 speakers in CroatiaCroatiaCroatia , officially the Republic of Croatia , is a unitary democratic parliamentary republic in Europe at the crossroads of the Mitteleuropa, the Balkans, and the Mediterranean. Its capital and largest city is Zagreb. The country is divided into 20 counties and the city of Zagreb. Croatia covers ...
(ethnic population, though: 1,500)
Italo-Dalmatian
- DalmatianDalmatian languageDalmatian was a Romance language spoken in the Dalmatia region of Croatia, and as far south as Kotor in Montenegro. The name refers to a pre-Roman tribe of the Illyrian linguistic group, Dalmatae...
(SIL Code, DLM; ISO 639-2 code, roa): Croatia, extinct in the 19th century- Regional varieties: Ragusan, Vegliot, Zara/Zadar
- Istriot (SIL Code, IST; ISO 639-2 code, roa): 1,000 speakers in IstriaIstriaIstria , formerly Histria , is the largest peninsula in the Adriatic Sea. The peninsula is located at the head of the Adriatic between the Gulf of Trieste and the Bay of Kvarner...
- Italian (SIL Code, ITN; ISO 639-1 code, it; ISO 639-2 code, ita): 60,000,000 in Italy; 3,000,000 in the Americas and 2,000,000 in Western Europe, Oceania and Africa. Italian dialectsItalian dialectsDialects of Italian are regional varieties of the Italian language, more commonly and more accurately referred to as Regional Italian. The dialects have features, most notably phonological and lexical, percolating from the underlying substrate languages...
:- Judeo-Italian (SIL Code, ITK; ISO 639-2 code, roa): 4,000 Italy
- CorsicanCorsican languageCorsican is a Italo-Dalmatian Romance language spoken and written on the islands of Corsica and northern Sardinia . Corsican is the traditional native language of the Corsican people, and was long the vernacular language alongside the Italian, official language in Corsica until 1859, which was...
(SIL Code, COI; ISO 639-1 code, co; ISO 639-2 code, cos), related to Italian, and particularly to the Tuscan dialects, is sometimes listed under Italian-Dalmatian languages, and other times under Southern Romance languages
- NeapolitanNeapolitan languageNeapolitan is the language of the city and region of Naples , and Campania. On October 14, 2008 a law by the Region of Campania stated that the Neapolitan language had to be protected....
(SIL Code, NPL; ISO 639-2 code, roa): about 8,000,000 in central-southern Italy - SicilianSicilian languageSicilian is a Romance language. Its dialects make up the Extreme-Southern Italian language group, which are spoken on the island of Sicily and its satellite islands; in southern and central Calabria ; in the southern parts of Apulia, the Salento ; and Campania, on the Italian mainland, where it is...
(SIL Code, SCN; ISO 639-2 code, scn): 6,000,000 in SicilySicilySicily is a region of Italy, and is the largest island in the Mediterranean Sea. Along with the surrounding minor islands, it constitutes an autonomous region of Italy, the Regione Autonoma Siciliana Sicily has a rich and unique culture, especially with regard to the arts, music, literature,...
, CalabriaCalabriaCalabria , in antiquity known as Bruttium, is a region in southern Italy, south of Naples, located at the "toe" of the Italian Peninsula. The capital city of Calabria is Catanzaro....
and Puglia
Western Romance
Western Romance languages comprise the Romance subgroup with the most languages and the most speakers. It includes the three major international languages of French, Portuguese, and Spanish as well as many regional languageRegional language
A regional language is a language spoken in an area of a nation state, whether it be a small area, a federal state or province, or some wider area....
s, dialects, and varieties.
Pyrenean–Mozarabic
- AragoneseAragonese languageAragonese is a Romance language now spoken in a number of local varieties by between 10,000 and 30,000 people over the valleys of the Aragón River, Sobrarbe and Ribagorza in Aragon, Spain...
: 10,000 in AragonAragonAragon is a modern autonomous community in Spain, coextensive with the medieval Kingdom of Aragon. Located in northeastern Spain, the Aragonese autonomous community comprises three provinces : Huesca, Zaragoza, and Teruel. Its capital is Zaragoza...
. - Mozarabic: Southern Iberia (extinct)
Gallo-Iberian Romance
The languages in this subfamily can be grouped into four main groups: Gallo-Rhaetian, Gallo‒Italic, Occitano RomanceOccitano-Romance languages
The Occitano-Romance branch of Romance languages encompasses the dialects pertaining to the Occitan and the Catalan languages situated in France , Spain , Andorra, Monaco, parts of Italy , and historically in the County of Tripoli and the...
, and Iberian Romance
Iberian Romance languages
The Iberian Romance languages or Ibero-Romance languages are the Romance languages that developed on the Iberian Peninsula, an area consisting primarily of Spain, Portugal, and Andorra....
. But there is no consensus on how these four groups relate. The Ethnologue groups the first two under Gallo-Romance
Gallo-Romance languages
The Gallo-Romance branch of Romance languages include French and the other langue d'oïl dialects, Occitan , Catalan, Franco-Provençal, Gallo-Italic, and other languages - Other possible classifications :...
(and generally lists Gallo-Italic first and Gallo-Rhaetian second), and considers Occitano Romance a subgroup of Iberian Romance. Sometimes, however, Occitano Romance is regarded as a group of its own. Yet another method is to lump Northern Italian and Occitano Romance as subgroups of a group of their own.
For simplicity of presentation, the four groups are listed separately below. However, note that all points of view among linguists reject a classifcation into four groups.
Gallo-Rhaetian or Gallo-Romance
- Oïl languages, most non-French Oïl languages now have some legal or administrative status as languages distinct from French, but have also been regarded by some as French dialects:
- French: 70 million Europe; 12 million AmericasAmericasThe Americas, or America , are lands in the Western hemisphere, also known as the New World. In English, the plural form the Americas is often used to refer to the landmasses of North America and South America with their associated islands and regions, while the singular form America is primarily...
. Official language of France and its Overseas Territories, MonacoMonacoMonaco , officially the Principality of Monaco , is a sovereign city state on the French Riviera. It is bordered on three sides by its neighbour, France, and its centre is about from Italy. Its area is with a population of 35,986 as of 2011 and is the most densely populated country in the...
, Belgium, LuxembourgLuxembourgLuxembourg , officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg , is a landlocked country in western Europe, bordered by Belgium, France, and Germany. It has two principal regions: the Oesling in the North as part of the Ardennes massif, and the Gutland in the south...
, Switzerland, Canada, HaitiHaitiHaiti , officially the Republic of Haiti , is a Caribbean country. It occupies the western, smaller portion of the island of Hispaniola, in the Greater Antillean archipelago, which it shares with the Dominican Republic. Ayiti was the indigenous Taíno or Amerindian name for the island...
, LebanonLebanonLebanon , officially the Republic of LebanonRepublic of Lebanon is the most common term used by Lebanese government agencies. The term Lebanese Republic, a literal translation of the official Arabic and French names that is not used in today's world. Arabic is the most common language spoken among...
, VanuatuVanuatuVanuatu , officially the Republic of Vanuatu , is an island nation located in the South Pacific Ocean. The archipelago, which is of volcanic origin, is some east of northern Australia, northeast of New Caledonia, west of Fiji, and southeast of the Solomon Islands, near New Guinea.Vanuatu was...
, parts of India and many countries in Africa. One of the six official languages of the United Nations, and one of its two working languages. A language of administration in SyriaSyriaSyria , officially the Syrian Arab Republic , is a country in Western Asia, bordering Lebanon and the Mediterranean Sea to the West, Turkey to the north, Iraq to the east, Jordan to the south, and Israel to the southwest....
, CambodiaCambodiaCambodia , officially known as the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country located in the southern portion of the Indochina Peninsula in Southeast Asia...
and LaosLaosLaos Lao: ສາທາລະນະລັດ ປະຊາທິປະໄຕ ປະຊາຊົນລາວ Sathalanalat Paxathipatai Paxaxon Lao, officially the Lao People's Democratic Republic, is a landlocked country in Southeast Asia, bordered by Burma and China to the northwest, Vietnam to the east, Cambodia to the south and Thailand to the west...
. Spoken and studied in many other countries - (SIL Code, FRN; ISO 639-1 code, fr; ISO 639-2(B) code, fre; ISO 639-2(T) code, fra).- French Dialects in Europe:
- Aostan French (Italy)
- Belgian FrenchBelgian FrenchBelgian French is the variety of French spoken mainly in the French Community of Belgium, alongside related minority regional languages such as Walloon, Picard, Champenois and Gaumais. The French spoken in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Rwanda, and Burundi, which were formerly Belgian...
(Belgium) - Metropolitan French (France; Standard French Language)
- Swiss FrenchSwiss FrenchSwiss French is the name used for the variety of French spoken in the French-speaking area of Switzerland known as Romandy. Swiss French is not to be confused with Franco-Provençal/Arpitan or Romansh, two other individual Romance languages spoken in areas not far from Romandy.The differences...
(Switzerland) - Meridional FrenchMeridional FrenchMeridional French is a regional variant of the French language. It is strongly influenced by Occitan and so widely spoken in Occitania...
(France)
- French Dialects in the Americas:
- Canadian FrenchCanadian FrenchCanadian French is an umbrella term referring to the varieties of French spoken in Canada. French is the mother tongue of nearly seven million Canadians, a figure constituting roughly 22% of the national population. At the federal level it has co-official status alongside English...
(Canada):- Acadian FrenchAcadian FrenchAcadian French , is a regionalized dialect of Canadian French. It is spoken by the francophone population of the Canadian province of New Brunswick, by small minorities in areas in the Gaspé region of eastern Quebec, by small groups of francophones in Prince Edward Island, in several tiny pockets...
- Newfoundland FrenchNewfoundland FrenchNewfoundland French or Newfoundland Peninsular French refers to the French spoken on the Port au Port Peninsula of Newfoundland. The francophones of the region are unique in Canada, tracing their origins to Continental French fishermen who settled in the late 1800s and early 1900s, and not to the...
- Quebec FrenchQuebec FrenchQuebec French , or Québécois French, is the predominant variety of the French language in Canada, in its formal and informal registers. Quebec French is used in everyday communication, as well as in education, the media, and government....
- Acadian French
- Cajun FrenchCajun FrenchCajun French is a variety or dialects of the French language spoken primarily in Louisiana, specifically in the southern and southwestern parishes....
(United States) - (SIL Code, FRC; ISO 639-2 code, roa)
- Canadian French
- ZarphaticZarphatic languageZarphatic or Judæo-French is an extinct Jewish language, formerly spoken among the Jewish communities of northern France and in parts of what is now west-central Germany, in such cities as Mainz, Frankfurt am Main, and Aachen....
- Jewish French, extinct - (SIL Code, ZRP; ISO 639-2 code, roa)
- French Dialects in Europe:
- Burgundian languageBurgundian language (Oïl)The Burgundian language, also known by French names Bourguignon-morvandiau, Bourguignon, and Morvandiau, is an Oïl language spoken in Burgundy and particularly in the Morvan area of the region....
(Bourguignon-Morvandiau) - ChampenoisChampenoisChampenois is a language spoken by a minority of people in Champagne in France and in Wallonia in Belgium. It is one of the langues d'oïl. It is classified as a regional language of France, and has the recognized status of a regional language of Wallonia....
: spoken in ChampagneChampagne, FranceChampagne is a historic province in the northeast of France, now best known for the sparkling white wine that bears its name.Formerly ruled by the counts of Champagne, its western edge is about 100 miles east of Paris. The cities of Troyes, Reims, and Épernay are the commercial centers of the area...
and Wallonia. - Franc-Comtois: spoken in Franche-ComtéFranche-ComtéFranche-Comté the former "Free County" of Burgundy, as distinct from the neighbouring Duchy, is an administrative region and a traditional province of eastern France...
and Romandy. - GalloGallo languageGallo is a regional language of France. Gallo is a Romance language, one of the Oïl languages. It is the historic language of the region of Upper Brittany and some neighboring portions of Normandy, but today is spoken by only a small minority of the population, having been largely superseded by...
: spoken in BrittanyBrittanyBrittany is a cultural and administrative region in the north-west of France. Previously a kingdom and then a duchy, Brittany was united to the Kingdom of France in 1532 as a province. Brittany has also been referred to as Less, Lesser or Little Britain... - LorrainLorrain languageLorrain is a language spoken by a minority of people in Lorraine in France and in Gaume in Belgium. It is one of the Langues d'oïl. It is classified as a regional language of France, and has the recognised status of a regional language of Wallonia...
: spoken in Lorraine regionLorraine (région)Lorraine is one of the 27 régions of France. The administrative region has two cities of equal importance, Metz and Nancy. Metz is considered to be the official capital since that is where the regional parliament is situated...
and Wallonia (as Gaumais). - NormanNorman languageNorman is a Romance language and one of the Oïl languages. Norman can be classified as one of the northern Oïl languages along with Picard and Walloon...
: a group of languages in NormandyNormandyNormandy is a geographical region corresponding to the former Duchy of Normandy. It is in France.The continental territory covers 30,627 km² and forms the preponderant part of Normandy and roughly 5% of the territory of France. It is divided for administrative purposes into two régions:...
and the Channel IslandsChannel IslandsThe Channel Islands are an archipelago of British Crown Dependencies in the English Channel, off the French coast of Normandy. They include two separate bailiwicks: the Bailiwick of Guernsey and the Bailiwick of Jersey...
:- Anglo-Norman languageAnglo-Norman languageAnglo-Norman is the name traditionally given to the kind of Old Norman used in England and to some extent elsewhere in the British Isles during the Anglo-Norman period....
: used in England after the Norman conquest of 1066. Extinct. - AuregnaisAuregnaisAuregnais, Aoeur'gnaeux or Aurignais is the Norman dialect of the Channel Island of Alderney . It is estimated that there are now possibly only 20 people still fluent in the language....
: AlderneyAlderneyAlderney is the most northerly of the Channel Islands. It is part of the Bailiwick of Guernsey, a British Crown dependency. It is long and wide. The area is , making it the third-largest island of the Channel Islands, and the second largest in the Bailiwick...
(extinct). - Continental dialects: including AugeronAugeronAugeron is the Norman dialect of the Pays d'Auge. It is highly endangered. This dialect includes both coastal and inland areas.-Phonology:Augeron can be characterised by means of its position within the isoglosses that traverse the Norman-speaking territory...
, CauchoisCauchoisCauchois is one of the eastern dialects of the Norman language, spoken in, and taking its name from, the Pays de Caux region of the Seine-Maritime départment.-Status:...
, CotentinaisCotentinaisCotentinais is the dialect of the Norman language spoken in the Cotentin Peninsula. It is one of the strongest dialects of the language on the mainland.-Dialects:... - Guernésiais: spoken in GuernseyGuernseyGuernsey, officially the Bailiwick of Guernsey is a British Crown dependency in the English Channel off the coast of Normandy.The Bailiwick, as a governing entity, embraces not only all 10 parishes on the Island of Guernsey, but also the islands of Herm, Jethou, Burhou, and Lihou and their islet...
. Endangered. - JèrriaisJèrriaisJèrriais is the form of the Norman language spoken in Jersey, in the Channel Islands, off the coast of France. It has been in decline over the past century as English has increasingly become the language of education, commerce and administration...
: spoken in JerseyJerseyJersey, officially the Bailiwick of Jersey is a British Crown Dependency off the coast of Normandy, France. As well as the island of Jersey itself, the bailiwick includes two groups of small islands that are no longer permanently inhabited, the Minquiers and Écréhous, and the Pierres de Lecq and...
. Endangered.- SercquiaisSercquiais' also known as Sarkese or Sark-French is the Norman dialect of the Channel Island of Sark. In the island it is sometimes known, slightly disparagingly, as the "patois", a French term meaning "regional language"....
: spoken in SarkSarkSark is a small island in the Channel Islands in southwestern English Channel, off the French coast of Normandy. It is a royal fief, geographically located in the Channel Islands in the Bailiwick of Guernsey, with its own set of laws based on Norman law and its own parliament. It has a population...
. Highly endangered.
- Sercquiais
- Anglo-Norman language
- PicardPicard languagePicard is a language closely related to French, and as such is one of the larger group of Romance languages. It is spoken in two regions in the far north of France – Nord-Pas-de-Calais and Picardy – and in parts of the Belgian region of Wallonia, the district of Tournai and a part of...
- (SIL Code, PCD; ISO 639-2 code, roa) - Poitevin
- SaintongeaisSaintongeaisSaintongeais is a dialect spoken halfway down the western coast of France in the former provinces of Saintonge, Aunis and Angoumois, all of which have been incorporated into the current départements of Charente and Charente-Maritime as well as in parts of their neighbouring départements of...
- WalloonWalloon languageWalloon is a Romance language which was spoken as a primary language in large portions of the Walloon Region of Belgium and some villages of Northern France until the middle of the 20th century. It belongs to the langue d'oïl language family, whose most prominent member is the French language...
- French: 70 million Europe; 12 million Americas
- Franco-ProvençalFranco-Provençal languageFranco-Provençal , Arpitan, or Romand is a Romance language with several distinct dialects that form a linguistic sub-group separate from Langue d'Oïl and Langue d'Oc. The name Franco-Provençal was given to the language by G.I...
: endangered - Italy: Aosta Valley, PiedmontPiedmontPiedmont is one of the 20 regions of Italy. It has an area of 25,402 square kilometres and a population of about 4.4 million. The capital of Piedmont is Turin. The main local language is Piedmontese. Occitan is also spoken by a minority in the Occitan Valleys situated in the Provinces of...
, FoggiaProvince of FoggiaThe Province of Foggia is a province in the Apulia region of Italy.This province is also known as Capitanata, originally Catapanata, because during the Middle Ages it was governed by a catapan, as part of the Catapanate of Italy...
; France: Rhône-AlpesRhône-AlpesRhône-Alpes is one of the 27 regions of France, located on the eastern border of the country, towards the south. The region was named after the Rhône River and the Alps mountain range. Its capital, Lyon, is the second-largest metropolitan area in France after Paris...
, Franche-ComtéFranche-ComtéFranche-Comté the former "Free County" of Burgundy, as distinct from the neighbouring Duchy, is an administrative region and a traditional province of eastern France...
; Switzerland: Romandy- Franco-Provençal dialects: see Franco-Provençal Dialect List
- Rhaeto-Romance languagesRhaeto-Romance languagesRhaeto-Romance languages are a Romance language sub-family which includes multiple languages spoken in north and north-eastern Italy, and Switzerland...
- FriulianFriulian languageFriulan , is a Romance language belonging to the Rhaeto-Romance family, spoken in the Friuli region of northeastern Italy. Friulan has around 800,000 speakers, the vast majority of whom also speak Italian...
: 2 million FriuliFriuliFriuli is an area of northeastern Italy with its own particular cultural and historical identity. It comprises the major part of the autonomous region Friuli-Venezia Giulia, i.e. the province of Udine, Pordenone, Gorizia, excluding Trieste...
, ArgentinaArgentinaArgentina , officially the Argentine Republic , is the second largest country in South America by land area, after Brazil. It is constituted as a federation of 23 provinces and an autonomous city, Buenos Aires...
, Canada, Australia, etc. - (SIL Code, FRL; ISO 639-2 code, fur) - Ladin: DolomitesDolomitesThe Dolomites are a mountain range located in north-eastern Italy. It is a part of Southern Limestone Alps and extends from the River Adige in the west to the Piave Valley in the east. The northern and southern borders are defined by the Puster Valley and the Sugana Valley...
- (SIL Code, LLD; ISO 639-2 code, roa) - Romansh: 66,000 Switzerland - (SIL Code, RHE; ISO 639-1 code, rm; ISO 639-2 code, roh).
- Friulian
Gallo-Italic Gallo-Romance
- Gallo-Italic languagesGallo-Italic languagesThe Gallo-Italic or Gallo-Italian is a linguistic set of Romance languages. In accordance with a source such as Ethnologue is a subset of the Gallo-Romance languages, which also include French and Occitan, among others; in accordance with the major Italian linguists and dialectologists The...
group- Emiliano-RomagnoloEmiliano-RomagnoloEmiliano-Romagnolo is a Romance language mostly spoken in Emilia-Romagna, Italy and San Marino. It belongs to the Northern Italian group within Romance languages , which is included in the wider group of western Romance languages...
- (SIL Code, EML; ISO 639-2 code, roa) - LigurianLigurian language (Romance)Ligurian is a Gallo-Romance language spoken in Liguria in Northern Italy, parts of the Mediterranean coastal zone of France, Monaco and in the villages of Carloforte and Calasetta in Sardinia. Genoese , spoken in Genoa, the capital of Liguria, is its most important dialect...
- (SIL Code, LIJ; ISO 639-2 code, roa)- GenoeseGenoese dialectGenoese is a dialect of the Ligurian language, the one spoken in Genoa .Ligurian is listed by Ethnologue as a language in its own right, of the Romance branch, and not to be confused with the ancient Ligurian language...
- Genoese
- Lombard: Over 3,500,000 speakers in Lombardy and neighboring regions. Many regional varieties. Most speakers bilingual in Standard Italian - (SIL Code, LMO; ISO 639-2 code, roa).
- Western LombardWestern LombardWestern Lombard is a Romance language spoken in Italy, in the Lombard provinces of Milan, Monza, Varese, Como, Lecco, Sondrio, a small part of Cremona , Lodi and Pavia, and the Piedmont provinces of Novara, Verbano-Cusio-Ossola and a small part of Vercelli , and Switzerland...
: - Eastern Lombard
- Gallo-Italic of Sicily (also related to SicilianSicilian languageSicilian is a Romance language. Its dialects make up the Extreme-Southern Italian language group, which are spoken on the island of Sicily and its satellite islands; in southern and central Calabria ; in the southern parts of Apulia, the Salento ; and Campania, on the Italian mainland, where it is...
and Piedmontese)
- Western Lombard
- PiedmontesePiedmontese languagePiedmontese is a Romance language spoken by over 2 million people in Piedmont, northwest Italy. It is geographically and linguistically included in the Northern Italian group . It is part of the wider western group of Romance languages, including French, Occitan, and Catalan.Many European and...
: 2,000,000 in PiedmontPiedmontPiedmont is one of the 20 regions of Italy. It has an area of 25,402 square kilometres and a population of about 4.4 million. The capital of Piedmont is Turin. The main local language is Piedmontese. Occitan is also spoken by a minority in the Occitan Valleys situated in the Provinces of...
- (SIL Code, PMS; ISO 639-2 code, roa)
- Emiliano-Romagnolo
- Venetian group
- VenetianVenetian languageVenetian or Venetan is a Romance language spoken as a native language by over two million people, mostly in the Veneto region of Italy, where of five million inhabitants almost all can understand it. It is sometimes spoken and often well understood outside Veneto, in Trentino, Friuli, Venezia...
: 4,500,000 in VenetoVenetoVeneto is one of the 20 regions of Italy. Its population is about 5 million, ranking 5th in Italy.Veneto had been for more than a millennium an independent state, the Republic of Venice, until it was eventually annexed by Italy in 1866 after brief Austrian and French rule...
, Trentino, FriuliFriuliFriuli is an area of northeastern Italy with its own particular cultural and historical identity. It comprises the major part of the autonomous region Friuli-Venezia Giulia, i.e. the province of Udine, Pordenone, Gorizia, excluding Trieste...
and Venezia Giulia-IstriaIstriaIstria , formerly Histria , is the largest peninsula in the Adriatic Sea. The peninsula is located at the head of the Adriatic between the Gulf of Trieste and the Bay of Kvarner...
, most speakers bilingual in Standard Italian - (SIL Code, VEC; ISO 639-2 code, roa); spoken also in South Brazil and Mexico, and small minorities in Dalmatia.
- Venetian
Occitano-Romance
There is a controversy about the classification of CatalanCatalan language
Catalan is a Romance language, the national and only official language of Andorra and a co-official language in the Spanish autonomous communities of Catalonia, the Balearic Islands and Valencian Community, where it is known as Valencian , as well as in the city of Alghero, on the Italian island...
and Occitan languages. One way is to list them as a distinct group of its own. A second way is to lump them into the Ibero-Romance group, under the claim that they serve as transitional languages between Ibero-Romance and Gallo-Romance. A third way is to lump it with the Gallo-Italic subclad of the Gallo-Romance.
- CatalanCatalan languageCatalan is a Romance language, the national and only official language of Andorra and a co-official language in the Spanish autonomous communities of Catalonia, the Balearic Islands and Valencian Community, where it is known as Valencian , as well as in the city of Alghero, on the Italian island...
: 11.5 million, spoken in Spain, France, AndorraAndorraAndorra , officially the Principality of Andorra , also called the Principality of the Valleys of Andorra, , is a small landlocked country in southwestern Europe, located in the eastern Pyrenees mountains and bordered by Spain and France. It is the sixth smallest nation in Europe having an area of...
, Italy. The only official language of Andorra. Official in CataloniaCataloniaCatalonia is an autonomous community in northeastern Spain, with the official status of a "nationality" of Spain. Catalonia comprises four provinces: Barcelona, Girona, Lleida, and Tarragona. Its capital and largest city is Barcelona. Catalonia covers an area of 32,114 km² and has an...
, Valencian CommunityValencian CommunityThe Valencian Community is an autonomous community of Spain located in central and south-eastern Iberian Peninsula. Its capital and largest city is Valencia...
and Balearic IslandsBalearic IslandsThe Balearic Islands are an archipelago of Spain in the western Mediterranean Sea, near the eastern coast of the Iberian Peninsula.The four largest islands are: Majorca, Minorca, Ibiza and Formentera. The archipelago forms an autonomous community and a province of Spain with Palma as the capital...
- (SIL Code, CAT; ISO 639-1 code, ca; ISO 639-2 code, cat). Dialects:- Eastern Catalan
- Algherese: spoken in the town of AlgheroAlgheroAlghero , is a town of about 44,000 inhabitants in Italy. It lies in the province of Sassari in northwestern Sardinia, next to the sea.-History:The area of today's Alghero has been settled since pre-historic times...
in Sardinia. - Balearic
- Central CatalanCentral CatalanCentral Catalan is the Eastern Catalan dialect with the highest number of speakers, since it is commonly spoken in densely populated areas such as the whole Barcelona province, the eastern half of Tarragona province and most of the Girona province, except for it is northern part, where a...
- Northern Catalan (Roussillonese)Northern CatalanNorthern Catalan is a Catalan dialect mostly spoken in Northern Catalonia, but also extending in the northeast part of Southern Catalonia in a transition zone with Central Catalan....
- Algherese: spoken in the town of Alghero
- Western Catalan
- RibagorçanRibagorçanRibagorçan is the name given to a number of Romance dialects spoken in the modern territories of the medieval County of Ribagorza, in northern Spain...
- North-Western Catalan
- ValencianValencianValencian is the traditional and official name of the Catalan language in the Valencian Community. There are dialectical differences from standard Catalan, and under the Valencian Statute of Autonomy, the Acadèmia Valenciana de la Llengua has been established as its regulator...
- Ribagorçan
- Eastern Catalan
- Occitan: circa 2 million in France, Italy, Spain and MonacoMonacoMonaco , officially the Principality of Monaco , is a sovereign city state on the French Riviera. It is bordered on three sides by its neighbour, France, and its centre is about from Italy. Its area is with a population of 35,986 as of 2011 and is the most densely populated country in the...
- Six dialects recognized; all are included in ISO 639-1 code, oc; ISO 639-2 code, oci; ISO 639-3 and SIL code, OCI) - all are from France:- Auvergnat also known as Auvernhat: Auvergne provinceAuvergne (province)Auvergne was a historic province in south central France. It was originally the feudal domain of the Counts of Auvergne. It is now the geographical and cultural area that corresponds to the former province....
- GasconGascon languageGascon is usually considered as a dialect of Occitan, even though some specialists regularly consider it a separate language. Gascon is mostly spoken in Gascony and Béarn in southwestern France and in the Aran Valley of Spain...
: Bordeaux (Bordèu) country to Val d'AranVal d'AranThe Val d'Aran is a valley in the Pyrenees mountains and a comarca in the northwestern part of the province of Lleida, in Catalonia, northern Spain. Most of the valley constitutes the only part of Spain, and of Catalonia, on the north face of the Pyrenees, hence the only part of Catalonia whose...
in Spain (araneseAranese languageAranese is a standardized form of the Pyrenean Gascon variety of the Occitan language spoken in the Val d'Aran, in north western Catalonia on the border between Spain and France, where it is one of the three official languages besides Catalan and Spanish...
) - Lengadocian: from Bergerac to Montpellier, including Toulouse, Agen, Montauban, Carcassonne, Aurillac
- LemosinLimousin languageLimousin is a dialect of the Occitan language, spoken in the three departments of Limousin, parts of Charente and the Dordogne in the southwest of France.The first Occitan documents are in this dialect, particularly the Boecis, written around the year 1000....
: LimousinLimousin (région)Limousin is one of the 27 regions of France. It is composed of three départements: Corrèze, Creuse and the Haute-Vienne.Situated largely in the Massif Central, as of January 1st 2008, the Limousin comprised 740,743 inhabitants on nearly 17 000 km2, making it the second least populated region of...
and CharenteCharenteCharente is a department in southwestern France, in the Poitou-Charentes region, named after the Charente River, the most important river in the department, and also the river beside which the department's two largest towns, Angoulême and Cognac, are sited.-History:Charente is one of the original... - ProvençalProvençal languageProvençal is a dialect of Occitan spoken by a minority of people in southern France, mostly in Provence. In the English-speaking world, "Provençal" is often used to refer to all dialects of Occitan, but it actually refers specifically to the dialect spoken in Provence."Provençal" is also the...
: Marseilles (Marselha) and Provence- NiçardNiçardNiçard , Nissart/Niçart , Niçois , or Nizzardo is considered a distinct subdialect of the Occitan language spoken in the city of Nice and in the historical County of Nice Niçard (Classical orthography), Nissart/Niçart (Mistralian orthography), Niçois (French, IPA: ), or Nizzardo (Italian, IPA: )...
: County of NiceCounty of NiceThe County of Nice or Niçard Country is a historical region of France, located in the south-eastern part, around the city of Nice.-History:Its territory lies between the Mediterranean Sea , Var River and the southernmost crest of the...
- generally considered as a subdialect of Provençal - Shuadit: Judeo-Provençal. Extinct since 1977 - Generally considered as Provençal and not as a language of its own (ISO 639-3 and SIL Code, SDT).
- Niçard
- Vivaro-AlpineVivaro-AlpineVivaro-Alpine or Vivaroalpenc, Vivaroaupenc is the northeastern dialect of the Occitan language. It belongs to the Northern Occitan dialectal group. Vivaro-Alpine is spoken in Southern France and North-Western Italy, and in the remote Guardia Piemontese, Calabria, where it is known as gardiol...
: Southern France and North-Western Italy, plus the Gardiol in Guardia PiemonteseGuardia PiemonteseGuardia Piemontese is a town and comune in the province of Cosenza in the Calabria region of southern Italy.- Location and language :...
, Calabria.- Cisalpenc: Piedmont western valleys
- Auvergnat also known as Auvernhat: Auvergne province
Iberian Romance
This group includes the West Iberian languagesWest Iberian languages
West Iberian is a branch of the Romance languages which includes Castilian, Ladino, the Astur-Leonese group , and the modern descendants of Galician-Portuguese...
- Asturian, Leonese, Mirandese, Spanish, Galician, Portuguese and their dialects.
- West Iberian languagesWest Iberian languagesWest Iberian is a branch of the Romance languages which includes Castilian, Ladino, the Astur-Leonese group , and the modern descendants of Galician-Portuguese...
- of Latin AmericaLatin AmericaLatin America is a region of the Americas where Romance languages – particularly Spanish and Portuguese, and variably French – are primarily spoken. Latin America has an area of approximately 21,069,500 km² , almost 3.9% of the Earth's surface or 14.1% of its land surface area...
, and Equatorial GuineaEquatorial GuineaEquatorial Guinea, officially the Republic of Equatorial Guinea where the capital Malabo is situated.Annobón is the southernmost island of Equatorial Guinea and is situated just south of the equator. Bioko island is the northernmost point of Equatorial Guinea. Between the two islands and to the...
. See Spanish dialects and varietiesSpanish dialects and varietiesSpanish dialects and varieties are the regional variants of the Spanish language, some of which are quite divergent from one another, especially in pronunciation and vocabulary, and less so in grammar....
for an exhaustive list - (SIL Code, SPN; ISO 639-1 code, es; ISO 639-2 code, spa).-
- Ladino (Judæo-Spanish) - (SIL Code, SPJ; ISO 639-2 code, lad).
- Spanish, Loreto-Ucayali (SIL Code, SPQ; ISO 639-2 code, roa), or Jungle Spanish
- Astur-Leonese
- AsturianAsturian languageAsturian is a Romance language of the West Iberian group, Astur-Leonese Subgroup, spoken in the Spanish Region of Asturias by the Asturian people...
- (SIL Code, AUB; ISO 639-2 code, ast) - LeoneseLeonese languageThe Leonese language is the endonym term used to refer to all vernacular Romance dialects of the Astur-Leonese linguistic group in the Spanish provinces of León and Zamora; Astur-Leonese also includes the dialects...
: 55.000 (Spain and Portugal) - (LS Code AAA-51-ccc) - MirandeseMirandese languageThe Mirandese language is a Romance language belonging to the Astur-Leonese linguistic group, sparsely spoken in a small area of northeastern Portugal, in the municipalities of Miranda do Douro, Mogadouro and Vimioso...
: 5,000 Portugal - (SIL Code, MWL; ISO 639-2 code, roa)
- Asturian
- Galician-PortugueseGalician-PortugueseGalician-Portuguese or Old Portuguese was a West Iberian Romance language spoken in the Middle Ages, in the northwest area of the Iberian Peninsula. It was first spoken in the area bounded in the north and west by the Atlantic Ocean and the Douro River in the south but it was later extended south...
- Portuguese: 230 million Portugal, BrazilBrazilBrazil , officially the Federative Republic of Brazil , is the largest country in South America. It is the world's fifth largest country, both by geographical area and by population with over 192 million people...
; 26 million Africa and a few thousands Asia - (SIL Code, POR; ISO 639-1 code, pt; ISO 639-2 code, por). Many mutually intelligible dialects, see Portuguese dialectsPortuguese dialectsPortuguese dialects are variants of the Portuguese language that are shared by a substantial number of speakers over several generations, but are not sufficiently distinct from the official norms to be considered separate languages...
for a full list. - Judeo-PortugueseJudeo-PortugueseJudaeo-Portuguese, Lusitanic, or "Lusitanico" in Judaeo-Portuguese is the generally extinct Jewish language of the Jews of Portugal.-Description:...
: extinct. - GalicianGalician languageGalician is a language of the Western Ibero-Romance branch, spoken in Galicia, an autonomous community located in northwestern Spain, where it is co-official with Castilian Spanish, as well as in border zones of the neighbouring territories of Asturias and Castile and León.Modern Galician and...
: 3 million in Galicia - (SIL Code, GLN; ISO 639-1 code, gl; ISO 639-2 code, glg). - FalaFala languageFala is a Romance linguistic variety commonly classified in the Portuguese-Galician subgroup, with some traits from Leonese, spoken in Spain by about 10,500 people, of whom 5,500 live in a valley of the northwestern part of Extremadura near the border with Portugal...
: 10,000 in ExtremaduraExtremaduraExtremadura is an autonomous community of western Spain whose capital city is Mérida. Its component provinces are Cáceres and Badajoz. It is bordered by Portugal to the west...
, Spain - (SIL Code, FAX; ISO 639-2 code, roa).
- Portuguese: 230 million Portugal, Brazil
-
- CalóCaló (Spanish Romani)Caló is a language spoken by the Spanish and Portuguese Romani. It is a mixed language based on Romance grammar, with an adstratum of Romani lexical items through language shift by the Romani community. It is often used as an argot, a secret language for discreet communication amongst Iberian...
(SIL Code, RMR; ISO 639-2 code, roa), or Spanish Romani is a Romani languageRomani languageRomani or Romany, Gypsy or Gipsy is any of several languages of the Romani people. They are Indic, sometimes classified in the "Central" or "Northwestern" zone, and sometimes treated as a branch of their own....
whose grammar has been heavily influenced by Spanish. The Ethnologue lists it in a separate group of mixed languages; it is not one of the 47.
Extinct branches of the Romance language tree
- African RomanceAfrican RomanceAfrican Romance or African Latin is an extinct Romance language that is supposed to have been spoken in the Roman province of Africa during the later Roman and early Byzantine Empires, prior to the annexation of the region by the Umayyad Caliphate in 696...
: Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia and Libya (extinct). - British RomanceBritish RomanceBritish Romance, British Vulgar Latin or British Latin are terms used for the Vulgar Latin spoken in southern Great Britain in Late Antiquity ....
: England and Wales (extinct). - The language of the MorlachsMorlachsMorlachs were a population of Vlachs. In another version their name comes from the slavic terms of "morski-Vlasi" or Sea Vlachs...
: Croatia, Bosnia-Herzegovina, Serbia, Montenegro and Slovenia (extinct). - It is believed there were Germano-Romance languages in present-day Southern Germany, Switzerland and Austria in the 11th century AD.
- Slavic-Romance: The hypothetical language of the BrodniciBrodniciThe Brodnici were a 13th-century people whose ethnicity is uncertain, as various authors suggest they were Slavic, mixed Romanian-Jassic, Romanian-Slavic, or Turkic-Slavic population, probably vassals of Galicia for a period. Brodnici did not leave any provable material or written traces, which...
of southern Moldavia and western Ukraine in the 13th to 15th century AD. - Pannonian RomancePannonian RomancePannonian Romance was the Romance language that developed in Pannonia after the fall of the Western Roman Empire. It seems to have lasted until the 10th century...
: Hungary (extinct).
Pidgins and creoles
The global spread of colonialColonialism
Colonialism is the establishment, maintenance, acquisition and expansion of colonies in one territory by people from another territory. It is a process whereby the metropole claims sovereignty over the colony and the social structure, government, and economics of the colony are changed by...
Romance languages has given rise to numerous creole language
Creole language
A creole language, or simply a creole, is a stable natural language developed from the mixing of parent languages; creoles differ from pidgins in that they have been nativized by children as their primary language, making them have features of natural languages that are normally missing from...
s and pidgin
Pidgin
A pidgin , or pidgin language, is a simplified language that develops as a means of communication between two or more groups that do not have a language in common. It is most commonly employed in situations such as trade, or where both groups speak languages different from the language of the...
s. Some of the lesser-used languages have also had influences on varieties spoken far from their traditional regions. The following is a partial list of creole languages and pidgins, grouped by their main source language.
- Mediterranean Lingua FrancaMediterranean Lingua FrancaThe Mediterranean Lingua Franca or Sabir was a pidgin language used as a lingua franca in the Mediterranean Basin from the 11th to the 19th century.-History:...
, influenced by the Romance languages of the Western Mediterranean and Arabic. - French-based creole languagesFrench-based creole languagesA French Creole, or French-based Creole language, is a creole language based on the French language, more specifically on a 17th century koiné French extant in Paris, the French Atlantic harbors, and the nascent French colonies...
- Portuguese-based creole languagesPortuguese CreolePortuguese creoles are creole languages which have been significantly influenced by Portuguese.- Origins :Portuguese overseas exploration in the 15th and 16th century's led to the establishment of a Portuguese Empire with trading posts, forts and colonies in the Americas, Asia and Africa...
- Spanish-based creole languagesSpanish-based Creole languages-Chavacano:Chavacano is a Spanish-based Creole language and the name of the Six Dialects of Spanish evolved words turned into a Creole language spoken in the Philippines...
While not being pidgins nor creoles, English (see Middle English creole hypothesis
Middle English creole hypothesis
The Middle English creole hypothesis is the concept that the English language is a creole, i.e., a language that developed from a pidgin. The vast differences between Old and Middle English have led some historical linguists to claim that the language underwent creolisation at the time of either...
), Basque
Basque language
Basque is the ancestral language of the Basque people, who inhabit the Basque Country, a region spanning an area in northeastern Spain and southwestern France. It is spoken by 25.7% of Basques in all territories...
and Albanian
Albanian language
Albanian is an Indo-European language spoken by approximately 7.6 million people, primarily in Albania and Kosovo but also in other areas of the Balkans in which there is an Albanian population, including western Macedonia, southern Montenegro, southern Serbia and northwestern Greece...
have a substantial Romance influence in their vocabularies.
For mixed languages based on Romance languages, see the main article on Mixed language
Mixed language
A mixed language is a language that arises through the fusion of two source languages, normally in situations of thorough bilingualism, so that it is not possible to classify the resulting language as belonging to either of the language families that were its source...
s.
Romance languages by usage
The 47 spoken varieties identified by the Ethnologue can be grouped by usage as follows:- 6 national languages: Spanish, Portuguese, French, Italian, RomanianRomanian languageRomanian Romanian Romanian (or Daco-Romanian; obsolete spellings Rumanian, Roumanian; self-designation: română, limba română ("the Romanian language") or românește (lit. "in Romanian") is a Romance language spoken by around 24 to 28 million people, primarily in Romania and Moldova...
and CatalanCatalan languageCatalan is a Romance language, the national and only official language of Andorra and a co-official language in the Spanish autonomous communities of Catalonia, the Balearic Islands and Valencian Community, where it is known as Valencian , as well as in the city of Alghero, on the Italian island... - 8 languages and 1 "macrolanguage" with 3 varieties, which have various forms of official recognition and at least some degree of formal education available in them:
- GalicianGalician languageGalician is a language of the Western Ibero-Romance branch, spoken in Galicia, an autonomous community located in northwestern Spain, where it is co-official with Castilian Spanish, as well as in border zones of the neighbouring territories of Asturias and Castile and León.Modern Galician and...
in Spain - Waloon in Belgium
- Romansh in Switzerland
- Occitan language and Corsican languageCorsican languageCorsican is a Italo-Dalmatian Romance language spoken and written on the islands of Corsica and northern Sardinia . Corsican is the traditional native language of the Corsican people, and was long the vernacular language alongside the Italian, official language in Corsica until 1859, which was...
in France - Franco-Provençal languageFranco-Provençal languageFranco-Provençal , Arpitan, or Romand is a Romance language with several distinct dialects that form a linguistic sub-group separate from Langue d'Oïl and Langue d'Oc. The name Franco-Provençal was given to the language by G.I...
, Friulian languageFriulian languageFriulan , is a Romance language belonging to the Rhaeto-Romance family, spoken in the Friuli region of northeastern Italy. Friulan has around 800,000 speakers, the vast majority of whom also speak Italian...
, and SardinianSardinian languageSardinian is a Romance language spoken and written on most of the island of Sardinia . It is considered the most conservative of the Romance languages in terms of phonology and is noted for its Paleosardinian substratum....
in Italy- LogudoreseSardo logudoreseLogudorese Sardinian is a standardised variety of Sardinian, often considered the most conservative of all Romance languages. Its ISO 639-3 code is src....
, CampidaneseSardo campidaneseCampidanese Sardinian is a standardised variety of Sardinian primarily spoken in the Province of Cagliari. Traditionally, the name Campidano refers to the fertile area located around the towns of Guspini and Villacidro. Campidanese and its variants of the dialect can be found across the entire...
, SassareseSassareseSassarese is an Italo-Dalmatian language and transitional between Corsican and Sardinian. It is regarded as a Corsican–Sardinian language because of Sassari's historic ties with Tuscany and Corsica...
and GallureseGallureseGallurese is a Italo-Dalmatian Romance language spoken in the northeastern part of Sardinia. It is often considered as a variety of Corsican, or a transitional language between Corsican and Sardinian....
- varieties making up the Sardinian (Note that the latter two can be classified as varieties of CorsicanCorsican languageCorsican is a Italo-Dalmatian Romance language spoken and written on the islands of Corsica and northern Sardinia . Corsican is the traditional native language of the Corsican people, and was long the vernacular language alongside the Italian, official language in Corsica until 1859, which was...
.)
- Logudorese
- Galician
- 7 endangered or partially endangered languages:
- AsturianAsturian languageAsturian is a Romance language of the West Iberian group, Astur-Leonese Subgroup, spoken in the Spanish Region of Asturias by the Asturian people...
, AragoneseAragonese languageAragonese is a Romance language now spoken in a number of local varieties by between 10,000 and 30,000 people over the valleys of the Aragón River, Sobrarbe and Ribagorza in Aragon, Spain...
and FalaFala languageFala is a Romance linguistic variety commonly classified in the Portuguese-Galician subgroup, with some traits from Leonese, spoken in Spain by about 10,500 people, of whom 5,500 live in a valley of the northwestern part of Extremadura near the border with Portugal...
in Spain - MirandeseMirandese languageThe Mirandese language is a Romance language belonging to the Astur-Leonese linguistic group, sparsely spoken in a small area of northeastern Portugal, in the municipalities of Miranda do Douro, Mogadouro and Vimioso...
in Portugal - Ladin in Italy
- Istro-RomanianIstro-Romanian languageIstro-Romanian is an Eastern Romance language that is still spoken today in a few villages and hamlets in the peninsula of Istria, on the northern part of the Adriatic Sea, in what is now Croatia as well as in other countries around the world where the Istro-Romanian people settled after the two...
in CroatiaCroatiaCroatia , officially the Republic of Croatia , is a unitary democratic parliamentary republic in Europe at the crossroads of the Mitteleuropa, the Balkans, and the Mediterranean. Its capital and largest city is Zagreb. The country is divided into 20 counties and the city of Zagreb. Croatia covers ... - Megleno-RomanianMegleno-Romanian languageMegleno-Romanian is a Romance language, similar to Aromanian and Romanian, or a dialect of the Romanian language...
in Greece and MacedoniaRepublic of MacedoniaMacedonia , officially the Republic of Macedonia , is a country located in the central Balkan peninsula in Southeast Europe. It is one of the successor states of the former Yugoslavia, from which it declared independence in 1991...
with a diaspora in RomaniaRomaniaRomania is a country located at the crossroads of Central and Southeastern Europe, on the Lower Danube, within and outside the Carpathian arch, bordering on the Black Sea... - AromanianAromanian languageAromanian , also known as Macedo-Romanian, Arumanian or Vlach is an Eastern Romance language spoken in Southeastern Europe...
in AlbaniaAlbaniaAlbania , officially known as the Republic of Albania , is a country in Southeastern Europe, in the Balkans region. It is bordered by Montenegro to the northwest, Kosovo to the northeast, the Republic of Macedonia to the east and Greece to the south and southeast. It has a coast on the Adriatic Sea...
, Macedonia, Greece, and BulgariaBulgariaBulgaria , officially the Republic of Bulgaria , is a parliamentary democracy within a unitary constitutional republic in Southeast Europe. The country borders Romania to the north, Serbia and Macedonia to the west, Greece and Turkey to the south, as well as the Black Sea to the east...
with a diaspora in Romania
- Asturian
- 14 varieties or dialects:
- Amazonic SpanishAmazonic SpanishAmazonic Spanish , also known as Loreto-Ucayali Spanish or Jungle Spanish , is a variety of Spanish spoken in the Amazon, especially in the Peruvian Amazon provinces of Loreto and Ucayali...
(in PeruPeruPeru , officially the Republic of Peru , is a country in western South America. It is bordered on the north by Ecuador and Colombia, on the east by Brazil, on the southeast by Bolivia, on the south by Chile, and on the west by the Pacific Ocean....
), Extremaduran varietyExtremaduran languageExtremaduran is a Romance language, spoken by several hundred thousand people in Spain, in an area covering the north-western part of the autonomous community of Extremadura and adjoining areas in the province of Salamanca....
(in Spain), and Ladino language (Judeo-Spanish) - Cajun FrenchCajun FrenchCajun French is a variety or dialects of the French language spoken primarily in Louisiana, specifically in the southern and southwestern parishes....
(in the USA) and PicardPicard languagePicard is a language closely related to French, and as such is one of the larger group of Romance languages. It is spoken in two regions in the far north of France – Nord-Pas-de-Calais and Picardy – and in parts of the Belgian region of Wallonia, the district of Tournai and a part of...
(in France) - Gallo-Italic varieties: Emiliano-RomagnoloEmiliano-RomagnoloEmiliano-Romagnolo is a Romance language mostly spoken in Emilia-Romagna, Italy and San Marino. It belongs to the Northern Italian group within Romance languages , which is included in the wider group of western Romance languages...
, LigurianLigurian language (Romance)Ligurian is a Gallo-Romance language spoken in Liguria in Northern Italy, parts of the Mediterranean coastal zone of France, Monaco and in the villages of Carloforte and Calasetta in Sardinia. Genoese , spoken in Genoa, the capital of Liguria, is its most important dialect...
, PiedmontesePiedmontese languagePiedmontese is a Romance language spoken by over 2 million people in Piedmont, northwest Italy. It is geographically and linguistically included in the Northern Italian group . It is part of the wider western group of Romance languages, including French, Occitan, and Catalan.Many European and...
, Lombard, and Venetian - proper Italian varietiesItalian dialectsDialects of Italian are regional varieties of the Italian language, more commonly and more accurately referred to as Regional Italian. The dialects have features, most notably phonological and lexical, percolating from the underlying substrate languages...
: Napoletano-CalabreseNeapolitan languageNeapolitan is the language of the city and region of Naples , and Campania. On October 14, 2008 a law by the Region of Campania stated that the Neapolitan language had to be protected....
, SicilianSicilian languageSicilian is a Romance language. Its dialects make up the Extreme-Southern Italian language group, which are spoken on the island of Sicily and its satellite islands; in southern and central Calabria ; in the southern parts of Apulia, the Salento ; and Campania, on the Italian mainland, where it is...
, IstriotIstriot languageIstriot is a Romance language spoken in the Western Region on the coast of the Istrian Peninsula, especially in the towns of Rovinj and Vodnjan , on the upper northern part of the Adriatic Sea, in Croatia.-Classification:...
, and Judeo-Italian
- Amazonic Spanish
- 4 extinct languages:
- MozarabicMozarabic languageMozarabic was a continuum of closely related Romance dialects spoken in Muslim-dominated areas of the Iberian Peninsula during the early stages of the Romance languages' development in Iberia. Mozarabic descends from Late Latin and early Romance dialects spoken in the Iberian Peninsula from the 5th...
(extinct), - ShuaditShuadit languageShuadit, also spelled Chouhadite, Chouhadit, Chouadite, Chouadit, and Shuhadit is the extinct Jewish language of southern France, also known as Judaeo-Provençal, Judéo-Comtadin, Hébraïco-Comtadin...
(Judeo-Provençal), itself a variety of Occitan - ZarphaticZarphatic languageZarphatic or Judæo-French is an extinct Jewish language, formerly spoken among the Jewish communities of northern France and in parts of what is now west-central Germany, in such cities as Mainz, Frankfurt am Main, and Aachen....
(Jewish French), and - DalmatianDalmatian languageDalmatian was a Romance language spoken in the Dalmatia region of Croatia, and as far south as Kotor in Montenegro. The name refers to a pre-Roman tribe of the Illyrian linguistic group, Dalmatae...
- Mozarabic
The Ethnologue classification does not include numerous other dialects and varieties of the Romance languages, such as:
- extinct Romance branches (African RomanceAfrican RomanceAfrican Romance or African Latin is an extinct Romance language that is supposed to have been spoken in the Roman province of Africa during the later Roman and early Byzantine Empires, prior to the annexation of the region by the Umayyad Caliphate in 696...
, the language of the MorlachsMorlachsMorlachs were a population of Vlachs. In another version their name comes from the slavic terms of "morski-Vlasi" or Sea Vlachs...
) - pidgins and creoles
- Medieval LatinMedieval LatinMedieval Latin was the form of Latin used in the Middle Ages, primarily as a medium of scholarly exchange and as the liturgical language of the medieval Roman Catholic Church, but also as a language of science, literature, law, and administration. Despite the clerical origin of many of its authors,...
as it is regarded only as a written language (it was the lingua francaLingua francaA lingua franca is a language systematically used to make communication possible between people not sharing a mother tongue, in particular when it is a third language, distinct from both mother tongues.-Characteristics:"Lingua franca" is a functionally defined term, independent of the linguistic...
of the scientists during the Middle AgesMiddle AgesThe Middle Ages is a periodization of European history from the 5th century to the 15th century. The Middle Ages follows the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 and precedes the Early Modern Era. It is the middle period of a three-period division of Western history: Classic, Medieval and Modern...
), not spoken by an ethnic population - numerous other Spanish dialects and varietiesSpanish dialects and varietiesSpanish dialects and varieties are the regional variants of the Spanish language, some of which are quite divergent from one another, especially in pronunciation and vocabulary, and less so in grammar....
, such as Cantabrian or Latin American - numerous Portuguese varieties and dialects, such as Brazilian Portuguese, African Portuguese, Judeo-Portuguese
- Niçard and other varieties of Occitan
- 8 other oïl languages (besides French, Wallon, and Picard)
- numerous American and African dialects of French
- central Italian varieties, including Romanesco, Salentino, Toscan dialect
See also
- Classification of Romance languagesClassification of Romance languagesThe internal classification of the Romance languages is a complex and sometimes controversial topic which may not have a unique answer. Several classifications have been proposed, based on different criteria....
- List of languages of Italy
- Legacy of the Roman EmpireLegacy of the Roman EmpireThe legacy of the Roman Empire refers to the set of cultural values, religious beliefs, as well as technological and other achievements of Ancient Rome which were passed on after the demise of the empire itself and continued to shape other civilizations, a process which continues to this day.-...

