
Early centers of Christianity
Encyclopedia
Early Christianity
(generally considered as Christianity
before 325
) spread from Western Asia, throughout the Roman Empire
, and beyond into East Africa
and South Asia
, reaching as far as India
. At first, this development was closely connected to centers of Hebrew faith
, in the Holy Land
and the Jewish diaspora
. Jesus
and his first followers were Jews
, or Jewish Proselytes, which historians refer to as Jewish Christians
.
After the Crucifixion
, James the Just
took leadership of the Jerusalem Church while many of the Apostles
, following the Great Commission
, traveled extensively and established Christian communities outside of Jerusalem
. Early Christians gathered in small private homes, known as house churches, but a city's whole Christian community would also be called a church - the Greek noun εκκλησια (or Ecclesia
) literally means assembly, gathering, or congregation but is translated as church
in most English translations of the New Testament
.
Many of these Early Christians were merchants and others who had practical reasons for traveling to northern Africa, Asia Minor, Arabia, Greece, and other places. Over 40 such communities were established by the year 100, many in Anatolia, also known as Asia Minor
, such as the Seven churches of Asia
. By the end of the first century
, Christianity had already spread to Rome, India, and major cities in Greece, Asia Minor and Syria, serving as foundations for the expansive spread of Christianity, eventually throughout the world.

Jesus and his apostles
, disciples
, and early followers, being Jewish or Jewish proselytes, traveled from Galilee
to the Jewish Temple
in Jerusalem, c. 33, at which time the city was under Roman occupation as part of Iudaea province
. After an incident in the Temple
, there he was crucified
, and there, according to Christian belief, he rose again
and then ascended to heaven with a prophecy to return
.
Jerusalem was the first center of the church, according to the Book of Acts, and according to the Catholic Encyclopedia
: the location of "the first Christian church". The apostles lived and taught there for some time after Pentecost
. Jesus' brother James
was a leader in the church, and his other kinsman
likely held leadership positions in the surrounding area after the destruction of the city until its rebuilding as Aelia Capitolina
, c. 130, when all Jews were banished from the city. In about 50, Barnabas and Paul went to Jerusalem to meet with the "pillars of the church": James, Peter, and John. Later called the Council of Jerusalem
, this meeting, among other things, confirmed the legitimacy of the mission of Barnabas and Paul to the gentiles, and the gentile converts' freedom from most Mosaic law, especially circumcision
, which was repulsive to the Hellenic
mind. Thus, the Apostolic Decree may be a major act of differentiation of the Church from its Jewish roots (the first major act being the Rejection of Jesus
as Messiah), though the decree may simply parallel Jewish Noahide Law and thus be a commonality rather than a differential. In roughly the same time period Rabbinic Judaism made their circumcision requirement of Jewish boys
even stricter.
When Peter left Jerusalem after Herod Agrippa I
tried to kill him, James appears as the principal authority. Clement of Alexandria
(c. 150-215) called him Bishop of Jerusalem
. A second-century
church historian, Hegesippus
, wrote that the Sanhedrin
martyred him in 62.
In 66, the Jews revolted against Rome. Rome besieged Jerusalem for four years, and the city fell in 70. The city was destroyed, including the Temple, and the population was mostly killed or removed. Though, according to Epiphanius of Salamis
, the Cenacle
survived at least to Hadrian
's visit in 130. A scattered population survived. Traditionally it is believed the Jerusalem Christians waited out the Jewish–Roman wars in Pella
in the Decapolis
. The Sanhedrin relocated to Jamnia
. Prophecies of the Second Temple's destruction are found in the synoptics
.
In the 2nd century, Hadrian
rebuilt Jerusalem as a pagan
city called Aelia Capitolina
, erecting statues of Jupiter and himself
on the site of the former Jewish Temple, the Temple Mount
. Bar Cochba led an unsuccessful revolt as a Messiah, but Christians refused to acknowledge him as such. When Bar Cochba was defeated, Hadrian barred Jews from the city, except for the day of Tisha B'Av
, thus the subsequent Jerusalem bishops were gentiles ("uncircumcised") for the first time.
The general significance of Jerusalem to Christians
entered a period of decline during the Persecution of Christians in the Roman Empire, but resumed again with the pilgrimage
of Helena (the mother of Constantine the Great) to the Holy Land
c. 326–28. According to the church historian Socrates of Constantinople, Helena (with the assistance of Bishop Macarius of Jerusalem
) claimed to have found the cross of Christ
, after removing a Temple to Venus
(attributed to Hadrian) that had been built over the site. (For that reason she is seen as the Patron Saint
of Archaeologists
.) Jerusalem had received special recognition in Canon VII of Nicaea
in 325. The traditional founding date for the Brotherhood of the Holy Sepulchre
(which guards the Christian Holy places in the Holy Land
) is 313 which corresponds with the date of the Edict of Milan
which legalized Christianity in the Roman Empire. Jerusalem was later named as one of the Pentarchy
, but this was never accepted by the church of Rome. See also East–West Schism#Prospects for reconciliation.
, a major center of Hellenistic Greece
, and the third-most important city of the Roman Empire, then part of Syria province
, today a ruin near Antakya
, Turkey, was where Christians were first so-called and also the location of the Incident at Antioch. It was the site of an early church, traditionally said to be founded by Peter who is considered the first bishop. The Gospel of Matthew
and the Apostolic Constitutions
may have been written there. The church father Ignatius of Antioch
was its third bishop. The School of Antioch, founded in 270, was one of two major centers of early church learning. The Curetonian Gospels
and the Syriac Sinaiticus are two early (pre-Peshitta
) New Testament text types associated with Syriac Christianity
. It was one of the three whose bishops were recognized at the First Council of Nicaea
(325) as exercising jurisdiction over the adjoining territories.
, in the Nile delta
, was established by Alexander the Great. Its famous libraries were a center of Hellenistic learning. The Septuagint translation of the Old Testament began there and the Alexandrian text-type
is recognized by scholars as one of the earliest New Testament types. It had a significant Jewish population, of which Philo of Alexandria is probably its most known author. It produced superior scripture and notable church fathers, such as Clement, Origen, and Athanasius, also noteworthy were the nearby Desert Fathers
. By the end of the era, Alexandria, Rome, and Antioch were accorded authority over nearby metropolitans
. The Council of Nicaea in canon VI affirmed Alexandria's traditional authority over Egypt, Libya, and Pentapolis (North Africa) (the Diocese of Egypt) and probably granted Alexandria the right to declare a universal date for the observance of Easter
, see also Easter controversy
.
 The tradition of John the Apostle
The tradition of John the Apostle
was strong in Anatolia
(the near-east, part of modern Turkey
, the western part was called the Roman province of Asia). The gospel of John was likely written in Ephesus
. According to the New Testament, the Apostle Paul was from Tarsus
(in south-central Anatolia) and his missionary journeys were primarily in Anatolia. The Book of Revelation
, believed to be authored by John of Patmos
(a Greek island about 30 miles off the Anatolian coast), mentions Seven churches of Asia
. The First Epistle of Peter
is addressed to Anatolian regions. On the southeast shore of the Black Sea
, Pontus was a Greek colony mentioned three times in the New Testament, inhabitants of Pontus were some of the very first converts to Christianity. Pliny, governor in 110
, in his letters, addressed Christians in Pontus. Of the extant letters of Ignatius of Antioch considered authentic, five of seven are to Anatolian cities, the sixth is to Polycarp
. Smyrna
was home to Polycarp, the bishop who reportedly knew the Apostle John personally, and probably also to his student Irenaeus
. Papias of Hierapolis is also believed to have been a student of John the Apostle. In the 2nd century, Anatolia was home to Quartodecimanism
, Montanism
, Marcion of Sinope
, and Melito of Sardis
who recorded an early Christian Biblical canon
. After the Crisis of the Third Century
, Nicomedia
became the capital of the Eastern Roman Empire
in 286. The Synod of Ancyra
was held in 314. In 325 the emperor Constantine
convoked the first Christian ecumenical council
in Nicaea and in 330 moved the capital of the reunified empire to Byzantium
(also an early Christian center and just across the Bosporus
from Anatolia, later called Constantinople
), referred to as the Byzantine Empire
, which lasted till 1453. The First seven Ecumenical Councils
were held either in Western Anatolia or Constantinople.
, c.25-13 BC, and was the capital of Iudaea province
(6-132) and later Palaestina Prima. It was there that Peter baptized the centurion Cornelius, considered the first gentile convert. Paul sought refuge there, once staying at the house of Philip the Evangelist
, and later being imprisoned there for two years (estimated to be 57-59). The Apostolic Constitutions
(7.46) state that the first Bishop of Caesarea was Zacchaeus the Publican
but the Catholic Encyclopedia
claims that: "...there is no record of any bishops of Caesarea until the second century. At the end of this century a council was held there to regulate the celebration of Easter
." According to another Catholic Encyclopedia article, after Hadrian's siege of Jerusalem (c.133), Caesarea became the metropolitan see with the bishop of Jerusalem as one of its "suffragans"
(subordinates). Origen
(d.254) compiled his Hexapla
there and it held a famous library and theological school
, St. Pamphilus
(d.309) was a noted scholar-priest. St. Gregory the Wonder-Worker (d.270), St. Basil the Great (d.379), and St. Jerome (d.420) visited and studied at the library which was later destroyed, probably by the Persians
in 614 or the Saracens around 637. The first major church historian, Eusebius of Caesarea
, was a bishop, c.314-339. F. J. A. Hort
and Adolf von Harnack
have argued that the Nicene Creed
originated in Caesarea. The Caesarean text-type
is recognized by scholars as one of the earliest New Testament types.
 Damascus
Damascus
is the capital of Syria
and claims to be the oldest continuously inhabited city in the world. According to the New Testament, the Apostle Paul was converted on the Road to Damascus. In the three accounts , he is described as being led by those he was traveling with, blinded by the light, to Damascus where his sight was restored by a disciple called Ananias
(who, according to the Catholic Encyclopedia, is thought to have been the first Bishop of Damascus) then he was baptized.
 Paphos
Paphos
was the capital of the island of Cyprus
during the Roman years and seat of a Roman commander. In 45 AD, the apostles Paul and Barnabas
(according to the Catholic Encyclopedia "a native of the island") came to Cyprus and reached Paphos preaching the Word of Christ, see also . The apostles were persecuted by the Romans but eventually succeeded to convince the Roman commander Sergius Paulus
into renouncing his old religion in favour of Christianity. 5 years later, Barnabas returned to the Cypriot town of Salamis
, where he became bishop and oversaw the spread of Christianity to the island.
, the major northern Greek city where it is believed Christianity was founded by Paul, thus an Apostolic See
, and the surrounding regions of Macedonia
, Western
and Eastern Thrace, and Epirus
, which also extend into the neighboring Balkan states of Albania and Bulgaria, were early centers of Christianity. Of note are Paul's Epistles to the Thessalonians and to Philippi
, which is often considered the first contact of Christianity with Europe. The Apostolic Father Polycarp
wrote a letter to the Philippians
, c.125.
Nicopolis
was a city in the Roman province of Epirus Vetus, today a ruin on the northern part of the western Greek coast. According to the Catholic Encyclopedia: "St. Paul intended going there and it is possible that even then it numbered some Christians among its population; Origen
(c. 185–254) sojourned there for a while (Eusebius, Church History VI.16)."
Ancient Corinth, today a ruin near modern Corinth
in southern Greece, was an early center of Christianity. According to the Catholic Encyclopedia: "St. Paul preached successfully at Corinth, where he lived in the house of Aquila and Priscilla , where Silas
and Timothy soon joined him. After his departure he was replaced by Apollo
, who had been sent from Ephesus by Priscilla. The Apostle visited Corinth at least once more. He wrote to the Corinthians in 57 from Ephesus
, and then from Macedonia in the same year, or in 58
. The famous letter of St. Clement of Rome to the Corinthian church
(about 96) exhibits the earliest evidence concerning the ecclesiastical primacy of the Roman Church. Besides St. Apollo, Lequien (II, 155) mentions forty-three bishops: among them, St. Sosthenes
(?), the disciple of St. Paul, St. Dionysius
; Paul, brother of St. Peter ..."
Athens
, the capital and largest city in Greece, was visited by Paul. According to the Catholic Encyclopedia: Paul "came to Athens from Berœa of Macedonia
, coming probably by water and landing in the Peiræevs
, the harbour of Athens. This was about the year 53. Having arrived at Athens, he at once sent for Silas and Timotheos who had remained behind in Berœa. While awaiting the coming of these he tarried in Athens, viewing the idolatrous city, and frequenting the synagogue
; for there were already Jews in Athens. ... It seems that a Christian community was rapidly formed, although for a considerable time it did not possess a numerous membership. The commoner tradition names the Areopagite
as the first head and bishop of the Christian Athenians. Another tradition, however, gives this honour to Hierotheos the Thesmothete
. The successors of the first bishop were not all Athenians by lineage. They are catalogued as Narkissos, Publius, and Quadratus
. Narkissos is stated to have come from Palestine, and Publius from Malta
. In some lists Narkissos is omitted. Quadratus is revered for having contributed to early Christian literature by writing an apology
, which he addressed to the Emperor Hadrian
. This was on the occasion of Hadrian's visit to Athens. Another Athenian who defended Christianity in writing at a somewhat later time was Aristeides. His apology was directed to the Emperor Marcus Aurelius. Athenagoras
also wrote an apology. In the second century there must have been a considerable community of Christians in Athens, for Hygeinos, Bishop of Rome
, is said to have written a letter to the community in the year 139."
Gortyn
on Crete
, was allied with Rome and was thus made capital of Roman Creta et Cyrenaica
. St. Titus is believed to have been the first bishop. The city was sacked by the pirate Abu Hafs
in 828.
and the surrounding region of Cyrenaica or the North African "Pentapolis
", south of the Mediterranean from Greece, the northeastern part of modern Libya
, was a Greek colony in North Africa later converted to a Roman colony. In addition to Greeks and Romans, there was also a significant Jewish population, at least up to the Kitos War
(115-117). According to , Simon of Cyrene
carried Jesus' cross. Cyrenians are also mentioned in , , , . According to the Catholic Encyclopedia: "Lequien mentions six bishops of Cyrene, and according to Byzantine legend the first was St. Lucius
(Acts 13:1); St. Theodorus suffered martyrdom under Diocletian;" (284-305).
 Exactly when Christians first appeared in Rome is difficult to determine, see Godfearers and Proselytes for the historical background. The Acts of the Apostles
Exactly when Christians first appeared in Rome is difficult to determine, see Godfearers and Proselytes for the historical background. The Acts of the Apostles
claims that the Jewish Christian couple Priscilla and Aquila had recently come from Rome to Corinth when, in about the year 50, Paul reached the latter city, indicating that belief in Jesus in Rome had preceded Paul. Irenaeus of Lyons believed in the second century
that Peter
and Paul had been the founders of the Church in Rome and had appointed Linus
as succeeding bishop
. There is no conclusive evidence, scripturally, historically or chronologically, that Peter was in fact the Bishop of Rome. While the church in Rome was already flourishing when Paul wrote his Epistle to the Romans
to them from Corinth, about 57, he greets some fifty people in Rome by name, but not Peter whom he knew. There is also no mention of Peter in Rome later during Paul's two year stay there in chapter 28 of Acts
, about 60-62. Church historians consistently consider Peter and Paul to have been martyr
ed under the reign of Nero
, in 64 such as after the Great Fire of Rome which, according to Tacitus
, Nero blamed on the Christians.
Paul's Epistle to the Romans
(c 58) attests to a large Christian community already there but does not mention Peter
. The tradition that the See of Rome was founded as an organized Christian community by Peter and Paul and that its episcopate owes to them its origin can be traced as far back as second-century
Irenaeus
. Irenaeus does not say that either Peter or Paul was "bishop" of the Church in Rome, and some historians have questioned whether Peter spent much time in Rome before his martyrdom.
Oscar Cullmann
sharply rejected the claim that Peter began the papal succession
, and concludes that while Peter was the original head of the apostles
, Peter was not the founder of any visible church succession.
The original seat of Roman imperial power soon became a center of church authority, grew in power decade by decade, and was recognized during the period of the Seven Ecumenical Councils, when the seat of government had been transferred to Constantinople, as the "head" of the church.
Rome and Alexandria, which by tradition held authority over sees outside their own province, were not yet referred to as patriarchates.
The earliest bishops of Rome were all Greek-speaking, the most notable of them being Pope Clement I
(c. 88-97), author of an Epistle to the Church in Corinth
; Pope Telesphorus
(c. 126-136), probably the only martyr among them; Pope Pius I
(c. 141-154), said by the Muratorian fragment
to be the brother of the author of the Shepherd of Hermas
; and Pope Anicetus
(c. 155-160), who received Saint Polycarp
and discussed with him the dating of Easter
.
Pope Victor I
(189-198) was the first ecclesiastical writer known to have written in Latin; however, his only extant works are his encyclicals, which would naturally have been issued in both Latin and Greek.
Greek New Testament texts were translated into Latin early on, well before Jerome
, and are classified as the Vetus Latina
and Western text-type
.
During the 2nd century, Christians and semi-Christians of diverse views congregated in Rome, notably Marcion and Valentinius, and in the following century there were schisms connected with Hippolytus of Rome and Novatian.
The Roman church survived various persecutions, and many clergy were martyred. In the "Massacre of 258", under Valerian
, the emperor killed a great many Christian clergy, including Pope Sixtus II
and Cyprian of Carthage and perhaps also Antipope Novatian
. Mass persecutions, of which that which broke out under Diocletian in 303 was particularly severe, finally ended in Rome, and the West in general, with the accession of Maxentius
in 306.
. According to the Catholic Encyclopedia: "Syracuse claims to be the second Church founded by St. Peter, after that of Antioch. It also claims that St. Paul preached there. ... In the times of St. Cyprian (the middle of the third century), Christianity certainly flourished at Syracuse, and the catacombs
clearly show that this was the case in the second century." Across the Strait of Messina
, Calabria
on the mainland was also an early center of Christianity.
at the head of the Adriatic Sea
, today one of the main archeological sites of Northern Italy
, was an early center of Christianity said to be founded by Mark
before his mission to Alexandria. Hermagoras of Aquileia
is believed to be its first bishop. The Aquileian Rite
is associated with Aquileia.
in northwest Italy was founded by the apostle Barnabas
in the 1st century. Gervasius and Protasius
and others were martyred there. It has long maintained its own rite known as the Ambrosian Rite
attributed to Ambrose
who was bishop c. 337-397 and one of the most influential ecclesiastical figures of the 4th century. Duchesne argues that the Gallican Rite originated in Milan.
, in the Roman province of Africa, south of the Mediterranean from Rome, gave the early church the Latin fathers Tertullian
(c.120-c.220) and Cyprian
(d. 258). Carthage fell to Islam
in 698.
(an island just south of Sicily
) for three months during which time he is said to have been bitten by a poisonous viper and survived , an event usually dated c. AD 60. Paul had been allowed passage from Caesarea Maritima to Rome by Porcius Festus
, procurator
of Iudaea province
, to stand trial before the Emperor. Many traditions are associated with this episode, and catacombs in Rabat testify to an Early Christian community on the islands. According to tradition, Publius
, the Roman Governor of Malta at the time of Saint Paul's shipwreck, became the first Bishop of Malta following his conversion to Christianity. After ruling the Maltese Church for thirty-one years, Publius was transferred to the See of Athens
in 90 AD, where he was martyred in 125 AD. There is scant information about the continuity of Christianity in Malta in subsequent years, although tradition has it that there was a continuous line of bishops from the days of St. Paul to the time of Emperor Constantine.
, the capital of the Roman province of Dalmatia
on the eastern shore of the Adriatic Sea
, was an early center of Christianity and today is a ruin in modern Croatia
. According to the Catholic Encyclopedia it was where: "...Titus the pupil of St. Paul preached, where the followers of Jesus Christ first shed their blood as martyrs, and where beautiful examples of basilicas and other early Christian sculpture have been discovered." According to the Catholic Encyclopedia article on Dalmatia: "Salona became the centre from which Christianity spread. In Pannonia St. Andronicus
founded the See of Syrmium (Mitrovica) and later those of Siscia and Mursia. The cruel persecution under Diocletian, who was a Dalmatian by birth, left numerous traces in Old Dalmatia
and Pannonia
. St. Quirinus, Bishop of Siscia, died a martyr A.D. 303. St. Jerome
was born in Strido
, a city on the border of Pannonia and Dalmatia."
was the capital of Hispania Baetica
or the Roman province of southern Spain. According to the Catholic Encyclopedia: "...the origin of the diocese goes back to Apostolic times, or at least to the first century of our era. St. Gerontius, Bishop of Italica (about four miles from Hispalis or Seville), preached in Baetica in Apostolic times, and without doubt must have left a pastor of its own to Seville. It is certain that in 303, when Sts. Justa and Rufina
, the potters, suffered martyrdom for refusing to adore the idol Salambo, there was a Bishop of Seville, Sabinus, who assisted at the Council of Illiberis (287). Before that time Marcellus had been bishop, as appears from a catalogue of the ancient prelates of Seville preserved in the "Codex Emilianensis", a manuscript of the year 1000, now in the Escorial. When Constantine brought peace to the Church
[313] Evodius was Bishop of Seville; he set himself to rebuild the ruined churches, among them he appears to have built the church of San Vicente, perhaps the first cathedral of Seville." Early Christianity also spread from the Iberian peninsula
south across the Strait of Gibraltar
into Roman Mauretania Tingitana
, of note is Marcellus of Tangier
who was martyred in 298.

The Mediterranean coast of France and the Rhone valley, then part of Roman Gallia Narbonensis
, were early centers of Christianity. Major cities are Arles
, Avignon
, Vienne
, Lyon
, and Marseille
(the oldest city in France). The Persecution in Lyon occurred in 177. The Apostolic Father Irenaeus
from Smyrna
of Anatolia was Bishop of Lyon near the end of the 2nd century and he claimed Saint Pothinus
was his predecessor. The Council of Arles in 314 is considered a forerunner of the Ecumenical councils. The Ephesine theory attributes the Gallican Rite to Lyon.
in 301 or 314, when Christianity was still illegal in the Roman Empire. Some claim the Armenian Apostolic Church
was founded by Gregory the Illuminator
of the late third - early fourth centuries while they trace their origins to the missions of Bartholomew the Apostle and Thaddeus (Jude the Apostle) in the 1st century.
(ancient Iberia
) extends back to the 4th century
, if not earlier. The Iberian king, Mirian III
, converted to Christianity, probably in 326.
, which was held by Rome from 116 to 118 and 212 to 214, but was mostly a client kingdom associated either with Rome or Persia, was an important Christian city. Shortly after 201 or even earlier, its royal house became Christian
Edessa
(now Şanlıurfa
) in northwestern Mesopotamia was from apostolic times the principal center of Syriac-speaking Christianity. it was the capital of an independent kingdom from 132 BC to AD 216, when it became tributary to Rome. Celebrated as an important centre of Greco-Syrian culture, Edessa was also noted for its Jewish community., with proselytes in the royal family. Strategically located on the main trade routes of the Fertile Crescent
, it was easily accessible from Antioch
, where the mission to the Gentiles was inaugurated. When early Christians were scattered abroad because of persecution, some found refuge at Edessa. Thus the Edessan church traced its origin to the apostolic age (which may account for its rapid growth), and Christianity
even became the state religion for a time.
The Church of the East had its inception at a very early date in the buffer zone between the Parthian
and Roman Empires in Upper Mesopotamia, known as the Assyrian Church of the East
. The vicissitudes of its later growth were rooted in its minority status in a situation of international tension. The rulers of the Parthian Empire
(250 BC - AD 226) were on the whole tolerant in spirit, and with the older faiths of Babylonia and Assyria in a state of decay, the time was ripe for a new and vital faith. The rulers of the Second Persian empire (226-640) also followed a policy of religious toleration to begin with, though later they gave Christians the same status as a subject race. However, these rulers also encouraged the revival of the ancient Persian dualistic faith of Zoroastrianism
and established it as the state religion, with the result that the Christians were increasingly subjected to repressive measures. Nevertheless, it was not until Christianity became the state religion in the West (380) that enmity toward Rome was focused on the Eastern Christians. After the Mohammedan conquest in the 7th century, the caliphate tolerated other faiths but forbade proselytism and subjected Christians to heavy taxation.
The missionary Addai evangelized Mesopotamia
(modern Iraq
) about the middle of the 2nd century. An ancient legend recorded by Eusebius (AD 260-340) and also found in the Doctrine of Addai (c. AD 400) (from information in the royal archives of Edessa) describes how King Abgar V of Edessa
communicated to Jesus, requesting he come and heal him, to which appeal he received a reply. It is said that after the resurrection, the Thomas sent Addai (or Thaddaeus), to the king, with the result that the city was won to the Christian faith. In this mission he was accompanied by a disciple, Mari, and the two are regarded as cofounders of the church, according to the Liturgy of Addai and Mari (c. AD 200), which is still the normal liturgy of the Assyrian church. The Doctrine of Addai
further states that Thomas was regarded as an apostle of the church, which long treasured a letter written by him from India.
Addai, who became the first bishop of Edessa, was succeeded by Aggai
, then by Palut, who was ordained about 200 by Serapion of Antioch
. Thence came to us in the 2nd century the famous Peshitta
, or Syriac translation of the Old Testament; also Tatian
's Diatessaron
, which was compiled about 172 and in common use until St. Rabbula
, Bishop of Edessa (412-435), forbade its use. This arrangement of the four Canonical gospels as a continuous narrative, whose original language may have been Syriac, Greek, or even Latin, circulated widely in Syriac-speaking Churches.
A Christian council was held at Edessa as early as 197. In 201 the city was devastated by a great flood, and the Christian church was destroyed. In 232 the relics of the Apostle Thomas
were brought from India
, on which occasion his Syriac Acts were written. Under Roman domination many martyrs suffered at Edessa: Sts. Scharbîl and Barsamya, under Decius
; Sts. Gûrja, Schâmôna, Habib, and others under Diocletian
. In the meanwhile Christian priests from Edessa had evangelized Eastern Mesopotamia and Persia
, and established the first Churches in the kingdom of the Sassanids. Atillâtiâ, Bishop of Edessa, assisted at the First Council of Nicaea (325).
, Persia, Parthia
, and Bactria
. The twenty bishops and many presbyters were more of the order of itinerant missionaries, passing from place to place as Paul did and supplying their needs with such occupations as merchant or craftsman. By AD 280
the metropolis of Seleucia assumed the title of “Catholicos,”and in A.D. 424
a council of the church at Seleucia elected the first patriarch to have jurisdiction over the whole church of the East, including India and Ceylon (Sri Lanka). The seat of the Patriarchate was fixed at Seleucia-Ctesiphon, since this was an important point on the East-West trade routes which extended both to India and China, Java and Japan. Thus the shift of ecclesiastical authority was away from Edessa, which in A.D. 216 had become tributary to Rome. the establishment of an independent patriarchate with nine subordinate metropoli contributed to a more favourable attitude by the Persian government, which no longer had to fear an ecclesiastical alliance with the common enemy, Rome.
By the time that Edessa was incorporated into the Persian Empire in 258, the city of Arbela
, situated on the Tigris
in what is now Iraq
, had taken on more and more the role that Edessa had played in the early years, as a centre from which Christianity spread to the rest of the Persian Empire.
Bardaisan, writing about 196, speaks of Christians throughout Media
, Parthia
and Bactria
(modern-day Afghanistan
) and, according to Tertullian
(c.160-230), there were already a number of bishoprics within the Persian Empire by 220. By 315, the bishop of Seleucia
-Ctesiphon
had assumed the title "Catholicos
". By this time, neither Edessa nor Arbela was the centre of the Church of the East anymore; ecclesiastical authority had moved east to the heart of the Persian Empire. The twin cities of Seleucia-Ctesiphon, well-situated on the main trade routes between East and West, became, in the words of John Stewart, "a magnificent centre for the missionary church that was entering on its great task of carrying the gospel to the far east."
Thus it was from Edessa that a missionary movement began which gradually spread throughout Mesopotamia
, Persia, Central Asia
and China
. According to another ancient tradition, Mari was sent as a missionary to Seleucia
(on the Tigris River near Baghdad), which, with its twin city of Ctesiphon
across the river, became another canter of missionary outreach. Mari was also regarded as the pioneer evangelist in the whole region of Adiabene
to the north, of which Arbil
(now Erbil) was the capital. By the latter half of the 2nd century, Christianity had spread east throughout Media
, Persia, Parthia
, and Bactria
. The twenty bishops and many presbyters were more of the order of itinerant missionaries, passing from place to place as Paul did and supplying their needs with such occupations as merchant or craftsman. By AD 280
the metropolis of Seleucia assumed the title of "Catholicos," and in AD 424
a council of the church at Seleucia elected the first patriarch to have jurisdiction over the whole church of the East, including India and Ceylon (Sri Lanka). The seat of the Patriarchate was fixed at Seleucia-Ctesiphon, since this was an important point on the East-West trade routes which extended both to India and China, Java and Japan. Thus the shift of ecclesiastical authority was away from Edessa, which in AD 216 had become tributary to Rome. the establishment of an independent patriarchate with nine subordinate metropoli contributed to a more favourable attitude by the Persian government, which no longer had to fear an ecclesiastical alliance with the common enemy, Rome.
When Constantine converted to Christianity, and the Roman Empire which was previously violently anti-Christian became pro-Christian, the Persian Empire, suspecting a new "enemy within," became violently anti-Christian. Within a few years, Shapur II
(309-379) inaugurated a twenty-year long persecution of the church with the murder of Mar Shimun, the Catholicos of Seleucia-Ctesiphon, five bishops and 100 priests on Good Friday, 344, after the Patriarch refused to collect a double tax from the Christians to help the Persian war effort against Rome. See also Christianity in Iran
.
by the Christian gospel, it is helpful to distinguish between the marauding Bedouin
nomads of the interior, who were chiefly herdsmen and unreceptive to foreign influence, and the inhabitants of the settled communities of the coastal areas and oases, who were either middlemen traders or farmers and were receptive to influences from abroad. Christianity apparently gained its strongest foothold in the ancient center of Semitic civilisation in South-west Arabia or Yemen
, (sometimes known as Seba or Sheba
), whose queen visited Solomon
. Because of geographic proximity, acculturation with Ethiopia
was always strong, and the royal family traces its ancestry to this queen.
The presence of Arabians at Pentecost and Paul's three-year sojourn in Arabia suggest a very early gospel witness. A 4th-century church history, states that the apostle Bartholomew
preached in Arabia and that Himyarites were among his converts. The Al-Jubail Church
in what is now Saudi Arabia
was built in the 4th century. Arabia's close relations with Ethiopia
give significance to the conversion of the treasurer to the queen of Ethiopia, not to mention the tradition that the Apostle Matthew was assigned to this land. Eusebius says that “one Pantaneous
(c. A.D. 190
) was sent from Alexandria
as a missionary to the nations of the East,” including southwest Arabia, on his way to India.
, see also Ethiopian Orthodox Tewahedo Church
, the region today known as Ethiopia
converted to Judaism during the time of the biblical Queen of Sheba and Solomon
. According to the fourth century western historian Rufinius
, it was Frumentius who brought Christianity to Ethiopia (the city of Axum
) and served as its first bishop, probably shortly after 325.
, Thomas
and Bartholomew were assigned to Parthia
(modern Iran) and India. The Didache
(dating from the end of the first century) states, "India and all countries condering it, even to the farthest seas...received the apostolic ordinances from Judas Thomas (same as the Apostle Thomas), who was a guide and ruler in the church which he built." Moreover, there is a wealth of confirmatory information in the Syriac writings, liturgical book
s, and calendars of the Church of the East, not to mention the writings of the Fathers, the calendars, the sacramentaries, and the martyrologies of the Roman, Greek and Ethiopian churches.
Since trade routes from the East were wide open at the time and were used by early missionaries, historian Vincent A. Smith says, "It must be admitted that a personal visit of the Apostle Thomas to South India was easily feasible in the traditional belief that he came by way of Socotra
, where an ancient Christian settlement undoubtedly existed. I am now satisfied that the Christian church of South India is extremely ancient...' Although there was a lively trade between the Near East and India via Mesopotamia and the Persian Gulf, the most direct route to India in the 1st century was via Alexandria
and the Red Sea
, taking advantage of the Monsoon winds, which could carry ships directly to and from the Malabar coast. The discovery of large hoards of Roman coins of 1st-century Caesars and the remains of Roman trading posts testify to the frequency of that trade. in addition, thriving Jewish colonies were to be found at the various trading centers, thereby furnishing obvious bases for the apostolic witness.
Piecing together the various traditions, one may conclude that Thomas left northwest India when invasion threatened and traveled by vessel to the Malabar coast
, possibly visiting southeast Arabia and Socotra enroute and landing at the former flourishing port of Muziris
on an island near Cochin (c. 51
-52
). From there he is said to have preached the gospel throughout the Malabar coast, though the various churches he founded were located mainly on the Periyar River
and its tributaries and along the coast, where there were Jewish colonies. he reputedly preached to all classes of people and had about seventeen thousand converts, including members of the four principal castes. Later, stone crosses were erected at the places where churches were founded, and they became pilgrimage centres. In accordance with apostolic custom thomas ordained teachers and leaders or elders, who were reported to be the earliest ministry of the Malabar church.
Thomas next proceeded overland to the Coromandel coast
and ministered in what is now the Madras area, where a local king and many people were converted. One tradition related that he went from there to China
via Malacca
and, after spending some time there, returned to the Madras area (Breviary of the Mar Thoma Church in Malabar). According to the Syriac version of the Acts of Thomas, Masdai, the local king at Mylapore
, after questioning the apostle condemned him to death about the year 72
. Anxious to avoid popular excitement, “for many had believed in our Lord, including some of the nobles,”the king ordered Thomas conducted to a nearby mountain, where, after being allowed to pray, he was then stoned and stabbed to death with a lance wielded by a hunter. A number of Christians fled to malabar and joined that Christian community.
An early 3rd-century Syriac work known as the Acts of Thomas
connects the apostle's Indian ministry with two kings, one in the north and the other in the south. According to one of the legends in the Acts, Thomas was at first reluctant to accept this mission, but the Lord appeared to him in a night vision and said, “Fear not, Thomas. Go away to India and proclaim the Word, for my grace shall be with you.”But the Apostle still demurred, do the Lord overruled the stubborn disciple by ordering circumstances so compelling that he was forced to accompany an Indian merchant, Abbanes, to his native place in northwest India, where he found himself in the service of the Indo-Parthian king, Gondophares
. The apostle's ministry resulted in many conversions throughout the kingdom, including the king and his brother.
Critical historians treated this legend as an idle tale and denied the historicity of King Gundaphorus until modern archeology established him as an important figure in North India in the latter half of the 1st century. Many coins of his reign have turned up in Afghanistan, the Punjab
, and the Indus Valley. Remains of some of his buildings , influenced by Greek architecture, indicate that he was a great builder. Interestingly enough, according to the legend, Thomas was a skilled carpenter and was bidden to build a palace for the king. However, the Apostle decided to teach the king a lesson by devoting the royal grant to acts of charity and thereby laying up treasure for the heavenly abode.
Although little is known of the immediate growth of the church, Bar-Daisan ( 154-223) reports that in his time there were Christian tribes in North India which claimed to have been converted by Thomas and to have books and relics to prove it. But at least by the time of the establishment of the Second Persian Empire ( 226), there were bishops of the Church of the East in northwest India, Afghanistan and Baluchistan
, with laymen and clergy alike engaging in missionary activity.
The apocryphal Acts of Thomas
(3rd century) identifies his second mission in India with a kingdom ruled by King Mahadwa, one of the rulers of a 1st-century dynasty in southern India. It is most significant that, aside from a small remnant of the Church of the East in Kurdistan, the only other church to maintain a distinctive identity is the Mar Thoma
or “Church of Thomas” congregations along the Malabar Coast
of Kerala
State in southwest India. According to the most ancient tradition of this church, Thomas evangelized this area and then crossed to the Coromandel Coast
of southeast India, where, after carrying out a second mission, he suffered martyrdom near Madras. Throughout the period under review, the church in India was under the jurisdiction of Edessa
, which was then under the Mesopotamian patriarchate at Seleucia-Ctesiphon and later at Baghdad and Mosul.
Early Christianity
Early Christianity is generally considered as Christianity before 325. The New Testament's Book of Acts and Epistle to the Galatians records that the first Christian community was centered in Jerusalem and its leaders included James, Peter and John....
(generally considered as Christianity
Christianity
Christianity is a monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus as presented in canonical gospels and other New Testament writings...
before 325
First Council of Nicaea
The First Council of Nicaea was a council of Christian bishops convened in Nicaea in Bithynia by the Roman Emperor Constantine I in AD 325...
) spread from Western Asia, throughout the Roman Empire
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of the ancient Roman civilization, characterised by an autocratic form of government and large territorial holdings in Europe and around the Mediterranean....
, and beyond into East Africa
East Africa
East Africa or Eastern Africa is the easterly region of the African continent, variably defined by geography or geopolitics. In the UN scheme of geographic regions, 19 territories constitute Eastern Africa:...
and South Asia
South Asia
South Asia, also known as Southern Asia, is the southern region of the Asian continent, which comprises the sub-Himalayan countries and, for some authorities , also includes the adjoining countries to the west and the east...
, reaching as far as India
Christianity in India
Christianity is India's third-largest religion, with approximately 24 million followers, constituting 2.3% of India's population. The works of scholars and Eastern Christian writings and 14th century Portuguese missionaries created an illusion to convert Indians that Christianity was introduced to...
. At first, this development was closely connected to centers of Hebrew faith
Faith
Faith is confidence or trust in a person or thing, or a belief that is not based on proof. In religion, faith is a belief in a transcendent reality, a religious teacher, a set of teachings or a Supreme Being. Generally speaking, it is offered as a means by which the truth of the proposition,...
, in the Holy Land
Holy Land
The Holy Land is a term which in Judaism refers to the Kingdom of Israel as defined in the Tanakh. For Jews, the Land's identifiction of being Holy is defined in Judaism by its differentiation from other lands by virtue of the practice of Judaism often possible only in the Land of Israel...
and the Jewish diaspora
Jewish diaspora
The Jewish diaspora is the English term used to describe the Galut גלות , or 'exile', of the Jews from the region of the Kingdom of Judah and Roman Iudaea and later emigration from wider Eretz Israel....
. Jesus
Jesus
Jesus of Nazareth , commonly referred to as Jesus Christ or simply as Jesus or Christ, is the central figure of Christianity...
and his first followers were Jews
Jews
The Jews , also known as the Jewish people, are a nation and ethnoreligious group originating in the Israelites or Hebrews of the Ancient Near East. The Jewish ethnicity, nationality, and religion are strongly interrelated, as Judaism is the traditional faith of the Jewish nation...
, or Jewish Proselytes, which historians refer to as Jewish Christians
Jewish Christians
Jewish Christians is a term which appears in historical texts contrasting Christians of Jewish origin with Gentile Christians, both in discussion of the New Testament church and the second and following centuries....
.
After the Crucifixion
Crucifixion of Jesus
The crucifixion of Jesus and his ensuing death is an event that occurred during the 1st century AD. Jesus, who Christians believe is the Son of God as well as the Messiah, was arrested, tried, and sentenced by Pontius Pilate to be scourged, and finally executed on a cross...
, James the Just
James the Just
James , first Bishop of Jerusalem, who died in 62 AD, was an important figure in Early Christianity...
took leadership of the Jerusalem Church while many of the Apostles
Apostle (Christian)
The term apostle is derived from Classical Greek ἀπόστολος , meaning one who is sent away, from στέλλω + από . The literal meaning in English is therefore an "emissary", from the Latin mitto + ex...
, following the Great Commission
Great Commission
The Great Commission, in Christian tradition, is the instruction of the resurrected Jesus Christ to his disciples, that they spread his teachings to all the nations of the world. It has become a tenet in Christian theology emphasizing missionary work, evangelism, and baptism...
, traveled extensively and established Christian communities outside of Jerusalem
Dispersion of the Apostles
The Dispersion of the Apostles is a feast in commemoration of the missionary work of the Twelve Apostles. It is celebrated as a double major on 15 July. The first vestige of this feast is found in the sequence composed for it by a certain Godescalc The Dispersion of the Apostles (Lat. Divisio...
. Early Christians gathered in small private homes, known as house churches, but a city's whole Christian community would also be called a church - the Greek noun εκκλησια (or Ecclesia
Ecclesia
-Ecclesia:* the Christian Church**See Church militant and church triumphant for ecclesia militans, ecclesia penitens, ecclesia triumphans* Congregation among many English-speaking Christadelphians....
) literally means assembly, gathering, or congregation but is translated as church
Christian Church
The Christian Church is the assembly or association of followers of Jesus Christ. The Greek term ἐκκλησία that in its appearances in the New Testament is usually translated as "church" basically means "assembly"...
in most English translations of the New Testament
English translations of the Bible
The efforts of translating the Bible from its original languages into over 2,000 others have spanned more than two millennia. Partial translations of the Bible into languages of the English people can be traced back to the end of the 7th century, including translations into Old English and Middle...
.
Many of these Early Christians were merchants and others who had practical reasons for traveling to northern Africa, Asia Minor, Arabia, Greece, and other places. Over 40 such communities were established by the year 100, many in Anatolia, also known as Asia Minor
Asia Minor
Asia Minor is a geographical location at the westernmost protrusion of Asia, also called Anatolia, and corresponds to the western two thirds of the Asian part of Turkey...
, such as the Seven churches of Asia
Seven churches of Asia
The Seven Churches of Revelation, also known as The Seven Churches of the Apocalypse and The Seven Churches of Asia , are seven major churches of Early Christianity, as mentioned in the New Testament Book of Revelation and written to by Ignatius of Antioch...
. By the end of the first century
Christianity in the 1st century
The earliest followers of Jesus composed an apocalyptic, Jewish sect, which historians refer to as Jewish Christianity. The Apostles and others following the Great Commission's decree to spread the teachings of Jesus to "all nations," had great success spreading the religion to gentiles. Peter,...
, Christianity had already spread to Rome, India, and major cities in Greece, Asia Minor and Syria, serving as foundations for the expansive spread of Christianity, eventually throughout the world.
Jerusalem


Jesus and his apostles
Apostle (Christian)
The term apostle is derived from Classical Greek ἀπόστολος , meaning one who is sent away, from στέλλω + από . The literal meaning in English is therefore an "emissary", from the Latin mitto + ex...
, disciples
Disciple (Christianity)
In Christianity, the disciples were the students of Jesus during his ministry. While Jesus attracted a large following, the term disciple is commonly used to refer specifically to "the Twelve", an inner circle of men whose number perhaps represented the twelve tribes of Israel...
, and early followers, being Jewish or Jewish proselytes, traveled from Galilee
Galilee
Galilee , is a large region in northern Israel which overlaps with much of the administrative North District of the country. Traditionally divided into Upper Galilee , Lower Galilee , and Western Galilee , extending from Dan to the north, at the base of Mount Hermon, along Mount Lebanon to the...
to the Jewish Temple
Second Temple
The Jewish Second Temple was an important shrine which stood on the Temple Mount in Jerusalem between 516 BCE and 70 CE. It replaced the First Temple which was destroyed in 586 BCE, when the Jewish nation was exiled to Babylon...
in Jerusalem, c. 33, at which time the city was under Roman occupation as part of Iudaea province
Iudaea Province
Judaea or Iudaea are terms used by historians to refer to the Roman province that extended over parts of the former regions of the Hasmonean and Herodian kingdoms of Israel...
. After an incident in the Temple
Jesus and the Money Changers
The narrative of Jesus and the money changers, commonly referred to as the cleansing of the Temple, occurs in all four canonical gospels of the New Testament....
, there he was crucified
Crucifixion of Jesus
The crucifixion of Jesus and his ensuing death is an event that occurred during the 1st century AD. Jesus, who Christians believe is the Son of God as well as the Messiah, was arrested, tried, and sentenced by Pontius Pilate to be scourged, and finally executed on a cross...
, and there, according to Christian belief, he rose again
Resurrection appearances of Jesus
The major Resurrection appearances of Jesus in the Canonical gospels are reported to have occurred after his death, burial and resurrection, but prior to his Ascension. Among these primary sources, most scholars believe First Corinthians was written first, authored by Paul of Tarsus along with...
and then ascended to heaven with a prophecy to return
Second Coming
In Christian doctrine, the Second Coming of Christ, the Second Advent, or the Parousia, is the anticipated return of Jesus Christ from Heaven, where he sits at the Right Hand of God, to Earth. This prophecy is found in the canonical gospels and in most Christian and Islamic eschatologies...
.
Jerusalem was the first center of the church, according to the Book of Acts, and according to the Catholic Encyclopedia
Catholic Encyclopedia
The Catholic Encyclopedia, also referred to as the Old Catholic Encyclopedia and the Original Catholic Encyclopedia, is an English-language encyclopedia published in the United States. The first volume appeared in March 1907 and the last three volumes appeared in 1912, followed by a master index...
: the location of "the first Christian church". The apostles lived and taught there for some time after Pentecost
Pentecost
Pentecost is a prominent feast in the calendar of Ancient Israel celebrating the giving of the Law on Sinai, and also later in the Christian liturgical year commemorating the descent of the Holy Spirit upon the disciples of Christ after the Resurrection of Jesus...
. Jesus' brother James
James the Just
James , first Bishop of Jerusalem, who died in 62 AD, was an important figure in Early Christianity...
was a leader in the church, and his other kinsman
Desposyni
The term Desposyni refers to alleged blood relatives of Jesus. The term was coined by Sextus Julius Africanus, a writer of the early 3rd century. Some scholars argue that Jesus' relatives held positions of special honor in the Early Christian Church...
likely held leadership positions in the surrounding area after the destruction of the city until its rebuilding as Aelia Capitolina
Aelia Capitolina
Aelia Capitolina was a city built by the emperor Hadrian, and occupied by a Roman colony, on the site of Jerusalem, which was in ruins since 70 AD, leading in part to the Bar Kokhba revolt of 132–136.-Politics:...
, c. 130, when all Jews were banished from the city. In about 50, Barnabas and Paul went to Jerusalem to meet with the "pillars of the church": James, Peter, and John. Later called the Council of Jerusalem
Council of Jerusalem
The Council of Jerusalem is a name applied by historians and theologians to an Early Christian council that was held in Jerusalem and dated to around the year 50. It is considered by Catholics and Orthodox to be a prototype and forerunner of the later Ecumenical Councils...
, this meeting, among other things, confirmed the legitimacy of the mission of Barnabas and Paul to the gentiles, and the gentile converts' freedom from most Mosaic law, especially circumcision
Circumcision controversy in early Christianity
There is evidence of a controversy over religious male circumcision in Early Christianity. A Council of Jerusalem, possibly held in approximately 50 AD, decreed that male circumcision was not a requirement for Gentile converts. This became known as the "Apostolic Decree" and may be one of the...
, which was repulsive to the Hellenic
Hellenization
Hellenization is a term used to describe the spread of ancient Greek culture, and, to a lesser extent, language. It is mainly used to describe the spread of Hellenistic civilization during the Hellenistic period following the campaigns of Alexander the Great of Macedon...
mind. Thus, the Apostolic Decree may be a major act of differentiation of the Church from its Jewish roots (the first major act being the Rejection of Jesus
Rejection of Jesus
The Canonical Gospels of the New Testament include some accounts of the rejection of Jesus in the course of his ministry. Judaism's view of Jesus, Jesus in Islam, and the view of the Historical Jesus all differ from Christian views of Jesus.-Hometown rejection:...
as Messiah), though the decree may simply parallel Jewish Noahide Law and thus be a commonality rather than a differential. In roughly the same time period Rabbinic Judaism made their circumcision requirement of Jewish boys
Brit milah
The brit milah is a Jewish religious circumcision ceremony performed on 8-day old male infants by a mohel. The brit milah is followed by a celebratory meal .-Biblical references:...
even stricter.
When Peter left Jerusalem after Herod Agrippa I
Agrippa I
Agrippa I also known as Herod Agrippa or simply Herod , King of the Jews, was the grandson of Herod the Great, and son of Aristobulus IV and Berenice. His original name was Marcus Julius Agrippa, so named in honour of Roman statesman Marcus Vipsanius Agrippa, and he is the king named Herod in the...
tried to kill him, James appears as the principal authority. Clement of Alexandria
Clement of Alexandria
Titus Flavius Clemens , known as Clement of Alexandria , was a Christian theologian and the head of the noted Catechetical School of Alexandria. Clement is best remembered as the teacher of Origen...
(c. 150-215) called him Bishop of Jerusalem
Greek Orthodox Patriarch of Jerusalem
The Greek Orthodox Patriarch of Jerusalem is the head bishop of the Orthodox Church of Jerusalem, ranking fourth of nine Patriarchs in the Eastern Orthodox Church. Since 2005, the Orthodox Patriarch of Jerusalem has been Theophilos III...
. A second-century
Christianity in the 2nd century
The 2nd century of Christianity was largely the time of the Apostolic Fathers who were the students of the apostles of Jesus, though there is some overlap as John the Apostle may have survived into the 2nd century and the early Apostolic Father Clement of Rome is said to have died at the end of the...
church historian, Hegesippus
Hegesippus (chronicler)
Saint Hegesippus , was a Christian chronicler of the early Church who may have been a Jewish convert and certainly wrote against heresies of the Gnostics and of Marcion...
, wrote that the Sanhedrin
Sanhedrin
The Sanhedrin was an assembly of twenty-three judges appointed in every city in the Biblical Land of Israel.The Great Sanhedrin was the supreme court of ancient Israel made of 71 members...
martyred him in 62.
In 66, the Jews revolted against Rome. Rome besieged Jerusalem for four years, and the city fell in 70. The city was destroyed, including the Temple, and the population was mostly killed or removed. Though, according to Epiphanius of Salamis
Epiphanius of Salamis
Epiphanius of Salamis was bishop of Salamis at the end of the 4th century. He is considered a saint and a Church Father by both the Eastern Orthodox and Catholic Churches. He gained a reputation as a strong defender of orthodoxy...
, the Cenacle
Cenacle
The Cenacle , also known as the "Upper Room", is the term used for the site of The Last Supper. The word is a derivative of the Latin word cena, which means dinner....
survived at least to Hadrian
Hadrian
Hadrian , was Roman Emperor from 117 to 138. He is best known for building Hadrian's Wall, which marked the northern limit of Roman Britain. In Rome, he re-built the Pantheon and constructed the Temple of Venus and Roma. In addition to being emperor, Hadrian was a humanist and was philhellene in...
's visit in 130. A scattered population survived. Traditionally it is believed the Jerusalem Christians waited out the Jewish–Roman wars in Pella
Pella, Jordan
Pella is a village and the site of ancient ruins in northwestern Jordan. It is half an hour by car from Irbid, in the north of the country....
in the Decapolis
Decapolis
The Decapolis was a group of ten cities on the eastern frontier of the Roman Empire in Judea and Syria. The ten cities were not an official league or political unit, but they were grouped together because of their language, culture, location, and political status...
. The Sanhedrin relocated to Jamnia
Council of Jamnia
The Council of Jamnia or Council of Yavne is a hypothetical late 1st-century council at which it is postulated the canon of the Hebrew Bible was finalized....
. Prophecies of the Second Temple's destruction are found in the synoptics
Synoptic Gospels
The gospels of Matthew, Mark, and Luke are known as the Synoptic Gospels because they include many of the same stories, often in the same sequence, and sometimes exactly the same wording. This degree of parallelism in content, narrative arrangement, language, and sentence structures can only be...
.
In the 2nd century, Hadrian
Hadrian
Hadrian , was Roman Emperor from 117 to 138. He is best known for building Hadrian's Wall, which marked the northern limit of Roman Britain. In Rome, he re-built the Pantheon and constructed the Temple of Venus and Roma. In addition to being emperor, Hadrian was a humanist and was philhellene in...
rebuilt Jerusalem as a pagan
Religion in ancient Rome
Religion in ancient Rome encompassed the religious beliefs and cult practices regarded by the Romans as indigenous and central to their identity as a people, as well as the various and many cults imported from other peoples brought under Roman rule. Romans thus offered cult to innumerable deities...
city called Aelia Capitolina
Aelia Capitolina
Aelia Capitolina was a city built by the emperor Hadrian, and occupied by a Roman colony, on the site of Jerusalem, which was in ruins since 70 AD, leading in part to the Bar Kokhba revolt of 132–136.-Politics:...
, erecting statues of Jupiter and himself
Imperial cult (ancient Rome)
The Imperial cult of ancient Rome identified emperors and some members of their families with the divinely sanctioned authority of the Roman State...
on the site of the former Jewish Temple, the Temple Mount
Temple Mount
The Temple Mount, known in Hebrew as , and in Arabic as the Haram Ash-Sharif , is one of the most important religious sites in the Old City of Jerusalem. It has been used as a religious site for thousands of years...
. Bar Cochba led an unsuccessful revolt as a Messiah, but Christians refused to acknowledge him as such. When Bar Cochba was defeated, Hadrian barred Jews from the city, except for the day of Tisha B'Av
Tisha B'Av
|Av]],") is an annual fast day in Judaism, named for the ninth day of the month of Av in the Hebrew calendar. The fast commemorates the destruction of both the First Temple and Second Temple in Jerusalem, which occurred about 655 years apart, but on the same Hebrew calendar date...
, thus the subsequent Jerusalem bishops were gentiles ("uncircumcised") for the first time.
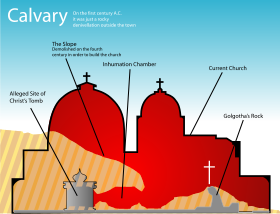
The general significance of Jerusalem to Christians
Jerusalem in Christianity
For Christians, Jerusalem's place in the ministry of Jesus and the Apostolic Age gives it great importance, in addition to its place in the Old Testament, the Hebrew Bible.-Jerusalem in the New Testament and early Christianity:...
entered a period of decline during the Persecution of Christians in the Roman Empire, but resumed again with the pilgrimage
Christian pilgrimage
Christian pilgrimage was first made to sites connected with the ministry of Jesus. Surviving descriptions of Christian pilgrimages to the Holy Land and Jerusalem date from the 4th century, when pilgrimage was encouraged by church fathers like Saint Jerome and established by Helena, the mother of...
of Helena (the mother of Constantine the Great) to the Holy Land
Holy Land
The Holy Land is a term which in Judaism refers to the Kingdom of Israel as defined in the Tanakh. For Jews, the Land's identifiction of being Holy is defined in Judaism by its differentiation from other lands by virtue of the practice of Judaism often possible only in the Land of Israel...
c. 326–28. According to the church historian Socrates of Constantinople, Helena (with the assistance of Bishop Macarius of Jerusalem
Macarius of Jerusalem
Saint Macarius of Jerusalem was Bishop of Jerusalem from 312 to shortly before 335, according to Sozomen.St. Athanasius, in one of his orations against Arianism, refers to St. Macarius as an example of "the honest and simple style of apostolical men." The date 312 for Macarius's accession to the...
) claimed to have found the cross of Christ
True Cross
The True Cross is the name for physical remnants which, by a Christian tradition, are believed to be from the cross upon which Jesus was crucified.According to post-Nicene historians, Socrates Scholasticus and others, the Empress Helena The True Cross is the name for physical remnants which, by a...
, after removing a Temple to Venus
Venus (mythology)
Venus is a Roman goddess principally associated with love, beauty, sex,sexual seduction and fertility, who played a key role in many Roman religious festivals and myths...
(attributed to Hadrian) that had been built over the site. (For that reason she is seen as the Patron Saint
Patron saint
A patron saint is a saint who is regarded as the intercessor and advocate in heaven of a nation, place, craft, activity, class, clan, family, or person...
of Archaeologists
Archaeology
Archaeology, or archeology , is the study of human society, primarily through the recovery and analysis of the material culture and environmental data that they have left behind, which includes artifacts, architecture, biofacts and cultural landscapes...
.) Jerusalem had received special recognition in Canon VII of Nicaea
First Council of Nicaea
The First Council of Nicaea was a council of Christian bishops convened in Nicaea in Bithynia by the Roman Emperor Constantine I in AD 325...
in 325. The traditional founding date for the Brotherhood of the Holy Sepulchre
Brotherhood of the Holy Sepulchre
The Brotherhood of the Holy Sepulchre, or The Holy Community of the All-Holy Sepulchre, is the Orthodox monastic fraternity that for centuries has guarded and protected the Christian Holy places in the Holy Land...
(which guards the Christian Holy places in the Holy Land
Holy Land
The Holy Land is a term which in Judaism refers to the Kingdom of Israel as defined in the Tanakh. For Jews, the Land's identifiction of being Holy is defined in Judaism by its differentiation from other lands by virtue of the practice of Judaism often possible only in the Land of Israel...
) is 313 which corresponds with the date of the Edict of Milan
Edict of Milan
The Edict of Milan was a letter signed by emperors Constantine I and Licinius that proclaimed religious toleration in the Roman Empire...
which legalized Christianity in the Roman Empire. Jerusalem was later named as one of the Pentarchy
Pentarchy
Pentarchy is a term in the history of Christianity for the idea of universal rule over all Christendom by the heads of five major episcopal sees, or patriarchates, of the Roman Empire: Rome, Constantinople, Alexandria, Antioch, and Jerusalem...
, but this was never accepted by the church of Rome. See also East–West Schism#Prospects for reconciliation.
Antioch
AntiochAntioch
Antioch on the Orontes was an ancient city on the eastern side of the Orontes River. It is near the modern city of Antakya, Turkey.Founded near the end of the 4th century BC by Seleucus I Nicator, one of Alexander the Great's generals, Antioch eventually rivaled Alexandria as the chief city of the...
, a major center of Hellenistic Greece
Hellenistic Greece
In the context of Ancient Greek art, architecture, and culture, Hellenistic Greece corresponds to the period between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the annexation of the classical Greek heartlands by Rome in 146 BC...
, and the third-most important city of the Roman Empire, then part of Syria province
Syria (Roman province)
Syria was a Roman province, annexed in 64 BC by Pompey, as a consequence of his military presence after pursuing victory in the Third Mithridatic War. It remained under Roman, and subsequently Byzantine, rule for seven centuries, until 637 when it fell to the Islamic conquests.- Principate :The...
, today a ruin near Antakya
Antakya
Antakya is the seat of the Hatay Province in southern Turkey, near the border with Syria. The mayor is Lütfü Savaş.Known as Antioch in ancient times, the city has historical significance for Christianity, as it was the place where the followers of Jesus Christ were called Christians for the first...
, Turkey, was where Christians were first so-called and also the location of the Incident at Antioch. It was the site of an early church, traditionally said to be founded by Peter who is considered the first bishop. The Gospel of Matthew
Gospel of Matthew
The Gospel According to Matthew is one of the four canonical gospels, one of the three synoptic gospels, and the first book of the New Testament. It tells of the life, ministry, death, and resurrection of Jesus of Nazareth...
and the Apostolic Constitutions
Apostolic Constitutions
The Apostolic Constitutions is a Christian collection of eight treatises which belongs to genre of the Church Orders. The work can be dated from 375 to 380 AD. The provenience is usually regarded as Syria, probably Antioch...
may have been written there. The church father Ignatius of Antioch
Ignatius of Antioch
Ignatius of Antioch was among the Apostolic Fathers, was the third Bishop of Antioch, and was a student of John the Apostle. En route to his martyrdom in Rome, Ignatius wrote a series of letters which have been preserved as an example of very early Christian theology...
was its third bishop. The School of Antioch, founded in 270, was one of two major centers of early church learning. The Curetonian Gospels
Curetonian Gospels
The Curetonian Gospels, designated by the siglum syrcur, are contained in a manuscript of the four gospels of the New Testament in Old Syriac, a translation from the Aramaic originals, according to William Cureton differing considerably from the canonical Greek texts, with which they had been...
and the Syriac Sinaiticus are two early (pre-Peshitta
Peshitta
The Peshitta is the standard version of the Bible for churches in the Syriac tradition.The Old Testament of the Peshitta was translated into Syriac from the Hebrew, probably in the 2nd century AD...
) New Testament text types associated with Syriac Christianity
Syriac Christianity
Syriac or Syrian Christianity , the Syriac-speaking Christians of Mesopotamia, comprises multiple Christian traditions of Eastern Christianity. With a history going back to the 1st Century AD, in modern times it is represented by denominations primarily in the Middle East and in Kerala, India....
. It was one of the three whose bishops were recognized at the First Council of Nicaea
First Council of Nicaea
The First Council of Nicaea was a council of Christian bishops convened in Nicaea in Bithynia by the Roman Emperor Constantine I in AD 325...
(325) as exercising jurisdiction over the adjoining territories.
Alexandria
AlexandriaAlexandria
Alexandria is the second-largest city of Egypt, with a population of 4.1 million, extending about along the coast of the Mediterranean Sea in the north central part of the country; it is also the largest city lying directly on the Mediterranean coast. It is Egypt's largest seaport, serving...
, in the Nile delta
Nile Delta
The Nile Delta is the delta formed in Northern Egypt where the Nile River spreads out and drains into the Mediterranean Sea. It is one of the world's largest river deltas—from Alexandria in the west to Port Said in the east, it covers some 240 km of Mediterranean coastline—and is a rich...
, was established by Alexander the Great. Its famous libraries were a center of Hellenistic learning. The Septuagint translation of the Old Testament began there and the Alexandrian text-type
Alexandrian text-type
The Alexandrian text-type , associated with Alexandria, is one of several text-types used in New Testament textual criticism to describe and group the textual character of biblical manuscripts...
is recognized by scholars as one of the earliest New Testament types. It had a significant Jewish population, of which Philo of Alexandria is probably its most known author. It produced superior scripture and notable church fathers, such as Clement, Origen, and Athanasius, also noteworthy were the nearby Desert Fathers
Desert Fathers
The Desert Fathers were hermits, ascetics, monks, and nuns who lived mainly in the Scetes desert of Egypt beginning around the third century AD. The most well known was Anthony the Great, who moved to the desert in 270–271 and became known as both the father and founder of desert monasticism...
. By the end of the era, Alexandria, Rome, and Antioch were accorded authority over nearby metropolitans
Metropolitan bishop
In Christian churches with episcopal polity, the rank of metropolitan bishop, or simply metropolitan, pertains to the diocesan bishop or archbishop of a metropolis; that is, the chief city of a historical Roman province, ecclesiastical province, or regional capital.Before the establishment of...
. The Council of Nicaea in canon VI affirmed Alexandria's traditional authority over Egypt, Libya, and Pentapolis (North Africa) (the Diocese of Egypt) and probably granted Alexandria the right to declare a universal date for the observance of Easter
Easter
Easter is the central feast in the Christian liturgical year. According to the Canonical gospels, Jesus rose from the dead on the third day after his crucifixion. His resurrection is celebrated on Easter Day or Easter Sunday...
, see also Easter controversy
Easter controversy
The Easter controversy is a series of controversies about the proper date to celebrate the Christian holiday of Easter. To date, there are four distinct historical phases of the dispute and the dispute has yet to be resolved...
.
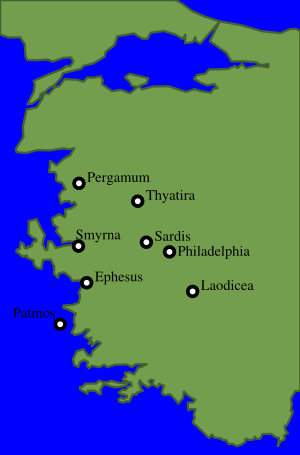
Anatolia


John the Apostle
John the Apostle, John the Apostle, John the Apostle, (Aramaic Yoħanna, (c. 6 - c. 100) was one of the Twelve Apostles of Jesus. He was the son of Zebedee and Salome, and brother of James, another of the Twelve Apostles...
was strong in Anatolia
Anatolia
Anatolia is a geographic and historical term denoting the westernmost protrusion of Asia, comprising the majority of the Republic of Turkey...
(the near-east, part of modern Turkey
Turkey
Turkey , known officially as the Republic of Turkey , is a Eurasian country located in Western Asia and in East Thrace in Southeastern Europe...
, the western part was called the Roman province of Asia). The gospel of John was likely written in Ephesus
Ephesus
Ephesus was an ancient Greek city, and later a major Roman city, on the west coast of Asia Minor, near present-day Selçuk, Izmir Province, Turkey. It was one of the twelve cities of the Ionian League during the Classical Greek era...
. According to the New Testament, the Apostle Paul was from Tarsus
Tarsus (city)
Tarsus is a historic city in south-central Turkey, 20 km inland from the Mediterranean Sea. It is part of the Adana-Mersin Metropolitan Area, the fourth-largest metropolitan area in Turkey with a population of 2.75 million...
(in south-central Anatolia) and his missionary journeys were primarily in Anatolia. The Book of Revelation
Book of Revelation
The Book of Revelation is the final book of the New Testament. The title came into usage from the first word of the book in Koine Greek: apokalupsis, meaning "unveiling" or "revelation"...
, believed to be authored by John of Patmos
John of Patmos
John of Patmos is the name given, in the Book of Revelation, as the author of the apocalyptic text that is traditionally cannonized in the New Testament...
(a Greek island about 30 miles off the Anatolian coast), mentions Seven churches of Asia
Seven churches of Asia
The Seven Churches of Revelation, also known as The Seven Churches of the Apocalypse and The Seven Churches of Asia , are seven major churches of Early Christianity, as mentioned in the New Testament Book of Revelation and written to by Ignatius of Antioch...
. The First Epistle of Peter
First Epistle of Peter
The First Epistle of Peter, usually referred to simply as First Peter and often written 1 Peter, is a book of the New Testament. The author claims to be Saint Peter the apostle, and the epistle was traditionally held to have been written during his time as bishop of Rome or Bishop of Antioch,...
is addressed to Anatolian regions. On the southeast shore of the Black Sea
Black Sea
The Black Sea is bounded by Europe, Anatolia and the Caucasus and is ultimately connected to the Atlantic Ocean via the Mediterranean and the Aegean seas and various straits. The Bosphorus strait connects it to the Sea of Marmara, and the strait of the Dardanelles connects that sea to the Aegean...
, Pontus was a Greek colony mentioned three times in the New Testament, inhabitants of Pontus were some of the very first converts to Christianity. Pliny, governor in 110
Pliny the Younger on Christ
Pliny the Younger's evidence for the historical existence of Christ and early Christians is found in one of his collected letters. Pliny was a governor of the Roman province of Bithynia and Pontus, as well as a priest of the traditional religion of ancient Rome and a jurist...
, in his letters, addressed Christians in Pontus. Of the extant letters of Ignatius of Antioch considered authentic, five of seven are to Anatolian cities, the sixth is to Polycarp
Polycarp
Saint Polycarp was a 2nd century Christian bishop of Smyrna. According to the Martyrdom of Polycarp, he died a martyr, bound and burned at the stake, then stabbed when the fire failed to touch him...
. Smyrna
Smyrna
Smyrna was an ancient city located at a central and strategic point on the Aegean coast of Anatolia. Thanks to its advantageous port conditions, its ease of defence and its good inland connections, Smyrna rose to prominence. The ancient city is located at two sites within modern İzmir, Turkey...
was home to Polycarp, the bishop who reportedly knew the Apostle John personally, and probably also to his student Irenaeus
Irenaeus
Saint Irenaeus , was Bishop of Lugdunum in Gaul, then a part of the Roman Empire . He was an early church father and apologist, and his writings were formative in the early development of Christian theology...
. Papias of Hierapolis is also believed to have been a student of John the Apostle. In the 2nd century, Anatolia was home to Quartodecimanism
Quartodecimanism
Quartodecimanism refers to the custom of some early Christians celebrating Passover beginning with the eve of the 14th day of Nisan , which at dusk is Biblically the "Lord's passover".The modern Jewish Passover and Feast of Unleavened Bread is seven days, starting with the sunset at...
, Montanism
Montanism
Montanism was an early Christian movement of the late 2nd century, later referred to by the name of its founder, Montanus, but originally known by its adherents as the New Prophecy...
, Marcion of Sinope
Marcion of Sinope
Marcion of Sinope was a bishop in early Christianity. His theology, which rejected the deity described in the Jewish Scriptures as inferior or subjugated to the God proclaimed in the Christian gospel, was denounced by the Church Fathers and he was excommunicated...
, and Melito of Sardis
Melito of Sardis
Melito of Sardis was the bishop of Sardis near Smyrna in western Anatolia, and a great authority in Early Christianity: Jerome, speaking of the Old Testament canon established by Melito, quotes Tertullian to the effect that he was esteemed a prophet by many of the faithful...
who recorded an early Christian Biblical canon
Development of the Christian Biblical canon
The Christian Biblical canon is the set of books Christians regard as divinely inspired and constituting the Christian Bible. Books included in the Christian Biblical canons of both the Old and New Testament were decided at the Council of Trent , by the Thirty-Nine Articles , the Westminster...
. After the Crisis of the Third Century
Crisis of the Third Century
The Crisis of the Third Century was a period in which the Roman Empire nearly collapsed under the combined pressures of invasion, civil war, plague, and economic depression...
, Nicomedia
Nicomedia
Nicomedia was an ancient city in what is now Turkey, founded in 712/11 BC as a Megarian colony and was originally known as Astacus . After being destroyed by Lysimachus, it was rebuilt by Nicomedes I of Bithynia in 264 BC under the name of Nicomedia, and has ever since been one of the most...
became the capital of the Eastern Roman Empire
History of the Eastern Roman Empire
This article continues the History of the Roman Empire, referring mainly to the Eastern Roman or Byzantine Empire. It begins with the division of the Roman Empire by Diocletian in 286 AD, and the founding of Constantinople as the capital of the Roman Empire by Constantine I in 330, while it...
in 286. The Synod of Ancyra
Synod of Ancyra
The Synod of Ancyra was an ecclesiastical council, or synod, convened in Ancyra , the seat of the Roman administration for the province of Galatia, in 314...
was held in 314. In 325 the emperor Constantine
Constantine I and Christianity
During the reign of the Emperor Constantine the Great, Christianity became the dominant religion of the Roman Empire. Constantine, also known as Constantine I, had a significant religious experience following his victory at the Battle of Milvian Bridge in 312...
convoked the first Christian ecumenical council
Ecumenical council
An ecumenical council is a conference of ecclesiastical dignitaries and theological experts convened to discuss and settle matters of Church doctrine and practice....
in Nicaea and in 330 moved the capital of the reunified empire to Byzantium
Byzantium
Byzantium was an ancient Greek city, founded by Greek colonists from Megara in 667 BC and named after their king Byzas . The name Byzantium is a Latinization of the original name Byzantion...
(also an early Christian center and just across the Bosporus
Bosporus
The Bosphorus or Bosporus , also known as the Istanbul Strait , is a strait that forms part of the boundary between Europe and Asia. It is one of the Turkish Straits, along with the Dardanelles...
from Anatolia, later called Constantinople
Constantinople
Constantinople was the capital of the Roman, Eastern Roman, Byzantine, Latin, and Ottoman Empires. Throughout most of the Middle Ages, Constantinople was Europe's largest and wealthiest city.-Names:...
), referred to as the Byzantine Empire
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire was the Eastern Roman Empire during the periods of Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, centred on the capital of Constantinople. Known simply as the Roman Empire or Romania to its inhabitants and neighbours, the Empire was the direct continuation of the Ancient Roman State...
, which lasted till 1453. The First seven Ecumenical Councils
First seven Ecumenical Councils
In the history of Christianity, the first seven Ecumenical Councils, from the First Council of Nicaea to the Second Council of Nicaea , represent an attempt to reach an orthodox consensus and to establish a unified Christendom as the State church of the Roman Empire...
were held either in Western Anatolia or Constantinople.
Caesarea
Caesarea, on the seacoast just northwest of Jerusalem, at first Caesarea Maritima, then after 133 Caesarea Palaestina, was built by Herod the GreatHerod the Great
Herod , also known as Herod the Great , was a Roman client king of Judea. His epithet of "the Great" is widely disputed as he is described as "a madman who murdered his own family and a great many rabbis." He is also known for his colossal building projects in Jerusalem and elsewhere, including his...
, c.25-13 BC, and was the capital of Iudaea province
Iudaea Province
Judaea or Iudaea are terms used by historians to refer to the Roman province that extended over parts of the former regions of the Hasmonean and Herodian kingdoms of Israel...
(6-132) and later Palaestina Prima. It was there that Peter baptized the centurion Cornelius, considered the first gentile convert. Paul sought refuge there, once staying at the house of Philip the Evangelist
Philip the Evangelist
Saint Philip the Evangelist appears several times in the Acts of the Apostles. He was one of the Seven Deacons chosen to care for the poor of the Christian community in Jerusalem . He preached and performed miracles in Samaria, converted Simon Magus, and met and baptised an Ethiopian man, an...
, and later being imprisoned there for two years (estimated to be 57-59). The Apostolic Constitutions
Apostolic Constitutions
The Apostolic Constitutions is a Christian collection of eight treatises which belongs to genre of the Church Orders. The work can be dated from 375 to 380 AD. The provenience is usually regarded as Syria, probably Antioch...
(7.46) state that the first Bishop of Caesarea was Zacchaeus the Publican
Zacchaeus
Zacchaeus , according to chapter 19 of the gospel of Luke, was a superintendent of customs; a chief tax-gatherer at Jericho...
but the Catholic Encyclopedia
Catholic Encyclopedia
The Catholic Encyclopedia, also referred to as the Old Catholic Encyclopedia and the Original Catholic Encyclopedia, is an English-language encyclopedia published in the United States. The first volume appeared in March 1907 and the last three volumes appeared in 1912, followed by a master index...
claims that: "...there is no record of any bishops of Caesarea until the second century. At the end of this century a council was held there to regulate the celebration of Easter
Easter controversy
The Easter controversy is a series of controversies about the proper date to celebrate the Christian holiday of Easter. To date, there are four distinct historical phases of the dispute and the dispute has yet to be resolved...
." According to another Catholic Encyclopedia article, after Hadrian's siege of Jerusalem (c.133), Caesarea became the metropolitan see with the bishop of Jerusalem as one of its "suffragans"
Suffragan bishop
A suffragan bishop is a bishop subordinate to a metropolitan bishop or diocesan bishop. He or she may be assigned to an area which does not have a cathedral of its own.-Anglican Communion:...
(subordinates). Origen
Origen
Origen , or Origen Adamantius, 184/5–253/4, was an early Christian Alexandrian scholar and theologian, and one of the most distinguished writers of the early Church. As early as the fourth century, his orthodoxy was suspect, in part because he believed in the pre-existence of souls...
(d.254) compiled his Hexapla
Hexapla
Hexapla is the term for an edition of the Bible in six versions. Especially it applies to the edition of the Old Testament compiled by Origen of Alexandria, which placed side by side:#Hebrew...
there and it held a famous library and theological school
Theological Library of Caesarea Maritima
The Theological Library of Caesarea Maritima or simply the Library of Caesarea was the library of the Christians of Caesarea Maritima in Palestine in ancient times.-History:...
, St. Pamphilus
Pamphilus of Caesarea
Saint Pamphilus , was a presbyter of Caesarea and chief among Catholic Biblical scholars of his generation...
(d.309) was a noted scholar-priest. St. Gregory the Wonder-Worker (d.270), St. Basil the Great (d.379), and St. Jerome (d.420) visited and studied at the library which was later destroyed, probably by the Persians
Sassanid Empire
The Sassanid Empire , known to its inhabitants as Ērānshahr and Ērān in Middle Persian and resulting in the New Persian terms Iranshahr and Iran , was the last pre-Islamic Persian Empire, ruled by the Sasanian Dynasty from 224 to 651...
in 614 or the Saracens around 637. The first major church historian, Eusebius of Caesarea
Eusebius of Caesarea
Eusebius of Caesarea also called Eusebius Pamphili, was a Roman historian, exegete and Christian polemicist. He became the Bishop of Caesarea in Palestine about the year 314. Together with Pamphilus, he was a scholar of the Biblical canon...
, was a bishop, c.314-339. F. J. A. Hort
Fenton John Anthony Hort
Fenton John Anthony Hort was an Irish theologian and editor, with Brooke Westcott of a critical edition of The New Testament in the Original Greek.-Life:...
and Adolf von Harnack
Adolf von Harnack
Adolf von Harnack , was a German theologian and prominent church historian.He produced many religious publications from 1873-1912....
have argued that the Nicene Creed
Nicene Creed
The Nicene Creed is the creed or profession of faith that is most widely used in Christian liturgy. It is called Nicene because, in its original form, it was adopted in the city of Nicaea by the first ecumenical council, which met there in the year 325.The Nicene Creed has been normative to the...
originated in Caesarea. The Caesarean text-type
Caesarean text-type
Caesarean text-type is the term proposed by certain scholars to denote a consistent pattern of variant readings that is claimed to be apparent in certain Greek manuscripts of the four Gospels, but which is not found in any of the other commonly recognized New Testament text-types; the Byzantine...
is recognized by scholars as one of the earliest New Testament types.
Damascus

Damascus
Damascus , commonly known in Syria as Al Sham , and as the City of Jasmine , is the capital and the second largest city of Syria after Aleppo, both are part of the country's 14 governorates. In addition to being one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world, Damascus is a major...
is the capital of Syria
Syria
Syria , officially the Syrian Arab Republic , is a country in Western Asia, bordering Lebanon and the Mediterranean Sea to the West, Turkey to the north, Iraq to the east, Jordan to the south, and Israel to the southwest....
and claims to be the oldest continuously inhabited city in the world. According to the New Testament, the Apostle Paul was converted on the Road to Damascus. In the three accounts , he is described as being led by those he was traveling with, blinded by the light, to Damascus where his sight was restored by a disciple called Ananias
Ananias of Damascus
Ananias , was a disciple of Jesus at Damascus mentioned in the Acts of the Apostles in the Bible, which describes how he was sent by Jesus to restore the sight of "Saul, of Tarsus" and provide him with additional instruction in the way of the...
(who, according to the Catholic Encyclopedia, is thought to have been the first Bishop of Damascus) then he was baptized.
Cyprus

Paphos
Paphos , sometimes referred to as Pafos, is a coastal city in the southwest of Cyprus and the capital of Paphos District. In antiquity, two locations were called Paphos: Old Paphos and New Paphos. The currently inhabited city is New Paphos. It lies on the Mediterranean coast, about west of the...
was the capital of the island of Cyprus
Cyprus
Cyprus , officially the Republic of Cyprus , is a Eurasian island country, member of the European Union, in the Eastern Mediterranean, east of Greece, south of Turkey, west of Syria and north of Egypt. It is the third largest island in the Mediterranean Sea.The earliest known human activity on the...
during the Roman years and seat of a Roman commander. In 45 AD, the apostles Paul and Barnabas
Barnabas
Barnabas , born Joseph, was an Early Christian, one of the earliest Christian disciples in Jerusalem. In terms of culture and background, he was a Hellenised Jew, specifically a Levite. Named an apostle in , he and Saint Paul undertook missionary journeys together and defended Gentile converts...
(according to the Catholic Encyclopedia "a native of the island") came to Cyprus and reached Paphos preaching the Word of Christ, see also . The apostles were persecuted by the Romans but eventually succeeded to convince the Roman commander Sergius Paulus
Sergius Paulus
Lucius Sergius Paullus was a Proconsul of Cyprus under Claudius . He appears in Acts , where in Paphos Paul, accompanied by Barnabas and John Mark, overcame the attempts of Bar-Jesus or Elymas and converted Sergius to Christianity....
into renouncing his old religion in favour of Christianity. 5 years later, Barnabas returned to the Cypriot town of Salamis
Salamis, Cyprus
Salamis was an ancient Greek city-state on the east coast of Cyprus, at the mouth of the river Pedieos, 6 km north of modern Famagusta. According to tradition the founder of Salamis was Teucer, son of Telamon, who could not return home after the Trojan war because he had failed to avenge his...
, where he became bishop and oversaw the spread of Christianity to the island.
Greece
ThessalonikiThessaloniki
Thessaloniki , historically also known as Thessalonica, Salonika or Salonica, is the second-largest city in Greece and the capital of the region of Central Macedonia as well as the capital of the Decentralized Administration of Macedonia and Thrace...
, the major northern Greek city where it is believed Christianity was founded by Paul, thus an Apostolic See
Apostolic See
In Christianity, an apostolic see is any episcopal see whose foundation is attributed to one or more of the apostles of Jesus.Out of the many such sees, five acquired special importance in Chalcedonian Christianity and became classified as the Pentarchy in Eastern Orthodox Christianity...
, and the surrounding regions of Macedonia
Macedonia (region)
Macedonia is a geographical and historical region of the Balkan peninsula in southeastern Europe. Its boundaries have changed considerably over time, but nowadays the region is considered to include parts of five Balkan countries: Greece, the Republic of Macedonia, Bulgaria, Albania, Serbia, as...
, Western
Western Thrace
Western Thrace or simply Thrace is a geographic and historical region of Greece, located between the Nestos and Evros rivers in the northeast of the country. Together with the regions of Macedonia and Epirus, it is often referred to informally as northern Greece...
and Eastern Thrace, and Epirus
Epirus
The name Epirus, from the Greek "Ήπειρος" meaning continent may refer to:-Geographical:* Epirus - a historical and geographical region of the southwestern Balkans, straddling modern Greece and Albania...
, which also extend into the neighboring Balkan states of Albania and Bulgaria, were early centers of Christianity. Of note are Paul's Epistles to the Thessalonians and to Philippi
Philippi
Philippi was a city in eastern Macedonia, established by Philip II in 356 BC and abandoned in the 14th century after the Ottoman conquest...
, which is often considered the first contact of Christianity with Europe. The Apostolic Father Polycarp
Polycarp
Saint Polycarp was a 2nd century Christian bishop of Smyrna. According to the Martyrdom of Polycarp, he died a martyr, bound and burned at the stake, then stabbed when the fire failed to touch him...
wrote a letter to the Philippians
Polycarp's letter to the Philippians
The Letter to the Philippians is an epistle composed around 110 to 140 ADby one of the Apostolic Fathers, Polycarp of Smyrna from Antioch, to the early Christian church in Philippi...
, c.125.
Nicopolis
Nicopolis
Nicopolis — or Actia Nicopolis — was an ancient city of Epirus, founded 31 BC by Octavian in memory of his victory over Antony and Cleopatra at Actium the previous year. It was later the capital of Epirus Vetus...
was a city in the Roman province of Epirus Vetus, today a ruin on the northern part of the western Greek coast. According to the Catholic Encyclopedia: "St. Paul intended going there and it is possible that even then it numbered some Christians among its population; Origen
Origen
Origen , or Origen Adamantius, 184/5–253/4, was an early Christian Alexandrian scholar and theologian, and one of the most distinguished writers of the early Church. As early as the fourth century, his orthodoxy was suspect, in part because he believed in the pre-existence of souls...
(c. 185–254) sojourned there for a while (Eusebius, Church History VI.16)."
Ancient Corinth, today a ruin near modern Corinth
Corinth
Corinth is a city and former municipality in Corinthia, Peloponnese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Corinth, of which it is the seat and a municipal unit...
in southern Greece, was an early center of Christianity. According to the Catholic Encyclopedia: "St. Paul preached successfully at Corinth, where he lived in the house of Aquila and Priscilla , where Silas
Silas
Saint Silas or Saint Silvanus was a leading member of the Early Christian community, who later accompanied Paul in some of his missionary journeys....
and Timothy soon joined him. After his departure he was replaced by Apollo
Apollos
Saint Apollos is an apostle who is also a 1st century Alexandrian Jewish Christian mentioned several times in the New Testament...
, who had been sent from Ephesus by Priscilla. The Apostle visited Corinth at least once more. He wrote to the Corinthians in 57 from Ephesus
First Epistle to the Corinthians
The first epistle of Paul the apostle to the Corinthians, often referred to as First Corinthians , is the seventh book of the New Testament of the Bible...
, and then from Macedonia in the same year, or in 58
Second Epistle to the Corinthians
The second epistle of Paul the apostle to the Corinthians, often referred to as Second Corinthians , is the eighth book of the New Testament of the Bible...
. The famous letter of St. Clement of Rome to the Corinthian church
First Epistle of Clement
The First Epistle of Clement, is a letter addressed to the Christians in the city of Corinth. The letter dates from the late 1st or early 2nd century, and ranks with Didache as one of the earliest — if not the earliest — of extant Christian documents outside the canonical New Testament...
(about 96) exhibits the earliest evidence concerning the ecclesiastical primacy of the Roman Church. Besides St. Apollo, Lequien (II, 155) mentions forty-three bishops: among them, St. Sosthenes
Sosthenes
Sosthenes was the chief ruler of the synagogue at Corinth, who, according to the New Testament, was seized and beaten by the mob in the presence of Gallio, the Roman governor, when he refused to proceed against Paul at the instigation of the Jews...
(?), the disciple of St. Paul, St. Dionysius
Saint Dionysius (disambiguation)
Saint Dionysius may refer to:* Pope Saint Dionysius , Greek pope* Saint Dionysius of Alexandria , Oriental Orthodox Patriarch* Saint Dionysius of Paris , Christian martyr...
; Paul, brother of St. Peter ..."
Athens
Athens
Athens , is the capital and largest city of Greece. Athens dominates the Attica region and is one of the world's oldest cities, as its recorded history spans around 3,400 years. Classical Athens was a powerful city-state...
, the capital and largest city in Greece, was visited by Paul. According to the Catholic Encyclopedia: Paul "came to Athens from Berœa of Macedonia
Beroea
Beroea is:*Veria , a city in northern Greece*a former name of Aleppo, Syria*mentioned in Thucydides, History of the Peloponnesian War; I,61,2...
, coming probably by water and landing in the Peiræevs
Piraeus
Piraeus is a city in the region of Attica, Greece. Piraeus is located within the Athens Urban Area, 12 km southwest from its city center , and lies along the east coast of the Saronic Gulf....
, the harbour of Athens. This was about the year 53. Having arrived at Athens, he at once sent for Silas and Timotheos who had remained behind in Berœa. While awaiting the coming of these he tarried in Athens, viewing the idolatrous city, and frequenting the synagogue
Synagogue
A synagogue is a Jewish house of prayer. This use of the Greek term synagogue originates in the Septuagint where it sometimes translates the Hebrew word for assembly, kahal...
; for there were already Jews in Athens. ... It seems that a Christian community was rapidly formed, although for a considerable time it did not possess a numerous membership. The commoner tradition names the Areopagite
Dionysius the Areopagite
Dionysius the Areopagite was a judge of the Areopagus who, as related in the Acts of the Apostles, , was converted to Christianity by the preaching of the Apostle Paul during the Areopagus sermon...
as the first head and bishop of the Christian Athenians. Another tradition, however, gives this honour to Hierotheos the Thesmothete
Hierotheos the Thesmothete
Hierotheos the Thesmothete is the reputed first head and bishop of the Christian Athenians. The title thesmothete means ruler, or junior archon, of Athens .- Biography :...
. The successors of the first bishop were not all Athenians by lineage. They are catalogued as Narkissos, Publius, and Quadratus
Quadratus of Athens
Saint Quadratus of Athens is said to have been the first of the Christian apologists. He is said by Eusebius of Caesarea to have been a disciple of the Apostles...
. Narkissos is stated to have come from Palestine, and Publius from Malta
Saint Publius
Saint Publius is the first maltese Saint. He is venerated as the first Bishop of Malta. Publius' conversion led to Malta being the first Christian nation in the West, and one of the first in the world....
. In some lists Narkissos is omitted. Quadratus is revered for having contributed to early Christian literature by writing an apology
Christian apologetics
Christian apologetics is a field of Christian theology that aims to present a rational basis for the Christian faith, defend the faith against objections, and expose the perceived flaws of other world views...
, which he addressed to the Emperor Hadrian
Hadrian
Hadrian , was Roman Emperor from 117 to 138. He is best known for building Hadrian's Wall, which marked the northern limit of Roman Britain. In Rome, he re-built the Pantheon and constructed the Temple of Venus and Roma. In addition to being emperor, Hadrian was a humanist and was philhellene in...
. This was on the occasion of Hadrian's visit to Athens. Another Athenian who defended Christianity in writing at a somewhat later time was Aristeides. His apology was directed to the Emperor Marcus Aurelius. Athenagoras
Athenagoras of Athens
Athenagoras was a Father of the Church, a Proto-orthodox Christian apologist who lived during the second half of the 2nd century of whom little is known for certain, besides that he was Athenian , a philosopher, and a convert to Christianity. In his writings he styles himself as "Athenagoras, the...
also wrote an apology. In the second century there must have been a considerable community of Christians in Athens, for Hygeinos, Bishop of Rome
Pope Hyginus
Pope Saint Hyginus was bishop of Rome from about 136 or 138 to about 140 or 142. Tradition holds that during his papacy he determined the various prerogatives of the clergy and defined the grades of the ecclesiastical hierarchy...
, is said to have written a letter to the community in the year 139."
Gortyn
Gortyn
Gortyn, Gortys or Gortyna is a municipality and an archaeological site on the Mediterranean island of Crete, 45 km away from the modern capital Heraklion. The seat of the municipality is the village Agioi Deka...
on Crete
Crete
Crete is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, and one of the thirteen administrative regions of Greece. It forms a significant part of the economy and cultural heritage of Greece while retaining its own local cultural traits...
, was allied with Rome and was thus made capital of Roman Creta et Cyrenaica
Creta et Cyrenaica
Creta et Cyrenaica was a senatorial province of the Roman empire created in 20 BC. It comprised the island of Crete and the region of Cyrenaica in north Africa ....
. St. Titus is believed to have been the first bishop. The city was sacked by the pirate Abu Hafs
Abu Hafs (pirate)
Umar ibn Hafs ibn Shuayb ibn Isa al Balluti, surnamed al-Ghaliz and later al-Ikritishi , and usually known as Abu Hafs , was a Muwallad corsair who was primarily active between 816 and 827...
in 828.
Cyrene
CyreneCyrene, Libya
Cyrene was an ancient Greek colony and then a Roman city in present-day Shahhat, Libya, the oldest and most important of the five Greek cities in the region. It gave eastern Libya the classical name Cyrenaica that it has retained to modern times.Cyrene lies in a lush valley in the Jebel Akhdar...
and the surrounding region of Cyrenaica or the North African "Pentapolis
Pentapolis
A pentapolis, from the Greek words , "five" and , "city" is a geographic and/or institutional grouping of five cities...
", south of the Mediterranean from Greece, the northeastern part of modern Libya
Libya
Libya is an African country in the Maghreb region of North Africa bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to the east, Sudan to the southeast, Chad and Niger to the south, and Algeria and Tunisia to the west....
, was a Greek colony in North Africa later converted to a Roman colony. In addition to Greeks and Romans, there was also a significant Jewish population, at least up to the Kitos War
Kitos War
The Kitos War , translation: Rebellion of the exile) is the name given to the second of the Jewish–Roman wars. Major revolts by diasporic Jews in Cyrene , Cyprus, Mesopotamia and Aegyptus spiraled out of control resulting in a widespread slaughter of Roman citizens and others by the Jewish rebels...
(115-117). According to , Simon of Cyrene
Simon of Cyrene
Simon of Cyrene was the man compelled by the Romans to carry the cross of Jesus as Jesus was taken to his crucifixion, according to all three Synoptic Gospels...
carried Jesus' cross. Cyrenians are also mentioned in , , , . According to the Catholic Encyclopedia: "Lequien mentions six bishops of Cyrene, and according to Byzantine legend the first was St. Lucius
Lucius of Cyrene
Lucius of Cyrene was, according to the Book of Acts, one of the founders of the Christian Church in Antioch, then part of Roman Syria. He is mentioned by name as a member of the church there, after King Herod's Death:...
(Acts 13:1); St. Theodorus suffered martyrdom under Diocletian;" (284-305).
Rome

Acts of the Apostles
The Acts of the Apostles , usually referred to simply as Acts, is the fifth book of the New Testament; Acts outlines the history of the Apostolic Age...
claims that the Jewish Christian couple Priscilla and Aquila had recently come from Rome to Corinth when, in about the year 50, Paul reached the latter city, indicating that belief in Jesus in Rome had preceded Paul. Irenaeus of Lyons believed in the second century
Christianity in the 2nd century
The 2nd century of Christianity was largely the time of the Apostolic Fathers who were the students of the apostles of Jesus, though there is some overlap as John the Apostle may have survived into the 2nd century and the early Apostolic Father Clement of Rome is said to have died at the end of the...
that Peter
Saint Peter
Saint Peter or Simon Peter was an early Christian leader, who is featured prominently in the New Testament Gospels and the Acts of the Apostles. The son of John or of Jonah and from the village of Bethsaida in the province of Galilee, his brother Andrew was also an apostle...
and Paul had been the founders of the Church in Rome and had appointed Linus
Pope Linus
Pope Saint Linus was, according to several early sources, Bishop of the diocese of Rome after Saint Peter. This makes Linus the second Pope. According to other early sources Pope Clement I was the Pope after Peter...
as succeeding bishop
Bishop
A bishop is an ordained or consecrated member of the Christian clergy who is generally entrusted with a position of authority and oversight. Within the Catholic Church, Eastern Orthodox, Oriental Orthodox Churches, in the Assyrian Church of the East, in the Independent Catholic Churches, and in the...
. There is no conclusive evidence, scripturally, historically or chronologically, that Peter was in fact the Bishop of Rome. While the church in Rome was already flourishing when Paul wrote his Epistle to the Romans
Epistle to the Romans
The Epistle of Paul to the Romans, often shortened to Romans, is the sixth book in the New Testament. Biblical scholars agree that it was composed by the Apostle Paul to explain that Salvation is offered through the Gospel of Jesus Christ...
to them from Corinth, about 57, he greets some fifty people in Rome by name, but not Peter whom he knew. There is also no mention of Peter in Rome later during Paul's two year stay there in chapter 28 of Acts
Acts of the Apostles
The Acts of the Apostles , usually referred to simply as Acts, is the fifth book of the New Testament; Acts outlines the history of the Apostolic Age...
, about 60-62. Church historians consistently consider Peter and Paul to have been martyr
Martyr
A martyr is somebody who suffers persecution and death for refusing to renounce, or accept, a belief or cause, usually religious.-Meaning:...
ed under the reign of Nero
Nero
Nero , was Roman Emperor from 54 to 68, and the last in the Julio-Claudian dynasty. Nero was adopted by his great-uncle Claudius to become his heir and successor, and succeeded to the throne in 54 following Claudius' death....
, in 64 such as after the Great Fire of Rome which, according to Tacitus
Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus was a senator and a historian of the Roman Empire. The surviving portions of his two major works—the Annals and the Histories—examine the reigns of the Roman Emperors Tiberius, Claudius, Nero and those who reigned in the Year of the Four Emperors...
, Nero blamed on the Christians.
Paul's Epistle to the Romans
Epistle to the Romans
The Epistle of Paul to the Romans, often shortened to Romans, is the sixth book in the New Testament. Biblical scholars agree that it was composed by the Apostle Paul to explain that Salvation is offered through the Gospel of Jesus Christ...
(c 58) attests to a large Christian community already there but does not mention Peter
Saint Peter
Saint Peter or Simon Peter was an early Christian leader, who is featured prominently in the New Testament Gospels and the Acts of the Apostles. The son of John or of Jonah and from the village of Bethsaida in the province of Galilee, his brother Andrew was also an apostle...
. The tradition that the See of Rome was founded as an organized Christian community by Peter and Paul and that its episcopate owes to them its origin can be traced as far back as second-century
Christianity in the 2nd century
The 2nd century of Christianity was largely the time of the Apostolic Fathers who were the students of the apostles of Jesus, though there is some overlap as John the Apostle may have survived into the 2nd century and the early Apostolic Father Clement of Rome is said to have died at the end of the...
Irenaeus
Irenaeus
Saint Irenaeus , was Bishop of Lugdunum in Gaul, then a part of the Roman Empire . He was an early church father and apologist, and his writings were formative in the early development of Christian theology...
. Irenaeus does not say that either Peter or Paul was "bishop" of the Church in Rome, and some historians have questioned whether Peter spent much time in Rome before his martyrdom.
Oscar Cullmann
Oscar Cullmann
Oscar Cullmann was a Christian theologian in the Lutheran tradition. He is best known for his work in the ecumenical movement, being in part responsible for the establishment of dialogue between the Lutheran and Roman Catholic traditions...
sharply rejected the claim that Peter began the papal succession
Historical development of the doctrine of Papal Primacy
The doctrines of Primacy of Simon Peter and Primacy of the Roman Pontiff are perhaps the most contentiously disputed in the history of Christianity. Many theologians regard the doctrine of Papal Primacy as having developed gradually in the West due to the convergence of a number of factors, e.g.,...
, and concludes that while Peter was the original head of the apostles
Primacy of Simon Peter
Most Christians hold that Simon Peter was the most prominent of the Apostles, called the Prince of the Apostles and favored by Jesus of Nazareth. As such, it is argued that Peter held the first place of honor and authority...
, Peter was not the founder of any visible church succession.
The original seat of Roman imperial power soon became a center of church authority, grew in power decade by decade, and was recognized during the period of the Seven Ecumenical Councils, when the seat of government had been transferred to Constantinople, as the "head" of the church.
Rome and Alexandria, which by tradition held authority over sees outside their own province, were not yet referred to as patriarchates.
The earliest bishops of Rome were all Greek-speaking, the most notable of them being Pope Clement I
Pope Clement I
Starting in the 3rd and 4th century, tradition has identified him as the Clement that Paul mentioned in Philippians as a fellow laborer in Christ.While in the mid-19th century it was customary to identify him as a freedman of Titus Flavius Clemens, who was consul with his cousin, the Emperor...
(c. 88-97), author of an Epistle to the Church in Corinth
First Epistle of Clement
The First Epistle of Clement, is a letter addressed to the Christians in the city of Corinth. The letter dates from the late 1st or early 2nd century, and ranks with Didache as one of the earliest — if not the earliest — of extant Christian documents outside the canonical New Testament...
; Pope Telesphorus
Pope Telesphorus
Pope Saint Telesphorus was Pope from 126 or 127 to 136 or 137 or 138, during the reigns of Roman Emperors Hadrian and Antoninus Pius. He was Greek by birth....
(c. 126-136), probably the only martyr among them; Pope Pius I
Pope Pius I
Pope Saint Pius I was Bishop of Rome, according to the Annuario Pontificio, from 142 or 146 to 157 or 161, respectively. Others suggest that his pontificate was perhaps from 140 to 154.-Early life:...
(c. 141-154), said by the Muratorian fragment
Muratorian fragment
The Muratorian fragment is a copy of perhaps the oldest known list of the books of the New Testament. The fragment, consisting of 85 lines, is a 7th-century Latin manuscript bound in an eighth or 7th century codex that came from the library of Columban's monastery at Bobbio; it contains internal...
to be the brother of the author of the Shepherd of Hermas
The Shepherd of Hermas
The Shepherd of Hermas is a Christian literary work of the 1st or 2nd century, considered a valuable book by many Christians, and considered canonical scripture by some of the early Church fathers such as Irenaeus. The Shepherd had great authority in the 2nd and 3rd centuries...
; and Pope Anicetus
Pope Anicetus
Pope Saint Anicetus was Pope of the Catholic Church from about 150 to about 167 . His name is Greek for unconquered...
(c. 155-160), who received Saint Polycarp
Polycarp
Saint Polycarp was a 2nd century Christian bishop of Smyrna. According to the Martyrdom of Polycarp, he died a martyr, bound and burned at the stake, then stabbed when the fire failed to touch him...
and discussed with him the dating of Easter
Easter controversy
The Easter controversy is a series of controversies about the proper date to celebrate the Christian holiday of Easter. To date, there are four distinct historical phases of the dispute and the dispute has yet to be resolved...
.
Pope Victor I
Pope Victor I
Pope Saint Victor I was Pope from 189 to 199 .Pope Victor I was the first bishop of Rome born in the Roman Province of Africa: probably he was born in Leptis Magna . He was later canonized...
(189-198) was the first ecclesiastical writer known to have written in Latin; however, his only extant works are his encyclicals, which would naturally have been issued in both Latin and Greek.
Greek New Testament texts were translated into Latin early on, well before Jerome
Jerome
Saint Jerome was a Roman Christian priest, confessor, theologian and historian, and who became a Doctor of the Church. He was the son of Eusebius, of the city of Stridon, which was on the border of Dalmatia and Pannonia...
, and are classified as the Vetus Latina
Vetus Latina
Vetus Latina is a collective name given to the Biblical texts in Latin that were translated before St Jerome's Vulgate Bible became the standard Bible for Latin-speaking Western Christians. The phrase Vetus Latina is Latin for Old Latin, and the Vetus Latina is sometimes known as the Old Latin Bible...
and Western text-type
Western text-type
The Western text-type is one of several text-types used in textual criticism to describe and group the textual character of Greek New Testament manuscripts...
.
During the 2nd century, Christians and semi-Christians of diverse views congregated in Rome, notably Marcion and Valentinius, and in the following century there were schisms connected with Hippolytus of Rome and Novatian.
The Roman church survived various persecutions, and many clergy were martyred. In the "Massacre of 258", under Valerian
Valerian (emperor)
Valerian , also known as Valerian the Elder, was Roman Emperor from 253 to 260. He was taken captive by Persian king Shapur I after the Battle of Edessa, becoming the only Roman Emperor who was captured as a prisoner of war, resulting in wide-ranging instability across the Empire.-Origins and rise...
, the emperor killed a great many Christian clergy, including Pope Sixtus II
Pope Sixtus II
Pope Sixtus II or Pope Saint Sixtus II was Pope from August 30, 257 to August 6, 258. He died as a martyr during the persecution by Emperor Valerian....
and Cyprian of Carthage and perhaps also Antipope Novatian
Antipope Novatian
Novatian was a scholar, priest, theologian and antipope who held the title between 251 and 258. According to Greek authors, pope Damasus I and Prudentius gave his name as Novatus....
. Mass persecutions, of which that which broke out under Diocletian in 303 was particularly severe, finally ended in Rome, and the West in general, with the accession of Maxentius
Maxentius
Maxentius was a Roman Emperor from 306 to 312. He was the son of former Emperor Maximian, and the son-in-law of Emperor Galerius.-Birth and early life:Maxentius' exact date of birth is unknown; it was probably around 278...
in 306.
Syracuse and Calabria
Syracuse was founded by Greek colonists in 734 or 733 BC, part of Magna GraeciaMagna Graecia
Magna Græcia is the name of the coastal areas of Southern Italy on the Tarentine Gulf that were extensively colonized by Greek settlers; particularly the Achaean colonies of Tarentum, Crotone, and Sybaris, but also, more loosely, the cities of Cumae and Neapolis to the north...
. According to the Catholic Encyclopedia: "Syracuse claims to be the second Church founded by St. Peter, after that of Antioch. It also claims that St. Paul preached there. ... In the times of St. Cyprian (the middle of the third century), Christianity certainly flourished at Syracuse, and the catacombs
Catacombs
Catacombs, human-made subterranean passageways for religious practice. Any chamber used as a burial place can be described as a catacomb, although the word is most commonly associated with the Roman empire...
clearly show that this was the case in the second century." Across the Strait of Messina
Strait of Messina
The Strait of Messina is the narrow passage between the eastern tip of Sicily and the southern tip of Calabria in the south of Italy. It connects the Tyrrhenian Sea with the Ionian Sea, within the central Mediterranean...
, Calabria
Calabria
Calabria , in antiquity known as Bruttium, is a region in southern Italy, south of Naples, located at the "toe" of the Italian Peninsula. The capital city of Calabria is Catanzaro....
on the mainland was also an early center of Christianity.
Aquileia
The ancient Roman city of AquileiaAquileia
Aquileia is an ancient Roman city in what is now Italy, at the head of the Adriatic at the edge of the lagoons, about 10 km from the sea, on the river Natiso , the course of which has changed somewhat since Roman times...
at the head of the Adriatic Sea
Adriatic Sea
The Adriatic Sea is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan peninsula, and the system of the Apennine Mountains from that of the Dinaric Alps and adjacent ranges...
, today one of the main archeological sites of Northern Italy
Northern Italy
Northern Italy is a wide cultural, historical and geographical definition, without any administrative usage, used to indicate the northern part of the Italian state, also referred as Settentrione or Alta Italia...
, was an early center of Christianity said to be founded by Mark
Mark the Evangelist
Mark the Evangelist is the traditional author of the Gospel of Mark. He is one of the Seventy Disciples of Christ, and the founder of the Church of Alexandria, one of the original four main sees of Christianity....
before his mission to Alexandria. Hermagoras of Aquileia
Hermagoras of Aquileia
Saint Hermagoras of Aquileia is considered the first bishop of Aquileia, northern Italy. Christian tradition states that he was chosen by Saint Mark to serve as the leader of the nascent Christian community in Aquileia, and that he was consecrated bishop by Saint Peter...
is believed to be its first bishop. The Aquileian Rite
Aquileian Rite
The Aquileian Rite was a particular liturgical tradition within the schismatical province of the ancient patriarchal see of Aquileia.-History:...
is associated with Aquileia.
Milan
It is believed that the Church of MilanMilan
Milan is the second-largest city in Italy and the capital city of the region of Lombardy and of the province of Milan. The city proper has a population of about 1.3 million, while its urban area, roughly coinciding with its administrative province and the bordering Province of Monza and Brianza ,...
in northwest Italy was founded by the apostle Barnabas
Barnabas
Barnabas , born Joseph, was an Early Christian, one of the earliest Christian disciples in Jerusalem. In terms of culture and background, he was a Hellenised Jew, specifically a Levite. Named an apostle in , he and Saint Paul undertook missionary journeys together and defended Gentile converts...
in the 1st century. Gervasius and Protasius
Gervasius and Protasius
Saints Gervasius and Protasius are venerated as Christian martyrs, probably of the 2nd century....
and others were martyred there. It has long maintained its own rite known as the Ambrosian Rite
Ambrosian Rite
Ambrosian Rite, also called the Milanese Rite, is a Catholic liturgical Western Rite. The rite is named after Saint Ambrose, a bishop of Milan in the fourth century...
attributed to Ambrose
Ambrose
Aurelius Ambrosius, better known in English as Saint Ambrose , was a bishop of Milan who became one of the most influential ecclesiastical figures of the 4th century. He was one of the four original doctors of the Church.-Political career:Ambrose was born into a Roman Christian family between about...
who was bishop c. 337-397 and one of the most influential ecclesiastical figures of the 4th century. Duchesne argues that the Gallican Rite originated in Milan.
Carthage
CarthageCarthage
Carthage , implying it was a 'new Tyre') is a major urban centre that has existed for nearly 3,000 years on the Gulf of Tunis, developing from a Phoenician colony of the 1st millennium BC...
, in the Roman province of Africa, south of the Mediterranean from Rome, gave the early church the Latin fathers Tertullian
Tertullian
Quintus Septimius Florens Tertullianus, anglicised as Tertullian , was a prolific early Christian author from Carthage in the Roman province of Africa. He is the first Christian author to produce an extensive corpus of Latin Christian literature. He also was a notable early Christian apologist and...
(c.120-c.220) and Cyprian
Cyprian
Cyprian was bishop of Carthage and an important Early Christian writer, many of whose Latin works are extant. He was born around the beginning of the 3rd century in North Africa, perhaps at Carthage, where he received a classical education...
(d. 258). Carthage fell to Islam
Islam
Islam . The most common are and . : Arabic pronunciation varies regionally. The first vowel ranges from ~~. The second vowel ranges from ~~~...
in 698.
Malta
According to Acts, Paul was shipwrecked and ministered on an island which some scholars have identified as MaltaMalta
Malta , officially known as the Republic of Malta , is a Southern European country consisting of an archipelago situated in the centre of the Mediterranean, south of Sicily, east of Tunisia and north of Libya, with Gibraltar to the west and Alexandria to the east.Malta covers just over in...
(an island just south of Sicily
Sicily
Sicily is a region of Italy, and is the largest island in the Mediterranean Sea. Along with the surrounding minor islands, it constitutes an autonomous region of Italy, the Regione Autonoma Siciliana Sicily has a rich and unique culture, especially with regard to the arts, music, literature,...
) for three months during which time he is said to have been bitten by a poisonous viper and survived , an event usually dated c. AD 60. Paul had been allowed passage from Caesarea Maritima to Rome by Porcius Festus
Porcius Festus
Porcius Festus was procurator of Judea from about AD 59 to 62, succeeding Antonius Felix. His exact time in office is not known. The earliest proposed date for the start of his term is c. A.D. 55-6, while the latest is A.D. 61. These extremes have not gained much support and most scholars opt...
, procurator
Procurator (Roman)
A procurator was the title of various officials of the Roman Empire, posts mostly filled by equites . A procurator Augusti was the governor of the smaller imperial provinces...
of Iudaea province
Iudaea Province
Judaea or Iudaea are terms used by historians to refer to the Roman province that extended over parts of the former regions of the Hasmonean and Herodian kingdoms of Israel...
, to stand trial before the Emperor. Many traditions are associated with this episode, and catacombs in Rabat testify to an Early Christian community on the islands. According to tradition, Publius
Saint Publius
Saint Publius is the first maltese Saint. He is venerated as the first Bishop of Malta. Publius' conversion led to Malta being the first Christian nation in the West, and one of the first in the world....
, the Roman Governor of Malta at the time of Saint Paul's shipwreck, became the first Bishop of Malta following his conversion to Christianity. After ruling the Maltese Church for thirty-one years, Publius was transferred to the See of Athens
Athens
Athens , is the capital and largest city of Greece. Athens dominates the Attica region and is one of the world's oldest cities, as its recorded history spans around 3,400 years. Classical Athens was a powerful city-state...
in 90 AD, where he was martyred in 125 AD. There is scant information about the continuity of Christianity in Malta in subsequent years, although tradition has it that there was a continuous line of bishops from the days of St. Paul to the time of Emperor Constantine.
Salona
SalonaSalona
Salona was an ancient Illyrian Delmati city in the first millennium BC. The Greeks had set up an emporion there. After the conquest by the Romans, Salona became the capital of the Roman province of Dalmatia...
, the capital of the Roman province of Dalmatia
Dalmatia (Roman province)
Dalmatia was an ancient Roman province. Its name is probably derived from the name of an Illyrian tribe called the Dalmatae which lived in the area of the eastern Adriatic coast in Classical antiquity....
on the eastern shore of the Adriatic Sea
Adriatic Sea
The Adriatic Sea is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan peninsula, and the system of the Apennine Mountains from that of the Dinaric Alps and adjacent ranges...
, was an early center of Christianity and today is a ruin in modern Croatia
Croatia
Croatia , officially the Republic of Croatia , is a unitary democratic parliamentary republic in Europe at the crossroads of the Mitteleuropa, the Balkans, and the Mediterranean. Its capital and largest city is Zagreb. The country is divided into 20 counties and the city of Zagreb. Croatia covers ...
. According to the Catholic Encyclopedia it was where: "...Titus the pupil of St. Paul preached, where the followers of Jesus Christ first shed their blood as martyrs, and where beautiful examples of basilicas and other early Christian sculpture have been discovered." According to the Catholic Encyclopedia article on Dalmatia: "Salona became the centre from which Christianity spread. In Pannonia St. Andronicus
Andronicus of Pannonia
Andronicus of Pannonia was a 1st century Christian mentioned by the Apostle Paul: According to that verse, Andronicus was a kinsman of Paul and a fellow prisoner at some time, particularly well-known among the apostles, and had become a follower of Jesus Christ before Paul's Damascus road conversion...
founded the See of Syrmium (Mitrovica) and later those of Siscia and Mursia. The cruel persecution under Diocletian, who was a Dalmatian by birth, left numerous traces in Old Dalmatia
Dalmatia
Dalmatia is a historical region on the eastern coast of the Adriatic Sea. It stretches from the island of Rab in the northwest to the Bay of Kotor in the southeast. The hinterland, the Dalmatian Zagora, ranges from fifty kilometers in width in the north to just a few kilometers in the south....
and Pannonia
Pannonia
Pannonia was an ancient province of the Roman Empire bounded north and east by the Danube, coterminous westward with Noricum and upper Italy, and southward with Dalmatia and upper Moesia....
. St. Quirinus, Bishop of Siscia, died a martyr A.D. 303. St. Jerome
Jerome
Saint Jerome was a Roman Christian priest, confessor, theologian and historian, and who became a Doctor of the Church. He was the son of Eusebius, of the city of Stridon, which was on the border of Dalmatia and Pannonia...
was born in Strido
Stridon
Stridon was a town in the Roman province of Dalmatia. The town is located near modern Ljubljana but the exact location is unknown. The town is especially known as the birthplace of Saint Jerome. From Stridon also came Domnus of Stridon, a bishop who took part in the First Council of Nicaea, and...
, a city on the border of Pannonia and Dalmatia."
Seville
SevilleSeville
Seville is the artistic, historic, cultural, and financial capital of southern Spain. It is the capital of the autonomous community of Andalusia and of the province of Seville. It is situated on the plain of the River Guadalquivir, with an average elevation of above sea level...
was the capital of Hispania Baetica
Hispania Baetica
Hispania Baetica was one of three Imperial Roman provinces in Hispania, . Hispania Baetica was bordered to the west by Lusitania, and to the northeast by Hispania Tarraconensis. Baetica was part of Al-Andalus under the Moors in the 8th century and approximately corresponds to modern Andalucia...
or the Roman province of southern Spain. According to the Catholic Encyclopedia: "...the origin of the diocese goes back to Apostolic times, or at least to the first century of our era. St. Gerontius, Bishop of Italica (about four miles from Hispalis or Seville), preached in Baetica in Apostolic times, and without doubt must have left a pastor of its own to Seville. It is certain that in 303, when Sts. Justa and Rufina
Justa and Rufina
Saints Justa and Rufina are venerated as martyrs. They are said to have been martyred at Hispalis during the 3rd century.Only St...
, the potters, suffered martyrdom for refusing to adore the idol Salambo, there was a Bishop of Seville, Sabinus, who assisted at the Council of Illiberis (287). Before that time Marcellus had been bishop, as appears from a catalogue of the ancient prelates of Seville preserved in the "Codex Emilianensis", a manuscript of the year 1000, now in the Escorial. When Constantine brought peace to the Church
Peace of the Church
Peace of the Church is a designation usually applied to the condition of the Church after the publication of the Edict of Milan in 313 by the two Augusti, Western Roman Emperor Constantine I and his eastern colleague Licinius, an edict of toleration by which the Christians were accorded complete...
[313] Evodius was Bishop of Seville; he set himself to rebuild the ruined churches, among them he appears to have built the church of San Vicente, perhaps the first cathedral of Seville." Early Christianity also spread from the Iberian peninsula
Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula , sometimes called Iberia, is located in the extreme southwest of Europe and includes the modern-day sovereign states of Spain, Portugal and Andorra, as well as the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar...
south across the Strait of Gibraltar
Strait of Gibraltar
The Strait of Gibraltar is a narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Mediterranean Sea and separates Spain in Europe from Morocco in Africa. The name comes from Gibraltar, which in turn originates from the Arabic Jebel Tariq , albeit the Arab name for the Strait is Bab el-Zakat or...
into Roman Mauretania Tingitana
Mauretania Tingitana
Mauretania Tingitana was a Roman province located in northwestern Africa, coinciding roughly with the northern part of present-day Morocco. The province extended from the northern peninsula, opposite Gibraltar, to Chellah and Volubilis to the south, and as far east as the Oued Laou river. Its...
, of note is Marcellus of Tangier
Marcellus of Tangier
Saint Marcellus of Tangier or Saint Marcellus the Centurion is venerated as a Martyr Saint by the Roman Catholic Church and the Eastern Orthodox Church...
who was martyred in 298.
Southern Gaul

The Mediterranean coast of France and the Rhone valley, then part of Roman Gallia Narbonensis
Gallia Narbonensis
Gallia Narbonensis was a Roman province located in what is now Languedoc and Provence, in southern France. It was also known as Gallia Transalpina , which was originally a designation for that part of Gaul lying across the Alps from Italia and it contained a western region known as Septimania...
, were early centers of Christianity. Major cities are Arles
Arles
Arles is a city and commune in the south of France, in the Bouches-du-Rhône department, of which it is a subprefecture, in the former province of Provence....
, Avignon
Avignon
Avignon is a French commune in southeastern France in the départment of the Vaucluse bordered by the left bank of the Rhône river. Of the 94,787 inhabitants of the city on 1 January 2010, 12 000 live in the ancient town centre surrounded by its medieval ramparts.Often referred to as the...
, Vienne
Vienne, Isère
Vienne is a commune in south-eastern France, located south of Lyon, on the Rhône River. It is the second largest city after Grenoble in the Isère department, of which it is a subprefecture. The city's population was of 29,400 as of the 2001 census....
, Lyon
Lyon
Lyon , is a city in east-central France in the Rhône-Alpes region, situated between Paris and Marseille. Lyon is located at from Paris, from Marseille, from Geneva, from Turin, and from Barcelona. The residents of the city are called Lyonnais....
, and Marseille
Marseille
Marseille , known in antiquity as Massalia , is the second largest city in France, after Paris, with a population of 852,395 within its administrative limits on a land area of . The urban area of Marseille extends beyond the city limits with a population of over 1,420,000 on an area of...
(the oldest city in France). The Persecution in Lyon occurred in 177. The Apostolic Father Irenaeus
Irenaeus
Saint Irenaeus , was Bishop of Lugdunum in Gaul, then a part of the Roman Empire . He was an early church father and apologist, and his writings were formative in the early development of Christian theology...
from Smyrna
Smyrna
Smyrna was an ancient city located at a central and strategic point on the Aegean coast of Anatolia. Thanks to its advantageous port conditions, its ease of defence and its good inland connections, Smyrna rose to prominence. The ancient city is located at two sites within modern İzmir, Turkey...
of Anatolia was Bishop of Lyon near the end of the 2nd century and he claimed Saint Pothinus
Saint Pothinus
Saint Pothinus is a figure of uncertain historicity, who is first mentioned in a letter attributed to Irenaeus of Lyon. The letter was sent from the Christian communities of Lyon and Vienne to the Roman province of Asia....
was his predecessor. The Council of Arles in 314 is considered a forerunner of the Ecumenical councils. The Ephesine theory attributes the Gallican Rite to Lyon.
Outside the Roman Empire
Christianity was by no means confined to the Roman Empire during the early Christian period.Armenia
It became the official religion of ArmeniaArmenia
Armenia , officially the Republic of Armenia , is a landlocked mountainous country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia...
in 301 or 314, when Christianity was still illegal in the Roman Empire. Some claim the Armenian Apostolic Church
Armenian Apostolic Church
The Armenian Apostolic Church is the world's oldest National Church, is part of Oriental Orthodoxy, and is one of the most ancient Christian communities. Armenia was the first country to adopt Christianity as its official religion in 301 AD, in establishing this church...
was founded by Gregory the Illuminator
Gregory the Illuminator
Saint Gregory the Illuminator or Saint Gregory the Enlightener is the patron saint and first official head of the Armenian Apostolic Church...
of the late third - early fourth centuries while they trace their origins to the missions of Bartholomew the Apostle and Thaddeus (Jude the Apostle) in the 1st century.
Georgia
Christianity in GeorgiaGeorgia (country)
Georgia is a sovereign state in the Caucasus region of Eurasia. Located at the crossroads of Western Asia and Eastern Europe, it is bounded to the west by the Black Sea, to the north by Russia, to the southwest by Turkey, to the south by Armenia, and to the southeast by Azerbaijan. The capital of...
(ancient Iberia
Caucasian Iberia
Iberia , also known as Iveria , was a name given by the ancient Greeks and Romans to the ancient Georgian kingdom of Kartli , corresponding roughly to the eastern and southern parts of the present day Georgia...
) extends back to the 4th century
Christianity in the 4th century
Christianity in the 4th century was dominated by Constantine the Great, and the First Council of Nicea of 325, which was the beginning of the period of the First seven Ecumenical Councils and the attempt to reach an orthodox consensus and to establish a unified Christendom as the State church of...
, if not earlier. The Iberian king, Mirian III
Mirian III of Iberia
Mirian III was a king of Iberia , contemporaneous to the Roman emperor Constantine I .According to the early medieval Georgian annals and hagiography, Mirian was the first Christian king of Iberia, converted through the ministry of Nino, a Cappadocian female missionary...
, converted to Christianity, probably in 326.
Mesopotamia and the Parthian Empire
EdessaEdessa, Mesopotamia
Edessa is the Greek name of an Aramaic town in northern Mesopotamia, as refounded by Seleucus I Nicator. For the modern history of the city, see Şanlıurfa.-Names:...
, which was held by Rome from 116 to 118 and 212 to 214, but was mostly a client kingdom associated either with Rome or Persia, was an important Christian city. Shortly after 201 or even earlier, its royal house became Christian
Edessa
Edessa, Mesopotamia
Edessa is the Greek name of an Aramaic town in northern Mesopotamia, as refounded by Seleucus I Nicator. For the modern history of the city, see Şanlıurfa.-Names:...
(now Şanlıurfa
Sanliurfa
Şanlıurfa, , often simply known as Urfa in daily language , in ancient times Edessa, is a city with 482,323 inhabitants Şanlıurfa, , often simply known as Urfa in daily language (Syriac ܐܘܪܗܝ Urhoy,Armenian Ուռհա Owr'ha, Arabic الرها ar-Ruhā), in ancient times Edessa, is a city with 482,323...
) in northwestern Mesopotamia was from apostolic times the principal center of Syriac-speaking Christianity. it was the capital of an independent kingdom from 132 BC to AD 216, when it became tributary to Rome. Celebrated as an important centre of Greco-Syrian culture, Edessa was also noted for its Jewish community., with proselytes in the royal family. Strategically located on the main trade routes of the Fertile Crescent
Fertile Crescent
The Fertile Crescent, nicknamed "The Cradle of Civilization" for the fact the first civilizations started there, is a crescent-shaped region containing the comparatively moist and fertile land of otherwise arid and semi-arid Western Asia. The term was first used by University of Chicago...
, it was easily accessible from Antioch
Antioch
Antioch on the Orontes was an ancient city on the eastern side of the Orontes River. It is near the modern city of Antakya, Turkey.Founded near the end of the 4th century BC by Seleucus I Nicator, one of Alexander the Great's generals, Antioch eventually rivaled Alexandria as the chief city of the...
, where the mission to the Gentiles was inaugurated. When early Christians were scattered abroad because of persecution, some found refuge at Edessa. Thus the Edessan church traced its origin to the apostolic age (which may account for its rapid growth), and Christianity
Christianity
Christianity is a monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus as presented in canonical gospels and other New Testament writings...
even became the state religion for a time.
The Church of the East had its inception at a very early date in the buffer zone between the Parthian
Parthian Empire
The Parthian Empire , also known as the Arsacid Empire , was a major Iranian political and cultural power in ancient Persia...
and Roman Empires in Upper Mesopotamia, known as the Assyrian Church of the East
Assyrian Church of the East
The Assyrian Church of the East, officially the Holy Apostolic Catholic Assyrian Church of the East ʻIttā Qaddishtā w-Shlikhāitā Qattoliqi d-Madnĕkhā d-Āturāyē), is a Syriac Church historically centered in Mesopotamia. It is one of the churches that claim continuity with the historical...
. The vicissitudes of its later growth were rooted in its minority status in a situation of international tension. The rulers of the Parthian Empire
Parthian Empire
The Parthian Empire , also known as the Arsacid Empire , was a major Iranian political and cultural power in ancient Persia...
(250 BC - AD 226) were on the whole tolerant in spirit, and with the older faiths of Babylonia and Assyria in a state of decay, the time was ripe for a new and vital faith. The rulers of the Second Persian empire (226-640) also followed a policy of religious toleration to begin with, though later they gave Christians the same status as a subject race. However, these rulers also encouraged the revival of the ancient Persian dualistic faith of Zoroastrianism
Zoroastrianism
Zoroastrianism is a religion and philosophy based on the teachings of prophet Zoroaster and was formerly among the world's largest religions. It was probably founded some time before the 6th century BCE in Greater Iran.In Zoroastrianism, the Creator Ahura Mazda is all good, and no evil...
and established it as the state religion, with the result that the Christians were increasingly subjected to repressive measures. Nevertheless, it was not until Christianity became the state religion in the West (380) that enmity toward Rome was focused on the Eastern Christians. After the Mohammedan conquest in the 7th century, the caliphate tolerated other faiths but forbade proselytism and subjected Christians to heavy taxation.
The missionary Addai evangelized Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a toponym for the area of the Tigris–Euphrates river system, largely corresponding to modern-day Iraq, northeastern Syria, southeastern Turkey and southwestern Iran.Widely considered to be the cradle of civilization, Bronze Age Mesopotamia included Sumer and the...
(modern Iraq
Iraq
Iraq ; officially the Republic of Iraq is a country in Western Asia spanning most of the northwestern end of the Zagros mountain range, the eastern part of the Syrian Desert and the northern part of the Arabian Desert....
) about the middle of the 2nd century. An ancient legend recorded by Eusebius (AD 260-340) and also found in the Doctrine of Addai (c. AD 400) (from information in the royal archives of Edessa) describes how King Abgar V of Edessa
Abgar V of Edessa
Abgar V the black or Abgarus V of Edessa BC - AD 7 and AD 13 - 50) was a historical Syriac ruler of the Syriac kingdom of Osroene, holding his capital at Edessa....
communicated to Jesus, requesting he come and heal him, to which appeal he received a reply. It is said that after the resurrection, the Thomas sent Addai (or Thaddaeus), to the king, with the result that the city was won to the Christian faith. In this mission he was accompanied by a disciple, Mari, and the two are regarded as cofounders of the church, according to the Liturgy of Addai and Mari (c. AD 200), which is still the normal liturgy of the Assyrian church. The Doctrine of Addai
Doctrine of Addai
The Doctrine of Addai is a controversial book about Saint Addai.The story of how King Abgar and Jesus had corresponded was first recounted in the 4th century by the church historian Eusebius of Caesarea in his Ecclesiastical History and it was retold in elaborated form by Ephrem the Syrian.In the...
further states that Thomas was regarded as an apostle of the church, which long treasured a letter written by him from India.
Addai, who became the first bishop of Edessa, was succeeded by Aggai
Mar Aggai
Aggai was a legendary 1st-century primate of the Church of the East, reputedly the disciple of Mar Addai, who is conventionally believed to have sat from 66 to 87. His existence is disputed, and considered as one of several fictitious early church leaders whose lives were concocted in the 6th...
, then by Palut, who was ordained about 200 by Serapion of Antioch
Serapion of Antioch
Serapion was Patriarch of Antioch . He is known primarily through his theological writings. Eusebius refers to three works of Serapion in his history, but admits that others probably existed: first is a private letter addressed to Caricus and Pontius against Montanism, from which Eusebius quotes an...
. Thence came to us in the 2nd century the famous Peshitta
Peshitta
The Peshitta is the standard version of the Bible for churches in the Syriac tradition.The Old Testament of the Peshitta was translated into Syriac from the Hebrew, probably in the 2nd century AD...
, or Syriac translation of the Old Testament; also Tatian
Tatian
Tatian the Assyrian was an Assyrian early Christian writer and theologian of the 2nd century.Tatian's most influential work is the Diatessaron, a Biblical paraphrase, or "harmony", of the four gospels that became the standard text of the four gospels in the Syriac-speaking churches until the...
's Diatessaron
Diatessaron
The Diatessaron is the most prominent Gospel harmony created by Tatian, an early Christian apologist and ascetic. The term "diatessaron" is from Middle English by way of Latin, diatessarōn , and ultimately Greek, διὰ τεσσάρων The Diatessaron (c 160 - 175) is the most prominent Gospel harmony...
, which was compiled about 172 and in common use until St. Rabbula
Rabbula
Rabbula was a bishop of Edessa from 411 to August 435, noteworthy for his opposition to the views of Theodore of Mopsuestia, as well as those of Nestorius...
, Bishop of Edessa (412-435), forbade its use. This arrangement of the four Canonical gospels as a continuous narrative, whose original language may have been Syriac, Greek, or even Latin, circulated widely in Syriac-speaking Churches.
A Christian council was held at Edessa as early as 197. In 201 the city was devastated by a great flood, and the Christian church was destroyed. In 232 the relics of the Apostle Thomas
Thomas the Apostle
Thomas the Apostle, also called Doubting Thomas or Didymus was one of the Twelve Apostles of Jesus. He is best known for questioning Jesus' resurrection when first told of it, then proclaiming "My Lord and my God" on seeing Jesus in . He was perhaps the only Apostle who went outside the Roman...
were brought from India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
, on which occasion his Syriac Acts were written. Under Roman domination many martyrs suffered at Edessa: Sts. Scharbîl and Barsamya, under Decius
Decius
Trajan Decius , was Roman Emperor from 249 to 251. In the last year of his reign, he co-ruled with his son Herennius Etruscus until they were both killed in the Battle of Abrittus.-Early life and rise to power:...
; Sts. Gûrja, Schâmôna, Habib, and others under Diocletian
Diocletian
Diocletian |latinized]] upon his accession to Diocletian . c. 22 December 244 – 3 December 311), was a Roman Emperor from 284 to 305....
. In the meanwhile Christian priests from Edessa had evangelized Eastern Mesopotamia and Persia
Iran
Iran , officially the Islamic Republic of Iran , is a country in Southern and Western Asia. The name "Iran" has been in use natively since the Sassanian era and came into use internationally in 1935, before which the country was known to the Western world as Persia...
, and established the first Churches in the kingdom of the Sassanids. Atillâtiâ, Bishop of Edessa, assisted at the First Council of Nicaea (325).
Persia and Central Asia
By the latter half of the 2nd century, Christianity had spread east throughout MediaMedes
The MedesThe Medes...
, Persia, Parthia
Parthia
Parthia is a region of north-eastern Iran, best known for having been the political and cultural base of the Arsacid dynasty, rulers of the Parthian Empire....
, and Bactria
Bactria
Bactria and also appears in the Zend Avesta as Bukhdi. It is the ancient name of a historical region located between south of the Amu Darya and west of the Indus River...
. The twenty bishops and many presbyters were more of the order of itinerant missionaries, passing from place to place as Paul did and supplying their needs with such occupations as merchant or craftsman. By AD 280
280
Year 280 was a leap year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Messalla and Gratus...
the metropolis of Seleucia assumed the title of “Catholicos,”and in A.D. 424
424
Year 424 was a leap year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Castinus and Victor...
a council of the church at Seleucia elected the first patriarch to have jurisdiction over the whole church of the East, including India and Ceylon (Sri Lanka). The seat of the Patriarchate was fixed at Seleucia-Ctesiphon, since this was an important point on the East-West trade routes which extended both to India and China, Java and Japan. Thus the shift of ecclesiastical authority was away from Edessa, which in A.D. 216 had become tributary to Rome. the establishment of an independent patriarchate with nine subordinate metropoli contributed to a more favourable attitude by the Persian government, which no longer had to fear an ecclesiastical alliance with the common enemy, Rome.
By the time that Edessa was incorporated into the Persian Empire in 258, the city of Arbela
Arbil
Arbil / Hewlêr is the fourth largest city in Iraq after Baghdad, Basra and Mosul...
, situated on the Tigris
Tigris
The Tigris River is the eastern member of the two great rivers that define Mesopotamia, the other being the Euphrates. The river flows south from the mountains of southeastern Turkey through Iraq.-Geography:...
in what is now Iraq
Iraq
Iraq ; officially the Republic of Iraq is a country in Western Asia spanning most of the northwestern end of the Zagros mountain range, the eastern part of the Syrian Desert and the northern part of the Arabian Desert....
, had taken on more and more the role that Edessa had played in the early years, as a centre from which Christianity spread to the rest of the Persian Empire.
Bardaisan, writing about 196, speaks of Christians throughout Media
Medea
Medea is a woman in Greek mythology. She was the daughter of King Aeëtes of Colchis, niece of Circe, granddaughter of the sun god Helios, and later wife to the hero Jason, with whom she had two children, Mermeros and Pheres. In Euripides's play Medea, Jason leaves Medea when Creon, king of...
, Parthia
Parthia
Parthia is a region of north-eastern Iran, best known for having been the political and cultural base of the Arsacid dynasty, rulers of the Parthian Empire....
and Bactria
Bactria
Bactria and also appears in the Zend Avesta as Bukhdi. It is the ancient name of a historical region located between south of the Amu Darya and west of the Indus River...
(modern-day Afghanistan
Afghanistan
Afghanistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located in the centre of Asia, forming South Asia, Central Asia and the Middle East. With a population of about 29 million, it has an area of , making it the 42nd most populous and 41st largest nation in the world...
) and, according to Tertullian
Tertullian
Quintus Septimius Florens Tertullianus, anglicised as Tertullian , was a prolific early Christian author from Carthage in the Roman province of Africa. He is the first Christian author to produce an extensive corpus of Latin Christian literature. He also was a notable early Christian apologist and...
(c.160-230), there were already a number of bishoprics within the Persian Empire by 220. By 315, the bishop of Seleucia
Seleucia
Seleucia was the first capital of the Seleucid Empire, and one of the great cities of antiquity standing in Mesopotamia, on the Tigris River.Seleucia may refer to:...
-Ctesiphon
Ctesiphon
Ctesiphon, the imperial capital of the Parthian Arsacids and of the Persian Sassanids, was one of the great cities of ancient Mesopotamia.The ruins of the city are located on the east bank of the Tigris, across the river from the Hellenistic city of Seleucia...
had assumed the title "Catholicos
Catholicos
Catholicos, plural Catholicoi, is a title used for the head of certain churches in some Eastern Christian traditions. The title implies autocephaly and in some cases is borne by the designated head of an autonomous church, in which case the holder might have other titles such as Patriarch...
". By this time, neither Edessa nor Arbela was the centre of the Church of the East anymore; ecclesiastical authority had moved east to the heart of the Persian Empire. The twin cities of Seleucia-Ctesiphon, well-situated on the main trade routes between East and West, became, in the words of John Stewart, "a magnificent centre for the missionary church that was entering on its great task of carrying the gospel to the far east."
Thus it was from Edessa that a missionary movement began which gradually spread throughout Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a toponym for the area of the Tigris–Euphrates river system, largely corresponding to modern-day Iraq, northeastern Syria, southeastern Turkey and southwestern Iran.Widely considered to be the cradle of civilization, Bronze Age Mesopotamia included Sumer and the...
, Persia, Central Asia
Central Asia
Central Asia is a core region of the Asian continent from the Caspian Sea in the west, China in the east, Afghanistan in the south, and Russia in the north...
and China
China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
. According to another ancient tradition, Mari was sent as a missionary to Seleucia
Seleucia
Seleucia was the first capital of the Seleucid Empire, and one of the great cities of antiquity standing in Mesopotamia, on the Tigris River.Seleucia may refer to:...
(on the Tigris River near Baghdad), which, with its twin city of Ctesiphon
Ctesiphon
Ctesiphon, the imperial capital of the Parthian Arsacids and of the Persian Sassanids, was one of the great cities of ancient Mesopotamia.The ruins of the city are located on the east bank of the Tigris, across the river from the Hellenistic city of Seleucia...
across the river, became another canter of missionary outreach. Mari was also regarded as the pioneer evangelist in the whole region of Adiabene
Adiabene
Adiabene was an ancient Assyrian independent kingdom in Mesopotamia, with its capital at Arbela...
to the north, of which Arbil
Arbil
Arbil / Hewlêr is the fourth largest city in Iraq after Baghdad, Basra and Mosul...
(now Erbil) was the capital. By the latter half of the 2nd century, Christianity had spread east throughout Media
Medes
The MedesThe Medes...
, Persia, Parthia
Parthia
Parthia is a region of north-eastern Iran, best known for having been the political and cultural base of the Arsacid dynasty, rulers of the Parthian Empire....
, and Bactria
Bactria
Bactria and also appears in the Zend Avesta as Bukhdi. It is the ancient name of a historical region located between south of the Amu Darya and west of the Indus River...
. The twenty bishops and many presbyters were more of the order of itinerant missionaries, passing from place to place as Paul did and supplying their needs with such occupations as merchant or craftsman. By AD 280
280
Year 280 was a leap year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Messalla and Gratus...
the metropolis of Seleucia assumed the title of "Catholicos," and in AD 424
424
Year 424 was a leap year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Castinus and Victor...
a council of the church at Seleucia elected the first patriarch to have jurisdiction over the whole church of the East, including India and Ceylon (Sri Lanka). The seat of the Patriarchate was fixed at Seleucia-Ctesiphon, since this was an important point on the East-West trade routes which extended both to India and China, Java and Japan. Thus the shift of ecclesiastical authority was away from Edessa, which in AD 216 had become tributary to Rome. the establishment of an independent patriarchate with nine subordinate metropoli contributed to a more favourable attitude by the Persian government, which no longer had to fear an ecclesiastical alliance with the common enemy, Rome.
When Constantine converted to Christianity, and the Roman Empire which was previously violently anti-Christian became pro-Christian, the Persian Empire, suspecting a new "enemy within," became violently anti-Christian. Within a few years, Shapur II
Shapur II
Shapur II the Great was the ninth King of the Persian Sassanid Empire from 309 to 379 and son of Hormizd II. During his long reign, the Sassanid Empire saw its first golden era since the reign of Shapur I...
(309-379) inaugurated a twenty-year long persecution of the church with the murder of Mar Shimun, the Catholicos of Seleucia-Ctesiphon, five bishops and 100 priests on Good Friday, 344, after the Patriarch refused to collect a double tax from the Christians to help the Persian war effort against Rome. See also Christianity in Iran
Christianity in Iran
Christianity in Iran has a long history, dating back to the early years of the faith. It has always been a minority religion, with the majority state religions — Zoroastrianism before the Islamic conquest, Sunni Islam in the Middle Ages and Shia Islam in modern times — though it had a much larger...
.
Arabian Peninsula
To understand the penetration of the Arabian peninsulaArabian Peninsula
The Arabian Peninsula is a land mass situated north-east of Africa. Also known as Arabia or the Arabian subcontinent, it is the world's largest peninsula and covers 3,237,500 km2...
by the Christian gospel, it is helpful to distinguish between the marauding Bedouin
Bedouin
The Bedouin are a part of a predominantly desert-dwelling Arab ethnic group traditionally divided into tribes or clans, known in Arabic as ..-Etymology:...
nomads of the interior, who were chiefly herdsmen and unreceptive to foreign influence, and the inhabitants of the settled communities of the coastal areas and oases, who were either middlemen traders or farmers and were receptive to influences from abroad. Christianity apparently gained its strongest foothold in the ancient center of Semitic civilisation in South-west Arabia or Yemen
Yemen
The Republic of Yemen , commonly known as Yemen , is a country located in the Middle East, occupying the southwestern to southern end of the Arabian Peninsula. It is bordered by Saudi Arabia to the north, the Red Sea to the west, and Oman to the east....
, (sometimes known as Seba or Sheba
Sheba
Sheba was a kingdom mentioned in the Jewish scriptures and the Qur'an...
), whose queen visited Solomon
Solomon
Solomon , according to the Book of Kings and the Book of Chronicles, a King of Israel and according to the Talmud one of the 48 prophets, is identified as the son of David, also called Jedidiah in 2 Samuel 12:25, and is described as the third king of the United Monarchy, and the final king before...
. Because of geographic proximity, acculturation with Ethiopia
Ethiopia
Ethiopia , officially known as the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a country located in the Horn of Africa. It is the second-most populous nation in Africa, with over 82 million inhabitants, and the tenth-largest by area, occupying 1,100,000 km2...
was always strong, and the royal family traces its ancestry to this queen.
The presence of Arabians at Pentecost and Paul's three-year sojourn in Arabia suggest a very early gospel witness. A 4th-century church history, states that the apostle Bartholomew
Bartholomew
Bartholomew was one of the Twelve Apostles of Jesus, and is usually identified as Nathaniel . He was introduced to Christ through St. Philip, another of the twelve apostles as per , where the name Nathaniel first appears. He is also mentioned as “Nathaniel of Cana in Galilee” in...
preached in Arabia and that Himyarites were among his converts. The Al-Jubail Church
Jubail Church
Jubail Church is one of the oldest still remaining church buildings in the world. The abandoned structure is located in Jubail, Saudi Arabia. It dates to the fourth century and was discovered in 1986. The government hides it from locals and bans foreigners from visiting it, even archaeologists...
in what is now Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia
The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia , commonly known in British English as Saudi Arabia and in Arabic as as-Sa‘ūdiyyah , is the largest state in Western Asia by land area, constituting the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and the second-largest in the Arab World...
was built in the 4th century. Arabia's close relations with Ethiopia
Ethiopia
Ethiopia , officially known as the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a country located in the Horn of Africa. It is the second-most populous nation in Africa, with over 82 million inhabitants, and the tenth-largest by area, occupying 1,100,000 km2...
give significance to the conversion of the treasurer to the queen of Ethiopia, not to mention the tradition that the Apostle Matthew was assigned to this land. Eusebius says that “one Pantaneous
Pantaenus
Saint Pantaenus was a Christian theologian who founded the Catechetical School of Alexandria about AD 190. This school was the earliest catechetical school, and became influential in the development of Christian theology....
(c. A.D. 190
190
Year 190 was a common year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Aurelius and Sura...
) was sent from Alexandria
Alexandria
Alexandria is the second-largest city of Egypt, with a population of 4.1 million, extending about along the coast of the Mediterranean Sea in the north central part of the country; it is also the largest city lying directly on the Mediterranean coast. It is Egypt's largest seaport, serving...
as a missionary to the nations of the East,” including southwest Arabia, on his way to India.
Ethiopia
According to records written in the Ge'ez languageGe'ez language
Ge'ez is an ancient South Semitic language that developed in the northern region of Ethiopia and southern Eritrea in the Horn of Africa...
, see also Ethiopian Orthodox Tewahedo Church
Ethiopian Orthodox Tewahedo Church
The Ethiopian Orthodox Tewahedo Church is the predominant Oriental Orthodox Christian church in Ethiopia. The Ethiopian Church was administratively part of the Coptic Orthodox Church until 1959, when it was granted its own Patriarch by Coptic Orthodox Pope of Alexandria and Patriarch of All...
, the region today known as Ethiopia
Ethiopia
Ethiopia , officially known as the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a country located in the Horn of Africa. It is the second-most populous nation in Africa, with over 82 million inhabitants, and the tenth-largest by area, occupying 1,100,000 km2...
converted to Judaism during the time of the biblical Queen of Sheba and Solomon
Solomon
Solomon , according to the Book of Kings and the Book of Chronicles, a King of Israel and according to the Talmud one of the 48 prophets, is identified as the son of David, also called Jedidiah in 2 Samuel 12:25, and is described as the third king of the United Monarchy, and the final king before...
. According to the fourth century western historian Rufinius
Tyrannius Rufinus
Tyrannius Rufinus or Rufinus of Aquileia was a monk, historian, and theologian. He is most known as a translator of Greek patristic material into Latin—especially the work of Origen.-Life:...
, it was Frumentius who brought Christianity to Ethiopia (the city of Axum
Axum
Axum or Aksum is a city in northern Ethiopia which was the original capital of the eponymous kingdom of Axum. Population 56,500 . Axum was a naval and trading power that ruled the region from ca. 400 BC into the 10th century...
) and served as its first bishop, probably shortly after 325.
India
According to Eusebius' recordChurch History (Eusebius)
The Church History of Eusebius, the bishop of Caesarea was a 4th-century pioneer work giving a chronological account of the development of Early Christianity from the 1st century to the 4th century. It was written in Koine Greek, and survives also in Latin, Syriac and Armenian manuscripts...
, Thomas
Thomas the Apostle
Thomas the Apostle, also called Doubting Thomas or Didymus was one of the Twelve Apostles of Jesus. He is best known for questioning Jesus' resurrection when first told of it, then proclaiming "My Lord and my God" on seeing Jesus in . He was perhaps the only Apostle who went outside the Roman...
and Bartholomew were assigned to Parthia
Parthia
Parthia is a region of north-eastern Iran, best known for having been the political and cultural base of the Arsacid dynasty, rulers of the Parthian Empire....
(modern Iran) and India. The Didache
Didache
The Didache or The Teaching of the Twelve Apostles is a brief early Christian treatise, dated by most scholars to the late first or early 2nd century...
(dating from the end of the first century) states, "India and all countries condering it, even to the farthest seas...received the apostolic ordinances from Judas Thomas (same as the Apostle Thomas), who was a guide and ruler in the church which he built." Moreover, there is a wealth of confirmatory information in the Syriac writings, liturgical book
Liturgical book
A liturgical book is a book published by the authority of a church, that contains the text and directions for the liturgy of its official religious services.-Roman Catholic:...
s, and calendars of the Church of the East, not to mention the writings of the Fathers, the calendars, the sacramentaries, and the martyrologies of the Roman, Greek and Ethiopian churches.
Since trade routes from the East were wide open at the time and were used by early missionaries, historian Vincent A. Smith says, "It must be admitted that a personal visit of the Apostle Thomas to South India was easily feasible in the traditional belief that he came by way of Socotra
Socotra
Socotra , also spelt Soqotra, is a small archipelago of four islands in the Indian Ocean. The largest island, also called Socotra, is about 95% of the landmass of the archipelago. It lies some east of the Horn of Africa and south of the Arabian Peninsula. The island is very isolated and through...
, where an ancient Christian settlement undoubtedly existed. I am now satisfied that the Christian church of South India is extremely ancient...' Although there was a lively trade between the Near East and India via Mesopotamia and the Persian Gulf, the most direct route to India in the 1st century was via Alexandria
Alexandria
Alexandria is the second-largest city of Egypt, with a population of 4.1 million, extending about along the coast of the Mediterranean Sea in the north central part of the country; it is also the largest city lying directly on the Mediterranean coast. It is Egypt's largest seaport, serving...
and the Red Sea
Red Sea
The Red Sea is a seawater inlet of the Indian Ocean, lying between Africa and Asia. The connection to the ocean is in the south through the Bab el Mandeb strait and the Gulf of Aden. In the north, there is the Sinai Peninsula, the Gulf of Aqaba, and the Gulf of Suez...
, taking advantage of the Monsoon winds, which could carry ships directly to and from the Malabar coast. The discovery of large hoards of Roman coins of 1st-century Caesars and the remains of Roman trading posts testify to the frequency of that trade. in addition, thriving Jewish colonies were to be found at the various trading centers, thereby furnishing obvious bases for the apostolic witness.
Piecing together the various traditions, one may conclude that Thomas left northwest India when invasion threatened and traveled by vessel to the Malabar coast
Malabar Coast
The Malabar Coast is a long and narrow coastline on the south-western shore line of the mainland Indian subcontinent. Geographically, it comprises the wettest regions of southern India, as the Western Ghats intercept the moisture-laden monsoon rains, especially on their westward-facing mountain...
, possibly visiting southeast Arabia and Socotra enroute and landing at the former flourishing port of Muziris
Muziris
Muziris is an ancient sea-port in Southwestern India on the Periyar River 3.2 km from its mouth. The derivation of the name Muziris is said to be from "Mucciripattanam," "mucciri" means "cleft palate" and "pattanam" means "city". Near Muziris, Periyar River was branched into two like a...
on an island near Cochin (c. 51
51
Year 51 was a common year starting on Friday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Caesar and Scipio...
-52
52
Year 52 was a leap year starting on Saturday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Sulla and Otho...
). From there he is said to have preached the gospel throughout the Malabar coast, though the various churches he founded were located mainly on the Periyar River
Periyar River
Periyar is the longest river in the state of Kerala, India, with a length of 244 km. The Periyar is known as the lifeline of Kerala; it is one of the few perennial rivers in the region and provides drinking water for several major towns...
and its tributaries and along the coast, where there were Jewish colonies. he reputedly preached to all classes of people and had about seventeen thousand converts, including members of the four principal castes. Later, stone crosses were erected at the places where churches were founded, and they became pilgrimage centres. In accordance with apostolic custom thomas ordained teachers and leaders or elders, who were reported to be the earliest ministry of the Malabar church.
Thomas next proceeded overland to the Coromandel coast
Coromandel Coast
The Coromandel Coast is the name given to the southeastern coast of the Indian Subcontinent between Cape Comorin and False Divi Point...
and ministered in what is now the Madras area, where a local king and many people were converted. One tradition related that he went from there to China
China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
via Malacca
Malacca
Malacca , dubbed The Historic State or Negeri Bersejarah among locals) is the third smallest Malaysian state, after Perlis and Penang. It is located in the southern region of the Malay Peninsula, on the Straits of Malacca. It borders Negeri Sembilan to the north and the state of Johor to the south...
and, after spending some time there, returned to the Madras area (Breviary of the Mar Thoma Church in Malabar). According to the Syriac version of the Acts of Thomas, Masdai, the local king at Mylapore
Mylapore
Mylapore is a cultural hub and neighborhood in the southern part of the city of Chennai, the capital of Tamil Nadu, India. Earlier, Mylapore used to be called Vedapuri....
, after questioning the apostle condemned him to death about the year 72
72
Year 72 was a leap year starting on Wednesday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Augustus and Vespasianus...
. Anxious to avoid popular excitement, “for many had believed in our Lord, including some of the nobles,”the king ordered Thomas conducted to a nearby mountain, where, after being allowed to pray, he was then stoned and stabbed to death with a lance wielded by a hunter. A number of Christians fled to malabar and joined that Christian community.
An early 3rd-century Syriac work known as the Acts of Thomas
Acts of Thomas
The early 3rd century text called Acts of Thomas is one of the New Testament apocrypha, portraying Christ as the "Heavenly Redeemer", independent of and beyond creation, who can free souls from the darkness of the world. References to the work by Epiphanius of Salamis show that it was in...
connects the apostle's Indian ministry with two kings, one in the north and the other in the south. According to one of the legends in the Acts, Thomas was at first reluctant to accept this mission, but the Lord appeared to him in a night vision and said, “Fear not, Thomas. Go away to India and proclaim the Word, for my grace shall be with you.”But the Apostle still demurred, do the Lord overruled the stubborn disciple by ordering circumstances so compelling that he was forced to accompany an Indian merchant, Abbanes, to his native place in northwest India, where he found himself in the service of the Indo-Parthian king, Gondophares
Gondophares
Gondophares I a Seistani representative of the house of Suren as well as founder and first king of the Indo-Parthian Kingdom. He seems to have ruled c...
. The apostle's ministry resulted in many conversions throughout the kingdom, including the king and his brother.
Critical historians treated this legend as an idle tale and denied the historicity of King Gundaphorus until modern archeology established him as an important figure in North India in the latter half of the 1st century. Many coins of his reign have turned up in Afghanistan, the Punjab
Punjab region
The Punjab , also spelled Panjab |water]]s"), is a geographical region straddling the border between Pakistan and India which includes Punjab province in Pakistan and the states of the Punjab, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Chandigarh and some northern parts of the National Capital Territory of Delhi...
, and the Indus Valley. Remains of some of his buildings , influenced by Greek architecture, indicate that he was a great builder. Interestingly enough, according to the legend, Thomas was a skilled carpenter and was bidden to build a palace for the king. However, the Apostle decided to teach the king a lesson by devoting the royal grant to acts of charity and thereby laying up treasure for the heavenly abode.
Although little is known of the immediate growth of the church, Bar-Daisan ( 154-223) reports that in his time there were Christian tribes in North India which claimed to have been converted by Thomas and to have books and relics to prove it. But at least by the time of the establishment of the Second Persian Empire ( 226), there were bishops of the Church of the East in northwest India, Afghanistan and Baluchistan
Balochistan (region)
Balochistan or Baluchistan is an arid, mountainous region in the Iranian plateau in Southwest Asia; it includes part of southeastern Iran, western Pakistan, and southwestern Afghanistan. The area is named after the numerous Baloch tribes, Iranian peoples who moved into the area from the west...
, with laymen and clergy alike engaging in missionary activity.
The apocryphal Acts of Thomas
Acts of Thomas
The early 3rd century text called Acts of Thomas is one of the New Testament apocrypha, portraying Christ as the "Heavenly Redeemer", independent of and beyond creation, who can free souls from the darkness of the world. References to the work by Epiphanius of Salamis show that it was in...
(3rd century) identifies his second mission in India with a kingdom ruled by King Mahadwa, one of the rulers of a 1st-century dynasty in southern India. It is most significant that, aside from a small remnant of the Church of the East in Kurdistan, the only other church to maintain a distinctive identity is the Mar Thoma
Saint Thomas Christians
The Saint Thomas Christians are an ancient body of Christians from Kerala, India, who trace their origins to the evangelical activity of Thomas the Apostle in the 1st century. They are also known as "Nasranis" because they are followers of "Jesus of Nazareth". The term "Nasrani" is still used by St...
or “Church of Thomas” congregations along the Malabar Coast
Malabar Coast
The Malabar Coast is a long and narrow coastline on the south-western shore line of the mainland Indian subcontinent. Geographically, it comprises the wettest regions of southern India, as the Western Ghats intercept the moisture-laden monsoon rains, especially on their westward-facing mountain...
of Kerala
Kerala
or Keralam is an Indian state located on the Malabar coast of south-west India. It was created on 1 November 1956 by the States Reorganisation Act by combining various Malayalam speaking regions....
State in southwest India. According to the most ancient tradition of this church, Thomas evangelized this area and then crossed to the Coromandel Coast
Coromandel Coast
The Coromandel Coast is the name given to the southeastern coast of the Indian Subcontinent between Cape Comorin and False Divi Point...
of southeast India, where, after carrying out a second mission, he suffered martyrdom near Madras. Throughout the period under review, the church in India was under the jurisdiction of Edessa
Edessa, Mesopotamia
Edessa is the Greek name of an Aramaic town in northern Mesopotamia, as refounded by Seleucus I Nicator. For the modern history of the city, see Şanlıurfa.-Names:...
, which was then under the Mesopotamian patriarchate at Seleucia-Ctesiphon and later at Baghdad and Mosul.
See also
- History of ChristianityHistory of ChristianityThe history of Christianity concerns the Christian religion, its followers and the Church with its various denominations, from the first century to the present. Christianity was founded in the 1st century by the followers of Jesus of Nazareth who they believed to be the Christ or chosen one of God...
- Early ChristianityEarly ChristianityEarly Christianity is generally considered as Christianity before 325. The New Testament's Book of Acts and Epistle to the Galatians records that the first Christian community was centered in Jerusalem and its leaders included James, Peter and John....
- History of early ChristianityHistory of early ChristianityThe history of early Christianity covers Christianity before the First Council of Nicaea in 325.The first part of the period, during the lifetimes of the Twelve Apostles, is traditionally believed to have been initiated by the Great Commission of Jesus , and is called the Apostolic Age...
- Early Christian art and architectureEarly Christian art and architectureEarly Christian art and architecture is the art produced by Christians or under Christian patronage from about the year 100 to about the year 500. Prior to 100 there is no surviving art that can be called Christian with absolute certainty...
- Christianity in the 1st centuryChristianity in the 1st centuryThe earliest followers of Jesus composed an apocalyptic, Jewish sect, which historians refer to as Jewish Christianity. The Apostles and others following the Great Commission's decree to spread the teachings of Jesus to "all nations," had great success spreading the religion to gentiles. Peter,...
- Christianity in the 2nd centuryChristianity in the 2nd centuryThe 2nd century of Christianity was largely the time of the Apostolic Fathers who were the students of the apostles of Jesus, though there is some overlap as John the Apostle may have survived into the 2nd century and the early Apostolic Father Clement of Rome is said to have died at the end of the...
- Christianity in the 3rd centuryChristianity in the 3rd centuryThe 3rd century of Christianity was largely the time of the Ante-Nicene Fathers who wrote after the Apostolic Fathers of the 1st and 2nd centuries but before the First Council of Nicaea in 325...

