
Electric car
Encyclopedia
An electric car is an automobile
which is propelled
by electric motor
(s), using electrical energy stored in batteries or another energy storage device. Electric cars were popular in the late-19th century and early 20th century, until advances in internal combustion engine
technology and mass production
of cheaper gasoline vehicles led to a decline in the use of electric drive vehicle. The energy crises of the 1970s and 80s brought a short lived interest in electric cars, but in the mid 2000s took place a renewed interest in the production of electric cars due mainly to concerns about rapidly increasing oil prices and the need to curb greenhouse gas emissions. As of November 2011 series production models available in some countries include the Tesla Roadster
, REVAi, Renault Fluence Z.E.
, Buddy
, Mitsubishi i MiEV
, Tazzari Zero
, Nissan Leaf
, Smart ED
, Wheego Whip LiFe, Mia electric
, and BYD e6
. The Leaf, with more than 20,000 units sold worldwide by November 2011, and the i-MiEV, with global cumulative sales of more than 17,000 units through October 2011, are the world's top selling highway-capable electric cars.
Electric cars have several potential benefits as compared to conventional internal combustion automobiles that include a significant reduction of urban air pollution
as they do not emit harmful tailpipe pollutants
from the onboard source of power at the point of operation (zero tail pipe emissions
); reduced greenhouse gas
emissions from the onboard source of power depending on the fuel and technology used for electricity generation
to charge the batteries; and less dependence on foreign oil, which for the United States, other developed and emerging countries is cause of concerns about their vulnerability to price shocks
and supply
disruption
. Also for many developing countries, and particularly for the poorest in Africa
, high oil prices have an adverse impact on their balance of payments
, hindering their economic growth.
Despite their potential benefits, widespread adoption of electric cars faces several hurdles and limitations. As of 2011 electric cars are significantly more expensive than conventional internal combustion engine
vehicles and hybrid electric vehicle
s due to the additional cost of their lithium-ion battery pack. However, battery prices are coming down with mass production and expected to drop further.
Other factors discouraging the adoption of electric cars are the lack of public and private recharging infrastructure
and the driver's fear of the batteries running out of energy before reaching their destination (range anxiety
) due to the limited range of existing electric cars. Several governments have established policies and economic incentives to overcome existing barriers, to promote the sales of electric cars, and to fund further development of electric vehicles, more cost-effective battery technology and their components. The U.S. has pledged in federal grants for electric cars and batteries. China has announced it will provide to initiate an electric car industry within its borders. Several national and local governments have established tax credits, subsidies, and other incentives
to reduce the net purchase price of electric cars and other plug-ins
.
(EV); the term "electric vehicle" refers to any vehicle that uses electric motors for propulsion, while "electric car" generally refers to road-going automobiles powered by electricity. While an electric car's power source is not explicitly an on-board battery
, electric cars with motors powered by other energy sources are generally referred to by a different name: an electric car powered by sunlight is a solar car
, and an electric car powered by a gasoline generator is a form of hybrid car. Thus, an electric car that derives its power from an on-board battery pack is a form of battery electric vehicle
(BEV). Most often, the term "electric car" is used to refer to pure battery electric vehicles.

Electric cars enjoyed popularity between the mid-19th century and early 20th century, when electricity was among the preferred methods for automobile propulsion, providing a level of comfort and ease of operation that could not be achieved by the gasoline cars of the time. Advances in internal combustion
technology, especially the electric starter, soon rendered this advantage moot; the greater range of gasoline cars, quicker refueling times, and growing petroleum infrastructure, along with the mass production of gasoline vehicles by companies such as the Ford Motor Company
, which reduced prices of gasoline cars to less than half that of equivalent electric cars, led to a decline in the use of electric propulsion, effectively removing it from important markets such as the United States
by the 1930s. However, in recent years, increased concerns over the environmental impact of gasoline cars, higher gasoline prices, improvements in battery technology, and the prospect of peak oil
, have brought about renewed interest in electric cars, which are perceived to be more environmentally friendly and cheaper to maintain and run, despite high initial costs. Electric cars currently enjoy relative popularity in countries around the world, though they were absent from the roads of the United States
, after they briefly re-appeared in the late 90s.
on April 29, 1899 in his 'rocket-shaped' vehicle Jamais Contente, which reached a top speed of 105.88 km/h (65.8 mph). Before the 1920s, electric automobiles were competing with petroleum-fueled cars for urban use of a quality service car.
 Proposed as early as 1896 in order to overcome the lack of recharging infrastructure, an exchangeable battery service was first put into practice by Hartford Electric Light Company for electric trucks. The vehicle owner purchased the vehicle from General Electric Company (GVC) without a battery and the electricity was purchased from Hartford Electric through an exchangeable battery. The owner paid a variable per-mile charge and a monthly service fee to cover maintenance and storage of the truck. The service was provided between 1910 to 1924 and during that period covered more than 6 million miles. Beginning in 1917 a similar service was operated in Chicago
Proposed as early as 1896 in order to overcome the lack of recharging infrastructure, an exchangeable battery service was first put into practice by Hartford Electric Light Company for electric trucks. The vehicle owner purchased the vehicle from General Electric Company (GVC) without a battery and the electricity was purchased from Hartford Electric through an exchangeable battery. The owner paid a variable per-mile charge and a monthly service fee to cover maintenance and storage of the truck. The service was provided between 1910 to 1924 and during that period covered more than 6 million miles. Beginning in 1917 a similar service was operated in Chicago
for owners of Milburn Light Electric cars who also could buy the vehicle without the batteries.
In 1897, electric vehicles found their first commercial application in the U.S. as a fleet of electrical New York City taxis, built by the Electric Carriage and Wagon Company of Philadelphia. Electric cars were produced in the US by Anthony Electric, Baker
, Columbia
, Anderson
, , Fritchle, Studebaker
, Riker
, Milburn, and others during the early 20th century.
Despite their relatively slow speed, electric vehicles had a number of advantages over their early-1900s competitors. They did not have the vibration, smell, and noise associated with gasoline cars. They did not require gear changes, which for gasoline cars was the most difficult part of driving. Electric cars found popularity among well-heeled customers who used them as city cars, where their limited range was less of a disadvantage. The cars were also preferred because they did not require a manual effort to start, as did gasoline cars which featured a hand crank to start the engine. Electric cars were often marketed as suitable vehicles for women drivers due to this ease of operation.
 In 1911, the New York Times stated that the electric car has long been recognized as "ideal" because it was cleaner, quieter and much more economical than gasoline-powered cars. Reporting this in 2010, the Washington Post commented that "the same unreliability of electric car batteries that flummoxed Thomas Edison persists today."
In 1911, the New York Times stated that the electric car has long been recognized as "ideal" because it was cleaner, quieter and much more economical than gasoline-powered cars. Reporting this in 2010, the Washington Post commented that "the same unreliability of electric car batteries that flummoxed Thomas Edison persists today."
(CARB), the government of California
's began a push for more fuel-efficient, lower-emissions vehicles, with the ultimate goal being a move to zero-emissions vehicle
s such as electric vehicles. In response, automakers developed electric models, including the Chrysler TEVan
, Ford Ranger EV
pickup truck, GM EV1 and S10 EV
pickup, Honda EV Plus
hatchback, Nissan lithium-battery Altra EV miniwagon and Toyota RAV4 EV
. These cars were eventually withdrawn from the U.S. market.
The global economic recession in the late 2000s led to increased calls for automakers to abandon fuel-inefficient SUVs, which were seen as a symbol of the excess that caused the recession, in favor of small cars, hybrid cars, and electric cars. California
electric car maker Tesla Motors
began development in 2004 on the Tesla Roadster
, which was first delivered to customers in 2008. As of January 2011 Tesla had produced more than 1,500 Roadsters sold in at least 31 countries. The Mitsubishi i MiEV
was launched for fleet customers in Japan in July 2009, and for individual customers in April 2010, followed by sales to the public in Hong Kong in May 2010, and Australia in July 2010 via leasing.
Retail customer deliveries of the Nissan Leaf
in Japan and the United States began in December 2010, though initial availability is restricted to a few launch markets and in limited quantities. As of September 2011 other electric automobiles, city cars, and light trucks available in some markets included the REVAi, Buddy
, Citroën C1 ev'ie
, Transit Connect Electric, Mercedes-Benz Vito E-Cell, Smart ED
, Wheego Whip LiFe, and several neighborhood electric vehicle
s.
(ICEVs).
. The primary reason is the high cost of car batteries
. US and British car buyers seem to be unwilling to pay more for an electric car. This prohibits the mass transition from gasoline cars
to electric cars. A survey taken by Nielsen
for the Financial Times
has shown that 65 percent of Americans and 76 percent of Britons are not willing to pay more for an electric car above the price of a gasoline car
. Also a report by J.D. Power and Associates
claims that about 50 percent of U.S. car buyers are not even willing to spend more than on a green vehicle
above the price of a petrol car despite their concern about the environment.
The Nissan LEAF
is the most affordable five door family electric car in the U.S. at a price of going down to after federal tax rebate of , going further down to after the tax rebate in California and similar incentives in other states.
The Renault Fluence Z.E.
five door family saloon electric car will be priced at less than before any U.S. federal and state tax rebates are applied. It will be sold without the battery
thus the significant price difference. The customer will buy the Renault Fluence Z.E. with a contract to lease the battery from the company Better Place.
The electric car company Tesla Motors
is using laptop battery technology
for the battery packs of their electric cars that are 3 to 4 times cheaper than dedicated electric car battery packs that other auto makers are using. While dedicated battery packs cost $700–$800 per kilowatt hour, battery packs using small laptop cells cost about $200. That could potentially drive down the cost of electric cars that are using Tesla's battery technology such as the Toyota RAV4 EV
and the Smart ED
as well as their own upcoming 2014 models such as the Model X
.
A study published in 2011 by the Belfer Center
, Harvard University
, found that the gasoline costs savings of plug-in electric cars over the vehicles’ lifetimes do not offset their higher purchase prices. This finding was estimated comparing their lifetime net present value
at 2010 purchase and operating costs for the U.S. market, and assuming no government subidies. According to the study estimates, a PHEV-40 is more expensive than a conventional internal combustion engine, while a battery electric vehicle is more expensive. The study also examined how this balance will change over the next 10 to 20 years, assuming that battery costs will decrease while gasoline prices increase. Under the future scenarios considered, the study found that BEVs will be significantly less expensive than conventional cars ( to cheaper), while PHEVs, will be more expensive than BEVs in almost all comparison scenarios, and only less expensive than conventional cars in an scenario with very low battery costs and high gasoline prices. The reason for the different savings among plug-in cars is due to the fact that BEVs are simpler to build and do not use liquid fuel, while PHEVs have more complicated powertrains and still have gasoline-powered engines.
. Electric cars have expensive batteries that must be replaced but otherwise incur very low maintenance costs, particularly in the case of current Lithium based designs.
To calculate the cost per kilometer of an electric vehicle it is therefore necessary to assign a monetary value to the wear incurred on the battery. This can be difficult due to the fact that it will have a slightly lower capacity each time it is charged and is only considered to be at the end of its life when the owner decides its performance is no longer acceptable. Even then an 'end of life' battery is not completely worthless as it can be re-purposed, recycled or used as a spare.
Since a battery is made of many individual cells that do not necessarily wear evenly periodically replacing the worst of these can retain the vehicle's range.
The Tesla Roadster's very large battery pack is expected to last seven years with typical driving and costs when pre-purchased today. Driving 40 miles (64.4 km) per day for seven years or 102200 miles (164,474.5 km) leads to a battery consumption cost of per 1 miles (1.6 km) or per 40 miles (64.4 km). The company Better Place provides another cost comparison as they anticipate meeting contractual obligations to deliver batteries as well as clean electricity to recharge the batteries at a total cost of per 1 miles (1.6 km) in 2010, per mile by 2015 and per mile by 2020. 40 miles (64.4 km) of driving would initially cost and fall over time to .
In 2010 the U.S. government estimated that a battery with a 100 miles (160.9 km) range would cost about . Concerns remain about durability and longevity of the battery.
Nissan estimates that the Leaf's
5 year operating cost will be versus for a gasoline car. The documentary film Who Killed the Electric Car?
shows a comparison between the parts that require replacement in a gasoline powered cars and EV1s, with the garages stating that they bring the electric cars in every 5000 mi (8,046.7 km), rotate the tires, fill the windshield washer fluid and send them back out again.
sport car's plug-to-wheel energy use is 280 W·h/mi. In Northern California, the local electric utility company PG&E says that "The E-9 rate is mandatory for those customers that are currently on a residential electric rate and who plan on refueling an EV on their premises." Combining these two facts implies that driving a Tesla Roadster 40 miles (64.4 km) a day would use 11.2 kW·h of electricity costing between and depending on the time of day chosen for recharging. For comparison, driving an internal combustion engine-powered car the same 40 miles (64.4 km), at a mileage of 25 miles per US gallon (10.6 km/L), would use 1.6 gallons (6.1 l) of fuel and, at a cost of per 1 gallons (3.8 l), would cost .
The Tesla Roadster
uses about 17.4 kWh/100 km, the EV1 used about 11 kWh/100 km. Other electric vehicles such as the Nissan Leaf
are quoted at 21.25 kWh/100 km by the US Environmental Protection Agency. These differences reflect the different design and utility targets for the vehicles, and the varying testing standards. The actual energy use is greatly dependent on the actual driving conditions and driving style.
Electric cars often have less maximum range on one charge than cars powered by fossil fuels, and they can take considerable time to recharge. This is a reason that many automakers marketed EVs as "daily drivers" suitable for city trips and other short hauls. The average American drives less than 40 miles (64.4 km) per day; so the GM EV1 would have been adequate for the daily driving needs of about 90% of U.S. consumers. Nevertheless, people can be concerned that they would run out of energy from their battery before reaching their destination, a worry known as range anxiety
.
The Tesla Roadster
can travel 245 miles (394.3 km) per charge; more than double that of prototypes and evaluation
fleet cars currently on the roads. The Roadster can be fully recharged in about 3.5 hours from a 220-volt, 70-amp
outlet which can be installed in a home.
One way automakers can extend the short range of electric vehicles is by building them with battery switch technology. An EV with battery switch technology and a 100 miles (160.9 km) driving range will be able to go to a battery switch station and switch a depleted battery with a fully charged one in 59.1 seconds giving the EV an additional 100 miles (160.9 km) driving range. The process is cleaner and faster than filling a tank with gasoline and the driver remains in the car the entire time, but because of the high investment cost, its economics are unclear. As of late 2010 there are only 2 companies with plans to integrate battery switching technology to their electric vehicles: Better Place and Tesla Motors
. Better Place operated a battery-switch station in Japan until November 2010 and announced a commitment to open four battery switch stations in California, USA.
Another way is the installation of DC Fast Charging stations with high-speed charging capability from three-phase
industrial outlets so that consumers could recharge the 100 mile battery of their electric vehicle to 80 percent in about 30 minutes. A nationwide fast charging infrastructure is currently being deployed in the US that by 2013 will cover the entire nation. DC Fast Chargers are going to be installed at 45 BP
and ARCO
locations and will be made available to the public as early as March 2011. The EV Project will deploy charge infrastructure in 16 cities and major metropolitan areas in six states. Nissan has announced that 200 of its dealers in Japan will install fast chargers for the December 2010 launch of its Leaf
EV, with the goal of having fast chargers everywhere in Japan within a 25 mile radius.
In July 2011, there are hints that Whole Foods, Walmart, etc. will be adding various charging stations.
from the onboard source of power, such as particulates (soot
), volatile organic compound
s, hydrocarbon
s, carbon monoxide
, ozone
, lead
, and various oxides of nitrogen
. The clean air benefit is usually local because, depending on the source of the electricity used to recharge the batteries, air pollutant emissions are shifted to the location of the generation plants
. The amount of carbon dioxide emitted depends on the emission intensity
of the power source used to charge the vehicle, the efficiency of the said vehicle and the energy wasted in the charging process.
For mains electricity
the emission intensity varies significantly per country and within a particular country it will vary depending on demand, the availability of renewable sources and the efficiency of the fossil fuel-based generation used at a given time.
Charging a vehicle using off-grid renewable energy yields very low carbon intensity (only that to produce and install the off-grid generation system e.g. domestic wind turbine).
An EV recharged from the existing US grid electricity emits about 115 grams of per kilometer driven (6.5 oz/mi), whereas a conventional US-market gasoline powered car emits 250 gCO2/km (most from its tailpipe, some from the production and distribution of gasoline). The savings are questionable relative to hybrid or diesel cars (according to official British government testing, the most efficient European market cars are well below 115 grams of per kilometer driven, although a study in Scotland gave 149.5g/km as the average for new cars in the UK), but would be more significant in countries with cleaner electric infrastructure. In a worst-case scenario where incremental electricity demand would be met exclusively with coal, a 2009 study conducted by the World Wide Fund for Nature
and IZES found that a mid-size EV would emit roughly 200 gCO2/km, compared with an average of 170 gCO2/km for a gasoline-powered compact car. This study concluded that introducing 1 million EV cars to Germany would, in the best-case scenario, only reduce emissions by 0.1%, if nothing is done to upgrade the electricity infrastructure or manage demand.
In France
, which has a clean energy grid, emissions from electric car use would be about 12g per kilometer.
A study made in the UK in 2008 concluded that electric vehicles had the potential to cut down carbon dioxide
and greenhouse gas
emissions by at least 40%, even taking into account the emissions due to current electricity generation in the UK and emissions relating to the production and disposal of electric vehicles.
A 2011 report prepared by Ricardo
found that hybrid electric vehicle
s, plug-in hybrids and all-electric cars generate more carbon emissions during their production than current conventional vehicles, but still have a lower overall carbon footprint
over the full life cycle
. The initial higher carbon footprint is due mainly to battery production. As an example, the study estimated that 43 percent of production emissions for a mid-size
electric car are generated from the battery production.
s, and batteries can be designed to supply the large currents to support these motors.
Although some electric vehicles have very small motors, 15 kW or less and therefore have modest acceleration, many electric cars have large motors and brisk acceleration. In addition, the relatively constant torque of an electric motor, even at very low speeds tends to increase the acceleration performance of an electric vehicle relative to that of the same rated motor power
internal combustion engine. Another early solution was American Motors
’ experimental Amitron
piggyback system of batteries with one type designed for sustained speeds while a different set boosted acceleration when needed.
Electric vehicles can also use a direct motor-to-wheel configuration which increases the amount of available power
. Having multiple motors connected directly to the wheels allows for each of the wheels to be used for both propulsion and as braking systems, thereby increasing traction
. In some cases, the motor can be housed directly in the wheel, such as in the Whispering Wheel design, which lowers the vehicle's center of gravity
and reduces the number of moving parts. When not fitted with an axle
, differential
, or transmission
, electric vehicles have less drivetrain rotational inertia. However, housing the motor within the wheel can increase the unsprung weight
of the wheel, which can have an adverse effect on the handling of the vehicle.
The disadvantage of providing high acceleration by high torque from the motor is lowered efficiency due to higher losses in the form of Joule heating
in the motor windings caused by the high electric current. This energy loss increases fourfold as the input current is doubled, so the practical limit for sustained torque from an electric motor depends on how well it can be cooled during operation. There is always a compromise between torque and energy efficiency. This limits the top speed of electric vehicles operating on a single gear due to the need to limit the required torque and maintain efficiency at low vehicle speeds.
For example, the Venturi Fetish
delivers supercar
acceleration despite a relatively modest 220 kW (295 hp), and top speed of around 160 kilometre per hour. Some DC motor-equipped drag racer EVs, have simple two-speed manual transmission
s to improve top speed. The Tesla Roadster
2.5 Sport can accelerate from 0 to 60 mi/h in 3.7 seconds with a motor rated at 215 kW.
Also the Wrightspeed X1
prototype
created by Wrightspeed Inc
is the worlds fastest street legal electric car. With an acceleration of 0-60 mph in 2.9 seconds the X1 has bested some of the worlds fastest sports car
s.
s are relatively inefficient at converting on-board fuel energy to propulsion as most of the energy is wasted as heat. On the other hand, electric motor
s are more efficient
in converting stored energy into driving a vehicle, and electric drive vehicles do not consume energy while at rest or coasting, and some of the energy lost when braking is captured and reused through regenerative braking, which captures as much as one fifth of the energy normally lost during braking. Typically, conventional gasoline engines effectively use only 15% of the fuel energy content to move the vehicle or to power accessories, and diesel engine
s can reach on-board efficiencies of 20%, while electric drive vehicles have on-board efficiency of around 80%.
Production and conversion
electric cars typically use 10 to 23 kW·h/100 km (0.17 to 0.37 kW·h/mi). Approximately 20% of this power consumption is due to inefficiencies
in charging the batteries. Tesla Motors indicates that the vehicle efficiency (including charging inefficiencies) of their lithium-ion battery powered vehicle is 12.7 kW·h/100 km (0.21 kW·h/mi) and the well-to-wheels efficiency (assuming the electricity is generated from natural gas) is 24.4 kW·h/100 km (0.39 kW·h/mi).
In the United States, General Motors run in several cities a training program for firefighter
s and first responder
s to demonstrate the sequence of tasks required to safely disable the Chevrolet Volt
’s powertrain and its 12 volt electrical system, which controls its high-voltage components, and then proceed to extricate injured occupants. The Volt's high-voltage system is designed to shut down automatically in the event of an airbag deployment, and to detect a loss of communication from an airbag control module. GM also made available an Emergency Response Guide for the 2011 Volt for use by emergency responders. The guide also describes methods of disabling the high voltage system and identifies cut zone information.
As a result of a a crashed tested Chevolet Volt that caught fire in June 2011 three weeks after the testing, the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration
( NHTSA) issued an statement saying that the agency does not believe the Volt or other electric vehicles are at a greater risk of fire than gasoline-powered vehicles. "In fact, all vehicles – both electric and gasoline-powered – have some risk of fire in the event of a serious crash." The NHTSA announced in November 2011 that it was working with all automakers to develop postcrash procedures to keep occupants of electric vehicles and emergency personnel who respond to crash scenes safe. General Motors said the fire would have been avoided if GM's protocols for deactivating the battery after the crash had been followed, and also stated that they "are working with other vehicle manufacturers, first responders, tow truck operators, and salvage associations with the goal of implementing industrywide protocols." In further testing of the Volt's batteries carried out by NHTSA in November 2011, two of the three tests resulted in thermal events, including fire. Therefore the NHTSA opened a formal safety defect investigation on November 25, 2011, to examine the potential risks involved from intrusion damage to the battery in the Chevrolet Volt.
Some electric cars use low rolling resistance tires, which typically offer less grip than normal tires. Many electric cars have a small, light and fragile body, though, and therefore offer inadequate safety protection. The Insurance Institute for Highway Safety
in America had condemned the use of low speed vehicles and "mini trucks," referred to as neighborhood electric vehicles
(NEVs) when powered by electric motors, on public roads.
as compared to vehicles propelled by internal combustion engine
s. Blind people or the visually impaired
consider the noise of combustion engines a helpful aid while crossing streets, hence electric cars and hybrid
s could pose an unexpected hazard. Tests have shown that this is a valid concern, as vehicles operating in electric mode can be particularly hard to hear below 20 mile per hour for all types of road users and not only the visually impaired. At higher speeds, the sound created by tire friction and the air displaced by the vehicle start to make sufficient audible noise.
The US Congress and the Government of Japan
passed legislation to regulate the minimum level of sound for hybrids and plug-in electric vehicle
s when operating in electric mode, so that blind people and other pedestrians and cyclists can hear them coming and detect from which direction they are approaching. The Nissan Leaf
is the first electric car to use Nissan's Vehicle Sound for Pedestrians system, which includes one sound for forward motion and another for reverse.
that motorists are familiar with. Most models therefore have a PRNDL selector traditionally found in cars with automatic transmission despite the underlying mechanical differences. Push buttons are the easiest to implement as all modes are implemented through software on the vehicle's controller.
Even though the motor may be permanently connected to the wheels through a fixed-ratio gear and no parking pawl
may be present the modes "P" and "N" will still be provided on the selector. In this case the motor is disabled in "N" and an electrically actuated handbrake
provides the "P" mode.
In some cars the motor will spin slowly to provide a small amount of creep in "D", similar to a traditional automatic.
When the foot is lifted from the accelerator of an ICE
, engine braking
causes the car to slow. An EV would coast under these conditions, and applying mild regenerative braking instead provides a more familiar response. Selecting the L mode will increase this effect for sustained downhill driving, analogous to selecting a lower gear.
While heating can be simply provided with an electric resistance heater, higher efficiency and integral cooling can be obtained with a reversible heat pump
(this is currently implemented in the hybrid Toyota Prius
). Positive Temperature Coefficient (PTC) junction cooling is also attractive for its simplicity — this kind of system is used for example in the Tesla Roadster
.
Some electric cars, for example the Citroën Berlingo Electrique
, use an auxiliary heating system (for example gasoline
-fueled units manufactured by Webasto or Eberspächer) but sacrifice "green" and "Zero emissions" credentials. Cabin cooling can be augmented with solar power
, most simply and effectively by inducting outside air to avoid extreme heat buildup when the vehicle is closed and parked in the sunlight (such cooling mechanisms are available as aftermarket
kits for conventional vehicles). Two models of the 2010 Toyota Prius include this feature as an option.
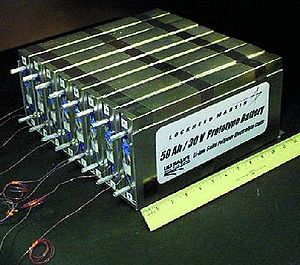 Finding the economic balance of range against performance, energy density
Finding the economic balance of range against performance, energy density
, and accumulator type versus cost challenges every EV manufacturer.
While most current highway-speed electric vehicle designs focus on lithium-ion
and other lithium-based variants a variety of alternative batteries can also be used. Lithium based batteries are often chosen for their high power and energy density but have a limited shelf-life and cycle lifetime which can significantly increase the running costs of the vehicle. Variants such as Lithium iron phosphate
and Lithium-titanate
attempt to solve the durability issues with traditional lithium-ion batteries.
Other battery technologies include:
Several battery technologies are also in development such as:
depends on the battery type:
horses were changed at coaching inn
s. Batteries could be leased
or rented
instead of bought, and then maintenance deferred to the leasing or rental company, and ensures availability.
Renault announced at the 2009 Frankfurt Motor Show that they have sponsored a network of charging stations and plug-in plug-out battery swap stations. Other vehicle manufacturers and companies are also investigating the possibility.
Replaceable batteries were used in the electric buses at the 2008 Summer Olympics
.
with high specific energy, power density, and long life, as all other aspects such as motors, motor controllers, and chargers are fairly mature and cost-competitive with internal combustion engine components. Diarmuid O'Connell, VP of Business Development at Tesla Motors, estimates that by the year 2020 30% of the cars driving on the road will be battery electric or plug-in hybrid.
Nissan CEO Carlos Ghosn
has predicted that one in 10 cars globally will run on battery power alone by 2020. Additionally a recent report claims that by 2020 electric cars and other green cars
will take a third of the total of global car sales.
It is estimated that there are sufficient lithium reserves to power 4 billion electric cars.
devices offer comparable storage capacity, faster charging, and lower volatility. They have the potential to overtake batteries as the preferred rechargeable storage for EVs. The FIA
included their use in its sporting regulations of energy systems for Formula One
race vehicles in 2007 (for supercapacitors) and 2009 (for flywheel energy storage devices).
established that solar race cars could exceed highway speeds, the specifications were changed to provide for vehicles that with little modification could be used for transportation.

Batteries in BEVs must be periodically recharged (see also Replacing, above).
Unlike vehicles powered by fossil fuels, BEVs are most commonly and conveniently charged from the power grid overnight at home, without the inconvenience of having to go to a filling station. Charging can also be done using a street or shop charging station.
The electricity on the grid is in turn generated from a variety of sources; such as coal
, hydroelectricity
, nuclear
and others. Power sources such as roof top photovoltaic solar cell panels, micro hydro
or wind
may also be used and are promoted because of concerns regarding global warming
.
classified levels of charging power that have been codified in title 13 of the California Code of Regulations, the U.S. 1999 National Electrical Code section 625 and SAE International
standards.
.* or potentially 208V x 37A, out of the strict specification but within circuit breaker and connector/cable power limits. Alternatively, this voltage would impose a lower power rating of 6.7 kW at 32A.
More recently the term "Level 3" has also been used by the SAE J1772 Standard Committee for a possible future higher-power AC fast charging standard. To distinguish from Level 3 DC fast charging, this would-be standard is written as "Level 3 AC".
SAE has not yet approved standards for either AC or DC Level 3 charging.
For comparison in Europe the IEC 61851-1 charging modes are used to classify charging equipment. The provisions of IEC 62196 charging modes for conductive charging of electric vehicles include Mode 1 (max. 16A / max. 250V a.c. or 480V three-phase), Mode 2 (max. 32A / max. 250V a.c. or 480V three-phase), Mode 3 (max. 63A (70A U.S.) / max. 690V a.c. or three-phase) and Mode 4 (max. 400A / max. 600V d.c.).
to supply electricity for recharging after the California Air Resources Board
settled on the SAE J1772
-2001 standard as the charging interface for electric vehicles in California in June 2001. In Europe the ACEA has decided to use the Type 2 connector from the range of IEC 62196 plug types for conductive charging of electric vehicles in the European Union as the Type 1 connector (SAE J1772-2009) does not provide for three-phase charging.
Another approach is inductive charging using a non-conducting "paddle" inserted into a slot in the car. Delco Electronics
developed the Magne Charge
inductive charging system around 1998 for the General Motors EV1
and it was also used for the Chevrolet S-10 EV and Toyota RAV4 EV
vehicles.
s, approximately 20% of the energy usually lost in the brakes is recovered to recharge the batteries.
outlet is between 1.5 kW (in the US, Canada, Japan, and other countries with 110 volt
supply) to 3 kW (in countries with 230V supply).
The main connection to a house may sustain 10, 15 or even 20 kW in addition to "normal" domestic loads - though it would be unwise to use all the apparent capability - and special wiring can be installed to use this.
As examples of on-board chargers, the Nissan Leaf
at launch has a 3.3 kW charger and the Tesla Roadster
appears to accept 16.8 kW (240V at 70A) from the Tesla Home Connector.
These power numbers are small compared to the effective power delivery rate of an average petrol pump
, about 5,000 kW.
Even if the electrical supply power can be increased, most batteries do not accept charge at greater than their charge rate ("1C"), because high charge rates have an adverse effect on the discharge capacities of batteries. Despite these power limitations, plugging in to even the least-powerful conventional home outlet provides more than 15 kilowatt-hours of energy overnight, sufficient to propel most electric cars more than 70 kilometres (43 mi) (see Energy efficiency above).
, LiFePO4 and even certain NiMH
variants can be charged almost to their full capacity in 10–20 minutes. Fast charging requires very high currents often derived from a three-phase power supply. Careful charge management is required to prevent damage to the batteries through overcharging.
Most people do not usually require fast recharging because they have enough time, six to eight hours (depending on discharge level) during the work day or overnight at home to recharge. BEV drivers frequently prefer recharging at home, avoiding the inconvenience of visiting a public charging station.
 Hobbyists often build their own EVs by converting
Hobbyists often build their own EVs by converting
existing production cars to run solely on electricity. There is a cottage industry supporting the conversion and construction of BEVs by hobbyists. Universities such as the University of California, Irvine
even build their own custom electric or hybrid-electric cars from scratch.
Short-range battery electric vehicles can offer the hobbyist comfort, utility, and quickness, sacrificing only range. Short-range EVs may be built using high-performance lead–acid batteries, using about half the mass needed for a 100 kilometre range. The result is a vehicle with about a 50 kilometre range, which, when designed with appropriate weight distribution (40/60 front to rear), does not require power steering
, offers exceptional acceleration in the lower end of its operating range, and is freeway capable and legal. But their EVs are expensive due to the higher cost for these higher-performance batteries. By including a manual transmission
, short-range EVs can obtain both better performance and greater efficiency than the single-speed EVs developed by major manufacturers. Unlike the converted golf carts used for neighborhood electric vehicle
s, short-range EVs may be operated on typical suburban throughways (where 60–80 km/h / 35-50 mph speed limits are typical) and can keep up with traffic typical on such roads and the short "slow-lane" on-and-off segments of freeways common in suburban areas.
Faced with chronic fuel shortage on the Gaza Strip
, Palestinian electrical engineer Waseem Othman al-Khozendar invented in 2008 a way to convert his car to run on 32 electric batteries. According to al-Khozendar, the batteries can be charged with worth of electricity to drive from 180 kilometre. After a 7-hour charge, the car should also be able to run up to a speed of 100 km/h (62.1 mph).
Japanese Professor Hiroshi Shimizu from Faculty of Environmental Information of the Keio University
created an electric limousine: the Eliica
(Electric Lithium-Ion Car) has eight wheels with electric 55 kW hub motors (8WD) with an output of 470 kW and zero emissions, a top speed of 370 km/h (229.9 mph), and a maximum range of 320 km (198.8 mi) provided by lithium-ion batteries. However, current models cost approximately , about one third of which is the cost of the batteries.
In 2008, several Chinese manufacturers began marketing lithium iron phosphate batteries
directly to hobbyists and vehicle conversion shops. These batteries offered much better power-to-weight ratios allowing vehicle conversions to typically achieve 75 mile per charge. Prices gradually declined to approximately per kW·h by mid 2009. As the cells feature life ratings of 3,000 cycles, compared to typical lead acid battery ratings of 300 cycles, the life expectancy of cells is around 10 years. This has led to a resurgence in the number of vehicles converted by individuals. cells do require more expensive battery management and charging systems than lead acid batteries.
Electric drag racing
is a sport where electric vehicles start from standstill and attempt the highest possible speed over a short given distance. Organizations such as NEDRA keep track of records world wide using certified equipment.

highway-capable models available in the market is limited. Most electric vehicles in the world roads are low-speed, low-range neighborhood electric vehicle
s, led by the Global Electric Motorcars
(GEM) vehicles, which as of December 2010 had sold more than 45,000 units worldwide since 1998. As if November 2011, the world's top selling highway-capable electric cars are the Nissan Leaf
, with more than 20,000 units sold worldwide by November 2011, and the Mitsubishi i-MiEV, with global cumulative sales of more than 17,000 units through October 2011. The i MiEV sales include units rebadged as Peugeot iOn and Citroën C-ZERO
for sale in Europe.
As of October 2011, Japan and the United States are the largest highway-capable electric car markets in the world, followed by several European countries. In Japan, more than 10,000 electric cars have been sold by July 2011, including more than 6,000 Nissan Leafs and more than 4,000 Mitsubishi i MiEVs. In the U.S. electric car sales are led by the Nissan Leaf with 8,066 units sold through October 2011. As of September 2011, Norway had almost 4,750 electric cars, the largest fleet of PEVs in Europe and the largest EV ownweship per capita in the world. By mid 2011, the UK had a fleet of almost 2,500 electric cars, and Germany 2,307 units registered by January 1st, 2011.
In the original 15 member states of the European Union
, 5,222 electric cars were sold during the first half of 2011. For year 2011 sales, the leading European countries are France and Norway, with 1,428 and 1,425 electric cars sold correspondingly through September, followed by Germany with 1,020 units sold through June, the UK with 812 units until August, and Austria with 347, Denmark with 283, and the Netherlands with 269 electric cars sold through June 2011.
There are also several pre-production models and plug-in conversions of existing internal combustion engine
models undergoing field trials or are part of demonstration programs, such as the Mini E
, Volvo C30 DRIVe Electric, Ford Focus Electric
, and the RAV4 EV second generation.
for the purchase of new electric cars depending on battery size. The U.S. offers a federal income tax credit up to , and several states have additional incentives. The U.K. offers a Plug-in Car Grant up to a maximum of . As of April 2011, 15 European Union member states provide economic incentives for the purchase of new electrically chargeable vehicles, which consist of tax reductions and exemptions, as well as of bonus payments for buyers of all-electric and plug-in hybrid vehicles, hybrid electric vehicle
s, and some alternative fuel vehicle
s.
Automobile
An automobile, autocar, motor car or car is a wheeled motor vehicle used for transporting passengers, which also carries its own engine or motor...
which is propelled
Ground propulsion
Ground propulsion is a different term than transport, because it refers to solid bodies being propelled. Those bodies may be mounted on vats or using wheels while the latter dominates for standard applications....
by electric motor
Electric motor
An electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.Most electric motors operate through the interaction of magnetic fields and current-carrying conductors to generate force...
(s), using electrical energy stored in batteries or another energy storage device. Electric cars were popular in the late-19th century and early 20th century, until advances in internal combustion engine
Internal combustion engine
The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer in a combustion chamber. In an internal combustion engine, the expansion of the high-temperature and high -pressure gases produced by combustion apply direct force to some component of the engine...
technology and mass production
Mass production
Mass production is the production of large amounts of standardized products, including and especially on assembly lines...
of cheaper gasoline vehicles led to a decline in the use of electric drive vehicle. The energy crises of the 1970s and 80s brought a short lived interest in electric cars, but in the mid 2000s took place a renewed interest in the production of electric cars due mainly to concerns about rapidly increasing oil prices and the need to curb greenhouse gas emissions. As of November 2011 series production models available in some countries include the Tesla Roadster
Tesla Roadster
The Tesla Roadster is a battery electric vehicle sports car produced by the electric car firm Tesla Motors in California. The Roadster was the first highway-capable all-electric vehicle in serial production available in the United States. Since 2008 Tesla has sold 2,024 Roadsters in 30 countries...
, REVAi, Renault Fluence Z.E.
Renault Fluence Z.E.
The Renault Fluence Z.E. is an upcoming electric version of the Renault Fluence, part of the Renault Z.E. program of battery electric vehicles. It was unveiled by Renault at the 2009 Frankfurt Motor Show. The Fluence Z.E...
, Buddy
Buddy (electric car)
Buddy is a Norwegian electric car, produced by Pure Mobility, formerly Elbil Norge AS, at Økern in Oslo. In 2007, the Buddy, and its predecessor, the Kewet, made up 20% of the electric cars in Norway.-History:...
, Mitsubishi i MiEV
Mitsubishi i MiEV
The Mitsubishi i-MiEV is a five-door hatchback electric car produced by Mitsubishi Motors, and is the electric version of the Mitsubishi i. According to the manufacturer, the i-MiEV all-electric range is on the Japanese test cycle...
, Tazzari Zero
Tazzari Zero
The Tazzari Zero is an battery electric microcar produced by the Tazzari Group, in Imola, Italy, and debuted in the 2009 Bologna Motor Show. The Tazzari Zero uses a lithium-ion battery pack that delivers an all-electric range of .-Specifications:...
, Nissan Leaf
Nissan Leaf
Nissan introduced its first battery electric vehicle, the Nissan Altra at the Los Angeles International Auto Show on 29 December 1997. The Altra EV was produced between 1998 and 2002, only about 200 vehicles were ever produced, and it was mainly used as a fleet vehicle for companies such as...
, Smart ED
Smart ED
The Smart fortwo electric drive is a battery electric vehicle version of the Smart Fortwo micro car. This electric car was formerly known as Smart fortwo EV...
, Wheego Whip LiFe, Mia electric
Mia electric
The Mia electric is a city electric car produced by the Franco-German company Mia Electric in Cerizay, France. The standard Mia has a electric motor with a 8 kWh lithium iron phosphate battery pack supplied by EVida that delivers a range of , and a maximum speed of .Production began in June 2011...
, and BYD e6
BYD e6
BYD e6 is an all-electric crossover car manufactured by BYD Auto with a range of according to the carmaker. Field testing began in China in May 2010 with 40 units operating as taxis in the city of Shenzhen...
. The Leaf, with more than 20,000 units sold worldwide by November 2011, and the i-MiEV, with global cumulative sales of more than 17,000 units through October 2011, are the world's top selling highway-capable electric cars.
Electric cars have several potential benefits as compared to conventional internal combustion automobiles that include a significant reduction of urban air pollution
Air pollution
Air pollution is the introduction of chemicals, particulate matter, or biological materials that cause harm or discomfort to humans or other living organisms, or cause damage to the natural environment or built environment, into the atmosphere....
as they do not emit harmful tailpipe pollutants
Motor vehicle emissions
Motor vehicle emissions are composed of the by-products that comes out of the exhaust systems or other emissions such as gasoline evaporation...
from the onboard source of power at the point of operation (zero tail pipe emissions
Zero-emissions vehicle
A zero-emissions vehicle, or ZEV, is a vehicle that emits no tailpipe pollutants from the onboard source of power. Harmful pollutants to the health and the environment include particulates , hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide, ozone, lead, and various oxides of nitrogen. Although not considered emission...
); reduced greenhouse gas
Greenhouse gas
A greenhouse gas is a gas in an atmosphere that absorbs and emits radiation within the thermal infrared range. This process is the fundamental cause of the greenhouse effect. The primary greenhouse gases in the Earth's atmosphere are water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozone...
emissions from the onboard source of power depending on the fuel and technology used for electricity generation
Electricity generation
Electricity generation is the process of generating electric energy from other forms of energy.The fundamental principles of electricity generation were discovered during the 1820s and early 1830s by the British scientist Michael Faraday...
to charge the batteries; and less dependence on foreign oil, which for the United States, other developed and emerging countries is cause of concerns about their vulnerability to price shocks
Shock (economics)
In economics a shock is an unexpected or unpredictable event that affects an economy, either positively or negatively. Technically, it refers to an unpredictable change in exogenous factors—that is, factors unexplained by economics—which may have an impact on endogenous economic variables.The...
and supply
Supply (economics)
In economics, supply is the amount of some product producers are willing and able to sell at a given price all other factors being held constant. Usually, supply is plotted as a supply curve showing the relationship of price to the amount of product businesses are willing to sell.In economics the...
disruption
Energy security
Energy security is a term for an association between national security and the availability of natural resources for energy consumption. Access to cheap energy has become essential to the functioning of modern economies. However, the uneven distribution of energy supplies among countries has led...
. Also for many developing countries, and particularly for the poorest in Africa
Africa
Africa is the world's second largest and second most populous continent, after Asia. At about 30.2 million km² including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of the Earth's total surface area and 20.4% of the total land area...
, high oil prices have an adverse impact on their balance of payments
Balance of payments
Balance of payments accounts are an accounting record of all monetary transactions between a country and the rest of the world.These transactions include payments for the country's exports and imports of goods, services, financial capital, and financial transfers...
, hindering their economic growth.
Despite their potential benefits, widespread adoption of electric cars faces several hurdles and limitations. As of 2011 electric cars are significantly more expensive than conventional internal combustion engine
Internal combustion engine
The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer in a combustion chamber. In an internal combustion engine, the expansion of the high-temperature and high -pressure gases produced by combustion apply direct force to some component of the engine...
vehicles and hybrid electric vehicle
Hybrid electric vehicle
A hybrid electric vehicle is a type of hybrid vehicle and electric vehicle which combines a conventional internal combustion engine propulsion system with an electric propulsion system. The presence of the electric powertrain is intended to achieve either better fuel economy than a conventional...
s due to the additional cost of their lithium-ion battery pack. However, battery prices are coming down with mass production and expected to drop further.
Other factors discouraging the adoption of electric cars are the lack of public and private recharging infrastructure
Charging station
An electric vehicle charging station, also called EV charging station, electric recharging point, charging point and EVSE , is an element in an infrastructure that supplies electric energy for the recharging of electric vehicles, plug-in hybrid electric-gasoline vehicles) or semi-static and mobile...
and the driver's fear of the batteries running out of energy before reaching their destination (range anxiety
Range anxiety
Range anxiety is the fear that a vehicle has insufficient range to reach its destination and would thus strand the vehicle's occupants.The term, which is primarily used in reference to electric vehicles, is considered to be one of the major barriers to large scale adoption of electric vehicles...
) due to the limited range of existing electric cars. Several governments have established policies and economic incentives to overcome existing barriers, to promote the sales of electric cars, and to fund further development of electric vehicles, more cost-effective battery technology and their components. The U.S. has pledged in federal grants for electric cars and batteries. China has announced it will provide to initiate an electric car industry within its borders. Several national and local governments have established tax credits, subsidies, and other incentives
Government incentives for plug-in electric vehicles
Government incentives for plug-in electric vehicles have been established by several national and local governments around the world as a financial incentive for consumers to purchase a plug-in electric vehicle....
to reduce the net purchase price of electric cars and other plug-ins
Plug-in electric vehicle
A plug-in electric vehicle is any motor vehicle that can be recharged from any external source of electricity, such as wall sockets, and the electricity stored in the rechargeable battery packs drives or contributes to drive the wheels...
.
Etymology
Electric cars are a variety of electric vehicleElectric vehicle
An electric vehicle , also referred to as an electric drive vehicle, uses one or more electric motors or traction motors for propulsion...
(EV); the term "electric vehicle" refers to any vehicle that uses electric motors for propulsion, while "electric car" generally refers to road-going automobiles powered by electricity. While an electric car's power source is not explicitly an on-board battery
Battery (electricity)
An electrical battery is one or more electrochemical cells that convert stored chemical energy into electrical energy. Since the invention of the first battery in 1800 by Alessandro Volta and especially since the technically improved Daniell cell in 1836, batteries have become a common power...
, electric cars with motors powered by other energy sources are generally referred to by a different name: an electric car powered by sunlight is a solar car
Solar car
A solar vehicle is an electric vehicle powered completely or significantly by direct solar energy. Usually, photovoltaic cells contained in solar panels convert the sun's energy directly into electric energy. The term "solar vehicle" usually implies that solar energy is used to power all or part...
, and an electric car powered by a gasoline generator is a form of hybrid car. Thus, an electric car that derives its power from an on-board battery pack is a form of battery electric vehicle
Battery electric vehicle
A battery electric vehicle, or BEV, is a type of electric vehicle that uses chemical energy stored in rechargeable battery packs. BEVs use electric motors and motor controllers instead of, or in addition to, internal combustion engines for propulsion.A battery-only electric vehicle or...
(BEV). Most often, the term "electric car" is used to refer to pure battery electric vehicles.
History

Electric cars enjoyed popularity between the mid-19th century and early 20th century, when electricity was among the preferred methods for automobile propulsion, providing a level of comfort and ease of operation that could not be achieved by the gasoline cars of the time. Advances in internal combustion
Internal combustion engine
The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer in a combustion chamber. In an internal combustion engine, the expansion of the high-temperature and high -pressure gases produced by combustion apply direct force to some component of the engine...
technology, especially the electric starter, soon rendered this advantage moot; the greater range of gasoline cars, quicker refueling times, and growing petroleum infrastructure, along with the mass production of gasoline vehicles by companies such as the Ford Motor Company
Ford Motor Company
Ford Motor Company is an American multinational automaker based in Dearborn, Michigan, a suburb of Detroit. The automaker was founded by Henry Ford and incorporated on June 16, 1903. In addition to the Ford and Lincoln brands, Ford also owns a small stake in Mazda in Japan and Aston Martin in the UK...
, which reduced prices of gasoline cars to less than half that of equivalent electric cars, led to a decline in the use of electric propulsion, effectively removing it from important markets such as the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
by the 1930s. However, in recent years, increased concerns over the environmental impact of gasoline cars, higher gasoline prices, improvements in battery technology, and the prospect of peak oil
Peak oil
Peak oil is the point in time when the maximum rate of global petroleum extraction is reached, after which the rate of production enters terminal decline. This concept is based on the observed production rates of individual oil wells, projected reserves and the combined production rate of a field...
, have brought about renewed interest in electric cars, which are perceived to be more environmentally friendly and cheaper to maintain and run, despite high initial costs. Electric cars currently enjoy relative popularity in countries around the world, though they were absent from the roads of the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
, after they briefly re-appeared in the late 90s.
1890s to 1900s: Early history
Before the pre-eminence of internal combustion engines, electric automobiles held many speed and distance records. Among the most notable of these records was the breaking of the 100 km/h (62.1 mph) speed barrier, by Camille JenatzyCamille Jenatzy
Camille Jenatzy was a Belgian race car driver. He is known for breaking the land speed record three times and being the first man to break the 100 km/h barrier....
on April 29, 1899 in his 'rocket-shaped' vehicle Jamais Contente, which reached a top speed of 105.88 km/h (65.8 mph). Before the 1920s, electric automobiles were competing with petroleum-fueled cars for urban use of a quality service car.

Chicago
Chicago is the largest city in the US state of Illinois. With nearly 2.7 million residents, it is the most populous city in the Midwestern United States and the third most populous in the US, after New York City and Los Angeles...
for owners of Milburn Light Electric cars who also could buy the vehicle without the batteries.
In 1897, electric vehicles found their first commercial application in the U.S. as a fleet of electrical New York City taxis, built by the Electric Carriage and Wagon Company of Philadelphia. Electric cars were produced in the US by Anthony Electric, Baker
Baker Motor Vehicle
Baker Motor Vehicle Company was a manufacturer of Brass Era electric automobiles in Cleveland, Ohio from 1899 to 1914.-History:The first Baker vehicle was a two seater with a selling price of US$850. One was sold to Thomas Edison as his first car. Edison also designed the nickel-iron batteries used...
, Columbia
Columbia Automobile Company
The Columbia Automobile Company was a leading early Hartford, Connecticut, United States manufacturer of automobiles.The Columbia Automobile Company was created as a joint venture of the Motor Vehicle Division of the Pope Manufacturing Company of Hartford, Connecticut, and the Electric Vehicle...
, Anderson
Detroit Electric
Detroit Electric was an automobile brand produced by the Anderson Electric Car Company in Detroit, Michigan. Nowadays, a Chinese British entrepreneur is leading Detroit Electric to develop affordable and high quality pure electric vehicles in mainland Europe...
, , Fritchle, Studebaker
Studebaker Electric (automobile)
The Studebaker Electric was an automobile produced by the Studebaker Brothers Manufacturing Company of South Bend, Indiana, a forerunner of the Studebaker Corporation. The battery-powered cars were sold from 1902 to 1912....
, Riker
Riker Electric Vehicle Company
The Riker was a veteran and brass era electric car founded in 1898 in Elizabeth, New Jersey.Designed by Andrew L. Riker, they were built in small numbers until the company was absorbed by the Electric Vehicle Company in 1901....
, Milburn, and others during the early 20th century.
Despite their relatively slow speed, electric vehicles had a number of advantages over their early-1900s competitors. They did not have the vibration, smell, and noise associated with gasoline cars. They did not require gear changes, which for gasoline cars was the most difficult part of driving. Electric cars found popularity among well-heeled customers who used them as city cars, where their limited range was less of a disadvantage. The cars were also preferred because they did not require a manual effort to start, as did gasoline cars which featured a hand crank to start the engine. Electric cars were often marketed as suitable vehicles for women drivers due to this ease of operation.

1990s to present: Revival of mass interest
The energy crises of the 1970s and 80s brought about renewed interest in the perceived independence that electric cars had from the fluctuations of the hydrocarbon energy market. In the early 1990s, the California Air Resources BoardCalifornia Air Resources Board
The California Air Resources Board, also known as CARB or ARB, is the "clean air agency" in the government of California. Established in 1967 in the Mulford-Carrell Act, combining the Bureau of Air Sanitation and the Motor Vehicle Pollution Control Board, CARB is a department within the...
(CARB), the government of California
California
California is a state located on the West Coast of the United States. It is by far the most populous U.S. state, and the third-largest by land area...
's began a push for more fuel-efficient, lower-emissions vehicles, with the ultimate goal being a move to zero-emissions vehicle
Zero-emissions vehicle
A zero-emissions vehicle, or ZEV, is a vehicle that emits no tailpipe pollutants from the onboard source of power. Harmful pollutants to the health and the environment include particulates , hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide, ozone, lead, and various oxides of nitrogen. Although not considered emission...
s such as electric vehicles. In response, automakers developed electric models, including the Chrysler TEVan
Chrysler TEVan
The Chrysler TEVan was a battery electric vehicle produced from 1993 to 1995 by Chrysler and sold primarily to electric utilities throughout the United States. The first generation used either nickel-iron or nickel-cadmium batteries. Only 56 were produced and were sold for approximately $120,000 each...
, Ford Ranger EV
Ford Ranger EV
The Ford Ranger EV is a battery electric vehicle produced by Ford Motor Company. It was produced starting in the 1998 model year through 2002 and is no longer in production. It is built upon a light truck chassis used in the Ford Ranger. A few vehicles with lead-acid batteries were sold, but most...
pickup truck, GM EV1 and S10 EV
Chevrolet S10 EV
The Chevrolet S-10 Electric was introduced in 1997 by General Motors, updated in 1998, and then discontinued. It was an OEM BEV variant of Chevrolet's S-10 pickup truck which ran solely upon electricity, and was marketed primarily to utility fleet customers....
pickup, Honda EV Plus
Honda EV Plus
The Honda EV Plus was the first battery electric vehicle from a major automaker with non-lead acid batteries. Roughly 340 EV Plus models were produced and released. The EV Plus was taken out of production in 1999 when Honda announced the release of its first hybrid electric vehicle, the Honda Insight...
hatchback, Nissan lithium-battery Altra EV miniwagon and Toyota RAV4 EV
Toyota RAV4 EV
The RAV4 EV was an all-electric version of the popular RAV4 SUV produced by Toyota. It was leased from 1997 to 2003, and at the lessees request, many units were sold after the vehicle was discontinued. A total of 1,485 were leased and/or sold in California to meet the state’s mandate for...
. These cars were eventually withdrawn from the U.S. market.
The global economic recession in the late 2000s led to increased calls for automakers to abandon fuel-inefficient SUVs, which were seen as a symbol of the excess that caused the recession, in favor of small cars, hybrid cars, and electric cars. California
California
California is a state located on the West Coast of the United States. It is by far the most populous U.S. state, and the third-largest by land area...
electric car maker Tesla Motors
Tesla Motors
Tesla Motors, Inc. is a Silicon Valley-based company that designs, manufactures and sells electric cars and electric vehicle powertrain components. It was the only automaker building and selling a zero-emission sports car, the Tesla Roadster, in serial production...
began development in 2004 on the Tesla Roadster
Tesla Roadster
The Tesla Roadster is a battery electric vehicle sports car produced by the electric car firm Tesla Motors in California. The Roadster was the first highway-capable all-electric vehicle in serial production available in the United States. Since 2008 Tesla has sold 2,024 Roadsters in 30 countries...
, which was first delivered to customers in 2008. As of January 2011 Tesla had produced more than 1,500 Roadsters sold in at least 31 countries. The Mitsubishi i MiEV
Mitsubishi i MiEV
The Mitsubishi i-MiEV is a five-door hatchback electric car produced by Mitsubishi Motors, and is the electric version of the Mitsubishi i. According to the manufacturer, the i-MiEV all-electric range is on the Japanese test cycle...
was launched for fleet customers in Japan in July 2009, and for individual customers in April 2010, followed by sales to the public in Hong Kong in May 2010, and Australia in July 2010 via leasing.
Retail customer deliveries of the Nissan Leaf
Nissan Leaf
Nissan introduced its first battery electric vehicle, the Nissan Altra at the Los Angeles International Auto Show on 29 December 1997. The Altra EV was produced between 1998 and 2002, only about 200 vehicles were ever produced, and it was mainly used as a fleet vehicle for companies such as...
in Japan and the United States began in December 2010, though initial availability is restricted to a few launch markets and in limited quantities. As of September 2011 other electric automobiles, city cars, and light trucks available in some markets included the REVAi, Buddy
Buddy (electric car)
Buddy is a Norwegian electric car, produced by Pure Mobility, formerly Elbil Norge AS, at Økern in Oslo. In 2007, the Buddy, and its predecessor, the Kewet, made up 20% of the electric cars in Norway.-History:...
, Citroën C1 ev'ie
Citroën C1 ev'ie
The Citroën C1 ev'ie is an electric car conversion from a standard Citroën C1 by the Electric Car Corporation. The model was first released on 30 April 2009, with a 2010 list price of £19,860 this makes the C1 ev'ie a competitively priced electric car.The Citroën C1 ev'ie's body and fittings are...
, Transit Connect Electric, Mercedes-Benz Vito E-Cell, Smart ED
Smart ED
The Smart fortwo electric drive is a battery electric vehicle version of the Smart Fortwo micro car. This electric car was formerly known as Smart fortwo EV...
, Wheego Whip LiFe, and several neighborhood electric vehicle
Neighborhood electric vehicle
A Neighborhood Electric Vehicle is a U.S. denomination for battery electric vehicles that are legally limited to roads with posted speed limits as high as depending on the particular laws of the state, usually are built to have a top speed of , and have a maximum loaded weight of 3,000 lbs...
s.
Comparison with internal combustion engine vehicles
An important goal for electric vehicles is overcoming the disparity between their costs of development, production, and operation, with respect to those of equivalent internal combustion engine vehiclesInternal combustion engine
The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer in a combustion chamber. In an internal combustion engine, the expansion of the high-temperature and high -pressure gases produced by combustion apply direct force to some component of the engine...
(ICEVs).
Price
Electric cars are generally more expensive than gasoline carsInternal combustion engine
The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer in a combustion chamber. In an internal combustion engine, the expansion of the high-temperature and high -pressure gases produced by combustion apply direct force to some component of the engine...
. The primary reason is the high cost of car batteries
Battery (electricity)
An electrical battery is one or more electrochemical cells that convert stored chemical energy into electrical energy. Since the invention of the first battery in 1800 by Alessandro Volta and especially since the technically improved Daniell cell in 1836, batteries have become a common power...
. US and British car buyers seem to be unwilling to pay more for an electric car. This prohibits the mass transition from gasoline cars
Internal combustion engine
The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer in a combustion chamber. In an internal combustion engine, the expansion of the high-temperature and high -pressure gases produced by combustion apply direct force to some component of the engine...
to electric cars. A survey taken by Nielsen
Nielsen
Nielsen , is a Danish patronymic surname, literally meaning son of Niels, Niels being the Danish version of the Greek male given name Νικόλαος, Nikolaos . It is the second most common surname in Denmark, shared by about 5% of the population. It is also used in Norway, although the form Nelsen and...
for the Financial Times
Financial Times
The Financial Times is an international business newspaper. It is a morning daily newspaper published in London and printed in 24 cities around the world. Its primary rival is the Wall Street Journal, published in New York City....
has shown that 65 percent of Americans and 76 percent of Britons are not willing to pay more for an electric car above the price of a gasoline car
Internal combustion engine
The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer in a combustion chamber. In an internal combustion engine, the expansion of the high-temperature and high -pressure gases produced by combustion apply direct force to some component of the engine...
. Also a report by J.D. Power and Associates
J.D. Power and Associates
J.D. Power and Associates is a global marketing information services firm founded in 1968 by James David Power III. The firm conducts surveys of customer satisfaction, product quality, and buyer behavior for industries ranging from cars to marketing and advertising firms. The firm is best known for...
claims that about 50 percent of U.S. car buyers are not even willing to spend more than on a green vehicle
Green vehicle
A green vehicle or environmentally friendly vehicle is a road motor vehicle that produces less harmful impacts to the environment than comparable conventional internal combustion engine vehicles running on gasoline or diesel, or one that uses alternative fuels...
above the price of a petrol car despite their concern about the environment.
The Nissan LEAF
Nissan Leaf
Nissan introduced its first battery electric vehicle, the Nissan Altra at the Los Angeles International Auto Show on 29 December 1997. The Altra EV was produced between 1998 and 2002, only about 200 vehicles were ever produced, and it was mainly used as a fleet vehicle for companies such as...
is the most affordable five door family electric car in the U.S. at a price of going down to after federal tax rebate of , going further down to after the tax rebate in California and similar incentives in other states.
The Renault Fluence Z.E.
Renault Fluence Z.E.
The Renault Fluence Z.E. is an upcoming electric version of the Renault Fluence, part of the Renault Z.E. program of battery electric vehicles. It was unveiled by Renault at the 2009 Frankfurt Motor Show. The Fluence Z.E...
five door family saloon electric car will be priced at less than before any U.S. federal and state tax rebates are applied. It will be sold without the battery
Battery (electricity)
An electrical battery is one or more electrochemical cells that convert stored chemical energy into electrical energy. Since the invention of the first battery in 1800 by Alessandro Volta and especially since the technically improved Daniell cell in 1836, batteries have become a common power...
thus the significant price difference. The customer will buy the Renault Fluence Z.E. with a contract to lease the battery from the company Better Place.
The electric car company Tesla Motors
Tesla Motors
Tesla Motors, Inc. is a Silicon Valley-based company that designs, manufactures and sells electric cars and electric vehicle powertrain components. It was the only automaker building and selling a zero-emission sports car, the Tesla Roadster, in serial production...
is using laptop battery technology
Battery (electricity)
An electrical battery is one or more electrochemical cells that convert stored chemical energy into electrical energy. Since the invention of the first battery in 1800 by Alessandro Volta and especially since the technically improved Daniell cell in 1836, batteries have become a common power...
for the battery packs of their electric cars that are 3 to 4 times cheaper than dedicated electric car battery packs that other auto makers are using. While dedicated battery packs cost $700–$800 per kilowatt hour, battery packs using small laptop cells cost about $200. That could potentially drive down the cost of electric cars that are using Tesla's battery technology such as the Toyota RAV4 EV
Toyota RAV4 EV
The RAV4 EV was an all-electric version of the popular RAV4 SUV produced by Toyota. It was leased from 1997 to 2003, and at the lessees request, many units were sold after the vehicle was discontinued. A total of 1,485 were leased and/or sold in California to meet the state’s mandate for...
and the Smart ED
Smart ED
The Smart fortwo electric drive is a battery electric vehicle version of the Smart Fortwo micro car. This electric car was formerly known as Smart fortwo EV...
as well as their own upcoming 2014 models such as the Model X
Tesla Model X
The Tesla Model X is a proposed full-sized battery electric crossover SUV being designed by Tesla Motors. Current plans are for a market launch by 2014, with an unveiling in late December 2011....
.
A study published in 2011 by the Belfer Center
Belfer Center for Science and International Affairs
The Belfer Center for Science and International Affairs is a permanent research center located within the John F. Kennedy School of Government at Harvard University. The center's current director is political scientist Graham T. Allison....
, Harvard University
Harvard University
Harvard University is a private Ivy League university located in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States, established in 1636 by the Massachusetts legislature. Harvard is the oldest institution of higher learning in the United States and the first corporation chartered in the country...
, found that the gasoline costs savings of plug-in electric cars over the vehicles’ lifetimes do not offset their higher purchase prices. This finding was estimated comparing their lifetime net present value
Net present value
In finance, the net present value or net present worth of a time series of cash flows, both incoming and outgoing, is defined as the sum of the present values of the individual cash flows of the same entity...
at 2010 purchase and operating costs for the U.S. market, and assuming no government subidies. According to the study estimates, a PHEV-40 is more expensive than a conventional internal combustion engine, while a battery electric vehicle is more expensive. The study also examined how this balance will change over the next 10 to 20 years, assuming that battery costs will decrease while gasoline prices increase. Under the future scenarios considered, the study found that BEVs will be significantly less expensive than conventional cars ( to cheaper), while PHEVs, will be more expensive than BEVs in almost all comparison scenarios, and only less expensive than conventional cars in an scenario with very low battery costs and high gasoline prices. The reason for the different savings among plug-in cars is due to the fact that BEVs are simpler to build and do not use liquid fuel, while PHEVs have more complicated powertrains and still have gasoline-powered engines.
Running costs and maintenance
Most of the running cost of an electric vehicle can be attributed to the maintenance and replacement of the battery pack because an electric vehicle has only around 5 moving parts in its motor, compared to a gasoline car that has hundreds of parts in its internal combustion engineInternal combustion engine
The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer in a combustion chamber. In an internal combustion engine, the expansion of the high-temperature and high -pressure gases produced by combustion apply direct force to some component of the engine...
. Electric cars have expensive batteries that must be replaced but otherwise incur very low maintenance costs, particularly in the case of current Lithium based designs.
To calculate the cost per kilometer of an electric vehicle it is therefore necessary to assign a monetary value to the wear incurred on the battery. This can be difficult due to the fact that it will have a slightly lower capacity each time it is charged and is only considered to be at the end of its life when the owner decides its performance is no longer acceptable. Even then an 'end of life' battery is not completely worthless as it can be re-purposed, recycled or used as a spare.
Since a battery is made of many individual cells that do not necessarily wear evenly periodically replacing the worst of these can retain the vehicle's range.
The Tesla Roadster's very large battery pack is expected to last seven years with typical driving and costs when pre-purchased today. Driving 40 miles (64.4 km) per day for seven years or 102200 miles (164,474.5 km) leads to a battery consumption cost of per 1 miles (1.6 km) or per 40 miles (64.4 km). The company Better Place provides another cost comparison as they anticipate meeting contractual obligations to deliver batteries as well as clean electricity to recharge the batteries at a total cost of per 1 miles (1.6 km) in 2010, per mile by 2015 and per mile by 2020. 40 miles (64.4 km) of driving would initially cost and fall over time to .
In 2010 the U.S. government estimated that a battery with a 100 miles (160.9 km) range would cost about . Concerns remain about durability and longevity of the battery.
Nissan estimates that the Leaf's
Nissan Leaf
Nissan introduced its first battery electric vehicle, the Nissan Altra at the Los Angeles International Auto Show on 29 December 1997. The Altra EV was produced between 1998 and 2002, only about 200 vehicles were ever produced, and it was mainly used as a fleet vehicle for companies such as...
5 year operating cost will be versus for a gasoline car. The documentary film Who Killed the Electric Car?
Who Killed the Electric Car?
Who Killed the Electric Car? is a 2006 documentary film that explores the creation, limited commercialization, and subsequent destruction of the battery electric vehicle in the United States, specifically the General Motors EV1 of the mid 1990s...
shows a comparison between the parts that require replacement in a gasoline powered cars and EV1s, with the garages stating that they bring the electric cars in every 5000 mi (8,046.7 km), rotate the tires, fill the windshield washer fluid and send them back out again.
Electricity vs. hydrocarbon fuel
"Fuel" cost comparison: the Tesla RoadsterTesla Roadster
The Tesla Roadster is a battery electric vehicle sports car produced by the electric car firm Tesla Motors in California. The Roadster was the first highway-capable all-electric vehicle in serial production available in the United States. Since 2008 Tesla has sold 2,024 Roadsters in 30 countries...
sport car's plug-to-wheel energy use is 280 W·h/mi. In Northern California, the local electric utility company PG&E says that "The E-9 rate is mandatory for those customers that are currently on a residential electric rate and who plan on refueling an EV on their premises." Combining these two facts implies that driving a Tesla Roadster 40 miles (64.4 km) a day would use 11.2 kW·h of electricity costing between and depending on the time of day chosen for recharging. For comparison, driving an internal combustion engine-powered car the same 40 miles (64.4 km), at a mileage of 25 miles per US gallon (10.6 km/L), would use 1.6 gallons (6.1 l) of fuel and, at a cost of per 1 gallons (3.8 l), would cost .
The Tesla Roadster
Tesla Roadster
The Tesla Roadster is a battery electric vehicle sports car produced by the electric car firm Tesla Motors in California. The Roadster was the first highway-capable all-electric vehicle in serial production available in the United States. Since 2008 Tesla has sold 2,024 Roadsters in 30 countries...
uses about 17.4 kWh/100 km, the EV1 used about 11 kWh/100 km. Other electric vehicles such as the Nissan Leaf
Nissan Leaf
Nissan introduced its first battery electric vehicle, the Nissan Altra at the Los Angeles International Auto Show on 29 December 1997. The Altra EV was produced between 1998 and 2002, only about 200 vehicles were ever produced, and it was mainly used as a fleet vehicle for companies such as...
are quoted at 21.25 kWh/100 km by the US Environmental Protection Agency. These differences reflect the different design and utility targets for the vehicles, and the varying testing standards. The actual energy use is greatly dependent on the actual driving conditions and driving style.
Range and refuelling time
Cars with internal combustion engines can be considered to have indefinite range, as they can be refuelled very quickly almost anywhere.Electric cars often have less maximum range on one charge than cars powered by fossil fuels, and they can take considerable time to recharge. This is a reason that many automakers marketed EVs as "daily drivers" suitable for city trips and other short hauls. The average American drives less than 40 miles (64.4 km) per day; so the GM EV1 would have been adequate for the daily driving needs of about 90% of U.S. consumers. Nevertheless, people can be concerned that they would run out of energy from their battery before reaching their destination, a worry known as range anxiety
Range anxiety
Range anxiety is the fear that a vehicle has insufficient range to reach its destination and would thus strand the vehicle's occupants.The term, which is primarily used in reference to electric vehicles, is considered to be one of the major barriers to large scale adoption of electric vehicles...
.
The Tesla Roadster
Tesla Roadster
The Tesla Roadster is a battery electric vehicle sports car produced by the electric car firm Tesla Motors in California. The Roadster was the first highway-capable all-electric vehicle in serial production available in the United States. Since 2008 Tesla has sold 2,024 Roadsters in 30 countries...
can travel 245 miles (394.3 km) per charge; more than double that of prototypes and evaluation
Evaluation
Evaluation is systematic determination of merit, worth, and significance of something or someone using criteria against a set of standards.Evaluation often is used to characterize and appraise subjects of interest in a wide range of human enterprises, including the arts, criminal justice,...
fleet cars currently on the roads. The Roadster can be fully recharged in about 3.5 hours from a 220-volt, 70-amp
Ampere
The ampere , often shortened to amp, is the SI unit of electric current and is one of the seven SI base units. It is named after André-Marie Ampère , French mathematician and physicist, considered the father of electrodynamics...
outlet which can be installed in a home.
One way automakers can extend the short range of electric vehicles is by building them with battery switch technology. An EV with battery switch technology and a 100 miles (160.9 km) driving range will be able to go to a battery switch station and switch a depleted battery with a fully charged one in 59.1 seconds giving the EV an additional 100 miles (160.9 km) driving range. The process is cleaner and faster than filling a tank with gasoline and the driver remains in the car the entire time, but because of the high investment cost, its economics are unclear. As of late 2010 there are only 2 companies with plans to integrate battery switching technology to their electric vehicles: Better Place and Tesla Motors
Tesla Motors
Tesla Motors, Inc. is a Silicon Valley-based company that designs, manufactures and sells electric cars and electric vehicle powertrain components. It was the only automaker building and selling a zero-emission sports car, the Tesla Roadster, in serial production...
. Better Place operated a battery-switch station in Japan until November 2010 and announced a commitment to open four battery switch stations in California, USA.
Another way is the installation of DC Fast Charging stations with high-speed charging capability from three-phase
Three-phase electric power
Three-phase electric power is a common method of alternating-current electric power generation, transmission, and distribution. It is a type of polyphase system and is the most common method used by grids worldwide to transfer power. It is also used to power large motors and other heavy loads...
industrial outlets so that consumers could recharge the 100 mile battery of their electric vehicle to 80 percent in about 30 minutes. A nationwide fast charging infrastructure is currently being deployed in the US that by 2013 will cover the entire nation. DC Fast Chargers are going to be installed at 45 BP
BP
BP p.l.c. is a global oil and gas company headquartered in London, United Kingdom. It is the third-largest energy company and fourth-largest company in the world measured by revenues and one of the six oil and gas "supermajors"...
and ARCO
ARCO
Atlantic Richfield Company is an oil company with operations in the United States as well as in Indonesia, the North Sea, and the South China Sea. It has more than 1,300 gas stations in the western part of the United States. ARCO was originally formed by the merger of East Coast-based Atlantic...
locations and will be made available to the public as early as March 2011. The EV Project will deploy charge infrastructure in 16 cities and major metropolitan areas in six states. Nissan has announced that 200 of its dealers in Japan will install fast chargers for the December 2010 launch of its Leaf
Nissan Leaf
Nissan introduced its first battery electric vehicle, the Nissan Altra at the Los Angeles International Auto Show on 29 December 1997. The Altra EV was produced between 1998 and 2002, only about 200 vehicles were ever produced, and it was mainly used as a fleet vehicle for companies such as...
EV, with the goal of having fast chargers everywhere in Japan within a 25 mile radius.
In July 2011, there are hints that Whole Foods, Walmart, etc. will be adding various charging stations.
Air pollution and carbon emissions
Electric cars contribute to cleaner air in cities because they produce no harmful pollution at the tailpipeMotor vehicle emissions
Motor vehicle emissions are composed of the by-products that comes out of the exhaust systems or other emissions such as gasoline evaporation...
from the onboard source of power, such as particulates (soot
Soot
Soot is a general term that refers to impure carbon particles resulting from the incomplete combustion of a hydrocarbon. It is more properly restricted to the product of the gas-phase combustion process but is commonly extended to include the residual pyrolyzed fuel particles such as cenospheres,...
), volatile organic compound
Volatile organic compound
Volatile organic compounds are organic chemicals that have a high vapor pressure at ordinary, room-temperature conditions. Their high vapor pressure results from a low boiling point, which causes large numbers of molecules to evaporate or sublimate from the liquid or solid form of the compound and...
s, hydrocarbon
Hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons from which one hydrogen atom has been removed are functional groups, called hydrocarbyls....
s, carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide , also called carbonous oxide, is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas that is slightly lighter than air. It is highly toxic to humans and animals in higher quantities, although it is also produced in normal animal metabolism in low quantities, and is thought to have some normal...
, ozone
Ozone
Ozone , or trioxygen, is a triatomic molecule, consisting of three oxygen atoms. It is an allotrope of oxygen that is much less stable than the diatomic allotrope...
, lead
Lead
Lead is a main-group element in the carbon group with the symbol Pb and atomic number 82. Lead is a soft, malleable poor metal. It is also counted as one of the heavy metals. Metallic lead has a bluish-white color after being freshly cut, but it soon tarnishes to a dull grayish color when exposed...
, and various oxides of nitrogen
NOx
NOx is a generic term for the mono-nitrogen oxides NO and NO2 . They are produced from the reaction of nitrogen and oxygen gases in the air during combustion, especially at high temperatures...
. The clean air benefit is usually local because, depending on the source of the electricity used to recharge the batteries, air pollutant emissions are shifted to the location of the generation plants
Electricity generation
Electricity generation is the process of generating electric energy from other forms of energy.The fundamental principles of electricity generation were discovered during the 1820s and early 1830s by the British scientist Michael Faraday...
. The amount of carbon dioxide emitted depends on the emission intensity
Emission intensity
An emission intensity is the average emission rate of a given pollutant from a given source relative to the intensity of a specific activity; for example grams of carbon dioxide released per megajoule of energy produced, or the ratio of greenhouse gas emissions produced to GDP...
of the power source used to charge the vehicle, the efficiency of the said vehicle and the energy wasted in the charging process.
For mains electricity
Mains electricity
Mains is the general-purpose alternating current electric power supply. In the US, electric power is referred to by several names including household power, household electricity, powerline, domestic power, wall power, line power, AC power, city power, street power, and grid power...
the emission intensity varies significantly per country and within a particular country it will vary depending on demand, the availability of renewable sources and the efficiency of the fossil fuel-based generation used at a given time.
Charging a vehicle using off-grid renewable energy yields very low carbon intensity (only that to produce and install the off-grid generation system e.g. domestic wind turbine).
An EV recharged from the existing US grid electricity emits about 115 grams of per kilometer driven (6.5 oz/mi), whereas a conventional US-market gasoline powered car emits 250 gCO2/km (most from its tailpipe, some from the production and distribution of gasoline). The savings are questionable relative to hybrid or diesel cars (according to official British government testing, the most efficient European market cars are well below 115 grams of per kilometer driven, although a study in Scotland gave 149.5g/km as the average for new cars in the UK), but would be more significant in countries with cleaner electric infrastructure. In a worst-case scenario where incremental electricity demand would be met exclusively with coal, a 2009 study conducted by the World Wide Fund for Nature
World Wide Fund for Nature
The World Wide Fund for Nature is an international non-governmental organization working on issues regarding the conservation, research and restoration of the environment, formerly named the World Wildlife Fund, which remains its official name in Canada and the United States...
and IZES found that a mid-size EV would emit roughly 200 gCO2/km, compared with an average of 170 gCO2/km for a gasoline-powered compact car. This study concluded that introducing 1 million EV cars to Germany would, in the best-case scenario, only reduce emissions by 0.1%, if nothing is done to upgrade the electricity infrastructure or manage demand.
In France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
, which has a clean energy grid, emissions from electric car use would be about 12g per kilometer.
A study made in the UK in 2008 concluded that electric vehicles had the potential to cut down carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
and greenhouse gas
Greenhouse gas
A greenhouse gas is a gas in an atmosphere that absorbs and emits radiation within the thermal infrared range. This process is the fundamental cause of the greenhouse effect. The primary greenhouse gases in the Earth's atmosphere are water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozone...
emissions by at least 40%, even taking into account the emissions due to current electricity generation in the UK and emissions relating to the production and disposal of electric vehicles.
A 2011 report prepared by Ricardo
Ricardo plc
Ricardo plc is a British publicly listed company named after its founder, Sir Harry Ricardo and founded on 30 June 1927 in Shoreham-by-Sea, West Sussex. The company is a leading global multi-industry engineering provider of technology, product innovation and strategic consulting...
found that hybrid electric vehicle
Hybrid electric vehicle
A hybrid electric vehicle is a type of hybrid vehicle and electric vehicle which combines a conventional internal combustion engine propulsion system with an electric propulsion system. The presence of the electric powertrain is intended to achieve either better fuel economy than a conventional...
s, plug-in hybrids and all-electric cars generate more carbon emissions during their production than current conventional vehicles, but still have a lower overall carbon footprint
Carbon footprint
A carbon footprint has historically been defined as "the total set of greenhouse gas emissions caused by an organization, event, product or person.". However, calculating a carbon footprint which conforms to this definition is often impracticable due to the large amount of data required, which is...
over the full life cycle
Life cycle assessment
A life-cycle assessment is a technique to assess environmental impacts associated with all the stages of a product's life from-cradle-to-grave A life-cycle assessment (LCA, also known as life-cycle analysis, ecobalance, and cradle-to-grave analysis) is a technique to assess environmental impacts...
. The initial higher carbon footprint is due mainly to battery production. As an example, the study estimated that 43 percent of production emissions for a mid-size
Mid-size car
A mid-size car is the North American/Australian standard for an automobile with a size equal to or greater than that of a compact...
electric car are generated from the battery production.
Acceleration and drivetrain design
Electric motors can provide high power-to-weight ratioPower-to-weight ratio
Power-to-weight ratio is a calculation commonly applied to engines and mobile power sources to enable the comparison of one unit or design to another. Power-to-weight ratio is a measurement of actual performance of any engine or power sources...
s, and batteries can be designed to supply the large currents to support these motors.
Although some electric vehicles have very small motors, 15 kW or less and therefore have modest acceleration, many electric cars have large motors and brisk acceleration. In addition, the relatively constant torque of an electric motor, even at very low speeds tends to increase the acceleration performance of an electric vehicle relative to that of the same rated motor power
Horsepower
Horsepower is the name of several units of measurement of power. The most common definitions equal between 735.5 and 750 watts.Horsepower was originally defined to compare the output of steam engines with the power of draft horses in continuous operation. The unit was widely adopted to measure the...
internal combustion engine. Another early solution was American Motors
American Motors
American Motors Corporation was an American automobile company formed by the 1954 merger of Nash-Kelvinator Corporation and Hudson Motor Car Company. At the time, it was the largest corporate merger in U.S. history.George W...
’ experimental Amitron
Amitron
The Amitron was an American electric concept car built in 1967 by American Motors Corporation and Gulton Industries of Metuchen, New Jersey.- Design :...
piggyback system of batteries with one type designed for sustained speeds while a different set boosted acceleration when needed.
Electric vehicles can also use a direct motor-to-wheel configuration which increases the amount of available power
Power (physics)
In physics, power is the rate at which energy is transferred, used, or transformed. For example, the rate at which a light bulb transforms electrical energy into heat and light is measured in watts—the more wattage, the more power, or equivalently the more electrical energy is used per unit...
. Having multiple motors connected directly to the wheels allows for each of the wheels to be used for both propulsion and as braking systems, thereby increasing traction
Traction (engineering)
Traction refers to the maximum frictional force that can be produced between surfaces without slipping.The units of traction are those of force, or if expressed as a coefficient of traction a ratio.-Traction:...
. In some cases, the motor can be housed directly in the wheel, such as in the Whispering Wheel design, which lowers the vehicle's center of gravity
Center of gravity
In physics, a center of gravity of a material body is a point that may be used for a summary description of gravitational interactions. In a uniform gravitational field, the center of mass serves as the center of gravity...
and reduces the number of moving parts. When not fitted with an axle
Axle
An axle is a central shaft for a rotating wheel or gear. On wheeled vehicles, the axle may be fixed to the wheels, rotating with them, or fixed to its surroundings, with the wheels rotating around the axle. In the former case, bearings or bushings are provided at the mounting points where the axle...
, differential
Differential (mechanics)
A differential is a device, usually, but not necessarily, employing gears, capable of transmitting torque and rotation through three shafts, almost always used in one of two ways: in one way, it receives one input and provides two outputs—this is found in most automobiles—and in the other way, it...
, or transmission
Transmission (mechanics)
A machine consists of a power source and a power transmission system, which provides controlled application of the power. Merriam-Webster defines transmission as: an assembly of parts including the speed-changing gears and the propeller shaft by which the power is transmitted from an engine to a...
, electric vehicles have less drivetrain rotational inertia. However, housing the motor within the wheel can increase the unsprung weight
Unsprung weight
In a ground vehicle with a suspension, the unsprung weight is the mass of the suspension, wheels or tracks , and other components directly connected to them, rather than supported by the suspension...
of the wheel, which can have an adverse effect on the handling of the vehicle.
Transmission
A gearless or single gear design in some EVs eliminates the need for gear shifting, giving such vehicles both smoother acceleration and smoother braking. Because the torque of an electric motor is a function of current, not rotational speed, electric vehicles have a high torque over a larger range of speeds during acceleration, as compared to an internal combustion engine. As there is no delay in developing torque in an EV, EV drivers report generally high satisfaction with acceleration.The disadvantage of providing high acceleration by high torque from the motor is lowered efficiency due to higher losses in the form of Joule heating
Joule heating
Joule heating, also known as ohmic heating and resistive heating, is the process by which the passage of an electric current through a conductor releases heat. It was first studied by James Prescott Joule in 1841. Joule immersed a length of wire in a fixed mass of water and measured the temperature...
in the motor windings caused by the high electric current. This energy loss increases fourfold as the input current is doubled, so the practical limit for sustained torque from an electric motor depends on how well it can be cooled during operation. There is always a compromise between torque and energy efficiency. This limits the top speed of electric vehicles operating on a single gear due to the need to limit the required torque and maintain efficiency at low vehicle speeds.
For example, the Venturi Fetish
Venturi Fetish
The Venturi Fétish is the world's first two-seater electric sports car . It is produced by Venturi in Monaco, and the futuristic design of the car was done by the Parisian designers Sacha Lakic. The Fétish was first introduced in concept form at the 2002 Salon International de l'Auto...
delivers supercar
Supercar
Supercar is a term used most often to describe an expensive high end car. It has been defined specifically as "a very expensive, fast or powerful car"...
acceleration despite a relatively modest 220 kW (295 hp), and top speed of around 160 kilometre per hour. Some DC motor-equipped drag racer EVs, have simple two-speed manual transmission
Manual transmission
A manual transmission, also known as a manual gearbox or standard transmission is a type of transmission used in motor vehicle applications...
s to improve top speed. The Tesla Roadster
Tesla Roadster
The Tesla Roadster is a battery electric vehicle sports car produced by the electric car firm Tesla Motors in California. The Roadster was the first highway-capable all-electric vehicle in serial production available in the United States. Since 2008 Tesla has sold 2,024 Roadsters in 30 countries...
2.5 Sport can accelerate from 0 to 60 mi/h in 3.7 seconds with a motor rated at 215 kW.
Also the Wrightspeed X1
Wrightspeed X1
The Wrightspeed X1 is a one-off Ariel Atom heavily modified to use an all-electric powertrain. The Atom was chosen for its light weight and efficient design. The electric motor and inverter are sourced from AC Propulsion, makers of the TZero concept car, while the batteries are low weight, high...
prototype
Prototype
A prototype is an early sample or model built to test a concept or process or to act as a thing to be replicated or learned from.The word prototype derives from the Greek πρωτότυπον , "primitive form", neutral of πρωτότυπος , "original, primitive", from πρῶτος , "first" and τύπος ,...
created by Wrightspeed Inc
Wrightspeed X1
The Wrightspeed X1 is a one-off Ariel Atom heavily modified to use an all-electric powertrain. The Atom was chosen for its light weight and efficient design. The electric motor and inverter are sourced from AC Propulsion, makers of the TZero concept car, while the batteries are low weight, high...
is the worlds fastest street legal electric car. With an acceleration of 0-60 mph in 2.9 seconds the X1 has bested some of the worlds fastest sports car
Sports car
A sports car is a small, usually two seat, two door automobile designed for high speed driving and maneuverability....
s.
Energy efficiency
Internal combustion engineInternal combustion engine
The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer in a combustion chamber. In an internal combustion engine, the expansion of the high-temperature and high -pressure gases produced by combustion apply direct force to some component of the engine...
s are relatively inefficient at converting on-board fuel energy to propulsion as most of the energy is wasted as heat. On the other hand, electric motor
Electric motor
An electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.Most electric motors operate through the interaction of magnetic fields and current-carrying conductors to generate force...
s are more efficient
Thermal efficiency
In thermodynamics, the thermal efficiency is a dimensionless performance measure of a device that uses thermal energy, such as an internal combustion engine, a boiler, a furnace, or a refrigerator for example.-Overview:...
in converting stored energy into driving a vehicle, and electric drive vehicles do not consume energy while at rest or coasting, and some of the energy lost when braking is captured and reused through regenerative braking, which captures as much as one fifth of the energy normally lost during braking. Typically, conventional gasoline engines effectively use only 15% of the fuel energy content to move the vehicle or to power accessories, and diesel engine
Diesel engine
A diesel engine is an internal combustion engine that uses the heat of compression to initiate ignition to burn the fuel, which is injected into the combustion chamber...
s can reach on-board efficiencies of 20%, while electric drive vehicles have on-board efficiency of around 80%.
Production and conversion
Electric vehicle conversion
An electric vehicle conversion is the modification of a conventional internal combustion engine vehicle to electric propulsion, creating an all-electric or plug-in hybrid electric vehicle.-Elements of a conversion:...
electric cars typically use 10 to 23 kW·h/100 km (0.17 to 0.37 kW·h/mi). Approximately 20% of this power consumption is due to inefficiencies
Energy conversion efficiency
Energy conversion efficiency is the ratio between the useful output of an energy conversion machine and the input, in energy terms. The useful output may be electric power, mechanical work, or heat.-Overview:...
in charging the batteries. Tesla Motors indicates that the vehicle efficiency (including charging inefficiencies) of their lithium-ion battery powered vehicle is 12.7 kW·h/100 km (0.21 kW·h/mi) and the well-to-wheels efficiency (assuming the electricity is generated from natural gas) is 24.4 kW·h/100 km (0.39 kW·h/mi).
Safety
The safety issues of BEVs are largely dealt with by the international standard ISO 6469. This document is divided in three parts dealing with specific issues:- On-board electrical energy storage, i.e. the battery
- Functional safety means and protection against failures
- Protection of persons against electrical hazards.
In the United States, General Motors run in several cities a training program for firefighter
Firefighter
Firefighters are rescuers extensively trained primarily to put out hazardous fires that threaten civilian populations and property, to rescue people from car incidents, collapsed and burning buildings and other such situations...
s and first responder
Certified first responder
A certified first responder is a person who has completed a course and received certification in providing pre-hospital care for medical emergencies. They have more skill than someone who is trained in basic first aid but they are not a substitute for advanced medical care rendered by emergency...
s to demonstrate the sequence of tasks required to safely disable the Chevrolet Volt
Chevrolet Volt
The Chevrolet Volt is a plug-in hybrid electric vehicle manufactured by General Motors. The Volt has been on sale in the U.S. market since mid-December 2010, and is the most fuel-efficient compact car sold in the United States, as rated by the United States Environmental Protection Agency...
’s powertrain and its 12 volt electrical system, which controls its high-voltage components, and then proceed to extricate injured occupants. The Volt's high-voltage system is designed to shut down automatically in the event of an airbag deployment, and to detect a loss of communication from an airbag control module. GM also made available an Emergency Response Guide for the 2011 Volt for use by emergency responders. The guide also describes methods of disabling the high voltage system and identifies cut zone information.
As a result of a a crashed tested Chevolet Volt that caught fire in June 2011 three weeks after the testing, the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration
National Highway Traffic Safety Administration
The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration is an agency of the Executive Branch of the U.S. government, part of the Department of Transportation...
( NHTSA) issued an statement saying that the agency does not believe the Volt or other electric vehicles are at a greater risk of fire than gasoline-powered vehicles. "In fact, all vehicles – both electric and gasoline-powered – have some risk of fire in the event of a serious crash." The NHTSA announced in November 2011 that it was working with all automakers to develop postcrash procedures to keep occupants of electric vehicles and emergency personnel who respond to crash scenes safe. General Motors said the fire would have been avoided if GM's protocols for deactivating the battery after the crash had been followed, and also stated that they "are working with other vehicle manufacturers, first responders, tow truck operators, and salvage associations with the goal of implementing industrywide protocols." In further testing of the Volt's batteries carried out by NHTSA in November 2011, two of the three tests resulted in thermal events, including fire. Therefore the NHTSA opened a formal safety defect investigation on November 25, 2011, to examine the potential risks involved from intrusion damage to the battery in the Chevrolet Volt.
Vehicle safety
Great effort is taken to keep the mass of an electric vehicle as low as possible to improve its range and endurance. However, the weight and bulk of the batteries themselves usually makes an EV heavier than a comparable gasoline vehicle, reducing range and leading to longer braking distances; it also has less interior space. However, in a collision, the occupants of a heavy vehicle will, on average, suffer fewer and less serious injuries than the occupants of a lighter vehicle; therefore, the additional weight brings safety benefits despite having a negative effect on the car's performance. An accident in a 2000 pound vehicle will on average cause about 50% more injuries to its occupants than a 3000 pound vehicle. In a single car accident, and for the other car in a two car accident, the increased mass causes an increase in accelerations and hence an increase in the severity of the accident.Some electric cars use low rolling resistance tires, which typically offer less grip than normal tires. Many electric cars have a small, light and fragile body, though, and therefore offer inadequate safety protection. The Insurance Institute for Highway Safety
Insurance Institute for Highway Safety
The Insurance Institute for Highway Safety is a U.S. non-profit organization funded by auto insurers, established in 1959 and headquartered in Arlington, Virginia. It works to reduce the number of motor vehicle crashes, and the rate of injuries and amount of property damage in the crashes that...
in America had condemned the use of low speed vehicles and "mini trucks," referred to as neighborhood electric vehicles
Neighborhood electric vehicle
A Neighborhood Electric Vehicle is a U.S. denomination for battery electric vehicles that are legally limited to roads with posted speed limits as high as depending on the particular laws of the state, usually are built to have a top speed of , and have a maximum loaded weight of 3,000 lbs...
(NEVs) when powered by electric motors, on public roads.
Hazard to pedestrians
At low speeds, electric cars produced less roadway noiseRoadway noise
Roadway noise is the collective sound energy emanating from motor vehicles. In the USA it contributes more to environmental noise exposure than any other noise source, and is constituted chiefly of engine, tire, aerodynamic and braking elements...
as compared to vehicles propelled by internal combustion engine
Internal combustion engine
The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer in a combustion chamber. In an internal combustion engine, the expansion of the high-temperature and high -pressure gases produced by combustion apply direct force to some component of the engine...
s. Blind people or the visually impaired
Visual impairment
Visual impairment is vision loss to such a degree as to qualify as an additional support need through a significant limitation of visual capability resulting from either disease, trauma, or congenital or degenerative conditions that cannot be corrected by conventional means, such as refractive...
consider the noise of combustion engines a helpful aid while crossing streets, hence electric cars and hybrid
Hybrid vehicle
A hybrid vehicle is a vehicle that uses two or more distinct power sources to move the vehicle. The term most commonly refers to hybrid electric vehicles , which combine an internal combustion engine and one or more electric motors.-Power:...
s could pose an unexpected hazard. Tests have shown that this is a valid concern, as vehicles operating in electric mode can be particularly hard to hear below 20 mile per hour for all types of road users and not only the visually impaired. At higher speeds, the sound created by tire friction and the air displaced by the vehicle start to make sufficient audible noise.
The US Congress and the Government of Japan
Government of Japan
The government of Japan is a constitutional monarchy where the power of the Emperor is very limited. As a ceremonial figurehead, he is defined by the 1947 constitution as "the symbol of the state and of the unity of the people". Power is held chiefly by the Prime Minister of Japan and other elected...
passed legislation to regulate the minimum level of sound for hybrids and plug-in electric vehicle
Plug-in electric vehicle
A plug-in electric vehicle is any motor vehicle that can be recharged from any external source of electricity, such as wall sockets, and the electricity stored in the rechargeable battery packs drives or contributes to drive the wheels...
s when operating in electric mode, so that blind people and other pedestrians and cyclists can hear them coming and detect from which direction they are approaching. The Nissan Leaf
Nissan Leaf
Nissan introduced its first battery electric vehicle, the Nissan Altra at the Los Angeles International Auto Show on 29 December 1997. The Altra EV was produced between 1998 and 2002, only about 200 vehicles were ever produced, and it was mainly used as a fleet vehicle for companies such as...
is the first electric car to use Nissan's Vehicle Sound for Pedestrians system, which includes one sound for forward motion and another for reverse.
Differences in controls
Presently most EV manufacturers do their best to emulate the driving experience as closely as possible to that of a car with a conventional automatic transmissionAutomatic transmission
An automatic transmission is one type of motor vehicle transmission that can automatically change gear ratios as the vehicle moves, freeing the driver from having to shift gears manually...
that motorists are familiar with. Most models therefore have a PRNDL selector traditionally found in cars with automatic transmission despite the underlying mechanical differences. Push buttons are the easiest to implement as all modes are implemented through software on the vehicle's controller.
Even though the motor may be permanently connected to the wheels through a fixed-ratio gear and no parking pawl
Parking pawl
A parking pawl is a device fitted to a motor vehicle's automatic transmission in order for it to lock up the transmission. It is engaged when the transmission shift lever selector is placed in the Park position, which is always the first position in all cars sold in the United States since 1965 A...
may be present the modes "P" and "N" will still be provided on the selector. In this case the motor is disabled in "N" and an electrically actuated handbrake
HandBrake
HandBrake is a general-purpose, open-source, cross-platform, multithreaded video transcoder software application. HandBrake was originally developed by titer in 2003 as a general-purpose video transcoder to make ripping a film from a DVD to a data storage device easier...
provides the "P" mode.
In some cars the motor will spin slowly to provide a small amount of creep in "D", similar to a traditional automatic.
When the foot is lifted from the accelerator of an ICE
Internal combustion engine
The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer in a combustion chamber. In an internal combustion engine, the expansion of the high-temperature and high -pressure gases produced by combustion apply direct force to some component of the engine...
, engine braking
Engine braking
Engine braking is where the retarding forces within an engine are used to slow a vehicle down, as opposed to using an external braking mechanism, for example friction brakes or magnetic brakes....
causes the car to slow. An EV would coast under these conditions, and applying mild regenerative braking instead provides a more familiar response. Selecting the L mode will increase this effect for sustained downhill driving, analogous to selecting a lower gear.
Cabin heating and cooling
Electric vehicles generate very little waste heat and resistance electric heat may have to be used to heat the interior of the vehicle if heat generated from battery charging/discharging can not be used to heat the interior.While heating can be simply provided with an electric resistance heater, higher efficiency and integral cooling can be obtained with a reversible heat pump
Heat pump
A heat pump is a machine or device that effectively "moves" thermal energy from one location called the "source," which is at a lower temperature, to another location called the "sink" or "heat sink", which is at a higher temperature. An air conditioner is a particular type of heat pump, but the...
(this is currently implemented in the hybrid Toyota Prius
Toyota Prius
The Toyota Prius is a full hybrid electric mid-size hatchback, formerly a compact sedan developed and manufactured by the Toyota Motor Corporation...
). Positive Temperature Coefficient (PTC) junction cooling is also attractive for its simplicity — this kind of system is used for example in the Tesla Roadster
Tesla Roadster
The Tesla Roadster is a battery electric vehicle sports car produced by the electric car firm Tesla Motors in California. The Roadster was the first highway-capable all-electric vehicle in serial production available in the United States. Since 2008 Tesla has sold 2,024 Roadsters in 30 countries...
.
Some electric cars, for example the Citroën Berlingo Electrique
Citroën Berlingo Electrique
The Citroën Berlingo électrique is a battery-powered version of the Berlingo range of vans. It has a 162 V Saft NiCd battery , a 28 kW Leroy Somer electric motor and has a maximum speed of 95 km/h , with a maximum range of in typical driving...
, use an auxiliary heating system (for example gasoline
Gasoline
Gasoline , or petrol , is a toxic, translucent, petroleum-derived liquid that is primarily used as a fuel in internal combustion engines. It consists mostly of organic compounds obtained by the fractional distillation of petroleum, enhanced with a variety of additives. Some gasolines also contain...
-fueled units manufactured by Webasto or Eberspächer) but sacrifice "green" and "Zero emissions" credentials. Cabin cooling can be augmented with solar power
Solar power
Solar energy, radiant light and heat from the sun, has been harnessed by humans since ancient times using a range of ever-evolving technologies. Solar radiation, along with secondary solar-powered resources such as wind and wave power, hydroelectricity and biomass, account for most of the available...
, most simply and effectively by inducting outside air to avoid extreme heat buildup when the vehicle is closed and parked in the sunlight (such cooling mechanisms are available as aftermarket
Aftermarket (automotive)
The automotive aftermarket is the secondary market of the automotive industry, concerned with the manufacturing, remanufacturing, distribution, retailing, and installation of all vehicle parts, chemicals, tools, equipment and accessories for light and heavy vehicles, after the sale of the...
kits for conventional vehicles). Two models of the 2010 Toyota Prius include this feature as an option.
Batteries

Energy density
Energy density is a term used for the amount of energy stored in a given system or region of space per unit volume. Often only the useful or extractable energy is quantified, which is to say that chemically inaccessible energy such as rest mass energy is ignored...
, and accumulator type versus cost challenges every EV manufacturer.
While most current highway-speed electric vehicle designs focus on lithium-ion
Lithium ion battery
A lithium-ion battery is a family of rechargeable battery types in which lithium ions move from the negative electrode to the positive electrode during discharge, and back when charging. Chemistry, performance, cost, and safety characteristics vary across LIB types...
and other lithium-based variants a variety of alternative batteries can also be used. Lithium based batteries are often chosen for their high power and energy density but have a limited shelf-life and cycle lifetime which can significantly increase the running costs of the vehicle. Variants such as Lithium iron phosphate
Lithium iron phosphate
Lithium iron phosphate , also known as LFP, is a compound used in lithium iron phosphate batteries . It is targeted for use in power tools and electric vehicles...
and Lithium-titanate
Lithium-titanate battery
The lithium–titanate battery is a type of rechargeable battery, which has the advantage of being faster to charge than other lithium-ion batteries. Some analysts speculate that lithium–titanate batteries will power electric cars of the future....
attempt to solve the durability issues with traditional lithium-ion batteries.
Other battery technologies include:
- Lead acid batteries are still the most used form of power for most of the electric vehicles used today. The initial construction costs are significantly lower than for other battery types, and while power output to weight is poorer than other designs, range and power can be easily added by increasing the number of batteries.
- NiCdNickel-cadmium batteryThe nickel–cadmium battery ' is a type of rechargeable battery using nickel oxide hydroxide and metallic cadmium as electrodes....
- Largely superseded by NiMH - Nickel metal hydride (NiMH)Nickel metal hydride batteryA nickel–metal hydride cell, abbreviated NiMH, is a type of rechargeable battery similar to the nickel–cadmium cell. The NiMH battery uses a hydrogen-absorbing alloy for the negative electrode instead of cadmium. As in NiCd cells, the positive electrode is nickel oxyhydroxide...
- Nickel iron battery - Known for its comparatively long lifetime and low power density
Several battery technologies are also in development such as:
- Zinc-air batteryZinc-air batteryZinc–air batteries , and zinc–air fuel cells, are electro-chemical batteries powered by oxidizing zinc with oxygen from the air. These batteries have high energy densities and are relatively inexpensive to produce...
- Molten salt batteryMolten salt batteryMolten salt batteries or liquid sodium battery are a class of primary cell and secondary cell high-temperature electric battery that use molten salts as an electrolyte. They offer both a higher energy density through the proper selection of reactant pairs as well as a higher power density by means...
- Zinc-bromine flow batteriesZinc-bromine flow batteryThe zinc–bromine flow battery is a type of hybrid flow battery. A solution of zinc bromide is stored in two tanks. When the battery is charged or discharged the solutions are pumped through a reactor stack and back into the tanks. One tank is used to store the electrolyte for the positive...
or Vanadium redox batteriesVanadium redox batteryThe vanadium redox battery is a type of rechargeable flow battery that employs vanadium ions in different oxidation states to store chemical potential energy...
can be refilled, instead of recharged, saving time. The depleted electrolyte can be recharged at the point of exchange, or taken away to a remote station.
Travel range before recharging
The range of an electric car depends on the number and type of batteries used. The weight and type of vehicle, and the performance demands of the driver, also have an impact just as they do on the range of traditional vehicles. The range of an electric vehicle conversionElectric vehicle conversion
An electric vehicle conversion is the modification of a conventional internal combustion engine vehicle to electric propulsion, creating an all-electric or plug-in hybrid electric vehicle.-Elements of a conversion:...
depends on the battery type:
Replacing
An alternative to quick recharging is to exchange the drained or nearly drained batteries (or battery range extender modules) with fully charged batteries, similar to how stagecoachStagecoach
A stagecoach is a type of covered wagon for passengers and goods, strongly sprung and drawn by four horses, usually four-in-hand. Widely used before the introduction of railway transport, it made regular trips between stages or stations, which were places of rest provided for stagecoach travelers...
horses were changed at coaching inn
Coaching inn
In Europe, from approximately the mid-17th century for a period of about 200 years, the coaching inn, sometimes called a coaching house or staging inn, was a vital part of the inland transport infrastructure, as an inn serving coach travelers...
s. Batteries could be leased
Leasing
Leasing is a process by which a firm can obtain the use of a certain fixed assets for which it must pay a series of contractual, periodic, tax deductible payments....
or rented
Renting
Renting is an agreement where a payment is made for the temporary use of a good, service or property owned by another. A gross lease is when the tenant pays a flat rental amount and the landlord pays for all property charges regularly incurred by the ownership from landowners...
instead of bought, and then maintenance deferred to the leasing or rental company, and ensures availability.
Renault announced at the 2009 Frankfurt Motor Show that they have sponsored a network of charging stations and plug-in plug-out battery swap stations. Other vehicle manufacturers and companies are also investigating the possibility.
Replaceable batteries were used in the electric buses at the 2008 Summer Olympics
2008 Summer Olympics
The 2008 Summer Olympics, officially known as the Games of the XXIX Olympiad, was a major international multi-sport event that took place in Beijing, China, from August 8 to August 24, 2008. A total of 11,028 athletes from 204 National Olympic Committees competed in 28 sports and 302 events...
.
Vehicle-to-grid: uploading and grid buffering
A Smart grid allows BEVs to provide power to the grid, specifically:- During peak load periods, when the cost of electricity can be very high. These vehicles can then be recharged during off-peak hours at cheaper rates while helping to absorb excess night time generation. Here the batteries in the vehicles serve as a distributed storage system to buffer power.
- During blackoutPower outageA power outage is a short- or long-term loss of the electric power to an area.There are many causes of power failures in an electricity network...
s, as an emergency backup supply.
Lifespan
Battery life should be considered when calculating the extended cost of ownership, as all batteries eventually wear out and must be replaced. The rate at which they expire depends on the type of battery technology and how they are used — many types of batteries are damaged by depleting them beyond a certain level. Lithium-ion batteries degrade faster when stored at higher temperatures.Future
The future of battery electric vehicles depends primarily upon the cost and availability of batteriesRechargeable battery
A rechargeable battery or storage battery is a group of one or more electrochemical cells. They are known as secondary cells because their electrochemical reactions are electrically reversible. Rechargeable batteries come in many different shapes and sizes, ranging anything from a button cell to...
with high specific energy, power density, and long life, as all other aspects such as motors, motor controllers, and chargers are fairly mature and cost-competitive with internal combustion engine components. Diarmuid O'Connell, VP of Business Development at Tesla Motors, estimates that by the year 2020 30% of the cars driving on the road will be battery electric or plug-in hybrid.
Nissan CEO Carlos Ghosn
Carlos Ghosn
Carlos Ghosn, KBE , born 9 March 1954, is a Brazilian-Lebanese-French businessman who is currently the Chairman and CEO of Yokohama, Japan-based Nissan and holds the same positions at Paris-based Renault, which together produce more than one in 10 cars worldwide...
has predicted that one in 10 cars globally will run on battery power alone by 2020. Additionally a recent report claims that by 2020 electric cars and other green cars
Green vehicle
A green vehicle or environmentally friendly vehicle is a road motor vehicle that produces less harmful impacts to the environment than comparable conventional internal combustion engine vehicles running on gasoline or diesel, or one that uses alternative fuels...
will take a third of the total of global car sales.
It is estimated that there are sufficient lithium reserves to power 4 billion electric cars.
Other methods of energy storage
Experimental supercapacitors and flywheel energy storageFlywheel energy storage
Flywheel energy storage works by accelerating a rotor to a very high speed and maintaining the energy in the system as rotational energy...
devices offer comparable storage capacity, faster charging, and lower volatility. They have the potential to overtake batteries as the preferred rechargeable storage for EVs. The FIA
Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile
The Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile is a non-profit association established as the Association Internationale des Automobile Clubs Reconnus on 20 June 1904 to represent the interests of motoring organisations and motor car users...
included their use in its sporting regulations of energy systems for Formula One
Formula One
Formula One, also known as Formula 1 or F1 and referred to officially as the FIA Formula One World Championship, is the highest class of single seater auto racing sanctioned by the Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile . The "formula" designation in the name refers to a set of rules with which...
race vehicles in 2007 (for supercapacitors) and 2009 (for flywheel energy storage devices).
Solar cars
Solar cars are electric cars that derive most or all of their electricity from built in solar panels. After the 2005 World Solar ChallengeWorld Solar Challenge
The World Solar Challenge is a solar-powered car race which covers through the Australian Outback, from Darwin to Adelaide.The race attracts teams from around the world, most of which are fielded by universities or corporations although some are fielded by high schools...
established that solar race cars could exceed highway speeds, the specifications were changed to provide for vehicles that with little modification could be used for transportation.
Charging

Batteries in BEVs must be periodically recharged (see also Replacing, above).
Unlike vehicles powered by fossil fuels, BEVs are most commonly and conveniently charged from the power grid overnight at home, without the inconvenience of having to go to a filling station. Charging can also be done using a street or shop charging station.
The electricity on the grid is in turn generated from a variety of sources; such as coal
Fossil fuel power plant
A fossil-fuel power station is a power station that burns fossil fuels such as coal, natural gas or petroleum to produce electricity. Central station fossil-fuel power plants are designed on a large scale for continuous operation...
, hydroelectricity
Hydroelectricity
Hydroelectricity is the term referring to electricity generated by hydropower; the production of electrical power through the use of the gravitational force of falling or flowing water. It is the most widely used form of renewable energy...
, nuclear
Nuclear power
Nuclear power is the use of sustained nuclear fission to generate heat and electricity. Nuclear power plants provide about 6% of the world's energy and 13–14% of the world's electricity, with the U.S., France, and Japan together accounting for about 50% of nuclear generated electricity...
and others. Power sources such as roof top photovoltaic solar cell panels, micro hydro
Micro hydro
Micro hydro is a term used for hydroelectric power installations that typically produce up to 100 kW of electricity. These installations can provide power to an isolated home or small community, or are sometimes connected to electric power networks....
or wind
Wind power
Wind power is the conversion of wind energy into a useful form of energy, such as using wind turbines to make electricity, windmills for mechanical power, windpumps for water pumping or drainage, or sails to propel ships....
may also be used and are promoted because of concerns regarding global warming
Global warming
Global warming refers to the rising average temperature of Earth's atmosphere and oceans and its projected continuation. In the last 100 years, Earth's average surface temperature increased by about with about two thirds of the increase occurring over just the last three decades...
.
Level 1, 2, and 3 charging
Around 1998 the California Air Resources BoardCalifornia Air Resources Board
The California Air Resources Board, also known as CARB or ARB, is the "clean air agency" in the government of California. Established in 1967 in the Mulford-Carrell Act, combining the Bureau of Air Sanitation and the Motor Vehicle Pollution Control Board, CARB is a department within the...
classified levels of charging power that have been codified in title 13 of the California Code of Regulations, the U.S. 1999 National Electrical Code section 625 and SAE International
SAE International
SAE International is an organization for engineering professionals in the aerospace, automotive, and commercial vehicle industries. The Society is a standards development organization for the engineering of powered vehicles of all kinds, including cars, trucks, boats, aircraft, and others.SAE...
standards.
| Level | Original definition | Coulomb Technologies Coulomb Technologies Coulomb Technologies is an electric vehicle infrastructure company, based in Campbell, California. Coulomb Technologies was founded in 2007 by Richard Lowenthal and Praveen Mandal.... ' definition |
Connectors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Level 1 | AC energy to the vehicle's on-board charger; from the most common U.S. grounded household receptacle, commonly referred to as a 120 volt outlet. | 120 V AC; 16 A (= 1.92 kW) | SAE J1772 SAE J1772 SAE J1772 is a North American standard for electrical connectors for electric vehicles maintained by the Society of Automotive Engineers and has the formal title "SAE Surface Vehicle Recommended Practice J1772, SAE Electric VehicleConductive Charge Coupler”... (16.8 kW), ordinary household 120 volt outlet |
| Level 2 | AC energy to the vehicle's on-board charger;208 - 240 volt, single phase. The maximum current specified is 32 amps (continuous) with a branch circuit breaker rated at 40 amps. Maximum continuous input power is specified as 7.68 kW (= 240V x 32A*). | 208-240 V AC; 12 A - 80 A (= 2.5 - 19.2 kW) |
SAE J1772 SAE J1772 SAE J1772 is a North American standard for electrical connectors for electric vehicles maintained by the Society of Automotive Engineers and has the formal title "SAE Surface Vehicle Recommended Practice J1772, SAE Electric VehicleConductive Charge Coupler”... (16.8 kW), IEC 62196 IEC 62196 IEC 62196 is an international standard for set of electrical connectors and charging modes for electric vehicles and is maintained by the International Electrotechnical Commission .... (44 kW), Magne Charge (Obsolete) Magne Charge Magne Charge is a largely obsolete inductive charging system, also known as J1773, used to charge battery electric vehicles formerly made by General Motors, for vehicles such as the EV1, Chevy S10 EV, and other electric vehicles. It was produced by the General Motors subsidiary Delco Electronics.... , Avcon Avcon Avcon is a company that manufactures charging interfaces for battery electric vehicles . The lettering convention is Avcon for the company and AVCON for the EV charging head.... , IEC 60309 16 A IEC 60309 IEC 60309 is an international standard from the International Electrotechnical Commission for "plugs, socket-outlets and couplers for industrial purposes". The highest voltage allowed by the standard is DC or AC; the highest current, ; and the highest frequency,... (3.8 kW) IEC 62198-2 Type2 same as VDE-AR-E 2623-2-2, also known as the Mennekes connector (43.5 kW)IEC 62198-2 Type3 also known as Scame |
| Level 3 | DC energy from an off-board charger; there is no minimum energy requirement but the maximum current specified is 400 amps and 240 kW continuous power supplied. | very high voltages (300-600 V DC); very high currents (hundreds of Amperes) | Magne Charge (Obsolete) Magne Charge Magne Charge is a largely obsolete inductive charging system, also known as J1773, used to charge battery electric vehicles formerly made by General Motors, for vehicles such as the EV1, Chevy S10 EV, and other electric vehicles. It was produced by the General Motors subsidiary Delco Electronics.... CHΛdeMO (62.5 kW), |
.* or potentially 208V x 37A, out of the strict specification but within circuit breaker and connector/cable power limits. Alternatively, this voltage would impose a lower power rating of 6.7 kW at 32A.
More recently the term "Level 3" has also been used by the SAE J1772 Standard Committee for a possible future higher-power AC fast charging standard. To distinguish from Level 3 DC fast charging, this would-be standard is written as "Level 3 AC".
SAE has not yet approved standards for either AC or DC Level 3 charging.
For comparison in Europe the IEC 61851-1 charging modes are used to classify charging equipment. The provisions of IEC 62196 charging modes for conductive charging of electric vehicles include Mode 1 (max. 16A / max. 250V a.c. or 480V three-phase), Mode 2 (max. 32A / max. 250V a.c. or 480V three-phase), Mode 3 (max. 63A (70A U.S.) / max. 690V a.c. or three-phase) and Mode 4 (max. 400A / max. 600V d.c.).
Connectors
Most electric cars have used conductive couplingConductive coupling
Conductive coupling is the transfer of electrical energy by means of physical contact via a conductive medium, in contrast to inductive coupling and capacitive coupling...
to supply electricity for recharging after the California Air Resources Board
California Air Resources Board
The California Air Resources Board, also known as CARB or ARB, is the "clean air agency" in the government of California. Established in 1967 in the Mulford-Carrell Act, combining the Bureau of Air Sanitation and the Motor Vehicle Pollution Control Board, CARB is a department within the...
settled on the SAE J1772
SAE J1772
SAE J1772 is a North American standard for electrical connectors for electric vehicles maintained by the Society of Automotive Engineers and has the formal title "SAE Surface Vehicle Recommended Practice J1772, SAE Electric VehicleConductive Charge Coupler”...
-2001 standard as the charging interface for electric vehicles in California in June 2001. In Europe the ACEA has decided to use the Type 2 connector from the range of IEC 62196 plug types for conductive charging of electric vehicles in the European Union as the Type 1 connector (SAE J1772-2009) does not provide for three-phase charging.
Another approach is inductive charging using a non-conducting "paddle" inserted into a slot in the car. Delco Electronics
Delco Electronics
Delco Electronics Corporation was the automotive electronics design and manufacturing subsidiary of General Motors based in Kokomo, Indiana.The name Delco came from the Dayton Engineering Laboratories Co., founded in Dayton, Ohio by Charles Kettering and Edward A...
developed the Magne Charge
Magne Charge
Magne Charge is a largely obsolete inductive charging system, also known as J1773, used to charge battery electric vehicles formerly made by General Motors, for vehicles such as the EV1, Chevy S10 EV, and other electric vehicles. It was produced by the General Motors subsidiary Delco Electronics....
inductive charging system around 1998 for the General Motors EV1
General Motors EV1
The General Motors EV1 was an electric car produced and leased by the General Motors Corporation from 1996 to 1999. It was the first mass-produced and purpose-designed electric vehicle of the modern era from a major automaker, and the first GM car designed to be an electric vehicle from the...
and it was also used for the Chevrolet S-10 EV and Toyota RAV4 EV
Toyota RAV4 EV
The RAV4 EV was an all-electric version of the popular RAV4 SUV produced by Toyota. It was leased from 1997 to 2003, and at the lessees request, many units were sold after the vehicle was discontinued. A total of 1,485 were leased and/or sold in California to meet the state’s mandate for...
vehicles.
Regenerative braking
Using regenerative braking, a feature which is present on many hybrid electric vehicleHybrid electric vehicle
A hybrid electric vehicle is a type of hybrid vehicle and electric vehicle which combines a conventional internal combustion engine propulsion system with an electric propulsion system. The presence of the electric powertrain is intended to achieve either better fuel economy than a conventional...
s, approximately 20% of the energy usually lost in the brakes is recovered to recharge the batteries.
Charging time
More electrical power to the car reduces charging time. Power is limited by the capacity of the grid connection, and, for level 1 and 2 charging, by the power rating of the car's on-board charger. A normal householdHousehold
The household is "the basic residential unit in which economic production, consumption, inheritance, child rearing, and shelter are organized and carried out"; [the household] "may or may not be synonymous with family"....
outlet is between 1.5 kW (in the US, Canada, Japan, and other countries with 110 volt
Volt
The volt is the SI derived unit for electric potential, electric potential difference, and electromotive force. The volt is named in honor of the Italian physicist Alessandro Volta , who invented the voltaic pile, possibly the first chemical battery.- Definition :A single volt is defined as the...
supply) to 3 kW (in countries with 230V supply).
The main connection to a house may sustain 10, 15 or even 20 kW in addition to "normal" domestic loads - though it would be unwise to use all the apparent capability - and special wiring can be installed to use this.
As examples of on-board chargers, the Nissan Leaf
Nissan Leaf
Nissan introduced its first battery electric vehicle, the Nissan Altra at the Los Angeles International Auto Show on 29 December 1997. The Altra EV was produced between 1998 and 2002, only about 200 vehicles were ever produced, and it was mainly used as a fleet vehicle for companies such as...
at launch has a 3.3 kW charger and the Tesla Roadster
Tesla Roadster
The Tesla Roadster is a battery electric vehicle sports car produced by the electric car firm Tesla Motors in California. The Roadster was the first highway-capable all-electric vehicle in serial production available in the United States. Since 2008 Tesla has sold 2,024 Roadsters in 30 countries...
appears to accept 16.8 kW (240V at 70A) from the Tesla Home Connector.
These power numbers are small compared to the effective power delivery rate of an average petrol pump
Filling station
A filling station, also known as a fueling station, garage, gasbar , gas station , petrol bunk , petrol pump , petrol garage, petrol kiosk , petrol station "'servo"' in Australia or service station, is a facility which sells fuel and lubricants...
, about 5,000 kW.
Even if the electrical supply power can be increased, most batteries do not accept charge at greater than their charge rate ("1C"), because high charge rates have an adverse effect on the discharge capacities of batteries. Despite these power limitations, plugging in to even the least-powerful conventional home outlet provides more than 15 kilowatt-hours of energy overnight, sufficient to propel most electric cars more than 70 kilometres (43 mi) (see Energy efficiency above).
Faster charging
Some types of batteries such as Lithium-titanateLithium-titanate battery
The lithium–titanate battery is a type of rechargeable battery, which has the advantage of being faster to charge than other lithium-ion batteries. Some analysts speculate that lithium–titanate batteries will power electric cars of the future....
, LiFePO4 and even certain NiMH
NIMH
NIMH or NiMH may refer to:*Nickel-metal hydride battery, a type of rechargeable battery*National Institute of Mental Health, a part of the United States National Institutes of Health...
variants can be charged almost to their full capacity in 10–20 minutes. Fast charging requires very high currents often derived from a three-phase power supply. Careful charge management is required to prevent damage to the batteries through overcharging.
Most people do not usually require fast recharging because they have enough time, six to eight hours (depending on discharge level) during the work day or overnight at home to recharge. BEV drivers frequently prefer recharging at home, avoiding the inconvenience of visiting a public charging station.
Hobbyists, conversions, and racing

Electric vehicle conversion
An electric vehicle conversion is the modification of a conventional internal combustion engine vehicle to electric propulsion, creating an all-electric or plug-in hybrid electric vehicle.-Elements of a conversion:...
existing production cars to run solely on electricity. There is a cottage industry supporting the conversion and construction of BEVs by hobbyists. Universities such as the University of California, Irvine
University of California, Irvine
The University of California, Irvine , founded in 1965, is one of the ten campuses of the University of California, located in Irvine, California, USA...
even build their own custom electric or hybrid-electric cars from scratch.
Short-range battery electric vehicles can offer the hobbyist comfort, utility, and quickness, sacrificing only range. Short-range EVs may be built using high-performance lead–acid batteries, using about half the mass needed for a 100 kilometre range. The result is a vehicle with about a 50 kilometre range, which, when designed with appropriate weight distribution (40/60 front to rear), does not require power steering
Power steering
Power steering helps drivers steer vehicles by augmenting steering effort of the steering wheel.Hydraulic or electric actuators add controlled energy to the steering mechanism, so the driver needs to provide only modest effort regardless of conditions. Power steering helps considerably when a...
, offers exceptional acceleration in the lower end of its operating range, and is freeway capable and legal. But their EVs are expensive due to the higher cost for these higher-performance batteries. By including a manual transmission
Manual transmission
A manual transmission, also known as a manual gearbox or standard transmission is a type of transmission used in motor vehicle applications...
, short-range EVs can obtain both better performance and greater efficiency than the single-speed EVs developed by major manufacturers. Unlike the converted golf carts used for neighborhood electric vehicle
Neighborhood electric vehicle
A Neighborhood Electric Vehicle is a U.S. denomination for battery electric vehicles that are legally limited to roads with posted speed limits as high as depending on the particular laws of the state, usually are built to have a top speed of , and have a maximum loaded weight of 3,000 lbs...
s, short-range EVs may be operated on typical suburban throughways (where 60–80 km/h / 35-50 mph speed limits are typical) and can keep up with traffic typical on such roads and the short "slow-lane" on-and-off segments of freeways common in suburban areas.
Faced with chronic fuel shortage on the Gaza Strip
Gaza Strip
thumb|Gaza city skylineThe Gaza Strip lies on the Eastern coast of the Mediterranean Sea. The Strip borders Egypt on the southwest and Israel on the south, east and north. It is about long, and between 6 and 12 kilometres wide, with a total area of...
, Palestinian electrical engineer Waseem Othman al-Khozendar invented in 2008 a way to convert his car to run on 32 electric batteries. According to al-Khozendar, the batteries can be charged with worth of electricity to drive from 180 kilometre. After a 7-hour charge, the car should also be able to run up to a speed of 100 km/h (62.1 mph).
Japanese Professor Hiroshi Shimizu from Faculty of Environmental Information of the Keio University
Keio University
,abbreviated as Keio or Keidai , is a Japanese university located in Minato, Tokyo. It is known as the oldest institute of higher education in Japan. Founder Fukuzawa Yukichi originally established it as a school for Western studies in 1858 in Edo . It has eleven campuses in Tokyo and Kanagawa...
created an electric limousine: the Eliica
Eliica
The Eliica is a battery electric vehicle prototype or concept car first shown in 2004 and designed by a team at Keio University in Tokyo, led by Professor Hiroshi Shimizu. The car runs on a lithium-ion battery and can accelerate from 0– in four seconds...
(Electric Lithium-Ion Car) has eight wheels with electric 55 kW hub motors (8WD) with an output of 470 kW and zero emissions, a top speed of 370 km/h (229.9 mph), and a maximum range of 320 km (198.8 mi) provided by lithium-ion batteries. However, current models cost approximately , about one third of which is the cost of the batteries.
In 2008, several Chinese manufacturers began marketing lithium iron phosphate batteries
Lithium iron phosphate battery
The lithium iron phosphate battery, also called LFP battery, is a type of rechargeable battery, specifically a lithium-ion battery, which uses LiFePO4 as a cathode material.-History:...
directly to hobbyists and vehicle conversion shops. These batteries offered much better power-to-weight ratios allowing vehicle conversions to typically achieve 75 mile per charge. Prices gradually declined to approximately per kW·h by mid 2009. As the cells feature life ratings of 3,000 cycles, compared to typical lead acid battery ratings of 300 cycles, the life expectancy of cells is around 10 years. This has led to a resurgence in the number of vehicles converted by individuals. cells do require more expensive battery management and charging systems than lead acid batteries.
Electric drag racing
Electric drag racing
Electric drag racing rules are very different from traditional drag racing. The common safety rules apply but additional rules apply depending on voltage, battery type, motor number and configuration....
is a sport where electric vehicles start from standstill and attempt the highest possible speed over a short given distance. Organizations such as NEDRA keep track of records world wide using certified equipment.
Currently available electric cars

Highway capable
As of late 2011 the number of mass productionMass production
Mass production is the production of large amounts of standardized products, including and especially on assembly lines...
highway-capable models available in the market is limited. Most electric vehicles in the world roads are low-speed, low-range neighborhood electric vehicle
Neighborhood electric vehicle
A Neighborhood Electric Vehicle is a U.S. denomination for battery electric vehicles that are legally limited to roads with posted speed limits as high as depending on the particular laws of the state, usually are built to have a top speed of , and have a maximum loaded weight of 3,000 lbs...
s, led by the Global Electric Motorcars
Global Electric Motorcars
Global Electric Motorcars , a wholly owned subsidiary of Polaris Industries, is a U.S. manufacturer in the low-speed vehicle category, producing neighborhood electric vehicles since 1998 and has sold more than 45,000 GEM battery-electric vehicles worldwide as of December 2010.Until June 2011, GEM...
(GEM) vehicles, which as of December 2010 had sold more than 45,000 units worldwide since 1998. As if November 2011, the world's top selling highway-capable electric cars are the Nissan Leaf
Nissan Leaf
Nissan introduced its first battery electric vehicle, the Nissan Altra at the Los Angeles International Auto Show on 29 December 1997. The Altra EV was produced between 1998 and 2002, only about 200 vehicles were ever produced, and it was mainly used as a fleet vehicle for companies such as...
, with more than 20,000 units sold worldwide by November 2011, and the Mitsubishi i-MiEV, with global cumulative sales of more than 17,000 units through October 2011. The i MiEV sales include units rebadged as Peugeot iOn and Citroën C-ZERO
Citroën C-ZERO
The Citroën C-Zero is a electric supermini/city car produced by Citroën. It was developed in collaboration with Mitsubishi Motors Corporation. Its sister will be marketed by Peugeot as the Peugeot iOn...
for sale in Europe.
As of October 2011, Japan and the United States are the largest highway-capable electric car markets in the world, followed by several European countries. In Japan, more than 10,000 electric cars have been sold by July 2011, including more than 6,000 Nissan Leafs and more than 4,000 Mitsubishi i MiEVs. In the U.S. electric car sales are led by the Nissan Leaf with 8,066 units sold through October 2011. As of September 2011, Norway had almost 4,750 electric cars, the largest fleet of PEVs in Europe and the largest EV ownweship per capita in the world. By mid 2011, the UK had a fleet of almost 2,500 electric cars, and Germany 2,307 units registered by January 1st, 2011.
In the original 15 member states of the European Union
European Union
The European Union is an economic and political union of 27 independent member states which are located primarily in Europe. The EU traces its origins from the European Coal and Steel Community and the European Economic Community , formed by six countries in 1958...
, 5,222 electric cars were sold during the first half of 2011. For year 2011 sales, the leading European countries are France and Norway, with 1,428 and 1,425 electric cars sold correspondingly through September, followed by Germany with 1,020 units sold through June, the UK with 812 units until August, and Austria with 347, Denmark with 283, and the Netherlands with 269 electric cars sold through June 2011.
There are also several pre-production models and plug-in conversions of existing internal combustion engine
Internal combustion engine
The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer in a combustion chamber. In an internal combustion engine, the expansion of the high-temperature and high -pressure gases produced by combustion apply direct force to some component of the engine...
models undergoing field trials or are part of demonstration programs, such as the Mini E
Mini E
The Mini E is a demonstration electric car developed by BMW as a conversion of its Mini Cooper car. The MINI E was developed for field trials and deployed in several countries, including the United States, Germany, UK, France, Japan and China...
, Volvo C30 DRIVe Electric, Ford Focus Electric
Ford Focus Electric
The Ford Focus Electric is a 5-door hatchback electric car being produced by Ford Motor Company. The Focus electric will be Ford's first full production, all-electric passenger vehicle. The initial U.S. market roll-out is scheduled to be limited to 19 regional markets, beginning with California and...
, and the RAV4 EV second generation.
Government subsidy
Several countries have established grants and tax creditsGovernment incentives for plug-in electric vehicles
Government incentives for plug-in electric vehicles have been established by several national and local governments around the world as a financial incentive for consumers to purchase a plug-in electric vehicle....
for the purchase of new electric cars depending on battery size. The U.S. offers a federal income tax credit up to , and several states have additional incentives. The U.K. offers a Plug-in Car Grant up to a maximum of . As of April 2011, 15 European Union member states provide economic incentives for the purchase of new electrically chargeable vehicles, which consist of tax reductions and exemptions, as well as of bonus payments for buyers of all-electric and plug-in hybrid vehicles, hybrid electric vehicle
Hybrid electric vehicle
A hybrid electric vehicle is a type of hybrid vehicle and electric vehicle which combines a conventional internal combustion engine propulsion system with an electric propulsion system. The presence of the electric powertrain is intended to achieve either better fuel economy than a conventional...
s, and some alternative fuel vehicle
Alternative fuel vehicle
An alternative fuel vehicle is a vehicle that runs on a fuel other than "traditional" petroleum fuels ; and also refers to any technology of powering an engine that does not involve solely petroleum...
s.
See also
- Electric Vehicle Racing in UKEV CupEV Cup is a multiple electric vehicle racing series to be held in accordance with MSA standards. The racing cup is run with a mix of different race classifications that are divided according to the performance parameters of each model....
- The Greenpower Challenge - EV racing for young peopleGreenpowerGreenpower is the trading name of a British Charitable organization: The Greenpower Education Trust whose legal objective is to inspire more young people to become engineers by presenting the engineering industry as an interesting and relevant career choice which could help to solve problems ...
- Compressed air car
- Electric car use by countryElectric car use by country-Australia and New Zealand:In 2008 Australia started producing its first commercial all-electric vehicle. Originally called the Blade Runner, its name was changed to Electron, and is already being exported to New Zealand with one purchased by the Environment Minister Dr. Nick Smith...
- Electric boatElectric boatWhile a significant majority of water vessels are powered by diesel engines, with sail power and gasoline engines also remaining popular, boats powered by electricity have been used for over 120 years. Electric boats were very popular from the 1880s until the 1920s, when the internal combustion...
- Electric busElectric busAn electric bus is a bus powered by electricity.There are two main electric bus categories:* Non-autonomous electric buses:**The trolleybus is a type of electric bus powered by two overhead electric wires, with electricity being drawn from one wire and returned via the other wire, using two...
- Electric motorcycles and scootersElectric motorcycles and scootersElectric motorcycles and scooters are vehicles with two or three wheels that use electric motors to attain locomotion. Electric motorcycles, as distinguished from scooters, do not have a step-through frame....
- Electric vehicle conversionElectric vehicle conversionAn electric vehicle conversion is the modification of a conventional internal combustion engine vehicle to electric propulsion, creating an all-electric or plug-in hybrid electric vehicle.-Elements of a conversion:...
- Hybrid electric vehicleHybrid electric vehicleA hybrid electric vehicle is a type of hybrid vehicle and electric vehicle which combines a conventional internal combustion engine propulsion system with an electric propulsion system. The presence of the electric powertrain is intended to achieve either better fuel economy than a conventional...
(HEV) - List of production battery electric vehicles
- Plug-in electric vehiclePlug-in electric vehicleA plug-in electric vehicle is any motor vehicle that can be recharged from any external source of electricity, such as wall sockets, and the electricity stored in the rechargeable battery packs drives or contributes to drive the wheels...
(PEV) - Plug-in hybrid (PHEV)
- Solar Golf CartSolar golf cartSolar golf carts are golf carts powered by mounting a photovoltaic or thin film panel on top of the existing roof or using a PV panel as the roof itself. A controller converts the sun's energy to charge the golf cart's 36-volt or 48-volt battery bank...
- Tesla electric carTesla electric carThe Tesla electric car anecdote refers to a supposed Tesla invention described by a Peter Savo , to one Derek Ahers on September 16, 1967. Savo said that Tesla took him to Buffalo, New York in 1931 and showed him a modified Pierce-Arrow automobile.Tesla, according to the story, had the stock...
- Patent encumbrance of large automotive NiMH batteriesPatent encumbrance of large automotive NiMH batteriesThe patent encumbrance of large automotive NiMH batteries is the encumbrance of the commercialization of nickel metal hydride battery technology by corporate interests...
External links
- NOW on PBS investigates if electric cars will bring a new global climate change plan
- Plugging In: A Consumer’s Guide to the Electric Vehicle Electric Power Research InstituteElectric Power Research InstituteThe Electric Power Research Institute conducts research on issues related to the electric power industry in USA. EPRI is a nonprofit organization funded by the electric utility industry. EPRI is primarily a US based organization, receives international participation...
Organizations
- Open Source Electric Car by Society for Sustainable Mobility [Dead Link]
- Plug In America (plug-in vehicle advocacy group)
- US Electric Auto Association (EAA) and recharging points
- Electric Car Society founded in 1982
- Electrification Coalition (business alliance)
- Better Place provides infrastructure for electric cars .

