
Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth
Encyclopedia
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth (or Union, since 1791 the Commonwealth of Poland) was a dualistic state
of Poland
and Lithuania
ruled by a common monarch
. It was the largest and one of the most populous countries of 16th- and 17th‑century Europe with some 400000 square miles (1,035,995.2 km²) and a multi-ethnic population of 11 million at its peak in the early 17th century. It was established at the Union of Lublin
in July 1569, disappeared as an independent state after the Third Partition of Poland
in 1795.
The Union possessed features unique among contemporary states: its political system was characterized by strict checks upon monarchical power. These checks were enacted by a legislature (Sejm
) controlled by the nobility (szlachta
). This idiosyncratic system was a precursor to modern concepts of democracy
, constitutional monarchy
and federation
. The two component states of the Commonwealth were formally equal, yet Poland was the dominant partner in the union.
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth was marked by high levels of ethnic diversity and by relative religious tolerance
guaranteed by Warsaw Confederation Act 1573
, though the degree of religious tolerance varied over time.
After several decades of prosperity, it entered a period of protracted political, military and economic decline. Its growing weakness led to its partitioning
among its more powerful neighbors, Austria
, Prussia
and the Russian Empire
, during the late 18th century. Shortly before its demise, the Commonwealth adopted a massive reform effort and enacted the Constitution of May 3, 1791
, described by Norman Davies
as the first of its kind in Europe
.
" (Ruthenian
: Рѣч Посполита, Lithuanian ). Western Europeans often simply called it Poland, applying the pars pro toto
synecdoche. The widespread term 'Commonwealth of the Two Nations' was coined in the 20th century.
, the Union of Krewo
, the Union of Vilnius and Radom, the Union of Grodno, and the Union of Horodło) were struck before the more permanent 1569 Union of Lublin
. This agreement was one of the signal achievements of Sigismund II Augustus
, last monarch of the Jagiellon dynasty
. Sigismund believed he could preserve his dynasty by adopting elective monarchy
. His death in 1572 was followed by a three-year interregnum
during which adjustments were made to the constitutional system; these adjustments significantly increased the power of the Polish nobility
and established a truly elective monarchy.
The Commonwealth reached its Golden Age
in the early 17th century. Its powerful parliament
was dominated by nobles (Pic. 2) who were reluctant to get involved in the Thirty Years' War
; this neutrality spared the country from the ravages of a political-religious conflict which devastated most of contemporary Europe. The Commonwealth was able to hold its own against Sweden
, Tsardom of Russia
, and vassals of the Ottoman Empire
, and even launched successful expansionist
offensives against its neighbors. In several invasions during the Time of Troubles
Commonwealth troops entered Russia and managed to take Moscow
and hold it from September 27, 1610 to November 4, 1612, until driven out after a siege.
Commonwealth power began waning after a series of blows during the following decades. A major rebellion of Cossack
s in the southeastern portion of the Commonwealth (the Khmelnytskyi Uprising in modern-day Ukraine
) began in 1648. It resulted in a Ukrainian request, under the terms of the Treaty of Pereyaslav
, for protection by the Muscovian Tsar. Muscovian annexation of part of Ukraine gradually supplanted Polish influence. The other blow to the Commonwealth was a Swedish invasion in 1655. Supported by troops of Transylvania
n duke George II Rakoczy and Friedrich Wilhelm I
, Elector
of Brandenburg
, The Deluge
was the Swedish royal
response to years of Commonwealth belligerence.
 In the late 17th century, the weakened Commonwealth's King John III Sobieski
In the late 17th century, the weakened Commonwealth's King John III Sobieski
allied himself with Leopold I, Holy Roman Emperor
to deal crushing defeats to the Ottoman Empire. In 1683, the Battle of Vienna
marked the final turning point in a 250-year struggle between the forces of Christian
Europe and the Islam
ic Ottoman Empire
. For its centuries-long stance against the Muslim advances, the Commonwealth would gain the name of Antemurale Christianitatis (bulwark of Christianity). During the next 16 years the Great Turkish War
would drive the Turks permanently south of the Danube River, never to threaten central Europe again.
By the 18th century, destabilization of its political system brought Poland to the brink of anarchy
. The Commonwealth was facing many internal problems and was vulnerable to foreign influences. An outright war between the King and the nobility broke out in 1715 and Tsar Peter the Great's mediation put him in a position to further weaken the state. The Russian army was present at the Silent Sejm
of 1717, which limited the armed forces to 24,000 and specified its funding, reaffirmed the liberum veto, and banished the King's Saxon army; the Tsar was to serve as guarantor of the agreement. Western Europe's increasing exploitation of resources in the Americas
rendered the Commonwealth's supplies less crucial. In 1768 the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth became a protectorate
of the Russian Empire
. Control of Poland was central to Catherine the Great's
diplomatic and military strategies. Attempts at reform, such as the Four-Year Sejm's May Constitution came too late. The country was partitioned in three stages
by the neighboring Russian Empire
, Kingdom of Prussia
, and the Habsburg Monarchy
. By 1795, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth had been completely erased from the map of Europe. Poland and Lithuania would not be re-established as independent countries until 1918; Ukraine and Belarus
established independence in the 1990s.
 The political doctrine of the Commonwealth was: our state is a republic under the presidency of the King. Chancellor
The political doctrine of the Commonwealth was: our state is a republic under the presidency of the King. Chancellor
Jan Zamoyski
summed up this doctrine when he said that Rex regnat et non gubernat ("The King reigns but does not govern"). The Commonwealth had a parliament, the Sejm, as well as a Senat and an elected king (Pic. 1). The king was obliged to respect citizens' rights specified in King Henry's Articles as well as in pacta conventa
, negotiated at the time of his election.
The monarch's power was limited, in favor of a sizable noble class. Each new king had to pledge to uphold the Henrician Articles, which were the basis of Poland's political system (and included near-unprecedented guarantees of religious tolerance
). Over time, the Henrician Articles were merged with the Pacta Conventa, specific pledges agreed to by the king-elect. From that point onwards, the king was effectively a partner with the noble class and was constantly supervised by a group of senators. The Sejm could veto the king on important matters, including legislation (the adoption of new laws), foreign affairs, declaration of war, and taxation (changes of existing taxes or the levying of new ones).
The foundation of the Commonwealth's political system, the "Golden Liberty
" , included:
 The three regions (see below) of the Commonwealth enjoyed a degree of autonomy. Each voivodship had its own parliament (sejmik), which exercised serious political power, including choice of poseł (deputy
The three regions (see below) of the Commonwealth enjoyed a degree of autonomy. Each voivodship had its own parliament (sejmik), which exercised serious political power, including choice of poseł (deputy
) to the national Sejm and charging of the deputy with specific voting instructions. The Grand Duchy of Lithuania
had its own separate army, treasury and most other official institutions.
Golden Liberty created a state that was unusual for its time, although somewhat similar political system
s existed in the contemporary city-state
s like the Republic of Venice
. Interestingly, both states were styled "Serenissima Respublica" or the "Most Serene Republic
". At a time when most European countries were headed toward centralization
, absolute monarchy
and religious and dynastic warfare, the Commonwealth experimented with decentralization
, confederation
and federation
, democracy, religious tolerance
, and even pacifism
. The Sejm's usual veto of wars has been described as an example of democratic peace theory
.
This political system unusual for its time stemmed from the ascendance of the szlachta noble class
over other social classes and over the political system
of monarchy
. In time, the szlachta accumulated enough privileges (such as those established by the Nihil novi
Act of 1505) that no monarch could hope to break the szlachta's grip on power. The Commonwealth's political system is difficult to fit into a simple category, but it can be tentatively described as a mixture of:
 The end of the Jagiellon dynasty
The end of the Jagiellon dynasty
in 1572after nearly two centuriesdisrupted the fragile equilibrium of the Commonwealth's government. Power increasingly slipped away from the central government to the nobility.
When presented with periodic opportunities to fill the throne, the szlachta exhibited a preference for foreign candidates who would not found another strong dynasty
. This policy often produced monarchs who were either totally ineffective or in constant debilitating conflict with the nobility. Furthermore, aside from notable exceptions such as the able Transylvania
n Stefan Batory
(1576–86), the kings of foreign origin were inclined to subordinate the interests of the Commonwealth to those of their own country and ruling house. This was especially visible in the policies and actions of the first two elected kings from the Swedish House of Vasa
, whose politics brought the Commonwealth into conflict with Sweden, culminating in the war known as The Deluge
(1655), one of the events that mark the end of the Commonwealth's Golden Age and the beginning of the Commonwealth's decline.
Zebrzydowski's rokosz (1606–07) marked a substantial increase in the power of the magnate
s, and the transformation of szlachta democracy into magnate oligarchy. The Commonwealth's political system was vulnerable to outside interference, as Sejm deputies bribed by foreign powers might use their liberum veto to block attempted reforms. This sapped the Commonwealth and plunged it into political paralysis and anarchy for over a century, from the mid-17th century to the end of the 18th, while its neighbors stabilized their internal affairs and increased their military might.
 The Commonwealth did eventually make a serious effort to reform its political system, adopting in 1791 the May 3rd Constitution, which historian Norman Davies
The Commonwealth did eventually make a serious effort to reform its political system, adopting in 1791 the May 3rd Constitution, which historian Norman Davies
calls the first of its kind in Europe. The revolutionary Constitution recast the erstwhile Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth as a Polish–Lithuanian federal state with a hereditary monarchy
and abolished many of the deleterious features of the old system. The new constitution:
These reforms came too late, however, as the Commonwealth was immediately invaded from all sides by its neighbors which were content to leave the Commonwealth alone as a weak buffer state, but reacted strongly to king Stanisław August Poniatowski's and other reformers' attempts to strengthen the country. Russia feared the revolutionary implications of the May 3rd Constitution's political reforms and the prospect of the Commonwealth regaining its position as a European empire. Catherine the Great regarded the May constitution as fatal to her influence and declared the Polish constitution Jacobinical
. Grigori Aleksandrovich Potemkin drafted the act for the Confederation of Targowica, referring to the constitution as the "contagion of democratic ideas". Meanwhile, Prussia
and Austria
, also afraid of a strengthened Poland, used it as a pretext for further territorial expansion. Prussian minister Ewald von Hertzberg called the constitution "a blow to the Prussian monarchy", fearing that strengthened Poland would once again dominate Prussia. In the end, the May 3rd Constitution was never fully implemented, and the Commonwealth entirely ceased to exist only four years after the Constitution's adoption.

 The economy
The economy
of the Commonwealth was dominated by feudal
agriculture
based on the plantation system
(serfs). Slavery
in Poland was forbidden in the 15th century; in Lithuania, slavery was formally abolished in 1588. They were replaced by the second enserfment. Typically a nobleman's landholding comprised a folwark
, a large farm
worked by serf
s to produce surpluses for internal and external trade. This economic arrangement worked well for the ruling classes in the early era of the Commonwealth, which was one of the most prosperous eras of the grain trade. The economic strength of Commonwealth grain trade waned from the late 17th century on. Trade relationships were disrupted by the wars and the Commonwealth proved unable to improve its transport infrastructure or its agricultural practices. Serfs in the region were increasingly tempted to flee. The Commonwealth's major attempts at countering this problem and improving productivity consisted of increasing serfs' workload and further restricting their freedoms in a process known as second serfdom.
Though the urban population of the Commonwealth was about 20% of the total in the 17th century, which was much lower than in some West European countries (approximately 50% in the Netherlands and Italy) the urbanization
of the country was of a specific character (Pic. 7). The Commonwealth's preoccupation with agriculture, coupled with the szlachta's privileged position when compared to the bourgeoisie
, resulted in a fairly slow process of urbanization and thus a rather slow development of industries
. While similar conflicts among social classes may be found all over Europe, nowhere were the nobility as dominant at the time as in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. There is, however, much debate among historians as to which processes most affected those developments, since until the wars and crises of the mid-17th century the cities of the Commonwealth had not markedly lagged in size and wealth behind their western counterparts. The Commonwealth did have numerous towns and cities
, commonly founded on Magdeburg rights
. Some of the largest trade fair
s in the Commonwealth were held at Lublin
. See the geography section, below, for a list of major cities in the Commonwealth (commonly capitals of voivodships).
Poland-Lithuania played a significant role in the supply of 16th century Western Europe
by the export of three sorts of goods, notably grain
(rye), cattle
(oxen) and fur
. These three articles amounted to nearly 90% of the country's exports to western markets by overland- and maritime trade.
 Although the Commonwealth was Europe's largest grain producer, the bulk of her grain was consumed domestically. Estimated grain consumption in the Polish Crown (Poland proper) and Prussia
Although the Commonwealth was Europe's largest grain producer, the bulk of her grain was consumed domestically. Estimated grain consumption in the Polish Crown (Poland proper) and Prussia
in 1560–70 was some 113,000 ton
s of wheat
(or 226,000 łaszt – a łaszt, or "last"
, being a large bulk measure; in the case of grain, about half a ton). Average yearly production of grain in the Commonwealth in the 16th Century was 120,000 tons, 6% of which was export
ed, while cities consumed some 19% and the remainder was consumed by the villages. Commonwealth grain achieved far more importance in poor crop years, as in the early 1590s and the 1620s, when governments throughout southern Europe arranged for large grain imports to cover shortfalls in their jurisdictions.
Still, grain was the largest export commodity of the Commonwealth. The owner of a folwark
usually signed a contract
with merchants of Gdańsk
, who controlled 80% of this inland trade, to ship the grain north to that seaport on the Baltic Sea
. Many rivers in the Commonwealth were used for shipping purposes: the Vistula
, Pilica, Bug
, San
, Nida
, Wieprz, Niemen. The rivers had relatively developed infrastructure, with river ports and granaries
. Most of the river shipping moved north, southward transport being less profitable, and barges and rafts were often sold off in Gdańsk for lumber. Hrodna
become an important site after formation of a customs post at Augustów
in 1569, which became a checkpoint for merchants travelling to the Crown lands from the Grand Duchy.
From Gdańsk, ships, mostly from the Netherlands
and Flanders
, carried the grain to ports such as Antwerp and Amsterdam
. Besides grain, other seaborne exports included carminic acid
from Polish cochineal
, lumber
and wood-related products such as ash
, and tar
. The land routes, mostly to the German lands of the Holy Roman Empire
such as the cities of Leipzig
and Nuremberg
, were used for export of live cattle
(herds of around 50,000 head) hides
, fur
s, salt
, tobacco
, hemp
, cotton
(mostly from Greater Poland
) and linen
.
The Commonwealth imported wine
, fruit
, spices, luxury good
s (e.g. tapestries
, Pic. 5), clothing
, fish
, beer
and industrial products like steel
and tool
s. A few riverboats carried south imports from Gdańsk like wine, fruit, spices and herring. Somewhere between the 16th and 17th centuries, the Commonwealth's trade balance shifted from positive to negative.
With the advent of the Age of Exploration, many old trading routes
such as the Amber Road
(Pic. 4) lost importance as new ones were created. Poland's importance as a caravan route between Asia and Europe diminished, while new local trading routes were created between the Commonwealth and Russia. Many goods and cultural artifacts continued to pass from one region to another via the Commonwealth. For example, Isfahan rug
s imported from Persia to the Commonwealth were actually known in the West as "Polish rugs" .
Commonwealth currency
included the złoty and the grosz
. The City of Gdańsk
had the privilege of minting its own coinage.
 The Commonwealth was an important European center for the development of modern social and political ideas. It was famous for its rare quasi-democratic political system, praised by philosophers
The Commonwealth was an important European center for the development of modern social and political ideas. It was famous for its rare quasi-democratic political system, praised by philosophers
such as Erasmus; and, during the Counter-Reformation
, was known for near-unparalleled religious tolerance
, with peacefully coexisting Catholic, Jewish
, Eastern Orthodox, Protestant and Muslim
communities. The Commonwealth gave rise to the famous Christian sect
of the Polish Brethren
, antecedents of British
and American Unitarianism
.
With its political system, the Commonwealth gave birth to political philosophers
such as Andrzej Frycz Modrzewski
(1503–1572) (Pic. 9), Wawrzyniec Grzymała Goślicki (1530–1607) and Piotr Skarga
(1536–1612). Later, works by Stanisław Staszic (1755–1826) and Hugo Kołłątaj (1750–1812) helped pave the way for the Constitution of May 3, 1791
, which Norman Davies
calls the first of its kind in Europe.
Kraków
's Jagiellonian University
is one of the oldest universities in the world (established in 1364), together with the Vilnius University
(established in 1579) they were the major scholarly and scientific centers in the Commonwealth. The Komisja Edukacji Narodowej, Polish for Commission for National Education, formed in 1773, was the world's first national Ministry of Education. Commonwealth scientists included: Martin Kromer (1512–1589), historian and cartographer; Michał Sędziwój (1566–1636), alchemist
and chemist; Jan Brożek
(Ioannes Broscius in Latin
) (1585–1652), polymath
: a mathematician
, physician
and astronomer
; Krzysztof Arciszewski
(Crestofle d'Artischau Arciszewski in Portuguese
) (1592–1656), engineer
, ethnographer, general and admiral of the Dutch West Indies Company army in the war with the Spanish Empire
for control of Brazil
; Kazimierz Siemienowicz
(1600–1651), military engineer, artillery
specialist and a founder of rocket
ry; Johannes Hevelius
(1611–1687), astronomer
, founder of lunar
topography
; Michał Boym (1612–1659), orientalist
, cartographer, naturalist
and diplomat in Ming Dynasty's service (Pic. 11); Adam Adamandy Kochański
(1631–1700), mathematician
and engineer; Baal Shem Tov (הבעל שם טוב in Hebrew
) (1698–1760), considered to be the founder of Hasidic Judaism
; Marcin Odlanicki Poczobutt (1728–1810), astronomer
and mathematician
(Pic. 12); Jan Krzysztof Kluk
(1739–1796), naturalist
, agronomist
and entomologist
. In 1628 the Czech teacher
, scientist
, educator, and writer
John Amos Comenius took refuge in the Commonwealth, when the Protestants
were persecuted under the Counter Reformation.
The works of many Commonwealth authors are considered classics, including those of Jan Kochanowski
(Pic. 10), Wacław Potocki, Ignacy Krasicki
, and Julian Ursyn Niemcewicz
. Many szlachta
members wrote memoir
s and diaries
. Perhaps the most famous are the Memoirs of Polish History by Albrycht Stanisław Radziwiłł (1595–1656) and the Memoirs of Jan Chryzostom Pasek
(ca. 1636–ca. 1701). Jakub Sobieski
(1590–1646) (father of John III Sobieski
) wrote notable diaries. During the Khotyn expedition
in 1621 he wrote a diary called Commentariorum chotinensis belli libri tres (Diary of the Chocim War), which was published in 1646 in Gdańsk
. It was used by Wacław Potocki as a basis for his epic poem, Transakcja wojny chocimskiej (The Progress of the War of Chocim). He also authored instructions for the journey of his sons to Kraków (1640) and France (1645), a good example of liberal education of the era.
 The two great culture
The two great culture
s of the Commonwealth, Latin
and Eastern Orthodox
, coexisted and penetrate each other, which is reflected in great popularity of icon
s (Pic. 13) and icon resembling effigies of Mary
, as well as metal dresses typical for the Orthodox Church in predominantly Latin territories of today's Poland (Black Madonna
) and Lithuania (Our Lady of the Gate of Dawn
). The implementation of post-renaissance
naturalism and sentimentality of Polish baroque in Orthodox painting as well as creation of Cossack Baroque
in architecture, also inspired by Polish patterns, were the major factors of Latin infiltration in Eastern art (Pic. 3).
A common art form of the Sarmatian
period were coffin portraits, particular to the culture of the Commonwealth, used in funerals and other important ceremonies. As a rule, such portraits were nailed to sheet metal, six – or eight – sided in shape, fixed to the front of a coffin placed on a high, ornate catafalque.
Another characteristic is common usage of black marble. Altars, fonts, portals, balustrades, columns, monuments, tombstones, headstones and whole rooms (e.g. Marble Room at the Royal Castle in Warsaw, St. Casimir Chapel of the Vilnius Cathedral
and Vasa Chapel of the Wawel Cathedral
) were decorated with black marble.
Music was a common feature of religious and secular events. To that end many noblemen founded church and school choirs, and employed their own ensembles of musicians. Some, like Stanisław Lubomirski build their own opera houses (in Nowy Wiśnicz
). Yet others, like Janusz Skumin Tyszkiewicz
and Krzysztof Radziwiłł were known for their sponsorship of arts which manifested itself in their permanently retained orchestras, at their courts in Vilnius
. Musical life further flourished during the reign of the Vasas. Both foreign and domestic composers were active in the Commonwealth. King Sigismund III
brought in Italian composers and conductors, such as Luca Marenzio
, Annibale Stabile
, Asprilio Pacelli
, Marco Scacchi
and Diomedes Cato
for the royal orchestra. Notable home grown musicians, who also composed and played for the King's court, included Bartłomiej Pękiel, Jacek Różycki
, Adam Jarzębski
, Marcin Mielczewski
, Stanisław Sylwester Szarzyński, Damian Stachowicz, Mikołaj Zieleński and Grzegorz Gorczycki.
Magnate
s often undertook construction projects as monuments to themselves: churches, cathedral
s, monasteries
(Pic. 14), and palace
s like the present-day Presidential Palace in Warsaw
and Pidhirtsi Castle
built by Grand Hetman Stanisław Koniecpolski herbu Pobóg. The largest projects involved entire towns, although in time many of them would lapse into obscurity or be totally abandoned. Usually they were named after the sponsoring magnate. Among the most famous is the town of Zamość
, founded by Jan Zamoyski
and designed by the Italian architect
Bernardo Morando
. The magnates throughout Poland competed with the kings. The monumental castle Krzyżtopór
, built in the style palazzo in fortezza between 1627 and 1644, had several courtyards surrounded by fortifications. Due to efforts of powerful Radziwiłł family, the town of Nesvizh
in today's Belarus
came to exercise significant influence in many domains – the Nesvizh manufactures of firearm
, carpet
s, kontusz sashes and tapestries
as well as school of painting produced renowned and luxury items. Late baroque fascination with the culture and art of the "central nation
" is reflected in Queen Masysieńka
's Chinese Palace
in Zolochiv
. 18th century magnate palaces represents the characteristic type of baroque
suburban residence built entre cour et jardin
(between the entrance court and the garden). Its architecture - a merger of European art with old Commonwealth building traditions are visible in Wilanów Palace
in Warsaw
(Pic. 15), Branicki Palace in Białystok and in Warsaw, Potocki Palace in Radzyń Podlaski
and in Krystynopol
, Raczyński Palace in Rogalin
and Sapieha Palace
in Ruzhany
.
 The prevalent ideology
The prevalent ideology
of the szlachta became "Sarmatism
", named after the Sarmatians
, alleged ancestors of the Poles. This belief system was an important part of the szlachta's culture
, penetrating all aspects of its life. Sarmatism enshrined equality among szlachta, horseback riding, tradition, provincial rural life, peace and pacifism
; championed oriental-inspired attire (żupan
, kontusz
, sukmana, pas kontuszowy
, delia, szabla
); and served to integrate the multi-ethnic nobility by creating an almost nationalistic
sense of unity and of pride in the szlachta's Golden Freedoms.
In its early, idealistic form, Sarmatism represented a positive cultural movement: it supported religious belief, honesty, national pride, courage, equality and freedom. In time, however, it became distorted. Late extreme Sarmatism turned belief into bigotry, honesty into political naïveté, pride into arrogance, courage into stubbornness and freedom into anarchy. The faults of Sarmatism were blamed for the demise of the country from the late 18th century onwards. Criticism, often one-sided and exaggerated, was used by the Polish reformists to push for radical changes. This self-deprecation was accompanied by works of Prussian, Russian
and Austrian
historians, who tried to prove that it was Poland itself that was to blame for its fall.
and confederation with Lithuania
, in both of which countries ethnic Poles were a distinct minority. The Commonwealth comprised primarily four nations: Lithuanians
, Poles
, Belarusians
and Ukrainians
; the latter two usually referred to as the Ruthenians
. Sometimes inhabitants of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania
were called Litvins, a Slavic term for people from Lithuania, regardless their ethnicity (with the exception of Jews, which were called Litvak
s). Shortly after the Union of Lublin
( 1569 ), the Commonwealth population was around 7 million, with a rough breakdown of 4.5 m Poles, 0.75 m Lithuanians, 0.7 m/10% Jews
and 2 m Ruthenians. In 1618, after the Truce of Deulino
, the Commonwealth population increased together with its territory, reaching 11.5 million people, which was composed roughly of 4.5 m Poles, 3.5 m Ukrainians, 1.5 m Belarusians, 0.75 m Lithuanians, 0.75 m Old Prussians
, 0.5 m Jews, and 0.5 m Livonians. At that time nobility was 10% of the population, and burghers
were 15%. The average population density per square kilometer was: 24 in Mazovia, 23 in Little Poland, 19 in Great Poland, 12 in Lublin palatinate, 10 in the Lvov area, 7 in Podolia and Volhynia, 3 in the Ukraine. There was a tendency for the people from the more densely inhabited western territories to migrate eastwards. In the period from 1648–57, populations losses are estimated at 4 m. Coupled with further population and territorial losses, in 1717 the Commonwealth population had fallen to 9 m, with roughly 4.5 m/50% Poles, 1.5 m/17% Ukrainians, 1.2 m Belarusians, 0.8 m Lithuanians, 0.5 m Jews, and 0.5 m others.
“Certainly, the wording and substance of the declaration of the Confederation of Warsaw of 28 January 1573 were extraordinary with regards to prevailing conditions elsewhere in Europe; and they governed the principles of religious life in the Republic for over two hundred years.” - Norman Davies
Poland has a long tradition of religious freedom. The right to worship freely was a basic right given to all inhabitants of the Commonwealth throughout the 15th and early 16th century, however, complete freedom of religion was officially recognized in Poland in 1573 during the Warsaw Confederation
. Poland kept religious freedom laws during an era when religious persecution was an everyday occurrence in the rest of Europe. Commonwealth was a place were the most radical religious sects, trying to escape persecution in other countries of the Christian world, sought refuge.
To be Polish, in the non-Polish lands of the Commonwealth, was then much less an index of ethnicity than of religion and rank
; it was a designation largely reserved for the landed noble class (szlachta), which included Poles but also many members of non-Polish origin who converted to Catholicism
in increasing numbers with each following generation. For the non-Polish noble
such conversion meant a final step of Polonization
that followed the adoption of the Polish language and culture. Poland, as the culturally most advanced part of the Commonwealth, with the royal court, the capital, the largest cities, the second-oldest university in Central Europe (after Prague
), and the more liberal and democratic social institutions had proven an irresistible magnet for the non-Polish nobility in the Commonwealth. Many referred to themselves as "gente Ruthenus, natione Polonus" (Ruthenian by blood, Polish by nationality) since 16th century onwards.
As a result, in the eastern territories a Polish (or Polonized) aristocracy dominated a peasantry whose great majority was neither Polish nor Roman Catholic. Moreover, the decades of peace brought huge colonization efforts to Ukraine, heightening the tensions among nobles
, Jews, Cossack
s (traditionally Orthodox), Polish and Ruthenian peasants. The latter, deprived of their native protectors among the Ruthenian nobility, turned for protection to cossack
s that facilitated violence that in the end broke the Commonwealth. The tensions were aggravated by conflicts between Eastern Orthodoxy and the Greek Catholic Church
following the Union of Brest
, overall discrimination of Orthodox religions by dominant Catholicism, and several Cossack
uprisings. In the west and north, many cities had sizable German minorities, often belonging to Reformed churches
. The Commonwealth had also one of the largest Jewish diaspora
s in the world – by the mid-16th century 80% of the world's Jews lived in Poland (Pic. 16).
Until the Reformation
, the szlachta were mostly Catholic or Eastern Orthodox (Pic. 3, 13). However, many families quickly adopted the Reformed religion. After the Counter-Reformation
, when the Roman Catholic Church regained power in Poland, the szlachta became almost exclusively Roman Catholic, despite the fact that Roman Catholicism was not a majority religion (the Roman Catholic and Orthodox churches counted approximately 40% of the population each, while the remaining 20% were Jews and members of various Protestant churches).
The Crown had about double the population of Lithuania and five times the income of the latter's treasury. As with other countries, the borders, area and population of the Commonwealth varied over time. After the Peace of Jam Zapolski
(1582), the Commonwealth had approximately 815,000 km² area and a population of 7.5 million. After the Truce of Deulino
(1618), the Commonwealth had an area of some 990,000 km² and a population of 10–11 million (including some 4 million Poles and close to a million Lithuanians).
, established in 1807, traced its origins to the Commonwealth. Other revival movements appeared during the November Uprising
(1830–31), the January Uprising
(1863–64) and in the 1920s, with Józef Piłsudski's failed attempt to create a Polish-led Międzymorze
("Between-Seas") federation
that would have included Lithuania and Ukraine
. Today's Republic of Poland considers itself a successor to the Commonwealth, whereas the Republic of Lithuania, re-established at the end of World War I
, saw the participation of the Lithuanian state in the old Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth mostly in a negative light at the early stages of regaining its independence, although this attitude has been changing recently.
The Commonwealth was further divided into smaller administrative units known as voivodships (województwa). Each voivodship was governed by a voivod (wojewoda, governor). Voivodships were further divided into starostwa
, each starostwo being governed by a starosta
. Cities were governed by castellan
s. There were frequent exceptions to these rules, often involving the ziemia
subunit of administration.
The lands that once belonged to the Commonwealth are now largely distributed among several Central and East European
countries: Poland, Ukraine, Moldova
(Transnistria
), Belarus, Russia, Lithuania, Latvia, and Estonia. Also some small towns in Slovakia
, then within the Kingdom of Hungary
, became a part of Poland in the Treaty of Lubowla
.
Other notable parts of the Commonwealth, without respect to region or voivodship divisions, include:
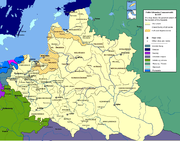
Commonwealth borders shifted with wars and treaties, sometimes several times in a decade, especially in the eastern and southern parts. After the Peace of Jam Zapolski (1582), the Commonwealth had approximately 815,000 km² area and a population of 7.5 million. After the Truce of Deulino (1618), the Commonwealth had an area of some 1 million km² (990,000 km²) and a population of about 11 million.
In the 16th century, the Polish bishop
and cartographer Martin Kromer published a Latin atlas, entitled Poland: about Its Location, People, Culture, Offices and the Polish Commonwealth
, which was regarded as the most comprehensive guide to the country.
Kromer's works and other contemporary maps, such as those of Gerardus Mercator
, show the Commonwealth as mostly plain
s. The Commonwealth's southeastern part, the Kresy
, was famous for its steppe
s. The Carpathian Mountains
formed part of the southern border, with the Tatra Mountain
chain the highest, and the Baltic Sea
formed the Commonwealth's northern border. As with most European countries at the time, the Commonwealth had extensive forest
cover, especially in the east. Today, what remains of the Białowieża Forest constitutes the last largely intact primeval forest in Europe.
Sovereign state
A sovereign state, or simply, state, is a state with a defined territory on which it exercises internal and external sovereignty, a permanent population, a government, and the capacity to enter into relations with other sovereign states. It is also normally understood to be a state which is neither...
of Poland
Poland
Poland , officially the Republic of Poland , is a country in Central Europe bordered by Germany to the west; the Czech Republic and Slovakia to the south; Ukraine, Belarus and Lithuania to the east; and the Baltic Sea and Kaliningrad Oblast, a Russian exclave, to the north...
and Lithuania
Lithuania
Lithuania , officially the Republic of Lithuania is a country in Northern Europe, the biggest of the three Baltic states. It is situated along the southeastern shore of the Baltic Sea, whereby to the west lie Sweden and Denmark...
ruled by a common monarch
Monarch
A monarch is the person who heads a monarchy. This is a form of government in which a state or polity is ruled or controlled by an individual who typically inherits the throne by birth and occasionally rules for life or until abdication...
. It was the largest and one of the most populous countries of 16th- and 17th‑century Europe with some 400000 square miles (1,035,995.2 km²) and a multi-ethnic population of 11 million at its peak in the early 17th century. It was established at the Union of Lublin
Union of Lublin
The Union of Lublin replaced the personal union of the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania with a real union and an elective monarchy, since Sigismund II Augustus, the last of the Jagiellons, remained childless after three marriages. In addition, the autonomy of Royal Prussia was...
in July 1569, disappeared as an independent state after the Third Partition of Poland
Third Partition of Poland
The Third Partition of Poland or Third Partition of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth took place in 1795 as the third and last of three partitions that ended the existence of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth.-Background:...
in 1795.
The Union possessed features unique among contemporary states: its political system was characterized by strict checks upon monarchical power. These checks were enacted by a legislature (Sejm
Sejm
The Sejm is the lower house of the Polish parliament. The Sejm is made up of 460 deputies, or Poseł in Polish . It is elected by universal ballot and is presided over by a speaker called the Marshal of the Sejm ....
) controlled by the nobility (szlachta
Szlachta
The szlachta was a legally privileged noble class with origins in the Kingdom of Poland. It gained considerable institutional privileges during the 1333-1370 reign of Casimir the Great. In 1413, following a series of tentative personal unions between the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the Kingdom of...
). This idiosyncratic system was a precursor to modern concepts of democracy
Democracy
Democracy is generally defined as a form of government in which all adult citizens have an equal say in the decisions that affect their lives. Ideally, this includes equal participation in the proposal, development and passage of legislation into law...
, constitutional monarchy
Constitutional monarchy
Constitutional monarchy is a form of government in which a monarch acts as head of state within the parameters of a constitution, whether it be a written, uncodified or blended constitution...
and federation
Federation
A federation , also known as a federal state, is a type of sovereign state characterized by a union of partially self-governing states or regions united by a central government...
. The two component states of the Commonwealth were formally equal, yet Poland was the dominant partner in the union.
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth was marked by high levels of ethnic diversity and by relative religious tolerance
Religious toleration
Toleration is "the practice of deliberately allowing or permitting a thing of which one disapproves. One can meaningfully speak of tolerating, ie of allowing or permitting, only if one is in a position to disallow”. It has also been defined as "to bear or endure" or "to nourish, sustain or preserve"...
guaranteed by Warsaw Confederation Act 1573
Warsaw Confederation
The Warsaw Confederation , an important development in the history of Poland and Lithuania that extended religious tolerance to nobility and free persons within the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. , is considered the formal beginning of religious freedom in the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, and...
, though the degree of religious tolerance varied over time.
After several decades of prosperity, it entered a period of protracted political, military and economic decline. Its growing weakness led to its partitioning
Partitions of Poland
The Partitions of Poland or Partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth took place in the second half of the 18th century and ended the existence of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, resulting in the elimination of sovereign Poland for 123 years...
among its more powerful neighbors, Austria
Habsburg Monarchy
The Habsburg Monarchy covered the territories ruled by the junior Austrian branch of the House of Habsburg , and then by the successor House of Habsburg-Lorraine , between 1526 and 1867/1918. The Imperial capital was Vienna, except from 1583 to 1611, when it was moved to Prague...
, Prussia
Kingdom of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia was a German kingdom from 1701 to 1918. Until the defeat of Germany in World War I, it comprised almost two-thirds of the area of the German Empire...
and the Russian Empire
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was a state that existed from 1721 until the Russian Revolution of 1917. It was the successor to the Tsardom of Russia and the predecessor of the Soviet Union...
, during the late 18th century. Shortly before its demise, the Commonwealth adopted a massive reform effort and enacted the Constitution of May 3, 1791
Constitution of May 3, 1791
The Constitution of May 3, 1791 was adopted as a "Government Act" on that date by the Sejm of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. Historian Norman Davies calls it "the first constitution of its type in Europe"; other scholars also refer to it as the world's second oldest constitution...
, described by Norman Davies
Norman Davies
Professor Ivor Norman Richard Davies FBA, FRHistS is a leading English historian of Welsh descent, noted for his publications on the history of Europe, Poland, and the United Kingdom.- Academic career :...
as the first of its kind in Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
.
Name
The official name of the Commonwealth was The Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania . Prior to the 17th century, international treaties and diplomatic texts referred to it by its Latin name . In the 17th century and later it became known as the Most Serene Republic of Poland (Polish , Latin ). Its inhabitants referred to it in everyday speech as "RzeczpospolitaRzeczpospolita
Rzeczpospolita is a traditional name of the Polish State, usually referred to as Rzeczpospolita Polska . It comes from the words: "rzecz" and "pospolita" , literally, a "common thing". It comes from latin word "respublica", meaning simply "republic"...
" (Ruthenian
Ruthenian language
Ruthenian, or Old Ruthenian , is a term used for the varieties of Eastern Slavonic spoken in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and later in the East Slavic territories of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth....
: Рѣч Посполита, Lithuanian ). Western Europeans often simply called it Poland, applying the pars pro toto
Pars pro toto
Pars pro toto is Latin for "a part for the whole" where the name of a portion of an object or concept represents the entire object or context....
synecdoche. The widespread term 'Commonwealth of the Two Nations' was coined in the 20th century.
History
Poland and Lithuania underwent an alternating series of wars and alliances during the 14th century and early 15th century. Several relatively weak agreements between the two (the Union of Kraków and VilnaUnion of Kraków and Vilna
The Union of Kraków and Vilna also known as Union of Vilnius was one of the agreements of the Polish–Lithuanian union. It was signed in Kraków by Polish nobility on 6 May 1499 and Vilnius by Lithuanian nobility on 24 July 1499....
, the Union of Krewo
Union of Krewo
In a strict sense, the Union of Krewo or Act of Krėva was a set of prenuptial promises made in the Kreva Castle on 14 August 1385 by Jogaila, Grand Duke of Lithuania, in exchange for marriage to the underage reigning Queen Jadwiga of Poland...
, the Union of Vilnius and Radom, the Union of Grodno, and the Union of Horodło) were struck before the more permanent 1569 Union of Lublin
Union of Lublin
The Union of Lublin replaced the personal union of the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania with a real union and an elective monarchy, since Sigismund II Augustus, the last of the Jagiellons, remained childless after three marriages. In addition, the autonomy of Royal Prussia was...
. This agreement was one of the signal achievements of Sigismund II Augustus
Sigismund II Augustus
Sigismund II Augustus I was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania, the only son of Sigismund I the Old, whom Sigismund II succeeded in 1548...
, last monarch of the Jagiellon dynasty
Jagiellon dynasty
The Jagiellonian dynasty was a royal dynasty originating from the Lithuanian House of Gediminas dynasty that reigned in Central European countries between the 14th and 16th century...
. Sigismund believed he could preserve his dynasty by adopting elective monarchy
Elective monarchy
An elective monarchy is a monarchy ruled by an elected rather than hereditary monarch. The manner of election, the nature of the candidacy and the electors vary from case to case...
. His death in 1572 was followed by a three-year interregnum
Interregnum
An interregnum is a period of discontinuity or "gap" in a government, organization, or social order...
during which adjustments were made to the constitutional system; these adjustments significantly increased the power of the Polish nobility
Szlachta
The szlachta was a legally privileged noble class with origins in the Kingdom of Poland. It gained considerable institutional privileges during the 1333-1370 reign of Casimir the Great. In 1413, following a series of tentative personal unions between the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the Kingdom of...
and established a truly elective monarchy.
The Commonwealth reached its Golden Age
Golden Age
The term Golden Age comes from Greek mythology and legend and refers to the first in a sequence of four or five Ages of Man, in which the Golden Age is first, followed in sequence, by the Silver, Bronze, and Iron Ages, and then the present, a period of decline...
in the early 17th century. Its powerful parliament
Sejm
The Sejm is the lower house of the Polish parliament. The Sejm is made up of 460 deputies, or Poseł in Polish . It is elected by universal ballot and is presided over by a speaker called the Marshal of the Sejm ....
was dominated by nobles (Pic. 2) who were reluctant to get involved in the Thirty Years' War
Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War was fought primarily in what is now Germany, and at various points involved most countries in Europe. It was one of the most destructive conflicts in European history....
; this neutrality spared the country from the ravages of a political-religious conflict which devastated most of contemporary Europe. The Commonwealth was able to hold its own against Sweden
Sweden
Sweden , officially the Kingdom of Sweden , is a Nordic country on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. Sweden borders with Norway and Finland and is connected to Denmark by a bridge-tunnel across the Öresund....
, Tsardom of Russia
Tsardom of Russia
The Tsardom of Russia was the name of the centralized Russian state from Ivan IV's assumption of the title of Tsar in 1547 till Peter the Great's foundation of the Russian Empire in 1721.From 1550 to 1700, Russia grew 35,000 km2 a year...
, and vassals of the Ottoman Empire
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman EmpireIt was usually referred to as the "Ottoman Empire", the "Turkish Empire", the "Ottoman Caliphate" or more commonly "Turkey" by its contemporaries...
, and even launched successful expansionist
Expansionism
In general, expansionism consists of expansionist policies of governments and states. While some have linked the term to promoting economic growth , more commonly expansionism refers to the doctrine of a state expanding its territorial base usually, though not necessarily, by means of military...
offensives against its neighbors. In several invasions during the Time of Troubles
Time of Troubles
The Time of Troubles was a period of Russian history comprising the years of interregnum between the death of the last Russian Tsar of the Rurik Dynasty, Feodor Ivanovich, in 1598, and the establishment of the Romanov Dynasty in 1613. In 1601-1603, Russia suffered a famine that killed one-third...
Commonwealth troops entered Russia and managed to take Moscow
Moscow
Moscow is the capital, the most populous city, and the most populous federal subject of Russia. The city is a major political, economic, cultural, scientific, religious, financial, educational, and transportation centre of Russia and the continent...
and hold it from September 27, 1610 to November 4, 1612, until driven out after a siege.
Commonwealth power began waning after a series of blows during the following decades. A major rebellion of Cossack
Cossack
Cossacks are a group of predominantly East Slavic people who originally were members of democratic, semi-military communities in what is today Ukraine and Southern Russia inhabiting sparsely populated areas and islands in the lower Dnieper and Don basins and who played an important role in the...
s in the southeastern portion of the Commonwealth (the Khmelnytskyi Uprising in modern-day Ukraine
Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It has an area of 603,628 km², making it the second largest contiguous country on the European continent, after Russia...
) began in 1648. It resulted in a Ukrainian request, under the terms of the Treaty of Pereyaslav
Treaty of Pereyaslav
The Treaty of Pereyaslav is known in history more as the Council of Pereiaslav.Council of Pereyalslav was a meeting between the representative of the Russian Tsar, Prince Vasili Baturlin who presented a royal decree, and Bohdan Khmelnytsky as the leader of Cossack Hetmanate. During the council...
, for protection by the Muscovian Tsar. Muscovian annexation of part of Ukraine gradually supplanted Polish influence. The other blow to the Commonwealth was a Swedish invasion in 1655. Supported by troops of Transylvania
Transylvania
Transylvania is a historical region in the central part of Romania. Bounded on the east and south by the Carpathian mountain range, historical Transylvania extended in the west to the Apuseni Mountains; however, the term sometimes encompasses not only Transylvania proper, but also the historical...
n duke George II Rakoczy and Friedrich Wilhelm I
Frederick William, Elector of Brandenburg
|align=right|Frederick William was Elector of Brandenburg and Duke of Prussia – and thus ruler of Brandenburg-Prussia – from 1640 until his death. A member of the House of Hohenzollern, he is popularly known as the "Great Elector" because of his military and political prowess...
, Elector
Prince-elector
The Prince-electors of the Holy Roman Empire were the members of the electoral college of the Holy Roman Empire, having the function of electing the Roman king or, from the middle of the 16th century onwards, directly the Holy Roman Emperor.The heir-apparent to a prince-elector was known as an...
of Brandenburg
Brandenburg
Brandenburg is one of the sixteen federal-states of Germany. It lies in the east of the country and is one of the new federal states that were re-created in 1990 upon the reunification of the former West Germany and East Germany. The capital is Potsdam...
, The Deluge
The Deluge (Polish history)
The term Deluge denotes a series of mid-17th century campaigns in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. In a wider sense it applies to the period between the Khmelnytsky Uprising of 1648 and the Truce of Andrusovo in 1667, thus comprising the Polish–Lithuanian theaters of the Russo-Polish and...
was the Swedish royal
House of Vasa
The House of Vasa was the Royal House of Sweden 1523-1654 and of Poland 1587-1668. It originated from a noble family in Uppland of which several members had high offices during the 15th century....
response to years of Commonwealth belligerence.

John III Sobieski
John III Sobieski was one of the most notable monarchs of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, from 1674 until his death King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania. Sobieski's 22-year-reign was marked by a period of the Commonwealth's stabilization, much needed after the turmoil of the Deluge and...
allied himself with Leopold I, Holy Roman Emperor
Leopold I, Holy Roman Emperor
| style="float:right;" | Leopold I was a Holy Roman Emperor, King of Hungary and King of Bohemia. A member of the Habsburg family, he was the second son of Emperor Ferdinand III and his first wife, Maria Anna of Spain. His maternal grandparents were Philip III of Spain and Margaret of Austria...
to deal crushing defeats to the Ottoman Empire. In 1683, the Battle of Vienna
Battle of Vienna
The Battle of Vienna took place on 11 and 12 September 1683 after Vienna had been besieged by the Ottoman Empire for two months...
marked the final turning point in a 250-year struggle between the forces of Christian
Christianity
Christianity is a monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus as presented in canonical gospels and other New Testament writings...
Europe and the Islam
Islam
Islam . The most common are and . : Arabic pronunciation varies regionally. The first vowel ranges from ~~. The second vowel ranges from ~~~...
ic Ottoman Empire
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman EmpireIt was usually referred to as the "Ottoman Empire", the "Turkish Empire", the "Ottoman Caliphate" or more commonly "Turkey" by its contemporaries...
. For its centuries-long stance against the Muslim advances, the Commonwealth would gain the name of Antemurale Christianitatis (bulwark of Christianity). During the next 16 years the Great Turkish War
Great Turkish War
The Great Turkish War refers to a series of conflicts between the Ottoman Empire and contemporary European powers, then joined into a Holy League, during the second half of the 17th century.-1667–1683:...
would drive the Turks permanently south of the Danube River, never to threaten central Europe again.
By the 18th century, destabilization of its political system brought Poland to the brink of anarchy
Anarchism
Anarchism is generally defined as the political philosophy which holds the state to be undesirable, unnecessary, and harmful, or alternatively as opposing authority in the conduct of human relations...
. The Commonwealth was facing many internal problems and was vulnerable to foreign influences. An outright war between the King and the nobility broke out in 1715 and Tsar Peter the Great's mediation put him in a position to further weaken the state. The Russian army was present at the Silent Sejm
Silent Sejm
Silent Sejm is the name given to the session of the Sejm of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth of 1 February 1717. A civil war in the Commonwealth was used by the Russian Tsar Peter the Great as an opportunity to intervene as a mediator...
of 1717, which limited the armed forces to 24,000 and specified its funding, reaffirmed the liberum veto, and banished the King's Saxon army; the Tsar was to serve as guarantor of the agreement. Western Europe's increasing exploitation of resources in the Americas
Americas
The Americas, or America , are lands in the Western hemisphere, also known as the New World. In English, the plural form the Americas is often used to refer to the landmasses of North America and South America with their associated islands and regions, while the singular form America is primarily...
rendered the Commonwealth's supplies less crucial. In 1768 the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth became a protectorate
Protectorate
In history, the term protectorate has two different meanings. In its earliest inception, which has been adopted by modern international law, it is an autonomous territory that is protected diplomatically or militarily against third parties by a stronger state or entity...
of the Russian Empire
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was a state that existed from 1721 until the Russian Revolution of 1917. It was the successor to the Tsardom of Russia and the predecessor of the Soviet Union...
. Control of Poland was central to Catherine the Great's
Catherine II of Russia
Catherine II, also known as Catherine the Great , Empress of Russia, was born in Stettin, Pomerania, Prussia on as Sophie Friederike Auguste von Anhalt-Zerbst-Dornburg...
diplomatic and military strategies. Attempts at reform, such as the Four-Year Sejm's May Constitution came too late. The country was partitioned in three stages
Partitions of Poland
The Partitions of Poland or Partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth took place in the second half of the 18th century and ended the existence of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, resulting in the elimination of sovereign Poland for 123 years...
by the neighboring Russian Empire
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was a state that existed from 1721 until the Russian Revolution of 1917. It was the successor to the Tsardom of Russia and the predecessor of the Soviet Union...
, Kingdom of Prussia
Kingdom of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia was a German kingdom from 1701 to 1918. Until the defeat of Germany in World War I, it comprised almost two-thirds of the area of the German Empire...
, and the Habsburg Monarchy
Habsburg Monarchy
The Habsburg Monarchy covered the territories ruled by the junior Austrian branch of the House of Habsburg , and then by the successor House of Habsburg-Lorraine , between 1526 and 1867/1918. The Imperial capital was Vienna, except from 1583 to 1611, when it was moved to Prague...
. By 1795, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth had been completely erased from the map of Europe. Poland and Lithuania would not be re-established as independent countries until 1918; Ukraine and Belarus
Belarus
Belarus , officially the Republic of Belarus, is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe, bordered clockwise by Russia to the northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. Its capital is Minsk; other major cities include Brest, Grodno , Gomel ,...
established independence in the 1990s.
Golden Liberty

Kanclerz
Kanclerz was one of the highest officials in the historic Poland. This office functioned from the early Polish kingdom of the 12th century until the end of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth in 1795. A respective office also existed in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania since the 16th...
Jan Zamoyski
Jan Zamoyski
Jan Zamoyski , was a Polish-Lithuanian nobleman, magnate, 1st duke/ordynat of Zamość. Royal Secretary since 1566, Lesser Kanclerz ) of the Crown since 1576, Lord Grand-Chancellor of the Crown since 1578, and Grand Hetman of the Crown since 1581...
summed up this doctrine when he said that Rex regnat et non gubernat ("The King reigns but does not govern"). The Commonwealth had a parliament, the Sejm, as well as a Senat and an elected king (Pic. 1). The king was obliged to respect citizens' rights specified in King Henry's Articles as well as in pacta conventa
Pacta conventa (Poland)
Pacta conventa was a contractual agreement, from 1573 to 1764 entered into between the "Polish nation" and a newly-elected king upon his "free election" to the throne.The pacta conventa affirmed the king-elect's pledge to respect the laws of the...
, negotiated at the time of his election.
The monarch's power was limited, in favor of a sizable noble class. Each new king had to pledge to uphold the Henrician Articles, which were the basis of Poland's political system (and included near-unprecedented guarantees of religious tolerance
Religious toleration
Toleration is "the practice of deliberately allowing or permitting a thing of which one disapproves. One can meaningfully speak of tolerating, ie of allowing or permitting, only if one is in a position to disallow”. It has also been defined as "to bear or endure" or "to nourish, sustain or preserve"...
). Over time, the Henrician Articles were merged with the Pacta Conventa, specific pledges agreed to by the king-elect. From that point onwards, the king was effectively a partner with the noble class and was constantly supervised by a group of senators. The Sejm could veto the king on important matters, including legislation (the adoption of new laws), foreign affairs, declaration of war, and taxation (changes of existing taxes or the levying of new ones).
The foundation of the Commonwealth's political system, the "Golden Liberty
Golden Liberty
Golden Liberty , sometimes referred to as Golden Freedoms, Nobles' Democracy or Nobles' Commonwealth refers to a unique aristocratic political system in the Kingdom of Poland and later, after the Union of Lublin , in the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth...
" , included:
- election of the king by all nobles wishing to participate, known as wolna elekcja (free election);;
- SejmSejmThe Sejm is the lower house of the Polish parliament. The Sejm is made up of 460 deputies, or Poseł in Polish . It is elected by universal ballot and is presided over by a speaker called the Marshal of the Sejm ....
, the Commonwealth parliament which the king was required to hold every two years; - Pacta conventaPacta conventaPacta conventa may mean:*Pacta conventa , a contractual agreement between the Polish nobility and king, in force from 1573 to 1764*Pacta conventa , a contractual agreement between the Croatian nobility and the Hungarian king, in force from 1102 to 1918...
(LatinLatinLatin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
), "agreed-to agreements" negotiated with the king-elect, including a bill of rights, binding on the king, derived from the earlier Henrician ArticlesHenrician ArticlesThe Henrician Articles or King Henry's Articles were a permanent contract that stated the fundamental principles of governance and constitutional law in the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth in the form of 21 Articles written and adopted by the nobility in 1573 at the town of Kamień, near Warsaw,...
. - religious freedomReligious tolerationToleration is "the practice of deliberately allowing or permitting a thing of which one disapproves. One can meaningfully speak of tolerating, ie of allowing or permitting, only if one is in a position to disallow”. It has also been defined as "to bear or endure" or "to nourish, sustain or preserve"...
guaranted by Warsaw Confederation Act 1573Warsaw ConfederationThe Warsaw Confederation , an important development in the history of Poland and Lithuania that extended religious tolerance to nobility and free persons within the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. , is considered the formal beginning of religious freedom in the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, and...
, - rokoszRokoszA rokosz originally was a gathering of all the Polish szlachta , not merely of deputies, for a sejm. The term was introduced to the Polish language from Hungary, where analogous gatherings took place at a field called Rákos....
(insurrection), the right of szlachta to form a legal rebellion against a king who violated their guaranteed freedoms; - liberum vetoLiberum vetoThe liberum veto was a parliamentary device in the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. It allowed any member of the Sejm to force an immediate end to the current session and nullify any legislation that had already been passed at the session by shouting Nie pozwalam! .From the mid-16th to the late 18th...
(Latin), the right of an individual Sejm deputy to oppose a decision by the majority in a Sejm session; the voicing of such a "free veto" nullified all the legislation that had been passed at that session; during the crisis of the second half of the 17th century, Polish nobles could also use the liberum vetoLiberum vetoThe liberum veto was a parliamentary device in the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. It allowed any member of the Sejm to force an immediate end to the current session and nullify any legislation that had already been passed at the session by shouting Nie pozwalam! .From the mid-16th to the late 18th...
in provincial sejmikSejmikA sejmik was a regional assembly in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, and earlier in the Kingdom of Poland. Sejmiks existed until the end of the Commonwealth in 1795 following the partitions of the Commonwealth...
s; - konfederacja (from the Latin confederatio), the right to form an organization to force through a common political aim.

Chamber of Deputies
Chamber of deputies is the name given to a legislative body such as the lower house of a bicameral legislature, or can refer to a unicameral legislature.-Description:...
) to the national Sejm and charging of the deputy with specific voting instructions. The Grand Duchy of Lithuania
Grand Duchy of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state from the 12th /13th century until 1569 and then as a constituent part of Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth until 1791 when Constitution of May 3, 1791 abolished it in favor of unitary state. It was founded by the Lithuanians, one of the polytheistic...
had its own separate army, treasury and most other official institutions.
Golden Liberty created a state that was unusual for its time, although somewhat similar political system
Political system
A political system is a system of politics and government. It is usually compared to the legal system, economic system, cultural system, and other social systems...
s existed in the contemporary city-state
City-state
A city-state is an independent or autonomous entity whose territory consists of a city which is not administered as a part of another local government.-Historical city-states:...
s like the Republic of Venice
Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice or Venetian Republic was a state originating from the city of Venice in Northeastern Italy. It existed for over a millennium, from the late 7th century until 1797. It was formally known as the Most Serene Republic of Venice and is often referred to as La Serenissima, in...
. Interestingly, both states were styled "Serenissima Respublica" or the "Most Serene Republic
Most Serene Republic
Most Serene Republic is a title attached to the following countries:* Republic of Venice , city-state that existed from 697 to 1797 based in the city of Venice with continuously controlled territory along the eastern Adriatic at its strongest period...
". At a time when most European countries were headed toward centralization
Centralization
Centralisation, or centralization , is the process by which the activities of an organisation, particularly those regarding planning and decision-making, become concentrated within a particular location and/or group....
, absolute monarchy
Absolute monarchy
Absolute monarchy is a monarchical form of government in which the monarch exercises ultimate governing authority as head of state and head of government, his or her power not being limited by a constitution or by the law. An absolute monarch thus wields unrestricted political power over the...
and religious and dynastic warfare, the Commonwealth experimented with decentralization
Decentralization
__FORCETOC__Decentralization or decentralisation is the process of dispersing decision-making governance closer to the people and/or citizens. It includes the dispersal of administration or governance in sectors or areas like engineering, management science, political science, political economy,...
, confederation
Confederation
A confederation in modern political terms is a permanent union of political units for common action in relation to other units. Usually created by treaty but often later adopting a common constitution, confederations tend to be established for dealing with critical issues such as defense, foreign...
and federation
Federation
A federation , also known as a federal state, is a type of sovereign state characterized by a union of partially self-governing states or regions united by a central government...
, democracy, religious tolerance
Religious toleration
Toleration is "the practice of deliberately allowing or permitting a thing of which one disapproves. One can meaningfully speak of tolerating, ie of allowing or permitting, only if one is in a position to disallow”. It has also been defined as "to bear or endure" or "to nourish, sustain or preserve"...
, and even pacifism
Pacifism
Pacifism is the opposition to war and violence. The term "pacifism" was coined by the French peace campaignerÉmile Arnaud and adopted by other peace activists at the tenth Universal Peace Congress inGlasgow in 1901.- Definition :...
. The Sejm's usual veto of wars has been described as an example of democratic peace theory
Democratic peace theory
Democratic peace theory is the theory that democracies don't go to war with each other. How well the theory matches reality depends a great deal on one's definition of "democracy" and "war"...
.
This political system unusual for its time stemmed from the ascendance of the szlachta noble class
Nobility
Nobility is a social class which possesses more acknowledged privileges or eminence than members of most other classes in a society, membership therein typically being hereditary. The privileges associated with nobility may constitute substantial advantages over or relative to non-nobles, or may be...
over other social classes and over the political system
Political system
A political system is a system of politics and government. It is usually compared to the legal system, economic system, cultural system, and other social systems...
of monarchy
Monarchy
A monarchy is a form of government in which the office of head of state is usually held until death or abdication and is often hereditary and includes a royal house. In some cases, the monarch is elected...
. In time, the szlachta accumulated enough privileges (such as those established by the Nihil novi
Nihil novi
Nihil novi nisi commune consensu is the original Latin title of a 1505 act adopted by the Polish Sejm , meeting in the royal castle at Radom.-History:...
Act of 1505) that no monarch could hope to break the szlachta's grip on power. The Commonwealth's political system is difficult to fit into a simple category, but it can be tentatively described as a mixture of:
- confederationConfederationA confederation in modern political terms is a permanent union of political units for common action in relation to other units. Usually created by treaty but often later adopting a common constitution, confederations tend to be established for dealing with critical issues such as defense, foreign...
and federationFederationA federation , also known as a federal state, is a type of sovereign state characterized by a union of partially self-governing states or regions united by a central government...
, with regard to the broad autonomy of its regions. It is, however, difficult to decisively call the Commonwealth either confederation or federation, as it had some qualities of both of them; - oligarchyOligarchyOligarchy is a form of power structure in which power effectively rests with an elite class distinguished by royalty, wealth, family ties, commercial, and/or military legitimacy...
, as only the szlachta—around 15% of the population—had political rights; - democracyDemocracyDemocracy is generally defined as a form of government in which all adult citizens have an equal say in the decisions that affect their lives. Ideally, this includes equal participation in the proposal, development and passage of legislation into law...
, since all the szlachta were equal in rights and privileges, and the Sejm could veto the king on important matters, including legislationLegislationLegislation is law which has been promulgated by a legislature or other governing body, or the process of making it...
(the adoption of new laws), foreign affairs, declaration of war, and taxation (changes of existing taxes or the levying of new ones). Also, the 15% of Commonwealth population who enjoyed those political rights (the szlachta) was a substantially larger percentage than in majority European countries; note that in 1789 in France only about 1% of the population had the right to vote, and in 1867 in the United Kingdom, only about 3%. - elective monarchyElective monarchyAn elective monarchy is a monarchy ruled by an elected rather than hereditary monarch. The manner of election, the nature of the candidacy and the electors vary from case to case...
, since the monarch, elected by the szlachta, was Head of State; - constitutional monarchyConstitutional monarchyConstitutional monarchy is a form of government in which a monarch acts as head of state within the parameters of a constitution, whether it be a written, uncodified or blended constitution...
, since the monarch was bound by pacta conventa and other laws, and the szlachta could disobey any king's decrees they deemed illegal.
Shortcomings

Jagiellon dynasty
The Jagiellonian dynasty was a royal dynasty originating from the Lithuanian House of Gediminas dynasty that reigned in Central European countries between the 14th and 16th century...
in 1572after nearly two centuriesdisrupted the fragile equilibrium of the Commonwealth's government. Power increasingly slipped away from the central government to the nobility.
When presented with periodic opportunities to fill the throne, the szlachta exhibited a preference for foreign candidates who would not found another strong dynasty
Dynasty
A dynasty is a sequence of rulers considered members of the same family. Historians traditionally consider many sovereign states' history within a framework of successive dynasties, e.g., China, Ancient Egypt and the Persian Empire...
. This policy often produced monarchs who were either totally ineffective or in constant debilitating conflict with the nobility. Furthermore, aside from notable exceptions such as the able Transylvania
Transylvania
Transylvania is a historical region in the central part of Romania. Bounded on the east and south by the Carpathian mountain range, historical Transylvania extended in the west to the Apuseni Mountains; however, the term sometimes encompasses not only Transylvania proper, but also the historical...
n Stefan Batory
Stefan Batory
Stephen Báthory was a Hungarian noble Prince of Transylvania , then King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania . He was a member of the Somlyó branch of the noble Hungarian Báthory family...
(1576–86), the kings of foreign origin were inclined to subordinate the interests of the Commonwealth to those of their own country and ruling house. This was especially visible in the policies and actions of the first two elected kings from the Swedish House of Vasa
House of Vasa
The House of Vasa was the Royal House of Sweden 1523-1654 and of Poland 1587-1668. It originated from a noble family in Uppland of which several members had high offices during the 15th century....
, whose politics brought the Commonwealth into conflict with Sweden, culminating in the war known as The Deluge
The Deluge (Polish history)
The term Deluge denotes a series of mid-17th century campaigns in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. In a wider sense it applies to the period between the Khmelnytsky Uprising of 1648 and the Truce of Andrusovo in 1667, thus comprising the Polish–Lithuanian theaters of the Russo-Polish and...
(1655), one of the events that mark the end of the Commonwealth's Golden Age and the beginning of the Commonwealth's decline.
Zebrzydowski's rokosz (1606–07) marked a substantial increase in the power of the magnate
Magnate
Magnate, from the Late Latin magnas, a great man, itself from Latin magnus 'great', designates a noble or other man in a high social position, by birth, wealth or other qualities...
s, and the transformation of szlachta democracy into magnate oligarchy. The Commonwealth's political system was vulnerable to outside interference, as Sejm deputies bribed by foreign powers might use their liberum veto to block attempted reforms. This sapped the Commonwealth and plunged it into political paralysis and anarchy for over a century, from the mid-17th century to the end of the 18th, while its neighbors stabilized their internal affairs and increased their military might.
Late reforms

Norman Davies
Professor Ivor Norman Richard Davies FBA, FRHistS is a leading English historian of Welsh descent, noted for his publications on the history of Europe, Poland, and the United Kingdom.- Academic career :...
calls the first of its kind in Europe. The revolutionary Constitution recast the erstwhile Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth as a Polish–Lithuanian federal state with a hereditary monarchy
Hereditary monarchy
A hereditary monarchy is the most common type of monarchy and is the form that is used by almost all of the world's existing monarchies.Under a hereditary monarchy, all the monarchs come from the same family, and the crown is passed down from one member to another member of the family...
and abolished many of the deleterious features of the old system. The new constitution:
- abolished the liberum vetoLiberum vetoThe liberum veto was a parliamentary device in the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. It allowed any member of the Sejm to force an immediate end to the current session and nullify any legislation that had already been passed at the session by shouting Nie pozwalam! .From the mid-16th to the late 18th...
and banned the szlachta's confederations; - provided for a separation of powersSeparation of powersThe separation of powers, often imprecisely used interchangeably with the trias politica principle, is a model for the governance of a state. The model was first developed in ancient Greece and came into widespread use by the Roman Republic as part of the unmodified Constitution of the Roman Republic...
among legislative, executiveExecutive (government)Executive branch of Government is the part of government that has sole authority and responsibility for the daily administration of the state bureaucracy. The division of power into separate branches of government is central to the idea of the separation of powers.In many countries, the term...
and judicial branches of government; - established "popular sovereigntyPopular sovereigntyPopular sovereignty or the sovereignty of the people is the political principle that the legitimacy of the state is created and sustained by the will or consent of its people, who are the source of all political power. It is closely associated with Republicanism and the social contract...
" and extended political rightsRightsRights are legal, social, or ethical principles of freedom or entitlement; that is, rights are the fundamental normative rules about what is allowed of people or owed to people, according to some legal system, social convention, or ethical theory...
to include not only the nobilityNobilityNobility is a social class which possesses more acknowledged privileges or eminence than members of most other classes in a society, membership therein typically being hereditary. The privileges associated with nobility may constitute substantial advantages over or relative to non-nobles, or may be...
but the bourgeoisieBourgeoisieIn sociology and political science, bourgeoisie describes a range of groups across history. In the Western world, between the late 18th century and the present day, the bourgeoisie is a social class "characterized by their ownership of capital and their related culture." A member of the...
; - increased the rights of the peasantry;
- preserved religious toleranceReligious tolerationToleration is "the practice of deliberately allowing or permitting a thing of which one disapproves. One can meaningfully speak of tolerating, ie of allowing or permitting, only if one is in a position to disallow”. It has also been defined as "to bear or endure" or "to nourish, sustain or preserve"...
(but with a condemnation of apostasyApostasyApostasy , 'a defection or revolt', from ἀπό, apo, 'away, apart', στάσις, stasis, 'stand, 'standing') is the formal disaffiliation from or abandonment or renunciation of a religion by a person. One who commits apostasy is known as an apostate. These terms have a pejorative implication in everyday...
from the Catholic faith).
These reforms came too late, however, as the Commonwealth was immediately invaded from all sides by its neighbors which were content to leave the Commonwealth alone as a weak buffer state, but reacted strongly to king Stanisław August Poniatowski's and other reformers' attempts to strengthen the country. Russia feared the revolutionary implications of the May 3rd Constitution's political reforms and the prospect of the Commonwealth regaining its position as a European empire. Catherine the Great regarded the May constitution as fatal to her influence and declared the Polish constitution Jacobinical
Jacobin (politics)
A Jacobin , in the context of the French Revolution, was a member of the Jacobin Club, a revolutionary far-left political movement. The Jacobin Club was the most famous political club of the French Revolution. So called from the Dominican convent where they originally met, in the Rue St. Jacques ,...
. Grigori Aleksandrovich Potemkin drafted the act for the Confederation of Targowica, referring to the constitution as the "contagion of democratic ideas". Meanwhile, Prussia
Prussia
Prussia was a German kingdom and historic state originating out of the Duchy of Prussia and the Margraviate of Brandenburg. For centuries, the House of Hohenzollern ruled Prussia, successfully expanding its size by way of an unusually well-organized and effective army. Prussia shaped the history...
and Austria
Austria
Austria , officially the Republic of Austria , is a landlocked country of roughly 8.4 million people in Central Europe. It is bordered by the Czech Republic and Germany to the north, Slovakia and Hungary to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland and Liechtenstein to the...
, also afraid of a strengthened Poland, used it as a pretext for further territorial expansion. Prussian minister Ewald von Hertzberg called the constitution "a blow to the Prussian monarchy", fearing that strengthened Poland would once again dominate Prussia. In the end, the May 3rd Constitution was never fully implemented, and the Commonwealth entirely ceased to exist only four years after the Constitution's adoption.
Economy


Economics
Economics is the social science that analyzes the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. The term economics comes from the Ancient Greek from + , hence "rules of the house"...
of the Commonwealth was dominated by feudal
Feudalism
Feudalism was a set of legal and military customs in medieval Europe that flourished between the 9th and 15th centuries, which, broadly defined, was a system for ordering society around relationships derived from the holding of land in exchange for service or labour.Although derived from the...
agriculture
Agriculture
Agriculture is the cultivation of animals, plants, fungi and other life forms for food, fiber, and other products used to sustain life. Agriculture was the key implement in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that nurtured the...
based on the plantation system
Plantation economy
A plantation economy is an economy which is based on agricultural mass production, usually of a few staple products grown on large farms called plantations. Plantation economies rely on the export of cash crops as a source of income...
(serfs). Slavery
Slavery
Slavery is a system under which people are treated as property to be bought and sold, and are forced to work. Slaves can be held against their will from the time of their capture, purchase or birth, and deprived of the right to leave, to refuse to work, or to demand compensation...
in Poland was forbidden in the 15th century; in Lithuania, slavery was formally abolished in 1588. They were replaced by the second enserfment. Typically a nobleman's landholding comprised a folwark
Folwark
Folwark is a Polish word for a primarily serfdom-based farm and agricultural enterprise , often very large. Folwarks were operated in the Crown of Poland from the 14th century and in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania since the 15th century, from the second half of the 16th century in the joint...
, a large farm
Farm
A farm is an area of land, or, for aquaculture, lake, river or sea, including various structures, devoted primarily to the practice of producing and managing food , fibres and, increasingly, fuel. It is the basic production facility in food production. Farms may be owned and operated by a single...
worked by serf
SERF
A spin exchange relaxation-free magnetometer is a type of magnetometer developed at Princeton University in the early 2000s. SERF magnetometers measure magnetic fields by using lasers to detect the interaction between alkali metal atoms in a vapor and the magnetic field.The name for the technique...
s to produce surpluses for internal and external trade. This economic arrangement worked well for the ruling classes in the early era of the Commonwealth, which was one of the most prosperous eras of the grain trade. The economic strength of Commonwealth grain trade waned from the late 17th century on. Trade relationships were disrupted by the wars and the Commonwealth proved unable to improve its transport infrastructure or its agricultural practices. Serfs in the region were increasingly tempted to flee. The Commonwealth's major attempts at countering this problem and improving productivity consisted of increasing serfs' workload and further restricting their freedoms in a process known as second serfdom.
Though the urban population of the Commonwealth was about 20% of the total in the 17th century, which was much lower than in some West European countries (approximately 50% in the Netherlands and Italy) the urbanization
Urbanization
Urbanization, urbanisation or urban drift is the physical growth of urban areas as a result of global change. The United Nations projected that half of the world's population would live in urban areas at the end of 2008....
of the country was of a specific character (Pic. 7). The Commonwealth's preoccupation with agriculture, coupled with the szlachta's privileged position when compared to the bourgeoisie
Bourgeoisie
In sociology and political science, bourgeoisie describes a range of groups across history. In the Western world, between the late 18th century and the present day, the bourgeoisie is a social class "characterized by their ownership of capital and their related culture." A member of the...
, resulted in a fairly slow process of urbanization and thus a rather slow development of industries
Industry
Industry refers to the production of an economic good or service within an economy.-Industrial sectors:There are four key industrial economic sectors: the primary sector, largely raw material extraction industries such as mining and farming; the secondary sector, involving refining, construction,...
. While similar conflicts among social classes may be found all over Europe, nowhere were the nobility as dominant at the time as in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. There is, however, much debate among historians as to which processes most affected those developments, since until the wars and crises of the mid-17th century the cities of the Commonwealth had not markedly lagged in size and wealth behind their western counterparts. The Commonwealth did have numerous towns and cities
City
A city is a relatively large and permanent settlement. Although there is no agreement on how a city is distinguished from a town within general English language meanings, many cities have a particular administrative, legal, or historical status based on local law.For example, in the U.S...
, commonly founded on Magdeburg rights
Magdeburg rights
Magdeburg Rights or Magdeburg Law were a set of German town laws regulating the degree of internal autonomy within cities and villages granted by a local ruler. Modelled and named after the laws of the German city of Magdeburg and developed during many centuries of the Holy Roman Empire, it was...
. Some of the largest trade fair
Trade fair
A trade fair is an exhibition organized so that companies in a specific industry can showcase and demonstrate their latest products, service, study activities of rivals and examine recent market trends and opportunities...
s in the Commonwealth were held at Lublin
Lublin
Lublin is the ninth largest city in Poland. It is the capital of Lublin Voivodeship with a population of 350,392 . Lublin is also the largest Polish city east of the Vistula river...
. See the geography section, below, for a list of major cities in the Commonwealth (commonly capitals of voivodships).
Poland-Lithuania played a significant role in the supply of 16th century Western Europe
Western Europe
Western Europe is a loose term for the collection of countries in the western most region of the European continents, though this definition is context-dependent and carries cultural and political connotations. One definition describes Western Europe as a geographic entity—the region lying in the...
by the export of three sorts of goods, notably grain
GRAIN
GRAIN is a small international non-profit organisation that works to support small farmers and social movements in their struggles for community-controlled and biodiversity-based food systems. Our support takes the form of independent research and analysis, networking at local, regional and...
(rye), cattle
Cattle
Cattle are the most common type of large domesticated ungulates. They are a prominent modern member of the subfamily Bovinae, are the most widespread species of the genus Bos, and are most commonly classified collectively as Bos primigenius...
(oxen) and fur
Fur
Fur is a synonym for hair, used more in reference to non-human animals, usually mammals; particularly those with extensives body hair coverage. The term is sometimes used to refer to the body hair of an animal as a complete coat, also known as the "pelage". Fur is also used to refer to animal...
. These three articles amounted to nearly 90% of the country's exports to western markets by overland- and maritime trade.

Prussia
Prussia was a German kingdom and historic state originating out of the Duchy of Prussia and the Margraviate of Brandenburg. For centuries, the House of Hohenzollern ruled Prussia, successfully expanding its size by way of an unusually well-organized and effective army. Prussia shaped the history...
in 1560–70 was some 113,000 ton
Ton
The ton is a unit of measure. It has a long history and has acquired a number of meanings and uses over the years. It is used principally as a unit of weight, and as a unit of volume. It can also be used as a measure of energy, for truck classification, or as a colloquial term.It is derived from...
s of wheat
Wheat
Wheat is a cereal grain, originally from the Levant region of the Near East, but now cultivated worldwide. In 2007 world production of wheat was 607 million tons, making it the third most-produced cereal after maize and rice...
(or 226,000 łaszt – a łaszt, or "last"
Last (disambiguation)
-Music:* "Last", a song by Nine Inch Nails from the 1992 album Broken * Last , a 2010 album by Uverworld* Last , a 2011 album by The Unthanks* Last.fm, a UK-based music-community website-Other:...
, being a large bulk measure; in the case of grain, about half a ton). Average yearly production of grain in the Commonwealth in the 16th Century was 120,000 tons, 6% of which was export
Export
The term export is derived from the conceptual meaning as to ship the goods and services out of the port of a country. The seller of such goods and services is referred to as an "exporter" who is based in the country of export whereas the overseas based buyer is referred to as an "importer"...
ed, while cities consumed some 19% and the remainder was consumed by the villages. Commonwealth grain achieved far more importance in poor crop years, as in the early 1590s and the 1620s, when governments throughout southern Europe arranged for large grain imports to cover shortfalls in their jurisdictions.
Still, grain was the largest export commodity of the Commonwealth. The owner of a folwark
Folwark
Folwark is a Polish word for a primarily serfdom-based farm and agricultural enterprise , often very large. Folwarks were operated in the Crown of Poland from the 14th century and in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania since the 15th century, from the second half of the 16th century in the joint...
usually signed a contract
Contract
A contract is an agreement entered into by two parties or more with the intention of creating a legal obligation, which may have elements in writing. Contracts can be made orally. The remedy for breach of contract can be "damages" or compensation of money. In equity, the remedy can be specific...
with merchants of Gdańsk
Gdansk
Gdańsk is a Polish city on the Baltic coast, at the centre of the country's fourth-largest metropolitan area.The city lies on the southern edge of Gdańsk Bay , in a conurbation with the city of Gdynia, spa town of Sopot, and suburban communities, which together form a metropolitan area called the...
, who controlled 80% of this inland trade, to ship the grain north to that seaport on the Baltic Sea
Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is a brackish mediterranean sea located in Northern Europe, from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from 20°E to 26°E longitude. It is bounded by the Scandinavian Peninsula, the mainland of Europe, and the Danish islands. It drains into the Kattegat by way of the Øresund, the Great Belt and...
. Many rivers in the Commonwealth were used for shipping purposes: the Vistula
Vistula
The Vistula is the longest and the most important river in Poland, at 1,047 km in length. The watershed area of the Vistula is , of which lies within Poland ....
, Pilica, Bug
Bug River
The Bug River is a left tributary of the Narew river flows from central Ukraine to the west, passing along the Ukraine-Polish and Polish-Belarusian border and into Poland, where it empties into the Narew river near Serock. The part between the lake and the Vistula River is sometimes referred to as...
, San
San River
The San is a river in southeastern Poland and western Ukraine, a tributary of the Vistula River, with a length of 433 km and a basin area of 16,861 km2...
, Nida
Nida River
Nida is a river in central Poland, a tributary of the Vistula river , with a length of 151 kilometres and a basin area of 3,865 km2. This includes the protected area called Nida Landscape Park.Towns and townships;...
, Wieprz, Niemen. The rivers had relatively developed infrastructure, with river ports and granaries
Granary
A granary is a storehouse for threshed grain or animal feed. In ancient or primitive granaries, pottery is the most common use of storage in these buildings. Granaries are often built above the ground to keep the stored food away from mice and other animals.-Early origins:From ancient times grain...
. Most of the river shipping moved north, southward transport being less profitable, and barges and rafts were often sold off in Gdańsk for lumber. Hrodna
Hrodna
Grodno or Hrodna , is a city in Belarus. It is located on the Neman River , close to the borders of Poland and Lithuania . It has 327,540 inhabitants...
become an important site after formation of a customs post at Augustów
Augustów
Augustów is a town in north-eastern Poland with 29,600 inhabitants . It lies on the Netta River and the Augustów Canal. It is situated in the Podlaskie Voivodeship , having previously been in Suwałki Voivodeship . It is the seat of Augustów County and of Gmina Augustów.In 1970 Augustów became...
in 1569, which became a checkpoint for merchants travelling to the Crown lands from the Grand Duchy.
From Gdańsk, ships, mostly from the Netherlands
Netherlands
The Netherlands is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, located mainly in North-West Europe and with several islands in the Caribbean. Mainland Netherlands borders the North Sea to the north and west, Belgium to the south, and Germany to the east, and shares maritime borders...
and Flanders
Flanders
Flanders is the community of the Flemings but also one of the institutions in Belgium, and a geographical region located in parts of present-day Belgium, France and the Netherlands. "Flanders" can also refer to the northern part of Belgium that contains Brussels, Bruges, Ghent and Antwerp...
, carried the grain to ports such as Antwerp and Amsterdam
Amsterdam
Amsterdam is the largest city and the capital of the Netherlands. The current position of Amsterdam as capital city of the Kingdom of the Netherlands is governed by the constitution of August 24, 1815 and its successors. Amsterdam has a population of 783,364 within city limits, an urban population...
. Besides grain, other seaborne exports included carminic acid
Carminic acid
Carminic acid is a red glucosidal hydroxyanthrapurin that occurs naturally in some scale insects, such as the cochineal and the Polish cochineal. The insects produce the acid as a deterrent to predators. Carminic acid is the colouring agent in carmine. Synonyms are C.I. 75470 and C.I...
from Polish cochineal
Polish cochineal
Polish cochineal , also known as Polish carmine scales, is a scale insect formerly used to produce a crimson dye of the same name, colloquially known as "Saint John's blood". The larvae of P...
, lumber
Lumber
Lumber or timber is wood in any of its stages from felling through readiness for use as structural material for construction, or wood pulp for paper production....
and wood-related products such as ash
Wood ash
Wood ash is the residue powder left after the combustion of wood. Main producers of wood ash are wood industries and power plants.-Composition:...
, and tar
Tar
Tar is modified pitch produced primarily from the wood and roots of pine by destructive distillation under pyrolysis. Production and trade in tar was a major contributor in the economies of Northern Europe and Colonial America. Its main use was in preserving wooden vessels against rot. The largest...
. The land routes, mostly to the German lands of the Holy Roman Empire
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a realm that existed from 962 to 1806 in Central Europe.It was ruled by the Holy Roman Emperor. Its character changed during the Middle Ages and the Early Modern period, when the power of the emperor gradually weakened in favour of the princes...
such as the cities of Leipzig
Leipzig
Leipzig Leipzig has always been a trade city, situated during the time of the Holy Roman Empire at the intersection of the Via Regia and Via Imperii, two important trade routes. At one time, Leipzig was one of the major European centres of learning and culture in fields such as music and publishing...
and Nuremberg
Nuremberg
Nuremberg[p] is a city in the German state of Bavaria, in the administrative region of Middle Franconia. Situated on the Pegnitz river and the Rhine–Main–Danube Canal, it is located about north of Munich and is Franconia's largest city. The population is 505,664...
, were used for export of live cattle
Cattle
Cattle are the most common type of large domesticated ungulates. They are a prominent modern member of the subfamily Bovinae, are the most widespread species of the genus Bos, and are most commonly classified collectively as Bos primigenius...
(herds of around 50,000 head) hides
Hides
A hide is an animal skin treated for human use. Hides include leather from cattle and other livestock animals, alligator skins, snake skins for shoes and fashion accessories and furs from wild cats, mink and bears. In some areas, leather is produced on a domestic or small industrial scale, but most...
, fur
Fur
Fur is a synonym for hair, used more in reference to non-human animals, usually mammals; particularly those with extensives body hair coverage. The term is sometimes used to refer to the body hair of an animal as a complete coat, also known as the "pelage". Fur is also used to refer to animal...
s, salt
Salt
In chemistry, salts are ionic compounds that result from the neutralization reaction of an acid and a base. They are composed of cations and anions so that the product is electrically neutral...
, tobacco
Tobacco
Tobacco is an agricultural product processed from the leaves of plants in the genus Nicotiana. It can be consumed, used as a pesticide and, in the form of nicotine tartrate, used in some medicines...
, hemp
Hemp
Hemp is mostly used as a name for low tetrahydrocannabinol strains of the plant Cannabis sativa, of fiber and/or oilseed varieties. In modern times, hemp has been used for industrial purposes including paper, textiles, biodegradable plastics, construction, health food and fuel with modest...
, cotton
Cotton
Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective capsule, around the seeds of cotton plants of the genus Gossypium. The fiber is almost pure cellulose. The botanical purpose of cotton fiber is to aid in seed dispersal....
(mostly from Greater Poland
Greater Poland
Greater Poland or Great Poland, often known by its Polish name Wielkopolska is a historical region of west-central Poland. Its chief city is Poznań.The boundaries of Greater Poland have varied somewhat throughout history...
) and linen
Linen
Linen is a textile made from the fibers of the flax plant, Linum usitatissimum. Linen is labor-intensive to manufacture, but when it is made into garments, it is valued for its exceptional coolness and freshness in hot weather....
.
The Commonwealth imported wine
Wine
Wine is an alcoholic beverage, made of fermented fruit juice, usually from grapes. The natural chemical balance of grapes lets them ferment without the addition of sugars, acids, enzymes, or other nutrients. Grape wine is produced by fermenting crushed grapes using various types of yeast. Yeast...
, fruit
Fruit
In broad terms, a fruit is a structure of a plant that contains its seeds.The term has different meanings dependent on context. In non-technical usage, such as food preparation, fruit normally means the fleshy seed-associated structures of certain plants that are sweet and edible in the raw state,...
, spices, luxury good
Luxury good
Luxury goods are products and services that are not considered essential and associated with affluence.The concept of luxury has been present in various forms since the beginning of civilization. Its role was just as important in ancient western and eastern empires as it is in modern societies...
s (e.g. tapestries
Tapestry
Tapestry is a form of textile art, traditionally woven on a vertical loom, however it can also be woven on a floor loom as well. It is composed of two sets of interlaced threads, those running parallel to the length and those parallel to the width ; the warp threads are set up under tension on a...
, Pic. 5), clothing
Clothing
Clothing refers to any covering for the human body that is worn. The wearing of clothing is exclusively a human characteristic and is a feature of nearly all human societies...
, fish
Fish
Fish are a paraphyletic group of organisms that consist of all gill-bearing aquatic vertebrate animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish, as well as various extinct related groups...
, beer
Beer
Beer is the world's most widely consumed andprobably oldest alcoholic beverage; it is the third most popular drink overall, after water and tea. It is produced by the brewing and fermentation of sugars, mainly derived from malted cereal grains, most commonly malted barley and malted wheat...
and industrial products like steel
Steel
Steel is an alloy that consists mostly of iron and has a carbon content between 0.2% and 2.1% by weight, depending on the grade. Carbon is the most common alloying material for iron, but various other alloying elements are used, such as manganese, chromium, vanadium, and tungsten...
and tool
Tool
A tool is a device that can be used to produce an item or achieve a task, but that is not consumed in the process. Informally the word is also used to describe a procedure or process with a specific purpose. Tools that are used in particular fields or activities may have different designations such...
s. A few riverboats carried south imports from Gdańsk like wine, fruit, spices and herring. Somewhere between the 16th and 17th centuries, the Commonwealth's trade balance shifted from positive to negative.
With the advent of the Age of Exploration, many old trading routes
Trade route
A trade route is a logistical network identified as a series of pathways and stoppages used for the commercial transport of cargo. Allowing goods to reach distant markets, a single trade route contains long distance arteries which may further be connected to several smaller networks of commercial...
such as the Amber Road
Amber Road
The Amber Road was an ancient trade route for the transfer of amber. As one of the waterways and ancient highways, for centuries the road led from Europe to Asia and back, and from northern Africa to the Baltic Sea....
(Pic. 4) lost importance as new ones were created. Poland's importance as a caravan route between Asia and Europe diminished, while new local trading routes were created between the Commonwealth and Russia. Many goods and cultural artifacts continued to pass from one region to another via the Commonwealth. For example, Isfahan rug
Isfahan rug
The Iranian city of Isfahan has long been one of the centres for production of the famous Persian Rug.Weaving in Isfahan flourished in the Safavid era. But when the Afghans invaded Iran, ending the Safavid dynasty, the craft also became stagnant.Not until 1920s, between two world wars, was weaving...
s imported from Persia to the Commonwealth were actually known in the West as "Polish rugs" .
Commonwealth currency
Currency
In economics, currency refers to a generally accepted medium of exchange. These are usually the coins and banknotes of a particular government, which comprise the physical aspects of a nation's money supply...
included the złoty and the grosz
Grosz
Grosz may refer to:* Grosz, a coin used in Poland as a hundredth part of 1 złoty. Złoty is Polish currency* Kraków grosz, 14th century coins of Kraków* Groschen, a coin used in various statesGrosz or Grósz is the surname of:...
. The City of Gdańsk
Gdansk
Gdańsk is a Polish city on the Baltic coast, at the centre of the country's fourth-largest metropolitan area.The city lies on the southern edge of Gdańsk Bay , in a conurbation with the city of Gdynia, spa town of Sopot, and suburban communities, which together form a metropolitan area called the...
had the privilege of minting its own coinage.
Culture
Science and literature


Philosophy
Philosophy is the study of general and fundamental problems, such as those connected with existence, knowledge, values, reason, mind, and language. Philosophy is distinguished from other ways of addressing such problems by its critical, generally systematic approach and its reliance on rational...
such as Erasmus; and, during the Counter-Reformation
Counter-Reformation
The Counter-Reformation was the period of Catholic revival beginning with the Council of Trent and ending at the close of the Thirty Years' War, 1648 as a response to the Protestant Reformation.The Counter-Reformation was a comprehensive effort, composed of four major elements:#Ecclesiastical or...
, was known for near-unparalleled religious tolerance
Religious toleration
Toleration is "the practice of deliberately allowing or permitting a thing of which one disapproves. One can meaningfully speak of tolerating, ie of allowing or permitting, only if one is in a position to disallow”. It has also been defined as "to bear or endure" or "to nourish, sustain or preserve"...
, with peacefully coexisting Catholic, Jewish
Judaism
Judaism ) is the "religion, philosophy, and way of life" of the Jewish people...
, Eastern Orthodox, Protestant and Muslim
Muslim
A Muslim, also spelled Moslem, is an adherent of Islam, a monotheistic, Abrahamic religion based on the Quran, which Muslims consider the verbatim word of God as revealed to prophet Muhammad. "Muslim" is the Arabic term for "submitter" .Muslims believe that God is one and incomparable...
communities. The Commonwealth gave rise to the famous Christian sect
Sect
A sect is a group with distinctive religious, political or philosophical beliefs. Although in past it was mostly used to refer to religious groups, it has since expanded and in modern culture can refer to any organization that breaks away from a larger one to follow a different set of rules and...
of the Polish Brethren
Polish Brethren
The Polish Brethren were members of the Minor Reformed Church of Poland, a Nontrinitarian Protestant church that existed in Poland from 1565 to 1658...
, antecedents of British
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
and American Unitarianism
Unitarianism
Unitarianism is a Christian theological movement, named for its understanding of God as one person, in direct contrast to Trinitarianism which defines God as three persons coexisting consubstantially as one in being....
.
With its political system, the Commonwealth gave birth to political philosophers
Political philosophy
Political philosophy is the study of such topics as liberty, justice, property, rights, law, and the enforcement of a legal code by authority: what they are, why they are needed, what, if anything, makes a government legitimate, what rights and freedoms it should protect and why, what form it...
such as Andrzej Frycz Modrzewski
Andrzej Frycz Modrzewski
Andrzej Frycz Modrzewski was a Polish Renaissance scholar, humanist and theologian, called "the father of Polish democracy." His book De Republica emendanda was widely read and praised across most of Renaissance Europe.-Life:Modrzewski was born in Wolbórz Andrzej Frycz Modrzewski (ca....
(1503–1572) (Pic. 9), Wawrzyniec Grzymała Goślicki (1530–1607) and Piotr Skarga
Piotr Skarga
Piotr Skarga was a Polish Jesuit, preacher, hagiographer, polemicist, and leading figure of the Counter-reformation in the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. He was called the "Polish Bossuet" due to his oratorical abilities.He was born February 2, 1536 in Grójec, to a family of lesser landless gentry...
(1536–1612). Later, works by Stanisław Staszic (1755–1826) and Hugo Kołłątaj (1750–1812) helped pave the way for the Constitution of May 3, 1791
Constitution of May 3, 1791
The Constitution of May 3, 1791 was adopted as a "Government Act" on that date by the Sejm of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. Historian Norman Davies calls it "the first constitution of its type in Europe"; other scholars also refer to it as the world's second oldest constitution...
, which Norman Davies
Norman Davies
Professor Ivor Norman Richard Davies FBA, FRHistS is a leading English historian of Welsh descent, noted for his publications on the history of Europe, Poland, and the United Kingdom.- Academic career :...
calls the first of its kind in Europe.
Kraków
Kraków
Kraków also Krakow, or Cracow , is the second largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula River in the Lesser Poland region, the city dates back to the 7th century. Kraków has traditionally been one of the leading centres of Polish academic, cultural, and artistic life...
's Jagiellonian University
Jagiellonian University
The Jagiellonian University was established in 1364 by Casimir III the Great in Kazimierz . It is the oldest university in Poland, the second oldest university in Central Europe and one of the oldest universities in the world....
is one of the oldest universities in the world (established in 1364), together with the Vilnius University
Vilnius University
Vilnius University is the oldest university in the Baltic states and one of the oldest in Eastern Europe. It is also the largest university in Lithuania....
(established in 1579) they were the major scholarly and scientific centers in the Commonwealth. The Komisja Edukacji Narodowej, Polish for Commission for National Education, formed in 1773, was the world's first national Ministry of Education. Commonwealth scientists included: Martin Kromer (1512–1589), historian and cartographer; Michał Sędziwój (1566–1636), alchemist
Alchemy
Alchemy is an influential philosophical tradition whose early practitioners’ claims to profound powers were known from antiquity. The defining objectives of alchemy are varied; these include the creation of the fabled philosopher's stone possessing powers including the capability of turning base...
and chemist; Jan Brożek
Jan Brozek
Jan Brożek was a Polish polymath: a mathematician, astronomer, physician, poet, writer, musician and rector of the Kraków Academy.-Life:...
(Ioannes Broscius in Latin
Latin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
) (1585–1652), polymath
Polymath
A polymath is a person whose expertise spans a significant number of different subject areas. In less formal terms, a polymath may simply be someone who is very knowledgeable...
: a mathematician
Mathematician
A mathematician is a person whose primary area of study is the field of mathematics. Mathematicians are concerned with quantity, structure, space, and change....
, physician
Physician
A physician is a health care provider who practices the profession of medicine, which is concerned with promoting, maintaining or restoring human health through the study, diagnosis, and treatment of disease, injury and other physical and mental impairments...
and astronomer
Astronomer
An astronomer is a scientist who studies celestial bodies such as planets, stars and galaxies.Historically, astronomy was more concerned with the classification and description of phenomena in the sky, while astrophysics attempted to explain these phenomena and the differences between them using...
; Krzysztof Arciszewski
Krzysztof Arciszewski
Krzysztof Arciszewski Krzysztof Arciszewski Krzysztof Arciszewski (December 9, 1592 in Rogalin – April 7, 1656 near Gdańsk (Danzig), Poland, was a Polish-Lithuanian nobleman (szlachcic), military officer, engineer, and ethnographer. General of artillery of Holland, and Poland ....
(Crestofle d'Artischau Arciszewski in Portuguese
Portuguese language
Portuguese is a Romance language that arose in the medieval Kingdom of Galicia, nowadays Galicia and Northern Portugal. The southern part of the Kingdom of Galicia became independent as the County of Portugal in 1095...
) (1592–1656), engineer
Engineer
An engineer is a professional practitioner of engineering, concerned with applying scientific knowledge, mathematics and ingenuity to develop solutions for technical problems. Engineers design materials, structures, machines and systems while considering the limitations imposed by practicality,...
, ethnographer, general and admiral of the Dutch West Indies Company army in the war with the Spanish Empire
Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire comprised territories and colonies administered directly by Spain in Europe, in America, Africa, Asia and Oceania. It originated during the Age of Exploration and was therefore one of the first global empires. At the time of Habsburgs, Spain reached the peak of its world power....
for control of Brazil
Brazil
Brazil , officially the Federative Republic of Brazil , is the largest country in South America. It is the world's fifth largest country, both by geographical area and by population with over 192 million people...
; Kazimierz Siemienowicz
Kazimierz Siemienowicz
Kazimierz Siemienowicz , was a Polish-Lithuanian general of artillery, gunsmith, military engineer, artillery specialist and pioneer of rocketry. Born in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, he served the armies of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, a federation of Poland and the Grand Duchy, and in the...
(1600–1651), military engineer, artillery
Artillery
Originally applied to any group of infantry primarily armed with projectile weapons, artillery has over time become limited in meaning to refer only to those engines of war that operate by projection of munitions far beyond the range of effect of personal weapons...
specialist and a founder of rocket
Rocket
A rocket is a missile, spacecraft, aircraft or other vehicle which obtains thrust from a rocket engine. In all rockets, the exhaust is formed entirely from propellants carried within the rocket before use. Rocket engines work by action and reaction...
ry; Johannes Hevelius
Johannes Hevelius
Johannes Hevelius Some sources refer to Hevelius as Polish:Some sources refer to Hevelius as German:*Encyplopedia Britannica * of the Royal Society was a councilor and mayor of Danzig , Pomeranian Voivodeship, in the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth...
(1611–1687), astronomer
Astronomer
An astronomer is a scientist who studies celestial bodies such as planets, stars and galaxies.Historically, astronomy was more concerned with the classification and description of phenomena in the sky, while astrophysics attempted to explain these phenomena and the differences between them using...
, founder of lunar
Moon
The Moon is Earth's only known natural satellite,There are a number of near-Earth asteroids including 3753 Cruithne that are co-orbital with Earth: their orbits bring them close to Earth for periods of time but then alter in the long term . These are quasi-satellites and not true moons. For more...
topography
Topography
Topography is the study of Earth's surface shape and features or those ofplanets, moons, and asteroids...
; Michał Boym (1612–1659), orientalist
Oriental studies
Oriental studies is the academic field of study that embraces Near Eastern and Far Eastern societies and cultures, languages, peoples, history and archaeology; in recent years the subject has often been turned into the newer terms of Asian studies and Middle Eastern studies...
, cartographer, naturalist
Naturalist
Naturalist may refer to:* Practitioner of natural history* Conservationist* Advocate of naturalism * Naturalist , autobiography-See also:* The American Naturalist, periodical* Naturalism...
and diplomat in Ming Dynasty's service (Pic. 11); Adam Adamandy Kochański
Adam Adamandy Kochanski
Adam Adamandy Kochański was a Polish mathematician.Kochański was born in Dobrzyń nad Wisłą. He began his education in Toruń, and in 1652 he entered the Society of Jesus in Vilnius under Cardinal Brandr Beekman-Ellner. He studied philosophy at Vilnius University . He also studied mathematics,...
(1631–1700), mathematician
Mathematician
A mathematician is a person whose primary area of study is the field of mathematics. Mathematicians are concerned with quantity, structure, space, and change....
and engineer; Baal Shem Tov (הבעל שם טוב in Hebrew
Hebrew language
Hebrew is a Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Culturally, is it considered by Jews and other religious groups as the language of the Jewish people, though other Jewish languages had originated among diaspora Jews, and the Hebrew language is also used by non-Jewish groups, such...
) (1698–1760), considered to be the founder of Hasidic Judaism
Hasidic Judaism
Hasidic Judaism or Hasidism, from the Hebrew —Ḥasidut in Sephardi, Chasidus in Ashkenazi, meaning "piety" , is a branch of Orthodox Judaism that promotes spirituality and joy through the popularisation and internalisation of Jewish mysticism as the fundamental aspects of the Jewish faith...
; Marcin Odlanicki Poczobutt (1728–1810), astronomer
Astronomer
An astronomer is a scientist who studies celestial bodies such as planets, stars and galaxies.Historically, astronomy was more concerned with the classification and description of phenomena in the sky, while astrophysics attempted to explain these phenomena and the differences between them using...
and mathematician
Mathematician
A mathematician is a person whose primary area of study is the field of mathematics. Mathematicians are concerned with quantity, structure, space, and change....
(Pic. 12); Jan Krzysztof Kluk
Jan Krzysztof Kluk
Jan Krzysztof Kluk was a Polish naturalist agronomist and entomologist.He was the son of Jan Krzysztof and Marianna Elżbieta. His father, a nobleman turned poor, was an architect, mainly of churches. Jan Krzysztof Kluk went to school in Warsaw, later in Drohiczyn, and finally in the Piarists...
(1739–1796), naturalist
Natural history
Natural history is the scientific research of plants or animals, leaning more towards observational rather than experimental methods of study, and encompasses more research published in magazines than in academic journals. Grouped among the natural sciences, natural history is the systematic study...
, agronomist
Agronomist
An agronomist is a scientist who specializes in agronomy, which is the science of utilizing plants for food, fuel, feed, and fiber. An agronomist is an expert in agricultural and allied sciences, with the exception veterinary sciences.Agronomists deal with interactions between plants, soils, and...
and entomologist
Entomology
Entomology is the scientific study of insects, a branch of arthropodology...
. In 1628 the Czech teacher
Teacher
A teacher or schoolteacher is a person who provides education for pupils and students . The role of teacher is often formal and ongoing, carried out at a school or other place of formal education. In many countries, a person who wishes to become a teacher must first obtain specified professional...
, scientist
Scientist
A scientist in a broad sense is one engaging in a systematic activity to acquire knowledge. In a more restricted sense, a scientist is an individual who uses the scientific method. The person may be an expert in one or more areas of science. This article focuses on the more restricted use of the word...
, educator, and writer
Writer
A writer is a person who produces literature, such as novels, short stories, plays, screenplays, poetry, or other literary art. Skilled writers are able to use language to portray ideas and images....
John Amos Comenius took refuge in the Commonwealth, when the Protestants
Protestantism
Protestantism is one of the three major groupings within Christianity. It is a movement that began in Germany in the early 16th century as a reaction against medieval Roman Catholic doctrines and practices, especially in regards to salvation, justification, and ecclesiology.The doctrines of the...
were persecuted under the Counter Reformation.
The works of many Commonwealth authors are considered classics, including those of Jan Kochanowski
Jan Kochanowski
Jan Kochanowski was a Polish Renaissance poet who established poetic patterns that would become integral to Polish literary language.He is commonly regarded as the greatest Polish poet before Adam Mickiewicz, and the greatest Slavic poet, prior to the 19th century.-Life:Kochanowski was born at...
(Pic. 10), Wacław Potocki, Ignacy Krasicki
Ignacy Krasicki
Ignacy Krasicki , from 1766 Prince-Bishop of Warmia and from 1795 Archbishop of Gniezno , was Poland's leading Enlightenment poet , a critic of the clergy, Poland's La Fontaine, author of the first Polish novel, playwright, journalist, encyclopedist, and translator from French and...
, and Julian Ursyn Niemcewicz
Julian Ursyn Niemcewicz
Julian Ursyn Niemcewicz was a Polish poet, playwright and statesman. He was a leading advocate for the Constitution of May 3, 1791.-Life:...
. Many szlachta
Szlachta
The szlachta was a legally privileged noble class with origins in the Kingdom of Poland. It gained considerable institutional privileges during the 1333-1370 reign of Casimir the Great. In 1413, following a series of tentative personal unions between the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the Kingdom of...
members wrote memoir
Memoir
A memoir , is a literary genre, forming a subclass of autobiography – although the terms 'memoir' and 'autobiography' are almost interchangeable. Memoir is autobiographical writing, but not all autobiographical writing follows the criteria for memoir set out below...
s and diaries
Diary
A diary is a record with discrete entries arranged by date reporting on what has happened over the course of a day or other period. A personal diary may include a person's experiences, and/or thoughts or feelings, including comment on current events outside the writer's direct experience. Someone...
. Perhaps the most famous are the Memoirs of Polish History by Albrycht Stanisław Radziwiłł (1595–1656) and the Memoirs of Jan Chryzostom Pasek
Jan Chryzostom Pasek
Jan Chryzostom Pasek was a Polish nobleman and writer in the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. He is best remembered for his memoirs , which are a valuable historical source about Baroque sarmatian culture and events in the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth.Born in Węgrzynowice near Rawa Mazowiecka in...
(ca. 1636–ca. 1701). Jakub Sobieski
Jakub Sobieski
Jakub Sobieski was a Polish-Lithuanian noble, parliamentarian, diarist, political activist, military leader and father of King Jan III Sobieski. Son of castellan and voivode Marek Sobieski and Jadwiga Snopkowska.- Life :...
(1590–1646) (father of John III Sobieski
John III Sobieski
John III Sobieski was one of the most notable monarchs of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, from 1674 until his death King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania. Sobieski's 22-year-reign was marked by a period of the Commonwealth's stabilization, much needed after the turmoil of the Deluge and...
) wrote notable diaries. During the Khotyn expedition
Battle of Khotyn (1621)
The Battle of Khotyn was a battle fought between a Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth army and an invading Ottoman Imperial army. Here, for a whole month , the Commonwealth forces halted the Ottoman advance...
in 1621 he wrote a diary called Commentariorum chotinensis belli libri tres (Diary of the Chocim War), which was published in 1646 in Gdańsk
Gdansk
Gdańsk is a Polish city on the Baltic coast, at the centre of the country's fourth-largest metropolitan area.The city lies on the southern edge of Gdańsk Bay , in a conurbation with the city of Gdynia, spa town of Sopot, and suburban communities, which together form a metropolitan area called the...
. It was used by Wacław Potocki as a basis for his epic poem, Transakcja wojny chocimskiej (The Progress of the War of Chocim). He also authored instructions for the journey of his sons to Kraków (1640) and France (1645), a good example of liberal education of the era.
Art and music

Culture
Culture is a term that has many different inter-related meanings. For example, in 1952, Alfred Kroeber and Clyde Kluckhohn compiled a list of 164 definitions of "culture" in Culture: A Critical Review of Concepts and Definitions...
s of the Commonwealth, Latin
Latin Europe
Latin Europe is a loose term for the region of Europe with an especially strong Latin cultural heritage inherited from the Roman Empire.-Application:...
and Eastern Orthodox
Eastern Orthodox Church
The Orthodox Church, officially called the Orthodox Catholic Church and commonly referred to as the Eastern Orthodox Church, is the second largest Christian denomination in the world, with an estimated 300 million adherents mainly in the countries of Belarus, Bulgaria, Cyprus, Georgia, Greece,...
, coexisted and penetrate each other, which is reflected in great popularity of icon
Icon
An icon is a religious work of art, most commonly a painting, from Eastern Christianity and in certain Eastern Catholic churches...
s (Pic. 13) and icon resembling effigies of Mary
Mary (mother of Jesus)
Mary , commonly referred to as "Saint Mary", "Mother Mary", the "Virgin Mary", the "Blessed Virgin Mary", or "Mary, Mother of God", was a Jewish woman of Nazareth in Galilee...
, as well as metal dresses typical for the Orthodox Church in predominantly Latin territories of today's Poland (Black Madonna
Black Madonna of Czestochowa
The Black Madonna of Częstochowa is a revered icon of the Virgin Mary housed at the Jasna Góra Monastery in Częstochowa, Poland.-The icon:The origins of the icon and the date of its composition are still hotly contested among scholars...
) and Lithuania (Our Lady of the Gate of Dawn
Our Lady of the Gate of Dawn
Our Lady of the Gate of Dawn is the prominent painting of the Blessed Virgin Mary venerated by the faithful in the Chapel of the Gate of Dawn in Vilnius, Lithuania. The Renaissance painting, completed possibly in the first half of the 17th century, is an unusual portrayal of Madonna as she is...
). The implementation of post-renaissance
Renaissance
The Renaissance was a cultural movement that spanned roughly the 14th to the 17th century, beginning in Italy in the Late Middle Ages and later spreading to the rest of Europe. The term is also used more loosely to refer to the historical era, but since the changes of the Renaissance were not...
naturalism and sentimentality of Polish baroque in Orthodox painting as well as creation of Cossack Baroque
Ukrainian Baroque
Ukrainian Baroque or Cossack Baroque is an architectural style that emerged in Ukraine during the Hetmanate era, in the 17th and 18th centuries....
in architecture, also inspired by Polish patterns, were the major factors of Latin infiltration in Eastern art (Pic. 3).
A common art form of the Sarmatian
Sarmatism
"Sarmatism" is a term designating the dominant lifestyle, culture and ideology of the szlachta of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth from the 16th to the 19th centuries. Together with "Golden Liberty," it formed a central aspect of the Commonwealth's culture...
period were coffin portraits, particular to the culture of the Commonwealth, used in funerals and other important ceremonies. As a rule, such portraits were nailed to sheet metal, six – or eight – sided in shape, fixed to the front of a coffin placed on a high, ornate catafalque.
Another characteristic is common usage of black marble. Altars, fonts, portals, balustrades, columns, monuments, tombstones, headstones and whole rooms (e.g. Marble Room at the Royal Castle in Warsaw, St. Casimir Chapel of the Vilnius Cathedral
Vilnius Cathedral
The Cathedral of Vilnius is the main Roman Catholic Cathedral of Lithuania.It is situated in Vilnius Old Town, just off of Cathedral Square. It is the heart of Lithuania's Catholic spiritual life....
and Vasa Chapel of the Wawel Cathedral
Wawel Cathedral
The Wawel Cathedral, also known as the Cathedral Basilica of Sts. Stanisław and Vaclav, is a church located on Wawel Hill in Kraków–Poland's national sanctuary. It has a 1,000-year history and was the traditional coronation site of Polish monarchs. It is the Cathedral of the Archdiocese of Kraków...
) were decorated with black marble.
Music was a common feature of religious and secular events. To that end many noblemen founded church and school choirs, and employed their own ensembles of musicians. Some, like Stanisław Lubomirski build their own opera houses (in Nowy Wiśnicz
Nowy Wisnicz
Nowy Wiśnicz is a small town in Bochnia County, Lesser Poland Voivodeship, Poland, with 2,724 inhabitants . It is located 4 miles south of Bochnia.-Former structures:...
). Yet others, like Janusz Skumin Tyszkiewicz
Janusz Skumin Tyszkiewicz
Janusz Skumin Tyszkiewicz was a noble of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, a politician, a sponsor of Baroque music and a writer...
and Krzysztof Radziwiłł were known for their sponsorship of arts which manifested itself in their permanently retained orchestras, at their courts in Vilnius
Vilnius
Vilnius is the capital of Lithuania, and its largest city, with a population of 560,190 as of 2010. It is the seat of the Vilnius city municipality and of the Vilnius district municipality. It is also the capital of Vilnius County...
. Musical life further flourished during the reign of the Vasas. Both foreign and domestic composers were active in the Commonwealth. King Sigismund III
Sigismund III Vasa
Sigismund III Vasa was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania, a monarch of the united Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth from 1587 to 1632, and King of Sweden from 1592 until he was deposed in 1599...
brought in Italian composers and conductors, such as Luca Marenzio
Luca Marenzio
Luca Marenzio was an Italian composer and singer of the late Renaissance. He was one of the most renowned composers of madrigals, and wrote some of the most famous examples of the form in its late stage of development, prior to its early Baroque transformation by Monteverdi...
, Annibale Stabile
Annibale Stabile
Annibale Stabile was an Italian composer of the Renaissance. He was a member of the Roman School of composition, and probably was a pupil of Palestrina. He was active mainly at Rome but moved briefly to Kraków, Poland at the end of his life.-Life:Records of his early life are inexact, but he was...
, Asprilio Pacelli
Asprilio Pacelli
Asprilio Pacelli was an Italian Baroque composer. He was born in Vasciano near Narni in Stroncone, Province of Terni, Umbria, Italy; and died in Warsaw.-Life:...
, Marco Scacchi
Marco Scacchi
Marco Scacchi was an Italian composer and writer on music.Scacchi was born in Gallese, Lazio. He studied under Giovanni Francesco Anerio in Rome. He was associated with the court at Warsaw from 1626, and was kapellmeister there from 1628 to 1649...
and Diomedes Cato
Diomedes Cato
Diomedes Cato was an Italian-born composer and lute player, who lived and worked entirely in Poland. He is known mainly for his instrumental music...
for the royal orchestra. Notable home grown musicians, who also composed and played for the King's court, included Bartłomiej Pękiel, Jacek Różycki
Jacek Różycki
Jacek Hyancithus Różycki was a Polish composer of Baroque music. He began his musical career in the court orchestra of Władysław IV. Eventually he took over the function of the director of the court musical ensemble...
, Adam Jarzębski
Adam Jarzebski
Adam Jarzębski was an early baroque Polish composer, violinist, poet, and writer. The first documented mention of Jarzębski was in 1612, when he became a member of the chapel of Johann Siegmund Hohenzollern in Berlin...
, Marcin Mielczewski
Marcin Mielczewski
Marcin Mielczewski was, together with his tutor Franciszek Lilius and Bartłomiej Pękiel, among the most notable Polish composers in the 17th century....
, Stanisław Sylwester Szarzyński, Damian Stachowicz, Mikołaj Zieleński and Grzegorz Gorczycki.
Magnate
Magnate
Magnate, from the Late Latin magnas, a great man, itself from Latin magnus 'great', designates a noble or other man in a high social position, by birth, wealth or other qualities...
s often undertook construction projects as monuments to themselves: churches, cathedral
Cathedral
A cathedral is a Christian church that contains the seat of a bishop...
s, monasteries
Monastery
Monastery denotes the building, or complex of buildings, that houses a room reserved for prayer as well as the domestic quarters and workplace of monastics, whether monks or nuns, and whether living in community or alone .Monasteries may vary greatly in size – a small dwelling accommodating only...
(Pic. 14), and palace
Palace
A palace is a grand residence, especially a royal residence or the home of a head of state or some other high-ranking dignitary, such as a bishop or archbishop. The word itself is derived from the Latin name Palātium, for Palatine Hill, one of the seven hills in Rome. In many parts of Europe, the...
s like the present-day Presidential Palace in Warsaw
Presidential Palace, Warsaw
The Presidential Palace in Warsaw, Poland, is the elegant classicist latest version of a building that has stood on the Krakowskie Przedmieście site since 1643. Over the years, it has been rebuilt and remodeled many times...
and Pidhirtsi Castle
Pidhirtsi Castle
Pidhirtsi Castle is a residential castle-fortress located in the village of Pidhirtsi in Lviv Oblast western Ukraine, located eighty kilometers east of Lviv. It was constructed by Guillaume Le Vasseur de Beauplan between 1635–1640 by order of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth's Grand Crown...
built by Grand Hetman Stanisław Koniecpolski herbu Pobóg. The largest projects involved entire towns, although in time many of them would lapse into obscurity or be totally abandoned. Usually they were named after the sponsoring magnate. Among the most famous is the town of Zamość
Zamosc
Zamość ukr. Замостя is a town in southeastern Poland with 66,633 inhabitants , situated in the south-western part of Lublin Voivodeship , about from Lublin, from Warsaw and from the border with Ukraine...
, founded by Jan Zamoyski
Jan Zamoyski
Jan Zamoyski , was a Polish-Lithuanian nobleman, magnate, 1st duke/ordynat of Zamość. Royal Secretary since 1566, Lesser Kanclerz ) of the Crown since 1576, Lord Grand-Chancellor of the Crown since 1578, and Grand Hetman of the Crown since 1581...
and designed by the Italian architect
Architect
An architect is a person trained in the planning, design and oversight of the construction of buildings. To practice architecture means to offer or render services in connection with the design and construction of a building, or group of buildings and the space within the site surrounding the...
Bernardo Morando
Bernardo Morando
Bernardo Morando, also known as Bernardino or Morandi was a Polish-Italian architect. He is notable as the author of a new town of Zamość, modelled on Renaissance theories of the 'ideal city'....
. The magnates throughout Poland competed with the kings. The monumental castle Krzyżtopór
Krzyztopór
Krzyżtopór is a castle located in the village of Ujazd, Iwaniska commune, Opatów County, Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship, in southern Poland. It was originally built by a Polish nobleman and Voivode of Sandomierz, Krzysztof Ossoliński...
, built in the style palazzo in fortezza between 1627 and 1644, had several courtyards surrounded by fortifications. Due to efforts of powerful Radziwiłł family, the town of Nesvizh
Nesvizh
Nesvizh is a city in Belarus. It is the administrative center of the Nesvizh District of Minsk Province and location of the Nesvizh Castle World Heritage Site. Its 2009 population is 14,300 .-History:...
in today's Belarus
Belarus
Belarus , officially the Republic of Belarus, is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe, bordered clockwise by Russia to the northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. Its capital is Minsk; other major cities include Brest, Grodno , Gomel ,...
came to exercise significant influence in many domains – the Nesvizh manufactures of firearm
Firearm
A firearm is a weapon that launches one, or many, projectile at high velocity through confined burning of a propellant. This subsonic burning process is technically known as deflagration, as opposed to supersonic combustion known as a detonation. In older firearms, the propellant was typically...
, carpet
Carpet
A carpet is a textile floor covering consisting of an upper layer of "pile" attached to a backing. The pile is generally either made from wool or a manmade fibre such as polypropylene,nylon or polyester and usually consists of twisted tufts which are often heat-treated to maintain their...
s, kontusz sashes and tapestries
Tapestry
Tapestry is a form of textile art, traditionally woven on a vertical loom, however it can also be woven on a floor loom as well. It is composed of two sets of interlaced threads, those running parallel to the length and those parallel to the width ; the warp threads are set up under tension on a...
as well as school of painting produced renowned and luxury items. Late baroque fascination with the culture and art of the "central nation
China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
" is reflected in Queen Masysieńka
Marie Casimire Louise de la Grange d'Arquien
Marie Casimire Louise de La Grange d'Arquien, in Polish: Maria Kazimiera, known also by the diminutive form "Marysieńka" was consort to King John III Sobieski, from 1674 to 1696.-Biography:...
's Chinese Palace
Zolochiv Castle
Zolochiv Castle was a residence of the Sobieski noble family on a hill at the confluence of two small rivers in the south-eastern part of Zolochiv, Galicia ....
in Zolochiv
Zolochiv
Zolochiv is a town located in the Lviv Oblast of western Ukraine. It is the administrative center of the Zolochiv Raion ....
. 18th century magnate palaces represents the characteristic type of baroque
Baroque
The Baroque is a period and the style that used exaggerated motion and clear, easily interpreted detail to produce drama, tension, exuberance, and grandeur in sculpture, painting, literature, dance, and music...
suburban residence built entre cour et jardin
Cour d'Honneur
Cour d'Honneur is the architectural term for defining a three-sided courtyard, created when the main central block, or corps de logis, is flanked by symmetrical advancing secondary wings, containing minor rooms...
(between the entrance court and the garden). Its architecture - a merger of European art with old Commonwealth building traditions are visible in Wilanów Palace
Wilanów Palace
Wilanów Palace is a royal palace located in the Wilanów district, Warsaw. Wilanów Palace survived the time of Poland's partitions and both World Wars and has preserved its authentic historical qualities, also is one of the most important monuments of Polish culture.The palace and park in Wilanów...
in Warsaw
Warsaw
Warsaw is the capital and largest city of Poland. It is located on the Vistula River, roughly from the Baltic Sea and from the Carpathian Mountains. Its population in 2010 was estimated at 1,716,855 residents with a greater metropolitan area of 2,631,902 residents, making Warsaw the 10th most...
(Pic. 15), Branicki Palace in Białystok and in Warsaw, Potocki Palace in Radzyń Podlaski
Radzyn Podlaski
Radzyń Podlaski is a town in eastern Poland, about 60 km north of Lublin, with 16,140 inhabitants . Situated in the Lublin Voivodeship , previously in Biała Podlaska Voivodeship . It is the capital of Radzyń Podlaski County.The town was founded in 1468. The most important landmark is the...
and in Krystynopol
Chervonohrad
Chervonohrad is a city located in the Lviv Oblast of western Ukraine. The city is designated as a separate raion within the oblast. It about 62 km north of Lviv and 7 km from Sokal. The population numbers 68,300 inhabitants....
, Raczyński Palace in Rogalin
Rogalin
Rogalin is a village in western Poland, situated on the Warta river. It lies approximately east of the town of Mosina, and south of the city of Poznań....
and Sapieha Palace
Ruzhany Palace
Ruzhany Palace is a ruined palace compound in Ruzhany village, Pruzhany Raion , Brest voblast , Western Belarus. Between the 16th and 19th centuries Ruzhany was the main seat of the senior line of the Sapieha noble family, known as the Sapiehowie-Różańscy...
in Ruzhany
Ruzhany
Ruzhany is a small town located in Pruzhany Raion of Brest Voblast, Belarus.-Geography:Ruzhany is situated on the river Ruzhanka and surrounded by picturesque hills...
.
Szlachta and Sarmatism

Ideology
An ideology is a set of ideas that constitutes one's goals, expectations, and actions. An ideology can be thought of as a comprehensive vision, as a way of looking at things , as in common sense and several philosophical tendencies , or a set of ideas proposed by the dominant class of a society to...
of the szlachta became "Sarmatism
Sarmatism
"Sarmatism" is a term designating the dominant lifestyle, culture and ideology of the szlachta of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth from the 16th to the 19th centuries. Together with "Golden Liberty," it formed a central aspect of the Commonwealth's culture...
", named after the Sarmatians
Sarmatians
The Iron Age Sarmatians were an Iranian people in Classical Antiquity, flourishing from about the 5th century BC to the 4th century AD....
, alleged ancestors of the Poles. This belief system was an important part of the szlachta's culture
Culture
Culture is a term that has many different inter-related meanings. For example, in 1952, Alfred Kroeber and Clyde Kluckhohn compiled a list of 164 definitions of "culture" in Culture: A Critical Review of Concepts and Definitions...
, penetrating all aspects of its life. Sarmatism enshrined equality among szlachta, horseback riding, tradition, provincial rural life, peace and pacifism
Pacifism
Pacifism is the opposition to war and violence. The term "pacifism" was coined by the French peace campaignerÉmile Arnaud and adopted by other peace activists at the tenth Universal Peace Congress inGlasgow in 1901.- Definition :...
; championed oriental-inspired attire (żupan
Zupan
Żupan was a long garment, always lined, worn by almost all males of the noble social class in the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, typical male attire from the beginning of the 16th to half of the 18th century, still surviving as a part of the Polishnational dress.- Derivation :The name żupan has...
, kontusz
Kontusz
Kontusz - a type of outer garment worn by the Hungarian, Polish, Belarusian, Lithuanian and Ukrainian male nobility...
, sukmana, pas kontuszowy
Pas kontuszowy
Pas kontuszowy was a cloth sash used for compassing a kontusz . It was one of the most distinctive items of dress of Polish and Lithuanian nobility from about 17th through the 19th centuries. In an earlier periods, sometimes narrower sashes of fine cloth or silk net were worn, but the wide...
, delia, szabla
Szabla
Szabla is the Polish word for sabre. It specifically refers to an Eastern European one-edged sabre-like mêlée weapon with a curved blade and, in most cases, a two-bladed tip called a feather . Initially used by light cavalry, with time it also evolved into a variety of arms used both for martial...
); and served to integrate the multi-ethnic nobility by creating an almost nationalistic
Nationalism
Nationalism is a political ideology that involves a strong identification of a group of individuals with a political entity defined in national terms, i.e. a nation. In the 'modernist' image of the nation, it is nationalism that creates national identity. There are various definitions for what...
sense of unity and of pride in the szlachta's Golden Freedoms.
In its early, idealistic form, Sarmatism represented a positive cultural movement: it supported religious belief, honesty, national pride, courage, equality and freedom. In time, however, it became distorted. Late extreme Sarmatism turned belief into bigotry, honesty into political naïveté, pride into arrogance, courage into stubbornness and freedom into anarchy. The faults of Sarmatism were blamed for the demise of the country from the late 18th century onwards. Criticism, often one-sided and exaggerated, was used by the Polish reformists to push for radical changes. This self-deprecation was accompanied by works of Prussian, Russian
Russians
The Russian people are an East Slavic ethnic group native to Russia, speaking the Russian language and primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries....
and Austrian
Austrians
Austrians are a nation and ethnic group, consisting of the population of the Republic of Austria and its historical predecessor states who share a common Austrian culture and Austrian descent....
historians, who tried to prove that it was Poland itself that was to blame for its fall.
Demographics and religion
The population of the Commonwealth was never overwhelmingly either Roman Catholic or Polish. This circumstance resulted from Poland's possession of UkraineUkraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It has an area of 603,628 km², making it the second largest contiguous country on the European continent, after Russia...
and confederation with Lithuania
Lithuania
Lithuania , officially the Republic of Lithuania is a country in Northern Europe, the biggest of the three Baltic states. It is situated along the southeastern shore of the Baltic Sea, whereby to the west lie Sweden and Denmark...
, in both of which countries ethnic Poles were a distinct minority. The Commonwealth comprised primarily four nations: Lithuanians
Lithuanians
Lithuanians are the Baltic ethnic group native to Lithuania, where they number around 2,765,600 people. Another million or more make up the Lithuanian diaspora, largely found in countries such as the United States, Brazil, Canada, Colombia, Russia, United Kingdom and Ireland. Their native language...
, Poles
Poles
thumb|right|180px|The state flag of [[Poland]] as used by Polish government and diplomatic authoritiesThe Polish people, or Poles , are a nation indigenous to Poland. They are united by the Polish language, which belongs to the historical Lechitic subgroup of West Slavic languages of Central Europe...
, Belarusians
Belarusians
Belarusians ; are an East Slavic ethnic group who populate the majority of the Republic of Belarus. Introduced to the world as a new state in the early 1990s, the Republic of Belarus brought with it the notion of a re-emerging Belarusian ethnicity, drawn upon the lines of the Old Belarusian...
and Ukrainians
Ukrainians
Ukrainians are an East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine, which is the sixth-largest nation in Europe. The Constitution of Ukraine applies the term 'Ukrainians' to all its citizens...
; the latter two usually referred to as the Ruthenians
Ruthenians
The name Ruthenian |Rus']]) is a culturally loaded term and has different meanings according to the context in which it is used. Initially, it was the ethnonym used for the East Slavic peoples who lived in Rus'. Later it was used predominantly for Ukrainians...
. Sometimes inhabitants of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania
Grand Duchy of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state from the 12th /13th century until 1569 and then as a constituent part of Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth until 1791 when Constitution of May 3, 1791 abolished it in favor of unitary state. It was founded by the Lithuanians, one of the polytheistic...
were called Litvins, a Slavic term for people from Lithuania, regardless their ethnicity (with the exception of Jews, which were called Litvak
Litvak
Litvak may refer to:* Lithuanian Jews* Lithuanian Yiddish dialectPeople:* Anatole Litvak* Lydia Litvak...
s). Shortly after the Union of Lublin
Union of Lublin
The Union of Lublin replaced the personal union of the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania with a real union and an elective monarchy, since Sigismund II Augustus, the last of the Jagiellons, remained childless after three marriages. In addition, the autonomy of Royal Prussia was...
( 1569 ), the Commonwealth population was around 7 million, with a rough breakdown of 4.5 m Poles, 0.75 m Lithuanians, 0.7 m/10% Jews
Jews
The Jews , also known as the Jewish people, are a nation and ethnoreligious group originating in the Israelites or Hebrews of the Ancient Near East. The Jewish ethnicity, nationality, and religion are strongly interrelated, as Judaism is the traditional faith of the Jewish nation...
and 2 m Ruthenians. In 1618, after the Truce of Deulino
Truce of Deulino
Truce of Deulino was signed on 11 December 1618 and took effect on 4 January 1619. It concluded the Polish–Muscovite War between the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and the Tsardom of Russia....
, the Commonwealth population increased together with its territory, reaching 11.5 million people, which was composed roughly of 4.5 m Poles, 3.5 m Ukrainians, 1.5 m Belarusians, 0.75 m Lithuanians, 0.75 m Old Prussians
Old Prussians
The Old Prussians or Baltic Prussians were an ethnic group, autochthonous Baltic tribes that inhabited Prussia, the lands of the southeastern Baltic Sea in the area around the Vistula and Curonian Lagoons...
, 0.5 m Jews, and 0.5 m Livonians. At that time nobility was 10% of the population, and burghers
Bourgeoisie
In sociology and political science, bourgeoisie describes a range of groups across history. In the Western world, between the late 18th century and the present day, the bourgeoisie is a social class "characterized by their ownership of capital and their related culture." A member of the...
were 15%. The average population density per square kilometer was: 24 in Mazovia, 23 in Little Poland, 19 in Great Poland, 12 in Lublin palatinate, 10 in the Lvov area, 7 in Podolia and Volhynia, 3 in the Ukraine. There was a tendency for the people from the more densely inhabited western territories to migrate eastwards. In the period from 1648–57, populations losses are estimated at 4 m. Coupled with further population and territorial losses, in 1717 the Commonwealth population had fallen to 9 m, with roughly 4.5 m/50% Poles, 1.5 m/17% Ukrainians, 1.2 m Belarusians, 0.8 m Lithuanians, 0.5 m Jews, and 0.5 m others.
“Certainly, the wording and substance of the declaration of the Confederation of Warsaw of 28 January 1573 were extraordinary with regards to prevailing conditions elsewhere in Europe; and they governed the principles of religious life in the Republic for over two hundred years.” - Norman Davies
Norman Davies
Professor Ivor Norman Richard Davies FBA, FRHistS is a leading English historian of Welsh descent, noted for his publications on the history of Europe, Poland, and the United Kingdom.- Academic career :...
Poland has a long tradition of religious freedom. The right to worship freely was a basic right given to all inhabitants of the Commonwealth throughout the 15th and early 16th century, however, complete freedom of religion was officially recognized in Poland in 1573 during the Warsaw Confederation
Warsaw Confederation
The Warsaw Confederation , an important development in the history of Poland and Lithuania that extended religious tolerance to nobility and free persons within the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. , is considered the formal beginning of religious freedom in the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, and...
. Poland kept religious freedom laws during an era when religious persecution was an everyday occurrence in the rest of Europe. Commonwealth was a place were the most radical religious sects, trying to escape persecution in other countries of the Christian world, sought refuge.
"This country became a place of shelter for heretics” - Cardinal HozjuszStanislaus HosiusStanislaus Hosius was a cardinal, since 1551 Prince-Bishop in Bishopric of Warmia, Poland since 1558 papal legate to the Holy Roman Emperor's Imperial Court in Vienna, Austria and since 1566 a papal legate to Poland.Hosius was born in Kraków as the son of Ulrich Hos of Pforzheim and studied law...
papal legatePapal legateA papal legate – from the Latin, authentic Roman title Legatus – is a personal representative of the pope to foreign nations, or to some part of the Catholic Church. He is empowered on matters of Catholic Faith and for the settlement of ecclesiastical matters....
to Poland.
To be Polish, in the non-Polish lands of the Commonwealth, was then much less an index of ethnicity than of religion and rank
Hierarchy
A hierarchy is an arrangement of items in which the items are represented as being "above," "below," or "at the same level as" one another...
; it was a designation largely reserved for the landed noble class (szlachta), which included Poles but also many members of non-Polish origin who converted to Catholicism
Religious conversion
Religious conversion is the adoption of a new religion that differs from the convert's previous religion. Changing from one denomination to another within the same religion is usually described as reaffiliation rather than conversion.People convert to a different religion for various reasons,...
in increasing numbers with each following generation. For the non-Polish noble
Nobility
Nobility is a social class which possesses more acknowledged privileges or eminence than members of most other classes in a society, membership therein typically being hereditary. The privileges associated with nobility may constitute substantial advantages over or relative to non-nobles, or may be...
such conversion meant a final step of Polonization
Polonization
Polonization was the acquisition or imposition of elements of Polish culture, in particular, Polish language, as experienced in some historic periods by non-Polish populations of territories controlled or substantially influenced by Poland...
that followed the adoption of the Polish language and culture. Poland, as the culturally most advanced part of the Commonwealth, with the royal court, the capital, the largest cities, the second-oldest university in Central Europe (after Prague
Prague
Prague is the capital and largest city of the Czech Republic. Situated in the north-west of the country on the Vltava river, the city is home to about 1.3 million people, while its metropolitan area is estimated to have a population of over 2.3 million...
), and the more liberal and democratic social institutions had proven an irresistible magnet for the non-Polish nobility in the Commonwealth. Many referred to themselves as "gente Ruthenus, natione Polonus" (Ruthenian by blood, Polish by nationality) since 16th century onwards.
As a result, in the eastern territories a Polish (or Polonized) aristocracy dominated a peasantry whose great majority was neither Polish nor Roman Catholic. Moreover, the decades of peace brought huge colonization efforts to Ukraine, heightening the tensions among nobles
Nobility
Nobility is a social class which possesses more acknowledged privileges or eminence than members of most other classes in a society, membership therein typically being hereditary. The privileges associated with nobility may constitute substantial advantages over or relative to non-nobles, or may be...
, Jews, Cossack
Cossack
Cossacks are a group of predominantly East Slavic people who originally were members of democratic, semi-military communities in what is today Ukraine and Southern Russia inhabiting sparsely populated areas and islands in the lower Dnieper and Don basins and who played an important role in the...
s (traditionally Orthodox), Polish and Ruthenian peasants. The latter, deprived of their native protectors among the Ruthenian nobility, turned for protection to cossack
Cossack
Cossacks are a group of predominantly East Slavic people who originally were members of democratic, semi-military communities in what is today Ukraine and Southern Russia inhabiting sparsely populated areas and islands in the lower Dnieper and Don basins and who played an important role in the...
s that facilitated violence that in the end broke the Commonwealth. The tensions were aggravated by conflicts between Eastern Orthodoxy and the Greek Catholic Church
Union of Brest
Union of Brest or Union of Brześć refers to the 1595-1596 decision of the Church of Rus', the "Metropolia of Kiev-Halych and all Rus'", to break relations with the Patriarch of Constantinople and place themselves under the Pope of Rome. At the time, this church included most Ukrainians and...
following the Union of Brest
Union of Brest
Union of Brest or Union of Brześć refers to the 1595-1596 decision of the Church of Rus', the "Metropolia of Kiev-Halych and all Rus'", to break relations with the Patriarch of Constantinople and place themselves under the Pope of Rome. At the time, this church included most Ukrainians and...
, overall discrimination of Orthodox religions by dominant Catholicism, and several Cossack
Cossack
Cossacks are a group of predominantly East Slavic people who originally were members of democratic, semi-military communities in what is today Ukraine and Southern Russia inhabiting sparsely populated areas and islands in the lower Dnieper and Don basins and who played an important role in the...
uprisings. In the west and north, many cities had sizable German minorities, often belonging to Reformed churches
Reformed churches
The Reformed churches are a group of Protestant denominations characterized by Calvinist doctrines. They are descended from the Swiss Reformation inaugurated by Huldrych Zwingli but developed more coherently by Martin Bucer, Heinrich Bullinger and especially John Calvin...
. The Commonwealth had also one of the largest Jewish diaspora
Jewish diaspora
The Jewish diaspora is the English term used to describe the Galut גלות , or 'exile', of the Jews from the region of the Kingdom of Judah and Roman Iudaea and later emigration from wider Eretz Israel....
s in the world – by the mid-16th century 80% of the world's Jews lived in Poland (Pic. 16).
Until the Reformation
Protestant Reformation
The Protestant Reformation was a 16th-century split within Western Christianity initiated by Martin Luther, John Calvin and other early Protestants. The efforts of the self-described "reformers", who objected to the doctrines, rituals and ecclesiastical structure of the Roman Catholic Church, led...
, the szlachta were mostly Catholic or Eastern Orthodox (Pic. 3, 13). However, many families quickly adopted the Reformed religion. After the Counter-Reformation
Counter-Reformation
The Counter-Reformation was the period of Catholic revival beginning with the Council of Trent and ending at the close of the Thirty Years' War, 1648 as a response to the Protestant Reformation.The Counter-Reformation was a comprehensive effort, composed of four major elements:#Ecclesiastical or...
, when the Roman Catholic Church regained power in Poland, the szlachta became almost exclusively Roman Catholic, despite the fact that Roman Catholicism was not a majority religion (the Roman Catholic and Orthodox churches counted approximately 40% of the population each, while the remaining 20% were Jews and members of various Protestant churches).
The Crown had about double the population of Lithuania and five times the income of the latter's treasury. As with other countries, the borders, area and population of the Commonwealth varied over time. After the Peace of Jam Zapolski
Peace of Jam Zapolski
The Truce or Treaty of Jam Zapolski, Yam Zapol'sky, Yam Zapol'skii or Zapole, signed on 15 January 1582 between the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth and the Tsardom of Russia, was one of the treaties that ended the Livonian War...
(1582), the Commonwealth had approximately 815,000 km² area and a population of 7.5 million. After the Truce of Deulino
Truce of Deulino
Truce of Deulino was signed on 11 December 1618 and took effect on 4 January 1619. It concluded the Polish–Muscovite War between the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and the Tsardom of Russia....
(1618), the Commonwealth had an area of some 990,000 km² and a population of 10–11 million (including some 4 million Poles and close to a million Lithuanians).
Languages
- PolishPolish languagePolish is a language of the Lechitic subgroup of West Slavic languages, used throughout Poland and by Polish minorities in other countries...
- officially recognized; dominant language, used by most of Commonwealth nobility and by peasantry in the Crown province; official language in Crown chancellery and since 1697 in Grand Duchy chancellery. Dominant language in the towns. - LatinLatinLatin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
- off. recog.; commonly used in foreign relations and popular as second language among the nobility. - FrenchFrench languageFrench is a Romance language spoken as a first language in France, the Romandy region in Switzerland, Wallonia and Brussels in Belgium, Monaco, the regions of Quebec and Acadia in Canada, and by various communities elsewhere. Second-language speakers of French are distributed throughout many parts...
- not officially recognized; replaced Latin at the royal court in Warsaw in the beginning of the 18th century as a language used in foreign relations and as genuine spoken languageWorld languageA world language is a language spoken internationally which is learned by many people as a second language. A world language is not only characterized by the number of its speakers , but also by its geographical distribution, and its use in international organizations and in diplomatic relations...
. It was commonly used as a language of science and literature and as second language among the nobility. - Chancellery RuthenianRuthenian languageRuthenian, or Old Ruthenian , is a term used for the varieties of Eastern Slavonic spoken in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and later in the East Slavic territories of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth....
- also known as Chancellery Slavonic; off. recog.; official language in Grand Duchy chancellery until 1697 (when replaced by Polish); used in some foreign relations its dialects were widely used in Grand Duchy and eastern parts of the Crown as spoken language. - LithuanianLithuanian languageLithuanian is the official state language of Lithuania and is recognized as one of the official languages of the European Union. There are about 2.96 million native Lithuanian speakers in Lithuania and about 170,000 abroad. Lithuanian is a Baltic language, closely related to Latvian, although they...
- not officially recognised; but used in some official documents in Grand Duchy and, mostly, used as a spoken language in the northwest part of the Grand Duchy (in Lithuania ProperLithuania properLithuania proper refers to a region which existed within Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and spoke Lithuanian language. The primary meaning is identical to the Duchy of Lithuania, a land around which Grand Duchy of Lithuania evolved...
) and the northern part of Polish PrussiaRoyal PrussiaRoyal Prussia was a Region of the Kingdom of Poland and of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth . Polish Prussia included Pomerelia, Chełmno Land , Malbork Voivodeship , Gdańsk , Toruń , and Elbląg . It is distinguished from Ducal Prussia...
(see Lithuania MinorLithuania MinorLithuania Minor or Prussian Lithuania is a historical ethnographic region of Prussia, later East Prussia in Germany, where Prussian Lithuanians or Lietuvininkai lived. Lithuania Minor enclosed the northern part of this province and got its name due to the territory's substantial...
). - GermanGerman languageGerman is a West Germanic language, related to and classified alongside English and Dutch. With an estimated 90 – 98 million native speakers, German is one of the world's major languages and is the most widely-spoken first language in the European Union....
- off. recog.; used in some foreign relations, in Polish Prussia and by minorities in cities. - HebrewHebrew languageHebrew is a Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Culturally, is it considered by Jews and other religious groups as the language of the Jewish people, though other Jewish languages had originated among diaspora Jews, and the Hebrew language is also used by non-Jewish groups, such...
- off. recog.; used by the Jews in their religion matters; - Yiddish, used by the Jews in their daily life but not recognized as official language.
- ItalianItalian languageItalian is a Romance language spoken mainly in Europe: Italy, Switzerland, San Marino, Vatican City, by minorities in Malta, Monaco, Croatia, Slovenia, France, Libya, Eritrea, and Somalia, and by immigrant communities in the Americas and Australia...
- not officially recognised; used in some foreign relations and by Italian minorities in cities. - ArmenianArmenian languageThe Armenian language is an Indo-European language spoken by the Armenian people. It is the official language of the Republic of Armenia as well as in the region of Nagorno-Karabakh. The language is also widely spoken by Armenian communities in the Armenian diaspora...
- off. recog. used by Armenian minority. - ArabicArabic languageArabic is a name applied to the descendants of the Classical Arabic language of the 6th century AD, used most prominently in the Quran, the Islamic Holy Book...
- not officially recognised; used in some foreign relations and by TatarsTatarsTatars are a Turkic speaking ethnic group , numbering roughly 7 million.The majority of Tatars live in the Russian Federation, with a population of around 5.5 million, about 2 million of which in the republic of Tatarstan.Significant minority populations are found in Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan,...
in their religion matters, they also wrote Ruthenian in the Arabic script.
Legacy
The Duchy of WarsawDuchy of Warsaw
The Duchy of Warsaw was a Polish state established by Napoleon I in 1807 from the Polish lands ceded by the Kingdom of Prussia under the terms of the Treaties of Tilsit. The duchy was held in personal union by one of Napoleon's allies, King Frederick Augustus I of Saxony...
, established in 1807, traced its origins to the Commonwealth. Other revival movements appeared during the November Uprising
November Uprising
The November Uprising , Polish–Russian War 1830–31 also known as the Cadet Revolution, was an armed rebellion in the heartland of partitioned Poland against the Russian Empire. The uprising began on 29 November 1830 in Warsaw when the young Polish officers from the local Army of the Congress...
(1830–31), the January Uprising
January Uprising
The January Uprising was an uprising in the former Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth against the Russian Empire...
(1863–64) and in the 1920s, with Józef Piłsudski's failed attempt to create a Polish-led Międzymorze
Miedzymorze
Międzymorze was a plan, pursued after World War I by Polish leader Józef Piłsudski, for a federation, under Poland's aegis, of Central and Eastern European countries...
("Between-Seas") federation
Federation
A federation , also known as a federal state, is a type of sovereign state characterized by a union of partially self-governing states or regions united by a central government...
that would have included Lithuania and Ukraine
Ukrainian People's Republic
The Ukrainian People's Republic or Ukrainian National Republic was a republic that was declared in part of the territory of modern Ukraine after the Russian Revolution, eventually headed by Symon Petliura.-Revolutionary Wave:...
. Today's Republic of Poland considers itself a successor to the Commonwealth, whereas the Republic of Lithuania, re-established at the end of World War I
World War I
World War I , which was predominantly called the World War or the Great War from its occurrence until 1939, and the First World War or World War I thereafter, was a major war centred in Europe that began on 28 July 1914 and lasted until 11 November 1918...
, saw the participation of the Lithuanian state in the old Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth mostly in a negative light at the early stages of regaining its independence, although this attitude has been changing recently.
Administrative division
While the term "Poland" was also commonly used to denote this whole polity, Poland was in fact only part of a greater whole—the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, which comprised primarily two parts:- the Crown of the Polish KingdomCrown of the Polish KingdomThe Crown of the Kingdom of Poland , or simply the Crown , is the name for the unit of administrative division, the territories under direct administration of Polish nobility from middle-ages to late 18th century...
(Poland proper), colloquially "the Crown"; and - the Grand Duchy of LithuaniaGrand Duchy of LithuaniaThe Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state from the 12th /13th century until 1569 and then as a constituent part of Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth until 1791 when Constitution of May 3, 1791 abolished it in favor of unitary state. It was founded by the Lithuanians, one of the polytheistic...
, colloquially "Lithuania".
The Commonwealth was further divided into smaller administrative units known as voivodships (województwa). Each voivodship was governed by a voivod (wojewoda, governor). Voivodships were further divided into starostwa
Starostwo
Starostwo , from the 14th century in the Polish Crown and later through the era of the joint state of Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth until the partitions of Poland in 1795, referred to the crown lands administered by the official known as starosta...
, each starostwo being governed by a starosta
Starosta
Starost is a title for an official or unofficial position of leadership that has been used in various contexts through most of Slavic history. It can be translated as "elder"...
. Cities were governed by castellan
Castellan
A castellan was the governor or captain of a castle. The word stems from the Latin Castellanus, derived from castellum "castle". Also known as a constable.-Duties:...
s. There were frequent exceptions to these rules, often involving the ziemia
Ziemia
Ziemia is a historical unit of administration in Poland. In Polish the term is not capitalized ....
subunit of administration.
The lands that once belonged to the Commonwealth are now largely distributed among several Central and East European
Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is the eastern part of Europe. The term has widely disparate geopolitical, geographical, cultural and socioeconomic readings, which makes it highly context-dependent and even volatile, and there are "almost as many definitions of Eastern Europe as there are scholars of the region"...
countries: Poland, Ukraine, Moldova
Moldova
Moldova , officially the Republic of Moldova is a landlocked state in Eastern Europe, located between Romania to the West and Ukraine to the North, East and South. It declared itself an independent state with the same boundaries as the preceding Moldavian Soviet Socialist Republic in 1991, as part...
(Transnistria
Transnistria
Transnistria is a breakaway territory located mostly on a strip of land between the Dniester River and the eastern Moldovan border to Ukraine...
), Belarus, Russia, Lithuania, Latvia, and Estonia. Also some small towns in Slovakia
Slovakia
The Slovak Republic is a landlocked state in Central Europe. It has a population of over five million and an area of about . Slovakia is bordered by the Czech Republic and Austria to the west, Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east and Hungary to the south...
, then within the Kingdom of Hungary
Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary comprised present-day Hungary, Slovakia and Croatia , Transylvania , Carpatho Ruthenia , Vojvodina , Burgenland , and other smaller territories surrounding present-day Hungary's borders...
, became a part of Poland in the Treaty of Lubowla
Treaty of Lubowla
Treaty of Lubowla of 1412 was a treaty between Władysław II, King of Poland, and Sigismund of Luxemburg, King of Hungary. Negotiated in the town of Stará Ľubovňa in modern Slovakia, it was confirmed later that year in Buda....
.
Other notable parts of the Commonwealth, without respect to region or voivodship divisions, include:
- Lesser PolandLesser PolandLesser Poland is one of the historical regions of Poland, with its capital in the city of Kraków. It forms the southeastern corner of the country, and should not be confused with the modern Lesser Poland Voivodeship, which covers only a small, southern part of Lesser Poland...
, southern Poland, with its capital at KrakówKrakówKraków also Krakow, or Cracow , is the second largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula River in the Lesser Poland region, the city dates back to the 7th century. Kraków has traditionally been one of the leading centres of Polish academic, cultural, and artistic life...
(Cracow); - Greater PolandGreater PolandGreater Poland or Great Poland, often known by its Polish name Wielkopolska is a historical region of west-central Poland. Its chief city is Poznań.The boundaries of Greater Poland have varied somewhat throughout history...
, west–central Poland around PoznańPoznanPoznań is a city on the Warta river in west-central Poland, with a population of 556,022 in June 2009. It is among the oldest cities in Poland, and was one of the most important centres in the early Polish state, whose first rulers were buried at Poznań's cathedral. It is sometimes claimed to be...
and the Warta RiverWarta RiverThe Warta is a river in western-central Poland, a tributary of the Oder river. With a length of approximately it is the country's third longest river. The Warta has a basin area of 54,529 square kilometers...
system; - Masovia , central Poland, with its capital at WarszawaWarsawWarsaw is the capital and largest city of Poland. It is located on the Vistula River, roughly from the Baltic Sea and from the Carpathian Mountains. Its population in 2010 was estimated at 1,716,855 residents with a greater metropolitan area of 2,631,902 residents, making Warsaw the 10th most...
(Warsaw); - Lithuania ProperLithuania properLithuania proper refers to a region which existed within Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and spoke Lithuanian language. The primary meaning is identical to the Duchy of Lithuania, a land around which Grand Duchy of Lithuania evolved...
, the catholic, or, perhaps, in some cases ethnically Lithuanian, part of Grand Duchy in the northwest of it; - SamogitiaEldership of SamogitiaThe Duchy of Samogitia had been the administrative unit of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania from 1422 . Between 1422 to 1441 it was known as the Eldership of Samogitia...
, an autonomous area of Grand Duchy of Lithuania in the westernmost part of it, the western part of Lithuania Proper; - Royal PrussiaRoyal PrussiaRoyal Prussia was a Region of the Kingdom of Poland and of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth . Polish Prussia included Pomerelia, Chełmno Land , Malbork Voivodeship , Gdańsk , Toruń , and Elbląg . It is distinguished from Ducal Prussia...
, at the southern shore of the Baltic SeaBaltic SeaThe Baltic Sea is a brackish mediterranean sea located in Northern Europe, from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from 20°E to 26°E longitude. It is bounded by the Scandinavian Peninsula, the mainland of Europe, and the Danish islands. It drains into the Kattegat by way of the Øresund, the Great Belt and...
, was an autonomous area since the Second Peace of Thorn (1466), incorporated into the Crown in 1569 with the Commonwealth's formationUnion of LublinThe Union of Lublin replaced the personal union of the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania with a real union and an elective monarchy, since Sigismund II Augustus, the last of the Jagiellons, remained childless after three marriages. In addition, the autonomy of Royal Prussia was...
;- PomereliaPomereliaPomerelia is a historical region in northern Poland. Pomerelia lay in eastern Pomerania: on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea and west of the Vistula and its delta. The area centered on the city of Gdańsk at the mouth of the Vistula...
, PomeraniaPomeraniaPomerania is a historical region on the south shore of the Baltic Sea. Divided between Germany and Poland, it stretches roughly from the Recknitz River near Stralsund in the West, via the Oder River delta near Szczecin, to the mouth of the Vistula River near Gdańsk in the East...
around GdańskGdanskGdańsk is a Polish city on the Baltic coast, at the centre of the country's fourth-largest metropolitan area.The city lies on the southern edge of Gdańsk Bay , in a conurbation with the city of Gdynia, spa town of Sopot, and suburban communities, which together form a metropolitan area called the...
(Danzig), western part of Royal Prussia;
- Pomerelia
- RutheniaRutheniaRuthenia is the Latin word used onwards from the 13th century, describing lands of the Ancient Rus in European manuscripts. Its geographic and culturo-ethnic name at that time was applied to the parts of Eastern Europe. Essentially, the word is a false Latin rendering of the ancient place name Rus...
, the eastern Commonwealth, adjoining Russia; - Duchy of LivoniaDuchy of LivoniaThe Duchy of Livonia was a territory of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania — and later the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth — that existed from 1561 to 1621...
, a joint domain of the Crown and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. Parts lost to Sweden in the 1620s and in 1660; - Duchy of Courland , a northern fief of the Commonwealth. It established a colonyColonyIn politics and history, a colony is a territory under the immediate political control of a state. For colonies in antiquity, city-states would often found their own colonies. Some colonies were historically countries, while others were territories without definite statehood from their inception....
in TobagoTobagoTobago is the smaller of the two main islands that make up the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago. It is located in the southern Caribbean, northeast of the island of Trinidad and southeast of Grenada. The island lies outside the hurricane belt...
in 1637 and on St. Andrews Island at the Gambia RiverGambia RiverThe Gambia River is a major river in West Africa, running from the Fouta Djallon plateau in north Guinea westward through Senegal and The Gambia to the Atlantic Ocean at the city of Banjul...
in 1651 (see Courland colonizationCourland colonizationThe Duchy of Courland and Semigallia, a vassal of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, being small but wealthy took a modest part in European colonialism, in West Africa and the Caribbean.- History :...
); - SilesiaSilesiaSilesia is a historical region of Central Europe located mostly in Poland, with smaller parts also in the Czech Republic, and Germany.Silesia is rich in mineral and natural resources, and includes several important industrial areas. Silesia's largest city and historical capital is Wrocław...
was not within the Commonwealth, but small parts belonged to various Commonwealth kings; in particular, the VasaHouse of VasaThe House of Vasa was the Royal House of Sweden 1523-1654 and of Poland 1587-1668. It originated from a noble family in Uppland of which several members had high offices during the 15th century....
kings were dukeDukeA duke or duchess is a member of the nobility, historically of highest rank below the monarch, and historically controlling a duchy...
s of OpoleOpoleOpole is a city in southern Poland on the Oder River . It has a population of 125,992 and is the capital of the Upper Silesia, Opole Voivodeship and, also the seat of Opole County...
(Oppeln) and RacibórzRacibórzRacibórz is a town in southern Poland with 60,218 inhabitants situated in the Silesian Voivodeship , previously in Katowice Voivodeship...
(Ratibor) from 1645 to 1666.
Commonwealth borders shifted with wars and treaties, sometimes several times in a decade, especially in the eastern and southern parts. After the Peace of Jam Zapolski (1582), the Commonwealth had approximately 815,000 km² area and a population of 7.5 million. After the Truce of Deulino (1618), the Commonwealth had an area of some 1 million km² (990,000 km²) and a population of about 11 million.
Geography
In the 16th century, the Polish bishop
Bishop
A bishop is an ordained or consecrated member of the Christian clergy who is generally entrusted with a position of authority and oversight. Within the Catholic Church, Eastern Orthodox, Oriental Orthodox Churches, in the Assyrian Church of the East, in the Independent Catholic Churches, and in the...
and cartographer Martin Kromer published a Latin atlas, entitled Poland: about Its Location, People, Culture, Offices and the Polish Commonwealth
Polonia sive de situ, populis, moribus, magistratibus et Republica regni Polonici libri duo
Polonia sive de situ, populis, moribus, magistratibus et Republica regni Polonici libri duo is a book, first published in Cologne in 1577 in Latin. The author of the book is Marcin Kromer....
, which was regarded as the most comprehensive guide to the country.
Kromer's works and other contemporary maps, such as those of Gerardus Mercator
Gerardus Mercator
thumb|right|200px|Gerardus MercatorGerardus Mercator was a cartographer, born in Rupelmonde in the Hapsburg County of Flanders, part of the Holy Roman Empire. He is remembered for the Mercator projection world map, which is named after him...
, show the Commonwealth as mostly plain
Plain
In geography, a plain is land with relatively low relief, that is flat or gently rolling. Prairies and steppes are types of plains, and the archetype for a plain is often thought of as a grassland, but plains in their natural state may also be covered in shrublands, woodland and forest, or...
s. The Commonwealth's southeastern part, the Kresy
Kresy
The Polish term Kresy refers to a land considered by Poles as historical eastern provinces of their country. Today, it makes western Ukraine, western Belarus, as well as eastern Lithuania, with such major cities, as Lviv, Vilnius, and Hrodna. This territory belonged to the Polish-Lithuanian...
, was famous for its steppe
Steppe
In physical geography, steppe is an ecoregion, in the montane grasslands and shrublands and temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biomes, characterized by grassland plains without trees apart from those near rivers and lakes...
s. The Carpathian Mountains
Carpathian Mountains
The Carpathian Mountains or Carpathians are a range of mountains forming an arc roughly long across Central and Eastern Europe, making them the second-longest mountain range in Europe...
formed part of the southern border, with the Tatra Mountain
Tatra Mountains
The Tatra Mountains, Tatras or Tatra , are a mountain range which forms a natural border between Slovakia and Poland, and are the highest mountain range in the Carpathian Mountains...
chain the highest, and the Baltic Sea
Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is a brackish mediterranean sea located in Northern Europe, from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from 20°E to 26°E longitude. It is bounded by the Scandinavian Peninsula, the mainland of Europe, and the Danish islands. It drains into the Kattegat by way of the Øresund, the Great Belt and...
formed the Commonwealth's northern border. As with most European countries at the time, the Commonwealth had extensive forest
Forest
A forest, also referred to as a wood or the woods, is an area with a high density of trees. As with cities, depending where you are in the world, what is considered a forest may vary significantly in size and have various classification according to how and what of the forest is composed...
cover, especially in the east. Today, what remains of the Białowieża Forest constitutes the last largely intact primeval forest in Europe.
See also
- Historical powersHistorical powersHistorical powers include great powers, nations, or empires in history.The term "Great power" represent the most important world powers. In a modern context, recognised great powers came about first in Europe during the post-Napoleonic era. The formalization of the division between small powers and...
- List of Polish Coats of Arms
- List of szlachta
- Polish heraldryPolish heraldryPolish heraldry is a branch of heraldry focused on studying the development of coats of arms in the lands of historical Poland , as well as specifically-Polish traits of heraldry. The term is also used to refer to Polish heraldic system, as opposed to systems used elsewhere, notably in Western Europe...
- History of the Jews in LithuaniaHistory of the Jews in LithuaniaThe history of the Jews in Lithuania spans the period from the eighth century to the present day. There is still a small community in that country, as well as an extensive Lithuanian Jewish diaspora in Israel, the United States and other countries. For more detail, see Lithuanian Jews.-Early...
- History of the Jews in PolandHistory of the Jews in PolandThe history of the Jews in Poland dates back over a millennium. For centuries, Poland was home to the largest and most significant Jewish community in the world. Poland was the centre of Jewish culture thanks to a long period of statutory religious tolerance and social autonomy. This ended with the...

