
History of film
Encyclopedia
The history of film
is the historical development of the medium known variously as cinema, motion pictures, film, or the movies.
The history of film spans over 100 years, from the latter part of the 19th century to the present day. Motion pictures developed gradually from a carnival novelty to one of the most important tools of communication
and entertainment
, and mass media
in the 20th century and into the 21st century. Motion picture films
have substantially affected the arts
, technology
, and politics
.
and dances had elements common to films- scripts, sets
, lighting
, costumes, production, direction
, actors, audiences
, storyboards, and scores. They preceded film by thousands of years. Much terminology later used in film theory and criticism applied, such as mise en scène
. Moving visual images
and sound
s were not recorded for replaying as in film.
People tend to have used very old camera obscura (which meanes darken chamber). The camera obscura was further described by Alhazen in his Book of Optics
(1021), and was later perfected near the year 1600 by Giambattista della Porta
. Light
is inverted through a small hole or lens
from outside, and projected onto a surface or screen
, creating a projected moving image, indistinguishable from a projected high quality film to an audience, but it is not preserved in a recording.
In 1739 and 1748, David Hume
published Treatise of Human Nature and An Enquiry concerning Human Understanding
, arguing for the associations and causes of ideas with visual images, in some sense forerunners to the language of film.
Moving images were produced on revolving drums and disks in the 1830s with independent invention by Simon von Stampfer
(Stroboscope) in Austria, Joseph Plateau (Phenakistoscope) in Belgium and William Horner (zoetrope) in Britain.
On June 19, 1878, under the sponsorship of Leland Stanford
, Eadweard Muybridge
successfully photographed a horse named "Sallie Gardner
" in fast motion using a series of 24 stereoscopic cameras. The experiment took place on June 11 at the Palo Alto farm in California with the press present. The exercise was meant to determine whether a running horse ever had all four legs lifted off the ground at once. The cameras were arranged along a track parallel to the horse's, and each camera shutter was controlled by a trip wire which was triggered by the horse's hooves. They were 21 inches apart to cover the 20 feet taken by the horse stride, taking pictures at one thousandth of a second.
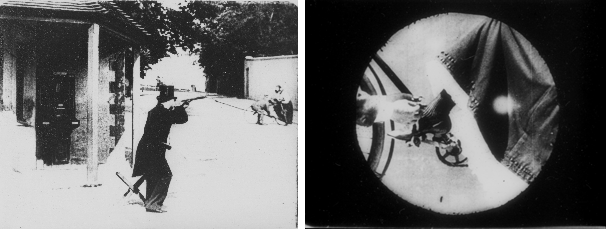
Étienne-Jules Marey
invented a chronophotographic gun in 1882, which was capable of taking 12 consecutive frames a second, recording all the frames on the same picture. He used the chronophotographic gun for studying animals and human locomotion.
The second experimental film, Roundhay Garden Scene
, filmed by Louis Le Prince
on October 14, 1888 in Roundhay
, Leeds
, West Yorkshire
, England
, UK is now known as the earliest surviving motion picture.
On June 21, 1889, William Friese-Greene
was issued patent
no. 10131 for his 'chronophotographic' camera. It was apparently capable of taking up to ten photographs per second using perforated celluloid film. A report on the camera was published in the British Photographic News on February 28, 1890. On 18 March, Friese-Greene sent a clipping of the story to Thomas Edison
, whose laboratory had been developing a motion picture system known as the Kinetoscope
. The report was reprinted in Scientific American
on April 19. Friese-Greene gave a public demonstration in 1890 but the low frame rate
combined with the device's apparent unreliability failed to make an impression.
As a result of the work of Etienne-Jules Marey and Eadweard Muybridge
, many researchers in the late 19th century realized that films as they are known today were a practical possibility, but the first to design a fully successful apparatus was W. K. L. Dickson, working under the direction of Thomas Alva Edison. His fully developed camera, called the Kinetograph, was patented in 1891 and took a series of instantaneous photographs on standard Eastman Kodak photographic emulsion coated on to a transparent celluloid strip
35 mm wide. The results of this work were first shown in public in 1893, using the viewing apparatus also designed by Dickson, and called the Kinetoscope
. This was contained within a large box, and only permitted the images to be viewed by one person at a time looking into it through a peephole, after starting the machine by inserting a coin. It was not a commercial success in this form, and left the way free for Charles Francis Jenkins
and his projector, the Phantoscope
, with the first showing before an audience in June 1894. The Louis and Auguste Lumière
perfected the Cinématographe
, an apparatus that took, printed, and projected film. They gave their first show of projected pictures to an audience in Paris in December 1895.
After this date, the Edison company developed its own form of projector, as did various other inventors. Some of these used different film widths and projection speeds, but after a few years the 35-mm wide Edison film, and the 16-frames-per-second projection speed of the Lumière Cinématographe became standard. The other important American competitor was the American Mutoscope & Biograph Company, which used a new camera designed by Dickson after he left the Edison company.
At the Chicago
1893 World's Columbian Exposition
, Muybridge gave a series of lectures on the Science of Animal Locomotion in the Zoopraxographical Hall, built specially for that purpose in the "Midway Plaisance" arm of the exposition. He used his zoopraxiscope
to show his moving pictures
to a paying public, making the Hall the first commercial film theater.
William Kennedy Laurie Dickson, chief engineer with the Edison Laboratories, is credited with the invention of a practicable form of a celluloid strip containing a sequence of images, the basis of a method of photographing and projecting moving images. Celluloid blocks were thinly sliced, then removed with heated pressure plates. After this, they were coated with a photosensitive gelatin emulsion. In 1893 at the Chicago World's Fair
, Thomas Edison
introduced to the public two pioneering inventions based on this innovation; the Kinetograph - the first practical moving picture camera - and the Kinetoscope
. The latter was a cabinet in which a continuous loop of Dickson's celluloid film (powered by an electric motor
) was back lit by an incandescent lamp
and seen through a magnifying lens
. The spectator viewed the image through an eye piece. Kinetoscope parlours were supplied with fifty-foot film snippets photographed by Dickson, in Edison's "Black Maria"
studio . These sequences recorded both mundane incidents, such as Fred Ott's Sneeze
, and entertainment acts, such as acrobats, music hall
performers and boxing demonstrations.
Kinetoscope parlors soon spread successfully to Europe. Edison, however, never attempted to patent these instruments on the other side of the Atlantic, since they relied so greatly on previous experiments and innovations
from Britain and Europe. This enabled the development of imitations, such as the camera devised by British electrician and scientific instrument maker Robert W. Paul
and his partner Birt Acres
.
Charles Francis Jenkins
, wanting to display moving pictures to large groups of people, invented the first patented film projector
. In 1894, his invention, called the Phantoscope, was the first to project a motion picture. At about the same time, in Lyon
, France, Auguste and Louis Lumière
invented the cinematograph, a portable camera, printer, and projector. In late 1895 in Paris, father Antoine Lumière began exhibitions of projected films before the paying public, beginning the general conversion of the medium to projection (Cook, 1990). They quickly became Europe's main producers with their actualités
like Workers Leaving the Lumière Factory
and comic vignettes like The Sprinkler Sprinkled
(both 1895). Even Edison, initially dismissive of projection, joined the trend with the Vitascope
, a modified Jenkins' Phantoscope, within less than six months. The first public motion-picture film presentation in Europe, though, belongs to Max
and Emil Skladanowsky of Berlin, who projected with their apparatus "Bioscop", a flickerfree duplex construction, November 1 through 31, 1895.
That same year in May, in the USA, Eugene Augustin Lauste
devised his Eidoloscope
for the Latham
family. But the first public screening of film ever is due to Jean Aimé "Acme" Le Roy, a French photographer. On February 5, 1894, his 40th birthday, he presented his "Marvellous Cinematograph" to a group of around twenty show business men in New York City.
The films of the time were seen mostly via temporary storefront spaces and traveling exhibitors or as acts in vaudeville programs. A film could be under a minute long and would usually present a single scene, authentic or staged, of everyday life, a public event, a sporting event or slapstick
. There was little to no cinematic technique: no editing and usually no camera movement, and flat, stagey compositions. But the novelty of realistically moving photographs was enough for a motion picture industry to mushroom before the end of the century, in countries around the world.
s and even commentary spoken by the showman or projectionist.
Illustrated songs
were a notable exception to this trend that began in 1894 in vaudeville
houses and persisted as late as the late 1930s in film theaters. In this early precursor to the music video
, live performance or sound recordings were paired with hand-colored glass slides projected through stereopticon
s and similar devices. In this way, song narrative was illustrated through a series of slides whose changes were simultaneous with the narrative development. The main purpose of illustrated songs was to encourage sheet music
sales, and they were highly successful with sales reaching into the millions for a single song. Later, with the birth of film, illustrated songs were used as filler material preceding films and during reel changes.
In most countries the need for spoken accompaniment quickly faded, with dialogue and narration presented in intertitle
s, but in Japanese cinema it remained popular throughout the silent era.
However, it was clear that Edison originally intended to create a sound film
system, which would not gain worldwide recognition until the release of "The Jazz Singer
" in 1927. In 1896 it became clear that more money was to be made by showing motion picture films with a projector to a large audience than exhibiting them in Edison's Kinetoscope
peep-show
machines. The Edison company took up a projector developed by Armat and Jenkins, the “Phantoscope”, which was renamed the Vitascope, and it joined various projecting machines made by other people to show the 480 mm. width films being made by the Edison company and others in France and the UK.
However, the most successful motion picture company in the United States, with the largest production until 1900, was the American Mutoscope
company. This was initially set up to exploit peep-show type films using designs made by W.K.L. Dickson after he left the Edison company in 1895. His equipment used 70 mm. wide film, and each frame was printed separately onto paper sheets for insertion into their viewing machine, called the Mutoscope
. The image sheets stood out from the periphery of a rotating drum, and flipped into view in succession. Besides the Mutoscope, they also made a projector called the Biograph, which could project a continuous positive film print made from the same negatives.
There were numerous other smaller producers in the United States, and some of them established a long-term presence in the new century. American Vitagraph
, one of these minor producers, built studios in Brooklyn, and expanded its operations in 1905. From 1896 there was continuous litigation in the United States over the patents covering the basic mechanisms that made motion pictures possible.
In France, the Lumière
company sent cameramen all round the world from 1896 onwards to shoot films, which were exhibited locally by the cameramen, and then sent back to the company factory in Lyon to make prints for sale to whoever wanted them. There were nearly a thousand of these films made up to 1901, nearly all of them actualities.
By 1898 Georges Méliès
was the largest producer of fiction films in France, and from this point onwards his output was almost entirely films featuring trick effects, which were very successful in all markets. The special popularity of his longer films, which were several minutes long from 1899 onwards (while most other films were still only a minute long), led other makers to start producing longer films.
From 1900 Charles Pathé
began film production under the Pathé-Frères brand, with Ferdinand Zecca
hired to actually make the films. By 1905, Pathé was the largest film company in the world, a position it retained until World War I. Léon Gaumont
began film production in 1896, with his production supervised by Alice Guy
.
In the UK, Robert W. Paul
, James Williamson and G.A. Smith
and the other lesser producers were joined by Cecil Hepworth
in 1899, and in a few years he was turning out 100 films a year, with his company becoming the largest on the British scene.
films, which were being produced of the most popular subjects before 1900, cost 2 to 3 times as much per foot. There were a few producers, such as the American Mutoscope and Biograph Company, which did not sell their films, but exploited them solely with their own exhibition units.
The first successful permanent theatre showing nothing but films was “The Nickelodeon”, which was opened in Pittsburgh in 1905. By this date there were finally enough films several minutes long available to fill a programme running for at least half an hour, and which could be changed weekly when the local audience became bored with it. Other exhibitors in the United States quickly followed suit, and within a couple of years there were thousands of these nickelodeons in operation. The American situation led to a worldwide boom in the production and exhibition of films from 1906 onwards.
 The first film cameras were fastened directly to the head of their tripod or other support, with only the crudest kind of levelling devices provided, in the manner of the still-camera tripod heads of the period. The earliest film cameras were thus effectively fixed during the shot, and hence the first camera movements were the result of mounting a camera on a moving vehicle. The first known of these was a film shot by a Lumière cameraman from the back platform of a train leaving Jerusalem in 1896, and by 1898 there were a number of films shot from moving trains. Although listed under the general heading of "panoramas" in the sales catalogues of the time, those films shot straight forward from in front of a railway engine were usually specifically referred to as "phantom ride
The first film cameras were fastened directly to the head of their tripod or other support, with only the crudest kind of levelling devices provided, in the manner of the still-camera tripod heads of the period. The earliest film cameras were thus effectively fixed during the shot, and hence the first camera movements were the result of mounting a camera on a moving vehicle. The first known of these was a film shot by a Lumière cameraman from the back platform of a train leaving Jerusalem in 1896, and by 1898 there were a number of films shot from moving trains. Although listed under the general heading of "panoramas" in the sales catalogues of the time, those films shot straight forward from in front of a railway engine were usually specifically referred to as "phantom ride
s".
In 1897, Robert W. Paul had the first real rotating camera head made to put on a tripod, so that he could follow the passing processions of Queen Victoria's Diamond Jubilee
in one uninterrupted shot. This device had the camera mounted on a vertical axis that could be rotated by a worm gear driven by turning a crank handle, and Paul put it on general sale the next year. Shots taken using such a "panning"
head were also referred to as "panoramas" in the film catalogues of the first decade of the cinema.
The standard pattern for early film studios was provided by the studio which Georges Méliès had built in 1897. This had a glass roof and three glass walls constructed after the model of large studios for still photography, and it was fitted with thin cotton cloths that could be stretched below the roof to diffuse the direct ray of the sun on sunny days. The soft overall light without real shadows that this arrangement produced, and which also exists naturally on lightly overcast days, was to become the basis for film lighting in film studios for the next decade.
This film was among those exported to Europe with the first Kinetoscope machines in 1895, and was seen by Georges Méliès, who was putting on magic shows in his Theatre Robert-Houdin in Paris at the time. He took up filmmaking
in 1896, and after making imitations of other films from Edison, Lumière, and Robert Paul
, he made Escamotage d’un dame chez Robert-Houdin (The Vanishing Lady). This film shows a woman being made to vanish by using the same stop motion
technique as the earlier Edison film. After this, Georges Méliès made many single shot films using this trick over the next couple of years.
The other basic set of techniques for trick cinematography involves double exposure
of the film in the camera, which was first done by G.A. Smith in July 1898 in the UK. His The Corsican Brothers was described in the catalogue of the Warwick Trading Company
, which took up the distribution of Smith's films in 1900, thus:

The ghost effect was simply done by draping the set in black velvet after the main action had been shot, and then re-exposing the negative with the actor playing the ghost going through the actions at the appropriate point. Likewise, the vision, which appeared within a circular vignette or matte
, was similarly superimposed over a black area in the backdrop to the scene, rather than over a part of the set with detail in it, so that nothing appeared through the image, which seemed quite solid. Smith used this technique again a year later in Santa Claus.
Georges Méliès first used superimposition on a dark background in la Caverne maudite (The Cave of the Demons) made a couple of months later in 1898, and then elaborated it further with multiple superimpositions in the one shot in l’Homme de têtes (The Troublesome Heads). He then did it with further variations in numerous subsequent films.
Cecil Hepworth took this technique further, by printing the negative of the forwards motion backwards frame by frame, so producing a print in which the original action was exactly reversed. To do this he built a special printer in which the negative running through a projector was projected into the gate of a camera through a special lens giving a same-size image. This arrangement came to be called a “projection printer”, and eventually an “optical printer
”. With it Hepworth made The Bathers in 1900, in which bathers who have undressed and jumped into the water appear to spring backwards out of it, and have their clothes magically fly back onto their bodies.
The use of different camera speeds also appeared around 1900. To make Robert Paul's On a Runaway Motor Car through Piccadilly Circus (1899), the camera was turned very slowly, so that when the film was projected at the usual 16 frames per second, the scenery appeared to be passing at great speed. Cecil Hepworth used the opposite effect in The Indian Chief and the Seidlitz Powder
(1901), in which a naïve Red Indian
eats a lot of the fizzy stomach medicine, causing his stomach to expand vastly. He leaps around in a way that is made balloon-like by cranking the camera much faster than 16 frames per second. This gives what we would call a “slow motion
” effect.
. The relative sophistication of this piece was not followed up for some time, with subsequent works in animation being limited to short, two or three frame effects, such as appeared in Edwin Porter's 1902 short "Fun in a Bakery Shop", where a lump of dough was made to smile over the course of a three-frame sequence. Works rivaling the British short in length did not appear until 1905, when Edwin Porter made How Jones Lost His Roll, and The Whole Dam Family and the Dam Dog. Both of these films had intertitles which were formed by the letters moving into place from a random scattering to form the words of the titles. This was done by exposing the film one frame at a time, and moving the letters a little bit towards their final position between each exposure. This is what has come to be called “single frame animation
” or “object animation”, and it needs a slightly adapted camera that exposes only one frame for each turn of the crank handle, rather than the usual eight frames per turn.
In 1906, Albert Edward Smith and James Stuart Blackton
at Vitagraph took the next step, and in their Humorous Phases of Funny Faces, what appear to be cartoon drawings of people move from one pose to another. This is done for most of the length of this film by moving jointed cut-outs of the figures frame by frame between the exposures, just as Porter moved his letters. However, there is a very short section of the film where things are made to appear to move by altering the drawings themselves from frame to frame, which is how standard animated cartoons
have since been made up to today.
Christ. The first of these was made in France in 1897, and it was followed in the same year by a film of the Passion play staged yearly in the Czech town of Horitz. This was filmed by Americans for exhibition outside the German-speaking world and was presented in special venues, not as a continuous film, but with the separate scenes interspersed with lantern slides, a lecture, and live choral numbers, to increase the running time of the spectacle to about 90 minutes.
Films of acted reproductions of scenes from the Greco-Turkish war
were made by Georges Méliès in 1897, and although sold separately, these were no doubt shown in continuous sequence by exhibitors. In 1898 a few films of similar kind were made, but still none had continuous action moving from one shot into the next. The multi-shot films that Georges Méliès made in 1899 were much longer than those made by anybody else, but l’Affaire Dreyfus (The Dreyfus Case) and Cendrillon (Cinderella) still contained no action moving from one shot to the next one. Also, from Cendrillon onwards, Méliès made a dissolve
between every shot in his films, which reduced any appearance of action continuity even further. To understand what is going on in both these films, the audience had to know their stories beforehand, or be told them by a presenter.
's Come Along, Do!
, made in 1898. In the first shot of this film, an old couple outside an art exhibition
follow other people inside through the door. The second shot showed what they do inside.
 The further development of action continuity in multi-shot films continued in 1899. In the latter part of that year, George Albert Smith
The further development of action continuity in multi-shot films continued in 1899. In the latter part of that year, George Albert Smith
, working in Brighton
, made The Kiss in the Tunnel. This started with a shot from a “phantom ride” at the point at which the train goes into a tunnel, and continued with the action on a set representing the interior of a railway carriage, where a man steals a kiss from a woman, and then cuts back to the phantom ride shot when the train comes out of the tunnel. A month later, the Bamforth company in Yorkshire made a restaged version of this film under the same title, and in this case they filmed shots of a train entering and leaving a tunnel from beside the tracks, which they joined before and after their version of the kiss inside the train compartment.
In 1900, continuity of action across successive shots was definitively established by George Albert Smith and James Williamson, who also worked in Brighton. In that year Smith made Seen Through the Telescope, in which the main shot shows street scene with a young man tying the shoelace and then caressing the foot of his girlfriend, while an old man observes this through a telescope. There is then a cut to close shot of the hands on the girl's foot shown inside a black circular mask, and then a cut back to the continuation of the original scene.
 Even more remarkable is James Williamson
Even more remarkable is James Williamson
's Attack on a China Mission Station, made around the same time in 1900. The first shot shows the gate to the mission station from the outside being attacked and broken open by Chinese Boxer rebels, then there is a cut to the garden of the mission station where the missionary and his family are seated. The Boxers rush in and after exchanging fire with the missionary, kill him, and pursue his family into the house. His wife appears on the balcony waving for help, which immediately comes with an armed party of British sailors appearing through the gate to the mission station, this time seen from the inside. They fire at the Boxers, and advance out of the frame into the next shot, which is taken from the opposite direction looking towards the house. This constitutes the first “reverse angle” cut in film history. The scene continues with the sailors rescuing the remaining members of the missionary's family.
G.A. Smith further developed the ideas of breaking a scene shot in one place into a series of shots taken from different camera positions over the next couple of years, starting with The Little Doctors of 1901. In this film a little girl is administering pretend medicine to a kitten, and Smith cuts in to a big Close Up
of the kitten as she does so, and then cuts back to the main shot. In this case the inserted close up is not shown as a Point of View shot in a circular mask. He summed up his work in Mary Jane's Mishap of 1903, with repeated cuts in to a close shot of a housemaid fooling around, along with superimpositions and other devices, before abandoning film-making to invent the Kinemacolor system of colour cinematography.
James Williamson concentrated on making films taking action from one place shown in one shot to the next shown in another shot in films like Stop Thief! and Fire!, made in 1901, and many others.
”, as we know it. The best known of these film-makers was Edwin S. Porter, who started making films for the Edison Company in 1901. When he began making longer films in 1902, he put a dissolve between every shot, just as Georges Méliès was already doing, and he frequently had the same action repeated across the dissolves. In other words, Edwin Porter did not develop the basics of film construction. The Pathé company in France also made imitations and variations of Smith and Williamson's films from 1902 onwards using cuts between the shots, which helped to standardize the basics of film construction.
In 1903 there was a substantial increase in the number of women film several minutes long, as a result of the great popularity of Georges Méliès’ le Voyage dans la lune (A Trip to the Moon), which came out in early 1902, though such films were still a very minor part of production. Most of them were what came to be called “chase films”. These were inspired by James Williamson
's Stop Thief!
of 1901, which showed a tramp stealing a leg of mutton from a butcher's boy in the first shot, then being chased through the second shot by the butcher's boy and assorted dogs, and finally being caught by the dogs in the third shot.
Several British films made in the first half of 1903 extended the chase method of film construction. These included An Elopement à la Mode and The Pickpocket: A Chase Through London, made by Alf Collins for the British branch of the French Gaumont company
, Daring Daylight Burglary, made by Frank Mottershaw
at the Sheffield Photographic Company, and Desperate Poaching Affray
, made by the Haggar
family, whose main business was exhibiting films made by others in their traveling tent theatre. All of these films, and indeed others of like nature were shown in the United States, and some them were certainly seen by Edwin Porter, before he made The Great Train Robbery towards the end of the year. The time continuity in The Great Train Robbery is actually more confusing than that in the films it was modeled on, but nevertheless it was a greater success than them worldwide, because of its Wild West
violence.
From 1900, the Pathé company films also frequently copied and varied the ideas of the British film-makers, without making any major innovations in narrative film construction, but eventually the sheer volume of their production led to their film-makers giving a further precision and polish to the details of film continuity.

films, but this changed fairly quickly as the American companies cranked up production. The programme was made up of just a few films, and the show lasted around 30 minutes. The reel of film, of maximum length 1000 feet (304.8 m), which usually contained one individual film, became the standard unit of film production and exhibition in this period. The programme was changed twice or more a week, but went up to five changes of programme a week after a couple of years. In general, cinemas were set up in the established entertainment districts of the cities. In other countries of the Western world the film exhibition situation was similar. With the change to “nickelodeon” exhibition there was also a change, led by Pathé in 1907, from selling films outright to renting them through film exchanges.
The litigation over patents between all the major American film-making companies had continued, and at the end of 1908 they decided to pool their patents and form a trust to use them to control the American film business. The companies concerned were Pathé
, Edison
, Biograph, Vitagraph
, Lubin
, Selig
, Essanay
, Kalem, and the Kleine Optical Company, a major importer of European films. The George Eastman
company, the only manufacturer of film stock in the United States, was also part of the combine, which was called the Motion Picture Patents Company
(MPPC), and Eastman Kodak
agreed to only supply the members with film stock. License fees for distributing and projecting films were extracted from all distributors and exhibitors. The producing companies that were part of the trust were allocated production quotas (two reels, i.e. films, a week for the biggest ones, one reel a week for the smaller), which were supposed to be enough to fill the programmes of the licensed exhibitors. Vitagraph and Edison already had multiple production units, and so had no difficulty meeting their quota, but in 1908 Biograph lost their one working director. They offered the job of making their films to D. W. Griffith
, an unimportant actor and playwright, who took up the job, and found he had a gift for it. Alone he made all the Biograph films from 1908 to 1910. This amounted to 30 minutes of screen time a week.
But the market was bigger than the Motion Picture Patents Company members could supply. Although 6,000 exhibitors signed with the MPPC, about 2,000 others did not. A minority of the exchanges (i.e. distributors) stayed outside the MPPC, and in 1909 these independent exchanges immediately began to fund new film producing companies. By 1911 there were enough independent and foreign films available to programme all the shows of the independent exhibitors, and in 1912 the independents had nearly half of the market. The MPPC had effectively been defeated in its plan to control the whole United States market, and the government anti-trust
action, which only now started against the MPPC, was not really necessary to defeat it.
, made in Australia in 1906. This was a four-reel version of the career of this famous (in Australia) outlaw, and was incomprehensible without explanation. More multi-reel films were made in Europe than in the United States after 1906, because the MPPC insisted on working on the basis of one-reel films up until 1912. However, before this, some MPPC members got around this restriction by occasionally making longer stories in separate parts, and releasing them in successive weeks, starting with Vitagraph's The Life of Moses in five parts (and five reels) at the end 1909. In other countries this film was shown straight through as one picture, and it inspired the creation of other multi-reel films in Europe.
Pathé-Frères set up a new subsidiary company
in the United States called Eclectic in 1913, and in 1914 this began production of features at the Pathé plant in New Jersey. The French Éclair company was already making films in the United States, and their production of features increased with the transfer of more film-makers when the French industry was shut down at the beginning of World War I.
Up to 1913, most American film production was still carried out around New York, but because of the monopoly of Thomas Edison
's film patents, many filmmakers had moved to Southern California, hoping to escape the litany of lawsuits that the Edison Company had been bringing to protect its monopoly. Once there in Southern California, the film industry grew continuously.
The move to filming in California had begun when Selig, one of the MPPC companies, sent a production unit there in 1909. Other companies, both independents and members of the MPPC, then sent units to work there in the summer to take advantage of the sunshine and scenery. The latter was important for the production of Westerns, which now formed a major American film genre. The first cowboy star was G.M. Anderson (“Broncho Billy”)
, directing his own Western dramas for Essanay, but in 1911 Tom Mix
brought the kind of costumes and stunt action used in live Wild West shows to Selig film productions, and became the biggest cowboy star for the next two decades.
Most of the major companies made films in all the genres, but some had a special interest in certain kinds of films. Once Selig had taken up production in California, they used the (fairly) wild animals from the zoo that Colonel Selig had set up there in a series of exotic adventures, with the actors being menaced or saved by the animals. Essanay specialized in Westerns featuring “Broncho Billy” Anderson, and Kalem sent Sidney Olcott
off with a film crew and a troupe of actors to various places in America and abroad to make film stories in the actual places they were supposed to have happened. Kalem also pioneered the female action heroine from 1912, with Ruth Roland
playing starring roles in their Westerns.
Minor curiosities were some of the films of Solax
directed by Herbert Blaché and his wife Alice Guy. They left American branch of the Gaumont company in 1912 to set up their own independent company. The distinguishing feature of some of their films was a deliberate attempt to use resolutely theatrical-type light comedy playing that was directed towards the audience. This went against the trend towards filmic restraint already visible in what were called “polite” comedies from other film companies.
In France, Pathé retained its dominant position, followed still by Gaumont, and then other new companies that appeared to cater to the film boom. A film company with a different approach was Film d’Art. This was set up at the beginning of 1908 to make films of a serious artistic nature. Their declared programme was to make films using only the best dramatists, artists and actors. The first of these was L’Assassinat du Duc de Guise
(The Assassination of the Duc de Guise), a historical subject set in the court of Henri III
. This film used leading actors from the Comédie Francaise
, and had a special accompanying score written by Camille Saint-Saens
. The other French majors followed suit, and this wave gave rise to the English-language description of films with artistic pretensions aimed at a sophisticated audience as “art films”
. By 1910, the French film companies were starting to make films as long as two, or even three reels, though most were still one reel long. This trend was followed in Italy, Denmark, and Sweden.
Although the British industry continued to expand after its brilliant beginning, the new companies that replaced the first innovative film-makers proved unable to preserve their drive and originality.
two-reel la Caduta di Troia (The Fall of Troy
) made a big impression worldwide, and it was followed by even bigger spectacles like Quo Vadis? (1912), which ran for 90 minutes, and Pastrone's Cabiria of 1914, which ran for two and a half hours.
 Italian companies also had a strong line in slapstick comedy, with actors like André Deed, known locally as “Cretinetti”, and elsewhere as “Foolshead” and “Gribouille”, achieving worldwide fame with his almost surrealistic gags.
Italian companies also had a strong line in slapstick comedy, with actors like André Deed, known locally as “Cretinetti”, and elsewhere as “Foolshead” and “Gribouille”, achieving worldwide fame with his almost surrealistic gags.
The most important film-producing country in Northern Europe up until the First World War was Denmark. The Nordisk
company was set up there in 1906 by Ole Olsen, a fairground showman, and after a brief period imitating the successes of French and British film-makers, in 1907 he produced 67 films, most directed by Viggo Larsen, with sensational subjects like Den hvide Slavinde (The White Slave), Isbjørnenjagt (Polar Bear Hunt) and Løvejagten (The Lion Hunt). By 1910 new smaller Danish companies began joining the business, and besides making more films about the white slave trade, they contributed other new subjects. The most important of these finds was Asta Nielsen
in Afgrunden (The Abyss), directed by Urban Gad
for Kosmorama, This combined the circus, sex, jealousy and murder, all put over with great conviction, and pushed the other Danish film-makers further in this direction. By 1912 the Danish film companies were multiplying rapidly.
The Swedish film industry
was smaller and slower to get started than the Danish industry. Here, the important man was Charles Magnusson, a newsreel cameraman for the Svenskabiografteatern cinema chain. He started fiction film production for them in 1909, directing a number of the films himself. Production increased in 1912, when the company engaged Victor Sjöström
and Mauritz Stiller
as directors. They started out by imitating the subjects favoured by the Danish film industry, but by 1913 they were producing their own strikingly original work, which sold very well.
Russia began its film industry in 1908 with Pathé shooting some fiction subjects there, and then the creation of real Russian film companies by Aleksandr Drankov and Aleksandr Khanzhonkov
. The Khanzhonkov company quickly became much the largest Russian film company, and remained so until 1918.
In Germany, Oskar Messter
had been involved in film-making from 1896, but did not make a significant number of films per year till 1910. When the worldwide film boom started, he, and the few other people in the German film business, continued to sell prints of their own films outright, which put them at a disadvantage. It was only when Paul Davidson, the owner of a chain of cinemas, brought Asta Nielsen and Urban Gad to Germany from Denmark in 1911, and set up a production company, Projektions-AG “Union” (PAGU), for them, that a change-over to renting prints began. Messter replied with a series of longer films starring Henny Porten, but although these did well in the German-speaking world, they were not particularly successful internationally, unlike the Asta Nielsen films. Another of the growing German film producers just before World War I was the German branch of the French Éclair company, Deutsche Éclair. This was expropriated by the German government, and turned into DECLA when the war started. But altogether, German producers only had a minor part of the German market in 1914.
Overall, from about 1910, American films had the largest share of the market in all European countries except France, and even in France, the American films had just pushed the local production out of first place on the eve of World War I. So even if the war had not happened, American films may have become dominant worldwide. Although the war made things much worse for European producers, the technical qualities of American films made them increasingly attractive to audiences everywhere.
 With the increased production required by the nickelodeon boom, extra artificial lighting was used more and more in the film studios to supplement diffuse sunlight, and so increase the hours that film could be shot during the day. The main sources used were modified arc lights
With the increased production required by the nickelodeon boom, extra artificial lighting was used more and more in the film studios to supplement diffuse sunlight, and so increase the hours that film could be shot during the day. The main sources used were modified arc lights
made for street lighting. These were either hung on battens suspended forward of the actors from the roof, or mounted in groups on floorstands. The addition of a metal reflector round the arc source directed a very broad sweep of light in the desired direction. Large mercury vapour tube lights (Cooper-Hewitts) were also used in racks placed in the same way. Arc lights had been used to produce special lighting effects in films like the light from a lamp or firelight before 1906, but this now became more common.
 A strong expressive use of a fire effect occurs in D.W. Griffith'sThe Drunkard's Reformation (1909). Here, the reformed drunkard is happily reunited with his family before the fire in the hearth, in a set-up reproducing that at the beginning of the film in which the fire is out, and the hearth is cold, and the family is destitute.
A strong expressive use of a fire effect occurs in D.W. Griffith'sThe Drunkard's Reformation (1909). Here, the reformed drunkard is happily reunited with his family before the fire in the hearth, in a set-up reproducing that at the beginning of the film in which the fire is out, and the hearth is cold, and the family is destitute.
Low-key lighting
(i.e. lighting in which most of the frame is dark) slowly began to be used for sinister scenes, but not in D.W. Griffith films. Vitagraph's thriller, The Mystery of Temple Court (1910) has low-key lighting for a scene of murder, and their Conscience (1912) shows low-key lighting done solely with artificial light for a scene of terror.
 This sort of lighting was appearing occasionally in European films by 1911, and in some cases was pushed much further. Lighting from a low angle was used more strongly in the Italian epic film Quo Vadis? in 1912, and then in the famous Cabiria
This sort of lighting was appearing occasionally in European films by 1911, and in some cases was pushed much further. Lighting from a low angle was used more strongly in the Italian epic film Quo Vadis? in 1912, and then in the famous Cabiria
(1914) to reinforce the weird atmosphere in one scene.
Silhouette effects in location scenes began to appear in 1909 in both the United States and Italy; though as things developed, European film-makers made more use of this than the Americans did.
The most important aspect of this was that such shots involved having the sun light the scene from behind, and this approach was extended by using the reflected sunlight from a white surface below the camera to light up the shadow on the actors faces from the front. This is the one novel technique that D.W. Griffith and his cameraman Billy Bitzer
may really have invented. The next step was to transfer this kind of back-lighting onto the lighting of actors on studio sets. Up to this point artificial lighting in studio scenes had always been put on from the front or side-front, but in 1912 there began to be a few cases where light was put onto the actors from arc floodlights out of shot behind them and to one side, to give a kind of backlighting. It was not until 1915 that the effect of backlighting of the actors by the sun was fully mimicked in studio lighting, by using a powerful arc spotlight shining from above and behind the set down onto the actors. This slowly became a standard component of the studio lighting of figures in American films, but it took much longer to catch on with European cameramen.
, in which sculptures were deformed from one thing into another thing frame by frame in Sculpture moderne (1908), and then Pathé made the next step to the animation of silhouette shapes. Also in France, Emile Cohl
fully developed drawn animation in a series of films starting with Fantasmagorie
(1908), in which humans and objects drawn as outline figures went though a series of remarkable interactions and transformations. In the United States the response was from the famous strip cartoon artist
Winsor McCay
, who drew much more realistic animated figures going through smoother, more naturalistic motion in a series of films starting with the film Little Nemo, made for Vitagraph in 1911. In the next few years various others took part in this development of animated cartoon
s in the United States and elsewhere.
In the United States, Vitagraph was also trying cross-cutting for suspense in 1907 and 1908 with The Mill Girl and Get Me a Stepladder. Before D.W. Griffith started directing at Biograph in May 1908, he had seen the two Pathé films just mentioned, and a number of Vitagraph films as well. But Griffith's first use of cross-cutting in The Fatal Hour, made in July 1908, has a much stronger suspense story served by this construction than those in the earlier Pathé examples. From this point onwards Griffith certainly developed the device much further, gradually increasing the number of alternations between two, and later three, sets of parallel scenes, and also their speed. This intensified usage was only slowly taken up by other American film-makers. So although he did not invent the technique of cross-cutting, he did consciously develop it into a powerful method of film construction. It is also important to note that Griffith described cross-cutting indiscriminately as the ‘switch-back’ or ‘cut-back’ or ‘flash-back’ technique, and that by the last of these terms he did not mean what we now understand by a ‘flash-back’. The true ‘flash-back’ was also developed in this period, but not at all by D.W. Griffith.
Although D. W. Griffith did not invent any new film techniques, he was the best film director working up to 1913, and this was because he made better dramatic and artistic use of the medium than other directors. One aspect of this was the structure he gave his films, with the final scene mirroring the opening scene, as in the example of A Drunkard's Reformation
already mentioned above. Many other examples of this like The Country Doctor
(1908) can easily be found in his work. But the most important thing Griffith did was work out significant and expressive natural gestures in intensive rehearsal periods with his actors, before the film was shot, such as the enraged and jealous husband in The Voice of the Child
(1911) walking around his office chomping on a cigar and puffing clouds of smoke out of it through clenched teeth.
Griffith's increased use of cross-cutting between parallel actions helped him to get more shots into his films than other directors, but he also had another method for doing this. This was to split a scene that could have been played in room (or other place), into two or more sections that moved backwards and forwards between adjoining rooms or spaces. The result of this was that D.W. Griffith's films had at least twice as many shots in them as did those of other American directors. Over this period, the other directors speeded up, but so did Griffith. At first, the technique of cutting in to a closer shot of an actor in a scene made no contribution to the increase in cutting rate, because it was still very rarely done, despite having been established as a possibility in the previous period. The exception to this was a close shot of an object, which was sometimes used to make clear exactly what a person was doing. It was only towards 1913 that film-makers began to cut into closer shots with any regularity.
However, American film-makers did get closer to the actors on the average by shooting the whole scene with the camera closer than previously. The Vitagraph company led the way here, by using what they called “the nine-foot line” from 1910 onwards. This meant that the actors played a scene up to a line marked on the ground nine feet from the camera lens, which meant that they were shown cut off at the waist in the image. Some, but not all, American film-makers followed their example, calling it the “American foreground”, while European film-makers stayed with the “French foreground” established by the Pathé about 1907, which only cut the actors off at the shins. This corresponded to the actors playing up to a line put down 4 metres in front of the camera lens.
. Previously, these had only been used to convey the idea of what someone in the film was seeing through a telescope (or other aperture), and this was indicated by having a black circular mask or vignette within the film frame. The true Point of View (POV) shot, in which a shot of someone looking at something is followed by a cut to a shot taken from their position without any mask, took longer to appear. In 1910, in Vitagraph's Back to Nature we see a Long Shot of people looking down over the rail of a ship taken from below, followed by a shot of the lifeboat they are looking at taken from their position.
 However, the Vitagraph film-makers continued to be a little uneasy with the device, as a true POV shot is introduced by an explanatory intertitle, “What they saw in the house across the court” in Larry Trimble's Jean and the Waif, made at the end of 1910. But a few months later, Trimble made Jean Rescues, another of the popular series starring the fictional exploits of his Border Collie
However, the Vitagraph film-makers continued to be a little uneasy with the device, as a true POV shot is introduced by an explanatory intertitle, “What they saw in the house across the court” in Larry Trimble's Jean and the Waif, made at the end of 1910. But a few months later, Trimble made Jean Rescues, another of the popular series starring the fictional exploits of his Border Collie
, which has Point of View [POV] shots introduced at an appropriate point without explanation. After this, un-vignetted POV shots began to appear fairly frequently in Vitagraph films, and also occasionally in films from other American companies. However, D.W. Griffith only used them in a theatrical situation, to show what the audience in a theatre were looking at, as did European film-makers.
 Another important development was in the use of reverse angle shots; that is, continuing a scene with a cut to a shot of the action taken from the opposite direction. There were isolated examples of this very early, and the first of these, Williamson's Attack on a China Mission (1900) has already been mentioned. But in 1908, starting with l’Assassinat du duc de Guise (The Assassination of the Duc de Guise)
Another important development was in the use of reverse angle shots; that is, continuing a scene with a cut to a shot of the action taken from the opposite direction. There were isolated examples of this very early, and the first of these, Williamson's Attack on a China Mission (1900) has already been mentioned. But in 1908, starting with l’Assassinat du duc de Guise (The Assassination of the Duc de Guise)
, there began to be other films in which a scene was shown from another direction by cutting to the opposite side. This effect was imitated occasionally in Europe and the United States over the next couple of years, and came to be called a “reverse scene”.
The next step, in which two actors facing each other are shown in successive close shots from taken opposite directions towards each of them, is first to be seen at the end of 1911 in The Loafer, made by Arthur Mackley for Essanay. This is what is called reverse-angle cutting, and it is used constantly in present day film-making. However, it took some years to catch on with other American film-makers, but by 1913, it was starting to occur with greater frequency in the work of a few directors. This happened entirely when they were filming exterior scenes, where there was no problem about shooting past the edge of the studio set. A leading example of this use of close in reverse-angle cutting is His Last Fight (1913), directed by Ralph Ince for Vitagraph, in which one-third of the cuts are between a shot and the reverse angle. However, this sort of thing never happened in D.W. Griffith's films, or in European films.
s at intervals down the length of the film. However, this was an exceptional case, and it is not until 1912 that there were the first signs of the special expressive use of Insert Shots; that is, shots of objects rather than people. In the Italian Ambrosio companies film La mala planta (The Evil Plant), directed by Mario Caserini
, which involves a case of poisoning, there is an Insert shot of a snake slithering over the ‘Evil Plant’. Another of the still very rare examples at this date is in Griffith's The Massacre, which was made at the end of 1912. This includes an Insert Shot of a candle at a sick man's bedside guttering out to indicate his death. Yet another is in the Ambrosio company version of Gli ultimi giorni di Pompei (The Last Days of Pompeii) (1913). This film includes a scene, preceded by the title “The thorns of jealousy”, in which a rejected woman overhears the man she loves with another woman, and this is followed by a fade to a shot of a pair of doves, which then dissolves into a shot of a bird of prey.
It was in 1914 that D.W. Griffith began to bend the use of the Insert towards truly dramatically expressive ends, but he had not done this often, and it is really only with his The Avenging Conscience
of 1914 that a new phase in the use of the Insert Shot starts. In this film the intertitle “The birth of the evil thought” precedes a series of three shots of the protagonist looking at a spider, and ants eating an insect, though at a later point in the film, when he prepares to kill someone, these shots are cut straight in without explanation. As well as the symbolic inserts already mentioned, The Avenging Conscience also made extensive use of large numbers of Big Close Up shots of clutching hands and tapping feet as a means of emphasizing those parts of the body as indicators of psychological tension. Griffith never went so far in this direction again, but his use of the Insert shot made its real impression on other American film-makers during the years 1915-1919.
 The vast increase in film production after 1906 inevitably brought specialist writers into film-making as part of the increasing sub-division of labour, but even so the film companies still had to buy stories from outsiders to get enough material for their productions. This introduced a greater variety into the types of story used in films. The use of more complex stories derived from literary and stage works of the recent past also contributed to developments in script film construction. The general American tendency was to simplify the plots borrowed from novels and plays so that they could be dealt with in one reel and with the minimum of titling and the maximum of straightforward narrative continuity, but there were exceptions to this. In these cases the information that was difficult to film and lacking in strong dramatic interest was put into narrative titles before each scene, and this was also mostly the custom in European films of the more seriously intended kind.
The vast increase in film production after 1906 inevitably brought specialist writers into film-making as part of the increasing sub-division of labour, but even so the film companies still had to buy stories from outsiders to get enough material for their productions. This introduced a greater variety into the types of story used in films. The use of more complex stories derived from literary and stage works of the recent past also contributed to developments in script film construction. The general American tendency was to simplify the plots borrowed from novels and plays so that they could be dealt with in one reel and with the minimum of titling and the maximum of straightforward narrative continuity, but there were exceptions to this. In these cases the information that was difficult to film and lacking in strong dramatic interest was put into narrative titles before each scene, and this was also mostly the custom in European films of the more seriously intended kind.
Motion pictures were classified into genres by the film industry following the divisions already established in other media, particularly the stage. The main division was into comedy and drama, but these categories were further subdivided. Comedy could be either slapstick (usually referred to as “burlesque farce”), or alternatively “polite comedy”, which later came to be referred to as “domestic comedy” or “sophisticated comedy”. D.W. Griffith made a small number of the latter type of film in his first two years at Biograph, but had little interest or aptitude for the genre. From 1910 he let Frank Powell
, and then Mack Sennett direct the Biograph comedies. Sennett left in 1912 to set up the Keystone company, where he could give his enthusiasm for the slapstick comedy style derived from the earlier Pathé comedies like le Cheval emballé (The Runaway Horse) full rein. In Europe the more restrained type of comedy was developed in substantial quantities in France, with the films of Max Linder
for Pathé representing the summit of the genre from 1910 onwards. Linder's comedy was set in an upper middle-class
milieu, and relied on clever and inventive ways of getting around the embarrassments and obstacles arising in his single-minded pursuit of a goal. Quite often a goal of a sexual nature.
D.W. Griffith had a major influence on the simplification of film stories. After he had been at Biograph for a year, Griffith started to make some films that had much less story content than any previous one-reel films. In The Country Doctor, the action is no more than various people, including the doctor, hurrying backwards and forwards between the doctor's house, where his child is sick, and a neighbouring cottage, where another child is also sick. By 1912 and 1913, there are beginning to be many films from many American companies that rely on applying novel decoration to the story, rather than supplying any twists to the drama itself to sustain interest.
From 1909 a small number of American films, and even one or two European ones, came to include a few dialogue titles, or “spoken titles” as they were called at the time. Film-makers slowly progressed from putting these dialogue titles before the scene in which they were spoken, to cutting them into the middle of the shot at the point at which they were understood to be actually spoken by the characters. This transition began in 1912. Once underway, the trend was aided by the move towards the increasing use of cuts within scenes in American films. In 1913 a substantial proportion of the dialogue titles that were used in American films were cut in at the point when they were spoken. Hardly any of the films where this happened were D.W. Griffith films, and indeed many of his 1913 films still contain no dialogue titles at all. Although some European film-makers picked up the trend towards using dialogue titles, they did not pick up on the move towards cutting them into the scene at the point at which they were actually spoken until a few years later.
The introduction of dialogue titles was far from being a trivial matter, for they entirely transformed the nature of film narrative. When dialogue titles came to be always cut into a scene just after a character starts speaking, and then left with a cut to the character just before they finish speaking, then one had something that was effectively the equivalent of a present-day sound film.
The Universal Film Manufacturing Company
had been formed in 1912 as an umbrella company for many of the independent producing companies, and continued to grow during the war. Other independent companies were grouped under the Mutual banner in 1912, and there were also important new entrants, particularly the Jesse Lasky
Feature Play Company, and Famous Players, which were both formed in 1913 to take advantage of the fact that films could reproduce the real substance of a stage play (plus embellishments), and so the best plays and actors from the legitimate stage could be enticed into films. In fact, the film industry adopted the term “photoplay” for motion pictures at this time. In 1914 the Lasky company and Famous Players were amalgamated into Famous Players-Lasky
, with distribution of their films handled by the new Paramount Pictures Corporation.
Another new major producing company formed during the war years was Triangle, with Mack Sennett
, D.W. Griffith and Thomas Ince heading its production units. Despite the talents involved, it only lasted from 1915 to 1917, after which its separate producers took their films to Paramount for distribution. Equally short-lived, but still very important, was the World Film Company, which recruited most of the French directors, cameramen, and designers who had previously been working at the Fort Lee, New Jersey
studios for Pathé and Éclair.
The biggest success of these years was D.W. Griffith's The Birth of a Nation
(1915), made for Triangle. Griffith applied all the ideas for film staging that he had worked out in his Biograph films to a bigoted white southerner's epic view of the Civil War and its aftermath. Despite protests in the northern cities of the United States organized by the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People
and others, it took many millions at the box office. Stung by the criticism of his film, Griffith made a new film he had just finished, The Mother and the Law, into one of the strands of an even bigger film with an even bigger theme, Intolerance
(1916).
of the country at the beginning of the war. Although film production began again in 1915, it was on a reduced scale, and the biggest companies gradually retired from production, to concentrate on film distribution
and exhibition. Hence the cinemas were given over to imported films, particularly American ones. New small companies entered the business, and new young directors arrived to replace those drafted or working in the United States. The most notable of these was Abel Gance
.
Italian film production held up during the war, with long features already established as the main form. However, there was a disastrous move in subject matter to what were called “diva films”. These romantic dramas had the female star (the “diva”) suffering from unhappy love, and striking endless anguished Art Nouveau
poses, while surrounded by male admirers and luxury. They were a commercial failure outside Italy.
In Denmark the Nordisk company increased its production so much in 1915 and 1916 that it could not sell all its films, which led to a very sharp decline in Danish production, and the end of Denmark's importance on the world film scene. The Nordisk distribution and cinema chain in Germany was effectively expropriated by the German government in 1917. The Swedish industry did not have this problem, as its production was more in balance with the market, and more importantly, the quality of its films was now superior to those from Denmark.
The German film industry was seriously weakened by the war, though with the major companies continuing as before. The distribution organization Projektions-AG “Union” (PAGU) acted as an umbrella company backing production by individual producers, and the Messter company also made many films. The most important of the new film producers at the time was Joe May
, who made a series of thrillers and adventure film
s through the war years, but Ernst Lubitsch
also came into prominence with a series of very successful comedies and dramas.
Because of the large local market for films in Russia, the industry there was not harmed by the war at first, although the isolation of the country led many Russian films to develop peculiarly distinctive features. The Khanzhonkov company retained its dominance, but the Ermoliev company, which had been formed in 1914, became its principal competitor, propelled by the work of its star, Ivan Mosjoukin
, and principal director, Yakov Protazanov
. The Bolshevik revolution
in October 1917 did not eliminate the privately owned film companies at first, though production was reduced through 1918. It was only in 1919 that the exodus of talent from the country took place, and fiction film production was reduced to practically nothing.
trucks for this purpose. All these developments took years to reach Europe
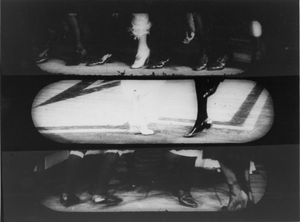 A very noticeable technical development was the widespread adoption of irising-in and out to begin and end scenes. This is the revelation of a film shot by its appearance inside a small circular vignette mask which gradually gets larger till it expands beyond the frame, and the whole image is in the clear. D.W. Griffith, who used it relentlessly, was responsible for the popularization of this device. By 1918 the use of the iris to begin and end sequences was starting to decrease in the United States, though in Europe it was just starting to become fashionable. At that date it is quite easy to find American films such as Stella Maris in which only fades are used.
A very noticeable technical development was the widespread adoption of irising-in and out to begin and end scenes. This is the revelation of a film shot by its appearance inside a small circular vignette mask which gradually gets larger till it expands beyond the frame, and the whole image is in the clear. D.W. Griffith, who used it relentlessly, was responsible for the popularization of this device. By 1918 the use of the iris to begin and end sequences was starting to decrease in the United States, though in Europe it was just starting to become fashionable. At that date it is quite easy to find American films such as Stella Maris in which only fades are used.
There were other variants of the simple iris as well and in these the mask opening or closing in front of the lens had shapes other than circular. One of the more frequent of these shapes was the opening slit; a vertical central split appears in the totally black frame, and widens till the whole frame is clear, revealing the scene that is about to start. Eventually the diagonally opening slit appeared as well, and then there was the diamond-shaped opening iris, as in Poor Little Peppina and Alsace (1916), rather than the usual circle. Again, all of these variant forms were very infrequently used, and when they did occur in American films it was usually in the introductory stages. By 1918 the edges of ordinary circular irises were becoming very fuzzy when they were used in American films.
Enclosing the image inside static vignettes or masks of shapes other than circular also began to appear in films during the years 1914-1919, including symbolic shapes such as a cruciform cut-out in the Mary Pickford
film Stella Maris (Marshall Neilan, 1918), and Maurice Elvey in Britain put romantic scenes inside a heart-shaped mask in Nelson; The Story of England's Immortal Naval Hero (1918) and The Rocks of Valpré (1919). The most elegant variants occur in some films Ernst Lubitsch made in 1919. In Die Austernprinzessin (The Oyster Princess) a triple layer of horizontal rectangles with rounded ends enclose sets of dancing feet at the frenzied peak of a foxtrot, and in Die Puppe (The Doll) a dozen gossiping mouths are each enclosed in individual small circular vignettes arranged in a matrix.
A new idea taken over from still photography was “soft focus
”. This began in 1915, with some shots being intentionally thrown out of focus for expressive effect, as in Mary Pickford's Fanchon the Cricket. The idea developed slowly through the war years, until in D.W. Griffith's Broken Blossoms
(1918) all the Close Ups of Lillian Gish
are heavily diffused by the use of layers of fine black cotton mesh placed in front of the lens. Heavy lens diffusion was also used on all the other shots carrying forward the romantic and sentimental parts of the story of this film.
The use of anamorphic (in the general sense of distorted shape) images first appears in these years with Abel Gance's la Folie du Docteur Tube (The Madness of Dr. Tube). In this film the effect of a drug administered to a group of people was suggested by shooting the scenes reflected in a distorting mirror
of the fair-ground type. Later we have Till the Clouds Roll By (Victor Fleming, 1919), where anamorphosis
is used to depict the nightmare effects of indigestion in a comic manner. In fact, like so many film effects that distort the representation of reality, anamorphosis was first used exclusively in comic contexts.
Hypocrites, Vitagraph's Youth, someone else's Purity, and so on. The Primrose Path starts with a large painting illustrating the concept, which dissolves into a replica of the same scene with actors posed, and then they come to life, as these would soon become popular aspects of film making. This is then amplified by closer detailed live action representations of stations on “The Primrose Path”. An interesting German example from a few years later is Robert Reinert's Opium (1919), which has some notable innovations in the use of Insert shots to help convey the sensation of the drug reveries. These are travelling landscape shots taken from a boat going down a river, and they are intentionally shot out of focus, or underexposed, or cut into the film upside down.
Symbolist art and literature from the turn of the century also had a more general effect on a small number of films made in Italy and Russia. The supine acceptance of death resulting from passion and forbidden longings was a major feature of this art, and states of delirium dwelt on at length were important as well. The first Russian examples were all made by Yevgeni Bauer
for Khanzhonkov during the First World War, and include Grezy, Schastye vechnoi nochi, and Posle smerti, all from 1915. These to some extent live up to the promise of the `decadent' aesthetic suggested by their titles; Daydreams, Happiness of Eternal Night, and After Death. Schastye vechnoi nochi includes a visually very striking vision of a medusa-like monster superimposed on a night-time snow scene, and *Posle smerti*has a somewhat subtler dream vision of a dead girl, picked out by extra arc lighting, walking through a wind-blown cornfield in the dusk. In Italy, another country somewhat isolated filmically by the war, the same kind of realization of the fin-de-siecle
decadent symbolist aesthetic can be found, mostly in films associated with the “diva” phenomenon. The most complete example, which also has decor to match, is Charles Kraus' Il gatto nero (The Black Cat). This last is one of the few films of this kind to use atmospheric insert shots to heighten the mood. The first film explicitly intended by its maker to be a visual analogue of poetry, Marcel L'Herbier's
Rose-France (1919), continues further along these same paths.
 The use of Insert Shots, i.e. Close Ups of objects other than faces, was established very early, but apart from the special case of Inserts of a letter that was being read by one of the characters, they were infrequently used before 1914. It is really only with his *The Avenging Conscience*of 1914 that a new phase in the use of the Insert Shot starts. As well as the symbolic inserts already mentioned, The Avenging Conscience also made extensive use of large numbers of Big Close Up shots of clutching hands and tapping feet as a means of emphasizing those parts of the body as indicators of psychological tension. Griffith never went so far in this direction again, but his use of the Insert made its real impression on other American film-makers during the years 1914-1919. Cecil B. DeMille was a leading figure in the increased use of the Insert, and by 1918 he had reached the point of including about 9 Inserts in every 100 shots in The Whispering Chorus. He also pushed the insert into areas of visual sensuality inaccessible to D.W. Griffith, with such images as a Close Up of a silver-plated revolver nestling in a pile of silken sexy ribbons in a drawer in Old Wives for New (1918).
The use of Insert Shots, i.e. Close Ups of objects other than faces, was established very early, but apart from the special case of Inserts of a letter that was being read by one of the characters, they were infrequently used before 1914. It is really only with his *The Avenging Conscience*of 1914 that a new phase in the use of the Insert Shot starts. As well as the symbolic inserts already mentioned, The Avenging Conscience also made extensive use of large numbers of Big Close Up shots of clutching hands and tapping feet as a means of emphasizing those parts of the body as indicators of psychological tension. Griffith never went so far in this direction again, but his use of the Insert made its real impression on other American film-makers during the years 1914-1919. Cecil B. DeMille was a leading figure in the increased use of the Insert, and by 1918 he had reached the point of including about 9 Inserts in every 100 shots in The Whispering Chorus. He also pushed the insert into areas of visual sensuality inaccessible to D.W. Griffith, with such images as a Close Up of a silver-plated revolver nestling in a pile of silken sexy ribbons in a drawer in Old Wives for New (1918).
The Narrow Trail, in which a single shot of the mouth of San Francisco Bay
taken against the light (the Golden Gate
) is preceded by a narrative title explaining its symbolic function in the story. This film also contains a shot of wild hills and valleys cut in as one character comments that the country far from the city is so clean and pure. By 1918 we can find a shot of the sky being used to reflect the mood of one of the characters without specific explanation in The Gun Woman (Frank Borzage
), but it must be emphasized that these examples are very rare, and did not either then, or within the next several years, constitute regular practice in the American cinema. The Tourneur example just mentioned also could stand as part of the beginning of the “montage sequence”. Maurice Elvey's
Nelson - England's Immortal Naval Hero (1919) has a symbolic sequence dissolving from a picture of Kaiser Wilhelm II
to a peacock, and then to a battleship. The atmospheric Insert began its notable career in European art cinema in Marcel L'Herbier's
Rose-France. Here amongst the intentionally “poetic” uses of vignettes and filters and literary intertitles, a shot of the empty path once trod by the lovers is used to evoke the past.
or Medium Long Shot (which were the shots he most used) to a Big Close Up of an insert detail, which only occupied a small part of the frame in the previous shot. This in itself introduces a fairly strong visual discontinuity across the cut, but as well as that, the cut-in shot might often have a circular vignette mask if it were a Close Up of a person, so reinforcing the effect. And sometimes the now-standard Griffith iris-out and iris-in might also be left on the inserted shot, even though it had action continuity with the shots on either side of it. As well as all this there was Griffith's habit of moving the action into another shot in an adjoining space, and then back again if it was at all possible, which produced a marked change in background, which also made its small contribution to the discontinuity between shots.
One of the advanced continuity techniques involves the exact way the movement of actors from a shot in one location to another in a neighbouring location is handled. At best this kind of transition had previously been dealt with by having the directions of travel of the actor in the two shots correspond on the screen, but in a film such as The Bank Burglar's Fate (Jack Adolfi, 1914), one can see shot transitions in which a cut is made from an actor just leaving the frame, to a shot of him well inside the frame in an adjoining location, which have the positions and directions so well chosen that to the casual eye his movement appears quite continuous, and the real space and time ellipsis between the shots is concealed. Other good examples of this technique for eliminating several yards of waste space and a few seconds of waste time can be seen in Ralph Ince's films, particularly The Right Girl (1915), and by 1919 it was widely diffused in American films, but not in those made in Europe. All this connects with the rise of the use of cutting to different angles within a scene during the years 1914-1919, and in particular to the development of reverse-angle cutting.
in Bad Buck of Santa Ynez.
As for Griffith, in Birth of a Nation there are just eight cuts to reverse-angle shots in the scene in Ford's Theatre, while elsewhere throughout the two-and-a-half hour length of this film there are only four more true reverse-angle cuts. Nevertheless, the Griffith style of film-making was still followed in its full idiosyncrasy, with extensive use of side by side spaces and a definite “front” for the camera, in most slapstick comedy. Directors of dramatic films who had worked Griffith also followed his style fairly closely, and it the standard for films made by his Fine Arts section of the Triangle company.
By 1916 there are a number of films in which there are around 15 to 20 true reverse-angle cuts per hundred shot transitions, such as The Deserter (Scott Sidney) and Going Straight. By the end of the war such films formed an appreciable but minor part of production: e.g. The Gun Woman (F. Borzage, 1918) and Jubilo (Clarence Badger, 1919). All this hardly concerned European cinema, where those few reverse-angle cuts used were mostly between a watcher and what he sees from his Point of View, both being filmed in a fairly distant shot. However, after the end of the war some of the brighter young directors such as Lubitsch started using a few reverse-angle cuts, mostly in association with Point of View cutting.
structures continued to develop in this period, and the usual way of entering and leaving a flash-back was through a dissolve, and this was in fact the principal use at this time for this device. The Vitagraph company's The Man That Might Have Been (William Humphrey, 1914), is even more complex, with a series of reveries and flash-backs that contrast the protagonist's real passage through life with what might have been, if his son had not died. In this film dissolves are used both to enter and leave the flash-backs, and also the wish-dreams, and also for a time-lapse
inside a reverie at one point. But fades are also used for these purposes in this and other films of the period, and flashback transitions are also done with irising in other films, and even straight cuts.
During World War I the use of flashbacks occurred in films from all the major European film-making countries as well, from Italy (Tigre reale) to Denmark (Evangeliemandens Liv) to Russia (Grezy and Posle smerti), where it arrived in 1915.
As the years moved on a sudden decline in the use of long flash-back sequences set in around 1917, but on the other hand the use of a transition to and from a brief single shot memory scene remained quite common in American films. However, there could still be an even more complex flash-back construction in American films in the case of W.S. Van Dyke'sThe Lady of the Dugout (1918). This film has a story that happened long before which is narrated by one character in the framing scene, and initially accompanied by his narrating dialogue in intertitles, though after a while this stops, and the intertitles then convey the dialogue occurring within the flashback. Inside this main flashback there develops cross-cutting to another story, happening at the same time, and at first apparently unconnected with it, though the connection eventually appears. Next, inside this first flashback, the Lady of the title narrates another story, presented in flashback form, but with cutaways inside it back to events occurring in the time frame in which she is doing her narrating. Actually, all this is fairly easy to follow while watching the film, in part because what happens in all these strings of action is relatively simple.
Cross-cutting was also used to get new effects of contrast, such as the cross-cut sequence in Cecil B. DeMille's The Whispering Chorus, in which a supposedly dead husband is having a liaison with a Chinese prostitute in an opium den, while simultaneously his unknowing wife is being remarried in church.
All this was simple compared to D.W. Griffith's Intolerance (1916), in which four parallel stories are intercut throughout the whole length of the film, though in this case the stories are more similar than contrasting in their nature. The use of cross-cutting within these parallel stories as well as between them produced a complexity that was beyond the comprehension of the average audience of the time. The influence of Intolerance produced a few other films that combined a number of similar stories having similar themes, such as Maurice Tourneur's Woman (1918), but the box-office failure of Intolerance ensured that these later films had simpler structures.
, whose films, such as The Cheat (1915), brought out the moral dilemmas facing their characters in a more subtle way than Griffith. DeMille was also in closer touch with the reality of contemporary American life. Maurice Tourneur
was also highly ranked for the pictorial beauties of his films, together with the subtlety of his handling of fantasy, while at the same time he was capable of getting greater naturalism
from his actors at appropriate moments, as in A Girl's Folly (1917).
Sidney Drew
was the leader in developing “polite comedy”, while slapstick was refined by Fatty Arbuckle and Charles Chaplin, who both started with Mack Sennet's
Keystone company. They reduced the usual frenetic pace of Sennett's films to give the audience a chance to appreciate the subtlety and finesse of their movement, and the cleverness of their gags. By 1917 Chaplin was also introducing more dramatic plot into his films, and mixing the comedy with sentiment.
In Russia, Yevgeni Bauer
put a slow intensity of acting combined with Symbolist overtones onto film in a unique way.
In Sweden, Victor Sjöström
made a series of films that combined the realities of people's lives with their surroundings in a striking manner, while Mauritz Stiller developed sophisticated comedy to a new level.
In Germany, Ernst Lubitsch
got his inspiration from the stage work of Max Reinhardt, both in bourgeois comedy and in spectacle, and applied this to his films, culminating in his die Puppe (The Doll), die Austernprinzessin (The Oyster Princess) and Madame Dubarry.
and Italy
had been the most globally popular and powerful. But the United States
was already gaining quickly when World War I
(1914–1918) caused a devastating interruption in the European film industries. The American industry, or "Hollywood", as it was becoming known after its new geographical center in California
, gained the position it has held, more or less, ever since: film factory for the world, exporting its product to most countries on earth and controlling the market in many of them.
By the 1920s, the U.S. reached what is still its era of greatest-ever output, producing an average of 800 feature films annually, or 82% of the global total (Eyman, 1997). The comedies of Charlie Chaplin
and Buster Keaton
, the swashbuckling
adventures of Douglas Fairbanks
and the romances of Clara Bow
, to cite just a few examples, made these performers’ faces well-known on every continent. The Western visual norm that would become classical continuity editing
was developed and exported - although its adoption was slower in some non-Western countries without strong realist
traditions in art and drama, such as Japan
.
This development was contemporary with the growth of the studio system
and its greatest publicity method, the star system
, which characterized American film for decades to come and provided models for other film industries. The studios’ efficient, top-down control over all stages of their product enabled a new and ever-growing level of lavish production and technical sophistication.
At the same time, the system's commercial regimentation and focus on glamorous escapism
discouraged daring and ambition beyond a certain degree, a prime example being the brief but still legendary directing career of the iconoclastic Erich von Stroheim
in the late teens and the ‘20s.
technology, both for recording and playback, was virtually constant throughout the silent era, but the twin problems of accurate synchronization and sufficient amplification had been difficult to overcome (Eyman, 1997). In 1926, Hollywood studio Warner Bros.
introduced the "Vitaphone
" system, producing short films of live entertainment acts and public figures and adding recorded sound
effects and orchestral scores to some of its major features. During late 1927, Warners released The Jazz Singer
, which was mostly silent but contained what is generally regarded as the first synchronized dialogue (and singing) in a feature film; but this process was actually accomplished first by Charles Taze Russell
in 1914 with the lengthy film The Photo-Drama of Creation
. This drama consisted of picture slides and moving pictures synchronized with phonograph records of talks and music. The early sound-on-disc
processes such as Vitaphone were soon superseded by sound-on-film
methods like Fox Movietone
, DeForest Phonofilm
, and RCA Photophone
. The trend convinced the largely reluctant industrialists that "talking pictures", or "talkies", were the future. A lot of attempts were done before the success of the Jazz Singer
, that can be seen in the List of film sound systems.
and Japan
, where silents co-existed successfully with sound well into the 1930s, indeed producing what would be some of the most revered classics in those countries, like Wu Yonggang
's The Goddess
(China, 1934) and Yasujiro Ozu
's Was Born, But... (Japan, 1932). But even in Japan, a figure such as the benshi, the live narrator who was a major part of Japanese silent cinema, found his acting career was ending.
Sound further tightened the grip of major studios in numerous countries: the vast expense of the transition overwhelmed smaller competitors, while the novelty of sound lured vastly larger audiences for those producers that remained. In the case of the U.S., some historians credit sound with saving the Hollywood studio system in the face of the Great Depression
(Parkinson, 1995). Thus began what is now often called "The Golden Age of Hollywood", which refers roughly to the period beginning with the introduction of sound until the late 1940s. The American cinema reached its peak of efficiently manufactured glamour and global appeal during this period. The top actors of the era are now thought of as the classic film stars, such as Clark Gable
, Katharine Hepburn
, Humphrey Bogart
, Greta Garbo
, and the greatest box office draw of the 1930s, child performer Shirley Temple
.
This awkward period was fairly short-lived. 1929 was a watershed year: William Wellman with Chinatown Nights and The Man I Love, Rouben Mamoulian
with Applause, Alfred Hitchcock
with Blackmail
(Britain's first sound feature), were among the directors to bring greater fluidity to talkies and experiment with the expressive use of sound (Eyman, 1997). In this,
they both benefited from, and pushed further, technical advances in microphones and cameras, and capabilities for editing and post-synchronizing sound (rather than recording all sound directly at the time of filming).
Sound films emphasized on black history and benefited different genres more so than silents did. Most obviously, the musical film
was born; the first classic-style Hollywood musical was The Broadway Melody (1929) and the form would find its first major creator in choreographer/director Busby Berkeley
(42nd Street
, 1933, Dames
, 1934). In France, avant-garde director René Clair
made surreal
use of song and dance in comedies like Under the Roofs of Paris (1930) and Le Million (1931). Universal Pictures
begin releasing gothic horror films like Dracula
and Frankenstein (both 1931). In 1933, RKO released Merian C. Cooper
's classic "giant monster" film King Kong. The trend thrived best in India
, where the influence of the country's traditional song-and-dance drama made the musical the basic form of most sound films (Cook, 1990); virtually unnoticed by the Western world for decades, this Indian popular cinema would nevertheless become the world's most prolific. (See also Bollywood
.)
At this time, American gangster films like Little Caesar
and Wellman's The Public Enemy
(both 1931) became popular. Dialogue now took precedence over "slapstick" in Hollywood comedies: the fast-paced, witty banter of The Front Page
(1931) or It Happened One Night
(1934), the sexual double entrendres of Mae West
(She Done Him Wrong
, 1933) or the often subversively anarchic nonsense talk of the Marx Brothers
(Duck Soup, 1933). Walt Disney
, who had previously been in the short cartoon business, stepped into feature films with the first English-speaking animated feature Snow White and the Seven Dwarfs
; released by RKO Pictures
in 1937. 1939, a major year for American cinema, brought such films as The Wizard of Oz
and Gone with The Wind
.
(1941), Went the Day Well?
(1942), The Way Ahead
(1944) and Noel Coward
and David Lean
's celebrated naval film In Which We Serve
in 1942, which won a special Academy Award
. These existed alongside more flamboyant films like Michael Powell
and Emeric Pressburger
's The Life and Death of Colonel Blimp
(1943), A Canterbury Tale
(1944) and A Matter of Life and Death (1946), as well as Laurence Olivier
's 1944 film
Henry V
, based on the Shakespearean history Henry V
. The success of Snow White and the Seven Dwarfs allowed Disney to make more animated features like Pinocchio
(1940), Fantasia
(1940), Dumbo
(1941) and Bambi
(1942).
The onset of US involvement in World War II
also brought a proliferation of films as both patriotism
and propaganda
. American propaganda films included Desperate Journey, Mrs. Miniver
, Forever and a Day and Objective Burma. Notable American films from the war years include the anti-Nazi Watch on the Rhine
(1943), scripted by Dashiell Hammett
; Shadow of a Doubt
(1943), Hitchcock's direction of a script by Thornton Wilder
; the George M. Cohan
biopic, Yankee Doodle Dandy
(1942), starring James Cagney
, and the immensely popular Casablanca
, with Humphrey Bogart
. Bogart would star in 36 films between 1934 and 1942 including John Huston
's The Maltese Falcon
(1941), one of the first films now considered a classic film noir
. In 1941, RKO Pictures
released Citizen Kane
made by Orson Welles
. It is often considered the greatest film of all time. It would set the stage for the modern motion picture, as it revolutionized film story telling.
The strictures of wartime also brought an interest in more fantastical subjects. These included Britain's Gainsborough
melodramas (including The Man in Grey
and The Wicked Lady
), and films like Here Comes Mr. Jordan
, Heaven Can Wait
, I Married a Witch and Blithe Spirit. Val Lewton
also produced a series of atmospheric and influential small-budget horror
films, some of the more famous examples being Cat People, Isle of the Dead
and The Body Snatcher
. The decade probably also saw the so-called "women's pictures", such as Now, Voyager
, Random Harvest and Mildred Pierce
at the peak of their popularity.
1946 saw RKO Radio releasing It's a Wonderful Life
directed by Frank Capra
. Soldiers returning from the war would provide the inspiration for films like The Best Years of Our Lives
, and many of those in the film industry had served in some capacity during the war. Samuel Fuller
's experiences in World War II would influence his largely autobiographical films of later decades such as The Big Red One
. The Actor's Studio was founded in October 1947 by Elia Kazan
, Robert Lewis, and Cheryl Crawford
, and the same year Oskar Fischinger
filmed Motion Painting No. 1
.
In 1943, Ossessione was screened in Italy, marking the beginning of Italian neorealism
. Major films of this type during the 1940s included Bicycle Thieves
, Rome, Open City
, and La Terra Trema
. In 1952 Umberto D was released, usually considered the last film of this type.
In the late 1940s, in Britain, Ealing Studios
embarked on their series of celebrated comedies, including Whisky Galore!
, Passport to Pimlico
, Kind Hearts and Coronets
and The Man in the White Suit
, and Carol Reed
directed his influential thrillers Odd Man Out
, The Fallen Idol and The Third Man
. David Lean
was also rapidly becoming a force in world cinema with Brief Encounter
and his Dickens
adaptations Great Expectations
and Oliver Twist
, and Michael Powell
and Emeric Pressburger
would experience the best of their creative partnership with films like Black Narcissus
and The Red Shoes.
 The House Un-American Activities Committee
The House Un-American Activities Committee
investigated Hollywood in the early 1950s. Protested by the Hollywood Ten
before the committee, the hearings resulted in the blacklist
ing of many actors, writers and directors, including Chayefsky, Charlie Chaplin
, and Dalton Trumbo
, and many of these fled to Europe, especially the United Kingdom.
The Cold War era
zeitgeist
translated into a type of near-paranoia
manifested in theme
s such as invading armies of evil aliens
, (Invasion of the Body Snatchers, The War of the Worlds
); and communist
fifth column
ists, (The Manchurian Candidate
).
During the immediate post-war years the cinematic industry was also threatened by television, and the increasing popularity of the medium meant that some film theatres would bankrupt and close. The demise of the "studio system" spurred the self-commentary
of films like Sunset Boulevard (1950) and The Bad and the Beautiful
(1952).
In 1950, the Lettrists avante-gardists caused riots at the Cannes Film Festival
, when Isidore Isou
's Treatise on Slime and Eternity was screened. After their criticism of Charlie Chaplin
and split with the movement, the Ultra-Lettrist
s continued to cause disruptions when they showed their new hypergraphical techniques.
The most notorious film is Guy Debord
's Howls for Sade of 1952.
Distressed by the increasing number of closed theatres, studios and companies would find new and innovative ways to bring audiences back. These included attempts to literally widen their appeal with new screen formats. Cinemascope
, which would remain a 20th Century Fox
distinction until 1967, was announced with 1953's The Robe
. VistaVision
, Cinerama
, and Todd-AO
boasted a "bigger is better" approach to marketing
films to a dwindling US audience. This resulted in the revival of epic films to take advantage of the new big screen formats. Some of the most successful examples of these Biblical
and historical
spectaculars include The Ten Commandments
(1956), The Vikings
(1958), Ben-Hur
(1959), Spartacus
(1960) and El Cid
(1961). Also during this period a number of other significant films were produced in Todd-AO
, developed by Mike Todd
shortly before his death, including Oklahoma!
(1955), Around the World in 80 Days (1956), South Pacific
(1958) and Cleopatra (1963) plus many more.
Gimmick
s also proliferated to lure in audiences. The fad for 3-D film
would last for only two years, 1952–1954, and helped sell House of Wax
and Creature from the Black Lagoon
. Producer William Castle
would tout films featuring "Emergo" "Percepto", the first of a series of gimmicks that would remain popular marketing tools for Castle and others throughout the 1960s.
In the U.S., a post-WW2 tendency toward questioning the establishment and societal norms and the early activism
of the Civil Rights Movement
was reflected in Hollywood films such as Blackboard Jungle
(1955), On the Waterfront
(1954), Paddy Chayefsky
's Marty
and Reginald Rose
's 12 Angry Men (1957). Disney continued making animated films, notably; Cinderella
(1950), Peter Pan
(1953), Lady and the Tramp
(1955), and Sleeping Beauty
(1959). He began, however, getting more involved in live action films, producing classics like 20,000 Leagues Under the Sea
(1954), and Old Yeller
(1957). Television began competing seriously with films projected in theatres, but surprisingly it promoted more filmgoing rather than curtailing it.
Limelight is probably a unique film in at least one interesting respect. Its two leads, Charlie Chaplin
and Claire Bloom
, were in the industry in no less than three different centuries. In the 19th Century, Chaplin made his theatrical debut at the age of eight, in 1897, in a clog dancing troupe, The Eight Lancaster Lads. In the 21st Century, Bloom is still enjoying a full and productive career, having appeared in dozens of films and television series produced up to and including 2010.
in the 1940s, the following decade, the 1950s, marked a 'Golden Age' for non-English world cinema
, especially for Asian cinema
. Many of the most critically acclaimed Asian films of all time were produced during this decade, including Yasujiro Ozu
's Tokyo Story
(1953), Satyajit Ray
's The Apu Trilogy (1955–1959) and The Music Room
(1958), Kenji Mizoguchi
's Ugetsu
(1954) and Sansho the Bailiff
(1954), Raj Kapoor
's Awaara
(1951), Mikio Naruse
's Floating Clouds
(1955), Guru Dutt
's Pyaasa
(1957) and Kaagaz Ke Phool
(1959), and the Akira Kurosawa
films Rashomon
(1950), Ikiru
(1952), Seven Samurai (1954) and Throne of Blood
(1957).
During Japanese cinema
's 'Golden Age' of the 1950s, successful films included Rashomon
(1950), Seven Samurai (1954) and The Hidden Fortress
(1958) by Akira Kurosawa
, as well as Yasujiro Ozu
's Tokyo Story
(1953) and Ishirō Honda
's Godzilla
(1954). These films have had a profound influence on world cinema. In particular, Kurosawa's Seven Samurai has been remade several times as Western films
, such as The Magnificent Seven
(1960) and Battle Beyond the Stars
(1980), and has also inspired several Bollywood
films, such as Sholay
(1975) and China Gate
(1998). Rashomon was also remade as The Outrage
(1964), and inspired films with "Rashomon effect
" storytelling methods, such as Andha Naal
(1954), The Usual Suspects
(1995) and Hero
(2002). The Hidden Fortress was also the inspiration behind George Lucas
' Star Wars
(1977). Other famous Japanese filmmakers from this period include Kenji Mizoguchi
, Mikio Naruse
, Hiroshi Inagaki
and Nagisa Oshima
. Japanese cinema later became one of the main inspirations behind the New Hollywood
movement of the 1960s to 1980s.
During Indian cinema
's 'Golden Age' of the 1950s, it was producing 200 films annually, while Indian independent films
gained greater recognition through international film festival
s. One of the most famous was The Apu Trilogy (1955–1959) from critically acclaimed Bengali film
director Satyajit Ray
, whose films had a profound influence on world cinema, with directors such as Akira Kurosawa, Martin Scorsese
, James Ivory
, Abbas Kiarostami
, Elia Kazan
, François Truffaut
, Steven Spielberg
, Carlos Saura
, Jean-Luc Godard
, Isao Takahata
, Gregory Nava
, Ira Sachs
, Wes Anderson
and Danny Boyle
being influenced by his cinematic style. According to Michael Sragow of The Atlantic Monthly, the "youthful coming-of-age
dramas
that have flooded art houses since the mid-fifties owe a tremendous debt to the Apu trilogy". Subrata Mitra
's cinematographic technique of bounce lighting also originates from The Apu Trilogy. Other famous Indian filmmakers from this period include Guru Dutt
, Ritwik Ghatak, Mrinal Sen
, Raj Kapoor
, Bimal Roy
, K. Asif
and Mehboob Khan.
The cinema of South Korea also experienced a 'Golden Age' in the 1950s, beginning with director Lee Kyu-hwan's tremendously successful remake of Chunhyang-jon (1955). That year also saw the release of Yangsan Province
by the renowned director, Kim Ki-young
, marking the beginning of his productive career. Both the quality and quantity of filmmaking had increased rapidly by the end of the 1950s. South Korean films, such as Lee Byeong-il's 1956 comedy Sijibganeun nal (The Wedding Day), had begun winning international awards. In contrast to the beginning of the 1950s, when only 5 films were made per year, 111 films were produced in South Korea in 1959.
The 1950s was also a 'Golden Age' for Philippine cinema
, with the emergence of more artistic and mature films, and significant improvement in cinematic techniques among filmmakers. The studio system produced frenetic activity in the local film industry as many films were made annually and several local talents started to earn recognition abroad. The premiere Philippine directors of the era included Gerardo de Leon
, Gregorio Fernandez
, Eddie Romero
, Lamberto Avellana, and Cirio Santiago.
in the UK and Cinecittà
in Rome
. "Hollywood" films were still largely aimed at family audiences, and it was often the more old-fashioned films that produced the studios' biggest successes. Productions like Mary Poppins
(1964), My Fair Lady
(1964) and The Sound of Music
(1965) were among the biggest money-makers of the decade. The growth in independent producers and production companies, and the increase in the power of individual actors also contributed to the decline of traditional Hollywood studio production.
There was also an increasing awareness of foreign language cinema during this period. During the late 1950s and 1960s the French New Wave
directors such as François Truffaut
and Jean-Luc Godard
produced films such as Les quatre cents coups
, Breathless and Jules et Jim which broke the rules of Hollywood cinema's narrative structure
. As well, audiences were becoming aware of Italian
films like Federico Fellini
's La dolce vita
and the stark dramas of Sweden
's Ingmar Bergman
.
In Britain, the "Free Cinema" of Lindsay Anderson
, Tony Richardson
and others lead to a group of realistic and innovative dramas including Saturday Night and Sunday Morning
, A Kind of Loving
and This Sporting Life
. Other British films such as Repulsion
, Darling
, Alfie, Blowup
and Georgy Girl
(all in 1965-1966) helped to reduce prohibitions sex and nudity on screen, while the casual sex and violence of the James Bond
films, beginning with Dr. No
in 1962 would render the series popular worldwide.
During the 1960s, Ousmane Sembène
produced several French- and Wolof-language
films and became the 'father' of African Cinema
. In Latin America
the dominance of the "Hollywood" model was challenged by many film makers. Fernando Solanas
and Octavio Gettino called for a politically engaged Third Cinema
in contrast to Hollywood and the European auteur cinema.
Further, the nuclear paranoia of the age, and the threat of an apocalyptic nuclear exchange (like the 1962 close-call with the USSR during the Cuban missile crisis
) prompted a reaction within the film community as well. Films like Stanley Kubrick
's Dr. Strangelove and Fail Safe
with Henry Fonda
were produced in a Hollywood that was once known for its overt patriotism and wartime propaganda.
In documentary film
the sixties saw the blossoming of Direct Cinema
, an observational style of film making as well as the advent of more overtly partisan films like In the Year of the Pig
about the Vietnam War
by Emile de Antonio
. By the late 1960s however, Hollywood filmmakers were beginning to create more innovative and groundbreaking films that reflected the social revolution taken over much of the western world such as Bonnie and Clyde
(1967), The Graduate
(1967), 2001: A Space Odyssey
(1968), Rosemary's Baby
(1968), Midnight Cowboy
(1969), Easy Rider
(1969) and The Wild Bunch
(1969). Bonnie and Clyde
is often considered the beginning of the so-called New Hollywood
.
In Japanese cinema, Academy Award winning director Akira Kurosawa
produced Yojimbo (1961), which like his previous films also had a profound influence around the world. The influence of this film is most apparent in Sergio Leone
's A Fistful of Dollars
(1964) and Walter Hill's Last Man Standing
(1996). Yojimbo was also the origin of the "Man with No Name
" trend.
Meanwhile in India
, the Academy Award winning Bengali
director Satyajit Ray
wrote a script for The Alien
in 1967, based on a Bangla science fiction
story he himself had written in 1962. The film was intended to be his debut in Hollywood but the production was eventually cancelled. Nevertheless, the script went on to influence later films such as Steven Spielberg
's E.T.
(1982) and Rakesh Roshan
's Koi... Mil Gaya
(2003).
' and 'post-classical cinema' are terms used to describe the period following the decline of the studio system
during the 1950s and 1960s and the end of the production code
, (which was replaced in 1968 by the MPAA film rating system
). During the 1970s, filmmakers increasingly depicted explicit sexual content and showed gunfight and battle scenes that included graphic images of bloody deaths.
'Post-classical cinema' is a term used to describe the changing methods of storytelling of the "New Hollywood" producers. The new methods of drama
and characterization played upon audience expectations acquired during the classical/Golden Age period: story chronology may be scrambled, storylines may feature unsettling "twist endings", main characters may behave in a morally ambiguous fashion, and the lines between the antagonist
and protagonist
may be blurred. The beginnings of post-classical storytelling may be seen in 1940s and 1950s film noir
films, in films such as Rebel Without a Cause
(1955), and in Hitchcock's Psycho
. 1971 marked the release of controversial films like Straw Dogs, A Clockwork Orange
, The French Connection
and Dirty Harry
. This sparked heated controversy over the perceived escalation of violence in cinema.
During the 1970s, a new group of American filmmakers emerged, such as Martin Scorsese
, Francis Ford Coppola
, Roman Polanski
, Steven Spielberg
, George Lucas
and Brian De Palma
. This coincided with the increasing popularity of the auteur theory
in film literature and the media, which posited that a film director's films express their personal vision and creative insights. The development of the auteur style of filmmaking helped to give these directors far greater control over their projects than would have been possible in earlier eras. This led to some great critical and commercial successes, like Scorsese's Taxi Driver
, Coppola's The Godfather
films, Polanski's Chinatown, Spielberg's Jaws
and Close Encounters of the Third Kind
and George Lucas
's Star Wars
. It also, however, resulted in some failures, including Peter Bogdanovich
's At Long Last Love
and Michael Cimino
's hugely expensive Western epic Heaven's Gate
, which helped to bring about the demise of its backer, United Artists
.
The financial disaster of Heaven's Gate marking the end of the visionary "auteur" directors of the "New Hollywood", who had unrestrained creative and financial freedom to develop films. The phenomenal success in the 1970s of Jaws and Star Wars in particular, led to the rise of the modern "blockbuster
". Hollywood studios increasingly focused on producing a smaller number of very large budget films with massive marketing and promotional campaigns. This trend had already been foreshadowed by the commercial success of disaster film
s such as The Poseidon Adventure and The Towering Inferno
.
During the mid-1970s, more pornographic theatres, euphemistically called "adult cinemas", were established, and the legal production of hardcore pornographic
films began. Porn films such as Deep Throat
and its star Linda Lovelace
became something of a popular culture phenomenon and resulted in a spate of similar sex films. The porn cinemas finally died out during the 1980s, when the popularization of the home VCR and pornography videotapes allowed audiences to watch sex films at home. In the early 1970s, English-language audiences became more aware of the new West German cinema, with Werner Herzog
, Rainer Werner Fassbinder
and Wim Wenders
among its leading exponents.
In world cinema
, the 1970s saw a dramatic increase in the popularity of martial arts film
s, largely due to its reinvention by Bruce Lee
, who departed from the artistic style of traditional Chinese martial arts
films and added a much greater sense of realism to them with his Jeet Kune Do
style. This began with The Big Boss
(1971), which was a major success across Asia
. However, he didn't gain fame in the Western world
until shortly after his death in 1973, when Enter the Dragon
was released. The film went on to become the most successful martial arts film in cinematic history, popularized the martial arts film genre across the world, and cemented Bruce Lee's status as a cultural icon. Hong Kong action cinema
, however, was in decline due to a wave of "Bruceploitation
" films. This trend eventually came to an end in 1978 with the martial arts comedy film
s, Snake in the Eagle's Shadow
and Drunken Master
, directed by Yuen Woo-ping
and starring Jackie Chan
, laying the foundations for the rise of Hong Kong action cinema in the 1980s.
While the musical film
genre had declined in Hollywood by this time, musical films were quickly gaining popularity in the cinema of India
, where the term "Bollywood
" was coined for the growing Hindi
film industry in Bombay
(now Mumbai) that ended up dominating South Asian cinema
, overtaking the more critically acclaimed Bengali film industry
in popularity. Hindi filmmakers combined the Hollywood musical formula with the conventions of ancient Indian theatre to create a new film genre called "Masala
", which dominated Indian cinema throughout the late 20th century. These "Masala" films portrayed action
, comedy, drama
, romance
and melodrama
all at once, with "filmi
" song and dance routines thrown in. This trend began with films directed by Manmohan Desai
and starring Amitabh Bachchan
, who remains one of the most popular film stars in South Asia
. The most popular Indian film of all time was Sholay
(1975), a "Masala" film inspired by a real-life dacoit
as well as Kurosawa's Seven Samurai and the Spaghetti Western
s.
The end of the decade saw the first major international marketing of Australian cinema, as Peter Weir
's films Picnic at Hanging Rock
and The Last Wave
and Fred Schepisi's The Chant of Jimmie Blacksmith
gained critical acclaim. In 1979, Australian filmmaker George Miller
also garnered international attention for his violent, low-budget action film Mad Max
.
, which proved unsuccessful. Eventually, the sale and rental of films on home video
became a significant "second venue" for exhibition of films, and an additional source of revenue for the film industries.
The Lucas
-Spielberg
combine would dominate "Hollywood" cinema for much of the 1980s, and lead to much imitation. Two follow-ups to Star Wars
, three to Jaws
, and three Indiana Jones
films helped to make sequels of successful films more of an expectation than ever before. Lucas also launched THX Ltd
, a division of Lucasfilm
in 1982, while Spielberg enjoyed one of the decade's greatest successes in E.T. the Extra-Terrestrial
the same year. 1982 also saw the release of Disney's Tron
which was one of the first films from a major studio to use computer graphics
extensively. American independent cinema struggled more during the decade, although Martin Scorsese
's Raging Bull (1980), After Hours
(1985), and The King of Comedy
(1983) helped to establish him as one of the most critically acclaimed American film makers of the era. Also during 1983 Scarface
was released, was very profitable and resulted in even greater fame for its leading actor Al Pacino
. Probably the most successful film commercially was vended during 1989: Tim Burton
's version of Bob Kane
's creation, Batman
, exceeded box-office records. Jack Nicholson
's portrayal of the demented Joker
earned him a total of $60,000,000 after figuring in his percentage of the gross.
British cinema was given a boost during the early 1980s by the arrival of David Puttnam
's company Goldcrest Films
. The films Chariots of Fire
, Gandhi
, The Killing Fields
and A Room with a View
appealed to a "middlebrow" audience which was increasingly being ignored by the major Hollywood studios. While the films of the 1970s had helped to define modern blockbuster
motion pictures, the way "Hollywood" released its films would now change. Films, for the most part, would premiere in a wider number of theatres, although, to this day, some films still premiere using the route of the limited/roadshow release system
. Against some expectations, the rise of the multiplex cinema did not allow less mainstream films to be shown, but simply allowed the major blockbusters to be given an even greater number of screenings. However, films that had been overlooked in cinemas were increasingly being given a second chance on home video.
During the 1980s, Japanese cinema experienced a revival, largely due to the success of anime
films. At the beginning of the 1980s, Space Battleship Yamato
(1973) and Mobile Suit Gundam
(1979), both of which were unsuccessful as television series, were remade as films and became hugely successful in Japan. In particular, Mobile Suit Gundam sparked the Gundam
franchise of Real Robot
mecha
anime. The success of Macross: Do You Remember Love?
also sparked a Macross
franchise of mecha anime. This was also the decade when Studio Ghibli
was founded. The studio produced Hayao Miyazaki
's first fantasy film
s, Nausicaä of the Valley of the Wind (1984) and Castle in the Sky
(1986), as well as Isao Takahata
's Grave of the Fireflies
(1988), all of which were very successful in Japan and received worldwide critical acclaim. Original video animation
(OVA) films also began during this decade; the most influential of these early OVA films was Noboru Ishiguro
's cyberpunk
film Megazone 23
(1985). The most famous anime film of this decade was Katsuhiro Otomo
's cyberpunk film Akira
(1988), which although initially unsuccessful at Japanese theaters, went on to become an international success.
Hong Kong action cinema
, which was in a state of decline due to endless Bruceploitation
films after the death of Bruce Lee
, also experienced a revival in the 1980s, largely due to the reinvention of the action film
genre by Jackie Chan
. He had previously combined the comedy film
and martial arts film
genres successfully in the 1978 films Snake in the Eagle's Shadow
and Drunken Master
. The next step he took was in combining this comedy martial arts genre with a new emphasis on elaborate and highly dangerous stunt
s, reminiscent of the silent film
era. The first film in this new style of action cinema was Project A
(1983), which saw the formation of the Jackie Chan Stunt Team
as well as the "Three Brothers" (Chan, Sammo Hung
and Yuen Biao
). The film added elaborate, dangerous stunts to the fights and slapstick
humor, and became a huge success throughout the Far East
. As a result, Chan continued this trend with martial arts action films containing even more elaborate and dangerous stunts, including Wheels on Meals
(1984), Police Story
(1985), Armour of God (1986), Project A Part II
(1987), Police Story 2
(1988), and Dragons Forever
(1988). Other new trends which began in the 1980s were the "girls with guns
" sub-genre, for which Michelle Yeoh
gained fame; and especially the "heroic bloodshed
" genre, revolving around Triads, largely pioneered by John Woo
and for which Chow Yun-fat
became famous. These Hong Kong action trends were later adopted by many Hollywood action films in the 1990s and 2000s.
 The early 1990s saw the development of a commercially successful independent cinema in the United States. Although cinema was increasingly dominated by special-effects films such as Terminator 2: Judgment Day
The early 1990s saw the development of a commercially successful independent cinema in the United States. Although cinema was increasingly dominated by special-effects films such as Terminator 2: Judgment Day
(1991), Jurassic Park
(1993) and Titanic
(1997), independent films like Steven Soderbergh
's sex, lies, and videotape
(1989) and Quentin Tarantino
's Reservoir Dogs
(1992) had significant commercial success both at the cinema and on home video. Filmmakers associated with the Danish filmmovement Dogme 95
introduced a manifesto aimed to purify filmmaking. Its first few films gained worldwide critical acclaim, after which the movement slowly faded out.
Major American studios began to create their own "independent" production companies
to finance and produce non-mainstream fare. One of the most successful independents of the 1990s, Miramax Films
, was bought by Disney the year before the release of Tarantino's runaway hit Pulp Fiction
in 1994. The same year marked the beginning of film and video distribution online. Animated films aimed at family audiences also regained their popularity, with Disney's Beauty and the Beast
(1991), Aladdin (1992), and The Lion King
(1994). During 1995 the first feature length computer-animated
feature, Toy Story
, was produced by Pixar Animation Studios
and released by Disney. After the success of Toy Story, computer animation would grow to become the dominant technique for feature length animation, which would allow competing film companies such as Dreamworks Animation
and 20th Century Fox
to effectively compete with Disney with successful films of their own. During the late 1990s, another cinematic transition began, from physical film stock to digital cinema
technology. Meanwhile DVD
s became the new standard for consumer video, replacing VHS tapes.
 The documentary film
The documentary film
also rose as a commercial genre for perhaps the first time, with the success of films such as March of the Penguins
and Michael Moore
's Bowling for Columbine
and Fahrenheit 9/11
. A new genre was created with Martin Kunert
and Eric Manes
' Voices of Iraq
, when 150 inexpensive DV cameras were distributed across Iraq, transforming ordinary people into collaborative filmmakers. The success of Gladiator
lead to a revival of interest in epic cinema
, and Moulin Rouge!
renewed interest in musical cinema
. Home theatre
systems became increasingly sophisticated, as did some of the special edition DVD
s designed to be shown on them. The Lord of the Rings trilogy
was released on DVD in both the theatrical version and in a special extended version intended only for home cinema audiences.
There is a growing problem of digital distribution
to be overcome with regards to expiration of copyrights, content security, and enforcing copyright. There is higher compression for films, and Moore's law
allows for increasingly cheaper technology.
More films were also being released simultaneously to IMAX
cinema, the first was in 2002's Disney animation Treasure Planet
; and the first live action was in 2003's The Matrix Revolutions
and a re-release of The Matrix Reloaded
. Later in the decade, The Dark Knight
was the first major feature film to have been at least partially shot in IMAX technology.
There has been an increasing globalization of cinema during this decade, with foreign-language films gaining popularity in English-speaking markets. Examples of such films include Crouching Tiger, Hidden Dragon
(Mandarin), Amelie
(French), Lagaan
(Hindi), Spirited Away
(Japanese), City of God (Portuguese), The Passion of the Christ
(Aramaic), Apocalypto
(Mayan), Slumdog Millionaire
(a third in Hindi), and Inglourious Basterds (multiple languages).
Recently there has been a revival in 3D film popularity the first being James Cameron's Ghosts of the Abyss
which was released as the first full-length 3-D IMAX feature filmed with the Reality Camera System. This camera system used the latest HD video cameras, not film, and was built for Cameron by Emmy nominated Director of Photography Vince Pace, to his specifications. The same camera system was used to film Spy Kids 3D: Game Over (2003), Aliens of the Deep
IMAX (2005), and The Adventures of Sharkboy and Lavagirl in 3-D
(2005).
's How To Train Your Dragon
and Walt Disney Pictures
/Pixar
's Toy Story 3
.
As of 2010, the largest film industries by number of feature films produced are those of India, the United States and China.
.
" tradition of small-budget, often self-produced works created outside of the studio system and without the involvement of labor unions.
Film
A film, also called a movie or motion picture, is a series of still or moving images. It is produced by recording photographic images with cameras, or by creating images using animation techniques or visual effects...
is the historical development of the medium known variously as cinema, motion pictures, film, or the movies.
The history of film spans over 100 years, from the latter part of the 19th century to the present day. Motion pictures developed gradually from a carnival novelty to one of the most important tools of communication
Communication
Communication is the activity of conveying meaningful information. Communication requires a sender, a message, and an intended recipient, although the receiver need not be present or aware of the sender's intent to communicate at the time of communication; thus communication can occur across vast...
and entertainment
Entertainment
Entertainment consists of any activity which provides a diversion or permits people to amuse themselves in their leisure time. Entertainment is generally passive, such as watching opera or a movie. Active forms of amusement, such as sports, are more often considered to be recreation...
, and mass media
Mass media
Mass media refers collectively to all media technologies which are intended to reach a large audience via mass communication. Broadcast media transmit their information electronically and comprise of television, film and radio, movies, CDs, DVDs and some other gadgets like cameras or video consoles...
in the 20th century and into the 21st century. Motion picture films
Film
A film, also called a movie or motion picture, is a series of still or moving images. It is produced by recording photographic images with cameras, or by creating images using animation techniques or visual effects...
have substantially affected the arts
The arts
The arts are a vast subdivision of culture, composed of many creative endeavors and disciplines. It is a broader term than "art", which as a description of a field usually means only the visual arts. The arts encompass visual arts, literary arts and the performing arts – music, theatre, dance and...
, technology
Technology
Technology is the making, usage, and knowledge of tools, machines, techniques, crafts, systems or methods of organization in order to solve a problem or perform a specific function. It can also refer to the collection of such tools, machinery, and procedures. The word technology comes ;...
, and politics
Politics
Politics is a process by which groups of people make collective decisions. The term is generally applied to the art or science of running governmental or state affairs, including behavior within civil governments, but also applies to institutions, fields, and special interest groups such as the...
.
Precursors of film
PlaysPlay (theatre)
A play is a form of literature written by a playwright, usually consisting of scripted dialogue between characters, intended for theatrical performance rather than just reading. There are rare dramatists, notably George Bernard Shaw, who have had little preference whether their plays were performed...
and dances had elements common to films- scripts, sets
Set construction
Set construction is the process by which a set designer works in collaboration with the director of a production to create the set for a theatrical, film or television production...
, lighting
Lighting
Lighting or illumination is the deliberate application of light to achieve some practical or aesthetic effect. Lighting includes the use of both artificial light sources such as lamps and light fixtures, as well as natural illumination by capturing daylight...
, costumes, production, direction
Film director
A film director is a person who directs the actors and film crew in filmmaking. They control a film's artistic and dramatic nathan roach, while guiding the technical crew and actors.-Responsibilities:...
, actors, audiences
Audiences
Audiences is an indie rock band based in Chicago, Illinois. They have self-released two live albums. Live at The Otterarium was self recorded and produced in their practice space. Live at Lincoln Hall was recorded live at Lincoln Hall Chicago and engineered by Flashpoint Academy graduate sound...
, storyboards, and scores. They preceded film by thousands of years. Much terminology later used in film theory and criticism applied, such as mise en scène
Mise en scène
Mise-en-scène is an expression used to describe the design aspects of a theatre or film production, which essentially means "visual theme" or "telling a story"—both in visually artful ways through storyboarding, cinematography and stage design, and in poetically artful ways through direction...
. Moving visual images
Film
A film, also called a movie or motion picture, is a series of still or moving images. It is produced by recording photographic images with cameras, or by creating images using animation techniques or visual effects...
and sound
Sound
Sound is a mechanical wave that is an oscillation of pressure transmitted through a solid, liquid, or gas, composed of frequencies within the range of hearing and of a level sufficiently strong to be heard, or the sensation stimulated in organs of hearing by such vibrations.-Propagation of...
s were not recorded for replaying as in film.
People tend to have used very old camera obscura (which meanes darken chamber). The camera obscura was further described by Alhazen in his Book of Optics
Book of Optics
The Book of Optics ; ; Latin: De Aspectibus or Opticae Thesaurus: Alhazeni Arabis; Italian: Deli Aspecti) is a seven-volume treatise on optics and other fields of study composed by the medieval Muslim scholar Alhazen .-See also:* Science in medieval Islam...
(1021), and was later perfected near the year 1600 by Giambattista della Porta
Giambattista della Porta
Giambattista della Porta , also known as Giovanni Battista Della Porta and John Baptist Porta, was an Italian scholar, polymath and playwright who lived in Naples at the time of the Scientific Revolution and Reformation....
. Light
Light
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that is visible to the human eye, and is responsible for the sense of sight. Visible light has wavelength in a range from about 380 nanometres to about 740 nm, with a frequency range of about 405 THz to 790 THz...
is inverted through a small hole or lens
Lens (optics)
A lens is an optical device with perfect or approximate axial symmetry which transmits and refracts light, converging or diverging the beam. A simple lens consists of a single optical element...
from outside, and projected onto a surface or screen
Projection screen
A projection screen is an installation consisting of a surface and a support structure used for displaying a projected image for the view of an audience. Projection screens may be permanently installed, as in a movie theater; painted on the wall; or semi-permanent or mobile, as in a conference room...
, creating a projected moving image, indistinguishable from a projected high quality film to an audience, but it is not preserved in a recording.
In 1739 and 1748, David Hume
David Hume
David Hume was a Scottish philosopher, historian, economist, and essayist, known especially for his philosophical empiricism and skepticism. He was one of the most important figures in the history of Western philosophy and the Scottish Enlightenment...
published Treatise of Human Nature and An Enquiry concerning Human Understanding
An Enquiry Concerning Human Understanding
An Enquiry Concerning Human Understanding is a book by the Scottish empiricist philosopher David Hume, published in 1748. It was a revision of an earlier effort, Hume's A Treatise of Human Nature, published anonymously in London in 1739–40...
, arguing for the associations and causes of ideas with visual images, in some sense forerunners to the language of film.
Moving images were produced on revolving drums and disks in the 1830s with independent invention by Simon von Stampfer
Simon von Stampfer
Simon Ritter von Stampfer was an Austrian mathematician, surveyor and inventor. His most famous invention is that of the stroboscopic disk which has a claim to be the first device to show moving images...
(Stroboscope) in Austria, Joseph Plateau (Phenakistoscope) in Belgium and William Horner (zoetrope) in Britain.
On June 19, 1878, under the sponsorship of Leland Stanford
Leland Stanford
Amasa Leland Stanford was an American tycoon, industrialist, robber baron, politician and founder of Stanford University.-Early years:...
, Eadweard Muybridge
Eadweard Muybridge
Eadweard J. Muybridge was an English photographer who spent much of his life in the United States. He is known for his pioneering work on animal locomotion which used multiple cameras to capture motion, and his zoopraxiscope, a device for projecting motion pictures that pre-dated the flexible...
successfully photographed a horse named "Sallie Gardner
Sallie Gardner at a Gallop
Sallie Gardner at a Gallop was an early production experiment on June 19, 1878 that led to the development of motion pictures. The motion picture consists of 24 photographs in a fast-motion series that were shown on a zoopraxiscope. The photographs were taken by Eadweard Muybridge, who was...
" in fast motion using a series of 24 stereoscopic cameras. The experiment took place on June 11 at the Palo Alto farm in California with the press present. The exercise was meant to determine whether a running horse ever had all four legs lifted off the ground at once. The cameras were arranged along a track parallel to the horse's, and each camera shutter was controlled by a trip wire which was triggered by the horse's hooves. They were 21 inches apart to cover the 20 feet taken by the horse stride, taking pictures at one thousandth of a second.
Étienne-Jules Marey
Étienne-Jules Marey
Étienne-Jules Marey was a French scientist and chronophotographer.His work was significant in the development of cardiology, physical instrumentation, aviation, cinematography and the science of labor photography...
invented a chronophotographic gun in 1882, which was capable of taking 12 consecutive frames a second, recording all the frames on the same picture. He used the chronophotographic gun for studying animals and human locomotion.
The second experimental film, Roundhay Garden Scene
Roundhay Garden Scene
Roundhay Garden Scene is an 1888 short film directed by inventor Louis Le Prince. It was recorded at 12 frames per second, runs for 2.11 seconds and is the oldest surviving film.-Overview:...
, filmed by Louis Le Prince
Louis Le Prince
Louis Aimé Augustin Le Prince was an inventor who is considered by many film historians as the true father of motion pictures, who shot the first moving pictures on paper film using a single lens camera....
on October 14, 1888 in Roundhay
Roundhay
Roundhay is a large suburb and City Council ward of north-east Leeds, West Yorkshire, England, largely within the LS8 postcode. The ward boundary is the A6120 ring road on the north and the A58 Wetherby Road on the south and east. The boundary follows Gledhow Valley Road to the west before heading...
, Leeds
Leeds
Leeds is a city and metropolitan borough in West Yorkshire, England. In 2001 Leeds' main urban subdivision had a population of 443,247, while the entire city has a population of 798,800 , making it the 30th-most populous city in the European Union.Leeds is the cultural, financial and commercial...
, West Yorkshire
West Yorkshire
West Yorkshire is a metropolitan county within the Yorkshire and the Humber region of England with a population of 2.2 million. West Yorkshire came into existence as a metropolitan county in 1974 after the passage of the Local Government Act 1972....
, England
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
, UK is now known as the earliest surviving motion picture.
On June 21, 1889, William Friese-Greene
William Friese-Greene
William Friese-Greene was a British portrait photographer and prolific inventor. He is principally known as a pioneer in the field of motion pictures and is credited by some as the inventor of cinematography.-Career:William Edward Green was born on 7 September 1855, in Bristol...
was issued patent
Patent
A patent is a form of intellectual property. It consists of a set of exclusive rights granted by a sovereign state to an inventor or their assignee for a limited period of time in exchange for the public disclosure of an invention....
no. 10131 for his 'chronophotographic' camera. It was apparently capable of taking up to ten photographs per second using perforated celluloid film. A report on the camera was published in the British Photographic News on February 28, 1890. On 18 March, Friese-Greene sent a clipping of the story to Thomas Edison
Thomas Edison
Thomas Alva Edison was an American inventor and businessman. He developed many devices that greatly influenced life around the world, including the phonograph, the motion picture camera, and a long-lasting, practical electric light bulb. In addition, he created the world’s first industrial...
, whose laboratory had been developing a motion picture system known as the Kinetoscope
Kinetoscope
The Kinetoscope is an early motion picture exhibition device. Though not a movie projector—it was designed for films to be viewed individually through the window of a cabinet housing its components—the Kinetoscope introduced the basic approach that would become the standard for all cinematic...
. The report was reprinted in Scientific American
Scientific American
Scientific American is a popular science magazine. It is notable for its long history of presenting science monthly to an educated but not necessarily scientific public, through its careful attention to the clarity of its text as well as the quality of its specially commissioned color graphics...
on April 19. Friese-Greene gave a public demonstration in 1890 but the low frame rate
Frame rate
Frame rate is the frequency at which an imaging device produces unique consecutive images called frames. The term applies equally well to computer graphics, video cameras, film cameras, and motion capture systems...
combined with the device's apparent unreliability failed to make an impression.
As a result of the work of Etienne-Jules Marey and Eadweard Muybridge
Eadweard Muybridge
Eadweard J. Muybridge was an English photographer who spent much of his life in the United States. He is known for his pioneering work on animal locomotion which used multiple cameras to capture motion, and his zoopraxiscope, a device for projecting motion pictures that pre-dated the flexible...
, many researchers in the late 19th century realized that films as they are known today were a practical possibility, but the first to design a fully successful apparatus was W. K. L. Dickson, working under the direction of Thomas Alva Edison. His fully developed camera, called the Kinetograph, was patented in 1891 and took a series of instantaneous photographs on standard Eastman Kodak photographic emulsion coated on to a transparent celluloid strip
Celluloid
Celluloid is the name of a class of compounds created from nitrocellulose and camphor, plus dyes and other agents. Generally regarded to be the first thermoplastic, it was first created as Parkesine in 1862 and as Xylonite in 1869, before being registered as Celluloid in 1870. Celluloid is...
35 mm wide. The results of this work were first shown in public in 1893, using the viewing apparatus also designed by Dickson, and called the Kinetoscope
Kinetoscope
The Kinetoscope is an early motion picture exhibition device. Though not a movie projector—it was designed for films to be viewed individually through the window of a cabinet housing its components—the Kinetoscope introduced the basic approach that would become the standard for all cinematic...
. This was contained within a large box, and only permitted the images to be viewed by one person at a time looking into it through a peephole, after starting the machine by inserting a coin. It was not a commercial success in this form, and left the way free for Charles Francis Jenkins
Charles Francis Jenkins
Charles Francis Jenkins was an American pioneer of early cinema and one of the inventors of television, though he used mechanical rather than electronic technologies...
and his projector, the Phantoscope
Phantascope
The Phantoscope was a film projection machine, a creation of Charles Francis Jenkins. Created in the early 1890s, he projected the first motion picture before an audience in his hometown of Richmond, Indiana on June 6, 1894. He later met Thomas Armat who provided financial backing for necessary...
, with the first showing before an audience in June 1894. The Louis and Auguste Lumière
Lumière
-Characters:*Lumière , one of the two main characters of the 2002 anime series Kiddy Grade*Lumiere, a character in the Disney version of Beauty and the Beast-Places:*Lumière, a restaurant in Vancouver, Canada...
perfected the Cinématographe
Cinematographe
A cinematograph is a film camera, which also serves as a film projector and developer. It was invented in the 1890s.Note that this was not the first 'moving picture' device. Louis Le Prince had built early devices in 1886. His 1888 film Roundhay Garden Scene still survives.There is much dispute as...
, an apparatus that took, printed, and projected film. They gave their first show of projected pictures to an audience in Paris in December 1895.
After this date, the Edison company developed its own form of projector, as did various other inventors. Some of these used different film widths and projection speeds, but after a few years the 35-mm wide Edison film, and the 16-frames-per-second projection speed of the Lumière Cinématographe became standard. The other important American competitor was the American Mutoscope & Biograph Company, which used a new camera designed by Dickson after he left the Edison company.
At the Chicago
Chicago
Chicago is the largest city in the US state of Illinois. With nearly 2.7 million residents, it is the most populous city in the Midwestern United States and the third most populous in the US, after New York City and Los Angeles...
1893 World's Columbian Exposition
World's Columbian Exposition
The World's Columbian Exposition was a World's Fair held in Chicago in 1893 to celebrate the 400th anniversary of Christopher Columbus's arrival in the New World in 1492. Chicago bested New York City; Washington, D.C.; and St...
, Muybridge gave a series of lectures on the Science of Animal Locomotion in the Zoopraxographical Hall, built specially for that purpose in the "Midway Plaisance" arm of the exposition. He used his zoopraxiscope
Zoopraxiscope
The zoopraxiscope is an early device for displaying motion pictures. Created by photographic pioneer Eadweard Muybridge in 1879, it may be considered the first movie projector. The zoopraxiscope projected images from rotating glass disks in rapid succession to give the impression of motion. The...
to show his moving pictures
Film
A film, also called a movie or motion picture, is a series of still or moving images. It is produced by recording photographic images with cameras, or by creating images using animation techniques or visual effects...
to a paying public, making the Hall the first commercial film theater.
William Kennedy Laurie Dickson, chief engineer with the Edison Laboratories, is credited with the invention of a practicable form of a celluloid strip containing a sequence of images, the basis of a method of photographing and projecting moving images. Celluloid blocks were thinly sliced, then removed with heated pressure plates. After this, they were coated with a photosensitive gelatin emulsion. In 1893 at the Chicago World's Fair
World's Columbian Exposition
The World's Columbian Exposition was a World's Fair held in Chicago in 1893 to celebrate the 400th anniversary of Christopher Columbus's arrival in the New World in 1492. Chicago bested New York City; Washington, D.C.; and St...
, Thomas Edison
Thomas Edison
Thomas Alva Edison was an American inventor and businessman. He developed many devices that greatly influenced life around the world, including the phonograph, the motion picture camera, and a long-lasting, practical electric light bulb. In addition, he created the world’s first industrial...
introduced to the public two pioneering inventions based on this innovation; the Kinetograph - the first practical moving picture camera - and the Kinetoscope
Kinetoscope
The Kinetoscope is an early motion picture exhibition device. Though not a movie projector—it was designed for films to be viewed individually through the window of a cabinet housing its components—the Kinetoscope introduced the basic approach that would become the standard for all cinematic...
. The latter was a cabinet in which a continuous loop of Dickson's celluloid film (powered by an electric motor
Electric motor
An electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.Most electric motors operate through the interaction of magnetic fields and current-carrying conductors to generate force...
) was back lit by an incandescent lamp
Incandescent light bulb
The incandescent light bulb, incandescent lamp or incandescent light globe makes light by heating a metal filament wire to a high temperature until it glows. The hot filament is protected from air by a glass bulb that is filled with inert gas or evacuated. In a halogen lamp, a chemical process...
and seen through a magnifying lens
Magnifying glass
A magnifying glass is a convex lens that is used to produce a magnified image of an object. The lens is usually mounted in a frame with a handle ....
. The spectator viewed the image through an eye piece. Kinetoscope parlours were supplied with fifty-foot film snippets photographed by Dickson, in Edison's "Black Maria"
Edison's Black Maria
The Black Maria was Thomas Edison's movie production studio in West Orange, New Jersey. It is widely referred to as America's First Movie Studio.- History :...
studio . These sequences recorded both mundane incidents, such as Fred Ott's Sneeze
Fred Ott's Sneeze
Fred Ott's Sneeze is an 1894 American, short, black-and-white, silent documentary film shot by William K.L. Dickson and starring Fred Ott. It was the first motion picture to be copyrighted in the United States.In the five-second film one of Thomas Edison's assistants, Fred Ott, takes a pinch of...
, and entertainment acts, such as acrobats, music hall
Music hall
Music Hall is a type of British theatrical entertainment which was popular between 1850 and 1960. The term can refer to:# A particular form of variety entertainment involving a mixture of popular song, comedy and speciality acts...
performers and boxing demonstrations.
Kinetoscope parlors soon spread successfully to Europe. Edison, however, never attempted to patent these instruments on the other side of the Atlantic, since they relied so greatly on previous experiments and innovations
Precursors of film
Film as an art form grew out of a long tradition of literature, storytelling, narrative drama, art, mythology, puppetry and shadow play. In addition, the technology of film emerged from developments and achievements much further back in human history....
from Britain and Europe. This enabled the development of imitations, such as the camera devised by British electrician and scientific instrument maker Robert W. Paul
Robert W. Paul
Robert W. Paul was a British electrician, scientific instrument maker and early pioneer of British film.-Early career:...
and his partner Birt Acres
Birt Acres
Birt Acres was a photographer and film pioneer.Born in Richmond, Virginia to English parents, he invented the first British 35 mm moving picture camera, the first daylight loading home movie camera and projector, Birtac, was the first travelling newsreel reporter in international film history and...
.
Charles Francis Jenkins
Charles Francis Jenkins
Charles Francis Jenkins was an American pioneer of early cinema and one of the inventors of television, though he used mechanical rather than electronic technologies...
, wanting to display moving pictures to large groups of people, invented the first patented film projector
Film projector
Film projection or Film projector may refer to:*Movie projector for projection of moving images from film*Slide projector for projection of still images from film...
. In 1894, his invention, called the Phantoscope, was the first to project a motion picture. At about the same time, in Lyon
Lyon
Lyon , is a city in east-central France in the Rhône-Alpes region, situated between Paris and Marseille. Lyon is located at from Paris, from Marseille, from Geneva, from Turin, and from Barcelona. The residents of the city are called Lyonnais....
, France, Auguste and Louis Lumière
Auguste and Louis Lumière
The Lumière brothers, Auguste Marie Louis Nicolas and Louis Jean , were among the earliest filmmakers in history...
invented the cinematograph, a portable camera, printer, and projector. In late 1895 in Paris, father Antoine Lumière began exhibitions of projected films before the paying public, beginning the general conversion of the medium to projection (Cook, 1990). They quickly became Europe's main producers with their actualités
Actuality film
The actuality film is a non-fiction film genre that like the documentary film uses footage of real events, places, and things, yet unlike the documentary is not structured into a larger argument, picture of the phenomenon or coherent whole. In practice, actuality films preceded the emergence of the...
like Workers Leaving the Lumière Factory
Workers Leaving the Lumiere Factory
Workers Leaving The Lumière Factory in Lyon Workers Leaving The Lumière Factory in Lyon Workers Leaving The Lumière Factory in Lyon (also known as La Sortie des usines Lumière à Lyon (original title), Employees Leaving the Lumière Factory and Exiting the Factory (US titles) is an 1895 French short...
and comic vignettes like The Sprinkler Sprinkled
L'Arroseur Arrosé
L'Arroseur arrosé is an 1895 French short black-and-white silent comedy film directed and produced by Louis Lumière and starring François Clerc and Benoît Duval...
(both 1895). Even Edison, initially dismissive of projection, joined the trend with the Vitascope
Vitascope
Vitascope was an early film projector first demonstrated in 1895 by Charles Francis Jenkins and Thomas Armat. They had made modifications to Jenkins patented "Phantoscope", which cast images via film & electric light onto a wall or screen...
, a modified Jenkins' Phantoscope, within less than six months. The first public motion-picture film presentation in Europe, though, belongs to Max
Max Skladanowsky
Max Skladanowsky was a German inventor and early filmmaker. Along with his brother Emil, he invented the Bioscop, an early movie projector the Skladanowsky brothers used to display the first moving picture show to a paying audience on November 1, 1895, some two months before the public debut of...
and Emil Skladanowsky of Berlin, who projected with their apparatus "Bioscop", a flickerfree duplex construction, November 1 through 31, 1895.
That same year in May, in the USA, Eugene Augustin Lauste
Eugene Augustin Lauste
Eugène Augustin Lauste was a French inventor instrumental in the technological development of the history of cinema....
devised his Eidoloscope
Eidoloscope
The Eidoloscope was an early motion picture system created by Woodville Latham and his two sons through their business, the Lambda Company, in New York City in 1894 and 1895.-History:...
for the Latham
Woodville Latham
Major Woodville Latham was an ordnance officer of the Confederacy during the American Civil War and professor of chemistry at West Virginia University. He was significant in the development of early film technology....
family. But the first public screening of film ever is due to Jean Aimé "Acme" Le Roy, a French photographer. On February 5, 1894, his 40th birthday, he presented his "Marvellous Cinematograph" to a group of around twenty show business men in New York City.
The films of the time were seen mostly via temporary storefront spaces and traveling exhibitors or as acts in vaudeville programs. A film could be under a minute long and would usually present a single scene, authentic or staged, of everyday life, a public event, a sporting event or slapstick
Slapstick
Slapstick is a type of comedy involving exaggerated violence and activities which may exceed the boundaries of common sense.- Origins :The phrase comes from the batacchio or bataccio — called the 'slap stick' in English — a club-like object composed of two wooden slats used in Commedia dell'arte...
. There was little to no cinematic technique: no editing and usually no camera movement, and flat, stagey compositions. But the novelty of realistically moving photographs was enough for a motion picture industry to mushroom before the end of the century, in countries around the world.
The silent era
In the silent era of film, marrying the image with synchronous sound was not possible for inventors and producers, since no practical method was devised until 1923. Thus, for the first thirty years of their history, films were silent, although accompanied by live musicians and sometimes sound effectSound effect
For the album by The Jam, see Sound Affects.Sound effects or audio effects are artificially created or enhanced sounds, or sound processes used to emphasize artistic or other content of films, television shows, live performance, animation, video games, music, or other media...
s and even commentary spoken by the showman or projectionist.
Illustrated songs
Illustrated songs
An illustrated song is a type of performance art and was a popular form of entertainment in the early 20th century in the United States.Live performers and music recordings were both used by different venues to accompany still images projected from glass slides...
were a notable exception to this trend that began in 1894 in vaudeville
Vaudeville
Vaudeville was a theatrical genre of variety entertainment in the United States and Canada from the early 1880s until the early 1930s. Each performance was made up of a series of separate, unrelated acts grouped together on a common bill...
houses and persisted as late as the late 1930s in film theaters. In this early precursor to the music video
Music video
A music video or song video is a short film integrating a song and imagery, produced for promotional or artistic purposes. Modern music videos are primarily made and used as a marketing device intended to promote the sale of music recordings...
, live performance or sound recordings were paired with hand-colored glass slides projected through stereopticon
Stereopticon
A stereopticon is a slide projector or "magic lantern", which has two lenses, usually one above the other.These devices date back to the mid 19th century, and were a popular form of entertainment and education before the advent of moving pictures...
s and similar devices. In this way, song narrative was illustrated through a series of slides whose changes were simultaneous with the narrative development. The main purpose of illustrated songs was to encourage sheet music
Sheet music
Sheet music is a hand-written or printed form of music notation that uses modern musical symbols; like its analogs—books, pamphlets, etc.—the medium of sheet music typically is paper , although the access to musical notation in recent years includes also presentation on computer screens...
sales, and they were highly successful with sales reaching into the millions for a single song. Later, with the birth of film, illustrated songs were used as filler material preceding films and during reel changes.
In most countries the need for spoken accompaniment quickly faded, with dialogue and narration presented in intertitle
Intertitle
In motion pictures, an intertitle is a piece of filmed, printed text edited into the midst of the photographed action, at various points, generally to convey character dialogue, or descriptive narrative material related to, but not necessarily covered by, the material photographed.Intertitles...
s, but in Japanese cinema it remained popular throughout the silent era.
Film history from 1895 to 1906
The first eleven years of motion pictures show the cinema moving from a novelty to an established large-scale entertainment industry. The films represent a movement from films consisting of one shot, completely made by one person with a few assistants, towards films several minutes long consisting of several shots, which were made by large companies in something like industrial conditions.Film business up to 1906
The first commercial exhibition of film took place on April 14, 1894 at the first Kinetoscope parlor ever built.However, it was clear that Edison originally intended to create a sound film
Sound film
A sound film is a motion picture with synchronized sound, or sound technologically coupled to image, as opposed to a silent film. The first known public exhibition of projected sound films took place in Paris in 1900, but decades would pass before sound motion pictures were made commercially...
system, which would not gain worldwide recognition until the release of "The Jazz Singer
The Jazz Singer (1927 film)
The Jazz Singer is a 1927 American musical film. The first feature-length motion picture with synchronized dialogue sequences, its release heralded the commercial ascendance of the "talkies" and the decline of the silent film era. Produced by Warner Bros. with its Vitaphone sound-on-disc system,...
" in 1927. In 1896 it became clear that more money was to be made by showing motion picture films with a projector to a large audience than exhibiting them in Edison's Kinetoscope
Kinetoscope
The Kinetoscope is an early motion picture exhibition device. Though not a movie projector—it was designed for films to be viewed individually through the window of a cabinet housing its components—the Kinetoscope introduced the basic approach that would become the standard for all cinematic...
peep-show
Peep show
A peep show or peepshow is an exhibition of pictures, objects or people viewed through a small hole or magnifying glass. Though historically a peep show was a form of entertainment provided by wandering showmen, nowadays it more commonly refers a presentation of a sex show or pornographic film...
machines. The Edison company took up a projector developed by Armat and Jenkins, the “Phantoscope”, which was renamed the Vitascope, and it joined various projecting machines made by other people to show the 480 mm. width films being made by the Edison company and others in France and the UK.
However, the most successful motion picture company in the United States, with the largest production until 1900, was the American Mutoscope
American Mutoscope and Biograph Company
The American Mutoscope and Biograph Company, was a motion picture company founded in 1895 and active until 1928. It was the first company in the United States devoted entirely to film production and exhibition, and for two decades was one of the most prolific, releasing over three thousand short...
company. This was initially set up to exploit peep-show type films using designs made by W.K.L. Dickson after he left the Edison company in 1895. His equipment used 70 mm. wide film, and each frame was printed separately onto paper sheets for insertion into their viewing machine, called the Mutoscope
Mutoscope
frame|right|An 1899 trade advertisementThe Mutoscope was an early motion picture device, patented by Herman Casler on November 21, 1894. Like Thomas Edison's Kinetoscope it did not project on a screen, and provided viewing to only one person at a time...
. The image sheets stood out from the periphery of a rotating drum, and flipped into view in succession. Besides the Mutoscope, they also made a projector called the Biograph, which could project a continuous positive film print made from the same negatives.
There were numerous other smaller producers in the United States, and some of them established a long-term presence in the new century. American Vitagraph
Vitagraph Studios
American Vitagraph was a United States movie studio, founded by J. Stuart Blackton and Albert E. Smith in 1897 in Brooklyn, New York. By 1907 it was the most prolific American film production company, producing many famous silent films. It was bought by Warner Bros...
, one of these minor producers, built studios in Brooklyn, and expanded its operations in 1905. From 1896 there was continuous litigation in the United States over the patents covering the basic mechanisms that made motion pictures possible.
In France, the Lumière
Auguste and Louis Lumière
The Lumière brothers, Auguste Marie Louis Nicolas and Louis Jean , were among the earliest filmmakers in history...
company sent cameramen all round the world from 1896 onwards to shoot films, which were exhibited locally by the cameramen, and then sent back to the company factory in Lyon to make prints for sale to whoever wanted them. There were nearly a thousand of these films made up to 1901, nearly all of them actualities.
By 1898 Georges Méliès
Georges Méliès
Georges Méliès , full name Marie-Georges-Jean Méliès, was a French filmmaker famous for leading many technical and narrative developments in the earliest cinema. He was very innovative in the use of special effects...
was the largest producer of fiction films in France, and from this point onwards his output was almost entirely films featuring trick effects, which were very successful in all markets. The special popularity of his longer films, which were several minutes long from 1899 onwards (while most other films were still only a minute long), led other makers to start producing longer films.
From 1900 Charles Pathé
Charles Pathé
Charles Pathé was a major French pioneer of the film and recording industries.The son of a butcher shop owner, Charles Pathé was born at Chevry-Cossigny, in the Seine-et-Marne département of France. In 1894, together with his brother Émile, he formed Pathé Records...
began film production under the Pathé-Frères brand, with Ferdinand Zecca
Ferdinand Zecca
Ferdinand Zecca was an early French film director.Zecca was a cafe entertainer, playing the cornet, before switching to film in his mid-30s...
hired to actually make the films. By 1905, Pathé was the largest film company in the world, a position it retained until World War I. Léon Gaumont
Léon Gaumont
Léon Gaumont was a French inventor, engineer, and industrialist who was a pioneer of the motion picture industry....
began film production in 1896, with his production supervised by Alice Guy
Alice Guy-Blaché
Alice Guy-Blaché was a French pioneer filmmaker who was the first female director in the motion picture industry and is considered to be one of the first directors of a fiction film.-Early years:...
.
In the UK, Robert W. Paul
Robert W. Paul
Robert W. Paul was a British electrician, scientific instrument maker and early pioneer of British film.-Early career:...
, James Williamson and G.A. Smith
George Albert Smith (inventor)
George Albert Smith was a stage hypnotist, psychic, magic lantern lecturer, astronomer, inventor, and one of the pioneers of British cinema, who is best known for his controversial work with Edmund Gurney at the Society for Psychical Research, his short-films from 1897-1903 which pioneered film...
and the other lesser producers were joined by Cecil Hepworth
Cecil Hepworth
Cecil Milton Hepworth was an English film director, producer and screenwriter. He was among the founders of the British film industry and continued making films into the 1920s....
in 1899, and in a few years he was turning out 100 films a year, with his company becoming the largest on the British scene.
Film exhibition
Initially films were mostly shown as a novelty in special venues, but the main methods of exhibition quickly became either as an item on the programmes of variety theatres, or by traveling showman in tent theatres, which they took around the fairs in country towns. It became the practice for the producing companies to sell prints outright to the exhibitors, at so much per foot, regardless of the subject. Typical prices initially were 15 cents a foot in the United States, and one shilling a foot in Britain. Hand-colouredHand-colouring
Hand-colouring refers to any method of manually adding colour to a black-and-white photograph, generally either to heighten the realism of the photograph or for artistic purposes...
films, which were being produced of the most popular subjects before 1900, cost 2 to 3 times as much per foot. There were a few producers, such as the American Mutoscope and Biograph Company, which did not sell their films, but exploited them solely with their own exhibition units.
The first successful permanent theatre showing nothing but films was “The Nickelodeon”, which was opened in Pittsburgh in 1905. By this date there were finally enough films several minutes long available to fill a programme running for at least half an hour, and which could be changed weekly when the local audience became bored with it. Other exhibitors in the United States quickly followed suit, and within a couple of years there were thousands of these nickelodeons in operation. The American situation led to a worldwide boom in the production and exhibition of films from 1906 onwards.
Film technique

Phantom ride
Phantom rides were an early genre of film popular in Britain and the US at the end of the 19th century. Known more generally as "panoramas" at the time, phantom rides were one of the first types of motion picture ever publicly demonstrated. Pre-dating true narrative, the films simply show the...
s".
In 1897, Robert W. Paul had the first real rotating camera head made to put on a tripod, so that he could follow the passing processions of Queen Victoria's Diamond Jubilee
Diamond Jubilee
A Diamond Jubilee is a celebration held to mark a 60th anniversary in the case of a person or a 75th anniversary in the case of an event.- Thailand :...
in one uninterrupted shot. This device had the camera mounted on a vertical axis that could be rotated by a worm gear driven by turning a crank handle, and Paul put it on general sale the next year. Shots taken using such a "panning"
Panning (camera)
In photography, panning refers to the horizontal movement or rotation of a still or video camera, or the scanning of a subject horizontally on video or a display device...
head were also referred to as "panoramas" in the film catalogues of the first decade of the cinema.
The standard pattern for early film studios was provided by the studio which Georges Méliès had built in 1897. This had a glass roof and three glass walls constructed after the model of large studios for still photography, and it was fitted with thin cotton cloths that could be stretched below the roof to diffuse the direct ray of the sun on sunny days. The soft overall light without real shadows that this arrangement produced, and which also exists naturally on lightly overcast days, was to become the basis for film lighting in film studios for the next decade.
Filmic effects
Unique among all the one minute long films made by the Edison company, which recorded parts of the acts of variety performers for their Kinetoscope viewing machines, was The Execution of Mary, Queen of Scots. This showed a person dressed as the queen placing her head on the execution block in front of a small group of bystanders in Elizabethan dress. The executioner brings his axe down, and the queen's severed head drops onto the ground. This trick was worked by stopping the camera and replacing the actor with a dummy, then restarting the camera before the axe falls. The two pieces of film were then trimmed and cemented together so that the action appeared continuous when the film was shown.This film was among those exported to Europe with the first Kinetoscope machines in 1895, and was seen by Georges Méliès, who was putting on magic shows in his Theatre Robert-Houdin in Paris at the time. He took up filmmaking
Filmmaking
Filmmaking is the process of making a film, from an initial story, idea, or commission, through scriptwriting, casting, shooting, directing, editing, and screening the finished product before an audience that may result in a theatrical release or television program...
in 1896, and after making imitations of other films from Edison, Lumière, and Robert Paul
Robert W. Paul
Robert W. Paul was a British electrician, scientific instrument maker and early pioneer of British film.-Early career:...
, he made Escamotage d’un dame chez Robert-Houdin (The Vanishing Lady). This film shows a woman being made to vanish by using the same stop motion
Stop motion
Stop motion is an animation technique to make a physically manipulated object appear to move on its own. The object is moved in small increments between individually photographed frames, creating the illusion of movement when the series of frames is played as a continuous sequence...
technique as the earlier Edison film. After this, Georges Méliès made many single shot films using this trick over the next couple of years.
The other basic set of techniques for trick cinematography involves double exposure
Multiple exposure
In photography, a multiple exposure is the superimposition of two or more individual exposures to create a single photograph. The exposure values may or may not be identical to each other.-Overview:...
of the film in the camera, which was first done by G.A. Smith in July 1898 in the UK. His The Corsican Brothers was described in the catalogue of the Warwick Trading Company
Warwick Trading Company
The Warwick Trading Company was formed in 1898 out of the British branch of the American firm Maguire and Baucus. It was the leading film producer in Britain at the turn of the century, specialising in actuality, travel and reportage. The managing director was Charles Urban. He left the company in...
, which took up the distribution of Smith's films in 1900, thus:

“One of the twin brothers returns home from shooting in the Corsican mountains, and is visited by the ghost of the other twin. By extremely careful photography the ghost appears *quite transparent*. After indicating that he has been killed by a sword-thrust, and appealing for vengeance, he disappears. A ‘vision’ then appears showing the fatal duel in the snow. To the Corsican's amazement, the duel and death of his brother are vividly depicted in the vision, and finally, overcome by his feelings, he falls to the floor just as his mother enters the room.”
The ghost effect was simply done by draping the set in black velvet after the main action had been shot, and then re-exposing the negative with the actor playing the ghost going through the actions at the appropriate point. Likewise, the vision, which appeared within a circular vignette or matte
Matte (filmmaking)
Mattes are used in photography and special effects filmmaking to combine two or more image elements into a single, final image. Usually, mattes are used to combine a foreground image with a background image . In this case, the matte is the background painting...
, was similarly superimposed over a black area in the backdrop to the scene, rather than over a part of the set with detail in it, so that nothing appeared through the image, which seemed quite solid. Smith used this technique again a year later in Santa Claus.
Georges Méliès first used superimposition on a dark background in la Caverne maudite (The Cave of the Demons) made a couple of months later in 1898, and then elaborated it further with multiple superimpositions in the one shot in l’Homme de têtes (The Troublesome Heads). He then did it with further variations in numerous subsequent films.
Other special techniques
The other special effect technique that G.A. Smith initiated was reverse motion and the quality of self-motivating images. He did this by repeating the action a second time, while filming it with an inverted camera, and then joining the tail of the second negative to that of the first. The first films made using this device were Tipsy, Topsy, Turvy and The Awkward Sign Painter. The Awkward Sign Painter showed a sign painter lettering a sign, and in the reverse printing of the same footage appended to the standard print, the painting on the sign vanished under the painter's brush. The earliest surviving example of this technique is Smith's The House That Jack Built, made before September 1901. Here, a small boy is shown knocking down a castle just constructed by a little girl out of children's building blocks. Then a title appears, saying “Reversed”, and the action is repeated in reverse, so that the castle re-erects itself under his blows.Cecil Hepworth took this technique further, by printing the negative of the forwards motion backwards frame by frame, so producing a print in which the original action was exactly reversed. To do this he built a special printer in which the negative running through a projector was projected into the gate of a camera through a special lens giving a same-size image. This arrangement came to be called a “projection printer”, and eventually an “optical printer
Optical printer
An optical printer is a device consisting of one or more film projectors mechanically linked to a movie camera. It allows filmmakers to re-photograph one or more strips of film...
”. With it Hepworth made The Bathers in 1900, in which bathers who have undressed and jumped into the water appear to spring backwards out of it, and have their clothes magically fly back onto their bodies.
The use of different camera speeds also appeared around 1900. To make Robert Paul's On a Runaway Motor Car through Piccadilly Circus (1899), the camera was turned very slowly, so that when the film was projected at the usual 16 frames per second, the scenery appeared to be passing at great speed. Cecil Hepworth used the opposite effect in The Indian Chief and the Seidlitz Powder
Seidlitz powder
Seidlitz powder is the name with which is commonly known a medication composed by a mixture of tartaric acid, sodium bicarbonate, and potassium sodium tartrate, used as a mild cathartic by dissolving in water and drinking....
(1901), in which a naïve Red Indian
Indigenous peoples of the Americas
The indigenous peoples of the Americas are the pre-Columbian inhabitants of North and South America, their descendants and other ethnic groups who are identified with those peoples. Indigenous peoples are known in Canada as Aboriginal peoples, and in the United States as Native Americans...
eats a lot of the fizzy stomach medicine, causing his stomach to expand vastly. He leaps around in a way that is made balloon-like by cranking the camera much faster than 16 frames per second. This gives what we would call a “slow motion
Slow motion
Slow motion is an effect in film-making whereby time appears to be slowed down. It was invented by the Austrian priest August Musger....
” effect.
Animation
The most important development in this area of special techniques occurred, arguably, in 1899, with the production of the short film Matches: An Appeal, a thirty-second long stop-motion animated piece intended to encourage the audience to send matches to British troops fighting the Boer WarBoer War
The Boer Wars were two wars fought between the British Empire and the two independent Boer republics, the Oranje Vrijstaat and the Republiek van Transvaal ....
. The relative sophistication of this piece was not followed up for some time, with subsequent works in animation being limited to short, two or three frame effects, such as appeared in Edwin Porter's 1902 short "Fun in a Bakery Shop", where a lump of dough was made to smile over the course of a three-frame sequence. Works rivaling the British short in length did not appear until 1905, when Edwin Porter made How Jones Lost His Roll, and The Whole Dam Family and the Dam Dog. Both of these films had intertitles which were formed by the letters moving into place from a random scattering to form the words of the titles. This was done by exposing the film one frame at a time, and moving the letters a little bit towards their final position between each exposure. This is what has come to be called “single frame animation
Animation
Animation is the rapid display of a sequence of images of 2-D or 3-D artwork or model positions in order to create an illusion of movement. The effect is an optical illusion of motion due to the phenomenon of persistence of vision, and can be created and demonstrated in several ways...
” or “object animation”, and it needs a slightly adapted camera that exposes only one frame for each turn of the crank handle, rather than the usual eight frames per turn.
In 1906, Albert Edward Smith and James Stuart Blackton
J. Stuart Blackton
James Stuart Blackton , usually known as J. Stuart Blackton, was an Anglo-American film producer of the Silent Era, the founder of Vitagraph Studios and among the first filmmakers to use the techniques of stop-motion and drawn animation...
at Vitagraph took the next step, and in their Humorous Phases of Funny Faces, what appear to be cartoon drawings of people move from one pose to another. This is done for most of the length of this film by moving jointed cut-outs of the figures frame by frame between the exposures, just as Porter moved his letters. However, there is a very short section of the film where things are made to appear to move by altering the drawings themselves from frame to frame, which is how standard animated cartoons
Traditional animation
Traditional animation, is an animation technique where each frame is drawn by hand...
have since been made up to today.
Narrative film construction
The way forward to making films made up of more than one shot was led by films of the life of JesusJesus
Jesus of Nazareth , commonly referred to as Jesus Christ or simply as Jesus or Christ, is the central figure of Christianity...
Christ. The first of these was made in France in 1897, and it was followed in the same year by a film of the Passion play staged yearly in the Czech town of Horitz. This was filmed by Americans for exhibition outside the German-speaking world and was presented in special venues, not as a continuous film, but with the separate scenes interspersed with lantern slides, a lecture, and live choral numbers, to increase the running time of the spectacle to about 90 minutes.
Films of acted reproductions of scenes from the Greco-Turkish war
Greco-Turkish War (1897)
The Greco-Turkish War of 1897, also called the Thirty Days' War and known as the Black '97 in Greece, was a war fought between the Kingdom of Greece and Ottoman Empire. Its immediate cause was the question over the status of the Ottoman province of Crete, whose Greek majority long desired union...
were made by Georges Méliès in 1897, and although sold separately, these were no doubt shown in continuous sequence by exhibitors. In 1898 a few films of similar kind were made, but still none had continuous action moving from one shot into the next. The multi-shot films that Georges Méliès made in 1899 were much longer than those made by anybody else, but l’Affaire Dreyfus (The Dreyfus Case) and Cendrillon (Cinderella) still contained no action moving from one shot to the next one. Also, from Cendrillon onwards, Méliès made a dissolve
Dissolve (film)
In the post-production process of film editing and video editing, a dissolve is a gradual transition from one image to another. The terms fade-out and fade-in and are used to describe a transition to and from a blank image. This is in contrast to a cut where there is no such transition. A dissolve...
between every shot in his films, which reduced any appearance of action continuity even further. To understand what is going on in both these films, the audience had to know their stories beforehand, or be told them by a presenter.
Film continuity
Real film continuity, which means showing action moving from one shot into another joined to it, can be dated to Robert W. PaulRobert W. Paul
Robert W. Paul was a British electrician, scientific instrument maker and early pioneer of British film.-Early career:...
's Come Along, Do!
Come Along, Do!
Come Along, Do! is an 1898 British short silent comedy film, produced and directed by Robert W. Paul, featuring an elderly man at an art gallery taking a great interest in a nude statue to the irritation of his wife. The film which, "sadly only survives as a fragment today," was according to...
, made in 1898. In the first shot of this film, an old couple outside an art exhibition
Art exhibition
Art exhibitions are traditionally the space in which art objects meet an audience. The exhibit is universally understood to be for some temporary period unless, as is rarely true, it is stated to be a "permanent exhibition". In American English, they may be called "exhibit", "exposition" or...
follow other people inside through the door. The second shot showed what they do inside.

George Albert Smith (inventor)
George Albert Smith was a stage hypnotist, psychic, magic lantern lecturer, astronomer, inventor, and one of the pioneers of British cinema, who is best known for his controversial work with Edmund Gurney at the Society for Psychical Research, his short-films from 1897-1903 which pioneered film...
, working in Brighton
Brighton
Brighton is the major part of the city of Brighton and Hove in East Sussex, England on the south coast of Great Britain...
, made The Kiss in the Tunnel. This started with a shot from a “phantom ride” at the point at which the train goes into a tunnel, and continued with the action on a set representing the interior of a railway carriage, where a man steals a kiss from a woman, and then cuts back to the phantom ride shot when the train comes out of the tunnel. A month later, the Bamforth company in Yorkshire made a restaged version of this film under the same title, and in this case they filmed shots of a train entering and leaving a tunnel from beside the tracks, which they joined before and after their version of the kiss inside the train compartment.
In 1900, continuity of action across successive shots was definitively established by George Albert Smith and James Williamson, who also worked in Brighton. In that year Smith made Seen Through the Telescope, in which the main shot shows street scene with a young man tying the shoelace and then caressing the foot of his girlfriend, while an old man observes this through a telescope. There is then a cut to close shot of the hands on the girl's foot shown inside a black circular mask, and then a cut back to the continuation of the original scene.

James Williamson (film pioneer)
James Williamson was an early film developer and film director.-Biography:...
's Attack on a China Mission Station, made around the same time in 1900. The first shot shows the gate to the mission station from the outside being attacked and broken open by Chinese Boxer rebels, then there is a cut to the garden of the mission station where the missionary and his family are seated. The Boxers rush in and after exchanging fire with the missionary, kill him, and pursue his family into the house. His wife appears on the balcony waving for help, which immediately comes with an armed party of British sailors appearing through the gate to the mission station, this time seen from the inside. They fire at the Boxers, and advance out of the frame into the next shot, which is taken from the opposite direction looking towards the house. This constitutes the first “reverse angle” cut in film history. The scene continues with the sailors rescuing the remaining members of the missionary's family.
G.A. Smith further developed the ideas of breaking a scene shot in one place into a series of shots taken from different camera positions over the next couple of years, starting with The Little Doctors of 1901. In this film a little girl is administering pretend medicine to a kitten, and Smith cuts in to a big Close Up
Close-up
In filmmaking, television production, still photography and the comic strip medium a close-up tightly frames a person or an object. Close-ups are one of the standard shots used regularly with medium shots and long shots . Close-ups display the most detail, but they do not include the broader scene...
of the kitten as she does so, and then cuts back to the main shot. In this case the inserted close up is not shown as a Point of View shot in a circular mask. He summed up his work in Mary Jane's Mishap of 1903, with repeated cuts in to a close shot of a housemaid fooling around, along with superimpositions and other devices, before abandoning film-making to invent the Kinemacolor system of colour cinematography.
James Williamson concentrated on making films taking action from one place shown in one shot to the next shown in another shot in films like Stop Thief! and Fire!, made in 1901, and many others.
Film continuity developed
Other film-makers then took up all these ideas, which is the basis of film construction, or “film language”, or “film grammarFilm grammar
In film, film grammar is defined as follows:# A frame is a single still image. It is analogous to a letter.# A shot is a single continuous recording made by a camera. It is analogous to a word....
”, as we know it. The best known of these film-makers was Edwin S. Porter, who started making films for the Edison Company in 1901. When he began making longer films in 1902, he put a dissolve between every shot, just as Georges Méliès was already doing, and he frequently had the same action repeated across the dissolves. In other words, Edwin Porter did not develop the basics of film construction. The Pathé company in France also made imitations and variations of Smith and Williamson's films from 1902 onwards using cuts between the shots, which helped to standardize the basics of film construction.
In 1903 there was a substantial increase in the number of women film several minutes long, as a result of the great popularity of Georges Méliès’ le Voyage dans la lune (A Trip to the Moon), which came out in early 1902, though such films were still a very minor part of production. Most of them were what came to be called “chase films”. These were inspired by James Williamson
James Williamson
James Robert Williamson is an American guitarist, songwriter, record producer and electronics engineer who is best known for his contribution to the protopunk rock band Iggy & The Stooges.-Early years:...
's Stop Thief!
Stop Thief!
Stop Thief! is a 1901 British short silent drama film, directed by James Williamson, showing tramp getting his come-uppance after stealing some meat from a butcher and his dogs. "One of the first true 'chase' films made not just in Britain but anywhere else", according to Michael Brooke of BFI...
of 1901, which showed a tramp stealing a leg of mutton from a butcher's boy in the first shot, then being chased through the second shot by the butcher's boy and assorted dogs, and finally being caught by the dogs in the third shot.
Several British films made in the first half of 1903 extended the chase method of film construction. These included An Elopement à la Mode and The Pickpocket: A Chase Through London, made by Alf Collins for the British branch of the French Gaumont company
Gaumont Film Company
Gaumont Film Company is a French film production company founded in 1895 by the engineer-turned-inventor, Léon Gaumont . Gaumont is the oldest continously operating film company in the world....
, Daring Daylight Burglary, made by Frank Mottershaw
Frank Mottershaw
Frank Mottershaw was an early English cinema director based in Sheffield, Yorkshire. His films, A Daring Daylight Burglary and The Robbery of the Mail Coach , made in April and September 1903, are regarded as highly influential on the development of Edwin Porter’s paradigmatic...
at the Sheffield Photographic Company, and Desperate Poaching Affray
Desperate Poaching Affray
Desperate Poaching Affray is a 1903 British chase film by William Haggar. Three minutes long, the film is recognised as an early influence on narrative drama in American film, especially in chase genre. The film used a number of innovative techniques including on location shooting, panning shots...
, made by the Haggar
William Haggar
William Haggar was a British pioneer of the cinema industry. Beginning his career as a travelling entertainer, Haggar, whose large family formed his theatre company, later bought a Bioscope show and earned his money in the fairgrounds of south Wales...
family, whose main business was exhibiting films made by others in their traveling tent theatre. All of these films, and indeed others of like nature were shown in the United States, and some them were certainly seen by Edwin Porter, before he made The Great Train Robbery towards the end of the year. The time continuity in The Great Train Robbery is actually more confusing than that in the films it was modeled on, but nevertheless it was a greater success than them worldwide, because of its Wild West
American Old West
The American Old West, or the Wild West, comprises the history, geography, people, lore, and cultural expression of life in the Western United States, most often referring to the latter half of the 19th century, between the American Civil War and the end of the century...
violence.
From 1900, the Pathé company films also frequently copied and varied the ideas of the British film-makers, without making any major innovations in narrative film construction, but eventually the sheer volume of their production led to their film-makers giving a further precision and polish to the details of film continuity.
Film history from 1906 to 1914

The film business
In 1907 there were about 4,000 small “nickelodeon” cinemas in the United States. The films were shown with the accompaniment of music provided by a pianist, though there could be more musicians. There were also a very few larger cinemas in some of the biggest cities. Initially, the majority of films in the programmes were PathéPathé
Pathé or Pathé Frères is the name of various French businesses founded and originally run by the Pathé Brothers of France.-History:...
films, but this changed fairly quickly as the American companies cranked up production. The programme was made up of just a few films, and the show lasted around 30 minutes. The reel of film, of maximum length 1000 feet (304.8 m), which usually contained one individual film, became the standard unit of film production and exhibition in this period. The programme was changed twice or more a week, but went up to five changes of programme a week after a couple of years. In general, cinemas were set up in the established entertainment districts of the cities. In other countries of the Western world the film exhibition situation was similar. With the change to “nickelodeon” exhibition there was also a change, led by Pathé in 1907, from selling films outright to renting them through film exchanges.
The litigation over patents between all the major American film-making companies had continued, and at the end of 1908 they decided to pool their patents and form a trust to use them to control the American film business. The companies concerned were Pathé
Pathé
Pathé or Pathé Frères is the name of various French businesses founded and originally run by the Pathé Brothers of France.-History:...
, Edison
Edison Studios
Edison Studios was an American motion picture production company owned by the Edison Company of inventor Thomas Edison. The studio made close to 1,200 films as the Edison Manufacturing Company and Thomas A. Edison, Inc. until the studio's closing in 1918...
, Biograph, Vitagraph
Vitagraph Studios
American Vitagraph was a United States movie studio, founded by J. Stuart Blackton and Albert E. Smith in 1897 in Brooklyn, New York. By 1907 it was the most prolific American film production company, producing many famous silent films. It was bought by Warner Bros...
, Lubin
Lubin Studios
The Lubin Manufacturing Company, was an American motion picture production company that produced silent films from 1902 to 1916. Lubin films were distributed with a Liberty Bell trademark.-History:...
, Selig
Selig Polyscope Company
The Selig Polyscope Company was an American motion picture company founded in 1896 by William Selig in Chicago, Illinois. Selig Polyscope is noted for establishing Southern California's first permanent movie studio, in the historic Edendale district of Los Angeles...
, Essanay
Essanay Studios
The Essanay Film Manufacturing Company was an American motion picture studio. It is best known today for its series of Charlie Chaplin comedies of 1915.-Founding:...
, Kalem, and the Kleine Optical Company, a major importer of European films. The George Eastman
George Eastman
George Eastman was an American innovator and entrepreneur who founded the Eastman Kodak Company and invented roll film, helping to bring photography to the mainstream...
company, the only manufacturer of film stock in the United States, was also part of the combine, which was called the Motion Picture Patents Company
Motion Picture Patents Company
The Motion Picture Patents Company , founded in December 1908, was a trust of all the major American film companies , the leading film distributor and the biggest supplier of raw film stock, Eastman Kodak...
(MPPC), and Eastman Kodak
Eastman Kodak
Eastman Kodak Company is a multinational imaging and photographic equipment, materials and services company headquarted in Rochester, New York, United States. It was founded by George Eastman in 1892....
agreed to only supply the members with film stock. License fees for distributing and projecting films were extracted from all distributors and exhibitors. The producing companies that were part of the trust were allocated production quotas (two reels, i.e. films, a week for the biggest ones, one reel a week for the smaller), which were supposed to be enough to fill the programmes of the licensed exhibitors. Vitagraph and Edison already had multiple production units, and so had no difficulty meeting their quota, but in 1908 Biograph lost their one working director. They offered the job of making their films to D. W. Griffith
D. W. Griffith
David Llewelyn Wark Griffith was a premier pioneering American film director. He is best known as the director of the controversial and groundbreaking 1915 film The Birth of a Nation and the subsequent film Intolerance .Griffith's film The Birth of a Nation made pioneering use of advanced camera...
, an unimportant actor and playwright, who took up the job, and found he had a gift for it. Alone he made all the Biograph films from 1908 to 1910. This amounted to 30 minutes of screen time a week.
But the market was bigger than the Motion Picture Patents Company members could supply. Although 6,000 exhibitors signed with the MPPC, about 2,000 others did not. A minority of the exchanges (i.e. distributors) stayed outside the MPPC, and in 1909 these independent exchanges immediately began to fund new film producing companies. By 1911 there were enough independent and foreign films available to programme all the shows of the independent exhibitors, and in 1912 the independents had nearly half of the market. The MPPC had effectively been defeated in its plan to control the whole United States market, and the government anti-trust
Antitrust
The United States antitrust law is a body of laws that prohibits anti-competitive behavior and unfair business practices. Antitrust laws are intended to encourage competition in the marketplace. These competition laws make illegal certain practices deemed to hurt businesses or consumers or both,...
action, which only now started against the MPPC, was not really necessary to defeat it.
Multi-reel films
It was around 1910 that the actors in American films, who up to this point had been anonymous, began to receive screen credit, and the way to the creation of film stars was opened. The appearance of films longer than one reel also helped this process. Such films were extremely rare, and almost entirely restricted to film versions of the life of Christ, which had reached three reels in length in the first few years of cinema. They were always shown as a special event in special venues, and supported by live commentary and music. A unique addition to this style of presentation was The Story of the Kelly GangThe Story of the Kelly Gang
The Story of the Kelly Gang is a 1906 Australian film that traces the life of the legendary bushranger Ned Kelly . It was written and directed by Charles Tait. The film ran for more than an hour, and was the longest narrative film yet seen in Australia, and the world. Its approximate reel length...
, made in Australia in 1906. This was a four-reel version of the career of this famous (in Australia) outlaw, and was incomprehensible without explanation. More multi-reel films were made in Europe than in the United States after 1906, because the MPPC insisted on working on the basis of one-reel films up until 1912. However, before this, some MPPC members got around this restriction by occasionally making longer stories in separate parts, and releasing them in successive weeks, starting with Vitagraph's The Life of Moses in five parts (and five reels) at the end 1909. In other countries this film was shown straight through as one picture, and it inspired the creation of other multi-reel films in Europe.
Pathé-Frères set up a new subsidiary company
Subsidiary
A subsidiary company, subsidiary, or daughter company is a company that is completely or partly owned and wholly controlled by another company that owns more than half of the subsidiary's stock. The subsidiary can be a company, corporation, or limited liability company. In some cases it is a...
in the United States called Eclectic in 1913, and in 1914 this began production of features at the Pathé plant in New Jersey. The French Éclair company was already making films in the United States, and their production of features increased with the transfer of more film-makers when the French industry was shut down at the beginning of World War I.
Up to 1913, most American film production was still carried out around New York, but because of the monopoly of Thomas Edison
Thomas Edison
Thomas Alva Edison was an American inventor and businessman. He developed many devices that greatly influenced life around the world, including the phonograph, the motion picture camera, and a long-lasting, practical electric light bulb. In addition, he created the world’s first industrial...
's film patents, many filmmakers had moved to Southern California, hoping to escape the litany of lawsuits that the Edison Company had been bringing to protect its monopoly. Once there in Southern California, the film industry grew continuously.
The move to filming in California had begun when Selig, one of the MPPC companies, sent a production unit there in 1909. Other companies, both independents and members of the MPPC, then sent units to work there in the summer to take advantage of the sunshine and scenery. The latter was important for the production of Westerns, which now formed a major American film genre. The first cowboy star was G.M. Anderson (“Broncho Billy”)
Broncho Billy Anderson
Gilbert M. "Broncho Billy" Anderson was an American actor, writer, film director, and film producer, who is best known as the first star of the Western film genre.-Early life:...
, directing his own Western dramas for Essanay, but in 1911 Tom Mix
Tom Mix
Thomas Edwin "Tom" Mix was an American film actor and the star of many early Western movies. He made a reported 336 films between 1910 and 1935, all but nine of which were silent features...
brought the kind of costumes and stunt action used in live Wild West shows to Selig film productions, and became the biggest cowboy star for the next two decades.
Most of the major companies made films in all the genres, but some had a special interest in certain kinds of films. Once Selig had taken up production in California, they used the (fairly) wild animals from the zoo that Colonel Selig had set up there in a series of exotic adventures, with the actors being menaced or saved by the animals. Essanay specialized in Westerns featuring “Broncho Billy” Anderson, and Kalem sent Sidney Olcott
Sidney Olcott
Sidney Olcott was a Canadian-born film producer, director, actor and screenwriter.-Biography:Born John Sidney Alcott in Toronto, he became one of the first great directors of the motion picture business...
off with a film crew and a troupe of actors to various places in America and abroad to make film stories in the actual places they were supposed to have happened. Kalem also pioneered the female action heroine from 1912, with Ruth Roland
Ruth Roland
Ruth Roland was an American stage and film actress and film producer.-Early life and career:Born in San Francisco, California, her father managed a theatre and she became a child actress who went on to work in vaudeville...
playing starring roles in their Westerns.
Minor curiosities were some of the films of Solax
Solax Studios
Solax Studios was an American motion picture studio founded in 1910 by executives from the Gaumont Film Company of France. Alice Guy-Blaché, her husband Herbert, and a third partner, George A. Magie established The Solax Company. Alice Guy-Blaché was artistic director and the director for many of...
directed by Herbert Blaché and his wife Alice Guy. They left American branch of the Gaumont company in 1912 to set up their own independent company. The distinguishing feature of some of their films was a deliberate attempt to use resolutely theatrical-type light comedy playing that was directed towards the audience. This went against the trend towards filmic restraint already visible in what were called “polite” comedies from other film companies.
In France, Pathé retained its dominant position, followed still by Gaumont, and then other new companies that appeared to cater to the film boom. A film company with a different approach was Film d’Art. This was set up at the beginning of 1908 to make films of a serious artistic nature. Their declared programme was to make films using only the best dramatists, artists and actors. The first of these was L’Assassinat du Duc de Guise
The Assassination of the Duke of Guise
The Assassination of the Duke of Guise is a French historical film directed by Charles Le Bargy and André Calmettes, adapted by Henri Lavedan, and featuring actors of the Comédie Française and prominent set designers...
(The Assassination of the Duc de Guise), a historical subject set in the court of Henri III
Henry III of France
Henry III was King of France from 1574 to 1589. As Henry of Valois, he was the first elected monarch of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth with the dual titles of King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1573 to 1575.-Childhood:Henry was born at the Royal Château de Fontainebleau,...
. This film used leading actors from the Comédie Francaise
Comédie-Française
The Comédie-Française or Théâtre-Français is one of the few state theaters in France. It is the only state theater to have its own troupe of actors. It is located in the 1st arrondissement of Paris....
, and had a special accompanying score written by Camille Saint-Saens
Camille Saint-Saëns
Charles-Camille Saint-Saëns was a French Late-Romantic composer, organist, conductor, and pianist. He is known especially for The Carnival of the Animals, Danse macabre, Samson and Delilah, Piano Concerto No. 2, Cello Concerto No. 1, Havanaise, Introduction and Rondo Capriccioso, and his Symphony...
. The other French majors followed suit, and this wave gave rise to the English-language description of films with artistic pretensions aimed at a sophisticated audience as “art films”
Art film
An art film is the result of filmmaking which is typically a serious, independent film aimed at a niche market rather than a mass market audience...
. By 1910, the French film companies were starting to make films as long as two, or even three reels, though most were still one reel long. This trend was followed in Italy, Denmark, and Sweden.
Although the British industry continued to expand after its brilliant beginning, the new companies that replaced the first innovative film-makers proved unable to preserve their drive and originality.
New film producing countries
With the worldwide film boom, yet more countries now joined Britain, France, and the United States in serious film production. In Italy, production was spread over several centres, with Turin being the first and biggest. There, Ambrosio was the first company in the field in 1905, and remained the largest in the country through this period. Its most substantial rival was Cines in Rome, which started producing in 1906. The great strength of the Italian industry was historical epics, with large casts and massive scenery. As early as 1911, Giovanni Pastrone'sGiovanni Pastrone
Giovanni Pastrone, also known by his artistic name Piero Fosco , was an Italian film pioneer, director, screenwriter, actor and technician.Pastrone was born in Montechiaro d'Asti...
two-reel la Caduta di Troia (The Fall of Troy
Trojan War
In Greek mythology, the Trojan War was waged against the city of Troy by the Achaeans after Paris of Troy took Helen from her husband Menelaus, the king of Sparta. The war is among the most important events in Greek mythology and was narrated in many works of Greek literature, including the Iliad...
) made a big impression worldwide, and it was followed by even bigger spectacles like Quo Vadis? (1912), which ran for 90 minutes, and Pastrone's Cabiria of 1914, which ran for two and a half hours.

The most important film-producing country in Northern Europe up until the First World War was Denmark. The Nordisk
Nordisk Film
Nordisk Film , established in Denmark in 1906 by Danish filmmaker Ole Olsen, is the oldest continuously operating film studio in the world. Olsen started his company in the Copenhagen suburb of Valby under the name "Ole Olsen's Film Factory" but soon changed it to the Nordisk Film Kompagni...
company was set up there in 1906 by Ole Olsen, a fairground showman, and after a brief period imitating the successes of French and British film-makers, in 1907 he produced 67 films, most directed by Viggo Larsen, with sensational subjects like Den hvide Slavinde (The White Slave), Isbjørnenjagt (Polar Bear Hunt) and Løvejagten (The Lion Hunt). By 1910 new smaller Danish companies began joining the business, and besides making more films about the white slave trade, they contributed other new subjects. The most important of these finds was Asta Nielsen
Asta Nielsen
Asta Nielsen , was a Danish silent film actress who was one of the most popular leading ladies of the 1910s and one of the first international movie stars. Seventy of Nielsen's 74 films were made in Germany where she was known simply as Die Asta...
in Afgrunden (The Abyss), directed by Urban Gad
Urban Gad
Peter Urban Gad was a Danish film director. He directed 40 film between 1910 and 1927. His wife Asta Nielsen starred in 30 of his films. Also in his debut the famous movie Afgrunden from 1910. They moved to Germany in 1911 where Gad worked until 1922.His uncle was Paul Gauguin...
for Kosmorama, This combined the circus, sex, jealousy and murder, all put over with great conviction, and pushed the other Danish film-makers further in this direction. By 1912 the Danish film companies were multiplying rapidly.
The Swedish film industry
Cinema of Sweden
Swedish cinema is known as producing many critically acclaimed movies, and during the 20th century was the most prominent of Scandinavia. This is largely due to the popularity and prominence of the directors Ingmar Bergman, Victor Sjöström, and more recently Lasse Hallström and Lukas...
was smaller and slower to get started than the Danish industry. Here, the important man was Charles Magnusson, a newsreel cameraman for the Svenskabiografteatern cinema chain. He started fiction film production for them in 1909, directing a number of the films himself. Production increased in 1912, when the company engaged Victor Sjöström
Victor Sjöström
Victor Sjöström was a Swedish actor, screenwriter, and film director.- Biography:Born in Silbodal, in the Värmland region of Sweden, he was only a year old when his father, Olof Adolf Sjöström, moved the family to Brooklyn, New York. His mother died when he was seven years old in 1886...
and Mauritz Stiller
Mauritz Stiller
Mauritz Stiller was a Finnish-Swedish actor, screenwriter and silent film director, who was mostly active in Sweden.-Life:...
as directors. They started out by imitating the subjects favoured by the Danish film industry, but by 1913 they were producing their own strikingly original work, which sold very well.
Russia began its film industry in 1908 with Pathé shooting some fiction subjects there, and then the creation of real Russian film companies by Aleksandr Drankov and Aleksandr Khanzhonkov
Aleksandr Khanzhonkov
Aleksandr Aleksejevich Khanzhonkov was Russia's first cinema entrepreneur. He produced Defence of Sevastopol, Russia's first feature film, and Ladislas Starevich's ground-breaking puppet animations....
. The Khanzhonkov company quickly became much the largest Russian film company, and remained so until 1918.
In Germany, Oskar Messter
Oskar Messter
Oskar Messter was a German inventor and film tycoon in the early years of cinema.-Biography:He was born in Berlin, where his father had founded a company selling and manufacturing optical equipment in 1859...
had been involved in film-making from 1896, but did not make a significant number of films per year till 1910. When the worldwide film boom started, he, and the few other people in the German film business, continued to sell prints of their own films outright, which put them at a disadvantage. It was only when Paul Davidson, the owner of a chain of cinemas, brought Asta Nielsen and Urban Gad to Germany from Denmark in 1911, and set up a production company, Projektions-AG “Union” (PAGU), for them, that a change-over to renting prints began. Messter replied with a series of longer films starring Henny Porten, but although these did well in the German-speaking world, they were not particularly successful internationally, unlike the Asta Nielsen films. Another of the growing German film producers just before World War I was the German branch of the French Éclair company, Deutsche Éclair. This was expropriated by the German government, and turned into DECLA when the war started. But altogether, German producers only had a minor part of the German market in 1914.
Overall, from about 1910, American films had the largest share of the market in all European countries except France, and even in France, the American films had just pushed the local production out of first place on the eve of World War I. So even if the war had not happened, American films may have become dominant worldwide. Although the war made things much worse for European producers, the technical qualities of American films made them increasingly attractive to audiences everywhere.
Film technique

Arc lamp
"Arc lamp" or "arc light" is the general term for a class of lamps that produce light by an electric arc . The lamp consists of two electrodes, first made from carbon but typically made today of tungsten, which are separated by a gas...
made for street lighting. These were either hung on battens suspended forward of the actors from the roof, or mounted in groups on floorstands. The addition of a metal reflector round the arc source directed a very broad sweep of light in the desired direction. Large mercury vapour tube lights (Cooper-Hewitts) were also used in racks placed in the same way. Arc lights had been used to produce special lighting effects in films like the light from a lamp or firelight before 1906, but this now became more common.

Low-key lighting
Low-key lighting
Low-key lighting is a style of lighting for photography, film or television. It is a necessary element in creating a chiaroscuro effect. Traditional photographic lighting, three-point lighting uses a key light, a fill light, and a back light for illumination...
(i.e. lighting in which most of the frame is dark) slowly began to be used for sinister scenes, but not in D.W. Griffith films. Vitagraph's thriller, The Mystery of Temple Court (1910) has low-key lighting for a scene of murder, and their Conscience (1912) shows low-key lighting done solely with artificial light for a scene of terror.

Cabiria
Cabiria is a silent movie from the early years of Italy's movie industry, directed by Giovanni Pastrone . The movie is set in ancient Sicily, Carthage, and Cirta during the period of the Second Punic War . It follows a melodramatic main plot about an abducted little girl, Cabiria, and features...
(1914) to reinforce the weird atmosphere in one scene.
Silhouette effects in location scenes began to appear in 1909 in both the United States and Italy; though as things developed, European film-makers made more use of this than the Americans did.
The most important aspect of this was that such shots involved having the sun light the scene from behind, and this approach was extended by using the reflected sunlight from a white surface below the camera to light up the shadow on the actors faces from the front. This is the one novel technique that D.W. Griffith and his cameraman Billy Bitzer
Billy Bitzer
Gottfried Wilhelm "Billy" Bitzer was a pioneering cinematographer notable for his close association with D. W. Griffith....
may really have invented. The next step was to transfer this kind of back-lighting onto the lighting of actors on studio sets. Up to this point artificial lighting in studio scenes had always been put on from the front or side-front, but in 1912 there began to be a few cases where light was put onto the actors from arc floodlights out of shot behind them and to one side, to give a kind of backlighting. It was not until 1915 that the effect of backlighting of the actors by the sun was fully mimicked in studio lighting, by using a powerful arc spotlight shining from above and behind the set down onto the actors. This slowly became a standard component of the studio lighting of figures in American films, but it took much longer to catch on with European cameramen.
Animation develops
The technique of single frame animation was further developed in 1907 by Edwin S. Porter in The Teddy Bears and by J. Stuart Blackton with Work Made Easy. In the first of these the toy bears were made to move, apparently on their own, and in the latter film building tools were made to perform construction tasks without human intervention, by using frame-by-frame animation. The technique got to Europe almost immediately, and Segundo de Chomon and others at Pathé took it further, adding clay animationClay animation
Clay animation or claymation is one of many forms of stop motion animation. Each animated piece, either character or background, is "deformable"—made of a malleable substance, usually Plasticine clay....
, in which sculptures were deformed from one thing into another thing frame by frame in Sculpture moderne (1908), and then Pathé made the next step to the animation of silhouette shapes. Also in France, Emile Cohl
Émile Cohl
Émile Cohl , born Émile Eugène Jean Louis Courtet, was a French caricaturist of the largely forgotten Incoherent Movement, cartoonist, and animator, called "The Father of the Animated Cartoon" and "The Oldest Parisian".-Biography:Émile's father Elie was a rubber salesman, and his mother, Emilie...
fully developed drawn animation in a series of films starting with Fantasmagorie
Fantasmagorie (1908 film)
Fantasmagorie is an 1908 French animated film by Émile Cohl. It is one of the earliest examples of traditional animation, and considered by film historians to be the first animated cartoon.-Description:...
(1908), in which humans and objects drawn as outline figures went though a series of remarkable interactions and transformations. In the United States the response was from the famous strip cartoon artist
Cartoonist
A cartoonist is a person who specializes in drawing cartoons. This work is usually humorous, mainly created for entertainment, political commentary or advertising...
Winsor McCay
Winsor McCay
Winsor McCay was an American cartoonist and animator.A prolific artist, McCay's pioneering early animated films far outshone the work of his contemporaries, and set a standard followed by Walt Disney and others in later decades...
, who drew much more realistic animated figures going through smoother, more naturalistic motion in a series of films starting with the film Little Nemo, made for Vitagraph in 1911. In the next few years various others took part in this development of animated cartoon
Animated cartoon
An animated cartoon is a short, hand-drawn film for the cinema, television or computer screen, featuring some kind of story or plot...
s in the United States and elsewhere.
Cross-cutting between parallel actions
As the film boom got under way, the Pathéa film-makers continued to refine the continuity of action from shot to shot in their films. In films like Pathéa's le Cheval emballé (The Runaway Horse) (1907), there appeared a new feature, which can be called cross-cutting between parallel actions. In this film, a delivery man is going about his lady's house inside an apartment house while his horse steals a big meal from a bag of oats outside a feed store. The film cuts back and forwards between the two chains of action four times before the delivery man comes out, and the horse runs away with him. More importantly, early next year the Pathé production unit down in the south of France in Nice made le Médecin du chateau (The Physician of the Castle), in which there are cuts back and forth between criminals threatening a doctor's wife and child, while the doctor himself drives home to rescue them after being warned by telephone. This film also contains a cut in to a closer shot of the doctor as he hears the dreadful news on the telephone, which uses the new idea of getting in closer to the actor to accentuate the emotion.In the United States, Vitagraph was also trying cross-cutting for suspense in 1907 and 1908 with The Mill Girl and Get Me a Stepladder. Before D.W. Griffith started directing at Biograph in May 1908, he had seen the two Pathé films just mentioned, and a number of Vitagraph films as well. But Griffith's first use of cross-cutting in The Fatal Hour, made in July 1908, has a much stronger suspense story served by this construction than those in the earlier Pathé examples. From this point onwards Griffith certainly developed the device much further, gradually increasing the number of alternations between two, and later three, sets of parallel scenes, and also their speed. This intensified usage was only slowly taken up by other American film-makers. So although he did not invent the technique of cross-cutting, he did consciously develop it into a powerful method of film construction. It is also important to note that Griffith described cross-cutting indiscriminately as the ‘switch-back’ or ‘cut-back’ or ‘flash-back’ technique, and that by the last of these terms he did not mean what we now understand by a ‘flash-back’. The true ‘flash-back’ was also developed in this period, but not at all by D.W. Griffith.
Although D. W. Griffith did not invent any new film techniques, he was the best film director working up to 1913, and this was because he made better dramatic and artistic use of the medium than other directors. One aspect of this was the structure he gave his films, with the final scene mirroring the opening scene, as in the example of A Drunkard's Reformation
A Drunkard's Reformation
A Drunkard's Reformation is a 1909 drama film directed by D. W. Griffith. Prints of the film survive in the film archive of the Library of Congress.-Cast:* Arthur V. Johnson - John Wharton* Linda Arvidson - Mrs. John Wharton...
already mentioned above. Many other examples of this like The Country Doctor
The Country Doctor (film)
The Country Doctor is a 1909 drama film directed by D. W. Griffith. Prints of the film exist in the film archives of the Museum of Modern Art and the Library of Congress.-Cast:* Kate Bruce as Poor Mother...
(1908) can easily be found in his work. But the most important thing Griffith did was work out significant and expressive natural gestures in intensive rehearsal periods with his actors, before the film was shot, such as the enraged and jealous husband in The Voice of the Child
The Voice of the Child
The Voice of the Child is a 1911 drama film directed by D. W. Griffith and starring Blanche Sweet. The film was made by the American Mutoscope and Biograph Company when it and many other early film studios in America's first motion picture industry were based in Fort Lee, New Jersey at the...
(1911) walking around his office chomping on a cigar and puffing clouds of smoke out of it through clenched teeth.
Griffith's increased use of cross-cutting between parallel actions helped him to get more shots into his films than other directors, but he also had another method for doing this. This was to split a scene that could have been played in room (or other place), into two or more sections that moved backwards and forwards between adjoining rooms or spaces. The result of this was that D.W. Griffith's films had at least twice as many shots in them as did those of other American directors. Over this period, the other directors speeded up, but so did Griffith. At first, the technique of cutting in to a closer shot of an actor in a scene made no contribution to the increase in cutting rate, because it was still very rarely done, despite having been established as a possibility in the previous period. The exception to this was a close shot of an object, which was sometimes used to make clear exactly what a person was doing. It was only towards 1913 that film-makers began to cut into closer shots with any regularity.
However, American film-makers did get closer to the actors on the average by shooting the whole scene with the camera closer than previously. The Vitagraph company led the way here, by using what they called “the nine-foot line” from 1910 onwards. This meant that the actors played a scene up to a line marked on the ground nine feet from the camera lens, which meant that they were shown cut off at the waist in the image. Some, but not all, American film-makers followed their example, calling it the “American foreground”, while European film-makers stayed with the “French foreground” established by the Pathé about 1907, which only cut the actors off at the shins. This corresponded to the actors playing up to a line put down 4 metres in front of the camera lens.
Point of view shots
An even more important development was the use of the Point of View shotPoint of view shot
A point of view shot is a short film scene that shows what a character is looking at . It is usually established by being positioned between a shot of a character looking at something, and a shot showing the character's reaction...
. Previously, these had only been used to convey the idea of what someone in the film was seeing through a telescope (or other aperture), and this was indicated by having a black circular mask or vignette within the film frame. The true Point of View (POV) shot, in which a shot of someone looking at something is followed by a cut to a shot taken from their position without any mask, took longer to appear. In 1910, in Vitagraph's Back to Nature we see a Long Shot of people looking down over the rail of a ship taken from below, followed by a shot of the lifeboat they are looking at taken from their position.

Border Collie
The Border Collie is a herding dog breed developed in the Anglo-Scottish border region for herding livestock, especially sheep. It is the most widespread of the collie breeds....
, which has Point of View [POV] shots introduced at an appropriate point without explanation. After this, un-vignetted POV shots began to appear fairly frequently in Vitagraph films, and also occasionally in films from other American companies. However, D.W. Griffith only used them in a theatrical situation, to show what the audience in a theatre were looking at, as did European film-makers.
Reverse-angle cutting

The Assassination of the Duke of Guise
The Assassination of the Duke of Guise is a French historical film directed by Charles Le Bargy and André Calmettes, adapted by Henri Lavedan, and featuring actors of the Comédie Française and prominent set designers...
, there began to be other films in which a scene was shown from another direction by cutting to the opposite side. This effect was imitated occasionally in Europe and the United States over the next couple of years, and came to be called a “reverse scene”.
The next step, in which two actors facing each other are shown in successive close shots from taken opposite directions towards each of them, is first to be seen at the end of 1911 in The Loafer, made by Arthur Mackley for Essanay. This is what is called reverse-angle cutting, and it is used constantly in present day film-making. However, it took some years to catch on with other American film-makers, but by 1913, it was starting to occur with greater frequency in the work of a few directors. This happened entirely when they were filming exterior scenes, where there was no problem about shooting past the edge of the studio set. A leading example of this use of close in reverse-angle cutting is His Last Fight (1913), directed by Ralph Ince for Vitagraph, in which one-third of the cuts are between a shot and the reverse angle. However, this sort of thing never happened in D.W. Griffith's films, or in European films.
Symbolism and insert shots
In this period the word “Art” was mentioned more and more in connection with motion pictures, and as a result of the increasing artistic ambitions of film-makers, poems began to be transposed directly into films. D.W. Griffith went further than this, by creating the visual equivalent of the poetic or musical refrain in The Way of the World (1910), by cutting in shots of church bellChurch bell
A church bell is a bell which is rung in a church either to signify the hour or the time for worshippers to go to church, perhaps to attend a wedding, funeral, or other service...
s at intervals down the length of the film. However, this was an exceptional case, and it is not until 1912 that there were the first signs of the special expressive use of Insert Shots; that is, shots of objects rather than people. In the Italian Ambrosio companies film La mala planta (The Evil Plant), directed by Mario Caserini
Mario Caserini
Mario Caserini was an Italian film director, as well as an actor, screenwriter, and early pioneer of film making in the early portion of the 20th century. Caserini was born in Rome, Italy, and was married to early 20th century Italian actress Maria Caserini...
, which involves a case of poisoning, there is an Insert shot of a snake slithering over the ‘Evil Plant’. Another of the still very rare examples at this date is in Griffith's The Massacre, which was made at the end of 1912. This includes an Insert Shot of a candle at a sick man's bedside guttering out to indicate his death. Yet another is in the Ambrosio company version of Gli ultimi giorni di Pompei (The Last Days of Pompeii) (1913). This film includes a scene, preceded by the title “The thorns of jealousy”, in which a rejected woman overhears the man she loves with another woman, and this is followed by a fade to a shot of a pair of doves, which then dissolves into a shot of a bird of prey.
It was in 1914 that D.W. Griffith began to bend the use of the Insert towards truly dramatically expressive ends, but he had not done this often, and it is really only with his The Avenging Conscience
The Avenging Conscience
The Avenging Conscience: or "Thou Shalt Not Kill" is a drama film directed by D. W. Griffith.The film is based on the Edgar Allan Poe short stories "The Tell-Tale Heart" and "Annabel Lee".-Plot:...
of 1914 that a new phase in the use of the Insert Shot starts. In this film the intertitle “The birth of the evil thought” precedes a series of three shots of the protagonist looking at a spider, and ants eating an insect, though at a later point in the film, when he prepares to kill someone, these shots are cut straight in without explanation. As well as the symbolic inserts already mentioned, The Avenging Conscience also made extensive use of large numbers of Big Close Up shots of clutching hands and tapping feet as a means of emphasizing those parts of the body as indicators of psychological tension. Griffith never went so far in this direction again, but his use of the Insert shot made its real impression on other American film-makers during the years 1915-1919.
Film art

Motion pictures were classified into genres by the film industry following the divisions already established in other media, particularly the stage. The main division was into comedy and drama, but these categories were further subdivided. Comedy could be either slapstick (usually referred to as “burlesque farce”), or alternatively “polite comedy”, which later came to be referred to as “domestic comedy” or “sophisticated comedy”. D.W. Griffith made a small number of the latter type of film in his first two years at Biograph, but had little interest or aptitude for the genre. From 1910 he let Frank Powell
Frank Powell
Frank E. Powell was a stage and silent film actor, screenwriter, and director in the United States. He was born in Hamilton, Ontario, Canada.Powell made his Broadway theatre debut in 1904 and began his career in film in 1909 as an actor and scriptwriter at Biograph Studios. There, he also...
, and then Mack Sennett direct the Biograph comedies. Sennett left in 1912 to set up the Keystone company, where he could give his enthusiasm for the slapstick comedy style derived from the earlier Pathé comedies like le Cheval emballé (The Runaway Horse) full rein. In Europe the more restrained type of comedy was developed in substantial quantities in France, with the films of Max Linder
Max Linder
Max Linder was an influential French pioneer of silent film.-Birth and early career:Born Gabriel-Maximilien Leuvielle in Saint-Loubès, Gironde, France to a Catholic wine-growing family, he grew up with a passion for the theatre and as a young man joined a theatre troupe touring the country...
for Pathé representing the summit of the genre from 1910 onwards. Linder's comedy was set in an upper middle-class
Upper middle class
The upper middle class is a sociological concept referring to the social group constituted by higher-status members of the middle class. This is in contrast to the term "lower middle class", which is used for the group at the opposite end of the middle class stratum, and to the broader term "middle...
milieu, and relied on clever and inventive ways of getting around the embarrassments and obstacles arising in his single-minded pursuit of a goal. Quite often a goal of a sexual nature.
D.W. Griffith had a major influence on the simplification of film stories. After he had been at Biograph for a year, Griffith started to make some films that had much less story content than any previous one-reel films. In The Country Doctor, the action is no more than various people, including the doctor, hurrying backwards and forwards between the doctor's house, where his child is sick, and a neighbouring cottage, where another child is also sick. By 1912 and 1913, there are beginning to be many films from many American companies that rely on applying novel decoration to the story, rather than supplying any twists to the drama itself to sustain interest.
Intertitles
Intertitles containing lines of dialogue began to be used consistently from 1908 onwards. In that year, Vitagraph's An Auto Heroine; or, The Race for the Vitagraph Cup and How It Was Won, contains a couple of dialogue titles, and the same firm's Julius Caesar includes three lines of dialogue from Shakespeare's play quoted in intertitles before the actors speak them, finishing with “This was the noblest Roman of them all”.From 1909 a small number of American films, and even one or two European ones, came to include a few dialogue titles, or “spoken titles” as they were called at the time. Film-makers slowly progressed from putting these dialogue titles before the scene in which they were spoken, to cutting them into the middle of the shot at the point at which they were understood to be actually spoken by the characters. This transition began in 1912. Once underway, the trend was aided by the move towards the increasing use of cuts within scenes in American films. In 1913 a substantial proportion of the dialogue titles that were used in American films were cut in at the point when they were spoken. Hardly any of the films where this happened were D.W. Griffith films, and indeed many of his 1913 films still contain no dialogue titles at all. Although some European film-makers picked up the trend towards using dialogue titles, they did not pick up on the move towards cutting them into the scene at the point at which they were actually spoken until a few years later.
The introduction of dialogue titles was far from being a trivial matter, for they entirely transformed the nature of film narrative. When dialogue titles came to be always cut into a scene just after a character starts speaking, and then left with a cut to the character just before they finish speaking, then one had something that was effectively the equivalent of a present-day sound film.
The film business from 1914 to 1919
The years of the First World War were a complex transitional period for the film industry. It was the period when the exhibition of films changed from short programmes of one-reel films to longer shows consisting of a feature film of four reels or longer, though still supported by short films. The exhibition venues also changed from small nickelodeon cinemas to larger cinemas charging higher prices. These higher prices were partly justified by the new film stars who were now being created. In the United States, nearly all the original film companies which formed the Motion Picture Patents Company went out of business in this period because of their resistance to the changeover to long feature films. The one exception to this was the Vitagraph company, which was already moving over to long films by 1914. The move towards shooting more films on the West coast around Los Angeles continued during World War I, until the bulk of American production was carried out there.The Universal Film Manufacturing Company
Universal Studios
Universal Pictures , a subsidiary of NBCUniversal, is one of the six major movie studios....
had been formed in 1912 as an umbrella company for many of the independent producing companies, and continued to grow during the war. Other independent companies were grouped under the Mutual banner in 1912, and there were also important new entrants, particularly the Jesse Lasky
Jesse L. Lasky
Jesse Louis Lasky, Sr. was a pioneer Hollywood film producer. He was a key founder of Paramount Pictures with Adolph Zukor, and father of screenwriter Jesse L...
Feature Play Company, and Famous Players, which were both formed in 1913 to take advantage of the fact that films could reproduce the real substance of a stage play (plus embellishments), and so the best plays and actors from the legitimate stage could be enticed into films. In fact, the film industry adopted the term “photoplay” for motion pictures at this time. In 1914 the Lasky company and Famous Players were amalgamated into Famous Players-Lasky
Famous Players-Lasky
Famous Players-Lasky Corporation was an American motion picture and distribution company created on July 19, 1916 from the merger of Adolph Zukor's Famous Players Film Company -- originally formed by Zukor as Famous Players in Famous Plays -- and Jesse L...
, with distribution of their films handled by the new Paramount Pictures Corporation.
Another new major producing company formed during the war years was Triangle, with Mack Sennett
Mack Sennett
Mack Sennett was a Canadian-born American director and was known as the innovator of slapstick comedy in film. During his lifetime he was known at times as the "King of Comedy"...
, D.W. Griffith and Thomas Ince heading its production units. Despite the talents involved, it only lasted from 1915 to 1917, after which its separate producers took their films to Paramount for distribution. Equally short-lived, but still very important, was the World Film Company, which recruited most of the French directors, cameramen, and designers who had previously been working at the Fort Lee, New Jersey
Fort Lee, New Jersey
Fort Lee is a borough in Bergen County, New Jersey, United States. As of the 2010 United States Census, the borough population was 35,345. Located atop the Hudson Palisades, the borough is the western terminus of the George Washington Bridge...
studios for Pathé and Éclair.
The biggest success of these years was D.W. Griffith's The Birth of a Nation
The Birth of a Nation
The Birth of a Nation is a 1915 American silent film directed by D. W. Griffith and based on the novel and play The Clansman, both by Thomas Dixon, Jr. Griffith also co-wrote the screenplay , and co-produced the film . It was released on February 8, 1915...
(1915), made for Triangle. Griffith applied all the ideas for film staging that he had worked out in his Biograph films to a bigoted white southerner's epic view of the Civil War and its aftermath. Despite protests in the northern cities of the United States organized by the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People
National Association for the Advancement of Colored People
The National Association for the Advancement of Colored People, usually abbreviated as NAACP, is an African-American civil rights organization in the United States, formed in 1909. Its mission is "to ensure the political, educational, social, and economic equality of rights of all persons and to...
and others, it took many millions at the box office. Stung by the criticism of his film, Griffith made a new film he had just finished, The Mother and the Law, into one of the strands of an even bigger film with an even bigger theme, Intolerance
Intolerance (film)
Intolerance is a 1916 American silent film directed by D. W. Griffith and is considered one of the great masterpieces of the Silent Era. The three-and-a-half hour epic intercuts four parallel storylines each separated by several centuries: A contemporary melodrama of crime and redemption; a...
(1916).
European film production
In France, film production and exhibition closed down as its personnel became part of the general military mobilizationMobilization
Mobilization is the act of assembling and making both troops and supplies ready for war. The word mobilization was first used, in a military context, in order to describe the preparation of the Prussian army during the 1850s and 1860s. Mobilization theories and techniques have continuously changed...
of the country at the beginning of the war. Although film production began again in 1915, it was on a reduced scale, and the biggest companies gradually retired from production, to concentrate on film distribution
Film distributor
A film distributor is a company or individual responsible for releasing films to the public either theatrically or for home viewing...
and exhibition. Hence the cinemas were given over to imported films, particularly American ones. New small companies entered the business, and new young directors arrived to replace those drafted or working in the United States. The most notable of these was Abel Gance
Abel Gance
Abel Gance was a French film director and producer, writer and actor. He is best known for three major silent films: J'accuse , La Roue , and the monumental Napoléon .-Early life:...
.
Italian film production held up during the war, with long features already established as the main form. However, there was a disastrous move in subject matter to what were called “diva films”. These romantic dramas had the female star (the “diva”) suffering from unhappy love, and striking endless anguished Art Nouveau
Art Nouveau
Art Nouveau is an international philosophy and style of art, architecture and applied art—especially the decorative arts—that were most popular during 1890–1910. The name "Art Nouveau" is French for "new art"...
poses, while surrounded by male admirers and luxury. They were a commercial failure outside Italy.
In Denmark the Nordisk company increased its production so much in 1915 and 1916 that it could not sell all its films, which led to a very sharp decline in Danish production, and the end of Denmark's importance on the world film scene. The Nordisk distribution and cinema chain in Germany was effectively expropriated by the German government in 1917. The Swedish industry did not have this problem, as its production was more in balance with the market, and more importantly, the quality of its films was now superior to those from Denmark.
The German film industry was seriously weakened by the war, though with the major companies continuing as before. The distribution organization Projektions-AG “Union” (PAGU) acted as an umbrella company backing production by individual producers, and the Messter company also made many films. The most important of the new film producers at the time was Joe May
Joe May
Joe May , born Julius Otto Mandl, was a film director and film producer born in Austria and one of the pioneers of German cinema....
, who made a series of thrillers and adventure film
Adventure film
Adventure films are a genre of film.Unlike pure, low-budget action films they often use their action scenes preferably to display and explore exotic locations in an energetic way....
s through the war years, but Ernst Lubitsch
Ernst Lubitsch
Ernst Lubitsch was a German-born film director. His urbane comedies of manners gave him the reputation of being Hollywood's most elegant and sophisticated director; as his prestige grew, his films were promoted as having "the Lubitsch touch."In 1947 he received an Honorary Academy Award for his...
also came into prominence with a series of very successful comedies and dramas.
Because of the large local market for films in Russia, the industry there was not harmed by the war at first, although the isolation of the country led many Russian films to develop peculiarly distinctive features. The Khanzhonkov company retained its dominance, but the Ermoliev company, which had been formed in 1914, became its principal competitor, propelled by the work of its star, Ivan Mosjoukin
Ivan Mozzhukhin
Ivan Ilyich Mozzhukhin Ivan Ilyich Mozzhukhin Ivan Ilyich Mozzhukhin (Russian: Иван Ильич Мозжухин was a Russian silent film actor.-Career in Russia:Mozzhukhin was born in Penza, Russia and studied law at Moscow State University. In 1910 he left academic life to join a troupe of traveling actors...
, and principal director, Yakov Protazanov
Yakov Protazanov
Yakov Alexandrovich Protazanov was Russian and Soviet film director and screenwriter, and one of the founding fathers of cinema of Russia....
. The Bolshevik revolution
October Revolution
The October Revolution , also known as the Great October Socialist Revolution , Red October, the October Uprising or the Bolshevik Revolution, was a political revolution and a part of the Russian Revolution of 1917...
in October 1917 did not eliminate the privately owned film companies at first, though production was reduced through 1918. It was only in 1919 that the exodus of talent from the country took place, and fiction film production was reduced to practically nothing.
Film studios
The major change in film production methods in the United States during this period was the change to shooting in “dark” studios. The existing glass-roofed studios were blacked out, and the many new ones being built around Los Angeles were constructed with solid walls and ceilings. This meant that shooting could continue all day and night, without being limited by the changing sunlight. The general diffuse daylighting in the old studios was completely replaced with floodlights, and the actors were individually lit with floodlights on floorstands. The use of a spotlight from high at the back onto the actors to rimlight them became more frequent, and around 1918 some American cameramen started to use spotlights to light the actors from the front. All this meant that the figures of the actors were modelled more by the lighting, and more separated from the background by the lower light levels now used on the sets. This was a major step towards the standard studio lighting methods of the sound period. At the same time there was the beginning of a move towards using artificial light to light the actors on location, and some of the biggest studios bought electric generatorElectrical generator
In electricity generation, an electric generator is a device that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy. A generator forces electric charge to flow through an external electrical circuit. It is analogous to a water pump, which causes water to flow...
trucks for this purpose. All these developments took years to reach Europe
Irising and soft focus

There were other variants of the simple iris as well and in these the mask opening or closing in front of the lens had shapes other than circular. One of the more frequent of these shapes was the opening slit; a vertical central split appears in the totally black frame, and widens till the whole frame is clear, revealing the scene that is about to start. Eventually the diagonally opening slit appeared as well, and then there was the diamond-shaped opening iris, as in Poor Little Peppina and Alsace (1916), rather than the usual circle. Again, all of these variant forms were very infrequently used, and when they did occur in American films it was usually in the introductory stages. By 1918 the edges of ordinary circular irises were becoming very fuzzy when they were used in American films.
Enclosing the image inside static vignettes or masks of shapes other than circular also began to appear in films during the years 1914-1919, including symbolic shapes such as a cruciform cut-out in the Mary Pickford
Mary Pickford
Mary Pickford was a Canadian-born motion picture actress, co-founder of the film studio United Artists and one of the original 36 founders of the Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences...
film Stella Maris (Marshall Neilan, 1918), and Maurice Elvey in Britain put romantic scenes inside a heart-shaped mask in Nelson; The Story of England's Immortal Naval Hero (1918) and The Rocks of Valpré (1919). The most elegant variants occur in some films Ernst Lubitsch made in 1919. In Die Austernprinzessin (The Oyster Princess) a triple layer of horizontal rectangles with rounded ends enclose sets of dancing feet at the frenzied peak of a foxtrot, and in Die Puppe (The Doll) a dozen gossiping mouths are each enclosed in individual small circular vignettes arranged in a matrix.
A new idea taken over from still photography was “soft focus
Soft Focus
Soft Focus is the fifth album released by the Norwegian band Euroboys. It peaked at #2 on the Norwegian album charts.-Track listing:#"Break Away"#"Sleep 'Til Tomorrow"#"Hold On"#"Fears Be Gone"#"Topanga"#"One-Way Street"#"24 Years"...
”. This began in 1915, with some shots being intentionally thrown out of focus for expressive effect, as in Mary Pickford's Fanchon the Cricket. The idea developed slowly through the war years, until in D.W. Griffith's Broken Blossoms
Broken Blossoms
Broken Blossoms or The Yellow Man and the Girl is a 1919 silent film directed by D.W. Griffith. It was distributed by United Artists and premiered on May 13, 1919...
(1918) all the Close Ups of Lillian Gish
Lillian Gish
Lillian Diana Gish was an American stage, screen and television actress whose film acting career spanned 75 years, from 1912 to 1987....
are heavily diffused by the use of layers of fine black cotton mesh placed in front of the lens. Heavy lens diffusion was also used on all the other shots carrying forward the romantic and sentimental parts of the story of this film.
Subjective effects
It was during this period that camera effects intended to convey the subjective feelings of characters in a film really began to be established. These could now be done as Point of View (POV) shots, as in Sidney Drew's The Story of the Glove (1915), where a wobbly hand-held shot of a door and its keyhole represents the POV of a drunken man. In Poor Little Rich Girl (1917) a camera shot tilting sideways is intended to convey delirium, and by 1918 the idea had got to Russia, in Baryshnya i khuligan (The Lady and the Hooligan), where the Hooligan's infatuation with the Lady is conveyed by his Point of View of her splitting into a multiply superimposed image.The use of anamorphic (in the general sense of distorted shape) images first appears in these years with Abel Gance's la Folie du Docteur Tube (The Madness of Dr. Tube). In this film the effect of a drug administered to a group of people was suggested by shooting the scenes reflected in a distorting mirror
Curved mirror
A curved mirror is a mirror with a curved reflective surface, which may be either convex or concave . Most curved mirrors have surfaces that are shaped like part of a sphere, but other shapes are sometimes used in optical devices...
of the fair-ground type. Later we have Till the Clouds Roll By (Victor Fleming, 1919), where anamorphosis
Anamorphosis
Anamorphosis or anamorphism may refer to any of the following:*Anamorphosis, in art, the representation of an object as seen, for instance, altered by reflection in a mirror...
is used to depict the nightmare effects of indigestion in a comic manner. In fact, like so many film effects that distort the representation of reality, anamorphosis was first used exclusively in comic contexts.
"Poetic Cinema" and symbolism
Symbolic effects taken over from conventional literary and artistic tradition continued to make some appearances in films during these years. In D.W. Griffith's The Avenging Conscience (1914), the title “The birth of the evil thought” precedes a series of three shots of the protagonist looking at a spider, and ants eating an insect, though at a later point in the film when he prepares to kill someone these shots are cut straight in without explanation. Possibly as a result of Griffith's influence, 1915 was a big year for symbolism, allegories, and parables in the American cinema. Films following this route invariably included female figures in light, skimpy draperies, and indeed sometimes wearing nothing at all, doing “expressive” dances or striking plastic poses in sylvan settings. Titles include Lois Weber'sLois Weber
Lois Weber was an American silent film actress, screenwriter, producer, and director, who is considered "the most important female director the American film industry has known", and "one of the most important and important and prolific film directors in the era of silent films". Film historian...
Hypocrites, Vitagraph's Youth, someone else's Purity, and so on. The Primrose Path starts with a large painting illustrating the concept, which dissolves into a replica of the same scene with actors posed, and then they come to life, as these would soon become popular aspects of film making. This is then amplified by closer detailed live action representations of stations on “The Primrose Path”. An interesting German example from a few years later is Robert Reinert's Opium (1919), which has some notable innovations in the use of Insert shots to help convey the sensation of the drug reveries. These are travelling landscape shots taken from a boat going down a river, and they are intentionally shot out of focus, or underexposed, or cut into the film upside down.
Symbolist art and literature from the turn of the century also had a more general effect on a small number of films made in Italy and Russia. The supine acceptance of death resulting from passion and forbidden longings was a major feature of this art, and states of delirium dwelt on at length were important as well. The first Russian examples were all made by Yevgeni Bauer
Yevgeni Bauer
Yevgeni Franzevich Bauer was a Russian film director of silent films, a theatre artist and a screenwriter. His work had a great influence on the aesthetics of Russian cinematography at the beginning of the 20th century....
for Khanzhonkov during the First World War, and include Grezy, Schastye vechnoi nochi, and Posle smerti, all from 1915. These to some extent live up to the promise of the `decadent' aesthetic suggested by their titles; Daydreams, Happiness of Eternal Night, and After Death. Schastye vechnoi nochi includes a visually very striking vision of a medusa-like monster superimposed on a night-time snow scene, and *Posle smerti*has a somewhat subtler dream vision of a dead girl, picked out by extra arc lighting, walking through a wind-blown cornfield in the dusk. In Italy, another country somewhat isolated filmically by the war, the same kind of realization of the fin-de-siecle
Fin de siècle
Fin de siècle is French for "end of the century". The term sometimes encompasses both the closing and onset of an era, as it was felt to be a period of degeneration, but at the same time a period of hope for a new beginning...
decadent symbolist aesthetic can be found, mostly in films associated with the “diva” phenomenon. The most complete example, which also has decor to match, is Charles Kraus' Il gatto nero (The Black Cat). This last is one of the few films of this kind to use atmospheric insert shots to heighten the mood. The first film explicitly intended by its maker to be a visual analogue of poetry, Marcel L'Herbier's
Marcel L'Herbier
Marcel L'Herbier, Légion d'honneur, was a French film-maker, who achieved prominence as an avant-garde theorist and imaginative practitioner with a series of silent films in the 1920s. His career as a director continued until the 1950s and he made more than 40 feature films in total...
Rose-France (1919), continues further along these same paths.
Insert Shots

The atmospheric insert
Like many other devices that were more fully developed in Europe during the next decade, what could be called the “atmospheric Insert Shot” made its first appearance in American films during the years before 1919. This kind of shot is one in a scene which neither contains any of the characters in the story, nor is a Point of View shot seen by one of them. An early example is in Maurice Tourneur's The Pride of the Clan (1917), in which there is a series of shots of waves beating on a rocky shore which are shown when the locale of the story, which is about the harsh lives of fisher folk, is being introduced. Simpler and cruder examples from the same year occurs in William S. Hart'sWilliam S. Hart
William Surrey Hart was an American silent film actor, screenwriter, director and producer. He is remembered for having "imbued all of his characters with honor and integrity."-Biography:...
The Narrow Trail, in which a single shot of the mouth of San Francisco Bay
San Francisco Bay
San Francisco Bay is a shallow, productive estuary through which water draining from approximately forty percent of California, flowing in the Sacramento and San Joaquin rivers from the Sierra Nevada mountains, enters the Pacific Ocean...
taken against the light (the Golden Gate
Golden Gate
The Golden Gate is the North American strait connecting San Francisco Bay to the Pacific Ocean. Since 1937 it has been spanned by the Golden Gate Bridge...
) is preceded by a narrative title explaining its symbolic function in the story. This film also contains a shot of wild hills and valleys cut in as one character comments that the country far from the city is so clean and pure. By 1918 we can find a shot of the sky being used to reflect the mood of one of the characters without specific explanation in The Gun Woman (Frank Borzage
Frank Borzage
Frank Borzage was an American film director and actor.-Biography:Frank Borzage's father, Luigi Borzaga, was born in Ronzone, in 1859. As a stonemason, he sometimes worked in Switzerland; he met his future wife, Maria Ruegg , where she worked in a silk factory...
), but it must be emphasized that these examples are very rare, and did not either then, or within the next several years, constitute regular practice in the American cinema. The Tourneur example just mentioned also could stand as part of the beginning of the “montage sequence”. Maurice Elvey's
Maurice Elvey
Maurice Elvey was the most prolific film director in British history. He directed nearly 200 films between 1913 and 1957. During the silent film era he directed as many as twenty films per year....
Nelson - England's Immortal Naval Hero (1919) has a symbolic sequence dissolving from a picture of Kaiser Wilhelm II
William II, German Emperor
Wilhelm II was the last German Emperor and King of Prussia, ruling the German Empire and the Kingdom of Prussia from 15 June 1888 to 9 November 1918. He was a grandson of the British Queen Victoria and related to many monarchs and princes of Europe...
to a peacock, and then to a battleship. The atmospheric Insert began its notable career in European art cinema in Marcel L'Herbier's
Marcel L'Herbier
Marcel L'Herbier, Légion d'honneur, was a French film-maker, who achieved prominence as an avant-garde theorist and imaginative practitioner with a series of silent films in the 1920s. His career as a director continued until the 1950s and he made more than 40 feature films in total...
Rose-France. Here amongst the intentionally “poetic” uses of vignettes and filters and literary intertitles, a shot of the empty path once trod by the lovers is used to evoke the past.
Continuity cinema
The years 1914-1919 in America also saw the consolidation of the forms of what was to become the dominant mode of commercial cinema: “continuity cinema”, or “classical cinema”. During this period there were other styles that were still important, and these can be considered to lie along a spectrum between the best examples of “continuity cinema” at one extreme, and at the other extreme the “DIS-continuity cinema” of D.W. Griffith. There are a number of factors involved in the strong and apparent visual discontinuities between successive shots in Griffith's films, and the use of cross-cutting between parallel actions is only the most obvious of these. In 1915, cuts within the duration of a scene were still relatively infrequent in his films, and when they do occur they were frequently from Long ShotLong shot
In photography, filmmaking and video production, a long shot typically shows the entire object or human figure and is usually intended to place it in some relation to its surroundings...
or Medium Long Shot (which were the shots he most used) to a Big Close Up of an insert detail, which only occupied a small part of the frame in the previous shot. This in itself introduces a fairly strong visual discontinuity across the cut, but as well as that, the cut-in shot might often have a circular vignette mask if it were a Close Up of a person, so reinforcing the effect. And sometimes the now-standard Griffith iris-out and iris-in might also be left on the inserted shot, even though it had action continuity with the shots on either side of it. As well as all this there was Griffith's habit of moving the action into another shot in an adjoining space, and then back again if it was at all possible, which produced a marked change in background, which also made its small contribution to the discontinuity between shots.
One of the advanced continuity techniques involves the exact way the movement of actors from a shot in one location to another in a neighbouring location is handled. At best this kind of transition had previously been dealt with by having the directions of travel of the actor in the two shots correspond on the screen, but in a film such as The Bank Burglar's Fate (Jack Adolfi, 1914), one can see shot transitions in which a cut is made from an actor just leaving the frame, to a shot of him well inside the frame in an adjoining location, which have the positions and directions so well chosen that to the casual eye his movement appears quite continuous, and the real space and time ellipsis between the shots is concealed. Other good examples of this technique for eliminating several yards of waste space and a few seconds of waste time can be seen in Ralph Ince's films, particularly The Right Girl (1915), and by 1919 it was widely diffused in American films, but not in those made in Europe. All this connects with the rise of the use of cutting to different angles within a scene during the years 1914-1919, and in particular to the development of reverse-angle cutting.
Reverse-angle cutting
Cutting to different angles within a scene now became well-established as a technique for dissecting a scene into shots in American films. This approach had appeared a few times in earlier years, but in general cuts to or from a closer shot within a scene were still being made more or less down the lens axis as established in the Long Shot of the scene in question. The particular form of cutting to different angles within a scene in which the direction changes by more than ninety degrees is called reverse-angle cutting by film-makers. The leading figure in the full development of reverse-angle cutting was Ralph Ince. Films that he made at Vitagraph in 1915 such as The Right Girl and His Phantom Sweetheart have a large number of reverse-angle cuts in interior, as well as exterior, scenes. Other directors were also just starting to take up this style in 1915, for instance William S. HartWilliam S. Hart
William Surrey Hart was an American silent film actor, screenwriter, director and producer. He is remembered for having "imbued all of his characters with honor and integrity."-Biography:...
in Bad Buck of Santa Ynez.
As for Griffith, in Birth of a Nation there are just eight cuts to reverse-angle shots in the scene in Ford's Theatre, while elsewhere throughout the two-and-a-half hour length of this film there are only four more true reverse-angle cuts. Nevertheless, the Griffith style of film-making was still followed in its full idiosyncrasy, with extensive use of side by side spaces and a definite “front” for the camera, in most slapstick comedy. Directors of dramatic films who had worked Griffith also followed his style fairly closely, and it the standard for films made by his Fine Arts section of the Triangle company.
By 1916 there are a number of films in which there are around 15 to 20 true reverse-angle cuts per hundred shot transitions, such as The Deserter (Scott Sidney) and Going Straight. By the end of the war such films formed an appreciable but minor part of production: e.g. The Gun Woman (F. Borzage, 1918) and Jubilo (Clarence Badger, 1919). All this hardly concerned European cinema, where those few reverse-angle cuts used were mostly between a watcher and what he sees from his Point of View, both being filmed in a fairly distant shot. However, after the end of the war some of the brighter young directors such as Lubitsch started using a few reverse-angle cuts, mostly in association with Point of View cutting.
The flash-back
The use of flash-backFlashback (narrative)
Flashback is an interjected scene that takes the narrative back in time from the current point the story has reached. Flashbacks are often used to recount events that happened before the story’s primary sequence of events or to fill in crucial backstory...
structures continued to develop in this period, and the usual way of entering and leaving a flash-back was through a dissolve, and this was in fact the principal use at this time for this device. The Vitagraph company's The Man That Might Have Been (William Humphrey, 1914), is even more complex, with a series of reveries and flash-backs that contrast the protagonist's real passage through life with what might have been, if his son had not died. In this film dissolves are used both to enter and leave the flash-backs, and also the wish-dreams, and also for a time-lapse
Time-lapse
Time-lapse photography is a cinematography technique whereby the frequency at which film frames are captured is much lower than that which will be used to play the sequence back. When replayed at normal speed, time appears to be moving faster and thus lapsing...
inside a reverie at one point. But fades are also used for these purposes in this and other films of the period, and flashback transitions are also done with irising in other films, and even straight cuts.
During World War I the use of flashbacks occurred in films from all the major European film-making countries as well, from Italy (Tigre reale) to Denmark (Evangeliemandens Liv) to Russia (Grezy and Posle smerti), where it arrived in 1915.
As the years moved on a sudden decline in the use of long flash-back sequences set in around 1917, but on the other hand the use of a transition to and from a brief single shot memory scene remained quite common in American films. However, there could still be an even more complex flash-back construction in American films in the case of W.S. Van Dyke'sThe Lady of the Dugout (1918). This film has a story that happened long before which is narrated by one character in the framing scene, and initially accompanied by his narrating dialogue in intertitles, though after a while this stops, and the intertitles then convey the dialogue occurring within the flashback. Inside this main flashback there develops cross-cutting to another story, happening at the same time, and at first apparently unconnected with it, though the connection eventually appears. Next, inside this first flashback, the Lady of the title narrates another story, presented in flashback form, but with cutaways inside it back to events occurring in the time frame in which she is doing her narrating. Actually, all this is fairly easy to follow while watching the film, in part because what happens in all these strings of action is relatively simple.
Cross-cutting between parallel actions
After 1914 cross cutting between parallel actions came to be used whenever appropriate in American films, though this was not the case in European films. It should be noted that a good deal of the American use of cross-cutting was not the rapid alternation between parallel chains of action developed by D.W. Griffith, but a limited number of alternations to make it possible to leave out uninteresting bits of action with no real plot function. In Europe, some of the most enterprising directors did use cross-cutting sometimes, but they never attained the speed of the many American examples of this technique.Cross-cutting was also used to get new effects of contrast, such as the cross-cut sequence in Cecil B. DeMille's The Whispering Chorus, in which a supposedly dead husband is having a liaison with a Chinese prostitute in an opium den, while simultaneously his unknowing wife is being remarried in church.
All this was simple compared to D.W. Griffith's Intolerance (1916), in which four parallel stories are intercut throughout the whole length of the film, though in this case the stories are more similar than contrasting in their nature. The use of cross-cutting within these parallel stories as well as between them produced a complexity that was beyond the comprehension of the average audience of the time. The influence of Intolerance produced a few other films that combined a number of similar stories having similar themes, such as Maurice Tourneur's Woman (1918), but the box-office failure of Intolerance ensured that these later films had simpler structures.
The development of film art
The general trend in the development of cinema, led from the United States, was towards using the newly developed specifically filmic devices for expression of the narrative content of film stories, and combining this with the standard dramatic structures already in use in commercial theatre. D.W. Griffith had the highest standing amongst American directors in the industry, basically because of the dramatic excitement he got into his films. But there were others who were also considered as major figures at the time. The first of these was Cecil B. DeMilleCecil B. DeMille
Cecil Blount DeMille was an American film director and Academy Award-winning film producer in both silent and sound films. He was renowned for the flamboyance and showmanship of his movies...
, whose films, such as The Cheat (1915), brought out the moral dilemmas facing their characters in a more subtle way than Griffith. DeMille was also in closer touch with the reality of contemporary American life. Maurice Tourneur
Maurice Tourneur
Maurice Tourneur was an important international film director and screenwriter.-Life:Born Maurice Thomas in the Belleville district of Paris, France, his father was a jeweler. As a young man, Maurice Thomas first trained as a graphic designer and a magazine illustrator but was soon drawn to the...
was also highly ranked for the pictorial beauties of his films, together with the subtlety of his handling of fantasy, while at the same time he was capable of getting greater naturalism
Naturalism (literature)
Naturalism was a literary movement taking place from the 1880s to 1940s that used detailed realism to suggest that social conditions, heredity, and environment had inescapable force in shaping human character...
from his actors at appropriate moments, as in A Girl's Folly (1917).
Sidney Drew
Mr. & Mrs. Sidney Drew
-Biography:Sidney Drew , or Mr. Sidney Drew as he was usually billed, was an uncle of actors Lionel, Ethel & John Barrymore. His origins have been the subject of much speculation. Sidney's mother Mrs. Louisa Drew said she adopted him not long after the death of her husband John Drew, Sr. in 1862....
was the leader in developing “polite comedy”, while slapstick was refined by Fatty Arbuckle and Charles Chaplin, who both started with Mack Sennet's
Mack Sennett
Mack Sennett was a Canadian-born American director and was known as the innovator of slapstick comedy in film. During his lifetime he was known at times as the "King of Comedy"...
Keystone company. They reduced the usual frenetic pace of Sennett's films to give the audience a chance to appreciate the subtlety and finesse of their movement, and the cleverness of their gags. By 1917 Chaplin was also introducing more dramatic plot into his films, and mixing the comedy with sentiment.
In Russia, Yevgeni Bauer
Yevgeni Bauer
Yevgeni Franzevich Bauer was a Russian film director of silent films, a theatre artist and a screenwriter. His work had a great influence on the aesthetics of Russian cinematography at the beginning of the 20th century....
put a slow intensity of acting combined with Symbolist overtones onto film in a unique way.
In Sweden, Victor Sjöström
Victor Sjöström
Victor Sjöström was a Swedish actor, screenwriter, and film director.- Biography:Born in Silbodal, in the Värmland region of Sweden, he was only a year old when his father, Olof Adolf Sjöström, moved the family to Brooklyn, New York. His mother died when he was seven years old in 1886...
made a series of films that combined the realities of people's lives with their surroundings in a striking manner, while Mauritz Stiller developed sophisticated comedy to a new level.
In Germany, Ernst Lubitsch
Ernst Lubitsch
Ernst Lubitsch was a German-born film director. His urbane comedies of manners gave him the reputation of being Hollywood's most elegant and sophisticated director; as his prestige grew, his films were promoted as having "the Lubitsch touch."In 1947 he received an Honorary Academy Award for his...
got his inspiration from the stage work of Max Reinhardt, both in bourgeois comedy and in spectacle, and applied this to his films, culminating in his die Puppe (The Doll), die Austernprinzessin (The Oyster Princess) and Madame Dubarry.
Hollywood triumphant
Until this point, the cinemas of FranceCinema of France
The Cinema of France comprises the art of film and creative movies made within the nation of France or by French filmmakers abroad.France is the birthplace of cinema and was responsible for many of its early significant contributions. Several important cinematic movements, including the Nouvelle...
and Italy
Cinema of Italy
The history of Italian cinema began just a few months after the Lumière brothers had patented their Cinematographe, when Pope Leo XIII was filmed for a few seconds in the act of blessing the camera.-Early years:...
had been the most globally popular and powerful. But the United States
Cinema of the United States
The cinema of the United States, also known as Hollywood, has had a profound effect on cinema across the world since the early 20th century. Its history is sometimes separated into four main periods: the silent film era, classical Hollywood cinema, New Hollywood, and the contemporary period...
was already gaining quickly when World War I
World War I
World War I , which was predominantly called the World War or the Great War from its occurrence until 1939, and the First World War or World War I thereafter, was a major war centred in Europe that began on 28 July 1914 and lasted until 11 November 1918...
(1914–1918) caused a devastating interruption in the European film industries. The American industry, or "Hollywood", as it was becoming known after its new geographical center in California
California
California is a state located on the West Coast of the United States. It is by far the most populous U.S. state, and the third-largest by land area...
, gained the position it has held, more or less, ever since: film factory for the world, exporting its product to most countries on earth and controlling the market in many of them.
By the 1920s, the U.S. reached what is still its era of greatest-ever output, producing an average of 800 feature films annually, or 82% of the global total (Eyman, 1997). The comedies of Charlie Chaplin
Charlie Chaplin
Sir Charles Spencer "Charlie" Chaplin, KBE was an English comic actor, film director and composer best known for his work during the silent film era. He became the most famous film star in the world before the end of World War I...
and Buster Keaton
Buster Keaton
Joseph Frank "Buster" Keaton was an American comic actor, filmmaker, producer and writer. He was best known for his silent films, in which his trademark was physical comedy with a consistently stoic, deadpan expression, earning him the nickname "The Great Stone Face".Keaton was recognized as the...
, the swashbuckling
Swashbuckler
Swashbuckler or swasher is a term that emerged in the 16th century and has been used for rough, noisy and boastful swordsmen ever since. A possible explanation for this term is that it derives from a fighting style using a side-sword with a buckler in the off-hand, which was applied with much...
adventures of Douglas Fairbanks
Douglas Fairbanks
Douglas Fairbanks, Sr. was an American actor, screenwriter, director and producer. He was best known for his swashbuckling roles in silent films such as The Thief of Bagdad, Robin Hood, and The Mark of Zorro....
and the romances of Clara Bow
Clara Bow
Clara Gordon Bow was an American actress who rose to stardom in the silent film era of the 1920s. It was her appearance as a spunky shopgirl in the film It that brought her global fame and the nickname "The It Girl." Bow came to personify the roaring twenties and is described as its leading sex...
, to cite just a few examples, made these performers’ faces well-known on every continent. The Western visual norm that would become classical continuity editing
Continuity editing
Continuity editing is the predominant style of film editing and video editing in the post-production process of filmmaking of narrative films and television programs...
was developed and exported - although its adoption was slower in some non-Western countries without strong realist
Realism (arts)
Realism in the visual arts and literature refers to the general attempt to depict subjects "in accordance with secular, empirical rules", as they are considered to exist in third person objective reality, without embellishment or interpretation...
traditions in art and drama, such as Japan
Cinema of Japan
The has a history that spans more than 100 years. Japan has one of the oldest and largest film industries in the world – as of 2009 the fourth largest by number of feature films produced. Movies have been produced in Japan since 1897, when the first foreign cameramen arrived...
.
This development was contemporary with the growth of the studio system
Studio system
The studio system was a means of film production and distribution dominant in Hollywood from the early 1920s through the early 1960s. The term studio system refers to the practice of large motion picture studios producing movies primarily on their own filmmaking lots with creative personnel under...
and its greatest publicity method, the star system
Star system (film)
The star system was the method of creating, promoting and exploiting movie stars in Classical Hollywood cinema. Studios would select promising young actors and glamorise and create personas for them, often inventing new names and even new backgrounds...
, which characterized American film for decades to come and provided models for other film industries. The studios’ efficient, top-down control over all stages of their product enabled a new and ever-growing level of lavish production and technical sophistication.
At the same time, the system's commercial regimentation and focus on glamorous escapism
Escapism
Escapism is mental diversion by means of entertainment or recreation, as an "escape" from the perceived unpleasant or banal aspects of daily life...
discouraged daring and ambition beyond a certain degree, a prime example being the brief but still legendary directing career of the iconoclastic Erich von Stroheim
Erich von Stroheim
Erich von Stroheim was an Austrian-born film star of the silent era, subsequently noted as an auteur for his directorial work.-Background:...
in the late teens and the ‘20s.
The sound era
Experimentation with sound filmSound film
A sound film is a motion picture with synchronized sound, or sound technologically coupled to image, as opposed to a silent film. The first known public exhibition of projected sound films took place in Paris in 1900, but decades would pass before sound motion pictures were made commercially...
technology, both for recording and playback, was virtually constant throughout the silent era, but the twin problems of accurate synchronization and sufficient amplification had been difficult to overcome (Eyman, 1997). In 1926, Hollywood studio Warner Bros.
Warner Bros.
Warner Bros. Entertainment, Inc., also known as Warner Bros. Pictures or simply Warner Bros. , is an American producer of film and television entertainment.One of the major film studios, it is a subsidiary of Time Warner, with its headquarters in Burbank,...
introduced the "Vitaphone
Vitaphone
Vitaphone was a sound film process used on feature films and nearly 1,000 short subjects produced by Warner Bros. and its sister studio First National from 1926 to 1930. Vitaphone was the last, but most successful, of the sound-on-disc processes...
" system, producing short films of live entertainment acts and public figures and adding recorded sound
Sound recording and reproduction
Sound recording and reproduction is an electrical or mechanical inscription and re-creation of sound waves, such as spoken voice, singing, instrumental music, or sound effects. The two main classes of sound recording technology are analog recording and digital recording...
effects and orchestral scores to some of its major features. During late 1927, Warners released The Jazz Singer
The Jazz Singer (1927 film)
The Jazz Singer is a 1927 American musical film. The first feature-length motion picture with synchronized dialogue sequences, its release heralded the commercial ascendance of the "talkies" and the decline of the silent film era. Produced by Warner Bros. with its Vitaphone sound-on-disc system,...
, which was mostly silent but contained what is generally regarded as the first synchronized dialogue (and singing) in a feature film; but this process was actually accomplished first by Charles Taze Russell
Charles Taze Russell
Charles Taze Russell , or Pastor Russell, was a prominent early 20th century Christian restorationist minister from Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, USA, and founder of what is now known as the Bible Student movement, from which Jehovah's Witnesses and numerous independent Bible Student groups emerged...
in 1914 with the lengthy film The Photo-Drama of Creation
The Photo-Drama of Creation
The Photo-Drama of Creation, or Creation-Drama, was a four-part Christian film produced by the Watch Tower Bible and Tract Society of Pennsylvania under the direction of Charles Taze Russell, the founder of the Bible Student movement.The film presented Russell's beliefs about God's plan from the...
. This drama consisted of picture slides and moving pictures synchronized with phonograph records of talks and music. The early sound-on-disc
Sound-on-disc
The term Sound-on-disc refers to a class of sound film processes using a phonograph or other disc to record or playback sound in sync with a motion picture...
processes such as Vitaphone were soon superseded by sound-on-film
Sound-on-film
Sound-on-film refers to a class of sound film processes where the sound accompanying picture is physically recorded onto photographic film, usually, but not always, the same strip of film carrying the picture. Sound-on-film processes can either record an analog sound track or digital sound track,...
methods like Fox Movietone
Movietone sound system
The Movietone sound system is a sound-on-film method of recording sound for motion pictures that guarantees synchronization between sound and picture. It achieves this by recording the sound as a variable-density optical track on the same strip of film that records the pictures...
, DeForest Phonofilm
Phonofilm
In 1919, Lee De Forest, inventor of the audion tube, filed his first patent on a sound-on-film process, DeForest Phonofilm, which recorded sound directly onto film as parallel lines. These parallel lines photographically recorded electrical waveforms from a microphone, which were translated back...
, and RCA Photophone
RCA Photophone
RCA Photophone was the trade name given to one of four major competing technologies that emerged in the American film industry in the late 1920s for synchronizing electrically recorded audio to a motion picture image. RCA Photophone was a sound-on-film, "variable-area" film exposure system, in...
. The trend convinced the largely reluctant industrialists that "talking pictures", or "talkies", were the future. A lot of attempts were done before the success of the Jazz Singer
The Jazz Singer (1927 film)
The Jazz Singer is a 1927 American musical film. The first feature-length motion picture with synchronized dialogue sequences, its release heralded the commercial ascendance of the "talkies" and the decline of the silent film era. Produced by Warner Bros. with its Vitaphone sound-on-disc system,...
, that can be seen in the List of film sound systems.
Industry impact of sound
The change was remarkably swift. By the end of 1929, Hollywood was almost all-talkie, with several competing sound systems (soon to be standardized). Total changeover was slightly slower in the rest of the world, principally for economic reasons. Cultural reasons were also a factor in countries like ChinaCinema of China
The Chinese-language cinema has three distinct historical threads: Cinema of Hong Kong, Cinema of China, and Cinema of Taiwan. Since 1949 the cinema of mainland China has operated under restrictions imposed by the Communist Party of China's State Administration of Radio, Film, and Television and...
and Japan
Cinema of Japan
The has a history that spans more than 100 years. Japan has one of the oldest and largest film industries in the world – as of 2009 the fourth largest by number of feature films produced. Movies have been produced in Japan since 1897, when the first foreign cameramen arrived...
, where silents co-existed successfully with sound well into the 1930s, indeed producing what would be some of the most revered classics in those countries, like Wu Yonggang
Wu Yonggang
Wu Yonggang was a prominent Chinese film director during the 1930s. Today Wu is best known for his directorial debut, The Goddess. Wu had a long career with the Lianhua Film Company in the 1930s, in Chongqing during the war, and in the mainland after the 1949 communist revolution...
's The Goddess
The Goddess (1934 film)
The Goddess is a 1934 Chinese silent film released by the United Photoplay Service. It starred Ruan Lingyu in one of her final roles, and was directed by Wu Yonggang....
(China, 1934) and Yasujiro Ozu
Yasujiro Ozu
was a prominent Japanese film director and script writer. He is known for his distinctive technical style, developed during the silent era. Marriage and family, especially the relationships between the generations, are among the most persistent themes in his body of work...
's Was Born, But... (Japan, 1932). But even in Japan, a figure such as the benshi, the live narrator who was a major part of Japanese silent cinema, found his acting career was ending.
Sound further tightened the grip of major studios in numerous countries: the vast expense of the transition overwhelmed smaller competitors, while the novelty of sound lured vastly larger audiences for those producers that remained. In the case of the U.S., some historians credit sound with saving the Hollywood studio system in the face of the Great Depression
Great Depression
The Great Depression was a severe worldwide economic depression in the decade preceding World War II. The timing of the Great Depression varied across nations, but in most countries it started in about 1929 and lasted until the late 1930s or early 1940s...
(Parkinson, 1995). Thus began what is now often called "The Golden Age of Hollywood", which refers roughly to the period beginning with the introduction of sound until the late 1940s. The American cinema reached its peak of efficiently manufactured glamour and global appeal during this period. The top actors of the era are now thought of as the classic film stars, such as Clark Gable
Clark Gable
William Clark Gable , known as Clark Gable, was an American film actor most famous for his role as Rhett Butler in the 1939 Civil War epic film Gone with the Wind, in which he starred with Vivien Leigh...
, Katharine Hepburn
Katharine Hepburn
Katharine Houghton Hepburn was an American actress of film, stage, and television. In a career that spanned 62 years as a leading lady, she was best known for playing strong-willed, sophisticated women in both dramas and comedies...
, Humphrey Bogart
Humphrey Bogart
Humphrey DeForest Bogart was an American actor. He is widely regarded as a cultural icon.The American Film Institute ranked Bogart as the greatest male star in the history of American cinema....
, Greta Garbo
Greta Garbo
Greta Garbo , born Greta Lovisa Gustafsson, was a Swedish film actress. Garbo was an international star and icon during Hollywood's silent and classic periods. Many of Garbo's films were sensational hits, and all but three were profitable...
, and the greatest box office draw of the 1930s, child performer Shirley Temple
Shirley Temple
Shirley Temple Black , born Shirley Jane Temple, is an American film and television actress, singer, dancer, autobiographer, and former U.S. Ambassador to Ghana and Czechoslovakia...
.
Creative impact of sound
Creatively, however, the rapid transition was a difficult one, and in some ways, film briefly reverted to the conditions of its earliest days. The late '20s were full of static, stagey talkies as artists in front of and behind the camera struggled with the stringent limitations of the early sound equipment and their own uncertainty as to how to utilize the new medium. Many stage performers, directors and writers were introduced to cinema as producers sought personnel experienced in dialogue-based storytelling. Many major silent filmmakers and actors were unable to adjust and found their careers severely curtailed or even ended.This awkward period was fairly short-lived. 1929 was a watershed year: William Wellman with Chinatown Nights and The Man I Love, Rouben Mamoulian
Rouben Mamoulian
Rouben Mamoulian was an Armenian-American film and theatre director.-Biography:Born in Tbilisi, Georgia to an Armenian family, Rouben relocated to England and started directing plays in London in 1922...
with Applause, Alfred Hitchcock
Alfred Hitchcock
Sir Alfred Joseph Hitchcock, KBE was a British film director and producer. He pioneered many techniques in the suspense and psychological thriller genres. After a successful career in British cinema in both silent films and early talkies, Hitchcock moved to Hollywood...
with Blackmail
Blackmail (1929 film)
Blackmail is a 1929 British thriller drama film directed by Alfred Hitchcock, starring Anny Ondra, John Longden, and Cyril Ritchard, and featuring Donald Calthrop, Sara Allgood and Charles Paton. The film is based on the play Blackmail by Charles Bennett, as adapted by Hitchcock, with dialogue by...
(Britain's first sound feature), were among the directors to bring greater fluidity to talkies and experiment with the expressive use of sound (Eyman, 1997). In this,
they both benefited from, and pushed further, technical advances in microphones and cameras, and capabilities for editing and post-synchronizing sound (rather than recording all sound directly at the time of filming).
Sound films emphasized on black history and benefited different genres more so than silents did. Most obviously, the musical film
Musical film
The musical film is a film genre in which songs sung by the characters are interwoven into the narrative, sometimes accompanied by dancing. The songs usually advance the plot or develop the film's characters, though in some cases they serve merely as breaks in the storyline, often as elaborate...
was born; the first classic-style Hollywood musical was The Broadway Melody (1929) and the form would find its first major creator in choreographer/director Busby Berkeley
Busby Berkeley
Busby Berkeley was a highly influential Hollywood movie director and musical choreographer. Berkeley was famous for his elaborate musical production numbers that often involved complex geometric patterns...
(42nd Street
42nd Street (film)
-Cast:*Warner Baxter as Julian Marsh, director*Bebe Daniels as Dorothy Brock, star*George Brent as Pat Denning, Dorothy's old vaudeville partner*Ruby Keeler as Peggy Sawyer, the newcomer*Guy Kibbee as Abner Dillon, the show's backer...
, 1933, Dames
Dames
Dames is a 1934 Warner Bros. musical comedy film directed by Ray Enright with dance numbers created by Busby Berkeley. The film stars Ruby Keeler, Dick Powell, Joan Blondell, Guy Kibbee, ZaSu Pitts, and Hugh Herbert...
, 1934). In France, avant-garde director René Clair
René Clair
René Clair born René-Lucien Chomette, was a French filmmaker.-Biography:He was born in Paris and grew up in the Les Halles quarter. He attended the Lycée Montaigne and the Lycée Louis-le-Grand. During World War I, he served as an ambulance driver. After the war, he started a career as a journalist...
made surreal
Surrealism
Surrealism is a cultural movement that began in the early 1920s, and is best known for the visual artworks and writings of the group members....
use of song and dance in comedies like Under the Roofs of Paris (1930) and Le Million (1931). Universal Pictures
Universal Pictures
-1920:* White Youth* The Flaming Disc* Am I Dreaming?* The Dragon's Net* The Adorable Savage* Putting It Over* The Line Runners-1921:* The Fire Eater* A Battle of Wits* Dream Girl* The Millionaire...
begin releasing gothic horror films like Dracula
Dracula (1931 film)
Dracula is a 1931 vampire-horror film directed by Tod Browning and starring Bela Lugosi as the title character. The film was produced by Universal and is based on the stage play of the same name by Hamilton Deane and John L...
and Frankenstein (both 1931). In 1933, RKO released Merian C. Cooper
Merian C. Cooper
Merian Caldwell Cooper was an American aviator, United States Air Force and Polish Air Force officer, adventurer, screenwriter, and film director and producer. His most famous film was the 1933 movie King Kong.-Early life:...
's classic "giant monster" film King Kong. The trend thrived best in India
Cinema of India
The cinema of India consists of films produced across India, which includes the cinematic culture of Andhra Pradesh, Assam, Gujarat, Haryana, Jammu and Kashmir, Karnataka, Kerala, Maharashtra, Orissa, Punjab, Tamil Nadu, and West Bengal. Indian films came to be followed throughout South Asia and...
, where the influence of the country's traditional song-and-dance drama made the musical the basic form of most sound films (Cook, 1990); virtually unnoticed by the Western world for decades, this Indian popular cinema would nevertheless become the world's most prolific. (See also Bollywood
Bollywood
Bollywood is the informal term popularly used for the Hindi-language film industry based in Mumbai , Maharashtra, India. The term is often incorrectly used to refer to the whole of Indian cinema; it is only a part of the total Indian film industry, which includes other production centers producing...
.)
At this time, American gangster films like Little Caesar
Little Caesar (film)
Little Caesar is a 1931 Warner Bros. Pre-Code crime film. It tells the story of a hoodlum who ascends the ranks of organized crime until he reaches its upper echelons. Directed by Mervyn LeRoy, the film stars Edward G. Robinson and Douglas Fairbanks, Jr.. The story was adapted by Francis Edward...
and Wellman's The Public Enemy
The Public Enemy
The Public Enemy is a 1931 American Pre-Code crime film starring James Cagney and directed by William A. Wellman. The film relates the story of a young man's rise in the criminal underworld in prohibition-era urban America...
(both 1931) became popular. Dialogue now took precedence over "slapstick" in Hollywood comedies: the fast-paced, witty banter of The Front Page
The Front Page
The Front Page is a hit Broadway comedy about tabloid newspaper reporters on the police beat, written by one-time Chicago reporters Ben Hecht and Charles MacArthur which was first produced in 1928.-Synopsis:...
(1931) or It Happened One Night
It Happened One Night
It Happened One Night is a 1934 American romantic comedy film with elements of screwball comedy directed by Frank Capra, in which a pampered socialite tries to get out from under her father's thumb, and falls in love with a roguish reporter . The plot was based on the story Night Bus by Samuel...
(1934), the sexual double entrendres of Mae West
Mae West
Mae West was an American actress, playwright, screenwriter and sex symbol whose entertainment career spanned seven decades....
(She Done Him Wrong
She Done Him Wrong
She Done Him Wrong is a Pre-Code 1933 Paramount Pictures comedy romance film starring Mae West and Cary Grant. Others in the cast include Owen Moore, Gilbert Roland, Noah Beery, Sr., Louise Beavers and Rochelle Hudson....
, 1933) or the often subversively anarchic nonsense talk of the Marx Brothers
Marx Brothers
The Marx Brothers were an American family comedy act, originally from New York City, that enjoyed success in Vaudeville, Broadway, and motion pictures from the early 1900s to around 1950...
(Duck Soup, 1933). Walt Disney
Walt Disney
Walter Elias "Walt" Disney was an American film producer, director, screenwriter, voice actor, animator, entrepreneur, entertainer, international icon, and philanthropist, well-known for his influence in the field of entertainment during the 20th century. Along with his brother Roy O...
, who had previously been in the short cartoon business, stepped into feature films with the first English-speaking animated feature Snow White and the Seven Dwarfs
Snow White and the Seven Dwarfs (1937 film)
Snow White and the Seven Dwarfs is a 1937 American animated film based on Snow White, a German fairy tale by the Brothers Grimm. It was the first full-length cel-animated feature in motion picture history, as well as the first animated feature film produced in America, the first produced in full...
; released by RKO Pictures
RKO Pictures
RKO Pictures is an American film production and distribution company. As RKO Radio Pictures Inc., it was one of the Big Five studios of Hollywood's Golden Age. The business was formed after the Keith-Albee-Orpheum theater chains and Joseph P...
in 1937. 1939, a major year for American cinema, brought such films as The Wizard of Oz
The Wizard of Oz (1939 film)
The Wizard of Oz is a 1939 American musical fantasy film produced by Metro-Goldwyn-Mayer. It was directed primarily by Victor Fleming. Noel Langley, Florence Ryerson and Edgar Allan Woolf received credit for the screenplay, but there were uncredited contributions by others. The lyrics for the songs...
and Gone with The Wind
Gone with the Wind (film)
Gone with the Wind is a 1939 American historical epic film adapted from Margaret Mitchell's Pulitzer-winning 1936 novel of the same name. It was produced by David O. Selznick and directed by Victor Fleming from a screenplay by Sidney Howard...
.
The 1940s: the war and post-war years
The desire for wartime propaganda created a renaissance in the film industry in Britain, with realistic war dramas like 49th Parallel49th Parallel (film)
49th Parallel is the third film made by the British writer-director team of Michael Powell and Emeric Pressburger. It was released in the United States as The Invaders. Despite the title, no scene in the movie is set at the 49th parallel, which forms much of the U.S.-Canadian border...
(1941), Went the Day Well?
Went the Day Well?
"Went the Day Well?" is a British war film produced by Ealing Studios in 1942 as unofficial propaganda. It tells of how an English village is taken over by German paratroopers . Made during the war, it reflects the greatest potential nightmares of many Britons of the time, although the threat of...
(1942), The Way Ahead
The Way Ahead
The Way Ahead is a British Second World War drama released in 1944. It stars David Niven and Stanley Holloway and follows a group of civilians who are conscripted into the British Army to fight in North Africa. In the U.S., an edited version was released as The Immortal Battalion.The film was...
(1944) and Noel Coward
Noël Coward
Sir Noël Peirce Coward was an English playwright, composer, director, actor and singer, known for his wit, flamboyance, and what Time magazine called "a sense of personal style, a combination of cheek and chic, pose and poise".Born in Teddington, a suburb of London, Coward attended a dance academy...
and David Lean
David Lean
Sir David Lean CBE was an English film director, producer, screenwriter, and editor best remembered for big-screen epics such as The Bridge on the River Kwai , Lawrence of Arabia ,...
's celebrated naval film In Which We Serve
In Which We Serve
In Which We Serve is a 1942 British patriotic war film directed by David Lean and Noël Coward. It was made during the Second World War with the assistance of the Ministry of Information ....
in 1942, which won a special Academy Award
Academy Awards
An Academy Award, also known as an Oscar, is an accolade bestowed by the American Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences to recognize excellence of professionals in the film industry, including directors, actors, and writers...
. These existed alongside more flamboyant films like Michael Powell
Michael Powell (director)
Michael Latham Powell was a renowned English film director, celebrated for his partnership with Emeric Pressburger...
and Emeric Pressburger
Emeric Pressburger
Emeric Pressburger was a Hungarian-British screenwriter, film director, and producer. He is best known for his series of film collaborations with Michael Powell, in a multiple-award-winning partnership known as The Archers and produced a series of classic British films, notably 49th Parallel , The...
's The Life and Death of Colonel Blimp
The Life and Death of Colonel Blimp
The Life and Death of Colonel Blimp is a 1943 film by the British film making team of Michael Powell and Emeric Pressburger under the production banner of The Archers. It stars Roger Livesey, Deborah Kerr and Anton Walbrook. The title derives from the satirical Colonel Blimp comic strip by David...
(1943), A Canterbury Tale
A Canterbury Tale
A Canterbury Tale is a 1944 British film by the film-making team of Michael Powell and Emeric Pressburger. It stars Eric Portman, Sheila Sim, Dennis Price and Sgt. John Sweet; Esmond Knight provided narration and played several small roles. For the postwar American release, Raymond Massey narrated...
(1944) and A Matter of Life and Death (1946), as well as Laurence Olivier
Laurence Olivier
Laurence Kerr Olivier, Baron Olivier, OM was an English actor, director, and producer. He was one of the most famous and revered actors of the 20th century. He married three times, to fellow actors Jill Esmond, Vivien Leigh, and Joan Plowright...
's 1944 film
1944 in film
The year 1944 in film involved some significant events, including the wholesome, award-winning Going My Way plus popular murder mysteries such as Double Indemnity, Gaslight and Laura.-Events:*July 20 - Since You Went Away is released....
Henry V
Henry V (1944 film)
Henry V is a 1944 film adaptation of William Shakespeare's play of the same name. The on-screen title is The Cronicle History of King Henry the Fift with His Battell Fought at Agincourt in France . It stars Laurence Olivier, who also directed. The play was adapted for the screen by Olivier, Dallas...
, based on the Shakespearean history Henry V
Henry V (play)
Henry V is a history play by William Shakespeare, believed to be written in approximately 1599. Its full titles are The Cronicle History of Henry the Fifth and The Life of Henry the Fifth...
. The success of Snow White and the Seven Dwarfs allowed Disney to make more animated features like Pinocchio
Pinocchio (1940 film)
Pinocchio is a 1940 American animated film produced by Walt Disney and based on the story The Adventures of Pinocchio by Carlo Collodi. It is the second film in the Walt Disney Animated Classics, and it was made after the success of Snow White and the Seven Dwarfs and was released to theaters by...
(1940), Fantasia
Fantasia (film)
Fantasia is a 1940 American animated film produced by Walt Disney and released by Walt Disney Productions. The third feature in the Walt Disney Animated Classics series, the film consists of eight animated segments set to pieces of classical music conducted by Leopold Stokowski, seven of which are...
(1940), Dumbo
Dumbo
Dumbo is a 1941 American animated film produced by Walt Disney and released on October 23, 1941, by RKO Radio Pictures.The fourth film in the Walt Disney Animated Classics series, Dumbo is based upon the storyline written by Helen Aberson and illustrated by Harold Pearl for the prototype of a...
(1941) and Bambi
Bambi
Bambi is a 1942 American animated film directed by David Hand , produced by Walt Disney and based on the book Bambi, A Life in the Woods by Austrian author Felix Salten...
(1942).
The onset of US involvement in World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
also brought a proliferation of films as both patriotism
Patriotism
Patriotism is a devotion to one's country, excluding differences caused by the dependencies of the term's meaning upon context, geography and philosophy...
and propaganda
Propaganda
Propaganda is a form of communication that is aimed at influencing the attitude of a community toward some cause or position so as to benefit oneself or one's group....
. American propaganda films included Desperate Journey, Mrs. Miniver
Mrs. Miniver (film)
Mrs. Miniver is a 1942 American drama film directed by William Wyler, and starring Greer Garson, Walter Pidgeon, and Teresa Wright. Based on the fictional English housewife created by Jan Struther in 1937 for a series of newspaper columns, the film won six Academy Awards, including Best Picture,...
, Forever and a Day and Objective Burma. Notable American films from the war years include the anti-Nazi Watch on the Rhine
Watch on the Rhine
Watch on the Rhine is a 1943 American drama film directed by Herman Shumlin. The screenplay by Dashiell Hammett is based on the 1941 play of the same title by Lillian Hellman.-Plot:...
(1943), scripted by Dashiell Hammett
Dashiell Hammett
Samuel Dashiell Hammett was an American author of hard-boiled detective novels and short stories, and political activist. Among the enduring characters he created are Sam Spade , Nick and Nora Charles , and the Continental Op .In addition to the significant influence his novels and stories had on...
; Shadow of a Doubt
Shadow of a Doubt
Shadow of a Doubt is a 1943 American thriller film directed by Alfred Hitchcock, and starring Teresa Wright and Joseph Cotten. Written by Thornton Wilder, Sally Benson, and Alma Reville, the film was nominated for an Academy Award for Best Story for Gordon McDonell...
(1943), Hitchcock's direction of a script by Thornton Wilder
Thornton Wilder
Thornton Niven Wilder was an American playwright and novelist. He received three Pulitzer Prizes, one for his novel The Bridge of San Luis Rey and two for his plays Our Town and The Skin of Our Teeth, and a National Book Award for his novel The Eighth Day.-Early years:Wilder was born in Madison,...
; the George M. Cohan
George M. Cohan
George Michael Cohan , known professionally as George M. Cohan, was a major American entertainer, playwright, composer, lyricist, actor, singer, dancer, and producer....
biopic, Yankee Doodle Dandy
Yankee Doodle Dandy
Yankee Doodle Dandy is a 1942 American biographical musical film about George M. Cohan, known as "The Man Who Owns Broadway". It stars James Cagney, Joan Leslie, Walter Huston, and Richard Whorf, and features Irene Manning, George Tobias, Rosemary DeCamp and Jeanne Cagney.The movie was written by...
(1942), starring James Cagney
James Cagney
James Francis Cagney, Jr. was an American actor, first on stage, then in film, where he had his greatest impact. Although he won acclaim and major awards for a wide variety of performances, he is best remembered for playing "tough guys." In 1999, the American Film Institute ranked him eighth...
, and the immensely popular Casablanca
Casablanca (film)
Casablanca is a 1942 American romantic drama film directed by Michael Curtiz, starring Humphrey Bogart, Ingrid Bergman and Paul Henreid, and featuring Claude Rains, Conrad Veidt, Sydney Greenstreet, Peter Lorre and Dooley Wilson. Set during World War II, it focuses on a man torn between, in...
, with Humphrey Bogart
Humphrey Bogart
Humphrey DeForest Bogart was an American actor. He is widely regarded as a cultural icon.The American Film Institute ranked Bogart as the greatest male star in the history of American cinema....
. Bogart would star in 36 films between 1934 and 1942 including John Huston
John Huston
John Marcellus Huston was an American film director, screenwriter and actor. He wrote most of the 37 feature films he directed, many of which are today considered classics: The Maltese Falcon , The Treasure of the Sierra Madre , Key Largo , The Asphalt Jungle , The African Queen , Moulin Rouge...
's The Maltese Falcon
The Maltese Falcon (1941 film)
The Maltese Falcon is a 1941 Warner Bros. film based on the novel of the same name by Dashiell Hammett and a remake of the 1931 film of the same name...
(1941), one of the first films now considered a classic film noir
Film noir
Film noir is a cinematic term used primarily to describe stylish Hollywood crime dramas, particularly those that emphasize cynical attitudes and sexual motivations. Hollywood's classic film noir period is generally regarded as extending from the early 1940s to the late 1950s...
. In 1941, RKO Pictures
RKO Pictures
RKO Pictures is an American film production and distribution company. As RKO Radio Pictures Inc., it was one of the Big Five studios of Hollywood's Golden Age. The business was formed after the Keith-Albee-Orpheum theater chains and Joseph P...
released Citizen Kane
Citizen Kane
Citizen Kane is a 1941 American drama film, directed by and starring Orson Welles. Many critics consider it the greatest American film of all time, especially for its innovative cinematography, music and narrative structure. Citizen Kane was Welles' first feature film...
made by Orson Welles
Orson Welles
George Orson Welles , best known as Orson Welles, was an American film director, actor, theatre director, screenwriter, and producer, who worked extensively in film, theatre, television and radio...
. It is often considered the greatest film of all time. It would set the stage for the modern motion picture, as it revolutionized film story telling.
The strictures of wartime also brought an interest in more fantastical subjects. These included Britain's Gainsborough
Gainsborough Pictures
Gainsborough Pictures was a British film studio based on the south bank of the Regent's Canal, in Poole Street, Hoxton in the former Metropolitan Borough of Shoreditch, London. Gainsborough Studios were active between 1924 and 1951. Built as a power station for the Great Northern & City Railway it...
melodramas (including The Man in Grey
The Man in Grey
The Man in Grey is a 1943 British film melodrama made by Gainsborough Pictures, and is widely considered as the first of its "Gainsborough melodramas"...
and The Wicked Lady
The Wicked Lady
The Wicked Lady is a 1945 film starring Margaret Lockwood in the title role as a nobleman's wife who secretly becomes a highwayman for the excitement...
), and films like Here Comes Mr. Jordan
Here Comes Mr. Jordan
Here Comes Mr. Jordan is a comedy film in which a boxer, mistakenly taken to Heaven before his time, is given a second chance back on Earth. It stars Robert Montgomery, Claude Rains and Evelyn Keyes. The movie was adapted by Sidney Buchman and Seton I. Miller from the play Heaven Can Wait by Harry...
, Heaven Can Wait
Heaven Can Wait (1943 film)
Heaven Can Wait is a 1943 American comedy film produced and directed by Ernst Lubitsch. The screenplay was by Samson Raphaelson based on the play Birthday by Leslie Bush-Fekete. The music score was by Alfred Newman and the cinematography by Edward Cronjager.The film tells the story of a man who has...
, I Married a Witch and Blithe Spirit. Val Lewton
Val Lewton
Val Lewton was an American film producer and screenwriter, best known for a string of low-budget horror films he produced for RKO Pictures in the 1940s.-Early life:...
also produced a series of atmospheric and influential small-budget horror
Horror film
Horror films seek to elicit a negative emotional reaction from viewers by playing on the audience's most primal fears. They often feature scenes that startle the viewer through the means of macabre and the supernatural, thus frequently overlapping with the fantasy and science fiction genres...
films, some of the more famous examples being Cat People, Isle of the Dead
Isle of the Dead (film)
Isle of the Dead is one of producer Val Lewton's horror films made for RKO Radio Pictures. The movie had a script inspired by the painting Isle of the Dead by Arnold Böcklin, which appears behind the title credits, though the film was originally titled "Camilla" during production...
and The Body Snatcher
The Body Snatcher (film)
The Body Snatcher is a 1945 horror film directed by Robert Wise based on the short story The Body Snatcher by Robert Louis Stevenson. The film's producer Val Lewton helped adapt the story for the screen, writing under the pen name of "Carlos Keith". The film was marketed with the tagline The...
. The decade probably also saw the so-called "women's pictures", such as Now, Voyager
Now, Voyager
Now, Voyager is a 1942 American drama film starring Bette Davis, Paul Henreid, and Claude Rains, and directed by Irving Rapper. The screenplay by Casey Robinson is based on the 1941 novel of the same name by Olive Higgins Prouty....
, Random Harvest and Mildred Pierce
Mildred Pierce (film)
Mildred Pierce is a 1945 American drama film starring Joan Crawford, Ann Blyth, Jack Carson, Zachary Scott, and Eve Arden in a film noir about a long-suffering mother and her ungrateful daughter. The screenplay by Ranald MacDougall, William Faulkner, and Catherine Turney was based upon the 1941...
at the peak of their popularity.
1946 saw RKO Radio releasing It's a Wonderful Life
It's a Wonderful Life
It's a Wonderful Life is a 1946 American Christmas drama film produced and directed by Frank Capra and based on the short story "The Greatest Gift" written by Philip Van Doren Stern....
directed by Frank Capra
Frank Capra
Frank Russell Capra was a Sicilian-born American film director. He emigrated to the U.S. when he was six, and eventually became a creative force behind major award-winning films during the 1930s and 1940s...
. Soldiers returning from the war would provide the inspiration for films like The Best Years of Our Lives
The Best Years of Our Lives
The Best Years of Our Lives is a 1946 American drama film directed by William Wyler, and starring Fredric March, Myrna Loy, Dana Andrews, Teresa Wright, and Harold Russell, a United States paratrooper who lost both hands in a military training accident. The film is about three United States...
, and many of those in the film industry had served in some capacity during the war. Samuel Fuller
Samuel Fuller
Samuel Michael Fuller was an American screenwriter, novelist, and film director known for low-budget genre movies with controversial themes.-Personal life:...
's experiences in World War II would influence his largely autobiographical films of later decades such as The Big Red One
The Big Red One
The Big Red One is a World War II war film starring Lee Marvin and Mark Hamill. Written and directed by Samuel Fuller, it was produced by Lorimar and released by United Artists in the US on July 18, 1980...
. The Actor's Studio was founded in October 1947 by Elia Kazan
Elia Kazan
Elia Kazan was an American director and actor, described by the New York Times as "one of the most honored and influential directors in Broadway and Hollywood history". Born in Istanbul, the capital of the Ottoman Empire, to Greek parents originally from Kayseri in Anatolia, the family emigrated...
, Robert Lewis, and Cheryl Crawford
Cheryl Crawford
Cheryl Crawford was an American theatre producer and director.Born in Akron, Ohio, Crawford majored in drama at Smith College. Following graduation, she moved to New York City and enrolled at the Theatre Guild's school...
, and the same year Oskar Fischinger
Oskar Fischinger
Oskar Fischinger was a German-American abstract animator, filmmaker, and painter. He made over 50 short animated films, and painted c. 800 canvases, many of which are in museums, galleries and collections worldwide. Among his film works is Motion Painting No. 1 , which is now listed on the...
filmed Motion Painting No. 1
Motion Painting No. 1
Motion Painting No. 1 is a 1947 short animated film in which film artist Oskar Fischinger put images in motion to the music of Johann Sebastian Bach's Brandenburg Concerto no. 3, BWV 1048. It is a film of a painting ; Fischinger filmed each brushstroke over the course of 9 months...
.
In 1943, Ossessione was screened in Italy, marking the beginning of Italian neorealism
Italian neorealism
Italian neorealism is a style of film characterized by stories set amongst the poor and working class, filmed on location, frequently using nonprofessional actors...
. Major films of this type during the 1940s included Bicycle Thieves
Bicycle Thieves
Bicycle Thieves , also known as The Bicycle Thief, is a 1948 Italian neorealist film directed by Vittorio De Sica. It tells the story of a poor man searching the streets of Rome for his stolen bicycle, which he needs to be able to work. The film is based on the novel of the same name by Luigi...
, Rome, Open City
Rome, open city
Rome, Open City is a 1945 Italian war drama film, directed by Roberto Rossellini. The picture features Aldo Fabrizi, Anna Magnani and Marcello Pagliero, and is set in Rome during the Nazi occupation in 1944...
, and La Terra Trema
La terra trema
La terra trema is a 1948 Italian dramatic film directed by Luchino Visconti...
. In 1952 Umberto D was released, usually considered the last film of this type.
In the late 1940s, in Britain, Ealing Studios
Ealing Studios
Ealing Studios is a television and film production company and facilities provider at Ealing Green in West London. Will Barker bought the White Lodge on Ealing Green in 1902 as a base for film making, and films have been made on the site ever since...
embarked on their series of celebrated comedies, including Whisky Galore!
Whisky Galore! (film)
Whisky Galore! was a 1949 Ealing comedy film based on the novel of the same name by Compton MacKenzie. Both the movie and the novel are based on the real-life 1941 shipwreck of the S.S. Politician near the island of Eriskay and the unauthorized taking of its cargo of whisky...
, Passport to Pimlico
Passport to Pimlico
Passport to Pimlico is a 1949 British comedy film made by Ealing Studios and starred Stanley Holloway, Margaret Rutherford, and Hermione Baddeley. It was directed by Henry Cornelius....
, Kind Hearts and Coronets
Kind Hearts and Coronets
Kind Hearts and Coronets is a 1949 British black comedy feature film. The plot is loosely based on the 1907 novel Israel Rank: The Autobiography of a Criminal by Roy Horniman, with the screenplay written by Robert Hamer and John Dighton and the film directed by Hamer...
and The Man in the White Suit
The Man in the White Suit
The Man In The White Suit is a 1951 satirical comedy film made by Ealing Studios. It starred Alec Guinness, Joan Greenwood, and Cecil Parker, and was directed by Alexander Mackendrick. It followed a common Ealing Studios theme of the "common man" against the Establishment...
, and Carol Reed
Carol Reed
Sir Carol Reed was an English film director best known for Odd Man Out , The Fallen Idol , The Third Man and Oliver!...
directed his influential thrillers Odd Man Out
Odd Man Out
Odd Man Out is a 1947 Anglo-Irish film noir directed by Carol Reed, starring James Mason, and is based on a novel of the same name by F. L. Green.-Plot:The film's opening intertitle reads:...
, The Fallen Idol and The Third Man
The Third Man
The Third Man is a 1949 British film noir, directed by Carol Reed and starring Joseph Cotten, Alida Valli, Orson Welles, and Trevor Howard. Many critics rank it as a masterpiece, particularly remembered for its atmospheric cinematography, performances, and unique musical score...
. David Lean
David Lean
Sir David Lean CBE was an English film director, producer, screenwriter, and editor best remembered for big-screen epics such as The Bridge on the River Kwai , Lawrence of Arabia ,...
was also rapidly becoming a force in world cinema with Brief Encounter
Brief Encounter
Brief Encounter is a 1945 British film directed by David Lean about the conventions of British suburban life, centring on a housewife for whom real love brings unexpectedly violent emotions. The film stars Celia Johnson, Trevor Howard, Stanley Holloway and Joyce Carey...
and his Dickens
Charles Dickens
Charles John Huffam Dickens was an English novelist, generally considered the greatest of the Victorian period. Dickens enjoyed a wider popularity and fame than had any previous author during his lifetime, and he remains popular, having been responsible for some of English literature's most iconic...
adaptations Great Expectations
Great Expectations (1946 film)
Great Expectations is a 1946 British film which won two Academy Awards and was nominated for three others...
and Oliver Twist
Oliver Twist (1948 film)
Oliver Twist is the second of David Lean's two film adaptations of Charles Dickens novels. Following the success of his 1946 version of Great Expectations, Lean re-assembled much of the same team for his adaptation of Dicken's 1838 novel, including producers Ronald Neame and Anthony...
, and Michael Powell
Michael Powell (director)
Michael Latham Powell was a renowned English film director, celebrated for his partnership with Emeric Pressburger...
and Emeric Pressburger
Emeric Pressburger
Emeric Pressburger was a Hungarian-British screenwriter, film director, and producer. He is best known for his series of film collaborations with Michael Powell, in a multiple-award-winning partnership known as The Archers and produced a series of classic British films, notably 49th Parallel , The...
would experience the best of their creative partnership with films like Black Narcissus
Black Narcissus
Black Narcissus is a 1947 film by the British director-writer team of Michael Powell and Emeric Pressburger, based on the novel of the same name by Rumer Godden...
and The Red Shoes.
The 1950s

House Un-American Activities Committee
The House Committee on Un-American Activities or House Un-American Activities Committee was an investigative committee of the United States House of Representatives. In 1969, the House changed the committee's name to "House Committee on Internal Security"...
investigated Hollywood in the early 1950s. Protested by the Hollywood Ten
Hollywood blacklist
The Hollywood blacklist—as the broader entertainment industry blacklist is generally known—was the mid-twentieth-century list of screenwriters, actors, directors, musicians, and other U.S. entertainment professionals who were denied employment in the field because of their political beliefs or...
before the committee, the hearings resulted in the blacklist
Blacklist
A blacklist is a list or register of entities who, for one reason or another, are being denied a particular privilege, service, mobility, access or recognition. As a verb, to blacklist can mean to deny someone work in a particular field, or to ostracize a person from a certain social circle...
ing of many actors, writers and directors, including Chayefsky, Charlie Chaplin
Charlie Chaplin
Sir Charles Spencer "Charlie" Chaplin, KBE was an English comic actor, film director and composer best known for his work during the silent film era. He became the most famous film star in the world before the end of World War I...
, and Dalton Trumbo
Dalton Trumbo
James Dalton Trumbo was an American screenwriter and novelist, and one of the Hollywood Ten, a group of film professionals who refused to testify before the House Un-American Activities Committee in 1947 during the committee's investigation of Communist influences in the motion picture industry...
, and many of these fled to Europe, especially the United Kingdom.
The Cold War era
Cold War
The Cold War was the continuing state from roughly 1946 to 1991 of political conflict, military tension, proxy wars, and economic competition between the Communist World—primarily the Soviet Union and its satellite states and allies—and the powers of the Western world, primarily the United States...
zeitgeist
Zeitgeist
Zeitgeist is "the spirit of the times" or "the spirit of the age."Zeitgeist is the general cultural, intellectual, ethical, spiritual or political climate within a nation or even specific groups, along with the general ambiance, morals, sociocultural direction, and mood associated with an era.The...
translated into a type of near-paranoia
Paranoia
Paranoia [] is a thought process believed to be heavily influenced by anxiety or fear, often to the point of irrationality and delusion. Paranoid thinking typically includes persecutory beliefs, or beliefs of conspiracy concerning a perceived threat towards oneself...
manifested in theme
Theme (literature)
A theme is a broad, message, or moral of a story. The message may be about life, society, or human nature. Themes often explore timeless and universal ideas and are almost always implied rather than stated explicitly. Along with plot, character,...
s such as invading armies of evil aliens
Alien invasion
The alien invasion is a common theme in science fiction stories and film, in which extraterrestrial life invades Earth either to exterminate and supplant human life, enslave it under a colonial system, harvest humans for food, steal the planet's resources, or destroy the planet altogether.The...
, (Invasion of the Body Snatchers, The War of the Worlds
The War of the Worlds (1953 film)
The War of the Worlds is a 1953 science fiction film starring Gene Barry and Ann Robinson. It was the first on-screen loose adaptation of the H. G. Wells classic novel of the same name...
); and communist
Communism
Communism is a social, political and economic ideology that aims at the establishment of a classless, moneyless, revolutionary and stateless socialist society structured upon common ownership of the means of production...
fifth column
Fifth column
A fifth column is a group of people who clandestinely undermine a larger group such as a nation from within.-Origin:The term originated with a 1936 radio address by Emilio Mola, a Nationalist General during the 1936–39 Spanish Civil War...
ists, (The Manchurian Candidate
The Manchurian Candidate (1962 film)
The Manchurian Candidate is a 1962 American Cold War political thriller film starring Frank Sinatra, Laurence Harvey, Janet Leigh and Angela Lansbury, and featuring Henry Silva, James Gregory, Leslie Parrish and John McGiver...
).
During the immediate post-war years the cinematic industry was also threatened by television, and the increasing popularity of the medium meant that some film theatres would bankrupt and close. The demise of the "studio system" spurred the self-commentary
Criticism
Criticism is the judgement of the merits and faults of the work or actions of an individual or group by another . To criticize does not necessarily imply to find fault, but the word is often taken to mean the simple expression of an objection against prejudice, or a disapproval.Another meaning of...
of films like Sunset Boulevard (1950) and The Bad and the Beautiful
The Bad and the Beautiful
The Bad and the Beautiful is a 1952 MGM melodramatic film that tells the story of a film producer who alienates all around him. It was directed by Vincente Minelli and stars Lana Turner, Kirk Douglas, Walter Pidgeon, Dick Powell, Barry Sullivan, Gloria Grahame and Gilbert Roland. The film was...
(1952).
In 1950, the Lettrists avante-gardists caused riots at the Cannes Film Festival
Cannes Film Festival
The Cannes International Film Festival , is an annual film festival held in Cannes, France, which previews new films of all genres including documentaries from around the world. Founded in 1946, it is among the world's most prestigious and publicized film festivals...
, when Isidore Isou
Isidore Isou
Isidore Isou , born Ioan-Isidor Goldstein, was a Romanian-born French poet, film critic and visual artist...
's Treatise on Slime and Eternity was screened. After their criticism of Charlie Chaplin
Charlie Chaplin
Sir Charles Spencer "Charlie" Chaplin, KBE was an English comic actor, film director and composer best known for his work during the silent film era. He became the most famous film star in the world before the end of World War I...
and split with the movement, the Ultra-Lettrist
Ultra-Lettrist
The Ultra-Lettrist movement was an art form developed by Jean-Louis Brau, Gil J Wolman, and Francois Dufrêne, in the 1950's, when they split from Isidore Isou's Lettrism....
s continued to cause disruptions when they showed their new hypergraphical techniques.
The most notorious film is Guy Debord
Guy Debord
Guy Ernest Debord was a French Marxist theorist, writer, filmmaker, member of the Letterist International, founder of a Letterist faction, and founding member of the Situationist International . He was also briefly a member of Socialisme ou Barbarie.-Early Life:Guy Debord was born in Paris in 1931...
's Howls for Sade of 1952.
Distressed by the increasing number of closed theatres, studios and companies would find new and innovative ways to bring audiences back. These included attempts to literally widen their appeal with new screen formats. Cinemascope
CinemaScope
CinemaScope was an anamorphic lens series used for shooting wide screen movies from 1953 to 1967. Its creation in 1953, by the president of 20th Century-Fox, marked the beginning of the modern anamorphic format in both principal photography and movie projection.The anamorphic lenses theoretically...
, which would remain a 20th Century Fox
20th Century Fox
Twentieth Century Fox Film Corporation — also known as 20th Century Fox, or simply 20th or Fox — is one of the six major American film studios...
distinction until 1967, was announced with 1953's The Robe
The Robe (film)
The Robe is a 1953 American Biblical epic film that tells the story of a Roman military tribune who commands the unit that crucifies Jesus. The film was made by 20th Century Fox and is notable for being the first film released in the widescreen process CinemaScope.It was directed by Henry Koster...
. VistaVision
VistaVision
VistaVision is a higher resolution, widescreen variant of the 35mm motion picture film format which was created by engineers at Paramount Pictures in 1954....
, Cinerama
Cinerama
Cinerama is the trademarked name for a widescreen process which works by simultaneously projecting images from three synchronized 35 mm projectors onto a huge, deeply-curved screen, subtending 146° of arc. It is also the trademarked name for the corporation which was formed to market it...
, and Todd-AO
Todd-AO
Todd-AO is a post-production company founded in 1953, providing sound-related services to the motion picture and television industries. The company operates three facilities in the Los Angeles area.-History:...
boasted a "bigger is better" approach to marketing
Marketing
Marketing is the process used to determine what products or services may be of interest to customers, and the strategy to use in sales, communications and business development. It generates the strategy that underlies sales techniques, business communication, and business developments...
films to a dwindling US audience. This resulted in the revival of epic films to take advantage of the new big screen formats. Some of the most successful examples of these Biblical
Bible
The Bible refers to any one of the collections of the primary religious texts of Judaism and Christianity. There is no common version of the Bible, as the individual books , their contents and their order vary among denominations...
and historical
History
History is the discovery, collection, organization, and presentation of information about past events. History can also mean the period of time after writing was invented. Scholars who write about history are called historians...
spectaculars include The Ten Commandments
The Ten Commandments (1956 film)
The Ten Commandments is a 1956 American epic film that dramatized the biblical story of the Exodus, in which the Hebrew-born Moses, an adopted Egyptian prince, becomes the deliverer of the Hebrew slaves. The film, released by Paramount Pictures in VistaVision on October 5, 1956, was directed by...
(1956), The Vikings
The Vikings (film)
The Vikings is an adventure film directed by Richard Fleischer in 1958 Technicolor, produced by and starring Kirk Douglas, and based on the novel The Viking by Edison Marshall, based in its turn on legendary material from the sagas of Ragnar Lodbrok and his sons. Other actors included Tony Curtis,...
(1958), Ben-Hur
Ben-Hur (1959 film)
Ben-Hur is a 1959 American epic film directed by William Wyler and starring Charlton Heston in the title role, the third film adaptation of Lew Wallace's 1880 novel Ben-Hur: A Tale of the Christ. The screenplay was written by Karl Tunberg, Gore Vidal, and Christopher Fry. The score was composed by...
(1959), Spartacus
Spartacus (film)
Spartacus is a 1960 American epic historical drama film directed by Stanley Kubrick and based on the novel of the same name by Howard Fast...
(1960) and El Cid
El Cid (film)
El Cid is a historical epic film, a romanticized story of the life of the Christian Castilian knight Don Rodrigo Díaz de Vivar, called "El Cid" who in the 11th century fought the North African Almoravides and ultimately contributed to the unification of Spain.Made by Samuel Bronston Productions in...
(1961). Also during this period a number of other significant films were produced in Todd-AO
Todd-AO
Todd-AO is a post-production company founded in 1953, providing sound-related services to the motion picture and television industries. The company operates three facilities in the Los Angeles area.-History:...
, developed by Mike Todd
Mike Todd
Michael Todd was an American theatre and film producer, best known for his 1956 production of Around the World in Eighty Days, which won an Academy Award for Best Picture...
shortly before his death, including Oklahoma!
Oklahoma!
Oklahoma! is the first musical written by composer Richard Rodgers and librettist Oscar Hammerstein II. The musical is based on Lynn Riggs' 1931 play, Green Grow the Lilacs. Set in Oklahoma Territory outside the town of Claremore in 1906, it tells the story of cowboy Curly McLain and his romance...
(1955), Around the World in 80 Days (1956), South Pacific
South Pacific (musical)
South Pacific is a musical with music by Richard Rodgers, lyrics by Oscar Hammerstein II and book by Hammerstein and Joshua Logan. The story draws from James A. Michener's Pulitzer Prize-winning 1947 book Tales of the South Pacific, weaving together characters and elements from several of its...
(1958) and Cleopatra (1963) plus many more.
Gimmick
Gimmick
In marketing language, a gimmick is a unique or quirky special feature that makes something "stand out" from its contemporaries. However, the special feature is typically thought to be of little relevance or use. Thus, a gimmick is a special feature for the sake of having a special feature...
s also proliferated to lure in audiences. The fad for 3-D film
3-D film
A 3-D film or S3D film is a motion picture that enhances the illusion of depth perception...
would last for only two years, 1952–1954, and helped sell House of Wax
House of Wax (1953 film)
House of Wax is a 1953 American horror film starring Vincent Price. It is a remake of Warners' Mystery of the Wax Museum without the comic relief featured in the earlier film, and was directed by André de Toth...
and Creature from the Black Lagoon
Creature from the Black Lagoon
Creature from the Black Lagoon is a 1954 monster horror film directed by Jack Arnold, and starring Richard Carlson, Julia Adams, Richard Denning, Antonio Moreno, and Whit Bissell. The eponymous creature was played by Ben Chapman on land and Ricou Browning in underwater scenes...
. Producer William Castle
William Castle
William Castle was an American film director, producer, screenwriter, and actor. Castle was known for directing films with many gimmicks which were ambitiously promoted, despite being reasonably low budget B-movies....
would tout films featuring "Emergo" "Percepto", the first of a series of gimmicks that would remain popular marketing tools for Castle and others throughout the 1960s.
In the U.S., a post-WW2 tendency toward questioning the establishment and societal norms and the early activism
Activism
Activism consists of intentional efforts to bring about social, political, economic, or environmental change. Activism can take a wide range of forms from writing letters to newspapers or politicians, political campaigning, economic activism such as boycotts or preferentially patronizing...
of the Civil Rights Movement
Civil rights movement
The civil rights movement was a worldwide political movement for equality before the law occurring between approximately 1950 and 1980. In many situations it took the form of campaigns of civil resistance aimed at achieving change by nonviolent forms of resistance. In some situations it was...
was reflected in Hollywood films such as Blackboard Jungle
Blackboard Jungle
Blackboard Jungle is a 1955 social commentary film about teachers in an inner-city school. It is based on the novel of the same name by Evan Hunter.-Plot:...
(1955), On the Waterfront
On the Waterfront
On the Waterfront is a 1954 American drama film about union violence and corruption among longshoremen. The film was directed by Elia Kazan and written by Budd Schulberg. It stars Marlon Brando, Rod Steiger, Eva Marie Saint, Lee J. Cobb and Karl Malden. The soundtrack score was composed by Leonard...
(1954), Paddy Chayefsky
Paddy Chayefsky
Sidney Aaron "Paddy" Chayefsky , was an American playwright, screenwriter, and novelist. He is the only person to have won three solo Academy Awards for Best Screenplay....
's Marty
Marty (film)
Marty is a 1955 American film directed by Delbert Mann. The screenplay was written by Paddy Chayefsky, expanding upon his 1953 teleplay of the same name. The film stars Ernest Borgnine and Betsy Blair. The film enjoyed international success, winning the 1955 Academy Award for Best Picture and...
and Reginald Rose
Reginald Rose
Reginald Rose was an American film and television writer most widely known for his work in the early years of television drama. Rose's work is marked by its treatment of controversial social and political issues...
's 12 Angry Men (1957). Disney continued making animated films, notably; Cinderella
Cinderella (1950 film)
Cinderella is a 1950 American animated film produced by Walt Disney and based on the fairy tale "Cendrillon" by Charles Perrault. Twelfth in the Walt Disney Animated Classics series, the film had a limited release on February 15, 1950 by RKO Radio Pictures. Directing credits go to Clyde Geronimi,...
(1950), Peter Pan
Peter Pan (1953 film)
Peter Pan is a 1953 American animated film produced by Walt Disney and based on the play Peter Pan, or The Boy Who Wouldn't Grow Up by J. M. Barrie. It is the fourteenth film in the Walt Disney Animated Classics series and was originally released on February 5, 1953 by RKO Pictures...
(1953), Lady and the Tramp
Lady and the Tramp
Lady and the Tramp is a 1955 American animated film produced by Walt Disney and released to theaters on June 22, 1955, by Buena Vista Distribution. The fifteenth animated feature in the Walt Disney Animated Classics series, it was the first animated feature filmed in the CinemaScope widescreen...
(1955), and Sleeping Beauty
Sleeping Beauty (1959 film)
Sleeping Beauty is a 1959 American animated film produced by Walt Disney and based on the fairy tale "La Belle au bois dormant" by Charles Perrault...
(1959). He began, however, getting more involved in live action films, producing classics like 20,000 Leagues Under the Sea
20,000 Leagues Under the Sea (1954 film)
20,000 Leagues Under the Sea is a 1954 adventure film starring Kirk Douglas as Ned Land, James Mason as Captain Nemo, Paul Lukas as Professor Pierre Aronnax, and Peter Lorre as Conseil. It was the first science fiction film produced by Walt Disney Productions, as well as the only science-fiction...
(1954), and Old Yeller
Old Yeller (1957 film)
Old Yeller is a 1957 Walt Disney Productions film starring Tommy Kirk, Dorothy McGuire and Beverly Washburn, and directed by Robert Stevenson. It is about a boy and a stray dog in post-Civil War Texas. The story is based upon the 1956 Newbery Honor-winning book Old Yeller by Fred Gipson. Gipson...
(1957). Television began competing seriously with films projected in theatres, but surprisingly it promoted more filmgoing rather than curtailing it.
Limelight is probably a unique film in at least one interesting respect. Its two leads, Charlie Chaplin
Charlie Chaplin
Sir Charles Spencer "Charlie" Chaplin, KBE was an English comic actor, film director and composer best known for his work during the silent film era. He became the most famous film star in the world before the end of World War I...
and Claire Bloom
Claire Bloom
Claire Bloom is an English film and stage actress.-Early life:Bloom was born in the North London suburb of Finchley, the daughter of Elizabeth and Edward Max Blume, who worked in sales...
, were in the industry in no less than three different centuries. In the 19th Century, Chaplin made his theatrical debut at the age of eight, in 1897, in a clog dancing troupe, The Eight Lancaster Lads. In the 21st Century, Bloom is still enjoying a full and productive career, having appeared in dozens of films and television series produced up to and including 2010.
Golden Age of Asian cinema
Following the end of World War IIWorld War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
in the 1940s, the following decade, the 1950s, marked a 'Golden Age' for non-English world cinema
World cinema
World cinema is a term used primarily in English language speaking countries to refer to the films and film industries of non-English speaking countries. It is therefore often used interchangeably with the term foreign film...
, especially for Asian cinema
Asian cinema
Asian cinema refers to the film industries and films produced in the continent of Asia, and is also sometimes known as Eastern cinema. More commonly however, it is used to refer to the cinema of Eastern, Southeastern and Southern Asia. West Asian cinema is sometimes classified as part of Middle...
. Many of the most critically acclaimed Asian films of all time were produced during this decade, including Yasujiro Ozu
Yasujiro Ozu
was a prominent Japanese film director and script writer. He is known for his distinctive technical style, developed during the silent era. Marriage and family, especially the relationships between the generations, are among the most persistent themes in his body of work...
's Tokyo Story
Tokyo Story
is a 1953 Japanese film directed by Yasujirō Ozu. It tells the story of an aging couple who travel to Tokyo to visit their grown children. The film contrasts the behavior of their biological children, who are too busy to pay them much attention, and their daughter-in-law, who treats them with...
(1953), Satyajit Ray
Satyajit Ray
Satyajit Ray was an Indian Bengali filmmaker. He is regarded as one of the greatest auteurs of 20th century cinema. Ray was born in the city of Kolkata into a Bengali family prominent in the world of arts and literature...
's The Apu Trilogy (1955–1959) and The Music Room
Jalsaghar
Jalsaghar is the fourth feature film directed by Satyajit Ray. Jalsaghar is a narration of the end days of a Zamindar in Bengal. The landlord, Roy , is a just but other-worldly man who loves to spend time listening to music and putting up spectacles rather than managing his fields ravaged by...
(1958), Kenji Mizoguchi
Kenji Mizoguchi
Kenji Mizoguchi was a Japanese film director and screenwriter. His film Ugetsu won the Silver Lion at the Venice Film Festival, and appeared in the Sight & Sound Critics' Top Ten Poll in 1962 and 1972. Mizoguchi is renowned for his mastery of the long take and mise-en-scène...
's Ugetsu
Ugetsu
Ugetsu is a 1953 Japanese film directed by Kenji Mizoguchi. Set in 16th century Japan, it stars Masayuki Mori and Machiko Kyō, and is inspired by short stories by Ueda Akinari and Guy de Maupassant...
(1954) and Sansho the Bailiff
Sansho the Bailiff
-External links:* at the Japanese Movie Database* * and QuickTime trailer* essay by Mark Le Fanu...
(1954), Raj Kapoor
Raj Kapoor
Known as Ranbir Raj Kapoor Rāj Kapūr, 14 December 1924 – 2 June 1988), also known as The Show-Man, was an Indian film actor, producer and director of Hindi cinema. He was the winner of nine Filmfare Awards, while his films Awaara and Boot Polish were nominated for the Palme d'Or at the...
's Awaara
Awaara
Awaara is a 1951 Hindi film directed and produced by Raj Kapoor who also plays the leading role. His real-life father Prithviraj Kapoor stars as his on-screen father Judge Raghunath. Kapoor's youngest real-life brother Shashi Kapoor plays the younger version of his character...
(1951), Mikio Naruse
Mikio Naruse
was a Japanese filmmaker, screenwriter, and producer who directed some 89 films spanning the period 1930 to 1967.Naruse is known for imbuing his films with a bleak and pessimistic outlook...
's Floating Clouds
Floating Clouds
is a 1955 black-and-white Japanese film drama directed by Mikio Naruse. It is based on the novel of the same name by Japanese author and poet Fumiko Hayashi....
(1955), Guru Dutt
Guru Dutt
Vasanth Kumar Shivashankar Padukone , popularly known as Guru Dutt, was an Indian film director, producer and actor. He is often credited with ushering in the golden era of Hindi cinema...
's Pyaasa
Pyaasa
Pyaasa is a 1957 Indian film produced and directed by Guru Dutt. The film tells the story of struggling poet, Vijay , trying to make his works known in post-independence India...
(1957) and Kaagaz Ke Phool
Kaagaz Ke Phool
Kaagaz Ke Phool, , is a 1959 Hindi film produced and directed by Guru Dutt, who also played the lead role in the film .The film was a box office disaster of its time but was later resurrected as a world cinema cult classic in the 1980s. The film's music was composed by S. D...
(1959), and the Akira Kurosawa
Akira Kurosawa
was a Japanese film director, producer, screenwriter and editor. Regarded as one of the most important and influential filmmakers in the history of cinema, Kurosawa directed 30 filmsIn 1946, Kurosawa co-directed, with Hideo Sekigawa and Kajiro Yamamoto, the feature Those Who Make Tomorrow ;...
films Rashomon
Rashomon (film)
The bandit's storyTajōmaru, a notorious brigand , claims that he tricked the samurai to step off the mountain trail with him and look at a cache of ancient swords he discovered. In the grove he tied the samurai to a tree, then brought the woman there. She initially tried to defend herself with a...
(1950), Ikiru
Ikiru
is a 1952 Japanese film co-written and directed by Akira Kurosawa. The film examines the struggles of a minor Tokyo bureaucrat and his final quest for meaning. The film stars Takashi Shimura as Kanji Watanabe.-Plot:...
(1952), Seven Samurai (1954) and Throne of Blood
Throne of Blood
Throne of Blood is a 1957 Japanese film directed by Akira Kurosawa. Its original Japanese title is Kumonosu-jō , which means "Spider Web Castle". The film transposes the plot of William Shakespeare's play Macbeth to feudal Japan.-Plot:...
(1957).
During Japanese cinema
Cinema of Japan
The has a history that spans more than 100 years. Japan has one of the oldest and largest film industries in the world – as of 2009 the fourth largest by number of feature films produced. Movies have been produced in Japan since 1897, when the first foreign cameramen arrived...
's 'Golden Age' of the 1950s, successful films included Rashomon
Rashomon (film)
The bandit's storyTajōmaru, a notorious brigand , claims that he tricked the samurai to step off the mountain trail with him and look at a cache of ancient swords he discovered. In the grove he tied the samurai to a tree, then brought the woman there. She initially tried to defend herself with a...
(1950), Seven Samurai (1954) and The Hidden Fortress
The Hidden Fortress
is a 1958 jidai-geki film directed by Akira Kurosawa and starring Toshirō Mifune as General and Misa Uehara as Princess Yuki. A literal translation of the Japanese title is The Three Villains of the Hidden Fortress.-Plot:...
(1958) by Akira Kurosawa
Akira Kurosawa
was a Japanese film director, producer, screenwriter and editor. Regarded as one of the most important and influential filmmakers in the history of cinema, Kurosawa directed 30 filmsIn 1946, Kurosawa co-directed, with Hideo Sekigawa and Kajiro Yamamoto, the feature Those Who Make Tomorrow ;...
, as well as Yasujiro Ozu
Yasujiro Ozu
was a prominent Japanese film director and script writer. He is known for his distinctive technical style, developed during the silent era. Marriage and family, especially the relationships between the generations, are among the most persistent themes in his body of work...
's Tokyo Story
Tokyo Story
is a 1953 Japanese film directed by Yasujirō Ozu. It tells the story of an aging couple who travel to Tokyo to visit their grown children. The film contrasts the behavior of their biological children, who are too busy to pay them much attention, and their daughter-in-law, who treats them with...
(1953) and Ishirō Honda
Ishiro Honda
Ishirō Honda , sometimes miscredited in foreign releases as "Inoshiro Honda", was a Japanese film director...
's Godzilla
Godzilla (1954 film)
is a 1954 Japanese science fiction film directed by Ishirō Honda and produced by Tomoyuki Tanaka. The film stars Akira Takarada, Momoko Kōchi, Akihiko Hirata and Takashi Shimura. The film tells the story of Godzilla, a giant monster mutated by nuclear radiation, who ravages Japan, bringing back the...
(1954). These films have had a profound influence on world cinema. In particular, Kurosawa's Seven Samurai has been remade several times as Western films
Western (genre)
The Western is a genre of various visual arts, such as film, television, radio, literature, painting and others. Westerns are devoted to telling stories set primarily in the latter half of the 19th century in the American Old West, hence the name. Some Westerns are set as early as the Battle of...
, such as The Magnificent Seven
The Magnificent Seven
The Magnificent Seven is an American Western film directed by John Sturges, and released in 1960. It is a fictional tale of a group of seven American gunmen who are hired to protect a small agricultural village in Mexico from a group of marauding Mexican bandits...
(1960) and Battle Beyond the Stars
Battle Beyond the Stars
Battle Beyond the Stars is a Roger Corman-produced science fiction film, directed by Jimmy T. Murakami and released in 1980. The film, intended as a "Magnificent Seven in outer space," is a pastiche of The Magnificent Seven, the Western remake of Akira Kurosawa's film Seven Samurai...
(1980), and has also inspired several Bollywood
Bollywood
Bollywood is the informal term popularly used for the Hindi-language film industry based in Mumbai , Maharashtra, India. The term is often incorrectly used to refer to the whole of Indian cinema; it is only a part of the total Indian film industry, which includes other production centers producing...
films, such as Sholay
Sholay
Sholay is a 1975 Indian action-adventure film produced by G.P. Sippy and directed by his son Ramesh Sippy. It is considered among the greatest films in the history of Indian cinema. Released on 15 August 1975, it stars Dharmendra, Amitabh Bachchan, Hema Malini, Sanjeev Kumar, Jaya Bhaduri and...
(1975) and China Gate
China Gate (1998 film)
China Gate is a 1998 Hindi film directed by Rajkumar Santoshi. The film is a "humble tribute to the late Akira Kurosawa", crediting Seven Samurai as its inspiration...
(1998). Rashomon was also remade as The Outrage
The Outrage
The Outrage is a remake of the 1950 Japanese film Rashomon, reformulated as a Western. Like the original Akira Kurosawa film, four people give contradictory accounts of a rape and murder. Kurosawa is credited with the screenplay. It was directed by Martin Ritt and is based on stories by Ryūnosuke...
(1964), and inspired films with "Rashomon effect
Rashomon effect
The Rashomon effect is the effect of the subjectivity of perception on recollection, by which observers of an event are able to produce substantially different but equally plausible accounts of it. A useful demonstration of this principle in scientific understanding can be found in an article by...
" storytelling methods, such as Andha Naal
Andha Naal
Andha Naal is a 1954 Tamil crime mystery film directed by Veenai S. Balachander. It is arguably the first film-noir in Tamil cinema and is the first Tamil film to be made without songs. The film was inspired by the 1950 Akira Kurosawa film Rashômon...
(1954), The Usual Suspects
The Usual Suspects
The Usual Suspects is a 1995 American neo-noir film written by Christopher McQuarrie and directed by Bryan Singer. It stars Stephen Baldwin, Gabriel Byrne, Benicio del Toro, Chazz Palminteri, Kevin Pollak, Kevin Spacey and Pete Postlethwaite....
(1995) and Hero
Hero (2002 film)
Hero is a 2002 wuxia film directed by Zhang Yimou. Starring Jet Li as the nameless protagonist, the film is based on the story of Jing Ke's assassination attempt on the King of Qin in 227 BC....
(2002). The Hidden Fortress was also the inspiration behind George Lucas
George Lucas
George Walton Lucas, Jr. is an American film producer, screenwriter, and director, and entrepreneur. He is the founder, chairman and chief executive of Lucasfilm. He is best known as the creator of the space opera franchise Star Wars and the archaeologist-adventurer character Indiana Jones...
' Star Wars
Star Wars
Star Wars is an American epic space opera film series created by George Lucas. The first film in the series was originally released on May 25, 1977, under the title Star Wars, by 20th Century Fox, and became a worldwide pop culture phenomenon, followed by two sequels, released at three-year...
(1977). Other famous Japanese filmmakers from this period include Kenji Mizoguchi
Kenji Mizoguchi
Kenji Mizoguchi was a Japanese film director and screenwriter. His film Ugetsu won the Silver Lion at the Venice Film Festival, and appeared in the Sight & Sound Critics' Top Ten Poll in 1962 and 1972. Mizoguchi is renowned for his mastery of the long take and mise-en-scène...
, Mikio Naruse
Mikio Naruse
was a Japanese filmmaker, screenwriter, and producer who directed some 89 films spanning the period 1930 to 1967.Naruse is known for imbuing his films with a bleak and pessimistic outlook...
, Hiroshi Inagaki
Hiroshi Inagaki
was a Japanese filmmaker most known for the Academy Award-winning Samurai I: Musashi Miyamoto, which he directed in 1954.-Career:Born in Tokyo as the son of a shinpa actor, Inagaki appeared on stage in his childhood before joining the Nikkatsu studio as an actor in 1922...
and Nagisa Oshima
Nagisa Oshima
is a Japanese film director and screenwriter. After graduating from Kyoto University he was hired by Shochiku Ltd. and quickly progressed to directing his own movies, making his debut feature A Town of Love and Hope in 1959....
. Japanese cinema later became one of the main inspirations behind the New Hollywood
New Hollywood
New Hollywood or post-classical Hollywood, sometimes referred to as the "American New Wave", refers to the time from roughly the late-1960s to the early 1980s when a new generation of young filmmakers came to prominence in America, influencing the types of films produced, their production and...
movement of the 1960s to 1980s.
During Indian cinema
Cinema of India
The cinema of India consists of films produced across India, which includes the cinematic culture of Andhra Pradesh, Assam, Gujarat, Haryana, Jammu and Kashmir, Karnataka, Kerala, Maharashtra, Orissa, Punjab, Tamil Nadu, and West Bengal. Indian films came to be followed throughout South Asia and...
's 'Golden Age' of the 1950s, it was producing 200 films annually, while Indian independent films
Parallel Cinema
The Indian New Wave, commonly known in India as Art Cinema or Parallel Cinema as an alternative to the mainstream commercial cinema, is a specific movement in Indian cinema, known for its serious content, realism and naturalism, with a keen eye on the sociopolitical climate of the times...
gained greater recognition through international film festival
Film festival
A film festival is an organised, extended presentation of films in one or more movie theaters or screening venues, usually in a single locality. More and more often film festivals show part of their films to the public by adding outdoor movie screenings...
s. One of the most famous was The Apu Trilogy (1955–1959) from critically acclaimed Bengali film
Bengali cinema
Bengali cinema refers to the Bengali language filmmaking industries in the Bengal region of South Asia. There are two major film-making hubs in the region: one in Kolkata, West Bengal, India and the other in Dhaka, Bangladesh .The history of cinema in Bengal dates back to the 1890s, when the first...
director Satyajit Ray
Satyajit Ray
Satyajit Ray was an Indian Bengali filmmaker. He is regarded as one of the greatest auteurs of 20th century cinema. Ray was born in the city of Kolkata into a Bengali family prominent in the world of arts and literature...
, whose films had a profound influence on world cinema, with directors such as Akira Kurosawa, Martin Scorsese
Martin Scorsese
Martin Charles Scorsese is an American film director, screenwriter, producer, actor, and film historian. In 1990 he founded The Film Foundation, a nonprofit organization dedicated to film preservation, and in 2007 he founded the World Cinema Foundation...
, James Ivory
James Ivory (director)
James Francis Ivory is an American film director, best known for the results of his long collaboration with Merchant Ivory Productions, which included both Indian-born film producer Ismail Merchant, and screenwriter Ruth Prawer Jhabvala...
, Abbas Kiarostami
Abbas Kiarostami
Abbas Kiarostami is an internationally acclaimed Iranian film director, screenwriter, photographer and film producer. An active filmmaker since 1970, Kiarostami has been involved in over forty films, including shorts and documentaries...
, Elia Kazan
Elia Kazan
Elia Kazan was an American director and actor, described by the New York Times as "one of the most honored and influential directors in Broadway and Hollywood history". Born in Istanbul, the capital of the Ottoman Empire, to Greek parents originally from Kayseri in Anatolia, the family emigrated...
, François Truffaut
François Truffaut
François Roland Truffaut was an influential film critic and filmmaker and one of the founders of the French New Wave. In a film career lasting over a quarter of a century, he remains an icon of the French film industry. He was also a screenwriter, producer, and actor working on over twenty-five...
, Steven Spielberg
Steven Spielberg
Steven Allan Spielberg KBE is an American film director, screenwriter, producer, video game designer, and studio entrepreneur. In a career of more than four decades, Spielberg's films have covered many themes and genres. Spielberg's early science-fiction and adventure films were seen as an...
, Carlos Saura
Carlos Saura
Carlos Saura Atarés is a Spanish film director and photographer.-Early life:Born into a family of artists , he developed his artistic sense in childhood as a photography enthusiast.He obtained his directing diploma in Madrid in 1957 at the Institute of Cinema Research and Studies...
, Jean-Luc Godard
Jean-Luc Godard
Jean-Luc Godard is a French-Swiss film director, screenwriter and film critic. He is often identified with the 1960s French film movement, French Nouvelle Vague, or "New Wave"....
, Isao Takahata
Isao Takahata
is a Japanese anime filmmaker that have earned critical international acclaim for his work as a director. Takahata is co-founder of Studio Ghibli with long-time collaborative partner Hayao Miyazaki. He has directed films such as the war-themed Grave of the Fireflies, the romantic-drama Only...
, Gregory Nava
Gregory Nava
Gregory Nava is a film director, producer and screenplay writer, of Mexican and Basque heritage.-Education:...
, Ira Sachs
Ira Sachs
Ira Sachs is an American filmmaker. His first film was the acclaimed short Lady .He directed Sundance Film Festival selection The Delta and directed Sundance Film Festival Grand Prize winning Forty Shades of Blue...
, Wes Anderson
Wes Anderson
Wesley Wales Anderson is an American film director, screenwriter, actor, and producer of features, short films and commercials....
and Danny Boyle
Danny Boyle
Daniel "Danny" Boyle is an English filmmaker and producer. He is best known for his work on films such as Slumdog Millionaire, 127 Hours, 28 Days Later, Sunshine and Trainspotting. For Slumdog Millionaire, Boyle won numerous awards in 2008, including the Academy Award for Best Director...
being influenced by his cinematic style. According to Michael Sragow of The Atlantic Monthly, the "youthful coming-of-age
Coming of age
Coming of age is a young person's transition from childhood to adulthood. The age at which this transition takes place varies in society, as does the nature of the transition. It can be a simple legal convention or can be part of a ritual, as practiced by many societies...
dramas
Drama film
A drama film is a film genre that depends mostly on in-depth development of realistic characters dealing with emotional themes. Dramatic themes such as alcoholism, drug addiction, infidelity, moral dilemmas, racial prejudice, religious intolerance, poverty, class divisions, violence against women...
that have flooded art houses since the mid-fifties owe a tremendous debt to the Apu trilogy". Subrata Mitra
Subrata Mitra
Subrata Mitra was an Indian cinematographer. Acclaimed for his work in The Apu Trilogy , Mitra is often considered one of the greatest of Indian cinematographers....
's cinematographic technique of bounce lighting also originates from The Apu Trilogy. Other famous Indian filmmakers from this period include Guru Dutt
Guru Dutt
Vasanth Kumar Shivashankar Padukone , popularly known as Guru Dutt, was an Indian film director, producer and actor. He is often credited with ushering in the golden era of Hindi cinema...
, Ritwik Ghatak, Mrinal Sen
Mrinal Sen
Mrinal Sen is a Bengali Indian filmmaker. He was born on 14 May 1923, in the town of Faridpur, now in Bangladesh in a Hindu family. After finishing his high school there, he left home to come to Calcutta as a student and studied physics at the well-known Scottish Church College and at the...
, Raj Kapoor
Raj Kapoor
Known as Ranbir Raj Kapoor Rāj Kapūr, 14 December 1924 – 2 June 1988), also known as The Show-Man, was an Indian film actor, producer and director of Hindi cinema. He was the winner of nine Filmfare Awards, while his films Awaara and Boot Polish were nominated for the Palme d'Or at the...
, Bimal Roy
Bimal Roy
Bimal Roy was one of the most acclaimed Indian film directors of all time. He is particularly noted for his realistic and socialistic films like Do Bigha Zamin, Parineeta, Biraj Bahu, Madhumati, Sujata, and Bandini, making him an important director of Hindi cinema...
, K. Asif
K. Asif
K. Asif was a film director, film producer and screenwriter who was famous for his work for the Hindi epic motion picture, Mughal-e-Azam .-Early life:...
and Mehboob Khan.
The cinema of South Korea also experienced a 'Golden Age' in the 1950s, beginning with director Lee Kyu-hwan's tremendously successful remake of Chunhyang-jon (1955). That year also saw the release of Yangsan Province
Yangsan Province (film)
Yangsan Province aka The Sunlit Path is a 1955 South Korean film directed by Kim Ki-young.-Synopsis:The film is a historical melodrama about a high government official who wants to marry a woman who is engaged to marry another man.-Cast:* Kim Sam-hwa... Ok-rang* Cho Yong-soo... Su-dong* Kim...
by the renowned director, Kim Ki-young
Kim Ki-young
Kim Ki-young was a South Korean film director, known for his intensely psychosexual and melodramatic horror films, often focusing on the psychology of their female characters. Kim was born in Seoul during the Japanese occupation, raised in Pyongyang and spent time in Japan, where he became...
, marking the beginning of his productive career. Both the quality and quantity of filmmaking had increased rapidly by the end of the 1950s. South Korean films, such as Lee Byeong-il's 1956 comedy Sijibganeun nal (The Wedding Day), had begun winning international awards. In contrast to the beginning of the 1950s, when only 5 films were made per year, 111 films were produced in South Korea in 1959.
The 1950s was also a 'Golden Age' for Philippine cinema
Cinema of the Philippines
Cinema of the Philippines started with the introduction of the first moving pictures to the country on January 1, 1897 at the Salón de Pertierra in Manila. The following year, local scenes were shot on film for the first time by a Spaniard, Antonio Ramos, using the Lumiere Cinematograph...
, with the emergence of more artistic and mature films, and significant improvement in cinematic techniques among filmmakers. The studio system produced frenetic activity in the local film industry as many films were made annually and several local talents started to earn recognition abroad. The premiere Philippine directors of the era included Gerardo de Leon
Gerardo de León
Gerardo de León was a Filipino actor turned film director, who made his acting debut in the 1934 film Ang Dangal....
, Gregorio Fernandez
Gregorio Fernández
Gregorio Fernández was a Spanish Baroque sculptor. He belongs to the Castilian school of sculpture, following the style of other great artists like Alonso Berruguete, Juan de Juni, Pompeyo Leoni and Juan de Arfe.-Biography:...
, Eddie Romero
Eddie Romero
Eddie Romero is an acclaimed and influential Filipino film director, film producer and screenwriter, considered one of the finest in the Cinema of the Philippines.Romero was named National Artist of the Philippines in 2003....
, Lamberto Avellana, and Cirio Santiago.
1960s
During the 1960s the studio system in Hollywood declined, because many films were now being made on location in other countries, or using studio facilities abroad, such as PinewoodPinewood Studios
Pinewood Studios is a major British film studio situated in Iver Heath, Buckinghamshire, approximately west of central London. The studios have played host to many productions over the years from huge blockbuster films to television shows to commercials to pop promos.The purchase of Shepperton...
in the UK and Cinecittà
Cinecittà
Cinecittà is a large film studio in Rome that is considered the hub of Italian cinema.-History:The studios were founded in 1937 by Benito Mussolini and his head of cinema Luigi Freddi for propaganda purposes, under the slogan "Il cinema è l'arma più forte"...
in Rome
Rome
Rome is the capital of Italy and the country's largest and most populated city and comune, with over 2.7 million residents in . The city is located in the central-western portion of the Italian Peninsula, on the Tiber River within the Lazio region of Italy.Rome's history spans two and a half...
. "Hollywood" films were still largely aimed at family audiences, and it was often the more old-fashioned films that produced the studios' biggest successes. Productions like Mary Poppins
Mary Poppins (film)
Mary Poppins is a 1964 musical film starring Julie Andrews and Dick Van Dyke, produced by Walt Disney, and based on the Mary Poppins books series by P. L. Travers with illustrations by Mary Shepard. The film was directed by Robert Stevenson and written by Bill Walsh and Don DaGradi, with songs by...
(1964), My Fair Lady
My Fair Lady (film)
My Fair Lady is a 1964 musical film adaptation of the Lerner and Loewe stage musical, of the same name, based on the 1938 film adaptation of the original stage play Pygmalion by George Bernard Shaw. The ballroom scene and the ending were taken from the previous film adaptation , rather than from...
(1964) and The Sound of Music
The Sound of Music (film)
Rodgers and Hammerstein's The Sound of Music is a 1965 American musical film directed by Robert Wise and starring Julie Andrews and Christopher Plummer. The film is based on the Broadway musical The Sound of Music, with songs written by Richard Rodgers and Oscar Hammerstein II, and with the musical...
(1965) were among the biggest money-makers of the decade. The growth in independent producers and production companies, and the increase in the power of individual actors also contributed to the decline of traditional Hollywood studio production.
There was also an increasing awareness of foreign language cinema during this period. During the late 1950s and 1960s the French New Wave
French New Wave
The New Wave was a blanket term coined by critics for a group of French filmmakers of the late 1950s and 1960s, influenced by Italian Neorealism and classical Hollywood cinema. Although never a formally organized movement, the New Wave filmmakers were linked by their self-conscious rejection of...
directors such as François Truffaut
François Truffaut
François Roland Truffaut was an influential film critic and filmmaker and one of the founders of the French New Wave. In a film career lasting over a quarter of a century, he remains an icon of the French film industry. He was also a screenwriter, producer, and actor working on over twenty-five...
and Jean-Luc Godard
Jean-Luc Godard
Jean-Luc Godard is a French-Swiss film director, screenwriter and film critic. He is often identified with the 1960s French film movement, French Nouvelle Vague, or "New Wave"....
produced films such as Les quatre cents coups
The 400 Blows
The 400 Blows is a 1959 French film directed by François Truffaut. One of the defining films of the French New Wave, it displays many of the characteristic traits of the movement. The story revolves around Antoine Doinel, an ordinary adolescent in Paris, who is thought by his parents and teachers...
, Breathless and Jules et Jim which broke the rules of Hollywood cinema's narrative structure
Narrative structure
Narrative structure is generally described as the structural framework that underlies the order and manner in which a narrative is presented to a reader, listener, or viewer....
. As well, audiences were becoming aware of Italian
Italy
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
films like Federico Fellini
Federico Fellini
Federico Fellini, Cavaliere di Gran Croce OMRI , was an Italian film director and scriptwriter. Known for a distinct style that blends fantasy and baroque images, he is considered one of the most influential and widely revered filmmakers of the 20th century...
's La dolce vita
La Dolce Vita
La Dolce Vita is a 1960 comedy-drama film written and directed by the critically acclaimed director Federico Fellini. The film is a story of a passive journalist's week in Rome, and his search for both happiness and love that will never come...
and the stark dramas of Sweden
Sweden
Sweden , officially the Kingdom of Sweden , is a Nordic country on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. Sweden borders with Norway and Finland and is connected to Denmark by a bridge-tunnel across the Öresund....
's Ingmar Bergman
Ingmar Bergman
Ernst Ingmar Bergman was a Swedish director, writer and producer for film, stage and television. Described by Woody Allen as "probably the greatest film artist, all things considered, since the invention of the motion picture camera", he is recognized as one of the most accomplished and...
.
In Britain, the "Free Cinema" of Lindsay Anderson
Lindsay Anderson
Lindsay Gordon Anderson was an Indian-born, British feature film, theatre and documentary director, film critic, and leading light of the Free Cinema movement and the British New Wave...
, Tony Richardson
Tony Richardson
Cecil Antonio "Tony" Richardson was an English theatre and film director and producer.-Early life:Richardson was born in Shipley, Yorkshire in 1928, the son of Elsie Evans and Clarence Albert Richardson, a chemist...
and others lead to a group of realistic and innovative dramas including Saturday Night and Sunday Morning
Saturday Night and Sunday Morning (film)
Saturday Night and Sunday Morning is a 1960 British film. It is an adaptation of the 1958 novel of the same name by Alan Sillitoe. Sillitoe wrote the screenplay adaptation and the film was directed by Karel Reisz.-Synopsis:...
, A Kind of Loving
A Kind of Loving (film)
A Kind of Loving is a 1962 British drama film directed by John Schlesinger, based on the 1960 novel of the same name by Stan Barstow. It stars Alan Bates and June Ritchie as two lovers in 1960s West Yorkshire. The photography was by Denys Coop, and the music by Ron Grainer...
and This Sporting Life
This Sporting Life
This Sporting Life is a 1963 British film based on a novel of the same name by David Storey which won the 1960 Macmillan Fiction Award. It tells the story of a rugby league footballer, Frank Machin, in Wakefield, a mining area of Yorkshire, whose romantic life is not as successful as his sporting...
. Other British films such as Repulsion
Repulsion
Repulsion is a 1965 British psychological thriller film directed by Roman Polanski, based on a scenario by Gérard Brach and Roman Polanski. It was Polanski's first English language film, and was shot in Britain, as such being his second film made outside his native Poland. The cast includes...
, Darling
Darling (film)
Darling is a 1965 British comedy/drama film written by Frederic Raphael, directed by John Schlesinger, and starring Julie Christie, Dirk Bogarde, and Laurence Harvey. It is considered one of Schlesinger's best films and an insightful satire of mid-sixties British culture...
, Alfie, Blowup
Blowup
Blowup is a 1966 film directed by Michelangelo Antonioni, his first English-language film.It tells of a British photographer's accidental involvement with a murder, inspired by Julio Cortázar's short story, "Las babas del diablo" or "The Devil's Drool" , translated also as Blow-Up, and by the life...
and Georgy Girl
Georgy Girl
Georgy Girl is a 1966 British film based on a novel by Margaret Forster. The film was directed by Silvio Narizzano and starred Lynn Redgrave as Georgy, Alan Bates, James Mason, Charlotte Rampling and Bill Owen....
(all in 1965-1966) helped to reduce prohibitions sex and nudity on screen, while the casual sex and violence of the James Bond
James Bond
James Bond, code name 007, is a fictional character created in 1953 by writer Ian Fleming, who featured him in twelve novels and two short story collections. There have been a six other authors who wrote authorised Bond novels or novelizations after Fleming's death in 1964: Kingsley Amis,...
films, beginning with Dr. No
Dr. No (film)
Dr. No is a 1962 spy film, starring Sean Connery; it is the first James Bond film. Based on the 1958 Ian Fleming novel of the same name, it was adapted by Richard Maibaum, Johanna Harwood, and Berkely Mather and was directed by Terence Young. The film was produced by Harry Saltzman and Albert R...
in 1962 would render the series popular worldwide.
During the 1960s, Ousmane Sembène
Ousmane Sembène
Ousmane Sembène , often credited in the French style as Sembène Ousmane in articles and reference works, was a Senegalese film director, producer and writer...
produced several French- and Wolof-language
Wolof language
Wolof is a language spoken in Senegal, The Gambia, and Mauritania, and is the native language of the Wolof people. Like the neighbouring languages Serer and Fula, it belongs to the Atlantic branch of the Niger–Congo language family...
films and became the 'father' of African Cinema
African cinema
The term African cinema refers to the film production in Africa, following formal independence. Some of the countries in North Africa developed a national film industry much earlier and are related to West Asian cinema...
. In Latin America
Latin America
Latin America is a region of the Americas where Romance languages – particularly Spanish and Portuguese, and variably French – are primarily spoken. Latin America has an area of approximately 21,069,500 km² , almost 3.9% of the Earth's surface or 14.1% of its land surface area...
the dominance of the "Hollywood" model was challenged by many film makers. Fernando Solanas
Fernando Solanas
Fernando Ezequiel 'Pino' Solanas is an Argentine film director, screenwriter and politician....
and Octavio Gettino called for a politically engaged Third Cinema
Third Cinema
Third Cinema is a Latin American film movement that started in the 1960s-70s which decries neocolonialism, the capitalist system, and the Hollywood model of cinema as mere entertainment to make money...
in contrast to Hollywood and the European auteur cinema.
Further, the nuclear paranoia of the age, and the threat of an apocalyptic nuclear exchange (like the 1962 close-call with the USSR during the Cuban missile crisis
Cuban Missile Crisis
The Cuban Missile Crisis was a confrontation among the Soviet Union, Cuba and the United States in October 1962, during the Cold War...
) prompted a reaction within the film community as well. Films like Stanley Kubrick
Stanley Kubrick
Stanley Kubrick was an American film director, writer, producer, and photographer who lived in England during most of the last four decades of his career...
's Dr. Strangelove and Fail Safe
Fail-Safe (1964 film)
Fail-Safe is a 1964 film directed by Sidney Lumet, based on the 1962 novel of the same name by Eugene Burdick and Harvey Wheeler. It tells the story of a fictional Cold War nuclear crisis...
with Henry Fonda
Henry Fonda
Henry Jaynes Fonda was an American film and stage actor.Fonda made his mark early as a Broadway actor. He also appeared in 1938 in plays performed in White Plains, New York, with Joan Tompkins...
were produced in a Hollywood that was once known for its overt patriotism and wartime propaganda.
In documentary film
Documentary film
Documentary films constitute a broad category of nonfictional motion pictures intended to document some aspect of reality, primarily for the purposes of instruction or maintaining a historical record...
the sixties saw the blossoming of Direct Cinema
Direct Cinema
Direct Cinema is a documentary genre that originated between 1958 and 1962 in North America, principally in the Canadian province of Quebec and the United States...
, an observational style of film making as well as the advent of more overtly partisan films like In the Year of the Pig
In the Year of the Pig
In the Year of the Pig is a 1968 American documentary film about the origins of the Vietnam War, directed by Emile de Antonio. It was nominated for an Academy award for best documentary....
about the Vietnam War
Vietnam War
The Vietnam War was a Cold War-era military conflict that occurred in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. This war followed the First Indochina War and was fought between North Vietnam, supported by its communist allies, and the government of...
by Emile de Antonio
Emile de Antonio
Emile de Antonio was a director and producer of documentary films, usually detailing political or social events circa 1960s–1980s...
. By the late 1960s however, Hollywood filmmakers were beginning to create more innovative and groundbreaking films that reflected the social revolution taken over much of the western world such as Bonnie and Clyde
Bonnie and Clyde (film)
The film was originally offered to François Truffaut, the best-known director of the New Wave movement, who made contributions to the script. He passed on the project to make Fahrenheit 451. The producers approached Jean-Luc Godard next...
(1967), The Graduate
The Graduate
The Graduate is a 1967 American comedy-drama motion picture directed by Mike Nichols. It is based on the 1963 novel The Graduate by Charles Webb, who wrote it shortly after graduating from Williams College. The screenplay was by Buck Henry, who makes a cameo appearance as a hotel clerk, and Calder...
(1967), 2001: A Space Odyssey
2001: A Space Odyssey (film)
2001: A Space Odyssey is a 1968 epic science fiction film produced and directed by Stanley Kubrick, and co-written by Kubrick and Arthur C. Clarke, partially inspired by Clarke's short story The Sentinel...
(1968), Rosemary's Baby
Rosemary's Baby (film)
Rosemary's Baby is a 1968 American horror film written and directed by Roman Polanski, based on the bestselling 1967 novel Rosemary's Baby by Ira Levin...
(1968), Midnight Cowboy
Midnight Cowboy
Midnight Cowboy is a 1969 American drama film based on the 1965 novel of the same name by James Leo Herlihy. It was written by Waldo Salt, directed by John Schlesinger, and stars Dustin Hoffman and newcomer Jon Voight in the title role. Notable smaller roles are filled by Sylvia Miles, John...
(1969), Easy Rider
Easy Rider
Easy Rider is a 1969 American road movie written by Peter Fonda, Dennis Hopper, and Terry Southern, produced by Fonda and directed by Hopper. It tells the story of two bikers who travel through the American Southwest and South with the aim of achieving freedom...
(1969) and The Wild Bunch
The Wild Bunch
The Wild Bunch is a 1969 American Western film directed by Sam Peckinpah about an aging outlaw gang on the Texas-Mexico border, trying to exist in the changing "modern" world of 1913...
(1969). Bonnie and Clyde
Bonnie and Clyde (film)
The film was originally offered to François Truffaut, the best-known director of the New Wave movement, who made contributions to the script. He passed on the project to make Fahrenheit 451. The producers approached Jean-Luc Godard next...
is often considered the beginning of the so-called New Hollywood
New Hollywood
New Hollywood or post-classical Hollywood, sometimes referred to as the "American New Wave", refers to the time from roughly the late-1960s to the early 1980s when a new generation of young filmmakers came to prominence in America, influencing the types of films produced, their production and...
.
In Japanese cinema, Academy Award winning director Akira Kurosawa
Akira Kurosawa
was a Japanese film director, producer, screenwriter and editor. Regarded as one of the most important and influential filmmakers in the history of cinema, Kurosawa directed 30 filmsIn 1946, Kurosawa co-directed, with Hideo Sekigawa and Kajiro Yamamoto, the feature Those Who Make Tomorrow ;...
produced Yojimbo (1961), which like his previous films also had a profound influence around the world. The influence of this film is most apparent in Sergio Leone
Sergio Leone
Sergio Leone was an Italian film director, producer and screenwriter most associated with the "Spaghetti Western" genre.Leone's film-making style includes juxtaposing extreme close-up shots with lengthy long shots...
's A Fistful of Dollars
A Fistful of Dollars
A Fistful of Dollars is a 1964 Italian Spaghetti Western film directed by Sergio Leone and starring Clint Eastwood alongside Gian Maria Volonté, Marianne Koch, Wolfgang Lukschy, Sieghardt Rupp, José Calvo, Antonio Prieto, and Joseph Egger. Released in Italy in 1964 then in the United States in...
(1964) and Walter Hill's Last Man Standing
Last Man Standing (film)
Last Man Standing is a 1996 action film written and directed by Walter Hill, starring Bruce Willis, Christopher Walken, and Bruce Dern. It is a credited remake of the Akira Kurosawa film Yojimbo.- Plot :...
(1996). Yojimbo was also the origin of the "Man with No Name
Man with No Name
The man with no name is a stock character in Western films, but the term usually applies specifically to the character played by Clint Eastwood in Sergio Leone's "Dollars Trilogy."...
" trend.
Meanwhile in India
Cinema of India
The cinema of India consists of films produced across India, which includes the cinematic culture of Andhra Pradesh, Assam, Gujarat, Haryana, Jammu and Kashmir, Karnataka, Kerala, Maharashtra, Orissa, Punjab, Tamil Nadu, and West Bengal. Indian films came to be followed throughout South Asia and...
, the Academy Award winning Bengali
Bengali cinema
Bengali cinema refers to the Bengali language filmmaking industries in the Bengal region of South Asia. There are two major film-making hubs in the region: one in Kolkata, West Bengal, India and the other in Dhaka, Bangladesh .The history of cinema in Bengal dates back to the 1890s, when the first...
director Satyajit Ray
Satyajit Ray
Satyajit Ray was an Indian Bengali filmmaker. He is regarded as one of the greatest auteurs of 20th century cinema. Ray was born in the city of Kolkata into a Bengali family prominent in the world of arts and literature...
wrote a script for The Alien
The Alien
The Alien was an Indian-American science fiction film under production in the late 1960s which was eventually cancelled. It was being directed by the celebrated Indian director Satyajit Ray and co-produced by Hollywood studio Columbia Pictures. The script was written by Ray in 1967, loosely based...
in 1967, based on a Bangla science fiction
Bangla Science Fiction
Bengali science fiction is a rich part of Bengali literature. Although it is not as established as other genres in the Bengali language, it is gaining popularity among Bengali readers, especially in Bangladesh.-Earliest writers:...
story he himself had written in 1962. The film was intended to be his debut in Hollywood but the production was eventually cancelled. Nevertheless, the script went on to influence later films such as Steven Spielberg
Steven Spielberg
Steven Allan Spielberg KBE is an American film director, screenwriter, producer, video game designer, and studio entrepreneur. In a career of more than four decades, Spielberg's films have covered many themes and genres. Spielberg's early science-fiction and adventure films were seen as an...
's E.T.
E.T. the Extra-Terrestrial
E.T. the Extra-Terrestrial is a 1982 American science fiction film co-produced and directed by Steven Spielberg, written by Melissa Mathison and starring Henry Thomas, Dee Wallace, Robert MacNaughton, Drew Barrymore, and Peter Coyote...
(1982) and Rakesh Roshan
Rakesh Roshan
Rakesh Roshan Rakesh Roshan Rakesh Roshan (Hindi: राकेश रोशन (born Rakesh Roshan Lal Nagrath on 6 September 1949 in Mumbai, Maharashtra, India) is a producer, director and former actor in Bollywood films who was born in a Punjabi Hindu Kayastha family...
's Koi... Mil Gaya
Koi... Mil Gaya
Koi... Mil Gaya is a 2003 Bollywood science fiction film, directed by Rakesh Roshan , starring Hrithik Roshan, Rekha, and Preity Zinta. It was released on 8 August 2003...
(2003).
1970s: The 'New Hollywood' or Post-classical cinema
'The New HollywoodNew Hollywood
New Hollywood or post-classical Hollywood, sometimes referred to as the "American New Wave", refers to the time from roughly the late-1960s to the early 1980s when a new generation of young filmmakers came to prominence in America, influencing the types of films produced, their production and...
' and 'post-classical cinema' are terms used to describe the period following the decline of the studio system
Studio system
The studio system was a means of film production and distribution dominant in Hollywood from the early 1920s through the early 1960s. The term studio system refers to the practice of large motion picture studios producing movies primarily on their own filmmaking lots with creative personnel under...
during the 1950s and 1960s and the end of the production code
Production Code
The Motion Picture Production Code was the set of industry moral censorship guidelines that governed the production of the vast majority of United States motion pictures released by major studios from 1930 to 1968. It is also popularly known as the Hays Code, after Hollywood's chief censor of the...
, (which was replaced in 1968 by the MPAA film rating system
MPAA film rating system
The Motion Picture Association of America's film-rating system is used in the U.S. and its territories to rate a film's thematic and content suitability for certain audiences. The MPAA system applies only to motion pictures that are submitted for rating. Other media may be rated by other entities...
). During the 1970s, filmmakers increasingly depicted explicit sexual content and showed gunfight and battle scenes that included graphic images of bloody deaths.
'Post-classical cinema' is a term used to describe the changing methods of storytelling of the "New Hollywood" producers. The new methods of drama
Drama
Drama is the specific mode of fiction represented in performance. The term comes from a Greek word meaning "action" , which is derived from "to do","to act" . The enactment of drama in theatre, performed by actors on a stage before an audience, presupposes collaborative modes of production and a...
and characterization played upon audience expectations acquired during the classical/Golden Age period: story chronology may be scrambled, storylines may feature unsettling "twist endings", main characters may behave in a morally ambiguous fashion, and the lines between the antagonist
Antagonist
An antagonist is a character, group of characters, or institution, that represents the opposition against which the protagonist must contend...
and protagonist
Protagonist
A protagonist is the main character of a literary, theatrical, cinematic, or musical narrative, around whom the events of the narrative's plot revolve and with whom the audience is intended to most identify...
may be blurred. The beginnings of post-classical storytelling may be seen in 1940s and 1950s film noir
Film noir
Film noir is a cinematic term used primarily to describe stylish Hollywood crime dramas, particularly those that emphasize cynical attitudes and sexual motivations. Hollywood's classic film noir period is generally regarded as extending from the early 1940s to the late 1950s...
films, in films such as Rebel Without a Cause
Rebel Without a Cause
Rebel Without a Cause is a 1955 American drama film about emotionally confused suburban, middle-class teenagers. Directed by Nicholas Ray, it offered both social commentary and an alternative to previous films depicting delinquents in urban slum environments...
(1955), and in Hitchcock's Psycho
Psycho (1960 film)
Psycho is a 1960 American suspense/psychological horror film directed by Alfred Hitchcock and starring Janet Leigh and Anthony Perkins. The film is based on the screenplay by Joseph Stefano, who adapted it from the 1959 novel of the same name by Robert Bloch...
. 1971 marked the release of controversial films like Straw Dogs, A Clockwork Orange
A Clockwork Orange (film)
A Clockwork Orange is a 1971 film adaptation of Anthony Burgess's 1962 novel of the same name. It was written, directed and produced by Stanley Kubrick...
, The French Connection
The French Connection (film)
This article is about the 1971 film. For the British fashion label, see French Connection .The French Connection is a 1971 American crime film directed by William Friedkin. The film was adapted and fictionalized by Ernest Tidyman from the non-fiction book by Robin Moore...
and Dirty Harry
Dirty Harry
Dirty Harry is a 1971 American crime thriller produced and directed by Don Siegel, the first in the Dirty Harry series. Clint Eastwood plays the title role, in his first outing as San Francisco Police Department Inspector "Dirty" Harry Callahan....
. This sparked heated controversy over the perceived escalation of violence in cinema.
During the 1970s, a new group of American filmmakers emerged, such as Martin Scorsese
Martin Scorsese
Martin Charles Scorsese is an American film director, screenwriter, producer, actor, and film historian. In 1990 he founded The Film Foundation, a nonprofit organization dedicated to film preservation, and in 2007 he founded the World Cinema Foundation...
, Francis Ford Coppola
Francis Ford Coppola
Francis Ford Coppola is an American film director, producer and screenwriter. He is widely acclaimed as one of Hollywood's most innovative and influential film directors...
, Roman Polanski
Roman Polanski
Roman Polanski is a French-Polish film director, producer, writer and actor. Having made films in Poland, Britain, France and the USA, he is considered one of the few "truly international filmmakers."...
, Steven Spielberg
Steven Spielberg
Steven Allan Spielberg KBE is an American film director, screenwriter, producer, video game designer, and studio entrepreneur. In a career of more than four decades, Spielberg's films have covered many themes and genres. Spielberg's early science-fiction and adventure films were seen as an...
, George Lucas
George Lucas
George Walton Lucas, Jr. is an American film producer, screenwriter, and director, and entrepreneur. He is the founder, chairman and chief executive of Lucasfilm. He is best known as the creator of the space opera franchise Star Wars and the archaeologist-adventurer character Indiana Jones...
and Brian De Palma
Brian De Palma
Brian Russell De Palma is an American film director and writer. In a career spanning over 40 years, he is probably best known for his suspense and crime thriller films, including such box office successes as the horror film Carrie, Dressed to Kill, Scarface, The Untouchables, and Mission:...
. This coincided with the increasing popularity of the auteur theory
Auteur theory
In film criticism, auteur theory holds that a director's film reflects the director's personal creative vision, as if they were the primary "auteur"...
in film literature and the media, which posited that a film director's films express their personal vision and creative insights. The development of the auteur style of filmmaking helped to give these directors far greater control over their projects than would have been possible in earlier eras. This led to some great critical and commercial successes, like Scorsese's Taxi Driver
Taxi Driver
Taxi Driver is a 1976 American drama film directed by Martin Scorsese and written by Paul Schrader. The film is set in New York City, soon after the Vietnam War. The film stars Robert De Niro and features Jodie Foster, Harvey Keitel, and Cybill Shepherd. The film was nominated for four Academy...
, Coppola's The Godfather
The Godfather
The Godfather is a 1972 American epic crime film directed by Francis Ford Coppola, based on the 1969 novel by Mario Puzo. With a screenplay by Puzo, Coppola and an uncredited Robert Towne, the film stars Marlon Brando, Al Pacino, James Caan, Robert Duvall, Sterling Hayden, John Marley, Richard...
films, Polanski's Chinatown, Spielberg's Jaws
Jaws (film)
Jaws is a 1975 American horror-thriller film directed by Steven Spielberg and based on Peter Benchley's novel of the same name. In the story, the police chief of Amity Island, a fictional summer resort town, tries to protect beachgoers from a giant man-eating great white shark by closing the beach,...
and Close Encounters of the Third Kind
Close Encounters of the Third Kind
Close Encounters of the Third Kind is a 1977 science fiction film written and directed by Steven Spielberg. The film stars Richard Dreyfuss, François Truffaut, Melinda Dillon, Teri Garr, Bob Balaban, and Cary Guffey...
and George Lucas
George Lucas
George Walton Lucas, Jr. is an American film producer, screenwriter, and director, and entrepreneur. He is the founder, chairman and chief executive of Lucasfilm. He is best known as the creator of the space opera franchise Star Wars and the archaeologist-adventurer character Indiana Jones...
's Star Wars
Star Wars Episode IV: A New Hope
Star Wars Episode IV: A New Hope, originally released as Star Wars, is a 1977 American epic space opera film, written and directed by George Lucas. It is the first of six films released in the Star Wars saga: two subsequent films complete the original trilogy, while a prequel trilogy completes the...
. It also, however, resulted in some failures, including Peter Bogdanovich
Peter Bogdanovich
Peter Bogdanovich is an American film historian, director, writer, actor, producer, and critic. He was part of the wave of "New Hollywood" directors, which included William Friedkin, Brian De Palma, George Lucas, Martin Scorsese, Michael Cimino, and Francis Ford Coppola...
's At Long Last Love
At Long Last Love
At Long Last Love is an American motion picture musical that was released in 1975. It was written, produced and directed by Peter Bogdanovich and stars Burt Reynolds and Cybill Shepherd....
and Michael Cimino
Michael Cimino
Michael Cimino is an American film director, screenwriter, producer and author. He is best known for writing and directing Academy Award-winning The Deer Hunter and the infamous Heaven's Gate. His films are characterized by their striking visual style and controversial subject...
's hugely expensive Western epic Heaven's Gate
Heaven's Gate (film)
Heaven's Gate is a 1980 American epic Western film based on the Johnson County War, a dispute between land barons and European immigrants in Wyoming in the 1890s...
, which helped to bring about the demise of its backer, United Artists
United Artists
United Artists Corporation is an American film studio. The original studio of that name was founded in 1919 by D. W. Griffith, Charles Chaplin, Mary Pickford and Douglas Fairbanks....
.
The financial disaster of Heaven's Gate marking the end of the visionary "auteur" directors of the "New Hollywood", who had unrestrained creative and financial freedom to develop films. The phenomenal success in the 1970s of Jaws and Star Wars in particular, led to the rise of the modern "blockbuster
Blockbuster (entertainment)
Blockbuster, as applied to film or theatre, denotes a very popular or successful production. The entertainment industry use was originally theatrical slang referring to a particularly successful play but is now used primarily by the film industry...
". Hollywood studios increasingly focused on producing a smaller number of very large budget films with massive marketing and promotional campaigns. This trend had already been foreshadowed by the commercial success of disaster film
Disaster film
A disaster film is a film genre that has an impending or ongoing disaster as its subject...
s such as The Poseidon Adventure and The Towering Inferno
The Towering Inferno (film)
The Towering Inferno is a 1974 American action disaster film produced by Irwin Allen featuring an all-star cast led by Steve McQueen and Paul Newman.A co-production between Twentieth Century-Fox and Warner Bros...
.
During the mid-1970s, more pornographic theatres, euphemistically called "adult cinemas", were established, and the legal production of hardcore pornographic
Hardcore pornography
Hardcore pornography is a form of pornography that features explicit sexual acts. The term was coined in the second half of the 20th century to distinguish it from softcore pornography. It usually takes the form of photographs, often displayed in magazines or on the Internet, or films. It can also...
films began. Porn films such as Deep Throat
Deep Throat (film)
Deep Throat is a 1972 American pornographic film written and directed by Gerard Damiano and produced by Louis Peraino and starring Linda Lovelace ....
and its star Linda Lovelace
Linda Lovelace
Linda Susan Boreman , better known by her stage name Linda Lovelace, was an American pornographic actress who was famous for her performance of deep throat fellatio in the enormously successful 1972 hardcore porn film Deep Throat...
became something of a popular culture phenomenon and resulted in a spate of similar sex films. The porn cinemas finally died out during the 1980s, when the popularization of the home VCR and pornography videotapes allowed audiences to watch sex films at home. In the early 1970s, English-language audiences became more aware of the new West German cinema, with Werner Herzog
Werner Herzog
Werner Herzog Stipetić , known as Werner Herzog, is a German film director, producer, screenwriter, actor, and opera director.He is often considered as one of the greatest figures of the New German Cinema, along with Rainer Werner Fassbinder, Margarethe von Trotta, Volker Schlöndorff, Werner...
, Rainer Werner Fassbinder
Rainer Werner Fassbinder
Rainer Werner Maria Fassbinder was a German movie director, screenwriter and actor. He is considered one of the most important representatives of the New German Cinema.He maintained a frenetic pace in film-making...
and Wim Wenders
Wim Wenders
Ernst Wilhelm "Wim" Wenders is a German film director, playwright, author, photographer and producer.-Early life:Wenders was born in Düsseldorf. He graduated from high school in Oberhausen in the Ruhr area. He then studied medicine and philosophy in Freiburg and Düsseldorf...
among its leading exponents.
In world cinema
World cinema
World cinema is a term used primarily in English language speaking countries to refer to the films and film industries of non-English speaking countries. It is therefore often used interchangeably with the term foreign film...
, the 1970s saw a dramatic increase in the popularity of martial arts film
Martial arts film
Martial arts film is a film genre. A sub-genre of the action film, martial arts films contain numerous fights between characters, usually as the films' primary appeal and entertainment value, and often as a method of storytelling and character expression and development. Martial arts are frequently...
s, largely due to its reinvention by Bruce Lee
Bruce Lee
Bruce Lee was a Chinese American, Hong Kong actor, martial arts instructor, philosopher, film director, film producer, screenwriter, and founder of the Jeet Kune Do martial arts movement...
, who departed from the artistic style of traditional Chinese martial arts
Chinese martial arts
Chinese martial arts, also referred to by the Mandarin Chinese term wushu and popularly as kung fu , are a number of fighting styles that have developed over the centuries in China. These fighting styles are often classified according to common traits, identified as "families" , "sects" or...
films and added a much greater sense of realism to them with his Jeet Kune Do
Jeet Kune Do
Jeet Kune Do is a hybrid martial arts system and life philosophy founded by martial artist Bruce Lee with direct, non classical and straightforward movements. Due to the way his style works they believe in minimal movement with maximum effect and extreme speed. The system works on the use of...
style. This began with The Big Boss
The Big Boss
The Big Boss, previously known by its U.S. title Fists Of Fury is a 1971 Hong Kong martial arts action crime thriller film. The Big Boss was Bruce Lee's first major film. It was written to star James Tien; however, Lee's strong performance relegated Tien, already a star in Hong Kong, to second...
(1971), which was a major success across Asia
Asian cinema
Asian cinema refers to the film industries and films produced in the continent of Asia, and is also sometimes known as Eastern cinema. More commonly however, it is used to refer to the cinema of Eastern, Southeastern and Southern Asia. West Asian cinema is sometimes classified as part of Middle...
. However, he didn't gain fame in the Western world
Western world
The Western world, also known as the West and the Occident , is a term referring to the countries of Western Europe , the countries of the Americas, as well all countries of Northern and Central Europe, Australia and New Zealand...
until shortly after his death in 1973, when Enter the Dragon
Enter the Dragon
Enter the Dragon is a 1973 Hong Kong martial arts co-production with Golden Harvest and Warner Bros. studios, directed by Robert Clouse; starring Bruce Lee, Jim Kelly and John Saxon. This is Bruce Lee's final film appearance before his death on July 20, 1973...
was released. The film went on to become the most successful martial arts film in cinematic history, popularized the martial arts film genre across the world, and cemented Bruce Lee's status as a cultural icon. Hong Kong action cinema
Hong Kong action cinema
Hong Kong action cinema is the principal source of the Hong Kong film industry's global fame. It combines elements from the action film, as codified by Hollywood, with Chinese storytelling and aesthetic traditions, to create a culturally distinctive form that nevertheless has a wide transcultural...
, however, was in decline due to a wave of "Bruceploitation
Bruceploitation
Bruceploitation is a cultural phenomenon mostly seen in the 1970s after the 1973 death of martial artist and actor Bruce Lee. Movie makers in mainland China, Hong Kong and Taiwan hired a great number of Bruce Lee look-alike actors to star in many cheap knock-off martial arts movies to cash in on...
" films. This trend eventually came to an end in 1978 with the martial arts comedy film
Comedy film
Comedy film is a genre of film in which the main emphasis is on humour. They are designed to elicit laughter from the audience. Comedies are mostly light-hearted dramas and are made to amuse and entertain the audiences...
s, Snake in the Eagle's Shadow
Snake in the Eagle's Shadow
Snake in the Eagle's Shadow is a 1978 Hong Kong martial arts action film directed by Yuen Woo-ping his directorial debut, who has since gained international stardom as the action choreographer for films such as Iron Monkey, Fist of Legend, Crouching Tiger, Hidden Dragon, The Matrix series, Kill...
and Drunken Master
Drunken Master
Drunken Master, also known as Drunk Monkey In The Tiger's Eye, is a 1978 Hong Kong martial arts comedy film directed by Yuen Woo-ping, and starring Jackie Chan, Yuen Siu-tien, and Hwang Jang Lee...
, directed by Yuen Woo-ping
Yuen Woo-ping
Yuen Woo-ping is a Chinese martial arts choreographer and film director, renowned as one of the most successful and influential figures in the world of Hong Kong action cinema. He is one of the inductees on the Avenue of Stars in Hong Kong...
and starring Jackie Chan
Jackie Chan
Jackie Chan, SBS, MBE is a Hong Kong actor, action choreographer, comedian, director, producer, martial artist, screenwriter, entrepreneur, singer and stunt performer. In his movies, he is known for his acrobatic fighting style, comic timing, use of improvised weapons, and innovative stunts...
, laying the foundations for the rise of Hong Kong action cinema in the 1980s.
While the musical film
Musical film
The musical film is a film genre in which songs sung by the characters are interwoven into the narrative, sometimes accompanied by dancing. The songs usually advance the plot or develop the film's characters, though in some cases they serve merely as breaks in the storyline, often as elaborate...
genre had declined in Hollywood by this time, musical films were quickly gaining popularity in the cinema of India
Cinema of India
The cinema of India consists of films produced across India, which includes the cinematic culture of Andhra Pradesh, Assam, Gujarat, Haryana, Jammu and Kashmir, Karnataka, Kerala, Maharashtra, Orissa, Punjab, Tamil Nadu, and West Bengal. Indian films came to be followed throughout South Asia and...
, where the term "Bollywood
Bollywood
Bollywood is the informal term popularly used for the Hindi-language film industry based in Mumbai , Maharashtra, India. The term is often incorrectly used to refer to the whole of Indian cinema; it is only a part of the total Indian film industry, which includes other production centers producing...
" was coined for the growing Hindi
Hindi
Standard Hindi, or more precisely Modern Standard Hindi, also known as Manak Hindi , High Hindi, Nagari Hindi, and Literary Hindi, is a standardized and sanskritized register of the Hindustani language derived from the Khariboli dialect of Delhi...
film industry in Bombay
Mumbai
Mumbai , formerly known as Bombay in English, is the capital of the Indian state of Maharashtra. It is the most populous city in India, and the fourth most populous city in the world, with a total metropolitan area population of approximately 20.5 million...
(now Mumbai) that ended up dominating South Asian cinema
South Asian cinema
South Asian cinema refers to the cinema of India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Afghanistan, Sri Lanka, Nepal, Bhutan and the Maldives.The terms Asian cinema, Eastern cinema and Oriental cinema in common usage often encompass South Asia as well as East Asia and South East Asia...
, overtaking the more critically acclaimed Bengali film industry
Bengali cinema
Bengali cinema refers to the Bengali language filmmaking industries in the Bengal region of South Asia. There are two major film-making hubs in the region: one in Kolkata, West Bengal, India and the other in Dhaka, Bangladesh .The history of cinema in Bengal dates back to the 1890s, when the first...
in popularity. Hindi filmmakers combined the Hollywood musical formula with the conventions of ancient Indian theatre to create a new film genre called "Masala
Masala (film genre)
Masala is a term given to films of Indian cinema that mix various genres in one film. Typically these films freely mix action, comedy, romance, and drama or melodrama. These films tend to be musicals that include songs filmed in picturesque locations...
", which dominated Indian cinema throughout the late 20th century. These "Masala" films portrayed action
Action film
Action film is a film genre where one or more heroes is thrust into a series of challenges that require physical feats, extended fights and frenetic chases...
, comedy, drama
Drama film
A drama film is a film genre that depends mostly on in-depth development of realistic characters dealing with emotional themes. Dramatic themes such as alcoholism, drug addiction, infidelity, moral dilemmas, racial prejudice, religious intolerance, poverty, class divisions, violence against women...
, romance
Romance film
Romance films are love stories that focus on passion, emotion, and the affectionate involvement of the main characters and the journey that their love takes through courtship or marriage. Romance films make the love story or the search for love the main plot focus...
and melodrama
Melodrama
The term melodrama refers to a dramatic work that exaggerates plot and characters in order to appeal to the emotions. It may also refer to the genre which includes such works, or to language, behavior, or events which resemble them...
all at once, with "filmi
Filmi
Filmi is Indian popular music as written and performed for Indian cinema. Music directors make up the main body of composers; the songs are performed by playback singers and it makes up 72% of the music sales in India....
" song and dance routines thrown in. This trend began with films directed by Manmohan Desai
Manmohan Desai
Manmohan Desai was a producer and director of Indian movies.- Background :His father, Kikubhai Desai, was an Indian film producer and owner of Paramount Studios from 1931 to 1941. His productions, mainly stunt films, included Circus Queen, Golden Gang, and Sheikh Challi...
and starring Amitabh Bachchan
Amitabh Bachchan
Amitabh Bachchan is an Indian film actor. He first gained popularity in the early 1970s as the "angry young man" of Hindi cinema, and has since appeared in over 180 Indian films in a career spanning more than four decades...
, who remains one of the most popular film stars in South Asia
South Asia
South Asia, also known as Southern Asia, is the southern region of the Asian continent, which comprises the sub-Himalayan countries and, for some authorities , also includes the adjoining countries to the west and the east...
. The most popular Indian film of all time was Sholay
Sholay
Sholay is a 1975 Indian action-adventure film produced by G.P. Sippy and directed by his son Ramesh Sippy. It is considered among the greatest films in the history of Indian cinema. Released on 15 August 1975, it stars Dharmendra, Amitabh Bachchan, Hema Malini, Sanjeev Kumar, Jaya Bhaduri and...
(1975), a "Masala" film inspired by a real-life dacoit
Dacoity
Dacoity is a term used for "banditry" in India. The spelling is the anglicized version of the Hindi word and as a colloquial Anglo-Indian word with this meaning, also appears in the Glossary of Colloquial Anglo-Indian Words and Phrases Banditry is criminal activity involving robbery by groups of...
as well as Kurosawa's Seven Samurai and the Spaghetti Western
Spaghetti Western
Spaghetti Western, also known as Italo-Western, is a nickname for a broad sub-genre of Western films that emerged in the mid-1960s in the wake of Sergio Leone's unique and much copied film-making style and international box-office success, so named by American critics because most were produced and...
s.
The end of the decade saw the first major international marketing of Australian cinema, as Peter Weir
Peter Weir
Peter Lindsay Weir, AM is an Australian film director. After playing a leading role in the Australian New Wave cinema with his films such as Picnic at Hanging Rock, The Last Wave and Gallipoli, Weir directed a diverse group of American and international films—many of them major box office...
's films Picnic at Hanging Rock
Picnic at Hanging Rock (film)
Picnic at Hanging Rock is a 1975 Australian feature film directed by Peter Weir and starring Anne-Louise Lambert, Helen Morse, Rachel Roberts and Vivean Gray. The film is adapted from the novel of the same name, by author Joan Lindsay....
and The Last Wave
The Last Wave
The Last Wave is a 1977 Australian film directed by Peter Weir. It is about a white Australian lawyer whose seemingly normal life is disrupted after he takes on a murder case for Aborigine defendants...
and Fred Schepisi's The Chant of Jimmie Blacksmith
The Chant of Jimmie Blacksmith
The Chant of Jimmie Blacksmith is a 1972 Booker Prize-nominated novel by Thomas Keneally, and a 1978 Australian film of the same name directed by Fred Schepisi. The novel is based on the life of bushranger Jimmy Governor....
gained critical acclaim. In 1979, Australian filmmaker George Miller
George Miller (producer)
George Miller is an Australian film director, screenwriter, producer, and former medical doctor. He is most well known for his work on the Mad Max movies, but has been involved in a wide range of projects, including the Oscar-winning Happy Feet and "Babe" family films.Miller is the older brother...
also garnered international attention for his violent, low-budget action film Mad Max
Mad Max
Mad Max is a 1979 Australian dystopian action film directed by George Miller and revised by Miller and Byron Kennedy over the original script by James McCausland. The film stars Mel Gibson, who was unknown at the time. Its narrative based around the traditional western genre, Mad Max tells a story...
.
1980s: sequels, blockbusters and videotape
During the 1980s, audiences began increasingly watching films on their home VCRs. In the early part of that decade, the film studios tried legal action to ban home ownership of VCRs as a violation of copyrightCopyright
Copyright is a legal concept, enacted by most governments, giving the creator of an original work exclusive rights to it, usually for a limited time...
, which proved unsuccessful. Eventually, the sale and rental of films on home video
Home video
Home video is a blanket term used for pre-recorded media that is either sold or rented/hired for home cinema entertainment. The term originates from the VHS/Betamax era but has carried over into current optical disc formats like DVD and Blu-ray Disc and, to a lesser extent, into methods of digital...
became a significant "second venue" for exhibition of films, and an additional source of revenue for the film industries.
The Lucas
George Lucas
George Walton Lucas, Jr. is an American film producer, screenwriter, and director, and entrepreneur. He is the founder, chairman and chief executive of Lucasfilm. He is best known as the creator of the space opera franchise Star Wars and the archaeologist-adventurer character Indiana Jones...
-Spielberg
Steven Spielberg
Steven Allan Spielberg KBE is an American film director, screenwriter, producer, video game designer, and studio entrepreneur. In a career of more than four decades, Spielberg's films have covered many themes and genres. Spielberg's early science-fiction and adventure films were seen as an...
combine would dominate "Hollywood" cinema for much of the 1980s, and lead to much imitation. Two follow-ups to Star Wars
Star Wars Episode IV: A New Hope
Star Wars Episode IV: A New Hope, originally released as Star Wars, is a 1977 American epic space opera film, written and directed by George Lucas. It is the first of six films released in the Star Wars saga: two subsequent films complete the original trilogy, while a prequel trilogy completes the...
, three to Jaws
Jaws (film)
Jaws is a 1975 American horror-thriller film directed by Steven Spielberg and based on Peter Benchley's novel of the same name. In the story, the police chief of Amity Island, a fictional summer resort town, tries to protect beachgoers from a giant man-eating great white shark by closing the beach,...
, and three Indiana Jones
Indiana Jones
Colonel Henry Walton "Indiana" Jones, Jr., Ph.D. is a fictional character and the protagonist of the Indiana Jones franchise. George Lucas and Steven Spielberg created the character in homage to the action heroes of 1930s film serials...
films helped to make sequels of successful films more of an expectation than ever before. Lucas also launched THX Ltd
THX
THX is a trade name of a high-fidelity audio/visual reproduction standard for movie theaters, screening rooms, home theaters, computer speakers, gaming consoles, and car audio systems. The current THX was created in 2001 when it spun off from Lucasfilm Ltd...
, a division of Lucasfilm
Lucasfilm
Lucasfilm Limited is an American film production company founded by George Lucas in 1971, based in San Francisco, California. Lucas is the company's current chairman and CEO, and Micheline Chau is the president and COO....
in 1982, while Spielberg enjoyed one of the decade's greatest successes in E.T. the Extra-Terrestrial
E.T. the Extra-Terrestrial
E.T. the Extra-Terrestrial is a 1982 American science fiction film co-produced and directed by Steven Spielberg, written by Melissa Mathison and starring Henry Thomas, Dee Wallace, Robert MacNaughton, Drew Barrymore, and Peter Coyote...
the same year. 1982 also saw the release of Disney's Tron
Tron
-Film:*Tron , a franchise that began in 1982 with the Walt Disney Pictures film Tron** Tron , a 1982 science fiction film by Disney, starring Jeff Bridges, Bruce Boxleitner, Cindy Morgan, Dan Shor and David Warner...
which was one of the first films from a major studio to use computer graphics
Computer graphics
Computer graphics are graphics created using computers and, more generally, the representation and manipulation of image data by a computer with help from specialized software and hardware....
extensively. American independent cinema struggled more during the decade, although Martin Scorsese
Martin Scorsese
Martin Charles Scorsese is an American film director, screenwriter, producer, actor, and film historian. In 1990 he founded The Film Foundation, a nonprofit organization dedicated to film preservation, and in 2007 he founded the World Cinema Foundation...
's Raging Bull (1980), After Hours
After Hours (film)
After Hours is a 1985 American black comedy film, written by Joseph Minion and directed by Martin Scorsese. Paul Hackett , a New Yorker, experiences a series of adventures and perils in trying to make his way home from SoHo.-Plot:...
(1985), and The King of Comedy
The King of Comedy (1983 film)
The King of Comedy is a 1983 American dark comedy film starring Robert De Niro and Jerry Lewis, and directed by Martin Scorsese. The subject of the movie is celebrity stalking...
(1983) helped to establish him as one of the most critically acclaimed American film makers of the era. Also during 1983 Scarface
Scarface (1983 film)
Scarface is a 1983 American epic crime drama movie directed by Brian De Palma, written by Oliver Stone, produced by Martin Bregman and starring Al Pacino as Tony Montana...
was released, was very profitable and resulted in even greater fame for its leading actor Al Pacino
Al Pacino
Alfredo James "Al" Pacino is an American film and stage actor and director. He is famous for playing mobsters, including Michael Corleone in The Godfather trilogy, Tony Montana in Scarface, Alphonse "Big Boy" Caprice in Dick Tracy and Carlito Brigante in Carlito's Way, though he has also appeared...
. Probably the most successful film commercially was vended during 1989: Tim Burton
Tim Burton
Timothy William "Tim" Burton is an American film director, film producer, writer and artist. He is famous for dark, quirky-themed movies such as Beetlejuice, Edward Scissorhands, The Nightmare Before Christmas, Ed Wood, Sleepy Hollow, Corpse Bride and Sweeney Todd: The Demon Barber of Fleet...
's version of Bob Kane
Bob Kane
Bob Kane was an American comic book artist and writer, credited as the creator of the DC Comics superhero Batman...
's creation, Batman
Batman (1989 film)
Batman is a 1989 superhero film based on the DC Comics character of the same name, directed by Tim Burton. The film stars Michael Keaton in the title role, as well as Jack Nicholson, Kim Basinger, Robert Wuhl and Jack Palance...
, exceeded box-office records. Jack Nicholson
Jack Nicholson
John Joseph "Jack" Nicholson is an American actor, film director, producer and writer. He is renowned for his often dark portrayals of neurotic characters. Nicholson has been nominated for an Academy Award twelve times, and has won the Academy Award for Best Actor twice: for One Flew Over the...
's portrayal of the demented Joker
Joker (comics)
The Joker is a fictional character, a comic book supervillain published by DC Comics. He is the archenemy of Batman, having been directly responsible for numerous tragedies in Batman's life, including the paralysis of Barbara Gordon and the death of Jason Todd, the second Robin...
earned him a total of $60,000,000 after figuring in his percentage of the gross.
British cinema was given a boost during the early 1980s by the arrival of David Puttnam
David Puttnam
David Terence Puttnam, Baron Puttnam, CBE, FRSA is a British film producer. He sits on the Labour benches in the House of Lords, although he is not principally a politician.-Early life:...
's company Goldcrest Films
Goldcrest Films
Goldcrest Films is a British film production company founded by Jake Eberts in January 1977. It enjoyed great success in the 1980s with films such as Local Hero , The Killing Fields and Hope and Glory mostly produced by David Puttnam on modest budgets. The company also benefited from the new...
. The films Chariots of Fire
Chariots of Fire
Chariots of Fire is a 1981 British film. It tells the fact-based story of two athletes in the 1924 Olympics: Eric Liddell, a devout Scottish Christian who runs for the glory of God, and Harold Abrahams, an English Jew who runs to overcome prejudice....
, Gandhi
Gandhi (film)
Gandhi is a 1982 biographical film based on the life of Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi, who led the nonviolent resistance movement against British colonial rule in India during the first half of the 20th century. The film was directed by Richard Attenborough and stars Ben Kingsley as Gandhi. They both...
, The Killing Fields
The Killing Fields (film)
The Killing Fields is a 1984 British drama film about the Khmer Rouge regime in Cambodia, which is based on the experiences of two journalists: Cambodian Dith Pran and American Sydney Schanberg. The film, which won three Academy Awards, was directed by Roland Joffé and stars Sam Waterston as...
and A Room with a View
A Room with a View (film)
A Room with a View is a 1985 British drama film directed by James Ivory and produced by Ismail Merchant. The film is a close adaptation of E. M...
appealed to a "middlebrow" audience which was increasingly being ignored by the major Hollywood studios. While the films of the 1970s had helped to define modern blockbuster
Blockbuster (entertainment)
Blockbuster, as applied to film or theatre, denotes a very popular or successful production. The entertainment industry use was originally theatrical slang referring to a particularly successful play but is now used primarily by the film industry...
motion pictures, the way "Hollywood" released its films would now change. Films, for the most part, would premiere in a wider number of theatres, although, to this day, some films still premiere using the route of the limited/roadshow release system
Roadshow theatrical release
A roadshow theatrical release was a term in the American motion picture industry for a practice in which a film opened in a limited number of theaters in large cities like Los Angeles, New York, Chicago, Houston, Atlanta, Dallas, and San Francisco for a specific period of time before the...
. Against some expectations, the rise of the multiplex cinema did not allow less mainstream films to be shown, but simply allowed the major blockbusters to be given an even greater number of screenings. However, films that had been overlooked in cinemas were increasingly being given a second chance on home video.
During the 1980s, Japanese cinema experienced a revival, largely due to the success of anime
Anime
is the Japanese abbreviated pronunciation of "animation". The definition sometimes changes depending on the context. In English-speaking countries, the term most commonly refers to Japanese animated cartoons....
films. At the beginning of the 1980s, Space Battleship Yamato
Space Battleship Yamato
is a Japanese science fiction anime series featuring an eponymous spacecraft. It is also known to English-speaking audiences as Space Cruiser Yamato; an English-dubbed and heavily edited version of the series was broadcast on North American and Australian television as Star Blazers...
(1973) and Mobile Suit Gundam
Mobile Suit Gundam
is a televised anime series, created by Sunrise. Created and directed by Yoshiyuki Tomino, it premiered in Japan on Nagoya Broadcasting Network on April 7, 1979, and lasted until January 26, 1980, spanning 43 episodes...
(1979), both of which were unsuccessful as television series, were remade as films and became hugely successful in Japan. In particular, Mobile Suit Gundam sparked the Gundam
Gundam
The is a metaseries of anime created by Sunrise studios that features giant robots called "Mobile Suits" ; usually the protagonist's MS will carry the name Gundam....
franchise of Real Robot
Real Robot
is a genre of Japanese animation. The genre contains mecha robots that are powered by conventional power sources and weapons explainable by real world science, and that use ranged weapons and speed to survive battle situations....
mecha
Mecha
A mech , is a science fiction term for a large walking bipedal tank or robot, including ones on treads and animal shapes.-Characteristics:...
anime. The success of Macross: Do You Remember Love?
The Super Dimension Fortress Macross: Do You Remember Love?
, also known as The Super Dimension Fortress Macross: Do You Remember Love? or Super Spacefortress Macross , is a 1984 Japanese animated movie based around the Macross television series.The movie is a film adaptation of the original Macross series, with new animation...
also sparked a Macross
Macross
is a series of science fiction mecha anime, directed by Shōji Kawamori of Studio Nue in 1982. The franchise features a fictional history of Earth/Humanity after the year 1999. It consists of three TV series, four movies, six OVAs, one light novel and five manga series, all sponsored by Big West...
franchise of mecha anime. This was also the decade when Studio Ghibli
Studio Ghibli
is a Japanese animation and film studio founded in June 1985. The company's logo features the character Totoro from Hayao Miyazaki's film My Neighbor Totoro...
was founded. The studio produced Hayao Miyazaki
Hayao Miyazaki
is a Japanese manga artist and prominent film director and animator of many popular anime feature films. Through a career that has spanned nearly fifty years, Miyazaki has attained international acclaim as a maker of animated feature films and, along with Isao Takahata, co-founded Studio Ghibli,...
's first fantasy film
Fantasy film
Fantasy films are films with fantastic themes, usually involving magic, supernatural events, make-believe creatures, or exotic fantasy worlds. The genre is considered to be distinct from science fiction film and horror film, although the genres do overlap...
s, Nausicaä of the Valley of the Wind (1984) and Castle in the Sky
Castle in the Sky
All compositions by Joe Hisaishi.#"The Girl Who Fell from the Sky" – 2:27#"Morning in Slag Ravine" – 3:04#"A Fun Brawl " – 4:27#"Memories of Gondoa" – 2:46#"Discouraged Pazu" – 1:46#"Robot Soldier " – 2:34...
(1986), as well as Isao Takahata
Isao Takahata
is a Japanese anime filmmaker that have earned critical international acclaim for his work as a director. Takahata is co-founder of Studio Ghibli with long-time collaborative partner Hayao Miyazaki. He has directed films such as the war-themed Grave of the Fireflies, the romantic-drama Only...
's Grave of the Fireflies
Grave of the Fireflies
is a 1988 Japanese animated war tragedy film written and directed by Isao Takahata. This is the first film produced by Shinchosha, who hired Studio Ghibli to do the animation production work...
(1988), all of which were very successful in Japan and received worldwide critical acclaim. Original video animation
Original video animation
, abbreviated as media , are animated films and series made specially for release in home-video formats. The term originated in relation to Japanese animation...
(OVA) films also began during this decade; the most influential of these early OVA films was Noboru Ishiguro
Noboru Ishiguro
is a Japanese animator who is noteworthy for directing the anime series The Super Dimension Fortress Macross, The Super Dimension Century Orguss, Yōkai Ningen Bem, Megazone 23, Legend of the Galactic Heroes, Noozles, and the 2008 completed series Tytania.He was in a hawaiian style music band in his...
's cyberpunk
Cyberpunk
Cyberpunk is a postmodern and science fiction genre noted for its focus on "high tech and low life." The name is a portmanteau of cybernetics and punk, and was originally coined by Bruce Bethke as the title of his short story "Cyberpunk," published in 1983...
film Megazone 23
Megazone 23
is a four-part original video animation created by AIC, written by Hiroyuki Hoshiyama, and directed by Noboru Ishiguro, Ichiro Itano, Kenichi Yatagai and Shinji Aramaki. The series was originally titled but the title was changed just before release....
(1985). The most famous anime film of this decade was Katsuhiro Otomo
Katsuhiro Otomo
is a Japanese comic book creator, screenwriter and film director. He is best known as the creator of the manga Akira and its animated film adaptation. Otomo has also directed several live-action films, such as the 2006 feature film adaptation of the manga Mushishi.-Biography:Katsuhiro Otomo was...
's cyberpunk film Akira
Akira (film)
is a 1988 Japanese animated cyberpunk science fiction film directed by Katsuhiro Otomo, written by Otomo and Izo Hashimoto, and starring the voices of Mitsuo Iwata, Nozomu Sasaki, Mami Koyama and Taro Ishida. The screenplay is based on Otomo's manga Akira....
(1988), which although initially unsuccessful at Japanese theaters, went on to become an international success.
Hong Kong action cinema
Hong Kong action cinema
Hong Kong action cinema is the principal source of the Hong Kong film industry's global fame. It combines elements from the action film, as codified by Hollywood, with Chinese storytelling and aesthetic traditions, to create a culturally distinctive form that nevertheless has a wide transcultural...
, which was in a state of decline due to endless Bruceploitation
Bruceploitation
Bruceploitation is a cultural phenomenon mostly seen in the 1970s after the 1973 death of martial artist and actor Bruce Lee. Movie makers in mainland China, Hong Kong and Taiwan hired a great number of Bruce Lee look-alike actors to star in many cheap knock-off martial arts movies to cash in on...
films after the death of Bruce Lee
Bruce Lee
Bruce Lee was a Chinese American, Hong Kong actor, martial arts instructor, philosopher, film director, film producer, screenwriter, and founder of the Jeet Kune Do martial arts movement...
, also experienced a revival in the 1980s, largely due to the reinvention of the action film
Action film
Action film is a film genre where one or more heroes is thrust into a series of challenges that require physical feats, extended fights and frenetic chases...
genre by Jackie Chan
Jackie Chan
Jackie Chan, SBS, MBE is a Hong Kong actor, action choreographer, comedian, director, producer, martial artist, screenwriter, entrepreneur, singer and stunt performer. In his movies, he is known for his acrobatic fighting style, comic timing, use of improvised weapons, and innovative stunts...
. He had previously combined the comedy film
Comedy film
Comedy film is a genre of film in which the main emphasis is on humour. They are designed to elicit laughter from the audience. Comedies are mostly light-hearted dramas and are made to amuse and entertain the audiences...
and martial arts film
Martial arts film
Martial arts film is a film genre. A sub-genre of the action film, martial arts films contain numerous fights between characters, usually as the films' primary appeal and entertainment value, and often as a method of storytelling and character expression and development. Martial arts are frequently...
genres successfully in the 1978 films Snake in the Eagle's Shadow
Snake in the Eagle's Shadow
Snake in the Eagle's Shadow is a 1978 Hong Kong martial arts action film directed by Yuen Woo-ping his directorial debut, who has since gained international stardom as the action choreographer for films such as Iron Monkey, Fist of Legend, Crouching Tiger, Hidden Dragon, The Matrix series, Kill...
and Drunken Master
Drunken Master
Drunken Master, also known as Drunk Monkey In The Tiger's Eye, is a 1978 Hong Kong martial arts comedy film directed by Yuen Woo-ping, and starring Jackie Chan, Yuen Siu-tien, and Hwang Jang Lee...
. The next step he took was in combining this comedy martial arts genre with a new emphasis on elaborate and highly dangerous stunt
Stunt
A stunt is an unusual and difficult physical feat, or any act requiring a special skill, performed for artistic purposes in TV, theatre, or cinema...
s, reminiscent of the silent film
Silent film
A silent film is a film with no synchronized recorded sound, especially with no spoken dialogue. In silent films for entertainment the dialogue is transmitted through muted gestures, pantomime and title cards...
era. The first film in this new style of action cinema was Project A
Project A
Project A is a 1983 Hong Kong martial arts action comedy film written and directed by Jackie Chan, and starring Chan, Sammo Hung and Yuen Biao....
(1983), which saw the formation of the Jackie Chan Stunt Team
Jackie Chan Stunt Team
The Jackie Chan Stunt Team , also known as Jackie Chan's Stuntmen Association is a group of stuntmen and martial artists who work alongside Jackie Chan.-History:...
as well as the "Three Brothers" (Chan, Sammo Hung
Sammo Hung
Sammo Hung is a Hong Kong actor, martial artist, film producer and director, known for his work in many martial arts films and Hong Kong action cinema...
and Yuen Biao
Yuen Biao
Yuen Biao is a Hong Kong actor, martial artist. He specialises in acrobatics and Chinese martial arts and has worked on over 80 films as actor, stuntman and action choreographer...
). The film added elaborate, dangerous stunts to the fights and slapstick
Slapstick
Slapstick is a type of comedy involving exaggerated violence and activities which may exceed the boundaries of common sense.- Origins :The phrase comes from the batacchio or bataccio — called the 'slap stick' in English — a club-like object composed of two wooden slats used in Commedia dell'arte...
humor, and became a huge success throughout the Far East
Far East
The Far East is an English term mostly describing East Asia and Southeast Asia, with South Asia sometimes also included for economic and cultural reasons.The term came into use in European geopolitical discourse in the 19th century,...
. As a result, Chan continued this trend with martial arts action films containing even more elaborate and dangerous stunts, including Wheels on Meals
Wheels on Meals
Wheels on Meals is a 1984 Hong Kong martial arts action film written and directed by Sammo Hung. Starring in the film are Hung, Jackie Chan and Yuen Biao...
(1984), Police Story
Police Story (film)
Police Story is a 1985 Hong Kong martial arts action comedy film directed by and starring Jackie Chan and written by Chan and Edward Tang. It is the first of the Police Story series featuring Chan as a Hong Kong police detective named "Kevin" Chan Ka-Kui.Chan began work on the film after a...
(1985), Armour of God (1986), Project A Part II
Project A Part II
Project A Part II is a 1987 Hong Kong martial arts action film directed by and starring Jackie Chan which serves as a sequel to his massive Asian hit film Project A...
(1987), Police Story 2
Police Story 2
Police Story 2 is a 1988 Hong Kong martial arts action comedy film directed by and starring Jackie Chan...
(1988), and Dragons Forever
Dragons Forever
Dragons Forever is a 1988 Hong Kong martial arts action comedy film directed by Sammo Hung. Film stars Hung, Jackie Chan and Yuen Biao. The three actors, known colloquially as the Three Brothers, had attended the famous China Drama Academy together, and became members of the Seven Little Fortunes...
(1988). Other new trends which began in the 1980s were the "girls with guns
Girls with guns
Girls with guns is a sub-genre of films and animation, especially Hong Kong action films and anime, with a female protagonist in a strong lead role, set in a modern context. The genre involves gun-play, stunts and martial arts action...
" sub-genre, for which Michelle Yeoh
Michelle Yeoh
Michelle Yeoh Choo-Kheng is a Hong Kong-based Malaysian Chinese actress, well known for performing her own stunts in the action films that brought her to fame in the early 1990s....
gained fame; and especially the "heroic bloodshed
Heroic bloodshed
Heroic Bloodshed is a genre of Hong Kong action cinema revolving around stylized action sequences and dramatic themes such as brotherhood, duty, honour, redemption and violence. The term heroic bloodshed was coined by editor Rick Baker in the magazine Eastern Heroes in the late 1980s, specifically...
" genre, revolving around Triads, largely pioneered by John Woo
John Woo
John Woo Yu-Sen SBS is a Hong Kong-based film director and producer. Recognized for his stylised films of highly choreographed action sequences, Mexican standoffs, and use of slow-motion, Woo has directed several notable Hong Kong action films, among them, A Better Tomorrow, The Killer, Hard...
and for which Chow Yun-fat
Chow Yun-Fat
Chow Yun-fat, SBS is an actor from Hong Kong. He is best known in Asia for his collaboration with filmmaker John Woo in heroic bloodshed genre films A Better Tomorrow, The Killer, and Hard Boiled; and to the West for his role as Li Mu-bai in Crouching Tiger, Hidden Dragon...
became famous. These Hong Kong action trends were later adopted by many Hollywood action films in the 1990s and 2000s.
1990s: New special effects, independent films, and DVDs

Terminator 2: Judgment Day
Terminator 2: Judgment Day is a 1991 science fiction action film directed by James Cameron and written by Cameron and William Wisher Jr.. It stars Arnold Schwarzenegger, Linda Hamilton, Robert Patrick, and Edward Furlong...
(1991), Jurassic Park
Jurassic Park (film)
Jurassic Park is a 1993 American science fiction adventure film directed by Steven Spielberg. The film is based on the novel of the same name by Michael Crichton. It stars Sam Neill, Laura Dern, Jeff Goldblum, Richard Attenborough, Martin Ferrero, and Bob Peck...
(1993) and Titanic
Titanic (1997 film)
Titanic is a 1997 American epic romance and disaster film directed, written, co-produced, and co-edited by James Cameron. A fictionalized account of the sinking of the RMS Titanic, it stars Leonardo DiCaprio as Jack Dawson, Kate Winslet as Rose DeWitt Bukater and Billy Zane as Rose's fiancé, Cal...
(1997), independent films like Steven Soderbergh
Steven Soderbergh
Steven Andrew Soderbergh is an American film producer, screenwriter, cinematographer, editor, and an Academy Award-winning film director. He is best known for directing commercial Hollywood films like Erin Brockovich, Traffic, and the remake of Ocean's Eleven, but he has also directed smaller less...
's sex, lies, and videotape
Sex, lies, and videotape
Sex, Lies, and Videotape is a 1989 independent film that brought director Steven Soderbergh to prominence. It tells the story of a man who films women discussing their sexuality, and his impact on the relationship of a troubled married couple....
(1989) and Quentin Tarantino
Quentin Tarantino
Quentin Jerome Tarantino is an American film director, screenwriter, producer, cinematographer and actor. In the early 1990s, he began his career as an independent filmmaker with films employing nonlinear storylines and the aestheticization of violence...
's Reservoir Dogs
Reservoir Dogs
Reservoir Dogs is an American crime film marking debut of director and writer Quentin Tarantino. It depicts the events before and after a botched diamond heist, but not the heist itself. Reservoir Dogs stars an ensemble cast: Harvey Keitel, Steve Buscemi, Tim Roth, Michael Madsen, Chris Penn, and...
(1992) had significant commercial success both at the cinema and on home video. Filmmakers associated with the Danish filmmovement Dogme 95
Dogme 95
Dogme 95 was an avant-garde filmmaking movement started in 1995 by the Danish directors Lars von Trier and Thomas Vinterberg, who created the "Dogme 95 Manifesto" and the "Vow of Chastity". These were rules to create filmmaking based on the traditional values of story, acting, and theme, and...
introduced a manifesto aimed to purify filmmaking. Its first few films gained worldwide critical acclaim, after which the movement slowly faded out.
Major American studios began to create their own "independent" production companies
Independent film
An independent film, or indie film, is a professional film production resulting in a feature film that is produced mostly or completely outside of the major film studio system. In addition to being produced and distributed by independent entertainment companies, independent films are also produced...
to finance and produce non-mainstream fare. One of the most successful independents of the 1990s, Miramax Films
Miramax Films
Miramax Films is an American entertainment company known for distributing independent and foreign films. For its first 14 years the company was privately owned by its founders, Bob and Harvey Weinstein...
, was bought by Disney the year before the release of Tarantino's runaway hit Pulp Fiction
Pulp Fiction (film)
Pulp Fiction is a 1994 American crime film directed by Quentin Tarantino, who co-wrote its screenplay with Roger Avary. The film is known for its rich, eclectic dialogue, ironic mix of humor and violence, nonlinear storyline, and host of cinematic allusions and pop culture references...
in 1994. The same year marked the beginning of film and video distribution online. Animated films aimed at family audiences also regained their popularity, with Disney's Beauty and the Beast
Beauty and the Beast (1991 film)
Beauty and the Beast is a 1991 American animated fantasy film produced by Walt Disney Animation Studios and distributed by Walt Disney Pictures. The thirtieth film in the Walt Disney Animated Classics series and the third film of the Disney Renaissance period...
(1991), Aladdin (1992), and The Lion King
The Lion King
The Lion King is a 1994 American animated film produced by Walt Disney Feature Animation and released by Walt Disney Pictures. It is the 32nd feature in the Walt Disney Animated Classics series...
(1994). During 1995 the first feature length computer-animated
Computer animation
Computer animation is the process used for generating animated images by using computer graphics. The more general term computer generated imagery encompasses both static scenes and dynamic images, while computer animation only refers to moving images....
feature, Toy Story
Toy Story
Toy Story is a 1995 American computer-animated film released by Walt Disney Pictures. It is Pixar's first feature film as well as the first ever feature film to be made entirely with CGI. The film was directed by John Lasseter and featuring the voices of Tom Hanks and Tim Allen...
, was produced by Pixar Animation Studios
Pixar
Pixar Animation Studios, pronounced , is an American computer animation film studio based in Emeryville, California. The studio has earned 26 Academy Awards, seven Golden Globes, and three Grammy Awards, among many other awards and acknowledgments. Its films have made over $6.3 billion worldwide...
and released by Disney. After the success of Toy Story, computer animation would grow to become the dominant technique for feature length animation, which would allow competing film companies such as Dreamworks Animation
DreamWorks Animation
DreamWorks Animation SKG, Inc. is an American animation studio based in Glendale, California that creates animated feature films, television program and online virtual worlds...
and 20th Century Fox
20th Century Fox
Twentieth Century Fox Film Corporation — also known as 20th Century Fox, or simply 20th or Fox — is one of the six major American film studios...
to effectively compete with Disney with successful films of their own. During the late 1990s, another cinematic transition began, from physical film stock to digital cinema
Digital cinema
Digital cinema refers to the use of digital technology to distribute and project motion pictures. A movie can be distributed via hard drives, optical disks or satellite and projected using a digital projector instead of a conventional film projector...
technology. Meanwhile DVD
DVD
A DVD is an optical disc storage media format, invented and developed by Philips, Sony, Toshiba, and Panasonic in 1995. DVDs offer higher storage capacity than Compact Discs while having the same dimensions....
s became the new standard for consumer video, replacing VHS tapes.
2000s

Documentary film
Documentary films constitute a broad category of nonfictional motion pictures intended to document some aspect of reality, primarily for the purposes of instruction or maintaining a historical record...
also rose as a commercial genre for perhaps the first time, with the success of films such as March of the Penguins
March of the Penguins
March of the Penguins is a 2005 French nature documentary film. It was directed and co-written by Luc Jacquet, and co-produced by Bonne Pioche and the National Geographic Society. The film depicts the yearly journey of the emperor penguins of Antarctica...
and Michael Moore
Michael Moore
Michael Francis Moore is an American filmmaker, author, social critic and activist. He is the director and producer of Fahrenheit 9/11, which is the highest-grossing documentary of all time. His films Bowling for Columbine and Sicko also place in the top ten highest-grossing documentaries...
's Bowling for Columbine
Bowling for Columbine
Bowling for Columbine is a 2002 documentary film written, directed, produced, and narrated by Michael Moore. The film explores what Michael Moore suggests are the causes for the Columbine High School massacre and other acts of violence with guns...
and Fahrenheit 9/11
Fahrenheit 9/11
Fahrenheit 9/11 is a 2004 documentary film by American filmmaker and political commentator Michael Moore. The film takes a critical look at the presidency of George W. Bush, the War on Terror, and its coverage in the news media...
. A new genre was created with Martin Kunert
Martin Kunert
Martin Kunert is a founding partner of Booya Studios and a feature film and television writer, director and producer. In 2004, Kunert conceived and directed the critically acclaimed documentary Voices of Iraq, made by sending 150 DV cameras to Iraqis to film their own lives...
and Eric Manes
Eric Manes
Eric Manes is a writer and producer in the film and television industry. As a producer, Manes made the groundbreaking documentary Voices of Iraq.-Biography:...
' Voices of Iraq
Voices of Iraq
Voices of Iraq is a 2004 documentary film about Iraq, created by distributing cameras to the subjects of a film, thus enabling subjects to film themselves...
, when 150 inexpensive DV cameras were distributed across Iraq, transforming ordinary people into collaborative filmmakers. The success of Gladiator
Gladiator (2000 film)
Gladiator is a 2000 historical epic film directed by Ridley Scott, starring Russell Crowe, Joaquin Phoenix, Connie Nielsen, Ralf Möller, Oliver Reed, Djimon Hounsou, Derek Jacobi, John Shrapnel and Richard Harris. Crowe portrays the loyal Roman General Maximus Decimus Meridius, who is betrayed...
lead to a revival of interest in epic cinema
Epic film
An epic is a genre of film that emphasizes human drama on a grand scale. Epics are more ambitious in scope than other film genres, and their ambitious nature helps to differentiate them from similar genres such as the period piece or adventure film...
, and Moulin Rouge!
Moulin Rouge!
Moulin Rouge! is a 2001 romantic jukebox musical film directed, produced, and co-written by Baz Luhrmann. Following the Red Curtain Cinema principles, the film is based on the Orphean myth, La Traviata, and La Bohème...
renewed interest in musical cinema
Musical film
The musical film is a film genre in which songs sung by the characters are interwoven into the narrative, sometimes accompanied by dancing. The songs usually advance the plot or develop the film's characters, though in some cases they serve merely as breaks in the storyline, often as elaborate...
. Home theatre
Home cinema
Home cinema, also commonly called home theater, are home entertainment set-ups that seek to reproduce a movie theater experience and mood with the help of video and audio equipment in a private home....
systems became increasingly sophisticated, as did some of the special edition DVD
DVD
A DVD is an optical disc storage media format, invented and developed by Philips, Sony, Toshiba, and Panasonic in 1995. DVDs offer higher storage capacity than Compact Discs while having the same dimensions....
s designed to be shown on them. The Lord of the Rings trilogy
The Lord of the Rings film trilogy
The Lord of the Rings is an epic film trilogy consisting of three fantasy adventure films based on the three-volume book of the same name by English author J. R. R. Tolkien. The films are The Fellowship of the Ring , The Two Towers and The Return of the King .The films were directed by Peter...
was released on DVD in both the theatrical version and in a special extended version intended only for home cinema audiences.
There is a growing problem of digital distribution
Digital distribution
Online distribution, digital distribution, or electronic software distribution is the practice of delivering content without the use of physical media, typically by downloading via the internet directly to a consumer's device. Online distribution bypasses conventional physical distribution media,...
to be overcome with regards to expiration of copyrights, content security, and enforcing copyright. There is higher compression for films, and Moore's law
Moore's Law
Moore's law describes a long-term trend in the history of computing hardware: the number of transistors that can be placed inexpensively on an integrated circuit doubles approximately every two years....
allows for increasingly cheaper technology.
More films were also being released simultaneously to IMAX
IMAX
IMAX is a motion picture film format and a set of proprietary cinema projection standards created by the Canadian company IMAX Corporation. IMAX has the capacity to record and display images of far greater size and resolution than conventional film systems...
cinema, the first was in 2002's Disney animation Treasure Planet
Treasure Planet
Treasure Planet is a 2002 animated science fiction film produced by Walt Disney Animation Studios, and released by Walt Disney Pictures on November 27, 2002...
; and the first live action was in 2003's The Matrix Revolutions
The Matrix Revolutions
The Matrix Revolutions is a 2003 American science fiction film and the third installment of The Matrix trilogy. The film was released six months following The Matrix Reloaded. The film was written and directed by the Wachowski brothers and released simultaneously in sixty countries on November 5,...
and a re-release of The Matrix Reloaded
The Matrix Reloaded
The Matrix Reloaded is a 2003 American science fiction film and the second installment in The Matrix trilogy, written and directed by the Wachowskis. It premiered on May 7, 2003, in Westwood, Los Angeles, California, and went on general release by Warner Bros. in North American theaters on May 15,...
. Later in the decade, The Dark Knight
The Dark Knight (film)
The Dark Knight is a 2008 superhero film directed, produced and co-written by Christopher Nolan. Based on the DC Comics character Batman, the film is part of Nolan's Batman film series and a sequel to 2005's Batman Begins...
was the first major feature film to have been at least partially shot in IMAX technology.
There has been an increasing globalization of cinema during this decade, with foreign-language films gaining popularity in English-speaking markets. Examples of such films include Crouching Tiger, Hidden Dragon
Crouching Tiger, Hidden Dragon
Crouching Tiger, Hidden Dragon is a 2000 wuxia film. An American-Chinese-Hong Kong-Taiwanese co-production, the film was directed by Ang Lee and featured an international cast of ethnic Chinese actors, including Chow Yun-Fat, Michelle Yeoh, Zhang Ziyi, and Chang Chen...
(Mandarin), Amelie
Amélie
Amélie is a 2001 romantic comedy film directed by Jean-Pierre Jeunet. Written by Jeunet with Guillaume Laurant, the film is a whimsical depiction of contemporary Parisian life, set in Montmartre...
(French), Lagaan
Lagaan
Lagaan is a 2001 Bollywood sports film written and directed by Ashutosh Gowariker. Aamir Khan, who was also the producer for the film, stars with Gracy Singh in the lead roles; British actors Rachel Shelley and Paul Blackthorne play the supporting roles...
(Hindi), Spirited Away
Spirited Away
is a 2001 Japanese animated fantasy-adventure film written and directed by Hayao Miyazaki and produced by Studio Ghibli. The film tells the story of Chihiro Ogino, a sullen ten-year-old girl who, while moving to a new neighborhood and after her parents are transformed into pigs by the witch Yubaba,...
(Japanese), City of God (Portuguese), The Passion of the Christ
The Passion of the Christ
The Passion of the Christ is a 2004 American drama film directed by Mel Gibson and starring Jim Caviezel as Jesus. It depicts the Passion of Jesus largely according to the New Testament Gospels of Matthew, Mark, Luke and John...
(Aramaic), Apocalypto
Apocalypto
Apocalypto is a 2006 American epic action-adventure film directed by Mel Gibson. Set in Yucatan, Mexico, during the declining period of the Maya civilization, Apocalypto depicts the journey of a Mesoamerican tribesman who must escape human sacrifice and rescue his family after the capture and...
(Mayan), Slumdog Millionaire
Slumdog Millionaire
Slumdog Millionaire is a 2008 British epic romantic drama adventure film directed by Danny Boyle, written by Simon Beaufoy, and co-directed in India by Loveleen Tandan. It is an adaptation of the novel Q & A by Indian author and diplomat Vikas Swarup...
(a third in Hindi), and Inglourious Basterds (multiple languages).
Recently there has been a revival in 3D film popularity the first being James Cameron's Ghosts of the Abyss
Ghosts of the Abyss
Ghosts of the Abyss is a 2003 documentary film released by Walt Disney Pictures and Walden Media. It was Disney's first film produced in 3-D and was directed by Academy Award winning filmmaker James Cameron after his Oscar winning film Titanic...
which was released as the first full-length 3-D IMAX feature filmed with the Reality Camera System. This camera system used the latest HD video cameras, not film, and was built for Cameron by Emmy nominated Director of Photography Vince Pace, to his specifications. The same camera system was used to film Spy Kids 3D: Game Over (2003), Aliens of the Deep
Aliens of the Deep
Aliens of the Deep is a 2005 documentary film, directed in part by James Cameron alongside fellow cameraman Steven Quale, who would later go on to direct Final Destination 5 six years later, and filmed in the IMAX 3D format. It was produced by Walden Media and Walt Disney Pictures...
IMAX (2005), and The Adventures of Sharkboy and Lavagirl in 3-D
The Adventures of Sharkboy and Lavagirl in 3-D
The Adventures of Sharkboy and Lavagirl in 3-D , is a 2005 adventure and fantasy film directed by Robert Rodriguez. The film uses the same anaglyph 3-D technology used in Spy Kids 3D: Game Over. The film stars Taylor Lautner, Cayden Boyd, Taylor Dooley and George Lopez...
(2005).
2010s
After James Cameron's 3D film Avatar became the highest-grossing film of all time, 3D films have gained increasing popularity with many other films being released in 3D, with the best critical and financial successes being in the field of feature film animation such as DreamWorks AnimationDreamWorks Animation
DreamWorks Animation SKG, Inc. is an American animation studio based in Glendale, California that creates animated feature films, television program and online virtual worlds...
's How To Train Your Dragon
How to Train Your Dragon (film)
How to Train Your Dragon is a 2010 3D computer-animated action fantasy film by DreamWorks Animation loosely based on the 2003 book of the same name. The film stars the voices of Jay Baruchel, Gerard Butler, Craig Ferguson, America Ferrera, Jonah Hill, T.J. Miller, Kristen Wiig, and Christopher...
and Walt Disney Pictures
Walt Disney Pictures
Walt Disney Pictures is an American film studio owned by The Walt Disney Company. Walt Disney Pictures and Television, a subsidiary of the Walt Disney Studios and the main production company for live-action feature films within the Walt Disney Motion Pictures Group, based at the Walt Disney...
/Pixar
Pixar
Pixar Animation Studios, pronounced , is an American computer animation film studio based in Emeryville, California. The studio has earned 26 Academy Awards, seven Golden Globes, and three Grammy Awards, among many other awards and acknowledgments. Its films have made over $6.3 billion worldwide...
's Toy Story 3
Toy Story 3
Toy Story 3 is a 2010 American 3D computer-animated comedy-adventure film, and the third installment in the Toy Story series. It was produced by Pixar and released by Walt Disney Pictures. It was directed by Lee Unkrich. The film was released worldwide from June through October in Disney Digital...
.
As of 2010, the largest film industries by number of feature films produced are those of India, the United States and China.
The Long Tail
One major new development in the early 21st century is the development of systems that make it much easier for regular people to write, shoot, edit and distribute their own films without the large apparatus of the film industry. This phenomenon and its repercussions are outlined in Chris Anderson's theory, The Long TailThe Long Tail
The Long Tail or long tail refers to the statistical property that a larger share of population rests within the tail of a probability distribution than observed under a 'normal' or Gaussian distribution...
.
The underground
Alongside the Hollywood tradition, there has also been an "underground filmUnderground film
An underground film is a film that is out of the mainstream either in its style, genre, or financing.-Definition and history:The first use of the term "underground film" occurs in a 1957 essay by American film critic Manny Farber, "Underground Films." Farber uses it to refer to the work of...
" tradition of small-budget, often self-produced works created outside of the studio system and without the involvement of labor unions.
See also
- B film
- Cinema of the world
- Culture history
- Experimental filmExperimental filmExperimental film or experimental cinema is a type of cinema. Experimental film is an artistic practice relieving both of visual arts and cinema. Its origins can be found in European avant-garde movements of the twenties. Experimental cinema has built its history through the texts of theoreticians...
- Fictional filmFictional filmFictional film or narrative film is film that tells a fictional story or narrative. Narrative cinema is usually contrasted to films that present information, such as a nature documentary, as well as to some experimental films...
- Film & HistoryFilm & HistoryFilm & History: An Interdisciplinary Journal is a peer-reviewed academic journal dedicated to the interdisciplinary study of film, television, and other moving-image arts. The editor-in-chief is Loren P. Q. Baybrook.-External links:...
- Film noirFilm noirFilm noir is a cinematic term used primarily to describe stylish Hollywood crime dramas, particularly those that emphasize cynical attitudes and sexual motivations. Hollywood's classic film noir period is generally regarded as extending from the early 1940s to the late 1950s...
- History of science fiction filmsHistory of science fiction filmsThe history of science fiction films parallels that of the motion picture industry as a whole, although it took several decades before the genre was taken seriously. Since the 1960s, major science fiction films have succeeded in pulling in large audience shares, and films of this genre have become...
- Kammerspielfilm
- List of film formats
- List of years in film
- Lists of film topics
- NewsreelNewsreelA newsreel was a form of short documentary film prevalent in the first half of the 20th century, regularly released in a public presentation place and containing filmed news stories and items of topical interest. It was a source of news, current affairs and entertainment for millions of moviegoers...
- Runaway productionRunaway productionRunaway production is a term used by the American film industry to describe filmmaking and television productions that are "intended for initial release/exhibition or television broadcast in the U.S., but are actually filmed in another country."...
- Silent filmSilent filmA silent film is a film with no synchronized recorded sound, especially with no spoken dialogue. In silent films for entertainment the dialogue is transmitted through muted gestures, pantomime and title cards...
- Sound filmSound filmA sound film is a motion picture with synchronized sound, or sound technologically coupled to image, as opposed to a silent film. The first known public exhibition of projected sound films took place in Paris in 1900, but decades would pass before sound motion pictures were made commercially...
- Women's cinemaWomen's cinemaThe term women's cinema usually refers to films made by women. Above all, it designates the work of women film directors and, to a lesser degree, the work of other women behind the camera such as cinematographers and screenwriters...
Further reading
- Abel, Richard. The Cine Goes to Town: French Cinema 1896-1914University of California PressUniversity of California PressUniversity of California Press, also known as UC Press, is a publishing house associated with the University of California that engages in academic publishing. It was founded in 1893 to publish books and papers for the faculty of the University of California, established 25 years earlier in 1868...
, 1998. - Acker, Ally. Reel Women: Pioneers of the Cinema, 1896 to the Present. London: B.T. Batsford, 1991.
- Barnes, John. The Cinema in England: 1894-1901 (5 Volumes) University of Exeter Press, 1997.
- Basten, Fred E. Glorious Technicolor: The Movies' Magic Rainbow. AS Barnes & Company, 1980.
- Bowser, Eileen. The Transformation of Cinema 1907-1915 (History of the American Cinema, Vol. 2) Charles Scribner's Sons, 1990.
- Cook, David A. A History of Narrative Film, 2nd edition. New York: W. W. NortonW. W. NortonW. W. Norton & Company is an independent American book publishing company based in New York City. It is well known for its "Norton Anthologies", particularly the Norton Anthology of English Literature and the "Norton Critical Editions" series of texts which are frequently assigned in university...
, 1990. - Cousins, Mark. The Story of Film: A Worldwide History, New York: Thunder's Mouth press, 2006.
- King, Geoff. New Hollywood Cinema: An Introduction. New York: Columbia University PressColumbia University PressColumbia University Press is a university press based in New York City, and affiliated with Columbia University. It is currently directed by James D. Jordan and publishes titles in the humanities and sciences, including the fields of literary and cultural studies, history, social work, sociology,...
, 2002. - Merritt, Greg. Celluloid Mavericks: A History of American Independent Film. Thunder's Mouth Press, 2001.
- Nowell-Smith, Geoffrey, ed. The Oxford History of World Cinema. Oxford University PressOxford University PressOxford University Press is the largest university press in the world. It is a department of the University of Oxford and is governed by a group of 15 academics appointed by the Vice-Chancellor known as the Delegates of the Press. They are headed by the Secretary to the Delegates, who serves as...
, 1999. - Parkinson, David. History of Film. New York: Thames & HudsonThames & HudsonThames & Hudson is a publisher of illustrated books on art, architecture, design, and visual culture. With its headquarters in London, England it has a sister company in New York and subsidiaries in Melbourne, Singapore and Hong Kong...
, 1995. ISBN 0-500-20277-X - Rocchio, Vincent F. Reel Racism. Confronting Hollywood's Construction of Afro-American Culture. Westview Press, 2000.
- Salt, Barry. Film Style and Technology: History and Analysis 2nd Ed. Starword, 1992.
- Salt, Barry. Moving Into Pictures Starword, 2001.
- Robin van Gils met zijn baardje School 2009.
- Schrader, Paul. "Notes on Film Noir." Film Comment, 1984.
- Thackway, Melissa. Africa shoots back: Alternative perspectives in sub-saharan Francophone African film. Indiana University Press, 2003.
- Tsivian, Yuri. Silent Witnesses: Russian Films 1908-1919 British Film InstituteBritish Film InstituteThe British Film Institute is a charitable organisation established by Royal Charter to:-Cinemas:The BFI runs the BFI Southbank and IMAX theatre, both located on the south bank of the River Thames in London...
, 1989. - Unterburger, Amy L. The St. James Women Filmmakers Encyclopedia: Women on the Other Side of the Camera. Visible Ink Press, 1999.
- Usai, P.C. & Codelli, L. (editors) Before Caligari: German Cinema, 1895-1920 Edizioni Biblioteca dell'Immagine, 1990.
External links
- View inside an ancient film camera *popup warning, possible vanity site*
- Museum Of Motion Picture History, Inc.
- History exhibit of filmmaking in Florida, presented by the State Archives of Florida
- American Cinematographer - January, 1930, THE EARLY HISTORY OF WIDE FILMS
- History of Film Formats
- Technicolor History
- What is a Camera Obscura?
- Film Sound History at FilmSound.org
- An Introduction to Early cinema
- List of Early Sound Films 1894-1929 at Silent Era website
- Official Web Site of Film Historian/Oral Historian Scott Feinberg
- Reality Film
- Film History by Decade *popup warning*
- Project "Westphalian History in the film"
- Cinema: From 1890 To Now
- A Brief, Early History of Computer Graphics in Film
- Film History @ Video-Film.info
- The Tex(t)-Mex Gallerblog Meditations on Latina/os in Cinema
- History of Film poster
- Burns, Paul The History of the Discovery of Cinematography An Illustrated Chronology
- The Film Experience : an undergraduate course taught by Prof. David Thorburn in the fall of 2007 at MIT
- hollywood Movies History

