
Nonbenzodiazepine
Encyclopedia
The nonbenzodiazepines, also called benzodiazepine-like drugs, are a class of psychoactive drug
s pharmacologically resembling the benzodiazepine
s, with similar benefits, side effects and risks, despite having dissimilar or entirely different chemical structures.
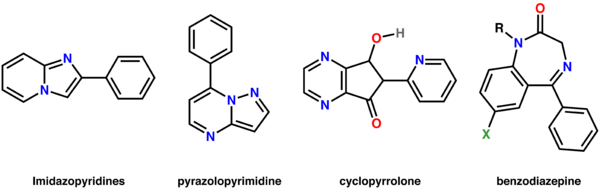 There are currently three major chemical classes of nonbenzodiazepines:
There are currently three major chemical classes of nonbenzodiazepines:
.
s used exclusively for the treatment of mild insomnia
. They are safer than the older barbiturates especially in overdosage and they may, when compared to the benzodiazepines, have less of a tendency to induce physical dependence
and addiction
, although these issues can still become a problem. This has led to the Z-drugs becoming widely prescribed for the treatment of insomnia particularly in elderly patients. Long term use is not recommended as tolerance and addiction
can occur. A survey of patients using nonbenzodiazepine Z drugs and benzodiazepine hypnotic users found that there was no difference in reports of adverse effects which were reported in over 41% of users and, in fact, Z drug users were more likely to report that they had tried to quit their hypnotic drug and were more likely to want to stop taking Z drugs than benzodiazepine users. Efficacy also didn't differ between Z drugs and benzodiazepine users.
and more rarely hallucinations, especially when used in large doses. More rarely these drugs can produce a fugue state
where the patient sleepwalks and may perform relatively complex actions, including cooking meals or driving cars, while effectively unconscious and with no recollection of the events upon awakening. While this effect is rare (and has also been reported to occur with some of the older sedative drugs such as temazepam
and secobarbital
) it can be potentially hazardous and so further development of this class of drugs has continued in an effort to find new compounds with further improved profiles.
Side effects can differ within the drug class due to differences in metabolism and pharmacology. For example long acting benzodiazepines have problems of drug accumulation especially in the elderly or those with liver disease and shorter acting benzodiazepines have a higher risk of more severe withdrawal symptoms. In the case of the nonbenzodiazepines, zaleplon
may be the safest in terms of next day sedation and unlike zolpidem
and zopiclone
, zaleplon has been found to have no association with increased motor vehicle accidents even when taken for middle of the night insomnia due to its ultra short elimination half life.
and hypothesized that insomnia medications may help to treat depression. However, an analysis of data of clinical trials submitted to the FDA concerning the drugs zolpidem
, zaleplon
and eszopiclone
found that these sedative hypnotic drugs more than doubled the risks of developing depression compared to those taking placebo pills. Hypnotic drugs therefore may be contraindicated in patients suffering from or at risk of depression. Hypnotics were found to be more likely to cause depression than to help it. Studies have found that long term users of sedative hypnotic drugs have a markedly raised suicide risk as well as an overall increased mortality
risk. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) for insomnia on the other hand has been found to both improve sleep quality as well as general mental health.
reactions which may resemble those seen during benzodiazepine withdrawal. Treatment usually entails gradually reducing the dosage over a period of weeks or several months depending on the individual, dosage and length of time the drug has been taken. If this approach fails a cross over to a benzodiazepine equivalent dose of a long acting benzodiazepine such as chlordiazepoxide
or preferably diazepam
can be tried followed by a gradual reduction in dosage. In extreme cases and particularly where severe addiction and or abuse is manifested an inpatient detoxification may be required with flumazenil as a possible detoxification tool.
The author was concerned that there is no discussion of adverse effects of benzodiazepine agonist hypnotics discussed in the medical literature such as significant increased levels of infection, cancers and increased mortality
in trials of hypnotic drugs and an overemphasis on the positive effects. No hypnotic manufacturer has yet tried to refute the epidemiology data that shows that use of their product is correlated with excess mortality. The author stated that "major hypnotic trials is needed to more carefully study potential adverse effects of hypnotics such as daytime impairment, infection
, cancer
, and death
and the resultant balance of benefits and risks." The author concluded that more independent research into daytime impairment, infection
, cancer
, and shortening of lives of sedative hypnotic users is needed to find the true balance of benefits and risks of benzodiazepine agonist hypnotic drugs in the treatment of insomnia
. Significant increases in skin cancers and tumors are found in clinical trial data of the nonbenzodiazepine hypnotics compared to trial subjects who took placebo tablets. Other cancers of the brain
, lung
, bowel, breast
and bladder
also occurred. An increase of infections, possibly due to decreased immune function also occurred in the nonbenzodiazepine users. It has been hypothesised that either depressed immune function or the viral infections themselves were the cause of the increased rates of cancer.
Initially the FDA was hesitant to approve some of the nonbenzodiazepines due to concerns regarding increases in cancers. The author reported that due to the fact that the FDA requires reporting of both favourable and unfavourable results of clinical trials that the FDA NDA data is more reliable than the peer reviewed literature which is subject to serious bias regarding hypnotics. In 2008 the FDA analysed their data again and confirmed an increased rate of cancers in the randomised trials compared to placebos but concluded that the rate of cancers did not warrant any regulatory action.
drugs, similar to benzodiazepines causes impairments in body balance and standing steadiness in individuals who wake up during the night or the next morning; falls and hip fractures are frequently reported. The combination with alcohol increases these impairments. Partial, but incomplete tolerance develops to these impairments. Nonbenzodiazepines are not generally recommended for older patients due to the increased risk of falls and fractures. An extensive review of the medical literature regarding the management of insomnia and the elderly found that there is considerable evidence of the effectiveness and lasting benefits of non-drug treatments for insomnia in adults of all age groups and that these interventions are under used. Compared with the benzodiazepines, the nonbenzodiazepine sedative-hypnotics offer little if any advantages in efficacy or tolerability in elderly persons. It was found that newer agents such as the melatonin agonists may be more suitable and effective for the management of chronic insomnia in elderly people. Long-term use of sedative-hypnotics for insomnia lacks an evidence base and is discouraged for reasons that include concerns about such potential adverse drug effects as cognitive impairment (anterograde amnesia
), daytime sedation, motor incoordination, and increased risk of motor vehicle accidents and falls. In addition, the effectiveness and safety of long-term use of these agents remain to be determined. It was concluded that further research is needed to evaluate the long-term effects of treatment and the most appropriate management strategy for elderly persons with chronic insomnia.
s including the nonbenzodiazepine Z drugs concluded that these drugs caused an unjustifiable risk to the individual and to public health and lack evidence of long term effectiveness due to tolerance. The risks include dependence
, accidents and other adverse effects. Gradual discontinuation of hypnotics leads to improved health without worsening of sleep. Preferably they should be prescribed for only a few days at the lowest effective dose and avoided altogether wherever possible in the elderly.
drugs derived from the same structural families as the Z-drugs have been developed, such as alpidem
and pagoclone
and are starting to be marketed. These drugs are also much more selective than the older benzodiazepine anxiolytics, producing effective relief of anxiety symptoms but with little or no sedative or amnestic side effects, and so offer considerable advantages over the older anxiolytic drugs; however, they are still new to the market and have not yet been widely prescribed.
Psychoactive drug
A psychoactive drug, psychopharmaceutical, or psychotropic is a chemical substance that crosses the blood–brain barrier and acts primarily upon the central nervous system where it affects brain function, resulting in changes in perception, mood, consciousness, cognition, and behavior...
s pharmacologically resembling the benzodiazepine
Benzodiazepine
A benzodiazepine is a psychoactive drug whose core chemical structure is the fusion of a benzene ring and a diazepine ring...
s, with similar benefits, side effects and risks, despite having dissimilar or entirely different chemical structures.
Classes

- ImidazopyridineImidazopyridineThe imidazopyridines are a class of drugs defined by their chemical structure. They are generally GABAA receptor agonists, however recently proton pump inhibitors in this class have been developed as well. Despite usually being similar to them in effect, they are not chemically related to...
s- ZolpidemZolpidemZolpidem is a prescription medication used for the short-term treatment of insomnia, as well as some brain disorders. It is a short-acting nonbenzodiazepine hypnotic of the imidazopyridine class that potentiates gamma-aminobutyric acid , an inhibitory neurotransmitter, by binding to GABAA...
(Ambien) - AlpidemAlpidemAlpidem is an anxiolytic drug from the imidazopyridine family, related to the more well known sleeping medication zolpidem. Unlike zolpidem however, alpidem does not produce sedative effects at normal doses, and is instead used specifically for the treatment of anxiety.Alipidem was developed by ...
- NecopidemNecopidemNecopidem is a drug in the imidazopyridine family, which is related to the better known drugs zolpidem and alpidem. It has sedative and anxiolytic effects....
- SaripidemSaripidemSaripidem is a sedative and anxiolytic drug in the imidazopyridine family, which is related to the better known drugs zolpidem and alpidem.Saripidem has a similar pharmacological profile to the benzodiazepine family of drugs including sedative and anxiolytic properties, but its chemical structure...
- Zolpidem
- PyrazolopyrimidinePyrazolopyrimidinePyrazolopyrimidine is a heterocyclic chemical compound with the molecular formula C6H5N3. It forms the central core of a variety of more complex chemical compounds including some pharmaceuticals and pesticides.-Pharmaceuticals:...
s- ZaleplonZaleplonZaleplon is a sedative/hypnotic, mainly used for insomnia. It is a nonbenzodiazepine hypnotic from the pyrazolopyrimidine class. In terms of adverse effects zaleplon appears to offer little improvement compared to both benzodiazepines and other non-benzodiazepine Z-drugs.Sonata is manufactured by...
(Sonata) - DivaplonDivaplonDivaplon is a nonbenzodiazepine, anxiolytic and anticonvulsant drug from the pyrazolopyrimidine family of drugs. It acts as a partial agonist at the "benzodiazepine site" of the GABAA receptor in the brain....
- FasiplonFasiplonFasiplon is a nonbenzodiazepine anxiolytic drug from the imidazopyrimidine family of drugs.Fasiplon binds strongly to benzodiazepine sites on the GABAA receptor and has similar anxiolytic effects in animals, but with less sedative or muscle relaxant action....
- IndiplonIndiplonIndiplon is a nonbenzodiazepine, hypnotic sedative being developed in 2 formulations - an immediate release product for sleep onset and a modified-release version for sleep maintenance.- Mode of action :...
- LorediplonLorediplonLorediplon is a nonbenzodiazepine anxiolytic drug of the pyrazolopyrimidine family of drugs....
- OcinaplonOcinaplonOcinaplon is an anxiolytic drug in the pyrazolopyrimidine family of drugs. Other pyrazolopyrimidine drugs include zaleplon and indiplon.Ocinaplon has a similar pharmacological profile to the benzodiazepine family of drugs, but with mainly anxiolytic properties and relatively little sedative or...
- PanadiplonPanadiplonPanadiplon is an anxiolytic drug with a novel chemical structure that is not closely related to other drugs of this type. It has a similar pharmacological profile to the benzodiazepine family of drugs, but with mainly anxiolytic properties and relatively little sedative or amnestic effect, and so...
- TaniplonTaniplonTaniplon is a nonbenzodiazepine anxiolytic drug from the imidazoquinazoline family of drugs.Taniplon binds strongly to benzodiazepine sites on the GABAA receptor and has similar anxiolytic effects in animals, but with less sedative or muscle relaxant action....
- Zaleplon
- Cyclopyrrolones
- EszopicloneEszopicloneEszopiclone, marketed by Sepracor under the brand-name Lunesta, is a nonbenzodiazepine hypnotic used as a treatment for insomnia. Eszopiclone is the active dextrorotatory stereoisomer of zopiclone, and belongs to the class of drugs known as cyclopyrrolones.Eszopiclone is a short acting...
(Lunesta) - ZopicloneZopicloneZopiclone is a non-benzodiazepine hypnotic agent used in the treatment of insomnia. In the United States, zopiclone is not commercially available, although its active stereoisomer, eszopiclone, is sold under the name Lunesta...
(Imovane) - PagoclonePagoclonePagoclone is an anxiolytic drug from the cyclopyrrolone family, related to better-known drugs such as the sleeping medication zopiclone. It is one of a relatively recently developed class of medicines known as the nonbenzodiazepines, which have similar effects to the older benzodiazepine group, but...
- PazinaclonePazinaclonePazinaclone is a sedative and anxiolytic drug in the cyclopyrrolone family of drugs. Other cyclopyrrolone drugs include zopiclone and eszopiclone....
- SuprocloneSuprocloneSuproclone is a sedative and anxiolytic drug in the cyclopyrrolone family of drugs, developed by the French pharmaceutical company Rhône-Poulenc. Other cyclopyrrolone drugs include zopiclone, pagoclone and suriclone....
- SuricloneSuricloneSuriclone is a sedative and anxiolytic drug in the cyclopyrrolone family of drugs. Other cyclopyrrolone drugs include zopiclone and pagoclone....
- Eszopiclone
- β-Carbolines
- AbecarnilAbecarnilAbecarnil is an anxiolytic drug from the β-Carboline family. It is one of a relatively recently developed class of medicines known as the nonbenzodiazepines, which have similar effects to the older benzodiazepine group, but with quite different chemical structures...
- GedocarnilGedocarnilGedocarnil is an anxiolytic....
- ZK-93423ZK-93423ZK-93423 is an anxiolytic drug from the β-Carboline family, closely related to abecarnil. It is a nonbenzodiazepine GABAA agonist which is not subtype selective and stimulates α1, α2, α3, and α5-subunit containing GABAA receptors equally. It has anticonvulsant, muscle relaxant and appetite...
- Abecarnil
- Others
- CGS-9896CGS-9896CGS-9896 is an anxiolytic drug used in scientific research. It has similar effects to benzodiazepine drugs, but is structurally distinct and so is classed as a nonbenzodiazepine anxiolytic....
- CGS-20625CGS-20625CGS-20625 is an anxiolytic drug used in scientific research. It has similar effects to, and binds to the same target as benzodiazepine drugs, but is structurally distinct and so is classed as a nonbenzodiazepine anxiolytic....
- CL-218,872CL-218,872CL-218,872 is a sedative and hypnotic drug used in scientific research. It has similar effects to sedative-hypnotic benzodiazepine drugs such as triazolam, but is structurally distinct and so is classed as a nonbenzodiazepine hypnotic....
- ELB-139ELB-139ELB-139 is an anxiolytic drug with a novel chemical structure, which is used in scientific research. It has similar effects to benzodiazepine drugs, but is structurally distinct and so is classed as a nonbenzodiazepine anxiolytic....
- GBLD-345GBLD-345GBLD-345 is an anxiolytic drug used in scientific research, which acts as a nonselective full agonist at GABAA receptors. It has similar effects to benzodiazepine drugs, but is structurally distinct and so is classed as a nonbenzodiazepine anxiolytic....
- L-838,417L-838,417L-838,417 is an anxiolytic drug used in scientific research. It has similar effects to benzodiazepine drugs, but is structurally distinct and so is classed as a nonbenzodiazepine anxiolytic...
- NS-2664NS-2664NS-2664 is an anxiolytic drug with a novel chemical structure, developed by the small pharmaceutical company Neurosearch. It has similar effects to benzodiazepine drugs, but is structurally distinct and so is classed as a nonbenzodiazepine anxiolytic...
- NS-2710NS-2710NS-2710 is an anxiolytic drug with a novel chemical structure, developed by the small pharmaceutical company Neurosearch. It has similar effects to benzodiazepine drugs, but is structurally distinct and so is classed as a nonbenzodiazepine anxiolytic...
- PipequalinePipequalinePipequaline is an anxiolytic drug with a novel chemical structure that is not closely related to other drugs of this type. It has a similar pharmacological profile to the benzodiazepine family of drugs, but with mainly anxiolytic properties and very little sedative, amnestic or anticonvulsant...
- RWJ-51204RWJ-51204RWJ-51204 is an anxiolytic drug used in scientific research. It has similar effects to benzodiazepine drugs, but is structurally distinct and so is classed as a nonbenzodiazepine anxiolytic.RWJ-51204 is a nonselective partial agonist at GABAA receptors...
- SB-205,384SB-205,384SB-205,384 is an anxiolytic drug. It has similar effects to benzodiazepine drugs, but is structurally distinct and so is classed as a nonbenzodiazepine anxiolytic....
- SL-651,498SL-651,498SL-651,498 is an anxiolytic and anticonvulsant drug used in scientific research, with a chemical structure most closely related to β-carboline derivatives such as abecarnil and gedocarnil...
- SX-3228SX-3228SX-3228 is a sedative and hypnotic drug used in scientific research. It has similar effects to sedative-hypnotic benzodiazepine drugs, but is structurally distinct and so is classed as a nonbenzodiazepine hypnotic....
- TP-003TP-003TP-003 is an anxiolytic drug with a novel chemical structure, which is used in scientific research. It has similar effects to benzodiazepine drugs, but is structurally distinct and so is classed as a nonbenzodiazepine anxiolytic...
- TP-13TP-13TP-13 is an anxiolytic drug with a novel chemical structure, which is used in scientific research. It has similar effects to benzodiazepine drugs, but is structurally distinct and so is classed as a nonbenzodiazepine anxiolytic. It is a subtype-selective partial agonist at GABAA receptors, binding...
- TPA-023TPA-023TPA-023 is an anxiolytic drug with a novel chemical structure, which is used in scientific research. It has similar effects to benzodiazepine drugs, but is structurally distinct and so is classed as a nonbenzodiazepine anxiolytic...
- Y-23684Y-23684Y-23684 is an anxiolytic drug with a novel chemical structure, which is used in scientific research. It has similar effects to benzodiazepine drugs, but is structurally distinct and so is classed as a nonbenzodiazepine anxiolytic....
- CGS-9896
Pharmacology
The nonbenzodiazepines are positive allosteric modulators of the GABA-A receptor. Like the benzodiazepines, they exert their effects by binding to and activating the benzodiazepine site of the receptor complex.Background
Nonbenzodiazepines have demonstrated efficacy in treating sleep disorders. There is some limited evidence that suggests that tolerance to nonbenzodiazepines is slower to develop than with benzodiazepines. However, data is limited so no conclusions can be drawn. Data is also limited into the long term effects of nonbenzodiazepines. Further research into the safety of nonbenzodiazepines and long term effectiveness of nonbenzodiazepines has been recommended in a review of the literature. Some differences exist between the Z-drugs, for example tolerance and rebound effects may not occur with zaleplonZaleplon
Zaleplon is a sedative/hypnotic, mainly used for insomnia. It is a nonbenzodiazepine hypnotic from the pyrazolopyrimidine class. In terms of adverse effects zaleplon appears to offer little improvement compared to both benzodiazepines and other non-benzodiazepine Z-drugs.Sonata is manufactured by...
.
Pharmaceuticals
The first three nonbenzodiazepine drugs to enter the market were the "Z-drugs", zopiclone, zolpidem and zaleplon. These three drugs are all sedativeSedative
A sedative or tranquilizer is a substance that induces sedation by reducing irritability or excitement....
s used exclusively for the treatment of mild insomnia
Insomnia
Insomnia is most often defined by an individual's report of sleeping difficulties. While the term is sometimes used in sleep literature to describe a disorder demonstrated by polysomnographic evidence of disturbed sleep, insomnia is often defined as a positive response to either of two questions:...
. They are safer than the older barbiturates especially in overdosage and they may, when compared to the benzodiazepines, have less of a tendency to induce physical dependence
Physical dependence
Physical dependence refers to a state resulting from chronic use of a drug that has produced tolerance and where negative physical symptoms of withdrawal result from abrupt discontinuation or dosage reduction...
and addiction
Substance dependence
The section about substance dependence in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders does not use the word addiction at all. It explains:...
, although these issues can still become a problem. This has led to the Z-drugs becoming widely prescribed for the treatment of insomnia particularly in elderly patients. Long term use is not recommended as tolerance and addiction
Substance dependence
The section about substance dependence in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders does not use the word addiction at all. It explains:...
can occur. A survey of patients using nonbenzodiazepine Z drugs and benzodiazepine hypnotic users found that there was no difference in reports of adverse effects which were reported in over 41% of users and, in fact, Z drug users were more likely to report that they had tried to quit their hypnotic drug and were more likely to want to stop taking Z drugs than benzodiazepine users. Efficacy also didn't differ between Z drugs and benzodiazepine users.
Side effects
The Z-drugs are not without disadvantages, and all three compounds are notable for producing side effects such as pronounced amnesiaAmnesia
Amnesia is a condition in which one's memory is lost. The causes of amnesia have traditionally been divided into categories. Memory appears to be stored in several parts of the limbic system of the brain, and any condition that interferes with the function of this system can cause amnesia...
and more rarely hallucinations, especially when used in large doses. More rarely these drugs can produce a fugue state
Fugue state
A fugue state, formally dissociative fugue or psychogenic fugue , is a rare psychiatric disorder characterized by reversible amnesia for personal identity, including the memories, personality and other identifying characteristics of individuality...
where the patient sleepwalks and may perform relatively complex actions, including cooking meals or driving cars, while effectively unconscious and with no recollection of the events upon awakening. While this effect is rare (and has also been reported to occur with some of the older sedative drugs such as temazepam
Temazepam
Temazepam is an intermediate-acting 3-hydroxy benzodiazepine. It is mostly prescribed for the short-term treatment of sleeplessness in patients who have difficulty maintaining sleep...
and secobarbital
Secobarbital
Secobarbital sodium is a barbiturate derivative drug that was first synthesized in 1928 in Germany. It possesses anaesthetic, anticonvulsant, sedative and hypnotic properties...
) it can be potentially hazardous and so further development of this class of drugs has continued in an effort to find new compounds with further improved profiles.
Side effects can differ within the drug class due to differences in metabolism and pharmacology. For example long acting benzodiazepines have problems of drug accumulation especially in the elderly or those with liver disease and shorter acting benzodiazepines have a higher risk of more severe withdrawal symptoms. In the case of the nonbenzodiazepines, zaleplon
Zaleplon
Zaleplon is a sedative/hypnotic, mainly used for insomnia. It is a nonbenzodiazepine hypnotic from the pyrazolopyrimidine class. In terms of adverse effects zaleplon appears to offer little improvement compared to both benzodiazepines and other non-benzodiazepine Z-drugs.Sonata is manufactured by...
may be the safest in terms of next day sedation and unlike zolpidem
Zolpidem
Zolpidem is a prescription medication used for the short-term treatment of insomnia, as well as some brain disorders. It is a short-acting nonbenzodiazepine hypnotic of the imidazopyridine class that potentiates gamma-aminobutyric acid , an inhibitory neurotransmitter, by binding to GABAA...
and zopiclone
Zopiclone
Zopiclone is a non-benzodiazepine hypnotic agent used in the treatment of insomnia. In the United States, zopiclone is not commercially available, although its active stereoisomer, eszopiclone, is sold under the name Lunesta...
, zaleplon has been found to have no association with increased motor vehicle accidents even when taken for middle of the night insomnia due to its ultra short elimination half life.
Increased risk of depression
It has been claimed that insomnia causes depressionDepression (mood)
Depression is a state of low mood and aversion to activity that can affect a person's thoughts, behaviour, feelings and physical well-being. Depressed people may feel sad, anxious, empty, hopeless, helpless, worthless, guilty, irritable, or restless...
and hypothesized that insomnia medications may help to treat depression. However, an analysis of data of clinical trials submitted to the FDA concerning the drugs zolpidem
Zolpidem
Zolpidem is a prescription medication used for the short-term treatment of insomnia, as well as some brain disorders. It is a short-acting nonbenzodiazepine hypnotic of the imidazopyridine class that potentiates gamma-aminobutyric acid , an inhibitory neurotransmitter, by binding to GABAA...
, zaleplon
Zaleplon
Zaleplon is a sedative/hypnotic, mainly used for insomnia. It is a nonbenzodiazepine hypnotic from the pyrazolopyrimidine class. In terms of adverse effects zaleplon appears to offer little improvement compared to both benzodiazepines and other non-benzodiazepine Z-drugs.Sonata is manufactured by...
and eszopiclone
Eszopiclone
Eszopiclone, marketed by Sepracor under the brand-name Lunesta, is a nonbenzodiazepine hypnotic used as a treatment for insomnia. Eszopiclone is the active dextrorotatory stereoisomer of zopiclone, and belongs to the class of drugs known as cyclopyrrolones.Eszopiclone is a short acting...
found that these sedative hypnotic drugs more than doubled the risks of developing depression compared to those taking placebo pills. Hypnotic drugs therefore may be contraindicated in patients suffering from or at risk of depression. Hypnotics were found to be more likely to cause depression than to help it. Studies have found that long term users of sedative hypnotic drugs have a markedly raised suicide risk as well as an overall increased mortality
Death
Death is the permanent termination of the biological functions that sustain a living organism. Phenomena which commonly bring about death include old age, predation, malnutrition, disease, and accidents or trauma resulting in terminal injury....
risk. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) for insomnia on the other hand has been found to both improve sleep quality as well as general mental health.
Dependence and withdrawal management
Nonbenzodiazepines should not be discontinued abruptly if taken for more than a few weeks due to the risk of rebound withdrawal effects and acute withdrawalWithdrawal
Withdrawal can refer to any sort of separation, but is most commonly used to describe the group of symptoms that occurs upon the abrupt discontinuation/separation or a decrease in dosage of the intake of medications, recreational drugs, and alcohol...
reactions which may resemble those seen during benzodiazepine withdrawal. Treatment usually entails gradually reducing the dosage over a period of weeks or several months depending on the individual, dosage and length of time the drug has been taken. If this approach fails a cross over to a benzodiazepine equivalent dose of a long acting benzodiazepine such as chlordiazepoxide
Chlordiazepoxide
Chlordiazepoxide, is a sedative/hypnotic drug and benzodiazepine. It is marketed under the trade names Angirex, Klopoxid, Librax , Libritabs, Librium, Mesural, Multum, Novapam, Risolid, Silibrin, Sonimen and Tropium.Chlordiazepoxide was the first benzodiazepine to be synthesised and...
or preferably diazepam
Diazepam
Diazepam , first marketed as Valium by Hoffmann-La Roche is a benzodiazepine drug. Diazepam is also marketed in Australia as Antenex. It is commonly used for treating anxiety, insomnia, seizures including status epilepticus, muscle spasms , restless legs syndrome, alcohol withdrawal,...
can be tried followed by a gradual reduction in dosage. In extreme cases and particularly where severe addiction and or abuse is manifested an inpatient detoxification may be required with flumazenil as a possible detoxification tool.
Carcinogenicity
The Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine published a paper which had carried out a systematic review of the medical literature concerning insomnia medications and raised concerns about benzodiazepine receptor agonist drugs, the benzodiazepines and the Z-drugs that are used as hypnotics in humans. The review found that almost all trials of sleep disorders and drugs are sponsored by the pharmaceutical industry. It was found that the odds ratio for finding results favorable to industry in industry-sponsored trials was 3.6 times higher than non-industry-sponsored studies and that 24% of authors did not disclose being funded by the drug companies in their published papers when they were funded by the drug companies. The paper found that there is little research into hypnotics that is independent from the drug manufacturers. Also of concern was the lack of focus in industry sponsored trials on their own results showing that use of hypnotics is correlated with depression.The author was concerned that there is no discussion of adverse effects of benzodiazepine agonist hypnotics discussed in the medical literature such as significant increased levels of infection, cancers and increased mortality
Death
Death is the permanent termination of the biological functions that sustain a living organism. Phenomena which commonly bring about death include old age, predation, malnutrition, disease, and accidents or trauma resulting in terminal injury....
in trials of hypnotic drugs and an overemphasis on the positive effects. No hypnotic manufacturer has yet tried to refute the epidemiology data that shows that use of their product is correlated with excess mortality. The author stated that "major hypnotic trials is needed to more carefully study potential adverse effects of hypnotics such as daytime impairment, infection
Infection
An infection is the colonization of a host organism by parasite species. Infecting parasites seek to use the host's resources to reproduce, often resulting in disease...
, cancer
Cancer
Cancer , known medically as a malignant neoplasm, is a large group of different diseases, all involving unregulated cell growth. In cancer, cells divide and grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors, and invade nearby parts of the body. The cancer may also spread to more distant parts of the...
, and death
Death
Death is the permanent termination of the biological functions that sustain a living organism. Phenomena which commonly bring about death include old age, predation, malnutrition, disease, and accidents or trauma resulting in terminal injury....
and the resultant balance of benefits and risks." The author concluded that more independent research into daytime impairment, infection
Infection
An infection is the colonization of a host organism by parasite species. Infecting parasites seek to use the host's resources to reproduce, often resulting in disease...
, cancer
Cancer
Cancer , known medically as a malignant neoplasm, is a large group of different diseases, all involving unregulated cell growth. In cancer, cells divide and grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors, and invade nearby parts of the body. The cancer may also spread to more distant parts of the...
, and shortening of lives of sedative hypnotic users is needed to find the true balance of benefits and risks of benzodiazepine agonist hypnotic drugs in the treatment of insomnia
Insomnia
Insomnia is most often defined by an individual's report of sleeping difficulties. While the term is sometimes used in sleep literature to describe a disorder demonstrated by polysomnographic evidence of disturbed sleep, insomnia is often defined as a positive response to either of two questions:...
. Significant increases in skin cancers and tumors are found in clinical trial data of the nonbenzodiazepine hypnotics compared to trial subjects who took placebo tablets. Other cancers of the brain
Brain
The brain is the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals—only a few primitive invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, sea squirts and starfishes do not have one. It is located in the head, usually close to primary sensory apparatus such as vision, hearing,...
, lung
Lung
The lung is the essential respiration organ in many air-breathing animals, including most tetrapods, a few fish and a few snails. In mammals and the more complex life forms, the two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of the heart...
, bowel, breast
Breast
The breast is the upper ventral region of the torso of a primate, in left and right sides, which in a female contains the mammary gland that secretes milk used to feed infants.Both men and women develop breasts from the same embryological tissues...
and bladder
Bladder
Bladder usually refers to an anatomical hollow organBladder may also refer to:-Biology:* Urinary bladder in humans** Urinary bladder ** Bladder control; see Urinary incontinence** Artificial urinary bladder, in humans...
also occurred. An increase of infections, possibly due to decreased immune function also occurred in the nonbenzodiazepine users. It has been hypothesised that either depressed immune function or the viral infections themselves were the cause of the increased rates of cancer.
Initially the FDA was hesitant to approve some of the nonbenzodiazepines due to concerns regarding increases in cancers. The author reported that due to the fact that the FDA requires reporting of both favourable and unfavourable results of clinical trials that the FDA NDA data is more reliable than the peer reviewed literature which is subject to serious bias regarding hypnotics. In 2008 the FDA analysed their data again and confirmed an increased rate of cancers in the randomised trials compared to placebos but concluded that the rate of cancers did not warrant any regulatory action.
Elderly
Nonbenzodiazepine hypnoticHypnotic
Hypnotic drugs are a class of psychoactives whose primary function is to induce sleep and to be used in the treatment of insomnia and in surgical anesthesia...
drugs, similar to benzodiazepines causes impairments in body balance and standing steadiness in individuals who wake up during the night or the next morning; falls and hip fractures are frequently reported. The combination with alcohol increases these impairments. Partial, but incomplete tolerance develops to these impairments. Nonbenzodiazepines are not generally recommended for older patients due to the increased risk of falls and fractures. An extensive review of the medical literature regarding the management of insomnia and the elderly found that there is considerable evidence of the effectiveness and lasting benefits of non-drug treatments for insomnia in adults of all age groups and that these interventions are under used. Compared with the benzodiazepines, the nonbenzodiazepine sedative-hypnotics offer little if any advantages in efficacy or tolerability in elderly persons. It was found that newer agents such as the melatonin agonists may be more suitable and effective for the management of chronic insomnia in elderly people. Long-term use of sedative-hypnotics for insomnia lacks an evidence base and is discouraged for reasons that include concerns about such potential adverse drug effects as cognitive impairment (anterograde amnesia
Anterograde amnesia
Anterograde amnesia is a loss of the ability to create new memories after the event that caused the amnesia, leading to a partial or complete inability to recall the recent past, while long-term memories from before the event remain intact. This is in contrast to retrograde amnesia, where memories...
), daytime sedation, motor incoordination, and increased risk of motor vehicle accidents and falls. In addition, the effectiveness and safety of long-term use of these agents remain to be determined. It was concluded that further research is needed to evaluate the long-term effects of treatment and the most appropriate management strategy for elderly persons with chronic insomnia.
Controversy
A review of the literature regarding hypnoticHypnotic
Hypnotic drugs are a class of psychoactives whose primary function is to induce sleep and to be used in the treatment of insomnia and in surgical anesthesia...
s including the nonbenzodiazepine Z drugs concluded that these drugs caused an unjustifiable risk to the individual and to public health and lack evidence of long term effectiveness due to tolerance. The risks include dependence
Substance dependence
The section about substance dependence in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders does not use the word addiction at all. It explains:...
, accidents and other adverse effects. Gradual discontinuation of hypnotics leads to improved health without worsening of sleep. Preferably they should be prescribed for only a few days at the lowest effective dose and avoided altogether wherever possible in the elderly.
New compounds
More recently, a range of non-sedating anxiolyticAnxiolytic
An anxiolytic is a drug used for the treatment of anxiety, and its related psychological and physical symptoms...
drugs derived from the same structural families as the Z-drugs have been developed, such as alpidem
Alpidem
Alpidem is an anxiolytic drug from the imidazopyridine family, related to the more well known sleeping medication zolpidem. Unlike zolpidem however, alpidem does not produce sedative effects at normal doses, and is instead used specifically for the treatment of anxiety.Alipidem was developed by ...
and pagoclone
Pagoclone
Pagoclone is an anxiolytic drug from the cyclopyrrolone family, related to better-known drugs such as the sleeping medication zopiclone. It is one of a relatively recently developed class of medicines known as the nonbenzodiazepines, which have similar effects to the older benzodiazepine group, but...
and are starting to be marketed. These drugs are also much more selective than the older benzodiazepine anxiolytics, producing effective relief of anxiety symptoms but with little or no sedative or amnestic side effects, and so offer considerable advantages over the older anxiolytic drugs; however, they are still new to the market and have not yet been widely prescribed.
See also
- BenzodiazepineBenzodiazepineA benzodiazepine is a psychoactive drug whose core chemical structure is the fusion of a benzene ring and a diazepine ring...
- Z-drugs
- ZaleplonZaleplonZaleplon is a sedative/hypnotic, mainly used for insomnia. It is a nonbenzodiazepine hypnotic from the pyrazolopyrimidine class. In terms of adverse effects zaleplon appears to offer little improvement compared to both benzodiazepines and other non-benzodiazepine Z-drugs.Sonata is manufactured by...
(Sonata) - ZolpidemZolpidemZolpidem is a prescription medication used for the short-term treatment of insomnia, as well as some brain disorders. It is a short-acting nonbenzodiazepine hypnotic of the imidazopyridine class that potentiates gamma-aminobutyric acid , an inhibitory neurotransmitter, by binding to GABAA...
(Ambien) - ZopicloneZopicloneZopiclone is a non-benzodiazepine hypnotic agent used in the treatment of insomnia. In the United States, zopiclone is not commercially available, although its active stereoisomer, eszopiclone, is sold under the name Lunesta...
(Imovane) - EszopicloneEszopicloneEszopiclone, marketed by Sepracor under the brand-name Lunesta, is a nonbenzodiazepine hypnotic used as a treatment for insomnia. Eszopiclone is the active dextrorotatory stereoisomer of zopiclone, and belongs to the class of drugs known as cyclopyrrolones.Eszopiclone is a short acting...
(Lunesta)
External links
- http://pharmacy.oregonstate.edu/drug_policy/pages/dur_board/reviews/articles/nonbenzodiazepine.html

