
Early modern period
Encyclopedia

History
History is the discovery, collection, organization, and presentation of information about past events. History can also mean the period of time after writing was invented. Scholars who write about history are called historians...
, the early modern period of modern history
Modern history
Modern history, or the modern era, describes the historical timeline after the Middle Ages. Modern history can be further broken down into the early modern period and the late modern period after the French Revolution and the Industrial Revolution...
follows the late Middle Ages
Late Middle Ages
The Late Middle Ages was the period of European history generally comprising the 14th to the 16th century . The Late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern era ....
. Although the chronological limits of the period are open to debate, the timeframe
Timeline
A timeline is a way of displaying a list of events in chronological order, sometimes described as a project artifact . It is typically a graphic design showing a long bar labeled with dates alongside itself and events labeled on points where they would have happened.-Uses of timelines:Timelines...
spans the period after the late portion of the Middle Ages
Middle Ages
The Middle Ages is a periodization of European history from the 5th century to the 15th century. The Middle Ages follows the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 and precedes the Early Modern Era. It is the middle period of a three-period division of Western history: Classic, Medieval and Modern...
(c. 1500) through the beginning of the Age of Revolutions (c. 1800). From a global standpoint, the most important feature of the early modern period was its globalizing
Proto-globalization
Proto-globalization or 'early modern globalization' is a period of the history of globalization roughly spanning the years between 1600 and 1800. First introduced by historians A. G...
character — it witnessed the exploration and colonization of the Americas and the rise of sustained contacts between previously isolated parts of the globe. The historical powers became involved in global trade. This world trading of goods plants, animals, and food crops saw exchange in the Old World
Old World
The Old World consists of those parts of the world known to classical antiquity and the European Middle Ages. It is used in the context of, and contrast with, the "New World" ....
and the New World
New World
The New World is one of the names used for the Western Hemisphere, specifically America and sometimes Oceania . The term originated in the late 15th century, when America had been recently discovered by European explorers, expanding the geographical horizon of the people of the European middle...
. The Columbian Exchange
Columbian Exchange
The Columbian Exchange was a dramatically widespread exchange of animals, plants, culture, human populations , communicable disease, and ideas between the Eastern and Western hemispheres . It was one of the most significant events concerning ecology, agriculture, and culture in all of human history...
greatly affected almost every society on Earth.
In the world, capitalist economies and institutions became more sophisticated and globally articulated. This process began in the medieval North Italian city-states, particularly Genoa
Genoa
Genoa |Ligurian]] Zena ; Latin and, archaically, English Genua) is a city and an important seaport in northern Italy, the capital of the Province of Genoa and of the region of Liguria....
, Venice
Venice
Venice is a city in northern Italy which is renowned for the beauty of its setting, its architecture and its artworks. It is the capital of the Veneto region...
, and Milan
Milan
Milan is the second-largest city in Italy and the capital city of the region of Lombardy and of the province of Milan. The city proper has a population of about 1.3 million, while its urban area, roughly coinciding with its administrative province and the bordering Province of Monza and Brianza ,...
. The early modern period also saw the rise and beginning of the dominance of the economic theory of mercantilism
Mercantilism
Mercantilism is the economic doctrine in which government control of foreign trade is of paramount importance for ensuring the prosperity and security of the state. In particular, it demands a positive balance of trade. Mercantilism dominated Western European economic policy and discourse from...
. It also saw the European colonization during the 15th to 19th centuries which resulted in the spread of Christianity around the world.
The early modern trends in various regions of the world represented a shift away from medieval modes of organization, sometimes politically and other-times economically. The period in Europe witnessed the decline of Christian theocracy
Theocracy
Theocracy is a form of organization in which the official policy is to be governed by immediate divine guidance or by officials who are regarded as divinely guided, or simply pursuant to the doctrine of a particular religious sect or religion....
, feudalism
Feudalism
Feudalism was a set of legal and military customs in medieval Europe that flourished between the 9th and 15th centuries, which, broadly defined, was a system for ordering society around relationships derived from the holding of land in exchange for service or labour.Although derived from the...
and serfdom
Serfdom
Serfdom is the status of peasants under feudalism, specifically relating to Manorialism. It was a condition of bondage or modified slavery which developed primarily during the High Middle Ages in Europe and lasted to the mid-19th century...
and includes the Reformation
Protestant Reformation
The Protestant Reformation was a 16th-century split within Western Christianity initiated by Martin Luther, John Calvin and other early Protestants. The efforts of the self-described "reformers", who objected to the doctrines, rituals and ecclesiastical structure of the Roman Catholic Church, led...
, the disastrous Thirty Years' War
Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War was fought primarily in what is now Germany, and at various points involved most countries in Europe. It was one of the most destructive conflicts in European history....
, the Commercial Revolution
Commercial Revolution
The Commercial Revolution was a period of European economic expansion, colonialism, and mercantilism which lasted from approximately the 16th century until the early 18th century. It was succeeded in the mid-18th century by the Industrial Revolution. Beginning with the Crusades, Europeans...
, the European colonization of the Americas
European colonization of the Americas
The start of the European colonization of the Americas is typically dated to 1492. The first Europeans to reach the Americas were the Vikings during the 11th century, who established several colonies in Greenland and one short-lived settlement in present day Newfoundland...
, and the Golden Age of Piracy
Golden Age of Piracy
The Golden Age of Piracy is a common designation given to one or more outbursts of piracy in maritime history of the early modern period. In its broadest accepted definition, the Golden Age of Piracy spans from the 1650s to the 1730s and covers three separate outbursts of piracy:the buccaneering...
. Ruling China at the beginning of the early modern period, the Ming Dynasty
Ming Dynasty
The Ming Dynasty, also Empire of the Great Ming, was the ruling dynasty of China from 1368 to 1644, following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan Dynasty. The Ming, "one of the greatest eras of orderly government and social stability in human history", was the last dynasty in China ruled by ethnic...
was "one of the greatest eras of orderly government and social stability in human history". By the 16th century the Ming economy was stimulated by trade with the Portuguese, the Spanish, and the Dutch. The Azuchi-Momoyama period
Azuchi-Momoyama period
The came at the end of the Warring States Period in Japan, when the political unification that preceded the establishment of the Tokugawa shogunate took place. It spans the years from approximately 1573 to 1603, during which time Oda Nobunaga and his successor, Toyotomi Hideyoshi, imposed order...
in Japan saw the Nanban trade
Nanban trade
The or the in Japanese history extends from the arrival of the first Europeans to Japan in 1543, to their near-total exclusion from the archipelago in 1614, under the promulgation of the "Sakoku" Seclusion Edicts.- Etymology :...
after the arrival of the first European Portuguese.
Other notable trends of the early modern period include the development of experimental science, the shrinkage of relative distances through improvements in transportation and communications, increasingly rapid technological progress
History of technology
The history of technology is the history of the invention of tools and techniques, and is similar in many ways to the history of humanity. Background knowledge has enabled people to create new things, and conversely, many scientific endeavors have become possible through technologies which assist...
, secularized civic politics and the early authoritarian nation states in various regions of the world.
Early modern timeline
-
-
- Dates are approximate, consult particular article for details
- Early modern themes Other
-
Europe and the West
This era in Western EuropeWestern Europe
Western Europe is a loose term for the collection of countries in the western most region of the European continents, though this definition is context-dependent and carries cultural and political connotations. One definition describes Western Europe as a geographic entity—the region lying in the...
is referred to as the early modern Europe
Early modern Europe
Early modern Europe is the term used by historians to refer to a period in the history of Europe which spanned the centuries between the end of the Middle Ages and the beginning of the Industrial Revolution, roughly the late 15th century to the late 18th century...
an period and includes the Protestant Reformation
Protestant Reformation
The Protestant Reformation was a 16th-century split within Western Christianity initiated by Martin Luther, John Calvin and other early Protestants. The efforts of the self-described "reformers", who objected to the doctrines, rituals and ecclesiastical structure of the Roman Catholic Church, led...
, the European wars of religion
European wars of religion
The European wars of religion were a series of wars waged in Europe from ca. 1524 to 1648, following the onset of the Protestant Reformation in Western and Northern Europe...
, the Age of Discovery
Age of Discovery
The Age of Discovery, also known as the Age of Exploration and the Great Navigations , was a period in history starting in the early 15th century and continuing into the early 17th century during which Europeans engaged in intensive exploration of the world, establishing direct contacts with...
and the beginning of European colonialism, the rise of strong centralized governments, the beginnings of recognizable nation-state
Nation-state
The nation state is a state that self-identifies as deriving its political legitimacy from serving as a sovereign entity for a nation as a sovereign territorial unit. The state is a political and geopolitical entity; the nation is a cultural and/or ethnic entity...
s that are the direct antecedents of today's states, the Age of Enlightenment
Age of Enlightenment
The Age of Enlightenment was an elite cultural movement of intellectuals in 18th century Europe that sought to mobilize the power of reason in order to reform society and advance knowledge. It promoted intellectual interchange and opposed intolerance and abuses in church and state...
and from the associated scientific advances
Science in the Age of Enlightenment
The scientific history of the Age of Enlightenment traces developments in science and technology during the Age of Reason, when Enlightenment ideas and ideals were being disseminated across Europe and North America...
the first phase of the Industrial Revolution
Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was a period from the 18th to the 19th century where major changes in agriculture, manufacturing, mining, transportation, and technology had a profound effect on the social, economic and cultural conditions of the times...
. The emergence of cultural and political dominance of the Western world
Western world
The Western world, also known as the West and the Occident , is a term referring to the countries of Western Europe , the countries of the Americas, as well all countries of Northern and Central Europe, Australia and New Zealand...
during this period is known as the Great Divergence
Great divergence
The Great Divergence, a term coined by Samuel Huntington , refers to the process by which the Western world The Great Divergence, a term coined by Samuel Huntington (also known as the European miracle, a term coined by Eric Jones in 1981), refers to the process by which the Western world The Great...
.
The early modern period is taken to end with the French Revolution
French Revolution
The French Revolution , sometimes distinguished as the 'Great French Revolution' , was a period of radical social and political upheaval in France and Europe. The absolute monarchy that had ruled France for centuries collapsed in three years...
, the Napoleonic Wars
Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars were a series of wars declared against Napoleon's French Empire by opposing coalitions that ran from 1803 to 1815. As a continuation of the wars sparked by the French Revolution of 1789, they revolutionised European armies and played out on an unprecedented scale, mainly due to...
, and the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a realm that existed from 962 to 1806 in Central Europe.It was ruled by the Holy Roman Emperor. Its character changed during the Middle Ages and the Early Modern period, when the power of the emperor gradually weakened in favour of the princes...
at the Congress of Vienna
Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna was a conference of ambassadors of European states chaired by Klemens Wenzel von Metternich, and held in Vienna from September, 1814 to June, 1815. The objective of the Congress was to settle the many issues arising from the French Revolutionary Wars, the Napoleonic Wars,...
.
At the end of the early modern period, the British and Russian
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was a state that existed from 1721 until the Russian Revolution of 1917. It was the successor to the Tsardom of Russia and the predecessor of the Soviet Union...
empires had emerged as world powers from the multipolar contest of colonial empire
Colonial empire
The Colonial empires were a product of the European Age of Exploration that began with a race of exploration between the then most advanced maritime powers, Portugal and Spain, in the 15th century...
s, while the three great Asia
Asia
Asia is the world's largest and most populous continent, located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres. It covers 8.7% of the Earth's total surface area and with approximately 3.879 billion people, it hosts 60% of the world's current human population...
n empires of the Early Modern period, Ottoman Turkey
Decline of the Ottoman Empire
The Decline of the Ottoman Empire is the period that followed after the Stagnation of the Ottoman Empire in which the empire experienced several economic and political setbacks. Directly affecting the Empire at this time was Russian imperialism...
Mughal India and Qing China, all entered a period of decline.
Renaissance and 'Early modern'
The expression "early modern" is sometimes incorrectly used as a substitute for the term RenaissanceRenaissance
The Renaissance was a cultural movement that spanned roughly the 14th to the 17th century, beginning in Italy in the Late Middle Ages and later spreading to the rest of Europe. The term is also used more loosely to refer to the historical era, but since the changes of the Renaissance were not...
. However, "Renaissance" is properly used in relation to a diverse series of cultural developments that occurred over several hundred years in many different parts of Europe — especially central and northern Italy
Italy
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
— and it spans the transition from late medieval civilization to the opening of the early modern period. In the visual arts and architecture, the term 'early modern' is not a common designation as the Renaissance period is clearly distinct from what came later. Only in the study of literature is the early modern period a standard designation. European music of the period is generally divided between Renaissance
Renaissance music
Renaissance music is European music written during the Renaissance. Defining the beginning of the musical era is difficult, given that its defining characteristics were adopted only gradually; musicologists have placed its beginnings from as early as 1300 to as late as the 1470s.Literally meaning...
and Baroque
Baroque music
Baroque music describes a style of Western Classical music approximately extending from 1600 to 1760. This era follows the Renaissance and was followed in turn by the Classical era...
. Similarly, philosophy is divided between Renaissance philosophy
Renaissance philosophy
Renaissance philosophy was the period of the history of philosophy in Europe that falls roughly between the Middle Ages and the Enlightenment. It includes the 15th century; some scholars extend it to as early as the 1350s or as late as the 16th century or early 17th century, overlapping the...
and the Enlightenment. In other fields, there is far more continuity through the period such as warfare
Gunpowder warfare
Early modern warfare is associated with the start of the widespread use of gunpowder and the development of suitable weapons to use the explosive, including artillery and handguns such as the arquebus and later the musket, and for this reason the era is also summarized as the age of gunpowder...
and science
History of science
The history of science is the study of the historical development of human understandings of the natural world and the domains of the social sciences....
.
The beginning of the early modern period is not clear-cut but is generally accepted to be in the late 15th century or early 16th century. Significant dates in this transitional phase from medieval to early modern Europe can be noted:
|
European kingdoms and movements
In the early modern period, the Holy Roman EmpireHoly Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a realm that existed from 962 to 1806 in Central Europe.It was ruled by the Holy Roman Emperor. Its character changed during the Middle Ages and the Early Modern period, when the power of the emperor gradually weakened in favour of the princes...
was a union of territories in Central Europe under a Holy Roman Emperor
Holy Roman Emperor
The Holy Roman Emperor is a term used by historians to denote a medieval ruler who, as German King, had also received the title of "Emperor of the Romans" from the Pope...
. The first emperor of the Holy Roman Empire was Otto I. The last was Francis II
Francis II, Holy Roman Emperor
Francis II was the last Holy Roman Emperor, ruling from 1792 until 6 August 1806, when he dissolved the Empire after the disastrous defeat of the Third Coalition by Napoleon at the Battle of Austerlitz...
, who abdicated
Abdication
Abdication occurs when a monarch, such as a king or emperor, renounces his office.-Terminology:The word abdication comes derives from the Latin abdicatio. meaning to disown or renounce...
and dissolved the Empire in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars
Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars were a series of wars declared against Napoleon's French Empire by opposing coalitions that ran from 1803 to 1815. As a continuation of the wars sparked by the French Revolution of 1789, they revolutionised European armies and played out on an unprecedented scale, mainly due to...
. Despite its name, for much of its history the Empire did not include Rome within its borders.
The Renaissance
Renaissance
The Renaissance was a cultural movement that spanned roughly the 14th to the 17th century, beginning in Italy in the Late Middle Ages and later spreading to the rest of Europe. The term is also used more loosely to refer to the historical era, but since the changes of the Renaissance were not...
was a cultural movement that spanned roughly the 14th to the 17th century, beginning in Italy in the Late Middle Ages
Late Middle Ages
The Late Middle Ages was the period of European history generally comprising the 14th to the 16th century . The Late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern era ....
and later spreading to the rest of Europe. The term is also used more loosely to refer to the historic era
Era
An era is a commonly used word for long period of time. When used in science, for example geology, eras denote clearly defined periods of time of arbitrary but well defined length, such as for example the Mesozoic era from 252 Ma–66 Ma, delimited by a start event and an end event. When used in...
, but since the changes of the Renaissance were not uniform across Europe, this is a general use of the term. As a cultural movement, it encompassed a rebellion of learning based on classical
Classical antiquity
Classical antiquity is a broad term for a long period of cultural history centered on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations of ancient Greece and ancient Rome, collectively known as the Greco-Roman world...
sources, the development of linear perspective
Perspective (graphical)
Perspective in the graphic arts, such as drawing, is an approximate representation, on a flat surface , of an image as it is seen by the eye...
in painting, and gradual but widespread educational
History of education
The history of education its part of the past and present teaching and learning. Each generation, since the beginning of human existence, has sought to pass on cultural and social values, traditions, morality, religion and skills to the next generation. The passing on of culture is also known as...
reform.
Notable individuals
Johannes Gutenberg is credited with being the first European to use movable typeMovable type
Movable type is the system of printing and typography that uses movable components to reproduce the elements of a document ....
printing
Printing
Printing is a process for reproducing text and image, typically with ink on paper using a printing press. It is often carried out as a large-scale industrial process, and is an essential part of publishing and transaction printing....
, around 1439, and the global inventor of the mechanical printing press
Printing press
A printing press is a device for applying pressure to an inked surface resting upon a print medium , thereby transferring the ink...
. Nicolaus Copernicus
Nicolaus Copernicus
Nicolaus Copernicus was a Renaissance astronomer and the first person to formulate a comprehensive heliocentric cosmology which displaced the Earth from the center of the universe....
formulated a comprehensive heliocentric
Heliocentrism
Heliocentrism, or heliocentricism, is the astronomical model in which the Earth and planets revolve around a stationary Sun at the center of the universe. The word comes from the Greek . Historically, heliocentrism was opposed to geocentrism, which placed the Earth at the center...
cosmology
Cosmology
Cosmology is the discipline that deals with the nature of the Universe as a whole. Cosmologists seek to understand the origin, evolution, structure, and ultimate fate of the Universe at large, as well as the natural laws that keep it in order...
, which displaced the Earth
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
from the center of the universe. His book, De revolutionibus orbium coelestium
De revolutionibus orbium coelestium
De revolutionibus orbium coelestium is the seminal work on the heliocentric theory of the Renaissance astronomer Nicolaus Copernicus...
(On the Revolutions of the Celestial Spheres) began modern astronomy
Astronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that deals with the study of celestial objects and phenomena that originate outside the atmosphere of Earth...
and was an epiphany
Epiphany (feeling)
An epiphany is the sudden realization or comprehension of the essence or meaning of something...
that sparked the Scientific Revolution
Scientific revolution
The Scientific Revolution is an era associated primarily with the 16th and 17th centuries during which new ideas and knowledge in physics, astronomy, biology, medicine and chemistry transformed medieval and ancient views of nature and laid the foundations for modern science...
. Another notable individual was Machiavelli, an Italian philosopher politician. He is considered a founder of modern political science
Political science
Political Science is a social science discipline concerned with the study of the state, government and politics. Aristotle defined it as the study of the state. It deals extensively with the theory and practice of politics, and the analysis of political systems and political behavior...
. Machiavelli is most famous for a short political treatise, The Prince
The Prince
The Prince is a political treatise by the Italian diplomat, historian and political theorist Niccolò Machiavelli. From correspondence a version appears to have been distributed in 1513, using a Latin title, De Principatibus . But the printed version was not published until 1532, five years after...
, a work of realist political theory.
Among the royalty of the time that were notable, Charles the Bold, known as Charles the Bold (or Rash) (not 'the Terrible') to his enemies, he was the last Valois Duke of Burgundy
Duke of Burgundy
Duke of Burgundy was a title borne by the rulers of the Duchy of Burgundy, a small portion of traditional lands of Burgundians west of river Saône which in 843 was allotted to Charles the Bald's kingdom of West Franks...
and his early death was a pivotal, if under-recognized, moment in European history. Charles has often been regarded as the last representative of the feudal spirit — a man who possessed no other quality than a blind bravery. Upon his death, Charles left an unmarried nineteen-year-old daughter, Mary of Burgundy
Mary of Burgundy
Mary of Burgundy ruled the Burgundian territories in Low Countries and was suo jure Duchess of Burgundy from 1477 until her death...
, as his heir; her marriage would have enormous implications for the political balance of Europe. The Habsburg Emperor secured the match for his son, the future Maximilian I, Holy Roman Emperor
Maximilian I, Holy Roman Emperor
Maximilian I , the son of Frederick III, Holy Roman Emperor and Eleanor of Portugal, was King of the Romans from 1486 and Holy Roman Emperor from 1493 until his death, though he was never in fact crowned by the Pope, the journey to Rome always being too risky...
, with the aid of Mary's stepmother, Margaret. In 1477, the territory of the Duchy of Burgundy
Duchy of Burgundy
The Duchy of Burgundy , was heir to an ancient and prestigious reputation and a large division of the lands of the Second Kingdom of Burgundy and in its own right was one of the geographically larger ducal territories in the emergence of Early Modern Europe from Medieval Europe.Even in that...
was annexed by France. In the same year, Mary married Maximilian, Archduke of Austria, giving the Habsburgs control of the remainder of the Burgundian Inheritance.
Claude de Lorraine was the first Duke of Guise from 1528 to his death. Claude distinguished himself at the battle of Marignano
Battle of Marignano
The Battle of Marignano was fought during the phase of the Italian Wars called the War of the League of Cambrai, between France and the Old Swiss Confederacy. It took place on September 13 and 15, 1515, near the town today called Melegnano, 16 km southeast of Milan...
(1515), and was long in recovering from the twenty-two wounds he received in the battle. In 1521, he fought at Fuenterrabia, and Louise of Savoy
Louise of Savoy
Louise of Savoy was a French noble, Duchess regnant of Auvergne and Bourbon, Duchess of Nemours, the mother of King Francis I of France...
ascribed the capture of the place to his efforts. In 1523 he became governor of Champagne
Champagne (province)
The Champagne wine region is a historic province within the Champagne administrative province in the northeast of France. The area is best known for the production of the sparkling white wine that bears the region's name...
and Burgundy, after defeating at Neufchâteau
Neufchâteau, Vosges
Neufchâteau is a commune in the Vosges department in Lorraine in northeastern France.Inhabitants are called Néocastriens.-Geography:Positioned at the confluence of the Rivers Meuse and Mouzon, the little town dominates the Vosges Plain...
the imperial
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a realm that existed from 962 to 1806 in Central Europe.It was ruled by the Holy Roman Emperor. Its character changed during the Middle Ages and the Early Modern period, when the power of the emperor gradually weakened in favour of the princes...
troops who had invaded this province. In 1525 he destroyed the Anabaptist
Anabaptist
Anabaptists are Protestant Christians of the Radical Reformation of 16th-century Europe, and their direct descendants, particularly the Amish, Brethren, Hutterites, and Mennonites....
peasant army
German Peasants' War
The German Peasants' War or Great Peasants' Revolt was a widespread popular revolt in the German-speaking areas of Central Europe, 1524–1526. At its height in the spring and summer of 1525, the conflict involved an estimated 300,000 peasants: contemporary estimates put the dead at 100,000...
, which was overrunning Lorraine
Lorraine (province)
The Duchy of Upper Lorraine was an historical duchy roughly corresponding with the present-day northeastern Lorraine region of France, including parts of modern Luxembourg and Germany. The main cities were Metz, Verdun, and the historic capital Nancy....
, at Lupstein
Lupstein
Lupstein is a commune in the Bas-Rhin department in Alsace in north-eastern France.-People:* Alois Kayser, Catholic pastor who was active in Nauru, was born in Lupstein.-References:* -External links:*...
, near Saverne
Saverne
Saverne is a commune in the Bas-Rhin department in Alsace in north-eastern France. It is situated on the Rhine-Marne canal at the foot of a pass over the Vosges Mountains, and 45 km N.W...
(Zabern). On the return of Francis I from captivity in 1528, Claude was made Duke of Guise in the peerage of France
Peerage of France
The Peerage of France was a distinction within the French nobility which appeared in the Middle Ages. It was abolished in 1789 during the French Revolution, but it reappeared in 1814 at the time of the Bourbon Restoration which followed the fall of the First French Empire...
, though up to this time only princes of the royal house had held the title of duke and peer of France. The Guises, as cadets of the sovereign house of Lorraine and descendants of the house of Anjou
House of Valois-Anjou
The Valois House of Anjou, or the Younger House of Anjou, was a noble French family, deriving from the royal family, the House of Valois. They were monarchs of Naples, as well as various other territories....
, claimed precedence of the Bourbon
House of Bourbon
The House of Bourbon is a European royal house, a branch of the Capetian dynasty . Bourbon kings first ruled Navarre and France in the 16th century. By the 18th century, members of the Bourbon dynasty also held thrones in Spain, Naples, Sicily, and Parma...
princes of Condé
Prince of Condé
The Most Serene House of Condé is a historical French house, a noble lineage of descent from a single ancestor...
and Conti
Prince of Conti
The title of Prince of Conti was a French noble title, assumed by a cadet branch of the house of Bourbon-Condé. It was taken from Conty, a small town of northern France, c. 35 km southwest of Amiens, which came into the Condé family by the marriage of Louis of Bourbon, first prince of Condé,...
.
The 3rd Duke of Alba
Fernando Álvarez de Toledo, 3rd Duke of Alba
Don Fernando Álvarez de Toledo y Pimentel, 3rd Duke of Alba was a Spanish general and governor of the Spanish Netherlands , nicknamed "the Iron Duke" in the Low Countries because of his harsh and cruel rule there and his role in the execution of his political opponents and the massacre of several...
was a nobleman of importance in the early modern period, nicknamed the "Iron Duke" by the Protestants of the Low Countries
Low Countries
The Low Countries are the historical lands around the low-lying delta of the Rhine, Scheldt, and Meuse rivers, including the modern countries of Belgium, the Netherlands, Luxembourg and parts of northern France and western Germany....
because of his harsh rule and cruelty. Tales of atrocities committed during his military operations in Flanders
Flanders
Flanders is the community of the Flemings but also one of the institutions in Belgium, and a geographical region located in parts of present-day Belgium, France and the Netherlands. "Flanders" can also refer to the northern part of Belgium that contains Brussels, Bruges, Ghent and Antwerp...
became part of Dutch and English folklore, forming a central component of the Black Legend
Black Legend
The Black Legend refers to a style of historical writing that demonizes Spain and in particular the Spanish Empire in a politically motivated attempt to morally disqualify Spain and its people, and to incite animosity against Spanish rule...
.
In England, Henry VIII
Henry VIII of England
Henry VIII was King of England from 21 April 1509 until his death. He was Lord, and later King, of Ireland, as well as continuing the nominal claim by the English monarchs to the Kingdom of France...
was the King of England and a significant figure in the history of the English monarchy. Although in the greater part of his reign he brutally suppressed the influence of the Protestant Reformation
Protestant Reformation
The Protestant Reformation was a 16th-century split within Western Christianity initiated by Martin Luther, John Calvin and other early Protestants. The efforts of the self-described "reformers", who objected to the doctrines, rituals and ecclesiastical structure of the Roman Catholic Church, led...
in England, a movement having some roots with John Wycliffe
John Wycliffe
John Wycliffe was an English Scholastic philosopher, theologian, lay preacher, translator, reformer and university teacher who was known as an early dissident in the Roman Catholic Church during the 14th century. His followers were known as Lollards, a somewhat rebellious movement, which preached...
in the 14th century, he is more popularly known for his political struggles with Rome
Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the world's largest Christian church, with over a billion members. Led by the Pope, it defines its mission as spreading the gospel of Jesus Christ, administering the sacraments and exercising charity...
. These struggles ultimately led to the separation of the Church of England
Church of England
The Church of England is the officially established Christian church in England and the Mother Church of the worldwide Anglican Communion. The church considers itself within the tradition of Western Christianity and dates its formal establishment principally to the mission to England by St...
from papal authority, the Dissolution of the Monasteries
Dissolution of the Monasteries
The Dissolution of the Monasteries, sometimes referred to as the Suppression of the Monasteries, was the set of administrative and legal processes between 1536 and 1541 by which Henry VIII disbanded monasteries, priories, convents and friaries in England, Wales and Ireland; appropriated their...
, and establishing himself as the Supreme Head of the Church of England. Though Henry reportedly became a Protestant on his death-bed, he advocated Catholic ceremony and doctrine throughout his life. Royal support for the English Reformation
English Reformation
The English Reformation was the series of events in 16th-century England by which the Church of England broke away from the authority of the Pope and the Roman Catholic Church....
began with his heirs, the devout Edward VI
Edward VI of England
Edward VI was the King of England and Ireland from 28 January 1547 until his death. He was crowned on 20 February at the age of nine. The son of Henry VIII and Jane Seymour, Edward was the third monarch of the Tudor dynasty and England's first monarch who was raised as a Protestant...
and the renowned Elizabeth I
Elizabeth I of England
Elizabeth I was queen regnant of England and Ireland from 17 November 1558 until her death. Sometimes called The Virgin Queen, Gloriana, or Good Queen Bess, Elizabeth was the fifth and last monarch of the Tudor dynasty...
, whilst daughter Mary I
Mary I of England
Mary I was queen regnant of England and Ireland from July 1553 until her death.She was the only surviving child born of the ill-fated marriage of Henry VIII and his first wife Catherine of Aragon. Her younger half-brother, Edward VI, succeeded Henry in 1547...
temporarily reinstated papal authority over England. Henry also oversaw the legal union of England and Wales
Wales
Wales is a country that is part of the United Kingdom and the island of Great Britain, bordered by England to its east and the Atlantic Ocean and Irish Sea to its west. It has a population of three million, and a total area of 20,779 km²...
with the Laws in Wales Acts 1535–1542. He is also noted for his six wives
Wives of Henry VIII
The wives of Henry VIII were the six queens consort married to Henry VIII of England between 1509 and 1547. The six women to hold the title 'queens consort' of King Henry VIII were, in order:* Catherine of Aragon ,* Anne Boleyn ,...
, two of whom were beheaded
Decapitation
Decapitation is the separation of the head from the body. Beheading typically refers to the act of intentional decapitation, e.g., as a means of murder or execution; it may be accomplished, for example, with an axe, sword, knife, wire, or by other more sophisticated means such as a guillotine...
.
Christians and Christendom
Christianity at the beginning of the modern period saw the fall of Constantinople in 1453, the end of the Hundred Years War, the discovery of the New World in 1492, and thereafter various movements to reform the church (Lutheran, Zwinglian, Calvinist, etc.), followed by the Counter Reformation.End of the Crusades and Unity
The Hussite CrusadesHussite Wars
The Hussite Wars, also called the Bohemian Wars involved the military actions against and amongst the followers of Jan Hus in Bohemia in the period 1419 to circa 1434. The Hussite Wars were notable for the extensive use of early hand-held gunpowder weapons such as hand cannons...
involved the military actions against and amongst the followers of Jan Hus
Jan Hus
Jan Hus , often referred to in English as John Hus or John Huss, was a Czech priest, philosopher, reformer, and master at Charles University in Prague...
in Bohemia ending ultimately with the Battle of Grotniki
Battle of Grotniki
The Battle of Grotniki took place on May 4, 1439 in the vicinity of Grotniki Duże, a village near Nowy Korczyn, currently in Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship....
. Also known as the Hussite Wars, they were arguably the first European war in which hand-held gunpowder weapons such as musket
Musket
A musket is a muzzle-loaded, smooth bore long gun, fired from the shoulder. Muskets were designed for use by infantry. A soldier armed with a musket had the designation musketman or musketeer....
s made a decisive contribution. The Taborite
Taborite
The Taborites were members of a religious community considered heretical by the Catholic Church. The Taborites were centered on the Bohemian city of Tábor during the Hussite Wars in the 15th century. The religious reform movement in Bohemia splintered into various religious sects...
faction of the Hussite
Hussite
The Hussites were a Christian movement following the teachings of Czech reformer Jan Hus , who became one of the forerunners of the Protestant Reformation...
warriors were basically infantry, and their many defeats of larger armies with heavily armored knights helped effect the infantry revolution. In totality, the Hussite Crusades were inconclusive.
The last crusade, the Crusade of 1456, was organized to counter the expanding Ottoman Empire and lift the Siege of Belgrade led by John Hunyadi
John Hunyadi
John Hunyadi John Hunyadi (Hungarian: Hunyadi János , Medieval Latin: Ioannes Corvinus or Ioannes de Hunyad, Romanian: Iancu (Ioan) de Hunedoara, Croatian: Janko Hunjadi, Serbian: Сибињанин Јанко / Sibinjanin Janko, Slovak: Ján Huňady) John Hunyadi (Hungarian: Hunyadi János , Medieval Latin: ...
and Giovanni da Capistrano
Giovanni da Capistrano
Saint John of Capistrano, O.F.M., was a Franciscan friar and Catholic priest from Italy...
. The siege eventually escalated into a major battle, during which Hunyadi led a sudden counterattack that overran the Turkish camp, ultimately compelling the wounded Sultan Mehmet II to lift the siege and retreat. The siege of Belgrade has been characterized as having "decided the fate of Christendom
Christendom
Christendom, or the Christian world, has several meanings. In a cultural sense it refers to the worldwide community of Christians, adherents of Christianity...
". The noon bell
Noon bell
During the Siege of Belgrade . In 1456, Hungarian noblemen John Hunyadi and Mihály Szilágyi defended the city against the onslaught of the Ottoman Sultan Mehmed II. The siege finished with a Christian victory...
ordered by Pope Callixtus III
Pope Callixtus III
Pope Callixtus III , né Alfons de Borja, was Pope from April 8, 1455 to his death in 1458.-Biography:...
commemorates the victory throughout the Christian world to this day.
Nearly a hundred years later, the Peace of Augsburg
Peace of Augsburg
The Peace of Augsburg, also called the Augsburg Settlement, was a treaty between Charles V and the forces of the Schmalkaldic League, an alliance of Lutheran princes, on September 25, 1555, at the imperial city of Augsburg, now in present-day Bavaria, Germany.It officially ended the religious...
officially ended the idea that all Christians could be united under one church. The principle of cuius regio, eius religio
Cuius regio, eius religio
Cuius regio, eius religio is a phrase in Latin translated as "Whose realm, his religion", meaning the religion of the ruler dictated the religion of the ruled...
("whose the region is, [it shall have] his religion") established the religious, political and geographic divisions of Christianity, and this was established in international law
International law
Public international law concerns the structure and conduct of sovereign states; analogous entities, such as the Holy See; and intergovernmental organizations. To a lesser degree, international law also may affect multinational corporations and individuals, an impact increasingly evolving beyond...
with the Treaty of Westphalia in 1648, which legally ended the concept of a single Christian hegemony
Hegemony
Hegemony is an indirect form of imperial dominance in which the hegemon rules sub-ordinate states by the implied means of power rather than direct military force. In Ancient Greece , hegemony denoted the politico–military dominance of a city-state over other city-states...
, i.e. the "One, Holy, Catholic, and Apostolic Church" of the Nicene Creed
Nicene Creed
The Nicene Creed is the creed or profession of faith that is most widely used in Christian liturgy. It is called Nicene because, in its original form, it was adopted in the city of Nicaea by the first ecumenical council, which met there in the year 325.The Nicene Creed has been normative to the...
. Each government determined the religion of their own state. Christians living in states where their denomination was not the established church were guaranteed the right to practice their faith in public during allotted hours and in private at their will. With the Treaty of Westphalia, the Wars of Religion
European wars of religion
The European wars of religion were a series of wars waged in Europe from ca. 1524 to 1648, following the onset of the Protestant Reformation in Western and Northern Europe...
came to an end, and in the Treaty of Utrecht
Treaty of Utrecht
The Treaty of Utrecht, which established the Peace of Utrecht, comprises a series of individual peace treaties, rather than a single document, signed by the belligerents in the War of Spanish Succession, in the Dutch city of Utrecht in March and April 1713...
of 1713 the concept of the sovereign national state
National sovereignty
National sovereignty is the doctrine that sovereignty belongs to and derives from the nation, an abstract entity normally linked to a physical territory and its past, present, and future citizens. It is an ideological concept or doctrine derived from liberal political theory...
was born. The Corpus Christianum has since existed with the modern idea of a tolerant and diverse society consisting of many different communities.
Inquisitions and Reformations
The modern InquisitionInquisition
The Inquisition, Inquisitio Haereticae Pravitatis , was the "fight against heretics" by several institutions within the justice-system of the Roman Catholic Church. It started in the 12th century, with the introduction of torture in the persecution of heresy...
refers to any one of several institutions charged with trying and convicting heretics
Christian heresy
Christian heresy refers to non-orthodox practices and beliefs that were deemed to be heretical by one or more of the Christian churches. In Western Christianity, the term "heresy" most commonly refers to those beliefs which were declared to be anathema by the Catholic Church prior to the schism of...
(or other offenders against canon law
Canon law
Canon law is the body of laws & regulations made or adopted by ecclesiastical authority, for the government of the Christian organization and its members. It is the internal ecclesiastical law governing the Catholic Church , the Eastern and Oriental Orthodox churches, and the Anglican Communion of...
) within the Catholic Church. In the modern era, the first manifestation was the Spanish Inquisition
Spanish Inquisition
The Tribunal of the Holy Office of the Inquisition , commonly known as the Spanish Inquisition , was a tribunal established in 1480 by Catholic Monarchs Ferdinand II of Aragon and Isabella I of Castile. It was intended to maintain Catholic orthodoxy in their kingdoms, and to replace the Medieval...
of 1478 to 1834. The Inquisition prosecuted individuals accused of a wide array of crimes related to heresy, including sorcery
Magic (paranormal)
Magic is the claimed art of manipulating aspects of reality either by supernatural means or through knowledge of occult laws unknown to science. It is in contrast to science, in that science does not accept anything not subject to either direct or indirect observation, and subject to logical...
, blasphemy
Blasphemy
Blasphemy is irreverence towards religious or holy persons or things. Some countries have laws to punish blasphemy, while others have laws to give recourse to those who are offended by blasphemy...
, Judaizing and witchcraft
Witchcraft
Witchcraft, in historical, anthropological, religious, and mythological contexts, is the alleged use of supernatural or magical powers. A witch is a practitioner of witchcraft...
, as well for censorship
Censorship
thumb|[[Book burning]] following the [[1973 Chilean coup d'état|1973 coup]] that installed the [[Military government of Chile |Pinochet regime]] in Chile...
of printed literature. Because of its objective — combating heresy — the Inquisition had jurisdiction only over baptized members of the Church (which, however, encompassed the vast majority of the population in Catholic countries). Secular courts could still try non-Christians for blasphemy. (Most of the witch trials went through secular courts.)
The Reformation and rise of modernity
Modernity
Modernity typically refers to a post-traditional, post-medieval historical period, one marked by the move from feudalism toward capitalism, industrialization, secularization, rationalization, the nation-state and its constituent institutions and forms of surveillance...
in the early 16th century entailed the start of a series of changes in the Corpus Christianum. Martin Luther
Martin Luther
Martin Luther was a German priest, professor of theology and iconic figure of the Protestant Reformation. He strongly disputed the claim that freedom from God's punishment for sin could be purchased with money. He confronted indulgence salesman Johann Tetzel with his Ninety-Five Theses in 1517...
challenged the Catholic Church to begin the Reformation
Protestant Reformation
The Protestant Reformation was a 16th-century split within Western Christianity initiated by Martin Luther, John Calvin and other early Protestants. The efforts of the self-described "reformers", who objected to the doctrines, rituals and ecclesiastical structure of the Roman Catholic Church, led...
. The Protestant Reformation
Protestant Reformation
The Protestant Reformation was a 16th-century split within Western Christianity initiated by Martin Luther, John Calvin and other early Protestants. The efforts of the self-described "reformers", who objected to the doctrines, rituals and ecclesiastical structure of the Roman Catholic Church, led...
was a Christian reform movement in Europe which is generally deemed to have begun with Martin Luther's Ninety-Five Theses although a number of precursors such as Johannes Hus predate that event. The Protestant movement of the 16th century was effected under the protection of the electors of Saxony. The Electorate of Saxony
Electorate of Saxony
The Electorate of Saxony , sometimes referred to as Upper Saxony, was a State of the Holy Roman Empire. It was established when Emperor Charles IV raised the Ascanian duchy of Saxe-Wittenberg to the status of an Electorate by the Golden Bull of 1356...
was an independent hereditary electorate
Prince-elector
The Prince-electors of the Holy Roman Empire were the members of the electoral college of the Holy Roman Empire, having the function of electing the Roman king or, from the middle of the 16th century onwards, directly the Holy Roman Emperor.The heir-apparent to a prince-elector was known as an...
of the Holy Roman Empire
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a realm that existed from 962 to 1806 in Central Europe.It was ruled by the Holy Roman Emperor. Its character changed during the Middle Ages and the Early Modern period, when the power of the emperor gradually weakened in favour of the princes...
. The Elector Frederick III
Frederick III, Elector of Saxony
Frederick III of Saxony , also known as Frederick the Wise , was Elector of Saxony from 1486 to his death. Frederick was the son of Ernest, Elector of Saxony and his wife Elisabeth, daughter of Albert III, Duke of Bavaria...
established a university at Wittenberg in 1502, at which the Augustinian monk Martin Luther was made professor of philosophy in 1508; at the same time he became one of the preachers at the castle church of Wittenberg. On 31 October 1517, he posted up the Ninety-Five Theses against the sale indulgence
Indulgence
In Catholic theology, an indulgence is the full or partial remission of temporal punishment due for sins which have already been forgiven. The indulgence is granted by the Catholic Church after the sinner has confessed and received absolution...
s on the door of the All Saints' Church
All Saints' Church, Wittenberg
All Saints' Church, commonly referred to as Schlosskirche, meaning "Castle Church" — to distinguish it from the "town church", the Stadtkirche of St. Mary — and sometimes known as the Reformation Memorial Church, is a Lutheran church in Lutherstadt Wittenberg, Germany...
, which served as a notice board for university-related announcements. These were points for debate that criticized the Church and the Pope. The most controversial points centered on the practice of selling indulgences and the Church's policy on purgatory
Purgatory
Purgatory is the condition or process of purification or temporary punishment in which, it is believed, the souls of those who die in a state of grace are made ready for Heaven...
. The reform movement soon split along certain doctrinal lines. Spiritual disagreements between various leading figures led to the emergence of rival Protestant churches. The most important denomination
Christian denomination
A Christian denomination is an identifiable religious body under a common name, structure, and doctrine within Christianity. In the Orthodox tradition, Churches are divided often along ethnic and linguistic lines, into separate churches and traditions. Technically, divisions between one group and...
s to emerge directly from the Reformation were the Lutherans, and the Reformed/Calvinists/Presbyterians. The process of reform had decidedly different causes and effects in other countries. In England, where it gave rise to Anglicanism
Anglicanism
Anglicanism is a tradition within Christianity comprising churches with historical connections to the Church of England or similar beliefs, worship and church structures. The word Anglican originates in ecclesia anglicana, a medieval Latin phrase dating to at least 1246 that means the English...
, the period became known as the English Reformation
English Reformation
The English Reformation was the series of events in 16th-century England by which the Church of England broke away from the authority of the Pope and the Roman Catholic Church....
. Subsequent Protestant denominations generally trace their roots back to the initial reforming movements.
Of the late Inquisitions in the modern era, there were two different manifestations:
- the Portuguese InquisitionPortuguese InquisitionThe Portuguese Inquisition was formally established in Portugal in 1536 at the request of the King of Portugal, João III. Manuel I had asked for the installation of the Inquisition in 1515 to fulfill the commitment of marriage with Maria of Aragon, but it was only after his death that the Pope...
(1536–1821) - the Roman InquisitionRoman InquisitionThe Roman Inquisition was a system of tribunals developed by the Holy See during the second half of the 16th century, responsible for prosecuting individuals accused of a wide array of crimes related to heresy, including Protestantism, sorcery, immorality, blasphemy, Judaizing and witchcraft, as...
(1542 – c.1860)
This Portuguese inquisition was a local analogue of the more famous Spanish Inquisition. The Roman Inquisition covered most of the Italian peninsula
Italian Peninsula
The Italian Peninsula or Apennine Peninsula is one of the three large peninsulas of Southern Europe , spanning from the Po Valley in the north to the central Mediterranean Sea in the south. The peninsula's shape gives it the nickname Lo Stivale...
as well as Malta
Malta
Malta , officially known as the Republic of Malta , is a Southern European country consisting of an archipelago situated in the centre of the Mediterranean, south of Sicily, east of Tunisia and north of Libya, with Gibraltar to the west and Alexandria to the east.Malta covers just over in...
and also existed in isolated pockets of papal jurisdiction in other parts of Europe, including Avignon
Avignon
Avignon is a French commune in southeastern France in the départment of the Vaucluse bordered by the left bank of the Rhône river. Of the 94,787 inhabitants of the city on 1 January 2010, 12 000 live in the ancient town centre surrounded by its medieval ramparts.Often referred to as the...
.
The Catholic Reformation began in 1545 when the Council of Trent
Council of Trent
The Council of Trent was the 16th-century Ecumenical Council of the Roman Catholic Church. It is considered to be one of the Church's most important councils. It convened in Trent between December 13, 1545, and December 4, 1563 in twenty-five sessions for three periods...
was called in reaction to the "Protestant Rebellion". The idea was to reform the state of worldliness and disarray which had befallen some of the clergy of the Church, while reaffirming the Catholic Church's spiritual authority and position as the sole true Church of Christ
Church of Christ
Churches of Christ are autonomous Christian congregations associated with one another through common beliefs and practices. They seek to base doctrine and practice on the Bible alone, and seek to be New Testament congregations as originally established by the authority of Christ. Historically,...
on Earth, as well as preventing further damage to the Church and her faithful at the hands of the newly formed Protestant denominations.
Tsardom of Russia
In development of the Third RomeThird Rome
The term Third Rome describes the idea that some European city, state, or country is the successor to the legacy of the Roman Empire and its successor state, the Byzantine Empire ....
ideas, the Grand Duke Ivan IV (the "Awesome" or "the Terrible") was officially crowned the first Tsar
Tsar
Tsar is a title used to designate certain European Slavic monarchs or supreme rulers. As a system of government in the Tsardom of Russia and Russian Empire, it is known as Tsarist autocracy, or Tsarism...
("Caesar
Caesar (title)
Caesar is a title of imperial character. It derives from the cognomen of Julius Caesar, the Roman dictator...
") of Russia in 1547. The Tsar promulgated a new code of laws (Sudebnik of 1550
Sudebnik of 1550
Sudebnik of tsar Ivan IV , a revised code of laws instituted by his grandfather Ivan the Great. This code can be considered as the result of the first Russian parliament of the feudal Estates type of 1549....
), established the first Russian feudal representative body (Zemsky Sobor
Zemsky Sobor
The zemsky sobor was the first Russian parliament of the feudal Estates type, in the 16th and 17th centuries. The term roughly means assembly of the land. It could be summoned either by tsar, or patriarch, or the Boyar Duma...
) and introduced local self-management into the rural regions. During his long reign, Ivan IV nearly doubled the already large Russian territory by annexing the three Tatar khanates (parts of disintegrated Golden Horde
Golden Horde
The Golden Horde was a Mongol and later Turkicized khanate that formed the north-western sector of the Mongol Empire...
): Kazan
Khanate of Kazan
The Khanate of Kazan was a medieval Tatar state which occupied the territory of former Volga Bulgaria between 1438 and 1552. Its khans were the patrilineal descendants of Toqa Temür, the thirteenth son of Jochi and grandson of Genghis Khan. The khanate covered contemporary Tatarstan, Mari El,...
and Astrakhan
Astrakhan Khanate
The Khanate of Astrakhan was a Tatar feudal state that appeared after the collapse of the Golden Horde. The Khanate existed in the 15th and 16th centuries in the area adjacent to the mouth of the Volga river, where the contemporary city of Astrakhan/Hajji Tarkhan is now located...
along the Volga River, and Sibirean Khanate in South Western Siberia. Thus by the end of the 16th century Russia was transformed into a multiethnic, multiconfessional and transcontinental state.
Discovery and trade
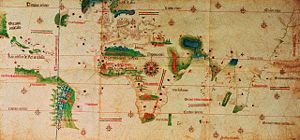
Age of Discovery
The Age of Discovery, also known as the Age of Exploration and the Great Navigations , was a period in history starting in the early 15th century and continuing into the early 17th century during which Europeans engaged in intensive exploration of the world, establishing direct contacts with...
was a period from the early 15th century and continuing into the early 17th century, during which European ships traveled around the world to search for new trading routes and partners to feed burgeoning capitalism in Europe. They also were in search of trading goods such as gold, silver and spices. In the process, Europeans encountered peoples and mapped lands previously unknown to them. This factor in the early European modern period was a globalizing
Proto-globalization
Proto-globalization or 'early modern globalization' is a period of the history of globalization roughly spanning the years between 1600 and 1800. First introduced by historians A. G...
character; the 'discovery' of the Americas and the rise of sustained contacts between previously isolated parts of the globe was an important historical event..
The search for new routes was based on the fact that the Silk Road
Silk Road
The Silk Road or Silk Route refers to a historical network of interlinking trade routes across the Afro-Eurasian landmass that connected East, South, and Western Asia with the Mediterranean and European world, as well as parts of North and East Africa...
was controlled by the Ottoman Empire, which was an impediment to European commercial interests, and other Eastern trade routes were not available to the Europeans due to Muslim control. The ability to outflank the Muslim states of North Africa was seen as crucial to European survival. At the same time, the Iberians learnt much from their Arab neighbors. The northwestern region of Eurasia
Eurasia
Eurasia is a continent or supercontinent comprising the traditional continents of Europe and Asia ; covering about 52,990,000 km2 or about 10.6% of the Earth's surface located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres...
has a very long coastline, and has arguably been influenced more by its maritime history
Maritime history
Maritime history is the study of human activity at sea. It covers a broad thematic element of history that often uses a global approach, although national and regional histories remain predominant...
than any other continent. Europe is uniquely situated between several navigable seas and intersected by navigable rivers running into them in a way which greatly facilitated the influence of maritime traffic and commerce. In the maritime history of Europe
Maritime history of Europe
Maritime history of Europe is a term used to describe significant past events relating to the northwestern region of Eurasia in areas concerning shipping and shipbuilding, shipwrecks, naval battles, and military installations and lighthouses constructed to protect or aid navigation and the...
, the carrack and caravel both incorporated the lateen sail that made ships far more maneuverable. By translating the Arab versions of lost ancient Greek geographical works into Latin, European navigators acquired a deeper knowledge of the shape of Africa and Asia.
Mercantile capitalism
MercantilismMercantilism
Mercantilism is the economic doctrine in which government control of foreign trade is of paramount importance for ensuring the prosperity and security of the state. In particular, it demands a positive balance of trade. Mercantilism dominated Western European economic policy and discourse from...
was the dominant school of economic thought throughout the early modern period (from the 16th to the 18th century). This led to some of the first instances of significant government intervention and control over the economy, and it was during this period that much of the modern capitalist system was established. Internationally, mercantilism encouraged the many European wars of the period and fueled European imperialism. Belief in mercantilism began to fade in the late 18th century, as the arguments of Adam Smith and the other classical economists won out.
The Commercial Revolution
Commercial Revolution
The Commercial Revolution was a period of European economic expansion, colonialism, and mercantilism which lasted from approximately the 16th century until the early 18th century. It was succeeded in the mid-18th century by the Industrial Revolution. Beginning with the Crusades, Europeans...
was a period of economic expansion, colonialism
Colonialism
Colonialism is the establishment, maintenance, acquisition and expansion of colonies in one territory by people from another territory. It is a process whereby the metropole claims sovereignty over the colony and the social structure, government, and economics of the colony are changed by...
, and mercantilism which lasted from approximately the 16th century until the early 18th century. Beginning with the Crusades
Crusades
The Crusades were a series of religious wars, blessed by the Pope and the Catholic Church with the main goal of restoring Christian access to the holy places in and near Jerusalem...
, Europeans rediscovered spices, silks, and other commodities rare in Europe. This development created a new desire for trade, and trade expanded in the second half of the Middle Ages
Middle Ages
The Middle Ages is a periodization of European history from the 5th century to the 15th century. The Middle Ages follows the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 and precedes the Early Modern Era. It is the middle period of a three-period division of Western history: Classic, Medieval and Modern...
. European nations, through voyages of discovery
Age of Discovery
The Age of Discovery, also known as the Age of Exploration and the Great Navigations , was a period in history starting in the early 15th century and continuing into the early 17th century during which Europeans engaged in intensive exploration of the world, establishing direct contacts with...
, were looking for new trade routes in the fifteenth and sixteenth centuries, which allowed the European powers to build vast, new international trade
International trade
International trade is the exchange of capital, goods, and services across international borders or territories. In most countries, such trade represents a significant share of gross domestic product...
networks. Nations also sought new sources of wealth. To deal with this new-found wealth, new economic theories and practices were created. Because of competing national interest, nations had the desire for increased world power through their colonial empires. The Commercial Revolution is marked by an increase in general commerce, and in the growth of non-manufacturing pursuits, such as banking, insurance, and investing.
Trade and the New Economy
In the Old World
Old World
The Old World consists of those parts of the world known to classical antiquity and the European Middle Ages. It is used in the context of, and contrast with, the "New World" ....
, the most desired trading goods were gold, silver and spice
Spice
A spice is a dried seed, fruit, root, bark, or vegetative substance used in nutritionally insignificant quantities as a food additive for flavor, color, or as a preservative that kills harmful bacteria or prevents their growth. It may be used to flavour a dish or to hide other flavours...
s. Western Europeans used the compass
Compass
A compass is a navigational instrument that shows directions in a frame of reference that is stationary relative to the surface of the earth. The frame of reference defines the four cardinal directions – north, south, east, and west. Intermediate directions are also defined...
, new sailing ship
Sailing ship
The term sailing ship is now used to refer to any large wind-powered vessel. In technical terms, a ship was a sailing vessel with a specific rig of at least three masts, square rigged on all of them, making the sailing adjective redundant. In popular usage "ship" became associated with all large...
technologies, new maps, and advances in astronomy to seek a viable trade route
Trade route
A trade route is a logistical network identified as a series of pathways and stoppages used for the commercial transport of cargo. Allowing goods to reach distant markets, a single trade route contains long distance arteries which may further be connected to several smaller networks of commercial...
to Asia for valuable spices which would be uncontested by Mediterranean powers.
Desired trading goods |
In terms of shipping advances, the most important developments were the creation of the carrack
Carrack
A carrack or nau was a three- or four-masted sailing ship developed in 15th century Western Europe for use in the Atlantic Ocean. It had a high rounded stern with large aftcastle, forecastle and bowsprit at the stem. It was first used by the Portuguese , and later by the Spanish, to explore and...
and caravel
Caravel
A caravel is a small, highly maneuverable sailing ship developed in the 15th century by the Portuguese to explore along the West African coast and into the Atlantic Ocean. The lateen sails gave her speed and the capacity for sailing to windward...
designs in Portugal
Portugal
Portugal , officially the Portuguese Republic is a country situated in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula. Portugal is the westernmost country of Europe, and is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the West and South and by Spain to the North and East. The Atlantic archipelagos of the...
. These vessels evolved from medieval
Middle Ages
The Middle Ages is a periodization of European history from the 5th century to the 15th century. The Middle Ages follows the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 and precedes the Early Modern Era. It is the middle period of a three-period division of Western history: Classic, Medieval and Modern...
European designs from the North Sea and both the Christian and Islamic Mediterranean. They were the first ships that could leave the relatively placid and calm Mediterranean
Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean surrounded by the Mediterranean region and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Anatolia and Europe, on the south by North Africa, and on the east by the Levant...
, Baltic
Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is a brackish mediterranean sea located in Northern Europe, from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from 20°E to 26°E longitude. It is bounded by the Scandinavian Peninsula, the mainland of Europe, and the Danish islands. It drains into the Kattegat by way of the Øresund, the Great Belt and...
or North Sea
North Sea
In the southwest, beyond the Straits of Dover, the North Sea becomes the English Channel connecting to the Atlantic Ocean. In the east, it connects to the Baltic Sea via the Skagerrak and Kattegat, narrow straits that separate Denmark from Norway and Sweden respectively...
and sail safely on the open Atlantic
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's oceanic divisions. With a total area of about , it covers approximately 20% of the Earth's surface and about 26% of its water surface area...
.
When the carrack
Carrack
A carrack or nau was a three- or four-masted sailing ship developed in 15th century Western Europe for use in the Atlantic Ocean. It had a high rounded stern with large aftcastle, forecastle and bowsprit at the stem. It was first used by the Portuguese , and later by the Spanish, to explore and...
and then the caravel
Caravel
A caravel is a small, highly maneuverable sailing ship developed in the 15th century by the Portuguese to explore along the West African coast and into the Atlantic Ocean. The lateen sails gave her speed and the capacity for sailing to windward...
were developed in Iberia
Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula , sometimes called Iberia, is located in the extreme southwest of Europe and includes the modern-day sovereign states of Spain, Portugal and Andorra, as well as the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar...
that European thoughts returned to the fabled East. These explorations have a number of causes. Monetarists believe the main reason the Age of Exploration began was because of a severe shortage of bullion in Europe. The European economy was dependent on gold and silver currency, but low domestic supplies had plunged much of Europe into a recession. Another factor was the centuries long conflict between the Iberians and the Muslims to the south.
Piracy's Golden Age
The Golden Age of Piracy
Golden Age of Piracy
The Golden Age of Piracy is a common designation given to one or more outbursts of piracy in maritime history of the early modern period. In its broadest accepted definition, the Golden Age of Piracy spans from the 1650s to the 1730s and covers three separate outbursts of piracy:the buccaneering...
is a designation given to one or more outbursts of piracy
Piracy
Piracy is an act of robbery or criminal violence at sea. The term can include acts committed on land, in the air, or in other major bodies of water or on a shore. It does not normally include crimes committed against persons traveling on the same vessel as the perpetrator...
in the early modern period. In its broadest accepted definition, this Age of Piracy spans from the mid-17th century to the mid-18th century. The buccaneering period covers approximately the late 17th century. The period is characterized by Anglo-French seamen based on Jamaica and Tortuga attacking Spanish colonies and shipping in the Caribbean and eastern Pacific. The turn of 18th century saw the Pirate Round
Pirate Round
The Pirate Round was a sailing route followed by certain Anglo-American pirates, mainly during the late 17th century. The course led from the western Atlantic, around the southern tip of Africa, stopping at Madagascar, then on to targets such as the coast of Yemen and India. The Pirate Round was...
. They associated with long-distance voyages from Bermuda and the Americas to rob Muslim and East India Company targets in the Indian Ocean and Red Sea. The post-Spanish Succession period extending into the early 18th century, when Anglo-American sailors and privateers left unemployed by the end of the War of the Spanish Succession turned en masse to piracy in the Caribbean, the American eastern seaboard, the West African coast, and the Indian Ocean.
European states and politics
The 15th to 18th century period is marked by the first European colonies, the rise of strong centralized governments, and the beginnings of recognizable European nation states that are the direct antecedents of today's states. Although the Renaissance saw revolutions in many intellectualIntellectual
An intellectual is a person who uses intelligence and critical or analytical reasoning in either a professional or a personal capacity.- Terminology and endeavours :"Intellectual" can denote four types of persons:...
pursuits, as well as social and political upheaval, it is perhaps best known for European artistic developments and the contributions of such polymath
Polymath
A polymath is a person whose expertise spans a significant number of different subject areas. In less formal terms, a polymath may simply be someone who is very knowledgeable...
s as Leonardo da Vinci
Leonardo da Vinci
Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci was an Italian Renaissance polymath: painter, sculptor, architect, musician, scientist, mathematician, engineer, inventor, anatomist, geologist, cartographer, botanist and writer whose genius, perhaps more than that of any other figure, epitomized the Renaissance...
and Michelangelo
Michelangelo
Michelangelo di Lodovico Buonarroti Simoni , commonly known as Michelangelo, was an Italian Renaissance painter, sculptor, architect, poet, and engineer who exerted an unparalleled influence on the development of Western art...
, who inspired the term "Renaissance man
Polymath
A polymath is a person whose expertise spans a significant number of different subject areas. In less formal terms, a polymath may simply be someone who is very knowledgeable...
".
The Baroque
Baroque
The Baroque is a period and the style that used exaggerated motion and clear, easily interpreted detail to produce drama, tension, exuberance, and grandeur in sculpture, painting, literature, dance, and music...
period saw the Thirty Years' War
Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War was fought primarily in what is now Germany, and at various points involved most countries in Europe. It was one of the most destructive conflicts in European history....
in Central Europe which decimated the population by up to 20%. The treaties in 1648 ended several wars in Europe and established the beginning of sovereign state
Sovereign state
A sovereign state, or simply, state, is a state with a defined territory on which it exercises internal and external sovereignty, a permanent population, a government, and the capacity to enter into relations with other sovereign states. It is also normally understood to be a state which is neither...
s. The Peace of Westphalia
Peace of Westphalia
The Peace of Westphalia was a series of peace treaties signed between May and October of 1648 in Osnabrück and Münster. These treaties ended the Thirty Years' War in the Holy Roman Empire, and the Eighty Years' War between Spain and the Dutch Republic, with Spain formally recognizing the...
refers to the two peace treaties
Peace treaty
A peace treaty is an agreement between two or more hostile parties, usually countries or governments, that formally ends a state of war between the parties...
of Osnabrück
Osnabrück
Osnabrück is a city in Lower Saxony, Germany, some 80 km NNE of Dortmund, 45 km NE of Münster, and some 100 km due west of Hanover. It lies in a valley penned between the Wiehen Hills and the northern tip of the Teutoburg Forest...
and Münster
Münster
Münster is an independent city in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is located in the northern part of the state and is considered to be the cultural centre of the Westphalia region. It is also capital of the local government region Münsterland...
, signed on May 15 and October 24, 1648, respectively, and written in French, that ended both the Thirty Years' War
Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War was fought primarily in what is now Germany, and at various points involved most countries in Europe. It was one of the most destructive conflicts in European history....
in the Holy Roman Empire
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a realm that existed from 962 to 1806 in Central Europe.It was ruled by the Holy Roman Emperor. Its character changed during the Middle Ages and the Early Modern period, when the power of the emperor gradually weakened in favour of the princes...
(today mostly Germany) and the Eighty Years' War
Dutch Revolt
The Dutch Revolt or the Revolt of the Netherlands This article adopts 1568 as the starting date of the war, as this was the year of the first battles between armies. However, since there is a long period of Protestant vs...
between Spain and the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands
Dutch Republic
The Dutch Republic — officially known as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands , the Republic of the United Netherlands, or the Republic of the Seven United Provinces — was a republic in Europe existing from 1581 to 1795, preceding the Batavian Republic and ultimately...
. The treaties involved the Holy Roman Emperor
Holy Roman Emperor
The Holy Roman Emperor is a term used by historians to denote a medieval ruler who, as German King, had also received the title of "Emperor of the Romans" from the Pope...
, Ferdinand III
Ferdinand III, Holy Roman Emperor
Ferdinand III was Holy Roman Emperor from 15 February 1637 until his death, as well as King of Hungary and Croatia, King of Bohemia and Archduke of Austria.-Life:...
(Habsburg
Habsburg
The House of Habsburg , also found as Hapsburg, and also known as House of Austria is one of the most important royal houses of Europe and is best known for being an origin of all of the formally elected Holy Roman Emperors between 1438 and 1740, as well as rulers of the Austrian Empire and...
), the Kingdoms of Spain, France and Sweden
Sweden
Sweden , officially the Kingdom of Sweden , is a Nordic country on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. Sweden borders with Norway and Finland and is connected to Denmark by a bridge-tunnel across the Öresund....
, the Netherlands
Dutch Republic
The Dutch Republic — officially known as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands , the Republic of the United Netherlands, or the Republic of the Seven United Provinces — was a republic in Europe existing from 1581 to 1795, preceding the Batavian Republic and ultimately...
and their respective allies among the princes
Princes of the Holy Roman Empire
The term Prince of the Holy Roman Empire denoted a secular or ecclesiastical Imperial State, who ruled over an immediate fief directly assigned by the Holy Roman Emperor...
and the Republican Imperial States
Free Imperial City
In the Holy Roman Empire, a free imperial city was a city formally ruled by the emperor only — as opposed to the majority of cities in the Empire, which were governed by one of the many princes of the Empire, such as dukes or prince-bishops...
of the Holy Roman Empire
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a realm that existed from 962 to 1806 in Central Europe.It was ruled by the Holy Roman Emperor. Its character changed during the Middle Ages and the Early Modern period, when the power of the emperor gradually weakened in favour of the princes...
.
The Peace of Westphalia resulted from the first modern diplomatic congress. Until 1806, the regulations became part of the constitutional laws of the Holy Roman Empire. The Treaty of the Pyrenees
Treaty of the Pyrenees
The Treaty of the Pyrenees was signed to end the 1635 to 1659 war between France and Spain, a war that was initially a part of the wider Thirty Years' War. It was signed on Pheasant Island, a river island on the border between the two countries...
, signed in 1659, ended the war
War
War is a state of organized, armed, and often prolonged conflict carried on between states, nations, or other parties typified by extreme aggression, social disruption, and usually high mortality. War should be understood as an actual, intentional and widespread armed conflict between political...
between France and Spain and is often considered part of the overall accord.
Absolutism
The Age of Absolutism describes the monarchical power
Monarch
A monarch is the person who heads a monarchy. This is a form of government in which a state or polity is ruled or controlled by an individual who typically inherits the throne by birth and occasionally rules for life or until abdication...
that was unrestrained by any other institutions, such as churches, legislature
Legislature
A legislature is a kind of deliberative assembly with the power to pass, amend, and repeal laws. The law created by a legislature is called legislation or statutory law. In addition to enacting laws, legislatures usually have exclusive authority to raise or lower taxes and adopt the budget and...
s, or social elites of the European monarchs during the transition from feudalism
Feudalism
Feudalism was a set of legal and military customs in medieval Europe that flourished between the 9th and 15th centuries, which, broadly defined, was a system for ordering society around relationships derived from the holding of land in exchange for service or labour.Although derived from the...
to capitalism. Monarchs described as absolute can especially be found in the 17th century through the 19th century. Absolutism is characterized by the ending of feudal partitioning, consolidation of power with the monarch, rise of state power
Political power
Political power is a type of power held by a group in a society which allows administration of some or all of public resources, including labour, and wealth. There are many ways to obtain possession of such power. At the nation-state level political legitimacy for political power is held by the...
, unification of the state law
State law
In the United States, state law is the law of each separate U.S. state, as passed by the state legislature and adjudicated by state courts. It exists in parallel, and sometimes in conflict with, United States federal law. These disputes are often resolved by the federal courts.-See also:*List of U.S...
s, and a decrease in the influence of nobility
Nobility
Nobility is a social class which possesses more acknowledged privileges or eminence than members of most other classes in a society, membership therein typically being hereditary. The privileges associated with nobility may constitute substantial advantages over or relative to non-nobles, or may be...
.
French power
For much of the reign of Louis XIV, who was known as the Sun King (French: le Roi Soleil), France stood as the leading power in Europe, engaging in three major war
War
War is a state of organized, armed, and often prolonged conflict carried on between states, nations, or other parties typified by extreme aggression, social disruption, and usually high mortality. War should be understood as an actual, intentional and widespread armed conflict between political...
s—the Franco-Dutch War
Franco-Dutch War
The Franco-Dutch War, often called simply the Dutch War was a war fought by France, Sweden, the Bishopric of Münster, the Archbishopric of Cologne and England against the United Netherlands, which were later joined by the Austrian Habsburg lands, Brandenburg and Spain to form a quadruple alliance...
, the War of the League of Augsburg, and the War of the Spanish Succession
War of the Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was fought among several European powers, including a divided Spain, over the possible unification of the Kingdoms of Spain and France under one Bourbon monarch. As France and Spain were among the most powerful states of Europe, such a unification would have...
—and two minor conflicts—the War of Devolution
War of Devolution
The War of Devolution saw Louis XIV's French armies overrun the Habsburg-controlled Spanish Netherlands and the Franche-Comté, but forced to give most of it back by a Triple Alliance of England, Sweden, and the Dutch Republic in the Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle.-Background:Louis's claims to the...
, and the War of the Reunions
War of the Reunions
The War of the Reunions was a short conflict between France and Spain and its allies. It was fueled by the long-running desire of Louis XIV to conquer new lands, many of them comprising part of the Spanish Netherlands, along France's northern and eastern borders...
. Louis believed in the Divine Right of Kings
Divine Right of Kings
The divine right of kings or divine-right theory of kingship is a political and religious doctrine of royal and political legitimacy. It asserts that a monarch is subject to no earthly authority, deriving his right to rule directly from the will of God...
, the theory that the King was crowned by God and accountable to him alone. Consequently, he has long been considered the archetypal absolute monarch
Absolute monarchy
Absolute monarchy is a monarchical form of government in which the monarch exercises ultimate governing authority as head of state and head of government, his or her power not being limited by a constitution or by the law. An absolute monarch thus wields unrestricted political power over the...
. Louis XIV continued the work of his predecessor to create a centralized state
Centralized government
A centralized or centralised government is one in which power or legal authority is exerted or coordinated by a de facto political executive to which federal states, local authorities, and smaller units are considered subject...
governed from the capital in order to sweep away the remnants of feudalism
Feudalism
Feudalism was a set of legal and military customs in medieval Europe that flourished between the 9th and 15th centuries, which, broadly defined, was a system for ordering society around relationships derived from the holding of land in exchange for service or labour.Although derived from the...
which had persisted in parts of France. He succeeded in breaking the power of the provincial nobility, much of which had risen in revolt during his minority called the Fronde, and forced many leading nobles to live with him in his lavish Palace of Versailles
Palace of Versailles
The Palace of Versailles , or simply Versailles, is a royal château in Versailles in the Île-de-France region of France. In French it is the Château de Versailles....
.
Men who featured prominently in the political and military life of France during this period include Mazarin, Jean-Baptiste Colbert
Jean-Baptiste Colbert
Jean-Baptiste Colbert was a French politician who served as the Minister of Finances of France from 1665 to 1683 under the rule of King Louis XIV. His relentless hard work and thrift made him an esteemed minister. He achieved a reputation for his work of improving the state of French manufacturing...
, Turenne
Henri de la Tour d'Auvergne, Vicomte de Turenne
Henri de la Tour d'Auvergne, Vicomte de Turenne,often called simply Turenne was the most illustrious member of the La Tour d'Auvergne family. He achieved military fame and became a Marshal of France...
, Vauban
Vauban
Sébastien Le Prestre, Seigneur de Vauban and later Marquis de Vauban , commonly referred to as Vauban, was a Marshal of France and the foremost military engineer of his age, famed for his skill in both designing fortifications and breaking through them...
. French culture likewise flourished during this era, producing a number of figures of great renown, including Molière
Molière
Jean-Baptiste Poquelin, known by his stage name Molière, was a French playwright and actor who is considered to be one of the greatest masters of comedy in Western literature...
, Racine
Jean Racine
Jean Racine , baptismal name Jean-Baptiste Racine , was a French dramatist, one of the "Big Three" of 17th-century France , and one of the most important literary figures in the Western tradition...
, Boileau
Nicolas Boileau-Despréaux
Nicolas Boileau-Despréaux was a French poet and critic.-Biography:Boileau was born in the rue de Jérusalem, in Paris, France. He was brought up to the law, but devoted to letters, associating himself with La Fontaine, Racine, and Molière...
, La Fontaine
Jean de La Fontaine
Jean de La Fontaine was the most famous French fabulist and one of the most widely read French poets of the 17th century. He is known above all for his Fables, which provided a model for subsequent fabulists across Europe and numerous alternative versions in France, and in French regional...
, Lully
Jean-Baptiste Lully
Jean-Baptiste de Lully was an Italian-born French composer who spent most of his life working in the court of Louis XIV of France. He is considered the chief master of the French Baroque style. Lully disavowed any Italian influence in French music of the period. He became a French subject in...
, Le Brun
Charles Le Brun
Charles Le Brun , a French painter and art theorist, became the all-powerful, peerless master of 17th-century French art.-Biography:-Early life and training:...
, Rigaud
Hyacinthe Rigaud
Hyacinthe Rigaud was a French baroque painter of Catalan origin whose career was based in Paris.He is renowned for his portrait paintings of Louis XIV, the royalty and nobility of Europe, and members of their courts and considered one of the most notable French portraitists of the classical period...
, Louis Le Vau
Louis Le Vau
Louis Le Vau was a French Classical architect who worked for Louis XIV of France. He was born and died in Paris.He was responsible, with André Le Nôtre and Charles Le Brun, for the redesign of the château of Vaux-le-Vicomte. His later works included the Palace of Versailles and his collaboration...
, Jules Hardouin Mansart
Jules Hardouin Mansart
Jules Hardouin-Mansart was a French architect whose work is generally considered to be the apex of French Baroque architecture, representing the power and grandeur of Louis XIV...
, Claude Perrault
Claude Perrault
Claude Perrault is best known as the architect of the eastern range of the Louvre Palace in Paris , but he also achieved success as a physician and anatomist, and as an author, who wrote treatises on physics and natural history.Perrault was born and died in Paris...
and Le Nôtre
André Le Nôtre
André Le Nôtre was a French landscape architect and the principal gardener of King Louis XIV of France...
.
Early English revolutions
Before the Age of Revolution, the English Civil War
English Civil War
The English Civil War was a series of armed conflicts and political machinations between Parliamentarians and Royalists...
was a series of armed conflicts and political machinations between Parliamentarians and Royalists. The first and second civil wars pitted the supporters of King Charles I against the supporters of the Long Parliament, while the third war saw fighting between supporters of King Charles II and supporters of the Rump Parliament. The Civil War ended with the Parliamentary victory at the Battle of Worcester. The monopoly of the Church of England on Christian worship in England ended with the victors consolidating the established Protestant Ascendancy in Ireland. Constitutionally, the wars established the precedent that an English monarch cannot govern without Parliament's consent. The English Restoration
English Restoration
The Restoration of the English monarchy began in 1660 when the English, Scottish and Irish monarchies were all restored under Charles II after the Interregnum that followed the Wars of the Three Kingdoms...
, or simply put as the Restoration, began in 1660 when the English, Scottish and Irish monarchies were all restored under Charles II after the Commonwealth of England that followed the English Civil War. The Glorious Revolution
Glorious Revolution
The Glorious Revolution, also called the Revolution of 1688, is the overthrow of King James II of England by a union of English Parliamentarians with the Dutch stadtholder William III of Orange-Nassau...
of 1688 establishes modern parliamentary democracy in England.
International balance of power
The War of the Spanish Succession
War of the Spanish Succession
The War of the Spanish Succession was fought among several European powers, including a divided Spain, over the possible unification of the Kingdoms of Spain and France under one Bourbon monarch. As France and Spain were among the most powerful states of Europe, such a unification would have...
was a war fought between 1701 to 1714, in which several European powers combined to stop a possible unification of the Kingdoms of Spain and France under a single Bourbon monarch, upsetting the European balance of power
Balance of power in international relations
In international relations, a balance of power exists when there is parity or stability between competing forces. The concept describes a state of affairs in the international system and explains the behavior of states in that system...
. It was fought mostly in Europe, but it included Queen Anne's War
Queen Anne's War
Queen Anne's War , as the North American theater of the War of the Spanish Succession was known in the British colonies, was the second in a series of French and Indian Wars fought between France and England, later Great Britain, in North America for control of the continent. The War of the...
in North America. The war was marked by the military leadership of notable generals like the duc de Villars, the Jacobite Duke of Berwick, the Duke of Marlborough
John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough
John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough, Prince of Mindelheim, KG, PC , was an English soldier and statesman whose career spanned the reigns of five monarchs through the late 17th and early 18th centuries...
and Prince Eugene of Savoy
Prince Eugene of Savoy
Prince Eugene of Savoy , was one of the most successful military commanders in modern European history, rising to the highest offices of state at the Imperial court in Vienna. Born in Paris to aristocratic Italian parents, Eugene grew up around the French court of King Louis XIV...
.
The Peace of Utrecht established after a series of individual peace treaties
Peace treaty
A peace treaty is an agreement between two or more hostile parties, usually countries or governments, that formally ends a state of war between the parties...
signed in the Dutch
Dutch Republic
The Dutch Republic — officially known as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands , the Republic of the United Netherlands, or the Republic of the Seven United Provinces — was a republic in Europe existing from 1581 to 1795, preceding the Batavian Republic and ultimately...
city of Utrecht
Utrecht (city)
Utrecht city and municipality is the capital and most populous city of the Dutch province of Utrecht. It is located in the eastern corner of the Randstad conurbation, and is the fourth largest city of the Netherlands with a population of 312,634 on 1 Jan 2011.Utrecht's ancient city centre features...
concluded between various European states helped end the War of the Spanish Succession. The representatives who met were Louis XIV of France and Philip V of Spain
Philip V of Spain
Philip V was King of Spain from 15 November 1700 to 15 January 1724, when he abdicated in favor of his son Louis, and from 6 September 1724, when he assumed the throne again upon his son's death, to his death.Before his reign, Philip occupied an exalted place in the royal family of France as a...
on the one hand, and representatives of Queen Anne
Anne of Great Britain
Anne ascended the thrones of England, Scotland and Ireland on 8 March 1702. On 1 May 1707, under the Act of Union, two of her realms, England and Scotland, were united as a single sovereign state, the Kingdom of Great Britain.Anne's Catholic father, James II and VII, was deposed during the...
of Great Britain
Kingdom of Great Britain
The former Kingdom of Great Britain, sometimes described as the 'United Kingdom of Great Britain', That the Two Kingdoms of Scotland and England, shall upon the 1st May next ensuing the date hereof, and forever after, be United into One Kingdom by the Name of GREAT BRITAIN. was a sovereign...
, the Duke of Savoy
Duchy of Savoy
From 1416 to 1847, the House of Savoy ruled the eponymous Duchy of Savoy . The Duchy was a state in the northern part of the Italian Peninsula, with some territories that are now in France. It was a continuation of the County of Savoy...
, and the United Provinces
Dutch Republic
The Dutch Republic — officially known as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands , the Republic of the United Netherlands, or the Republic of the Seven United Provinces — was a republic in Europe existing from 1581 to 1795, preceding the Batavian Republic and ultimately...
on the other. The treaty enregistred the defeat of French ambitions expressed in the wars of Louis XIV
Louis XIV of France
Louis XIV , known as Louis the Great or the Sun King , was a Bourbon monarch who ruled as King of France and Navarre. His reign, from 1643 to his death in 1715, began at the age of four and lasted seventy-two years, three months, and eighteen days...
and preserved the European system based on the balance of power
Balance of power in international relations
In international relations, a balance of power exists when there is parity or stability between competing forces. The concept describes a state of affairs in the international system and explains the behavior of states in that system...
. The Treaty of Utrecht
Treaty of Utrecht
The Treaty of Utrecht, which established the Peace of Utrecht, comprises a series of individual peace treaties, rather than a single document, signed by the belligerents in the War of Spanish Succession, in the Dutch city of Utrecht in March and April 1713...
marked the change from Spanish
Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire comprised territories and colonies administered directly by Spain in Europe, in America, Africa, Asia and Oceania. It originated during the Age of Exploration and was therefore one of the first global empires. At the time of Habsburgs, Spain reached the peak of its world power....
to British
Kingdom of Great Britain
The former Kingdom of Great Britain, sometimes described as the 'United Kingdom of Great Britain', That the Two Kingdoms of Scotland and England, shall upon the 1st May next ensuing the date hereof, and forever after, be United into One Kingdom by the Name of GREAT BRITAIN. was a sovereign...
naval supremacy.
Colonial expansion and possessions
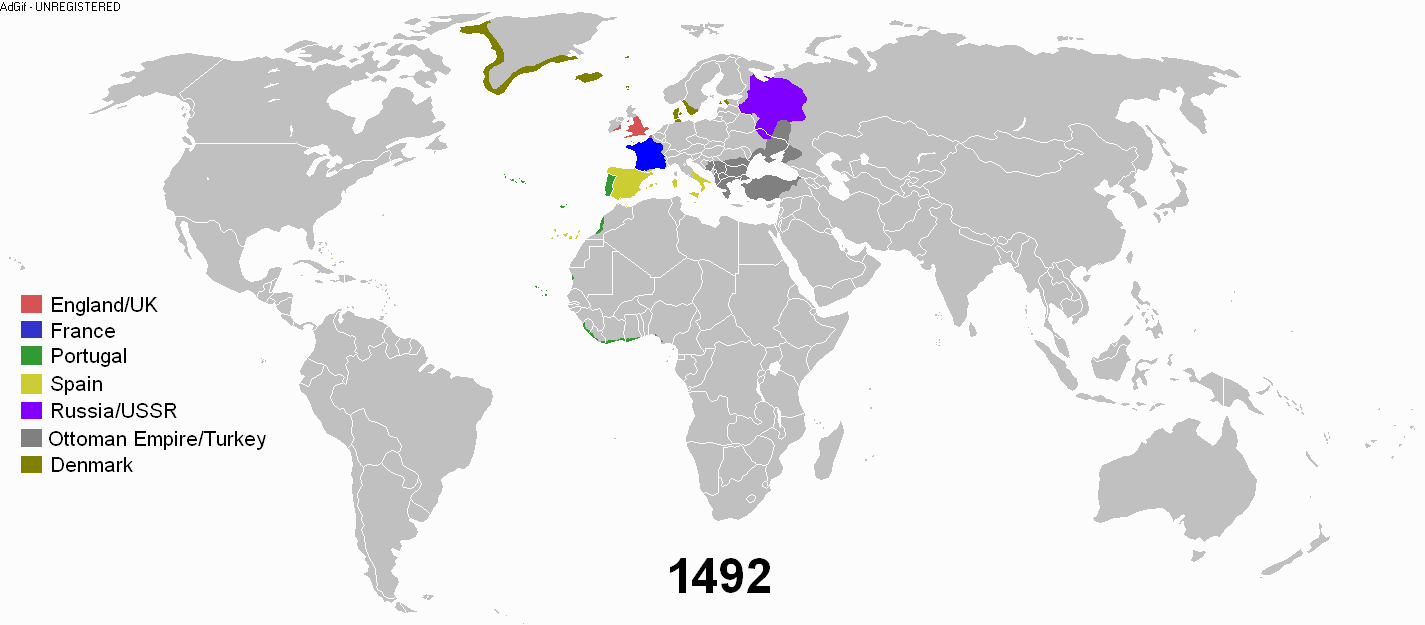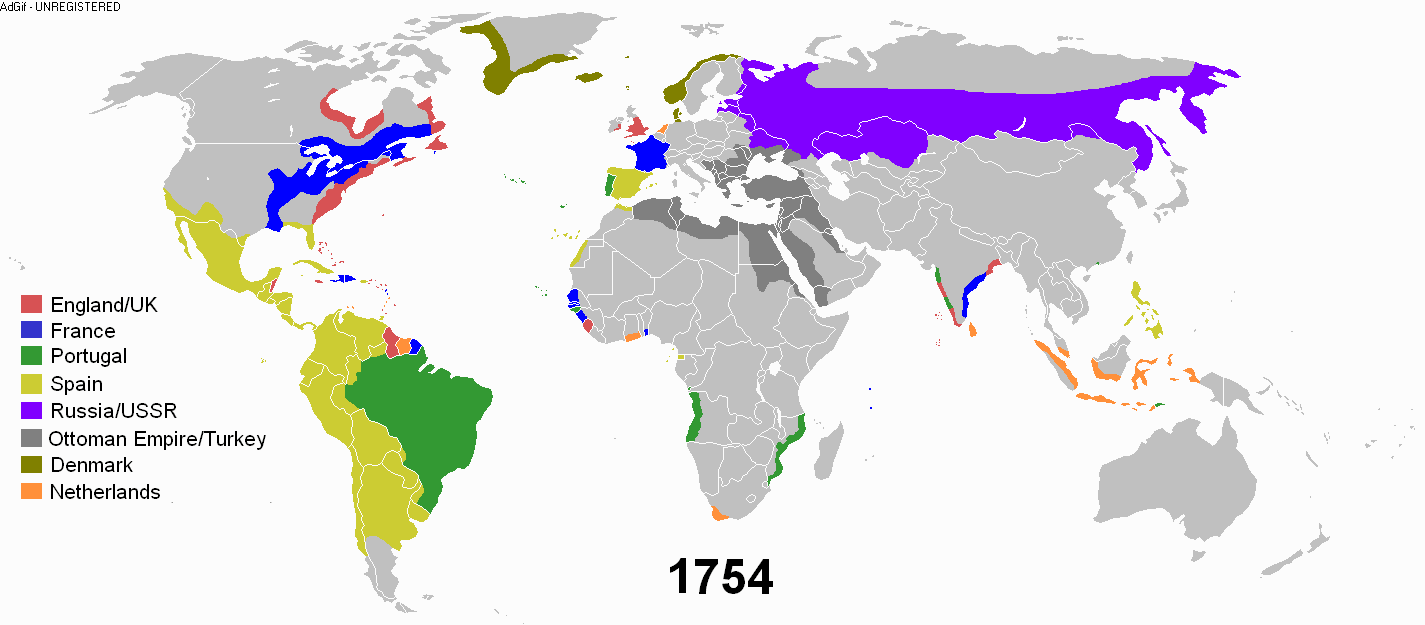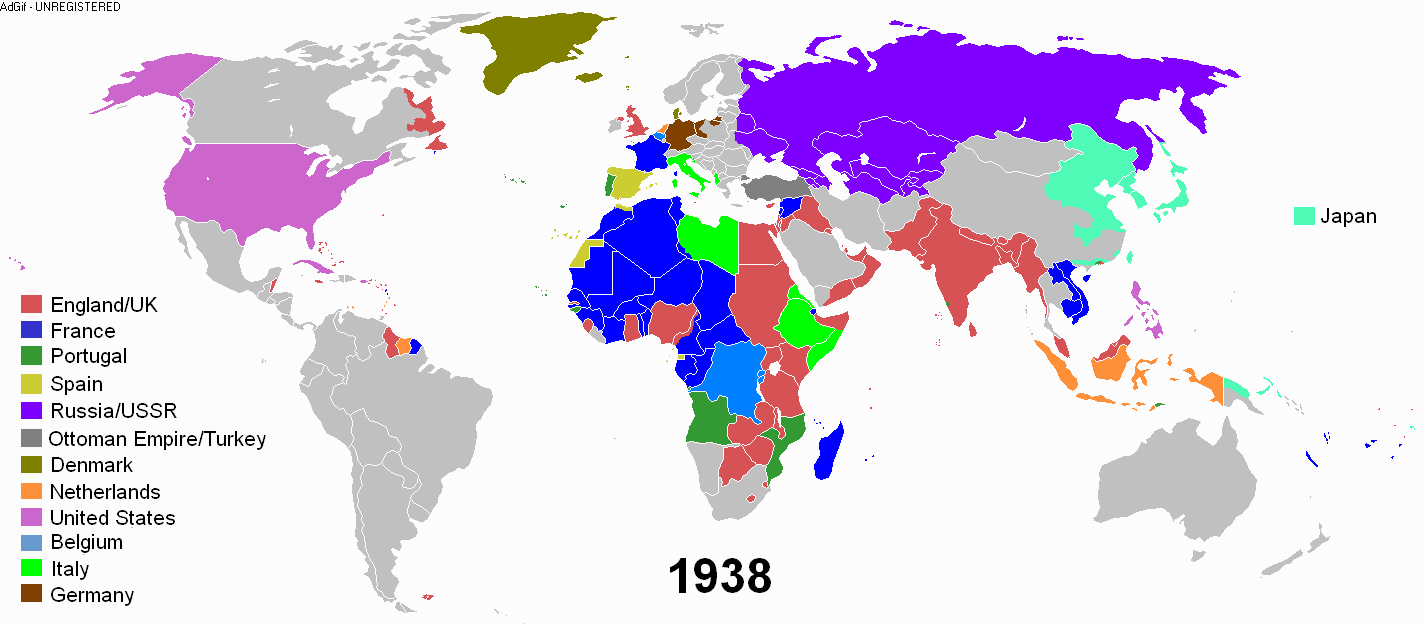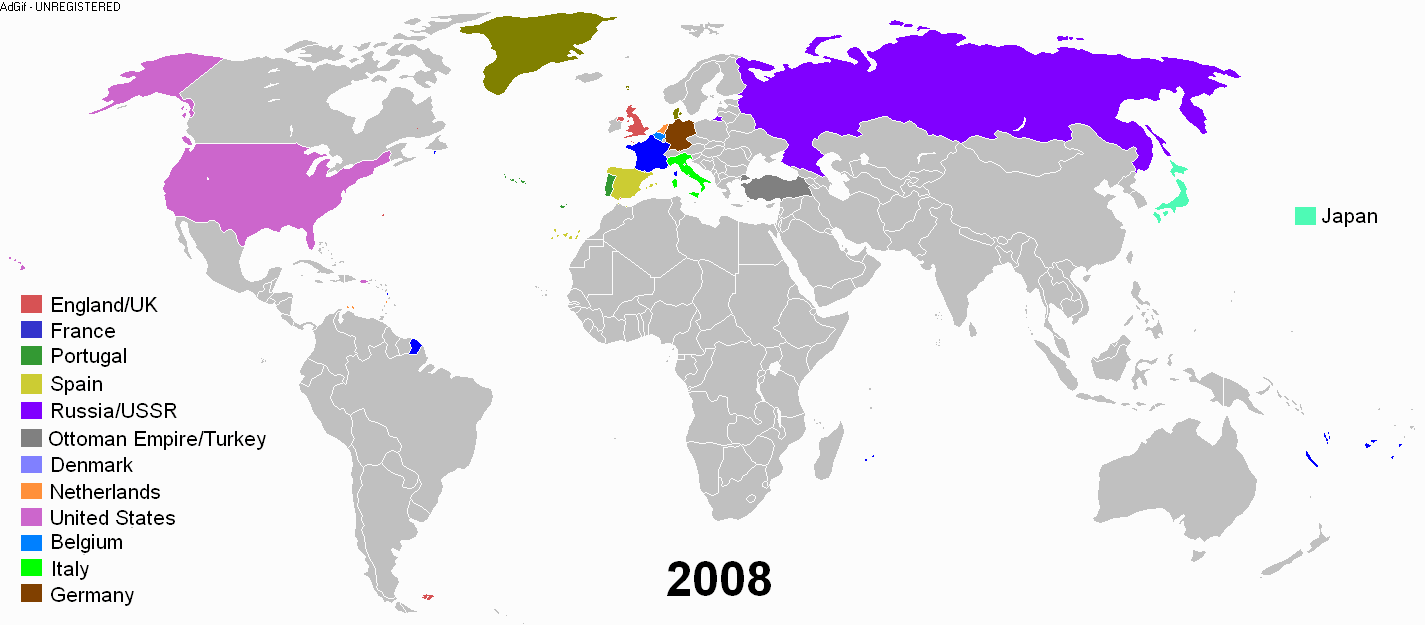
British Empire
The British Empire comprised the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom. It originated with the overseas colonies and trading posts established by England in the late 16th and early 17th centuries. At its height, it was the...
, although the term colonialism is normally used with reference to discontiguous overseas empires rather than contiguous land-based empires, European or otherwise. European colonization during the 15th to 19th centuries resulted in the spread of Christianity to Sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa as a geographical term refers to the area of the African continent which lies south of the Sahara. A political definition of Sub-Saharan Africa, instead, covers all African countries which are fully or partially located south of the Sahara...
, the Americas, Australia and the Philippines
Philippines
The Philippines , officially known as the Republic of the Philippines , is a country in Southeast Asia in the western Pacific Ocean. To its north across the Luzon Strait lies Taiwan. West across the South China Sea sits Vietnam...
.
Conquest and Americas exploration
Christopher ColumbusChristopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus was an explorer, colonizer, and navigator, born in the Republic of Genoa, in northwestern Italy. Under the auspices of the Catholic Monarchs of Spain, he completed four voyages across the Atlantic Ocean that led to general European awareness of the American continents in the...
discovered the Americas in 1492. Subsequently, the major sea powers in Europe sent expeditions to the New World
New World
The New World is one of the names used for the Western Hemisphere, specifically America and sometimes Oceania . The term originated in the late 15th century, when America had been recently discovered by European explorers, expanding the geographical horizon of the people of the European middle...
to build trade networks and colonies and to convert the native peoples to Christianity. Pope Alexander VI
Pope Alexander VI
Pope Alexander VI , born Roderic Llançol i Borja was Pope from 1492 until his death on 18 August 1503. He is one of the most controversial of the Renaissance popes, and his Italianized surname—Borgia—became a byword for the debased standards of the Papacy of that era, most notoriously the Banquet...
divided newly discovered lands outside Europe between Spain and Portugal along a north-south meridian 370 leagues west of the Cape Verde islands (off the west coast of Africa). This division was never accepted by the rulers of England or France. (See also the Treaty of Tordesillas
Treaty of Tordesillas
The Treaty of Tordesillas , signed at Tordesillas , , divided the newly discovered lands outside Europe between Spain and Portugal along a meridian 370 leagueswest of the Cape Verde islands...
, which followed the papal decree.)
Colonial North America
Great Britain held several colonies in North America and the West Indies. The colonies in North America were founded between 1607 (Virginia), and 1733 (Georgia). The British colonies in North America rebelled against British rule in 1775, largely due to the taxation that Great Britain was imposing on the colonies. The Thirteen ColoniesThirteen Colonies
The Thirteen Colonies were English and later British colonies established on the Atlantic coast of North America between 1607 and 1733. They declared their independence in the American Revolution and formed the United States of America...
were part of what became known as British America, a name that was used by Great Britain until the Treaty of Paris recognized the independence of the original thirteen United States of America in 1783. A provisional government was formed which proclaimed their independence, which is now celebrated as having occurred on July 4, 1776, and subsequently became the original thirteen United States of America.
Colonial Latin America
Spain concentrated building its empire on the central and southern parts of the Americas allotted to it by the Treaty of TordesillasTreaty of Tordesillas
The Treaty of Tordesillas , signed at Tordesillas , , divided the newly discovered lands outside Europe between Spain and Portugal along a meridian 370 leagueswest of the Cape Verde islands...
, because of presence of indigenous states whose human and material resources it could exploit, and large concentrations of silver and gold. The Portuguese built its empire in Brazil, which fell in its sphere of influence per the Treaty of Tordesillas, by developing the land for sugar production since there was a lack of a large, complex society or mineral resources.
Africa and the Near East
The Ottoman Empire
In this period, the growth of the Ottoman EmpireGrowth of the Ottoman Empire
The Growth of the Ottoman Empire is the period followed after the Rise of the Ottoman Empire in which the Ottoman state reached the Pax Ottomana. In this period, the Ottoman Empire expanded southwestwards into North Africa and battled with the re-emergent Persian Shi'ia Safavid Empire to the east...
is the period followed after the rise of the Ottoman Empire
Rise of the Ottoman Empire
The Foundation and Rise of the Ottoman Empire refers to the period which started with the weakening of the Seljuq Sultanate of Rûm in the very early 14th century and ended with the Byzantine Empire decline and the Fall of Constantinople on May 29, 1453.The rise of the Ottomans correlates with the...
in which the Ottoman state reached the Pax Ottomana
Pax Ottomana
Pax Ottomana is a term used to describe the economic and social stability attained in the conquered provinces of the Ottoman Empire, which, at the height of the Empire's power during the 16th and 17th centuries, applied to lands in the Balkans, Anatolia, the Middle East, North Africa and the...
. This era was perhaps the golden age for the Ottoman Empire
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman EmpireIt was usually referred to as the "Ottoman Empire", the "Turkish Empire", the "Ottoman Caliphate" or more commonly "Turkey" by its contemporaries...
.
North and East Africa
In North Africa, the Ottomans expanded southwestwards into North Africa and battled with the re-emergent Persian Shi'ia Safavid Empire to the east.In the Saracen
Saracen
Saracen was a term used by the ancient Romans to refer to a people who lived in desert areas in and around the Roman province of Arabia, and who were distinguished from Arabs. In Europe during the Middle Ages the term was expanded to include Arabs, and then all who professed the religion of Islam...
sphere of power, the Ottoman Empire, who had conquered Constantinople
Constantinople
Constantinople was the capital of the Roman, Eastern Roman, Byzantine, Latin, and Ottoman Empires. Throughout most of the Middle Ages, Constantinople was Europe's largest and wealthiest city.-Names:...
in 1453, and had seized Egypt in 1517, established the regencies of Algeria
Algeria
Algeria , officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria , also formally referred to as the Democratic and Popular Republic of Algeria, is a country in the Maghreb region of Northwest Africa with Algiers as its capital.In terms of land area, it is the largest country in Africa and the Arab...
, Tunisia and Tripoli
Tripolitania
Tripolitania or Tripolitana is a historic region and former province of Libya.Tripolitania was a separate Italian colony from 1927 to 1934...
(between 1519 and 1551), Morocco
Morocco
Morocco , officially the Kingdom of Morocco , is a country located in North Africa. It has a population of more than 32 million and an area of 710,850 km², and also primarily administers the disputed region of the Western Sahara...
remaining an independent Arabized Berber state under the Sharifan dynasty, which had its beginnings at the end of the 13th century.
In East Africa, the Solomonic dynasty
Solomonic dynasty
The Solomonic dynasty is the Imperial House of Abyssinia. Its members claim lineal descent from King Solomon and the Queen of Sheba, the latter of whom tradition asserts gave birth to the first King Menelik I after her Biblically described visit to Solomon in Jerusalem .-Overview:The dynasty, a...
came to rule in the 13th century and claimed direct descent from the old Axum
Axum
Axum or Aksum is a city in northern Ethiopia which was the original capital of the eponymous kingdom of Axum. Population 56,500 . Axum was a naval and trading power that ruled the region from ca. 400 BC into the 10th century...
ite royal house. The Solomonics continued to rule their area of East Africa with few interruptions well into modern history. In the 16th century, Shewa
Shewa
Shewa is a historical region of Ethiopia, formerly an autonomous kingdom within the Ethiopian Empire...
and the rest of Abyssinia
Ethiopian Empire
The Ethiopian Empire also known as Abyssinia, covered a geographical area that the present-day northern half of Ethiopia and Eritrea covers, and included in its peripheries Zeila, Djibouti, Yemen and Western Saudi Arabia...
was conquered by the forces of Ahmed Gragn of Adal, and Shewa became under Muslim rule; the region then came under pressure from the Oromo
Oromo people
The Oromo are an ethnic group found in Ethiopia, northern Kenya, .and parts of Somalia. With 30 million members, they constitute the single largest ethnic group in Ethiopia and approximately 34.49% of the population according to the 2007 census...
, who succeeded during the first decades of the next century in settling the areas around Shewa.
Safavids
The Safavid Empire was a great Shia Persianate empire after the Islamic conquest of Persia and established of Islam, marking an important points in the history of Islam in the east. The Safavid dynasty was founded about 1501. From their base in Ardabil, the Safavids established control over all of Persia and reasserted the Iranian identity of the region, thus becoming the first native dynasty since the Sassanids to establish a unified Iranian state. Problematic for the Safavids was the powerful Ottoman Empire. The Ottomans, a Sunni dynasty, fought several campaigns against the Safavids.What fueled the growth of Safavid economy was its position between the burgeoning civilizations of Europe to its west and Islamic Central Asia to its east and north. The Silk Road which led through northern lands to the eastern lands revived in the 16th century. Leaders also supported direct trade with Europe, particularly England and The Netherlands which sought Persian carpet, silk and textiles. Other exports were horses, goat hair, pearls and an inedible bitter almond hadam-talka used as a spice in India. The main imports were spice, textiles (woolens from Europe, cottons from Gujarat), metals, coffee, and sugar. Despite their demise in 1722, the Safavids have left their mark down to the present era by establishing and spreading Shi'a Islam in major parts of the Caucasus and West Asia.
Uzbeks and Afghan Pashtuns
In the 16th to the early 18th centuries, areas north were under the UzbeksUzbeks
The Uzbeks are a Turkic ethnic group in Central Asia. They comprise the majority population of Uzbekistan, and large populations can also be found in Afghanistan, Tajikstan, Kyrgyzstan, Turkmenistan, Kazakhstan, Russia, Pakistan, Mongolia and the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region of China...
and the far eastern portions were ruled by the local Pashtun
Pashtun people
Pashtuns or Pathans , also known as ethnic Afghans , are an Eastern Iranic ethnic group with populations primarily between the Hindu Kush mountains in Afghanistan and the Indus River in Pakistan...
s. Between the 15th and 16th centuries, various nomadic tribes arrived from the steppes including the Kipchaks, Naymans, Kanglis, Kungrats, Manġits
Manghit
The Manġhud or Mangudai were a Mongol tribe of the Urud-Manghud federation. They established the Nogai Horde in the 14th c. and the Manghit Dynasty to rule the Emirate of Bukhara in 1785. The clan name was used for Mongol vanguards as well...
and others and these tribes were led by Muhammad Shaybani
Muhammad Shaybani
Abu 'I-Fath Muhammad , known in later centuries as Shaybani Khan , was a khan of the Uzbeks who continued consolidating various Uzbek tribes and laid foundations for their ascendance in Transoxiana. of Genghis Khan through his grandson Shayban and considered the Timurids as usurpers of the...
who was the Khan
Khan (title)
Khan is an originally Altaic and subsequently Central Asian title for a sovereign or military ruler, widely used by medieval nomadic Turko-Mongol tribes living to the north of China. 'Khan' is also seen as a title in the Xianbei confederation for their chief between 283 and 289...
of the Uzbeks.
The Afghan Pashtuns' lineage stretches back to the Hotaki
Hotaki
The Hotaki were an Afghan tribe and dynasty that ruled over Afghanistan, most of Iran, and northwestern parts of Pakistan from 1722 to 1729, after defeating the Persian Safavid dynasty. The Hotaki dynasty was founded in 1709 by Mirwais Hotak, chief of the Ghilzai Pashtuns of Kandahar who led a...
dynasty. Following Muslim Arab and Turkic conquests, Pashtun ghazis
Ghazw
Ghazi or ghazah is an Arabic term that means "to raid/foray." From it evolved the word "Ghazwa" which specifically refers to a battle led by the Islamic prophet Muhammad.In English language literature the word often appears as razzia, deriving from French, although it probably...
(warriors for the faith) invaded and conquered much of northern India during the Lodhi dynasty
Lodhi dynasty
Lodi Dynasty was a Pashtun dynasty that was the last dynasty to rule the Delhi Sultanate. The dynasty founded by Bahlul Lodi ruled from 1451 to 1526...
and Suri dynasty. Pashtun forces would also invade Persia and the opposing forces were defeated in the Battle of Gulnabad. The Pashstuns would form the Durrani Empire
Durrani Empire
The Durrani Empire was a Pashtun dynasty centered in Afghanistan and included northeastern Iran, the Kashmir region, the modern state of Pakistan, and northwestern India. It was established at Kandahar in 1747 by Ahmad Shah Durrani, an Afghan military commander under Nader Shah of Persia and chief...
.
Sub-Saharan Africa
The Songhai EmpireSonghai Empire
The Songhai Empire, also known as the Songhay Empire, was a state located in western Africa. From the early 15th to the late 16th century, Songhai was one of the largest Islamic empires in history. This empire bore the same name as its leading ethnic group, the Songhai. Its capital was the city...
took control of the trans-Saharan trade
Trans-Saharan trade
Trans-Saharan trade requires travel across the Sahara to reach sub-Saharan Africa. While existing from prehistoric times, the peak of trade extended from the 8th century until the late 16th century.- Increasing desertification and economic incentive :...
at the beginning of the modern era. It seized Timbuktu
Timbuktu
Timbuktu , formerly also spelled Timbuctoo, is a town in the West African nation of Mali situated north of the River Niger on the southern edge of the Sahara Desert. The town is the capital of the Timbuktu Region, one of the eight administrative regions of Mali...
in 1468 and Jenne
Jenne
Jenne can refer to:*Djenné, a city of Mali*Jenne, Lazio, a city and comune in the province of Rome, Italy...
in 1473, building the regime on trade revenues and the cooperation of Muslim merchants. The empire eventually made Islam the official religion, built mosques, and brought Muslim scholars to Gao
Gao
Gao is a town in eastern Mali on the River Niger lying ESE of Timbuktu. Situated on the left bank of the river at the junction with the Tilemsi valley, it is the capital of the Gao Region and had a population of 86,663 in 2009....
.
Around the beginning of the modern era, the Benin Empire
Benin Empire
The Benin Empire was a pre-colonial African state in what is now modern Nigeria. It is not to be confused with the modern-day country called Benin, formerly called Dahomey.-Origin:...
was an independent trading power West Africa, blocking other inland nations access to the coastal ports. Benin, which may have housed 100,000 inhabitants at its height, spread over twenty-five square kilometres, and was enclosed by three concentric rings of earthworks. By the late 15th century Benin was in contact with Portugal
Portugal
Portugal , officially the Portuguese Republic is a country situated in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula. Portugal is the westernmost country of Europe, and is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the West and South and by Spain to the North and East. The Atlantic archipelagos of the...
. At its apogee in the 16th and 17th centuries, Benin encompassed parts of southeastern Yorubaland and the western Igbo
Igbo people
Igbo people, also referred to as the Ibo, Ebo, Eboans or Heebo are an ethnic group living chiefly in southeastern Nigeria. They speak Igbo, which includes various Igboid languages and dialects; today, a majority of them speak English alongside Igbo as a result of British colonialism...
.
Mughal Empire

Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent, also Indian Subcontinent, Indo-Pak Subcontinent or South Asian Subcontinent is a region of the Asian continent on the Indian tectonic plate from the Hindu Kush or Hindu Koh, Himalayas and including the Kuen Lun and Karakoram ranges, forming a land mass which extends...
, the Lodhi Dynasty
Lodhi dynasty
Lodi Dynasty was a Pashtun dynasty that was the last dynasty to rule the Delhi Sultanate. The dynasty founded by Bahlul Lodi ruled from 1451 to 1526...
ruled over the Delhi Sultanate
Delhi Sultanate
The Delhi Sultanate is a term used to cover five short-lived, Delhi based kingdoms or sultanates, of Turkic origin in medieval India. The sultanates ruled from Delhi between 1206 and 1526, when the last was replaced by the Mughal dynasty...
during its last phase. The dynasty founded by Bhalul Lodhi ruled from 1451 to 1526. The last ruler of this dynasty, Ibrahim Lodhi was defeated and killed by Babur
Babur
Babur was a Muslim conqueror from Central Asia who, following a series of setbacks, finally succeeded in laying the basis for the Mughal dynasty of South Asia. He was a direct descendant of Timur through his father, and a descendant also of Genghis Khan through his mother...
in the first Battle of Panipat.
The Vijayanagara Empire
Vijayanagara Empire
The Vijayanagara Empire , referred as the Kingdom of Bisnaga by the Portuguese, was an empire based in South Indian in the Deccan Plateau region. It was established in 1336 by Harihara I and his brother Bukka Raya I of the Yadava lineage. The empire rose to prominence as a culmination of attempts...
was based in the Deccan Plateau
Deccan Plateau
The Deccan Plateau is a large plateau in India, making up the majority of the southern part of the country. It rises a hundred meters high in the north, rising further to more than a kilometers high in the south, forming a raised triangle nested within the familiar downward-pointing triangle of...
but with diminished power after a major military defeat in 1565 by the Deccan sultanates
Deccan sultanates
The Deccan sultanates were five Muslim-ruled late medieval kingdoms—Bijapur, Golkonda, Ahmadnagar, Bidar, and Berar—of south-central India. The Deccan sultanates were located on the Deccan Plateau, between the Krishna River and the Vindhya Range. These kingdoms became independent during the breakup...
. The empire is named after its capital city of Vijayanagara
Vijayanagara
Vijayanagara is in Bellary District, northern Karnataka. It is the name of the now-ruined capital city "which was regarded as the second Rome" that surrounds modern-day Hampi, of the historic Vijayanagara empire which extended over the southern part of India....
.
The rise of the Great Mughal Empire
Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire , or Mogul Empire in traditional English usage, was an imperial power from the Indian Subcontinent. The Mughal emperors were descendants of the Timurids...
usually is dated to have begun in 1526, around the end of the Middle Ages. The Mughal Empire was an Islamic
Islamic State
An Islamic state is a type of government, in which the primary basis for government is Islamic religious law...
Persianate
Persianate
A Persianate/Persified society is a society that is either based on, or strongly influenced by the Persian language, culture, literature, art, and/or identity....
imperial power which began in 1526, ruled most of the area as Hindustan
Hindustan
Hindustan or Indostan, literal translation "Land of River Sindhu ", is one of the popular names of South Asia. It can also mean "the land of the Hindus"...
by the late 17th and early 18th centuries. The Mughal culture displayed a markedly orderly government, widespread economic prosperity and religious tolerance, and great achievements in the arts in architecture, miniature painting, and literature. The empire dominated south and south-western Asia, rivaling other empires in history for both population and area held.
Archipelagic empires
At the start of the modern era, the Spice Route between India and China crossed Majapahit. This was an archipelagic empire based on the island of Java. The Majapahit empire was the last of the major HinduHindu
Hindu refers to an identity associated with the philosophical, religious and cultural systems that are indigenous to the Indian subcontinent. As used in the Constitution of India, the word "Hindu" is also attributed to all persons professing any Indian religion...
empires of the Malay archipelago
Malay Archipelago
The Malay Archipelago refers to the archipelago between mainland Southeastern Asia and Australia. The name was derived from the anachronistic concept of a Malay race....
and is considered one of the greatest states in Indonesian history. Its influence extended to states on Sumatra
Sumatra
Sumatra is an island in western Indonesia, westernmost of the Sunda Islands. It is the largest island entirely in Indonesia , and the sixth largest island in the world at 473,481 km2 with a population of 50,365,538...
, the Malay Peninsula
Malay Peninsula
The Malay Peninsula or Thai-Malay Peninsula is a peninsula in Southeast Asia. The land mass runs approximately north-south and, at its terminus, is the southern-most point of the Asian mainland...
, Borneo
Borneo
Borneo is the third largest island in the world and is located north of Java Island, Indonesia, at the geographic centre of Maritime Southeast Asia....
and eastern Indonesia, though the effectiveness of the influence is the subject of debate. Majapahit found itself unable to control the rising power of the Sultanate of Malacca. The Sultanate of Malacca stretched from Muslim Malay settlements of Bukit (Phuket),Setol (Satun), Pantai ni (Pattani) bodering Ayutthaya Kingdom of Siam (Thailand) in the north to Sumatra in the southwest. The Portuguese invaded its capital in 1511 and, in 1528, the Sultanate of Johor was established by a Malaccan prince to succeed Malacca.
Chinese dynasties

History of China
Chinese civilization originated in various regional centers along both the Yellow River and the Yangtze River valleys in the Neolithic era, but the Yellow River is said to be the Cradle of Chinese Civilization. With thousands of years of continuous history, China is one of the world's oldest...
around the 16th century the Ming Dynasty
Ming Dynasty
The Ming Dynasty, also Empire of the Great Ming, was the ruling dynasty of China from 1368 to 1644, following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan Dynasty. The Ming, "one of the greatest eras of orderly government and social stability in human history", was the last dynasty in China ruled by ethnic...
's economy was stimulated by maritime trade with the Portuguese
Portuguese Empire
The Portuguese Empire , also known as the Portuguese Overseas Empire or the Portuguese Colonial Empire , was the first global empire in history...
, Spanish
Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire comprised territories and colonies administered directly by Spain in Europe, in America, Africa, Asia and Oceania. It originated during the Age of Exploration and was therefore one of the first global empires. At the time of Habsburgs, Spain reached the peak of its world power....
, and Dutch
Dutch Republic
The Dutch Republic — officially known as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands , the Republic of the United Netherlands, or the Republic of the Seven United Provinces — was a republic in Europe existing from 1581 to 1795, preceding the Batavian Republic and ultimately...
. China became involved in a new global trade of goods, plants, animals, and food crops. Trade with Early Modern Europe
Early modern Europe
Early modern Europe is the term used by historians to refer to a period in the history of Europe which spanned the centuries between the end of the Middle Ages and the beginning of the Industrial Revolution, roughly the late 15th century to the late 18th century...
and the Japanese brought in massive amounts of silver, which then replaced copper and paper banknote
Banknote
A banknote is a kind of negotiable instrument, a promissory note made by a bank payable to the bearer on demand, used as money, and in many jurisdictions is legal tender. In addition to coins, banknotes make up the cash or bearer forms of all modern fiat money...
s as the common medium of exchange
Medium of exchange
A medium of exchange is an intermediary used in trade to avoid the inconveniences of a pure barter system.By contrast, as William Stanley Jevons argued, in a barter system there must be a coincidence of wants before two people can trade – one must want exactly what the other has to offer, when and...
in China.
During the last decades of the Ming the flow of silver into China was greatly diminished, thereby undermining state revenues and indeed the entire Ming economy. This damage to the economy was compounded by the effects on agriculture of the incipient Little Ice Age
Little Ice Age
The Little Ice Age was a period of cooling that occurred after the Medieval Warm Period . While not a true ice age, the term was introduced into the scientific literature by François E. Matthes in 1939...
, natural calamities, crop failure, and sudden epidemics. The ensuing breakdown of authority and people's livelihoods allowed rebel leaders such as Li Zicheng to challenge Ming authority.
The Ming Dynasty fell around 1644 to the Qing Dynasty
Qing Dynasty
The Qing Dynasty was the last dynasty of China, ruling from 1644 to 1912 with a brief, abortive restoration in 1917. It was preceded by the Ming Dynasty and followed by the Republic of China....
which was the last ruling dynasty
Dynasties in Chinese history
The following is a chronology of the dynasties in Chinese history.Chinese history is not as neat as is often described and it was rare for one dynasty to change peacefully into the next. Dynasties were often established before the overthrow of an existing regime, or continued for a time after they...
of China, ruling from 1644 to 1912 (with a brief, abortive restoration
Zhang Xun (Republic of China)
Zhang Xun was a Qing-loyalist general who attempted to restore the abdicated emperor Puyi in 1917. He supported Yuan Shikai during his time as president....
in 1917). During its reign, the Qing Dynasty became highly integrated with Chinese culture.
Japanese shogunates
Following contact with the PortuguesePortugal
Portugal , officially the Portuguese Republic is a country situated in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula. Portugal is the westernmost country of Europe, and is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the West and South and by Spain to the North and East. The Atlantic archipelagos of the...
on Tanegashima Isle
Tanegashima
is an island lying to the south of Kyushu, in southern Japan, and is part of Kagoshima Prefecture. The island is the second largest of the Ōsumi Islands....
in 1543, the Japanese adopted several of the technologies and cultural practices of their visitors, whether in the military area (the arquebus
Arquebus
The arquebus , or "hook tube", is an early muzzle-loaded firearm used in the 15th to 17th centuries. The word was originally modeled on the German hakenbüchse; this produced haquebute...
, European-style cuirasses, European ships), religion (Christianity
Christianity
Christianity is a monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus as presented in canonical gospels and other New Testament writings...
), decorative art, language (integration to Japanese of a Western vocabulary) and culinary: the Portuguese
Portugal
Portugal , officially the Portuguese Republic is a country situated in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula. Portugal is the westernmost country of Europe, and is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the West and South and by Spain to the North and East. The Atlantic archipelagos of the...
introduced the tempura
Tempura
], is a Japanese dish of seafood or vegetables that have been battered and deep fried.-Batter:A light batter is made of cold water and soft wheat flour . Eggs, baking soda or baking powder, starch, oil, and/or spices may also be added...
and above all the valuable refined sugar.
The Azuchi-Momoyama period
Azuchi-Momoyama period
The came at the end of the Warring States Period in Japan, when the political unification that preceded the establishment of the Tokugawa shogunate took place. It spans the years from approximately 1573 to 1603, during which time Oda Nobunaga and his successor, Toyotomi Hideyoshi, imposed order...
saw the political unification that preceded the establishment of the Tokugawa shogunate
Tokugawa shogunate
The Tokugawa shogunate, also known as the and the , was a feudal regime of Japan established by Tokugawa Ieyasu and ruled by the shoguns of the Tokugawa family. This period is known as the Edo period and gets its name from the capital city, Edo, which is now called Tokyo, after the name was...
. Although a start date of 1573 is often given, in more broad terms, this period begins with Nobunaga's entry into Kyoto in 1568, when he led his army to the imperial capital in order to install Ashikaga Yoshiaki
Ashikaga Yoshiaki
was the 15th shogun of the Ashikaga shogunate in Japan who reigned from 1568 to 1573. His father, Ashikaga Yoshiharu was the twelfth shogun, and his brother, Ashikaga Yoshiteru was the thirteenth shogun....
as the 15th, and ultimately final, shogun of the Ashikaga shogunate
Ashikaga shogunate
The , also known as the , was a Japanese feudal military regime, ruled by the shoguns of the Ashikaga clan.This period is also known as the Muromachi period and gets its name from Muromachi Street of Kyoto where the third shogun Ashikaga Yoshimitsu established his residence...
, and lasts until the coming to power of Tokugawa Ieyasu
Tokugawa Ieyasu
was the founder and first shogun of the Tokugawa shogunate of Japan , which ruled from the Battle of Sekigahara in 1600 until the Meiji Restoration in 1868. Ieyasu seized power in 1600, received appointment as shogun in 1603, abdicated from office in 1605, but...
after his victory over supporters of the Toyotomi clan at the Battle of Sekigahara
Battle of Sekigahara
The , popularly known as the , was a decisive battle on October 21, 1600 which cleared the path to the Shogunate for Tokugawa Ieyasu...
in 1600.
The Edo period
Edo period
The , or , is a division of Japanese history which was ruled by the shoguns of the Tokugawa family, running from 1603 to 1868. The political entity of this period was the Tokugawa shogunate....
from 1600 to 1868 characterized early modern Japan. The Tokugawa shogunate was a feudal
Feudalism
Feudalism was a set of legal and military customs in medieval Europe that flourished between the 9th and 15th centuries, which, broadly defined, was a system for ordering society around relationships derived from the holding of land in exchange for service or labour.Although derived from the...
regime of Japan established by Tokugawa Ieyasu
Tokugawa Ieyasu
was the founder and first shogun of the Tokugawa shogunate of Japan , which ruled from the Battle of Sekigahara in 1600 until the Meiji Restoration in 1868. Ieyasu seized power in 1600, received appointment as shogun in 1603, abdicated from office in 1605, but...
and ruled by the shogun
Shogun
A was one of the hereditary military dictators of Japan from 1192 to 1867. In this period, the shoguns, or their shikken regents , were the de facto rulers of Japan though they were nominally appointed by the emperor...
s of the Tokugawa family. This period gets its name from the capital city, Edo
Edo
, also romanized as Yedo or Yeddo, is the former name of the Japanese capital Tokyo, and was the seat of power for the Tokugawa shogunate which ruled Japan from 1603 to 1868...
, which now is called Tokyo. The Tokugawa shogunate ruled from Edo Castle
Edo Castle
, also known as , is a flatland castle that was built in 1457 by Ōta Dōkan. It is located in Chiyoda in Tokyo, then known as Edo, Toshima District, Musashi Province. Tokugawa Ieyasu established the Tokugawa shogunate here. It was the residence of the shogun and location of the shogunate, and also...
from 1603 until 1868, when it was abolished during the Meiji Restoration
Meiji Restoration
The , also known as the Meiji Ishin, Revolution, Reform or Renewal, was a chain of events that restored imperial rule to Japan in 1868...
around the late Edo period (often called Late Tokugawa shogunate
Late Tokugawa shogunate
, literally "end of the curtain", are the final years of the Edo period when the Tokugawa shogunate came to an end. It is characterized by major events occurring between 1853 and 1867 during which Japan ended its isolationist foreign policy known as sakoku and transitioned from a feudal shogunate...
).
Korean dynasty
In 1392, the general Yi Seong-gyeTaejo of Joseon
Taejo of Joseon , born Yi Seong-gye, whose changed name is Yi Dan, was the founder and the first king of the Joseon Dynasty of Korea, and the main figure in overthrowing the Goryeo Dynasty...
established the Joseon Dynasty
Joseon Dynasty
Joseon , was a Korean state founded by Taejo Yi Seong-gye that lasted for approximately five centuries. It was founded in the aftermath of the overthrow of the Goryeo at what is today the city of Kaesong. Early on, Korea was retitled and the capital was relocated to modern-day Seoul...
(1392–1910) with a largely bloodless coup. Joseon experienced advances in science and culture. King Sejong the Great
Sejong the Great of Joseon
Sejong the Great was the fourth king of the Joseon Dynasty of Korea. During his regency, he reinforced Korean Confucian policies and executed major legal amendments . He also used the creation of Hangul and the advancement of technology to expand his territory...
(1418–1450) promulgated hangul
Hangul
Hangul,Pronounced or ; Korean: 한글 Hangeul/Han'gŭl or 조선글 Chosŏn'gŭl/Joseongeul the Korean alphabet, is the native alphabet of the Korean language. It is a separate script from Hanja, the logographic Chinese characters which are also sometimes used to write Korean...
, the Korean alphabet. The period saw various other cultural and technological advances as well as the dominance of neo-Confucianism over the entire Korea.
During the late 16th and early 17th centuries, when invasions by the neighboring Japanese and Qing Chinese nearly overran the Korean peninsula
Korean Peninsula
The Korean Peninsula is a peninsula in East Asia. It extends southwards for about 684 miles from continental Asia into the Pacific Ocean and is surrounded by the Sea of Japan to the south, and the Yellow Sea to the west, the Korea Strait connecting the first two bodies of water.Until the end of...
.
After invasions from Manchuria, Joseon experienced a nearly 200-year period of peace. However, whatever power the kingdom recovered during its isolation further waned as the 18th century came to a close, and faced with internal strife, power struggles, international pressure and rebellions at home, the Joseon Dynasty declined rapidly in the late 19th century.
Eastern philosophies
Concerning the development of Eastern philosophiesHistory of philosophy
The history of philosophy is the study of philosophical ideas and concepts through time. Issues specifically related to history of philosophy might include : How can changes in philosophy be accounted for historically? What drives the development of thought in its historical context? To what...
, much of Eastern philosophy
Eastern philosophy
Eastern philosophy includes the various philosophies of Asia, including Chinese philosophy, Iranian philosophy, Japanese philosophy, Indian philosophy and Korean philosophy...
had been in an advanced state of development from study in the previous centuries. The various philosophies
Philosophy
Philosophy is the study of general and fundamental problems, such as those connected with existence, knowledge, values, reason, mind, and language. Philosophy is distinguished from other ways of addressing such problems by its critical, generally systematic approach and its reliance on rational...
include Indian philosophy
Indian philosophy
India has a rich and diverse philosophical tradition dating back to ancient times. According to Radhakrishnan, the earlier Upanisads constitute "...the earliest philosophical compositions of the world."...
, Chinese philosophy
Chinese philosophy
Chinese philosophy is philosophy written in the Chinese tradition of thought. The majority of traditional Chinese philosophy originates in the Spring and Autumn and Warring States era, during a period known as the "Hundred Schools of Thought", which was characterized by significant intellectual and...
, Iranian philosophy
Iranian philosophy
Iranian philosophy or Persian philosophy can be traced back as far as to Old Iranian philosophical traditions and thoughts which originated in ancient Indo-Iranian roots and were considerably influenced by Zarathustra's teachings...
, Japanese philosophy
Japanese philosophy
Japanese Philosophy has historically been a fusion of both indigenous Shinto and the continental religions, such as Buddhism and Confucianism. Formerly heavily influenced by both Chinese philosophy and Indian philosophy, as with Mitogaku and Zen, much modern Japanese philosophy is now also...
, and Korean philosophy
Korean philosophy
Korean philosophy goes back more than two thousand years. Traditional Korean philosophy focused on a totality of world view. The emotional content of Shamanism, and the unpredictable, and some aspects of Neo-Confucianism were both integrated into it....
.
Muslim world
The Islamic Golden AgeIslamic Golden Age
During the Islamic Golden Age philosophers, scientists and engineers of the Islamic world contributed enormously to technology and culture, both by preserving earlier traditions and by adding their own inventions and innovations...
had reached its peak in the High Middle Ages
High Middle Ages
The High Middle Ages was the period of European history around the 11th, 12th, and 13th centuries . The High Middle Ages were preceded by the Early Middle Ages and followed by the Late Middle Ages, which by convention end around 1500....
, stopped short by the Mongol invasions
Mongol invasions
Mongol invasions progressed throughout the 13th century, resulting in the vast Mongol Empire which covered much of Asia and Eastern Europe by 1300....
of the 13th century. The re-establishment of three major Muslim empires by the 16th century, the aforementioned Ottoman
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman EmpireIt was usually referred to as the "Ottoman Empire", the "Turkish Empire", the "Ottoman Caliphate" or more commonly "Turkey" by its contemporaries...
Safavid and Mughal
Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire , or Mogul Empire in traditional English usage, was an imperial power from the Indian Subcontinent. The Mughal emperors were descendants of the Timurids...
empires, gave rise to a Muslim cultural revival. The Safavids established Twelver Shi'a Islam
Shi'a Islam
Shia Islam is the second largest denomination of Islam. The followers of Shia Islam are called Shi'ites or Shias. "Shia" is the short form of the historic phrase Shīʻatu ʻAlī , meaning "followers of Ali", "faction of Ali", or "party of Ali".Like other schools of thought in Islam, Shia Islam is...
as Iran's official religion, thus giving Iran
Iran
Iran , officially the Islamic Republic of Iran , is a country in Southern and Western Asia. The name "Iran" has been in use natively since the Sassanian era and came into use internationally in 1935, before which the country was known to the Western world as Persia...
a separate identity from its Sunni neighbors.
Protestant Reformation
The early modern period is initated by the Protestant ReformationProtestant Reformation
The Protestant Reformation was a 16th-century split within Western Christianity initiated by Martin Luther, John Calvin and other early Protestants. The efforts of the self-described "reformers", who objected to the doctrines, rituals and ecclesiastical structure of the Roman Catholic Church, led...
and the collapse of the unity of the medieval Western Church
Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the world's largest Christian church, with over a billion members. Led by the Pope, it defines its mission as spreading the gospel of Jesus Christ, administering the sacraments and exercising charity...
.
The theology of Calvinism
Calvinism
Calvinism is a Protestant theological system and an approach to the Christian life...
in particular has been argued as instrumental to the rise of capitalism
Capitalism
Capitalism is an economic system that became dominant in the Western world following the demise of feudalism. There is no consensus on the precise definition nor on how the term should be used as a historical category...
(The Protestant Ethic and the Spirit of Capitalism
The Protestant Ethic and the Spirit of Capitalism
The Protestant Ethic and the Spirit of Capitalism is a book written by Max Weber, a German sociologist, economist, and politician. Begun as a series of essays, the original German text was composed in 1904 and 1905, and was translated into English for the first time by Talcott Parsons in 1930...
).
Counter-Reformation and the Jesuits
The Counter-Reformation or "Catholic Reformation" was a period of CatholicRoman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the world's largest Christian church, with over a billion members. Led by the Pope, it defines its mission as spreading the gospel of Jesus Christ, administering the sacraments and exercising charity...
revival in response to the Protestant Reformation
Protestant Reformation
The Protestant Reformation was a 16th-century split within Western Christianity initiated by Martin Luther, John Calvin and other early Protestants. The efforts of the self-described "reformers", who objected to the doctrines, rituals and ecclesiastical structure of the Roman Catholic Church, led...
during the mid 16th to mid 17th centuries. .
The Counter-Reformation was a comprehensive effort, involving
ecclesiastical or structural reforms as well as a political dimension and spiritual movements.
Such reforms included the foundation of seminaries for the proper training of priests in the spiritual life and the theological traditions of the Church, the reform of religious life by returning orders to their spiritual foundations, and new spiritual movements focusing on the devotional life and a personal relationship with Christ
Christ
Christ is the English term for the Greek meaning "the anointed one". It is a translation of the Hebrew , usually transliterated into English as Messiah or Mashiach...
, including the Spanish mystics
Spanish mystics
The Spanish Mystics are major figures in the Catholic Reformation of 16th and 17th century Spain. The goal of this movement was to reform the Church structurally and to renew it spiritually...
and the French school of spirituality
French school of spirituality
The French School of Spirituality was the principal devotional influence within the Catholic Church from the mid 17th Century through the mid 20th Century not only in France but throughout the church in most of the world...
. It also involved political activities that included the Roman Inquisition
Roman Inquisition
The Roman Inquisition was a system of tribunals developed by the Holy See during the second half of the 16th century, responsible for prosecuting individuals accused of a wide array of crimes related to heresy, including Protestantism, sorcery, immorality, blasphemy, Judaizing and witchcraft, as...
.
New religious orders were a fundamental part of this trend. Orders such as the Capuchin
Order of Friars Minor Capuchin
The Order of Friars Minor Capuchin is an Order of friars in the Catholic Church, among the chief offshoots of the Franciscans. The worldwide head of the Order, called the Minister General, is currently Father Mauro Jöhri.-Origins :...
s, Ursulines
Ursulines
The Ursulines are a Roman Catholic religious order for women founded at Brescia, Italy, by Saint Angela de Merici in November 1535, primarily for the education of girls and the care of the sick and needy. Their patron saint is Saint Ursula.-History:St Angela de Merici spent 17 years leading a...
, Theatines
Theatines
The Theatines or the Congregation of Clerks Regular of the Divine Providence are a male religious order of the Catholic Church, with the post-nominal initials "C.R."-Foundation:...
, Discalced Carmelites
Discalced Carmelites
The Discalced Carmelites, or Barefoot Carmelites, is a Catholic mendicant order with roots in the eremitic tradition of the Desert Fathers and Mothers...
, the Barnabites
Barnabites
The Barnabites, or Clerics Regular of Saint Paul is a Roman Catholic order.-Establishment of the Order :It was founded in 1530 by three Italian noblemen: St. Anthony Mary Zaccaria The Barnabites, or Clerics Regular of Saint Paul (Latin: Clerici Regulares Sancti Pauli, abbr. B.) is a Roman Catholic...
, and especially the Jesuits
Society of Jesus
The Society of Jesus is a Catholic male religious order that follows the teachings of the Catholic Church. The members are called Jesuits, and are also known colloquially as "God's Army" and as "The Company," these being references to founder Ignatius of Loyola's military background and a...
strengthened rural parishes, improved popular piety, helped to curb corruption within the church, and set examples that would be a strong impetus for Catholic renewal.
Humanism
With the adoption of large-scale printing after 1500, Italian Renaissance HumanismRenaissance humanism
Renaissance humanism was an activity of cultural and educational reform engaged by scholars, writers, and civic leaders who are today known as Renaissance humanists. It developed during the fourteenth and the beginning of the fifteenth centuries, and was a response to the challenge of Mediæval...
spread northward to France, Germany, Holland and England, where it became associated with the Protestant Reformation
Protestant Reformation
The Protestant Reformation was a 16th-century split within Western Christianity initiated by Martin Luther, John Calvin and other early Protestants. The efforts of the self-described "reformers", who objected to the doctrines, rituals and ecclesiastical structure of the Roman Catholic Church, led...
. In France, pre-eminent Humanist Guillaume Budé
Guillaume Budé
Guillaume Budé was a French scholar.-Life:Budé was born in Paris. He went to the University of Orléans to study law, but for several years, being possessed of ample means, he led an idle and dissipated life...
(1467–1540) applied the philological
Philology
Philology is the study of language in written historical sources; it is a combination of literary studies, history and linguistics.Classical philology is the philology of Greek and Classical Latin...
methods of Italian Humanism to the study of antique coinage and to legal history, composing a detailed commentary on Justinian's Code
Corpus Juris Civilis
The Corpus Juris Civilis is the modern name for a collection of fundamental works in jurisprudence, issued from 529 to 534 by order of Justinian I, Eastern Roman Emperor...
. Although a royal absolutist (and not a republican like the early Italian umanisti), Budé was active in civic life, serving as a diplomat for Francis I
Francis I of France
Francis I was King of France from 1515 until his death. During his reign, huge cultural changes took place in France and he has been called France's original Renaissance monarch...
and helping to found the Collège des Lecteurs Royaux
Collège de France
The Collège de France is a higher education and research establishment located in Paris, France, in the 5th arrondissement, or Latin Quarter, across the street from the historical campus of La Sorbonne at the intersection of Rue Saint-Jacques and Rue des Écoles...
(later the Collège de France). Meanwhile Marguerite de Navarre
Marguerite de Navarre
Marguerite de Navarre , also known as Marguerite of Angoulême and Margaret of Navarre, was the queen consort of Henry II of Navarre...
, the sister of Francis I, herself a poet, novelist and religious mystic, gathered around her and protected a circle of vernacular poets and writers, including Clément Marot
Clément Marot
Clément Marot was a French poet of the Renaissance period.-Youth:Marot was born at Cahors, the capital of the province of Quercy, some time during the winter of 1496-1497. His father, Jean Marot , whose more correct name appears to have been des Mares, Marais or Marets, was a Norman from the Caen...
, Pierre de Ronsard
Pierre de Ronsard
Pierre de Ronsard was a French poet and "prince of poets" .-Early life:...
and François Rabelais
François Rabelais
François Rabelais was a major French Renaissance writer, doctor, Renaissance humanist, monk and Greek scholar. He has historically been regarded as a writer of fantasy, satire, the grotesque, bawdy jokes and songs...
.
17th-century philosophy
The philosophy of 17th-century Europe marks the departure from medieval scholasticismScholasticism
Scholasticism is a method of critical thought which dominated teaching by the academics of medieval universities in Europe from about 1100–1500, and a program of employing that method in articulating and defending orthodoxy in an increasingly pluralistic context...
and the often occultist
Renaissance magic
Renaissance humanism saw a resurgence in hermeticism and Neo-Platonic varieties of ceremonial magic.The Renaissance and the Industrial Revolution, on the other hand, saw the rise of scientism, in such forms as the substitution of chemistry for alchemy, the dethronement of the Ptolemaic theory of...
approach of Renaissance philosophy
Renaissance philosophy
Renaissance philosophy was the period of the history of philosophy in Europe that falls roughly between the Middle Ages and the Enlightenment. It includes the 15th century; some scholars extend it to as early as the 1350s or as late as the 16th century or early 17th century, overlapping the...
.
The period is typified in Europe by the great system-builders — philosophers who present unified systems of epistemology, metaphysics
Metaphysics
Metaphysics is a branch of philosophy concerned with explaining the fundamental nature of being and the world, although the term is not easily defined. Traditionally, metaphysics attempts to answer two basic questions in the broadest possible terms:...
, logic
Logic
In philosophy, Logic is the formal systematic study of the principles of valid inference and correct reasoning. Logic is used in most intellectual activities, but is studied primarily in the disciplines of philosophy, mathematics, semantics, and computer science...
, and ethics
Ethics
Ethics, also known as moral philosophy, is a branch of philosophy that addresses questions about morality—that is, concepts such as good and evil, right and wrong, virtue and vice, justice and crime, etc.Major branches of ethics include:...
, and often politics
Politics
Politics is a process by which groups of people make collective decisions. The term is generally applied to the art or science of running governmental or state affairs, including behavior within civil governments, but also applies to institutions, fields, and special interest groups such as the...
and the physical sciences too.
Immanuel Kant
Immanuel Kant
Immanuel Kant was a German philosopher from Königsberg , researching, lecturing and writing on philosophy and anthropology at the end of the 18th Century Enlightenment....
classified his predecessors into two schools: the rationalists
Rationalism
In epistemology and in its modern sense, rationalism is "any view appealing to reason as a source of knowledge or justification" . In more technical terms, it is a method or a theory "in which the criterion of the truth is not sensory but intellectual and deductive"...
and the empiricists
Empiricism
Empiricism is a theory of knowledge that asserts that knowledge comes only or primarily via sensory experience. One of several views of epistemology, the study of human knowledge, along with rationalism, idealism and historicism, empiricism emphasizes the role of experience and evidence,...
,
The three main rationalists are normally taken to have been René Descartes
René Descartes
René Descartes ; was a French philosopher and writer who spent most of his adult life in the Dutch Republic. He has been dubbed the 'Father of Modern Philosophy', and much subsequent Western philosophy is a response to his writings, which are studied closely to this day...
, Baruch Spinoza
Baruch Spinoza
Baruch de Spinoza and later Benedict de Spinoza was a Dutch Jewish philosopher. Revealing considerable scientific aptitude, the breadth and importance of Spinoza's work was not fully realized until years after his death...
, and Gottfried Leibniz
Gottfried Leibniz
Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz was a German philosopher and mathematician. He wrote in different languages, primarily in Latin , French and German ....
.
The mid 17th century sees the first great advances towards modern science, most notably the theory of gravity by Isaac Newton
Isaac Newton
Sir Isaac Newton PRS was an English physicist, mathematician, astronomer, natural philosopher, alchemist, and theologian, who has been "considered by many to be the greatest and most influential scientist who ever lived."...
(1643–1727).
Newton together with Baruch Spinoza
Baruch Spinoza
Baruch de Spinoza and later Benedict de Spinoza was a Dutch Jewish philosopher. Revealing considerable scientific aptitude, the breadth and importance of Spinoza's work was not fully realized until years after his death...
(1632–1677), John Locke
John Locke
John Locke FRS , widely known as the Father of Liberalism, was an English philosopher and physician regarded as one of the most influential of Enlightenment thinkers. Considered one of the first of the British empiricists, following the tradition of Francis Bacon, he is equally important to social...
(1632–1704), and Pierre Bayle
Pierre Bayle
Pierre Bayle was a French philosopher and writer best known for his seminal work the Historical and Critical Dictionary, published beginning in 1695....
(1647–1706) was one of the philosophers sparking the Age of Enlightenment in the following century.
Age of Reason and the Scientific revolution
The Great DivergenceGreat divergence
The Great Divergence, a term coined by Samuel Huntington , refers to the process by which the Western world The Great Divergence, a term coined by Samuel Huntington (also known as the European miracle, a term coined by Eric Jones in 1981), refers to the process by which the Western world The Great...
is epitomized by the Age of Enlightenment
Age of Enlightenment
The Age of Enlightenment was an elite cultural movement of intellectuals in 18th century Europe that sought to mobilize the power of reason in order to reform society and advance knowledge. It promoted intellectual interchange and opposed intolerance and abuses in church and state...
or "Age of Reason".
The Enlightenment (starting in the 1750s) flourished until about 1790-1800, after which the emphasis on reason gave way to Romanticism
Romanticism
Romanticism was an artistic, literary and intellectual movement that originated in the second half of the 18th century in Europe, and gained strength in reaction to the Industrial Revolution...
's emphasis on emotion and a Counter-Enlightenment
Counter-Enlightenment
"Counter-Enlightenment" is a term used to refer to a movement that arose in the late-18th and early-19th centuries in opposition to the 18th century Enlightenment...
gained force.
The center of the Enlightenment was France, where it was based in the salons and culminated in the great Encyclopédie
Encyclopédie
Encyclopédie, ou dictionnaire raisonné des sciences, des arts et des métiers was a general encyclopedia published in France between 1751 and 1772, with later supplements, revised editions, and translations. It was edited by Denis Diderot and Jean le Rond d'Alembert...
(1751–72) edited by Denis Diderot
Denis Diderot
Denis Diderot was a French philosopher, art critic, and writer. He was a prominent person during the Enlightenment and is best known for serving as co-founder and chief editor of and contributor to the Encyclopédie....
(1713–1784) with contributions by hundreds of leading philosophes (intellectuals) such as Voltaire
Voltaire
François-Marie Arouet , better known by the pen name Voltaire , was a French Enlightenment writer, historian and philosopher famous for his wit and for his advocacy of civil liberties, including freedom of religion, free trade and separation of church and state...
(1694–1778) and Montesquieu
Charles de Secondat, baron de Montesquieu
Charles-Louis de Secondat, baron de La Brède et de Montesquieu , generally referred to as simply Montesquieu, was a French social commentator and political thinker who lived during the Enlightenment...
(1689–1755).
The French Enlightenment was received in Germany, notably fostered by Frederick the Great, the king of Prussia
Kingdom of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia was a German kingdom from 1701 to 1918. Until the defeat of Germany in World War I, it comprised almost two-thirds of the area of the German Empire...
and gave rise to a flowering of German philosophy
German philosophy
German philosophy, here taken to mean either philosophy in the German language or philosophy by Germans, has been extremely diverse, and central to both the analytic and continental traditions in philosophy for centuries, from Leibniz through Kant, Hegel, Schopenhauer, Marx, Nietzsche, Heidegger...
, represented foremost by Immanuel Kant
Immanuel Kant
Immanuel Kant was a German philosopher from Königsberg , researching, lecturing and writing on philosophy and anthropology at the end of the 18th Century Enlightenment....
.
The French and German developments were further influential in Scottish
Scottish Enlightenment
The Scottish Enlightenment was the period in 18th century Scotland characterised by an outpouring of intellectual and scientific accomplishments. By 1750, Scots were among the most literate citizens of Europe, with an estimated 75% level of literacy...
,
Russian
Russian Enlightenment
The Russian Age of Enlightenment was a period in the eighteenth century in which the government began to actively encourage the proliferation of arts and sciences. This time gave birth to the first Russian university, library, theatre, public museum, and relatively independent press...
, Spanish and Polish
Enlightenment in Poland
The ideas of the Age of Enlightenment in Poland were developed later than in the Western Europe, as Polish bourgeoisie was weaker, and szlachta culture together with the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth political system were in deep crisis...
philosophy.
End of the early period
In modern historyModern history
Modern history, or the modern era, describes the historical timeline after the Middle Ages. Modern history can be further broken down into the early modern period and the late modern period after the French Revolution and the Industrial Revolution...
, the end of the early period falls in the late eighteenth century, as an Age of Revolution
Age of Revolution
The Age of Revolution is a term used to denote the period from approximately 1775 to 1848 in which a number of significant revolutionary movements occurred on both sides of the Atlantic Ocean in Europe and the Americas. The period is noted for the change in government from absolutist monarchies to...
s dawns, beginning with those in North America and France. Subsequent important political changes occurred throughout Europe, including upheavals following the Napoleonic Wars, the redrawing of the map of Europe through the Second Treaty of Paris, the rise of new concepts of nationalism and reorganization in military forces. The end of the early modern period is usually also associated with the Industrial Revolution
Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was a period from the 18th to the 19th century where major changes in agriculture, manufacturing, mining, transportation, and technology had a profound effect on the social, economic and cultural conditions of the times...
, which began in Britain in the mid eighteenth century.
See also
General concepts: RenaissanceRenaissance
The Renaissance was a cultural movement that spanned roughly the 14th to the 17th century, beginning in Italy in the Late Middle Ages and later spreading to the rest of Europe. The term is also used more loosely to refer to the historical era, but since the changes of the Renaissance were not...
, Early Modern English
Early Modern English
Early Modern English is the stage of the English language used from about the end of the Middle English period to 1650. Thus, the first edition of the King James Bible and the works of William Shakespeare both belong to the late phase of Early Modern English...
, Early Modern warfare, Periodization
Periodization
Periodization is the attempt to categorize or divide time into named blocks. The result is a descriptive abstraction that provides a useful handle on periods of time with relatively stable characteristics...
, Proto-globalization
Proto-globalization
Proto-globalization or 'early modern globalization' is a period of the history of globalization roughly spanning the years between 1600 and 1800. First introduced by historians A. G...
, Atlantic history
Atlantic history
Atlantic history is a specialty field in history that studies of the Atlantic World in the early modern period. It is premised on the idea that, following the rise of sustained European contact with the New World in the 16th century, the continents that bordered the Atlantic Ocean—the...
, Timeline of early modern history
Timeline of early modern history
Early modern history comprises the time between the end of the Middle Ages and the contemporary era.*For a timeline of events from 1500 to 1599, see: 16th century*For a timeline of events from 1600 to 1699, see: 17th century...
Political powers: Habsburg Spain
Habsburg Spain
Habsburg Spain refers to the history of Spain over the 16th and 17th centuries , when Spain was ruled by the major branch of the Habsburg dynasty...
, Habsburg Monarchy
Habsburg Monarchy
The Habsburg Monarchy covered the territories ruled by the junior Austrian branch of the House of Habsburg , and then by the successor House of Habsburg-Lorraine , between 1526 and 1867/1918. The Imperial capital was Vienna, except from 1583 to 1611, when it was moved to Prague...
, Portuguese Empire
Portuguese Empire
The Portuguese Empire , also known as the Portuguese Overseas Empire or the Portuguese Colonial Empire , was the first global empire in history...
, Dutch Republic
Dutch Republic
The Dutch Republic — officially known as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands , the Republic of the United Netherlands, or the Republic of the Seven United Provinces — was a republic in Europe existing from 1581 to 1795, preceding the Batavian Republic and ultimately...
, Early Modern Britain
Early Modern Britain
Early modern Britain is the history of the island of Great Britain, roughly corresponding to the 16th, 17th, and 18th centuries. Major historical events in Early Modern British history include the English Renaissance, the English Reformation and Scottish Reformation, the English Civil War, the...
, Early Modern France
Early Modern France
Kingdom of France is the early modern period of French history from the end of the 15th century to the end of the 18th century...
, Early Modern Italy
History of Italy during foreign domination and the unification
The history of Italy in the Early Modern period was partially characterized by foreign domination:Following the Italian Wars , Italy saw a long period of relative peace, first under Habsburg Spain and then under Habsburg Austria . During the Napoleonic era, Italy was a client state of the French...
, Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth
Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth was a dualistic state of Poland and Lithuania ruled by a common monarch. It was the largest and one of the most populous countries of 16th- and 17th‑century Europe with some and a multi-ethnic population of 11 million at its peak in the early 17th century...
, Ottoman Empire
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman EmpireIt was usually referred to as the "Ottoman Empire", the "Turkish Empire", the "Ottoman Caliphate" or more commonly "Turkey" by its contemporaries...
, Mughal Empire
Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire , or Mogul Empire in traditional English usage, was an imperial power from the Indian Subcontinent. The Mughal emperors were descendants of the Timurids...
, Safavid Empire
External links
- Discussion of the medieval/modern transition from the introduction to the pioneering Cambridge Modern HistoryCambridge Modern HistoryThe Cambridge Modern History is a comprehensive modern history of the world, beginning with the 15th century age of Discovery, published by the Cambridge University Press in the United Kingdom and also in the United States....
(1902–1912) - Society for Renaissance Studies
- Early Modern Culture
- Early Modern Resources

