Mößbauer spectroscopy
Encyclopedia
Spectroscopy
Spectroscopy is the study of the interaction between matter and radiated energy. Historically, spectroscopy originated through the study of visible light dispersed according to its wavelength, e.g., by a prism. Later the concept was expanded greatly to comprise any interaction with radiative...
technique based on the Mössbauer effect
Mössbauer effect
The Mössbauer effect, or recoilless nuclear resonance fluorescence, is a physical phenomenon discovered by Rudolf Mössbauer in 1958. It involves the resonant and recoil-free emission and absorption of γ radiation by atomic nuclei bound in a solid...
. This effect, discovered by Rudolf Mössbauer in 1957, consists in the recoil-free, resonant absorption and emission of gamma ray
Gamma ray
Gamma radiation, also known as gamma rays or hyphenated as gamma-rays and denoted as γ, is electromagnetic radiation of high frequency . Gamma rays are usually naturally produced on Earth by decay of high energy states in atomic nuclei...
s in solid
Solid
Solid is one of the three classical states of matter . It is characterized by structural rigidity and resistance to changes of shape or volume. Unlike a liquid, a solid object does not flow to take on the shape of its container, nor does it expand to fill the entire volume available to it like a...
s.
Like NMR spectroscopy
NMR spectroscopy
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, most commonly known as NMR spectroscopy, is a research technique that exploits the magnetic properties of certain atomic nuclei to determine physical and chemical properties of atoms or the molecules in which they are contained...
, Mössbauer spectroscopy probes tiny changes in the energy levels of an atomic nucleus in response to its environment. Typically, three types of nuclear interaction may be observed: an isomer shift, also known as a chemical shift
Chemical shift
In nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, the chemical shift is the resonant frequency of a nucleus relative to a standard. Often the position and number of chemical shifts are diagnostic of the structure of a molecule...
; quadrupole splitting
Quadrupole splitting
Quadrupole splitting is an example of a hyperfine interaction found in gamma-ray spectroscopy, in the circumstance where nuclei with a non-radially-symmetric shape are found immersed in an external electric field gradient...
; and, magnetic or hyperfine splitting, also known as the Zeeman effect
Zeeman effect
The Zeeman effect is the splitting of a spectral line into several components in the presence of a static magnetic field. It is analogous to the Stark effect, the splitting of a spectral line into several components in the presence of an electric field...
. Due to the high energy and extremely narrow line
Spectral line
A spectral line is a dark or bright line in an otherwise uniform and continuous spectrum, resulting from a deficiency or excess of photons in a narrow frequency range, compared with the nearby frequencies.- Types of line spectra :...
widths of gamma rays, Mössbauer spectroscopy is one of the most sensitive techniques in terms of energy (and hence frequency) resolution, capable of detecting change in just a few parts per 1011.
Basic principle
Just as a gun recoils when a bullet is fired, conservation of momentum requires a free nucleus (such as in a gas) to recoil during emission or absorption of a gamma ray. If a nucleus at rest emits a gamma ray, the energy of the gamma ray is slightly less than the natural energy of the transition, but in order for a nucleus at rest to absorb a gamma ray, the gamma ray's energy must be slightly greater than the natural energy, because in both cases energy is lost to recoil. This means that nuclear resonance (emission and absorption of the same gamma ray) is unobservable with free nuclei, because the shift in energy is too great and the emission and absorption spectra have no significant overlap.Nuclei in a solid crystal
Crystal
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituent atoms, molecules, or ions are arranged in an orderly repeating pattern extending in all three spatial dimensions. The scientific study of crystals and crystal formation is known as crystallography...
, however, are not free to recoil because they are bound in place in the crystal lattice. When a nucleus in a solid emits or absorbs a gamma ray, some energy can still be lost as recoil energy, but in this case it always occurs in discrete packets called phonon
Phonon
In physics, a phonon is a collective excitation in a periodic, elastic arrangement of atoms or molecules in condensed matter, such as solids and some liquids...
s (quantized vibrations of the crystal lattice). Any whole number of phonons can be emitted, including zero, which is known as a "recoil-free" event. In this case conservation of momentum is satisfied by the momentum of the crystal as a whole, so practically no energy is lost.
As an analogy, imagine jumping from a boat to shore, and imagine that the distance from the boat to shore is the longest you can possibly jump (on land). If the boat is floating in water, you will fall short because some of your energy goes into pushing the boat back. If the water is frozen solid, however, you will be able to make it.
Mössbauer found that a significant fraction of emission and absorption events will be recoil-free, which is quantified using the Lamb–Mössbauer factor
Lamb–Mössbauer factor
In physics, the Lamb–Mössbauer factor or elastic incoherent structure factor is the ratio of elastic to total incoherent neutron scattering, or the ratio of recoil-free to total nuclear resonant absorption in Mössbauer spectroscopy...
. This fact is what makes Mössbauer spectroscopy possible, because it means gamma rays emitted by one nucleus can be resonantly absorbed by a sample containing nuclei of the same isotope, and this absorption can be measured.
Typical method
In its most common form, Mössbauer absorption spectroscopy, a solid sample is exposed to a beam of gamma radiationGamma ray
Gamma radiation, also known as gamma rays or hyphenated as gamma-rays and denoted as γ, is electromagnetic radiation of high frequency . Gamma rays are usually naturally produced on Earth by decay of high energy states in atomic nuclei...
, and a detector measures the intensity of the beam transmitted through the sample. The atoms in the source emitting the gamma rays must be of the same isotope as the atoms in the sample absorbing them.
If the emitting and absorbing nuclei were in identical chemical environments, the nuclear transition energies would be exactly equal and resonant absorption would be observed with both materials at rest. The difference in chemical environments, however, causes the nuclear energy levels to shift in a few different ways, as described below. Although these energy shifts are tiny (often less than a micro-electronvolt
Electronvolt
In physics, the electron volt is a unit of energy equal to approximately joule . By definition, it is equal to the amount of kinetic energy gained by a single unbound electron when it accelerates through an electric potential difference of one volt...
), the extremely narrow spectral linewidth
Spectral linewidth
The spectral linewidth characterizes the width of a spectral line, such as in the electromagnetic emission spectrum of an atom, or the frequency spectrum of an acoustic or electronic system...
s of gamma rays for some radionuclides make the small energy shifts correspond to large changes in absorbance. To bring the two nuclei back into resonance it is necessary to change the energy of the gamma ray slightly, and in practice this is always done using the Doppler effect
Doppler effect
The Doppler effect , named after Austrian physicist Christian Doppler who proposed it in 1842 in Prague, is the change in frequency of a wave for an observer moving relative to the source of the wave. It is commonly heard when a vehicle sounding a siren or horn approaches, passes, and recedes from...
.
During Mössbauer absorption spectroscopy, the source is accelerated through a range of velocities using a linear motor
Linear motor
A linear motor is an electric motor that has had its stator and rotor "unrolled" so that instead of producing a torque it produces a linear force along its length...
to produce a Doppler effect and scan the gamma ray energy through a given range. A typical range of velocities for 57Fe, for example, may be ± .
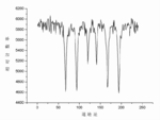
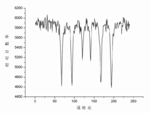
In the resulting spectra, gamma ray intensity is plotted as a function of the source velocity. At velocities corresponding to the resonant energy levels of the sample, a fraction of the gamma rays are absorbed, resulting in a drop in the measured intensity and a corresponding dip in the spectrum. The number, positions, and intensities of the dips (also called peaks; dips in transmitted intensity are peaks in absorbance) provide information about the chemical environment of the absorbing nuclei and can be used to characterize the sample.
Selecting a suitable source
Mössbauer spectroscopy is limited by the need for a suitable gamma-ray source. Usually, this consists of a radioactive parent that decays to the desired isotope. For example, the source for 57Fe consists of 57Co, which decays by electron captureElectron capture
Electron capture is a process in which a proton-rich nuclide absorbs an inner atomic electron and simultaneously emits a neutrino...
to an excited state
Excited state
Excitation is an elevation in energy level above an arbitrary baseline energy state. In physics there is a specific technical definition for energy level which is often associated with an atom being excited to an excited state....
of 57Fe, then subsequently decays to a ground state
Ground state
The ground state of a quantum mechanical system is its lowest-energy state; the energy of the ground state is known as the zero-point energy of the system. An excited state is any state with energy greater than the ground state...
emitting the desired gamma-ray. The radioactive cobalt is prepared on a foil, often of rhodium. Ideally the parent
Parent
A parent is a caretaker of the offspring in their own species. In humans, a parent is of a child . Children can have one or more parents, but they must have two biological parents. Biological parents consist of the male who sired the child and the female who gave birth to the child...
isotope will have a sufficiently long half-life to remain useful, but will also have a sufficient decay rate to supply the required intensity of radiation. Also, the gamma-ray energy should be relatively low, otherwise the system will have a low recoil-free fraction resulting in a poor signal-to-noise ratio
Signal-to-noise ratio
Signal-to-noise ratio is a measure used in science and engineering that compares the level of a desired signal to the level of background noise. It is defined as the ratio of signal power to the noise power. A ratio higher than 1:1 indicates more signal than noise...
and requiring long collection times. The periodic table below indicates those elements having an isotope suitable for Mössbauer spectroscopy. Of these, 57Fe is by far the most common element studied using the technique, although 129I
Iodine-129
Iodine-129 is long-lived radioisotope of iodine which occurs naturally, but also is of special interest in the monitoring and effects of man-made nuclear fission decay products, where it serves as both tracer and potential radiological contaminant....
, 119Sn, and 121Sb are also frequently studied.
Periodic table The periodic table of the chemical elements is a tabular display of the 118 known chemical elements organized by selected properties of their atomic structures. Elements are presented by increasing atomic number, the number of protons in an atom's atomic nucleus... of Mössbauer active elements |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H Hydrogen Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly... |
He Helium Helium is the chemical element with atomic number 2 and an atomic weight of 4.002602, which is represented by the symbol He. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas that heads the noble gas group in the periodic table... |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Li Lithium Lithium is a soft, silver-white metal that belongs to the alkali metal group of chemical elements. It is represented by the symbol Li, and it has the atomic number 3. Under standard conditions it is the lightest metal and the least dense solid element. Like all alkali metals, lithium is highly... |
Be Beryllium Beryllium is the chemical element with the symbol Be and atomic number 4. It is a divalent element which occurs naturally only in combination with other elements in minerals. Notable gemstones which contain beryllium include beryl and chrysoberyl... |
B Boron Boron is the chemical element with atomic number 5 and the chemical symbol B. Boron is a metalloid. Because boron is not produced by stellar nucleosynthesis, it is a low-abundance element in both the solar system and the Earth's crust. However, boron is concentrated on Earth by the... |
C Carbon Carbon is the chemical element with symbol C and atomic number 6. As a member of group 14 on the periodic table, it is nonmetallic and tetravalent—making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds... |
N Nitrogen Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere... |
O Oxygen Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition... |
F Fluorine Fluorine is the chemical element with atomic number 9, represented by the symbol F. It is the lightest element of the halogen column of the periodic table and has a single stable isotope, fluorine-19. At standard pressure and temperature, fluorine is a pale yellow gas composed of diatomic... |
Ne Neon Neon is the chemical element that has the symbol Ne and an atomic number of 10. Although a very common element in the universe, it is rare on Earth. A colorless, inert noble gas under standard conditions, neon gives a distinct reddish-orange glow when used in either low-voltage neon glow lamps or... |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Na Sodium Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal and is a member of the alkali metals; its only stable isotope is 23Na. It is an abundant element that exists in numerous minerals, most commonly as sodium chloride... |
Mg Magnesium Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg, atomic number 12, and common oxidation number +2. It is an alkaline earth metal and the eighth most abundant element in the Earth's crust and ninth in the known universe as a whole... |
Al Aluminium Aluminium or aluminum is a silvery white member of the boron group of chemical elements. It has the symbol Al, and its atomic number is 13. It is not soluble in water under normal circumstances.... |
Si Silicon Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. A tetravalent metalloid, it is less reactive than its chemical analog carbon, the nonmetal directly above it in the periodic table, but more reactive than germanium, the metalloid directly below it in the table... |
P Phosphorus Phosphorus is the chemical element that has the symbol P and atomic number 15. A multivalent nonmetal of the nitrogen group, phosphorus as a mineral is almost always present in its maximally oxidized state, as inorganic phosphate rocks... |
S Sulfur Sulfur or sulphur is the chemical element with atomic number 16. In the periodic table it is represented by the symbol S. It is an abundant, multivalent non-metal. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow... |
Cl Chlorine Chlorine is the chemical element with atomic number 17 and symbol Cl. It is the second lightest halogen, found in the periodic table in group 17. The element forms diatomic molecules under standard conditions, called dichlorine... |
Ar Argon Argon is a chemical element represented by the symbol Ar. Argon has atomic number 18 and is the third element in group 18 of the periodic table . Argon is the third most common gas in the Earth's atmosphere, at 0.93%, making it more common than carbon dioxide... |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| K Potassium Potassium is the chemical element with the symbol K and atomic number 19. Elemental potassium is a soft silvery-white alkali metal that oxidizes rapidly in air and is very reactive with water, generating sufficient heat to ignite the hydrogen emitted in the reaction.Potassium and sodium are... |
Ca Calcium Calcium is the chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. It has an atomic mass of 40.078 amu. Calcium is a soft gray alkaline earth metal, and is the fifth-most-abundant element by mass in the Earth's crust... |
Sc Scandium Scandium is a chemical element with symbol Sc and atomic number 21. A silvery-white metallic transition metal, it has historically been sometimes classified as a rare earth element, together with yttrium and the lanthanoids... |
Ti Titanium Titanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ti and atomic number 22. It has a low density and is a strong, lustrous, corrosion-resistant transition metal with a silver color.... |
V Vanadium Vanadium is a chemical element with the symbol V and atomic number 23. It is a hard, silvery gray, ductile and malleable transition metal. The formation of an oxide layer stabilizes the metal against oxidation. The element is found only in chemically combined form in nature... |
Cr Chromium Chromium is a chemical element which has the symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in Group 6. It is a steely-gray, lustrous, hard metal that takes a high polish and has a high melting point. It is also odorless, tasteless, and malleable... |
Mn Manganese Manganese is a chemical element, designated by the symbol Mn. It has the atomic number 25. It is found as a free element in nature , and in many minerals... |
Fe Iron Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust... |
Co Cobalt Cobalt is a chemical element with symbol Co and atomic number 27. It is found naturally only in chemically combined form. The free element, produced by reductive smelting, is a hard, lustrous, silver-gray metal.... |
Ni Nickel Nickel is a chemical element with the chemical symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel belongs to the transition metals and is hard and ductile... |
Cu Copper Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29. It is a ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. Pure copper is soft and malleable; an exposed surface has a reddish-orange tarnish... |
Zn Zinc Zinc , or spelter , is a metallic chemical element; it has the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is the first element in group 12 of the periodic table. Zinc is, in some respects, chemically similar to magnesium, because its ion is of similar size and its only common oxidation state is +2... |
Ga Gallium Gallium is a chemical element that has the symbol Ga and atomic number 31. Elemental gallium does not occur in nature, but as the gallium salt in trace amounts in bauxite and zinc ores. A soft silvery metallic poor metal, elemental gallium is a brittle solid at low temperatures. As it liquefies... |
Ge Germanium Germanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ge and atomic number 32. It is a lustrous, hard, grayish-white metalloid in the carbon group, chemically similar to its group neighbors tin and silicon. The isolated element is a semiconductor, with an appearance most similar to elemental silicon.... |
As Arsenic Arsenic is a chemical element with the symbol As, atomic number 33 and relative atomic mass 74.92. Arsenic occurs in many minerals, usually in conjunction with sulfur and metals, and also as a pure elemental crystal. It was first documented by Albertus Magnus in 1250.Arsenic is a metalloid... |
Se Selenium Selenium is a chemical element with atomic number 34, chemical symbol Se, and an atomic mass of 78.96. It is a nonmetal, whose properties are intermediate between those of adjacent chalcogen elements sulfur and tellurium... |
Br Bromine Bromine ") is a chemical element with the symbol Br, an atomic number of 35, and an atomic mass of 79.904. It is in the halogen element group. The element was isolated independently by two chemists, Carl Jacob Löwig and Antoine Jerome Balard, in 1825–1826... |
Kr Krypton Krypton is a chemical element with the symbol Kr and atomic number 36. It is a member of Group 18 and Period 4 elements. A colorless, odorless, tasteless noble gas, krypton occurs in trace amounts in the atmosphere, is isolated by fractionally distilling liquified air, and is often used with other... |
||||||||||||||
| Rb Rubidium Rubidium is a chemical element with the symbol Rb and atomic number 37. Rubidium is a soft, silvery-white metallic element of the alkali metal group. Its atomic mass is 85.4678. Elemental rubidium is highly reactive, with properties similar to those of other elements in group 1, such as very rapid... |
Sr Strontium Strontium is a chemical element with the symbol Sr and the atomic number 38. An alkaline earth metal, strontium is a soft silver-white or yellowish metallic element that is highly reactive chemically. The metal turns yellow when exposed to air. It occurs naturally in the minerals celestine and... |
Y Yttrium Yttrium is a chemical element with symbol Y and atomic number 39. It is a silvery-metallic transition metal chemically similar to the lanthanides and it has often been classified as a "rare earth element". Yttrium is almost always found combined with the lanthanides in rare earth minerals and is... |
Zr Zirconium Zirconium is a chemical element with the symbol Zr and atomic number 40. The name of zirconium is taken from the mineral zircon. Its atomic mass is 91.224. It is a lustrous, grey-white, strong transition metal that resembles titanium... |
Nb Niobium Niobium or columbium , is a chemical element with the symbol Nb and atomic number 41. It's a soft, grey, ductile transition metal, which is often found in the pyrochlore mineral, the main commercial source for niobium, and columbite... |
Mo Molybdenum Molybdenum , is a Group 6 chemical element with the symbol Mo and atomic number 42. The name is from Neo-Latin Molybdaenum, from Ancient Greek , meaning lead, itself proposed as a loanword from Anatolian Luvian and Lydian languages, since its ores were confused with lead ores... |
Tc Technetium Technetium is the chemical element with atomic number 43 and symbol Tc. It is the lowest atomic number element without any stable isotopes; every form of it is radioactive. Nearly all technetium is produced synthetically and only minute amounts are found in nature... |
Ru Ruthenium Ruthenium is a chemical element with symbol Ru and atomic number 44. It is a rare transition metal belonging to the platinum group of the periodic table. Like the other metals of the platinum group, ruthenium is inert to most chemicals. The Russian scientist Karl Ernst Claus discovered the element... |
Rh Rhodium Rhodium is a chemical element that is a rare, silvery-white, hard and chemically inert transition metal and a member of the platinum group. It has the chemical symbol Rh and atomic number 45. It is composed of only one isotope, 103Rh. Naturally occurring rhodium is found as the free metal, alloyed... |
Pd Palladium Palladium is a chemical element with the chemical symbol Pd and an atomic number of 46. It is a rare and lustrous silvery-white metal discovered in 1803 by William Hyde Wollaston. He named it after the asteroid Pallas, which was itself named after the epithet of the Greek goddess Athena, acquired... |
Ag Silver Silver is a metallic chemical element with the chemical symbol Ag and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it has the highest electrical conductivity of any element and the highest thermal conductivity of any metal... |
Cd Cadmium Cadmium is a chemical element with the symbol Cd and atomic number 48. This soft, bluish-white metal is chemically similar to the two other stable metals in group 12, zinc and mercury. Similar to zinc, it prefers oxidation state +2 in most of its compounds and similar to mercury it shows a low... |
In Indium Indium is a chemical element with the symbol In and atomic number 49. This rare, very soft, malleable and easily fusible post-transition metal is chemically similar to gallium and thallium, and shows the intermediate properties between these two... |
Sn Tin Tin is a chemical element with the symbol Sn and atomic number 50. It is a main group metal in group 14 of the periodic table. Tin shows chemical similarity to both neighboring group 14 elements, germanium and lead and has two possible oxidation states, +2 and the slightly more stable +4... |
Sb Antimony Antimony is a toxic chemical element with the symbol Sb and an atomic number of 51. A lustrous grey metalloid, it is found in nature mainly as the sulfide mineral stibnite... |
Te | I Iodine Iodine is a chemical element with the symbol I and atomic number 53. The name is pronounced , , or . The name is from the , meaning violet or purple, due to the color of elemental iodine vapor.... |
Xe Xenon Xenon is a chemical element with the symbol Xe and atomic number 54. The element name is pronounced or . A colorless, heavy, odorless noble gas, xenon occurs in the Earth's atmosphere in trace amounts... |
||||||||||||||
| Cs Caesium Caesium or cesium is the chemical element with the symbol Cs and atomic number 55. It is a soft, silvery-gold alkali metal with a melting point of 28 °C , which makes it one of only five elemental metals that are liquid at room temperature... |
Ba Barium Barium is a chemical element with the symbol Ba and atomic number 56. It is the fifth element in Group 2, a soft silvery metallic alkaline earth metal. Barium is never found in nature in its pure form due to its reactivity with air. Its oxide is historically known as baryta but it reacts with... |
La Lanthanum Lanthanum is a chemical element with the symbol La and atomic number 57.Lanthanum is a silvery white metallic element that belongs to group 3 of the periodic table and is the first element of the lanthanide series. It is found in some rare-earth minerals, usually in combination with cerium and... |
Hf Hafnium Hafnium is a chemical element with the symbol Hf and atomic number 72. A lustrous, silvery gray, tetravalent transition metal, hafnium chemically resembles zirconium and is found in zirconium minerals. Its existence was predicted by Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869. Hafnium was the penultimate stable... |
Ta Tantalum Tantalum is a chemical element with the symbol Ta and atomic number 73. Previously known as tantalium, the name comes from Tantalus, a character in Greek mythology. Tantalum is a rare, hard, blue-gray, lustrous transition metal that is highly corrosion resistant. It is part of the refractory... |
W Tungsten Tungsten , also known as wolfram , is a chemical element with the chemical symbol W and atomic number 74.A hard, rare metal under standard conditions when uncombined, tungsten is found naturally on Earth only in chemical compounds. It was identified as a new element in 1781, and first isolated as... |
Re Rhenium Rhenium is a chemical element with the symbol Re and atomic number 75. It is a silvery-white, heavy, third-row transition metal in group 7 of the periodic table. With an average concentration of 1 part per billion , rhenium is one of the rarest elements in the Earth's crust. The free element has... |
Os Osmium Osmium is a chemical element with the symbol Os and atomic number 76. Osmium is a hard, brittle, blue-gray or blue-blacktransition metal in the platinum family, and is the densest natural element. Osmium is twice as dense as lead. The density of osmium is , slightly greater than that of iridium,... |
Ir Iridium Iridium is the chemical element with atomic number 77, and is represented by the symbol Ir. A very hard, brittle, silvery-white transition metal of the platinum family, iridium is the second-densest element and is the most corrosion-resistant metal, even at temperatures as high as 2000 °C... |
Pt Platinum Platinum is a chemical element with the chemical symbol Pt and an atomic number of 78. Its name is derived from the Spanish term platina del Pinto, which is literally translated into "little silver of the Pinto River." It is a dense, malleable, ductile, precious, gray-white transition metal... |
Au Gold Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au and an atomic number of 79. Gold is a dense, soft, shiny, malleable and ductile metal. Pure gold has a bright yellow color and luster traditionally considered attractive, which it maintains without oxidizing in air or water. Chemically, gold is a... |
Hg Mercury (element) Mercury is a chemical element with the symbol Hg and atomic number 80. It is also known as quicksilver or hydrargyrum... |
Tl Thallium Thallium is a chemical element with the symbol Tl and atomic number 81. This soft gray poor metal resembles tin but discolors when exposed to air. The two chemists William Crookes and Claude-Auguste Lamy discovered thallium independently in 1861 by the newly developed method of flame spectroscopy... |
Pb Lead Lead is a main-group element in the carbon group with the symbol Pb and atomic number 82. Lead is a soft, malleable poor metal. It is also counted as one of the heavy metals. Metallic lead has a bluish-white color after being freshly cut, but it soon tarnishes to a dull grayish color when exposed... |
Bi Bismuth Bismuth is a chemical element with symbol Bi and atomic number 83. Bismuth, a trivalent poor metal, chemically resembles arsenic and antimony. Elemental bismuth may occur naturally uncombined, although its sulfide and oxide form important commercial ores. The free element is 86% as dense as lead... |
Po Polonium Polonium is a chemical element with the symbol Po and atomic number 84, discovered in 1898 by Marie Skłodowska-Curie and Pierre Curie. A rare and highly radioactive element, polonium is chemically similar to bismuth and tellurium, and it occurs in uranium ores. Polonium has been studied for... |
At Astatine Astatine is a radioactive chemical element with the symbol At and atomic number 85. It occurs on the Earth only as the result of decay of heavier elements, and decays away rapidly, so much less is known about this element than its upper neighbors in the periodic table... |
Rn Radon Radon is a chemical element with symbol Rn and atomic number 86. It is a radioactive, colorless, odorless, tasteless noble gas, occurring naturally as the decay product of uranium or thorium. Its most stable isotope, 222Rn, has a half-life of 3.8 days... |
||||||||||||||
| Fr Francium Francium is a chemical element with symbol Fr and atomic number 87. It was formerly known as eka-caesium and actinium K.Actually the least unstable isotope, francium-223 It has the lowest electronegativity of all known elements, and is the second rarest naturally occurring element... |
Ra Radium Radium is a chemical element with atomic number 88, represented by the symbol Ra. Radium is an almost pure-white alkaline earth metal, but it readily oxidizes on exposure to air, becoming black in color. All isotopes of radium are highly radioactive, with the most stable isotope being radium-226,... |
Ac Actinium Actinium is a radioactive chemical element with the symbol Ac and atomic number 89, which was discovered in 1899. It was the first non-primordial radioactive element to be isolated. Polonium, radium and radon were observed before actinium, but they were not isolated until 1902... |
Rf Rutherfordium Rutherfordium is a chemical element with symbol Rf and atomic number 104, named in honor of New Zealand physicist Ernest Rutherford. It is a synthetic element and radioactive; the most stable known isotope, 267Rf, has a half-life of approximately 1.3 hours.In the periodic table of the elements,... |
Db Dubnium The Soviet team proposed the name nielsbohrium in honor of the Danish nuclear physicist Niels Bohr. The American team proposed that the new element should be named hahnium , in honor of the late German chemist Otto Hahn... |
Sg Seaborgium Seaborgium is a synthetic chemical element with the symbol Sg and atomic number 106.Seaborgium is a synthetic element whose most stable isotope 271Sg has a half-life of 1.9 minutes. A new isotope 269Sg has a potentially slightly longer half-life based on the observation of a single decay... |
Bh Bohrium Bohrium is a chemical element with the symbol Bh and atomic number 107 and is the heaviest member of group 7 .It is a synthetic element whose most stable known isotope, 270Bh, has a half-life of 61 seconds... |
Hs Hassium Hassium is a synthetic element with the symbol Hs and atomic number 108. It is the heaviest member of the group 8 elements. The element was first observed in 1984... |
Mt Meitnerium Meitnerium is a chemical element with the symbol Mt and atomic number 109. It is placed as the heaviest member of group 9 in the periodic table but a sufficiently stable isotope is not known at this time which would allow chemical experiments to confirm its position, unlike its lighter... |
Ds Darmstadtium Darmstadtium is a chemical element with the symbol Ds and atomic number 110. It is placed as the heaviest member of group 10, but no known isotope is sufficiently stable to allow chemical experiments to confirm its placing in that group... |
Rg Roentgenium Roentgenium is a synthetic radioactive chemical element with the symbol Rg and atomic number 111. It is placed as the heaviest member of the group 11 elements, although a sufficiently stable isotope has not yet been produced in a sufficient amount that would confirm this position as a heavier... |
Cn | Uut Ununtrium Ununtrium is the temporary name of a synthetic element with the temporary symbol Uut and atomic number 113.It is placed as the heaviest member of the group 13 elements although a sufficiently stable isotope is not known at this time that would allow chemical experiments to confirm its position... |
Uuq Ununquadium Ununquadium is the temporary name of a radioactive chemical element with the temporary symbol Uuq and atomic number 114. There is no proposed name yet, although flerovium has been discussed in the media.About 80 decays of atoms of... |
Uup Ununpentium Ununpentium is the temporary name of a synthetic superheavy element in the periodic table that has the temporary symbol Uup and has the atomic number 115.... |
Uuh Ununhexium Ununhexium is the temporary name of a synthetic superheavy element with the temporary symbol Uuh and atomic number 116. There is no proposed name yet although moscovium has been discussed in the media.It is placed as the heaviest member of group 16 although a sufficiently stable isotope is... |
Uus Ununseptium Ununseptium is the temporary name of a superheavy artificial chemical element with temporary symbol Uus and atomic number 117. Six atoms were detected by a joint Russia–US collaboration at Dubna, Moscow Oblast, Russia, in 2009–10... |
Uuo Ununoctium Ununoctium is the temporary IUPAC name for the transactinide element having the atomic number 118 and temporary element symbol Uuo. It is also known as eka-radon or element 118, and on the periodic table of the elements it is a p-block element and the last one of the 7th period. Ununoctium is... |
||||||||||||||
| Ce Cerium Cerium is a chemical element with the symbol Ce and atomic number 58. It is a soft, silvery, ductile metal which easily oxidizes in air. Cerium was named after the dwarf planet . Cerium is the most abundant of the rare earth elements, making up about 0.0046% of the Earth's crust by weight... |
Pr Praseodymium Praseodymium is a chemical element that has the symbol Pr and atomic number 59. Praseodymium is a soft, silvery, malleable and ductile metal in the lanthanide group. It is too reactive to be found in native form, and when artificially prepared, it slowly develops a green oxide coating.The element... |
Nd Neodymium Neodymium is a chemical element with the symbol Nd and atomic number 60. It is a soft silvery metal that tarnishes in air. Neodymium was discovered in 1885 by the Austrian chemist Carl Auer von Welsbach. It is present in significant quantities in the ore minerals monazite and bastnäsite... |
Pm Promethium Promethium is a chemical element with the symbol Pm and atomic number 61. It is notable for being the only exclusively radioactive element besides technetium that is followed by chemical elements with stable isotopes.- Prediction :... |
Sm Samarium Samarium is a chemical element with the symbol Sm, atomic number 62 and atomic weight 150.36. It is a moderately hard silvery metal which readily oxidizes in air. Being a typical member of the lanthanide series, samarium usually assumes the oxidation state +3... |
Eu Europium Europium is a chemical element with the symbol Eu and atomic number 63. It is named after the continent of Europe. It is a moderately hard silvery metal which readily oxidizes in air and water... |
Gd Gadolinium Gadolinium is a chemical element with the symbol Gd and atomic number 64. It is a silvery-white, malleable and ductile rare-earth metal. It is found in nature only in combined form. Gadolinium was first detected spectroscopically in 1880 by de Marignac who separated its oxide and is credited with... |
Tb Terbium Terbium is a chemical element with the symbol Tb and atomic number 65. It is a silvery-white rare earth metal that is malleable, ductile and soft enough to be cut with a knife... |
Dy Dysprosium Dysprosium is a chemical element with the symbol Dy and atomic number 66. It is a rare earth element with a metallic silver luster. Dysprosium is never found in nature as a free element, though it is found in various minerals, such as xenotime... |
Ho Holmium Holmium is a chemical element with the symbol Ho and atomic number 67. Part of the lanthanide series, holmium is a rare earth element. Its oxide was first isolated from rare earth ores in 1878 and the element was named after the city of Stockholm.... |
Er Erbium Erbium is a chemical element in the lanthanide series, with the symbol Er and atomic number 68. A silvery-white solid metal when artificially isolated, natural erbium is always found in chemical combination with other elements on Earth... |
Tm Thulium Thulium is a chemical element that has the symbol Tm and atomic number 69. Thulium is the second least abundant of the lanthanides . It is an easily workable metal with a bright silvery-gray luster... |
Yb Ytterbium Ytterbium is a chemical element with the symbol Yb and atomic number 70. A soft silvery metallic element, ytterbium is a rare earth element of the lanthanide series and is found in the minerals gadolinite, monazite, and xenotime. The element is sometimes associated with yttrium or other related... |
Lu | ||||||||||||||||||
| Th Thorium Thorium is a natural radioactive chemical element with the symbol Th and atomic number 90. It was discovered in 1828 and named after Thor, the Norse god of thunder.... |
Pa Protactinium Protactinium is a chemical element with the symbol Pa and atomic number 91. It is a dense, silvery-gray metal which readily reacts with oxygen, water vapor and inorganic acids. It forms various chemical compounds where protactinium is usually present in the oxidation state +5, but can also assume... |
U Uranium Uranium is a silvery-white metallic chemical element in the actinide series of the periodic table, with atomic number 92. It is assigned the chemical symbol U. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons... |
Np Neptunium Neptunium is a chemical element with the symbol Np and atomic number 93. A radioactive metal, neptunium is the first transuranic element and belongs to the actinide series. Its most stable isotope, 237Np, is a by-product of nuclear reactors and plutonium production and it can be used as a... |
Pu Plutonium Plutonium is a transuranic radioactive chemical element with the chemical symbol Pu and atomic number 94. It is an actinide metal of silvery-gray appearance that tarnishes when exposed to air, forming a dull coating when oxidized. The element normally exhibits six allotropes and four oxidation... |
Am Americium Americium is a synthetic element that has the symbol Am and atomic number 95. This transuranic element of the actinide series is located in the periodic table below the lanthanide element europium, and thus by analogy was named after another continent, America.Americium was first produced in 1944... |
Cm Curium Curium is a synthetic chemical element with the symbol Cm and atomic number 96. This radioactive transuranic element of the actinide series was named after Marie Skłodowska-Curie and her husband Pierre Curie. Curium was first intentionally produced and identified in summer 1944 by the group of... |
Bk Berkelium Berkelium , is a synthetic element with the symbol Bk and atomic number 97, a member of the actinide and transuranium element series. It is named after the city of Berkeley, California, the location of the University of California Radiation Laboratory where it was discovered in December 1949... |
Cf Californium Californium is a radioactive metallic chemical element with the symbol Cf and atomic number 98. The element was first made in the laboratory in 1950 by bombarding curium with alpha particles at the University of California, Berkeley. It is the ninth member of the actinide series and was the... |
Es Einsteinium Einsteinium is a synthetic element with the symbol Es and atomic number 99. It is the seventh transuranic element, and an actinide.Einsteinium was discovered in the debris of the first hydrogen bomb explosion in 1952, and named after Albert Einstein... |
Fm Fermium Fermium is a synthetic element with the symbol Fm. It is the 100th element in the periodic table and a member of the actinide series. It is the heaviest element that can be formed by neutron bombardment of lighter elements, and hence the last element that can be prepared in macroscopic quantities,... |
Md Mendelevium Mendelevium is a synthetic element with the symbol Md and the atomic number 101. A metallic radioactive transuranic element in the actinide series, mendelevium is usually synthesized by bombarding einsteinium with alpha particles. It was named after Dmitri Ivanovich Mendeleev, who created the... |
No Nobelium Nobelium is a synthetic element with the symbol No and atomic number 102. It was first correctly identified in 1966 by scientists at the Flerov Laboratory of Nuclear Reactions in Dubna, Soviet Union... |
Lr Lawrencium Lawrencium is a radioactive synthetic chemical element with the symbol Lr and atomic number 103. In the periodic table of the elements, it is a period 7 d-block element and the last element of actinide series... |
||||||||||||||||||
EWLINE
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Analysis of Mössbauer spectra
As described above, Mössbauer spectroscopy has an extremely fine energy resolution and can detect even subtle changes in the nuclear environment of the relevant atoms. Typically, there are three types of nuclear interactions that are observed, isomer shift (or chemical shiftChemical shift
In nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, the chemical shift is the resonant frequency of a nucleus relative to a standard. Often the position and number of chemical shifts are diagnostic of the structure of a molecule...
), quadrupole splitting
Quadrupole splitting
Quadrupole splitting is an example of a hyperfine interaction found in gamma-ray spectroscopy, in the circumstance where nuclei with a non-radially-symmetric shape are found immersed in an external electric field gradient...
and hyperfine splitting (or Zeeman splitting).
Quadrupole Splitting reflects the interaction between the nuclear energy levels and surrounding electric field gradient
Electric field gradient
In atomic, molecular, and solid-state physics, the electric field gradient measures the rate of change of the electric field at an atomic nucleus generated by the electronic charge distribution and the other nuclei...
(EFG). Nuclei in states with non-spherical charge distributions, i.e. all those with angular quantum number (I) greater than 1/2, produce an asymmetrical electric field which splits the nuclear energy levels. This produces a nuclear quadrupole moment.
In the case of an isotope with a I=3/2 excited state, such as 57Fe or 119Sn, the 3/2 to 1/2 transition is split into two substates mI=±1/2 and mI=±3/2. These appear as two specific peaks in a spectrum, sometimes referred to as a 'doublet'. Quadrupole splitting
Quadrupole splitting
Quadrupole splitting is an example of a hyperfine interaction found in gamma-ray spectroscopy, in the circumstance where nuclei with a non-radially-symmetric shape are found immersed in an external electric field gradient...
is measured as the separation between these two peaks and reflects the character of the electric field at the nucleus.
Magnetic splitting (hyperfine splitting) is a result of the interaction between the nucleus any surrounding magnetic field. A nucleus with spin, I, splits into 2I + 1 sub-energy levels in the presence of magnetic field. For example, a nucleus with spin state I= 3/2 will split into 4 non-degenerate sub-states with mI values of +3/2, +1/2, -1/2 and −3/2. Each split is hyperfine, being in the order of 10−7eV. The restriction rule of magnetic dipoles means that transitions between the excited state and ground state can only occur where mI changes by 0 or 1. This gives six possible transitions for a 3/2 to 1/2 transition. Generally speaking therefore, in the majority of cases only six peaks can be monitored in a spectrum produced by a hyperfine splitting nucleus.
The three Mössbauer parameters: isomer shift, quadrupole splitting, and hyperfine splitting can often be used to identify a particular compound by comparing it to known spectra. A large database including most of the published Mössbauer parameters available in the literature is maintained by the Mössbauer Effect Data Center. In some cases, a compound may have more than one possible crystal structure. For example, the crystal structure of hematite
Hematite
Hematite, also spelled as haematite, is the mineral form of iron oxide , one of several iron oxides. Hematite crystallizes in the rhombohedral system, and it has the same crystal structure as ilmenite and corundum...
(Fe2O3) supports two unique sites for each of the six iron atoms. The corresponding spectrum therefore has twelve peaks, two for each potential atomic site. Thus, hematite also has two sets of Mössbauer parameters, one for each site.
Combination of all: Many times it is very common to observe all effects-isomer shift, quadrupole splitting and magnetic Zeeman effect- in a spectrum. In such cases the isomer shift is given by the average of all lines. The quadrupole splitting when all the four excited substates are equally shifted (two substates are lifted and other two are lowered) is given the shift of the outer two lines relative to the inner two lines (generally innermost two lines are not considered). If the shifting of four substates are not equal then the quadrupole splitting is often extracted using fitting software where all the six lines are taken in to account.
In addition, the relative intensities of the various peaks reflect the relative concentrations of compounds in a sample and can be used for semi-quantitative analysis. Also, since ferromagnetic phenomena are size-dependent, in some cases spectra can provide insight into the crystallite size and grain structure of a material.
Applications of Mössbauer spectroscopy
Among the drawbacks of the technique are the limited number of gamma ray sources and the requirement that samples be solid in order to eliminate the recoil of the nucleus. Mössbauer spectroscopy is unique in its sensitivity to subtle changes in the chemical environment of the nucleus including oxidation state changes, the effect of different ligandLigand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding between metal and ligand generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electron pairs. The nature of metal-ligand bonding can range from...
s on a particular atom, and the magnetic environment of the sample.
As an analytical tool Mössbauer spectroscopy offers detection limits in the order of billionths of an electron volt. It has been especially useful in the field of geology for identifying the composition of iron-containing specimens including meteors and moon rocks. In situ data collection of Mössbauer spectra has also been carried out on iron rich rocks on Mars.
Another significant application of Mössbauer spectroscopy is the study of phase transformations that occur in iron catalysts during Fischer–Tropsch synthesis. While these catalysts initially consist of hematite (Fe2O3), during reaction they are transformed into a mixture of magnetite
Magnetite
Magnetite is a ferrimagnetic mineral with chemical formula Fe3O4, one of several iron oxides and a member of the spinel group. The chemical IUPAC name is iron oxide and the common chemical name is ferrous-ferric oxide. The formula for magnetite may also be written as FeO·Fe2O3, which is one part...
(Fe3O4) and several iron carbides
Cementite
Cementite, also known as iron carbide, is a chemical compound of iron and carbon, with the formula Fe3C . By weight, it is 6.67% carbon and 93.3% iron. It has an orthorhombic crystal structure. It is a hard, brittle material, normally classified as a ceramic in its pure form, though it is more...
. The formation of carbides appears to improve catalytic activity, however it can also lead to the mechanical break-up and attrition of the catalyst particles. This can cause difficulties in the final separation of catalyst from reaction products.
Mössbauer spectroscopy has also been used to determine the relative concentration change in the oxidation state of antimony (Sb
Antimony
Antimony is a toxic chemical element with the symbol Sb and an atomic number of 51. A lustrous grey metalloid, it is found in nature mainly as the sulfide mineral stibnite...
) during the selective oxidation of olefins. During calcination
Calcination
Calcination is a thermal treatment process applied to ores and other solid materials to bring about a thermal decomposition, phase transition, or removal of a volatile fraction. The calcination process normally takes place at temperatures below the melting point of the product materials...
all the Sb ions in an antimony-containing tin dioxide catalyst transform into the +5 oxidation state. Following the catalytic reaction, almost all Sb ions revert from the +5 to the +3 oxidation state. A significant change in the chemical environment surrounding the antimony nucleus occurs during the oxidation state change which can easily be monitored as an isomer shift in the Mössbauer spectrum.
This technique has also been used to observe the second-order transverse Doppler effect predicted by the theory of relativity
Theory of relativity
The theory of relativity, or simply relativity, encompasses two theories of Albert Einstein: special relativity and general relativity. However, the word relativity is sometimes used in reference to Galilean invariance....
, because of very high energy resolution.
More recently, Mössbauer spectroscopy has been instrumental in developing an understanding of the structure and function of iron containing enzymes and the model complexes synthesized to mimic the functions of these enzymes. Some examples of enzyes characterized in this way are: ribonucleotide reductase
Ribonucleotide reductase
Ribonucleotide reductase is an enzyme that catalyzes the formation of deoxyribonucleotides from ribonucleotides. Deoxyribonucleotides in turn are used in the synthesis of DNA. The reaction catalyzed by RNR is strictly conserved in all living organisms...
methane monooxygenase
Methane monooxygenase
Methane monooxygenase, or MMO, is an enzyme capable of oxidizing the C-H bond in methane as well as other alkanes. Methane monooxygenase belongs to the class of oxidoreductase enzymes ....
, tryptophan dioxygenase, deoxypusine hydroxylase, protocatechuate 2,3 dioxygenase, and cytochrome ba3.
Mossbauer spectroscopy has also been used very successfully to investigate the electronic structure of heterobimetallic complexes.
Mössbauer spectrometers
A Mössbauer spectrometer is a device that performs Mössbauer spectroscopy, or a device that uses the Mössbauer effect to determine the chemical environment of Mössbauer nuclei present in the sample. It is formed by three main parts; a source that moves back and forth to generate a doppler effectDoppler effect
The Doppler effect , named after Austrian physicist Christian Doppler who proposed it in 1842 in Prague, is the change in frequency of a wave for an observer moving relative to the source of the wave. It is commonly heard when a vehicle sounding a siren or horn approaches, passes, and recedes from...
, a collimator
Collimator
A collimator is a device that narrows a beam of particles or waves. To "narrow" can mean either to cause the directions of motion to become more aligned in a specific direction or to cause the spatial cross section of the beam to become smaller.- Optical collimators :In optics, a collimator may...
that filters out non-parallel gamma rays and a detector.
A miniature Mössbauer Spectrometer, named (MB) MIMOS II
MIMOS II
MIMOS II is the miniaturised Mössbauer spectrometer, developed by Dr. Göstar Klingelhöfer at the Johannes Gutenberg University in Mainz, Germany, that is used on the Mars Exploration Rovers Spirit and Opportunity for close-up investigations on the Martian surface of the mineralogy of iron-bearing...
, was used by the two rovers in NASA
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research...
's Mars Exploration Rover
Mars Exploration Rover
NASA's Mars Exploration Rover Mission is an ongoing robotic space mission involving two rovers, Spirit and Opportunity, exploring the planet Mars...
missions.

