
Art in Roman Catholicism
Encyclopedia


Old Testament
The Old Testament, of which Christians hold different views, is a Christian term for the religious writings of ancient Israel held sacred and inspired by Christians which overlaps with the 24-book canon of the Masoretic Text of Judaism...
.
The earliest surviving Catholic art works are the painted frescoes on the walls of the catacombs and meeting houses of the persecuted Christians of the Roman Empire. The stone sarcophagi
Sarcophagus
A sarcophagus is a funeral receptacle for a corpse, most commonly carved or cut from stone. The word "sarcophagus" comes from the Greek σαρξ sarx meaning "flesh", and φαγειν phagein meaning "to eat", hence sarkophagus means "flesh-eating"; from the phrase lithos sarkophagos...
of Roman Christians exhibit the earliest surviving carved statuary of Jesus, Mary and other biblical figures. The legalisation of Christianity transformed Catholic art, which adopted richer forms such as mosaics and illuminated manuscripts. The iconoclasm
Iconoclasm
Iconoclasm is the deliberate destruction of religious icons and other symbols or monuments, usually with religious or political motives. It is a frequent component of major political or religious changes...
controversy briefly divided the eastern and western churches, after which artistic development progressed in separate directions. Romanesque
Romanesque art
Romanesque art refers to the art of Western Europe from approximately 1000 AD to the rise of the Gothic style in the 13th century, or later, depending on region. The preceding period is increasingly known as the Pre-Romanesque...
and Gothic art
Gothic art
Gothic art was a Medieval art movement that developed in France out of Romanesque art in the mid-12th century, led by the concurrent development of Gothic architecture. It spread to all of Western Europe, but took over art more completely north of the Alps, never quite effacing more classical...
flowered in the Western Church as the style of painting and statuary moved in an increasingly naturalistic direction. The Protestant Reformation, produced new waves of image-destruction, to which the Church responded with the dramatic and emotive Baroque
Baroque
The Baroque is a period and the style that used exaggerated motion and clear, easily interpreted detail to produce drama, tension, exuberance, and grandeur in sculpture, painting, literature, dance, and music...
and Rococo
Rococo
Rococo , also referred to as "Late Baroque", is an 18th-century style which developed as Baroque artists gave up their symmetry and became increasingly ornate, florid, and playful...
styles. In the 19th century the leadership in western art moved away from the Catholic Church which, after embracing historical revivalism was increasingly affected by the modernist movement, a movement that in its "rebellion" against nature, counters the Church's emphasis on nature as a good creation of God.
Beginnings
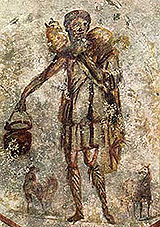
Christian art
Christian art
Christian art is sacred art produced in an attempt to illustrate, supplement and portray in tangible form the principles of Christianity, though other definitions are possible. Most Christian groups use or have used art to some extent, although some have had strong objections to some forms of...
is nearly as old as Christianity itself. The oldest Christian sculptures are from Roman sarcophagi, dating to the beginning of the 2nd century. As a persecuted sect, however, the earliest Christian images were arcane and meant to be intelligible only to the initiated. Early Christian symbols include the dove, the fish, the lamb, the cross, symbolic representation of the Four Evangelists
Four Evangelists
In Christian tradition the Four Evangelists are Matthew, Mark, Luke, and John, the authors attributed with the creation of the four Gospel accounts in the New Testament that bear the following titles:*Gospel according to Matthew*Gospel according to Mark...
as beasts, and the Good Shepherd. Early Christians also adapted Roman decorative motifs like the peacock, grapevines, and the good shepherd. It is in the Catacombs of Rome
Catacombs of Rome
The Catacombs of Rome are ancient catacombs, underground burial places under or near Rome, Italy, of which there are at least forty, some discovered only in recent decades. Though most famous for Christian burials, either in separate catacombs or mixed together, they began in the 2nd century, much...
that recognizable representations of Christian figures first appear in number. The recently-excavated Dura-Europos
Dura-Europos
Dura-Europos , also spelled Dura-Europus, was a Hellenistic, Parthian and Roman border city built on an escarpment 90 m above the right bank of the Euphrates river. It is located near the village of Salhiyé, in today's Syria....
house church on the borders of Syria dates from around 265 holds many images from the persecution period. The surviving fresco
Fresco
Fresco is any of several related mural painting types, executed on plaster on walls or ceilings. The word fresco comes from the Greek word affresca which derives from the Latin word for "fresh". Frescoes first developed in the ancient world and continued to be popular through the Renaissance...
es of the baptistry room are among the most ancient Christian paintings. We can see the "Good Shepherd", the "Healing of the paralytic" and "Christ and Peter walking on the water". A much larger fresco depicts the two Marys visiting Christ's tomb.

Edict of Milan
The Edict of Milan was a letter signed by emperors Constantine I and Licinius that proclaimed religious toleration in the Roman Empire...
allowed public Christian worship and led to the development of a monumental Christian art. Christians were able to build edifices for worship larger and more handsome than the furtive meeting places they had been using. Existing architectural formulas for temples were unsuitable because pagan sacrifices occurred outdoors in the sight of the gods, with the temple, housing the cult figures and the treasury, as a backdrop. As an architectural model for large churches, Christians chose the basilica
Basilica
The Latin word basilica , was originally used to describe a Roman public building, usually located in the forum of a Roman town. Public basilicas began to appear in Hellenistic cities in the 2nd century BC.The term was also applied to buildings used for religious purposes...
, the Roman public building used for justice and administration. These basilica had a center nave
Nave
In Romanesque and Gothic Christian abbey, cathedral basilica and church architecture, the nave is the central approach to the high altar, the main body of the church. "Nave" was probably suggested by the keel shape of its vaulting...
with one or more aisle
Aisle
An aisle is, in general, a space for walking with rows of seats on both sides or with rows of seats on one side and a wall on the other...
s at each side and a rounded apse
Apse
In architecture, the apse is a semicircular recess covered with a hemispherical vault or semi-dome...
at one end: on this raised platform sat the bishop and priests. Richer materials could now be used for art, such as the mosaics that decorate Santa Maria Maggiore
Basilica di Santa Maria Maggiore
The Papal Basilica of Saint Mary Major , known also by other names, is the largest Roman Catholic Marian church in Rome, Italy.There are other churches in Rome dedicated to Mary, such as Santa Maria in Trastevere, Santa Maria in Aracoeli, Santa Maria sopra Minerva, but the greater size of the...
in Rome and the 5th century basilicas of Ravenna
Ravenna
Ravenna is the capital city of the Province of Ravenna in the Emilia-Romagna region of Italy and the second largest comune in Italy by land area, although, at , it is little more than half the size of the largest comune, Rome...
, where narrative sequences begin to develop.
Much Christian art borrowed from Imperial imagery, including Christ in Majesty
Christ in Majesty
Christ in Majesty, or Christ in Glory, in Latin Majestas Domini, is the Western Christian image of Christ seated on a throne as ruler of the world, always seen frontally in the centre of the composition, and often flanked by other sacred figures, whose membership changes over time and according to...
, and the use of the halo
Halo (religious iconography)
A halo is a ring of light that surrounds a person in art. They have been used in the iconography of many religions to indicate holy or sacred figures, and have at various periods also been used in images of rulers or heroes...
as a symbol of sanctity. Late Antique Christian art replaced classical Hellenistic
Hellenistic Greece
In the context of Ancient Greek art, architecture, and culture, Hellenistic Greece corresponds to the period between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the annexation of the classical Greek heartlands by Rome in 146 BC...
naturalism with a more abstract aesthetic. The primary purpose of this new style was to convey religious meaning rather than accurately render objects and people. Realistic perspective, proportions, light and colour were ignored in favor of geometric simplification, reverse perspective
Reverse perspective
Reverse perspective, also called inverse perspective, inverted perspective or Byzantine perspective, is a convention of perspective drawing where the further the objects are, the larger they are drawn. The lines diverge against the horizon, rather than converge as in linear perspective...
and standardized conventions to portray individuals and events. Icon
Icon
An icon is a religious work of art, most commonly a painting, from Eastern Christianity and in certain Eastern Catholic churches...
s of Christ, Mary and the saints, ivory carving
Ivory carving
Ivory carving is the carving of ivory, that is to say animal tooth or tusk, by using sharp cutting tools, either mechanically or manually. The ancient craft has now virtually ceased, as since CITES it is illegal under most circumstances throughout the world....
, and illuminated manuscript
Illuminated manuscript
An illuminated manuscript is a manuscript in which the text is supplemented by the addition of decoration, such as decorated initials, borders and miniature illustrations...
s became important media - even more important in terms of modern understanding, as nearly all of the few surviving works, other than buildings, from the period consist of these portable objects.
Byzantine and Orthodox art

The dedication of Constantinople
Constantinople
Constantinople was the capital of the Roman, Eastern Roman, Byzantine, Latin, and Ottoman Empires. Throughout most of the Middle Ages, Constantinople was Europe's largest and wealthiest city.-Names:...
as capital in 330 AD created a great new Christian artistic centre for the Eastern Roman Empire, which soon became a separate political unit. Major Constantinopolitan churches built under Constantine and his son, Constantius II
Constantius II
Constantius II , was Roman Emperor from 337 to 361. The second son of Constantine I and Fausta, he ascended to the throne with his brothers Constantine II and Constans upon their father's death....
, included the original foundations of Hagia Sophia
Hagia Sophia
Hagia Sophia is a former Orthodox patriarchal basilica, later a mosque, and now a museum in Istanbul, Turkey...
and the Church of the Holy Apostles
Church of the Holy Apostles
The Church of the Holy Apostles , also known as the Imperial Polyandreion, was a Christian church built in Constantinople, capital of the Eastern Roman Empire, in 550. It was second only to the Church of the Holy Wisdom among the great churches of the capital...
. As the Western Roman Empire
Western Roman Empire
The Western Roman Empire was the western half of the Roman Empire after its division by Diocletian in 285; the other half of the Roman Empire was the Eastern Roman Empire, commonly referred to today as the Byzantine Empire....
disintegrated and was taken over by "barbarian" peoples, the art of the Byzantine Empire reached levels of sophistication, power and artistry not previously seen in Christian art, and set the standards for those parts of the West still in touch with Constantinople.
This achievement was checked by the controversy over the use of graven images, and the proper interpretation of the Second Commandment, which led to the crisis of Iconoclasm or destruction of religious images, which racked the Empire between 726 and 843. The restoration of Orthodoxy resulted in a strict standardization of religious imagery within the Eastern Church. Byzantine art became increasingly conservative, as the form of images themselves, many accorded divine origin
Acheiropoieta
Acheiropoieta — also called Icons Made Without Hands — are a particular kind of icon which are alleged to have come into existence miraculously, not created by a human painter. Invariably these are images of Jesus or the Virgin Mary...
or thought to have been be painted by Saint Luke or other figures, was held to have a status not far off that of a scriptural text. They could be copied, but not improved upon. As a concession to Iconoclast sentiment, monumental religious sculpture was effectively banned. Neither of these attitudes were held in Western Europe, but Byzantine art nonetheless had great influence there until the High Middle Ages
High Middle Ages
The High Middle Ages was the period of European history around the 11th, 12th, and 13th centuries . The High Middle Ages were preceded by the Early Middle Ages and followed by the Late Middle Ages, which by convention end around 1500....
, and remained very popular long after that, with vast numbers of icons of the Cretan School
Cretan School
The term Cretan School describes an important school of icon painting, also known as Post-Byzantine art, which flourished while Crete was under Venetian rule during the late Middle Ages, reaching its climax after the Fall of Constantinople, becoming the central force in Greek painting during the...
exported to Europe as late as the Renaissance
Renaissance
The Renaissance was a cultural movement that spanned roughly the 14th to the 17th century, beginning in Italy in the Late Middle Ages and later spreading to the rest of Europe. The term is also used more loosely to refer to the historical era, but since the changes of the Renaissance were not...
. Where possible, Byzantine artists were borrowed for projects such as mosaics in Venice
Venice
Venice is a city in northern Italy which is renowned for the beauty of its setting, its architecture and its artworks. It is the capital of the Veneto region...
and Palermo
Palermo
Palermo is a city in Southern Italy, the capital of both the autonomous region of Sicily and the Province of Palermo. The city is noted for its history, culture, architecture and gastronomy, playing an important role throughout much of its existence; it is over 2,700 years old...
. The enigmatic frescoes at Castelseprio
Castelseprio
Castelseprio was the site of a Roman fort in antiquity, and a significant Lombard town in the early Middle Ages, before being destroyed and abandoned in 1287. It is today preserved as an archaeological park in the modern comune of Castelseprio, near the modern village of the same name...
may be an example of work by a Greek artist working in Italy.
The art of Eastern Catholicism has always been rather closer to the Orthodox art of Greece and Russia, and in countries near the Orthodox world, notably Poland
Poland
Poland , officially the Republic of Poland , is a country in Central Europe bordered by Germany to the west; the Czech Republic and Slovakia to the south; Ukraine, Belarus and Lithuania to the east; and the Baltic Sea and Kaliningrad Oblast, a Russian exclave, to the north...
, Catholic art has many Orthodox influences. The Black Madonna of Częstochowa
Black Madonna of Czestochowa
The Black Madonna of Częstochowa is a revered icon of the Virgin Mary housed at the Jasna Góra Monastery in Częstochowa, Poland.-The icon:The origins of the icon and the date of its composition are still hotly contested among scholars...
may well have been of Byzantine origin - it has been repainted and this is hard to tell. Other images that are certainly of Greek origin, like the Salus Populi Romani
Salus Populi Romani
Salus Populi Romani -Protectress translates literally as "salvation or health" -is a title given in the 19th century to the Byzantine icon of the Madonna and Child, reputed to date to the Early Christian era, in the Borghese or Pauline Chapel of the Santa Maria Maggiore Basilica in Rome.It has...
and Our Lady of Perpetual Help, both icons in Rome, have been subjects of specific veneration for centuries.
Although the influence has often been resisted, especially in Russia, Catholic art has also affected Orthodox depictions in many respects, especially in countries like Romania
Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central and Southeastern Europe, on the Lower Danube, within and outside the Carpathian arch, bordering on the Black Sea...
, and in the post-Byzantine Cretan School
Cretan School
The term Cretan School describes an important school of icon painting, also known as Post-Byzantine art, which flourished while Crete was under Venetian rule during the late Middle Ages, reaching its climax after the Fall of Constantinople, becoming the central force in Greek painting during the...
, which led Greek Orthodox art under Venetian rule in the 15th and 16th centuries. El Greco
El Greco
El Greco was a painter, sculptor and architect of the Spanish Renaissance. "El Greco" was a nickname, a reference to his ethnic Greek origin, and the artist normally signed his paintings with his full birth name in Greek letters, Δομήνικος Θεοτοκόπουλος .El Greco was born on Crete, which was at...
left Crete when relatively young, but Michael Damaskinos
Michael Damaskinos
Michael Damaskenos or Michail Damaskenos was a leading post-Byzantine Cretan painter. He is a major representative of the Cretan School of painting that flourished in the 16th and 17th centuries, whilst Crete was under Venetian rule...
returned after a brief period in Venice, and was able to switch between Italian and Greek styles. Even the traditionalist Theophanes the Cretan
Theophanes the Cretan
Theophanis Strelitzas , also known as Theophanes the Cretan or "of Crete" or "Theophanes Bathas", was a leading icon painter of the Cretan school in the first half of the sixteenth century, and in particular the most important figure in Greek wall-painting of the period.He was born in Heraklion...
, working mainly on Mount Athos
Mount Athos
Mount Athos is a mountain and peninsula in Macedonia, Greece. A World Heritage Site, it is home to 20 Eastern Orthodox monasteries and forms a self-governed monastic state within the sovereignty of the Hellenic Republic. Spiritually, Mount Athos comes under the direct jurisdiction of the...
, nevertheless shows unmistakable Western influence.
Catholic doctrine on sacred images
The Catholic theological position on sacred images has remained effectively identical to that set out in the Libri CaroliniLibri Carolini
The Libri Carolini , Opus Caroli regis contra synodum , also called Charlemagne's Books or simply the Carolines, are the work in four books composed on the command of Charlemagne, around 790, to refute the supposed conclusions of the Byzantine Second Council of Nicaea , particularly as...
, although this, the fullest medieval expression of Western views on images, was in fact unknown during the Middle Ages. It was prepared for in about 790 for Charlemagne
Charlemagne
Charlemagne was King of the Franks from 768 and Emperor of the Romans from 800 to his death in 814. He expanded the Frankish kingdom into an empire that incorporated much of Western and Central Europe. During his reign, he conquered Italy and was crowned by Pope Leo III on 25 December 800...
after a bad translation had led his court to believe that the Byzantine Second Council of Nicaea
Second Council of Nicaea
The Second Council of Nicaea is regarded as the Seventh Ecumenical Council by Roman Catholics, Eastern Orthodox, Eastern Catholic Churches and various other Western Christian groups...
had approved the worship of images, which in fact was not the case. The Catholic counterblast set out a middle course between the extreme positions of Byzantine iconoclasm and the iconodules, approving the veneration of images for what they represented, but not accepting what became the Orthodox position, that images partook in some degree of the nature of the thing they represented (a belief later to resurface in the West in Renaissance Neo-Platonism).
To the Western church images were just objects made by craftsmen, to be utilized for stimulating the senses of the faithful, and to be respected for the sake of the subject represented, not in themselves. Although in popular devotional practice a tendency to go beyond these limits has often been present, the church was, before the advent of the idea of collecting old art, usually brutal in disposing of images no longer needed, much to the regret of art historians. Most monumental sculpture
Monumental sculpture
The term monumental sculpture is often used in art history and criticism, but not always consistently. It combines two concepts, one of function, and one of size, and may include an element of a third more subjective concept. It is often used for all sculptures that are large...
of the first millennium that has survived was broken up and reused as rubble in the re-building of churches.
In practical matters relating to the use of images, as opposed to their theoretical place in theology, the Libri Carolini were at the anti-iconic end of the spectrum of Catholic views, being for example rather disapproving of the lighting of candles before images. Such views were often expressed by individual church leaders, such as the famous example of Saint Bernard of Clairvaux
Bernard of Clairvaux
Bernard of Clairvaux, O.Cist was a French abbot and the primary builder of the reforming Cistercian order.After the death of his mother, Bernard sought admission into the Cistercian order. Three years later, he was sent to found a new abbey at an isolated clearing in a glen known as the Val...
, although many others leant the other way, and encouraged and commissioned art for their churches. Bernard was in fact only opposed to decorative imagery in monasteries that was not specifically religious, and popular preachers like Saint Bernardino of Siena
Bernardino of Siena
Saint Bernardino of Siena, O.F.M., was an Italian priest, Franciscan missionary, and is a Catholic saint.-Early life:...
and Savonarola regularly targeted secular images owned by the laiety.
Early Middle Ages

While the Western Roman Empire's political structure collapsed after the fall of Rome, the Church continued to fund art where it could. The most numerous surviving works of the early period are illuminated manuscripts, at this date all presumably created by the clergy, often including abbots and other senior figures. The monastic hybrid between "barbarian" decorative styles and the book in the Insular art
Insular art
Insular art, also known as Hiberno-Saxon art, is the style of art produced in the post-Roman history of Ireland and Great Britain. The term derives from insula, the Latin term for "island"; in this period Britain and Ireland shared a largely common style different from that of the rest of Europe...
of the British Isles
British Isles
The British Isles are a group of islands off the northwest coast of continental Europe that include the islands of Great Britain and Ireland and over six thousand smaller isles. There are two sovereign states located on the islands: the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland and...
from the 7th century was to be enormously influential in European art for the rest of the Middle Ages
Middle Ages
The Middle Ages is a periodization of European history from the 5th century to the 15th century. The Middle Ages follows the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 and precedes the Early Modern Era. It is the middle period of a three-period division of Western history: Classic, Medieval and Modern...
, providing an alternative path to classicism, transmitted to the continent by the Hiberno-Scottish mission
Hiberno-Scottish mission
The Hiberno-Scottish mission was a mission led by Irish and Scottish monks which spread Christianity and established monasteries in Great Britain and continental Europe during the Middle Ages...
. At this period the Gospel book
Gospel Book
The Gospel Book, Evangelion, or Book of the Gospels is a codex or bound volume containing one or more of the four Gospels of the Christian New Testament...
, with figurative art confined mostly to Evangelist portrait
Evangelist portrait
Evangelist portraits are a specific type of miniature included in ancient and mediæval illuminated manuscript Gospel Books, and later in Bibles and other books, as well as other media. Each Gospel of the Four Evangelists, the books of Matthew, Mark, Luke, and John, may be prefaced by a portrait of...
s, was usually the type of book most lavishly decorated; the Book of Kells
Book of Kells
The Book of Kells is an illuminated manuscript Gospel book in Latin, containing the four Gospels of the New Testament together with various prefatory texts and tables. It was created by Celtic monks ca. 800 or slightly earlier...
is the most famous example.
The 9th century Emperor Charlemagne
Charlemagne
Charlemagne was King of the Franks from 768 and Emperor of the Romans from 800 to his death in 814. He expanded the Frankish kingdom into an empire that incorporated much of Western and Central Europe. During his reign, he conquered Italy and was crowned by Pope Leo III on 25 December 800...
set out to create works of art appropriate to the status of his revived Empire. Carolingian
Carolingian art
Carolingian art comes from the Frankish Empire in the period of roughly 120 years from about AD 780 to 900 — during the reign of Charlemagne and his immediate heirs — popularly known as the Carolingian Renaissance. The art was produced by and for the court circle and a group of...
and Ottonian art
Ottonian art
In pre-romanesque Germany, the prevailing style was what has come to be known as Ottonian art. With Ottonian architecture, it is a key component of the Ottonian Renaissance named for the emperors Otto I, Otto II, and Otto III...
was largely confined to the circle of the Imperial court and different monastic centres, each of which had its own distinct artistic style. Carolingian artists consciously tried to emulate such examples of Byzantine and Late Antique art as were available to them, copying manuscripts like the Chronography of 354
Chronography of 354
The Chronography of 354, also known as the Calendar of 354, was a 4th century illuminated manuscript, which was produced in 354 AD for a wealthy Roman Christian named Valentinus. It is the earliest dated codex to have full page illustrations. None of the original has survived...
and producing works like the Utrecht Psalter
Utrecht Psalter
The Utrecht Psalter is a ninth century illuminated psalter which is a key masterpiece of Carolingian art; it is probably the most valuable manuscript in the Netherlands. It is famous for its 166 lively pen illustrations, with one accompanying each psalm and the other texts in the manuscript...
, which still divides art historians as to whether it is a copy of a much earlier manuscript, or an original Carolingian creation. This in turn was copied three times in England, lastly in an Early Gothic style.
Ivory carvings, often for book covers, drew on the diptych
Diptych
A diptych di "two" + ptychē "fold") is any object with two flat plates attached at a hinge. Devices of this form were quite popular in the ancient world, wax tablets being coated with wax on inner faces, for recording notes and for measuring time and direction.In Late Antiquity, ivory diptychs with...
s of Late Antiquity
Late Antiquity
Late Antiquity is a periodization used by historians to describe the time of transition from Classical Antiquity to the Middle Ages, in both mainland Europe and the Mediterranean world. Precise boundaries for the period are a matter of debate, but noted historian of the period Peter Brown proposed...
. For example the front and back covers of the Lorsch Gospels are of a 6th century Imperial triumph, adapted to the triumph of Christ and the Virgin. However they also drew on the Insular tradition, especially for decorative detail, whilst greatly improving on that in terms of the depiction of the human figure. Copies of the scriptures or liturgical books illustrated on vellum
Vellum
Vellum is mammal skin prepared for writing or printing on, to produce single pages, scrolls, codices or books. It is generally smooth and durable, although there are great variations depending on preparation, the quality of the skin and the type of animal used...
and adorned with precious metals were produced in abbeys and nunneries across Western Europe. A work like the Stockholm codex aureus might be written in gold leaf on purple vellum, in imitation of Roman and Byzantine Imperial manuscripts. Anglo-Saxon art
Anglo-Saxon art
Anglo-Saxon art covers art produced within the Anglo-Saxon period of English history, beginning with the Migration period style that the Anglo-Saxons brought with them from the continent in the 5th century, and ending in 1066 with the Norman Conquest of a large Anglo-Saxon nation-state whose...
was often freer, making more use of lively line drawings, and there were other distinct traditions, such as the group of extraordinary Mozarabic manuscripts from Spain, including the Saint-Sever Beatus
Saint-Sever Beatus
The Saint-Sever Beatus, also known as the Apocalypse of Saint-Sever , is a French Romanesque illuminated Apocalypse manuscript from the 11th century. It was made at the Abbey of Saint-Sever. It contains the Commentary on the Apocalypse of Beatus of Liébana...
, and those in Girona and the Morgan Library
Morgan Beatus
The Morgan Beatus is an illuminated manuscript with miniatures by the artist Magius of the Commentary on the Book of the Apocalypse by the eighth-century Spanish monk Beatus, which described the end of days and the Last Judgment...
.
We know Charlemagne had a life-size crucifix with the figure of Christ in precious metal in his Palatine Chapel in Aachen
Palatine Chapel in Aachen
The Palatine Chapel is an Early Medieval chapel that is the remaining component of Charlemagne's Palace of Aachen. Although the palace no longer exists, the chapel has been incorporated into the Aachen Cathedral, Germany. It is the city's major landmark and the central monument of the Carolingian...
, and many such objects, all now vanished, are recorded in large Anglo-Saxon churches and elsewhere. The Golden Madonna of Essen
Golden Madonna of Essen
The Golden Madonna of Essen is a sculpture with a wooden core covered all over with sheets of thin gold leaf of the Virgin Mary and the infant Jesus...
and a few smaller reliquary figures are now all that remain of this spectacular tradition, completely outside Byzantine norms. Like the Essen figure, these were presumably all made of thin sheets of gold or silver supported by a wooden core.
Romanesque

Romanesque art, long preceded by the Pre-Romanesque, developed in Western Europe from approximately 1000 AD until the rise of the Gothic style. Church-building was characterized by an increase in height and overall size. Vaulted roofs were supported by thick stone walls, massive pillars and rounded arches. The dark interiors were illumined by frescoes of Jesus, Mary and the saints, often based on Byzantine models.
Carvings in stone adorned the exteriors and interiors, particularly the tympanum
Tympanum (architecture)
In architecture, a tympanum is the semi-circular or triangular decorative wall surface over an entrance, bounded by a lintel and arch. It often contains sculpture or other imagery or ornaments. Most architectural styles include this element....
above the main entrance, which often featured a Christ in Majesty or in Judgement, and the large wooden crucifix
Crucifix
A crucifix is an independent image of Jesus on the cross with a representation of Jesus' body, referred to in English as the corpus , as distinct from a cross with no body....
was a German innovation right at the start of the period. The capitals of columns were also often elaborately carved with figurative scenes. The ensemble of large and well-preserved churches at Cologne
Cologne
Cologne is Germany's fourth-largest city , and is the largest city both in the Germany Federal State of North Rhine-Westphalia and within the Rhine-Ruhr Metropolitan Area, one of the major European metropolitan areas with more than ten million inhabitants.Cologne is located on both sides of the...
, then the largest city north of the Alps, and Segovia
Segovia
Segovia is a city in Spain, the capital of Segovia Province in the autonomous community of Castile and León. It is situated north of Madrid, 30 minutes by high speed train. The municipality counts some 55,500 inhabitants.-Etymology:...
in Spain, are among the best places today to appreciate the impact of the new larger churches on a city landscape, but many individual buildings exist, from Durham
Durham Cathedral
The Cathedral Church of Christ, Blessed Mary the Virgin and St Cuthbert of Durham is a cathedral in the city of Durham, England, the seat of the Anglican Bishop of Durham. The Bishopric dates from 995, with the present cathedral being founded in AD 1093...
, Ely
Ely Cathedral
Ely Cathedral is the principal church of the Diocese of Ely, in Cambridgeshire, England, and is the seat of the Bishop of Ely and a suffragan bishop, the Bishop of Huntingdon...
and Tournai Cathedral
Tournai Cathedral
The Cathedral of Our Lady is Roman Catholic church, see of the Diocese of Tournai in Tournai, Belgium. It has been classified both as a Wallonia's major heritage since 1936 and as a World Heritage Site since 2000.-History:...
s to large numbers of individual churches, especially in Southern France and Italy. In more prosperous areas, many Romanesque churches survive covered up by a Baroque makeover, much easier to do with these than a Gothic church.
Few of the large wall-paintings that originally covered most churches have survived in good condition. The Last Judgement was normally shown on the western wall, with a Christ in Majesty
Christ in Majesty
Christ in Majesty, or Christ in Glory, in Latin Majestas Domini, is the Western Christian image of Christ seated on a throne as ruler of the world, always seen frontally in the centre of the composition, and often flanked by other sacred figures, whose membership changes over time and according to...
in the apse semi-dome. Extensive narrative cycles of the Life of Christ were developed, and the Bible, with the Psalter
Psalter
A psalter is a volume containing the Book of Psalms, often with other devotional material bound in as well, such as a liturgical calendar and litany of the Saints. Until the later medieval emergence of the book of hours, psalters were the books most widely owned by wealthy lay persons and were...
, became the typical focus of illumination, with much use of historiated initial
Historiated initial
A historiated initial is an enlarged letter at the beginning of a paragraph or other section of text, which contains a picture. Strictly speaking, an inhabited initial contains figures that are decorative only, without forming a subject, whereas in a historiated initial there is an identifiable...
s. Metalwork, including decoration in enamel
Vitreous enamel
Vitreous enamel, also porcelain enamel in U.S. English, is a material made by fusing powdered glass to a substrate by firing, usually between 750 and 850 °C...
, became very sophisticated, and many spectacular shrines made to hold relics have survived, of which the best known is the Shrine of the Three Kings at Cologne Cathedral
Shrine of the Three Kings at Cologne Cathedral
The Shrine of the Three Kings is a reliquary said to contain the bones of the Biblical Magi, also known as the Three Kings or the Three Wise Men. The shrine is a large gilded and decorated triple sarcophagus placed above and behind the high altar of Cologne Cathedral...
by Nicholas of Verdun
Nicholas of Verdun
Nicholas of Verdun was a French artist, one of the most famous goldsmiths and enamellists of the Middle Ages, a major figure in Romanesque art, and the leading figure of Mosan art in his day...
and others (ca 1180-1225).
Gothic Art

Abbot Suger
Suger was one of the last Frankish abbot-statesmen, an historian, and the influential first patron of Gothic architecture....
was the first major building in the Gothic style. New monastic orders, especially the Cistercians and the Carthusian
Carthusian
The Carthusian Order, also called the Order of St. Bruno, is a Roman Catholic religious order of enclosed monastics. The order was founded by Saint Bruno of Cologne in 1084 and includes both monks and nuns...
s, were important builders who developed distinctive styles which they disseminated across Europe. The Franciscan
Franciscan
Most Franciscans are members of Roman Catholic religious orders founded by Saint Francis of Assisi. Besides Roman Catholic communities, there are also Old Catholic, Anglican, Lutheran, ecumenical and Non-denominational Franciscan communities....
friar
Friar
A friar is a member of one of the mendicant orders.-Friars and monks:...
s built functional city churches with huge open naves for preaching to large congregations. However regional variations
Cathedral architecture of Western Europe
The architecture of cathedrals, basilicas and abbey churches is the architecture of those church buildings which are usually of large size, including most cathedrals, and follow one of several branching traditions of form, function and style that stem initially from Early Christian traditions of...
remained important, even when, by the late 14th century, a coherent universal style known as International Gothic
International Gothic
International Gothic is a phase of Gothic art which developed in Burgundy, Bohemia, France and northern Italy in the late 14th century and early 15th century...
had evolved, which continued until the late 15th century, and beyond in many areas. The principal media of Gothic art were sculpture, panel painting
Panel painting
A panel painting is a painting made on a flat panel made of wood, either a single piece, or a number of pieces joined together. Until canvas became the more popular support medium in the 16th century, it was the normal form of support for a painting not on a wall or vellum, which was used for...
, stained glass
Stained glass
The term stained glass can refer to coloured glass as a material or to works produced from it. Throughout its thousand-year history, the term has been applied almost exclusively to the windows of churches and other significant buildings...
, fresco
Fresco
Fresco is any of several related mural painting types, executed on plaster on walls or ceilings. The word fresco comes from the Greek word affresca which derives from the Latin word for "fresh". Frescoes first developed in the ancient world and continued to be popular through the Renaissance...
and the illuminated manuscript
Illuminated manuscript
An illuminated manuscript is a manuscript in which the text is supplemented by the addition of decoration, such as decorated initials, borders and miniature illustrations...
, though religious imagery was also expressed in metalwork, tapestries and embroidered vestments. The architectural innovations of the pointed arch and the flying buttress
Flying buttress
A flying buttress is a specific form of buttressing most strongly associated with Gothic church architecture. The purpose of any buttress is to resist the lateral forces pushing a wall outwards by redirecting them to the ground...
, allowed taller, lighter churches with large areas of glazed window. Gothic art made full use of this new environment, telling a narrative story
Biblia pauperum
The Biblia pauperum was a tradition of picture Bibles beginning in the later Middle Ages. They sought to portray the historical books of the Bible visually. Unlike a simple "illustrated Bible", where the pictures are subordinated to the text, these Bibles placed the illustration in the centre,...
through pictures, sculpture, stained glass and soaring architecture. Chartres cathedral is a prime example of this.
Gothic art was often typological
Typology (theology)
Typology in Christian theology and Biblical exegesis is a doctrine or theory concerning the relationship between the Old and New Testaments...
in nature, reflecting a belief that the events of the Old Testament pre-figured those of the New, and that that was indeed their main significance. Old and New Testament scenes were shown side by side in works like the Speculum Humanae Salvationis
Speculum Humanae Salvationis
The Speculum Humanae Salvationis or Mirror of Human Salvation was a bestselling anonymous illustrated work of popular theology in the late Middle Ages, part of the genre of encyclopedic speculum literature, in this case concentrating on the medieval theory of typology, whereby the events of the Old...
, and the decoration of churches. The Gothic period coincided with a great resurgence in Marian devotion, in which the visual arts played a major part. Images of the Virgin Mary developed from the Byzantine hieratic types, through the Coronation of the Virgin
Coronation of the Virgin
The Coronation of the Virgin or Coronation of Mary is a subject in Christian art, especially popular in Italy in the 13th to 15th centuries, but continuing in popularity until the 18th century and beyond. Christ, sometimes accompanied by God the Father and the Holy Spirit in the form of a dove,...
, to more human and initimate types, and cycles of the Life of the Virgin
Life of the Virgin
The Life of the Virgin, showing narrative scenes from the life of Mary, the mother of Jesus, is a common subject for pictorial cycles in Christian art, often complementing, or forming part of, a cycle on the Life of Christ. In both cases the number of scenes shown varies greatly with the space...
were very popular. Artists like Giotto, Fra Angelico
Fra Angelico
Fra Angelico , born Guido di Pietro, was an Early Italian Renaissance painter described by Vasari in his Lives of the Artists as having "a rare and perfect talent"...
and Pietro Lorenzetti
Pietro Lorenzetti
Pietro Lorenzetti was an Italian painter, active between approximately 1306 and 1345. His younger brother was the painter Ambrogio Lorenzetti....
in Italy, and Early Netherlandish painting
Early Netherlandish painting
Early Netherlandish painting refers to the work of artists active in the Low Countries during the 15th- and early 16th-century Northern renaissance, especially in the flourishing Burgundian cities of Bruges and Ghent...
, brought realism and a more natural humanity to art. Western artists, and their patrons, became much more confident in innovative iconography
Iconography
Iconography is the branch of art history which studies the identification, description, and the interpretation of the content of images. The word iconography literally means "image writing", and comes from the Greek "image" and "to write". A secondary meaning is the painting of icons in the...
, and much more originality is seen, although copied formulae were still used by most artists. The book of hours
Book of Hours
The book of hours was a devotional book popular in the later Middle Ages. It is the most common type of surviving medieval illuminated manuscript. Like every manuscript, each manuscript book of hours is unique in one way or another, but most contain a similar collection of texts, prayers and...
was developed, mainly for the lay user able to afford them - the earliest known example
William de Brailes
William de Brailes was an English Early Gothic manuscript illuminator, presumably born in Brailes, Warwickshire. He signed two manuscripts, and apparently worked in Oxford, where he is documented from 1238 to 1252, owning property in Catte Street near the University Church of St Mary the Virgin,...
seems to have written for an unknown laywoman living in a small village
North Hinksey
North Hinksey , is a small civil parish in county Berkshire, 2 miles west of Oxford, and 5 miles north of of Abingdon,situated on the right bank of the Isis...
near Oxford
Oxford
The city of Oxford is the county town of Oxfordshire, England. The city, made prominent by its medieval university, has a population of just under 165,000, with 153,900 living within the district boundary. It lies about 50 miles north-west of London. The rivers Cherwell and Thames run through...
in about 1240 - and now royal and aristocratic examples became the type of manuscript most often lavishly decorated. Most religious art, including illuminated manuscripts, was now produced by lay artists, but the commissioning patron often specified in detail what the work was to contain.
Iconography was affected by changes in theology, with depictions of the Assumption of Mary
Assumption of Mary
According to the belief of Christians of the Roman Catholic Church, Eastern Orthodoxy, Oriental Orthodoxy, and parts of the Anglican Communion and Continuing Anglicanism, the Assumption of Mary was the bodily taking up of the Virgin Mary into Heaven at the end of her life...
gaining ground on the older Death of the Virgin
Death of the Virgin
The Death of the Virgin Mary is a common theme in Western Christian art, comparable to the Dormition in Eastern Orthodox art. It becomes less common as the doctrine of the Assumption gains support in the Roman Catholic Church from the late Middle Ages onwards...
, and in devotional practices such as the Devotio Moderna
Devotio Moderna
Devotio Moderna, or Modern Devotion, was a 14th century new religious movement, with Gerard Groote as a key founder. Other well known members included Thomas à Kempis who was the likely author of the book The Imitation of Christ which proved to be highly influential for centuries.Groote's initial...
, which produced new treatments of Christ in andachtsbilder
Andachtsbilder
Andachtsbilder is a German term often used in English in art history for Christian devotional images designed as aids for prayer or contemplation...
subjects such as the Man of Sorrows
Man of Sorrows
Among the passages in the Hebrew Bible that have been identified by Christians as prefigurations of the Messiah, the Man of Sorrows of Isaiah 53 is paramount - the various theological traditions are discussed at that article...
, Pensive Christ
Pensive Christ
The Pensive Christ or Christus im Elend is a subject in Christian iconography depicting a contemplating Jesus, sitting with his head supported by his hand with the Crown of Thorns and marks of his flagellation...
and Pietà
Pietà
The Pietà is a subject in Christian art depicting the Virgin Mary cradling the dead body of Jesus, most often found in sculpture. As such, it is a particular form of the Lamentation of Christ, a scene from the Passion of Christ found in cycles of the Life of Christ...
, which emphasized his human suffering and vulnerability, in a parallel movement to that in depictions of the Virgin. Many such images were now small oil painting
Oil painting
Oil painting is the process of painting with pigments that are bound with a medium of drying oil—especially in early modern Europe, linseed oil. Often an oil such as linseed was boiled with a resin such as pine resin or even frankincense; these were called 'varnishes' and were prized for their body...
s intended for private meditation and devotion in the homes of the wealthy. Even in Last Judgements Christ was now usually shown exposing his chest to show the wounds of his Passion. Saints were shown more frequently, and altarpiece
Altarpiece
An altarpiece is a picture or relief representing a religious subject and suspended in a frame behind the altar of a church. The altarpiece is often made up of two or more separate panels created using a technique known as panel painting. It is then called a diptych, triptych or polyptych for two,...
s showed saints relevant to the particular church or donor in attendance on a Crucifixion
Crucifixion
Crucifixion is an ancient method of painful execution in which the condemned person is tied or nailed to a large wooden cross and left to hang until dead...
or enthroned Virgin and Child, or occupying the central space themselves (this usually for works designed for side-chapels). Over the period many ancient iconographical features that originated in New Testament apocrypha
New Testament apocrypha
The New Testament apocrypha are a number of writings by early Christians that claim to be accounts of Jesus and his teachings, the nature of God, or the teachings of his apostles and of their lives. These writings often have links with books regarded as "canonical"...
were gradually eliminated under clerical pressure, like the midwives at the Nativity, though others were too well-established, and considered harmless.
In Early Netherlandish painting, from the richest cities of Northern Europe, a new minute realism in oil painting
Oil painting
Oil painting is the process of painting with pigments that are bound with a medium of drying oil—especially in early modern Europe, linseed oil. Often an oil such as linseed was boiled with a resin such as pine resin or even frankincense; these were called 'varnishes' and were prized for their body...
was combined with subtle and complex theological allusions, expressed precisely through the highly detailed settings of religious scenes. The Mérode Altarpiece (1420s) of Robert Campin
Robert Campin
Robert Campin , now usually identified as the artist known as the Master of Flémalle, is usually considered the first great master of Early Netherlandish painting...
, and the Washington Van Eyck Annunciation
Annunciation (van Eyck, Washington)
The Annunciation is an oil painting by the Early Netherlandish master Jan van Eyck, from around 1434-1436. It is in the National Gallery of Art, in Washington D.C. It was originally on panel but has been transferred to canvas. It is thought that it was the left wing of a triptych; there has...
or Madonna of Chancellor Rolin
Madonna of Chancellor Rolin
The Madonna of Chancellor Rolin is an oil painting by the Early Netherlandish master Jan van Eyck, dating from around 1435. It is on display in the Musée du Louvre, Paris....
(both 1430s, by Jan van Eyck
Jan van Eyck
Jan van Eyck was a Flemish painter active in Bruges and considered one of the best Northern European painters of the 15th century....
) are examples.
In the 15th century, the introduction of cheap prints
Old master print
An old master print is a work of art produced by a printing process within the Western tradition . A date of about 1830 is usually taken as marking the end of the period whose prints are covered by this term. The main techniques concerned are woodcut, engraving and etching, although there are...
, mostly in woodcut
Woodcut
Woodcut—occasionally known as xylography—is a relief printing artistic technique in printmaking in which an image is carved into the surface of a block of wood, with the printing parts remaining level with the surface while the non-printing parts are removed, typically with gouges...
, made it possible even for peasants to have devotional images at home. These images, tiny at the bottom of the market, often crudely coloured, were sold in thousands but are now extremely rare, most having been pasted to walls. Souvenirs of pilgrimages to shrines, such as clay or lead badges, medals and ampullae stamped with images were also popular and cheap. From the mid-century blockbooks, with both text and images cut as woodcut, seem to have been affordable by parish priests
Priest
A priest is a person authorized to perform the sacred rites of a religion, especially as a mediatory agent between humans and deities. They also have the authority or power to administer religious rites; in particular, rites of sacrifice to, and propitiation of, a deity or deities...
in the Low Countries
Low Countries
The Low Countries are the historical lands around the low-lying delta of the Rhine, Scheldt, and Meuse rivers, including the modern countries of Belgium, the Netherlands, Luxembourg and parts of northern France and western Germany....
, where they were most popular. By the end of the century, printed books with illustrations, still mostly on religious subjects, were rapidly becoming accessible to the prosperous middle class, as were engraving
Engraving
Engraving is the practice of incising a design on to a hard, usually flat surface, by cutting grooves into it. The result may be a decorated object in itself, as when silver, gold, steel, or glass are engraved, or may provide an intaglio printing plate, of copper or another metal, for printing...
s of fairly high-quality by printmakers like Israhel van Meckenem
Israhel van Meckenem
Israhel van Meckenem , also known as Israhel van Meckenem the Younger, was a German printmaker and goldsmith.He was the most prolific engraver of the fifteenth century and an important figure in the early history of old master prints. He was active from 1465 until his death.-Life:His birth date is...
and Master E. S.
Master E. S.
Master E. S. , is an unidentified German engraver, goldsmith, and printmaker of the late Gothic period. He was the first major German artist of old master prints and was greatly copied and imitated. The name assigned to him by art historians, Master E. S., is derived from the monogram, E...
.
For the wealthy, small panel painting
Panel painting
A panel painting is a painting made on a flat panel made of wood, either a single piece, or a number of pieces joined together. Until canvas became the more popular support medium in the 16th century, it was the normal form of support for a painting not on a wall or vellum, which was used for...
s, even polyptych
Polyptych
A polyptych generally refers to a painting which is divided into sections, or panels. The terminology that follows is in relevance to the number of panels integrated into a particular piece of work: "diptych" describes a two-part work of art; "triptych" describes a three-part work; "tetraptych"...
s in oil painting
Oil painting
Oil painting is the process of painting with pigments that are bound with a medium of drying oil—especially in early modern Europe, linseed oil. Often an oil such as linseed was boiled with a resin such as pine resin or even frankincense; these were called 'varnishes' and were prized for their body...
were becoming increasingly popular, often showing donor portrait
Donor portrait
A donor portrait or votive portrait is a portrait in a larger painting or other work showing the person who commissioned and paid for the image, or a member of his, or her, family...
s alongside, though often much smaller than, the Virgin or saints depicted. These were usually displayed in the home.
Renaissance art
Tornabuoni Chapel
The Tornabuoni Chapel is the main chapel in the church of Santa Maria Novella, Florence, Italy. It is famous for the extensive and well-preserved fresco cycle on its walls, one of the most complete in the city, which was created by Domenico Ghirlandaio and his workshop between 1485 and...
by Domenico Ghirlandaio
Domenico Ghirlandaio
Domenico Ghirlandaio was an Italian Renaissance painter from Florence. Among his many apprentices was Michelangelo.-Early years:Ghirlandaio's full name is given as Domenico di Tommaso di Currado di Doffo Bigordi...
(1485–90) seem more interested in the detailed depiction of scenes of bourgeois city life than their actual subjects, the Life of the Virgin and that of John the Baptist
John the Baptist
John the Baptist was an itinerant preacher and a major religious figure mentioned in the Canonical gospels. He is described in the Gospel of Luke as a relative of Jesus, who led a movement of baptism at the Jordan River...
, and the Magi Chapel
Magi Chapel
The Magi Chapel is a chapel in Palazzo Medici Riccardi of Florence, Italy. It includes a famous cycle of frescoes by the Renaissance master Benozzo Gozzoli, painted in 1459-1461....
of Benozzo Gozzoli
Benozzo Gozzoli
Benozzo Gozzoli was an Italian Renaissance painter from Florence. He is best known for a series of murals in the Palazzo Medici-Riccardi depicting festive, vibrant processions with wonderful attention to detail and a pronounced International Gothic influence.-Apprenticeship:He was born Benozzo di...
(1459–61) is more a celebration of Medici
Medici
The House of Medici or Famiglia de' Medici was a political dynasty, banking family and later royal house that first began to gather prominence under Cosimo de' Medici in the Republic of Florence during the late 14th century. The family originated in the Mugello region of the Tuscan countryside,...
status than an Arrival of the Magi. Both these examples (which still used contemporary clothes) come from Florence
Florence
Florence is the capital city of the Italian region of Tuscany and of the province of Florence. It is the most populous city in Tuscany, with approximately 370,000 inhabitants, expanding to over 1.5 million in the metropolitan area....
, the heart of the Early Renaissance, and the place where the charismatic Dominican
Dominican Order
The Order of Preachers , after the 15th century more commonly known as the Dominican Order or Dominicans, is a Catholic religious order founded by Saint Dominic and approved by Pope Honorius III on 22 December 1216 in France...
preacher Savonarola launched his attack on the worldliness of the life and art of the citizens, culminating in his famous Bonfire of the Vanities
Bonfire of the Vanities
Bonfire of the Vanities refers to the burning of objects that are deemed to be occasions of sin. The most infamous one took place on 7 February 1497, when supporters of the Dominican priest Girolamo Savonarola collected and publicly burned thousands of objects like cosmetics, art, and books in...
in 1497; in fact other preachers had been holding similar events for decades, but on a smaller scale. Many Early Renaissance artists, such as Fra Angelico
Fra Angelico
Fra Angelico , born Guido di Pietro, was an Early Italian Renaissance painter described by Vasari in his Lives of the Artists as having "a rare and perfect talent"...
and Botticelli were extremely devout, and the latter was one of many who fell under the influence of Savonarola.
The brief High Renaissance
High Renaissance
The expression High Renaissance, in art history, is a periodizing convention used to denote the apogee of the visual arts in the Italian Renaissance...
(c. 1490–1520) of Leonardo da Vinci
Leonardo da Vinci
Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci was an Italian Renaissance polymath: painter, sculptor, architect, musician, scientist, mathematician, engineer, inventor, anatomist, geologist, cartographer, botanist and writer whose genius, perhaps more than that of any other figure, epitomized the Renaissance...
, Michelangelo
Michelangelo
Michelangelo di Lodovico Buonarroti Simoni , commonly known as Michelangelo, was an Italian Renaissance painter, sculptor, architect, poet, and engineer who exerted an unparalleled influence on the development of Western art...
and Raphael
Raphael
Raffaello Sanzio da Urbino , better known simply as Raphael, was an Italian painter and architect of the High Renaissance. His work is admired for its clarity of form and ease of composition and for its visual achievement of the Neoplatonic ideal of human grandeur...
transformed Catholic art more fundamentally, breaking with the old iconography that was thoroughly integrated with theological conventions for original compositions that reflected both artistic imperatives, and the influence of Renaissance humanism
Renaissance humanism
Renaissance humanism was an activity of cultural and educational reform engaged by scholars, writers, and civic leaders who are today known as Renaissance humanists. It developed during the fourteenth and the beginning of the fifteenth centuries, and was a response to the challenge of Mediæval...
. Both Michelangelo and Raphael worked almost exclusively for the Papacy for much of their careers, including the year of 1517, when Martin Luther
Martin Luther
Martin Luther was a German priest, professor of theology and iconic figure of the Protestant Reformation. He strongly disputed the claim that freedom from God's punishment for sin could be purchased with money. He confronted indulgence salesman Johann Tetzel with his Ninety-Five Theses in 1517...
wrote his Ninety-Five Theses. The connection between the events was not just chronological, as the indulgence
Indulgence
In Catholic theology, an indulgence is the full or partial remission of temporal punishment due for sins which have already been forgiven. The indulgence is granted by the Catholic Church after the sinner has confessed and received absolution...
s that provoked Luther helped to finance the Papal artistic programme, as many historians have pointed out.
The Protestant Reformation
Protestant Reformation
The Protestant Reformation was a 16th-century split within Western Christianity initiated by Martin Luther, John Calvin and other early Protestants. The efforts of the self-described "reformers", who objected to the doctrines, rituals and ecclesiastical structure of the Roman Catholic Church, led...
was a holocaust of art in many parts of Europe. Although Lutheranism
Lutheranism
Lutheranism is a major branch of Western Christianity that identifies with the theology of Martin Luther, a German reformer. Luther's efforts to reform the theology and practice of the church launched the Protestant Reformation...
was prepared to live with much existing Catholic art so long as it did not become a focus of devotion, the more radical views of Calvin
John Calvin
John Calvin was an influential French theologian and pastor during the Protestant Reformation. He was a principal figure in the development of the system of Christian theology later called Calvinism. Originally trained as a humanist lawyer, he broke from the Roman Catholic Church around 1530...
, Zwingli and others saw public religious images of any sort as idolatry
Idolatry
Idolatry is a pejorative term for the worship of an idol, a physical object such as a cult image, as a god, or practices believed to verge on worship, such as giving undue honour and regard to created forms other than God. In all the Abrahamic religions idolatry is strongly forbidden, although...
, and art was systematically destroyed in areas where their followers held sway. This destructive process continued until the mid 17th century, as religious wars brought periods of iconoclast
Iconoclasm
Iconoclasm is the deliberate destruction of religious icons and other symbols or monuments, usually with religious or political motives. It is a frequent component of major political or religious changes...
Protestant control over much of the continent. In England and Scotland destruction of religious art, most intense during the English Commonwealth, was especially heavy. Some stone sculpture, illuminated manuscripts and stained glass windows (expensive to replace) survived, but of the thousands of high quality works of painted and wood-carved art produced in medieval Britain, virtually none remain.
In Rome, the sack of 1527
Sack of Rome (1527)
The Sack of Rome on 6 May 1527 was a military event carried out by the mutinous troops of Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor in Rome, then part of the Papal States...
by the Catholic Emperor
Holy Roman Emperor
The Holy Roman Emperor is a term used by historians to denote a medieval ruler who, as German King, had also received the title of "Emperor of the Romans" from the Pope...
Charles V
Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor
Charles V was ruler of the Holy Roman Empire from 1519 and, as Charles I, of the Spanish Empire from 1516 until his voluntary retirement and abdication in favor of his younger brother Ferdinand I and his son Philip II in 1556.As...
and his largely Protestant mercenary troops was enormously destructive both of art and artists, many of whose biographical records end abruptly. Other artists managed to escape to different parts of Italy, often finding difficulty in picking up the thread of their careers. Italian artists, with the odd exception like Girolamo da Treviso
Girolamo da Treviso
Girolamo da Treviso , also known as Girolamo di Tommaso da Treviso the Younger and Girolamo Trevigi, was an Italian Renaissance painter. Born in Treviso, he might have been a pupil of Pier Maria Pennacchi...
, seem to have had little attraction to Protestantism. In Germany, however, the leading figures such as Albrecht Dürer
Albrecht Dürer
Albrecht Dürer was a German painter, printmaker, engraver, mathematician, and theorist from Nuremberg. His prints established his reputation across Europe when he was still in his twenties, and he has been conventionally regarded as the greatest artist of the Northern Renaissance ever since...
and his pupils, Lucas Cranach the Elder
Lucas Cranach the Elder
Lucas Cranach the Elder , was a German Renaissance painter and printmaker in woodcut and engraving...
, Albrecht Altdorfer
Albrecht Altdorfer
Albrecht Altdorfer was a German painter, printmaker and architect of the Renaissance era.-Biography:Altdorfer was born in Regensburg or Altdorf around 1480....
and the Danube school
Danube school
The Danube School or Donau School is the name of a circle of painters of the first third of the 16th century in Bavaria and Austria . Many also were innovative printmakers, usually in etching...
, and Hans Holbein the Younger
Hans Holbein the Younger
Hans Holbein the Younger was a German artist and printmaker who worked in a Northern Renaissance style. He is best known as one of the greatest portraitists of the 16th century. He also produced religious art, satire and Reformation propaganda, and made a significant contribution to the history...
all followed the Reformers. The development of German religious painting had come to an abrupt halt by about 1540, although many prints
Printmaking
Printmaking is the process of making artworks by printing, normally on paper. Printmaking normally covers only the process of creating prints with an element of originality, rather than just being a photographic reproduction of a painting. Except in the case of monotyping, the process is capable...
and book illustrations, especially of Old Testament subjects, continued to be produced.
Council of Trent

Venice
Venice is a city in northern Italy which is renowned for the beauty of its setting, its architecture and its artworks. It is the capital of the Veneto region...
, developed into Mannerism
Mannerism
Mannerism is a period of European art that emerged from the later years of the Italian High Renaissance around 1520. It lasted until about 1580 in Italy, when a more Baroque style began to replace it, but Northern Mannerism continued into the early 17th century throughout much of Europe...
, a highly sophisticated style, striving for effect, that concerned many churchman as lacking appeal for the mass of the population. Church pressure to restrain religious imagery affected art from the 1530s and resulted in the decrees of the final session of the Council of Trent
Council of Trent
The Council of Trent was the 16th-century Ecumenical Council of the Roman Catholic Church. It is considered to be one of the Church's most important councils. It convened in Trent between December 13, 1545, and December 4, 1563 in twenty-five sessions for three periods...
in 1563 including short and rather inexplicit passages concerning religious images, which were to have great impact on the development of Catholic art. Previous Catholic Church councils had rarely felt the need to pronounce on these matters, unlike Orthodox ones which have often ruled on specific types of images.
The decree confirmed the traditional doctrine that images only represented the person depicted, and that veneration to them was paid to the person themselves, not the image, and further instructed that:
...every superstition shall be removed ... all lasciviousness be avoided; in such wise that figures shall not be painted or adorned with a beauty exciting to lust... there be nothing seen that is disorderly, or that is unbecomingly or confusedly arranged, nothing that is profane, nothing indecorous, seeing that holiness becometh the house of God.
And that these things may be the more faithfully observed, the holy Synod ordains, that no one be allowed to place, or cause to be placed, any unusual image, in any place, or church, howsoever exempted, except that image have been approved of by the bishop ...
Ten years after the decree Paolo Veronese
Paolo Veronese
Paolo Veronese was an Italian painter of the Renaissance in Venice, famous for paintings such as The Wedding at Cana and The Feast in the House of Levi...
was summoned by the Inquisition
Inquisition
The Inquisition, Inquisitio Haereticae Pravitatis , was the "fight against heretics" by several institutions within the justice-system of the Roman Catholic Church. It started in the 12th century, with the introduction of torture in the persecution of heresy...
to explain why his Last Supper, a huge canvas for the refectory
Refectory
A refectory is a dining room, especially in monasteries, boarding schools and academic institutions. One of the places the term is most often used today is in graduate seminaries...
of a monastery, contained, in the words of the Inquisition: "buffoons, drunken Germans, dwarfs and other such scurrilities" as well as extravagant costumes and settings, in what is indeed a fantasy version of a Venetian patrician feast. Veronese was told that he must change his painting within a three month period - in fact he just changed the title to The Feast in the House of Levi
The Feast in the House of Levi
The Feast in the House of Levi is a 1573 painting by Italian painter Paolo Veronese and one of the largest canvases of the 16th century measuring 555 x 1280 cm . It is now in the Gallerie dell'Accademia, in Venice. It was painted by Veronese for the Dominican order of SS...
, still an episode from the Gospels, but a less doctrinally central one, and no more was said. But the number of such decorative treatments of religious subjects declined sharply, as did "unbecomingly or confusedly arranged" Mannerist pieces, as a number of books, notably by the Flemish theologian Molanus
Molanus
Jan Vermeulen or Jan van der Meulen, also known as Molanus was an influential Counter Reformation Flemish Catholic theologian of Louvain University, where he was Professor of Theology, and Rector from 1578...
, Saint Charles Borromeo
Charles Borromeo
Charles Borromeo was the cardinal archbishop of the Catholic Archdiocese of Milan from 1564 to 1584. He was a leading figure during the Counter-Reformation and was responsible for significant reforms in the Catholic Church, including the founding of seminaries for the education of priests...
and Cardinal Gabriele Paleotti
Gabriele Paleotti
Gabriele Paleotti was an Italian Cardinal and Archbishop of Bologna.-Life:Paleotti was born at Bologna. Having acquired, in 1546, the title of Doctor of Civil and Canon Law, he was appointed to teach civil law. In 1549 he became a canon of the cathedral, but he did not become a priest until later...
, and instructions by local bishops, amplified the decrees, often going into minute detail on what was acceptable. One of the earliest of these, Degli Errori dei Pittori (1564), by the Dominican
Dominican Order
The Order of Preachers , after the 15th century more commonly known as the Dominican Order or Dominicans, is a Catholic religious order founded by Saint Dominic and approved by Pope Honorius III on 22 December 1216 in France...
theologian Andrea Gilio da Fabriano, joined the chorus of criticism of Michelangelo's Last Judgement and defended the devout and simple nature of much medieval imagery. But other writers were less sympathetic to medieval art and many traditional iconographies considered without adequate scriptural foundation were in effect prohibited, as was any inclusion of classical pagan elements in religious art, and almost all nudity, including that of the infant Jesus. According to the great medievalist Émile Mâle
Émile Mâle
Émile Mâle was a French art historian, one of the first to study medieval, mostly sacral French art and the influence of eastern European iconography thereon. He was a member of the Académie Française, and a director of the Académie de France à Rome....
, this was "the death of medieval art".
Baroque art

Accademia degli Incamminati
The Accademia degli Incamminati was one of the first art academies in Italy. It was originally created around 1580 in Bologna as the Accademia dei Desiderosi and was sometimes known as the Accademia dei Carracci after its founders the Carracci cousins , with Annibale heading the institution thanks...
and Caravaggio
Caravaggio
Michelangelo Merisi da Caravaggio was an Italian artist active in Rome, Naples, Malta, and Sicily between 1593 and 1610. His paintings, which combine a realistic observation of the human state, both physical and emotional, with a dramatic use of lighting, had a formative influence on the Baroque...
, who nonetheless met with clerical opposition over the realism of his sacred figures. Subjects were shown in a direct and dramatic fashion, with relatively few abstruse allusions. Choice of subjects was widened considerably, as Baroque artists delighted in finding new biblical episodes and dramatic moments from the lives of saints. As the movement continued into the 17th century simplicity and realism tended to reduce, more slowly in Spain and France, but the drama remained, produced by the depiction of extreme moments, dramatic movement, colour and chiaroscuro
Chiaroscuro
Chiaroscuro in art is "an Italian term which literally means 'light-dark'. In paintings the description refers to clear tonal contrasts which are often used to suggest the volume and modelling of the subjects depicted"....
lighting, and if necessary hosts of agitated cherubs
CHERUBS
CHERUBS is a Non-Profit Organization. It was founded in February, 1995 for families of children born with Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia, a severe and often lethal birth defect. It was founded and currently led by Dawn M...
and swirling clouds, all intended to overwhelm the worshipper. Architecture and sculpture aimed for the same effects; Bernini (1598–1680) epitomises the Baroque style in those arts. Baroque art spread across Catholic Europe and into the overseas missions of Asia and the Americas, promoted by the Jesuits and Franciscans.
New iconic subjects popularized in the Baroque period included the Sacred Heart
Sacred Heart
The Sacred Heart is one of the most famous religious devotions to Jesus' physical heart as the representation of His divine love for Humanity....
of Jesus, and the Immaculate Conception
Immaculate Conception
The Immaculate Conception of Mary is a dogma of the Roman Catholic Church, according to which the Virgin Mary was conceived without any stain of original sin. It is one of the four dogmata in Roman Catholic Mariology...
of Mary; the definitive iconography for the latter seems to have been established by the master and then father-in-law of Diego Velázquez
Diego Velázquez
Diego Rodríguez de Silva y Velázquez was a Spanish painter who was the leading artist in the court of King Philip IV. He was an individualistic artist of the contemporary Baroque period, important as a portrait artist...
, the painter and theorist Francisco Pacheco
Francisco Pacheco
Francisco Pacheco was a Spanish painter, best known as the teacher of Diego Velázquez and Alonso Cano, and for his textbook on painting that is an important source for the study of 17th-century practice in Spain...
, to whom the Inquisition in Seville
Seville
Seville is the artistic, historic, cultural, and financial capital of southern Spain. It is the capital of the autonomous community of Andalusia and of the province of Seville. It is situated on the plain of the River Guadalquivir, with an average elevation of above sea level...
also contracted the approval of new images. The Assumption of Mary
Assumption of Mary
According to the belief of Christians of the Roman Catholic Church, Eastern Orthodoxy, Oriental Orthodoxy, and parts of the Anglican Communion and Continuing Anglicanism, the Assumption of Mary was the bodily taking up of the Virgin Mary into Heaven at the end of her life...
became a very common subject, and (despite a Caravaggio of the subject) the Death of the Virgin
Death of the Virgin
The Death of the Virgin Mary is a common theme in Western Christian art, comparable to the Dormition in Eastern Orthodox art. It becomes less common as the doctrine of the Assumption gains support in the Roman Catholic Church from the late Middle Ages onwards...
became almost extinct in Catholic art; Molanus and others had written against it.
18th century

Rococo
Rococo , also referred to as "Late Baroque", is an 18th-century style which developed as Baroque artists gave up their symmetry and became increasingly ornate, florid, and playful...
style, which was difficult to adapt to religious themes, although Gianbattista Tiepolo was able to do so. In the later part of the century there was a reaction, especially in architecture, against the Baroque, and a turning back to more austere classical and Palladian forms.
By now the rate of production of religious art was noticeably slowing down. After a spate of building and re-building in the Baroque period, Catholic countries were mostly clearly overstocked with churches, monasteries and convents, in the case of some places such as Naples
Naples
Naples is a city in Southern Italy, situated on the country's west coast by the Gulf of Naples. Lying between two notable volcanic regions, Mount Vesuvius and the Phlegraean Fields, it is the capital of the region of Campania and of the province of Naples...
, almost absurdly so. The Church was now less important as a patron than royalty and the aristocracy, and the middle class demand for art, mostly secular, was increasing rapidly. Artists could now have a successful career painting portraits, landscapes, still lifes or other genre specialisms, without ever painting a religious subject - something unusual hitherto unusual in the Catholic countries, though long the norm in Protestant ones. The number of sales of paintings, metalwork and other church fittings to private collectors increased during the century, especially in Italy, where the Grand Tour
Grand Tour
The Grand Tour was the traditional trip of Europe undertaken by mainly upper-class European young men of means. The custom flourished from about 1660 until the advent of large-scale rail transit in the 1840s, and was associated with a standard itinerary. It served as an educational rite of passage...
gave rise to networks of dealers and agents. Leonardo da Vinci
Leonardo da Vinci
Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci was an Italian Renaissance polymath: painter, sculptor, architect, musician, scientist, mathematician, engineer, inventor, anatomist, geologist, cartographer, botanist and writer whose genius, perhaps more than that of any other figure, epitomized the Renaissance...
's London Virgin of the Rocks
Virgin of the Rocks
The Virgin of the Rocks is the name used for both of two paintings by Leonardo da Vinci, of the same subject, and of a composition which is identical except for two significant details...
was sold to the Scottish artist and dealer Gavin Hamilton
Gavin Hamilton (artist)
Gavin Hamilton was a Scottish neoclassical history painterwho is more widely remembered for his hunts for antiquities in the neighborhood of Rome...
by the church in Milan that it was painted for in about 1781; the version in the Louvre
Louvre
The Musée du Louvre – in English, the Louvre Museum or simply the Louvre – is one of the world's largest museums, the most visited art museum in the world and a historic monument. A central landmark of Paris, it is located on the Right Bank of the Seine in the 1st arrondissement...
having apparently been diverted from the same church three centuries earlier by Leonardo himself, to go to the King of France.
The wars following the French Revolution
French Revolution
The French Revolution , sometimes distinguished as the 'Great French Revolution' , was a period of radical social and political upheaval in France and Europe. The absolute monarchy that had ruled France for centuries collapsed in three years...
saw large quantities of the finest art, paintings in particular, carefully selected for appropriation by the French armies or the secular regimes they established. Many were sent to Paris for the Louvre
Louvre
The Musée du Louvre – in English, the Louvre Museum or simply the Louvre – is one of the world's largest museums, the most visited art museum in the world and a historic monument. A central landmark of Paris, it is located on the Right Bank of the Seine in the 1st arrondissement...
(some to eventually be returned, others not) or local museums established by the French, like the Brera
Brera
Brera is a district of Milan, ItalyBrera may also refer to:* the Palazzo Brera, a historical building in Brera; the palace also houses:** the Brera Art Academy** the Brera Art Gallery** the Brera Astronomical Observatory...
in Milan
Milan
Milan is the second-largest city in Italy and the capital city of the region of Lombardy and of the province of Milan. The city proper has a population of about 1.3 million, while its urban area, roughly coinciding with its administrative province and the bordering Province of Monza and Brianza ,...
. Suppression of monasteries, which had been under way for decades under Catholic Enlightened despots of the Ancien Regime, for example in the Edict on Idle Institutions
Edict on Idle Institutions
The Edict on Idle Institutions was one of over 10,000 ordinances issued by Joseph II, Holy Roman Emperor pertaining to religious issues. Promulgated in 1780, it outlawed contemplative monastic orders. The act permitted only monastic orders that dealt with teaching, nursing and other practical work...
(1780) of Joseph II of Austria, intensified considerably. By 1830 much of the best Catholic religious art was on public display in museums, as has been the case ever since. This undoubtedly widened access to many works, and promoted public awareness of the heritage of Catholic art, but at a cost, as objects came to regarded as of primarily artistic rather than religious significance, and were seen out of their original context and the setting they were designed for.
19th and 20th centuries
The 19th Century saw a widespread repudiation by both Catholic and Protestant churches of Classicism, which was associated with the French RevolutionFrench Revolution
The French Revolution , sometimes distinguished as the 'Great French Revolution' , was a period of radical social and political upheaval in France and Europe. The absolute monarchy that had ruled France for centuries collapsed in three years...
and Enlightenment
Age of Enlightenment
The Age of Enlightenment was an elite cultural movement of intellectuals in 18th century Europe that sought to mobilize the power of reason in order to reform society and advance knowledge. It promoted intellectual interchange and opposed intolerance and abuses in church and state...
secularism. This led to the Gothic Revival, a return to Gothic-influenced forms in architecture, sculpture and painting, led by people such as Augustus Pugin
Augustus Pugin
Augustus Welby Northmore Pugin was an English architect, designer, and theorist of design, now best remembered for his work in the Gothic Revival style, particularly churches and the Palace of Westminster. Pugin was the father of E. W...
in England and Eugène Viollet-le-Duc
Eugène Viollet-le-Duc
Eugène Emmanuel Viollet-le-Duc was a French architect and theorist, famous for his interpretive "restorations" of medieval buildings. Born in Paris, he was a major Gothic Revival architect.-Early years:...
in France. Across the world, thousands of Gothic churches and Cathedrals were produced in a new wave of church-building, and the collegiate Gothic style became the norm for other church institutions. Medieval Gothic churches, especially in England and France, were restored, often very heavy-handedly. In painting, similar attitudes led to the German Nazarene movement
Nazarene movement
The name Nazarene was adopted by a group of early 19th century German Romantic painters who aimed to revive honesty and spirituality in Christian art...
and the English Pre-Raphaelites. Both movements embraced both Catholic and Protestant members, but included some artists who converted to Catholicism.

Holy card
In the Catholic tradition, holy cards or prayer cards are small, devotional pictures mass-produced for the use of the faithful. They typically depict a religious scene or a saint in an image about the size of a playing card. The reverse typically contains a prayer, some of which promise an...
s. Much of this art continued to use watered-down versions of Baroque styles. The Immaculate Heart of Mary
Immaculate Heart of Mary
The Immaculate Heart of Mary originally The Sacred Heart of Mary is a devotional name used to refer to the interior life of Mary, her joys and sorrows, her virtues and hidden perfections, and, above all, her virginal love for God, her maternal love for her Son, Jesus, and her compassionate love for...
was a new subject of the 19th century, and new apparitions at Lourdes
Lourdes
Lourdes is a commune in the Hautes-Pyrénées department in the Midi-Pyrénées region in south-western France.Lourdes is a small market town lying in the foothills of the Pyrenees, famous for the Marian apparitions of Our Lady of Lourdes occurred in 1858 to Bernadette Soubirous...
and Fátima
Fátima, Portugal
Fátima is a city in Portugal famous for the Marian apparitions, recognized by the Catholic Church, that took place there in 1917. The town itself has a population of 7,756 and is located in the municipality of Ourém, in the Centro Region and Médio Tejo Subregion...
, as well as new saints, provided new subjects for art.
Architects began to revive other earlier Christian styles, and experiment with new ones, producing results such as Sacre Coeur in Paris, Sagrada Familia
Sagrada Familia
The ' , commonly known as the Sagrada Família, is a large Roman Catholic church in Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain, designed by Catalan architect Antoni Gaudí...
in Barcelona and the Byzantine influenced Westminster Cathedral
Westminster Cathedral
Westminster Cathedral in London is the mother church of the Catholic community in England and Wales and the Metropolitan Church and Cathedral of the Archbishop of Westminster...
in London. The 20th century led to the adoption of modernist styles of architecture and art. This movement rejected traditional forms in favour of utilitarian shapes with a bare minimum of decoration. Such art as there was eschewed naturalism and human qualities, favouring stylised and abstract forms. Examples of modernism include the Liverpool Metropolitan Cathedral
Liverpool Metropolitan Cathedral
The Metropolitan Cathedral Church of Christ the King is a Roman Catholic cathedral in Liverpool, Merseyside, England. The cathedral is the seat of the Archbishop of Liverpool and the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Liverpool. The Metropolitan Cathedral is one of two cathedrals in the city...
of Christ the King, and Los Angeles Cathedral.
Themes

Common themes of Catholic art:
:Category:Christian iconography
Life of Jesus:
- AnnunciationAnnunciationThe Annunciation, also referred to as the Annunciation to the Blessed Virgin Mary or Annunciation of the Lord, is the Christian celebration of the announcement by the angel Gabriel to Virgin Mary, that she would conceive and become the mother of Jesus the Son of God. Gabriel told Mary to name her...
- Nativity of Jesus in artNativity of Jesus in artThe Nativity of Jesus has been a major subject of Christian art since the 4th century. The artistic depictions of the Nativity or birth of Jesus, celebrated at Christmas, are based on the narratives in the Bible, in the Gospels of Matthew and Luke, and further elaborated by written, oral and...
- Adoration of the MagiAdoration of the Magi in ArtThe Adoration of the Magi is the name traditionally given to the Christian subject in the Nativity of Jesus in art in which the three Magi, represented as kings, especially in the West, having found Jesus by following a star, lay before him gifts of gold, frankincense, and myrrh, and worship him...
- Adoration of the shepherdsAdoration of the shepherdsThe Adoration of the shepherds, in the Nativity of Jesus in art, is a scene in which shepherds are near witnesses to the birth of Jesus in Bethlehem. It is often combined with the Adoration of the Magi, in which case it is typically just referred to by the latter title...
- Baptism of JesusBaptism of JesusThe baptism of Jesus marks the beginning of Jesus Christ's public ministry. This event is recorded in the Canonical Gospels of Matthew, Mark and Luke. In John 1:29-33 rather than a direct narrative, the Baptist bears witness to the episode...
- The Last Supper
- Arrest of JesusArrest of JesusThe arrest of Jesus is a pivotal event recorded in the Canonical gospels. The event ultimately leads, in the Gospel accounts, to Jesus' crucifixion...
- The Raising of the Cross
- The CrucifixionCrucifixA crucifix is an independent image of Jesus on the cross with a representation of Jesus' body, referred to in English as the corpus , as distinct from a cross with no body....
- Descent from the CrossDescent from the CrossThe Descent from the Cross , or Deposition of Christ, is the scene, as depicted in art, from the Gospels' accounts of Joseph of Arimathea and Nicodemus taking Christ down from the cross after his crucifixion . In Byzantine art the topic became popular in the 9th century, and in the West from the...
- Noli me tangereNoli me tangereNoli me tangere, meaning "don't touch me" / "touch me not", is the Latin version of words spoken, according to , by Jesus to Mary Magdalene when she recognizes him after his resurrection....
- Ascension of Jesus
- Christ in MajestyChrist in MajestyChrist in Majesty, or Christ in Glory, in Latin Majestas Domini, is the Western Christian image of Christ seated on a throne as ruler of the world, always seen frontally in the centre of the composition, and often flanked by other sacred figures, whose membership changes over time and according to...
Mary:
- Roman Catholic Marian artRoman Catholic Marian artThe Blessed Virgin Mary has been one of the major subjects of Christian Art, Catholic Art and Western Art for many centuries. Literally hundreds of thousands of pieces of...
- Life of the VirginLife of the VirginThe Life of the Virgin, showing narrative scenes from the life of Mary, the mother of Jesus, is a common subject for pictorial cycles in Christian art, often complementing, or forming part of, a cycle on the Life of Christ. In both cases the number of scenes shown varies greatly with the space...
- Christ taking leave of his MotherChrist taking leave of his MotherChrist taking leave of his Mother is a subject in Christian art, most commonly found in Northern art of the 15th and 16th centuries. Christ says farewell to his mother Mary, often blessing her, before leaving for his final journey to Jerusalem, which he knows will lead to his Passion and death;...
- Death of the VirginDeath of the VirginThe Death of the Virgin Mary is a common theme in Western Christian art, comparable to the Dormition in Eastern Orthodox art. It becomes less common as the doctrine of the Assumption gains support in the Roman Catholic Church from the late Middle Ages onwards...
- Assumption of the Virgin Mary in art
- Coronation of the VirginCoronation of the VirginThe Coronation of the Virgin or Coronation of Mary is a subject in Christian art, especially popular in Italy in the 13th to 15th centuries, but continuing in popularity until the 18th century and beyond. Christ, sometimes accompanied by God the Father and the Holy Spirit in the form of a dove,...
- The Holy familyHoly FamilyThe Holy Family consists of the Child Jesus, the Virgin Mary, and Saint Joseph.The Feast of the Holy Family is a liturgical celebration in the Roman Catholic Church in honor of Jesus of Nazareth, his mother, the Blessed Virgin Mary, and his foster father, Saint Joseph, as a family...
- Madonna (art)Madonna (art)Images of the Madonna and the Madonna and Child or Virgin and Child are pictorial or sculptured representations of Mary, Mother of Jesus, either alone, or more frequently, with the infant Jesus. These images are central icons of Roman Catholicism and Eastern Orthodox Christianity where Mary remains...
- Madonna and Child
- Hortus conclususHortus conclususHortus conclusus is a Latin term, meaning literally "enclosed garden". "The word 'garden' is at root the same as the word 'yard'. It means an enclosure", observed Derek Clifford, at the outset of a series of essays on garden design, in which he skirted the conventions of the hortus conclusus...
- Holy KinshipHoly KinshipHoly Kinship was a popular theme in religious art throughout Germany and the Low Countries, especially during the late 15th and early 16th centuries. The Holy Kin were the extended family of Jesus descended from his maternal grandmother St. Anne. According to this tradition, St...
Other:
- The Trinity in Art
- Angels in artAngels in artAngels have appeared in works of art for millennia.Angel-shaped beings appear in ancient Mesopotamian and Greek art and were probably the inspiration for the popular Christian image of angels....
- Evangelist portraitEvangelist portraitEvangelist portraits are a specific type of miniature included in ancient and mediæval illuminated manuscript Gospel Books, and later in Bibles and other books, as well as other media. Each Gospel of the Four Evangelists, the books of Matthew, Mark, Luke, and John, may be prefaced by a portrait of...
- MaestàMaestàMaestà, the Italian word for "majesty", designates an iconic formula of the enthroned Madonna with the child Jesus, whether or not accompanied with angels and saints...
- Stations of the CrossStations of the CrossStations of the Cross refers to the depiction of the final hours of Jesus, and the devotion commemorating the Passion. The tradition as chapel devotion began with St...
- Tree of JesseTree of JesseThe Tree of Jesse is a depiction in art of the Ancestors of Christ, shown in a tree which rises from Jesse of Bethlehem, the father of King David; the original use of the family tree as a schematic representation of a genealogy...
See also
- Roman Catholic Marian artRoman Catholic Marian artThe Blessed Virgin Mary has been one of the major subjects of Christian Art, Catholic Art and Western Art for many centuries. Literally hundreds of thousands of pieces of...
- Early Renaissance paintingEarly Renaissance paintingRenaissance art is the painting, sculpture and decorative arts of that period of European history known as the Renaissance, emerging as a distinct style in Italy in about 1400, in parallel with developments which occurred in philosophy, literature, music and science...
- Baroque architectureBaroque architectureBaroque architecture is a term used to describe the building style of the Baroque era, begun in late sixteenth century Italy, that took the Roman vocabulary of Renaissance architecture and used it in a new rhetorical and theatrical fashion, often to express the triumph of the Catholic Church and...
- List of illuminated manuscripts
- Western PaintingWestern paintingThe history of Western painting represents a continuous, though disrupted, tradition from antiquity. Until the mid-19th century it was primarily concerned with representational and Classical modes of production, after which time more modern, abstract and conceptual forms gained favor.Developments...
External links
- Christian Iconography from Augusta State University.

