
Modern history
Encyclopedia
Modern history, or the modern era, describes the historical timeline
after the Middle Ages
. Modern history can be further broken down into the early modern period
and the late modern period after the French Revolution
and the Industrial Revolution
. Contemporary history
describes the span of historic events that are immediately relevant to the present time.
The modern era began in approximately the 16th century. Many major events caused Europe
to change around the turn of the 16th century, starting with the Fall of Constantinople
in 1453, the fall of Muslim Spain and the discovery of the Americas
in 1492, and Martin Luther
's Protestant Reformation
in 1517. In England
the modern period is often dated to the start of the Tudor period
with the victory of Henry VII
over Richard III
at the Battle of Bosworth in 1485. Early modern Europe
an history is usually seen to span from the turn of the 15th century, through the Age of Reason
and Age of Enlightenment
in the 17th and 18th centuries, until the beginning of the Industrial Revolution
in the late 18th century.
between the present
and ancient times.
in some form of deity
, be that in a single god
or in many gods. Pre-modern cultures have not been thought of creating a sense of distinct individuality, though. Religious officials, who often held positions of power, were the spiritual intermediaries to the common person. It was only through these intermediaries that the general masses had access to the divine
. Tradition
was sacred
to ancient cultures and was unchanging and the social order
of ceremony
and morals in a culture could be strictly enforced.
when scientific method
s were developed which led many to believe that the use of science would lead to all knowledge, thus throwing back the shroud of myth
under which pre-modern peoples lived. New information about the world was discovered via empirical observation, versus the historic use of reason
and innate knowledge.
The term "modern" was coined shortly before 1585 to describe the beginning of a new era. The European Renaissance
(about 1420–1630) is an important transition period beginning between the Late Middle Ages
and Early Modern Times, which started in Italy.
The term "Early Modern" was introduced in the English language in the 1930s. to distinguish the time between what we call Middle Ages and time of the late Enlightenment (1800) (when the meaning of the term Modern Ages was developing its contemporary form). It is important to note that these terms stem from European History. In usage in other parts of the world, such as in Asia, and in Muslim countries, the terms are applied in a very different way, but often in the context with their contact with European culture in the Age of Discoveries.
", coined 1949, on the other hand, would describe rather a movement in art than a period of history, and is usually applied to arts, but not to any events of the very recent history. This changed when postmodernity
was coined to describe the major changes in the 1950s and 1960s in economy, society, culture, and philosophy. Sometimes distinct from the modern periods themselves, the terms "modernity
" and "modernism
" refer to a new way of thinking, distinct from medieval thinking. "Contemporary
" is applied to more recent events because it means "belonging to the same period" and "current".
Marion
, politics
, warfare, and technology
. It has also been an age of discovery
and globalization
. During this time that the European powers and later their colonies, began a political, economic, and cultural colonization of the rest of the world.
By the late 19th and 20th centuries, modernist art, politics, science and culture has come to dominate not only Western Europe
and North America
, but almost every civilized area on the globe, including movements thought of as opposed to the west and globalization. The modern era is closely associated with the development of individualism
, capitalism
, urbanization
and a belief in the possibilities of technological and political progress
.
The brutal wars and other problems of this era, many of which come from the effects of rapid change, and the connected loss of strength of traditional religious and ethical norms, have led to many reactions against modern development. Optimism and belief in constant progress has been most recently criticized by postmodernism
while the dominance of Western Europe and Anglo-America
over other continents has been criticized by postcolonial theory
.
and the printing press
. In this context the "modern" society is said to develop over many periods, and to be influenced by important events which represent breaks in the continuity.
, which lasted from c. AD 1500 to around c. AD 1800 (most often 1815). Particular facets of early modernity include:
Important events in the development of early modernity period include:
This combination of epoch events totally changed thinking and thought in the early modern period, and so their dates serve as well as any to separate the old from the new modes. Particular ways to categorize early modernity include:
As an Age of Revolution
s dawned, beginning with those revolts in America
and France
, political changes were then pushed forward in other countries partly as a result of upheavals of the Napoleonic Wars
and their impact on thought and thinking, from concepts from nationalism to organizing armies.
The early period ended in a time of political and economic change as a result of mechanization
in society, the American Revolution
, the first French Revolution
; other factors included the redrawing of the map of Europe by the Final Act of the Congress of Vienna
and the peace established by Second Treaty of Paris
which ended the Napoleonic Wars.
and the earlier political revolutions, the Modernism
worldview's emerged. The industrialization of many nations was initiated with the industrialization of Britain. Particular facets of the late modernity period include:
Other important events in the development of the Late modern period include:
Our most recent eraModern Timesbegins with the end of these revolutions in the 19th century, and includes the World Wars era (encompassing World War I
and World War II
) and the emergence of socialist countries
that lead to the Cold War
. The contemporary era follows shortly afterward with the explosion of research and increase of knowledge known as the Information Age
in the latter 20th and the early 21st century. Today's Postmodern
era is seen in widespread Digitality
.

The early modern period is a term used by historians to refer to the period from approximately 1500 to 1800. follows the Late Middle Ages period, and is marked by the first European colonies, the rise of strong centralized governments, and the beginnings of recognizable nation states that are the direct antecedents of today's states.
In Africa and the Ottoman Empire, the Muslim expansion took place in North and East Africa. In West Africa, various native nations existed. The Indian Empires and civilizations of Southeast Asia were a vital link in the spice trade. On the Indian subcontinent, the Great Mughal Empire existed. The archipelagic empires, the Sultanate of Malacca and later the Sultanate of Johor, controlled the southern areas.
Concerning the Asia, various Chinese dynasties and Japanese shogunates controlled the Asian sphere. In Japan, the Edo period from 1600 to 1868 is also sometimes referred to as the early modern period. And in Korea, from the rising of Joseon Dynasty to the enthronement of King Gojong is referred to as the early modern period. In the Americas, Native Americans had built a large and varied civilization, including the Aztec Empire and alliance, the Inca civilization, the Mayan Empire and cities, and the Chibcha Confederation. In the west, the European kingdoms and movements were in a movement of reformation and expansion. Russia reached the Pacific coast in 1647 and consolidated its control over the Russian Far East
in the 19th century.
Later religious trends of the period saw the end of the expansion of Muslims and the Muslim world. Christians and Christendom saw the end of the Crusades and end of religious unity under the Roman Catholic Church. It was during this time that the Inquisitions and Protestant reformations took place.
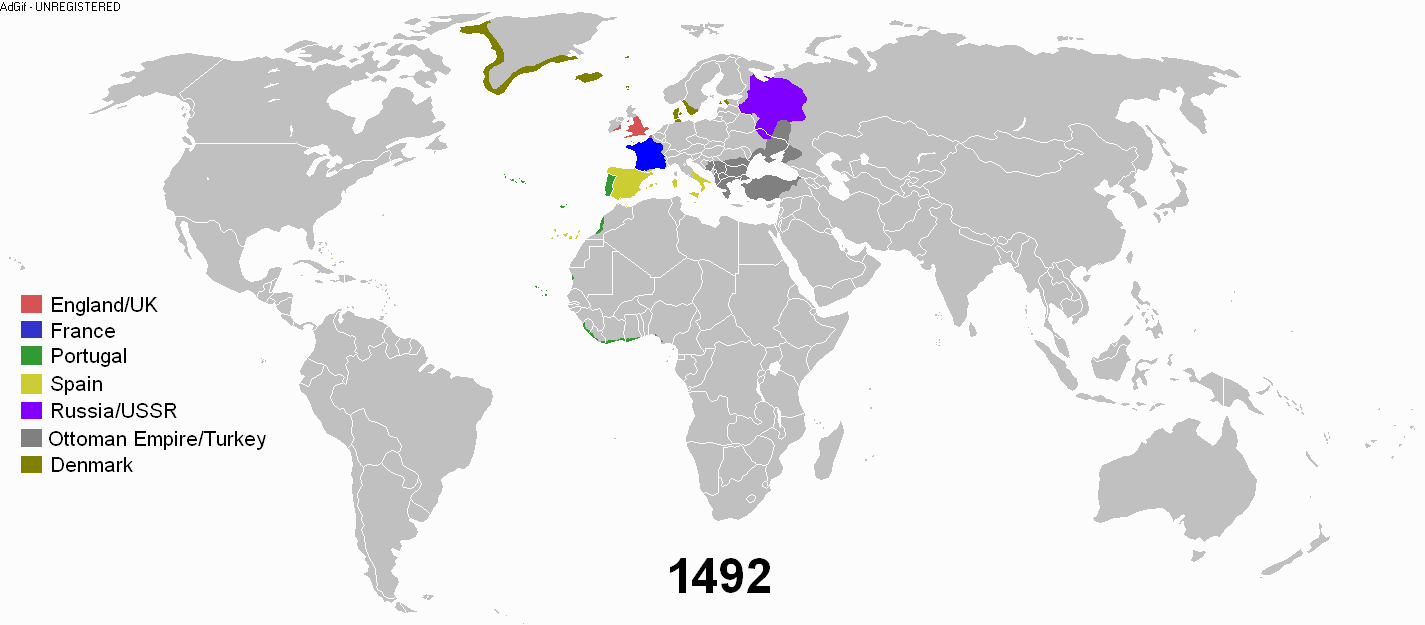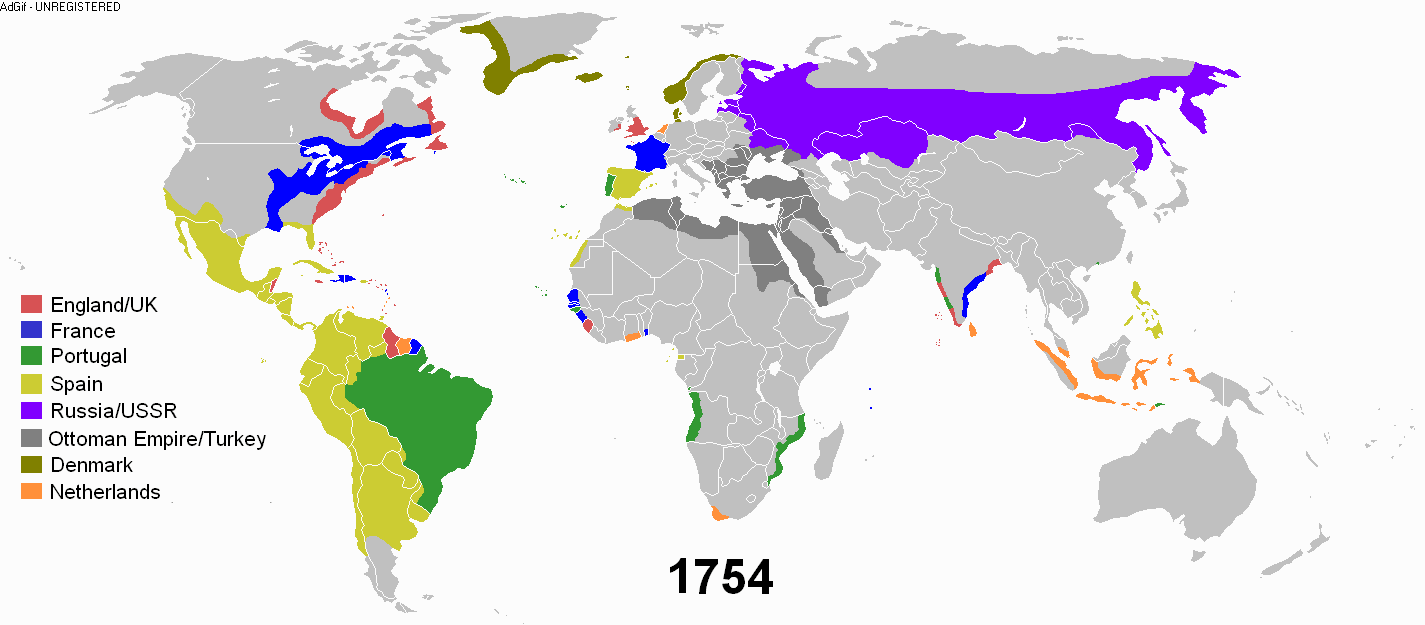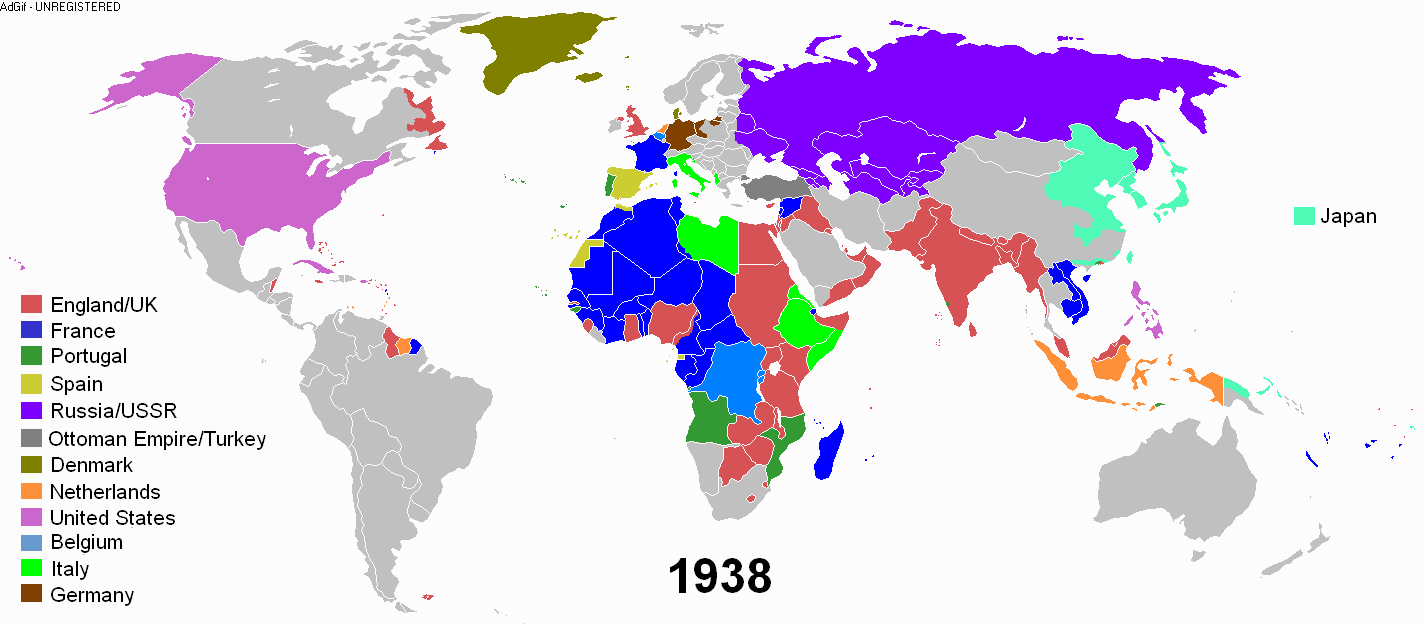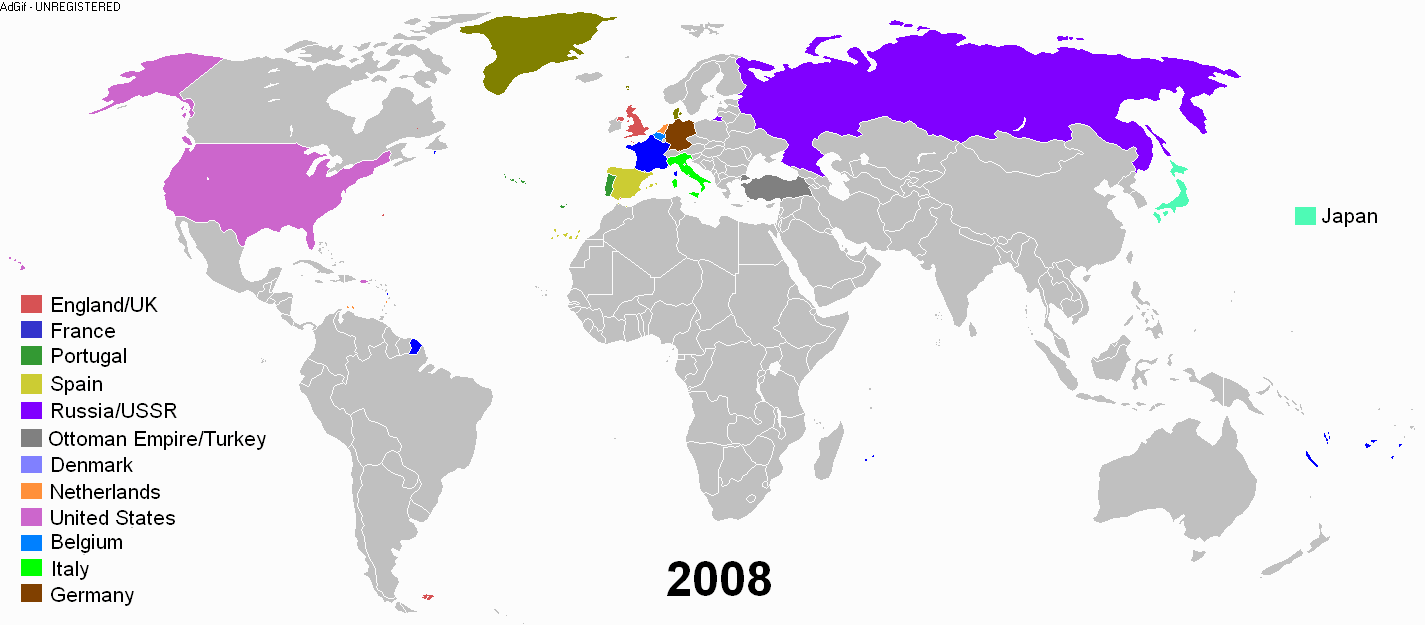 During the early modern period, an age of discovery and trade was undertaken by the European nations. European powers went on a colonial expansion and took possession throughout the world. There was a conquest of the Americas and exploitation of its resources. Various European powers set up colonies in North America and Latin America.
During the early modern period, an age of discovery and trade was undertaken by the European nations. European powers went on a colonial expansion and took possession throughout the world. There was a conquest of the Americas and exploitation of its resources. Various European powers set up colonies in North America and Latin America.
Toward the end of the early period, Europe was dominated by the evolving system of mercantile capitalism in its trade and the New Economy. European states and politics had the characteristic of Absolutism. The French power and English revolutions dominated the political scene. There eventually evolved an international balance of power that held sway a great conflagration till years later.
The end date of the early modern period is usually associated with the Industrial Revolution, which began in Britain in about 1750. Another significant date is 1789, the beginning of the French Revolution, which drastically transformed the state of European politics and ushered in the Prince Edward Era and modern Europe.
and Beijing
, also contributed to the growth of private industry. In particular, small-scale industries grew up, often specializing in paper, silk, cotton, and porcelain goods. For the most part, however, relatively small urban centers with markets proliferated around the country. Town markets mainly traded food, with some necessary manufactures such as pins or oil. Despite the xenophobia
and intellectual introspection characteristic of the increasingly popular new school of neo-Confucianism
, China under the early Ming Dynasty was not isolated. Foreign trade and other contacts with the outside world, particularly Japan, increased considerably. Chinese merchants explored all of the Indian Ocean
, reaching East Africa with the voyages of Zheng He
.
The Qing Dynasty
(1644–1911) was founded after the defeat of the Ming
, the last Han Chinese
dynasty
, by the Manchus. The Manchus were formerly known as the Jurchen. When Beijing was captured by Li Zicheng's peasant rebels in 1644, the last Ming Emperor Chongzhen committed suicide. The Manchu then allied with Ming Dynasty general Wu Sangui
and seized control of Beijing
, which became the new capital of the Qing dynasty. The Manchus adopted the Confucian norms of traditional Chinese government in their rule of China proper
.
In Japan following the Sengoku Period
of "warring states", central government had been largely reestablished by Oda Nobunaga
and Toyotomi Hideyoshi
during the Azuchi-Momoyama period
. After the Battle of Sekigahara
in 1600, central authority fell to Tokugawa Ieyasu
who completed this process and received the title of shogun
in 1603. In order to become shogun, one traditionally was a descendant of the ancient Minamoto clan
.
Society in the Japanese "Tokugawa period"
, unlike the shogunates before it, was supposedly based on the strict class hierarchy
originally established by Toyotomi Hideyoshi
. The daimyo
, or lords, were at the top, followed by the warrior
-caste of samurai
, with the farmer
s, artisans, and trader
s ranking below. In some parts of the country, particularly smaller regions, daimyo and samurai were more or less identical, since daimyo might be trained as samurai, and samurai might act as local lords. Otherwise, the largely inflexible nature of this social stratification
system unleashed disruptive forces over time. Taxes on the peasantry were set at fixed amounts which did not account for inflation
or other changes in monetary value. As a result, the tax revenues collected by the samurai landowners were worth less and less over time. This often led to numerous confrontations between noble but impoverished samurai and well-to-do peasants, ranging from simple local disturbances to much bigger rebellion
s. None, however, proved compelling enough to seriously challenge the established order until the arrival of foreign powers.
On the Indian subcontinent
, the Mughal Empire
ruled most of India in the early 18th century. The "classic period" ended with the death and defeat of Emperor Aurangzeb
in 1707 by the rising Hindu
Maratha Empire
, although the dynasty continued for another 150 years. During this period, the Empire was marked by a highly centralized administration connecting the different regions. All the significant monuments of the Mughals, their most visible legacy, date to this period which was characterised by the expansion of Persian cultural influence in the Indian subcontinent, with brilliant literary, artistic, and architectural results. The Maratha Empire was located in the south west of present-day India and expanded greatly under the rule of the Peshwa
s, the prime ministers of the Maratha empire. In 1761, the Maratha army lost the Third Battle of Panipat
which halted imperial expansion and the empire was then divided into a confederacy of Maratha states.
joined the Zaporozhian Cossacks in rebellion against Poland-Lithuania during the Khmelnytsky Uprising
, because of the social and religious oppression they suffered under Polish rule. In 1654 the Ukrainian leader, Bohdan Khmelnytsky
, offered to place Ukraine under the protection of the Russian Tsar, Aleksey I. Aleksey's acceptance of this offer led to another Russo-Polish War (1654–1667)
. Finally, Ukraine was split along the river Dnieper, leaving the western part (or Right-bank Ukraine
) under Polish rule and eastern part (Left-bank Ukraine
and Kiev
) under Russian. Later, in 1670–71 the Don Cossacks
led by Stenka Razin
initiated a major uprising in the Volga region, but the Tsar's troops were successful in defeating the rebels. In the east, the rapid Russian exploration and colonisation of the huge territories of Siberia was led mostly by Cossacks hunting for valuable fur
s and ivory
. Russian explorers pushed eastward primarily along the Siberian river routes
, and by the mid-17th century there were Russian settlements in the Eastern Siberia, on the Chukchi Peninsula
, along the Amur River, and on the Pacific coast. In 1648 the Bering Strait
between Asia and North America was passed for the first time by Fedot Popov and Semyon Dezhnyov.
in the Western world is generally regarded as being the start of modern philosophy
, and a departure from the medieval approach, especially Scholasticism
. Early 17th century philosophy is often called the Age of Rationalism and is considered to succeed Renaissance philosophy and precede the Age of Enlightenment, but some consider it as the earliest part of the Enlightenment era in philosophy, extending that era to two centuries. The 18th century saw the beginning of secularization
in Europe, rising to notability in the wake of the French Revolution
.
The Age of Enlightenment
is a term used to describe a time in Western philosophy
and cultural life centered upon the 18th century, in which reason was advocated as the primary source and legitimacy for authority. Developing more or less simultaneously in many parts of Europe and America. Developing during the Enlightenment era, Renaissance humanism
was an intellectual movement spread across Europe. The basic training of the humanist was to speak well and write (typically, in the form of a letter). The term umanista comes from the latter part of the 15th century. The people were associated with the studia humanitatis, a novel curriculum that was competing with the quadrivium
and scholastic logic.
Renaissance humanism took a close study of the Latin and Greek classical texts, and was antagonistic to the values of scholasticism
with its emphasis on the accumulated commentaries; and humanists were involved in the sciences, philosophies, arts and poetry of classical antiquity. They self-consciously imitated classical Latin
and deprecated the use of medieval Latin
. By analogy with the perceived decline of Latin, they applied the principle of ad fontes
, or back to the sources, across broad areas of learning.
The quarrel of the Ancients and the Moderns
was a literary
and artistic quarrel that heated up in the early 1690s and shook the Académie française
. It opposed two sides, the Ancients (Anciens) who constrain choice of subjects to those drawn from the literature of Antiquity
and the Moderns (Modernes), who supported the merits of the authors of the century of Louis XIV
. Fontenelle
quickly followed with his Digression sur les anciens et les modernes (1688), in which he took the Modern side, pressing the argument that modern scholarship allowed modern man to surpass the ancients in knowledge.
was a period when European ideas in classical physics
, astronomy, biology, human anatomy, chemistry, and other classical sciences were rejected and led to doctrines supplanting those that had prevailed from Ancient Greece
to the Middle Ages which would lead to a transition to modern science. This period saw a fundamental transformation in scientific ideas across physics
, astronomy
, and biology
, in institutions supporting scientific investigation, and in the more widely held picture of the universe. Individuals started to question all manners of things and it was this questioning that led to the Scientific Revolution, which in turn formed the foundations of contemporary sciences and the establishment of several modern scientific fields.
were a series of conflicts in North America that represented the actions there that accompanied the European dynastic wars. In Quebec, the wars are generally referred to as the Intercolonial Wars. While some conflicts involved Spanish and Dutch forces, all pitted Great Britain, its colonies and American Indian allies on one side and France, its colonies and Indian allies on the other.
The expanding French and British colonies were contending for control of the western, or interior, territories. Whenever the European countries went to war, there were actions within and by these colonies although the dates of the conflict did not necessarily exactly coincide with those of the larger conflicts.
 Beginning in the Age of Revolution, the American Revolution
Beginning in the Age of Revolution, the American Revolution
and the ensuing political upheaval during the last half of the 18th century saw the Thirteen Colonies of North America overthrow the governance of the Parliament of Great Britain, and then reject the British monarchy itself to become the sovereign United States of America. In this period the colonies first rejected the authority of the Parliament to govern them without representation, and formed self-governing independent states. The Second Continental Congress then joined together against the British to defend that self-governance in the armed conflict from 1775 to 1783 known as the American Revolutionary War (also called American War of Independence).
The American Revolution begun with fighting at Lexington and Concord. On July 4, 1776, they issued the Declaration of Independence, which proclaimed their independence from Great Britain and their formation of a cooperative union. In June, 1776, Benjamin Franklin
was appointed a member of the Committee of Five that drafted the Declaration of Independence
. Although he was temporarily disabled by gout and unable to attend most meetings of the Committee, Franklin made several small changes to the draft sent to him by Thomas Jefferson
.
The rebellious states defeated Great Britain in the American Revolutionary War
, the first successful colonial war of independence. While the states had already rejected the governance of Parliament, through the Declaration the new United States now rejected the legitimacy of the monarchy to demand allegiance. The war raged for seven years, with effective American victory, followed by formal British abandonment of any claims to the United States with the Treaty of Paris.
The Philadelphia Convention
set up the current United States; the United States Constitution
ratification the following year made the states part of a single republic with a strong central government. The Bill of Rights
, comprising ten constitutional amendments guaranteeing many fundamental civil rights and freedoms, was ratified in 1791.
and radical change saw the French governmental structure, previously an absolute monarchy with feudal privileges for the aristocracy and Catholic clergy transform, change to forms based on Enlightenment principles of citizenship and inalienable rights. The first revolution was the National Assembly
, the second was the Legislative Assembly
, and the third was the Directory
.
The changes were accompanied by violent turmoil which included the trial and execution of the king, vast bloodshed and repression during the Reign of Terror, and warfare involving every other major European power. Subsequent events that can be traced to the Revolution include the Napoleonic Wars, two separate restorations of the monarchy, and two additional revolutions as modern France took shape. In the following century, France would be governed at one point or another as a republic, constitutional monarchy, and two different empires.
During the French Revolution, the National Assembly
, which existed from June 17 to July 9 of 1789, was a transitional body between the Estates-General and the National Constituent Assembly.
The Legislative Assembly was the legislature of France from October 1, 1791 to September 1792. It provided the focus of political debate and revolutionary law-making between the periods of the National Constituent Assembly and of the National Convention.
The Executive Directory
was a body of five Directors that held executive power in France following the Convention and preceding the Consulate. The period of this regime (2 November 1795 until 10 November 1799), commonly known as the Directory (or Directoire) era, constitutes the second to last stage of the French Revolution.
The Napoleonic Era is a period in the History of France
and Europe. It is generally classified as the fourth stage of the French Revolution. The Napoleonic Era begins roughly with Napoleon
's coup d'état
, overthrowing the Directory and ends at the Hundred Days
and his defeat at Waterloo
(November 9, 1799 – June 28, 1815). The congress of Vienna soon set out to restore Europe to pre-French revolution days.
was the political and social movement that annexed different states of the Italian peninsula
into the single state of Italy in the 19th century. There is a lack of consensus on the exact dates for the beginning and the end of this period, but many scholars agree that the process began with the end of Napoleonic rule and the Congress of Vienna
in 1815, and approximately ended with the Franco-Prussian War
in 1871, though the last città irredente
did not join the Kingdom of Italy
until after World War I.
saw the conquest of nearly all eastern hemisphere territories by colonial powers. The commercial colonization of India
commenced in 1757, after the Battle of Plassey
, when the Nawab of Bengal
surrendered his dominions to the Company, in 1765, when the Company was granted the diwani, or the right to collect revenue, in Bengal
and Bihar
, or in 1772, when the Company established a capital in Calcutta, appointed its first Governor-General
, Warren Hastings
, and became directly involved in governance.
The Maratha states
, following the Anglo-Maratha wars
, eventually lost to the British East India Company
in 1818. The rule lasted until 1858, when, after the Indian rebellion of 1857
and consequent of the Government of India Act 1858
, the British government
assumed the task of directly administering India in the new British Raj
. In 1819 Stamford Raffles
established Singapore
as a key trading post for Britain in their rivalry with the Dutch. However, their rivalry cooled in 1824 when an Anglo-Dutch treaty
demarcated their respective interests in Southeast Asia. From the 1850s onwards, the pace of colonization shifted to a significantly higher gear.
The Dutch East India Company
(1800) and British East India Company
(1858) were dissolved by their respective governments, who took over the direct administration of the colonies. Only Thailand
was spared the experience of foreign rule, although, Thailand itself was also greatly affected by the power politics of the Western powers. Colonial rule had a profound effect on Southeast Asia. While the colonial powers profited much from the region's vast resources and large market, colonial rule did develop the region to a varying extent.
refers to the process by which the countries in the Americas gained their independence from European rule. Decolonization began with a series of revolutions in the late 18th and early to mid-19th centuries. The Spanish American wars of independence were the numerous wars against Spanish rule in Spanish America that took place during the early 19th century, from 1808 until 1829, directly related to the Napoleonic French invasion of Spain. The conflict started with short-lived governing juntas established in Chuquisaca and Quito opposing the composition of the Supreme Central Junta of Seville.
When the Central Junta fell to the French, numerous new Juntas appeared all across the Americas, eventually resulting in a chain of newly independent countries stretching from Argentina and Chile in the south, to Mexico in the north. After the death of the king Ferdinand VII, in 1833, only Cuba and Puerto Rico remained under Spanish rule, until the Spanish–American War in 1898. Unlike the Spanish, the Portuguese did not divide their colonial territory in America. The captaincies they created were subdued to a centralized administration in Salvador which reported directly to the Crown in Lisbon.
 The date of the Industrial Revolution
The date of the Industrial Revolution
is not exact. Eric Hobsbawm
held that it 'broke out' in the 1780s and was not fully felt until the 1830s or 1840s, while T.S. Ashton
held that it occurred roughly between 1760 and 1830 (in effect the reigns of George III
, The Regency
, and George IV
). The great changes of centuries before the 19th were more connected with ideas, religion or military conquest, and technological advance had only made small changes in the material wealth of ordinary people.
The first Industrial Revolution merged into the Second Industrial Revolution
around 1850, when technological and economic progress gained momentum with the development of steam-powered ships and railways, and later in the 19th century with the internal combustion engine
and electric power
generation. The Second Industrial Revolution was a phase of the Industrial Revolution; sometimes labeled as the separate Technical Revolution. From a technological and a social point of view there is no clean break between the two. Major innovations during the period occurred in the chemical, electrical, petroleum, and steel industries. Specific advancements included the introduction of oil fired steam turbine and internal combustion driven steel ships, the development of the airplane, the practical commercialization of the automobile, mass production of consumer goods, the perfection of canning, mechanical refrigeration and other food preservation techniques, and the invention of the telephone.
, where social change
and economic development
are closely related with technological innovation
, particularly with the development of large-scale energy and metallurgy production. It is the extensive organization of an economy for the purpose of manufacturing. Industrialization also introduces a form of philosophical change, where people obtain a different attitude towards their perception of nature
.
based on manual labour
was replaced by one dominated by industry and the manufacture
of machine
ry. It began with the mechanization of the textile
industries and the development of iron
-making techniques, and trade expansion was enabled by the introduction of canal
s, improved roads, and then railways
.
The introduction of steam power
(fuelled primarily by coal
) and powered machinery (mainly in textile manufacturing
) underpinned the dramatic increases in production capacity. The development of all-metal machine tool
s in the first two decades of the 19th century facilitated the manufacture of more production machines for manufacturing in other industries.
The modern petroleum industry
started in 1846 with the discovery of the process of refining kerosene
from coal
by Nova Scotia
n Abraham Pineo Gesner
. Ignacy Łukasiewicz improved Gesner's method to develop a means of refining kerosene from the more readily available "rock oil" ("petr-oleum") seep
s in 1852 and the first rock oil mine was built in Bóbrka
, near Krosno
in Galicia in the following year. In 1854, Benjamin Silliman
, a science professor at Yale University
in New Haven
, was the first to fractionate petroleum by distillation. These discoveries rapidly spread around the world.
was the original inventor of roller spinning, the basis of the water frame for spinning cotton in a cotton mill. Matthew Boulton
and James Watt
's improvements to the steam engine were fundamental to the changes brought by the Industrial Revolution in both the Kingdom of Great Britain and the world.
 In the latter part of the second revolution, Thomas Alva Edison developed many devices that greatly influenced life around the world and is often credited with the creation of the first industrial research laboratory. In 1882, Edison switched on the world's first large-scale electrical supply network that provided 110 volts direct current to fifty-nine customers in lower Manhattan. Also toward the end of the second industrial revolution, Nikola Tesla
In the latter part of the second revolution, Thomas Alva Edison developed many devices that greatly influenced life around the world and is often credited with the creation of the first industrial research laboratory. In 1882, Edison switched on the world's first large-scale electrical supply network that provided 110 volts direct current to fifty-nine customers in lower Manhattan. Also toward the end of the second industrial revolution, Nikola Tesla
made many contributions in the field of electricity
and magnetism
in the late 19th century and early 20th century. Much of Tesla's early work in electrical engineering and many of his discoveries were of importance. Tesla's patents and theoretical work formed the basis of modern alternating current electric power systems, including the polyphase system
s power distribution and the alternating current motor, with which he helped usher in the Second Industrial Revolution. In 1887, Tesla filed a number of patents related to a competing form of power distribution known as alternating current. In the following years a bitter rivalry between Tesla and Edison, known as the "War of Currents
", took place over the preferred method of distribution. After Tesla's demonstration of wireless communication (radio) in 1894 and after being the victor in the "War of Currents", he was widely respected as one of the greatest electrical engineers who worked in America.
, socioeconomic
, and cultural
changes in late 18th century and early 19th century that began in Britain and spread throughout the world. The effects spread throughout Western Europe
and North America during the 19th century, eventually affecting the majority of the world. The impact of this change on society
was enormous and is often compared to the Neolithic revolution
, when mankind developed agriculture
and gave up its nomadic lifestyle
.
It has been argued that GDP
per capita was much more stable and progressed at a much slower rate until the industrial revolution and the emergence of the modern capitalist
economy, and that it has since increased rapidly in capitalist countries.
The European Revolutions of 1848
, known in some countries as the Spring of Nations or the Year of Revolution, were a series of political upheavals throughout the European continent. Described as a revolutionary wave, the period of unrest began in France and then, further propelled by the French Revolution of 1848, soon spread to the rest of Europe. Although most of the revolutions were quickly put down, there was a significant amount of violence in many areas, with tens of thousands of people tortured and killed. While the immediate political effects of the revolutions were reversed, the long-term reverberations of the events were far-reaching.
Industrial age reform movement
s began the gradual change of society rather with episodes of rapid fundamental changes. The reformists' ideas were often grounded in liberalism, although they also possessed aspects of utopian, socialist or religious concepts. The Radical movement campaigned for electoral reform, a reform of the Poor Laws, free trade, educational reform, postal reform, prison reform, and public sanitation.
Following the Enlightenment's ideas, the reformers looked to the Scientific Revolution and industrial progress to solve the social problems which arose with the Industrial Revolution. Newton's natural philosophy combined a mathematics of axiomatic proof with the mechanics of physical observation, yielding a coherent system of verifiable predictions and replacing a previous reliance on revelation and inspired truth. Applied to public life, this approach yielded several successful campaigns for changes in social policy.
(the Great), Russia was proclaimed an Empire in 1721 and became recognized as a world power. Ruling from 1682 to 1725, Peter defeated Sweden in the Great Northern War
, forcing it to cede West Karelia
and Ingria
(two regions lost by Russia in the Time of Troubles
), as well as Estland
and Livland, securing Russia's access to the sea and sea trade. On the Baltic Sea
Peter founded a new capital called Saint Petersburg
, later known as Russia's Window to Europe. Peter the Great's reforms brought considerable Western European cultural influences to Russia. Catherine II (the Great), who ruled in 1762–96, extended Russian political control over the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth and incorporated most of its territories into Russia during the Partitions of Poland
, pushing the Russian frontier westward into Central Europe. In the south, after successful Russo-Turkish Wars against the Ottoman Empire
, Catherine advanced Russia's boundary to the Black Sea, defeating the Crimean khanate
.
) to 1914 (the outbreak of the First World War
); alternatively, Eric Hobsbawm
defined the "Long Nineteenth Century"
as spanning the years 1789 to 1914. During this time, the fall of the Spanish Armada
enabled the rise of the British Empire
.
, Portuguese
, and Ottoman
empires began to crumble and the Holy Roman
and Mughal
empires ceased. Following the Napoleonic Wars
, the British Empire
became the world's leading power, controlling one quarter of the World's population and one third of the land area. It enforced a Pax Britannica
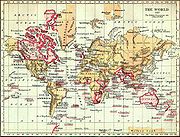
, encouraged trade, and battled rampant piracy.
Electricity, steel, and petroleum enabled Germany to become great international power that raced to create empires of its own
. The Meiji Restoration
was a chain of events that led to enormous changes in Japan's political and social structure that was taking a firm hold at the beginning of the Meiji Era which coincided the opening of Japan by the arrival of the Black Ships
of Commodore
Matthew Perry and made Imperial Japan a great power
. However, Russia and Qing Dynasty
China failed to keep pace with the other world powers which led to massive social unrest in both empires. The Qing Dynasty's military power weakened during the 19th century, and faced with international pressure, massive rebellion
s and defeats in wars, the dynasty declined after the mid-19th century. European powers controlled parts of Oceania, with French New Caledonia
from 1853 and French Polynesia
from 1889; the Germans established colonies in New Guinea
in 1884, and Samoa
in 1900. The United States expanded into the Pacific with Hawaii becoming a U.S. territory
from 1898. Disagreements between the US, Germany and UK over Samoa led to the Tripartite Convention of 1899.
 The Victorian era
The Victorian era
of the United Kingdom was the period of Queen Victoria's reign from June 1837 to January 1901. This was a long period of prosperity for the British people, as profits gained from the overseas British Empire, as well as from industrial improvements at home, allowed a large, educated middle class to develop. Some scholars would extend the beginning of the period—as defined by a variety of sensibilities and political games that have come to be associated with the Victorians—back five years to the passage of the Reform Act 1832.
 In Britain's "imperial century", Victory over Napoleon left Britain without any serious international rival, other than Russia in central Asia. Unchallenged at sea, Britain adopted the role of global policeman, a state of affairs later known as the Pax Britannica
In Britain's "imperial century", Victory over Napoleon left Britain without any serious international rival, other than Russia in central Asia. Unchallenged at sea, Britain adopted the role of global policeman, a state of affairs later known as the Pax Britannica
, and a foreign policy of "splendid isolation
". Alongside the formal control it exerted over its own colonies, Britain's dominant position in world trade meant that it effectively controlled the economies of many nominally independent countries, such as China, Argentina
and Siam
, which has been generally characterized as "informal empire
". Of note during this time was the Anglo-Zulu War
, which was fought in 1879 between the British Empire and the Zulu Empire.
British imperial strength was underpinned by the steamship
and the telegraph
, new technologies invented in the second half of the 19th century, allowing it to control and defend the Empire. By 1902, the British Empire was linked together by a network of telegraph cables, the so-called All Red Line
. Growing till 1922, around 13000000 square miles (33,669,845.4 km²) of territory and roughly 458 million people were added to the British Empire. The British established colonies in Australia in 1788, New Zealand in 1840 and Fiji
in 1872, with much of Oceania
becoming part of the British Empire.
followed the ousting of Napoleon I of France in 1814. The Allies restored the Bourbon Dynasty to the French throne. The ensuing period is called the Restoration, following French usage, and is characterized by a sharp conservative reaction and the re-establishment of the Roman Catholic Church as a power in French politics. The July Monarchy
was a period of liberal constitutional monarchy in France under King Louis-Philippe starting with the July Revolution (or Three Glorious Days) of 1830 and ending with the Revolution of 1848. The Second Empire
was the Imperial Bonapartist regime of Napoleon III from 1852 to 1870, between the Second Republic and the Third Republic, in France.
 The Franco-Prussian War
The Franco-Prussian War
was a conflict between France and Prussia, while Prussia was backed up by the North German Confederation, of which it was a member, and the South German states of Baden, Württemberg and Bavaria. The complete Prussian and German victory brought about the final unification of Germany under King Wilhelm I of Prussia. It also marked the downfall of Napoleon III and the end of the Second French Empire, which was replaced by the Third Republic. As part of the settlement, almost all of the territory of Alsace-Lorraine was taken by Prussia to become a part of Germany, which it would retain until the end of World War I.
The French Third Republic
was the republican government of France between the end of the Second French Empire following the defeat of Louis-Napoléon in the Franco-Prussian war in 1870 and the Vichy Regime after the invasion of France by the German Third Reich in 1940. The Third Republic endured seventy years, making it the most long-lasting regime in France since the collapse of the Ancien Régime in the French Revolution of 1789.
was greatly reduced around the world in the 19th century. Following a successful slave revolt in Haiti
, Britain forced the Barbary pirates to halt their practice of kidnapping and enslaving Europeans, banned slavery throughout its domain
, and charged its navy with ending the global slave trade. Slavery was then abolished in Russia, America
, and Brazil
(see Abolitionism
).
was initiated formally at the Berlin West Africa Conference in 1884–1885. All the major European powers laid claim to the areas of Africa where they could exhibit a sphere of influence over the area. These claims did not have to have any substantial land holdings or treaties to be legitimate. The French gained major ground in West Africa, the British in East Africa, and the Portuguese
and Spanish at various points throughout the continent, while King Leopold
was able to retain his personal fiefdom, Congo
.
. During this time, Japan started its modernization and rose to world power status. This era name
means "Enlightened Rule". It was not until the beginning of the Meiji Era that the Japanese government began taking modernization seriously. Japan expanded its military production base by opening arsenals in various locations. The hyobusho (war office) was replaced with a War Department and a Naval Department. The samurai
class suffered great disappointment the following years.
Laws were instituted that required every able-bodied male Japanese citizen, regardless of class, to serve a mandatory term of three years with the first reserves and two additional years with the second reserves. This action, the deathblow for the samurai warriors and their daimyo
feudal lords, initially met resistance from both the peasant and warrior alike. The peasant class interpreted the term for military service, ketsu-eki (blood tax) literally, and attempted to avoid service by any means necessary. The Japanese government began modelling their ground forces after the French military. The French government contributed greatly to the training of Japanese officers. Many were employed at the military academy in Kyoto, and many more still were feverishly translating French field manuals for use in the Japanese ranks.
After the death of the Meiji Emperor, the Taishō Emperor
took the throne, thus beginning the Taishō period
. A key foreign observer of the remarkable and rapid changes in Japanese society
in this period was Ernest Mason Satow
.
 "Manifest Destiny
"Manifest Destiny
" was the territorial expansion of the United States from 1812 to 1860. Manifest Destiny incorporated the belief that the United States was destined, even divinely ordained, to expand across the North American continent, from the Atlantic seaboard to the Pacific Ocean. This era, from the end of the War of 1812 to the beginning of the American Civil War, has been called the "Age of Manifest Destiny." During this time, the United States expanded to the Pacific Ocean—"from sea to shining sea"—largely defining the borders of the contiguous United States as they are today.
was a civil war
in the United States of America. Eleven Southern slave states
declared their secession
from the U.S. and formed the Confederate States of America (the Confederacy)
. Led by Jefferson Davis
, they fought against the U.S. federal government (the Union
), which was supported by all the free states and the five border slave states in the north.
Northern leaders agreed that victory would require more than the end of fighting. It had to encompass the two strategies
: secession had to be totally repudiated and all forms of slavery had to be eliminated. They disagreed sharply on the military tactics
and political tactics for these goals. They also disagreed on the degree of federal control, that should be imposed on the South and the process by which Southern states should be reintegrated into the Union. The Reconstruction Era in United States history existed in the post-Civil War era in the entire United States between 1865 and 1877.
saw a substantial growth in population in the United States and extravagant displays of wealth and excess of America's upper-class during the post-Civil War and post-Reconstruction era, in the late 19th century. The wealth polarization derived primarily from industrial and population expansion. The businessmen of the Second Industrial Revolution created industrial towns and cities in the Northeast with new factories, and contributed to the creation of an ethnically diverse industrial working class
which produced the wealth owned by rising super-rich industrialists and financiers called the "robber barons"
. An example is the company of John D. Rockefeller
, who was an important figure in shaping the new oil industry. Using highly effective tactics and aggressive practices, later widely criticized, Standard Oil
absorbed or destroyed most of its competition.
The creation of a modern industrial economy took place. With the creation of a transportation and communication infrastructure
, the corporation
became the dominant form of business organization and a managerial revolution
transformed business operation
s. In 1890, Congress passed the Sherman Antitrust Act
— the source of all American anti-monopoly laws. The law forbade every contract, scheme, deal, or conspiracy to restrain trade, though the phrase "restraint of trade" remained subjective. By the beginning of the 20th century, per capita income and industrial production
in the United States exceeded that of any other country except Britain. Long hours and hazardous working conditions led many workers to attempt to form labor unions despite strong opposition from industrialists and the courts. But the courts did protect the marketplace, declaring the Standard Oil group to be an "unreasonable" monopoly
under the Sherman Antitrust Act in 1911. It ordered Standard to break up into 34 independent companies with different boards of directors.
since the end of the scientific revolution, modern physics
arose with the advent of quantum physics; substituting mathematics studies
for experimental studies
and examining equation
s to build a theoretical structure. The old quantum theory
was a collection of results which predate modern quantum mechanics
, but were never complete or self-consistent. The collection of heuristic
prescriptions for quantum mechanics were the first corrections to classical mechanics
. In addition, the various number of aether theories
in classical physics which supposed a "fifth element", such as the Luminiferous aether
, was nullified by the Michelson-Morley experiment
in an attempt to detect the motion of earth through the aether. In biology, Darwinism
gained acceptance and exposed adaptation
in the theory of natural selection
. The fields of geology, astronomy and psychology also made strides and gained new insights. In medicine, there were advances of medical theory and treatments.
 Another philosophical trend was Chinese philosophy began to integrate concepts of Western philosophy, as steps toward modernization. By the time of the Xinhai Revolution
Another philosophical trend was Chinese philosophy began to integrate concepts of Western philosophy, as steps toward modernization. By the time of the Xinhai Revolution
in 1911, there were many calls, such as the May Fourth Movement
, to completely abolish the old imperial institutions and practices of China. There have been attempts to incorporate democracy
, republicanism
, and industrialism into Chinese philosophy, notably by Sun Yat-Sen
(Sūn yì xiān, in one Mandarin form of the name) at the beginning of the 20th century. Mao Zedong
(Máo zé dōng) added Marxism
, Stalinism
, and other communist
thought. When the Communist Party of China
took over
power, previous schools of thought, excepting notably Legalism
, were denounced as backward, and later even purged during the Cultural Revolution
.
Developed from earlier secular traditions, modern Humanism
ethical philosophies
affirm the dignity and worth of all people, based on the ability to determine right and wrong by appealing to universal human qualities, particularly rationality
, without resorting to the supernatural or alleged divine authority from religious texts. For liberal humanists such as Rousseau
or Kant
, the universal law of reason
guided the way towards total emancipation from any kind of tyranny. These ideas were challenged. The young Karl Marx
criticized the project of political emancipation (embodied in the form of human rights
), asserting it to be symptomatic of the very dehumanization it is supposed to oppose. For Friedrich Nietzsche
, humanism was nothing more than a secular version of theism
. In his Genealogy of Morals, he argues that human rights exist as a means for the weak to collectively constrain the strong. On this view, such rights do not facilitate emancipation of life, but rather deny it. In the 20th century, the notion that human beings are rationally autonomous was challenged by the concept that humans were driven by unconscious irrational desires.
is renowned for his redefinition of sexual desire as the primary motivational energy of human life, as well as his therapeutic techniques, including the use of free association
, his theory of transference
in the therapeutic relationship, and the interpretation of dreams
as sources of insight into unconscious desires.
Albert Einstein
is known for his theories of special relativity
and general relativity
. He also made important contributions to statistical mechanics
, especially his mathematical treatment of Brownian motion
, his resolution of the paradox of specific heats
, and his connection of fluctuations and dissipation
. Despite his reservations about its interpretation, Einstein also made contributions to quantum mechanics and, indirectly, quantum field theory
, primarily through his theoretical studies of the photon
.
was promoted and included the various ideologies based on a concept that competition among all individuals, groups, nations, or ideas was the framework of social evolution in human societies. In this view, society's advancement was dependent on the "survival of the fittest
", the term was in fact coined by Herbert Spencer
and referred to in "The Gospel of Wealth
" theory written by Andrew Carnegie
.
 Karl Marx
Karl Marx
summarized his approach to history and politics in the opening line of the first chapter of The Communist Manifesto
(1848). He wrote:
The Manifesto went through a number of editions from 1872 to 1890; notable new prefaces were written by Marx and Engels for the 1872 German edition, the 1882 Russian edition, the 1883 German edition, and the 1888 English edition. In general, Marxism
identified five (and one transitional) successive stages of development in Western Europe.
lose most of its remaining political power over commonwealth countries. The Trans-Siberian Railway
, crossing Asia by train, was complete by 1916. Other events include the Israeli–Palestinian conflict
, two world wars, and the Cold War
.
was the process by which the six separate British self-governing colonies
of New South Wales
, Queensland
, South Australia
, Tasmania
, Victoria
and Western Australia
formed one nation. They kept the systems of government that they had developed as separate colonies but also would have a federal government that was responsible for matters concerning the whole nation. When the Constitution of Australia
came into force, the colonies collectively became states
of the Commonwealth of Australia
.
were marked by civil unrest and foreign invasions. Responding to these civil failures and discontent, the Qing Imperial Court did attempt to reform the government in various ways, such as the decision to draft a constitution in 1906, the establishment of provincial legislatures in 1909, and the preparation for a national parliament in 1910. However, many of these measures were opposed by the conservatives of the Qing Court, and many reformers were either imprisoned or executed outright. The failures of the Imperial Court to enact such reforming measures of political liberalization and modernization caused the reformists to steer toward the road of revolution.
In 1912, the Republic of China was established and was inaugurated in Nanjing
as the first Provisional President
. But power in Beijing
already had passed to Yuan Shikai
, who had effective control of the Beiyang Army
, the most powerful military force in China at the time. To prevent civil war
and possible foreign intervention from undermining the infant republic, leaders agreed to Army's demand that China be united under a Beijing government. On March 10, in Beijing, Shikai was sworn in as the second Provisional President of the Republic of China.
After the early 1900s revolutions, shifting alliances of China's regional warlords fought for control of the Beijing government. Despite the fact that various warlords gained control of the government in Beijing during the warlord era, this did not constitute a new era of control or governance, because other warlords did not acknowledge the transitory governments in this period and were a law unto themselves. These military-dominated governments were collectively known as the Beiyang government
. The warlord era is ends around in 1927.
Begun at the Battle of Port Arthur
, the Russo-Japanese War
establishes the Empire of Japan
as a world power. The Russians were in constant pursuit of a warm water port on the Pacific Ocean, for their navy as well as for maritime trade. The Manchurian Campaign of the Russian Empire
was fought against the Japanese over Manchuria
and Korea
. The major theatres of operations were Southern Manchuria, specifically the area around the Liaodong Peninsula and Mukden, and the seas around Korea, Japan, and the Yellow Sea
. The resulting campaigns, in which the fledgling Japanese military consistently attained victory over the Russian forces arrayed against them, were unexpected by world observers. These victories, as time transpired, would dramatically transform the distribution of power in East Asia, resulting in a reassessment of Japan's recent entry onto the world stage. The embarrassing string of defeats increased Russian popular dissatisfaction with the inefficient and corrupt Tsarist government.
The Russian Revolution of 1905
was a wave of mass political unrest through vast areas of the Russian Empire
. Some of it was directed against the government, while some was undirected. It included terrorism
, worker strikes, peasant unrests, and military mutinies. It led to the establishment of the limited constitutional monarchy, the establishment of State Duma of the Russian Empire
, the multi-party system
and Russian Constitution of 1906
.
In China, the Qing Dynasty was overthrown following the Xinhai Revolution
. The Xinhai Revolution began with the Wuchang Uprising
on October 10, 1911 and ended with the abdication of Emperor Puyi on February 12, 1912. The primary parties to the conflict were the Imperial forces of the Qing Dynasty
(1644–1911), and the revolutionary forces of the Chinese Revolutionary Alliance
(Tongmenghui).
The Edwardian era in the United Kingdom is the period spanning the reign of King Edward VII
up to the end of the First World War, including the years surrounding the sinking of the RMS Titanic. In the early years of the period, the Second Boer War
in South Africa split the country into anti- and pro-war factions. The imperial policies of the Conservatives eventually proved unpopular and in the general election of 1906
the Liberals won a huge landslide. The Liberal government was unable to proceed with all of its radical programme without the support of the House of Lords
, which was largely Conservative. Conflict between the two Houses of Parliament over the People's Budget
led to a reduction in the power of the peers in 1910. The general election in January that year returned a hung parliament
with the balance of power held by Labour
and Irish Nationalist
members.
The causes of World War I
included many factors, including the conflicts and antagonisms of the four decades leading up to the war. The Triple Entente
was the name given to the loose alignment between the United Kingdom
, France
, and Russia
after the signing of the Anglo-Russian Entente
in 1907. The alignment of the three powers, supplemented by various agreements with Japan
, the United States, and Spain
, constituted a powerful counterweight to the Triple Alliance
of Germany
, Austria-Hungary
, and Italy
, the third having concluded an additional secret agreement with France effectively nullifying her Alliance commitments. Militarism, alliances, imperialism, and nationalism played major roles in the conflict. The immediate origins of the war lay in the decisions taken by statesmen and generals during the July crisis of 1914, the spark (or casus belli) for which was the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria.
However, the crisis did not exist in a void; it came after a long series of diplomatic clashes between the Great Powers over European and colonial issues in the decade prior to 1914 which had left tensions high. The diplomatic clashes can be traced to changes in the balance of power in Europe since 1870. An example is the Baghdad Railway
which was planned to connect the Ottoman Empire
cities of Konya
and Baghdad
with a line through modern-day Turkey, Syria and Iraq. The railway became a source of international disputes during the years immediately preceding World War I. Although it has been argued that they were resolved in 1914 before the war began, it has also been argued that the railroad was a cause of the First World War. Fundamentally the war was sparked by tensions over territory in the Balkans
. Austria-Hungary competed with Serbia and Russia for territory and influence in the region and they pulled the rest of the great powers into the conflict through their various alliances and treaties. The Balkan Wars
were two wars in South-eastern Europe in 1912–1913 in the course of which the Balkan League (Bulgaria, Montenegro, Greece, and Serbia) first captured Ottoman-held remaining part of Thessaly, Macedonia, Epirus, Albania and most of Thrace and then fell out over the division of the spoils, with incorporation of Romania this time.
 The First World War began in 1914 and lasted to the final Armistice
The First World War began in 1914 and lasted to the final Armistice
in 1918. The Allied Powers
, led by the British Empire, France
, Russia until March 1918, Japan and the United States after 1917, defeated the Central Powers
, led by the German Empire
, Austro-Hungarian Empire and the Ottoman Empire
. The war caused the disintegration of four empires — the Austro-Hungarian, German, Ottoman, and Russian ones — as well as radical change in the European and Middle Eastern maps. The Allied powers before 1917 are sometimes referred to as the Triple Entente
, and the Central Powers are sometimes referred to as the Triple Alliance
.
Much of the fighting in World War I took place along the Western Front
, within a system of opposing manned trenches and fortifications (separated by a "No man's land
") running from the North Sea
to the border of Switzerland. On the Eastern Front
, the vast eastern plains and limited rail network prevented a trench warfare stalemate from developing, although the scale of the conflict was just as large. Hostilities also occurred on and under the sea and — for the first time — from the air. More than 9 million soldiers died on the various battlefields, and nearly that many more in the participating countries' home fronts on account of food shortages and genocide
committed under the cover of various civil wars and internal conflicts. Notably, more people died of the worldwide influenza outbreak
at the end of the war and shortly after than died in the hostilities. The unsanitary conditions engendered by the war, severe overcrowding in barracks, wartime propaganda interfering with public health warnings, and migration of so many soldiers around the world helped the outbreak become a pandemic
.
Ultimately, World War I created a decisive break with the old world order that had emerged after the Napoleonic Wars
, which was modified by the mid-19th century's nationalistic revolutions. The results of World War I would be important factors in the development of World War II approximately 20 years later. More immediate to the time, the partitioning of the Ottoman Empire
was a political event that redrew the political boundaries of the Middle East. The huge conglomeration of territories and peoples formerly ruled by the Sultan of the Ottoman Empire was divided into several new nations. The partitioning brought the creation of the modern Arab world
and the Republic of Turkey. The League of Nations
granted France mandates over Syria
and Lebanon
and granted the United Kingdom mandates over Mesopotamia and Palestine (which was later divided into two regions: Palestine
and Transjordan
). Parts of the Ottoman Empire on the Arabian Peninsula
became parts of what are today Saudi Arabia
and Yemen
.
 The Russian Revolution is the series of revolutions in Russia in 1917, which destroyed the Tsarist autocracy
The Russian Revolution is the series of revolutions in Russia in 1917, which destroyed the Tsarist autocracy
and led to the creation of the Soviet Union. Following the abdication of Nicholas II of Russia
, the Russian Provisional Government
was established. In October 1917, a red faction revolution
occurred in which the Red Guard
, armed groups of workers and deserting soldiers directed by the Bolshevik Party, seized control of Saint Petersburg
(then known as Petrograd) and began an immediate armed takeover of cities and villages throughout the former Russian Empire
.
Another action in 1917 that is of note was the armistice signed between Russia and the Central Powers at Brest-Litovsk. As a condition for peace, the treaty by the Central Powers
conceded huge portions of the former Russian Empire to Imperial Germany
and the Ottoman Empire, greatly upsetting nationalists and conservative
s. The Bolsheviks made peace with the German Empire
and the Central Powers
, as they had promised the Russian people prior to the Revolution. Vladimir Lenin's decision has been attributed to his sponsorship by the foreign office of Wilhelm II, German Emperor, offered by the latter in hopes that with a revolution, Russia would withdraw from World War I. This suspicion was bolstered by the German Foreign Ministry's sponsorship of Lenin's return to Petrograd
. The Western Allies
, expressed their dismay at the Bolsheviks, upset at:
In addition, there was a concern, shared by many Central Powers
as well, that the socialist revolutionary ideas would spread to the West. Hence, many of these countries expressed their support for the Whites, including the provision of troops and supplies. Winston Churchill
declared that Bolshevism must be "strangled in its cradle".
The Russian Civil War
was a multi-party war that occurred within the former Russian Empire
after the Russian provisional government
collapsed and the Soviets
under the domination of the Bolshevik
party assumed power, first in Petrograd (St. Petersburg)
and then in other places. In the wake of the October Revolution
, the old Russian Imperial Army had been demobilized; the volunteer-based Red Guard was the Bolsheviks' main military force, augmented by an armed military component of the Cheka
, the Bolshevik state security apparatus. There was an instituted mandatory conscription of the rural peasantry into the Red Army. Opposition of rural Russians to Red Army conscription units was overcome by taking hostages and shooting them when necessary in order to force compliance. Former Tsarist officers were utilized as "military specialists" (voenspetsy), sometimes taking their families hostage in order to ensure loyalty. At the start of the war, three-fourths of the Red Army officer corps was composed of former Tsarist officers. By its end, 83% of all Red Army divisional and corps commanders were ex-Tsarist soldiers.
The principal fighting occurred between the Bolshevik
Red Army
and the forces of the White Army
. Many foreign armies warred against the Red Army, notably the Allied Forces
, yet many volunteer foreigners fought in both sides of the Russian Civil War. Other nationalist and regional political groups also participated in the war, including the Ukrainian nationalist Green Army, the Ukrainian anarchist Black Army
and Black Guards
, and warlords such as Ungern von Sternberg. The most intense fighting took place from 1918 to 1920. Major military operations ended on 25 October 1922 when the Red Army occupied Vladivostok
, previously held by the Provisional Priamur Government. The last enclave of the White Forces was the Ayano-Maysky District
on the Pacific coast. The majority of the fighting ended in 1920 with the defeat of General Pyotr Wrangel in the Crimea
, but a notable resistance in certain areas continued until 1923 (e.g., Kronstadt Uprising, Tambov Rebellion
, Basmachi Revolt
, and the final resistance of the White movement
in the Far East
).
In 1917, China declared war on Germany in the hope of recovering its lost province, then under Japanese control. The New Culture Movement
occupied the period from 1917 to 1923. Chinese representatives refused to sign the Treaty of Versailles
, due to intense pressure from the student protesters and public opinion alike.
The May Fourth Movement helped to rekindle the then-fading cause of republican revolution. In 1917 Sun Yat-sen
had become commander-in-chief of a rival military government in Guangzhou
in collaboration with southern warlords. Sun efforts to obtain aid from the Western democracies were ignored, however, and in 1920 he turned to the Soviet Union, which had recently achieved its own revolution. The Soviets sought to befriend the Chinese revolutionists by offering scathing attacks on Western imperialism. But for political expediency, the Soviet leadership initiated a dual policy of support for both Sun and the newly established Chinese Communist Party (CCP).
 The policy of working with the Kuomintang
The policy of working with the Kuomintang
and Chiang Kai-shek
had been recommended by the Dutch
Communist Henk Sneevliet
, chosen in 1923 to be the Comintern
representative in China due to his revolutionary experience in the Dutch Indies, where he had a major role in founding the Partai Komunis Indonesia (PKI) - and who felt that the Chinese party was too small and weak to undertake a major effort on its own (see Henk Sneevliet's work for the Comintern).
In early 1927, the Kuomintang-CCP rivalry led to a split in the revolutionary ranks. The CCP and the left wing of the Kuomintang had decided to move the seat of the Nationalist government from Guangzhou to Wuhan
. But Chiang Kai-shek
, whose Northern Expedition was proving successful, set his forces to destroying the Shanghai CCP apparatus and established an anti-Communist government at Nanjing in April 1927 - bloody events
.
The interwar period
was the period between the end of the First World War and the beginning of the Second World War. This period was marked by turmoil in much of the world, as Europe struggled to recover from the devastation of the First World War.
In North America, especially the first half of this period, people experienced considerable prosperity in the Roaring Twenties
. The social and societal upheaval known as the Roaring Twenties began in North America and spread to Europe in the aftermath of World War I
. The Roaring Twenties, often called "The Jazz Age
", saw a exposition of social, artistic, and cultural dynamism. 'Normalcy
' returned to politics, jazz music blossomed, the flapper
redefined modern womanhood, Art Deco
peaked. The spirit of the Roaring Twenties was marked by a general feeling of discontinuity associated with modernity, a break with traditions. Everything seemed to be feasible through modern technology. New technologies, especially automobiles, movies and radio proliferated 'modernity' to a large part of the population. The Twenties saw the general favor of practicality, in architecture as well as in daily life. The Twenties was further distinguished by several inventions and discoveries, extensive industrial growth and the rise in consumer demand and aspirations, and significant changes in lifestyle.
Europe spent these years rebuilding and coming to terms with the vast human cost of the conflict. The economy of the United States became increasingly intertwined with that of Europe. In Germany, the Weimar Republic
gave way to episodes of political and economic turmoil, which culminated with the German hyperinflation
of 1923 and the failed Beer Hall Putsch
of that same year. When Germany could no longer afford war payments, Wall Street invested heavily in European debts to keep the European economy afloat as a large consumer market for American mass produced goods. By the middle of the decade, economic development
soared in Europe, and the Roaring Twenties broke out in Germany, Britain and France, the second half of the decade becoming known as the "Golden Twenties
". In France and francophone Canada, they were also called the "années folles" ("Crazy Years").
Worldwide prosperity changed dramatically with the onset of the Great Depression
in 1929. The Wall Street Crash of 1929
served to punctuate the end of the previous era, as The Great Depression set in. The Great Depression was a worldwide economic downturn
starting in most places in 1929 and ending at different times in the 1930s or early 1940s for different countries. It was the largest and most important economic depression
in the 20th century, and is used in the 21st century as an example of how far the world's economy can fall.
The depression had devastating effects in virtually every country, rich or poor. International trade plunged by half to two-thirds, as did personal income, tax revenue, prices and profits. Cities all around the world
were hit hard, especially those dependent on heavy industry
. Construction was virtually halted in many countries. Farming and rural areas suffered as crop prices fell by roughly 60 percent. Facing plummeting demand with few alternate sources of jobs, areas dependent on primary sector industries suffered the most.
The Great Depression ended at different times in different countries with the effect lasting into the next era
. America's Great Depression ended in 1941 with America's entry into World War II. The majority of countries set up relief programs, and most underwent some sort of political upheaval, pushing them to the left or right. In some world states, the desperate citizens turned toward nationalist demagogues
— the most infamous being Adolf Hitler
— setting the stage for the next era of war. The convulsion brought on by the worldwide depression resulted in the rise of Nazism
. In Asia, Japan became an ever more assertive power, especially with regards to China.
 The "Nanjing Decade
The "Nanjing Decade
" of 1928-37 was one of consolidation and accomplishment under the leadership of the Nationalists, with a mixed but generally positive record in the economy, social progress, development of democracy
, and cultural creativity. Some of the harsh aspects of foreign concessions and privileges in China were moderated through diplomacy.
The interwar period was also marked by a radical change in the international order, away from the balance of power
that had dominated pre–World War I Europe. One main institution that was meant to bring stability was the League of Nations
, which was created after the First World War with the intention of maintaining world security and peace and encouraging economic growth between member countries. The League was undermined by the bellicosity of Nazi Germany
, Imperial Japan, the Soviet Union, and Mussolini's
Italy, and by the non-participation of the United States, leading many to question its effectiveness and legitimacy.
A series of international crises strained the League to its limits, the earliest being the invasion of Manchuria by Japan and the Abyssinian crisis of 1935/36 in which Italy invaded Abyssinia
, one of the only free African nations at that time. The League tried to enforce economic sanctions upon Italy, but to no avail. The incident highlighted French and British weakness, exemplified by their reluctance to alienate Italy and lose her as their ally. The limited actions taken by the Western powers pushed Mussolini's Italy towards alliance with Hitler's Germany anyway. The Abyssinian war showed Hitler how weak the League was and encouraged the remilitarization of the Rhineland in flagrant disregard of the Treaty of Versailles. This was the first in a series of provocative acts culminating in the invasion of Poland
in September 1939 and the beginning of the Second World War.
Few Chinese had any illusions about Japanese designs on China. Hungry for raw materials and pressed by a growing population, Japan initiated the seizure of Manchuria
in September 1931 and established ex-Qing emperor Puyi
as head of the puppet state
of Manchukuo
in 1932. During the Sino-Japanese War (1937-1945), the loss of Manchuria, and its vast potential for industrial development and war industries, was a blow to the Kuomintang economy. The League of Nations
, established at the end of World War I, was unable to act in the face of the Japanese defiance. After 1940, conflicts between the Kuomintang and Communists became more frequent in the areas not under Japanese control
. The Communists expanded their influence wherever opportunities presented themselves through mass organizations, administrative reforms, and the land- and tax-reform measures favoring the peasants — while the Kuomintang attempted to neutralize the spread of Communist influence.
The Second Sino-Japanese War
had seen tensions rise between Imperial Japan and the United States; events such as the Panay incident
and the Nanking Massacre
turned American public opinion against Japan. With the occupation of French Indochina
in the years of 1940–41, and with the continuing war in China, the United States placed embargoes on Japan of strategic materials such as scrap metal and oil, which were vitally needed for the war effort. The Japanese were faced with the option of either withdrawing from China and losing face or seizing and securing new sources of raw materials in the resource-rich, European-controlled colonies of South East Asia—specifically British Malaya
and the Dutch East Indies
(modern-day Indonesia
). In 1940, Imperial Japan signed the Tripartite Pact
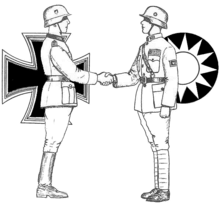
with Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy.
The Second World War was a global
military conflict
that took place in 1939–1945. It was the largest and deadliest war in history, culminating in the Holocaust and ending with the dropping of the atom bomb.
 Even though Japan had been fighting in China since 1937, the conventional view is that the war began on September 1, 1939, when Nazi Germany
Even though Japan had been fighting in China since 1937, the conventional view is that the war began on September 1, 1939, when Nazi Germany
invaded Poland, the Drang nach Osten
. Within two days the United Kingdom and France declared war on Germany, even though the fighting was confined to Poland. Pursuant to a then-secret provision of its non-aggression Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact
, the Soviet Union joined with Germany on September 17, 1939, to conquer Poland and to divide Eastern Europe.
The Allies
were initially made up of Poland, the United Kingdom, France, Australia, Canada, New Zealand, South Africa, as well as British Commonwealth
countries which were controlled directly by the UK, such as the Indian Empire
. All of these countries declared war on Germany in September 1939.
Following the lull in fighting, known as the "Phoney War", Germany invaded western Europe in May 1940. Six weeks later, France, in the mean time attacked by Italy as well, surrendered to Germany, which then tried unsuccessfully to conquer Britain. On September 27, Germany, Italy, and Japan signed a mutual defense agreement, the Tripartite Pact
, and were known as the Axis Powers
.
Nine months later, on June 22, 1941, Germany launched a massive invasion of the Soviet Union, which promptly joined the Allies. Germany was now engaged in fighting a war on two fronts. This proved to be a mistake by Germany - Germany had not successfully carried out the invasion of Britain and the war turned against of the Axis.
 On December 7, 1941, Japan attacked the United States at Pearl Harbor
On December 7, 1941, Japan attacked the United States at Pearl Harbor
, bringing it too into the war on the Allied side. China also joined the Allies, as eventually did most of the rest of the world. China was in turmoil at the time, and attacked Japanese armies through guerilla-type warfare. By the beginning of 1942, the major combatants were aligned as follows: the British Commonwealth, the United States, and the Soviet Union were fighting Germany and Italy; and the British Commonwealth, China, and the United States were fighting Japan. From then through August 1945, battles raged across all of Europe, in the North Atlantic Ocean, across North Africa, throughout Southeast Asia
, throughout China, across the Pacific Ocean and in the air over Japan.
Italy surrendered in September 1943 and split in a northern Germany-occupied puppet state
and in an Allies-friendly state in the South; Germany surrendered in May 1945. Following the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki
, Japan surrendered
, marking the end of the war on September 2, 1945.
It is possible that around 62 million people died in the war
; estimates vary greatly. About 60% of all casualties were civilians, who died as a result of disease, starvation, genocide
(in particular, the Holocaust), and aerial bombing. The former Soviet Union and China suffered the most casualties. Estimates place deaths in the Soviet Union at around 23 million, while China suffered about 10 million. No country lost a greater portion of its population than Poland: approximately 5.6 million, or 16%, of its pre-war population of 34.8 million died.
The Holocaust (which roughly means "burnt whole") was the deliberate and systematic murder of millions of Jews and other "unwanted" during World War II by the Nazi regime in Germany. Several differing views exist regarding whether it was intended to occur from the war's beginning, or if the plans for it came about later. Regardless, persecution of Jews extended well before the war even started, such as in the Kristallnacht
(Night of Broken Glass). The Nazis used propaganda to great effect to stir up anti-Semitic feelings within ordinary Germans.
After World War II, Europe was informally split into Western and Soviet spheres of influence
. Western Europe
later aligned as North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) and Eastern Europe
as the Warsaw Pact
. There was a shift in power from Western Europe and the British Empire
to the two new superpowers, the United States and the Soviet Union. These two rivals would later face off in the Cold War
. In Asia, the defeat of Japan led to its democratization
. China's civil war
continued through and after the war, resulting eventually in the establishment of the People's Republic of China
. The former colonies of the European powers began their road to independence.
 The mid-20th century is distinguished from most of human history in that its most significant changes were directly or indirectly economic and technological in nature. Economic development was the force behind vast changes in everyday life, to a degree which was unprecedented in human history.
The mid-20th century is distinguished from most of human history in that its most significant changes were directly or indirectly economic and technological in nature. Economic development was the force behind vast changes in everyday life, to a degree which was unprecedented in human history.
Over the course of the 20th century, the world's per-capita gross domestic product
grew by a factor of five, much more than all earlier centuries combined (including the 19th with its Industrial Revolution). Many economists make the case that this understates the magnitude of growth, as many of the goods and services consumed at the end of the century, such as improved medicine (causing world life expectancy to increase by more than two decades) and communications technologies, were not available at any price at its beginning. However, the gulf between the world's rich and poor grew wider, and the majority of the global population remained in the poor side of the divide.
Still, advancing technology and medicine has had a great impact even in the Global South. Large-scale industry and more centralized media
made brutal dictatorships possible on an unprecedented scale in the middle of the century, leading to wars that were also unprecedented. However, the increased communications contributed to democratization
. Technological developments included the development of airplanes and space exploration
, nuclear technology
, advancement in genetics
, and the dawning of the Information Age
.
 Pax Americana
Pax Americana
is an appellation applied to the historical concept of relative liberal peace in the Western world, resulting from the preponderance of power enjoyed by the United States of America starting around the turn of the 20th century. Although the term finds its primary utility in the latter half of the 20th century, it has been used in various places and eras. Its modern connotations concern the peace established after the end of World War II in 1945.
The Cold War
began in the mid-1940s and lasted into the early 1990s. Throughout this period, the conflict was expressed through military coalitions, espionage, weapons development, invasions, propaganda, and competitive technological development. The conflict included costly defense spending, a massive conventional
and nuclear
arms race
, and numerous proxy war
s; the two superpower
s never fought one another directly.
.png) The Soviet Union created the Eastern Bloc
The Soviet Union created the Eastern Bloc
of countries that it occupied, annexing some as Soviet Socialist Republics and maintaining others as satellite states that would later form the Warsaw Pact
. The United States and various western European countries began a policy of "containment
" of communism
and forged myriad alliances to this end, including NATO. Several of these western countries also coordinated efforts regarding the rebuilding of western Europe, including western Germany, which the Soviets opposed. In other regions of the world, such as Latin America and Southeast Asia
, the Soviet Union fostered communist revolution
ary movements, which the United States and many of its allies opposed and, in some cases, attempted to "roll back
". Many countries were prompted to align themselves with the nations that would later form either NATO or the Warsaw Pact, though other movements would also emerge.
The Cold War saw periods of both heightened tension and relative calm. International crises arose, such as the Berlin Blockade
(1948–1949), the Korean War
(1950–1953), the Berlin Crisis of 1961
, the Vietnam War
(1959–1975), the Cuban Missile Crisis
(1962), the Soviet war in Afghanistan
(1979–1989) and NATO exercises in November 1983
. There were also periods of reduced tension as both sides sought détente
. Direct military attacks on adversaries were deterred by the potential for mutual assured destruction
using deliverable nuclear weapon
s. In the Cold War era, the Generation of Love
and the rise of computer
s changed society in very different, complex ways, including higher social and local mobility.
The Cold War drew to a close in the late 1980s and the early 1990s. The United States under President Ronald Reagan
increased diplomatic, military, and economic pressure on the Soviet Union, which was already suffering from severe economic stagnation
. In the second half of the 1980s, newly appointed Soviet leader Mikhail Gorbachev
introduced the perestroika
and glasnost
reforms. The Soviet Union collapsed in 1991, leaving the United States as the dominant military power, though Russia retained much of the massive Soviet nuclear arsenal.
In Latin America, the 1970s saw leftists acquire a significant political influence which prompted the right-wing, ecclesiastical authorities and a large portion of the individual country's upper class to support coup d'états to avoid what they perceived as a communist threat. This was further fueled by Cuban and United States intervention which led to a political polarization. Most South American countries were in some periods ruled by military dictatorship
s that were supported by the United States of America. Around the 1970s, the regimes of the Southern Cone
collaborated in Operation Condor
killing many leftist dissidents, including some urban guerrillas. However, by the early 1990s all countries had restored their democracies.
 The Space Age
The Space Age
is a period encompassing the activities related to the Space Race
, space exploration
, space technology, and the cultural developments influenced by these events. The Space Age began with the development of several technologies that culminated with the launch of Sputnik 1
by the Soviet Union. This was the world's first artificial satellite, orbiting the Earth in 98.1 minutes and weighing in at 83 kg. The launch of Sputnik 1 ushered a new era of political, scientific and technological achievements that became known as the Space Age. The Space Age was characterized by rapid development of new technology in a close race mostly between the United States and the Soviet Union. The Space Age reached its peak with the Apollo program which captured the imagination of much of the world's population. The landing of Apollo 11
was an event watched by over 500 million people around the world and is widely recognized as one of the defining moments of the 20th century. Since then and with the end of the space race due to the dissolution of the Soviet Union
, public attention has largely moved to other areas.
are academic disciplines which study the human condition
, using methods that are primarily analytic
, critical, or speculative, as distinguished from the mainly empirical
approaches of the natural
and social sciences
. Although many of the subjects of modern history coincide with that of standard history, the subject is taught independently by various systems of education in the world.
. The material covered includes from the mid-18th century, to analysis of the present day
. Virtually all colleges and sixth forms that do teach modern history do it alongside standard history; very few teach the subject exclusively.
'Modern History' has a somewhat different meaning. The contrast is not with the Middle Ages but with Antiquity. The earliest period that can be studied in the Final Honour School of Modern History begins in 285.
, Atheism
, Ancestor worship, Muslim
s and the Muslim world
, Christian
s and Christendom
, Huguenots, Puritan
s, Church Missionary Society, Robert College
, Pietist, London Missionary Society
, Society of Jesus
(Jesuits), European wars of religion
People and groups: Andreas Karlstadt
, Anne Boleyn
, Menocchio
, Descartes, Goethe, Voltaire
, Nostradamus
, Isaac Newton
, Fugger
, Charles VII, Holy Roman Emperor
, Boers, Congress of Berlin
, Lenin, Yamagata Aritomo
, Tojo Hideki, Balkan League
, Tutsi
, William Paley
, British Whig Party and the Radical Whigs
, US Whig Party
, John Stuart Mill
, John Partridge
, Sir Frederick Pollock, William Ashley, American Historical Association
, John Adams
, Andrew Jackson
and Jacksonian Democracy
, United States Republican party, Joseph Galloway
, Frederick Jackson Turner
, American Anti-Slavery Society
, A. P. Herbert
, Rosa Parks
, Jackie Robinson
, Institute of Contemporary History
Companies and businesses: Laissez-faire
, Marconi Company
, Electric Vehicle Company
, Henry Ford
and the Ford Motor Company
, AT&T
, Bechtel
, Asahi Shimbun
, Daily Mail
Areas and histories: List of World Map changes, Duchy of Warsaw
, Bohemia
, Cape Colony
, Transvaal, History of the Netherlands
, History of Iran
, History of Korea
, History of Manchuria, History of Vladivostok
, History of Pakistan
, History of Saudi Arabia
, History of Kuwait
, History of Cambodia
, Kansas-Nebraska Act
, History of New York City
, Moabit
, Levittown
Culture and society: Iconoclasm
, Le Corbusier
, Apsley House
, Yosano Akiko
, Romanticist, Television
and Cable television
, History of modern literature
, Symbolist
, The Beatles, Rodgers and Hammerstein
, I Love Lucy
, Mass Observation
Legal:letter of credence
, prisoner of war
, laws of war
, exequatur
, extradition
, right of asylum
, jus soli
, jus sanguinis
, exterritoriality
Other: Modernity
, Postmodernity
, Romanticism
, Free silver
, political consciousness
, Sophisms, Fire of London, Tower of London
, utilitarian, Uitlanders, Pan-Slavism
, Sinn Féin
, UNESCO
, Women's suffrage
, The Nobel
and the Peace Prize
, Origin of Species, human evolution
, Social evolution
, Bakelite, Transistor
s, Infidelity
, Penicillin
, Ethanol
, Gasoline
, Fuel Cell
, Automobile
, personal computers, mobile phone
, Falklands War
Modernism Framework
Western Philosophy
20th century sources
19th century sources
Timeline
A timeline is a way of displaying a list of events in chronological order, sometimes described as a project artifact . It is typically a graphic design showing a long bar labeled with dates alongside itself and events labeled on points where they would have happened.-Uses of timelines:Timelines...
after the Middle Ages
Middle Ages
The Middle Ages is a periodization of European history from the 5th century to the 15th century. The Middle Ages follows the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 and precedes the Early Modern Era. It is the middle period of a three-period division of Western history: Classic, Medieval and Modern...
. Modern history can be further broken down into the early modern period
Early modern period
In history, the early modern period of modern history follows the late Middle Ages. Although the chronological limits of the period are open to debate, the timeframe spans the period after the late portion of the Middle Ages through the beginning of the Age of Revolutions...
and the late modern period after the French Revolution
French Revolution
The French Revolution , sometimes distinguished as the 'Great French Revolution' , was a period of radical social and political upheaval in France and Europe. The absolute monarchy that had ruled France for centuries collapsed in three years...
and the Industrial Revolution
Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was a period from the 18th to the 19th century where major changes in agriculture, manufacturing, mining, transportation, and technology had a profound effect on the social, economic and cultural conditions of the times...
. Contemporary history
Contemporary history
Contemporary history describes the period timeframe that is without any intervening time closely connected to the present and is a certain perspective of modern history. The term "contemporary history" has been in use at least by the early 19th century. In the widest context of this use,...
describes the span of historic events that are immediately relevant to the present time.
The modern era began in approximately the 16th century. Many major events caused Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
to change around the turn of the 16th century, starting with the Fall of Constantinople
Fall of Constantinople
The Fall of Constantinople was the capture of the capital of the Byzantine Empire, which occurred after a siege by the Ottoman Empire, under the command of Ottoman Sultan Mehmed II, against the defending army commanded by Byzantine Emperor Constantine XI...
in 1453, the fall of Muslim Spain and the discovery of the Americas
Americas
The Americas, or America , are lands in the Western hemisphere, also known as the New World. In English, the plural form the Americas is often used to refer to the landmasses of North America and South America with their associated islands and regions, while the singular form America is primarily...
in 1492, and Martin Luther
Martin Luther
Martin Luther was a German priest, professor of theology and iconic figure of the Protestant Reformation. He strongly disputed the claim that freedom from God's punishment for sin could be purchased with money. He confronted indulgence salesman Johann Tetzel with his Ninety-Five Theses in 1517...
's Protestant Reformation
Protestant Reformation
The Protestant Reformation was a 16th-century split within Western Christianity initiated by Martin Luther, John Calvin and other early Protestants. The efforts of the self-described "reformers", who objected to the doctrines, rituals and ecclesiastical structure of the Roman Catholic Church, led...
in 1517. In England
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
the modern period is often dated to the start of the Tudor period
Tudor period
The Tudor period usually refers to the period between 1485 and 1603, specifically in relation to the history of England. This coincides with the rule of the Tudor dynasty in England whose first monarch was Henry VII...
with the victory of Henry VII
Henry VII of England
Henry VII was King of England and Lord of Ireland from his seizing the crown on 22 August 1485 until his death on 21 April 1509, as the first monarch of the House of Tudor....
over Richard III
Richard III of England
Richard III was King of England for two years, from 1483 until his death in 1485 during the Battle of Bosworth Field. He was the last king of the House of York and the last of the Plantagenet dynasty...
at the Battle of Bosworth in 1485. Early modern Europe
Early modern Europe
Early modern Europe is the term used by historians to refer to a period in the history of Europe which spanned the centuries between the end of the Middle Ages and the beginning of the Industrial Revolution, roughly the late 15th century to the late 18th century...
an history is usually seen to span from the turn of the 15th century, through the Age of Reason
Age of reason
Age of reason may refer to:* 17th-century philosophy, as a successor of the Renaissance and a predecessor to the Age of Enlightenment* Age of Enlightenment in its long form of 1600-1800* The Age of Reason, a book by Thomas Paine...
and Age of Enlightenment
Age of Enlightenment
The Age of Enlightenment was an elite cultural movement of intellectuals in 18th century Europe that sought to mobilize the power of reason in order to reform society and advance knowledge. It promoted intellectual interchange and opposed intolerance and abuses in church and state...
in the 17th and 18th centuries, until the beginning of the Industrial Revolution
Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was a period from the 18th to the 19th century where major changes in agriculture, manufacturing, mining, transportation, and technology had a profound effect on the social, economic and cultural conditions of the times...
in the late 18th century.
The study of modern history
Some events, though born out of context not entirely new, show a new way of perceiving the world. The concept of modernity interprets the general meaning of these events and seeks explanations for major developments. Historians analyze the events taking place in Modern Times, since the Middle AgesMiddle Ages
The Middle Ages is a periodization of European history from the 5th century to the 15th century. The Middle Ages follows the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 and precedes the Early Modern Era. It is the middle period of a three-period division of Western history: Classic, Medieval and Modern...
between the present
Present
Present is a time that is neither past nor future.Present may also refer to:- Time and timing :* Present tense, the grammatical tense of a verb* Before Present, radiocarbon dates relative to AD 1950* Presenting, a medical term* Presenteeism...
and ancient times.
Source text
The fundamental difficulty of studying modern history is the fact that a plethora of it has been documented up to the present day. It is imperative to consider the reliability of the information obtained from these records.Pre-Modern
In the Pre-Modern era, many people's sense of self and purpose was often expressed via a faithFaith
Faith is confidence or trust in a person or thing, or a belief that is not based on proof. In religion, faith is a belief in a transcendent reality, a religious teacher, a set of teachings or a Supreme Being. Generally speaking, it is offered as a means by which the truth of the proposition,...
in some form of deity
Deity
A deity is a recognized preternatural or supernatural immortal being, who may be thought of as holy, divine, or sacred, held in high regard, and respected by believers....
, be that in a single god
God
God is the English name given to a singular being in theistic and deistic religions who is either the sole deity in monotheism, or a single deity in polytheism....
or in many gods. Pre-modern cultures have not been thought of creating a sense of distinct individuality, though. Religious officials, who often held positions of power, were the spiritual intermediaries to the common person. It was only through these intermediaries that the general masses had access to the divine
Divinity
Divinity and divine are broadly applied but loosely defined terms, used variously within different faiths and belief systems — and even by different individuals within a given faith — to refer to some transcendent or transcendental power or deity, or its attributes or manifestations in...
. Tradition
Tradition
A tradition is a ritual, belief or object passed down within a society, still maintained in the present, with origins in the past. Common examples include holidays or impractical but socially meaningful clothes , but the idea has also been applied to social norms such as greetings...
was sacred
Sacred
Holiness, or sanctity, is in general the state of being holy or sacred...
to ancient cultures and was unchanging and the social order
Social order
Social order is a concept used in sociology, history and other social sciences. It refers to a set of linked social structures, social institutions and social practices which conserve, maintain and enforce "normal" ways of relating and behaving....
of ceremony
Ceremony
A ceremony is an event of ritual significance, performed on a special occasion. The word may be of Etruscan origin.-Ceremonial occasions:A ceremony may mark a rite of passage in a human life, marking the significance of, for example:* birth...
and morals in a culture could be strictly enforced.
Modern
In contrast to the pre-modern era, Western civilization made a gradual transition from premodernity to modernityModernity
Modernity typically refers to a post-traditional, post-medieval historical period, one marked by the move from feudalism toward capitalism, industrialization, secularization, rationalization, the nation-state and its constituent institutions and forms of surveillance...
when scientific method
Scientific method
Scientific method refers to a body of techniques for investigating phenomena, acquiring new knowledge, or correcting and integrating previous knowledge. To be termed scientific, a method of inquiry must be based on gathering empirical and measurable evidence subject to specific principles of...
s were developed which led many to believe that the use of science would lead to all knowledge, thus throwing back the shroud of myth
Mythology
The term mythology can refer either to the study of myths, or to a body or collection of myths. As examples, comparative mythology is the study of connections between myths from different cultures, whereas Greek mythology is the body of myths from ancient Greece...
under which pre-modern peoples lived. New information about the world was discovered via empirical observation, versus the historic use of reason
Reason
Reason is a term that refers to the capacity human beings have to make sense of things, to establish and verify facts, and to change or justify practices, institutions, and beliefs. It is closely associated with such characteristically human activities as philosophy, science, language, ...
and innate knowledge.
The term "modern" was coined shortly before 1585 to describe the beginning of a new era. The European Renaissance
Renaissance
The Renaissance was a cultural movement that spanned roughly the 14th to the 17th century, beginning in Italy in the Late Middle Ages and later spreading to the rest of Europe. The term is also used more loosely to refer to the historical era, but since the changes of the Renaissance were not...
(about 1420–1630) is an important transition period beginning between the Late Middle Ages
Late Middle Ages
The Late Middle Ages was the period of European history generally comprising the 14th to the 16th century . The Late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern era ....
and Early Modern Times, which started in Italy.
The term "Early Modern" was introduced in the English language in the 1930s. to distinguish the time between what we call Middle Ages and time of the late Enlightenment (1800) (when the meaning of the term Modern Ages was developing its contemporary form). It is important to note that these terms stem from European History. In usage in other parts of the world, such as in Asia, and in Muslim countries, the terms are applied in a very different way, but often in the context with their contact with European culture in the Age of Discoveries.
Postmodern and contemporary
"PostmodernismPostmodernism
Postmodernism is a philosophical movement evolved in reaction to modernism, the tendency in contemporary culture to accept only objective truth and to be inherently suspicious towards a global cultural narrative or meta-narrative. Postmodernist thought is an intentional departure from the...
", coined 1949, on the other hand, would describe rather a movement in art than a period of history, and is usually applied to arts, but not to any events of the very recent history. This changed when postmodernity
Postmodernity
Postmodernity is generally used to describe the economic or cultural state or condition of society which is said to exist after modernity...
was coined to describe the major changes in the 1950s and 1960s in economy, society, culture, and philosophy. Sometimes distinct from the modern periods themselves, the terms "modernity
Modernity
Modernity typically refers to a post-traditional, post-medieval historical period, one marked by the move from feudalism toward capitalism, industrialization, secularization, rationalization, the nation-state and its constituent institutions and forms of surveillance...
" and "modernism
Modernism
Modernism, in its broadest definition, is modern thought, character, or practice. More specifically, the term describes the modernist movement, its set of cultural tendencies and array of associated cultural movements, originally arising from wide-scale and far-reaching changes to Western society...
" refer to a new way of thinking, distinct from medieval thinking. "Contemporary
Contemporary history
Contemporary history describes the period timeframe that is without any intervening time closely connected to the present and is a certain perspective of modern history. The term "contemporary history" has been in use at least by the early 19th century. In the widest context of this use,...
" is applied to more recent events because it means "belonging to the same period" and "current".
Marion
Significant developments
The modern period has been a period of significant development in the fields of scienceScience
Science is a systematic enterprise that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe...
, politics
Politics
Politics is a process by which groups of people make collective decisions. The term is generally applied to the art or science of running governmental or state affairs, including behavior within civil governments, but also applies to institutions, fields, and special interest groups such as the...
, warfare, and technology
Technology
Technology is the making, usage, and knowledge of tools, machines, techniques, crafts, systems or methods of organization in order to solve a problem or perform a specific function. It can also refer to the collection of such tools, machinery, and procedures. The word technology comes ;...
. It has also been an age of discovery
Age of Discovery
The Age of Discovery, also known as the Age of Exploration and the Great Navigations , was a period in history starting in the early 15th century and continuing into the early 17th century during which Europeans engaged in intensive exploration of the world, establishing direct contacts with...
and globalization
Globalization
Globalization refers to the increasingly global relationships of culture, people and economic activity. Most often, it refers to economics: the global distribution of the production of goods and services, through reduction of barriers to international trade such as tariffs, export fees, and import...
. During this time that the European powers and later their colonies, began a political, economic, and cultural colonization of the rest of the world.
By the late 19th and 20th centuries, modernist art, politics, science and culture has come to dominate not only Western Europe
Western Europe
Western Europe is a loose term for the collection of countries in the western most region of the European continents, though this definition is context-dependent and carries cultural and political connotations. One definition describes Western Europe as a geographic entity—the region lying in the...
and North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
, but almost every civilized area on the globe, including movements thought of as opposed to the west and globalization. The modern era is closely associated with the development of individualism
Individualism
Individualism is the moral stance, political philosophy, ideology, or social outlook that stresses "the moral worth of the individual". Individualists promote the exercise of one's goals and desires and so value independence and self-reliance while opposing most external interference upon one's own...
, capitalism
Capitalism
Capitalism is an economic system that became dominant in the Western world following the demise of feudalism. There is no consensus on the precise definition nor on how the term should be used as a historical category...
, urbanization
Urbanization
Urbanization, urbanisation or urban drift is the physical growth of urban areas as a result of global change. The United Nations projected that half of the world's population would live in urban areas at the end of 2008....
and a belief in the possibilities of technological and political progress
Progress (history)
In historiography and the philosophy of history, progress is the idea that the world can become increasingly better in terms of science, technology, modernization, liberty, democracy, quality of life, etc...
.
The brutal wars and other problems of this era, many of which come from the effects of rapid change, and the connected loss of strength of traditional religious and ethical norms, have led to many reactions against modern development. Optimism and belief in constant progress has been most recently criticized by postmodernism
Postmodernism
Postmodernism is a philosophical movement evolved in reaction to modernism, the tendency in contemporary culture to accept only objective truth and to be inherently suspicious towards a global cultural narrative or meta-narrative. Postmodernist thought is an intentional departure from the...
while the dominance of Western Europe and Anglo-America
Anglo-America
Anglo-America is a region in the Americas in which English is a main language, or one which has significant British historical, ethnic, linguistic, and cultural links...
over other continents has been criticized by postcolonial theory
Postcolonialism
Post-colonialism is a specifically post-modern intellectual discourse that consists of reactions to, and analysis of, the cultural legacy of colonialism...
.
Modern as post-medieval
One common use of the term is to describe the condition of Western history since the mid-15th century, or roughly the European development of movable typeMovable type
Movable type is the system of printing and typography that uses movable components to reproduce the elements of a document ....
and the printing press
Printing press
A printing press is a device for applying pressure to an inked surface resting upon a print medium , thereby transferring the ink...
. In this context the "modern" society is said to develop over many periods, and to be influenced by important events which represent breaks in the continuity.
Early modern period
The modern era includes the early period, sometimes called the early modern periodEarly modern period
In history, the early modern period of modern history follows the late Middle Ages. Although the chronological limits of the period are open to debate, the timeframe spans the period after the late portion of the Middle Ages through the beginning of the Age of Revolutions...
, which lasted from c. AD 1500 to around c. AD 1800 (most often 1815). Particular facets of early modernity include:
- The RenaissanceRenaissanceThe Renaissance was a cultural movement that spanned roughly the 14th to the 17th century, beginning in Italy in the Late Middle Ages and later spreading to the rest of Europe. The term is also used more loosely to refer to the historical era, but since the changes of the Renaissance were not...
- The ReformationProtestant ReformationThe Protestant Reformation was a 16th-century split within Western Christianity initiated by Martin Luther, John Calvin and other early Protestants. The efforts of the self-described "reformers", who objected to the doctrines, rituals and ecclesiastical structure of the Roman Catholic Church, led...
and Counter Reformation. - The Age of DiscoveryAge of DiscoveryThe Age of Discovery, also known as the Age of Exploration and the Great Navigations , was a period in history starting in the early 15th century and continuing into the early 17th century during which Europeans engaged in intensive exploration of the world, establishing direct contacts with...
- Rise of capitalismCapitalismCapitalism is an economic system that became dominant in the Western world following the demise of feudalism. There is no consensus on the precise definition nor on how the term should be used as a historical category...
Important events in the development of early modernity period include:
- The arrival of the printing pressPrinting pressA printing press is a device for applying pressure to an inked surface resting upon a print medium , thereby transferring the ink...
- The English Civil WarEnglish Civil WarThe English Civil War was a series of armed conflicts and political machinations between Parliamentarians and Royalists...
The concept of the modern world as distinct from an ancient or medieval world rests on a sense that the modern world is not just another era Era An era is a commonly used word for long period of time. When used in science, for example geology, eras denote clearly defined periods of time of arbitrary but well defined length, such as for example the Mesozoic era from 252 Ma–66 Ma, delimited by a start event and an end event. When used in... in history, but rather the result of a new type of change. This is usually conceived of as progress driven by deliberate human efforts to better their situation. Advances in all areas of human activity—politics Politics Politics is a process by which groups of people make collective decisions. The term is generally applied to the art or science of running governmental or state affairs, including behavior within civil governments, but also applies to institutions, fields, and special interest groups such as the... , industry Industry Industry refers to the production of an economic good or service within an economy.-Industrial sectors:There are four key industrial economic sectors: the primary sector, largely raw material extraction industries such as mining and farming; the secondary sector, involving refining, construction,... , society Society A society, or a human society, is a group of people related to each other through persistent relations, or a large social grouping sharing the same geographical or virtual territory, subject to the same political authority and dominant cultural expectations... , economics Economics Economics is the social science that analyzes the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. The term economics comes from the Ancient Greek from + , hence "rules of the house"... , commerce Commerce While business refers to the value-creating activities of an organization for profit, commerce means the whole system of an economy that constitutes an environment for business. The system includes legal, economic, political, social, cultural, and technological systems that are in operation in any... , transport Transport Transport or transportation is the movement of people, cattle, animals and goods from one location to another. Modes of transport include air, rail, road, water, cable, pipeline, and space. The field can be divided into infrastructure, vehicles, and operations... , communication Communication Communication is the activity of conveying meaningful information. Communication requires a sender, a message, and an intended recipient, although the receiver need not be present or aware of the sender's intent to communicate at the time of communication; thus communication can occur across vast... , mechanization Mechanization Mechanization or mechanisation is providing human operators with machinery that assists them with the muscular requirements of work or displaces muscular work. In some fields, mechanization includes the use of hand tools... , automation Automation Automation is the use of control systems and information technologies to reduce the need for human work in the production of goods and services. In the scope of industrialization, automation is a step beyond mechanization... , science Science Science is a systematic enterprise that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe... , medicine Medicine Medicine is the science and art of healing. It encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention and treatment of illness.... , technology Technology Technology is the making, usage, and knowledge of tools, machines, techniques, crafts, systems or methods of organization in order to solve a problem or perform a specific function. It can also refer to the collection of such tools, machinery, and procedures. The word technology comes ;... , and culture Culture Culture is a term that has many different inter-related meanings. For example, in 1952, Alfred Kroeber and Clyde Kluckhohn compiled a list of 164 definitions of "culture" in Culture: A Critical Review of Concepts and Definitions... — appear to have transformed an Old World into the Modern or New World. In each case, the identification of the old Revolutionary change can be used to demarcate the old and old-fashioned from the modern. Portions of the Modern world altered its relationship with the Biblical Bible The Bible refers to any one of the collections of the primary religious texts of Judaism and Christianity. There is no common version of the Bible, as the individual books , their contents and their order vary among denominations... value system Value system A value system is a set of consistent ethic values and measures used for the purpose of ethical or ideological integrity. A well defined value system is a moral code.-Personal and communal:... , revalued the monarchical Monarchy A monarchy is a form of government in which the office of head of state is usually held until death or abdication and is often hereditary and includes a royal house. In some cases, the monarch is elected... government system, and abolished the feudal Feudalism Feudalism was a set of legal and military customs in medieval Europe that flourished between the 9th and 15th centuries, which, broadly defined, was a system for ordering society around relationships derived from the holding of land in exchange for service or labour.Although derived from the... economic system, with new democratic and liberal Liberalism Liberalism is the belief in the importance of liberty and equal rights. Liberals espouse a wide array of views depending on their understanding of these principles, but generally, liberals support ideas such as constitutionalism, liberal democracy, free and fair elections, human rights,... ideas in the areas of politics Politics Politics is a process by which groups of people make collective decisions. The term is generally applied to the art or science of running governmental or state affairs, including behavior within civil governments, but also applies to institutions, fields, and special interest groups such as the... , science Science Science is a systematic enterprise that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe... , psychology Psychology Psychology is the study of the mind and behavior. Its immediate goal is to understand individuals and groups by both establishing general principles and researching specific cases. For many, the ultimate goal of psychology is to benefit society... , sociology Sociology Sociology is the study of society. It is a social science—a term with which it is sometimes synonymous—which uses various methods of empirical investigation and critical analysis to develop a body of knowledge about human social activity... , and economics Economics Economics is the social science that analyzes the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. The term economics comes from the Ancient Greek from + , hence "rules of the house"... . |
This combination of epoch events totally changed thinking and thought in the early modern period, and so their dates serve as well as any to separate the old from the new modes. Particular ways to categorize early modernity include:
- The Age of ReasonAge of reasonAge of reason may refer to:* 17th-century philosophy, as a successor of the Renaissance and a predecessor to the Age of Enlightenment* Age of Enlightenment in its long form of 1600-1800* The Age of Reason, a book by Thomas Paine...
- The Enlightenment
- the RomanticRomanticismRomanticism was an artistic, literary and intellectual movement that originated in the second half of the 18th century in Europe, and gained strength in reaction to the Industrial Revolution...
era - the VictorianVictorianismVictorianism is the name given to the attitudes, art, and culture of the later two-thirds of the 19th century. This usage is strong within social history and the study of literature, less so in philosophy. Many disciplines do not use the term, but instead prefer Victorian Era, or simply "Late 19th...
era
As an Age of Revolution
Age of Revolution
The Age of Revolution is a term used to denote the period from approximately 1775 to 1848 in which a number of significant revolutionary movements occurred on both sides of the Atlantic Ocean in Europe and the Americas. The period is noted for the change in government from absolutist monarchies to...
s dawned, beginning with those revolts in America
American Revolution
The American Revolution was the political upheaval during the last half of the 18th century in which thirteen colonies in North America joined together to break free from the British Empire, combining to become the United States of America...
and France
French Revolution
The French Revolution , sometimes distinguished as the 'Great French Revolution' , was a period of radical social and political upheaval in France and Europe. The absolute monarchy that had ruled France for centuries collapsed in three years...
, political changes were then pushed forward in other countries partly as a result of upheavals of the Napoleonic Wars
Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars were a series of wars declared against Napoleon's French Empire by opposing coalitions that ran from 1803 to 1815. As a continuation of the wars sparked by the French Revolution of 1789, they revolutionised European armies and played out on an unprecedented scale, mainly due to...
and their impact on thought and thinking, from concepts from nationalism to organizing armies.
The early period ended in a time of political and economic change as a result of mechanization
Mechanization
Mechanization or mechanisation is providing human operators with machinery that assists them with the muscular requirements of work or displaces muscular work. In some fields, mechanization includes the use of hand tools...
in society, the American Revolution
American Revolution
The American Revolution was the political upheaval during the last half of the 18th century in which thirteen colonies in North America joined together to break free from the British Empire, combining to become the United States of America...
, the first French Revolution
French Revolution
The French Revolution , sometimes distinguished as the 'Great French Revolution' , was a period of radical social and political upheaval in France and Europe. The absolute monarchy that had ruled France for centuries collapsed in three years...
; other factors included the redrawing of the map of Europe by the Final Act of the Congress of Vienna
Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna was a conference of ambassadors of European states chaired by Klemens Wenzel von Metternich, and held in Vienna from September, 1814 to June, 1815. The objective of the Congress was to settle the many issues arising from the French Revolutionary Wars, the Napoleonic Wars,...
and the peace established by Second Treaty of Paris
Treaty of Paris (1815)
Treaty of Paris of 1815, was signed on 20 November 1815 following the defeat and second abdication of Napoleon Bonaparte. In February, Napoleon had escaped from his exile on Elba; he entered Paris on 20 March, beginning the Hundred Days of his restored rule. Four days after France's defeat in the...
which ended the Napoleonic Wars.
Late modern period
As a result of the Industrial RevolutionIndustrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was a period from the 18th to the 19th century where major changes in agriculture, manufacturing, mining, transportation, and technology had a profound effect on the social, economic and cultural conditions of the times...
and the earlier political revolutions, the Modernism
Modernism
Modernism, in its broadest definition, is modern thought, character, or practice. More specifically, the term describes the modernist movement, its set of cultural tendencies and array of associated cultural movements, originally arising from wide-scale and far-reaching changes to Western society...
worldview's emerged. The industrialization of many nations was initiated with the industrialization of Britain. Particular facets of the late modernity period include:
- Increasing role of scienceScienceScience is a systematic enterprise that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe...
and technologyTechnologyTechnology is the making, usage, and knowledge of tools, machines, techniques, crafts, systems or methods of organization in order to solve a problem or perform a specific function. It can also refer to the collection of such tools, machinery, and procedures. The word technology comes ;... - Mass literacyLiteracyLiteracy has traditionally been described as the ability to read for knowledge, write coherently and think critically about printed material.Literacy represents the lifelong, intellectual process of gaining meaning from print...
and proliferation of mass mediaMass mediaMass media refers collectively to all media technologies which are intended to reach a large audience via mass communication. Broadcast media transmit their information electronically and comprise of television, film and radio, movies, CDs, DVDs and some other gadgets like cameras or video consoles... - Spread of social movements
- Institution of representative democracyRepresentative democracyRepresentative democracy is a form of government founded on the principle of elected individuals representing the people, as opposed to autocracy and direct democracy...
- IndividualismIndividualismIndividualism is the moral stance, political philosophy, ideology, or social outlook that stresses "the moral worth of the individual". Individualists promote the exercise of one's goals and desires and so value independence and self-reliance while opposing most external interference upon one's own...
- Industrialization
- UrbanizationUrbanizationUrbanization, urbanisation or urban drift is the physical growth of urban areas as a result of global change. The United Nations projected that half of the world's population would live in urban areas at the end of 2008....
Other important events in the development of the Late modern period include:
- The Revolutions of 1848Revolutions of 1848The European Revolutions of 1848, known in some countries as the Spring of Nations, Springtime of the Peoples or the Year of Revolution, were a series of political upheavals throughout Europe in 1848. It was the first Europe-wide collapse of traditional authority, but within a year reactionary...
- The Russian Revolution
- The First World War and the Second World War
Our most recent eraModern Timesbegins with the end of these revolutions in the 19th century, and includes the World Wars era (encompassing World War I
World War I
World War I , which was predominantly called the World War or the Great War from its occurrence until 1939, and the First World War or World War I thereafter, was a major war centred in Europe that began on 28 July 1914 and lasted until 11 November 1918...
and World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
) and the emergence of socialist countries
Socialism
Socialism is an economic system characterized by social ownership of the means of production and cooperative management of the economy; or a political philosophy advocating such a system. "Social ownership" may refer to any one of, or a combination of, the following: cooperative enterprises,...
that lead to the Cold War
Cold War
The Cold War was the continuing state from roughly 1946 to 1991 of political conflict, military tension, proxy wars, and economic competition between the Communist World—primarily the Soviet Union and its satellite states and allies—and the powers of the Western world, primarily the United States...
. The contemporary era follows shortly afterward with the explosion of research and increase of knowledge known as the Information Age
Information Age
The Information Age, also commonly known as the Computer Age or Digital Age, is an idea that the current age will be characterized by the ability of individuals to transfer information freely, and to have instant access to knowledge that would have been difficult or impossible to find previously...
in the latter 20th and the early 21st century. Today's Postmodern
Postmodernism
Postmodernism is a philosophical movement evolved in reaction to modernism, the tendency in contemporary culture to accept only objective truth and to be inherently suspicious towards a global cultural narrative or meta-narrative. Postmodernist thought is an intentional departure from the...
era is seen in widespread Digitality
Digitality
Digitality is used to mean the condition of living in a digital culture, derived from Nicholas Negroponte's book Being Digital in analogy with modernity and post-modernity....
.
Early modern period

The early modern period is a term used by historians to refer to the period from approximately 1500 to 1800. follows the Late Middle Ages period, and is marked by the first European colonies, the rise of strong centralized governments, and the beginnings of recognizable nation states that are the direct antecedents of today's states.
In Africa and the Ottoman Empire, the Muslim expansion took place in North and East Africa. In West Africa, various native nations existed. The Indian Empires and civilizations of Southeast Asia were a vital link in the spice trade. On the Indian subcontinent, the Great Mughal Empire existed. The archipelagic empires, the Sultanate of Malacca and later the Sultanate of Johor, controlled the southern areas.
Concerning the Asia, various Chinese dynasties and Japanese shogunates controlled the Asian sphere. In Japan, the Edo period from 1600 to 1868 is also sometimes referred to as the early modern period. And in Korea, from the rising of Joseon Dynasty to the enthronement of King Gojong is referred to as the early modern period. In the Americas, Native Americans had built a large and varied civilization, including the Aztec Empire and alliance, the Inca civilization, the Mayan Empire and cities, and the Chibcha Confederation. In the west, the European kingdoms and movements were in a movement of reformation and expansion. Russia reached the Pacific coast in 1647 and consolidated its control over the Russian Far East
Russian Far East
Russian Far East is a term that refers to the Russian part of the Far East, i.e., extreme east parts of Russia, between Lake Baikal in Eastern Siberia and the Pacific Ocean...
in the 19th century.
Later religious trends of the period saw the end of the expansion of Muslims and the Muslim world. Christians and Christendom saw the end of the Crusades and end of religious unity under the Roman Catholic Church. It was during this time that the Inquisitions and Protestant reformations took place.

Toward the end of the early period, Europe was dominated by the evolving system of mercantile capitalism in its trade and the New Economy. European states and politics had the characteristic of Absolutism. The French power and English revolutions dominated the political scene. There eventually evolved an international balance of power that held sway a great conflagration till years later.
The end date of the early modern period is usually associated with the Industrial Revolution, which began in Britain in about 1750. Another significant date is 1789, the beginning of the French Revolution, which drastically transformed the state of European politics and ushered in the Prince Edward Era and modern Europe.
Eastern foundations
In China, urbanization increased as the population grew and as the division of labor grew more complex. Large urban centers, such as NanjingNanjing
' is the capital of Jiangsu province in China and has a prominent place in Chinese history and culture, having been the capital of China on several occasions...
and Beijing
Beijing
Beijing , also known as Peking , is the capital of the People's Republic of China and one of the most populous cities in the world, with a population of 19,612,368 as of 2010. The city is the country's political, cultural, and educational center, and home to the headquarters for most of China's...
, also contributed to the growth of private industry. In particular, small-scale industries grew up, often specializing in paper, silk, cotton, and porcelain goods. For the most part, however, relatively small urban centers with markets proliferated around the country. Town markets mainly traded food, with some necessary manufactures such as pins or oil. Despite the xenophobia
Xenophobia
Xenophobia is defined as "an unreasonable fear of foreigners or strangers or of that which is foreign or strange". It comes from the Greek words ξένος , meaning "stranger," "foreigner" and φόβος , meaning "fear."...
and intellectual introspection characteristic of the increasingly popular new school of neo-Confucianism
Neo-Confucianism
Neo-Confucianism is an ethical and metaphysical Chinese philosophy influenced by Confucianism, that was primarily developed during the Song Dynasty and Ming Dynasty, but which can be traced back to Han Yu and Li Ao in the Tang Dynasty....
, China under the early Ming Dynasty was not isolated. Foreign trade and other contacts with the outside world, particularly Japan, increased considerably. Chinese merchants explored all of the Indian Ocean
Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third largest of the world's oceanic divisions, covering approximately 20% of the water on the Earth's surface. It is bounded on the north by the Indian Subcontinent and Arabian Peninsula ; on the west by eastern Africa; on the east by Indochina, the Sunda Islands, and...
, reaching East Africa with the voyages of Zheng He
Zheng He
Zheng He , also known as Ma Sanbao and Hajji Mahmud Shamsuddin was a Hui-Chinese mariner, explorer, diplomat and fleet admiral, who commanded voyages to Southeast Asia, South Asia, the Middle East, and East Africa, collectively referred to as the Voyages of Zheng He or Voyages of Cheng Ho from...
.
The Qing Dynasty
Qing Dynasty
The Qing Dynasty was the last dynasty of China, ruling from 1644 to 1912 with a brief, abortive restoration in 1917. It was preceded by the Ming Dynasty and followed by the Republic of China....
(1644–1911) was founded after the defeat of the Ming
Ming Dynasty
The Ming Dynasty, also Empire of the Great Ming, was the ruling dynasty of China from 1368 to 1644, following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan Dynasty. The Ming, "one of the greatest eras of orderly government and social stability in human history", was the last dynasty in China ruled by ethnic...
, the last Han Chinese
Han Chinese
Han Chinese are an ethnic group native to China and are the largest single ethnic group in the world.Han Chinese constitute about 92% of the population of the People's Republic of China , 98% of the population of the Republic of China , 78% of the population of Singapore, and about 20% of the...
dynasty
Dynasty
A dynasty is a sequence of rulers considered members of the same family. Historians traditionally consider many sovereign states' history within a framework of successive dynasties, e.g., China, Ancient Egypt and the Persian Empire...
, by the Manchus. The Manchus were formerly known as the Jurchen. When Beijing was captured by Li Zicheng's peasant rebels in 1644, the last Ming Emperor Chongzhen committed suicide. The Manchu then allied with Ming Dynasty general Wu Sangui
Wu Sangui
Wu Sangui was a Ming Chinese general who was instrumental in the succession of rule to the Qing Dynasty in 1644...
and seized control of Beijing
Beijing
Beijing , also known as Peking , is the capital of the People's Republic of China and one of the most populous cities in the world, with a population of 19,612,368 as of 2010. The city is the country's political, cultural, and educational center, and home to the headquarters for most of China's...
, which became the new capital of the Qing dynasty. The Manchus adopted the Confucian norms of traditional Chinese government in their rule of China proper
China proper
China proper or Eighteen Provinces was a term used by Western writers on the Qing Dynasty to express a distinction between the core and frontier regions of China. There is no fixed extent for China proper, as many administrative, cultural, and linguistic shifts have occurred in Chinese history...
.
In Japan following the Sengoku Period
Sengoku period
The or Warring States period in Japanese history was a time of social upheaval, political intrigue, and nearly constant military conflict that lasted roughly from the middle of the 15th century to the beginning of the 17th century. The name "Sengoku" was adopted by Japanese historians in reference...
of "warring states", central government had been largely reestablished by Oda Nobunaga
Oda Nobunaga
was the initiator of the unification of Japan under the shogunate in the late 16th century, which ruled Japan until the Meiji Restoration in 1868. He was also a major daimyo during the Sengoku period of Japanese history. His opus was continued, completed and finalized by his successors Toyotomi...
and Toyotomi Hideyoshi
Toyotomi Hideyoshi
was a daimyo warrior, general and politician of the Sengoku period. He unified the political factions of Japan. He succeeded his former liege lord, Oda Nobunaga, and brought an end to the Sengoku period. The period of his rule is often called the Momoyama period, named after Hideyoshi's castle...
during the Azuchi-Momoyama period
Azuchi-Momoyama period
The came at the end of the Warring States Period in Japan, when the political unification that preceded the establishment of the Tokugawa shogunate took place. It spans the years from approximately 1573 to 1603, during which time Oda Nobunaga and his successor, Toyotomi Hideyoshi, imposed order...
. After the Battle of Sekigahara
Battle of Sekigahara
The , popularly known as the , was a decisive battle on October 21, 1600 which cleared the path to the Shogunate for Tokugawa Ieyasu...
in 1600, central authority fell to Tokugawa Ieyasu
Tokugawa Ieyasu
was the founder and first shogun of the Tokugawa shogunate of Japan , which ruled from the Battle of Sekigahara in 1600 until the Meiji Restoration in 1868. Ieyasu seized power in 1600, received appointment as shogun in 1603, abdicated from office in 1605, but...
who completed this process and received the title of shogun
Shogun
A was one of the hereditary military dictators of Japan from 1192 to 1867. In this period, the shoguns, or their shikken regents , were the de facto rulers of Japan though they were nominally appointed by the emperor...
in 1603. In order to become shogun, one traditionally was a descendant of the ancient Minamoto clan
Minamoto clan
was one of the surnames bestowed by the Emperors of Japan upon members of the imperial family who were demoted into the ranks of the nobility. The practice was most prevalent during the Heian Period , although its last occurrence was during the Sengoku Era. The Taira were another such offshoot of...
.
Society in the Japanese "Tokugawa period"
Edo society
Society during the Edo period in Japan was ruled by strict customs and regulations intended to promote stability. Confucian ideas provided the foundation for a system of strict social prescriptions. At the top of the social order, though below emperor, shogun, and daimyo , were the samurai who...
, unlike the shogunates before it, was supposedly based on the strict class hierarchy
Hierarchy
A hierarchy is an arrangement of items in which the items are represented as being "above," "below," or "at the same level as" one another...
originally established by Toyotomi Hideyoshi
Toyotomi Hideyoshi
was a daimyo warrior, general and politician of the Sengoku period. He unified the political factions of Japan. He succeeded his former liege lord, Oda Nobunaga, and brought an end to the Sengoku period. The period of his rule is often called the Momoyama period, named after Hideyoshi's castle...
. The daimyo
Daimyo
is a generic term referring to the powerful territorial lords in pre-modern Japan who ruled most of the country from their vast, hereditary land holdings...
, or lords, were at the top, followed by the warrior
Warrior
A warrior is a person skilled in combat or warfare, especially within the context of a tribal or clan-based society that recognizes a separate warrior class.-Warrior classes in tribal culture:...
-caste of samurai
Samurai
is the term for the military nobility of pre-industrial Japan. According to translator William Scott Wilson: "In Chinese, the character 侍 was originally a verb meaning to wait upon or accompany a person in the upper ranks of society, and this is also true of the original term in Japanese, saburau...
, with the farmer
Farmer
A farmer is a person engaged in agriculture, who raises living organisms for food or raw materials, generally including livestock husbandry and growing crops, such as produce and grain...
s, artisans, and trader
Merchant
A merchant is a businessperson who trades in commodities that were produced by others, in order to earn a profit.Merchants can be one of two types:# A wholesale merchant operates in the chain between producer and retail merchant...
s ranking below. In some parts of the country, particularly smaller regions, daimyo and samurai were more or less identical, since daimyo might be trained as samurai, and samurai might act as local lords. Otherwise, the largely inflexible nature of this social stratification
Social stratification
In sociology the social stratification is a concept of class, involving the "classification of persons into groups based on shared socio-economic conditions ... a relational set of inequalities with economic, social, political and ideological dimensions."...
system unleashed disruptive forces over time. Taxes on the peasantry were set at fixed amounts which did not account for inflation
Inflation
In economics, inflation is a rise in the general level of prices of goods and services in an economy over a period of time.When the general price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services. Consequently, inflation also reflects an erosion in the purchasing power of money – a...
or other changes in monetary value. As a result, the tax revenues collected by the samurai landowners were worth less and less over time. This often led to numerous confrontations between noble but impoverished samurai and well-to-do peasants, ranging from simple local disturbances to much bigger rebellion
Rebellion
Rebellion, uprising or insurrection, is a refusal of obedience or order. It may, therefore, be seen as encompassing a range of behaviors aimed at destroying or replacing an established authority such as a government or a head of state...
s. None, however, proved compelling enough to seriously challenge the established order until the arrival of foreign powers.
On the Indian subcontinent
Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent, also Indian Subcontinent, Indo-Pak Subcontinent or South Asian Subcontinent is a region of the Asian continent on the Indian tectonic plate from the Hindu Kush or Hindu Koh, Himalayas and including the Kuen Lun and Karakoram ranges, forming a land mass which extends...
, the Mughal Empire
Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire , or Mogul Empire in traditional English usage, was an imperial power from the Indian Subcontinent. The Mughal emperors were descendants of the Timurids...
ruled most of India in the early 18th century. The "classic period" ended with the death and defeat of Emperor Aurangzeb
Aurangzeb
Abul Muzaffar Muhy-ud-Din Muhammad Aurangzeb Alamgir , more commonly known as Aurangzeb or by his chosen imperial title Alamgir , was the sixth Mughal Emperor of India, whose reign lasted from 1658 until his death in 1707.Badshah Aurangzeb, having ruled most of the Indian subcontinent for nearly...
in 1707 by the rising Hindu
Hindu
Hindu refers to an identity associated with the philosophical, religious and cultural systems that are indigenous to the Indian subcontinent. As used in the Constitution of India, the word "Hindu" is also attributed to all persons professing any Indian religion...
Maratha Empire
Maratha Empire
The Maratha Empire or the Maratha Confederacy was an Indian imperial power that existed from 1674 to 1818. At its peak, the empire covered much of South Asia, encompassing a territory of over 2.8 million km²....
, although the dynasty continued for another 150 years. During this period, the Empire was marked by a highly centralized administration connecting the different regions. All the significant monuments of the Mughals, their most visible legacy, date to this period which was characterised by the expansion of Persian cultural influence in the Indian subcontinent, with brilliant literary, artistic, and architectural results. The Maratha Empire was located in the south west of present-day India and expanded greatly under the rule of the Peshwa
Peshwa
A Peshwa is the titular equivalent of a modern Prime Minister. Emporer Shivaji created the Peshwa designation in order to more effectively delegate administrative duties during the growth of the Maratha Empire. Prior to 1749, Peshwas held office for 8-9 years and controlled the Maratha army...
s, the prime ministers of the Maratha empire. In 1761, the Maratha army lost the Third Battle of Panipat
Third battle of Panipat
The Third Battle of Panipat took place on 14 January 1761, at Panipat , about 60 miles north of Delhi between a northern expeditionary force of the Maratha Confederacy and a coalition of the King of Afghanistan, Ahmad Shah Abdali with 2 Indian Muslim allies—the Rohilla Afghans of the Doab, and the...
which halted imperial expansion and the empire was then divided into a confederacy of Maratha states.
Tsardom of Russia
Russia experienced territorial growth through the 17th century, which was the age of Cossacks. Cossacks were warriors organized into military communities, resembling pirates and pioneers of the New World. In 1648, the peasants of UkraineUkraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It has an area of 603,628 km², making it the second largest contiguous country on the European continent, after Russia...
joined the Zaporozhian Cossacks in rebellion against Poland-Lithuania during the Khmelnytsky Uprising
Khmelnytsky Uprising
The Khmelnytsky Uprising, was a Cossack rebellion in the Ukraine between the years 1648–1657 which turned into a Ukrainian war of liberation from Poland...
, because of the social and religious oppression they suffered under Polish rule. In 1654 the Ukrainian leader, Bohdan Khmelnytsky
Bohdan Khmelnytsky
Bohdan Zynoviy Mykhailovych Khmelnytsky was a hetman of the Zaporozhian Cossack Hetmanate of Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth . He led an uprising against the Commonwealth and its magnates which resulted in the creation of a Cossack state...
, offered to place Ukraine under the protection of the Russian Tsar, Aleksey I. Aleksey's acceptance of this offer led to another Russo-Polish War (1654–1667)
Russo-Polish War (1654–1667)
The Russo-Polish War of 1654–1667, also called Thirteen Years' War, First Northern War, War for Ukraine was the last major conflict between Tsardom of Russia and the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. Between 1655 and 1660, the Second Northern War was also fought in the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth,...
. Finally, Ukraine was split along the river Dnieper, leaving the western part (or Right-bank Ukraine
Right-bank Ukraine
Right-bank Ukraine , a historical name of a part of Ukraine on the right bank of the Dnieper River, corresponding with modern-day oblasts of Volyn, Rivne, Vinnitsa, Zhytomyr, Kirovohrad and Kiev, as well as part of Cherkasy and Ternopil...
) under Polish rule and eastern part (Left-bank Ukraine
Left-bank Ukraine
Left-bank Ukraine is a historic name of the part of Ukraine on the left bank of the Dnieper River, comprising the modern-day oblasts of Chernihiv, Poltava and Sumy as well as the eastern parts of the Kiev and Cherkasy....
and Kiev
Kiev
Kiev or Kyiv is the capital and the largest city of Ukraine, located in the north central part of the country on the Dnieper River. The population as of the 2001 census was 2,611,300. However, higher numbers have been cited in the press....
) under Russian. Later, in 1670–71 the Don Cossacks
Don Cossacks
Don Cossacks were Cossacks who settled along the middle and lower Don.- Etymology and origins :The Don Cossack Host was a frontier military organization from the end of the 16th until the early 20th century....
led by Stenka Razin
Stenka Razin
Stepan Timofeyevich Razin Тимофеевич Разин, ; 1630 – ) was a Cossack leader who led a major uprising against the nobility and Tsar's bureaucracy in South Russia.-Early life:...
initiated a major uprising in the Volga region, but the Tsar's troops were successful in defeating the rebels. In the east, the rapid Russian exploration and colonisation of the huge territories of Siberia was led mostly by Cossacks hunting for valuable fur
Fur
Fur is a synonym for hair, used more in reference to non-human animals, usually mammals; particularly those with extensives body hair coverage. The term is sometimes used to refer to the body hair of an animal as a complete coat, also known as the "pelage". Fur is also used to refer to animal...
s and ivory
Ivory
Ivory is a term for dentine, which constitutes the bulk of the teeth and tusks of animals, when used as a material for art or manufacturing. Ivory has been important since ancient times for making a range of items, from ivory carvings to false teeth, fans, dominoes, joint tubes, piano keys and...
. Russian explorers pushed eastward primarily along the Siberian river routes
Siberian River Routes
Siberian River Routes were the main ways of communication in the Russian Siberia before the 1730s, when roads began to be built. The rivers also were of primary importance in the process of Russian exploration and colonisation of vast Siberian territories...
, and by the mid-17th century there were Russian settlements in the Eastern Siberia, on the Chukchi Peninsula
Chukchi Peninsula
The Chukchi Peninsula, Chukotka Peninsula or Chukotski Peninsula , at about 66° N 172° W, is the northeastern extremity of Asia. Its eastern end is at Cape Dezhnev near the village of Uelen. It is bordered by the Chukchi Sea to the north, the Bering Sea to the south, and the Bering Strait to the...
, along the Amur River, and on the Pacific coast. In 1648 the Bering Strait
Bering Strait
The Bering Strait , known to natives as Imakpik, is a sea strait between Cape Dezhnev, Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, Russia, the easternmost point of the Asian continent and Cape Prince of Wales, Alaska, USA, the westernmost point of the North American continent, with latitude of about 65°40'N,...
between Asia and North America was passed for the first time by Fedot Popov and Semyon Dezhnyov.
Reason and Enlightenment
Traditionally, the European intellectual transformation of and after the Renaissance bridged the Middle Ages and the Modern era. The Age of ReasonAge of reason
Age of reason may refer to:* 17th-century philosophy, as a successor of the Renaissance and a predecessor to the Age of Enlightenment* Age of Enlightenment in its long form of 1600-1800* The Age of Reason, a book by Thomas Paine...
in the Western world is generally regarded as being the start of modern philosophy
Modern philosophy
Modern philosophy is a type of philosophy that originated in Western Europe in the 17th century, and is now common worldwide. It is not a specific doctrine or school , although there are certain assumptions common to much of it, which helps to distinguish it from earlier philosophy.The 17th and...
, and a departure from the medieval approach, especially Scholasticism
Scholasticism
Scholasticism is a method of critical thought which dominated teaching by the academics of medieval universities in Europe from about 1100–1500, and a program of employing that method in articulating and defending orthodoxy in an increasingly pluralistic context...
. Early 17th century philosophy is often called the Age of Rationalism and is considered to succeed Renaissance philosophy and precede the Age of Enlightenment, but some consider it as the earliest part of the Enlightenment era in philosophy, extending that era to two centuries. The 18th century saw the beginning of secularization
Secularization
Secularization is the transformation of a society from close identification with religious values and institutions toward non-religious values and secular institutions...
in Europe, rising to notability in the wake of the French Revolution
French Revolution
The French Revolution , sometimes distinguished as the 'Great French Revolution' , was a period of radical social and political upheaval in France and Europe. The absolute monarchy that had ruled France for centuries collapsed in three years...
.
The Age of Enlightenment
Age of Enlightenment
The Age of Enlightenment was an elite cultural movement of intellectuals in 18th century Europe that sought to mobilize the power of reason in order to reform society and advance knowledge. It promoted intellectual interchange and opposed intolerance and abuses in church and state...
is a term used to describe a time in Western philosophy
Western philosophy
Western philosophy is the philosophical thought and work of the Western or Occidental world, as distinct from Eastern or Oriental philosophies and the varieties of indigenous philosophies....
and cultural life centered upon the 18th century, in which reason was advocated as the primary source and legitimacy for authority. Developing more or less simultaneously in many parts of Europe and America. Developing during the Enlightenment era, Renaissance humanism
Renaissance humanism
Renaissance humanism was an activity of cultural and educational reform engaged by scholars, writers, and civic leaders who are today known as Renaissance humanists. It developed during the fourteenth and the beginning of the fifteenth centuries, and was a response to the challenge of Mediæval...
was an intellectual movement spread across Europe. The basic training of the humanist was to speak well and write (typically, in the form of a letter). The term umanista comes from the latter part of the 15th century. The people were associated with the studia humanitatis, a novel curriculum that was competing with the quadrivium
Quadrivium
The quadrivium comprised the four subjects, or arts, taught in medieval universities, after teaching the trivium. The word is Latin, meaning "the four ways" , and its use for the 4 subjects has been attributed to Boethius or Cassiodorus in the 6th century...
and scholastic logic.
Renaissance humanism took a close study of the Latin and Greek classical texts, and was antagonistic to the values of scholasticism
Scholasticism
Scholasticism is a method of critical thought which dominated teaching by the academics of medieval universities in Europe from about 1100–1500, and a program of employing that method in articulating and defending orthodoxy in an increasingly pluralistic context...
with its emphasis on the accumulated commentaries; and humanists were involved in the sciences, philosophies, arts and poetry of classical antiquity. They self-consciously imitated classical Latin
Classical Latin
Classical Latin in simplest terms is the socio-linguistic register of the Latin language regarded by the enfranchised and empowered populations of the late Roman republic and the Roman empire as good Latin. Most writers during this time made use of it...
and deprecated the use of medieval Latin
Medieval Latin
Medieval Latin was the form of Latin used in the Middle Ages, primarily as a medium of scholarly exchange and as the liturgical language of the medieval Roman Catholic Church, but also as a language of science, literature, law, and administration. Despite the clerical origin of many of its authors,...
. By analogy with the perceived decline of Latin, they applied the principle of ad fontes
Ad fontes
Ad fontes is a Latin expression which means "to the sources" . The phrase epitomizes the renewed study of Greek and Latin classics in Renaissance humanism. Similarly, the Protestant Reformation called for renewed attention to the Bible as the primary source of Christian faith...
, or back to the sources, across broad areas of learning.
The quarrel of the Ancients and the Moderns
Quarrel of the Ancients and the Moderns
The quarrel of the Ancients and the Moderns was a literary and artistic debate that heated up in the early 1690s and shook the Académie française.-Description:...
was a literary
Literature
Literature is the art of written works, and is not bound to published sources...
and artistic quarrel that heated up in the early 1690s and shook the Académie française
Académie française
L'Académie française , also called the French Academy, is the pre-eminent French learned body on matters pertaining to the French language. The Académie was officially established in 1635 by Cardinal Richelieu, the chief minister to King Louis XIII. Suppressed in 1793 during the French Revolution,...
. It opposed two sides, the Ancients (Anciens) who constrain choice of subjects to those drawn from the literature of Antiquity
Classical antiquity
Classical antiquity is a broad term for a long period of cultural history centered on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations of ancient Greece and ancient Rome, collectively known as the Greco-Roman world...
and the Moderns (Modernes), who supported the merits of the authors of the century of Louis XIV
Louis XIV of France
Louis XIV , known as Louis the Great or the Sun King , was a Bourbon monarch who ruled as King of France and Navarre. His reign, from 1643 to his death in 1715, began at the age of four and lasted seventy-two years, three months, and eighteen days...
. Fontenelle
Bernard le Bovier de Fontenelle
Bernard Le Bovier de Fontenelle , also called Bernard Le Bouyer de Fontenelle, was a French author.Fontenelle was born in Rouen, France and died in Paris just one month before his 100th birthday. His mother was the sister of great French dramatists Pierre and Thomas Corneille...
quickly followed with his Digression sur les anciens et les modernes (1688), in which he took the Modern side, pressing the argument that modern scholarship allowed modern man to surpass the ancients in knowledge.
Scientific Revolution
The Scientific RevolutionScientific revolution
The Scientific Revolution is an era associated primarily with the 16th and 17th centuries during which new ideas and knowledge in physics, astronomy, biology, medicine and chemistry transformed medieval and ancient views of nature and laid the foundations for modern science...
was a period when European ideas in classical physics
Classical physics
What "classical physics" refers to depends on the context. When discussing special relativity, it refers to the Newtonian physics which preceded relativity, i.e. the branches of physics based on principles developed before the rise of relativity and quantum mechanics...
, astronomy, biology, human anatomy, chemistry, and other classical sciences were rejected and led to doctrines supplanting those that had prevailed from Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece is a civilization belonging to a period of Greek history that lasted from the Archaic period of the 8th to 6th centuries BC to the end of antiquity. Immediately following this period was the beginning of the Early Middle Ages and the Byzantine era. Included in Ancient Greece is the...
to the Middle Ages which would lead to a transition to modern science. This period saw a fundamental transformation in scientific ideas across physics
Physics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
, astronomy
Astronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that deals with the study of celestial objects and phenomena that originate outside the atmosphere of Earth...
, and biology
Biology
Biology is a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, growth, origin, evolution, distribution, and taxonomy. Biology is a vast subject containing many subdivisions, topics, and disciplines...
, in institutions supporting scientific investigation, and in the more widely held picture of the universe. Individuals started to question all manners of things and it was this questioning that led to the Scientific Revolution, which in turn formed the foundations of contemporary sciences and the establishment of several modern scientific fields.
American wars and revolution
The French and Indian WarsFrench and Indian Wars
The French and Indian Wars is a name used in the United States for a series of conflicts lasting 74 years in North America that represented colonial events related to the European dynastic wars...
were a series of conflicts in North America that represented the actions there that accompanied the European dynastic wars. In Quebec, the wars are generally referred to as the Intercolonial Wars. While some conflicts involved Spanish and Dutch forces, all pitted Great Britain, its colonies and American Indian allies on one side and France, its colonies and Indian allies on the other.
The expanding French and British colonies were contending for control of the western, or interior, territories. Whenever the European countries went to war, there were actions within and by these colonies although the dates of the conflict did not necessarily exactly coincide with those of the larger conflicts.

American Revolution
The American Revolution was the political upheaval during the last half of the 18th century in which thirteen colonies in North America joined together to break free from the British Empire, combining to become the United States of America...
and the ensuing political upheaval during the last half of the 18th century saw the Thirteen Colonies of North America overthrow the governance of the Parliament of Great Britain, and then reject the British monarchy itself to become the sovereign United States of America. In this period the colonies first rejected the authority of the Parliament to govern them without representation, and formed self-governing independent states. The Second Continental Congress then joined together against the British to defend that self-governance in the armed conflict from 1775 to 1783 known as the American Revolutionary War (also called American War of Independence).
The American Revolution begun with fighting at Lexington and Concord. On July 4, 1776, they issued the Declaration of Independence, which proclaimed their independence from Great Britain and their formation of a cooperative union. In June, 1776, Benjamin Franklin
Benjamin Franklin
Dr. Benjamin Franklin was one of the Founding Fathers of the United States. A noted polymath, Franklin was a leading author, printer, political theorist, politician, postmaster, scientist, musician, inventor, satirist, civic activist, statesman, and diplomat...
was appointed a member of the Committee of Five that drafted the Declaration of Independence
Declaration of independence
A declaration of independence is an assertion of the independence of an aspiring state or states. Such places are usually declared from part or all of the territory of another nation or failed nation, or are breakaway territories from within the larger state...
. Although he was temporarily disabled by gout and unable to attend most meetings of the Committee, Franklin made several small changes to the draft sent to him by Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson was the principal author of the United States Declaration of Independence and the Statute of Virginia for Religious Freedom , the third President of the United States and founder of the University of Virginia...
.
The rebellious states defeated Great Britain in the American Revolutionary War
American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War , the American War of Independence, or simply the Revolutionary War, began as a war between the Kingdom of Great Britain and thirteen British colonies in North America, and ended in a global war between several European great powers.The war was the result of the...
, the first successful colonial war of independence. While the states had already rejected the governance of Parliament, through the Declaration the new United States now rejected the legitimacy of the monarchy to demand allegiance. The war raged for seven years, with effective American victory, followed by formal British abandonment of any claims to the United States with the Treaty of Paris.
The Philadelphia Convention
Philadelphia Convention
The Constitutional Convention took place from May 14 to September 17, 1787, in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, to address problems in governing the United States of America, which had been operating under the Articles of Confederation following independence from...
set up the current United States; the United States Constitution
United States Constitution
The Constitution of the United States is the supreme law of the United States of America. It is the framework for the organization of the United States government and for the relationship of the federal government with the states, citizens, and all people within the United States.The first three...
ratification the following year made the states part of a single republic with a strong central government. The Bill of Rights
Bill of rights
A bill of rights is a list of the most important rights of the citizens of a country. The purpose of these bills is to protect those rights against infringement. The term "bill of rights" originates from England, where it referred to the Bill of Rights 1689. Bills of rights may be entrenched or...
, comprising ten constitutional amendments guaranteeing many fundamental civil rights and freedoms, was ratified in 1791.
The French Revolutions
Toward the middle and latter stages of the Age of Revolution, the French political and social revolutionsFrench Revolution
The French Revolution , sometimes distinguished as the 'Great French Revolution' , was a period of radical social and political upheaval in France and Europe. The absolute monarchy that had ruled France for centuries collapsed in three years...
and radical change saw the French governmental structure, previously an absolute monarchy with feudal privileges for the aristocracy and Catholic clergy transform, change to forms based on Enlightenment principles of citizenship and inalienable rights. The first revolution was the National Assembly
National Assembly
National Assembly is either a legislature, or the lower house of a bicameral legislature in some countries. The best known National Assembly, and the first legislature to be known by this title, was that established during the French Revolution in 1789, known as the Assemblée nationale...
, the second was the Legislative Assembly
Legislative Assembly (France)
During the French Revolution, the Legislative Assembly was the legislature of France from 1 October 1791 to September 1792. It provided the focus of political debate and revolutionary law-making between the periods of the National Constituent Assembly and of the National Convention.The Legislative...
, and the third was the Directory
French Directory
The Directory was a body of five Directors that held executive power in France following the Convention and preceding the Consulate...
.
The changes were accompanied by violent turmoil which included the trial and execution of the king, vast bloodshed and repression during the Reign of Terror, and warfare involving every other major European power. Subsequent events that can be traced to the Revolution include the Napoleonic Wars, two separate restorations of the monarchy, and two additional revolutions as modern France took shape. In the following century, France would be governed at one point or another as a republic, constitutional monarchy, and two different empires.
National and Legislative Assembly
During the French Revolution, the National Assembly
National Assembly (French Revolution)
During the French Revolution, the National Assembly , which existed from June 17 to July 9, 1789, was a transitional body between the Estates-General and the National Constituent Assembly.-Background:...
, which existed from June 17 to July 9 of 1789, was a transitional body between the Estates-General and the National Constituent Assembly.
The Legislative Assembly was the legislature of France from October 1, 1791 to September 1792. It provided the focus of political debate and revolutionary law-making between the periods of the National Constituent Assembly and of the National Convention.
The Directory and Napoleonic Era
The Executive Directory
French Directory
The Directory was a body of five Directors that held executive power in France following the Convention and preceding the Consulate...
was a body of five Directors that held executive power in France following the Convention and preceding the Consulate. The period of this regime (2 November 1795 until 10 November 1799), commonly known as the Directory (or Directoire) era, constitutes the second to last stage of the French Revolution.
The Napoleonic Era is a period in the History of France
History of France
The history of France goes back to the arrival of the earliest human being in what is now France. Members of the genus Homo entered the area hundreds of thousands years ago, while the first modern Homo sapiens, the Cro-Magnons, arrived around 40,000 years ago...
and Europe. It is generally classified as the fourth stage of the French Revolution. The Napoleonic Era begins roughly with Napoleon
Napoleon I of France
Napoleon Bonaparte was a French military and political leader during the latter stages of the French Revolution.As Napoleon I, he was Emperor of the French from 1804 to 1815...
's coup d'état
Coup d'état
A coup d'état state, literally: strike/blow of state)—also known as a coup, putsch, and overthrow—is the sudden, extrajudicial deposition of a government, usually by a small group of the existing state establishment—typically the military—to replace the deposed government with another body; either...
, overthrowing the Directory and ends at the Hundred Days
Hundred Days
The Hundred Days, sometimes known as the Hundred Days of Napoleon or Napoleon's Hundred Days for specificity, marked the period between Emperor Napoleon I of France's return from exile on Elba to Paris on 20 March 1815 and the second restoration of King Louis XVIII on 8 July 1815...
and his defeat at Waterloo
Waterloo, Belgium
Waterloo is a Walloon municipality located in the province of Walloon Brabant, Belgium. On December 31, 2009, Waterloo had a total population of 29,573. The total area is 21.03 km² which gives a population density of 1,407 inhabitants per km²...
(November 9, 1799 – June 28, 1815). The congress of Vienna soon set out to restore Europe to pre-French revolution days.
Italian unification
Italian unificationItalian unification
Italian unification was the political and social movement that agglomerated different states of the Italian peninsula into the single state of Italy in the 19th century...
was the political and social movement that annexed different states of the Italian peninsula
Italian Peninsula
The Italian Peninsula or Apennine Peninsula is one of the three large peninsulas of Southern Europe , spanning from the Po Valley in the north to the central Mediterranean Sea in the south. The peninsula's shape gives it the nickname Lo Stivale...
into the single state of Italy in the 19th century. There is a lack of consensus on the exact dates for the beginning and the end of this period, but many scholars agree that the process began with the end of Napoleonic rule and the Congress of Vienna
Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna was a conference of ambassadors of European states chaired by Klemens Wenzel von Metternich, and held in Vienna from September, 1814 to June, 1815. The objective of the Congress was to settle the many issues arising from the French Revolutionary Wars, the Napoleonic Wars,...
in 1815, and approximately ended with the Franco-Prussian War
Franco-Prussian War
The Franco-Prussian War or Franco-German War, often referred to in France as the 1870 War was a conflict between the Second French Empire and the Kingdom of Prussia. Prussia was aided by the North German Confederation, of which it was a member, and the South German states of Baden, Württemberg and...
in 1871, though the last città irredente
Italia irredenta
Italian irredentism was an Italian Irredentist movement that aimed at the unification of all ethnically Italian peoples....
did not join the Kingdom of Italy
Kingdom of Italy (1861–1946)
The Kingdom of Italy was a state forged in 1861 by the unification of Italy under the influence of the Kingdom of Sardinia, which was its legal predecessor state...
until after World War I.
Eastern colonization
The development of New ImperialismNew Imperialism
New Imperialism refers to the colonial expansion adopted by Europe's powers and, later, Japan and the United States, during the 19th and early 20th centuries; expansion took place from the French conquest of Algeria until World War I: approximately 1830 to 1914...
saw the conquest of nearly all eastern hemisphere territories by colonial powers. The commercial colonization of India
Company rule in India
Company rule in India refers to the rule or dominion of the British East India Company on the Indian subcontinent...
commenced in 1757, after the Battle of Plassey
Battle of Plassey
The Battle of Plassey , 23 June 1757, was a decisive British East India Company victory over the Nawab of Bengal and his French allies, establishing Company rule in South Asia which expanded over much of the Indies for the next hundred years...
, when the Nawab of Bengal
Nawab of Bengal
The Nawabs of Bengal were the hereditary nazims or subadars of the subah of Bengal during the Mughal rule and the de-facto rulers of the province.-History:...
surrendered his dominions to the Company, in 1765, when the Company was granted the diwani, or the right to collect revenue, in Bengal
Bengal
Bengal is a historical and geographical region in the northeast region of the Indian Subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal. Today, it is mainly divided between the sovereign land of People's Republic of Bangladesh and the Indian state of West Bengal, although some regions of the previous...
and Bihar
Bihar
Bihar is a state in eastern India. It is the 12th largest state in terms of geographical size at and 3rd largest by population. Almost 58% of Biharis are below the age of 25, which is the highest proportion in India....
, or in 1772, when the Company established a capital in Calcutta, appointed its first Governor-General
Governor-General of India
The Governor-General of India was the head of the British administration in India, and later, after Indian independence, the representative of the monarch and de facto head of state. The office was created in 1773, with the title of Governor-General of the Presidency of Fort William...
, Warren Hastings
Warren Hastings
Warren Hastings PC was the first Governor-General of India, from 1773 to 1785. He was famously accused of corruption in an impeachment in 1787, but was acquitted in 1795. He was made a Privy Councillor in 1814.-Early life:...
, and became directly involved in governance.
The Maratha states
Maratha Empire
The Maratha Empire or the Maratha Confederacy was an Indian imperial power that existed from 1674 to 1818. At its peak, the empire covered much of South Asia, encompassing a territory of over 2.8 million km²....
, following the Anglo-Maratha wars
Anglo-Maratha Wars
The Anglo-Maratha Wars were three wars fought in India between the Maratha Empire and the British East India Company:* First Anglo-Maratha War * Second Anglo-Maratha War...
, eventually lost to the British East India Company
British East India Company
The East India Company was an early English joint-stock company that was formed initially for pursuing trade with the East Indies, but that ended up trading mainly with the Indian subcontinent and China...
in 1818. The rule lasted until 1858, when, after the Indian rebellion of 1857
Indian Rebellion of 1857
The Indian Rebellion of 1857 began as a mutiny of sepoys of the British East India Company's army on 10 May 1857, in the town of Meerut, and soon escalated into other mutinies and civilian rebellions largely in the upper Gangetic plain and central India, with the major hostilities confined to...
and consequent of the Government of India Act 1858
Government of India Act 1858
The Government of India Act 1858 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom passed on August 2, 1858. Its provisions called for the liquidation of the British East India Company and the transference of its functions to the British Crown...
, the British government
India Office
The India Office was a British government department created in 1858 to oversee the colonial administration of India, i.e. the modern-day nations of Bangladesh, Burma, India, and Pakistan, as well as territories in South-east and Central Asia, the Middle East, and parts of the east coast of Africa...
assumed the task of directly administering India in the new British Raj
British Raj
British Raj was the British rule in the Indian subcontinent between 1858 and 1947; The term can also refer to the period of dominion...
. In 1819 Stamford Raffles
Stamford Raffles
Sir Thomas Stamford Bingley Raffles, FRS was a British statesman, best known for his founding of the city of Singapore . He is often described as the "Father of Singapore"...
established Singapore
Singapore
Singapore , officially the Republic of Singapore, is a Southeast Asian city-state off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, north of the equator. An island country made up of 63 islands, it is separated from Malaysia by the Straits of Johor to its north and from Indonesia's Riau Islands by the...
as a key trading post for Britain in their rivalry with the Dutch. However, their rivalry cooled in 1824 when an Anglo-Dutch treaty
Anglo-Dutch Treaty of 1824
The Anglo-Dutch Treaty of 1824, also known as the Treaty of London, was a treaty signed between the United Kingdom and the Netherlands in London on 17 March 1824. The treaty was to resolve disputes arising from the execution of the Anglo-Dutch Treaty of 1814...
demarcated their respective interests in Southeast Asia. From the 1850s onwards, the pace of colonization shifted to a significantly higher gear.
The Dutch East India Company
Dutch East India Company
The Dutch East India Company was a chartered company established in 1602, when the States-General of the Netherlands granted it a 21-year monopoly to carry out colonial activities in Asia...
(1800) and British East India Company
British East India Company
The East India Company was an early English joint-stock company that was formed initially for pursuing trade with the East Indies, but that ended up trading mainly with the Indian subcontinent and China...
(1858) were dissolved by their respective governments, who took over the direct administration of the colonies. Only Thailand
Thailand
Thailand , officially the Kingdom of Thailand , formerly known as Siam , is a country located at the centre of the Indochina peninsula and Southeast Asia. It is bordered to the north by Burma and Laos, to the east by Laos and Cambodia, to the south by the Gulf of Thailand and Malaysia, and to the...
was spared the experience of foreign rule, although, Thailand itself was also greatly affected by the power politics of the Western powers. Colonial rule had a profound effect on Southeast Asia. While the colonial powers profited much from the region's vast resources and large market, colonial rule did develop the region to a varying extent.
Decolonization of the Americas
Decolonization of the AmericasDecolonization of the Americas
Decolonization of the Americas refers to the process by which the countries in the Americas gained their independence from European rule. Decolonization began with a series of revolutions in the late 18th and early to mid-19th centuries...
refers to the process by which the countries in the Americas gained their independence from European rule. Decolonization began with a series of revolutions in the late 18th and early to mid-19th centuries. The Spanish American wars of independence were the numerous wars against Spanish rule in Spanish America that took place during the early 19th century, from 1808 until 1829, directly related to the Napoleonic French invasion of Spain. The conflict started with short-lived governing juntas established in Chuquisaca and Quito opposing the composition of the Supreme Central Junta of Seville.
Americas decolonization |
When the Central Junta fell to the French, numerous new Juntas appeared all across the Americas, eventually resulting in a chain of newly independent countries stretching from Argentina and Chile in the south, to Mexico in the north. After the death of the king Ferdinand VII, in 1833, only Cuba and Puerto Rico remained under Spanish rule, until the Spanish–American War in 1898. Unlike the Spanish, the Portuguese did not divide their colonial territory in America. The captaincies they created were subdued to a centralized administration in Salvador which reported directly to the Crown in Lisbon.
Industrial revolutions

Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was a period from the 18th to the 19th century where major changes in agriculture, manufacturing, mining, transportation, and technology had a profound effect on the social, economic and cultural conditions of the times...
is not exact. Eric Hobsbawm
Eric Hobsbawm
Eric John Ernest Hobsbawm , CH, FBA, is a British Marxist historian, public intellectual, and author...
held that it 'broke out' in the 1780s and was not fully felt until the 1830s or 1840s, while T.S. Ashton
T.S. Ashton
Thomas Southcliffe Ashton was an English economic historian. He was professor of economic history at the London School of Economics at the University of London from 1944 until 1954, and Emeritus Professor until his death in 1968...
held that it occurred roughly between 1760 and 1830 (in effect the reigns of George III
George III of the United Kingdom
George III was King of Great Britain and King of Ireland from 25 October 1760 until the union of these two countries on 1 January 1801, after which he was King of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland until his death...
, The Regency
English Regency
The Regency era in the United Kingdom is the period between 1811—when King George III was deemed unfit to rule and his son, the Prince of Wales, ruled as his proxy as Prince Regent—and 1820, when the Prince Regent became George IV on the death of his father....
, and George IV
George IV of the United Kingdom
George IV was the King of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland and also of Hanover from the death of his father, George III, on 29 January 1820 until his own death ten years later...
). The great changes of centuries before the 19th were more connected with ideas, religion or military conquest, and technological advance had only made small changes in the material wealth of ordinary people.
The first Industrial Revolution merged into the Second Industrial Revolution
Second Industrial Revolution
The Second Industrial Revolution, also known as the Technological Revolution, was a phase of the larger Industrial Revolution corresponding to the latter half of the 19th century until World War I...
around 1850, when technological and economic progress gained momentum with the development of steam-powered ships and railways, and later in the 19th century with the internal combustion engine
Internal combustion engine
The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer in a combustion chamber. In an internal combustion engine, the expansion of the high-temperature and high -pressure gases produced by combustion apply direct force to some component of the engine...
and electric power
Electric power
Electric power is the rate at which electric energy is transferred by an electric circuit. The SI unit of power is the watt.-Circuits:Electric power, like mechanical power, is represented by the letter P in electrical equations...
generation. The Second Industrial Revolution was a phase of the Industrial Revolution; sometimes labeled as the separate Technical Revolution. From a technological and a social point of view there is no clean break between the two. Major innovations during the period occurred in the chemical, electrical, petroleum, and steel industries. Specific advancements included the introduction of oil fired steam turbine and internal combustion driven steel ships, the development of the airplane, the practical commercialization of the automobile, mass production of consumer goods, the perfection of canning, mechanical refrigeration and other food preservation techniques, and the invention of the telephone.
Industrialization
Industrialization is the process of social and economic change whereby a human group is transformed from a pre-industrial society into an industrial one. It is a subdivision of a more general modernization processModernization
In the social sciences, modernization or modernisation refers to a model of an evolutionary transition from a 'pre-modern' or 'traditional' to a 'modern' society. The teleology of modernization is described in social evolutionism theories, existing as a template that has been generally followed by...
, where social change
Social change
Social change refers to an alteration in the social order of a society. It may refer to the notion of social progress or sociocultural evolution, the philosophical idea that society moves forward by dialectical or evolutionary means. It may refer to a paradigmatic change in the socio-economic...
and economic development
Economic development
Economic development generally refers to the sustained, concerted actions of policymakers and communities that promote the standard of living and economic health of a specific area...
are closely related with technological innovation
Innovation
Innovation is the creation of better or more effective products, processes, technologies, or ideas that are accepted by markets, governments, and society...
, particularly with the development of large-scale energy and metallurgy production. It is the extensive organization of an economy for the purpose of manufacturing. Industrialization also introduces a form of philosophical change, where people obtain a different attitude towards their perception of nature
Nature
Nature, in the broadest sense, is equivalent to the natural world, physical world, or material world. "Nature" refers to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general...
.
Revolution in manufacture and power
An economyEconomic system
An economic system is the combination of the various agencies, entities that provide the economic structure that defines the social community. These agencies are joined by lines of trade and exchange along which goods, money etc. are continuously flowing. An example of such a system for a closed...
based on manual labour
Manual labour
Manual labour , manual or manual work is physical work done by people, most especially in contrast to that done by machines, and also to that done by working animals...
was replaced by one dominated by industry and the manufacture
Manufacturing
Manufacturing is the use of machines, tools and labor to produce goods for use or sale. The term may refer to a range of human activity, from handicraft to high tech, but is most commonly applied to industrial production, in which raw materials are transformed into finished goods on a large scale...
of machine
Machine
A machine manages power to accomplish a task, examples include, a mechanical system, a computing system, an electronic system, and a molecular machine. In common usage, the meaning is that of a device having parts that perform or assist in performing any type of work...
ry. It began with the mechanization of the textile
Textile
A textile or cloth is a flexible woven material consisting of a network of natural or artificial fibres often referred to as thread or yarn. Yarn is produced by spinning raw fibres of wool, flax, cotton, or other material to produce long strands...
industries and the development of iron
Iron
Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust...
-making techniques, and trade expansion was enabled by the introduction of canal
Canal
Canals are man-made channels for water. There are two types of canal:#Waterways: navigable transportation canals used for carrying ships and boats shipping goods and conveying people, further subdivided into two kinds:...
s, improved roads, and then railways
Rail transport
Rail transport is a means of conveyance of passengers and goods by way of wheeled vehicles running on rail tracks. In contrast to road transport, where vehicles merely run on a prepared surface, rail vehicles are also directionally guided by the tracks they run on...
.
The introduction of steam power
Steam engine
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs mechanical work using steam as its working fluid.Steam engines are external combustion engines, where the working fluid is separate from the combustion products. Non-combustion heat sources such as solar power, nuclear power or geothermal energy may be...
(fuelled primarily by coal
Coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock usually occurring in rock strata in layers or veins called coal beds or coal seams. The harder forms, such as anthracite coal, can be regarded as metamorphic rock because of later exposure to elevated temperature and pressure...
) and powered machinery (mainly in textile manufacturing
Textile manufacturing
Textile manufacturing is a major industry. It is based in the conversion of three types of fibre into yarn, then fabric, then textiles. These are then fabricated into clothes or other artifacts. Cotton remains the most important natural fibre, so is treated in depth...
) underpinned the dramatic increases in production capacity. The development of all-metal machine tool
Machine tool
A machine tool is a machine, typically powered other than by human muscle , used to make manufactured parts in various ways that include cutting or certain other kinds of deformation...
s in the first two decades of the 19th century facilitated the manufacture of more production machines for manufacturing in other industries.
The modern petroleum industry
Petroleum industry
The petroleum industry includes the global processes of exploration, extraction, refining, transporting , and marketing petroleum products. The largest volume products of the industry are fuel oil and gasoline...
started in 1846 with the discovery of the process of refining kerosene
Kerosene
Kerosene, sometimes spelled kerosine in scientific and industrial usage, also known as paraffin or paraffin oil in the United Kingdom, Hong Kong, Ireland and South Africa, is a combustible hydrocarbon liquid. The name is derived from Greek keros...
from coal
Coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock usually occurring in rock strata in layers or veins called coal beds or coal seams. The harder forms, such as anthracite coal, can be regarded as metamorphic rock because of later exposure to elevated temperature and pressure...
by Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia is one of Canada's three Maritime provinces and is the most populous province in Atlantic Canada. The name of the province is Latin for "New Scotland," but "Nova Scotia" is the recognized, English-language name of the province. The provincial capital is Halifax. Nova Scotia is the...
n Abraham Pineo Gesner
Abraham Pineo Gesner
Abraham Pineo Gesner was a Canadian physician and geologist who invented kerosene. Although Ignacy Łukasiewicz developed the modern kerosene lamp, starting the world's oil industry, Gesner is considered a primary founder. Gesner was born in Cornwallis, Nova Scotia...
. Ignacy Łukasiewicz improved Gesner's method to develop a means of refining kerosene from the more readily available "rock oil" ("petr-oleum") seep
Seep
A petroleum seep is a place where natural liquid or gaseous hydrocarbons escape to the earth's atmosphere and surface, normally under low pressure or flow. Seeps generally occur above either terrestrial or offshore petroleum accumulation structures...
s in 1852 and the first rock oil mine was built in Bóbrka
Bóbrka, Krosno County
Bóbrka is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Chorkówka, within Krosno County, Subcarpathian Voivodeship, in south-eastern Poland...
, near Krosno
Krosno
Krosno is a town and county in Subcarpathian Voivodeship, Poland with 47,455 inhabitants, as of 2 June 2009.Notably Krosno is the site of the first oil well in the world....
in Galicia in the following year. In 1854, Benjamin Silliman
Benjamin Silliman
Benjamin Silliman was an American chemist, one of the first American professors of science , and the first to distill petroleum.-Early life:...
, a science professor at Yale University
Yale University
Yale University is a private, Ivy League university located in New Haven, Connecticut, United States. Founded in 1701 in the Colony of Connecticut, the university is the third-oldest institution of higher education in the United States...
in New Haven
New Haven, Connecticut
New Haven is the second-largest city in Connecticut and the sixth-largest in New England. According to the 2010 Census, New Haven's population increased by 5.0% between 2000 and 2010, a rate higher than that of the State of Connecticut, and higher than that of the state's five largest cities, and...
, was the first to fractionate petroleum by distillation. These discoveries rapidly spread around the world.
Notable Engineers
Engineering achievements of the revolution ranged from electrification to developments in materials science. The advancements made a great contribution to the quality of life. In the first revolution, Lewis PaulLewis Paul
Lewis Paul was the original inventor of roller spinning, the basis of the water frame for spinning cotton in a cotton mill.-Life and work:Lewis Paul was of Huguenot descent. His father was physician to Lord Shaftesbury...
was the original inventor of roller spinning, the basis of the water frame for spinning cotton in a cotton mill. Matthew Boulton
Matthew Boulton
Matthew Boulton, FRS was an English manufacturer and business partner of Scottish engineer James Watt. In the final quarter of the 18th century the partnership installed hundreds of Boulton & Watt steam engines, which were a great advance on the state of the art, making possible the...
and James Watt
James Watt
James Watt, FRS, FRSE was a Scottish inventor and mechanical engineer whose improvements to the Newcomen steam engine were fundamental to the changes brought by the Industrial Revolution in both his native Great Britain and the rest of the world.While working as an instrument maker at the...
's improvements to the steam engine were fundamental to the changes brought by the Industrial Revolution in both the Kingdom of Great Britain and the world.

Nikola Tesla
Nikola Tesla was a Serbian-American inventor, mechanical engineer, and electrical engineer...
made many contributions in the field of electricity
Electricity
Electricity is a general term encompassing a variety of phenomena resulting from the presence and flow of electric charge. These include many easily recognizable phenomena, such as lightning, static electricity, and the flow of electrical current in an electrical wire...
and magnetism
Magnetism
Magnetism is a property of materials that respond at an atomic or subatomic level to an applied magnetic field. Ferromagnetism is the strongest and most familiar type of magnetism. It is responsible for the behavior of permanent magnets, which produce their own persistent magnetic fields, as well...
in the late 19th century and early 20th century. Much of Tesla's early work in electrical engineering and many of his discoveries were of importance. Tesla's patents and theoretical work formed the basis of modern alternating current electric power systems, including the polyphase system
Polyphase system
A polyphase system is a means of distributing alternating current electrical power. Polyphase systems have three or more energized electrical conductors carrying alternating currents with a definite time offset between the voltage waves in each conductor. Polyphase systems are particularly useful...
s power distribution and the alternating current motor, with which he helped usher in the Second Industrial Revolution. In 1887, Tesla filed a number of patents related to a competing form of power distribution known as alternating current. In the following years a bitter rivalry between Tesla and Edison, known as the "War of Currents
War of Currents
In the "War of Currents" era in the late 1880s, George Westinghouse and Thomas Edison became adversaries due to Edison's promotion of direct current for electric power distribution over alternating current advocated by several European companies and Westinghouse Electric based out of Pittsburgh,...
", took place over the preferred method of distribution. After Tesla's demonstration of wireless communication (radio) in 1894 and after being the victor in the "War of Currents", he was widely respected as one of the greatest electrical engineers who worked in America.
Social effects and classes
The Industrial Revolutions were major technologicalTechnology
Technology is the making, usage, and knowledge of tools, machines, techniques, crafts, systems or methods of organization in order to solve a problem or perform a specific function. It can also refer to the collection of such tools, machinery, and procedures. The word technology comes ;...
, socioeconomic
Socioeconomics
Socioeconomics or socio-economics or social economics is an umbrella term with different usages. 'Social economics' may refer broadly to the "use of economics in the study of society." More narrowly, contemporary practice considers behavioral interactions of individuals and groups through social...
, and cultural
Culture
Culture is a term that has many different inter-related meanings. For example, in 1952, Alfred Kroeber and Clyde Kluckhohn compiled a list of 164 definitions of "culture" in Culture: A Critical Review of Concepts and Definitions...
changes in late 18th century and early 19th century that began in Britain and spread throughout the world. The effects spread throughout Western Europe
Western Europe
Western Europe is a loose term for the collection of countries in the western most region of the European continents, though this definition is context-dependent and carries cultural and political connotations. One definition describes Western Europe as a geographic entity—the region lying in the...
and North America during the 19th century, eventually affecting the majority of the world. The impact of this change on society
Society
A society, or a human society, is a group of people related to each other through persistent relations, or a large social grouping sharing the same geographical or virtual territory, subject to the same political authority and dominant cultural expectations...
was enormous and is often compared to the Neolithic revolution
Neolithic Revolution
The Neolithic Revolution was the first agricultural revolution. It was the transition from hunting and gathering to agriculture and settlement. Archaeological data indicates that various forms of plants and animal domestication evolved independently in 6 separate locations worldwide circa...
, when mankind developed agriculture
Agriculture
Agriculture is the cultivation of animals, plants, fungi and other life forms for food, fiber, and other products used to sustain life. Agriculture was the key implement in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that nurtured the...
and gave up its nomadic lifestyle
Nomad
Nomadic people , commonly known as itinerants in modern-day contexts, are communities of people who move from one place to another, rather than settling permanently in one location. There are an estimated 30-40 million nomads in the world. Many cultures have traditionally been nomadic, but...
.
It has been argued that GDP
Gross domestic product
Gross domestic product refers to the market value of all final goods and services produced within a country in a given period. GDP per capita is often considered an indicator of a country's standard of living....
per capita was much more stable and progressed at a much slower rate until the industrial revolution and the emergence of the modern capitalist
Capitalism
Capitalism is an economic system that became dominant in the Western world following the demise of feudalism. There is no consensus on the precise definition nor on how the term should be used as a historical category...
economy, and that it has since increased rapidly in capitalist countries.
Mid-19th century European revolts
The European Revolutions of 1848
Revolutions of 1848
The European Revolutions of 1848, known in some countries as the Spring of Nations, Springtime of the Peoples or the Year of Revolution, were a series of political upheavals throughout Europe in 1848. It was the first Europe-wide collapse of traditional authority, but within a year reactionary...
, known in some countries as the Spring of Nations or the Year of Revolution, were a series of political upheavals throughout the European continent. Described as a revolutionary wave, the period of unrest began in France and then, further propelled by the French Revolution of 1848, soon spread to the rest of Europe. Although most of the revolutions were quickly put down, there was a significant amount of violence in many areas, with tens of thousands of people tortured and killed. While the immediate political effects of the revolutions were reversed, the long-term reverberations of the events were far-reaching.
Industrial age reformism
Industrial age reform movement
Reform movement
A reform movement is a kind of social movement that aims to make gradual change, or change in certain aspects of society, rather than rapid or fundamental changes...
s began the gradual change of society rather with episodes of rapid fundamental changes. The reformists' ideas were often grounded in liberalism, although they also possessed aspects of utopian, socialist or religious concepts. The Radical movement campaigned for electoral reform, a reform of the Poor Laws, free trade, educational reform, postal reform, prison reform, and public sanitation.
Following the Enlightenment's ideas, the reformers looked to the Scientific Revolution and industrial progress to solve the social problems which arose with the Industrial Revolution. Newton's natural philosophy combined a mathematics of axiomatic proof with the mechanics of physical observation, yielding a coherent system of verifiable predictions and replacing a previous reliance on revelation and inspired truth. Applied to public life, this approach yielded several successful campaigns for changes in social policy.
Imperial Russia
Under Peter IPeter I of Russia
Peter the Great, Peter I or Pyotr Alexeyevich Romanov Dates indicated by the letters "O.S." are Old Style. All other dates in this article are New Style. ruled the Tsardom of Russia and later the Russian Empire from until his death, jointly ruling before 1696 with his half-brother, Ivan V...
(the Great), Russia was proclaimed an Empire in 1721 and became recognized as a world power. Ruling from 1682 to 1725, Peter defeated Sweden in the Great Northern War
Great Northern War
The Great Northern War was a conflict in which a coalition led by the Tsardom of Russia successfully contested the supremacy of the Swedish Empire in northern Central Europe and Eastern Europe. The initial leaders of the anti-Swedish alliance were Peter I the Great of Russia, Frederick IV of...
, forcing it to cede West Karelia
Karelia
Karelia , the land of the Karelian peoples, is an area in Northern Europe of historical significance for Finland, Russia, and Sweden...
and Ingria
Ingria
Ingria is a historical region in the eastern Baltic, now part of Russia, comprising the southern bank of the river Neva, between the Gulf of Finland, the Narva River, Lake Peipus in the west, and Lake Ladoga and the western bank of the Volkhov river in the east...
(two regions lost by Russia in the Time of Troubles
Time of Troubles
The Time of Troubles was a period of Russian history comprising the years of interregnum between the death of the last Russian Tsar of the Rurik Dynasty, Feodor Ivanovich, in 1598, and the establishment of the Romanov Dynasty in 1613. In 1601-1603, Russia suffered a famine that killed one-third...
), as well as Estland
Governorate of Estonia
The Governorate of Estonia or Estland, also known as the Government of Estonia or Province of Estonia, was a governorate of the Russian Empire in what is now northern Estonia.-Historical overview:...
and Livland, securing Russia's access to the sea and sea trade. On the Baltic Sea
Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is a brackish mediterranean sea located in Northern Europe, from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from 20°E to 26°E longitude. It is bounded by the Scandinavian Peninsula, the mainland of Europe, and the Danish islands. It drains into the Kattegat by way of the Øresund, the Great Belt and...
Peter founded a new capital called Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg is a city and a federal subject of Russia located on the Neva River at the head of the Gulf of Finland on the Baltic Sea...
, later known as Russia's Window to Europe. Peter the Great's reforms brought considerable Western European cultural influences to Russia. Catherine II (the Great), who ruled in 1762–96, extended Russian political control over the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth and incorporated most of its territories into Russia during the Partitions of Poland
Partitions of Poland
The Partitions of Poland or Partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth took place in the second half of the 18th century and ended the existence of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, resulting in the elimination of sovereign Poland for 123 years...
, pushing the Russian frontier westward into Central Europe. In the south, after successful Russo-Turkish Wars against the Ottoman Empire
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman EmpireIt was usually referred to as the "Ottoman Empire", the "Turkish Empire", the "Ottoman Caliphate" or more commonly "Turkey" by its contemporaries...
, Catherine advanced Russia's boundary to the Black Sea, defeating the Crimean khanate
Crimean Khanate
Crimean Khanate, or Khanate of Crimea , was a state ruled by Crimean Tatars from 1441 to 1783. Its native name was . Its khans were the patrilineal descendants of Toqa Temür, the thirteenth son of Jochi and grandson of Genghis Khan...
.
European Hegemony and the 19th century
Historians sometimes define the 19th century historical era stretching from 1815 (the Congress of ViennaCongress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna was a conference of ambassadors of European states chaired by Klemens Wenzel von Metternich, and held in Vienna from September, 1814 to June, 1815. The objective of the Congress was to settle the many issues arising from the French Revolutionary Wars, the Napoleonic Wars,...
) to 1914 (the outbreak of the First World War
World War I
World War I , which was predominantly called the World War or the Great War from its occurrence until 1939, and the First World War or World War I thereafter, was a major war centred in Europe that began on 28 July 1914 and lasted until 11 November 1918...
); alternatively, Eric Hobsbawm
Eric Hobsbawm
Eric John Ernest Hobsbawm , CH, FBA, is a British Marxist historian, public intellectual, and author...
defined the "Long Nineteenth Century"
The long 19th century
The long nineteenth century, defined by Eric Hobsbawm , a British Marxist historian and author, refers to the period between the years 1789 and 1914...
as spanning the years 1789 to 1914. During this time, the fall of the Spanish Armada
Spanish Armada
This article refers to the Battle of Gravelines, for the modern navy of Spain, see Spanish NavyThe Spanish Armada was the Spanish fleet that sailed against England under the command of the Duke of Medina Sidonia in 1588, with the intention of overthrowing Elizabeth I of England to stop English...
enabled the rise of the British Empire
British Empire
The British Empire comprised the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom. It originated with the overseas colonies and trading posts established by England in the late 16th and early 17th centuries. At its height, it was the...
.
Imperialism and empires
During the 19th century, the SpanishSpanish Empire
The Spanish Empire comprised territories and colonies administered directly by Spain in Europe, in America, Africa, Asia and Oceania. It originated during the Age of Exploration and was therefore one of the first global empires. At the time of Habsburgs, Spain reached the peak of its world power....
, Portuguese
Portuguese Empire
The Portuguese Empire , also known as the Portuguese Overseas Empire or the Portuguese Colonial Empire , was the first global empire in history...
, and Ottoman
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman EmpireIt was usually referred to as the "Ottoman Empire", the "Turkish Empire", the "Ottoman Caliphate" or more commonly "Turkey" by its contemporaries...
empires began to crumble and the Holy Roman
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a realm that existed from 962 to 1806 in Central Europe.It was ruled by the Holy Roman Emperor. Its character changed during the Middle Ages and the Early Modern period, when the power of the emperor gradually weakened in favour of the princes...
and Mughal
Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire , or Mogul Empire in traditional English usage, was an imperial power from the Indian Subcontinent. The Mughal emperors were descendants of the Timurids...
empires ceased. Following the Napoleonic Wars
Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars were a series of wars declared against Napoleon's French Empire by opposing coalitions that ran from 1803 to 1815. As a continuation of the wars sparked by the French Revolution of 1789, they revolutionised European armies and played out on an unprecedented scale, mainly due to...
, the British Empire
British Empire
The British Empire comprised the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom. It originated with the overseas colonies and trading posts established by England in the late 16th and early 17th centuries. At its height, it was the...
became the world's leading power, controlling one quarter of the World's population and one third of the land area. It enforced a Pax Britannica
Pax Britannica
Pax Britannica was the period of relative peace in Europe when the British Empire controlled most of the key maritime trade routes and enjoyed unchallenged sea power...
, encouraged trade, and battled rampant piracy.
Electricity, steel, and petroleum enabled Germany to become great international power that raced to create empires of its own
New Imperialism
New Imperialism refers to the colonial expansion adopted by Europe's powers and, later, Japan and the United States, during the 19th and early 20th centuries; expansion took place from the French conquest of Algeria until World War I: approximately 1830 to 1914...
. The Meiji Restoration
Meiji Restoration
The , also known as the Meiji Ishin, Revolution, Reform or Renewal, was a chain of events that restored imperial rule to Japan in 1868...
was a chain of events that led to enormous changes in Japan's political and social structure that was taking a firm hold at the beginning of the Meiji Era which coincided the opening of Japan by the arrival of the Black Ships
Black Ships
The Black Ships was the name given to Western vessels arriving in Japan in the 16th and 19th centuries.In 1543 Portuguese initiated the first contacts, establishing a trade route linking Goa to Nagasaki...
of Commodore
Commodore (USN)
Commodore was an early title and later a rank in the United States Navy and United States Coast Guard and a current honorary title in the U.S. Navy with an intricate history. Because the U.S. Congress was originally unwilling to authorize more than four ranks until 1862, considerable importance...
Matthew Perry and made Imperial Japan a great power
Great power
A great power is a nation or state that has the ability to exert its influence on a global scale. Great powers characteristically possess military and economic strength and diplomatic and cultural influence which may cause small powers to consider the opinions of great powers before taking actions...
. However, Russia and Qing Dynasty
Qing Dynasty
The Qing Dynasty was the last dynasty of China, ruling from 1644 to 1912 with a brief, abortive restoration in 1917. It was preceded by the Ming Dynasty and followed by the Republic of China....
China failed to keep pace with the other world powers which led to massive social unrest in both empires. The Qing Dynasty's military power weakened during the 19th century, and faced with international pressure, massive rebellion
Rebellion
Rebellion, uprising or insurrection, is a refusal of obedience or order. It may, therefore, be seen as encompassing a range of behaviors aimed at destroying or replacing an established authority such as a government or a head of state...
s and defeats in wars, the dynasty declined after the mid-19th century. European powers controlled parts of Oceania, with French New Caledonia
New Caledonia
New Caledonia is a special collectivity of France located in the southwest Pacific Ocean, east of Australia and about from Metropolitan France. The archipelago, part of the Melanesia subregion, includes the main island of Grande Terre, the Loyalty Islands, the Belep archipelago, the Isle of...
from 1853 and French Polynesia
French Polynesia
French Polynesia is an overseas country of the French Republic . It is made up of several groups of Polynesian islands, the most famous island being Tahiti in the Society Islands group, which is also the most populous island and the seat of the capital of the territory...
from 1889; the Germans established colonies in New Guinea
German New Guinea
German New Guinea was the first part of the German colonial empire. It was a protectorate from 1884 until 1914 when it fell to Australia following the outbreak of the First World War. It consisted of the northeastern part of New Guinea and several nearby island groups...
in 1884, and Samoa
German Samoa
German Samoa was a German protectorate from 1900 to 1914, consisting of the islands of Upolu, Savai'i, Apolima and Manono, now wholly within the independent state Samoa, formerly Western Samoa...
in 1900. The United States expanded into the Pacific with Hawaii becoming a U.S. territory
Territory of Hawaii
The Territory of Hawaii or Hawaii Territory was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from July 7, 1898, until August 21, 1959, when its territory, with the exception of Johnston Atoll, was admitted to the Union as the fiftieth U.S. state, the State of Hawaii.The U.S...
from 1898. Disagreements between the US, Germany and UK over Samoa led to the Tripartite Convention of 1899.
British Victorian era

Victorian era
The Victorian era of British history was the period of Queen Victoria's reign from 20 June 1837 until her death on 22 January 1901. It was a long period of peace, prosperity, refined sensibilities and national self-confidence...
of the United Kingdom was the period of Queen Victoria's reign from June 1837 to January 1901. This was a long period of prosperity for the British people, as profits gained from the overseas British Empire, as well as from industrial improvements at home, allowed a large, educated middle class to develop. Some scholars would extend the beginning of the period—as defined by a variety of sensibilities and political games that have come to be associated with the Victorians—back five years to the passage of the Reform Act 1832.

Pax Britannica
Pax Britannica was the period of relative peace in Europe when the British Empire controlled most of the key maritime trade routes and enjoyed unchallenged sea power...
, and a foreign policy of "splendid isolation
Splendid isolation
Splendid Isolation was the foreign policy pursued by Britain during the late 19th century, under the Conservative premierships of Benjamin Disraeli and the Marquess of Salisbury. The term was actually coined by a Canadian politician to praise Britain's lack of involvement in European affairs...
". Alongside the formal control it exerted over its own colonies, Britain's dominant position in world trade meant that it effectively controlled the economies of many nominally independent countries, such as China, Argentina
Argentina
Argentina , officially the Argentine Republic , is the second largest country in South America by land area, after Brazil. It is constituted as a federation of 23 provinces and an autonomous city, Buenos Aires...
and Siam
Thailand
Thailand , officially the Kingdom of Thailand , formerly known as Siam , is a country located at the centre of the Indochina peninsula and Southeast Asia. It is bordered to the north by Burma and Laos, to the east by Laos and Cambodia, to the south by the Gulf of Thailand and Malaysia, and to the...
, which has been generally characterized as "informal empire
Informal Empire
Informal Empire describes the spheres of influence which an empire may develop that translate into a degree of influence over a region or country, which is not a formal colony in the empire, as a result of the extension of commercial, strategic or military interests of the empire.In a 2010...
". Of note during this time was the Anglo-Zulu War
Anglo-Zulu War
The Anglo-Zulu War was fought in 1879 between the British Empire and the Zulu Kingdom.Following the imperialist scheme by which Lord Carnarvon had successfully brought about federation in Canada, it was thought that a similar plan might succeed with the various African kingdoms, tribal areas and...
, which was fought in 1879 between the British Empire and the Zulu Empire.
British imperial strength was underpinned by the steamship
Steamboat
A steamboat or steamship, sometimes called a steamer, is a ship in which the primary method of propulsion is steam power, typically driving propellers or paddlewheels...
and the telegraph
Telegraphy
Telegraphy is the long-distance transmission of messages via some form of signalling technology. Telegraphy requires messages to be converted to a code which is known to both sender and receiver...
, new technologies invented in the second half of the 19th century, allowing it to control and defend the Empire. By 1902, the British Empire was linked together by a network of telegraph cables, the so-called All Red Line
All Red Line
The All Red Line was an informal name for the system of electrical telegraphs that linked much of the British Empire.It was inaugurated on 31 October 1902. It had this name because on many political maps, British Empire territory was coloured red ....
. Growing till 1922, around 13000000 square miles (33,669,845.4 km²) of territory and roughly 458 million people were added to the British Empire. The British established colonies in Australia in 1788, New Zealand in 1840 and Fiji
Colonial Fiji
The United Kingdom declined its first opportunity to annex Fiji in 1852. Ratu Seru Epenisa Cakobau had offered to cede the islands, subject to being allowed to retain his Tui Viti title, a condition unacceptable to both the British and to many of his fellow chiefs, who regarded him only as first...
in 1872, with much of Oceania
Oceania
Oceania is a region centered on the islands of the tropical Pacific Ocean. Conceptions of what constitutes Oceania range from the coral atolls and volcanic islands of the South Pacific to the entire insular region between Asia and the Americas, including Australasia and the Malay Archipelago...
becoming part of the British Empire.
French governments and conflicts
The Bourbon RestorationBourbon Restoration
The Bourbon Restoration is the name given to the period following the successive events of the French Revolution , the end of the First Republic , and then the forcible end of the First French Empire under Napoleon – when a coalition of European powers restored by arms the monarchy to the...
followed the ousting of Napoleon I of France in 1814. The Allies restored the Bourbon Dynasty to the French throne. The ensuing period is called the Restoration, following French usage, and is characterized by a sharp conservative reaction and the re-establishment of the Roman Catholic Church as a power in French politics. The July Monarchy
July Monarchy
The July Monarchy , officially the Kingdom of France , was a period of liberal constitutional monarchy in France under King Louis-Philippe starting with the July Revolution of 1830 and ending with the Revolution of 1848...
was a period of liberal constitutional monarchy in France under King Louis-Philippe starting with the July Revolution (or Three Glorious Days) of 1830 and ending with the Revolution of 1848. The Second Empire
Second French Empire
The Second French Empire or French Empire was the Imperial Bonapartist regime of Napoleon III from 1852 to 1870, between the Second Republic and the Third Republic, in France.-Rule of Napoleon III:...
was the Imperial Bonapartist regime of Napoleon III from 1852 to 1870, between the Second Republic and the Third Republic, in France.

Franco-Prussian War
The Franco-Prussian War or Franco-German War, often referred to in France as the 1870 War was a conflict between the Second French Empire and the Kingdom of Prussia. Prussia was aided by the North German Confederation, of which it was a member, and the South German states of Baden, Württemberg and...
was a conflict between France and Prussia, while Prussia was backed up by the North German Confederation, of which it was a member, and the South German states of Baden, Württemberg and Bavaria. The complete Prussian and German victory brought about the final unification of Germany under King Wilhelm I of Prussia. It also marked the downfall of Napoleon III and the end of the Second French Empire, which was replaced by the Third Republic. As part of the settlement, almost all of the territory of Alsace-Lorraine was taken by Prussia to become a part of Germany, which it would retain until the end of World War I.
The French Third Republic
French Third Republic
The French Third Republic was the republican government of France from 1870, when the Second French Empire collapsed due to the French defeat in the Franco-Prussian War, to 1940, when France was overrun by Nazi Germany during World War II, resulting in the German and Italian occupations of France...
was the republican government of France between the end of the Second French Empire following the defeat of Louis-Napoléon in the Franco-Prussian war in 1870 and the Vichy Regime after the invasion of France by the German Third Reich in 1940. The Third Republic endured seventy years, making it the most long-lasting regime in France since the collapse of the Ancien Régime in the French Revolution of 1789.
Slavery and abolition
SlaverySlavery
Slavery is a system under which people are treated as property to be bought and sold, and are forced to work. Slaves can be held against their will from the time of their capture, purchase or birth, and deprived of the right to leave, to refuse to work, or to demand compensation...
was greatly reduced around the world in the 19th century. Following a successful slave revolt in Haiti
Haitian Revolution
The Haitian Revolution was a period of conflict in the French colony of Saint-Domingue, which culminated in the elimination of slavery there and the founding of the Haitian republic...
, Britain forced the Barbary pirates to halt their practice of kidnapping and enslaving Europeans, banned slavery throughout its domain
Slavery Abolition Act
The Slavery Abolition Act 1833 was an 1833 Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom abolishing slavery throughout the British Empire...
, and charged its navy with ending the global slave trade. Slavery was then abolished in Russia, America
Emancipation Proclamation
The Emancipation Proclamation is an executive order issued by United States President Abraham Lincoln on January 1, 1863, during the American Civil War using his war powers. It proclaimed the freedom of 3.1 million of the nation's 4 million slaves, and immediately freed 50,000 of them, with nearly...
, and Brazil
Lei Áurea
The Lei Áurea , adopted on May 13, 1888, was the law that abolished slavery in Brazil.It was preceded by the Rio Branco Law of September 28, 1871 , which freed all children born to slave parents, and by the Saraiva-Cotegipe Law , of September 28, 1885, that freed slaves when they reached the age of...
(see Abolitionism
Abolitionism
Abolitionism is a movement to end slavery.In western Europe and the Americas abolitionism was a movement to end the slave trade and set slaves free. At the behest of Dominican priest Bartolomé de las Casas who was shocked at the treatment of natives in the New World, Spain enacted the first...
).
African colonization
Following the abolition of the slave trade, and propelled by economic exploitation, the Scramble for AfricaScramble for Africa
The Scramble for Africa, also known as the Race for Africa or Partition of Africa was a process of invasion, occupation, colonization and annexation of African territory by European powers during the New Imperialism period, between 1881 and World War I in 1914...
was initiated formally at the Berlin West Africa Conference in 1884–1885. All the major European powers laid claim to the areas of Africa where they could exhibit a sphere of influence over the area. These claims did not have to have any substantial land holdings or treaties to be legitimate. The French gained major ground in West Africa, the British in East Africa, and the Portuguese
Portugal
Portugal , officially the Portuguese Republic is a country situated in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula. Portugal is the westernmost country of Europe, and is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the West and South and by Spain to the North and East. The Atlantic archipelagos of the...
and Spanish at various points throughout the continent, while King Leopold
Leopold II of Belgium
Leopold II was the second king of the Belgians. Born in Brussels the second son of Leopold I and Louise-Marie of Orléans, he succeeded his father to the throne on 17 December 1865 and remained king until his death.Leopold is chiefly remembered as the founder and sole owner of the Congo Free...
was able to retain his personal fiefdom, Congo
Belgian Congo
The Belgian Congo was the formal title of present-day Democratic Republic of the Congo between King Leopold II's formal relinquishment of his personal control over the state to Belgium on 15 November 1908, and Congolese independence on 30 June 1960.-Congo Free State, 1884–1908:Until the latter...
.
Meiji Japan
Around the end of the 19th century and into the 20th century, the Meiji era was a marked by the reign of the Meiji EmperorEmperor Meiji
The or was the 122nd emperor of Japan according to the traditional order of succession, reigning from 3 February 1867 until his death...
. During this time, Japan started its modernization and rose to world power status. This era name
Japanese era name
The Japanese era calendar scheme is a common calendar scheme used in Japan, which identifies a year by the combination of the and the year number within the era...
means "Enlightened Rule". It was not until the beginning of the Meiji Era that the Japanese government began taking modernization seriously. Japan expanded its military production base by opening arsenals in various locations. The hyobusho (war office) was replaced with a War Department and a Naval Department. The samurai
Samurai
is the term for the military nobility of pre-industrial Japan. According to translator William Scott Wilson: "In Chinese, the character 侍 was originally a verb meaning to wait upon or accompany a person in the upper ranks of society, and this is also true of the original term in Japanese, saburau...
class suffered great disappointment the following years.
Laws were instituted that required every able-bodied male Japanese citizen, regardless of class, to serve a mandatory term of three years with the first reserves and two additional years with the second reserves. This action, the deathblow for the samurai warriors and their daimyo
Daimyo
is a generic term referring to the powerful territorial lords in pre-modern Japan who ruled most of the country from their vast, hereditary land holdings...
feudal lords, initially met resistance from both the peasant and warrior alike. The peasant class interpreted the term for military service, ketsu-eki (blood tax) literally, and attempted to avoid service by any means necessary. The Japanese government began modelling their ground forces after the French military. The French government contributed greatly to the training of Japanese officers. Many were employed at the military academy in Kyoto, and many more still were feverishly translating French field manuals for use in the Japanese ranks.
After the death of the Meiji Emperor, the Taishō Emperor
Emperor Taishō
The was the 123rd emperor of Japan, according to the traditional order of succession, reigning from 30 July 1912, until his death in 1926.The Emperor’s personal name was . According to Japanese customs, the emperor has no name during his reign and is only called the Emperor...
took the throne, thus beginning the Taishō period
Taisho period
The , or Taishō era, is a period in the history of Japan dating from July 30, 1912 to December 25, 1926, coinciding with the reign of the Taishō Emperor. The health of the new emperor was weak, which prompted the shift in political power from the old oligarchic group of elder statesmen to the Diet...
. A key foreign observer of the remarkable and rapid changes in Japanese society
Culture of Japan
The culture of Japan has evolved greatly over the millennia, from the country's prehistoric Jōmon period to its contemporary hybrid culture, which combines influences from Asia, Europe and North America...
in this period was Ernest Mason Satow
Ernest Mason Satow
Sir Ernest Mason Satow PC, GCMG, , known in Japan as "" , known in China as "薩道義" or "萨道义", was a British scholar, diplomat and Japanologist....
.
Antebellum Expansion
The Antebellum Age was the a period of increasing sectionalism that led up to the American Civil War. The Antebellum Age was a time of great transition because of the industrial revolution in America. It also was a time of growth in slavery in the American South. In a sense, the Antebellum Period is often considered to have begun with the Kansas-Nebraska Act of 1854, though it is sometimes stipulated to extend back as early as 1812.
Manifest Destiny
Manifest Destiny was the 19th century American belief that the United States was destined to expand across the continent. It was used by Democrat-Republicans in the 1840s to justify the war with Mexico; the concept was denounced by Whigs, and fell into disuse after the mid-19th century.Advocates of...
" was the territorial expansion of the United States from 1812 to 1860. Manifest Destiny incorporated the belief that the United States was destined, even divinely ordained, to expand across the North American continent, from the Atlantic seaboard to the Pacific Ocean. This era, from the end of the War of 1812 to the beginning of the American Civil War, has been called the "Age of Manifest Destiny." During this time, the United States expanded to the Pacific Ocean—"from sea to shining sea"—largely defining the borders of the contiguous United States as they are today.
US Civil War and Reconstruction
The American Civil WarAmerican Civil War
The American Civil War was a civil war fought in the United States of America. In response to the election of Abraham Lincoln as President of the United States, 11 southern slave states declared their secession from the United States and formed the Confederate States of America ; the other 25...
was a civil war
Civil war
A civil war is a war between organized groups within the same nation state or republic, or, less commonly, between two countries created from a formerly-united nation state....
in the United States of America. Eleven Southern slave states
Slave state
In the United States of America prior to the American Civil War, a slave state was a U.S. state in which slavery was legal, whereas a free state was one in which slavery was either prohibited from its entry into the Union or eliminated over time...
declared their secession
Secession
Secession is the act of withdrawing from an organization, union, or especially a political entity. Threats of secession also can be a strategy for achieving more limited goals.-Secession theory:...
from the U.S. and formed the Confederate States of America (the Confederacy)
Confederate States of America
The Confederate States of America was a government set up from 1861 to 1865 by 11 Southern slave states of the United States of America that had declared their secession from the U.S...
. Led by Jefferson Davis
Jefferson Davis
Jefferson Finis Davis , also known as Jeff Davis, was an American statesman and leader of the Confederacy during the American Civil War, serving as President for its entire history. He was born in Kentucky to Samuel and Jane Davis...
, they fought against the U.S. federal government (the Union
Union (American Civil War)
During the American Civil War, the Union was a name used to refer to the federal government of the United States, which was supported by the twenty free states and five border slave states. It was opposed by 11 southern slave states that had declared a secession to join together to form the...
), which was supported by all the free states and the five border slave states in the north.
Northern leaders agreed that victory would require more than the end of fighting. It had to encompass the two strategies
Strategy
Strategy, a word of military origin, refers to a plan of action designed to achieve a particular goal. In military usage strategy is distinct from tactics, which are concerned with the conduct of an engagement, while strategy is concerned with how different engagements are linked...
: secession had to be totally repudiated and all forms of slavery had to be eliminated. They disagreed sharply on the military tactics
Military tactics
Military tactics, the science and art of organizing an army or an air force, are the techniques for using weapons or military units in combination for engaging and defeating an enemy in battle. Changes in philosophy and technology over time have been reflected in changes to military tactics. In...
and political tactics for these goals. They also disagreed on the degree of federal control, that should be imposed on the South and the process by which Southern states should be reintegrated into the Union. The Reconstruction Era in United States history existed in the post-Civil War era in the entire United States between 1865 and 1877.
The Gilded Age and legacy
The Gilded AgeGilded Age
In United States history, the Gilded Age refers to the era of rapid economic and population growth in the United States during the post–Civil War and post-Reconstruction eras of the late 19th century. The term "Gilded Age" was coined by Mark Twain and Charles Dudley Warner in their book The Gilded...
saw a substantial growth in population in the United States and extravagant displays of wealth and excess of America's upper-class during the post-Civil War and post-Reconstruction era, in the late 19th century. The wealth polarization derived primarily from industrial and population expansion. The businessmen of the Second Industrial Revolution created industrial towns and cities in the Northeast with new factories, and contributed to the creation of an ethnically diverse industrial working class
Working class
Working class is a term used in the social sciences and in ordinary conversation to describe those employed in lower tier jobs , often extending to those in unemployment or otherwise possessing below-average incomes...
which produced the wealth owned by rising super-rich industrialists and financiers called the "robber barons"
Robber baron (industrialist)
Robber baron is a pejorative term used for a powerful 19th century American businessman. By the 1890s the term was used to attack any businessman who used questionable practices to become wealthy...
. An example is the company of John D. Rockefeller
John D. Rockefeller
John Davison Rockefeller was an American oil industrialist, investor, and philanthropist. He was the founder of the Standard Oil Company, which dominated the oil industry and was the first great U.S. business trust. Rockefeller revolutionized the petroleum industry and defined the structure of...
, who was an important figure in shaping the new oil industry. Using highly effective tactics and aggressive practices, later widely criticized, Standard Oil
Standard Oil
Standard Oil was a predominant American integrated oil producing, transporting, refining, and marketing company. Established in 1870 as a corporation in Ohio, it was the largest oil refiner in the world and operated as a major company trust and was one of the world's first and largest multinational...
absorbed or destroyed most of its competition.
The creation of a modern industrial economy took place. With the creation of a transportation and communication infrastructure
Infrastructure
Infrastructure is basic physical and organizational structures needed for the operation of a society or enterprise, or the services and facilities necessary for an economy to function...
, the corporation
Corporation
A corporation is created under the laws of a state as a separate legal entity that has privileges and liabilities that are distinct from those of its members. There are many different forms of corporations, most of which are used to conduct business. Early corporations were established by charter...
became the dominant form of business organization and a managerial revolution
Management
Management in all business and organizational activities is the act of getting people together to accomplish desired goals and objectives using available resources efficiently and effectively...
transformed business operation
Business
A business is an organization engaged in the trade of goods, services, or both to consumers. Businesses are predominant in capitalist economies, where most of them are privately owned and administered to earn profit to increase the wealth of their owners. Businesses may also be not-for-profit...
s. In 1890, Congress passed the Sherman Antitrust Act
Sherman Antitrust Act
The Sherman Antitrust Act requires the United States federal government to investigate and pursue trusts, companies, and organizations suspected of violating the Act. It was the first Federal statute to limit cartels and monopolies, and today still forms the basis for most antitrust litigation by...
— the source of all American anti-monopoly laws. The law forbade every contract, scheme, deal, or conspiracy to restrain trade, though the phrase "restraint of trade" remained subjective. By the beginning of the 20th century, per capita income and industrial production
Industrial production
Industrial production is a measure of output of the industrial sector of the economy. The industrial sector includes manufacturing, mining, and utilities. Although these sectors contribute only a small portion of GDP , they are highly sensitive to interest rates and consumer demand...
in the United States exceeded that of any other country except Britain. Long hours and hazardous working conditions led many workers to attempt to form labor unions despite strong opposition from industrialists and the courts. But the courts did protect the marketplace, declaring the Standard Oil group to be an "unreasonable" monopoly
Monopoly
A monopoly exists when a specific person or enterprise is the only supplier of a particular commodity...
under the Sherman Antitrust Act in 1911. It ordered Standard to break up into 34 independent companies with different boards of directors.
Transitions and Enlightenment negation
Around the turn of the 20th century, Enlightenment philosophy was challenged in various quarters. After the use of classical physicsClassical physics
What "classical physics" refers to depends on the context. When discussing special relativity, it refers to the Newtonian physics which preceded relativity, i.e. the branches of physics based on principles developed before the rise of relativity and quantum mechanics...
since the end of the scientific revolution, modern physics
Modern physics
The term modern physics refers to the post-Newtonian conception of physics. The term implies that classical descriptions of phenomena are lacking, and that an accurate, "modern", description of reality requires theories to incorporate elements of quantum mechanics or Einsteinian relativity, or both...
arose with the advent of quantum physics; substituting mathematics studies
Mathematical physics
Mathematical physics refers to development of mathematical methods for application to problems in physics. The Journal of Mathematical Physics defines this area as: "the application of mathematics to problems in physics and the development of mathematical methods suitable for such applications and...
for experimental studies
Experimental physics
Within the field of physics, experimental physics is the category of disciplines and sub-disciplines concerned with the observation of physical phenomena in order to gather data about the universe...
and examining equation
Equation
An equation is a mathematical statement that asserts the equality of two expressions. In modern notation, this is written by placing the expressions on either side of an equals sign , for examplex + 3 = 5\,asserts that x+3 is equal to 5...
s to build a theoretical structure. The old quantum theory
Old quantum theory
The old quantum theory was a collection of results from the years 1900–1925 which predate modern quantum mechanics. The theory was never complete or self-consistent, but was a collection of heuristic prescriptions which are now understood to be the first quantum corrections to classical mechanics...
was a collection of results which predate modern quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics, also known as quantum physics or quantum theory, is a branch of physics providing a mathematical description of much of the dual particle-like and wave-like behavior and interactions of energy and matter. It departs from classical mechanics primarily at the atomic and subatomic...
, but were never complete or self-consistent. The collection of heuristic
Heuristic
Heuristic refers to experience-based techniques for problem solving, learning, and discovery. Heuristic methods are used to speed up the process of finding a satisfactory solution, where an exhaustive search is impractical...
prescriptions for quantum mechanics were the first corrections to classical mechanics
Classical mechanics
In physics, classical mechanics is one of the two major sub-fields of mechanics, which is concerned with the set of physical laws describing the motion of bodies under the action of a system of forces...
. In addition, the various number of aether theories
Aether theories
Aether theories in early modern physics proposed the existence of a medium, the aether , a space-filling substance or field, thought to be necessary as a transmission medium for the propagation of electromagnetic waves...
in classical physics which supposed a "fifth element", such as the Luminiferous aether
Luminiferous aether
In the late 19th century, luminiferous aether or ether, meaning light-bearing aether, was the term used to describe a medium for the propagation of light....
, was nullified by the Michelson-Morley experiment
Michelson-Morley experiment
The Michelson–Morley experiment was performed in 1887 by Albert Michelson and Edward Morley at what is now Case Western Reserve University in Cleveland, Ohio. Its results are generally considered to be the first strong evidence against the theory of a luminiferous ether and in favor of special...
in an attempt to detect the motion of earth through the aether. In biology, Darwinism
Darwinism
Darwinism is a set of movements and concepts related to ideas of transmutation of species or of evolution, including some ideas with no connection to the work of Charles Darwin....
gained acceptance and exposed adaptation
Adaptation
An adaptation in biology is a trait with a current functional role in the life history of an organism that is maintained and evolved by means of natural selection. An adaptation refers to both the current state of being adapted and to the dynamic evolutionary process that leads to the adaptation....
in the theory of natural selection
Natural selection
Natural selection is the nonrandom process by which biologic traits become either more or less common in a population as a function of differential reproduction of their bearers. It is a key mechanism of evolution....
. The fields of geology, astronomy and psychology also made strides and gained new insights. In medicine, there were advances of medical theory and treatments.

Xinhai Revolution
The Xinhai Revolution or Hsinhai Revolution, also known as Revolution of 1911 or the Chinese Revolution, was a revolution that overthrew China's last imperial dynasty, the Qing , and established the Republic of China...
in 1911, there were many calls, such as the May Fourth Movement
May Fourth Movement
The May Fourth Movement was an anti-imperialist, cultural, and political movement growing out of student demonstrations in Beijing on May 4, 1919, protesting the Chinese government's weak response to the Treaty of Versailles, especially the Shandong Problem...
, to completely abolish the old imperial institutions and practices of China. There have been attempts to incorporate democracy
Democracy
Democracy is generally defined as a form of government in which all adult citizens have an equal say in the decisions that affect their lives. Ideally, this includes equal participation in the proposal, development and passage of legislation into law...
, republicanism
Republicanism
Republicanism is the ideology of governing a nation as a republic, where the head of state is appointed by means other than heredity, often elections. The exact meaning of republicanism varies depending on the cultural and historical context...
, and industrialism into Chinese philosophy, notably by Sun Yat-Sen
Sun Yat-sen
Sun Yat-sen was a Chinese doctor, revolutionary and political leader. As the foremost pioneer of Nationalist China, Sun is frequently referred to as the "Father of the Nation" , a view agreed upon by both the People's Republic of China and the Republic of China...
(Sūn yì xiān, in one Mandarin form of the name) at the beginning of the 20th century. Mao Zedong
Mao Zedong
Mao Zedong, also transliterated as Mao Tse-tung , and commonly referred to as Chairman Mao , was a Chinese Communist revolutionary, guerrilla warfare strategist, Marxist political philosopher, and leader of the Chinese Revolution...
(Máo zé dōng) added Marxism
Marxism
Marxism is an economic and sociopolitical worldview and method of socioeconomic inquiry that centers upon a materialist interpretation of history, a dialectical view of social change, and an analysis and critique of the development of capitalism. Marxism was pioneered in the early to mid 19th...
, Stalinism
Stalinism
Stalinism refers to the ideology that Joseph Stalin conceived and implemented in the Soviet Union, and is generally considered a branch of Marxist–Leninist ideology but considered by some historians to be a significant deviation from this philosophy...
, and other communist
Communism
Communism is a social, political and economic ideology that aims at the establishment of a classless, moneyless, revolutionary and stateless socialist society structured upon common ownership of the means of production...
thought. When the Communist Party of China
Communist Party of China
The Communist Party of China , also known as the Chinese Communist Party , is the founding and ruling political party of the People's Republic of China...
took over
Chinese Civil War
The Chinese Civil War was a civil war fought between the Kuomintang , the governing party of the Republic of China, and the Communist Party of China , for the control of China which eventually led to China's division into two Chinas, Republic of China and People's Republic of...
power, previous schools of thought, excepting notably Legalism
Legalism (Chinese philosophy)
In Chinese history, Legalism was one of the main philosophic currents during the Warring States Period, although the term itself was invented in the Han Dynasty and thus does not refer to an organized 'school' of thought....
, were denounced as backward, and later even purged during the Cultural Revolution
Cultural Revolution
The Great Proletarian Cultural Revolution, commonly known as the Cultural Revolution , was a socio-political movement that took place in the People's Republic of China from 1966 through 1976...
.
Developed from earlier secular traditions, modern Humanism
Humanism
Humanism is an approach in study, philosophy, world view or practice that focuses on human values and concerns. In philosophy and social science, humanism is a perspective which affirms some notion of human nature, and is contrasted with anti-humanism....
ethical philosophies
Ethics
Ethics, also known as moral philosophy, is a branch of philosophy that addresses questions about morality—that is, concepts such as good and evil, right and wrong, virtue and vice, justice and crime, etc.Major branches of ethics include:...
affirm the dignity and worth of all people, based on the ability to determine right and wrong by appealing to universal human qualities, particularly rationality
Rationalism
In epistemology and in its modern sense, rationalism is "any view appealing to reason as a source of knowledge or justification" . In more technical terms, it is a method or a theory "in which the criterion of the truth is not sensory but intellectual and deductive"...
, without resorting to the supernatural or alleged divine authority from religious texts. For liberal humanists such as Rousseau
Jean-Jacques Rousseau
Jean-Jacques Rousseau was a Genevan philosopher, writer, and composer of 18th-century Romanticism. His political philosophy influenced the French Revolution as well as the overall development of modern political, sociological and educational thought.His novel Émile: or, On Education is a treatise...
or Kant
Immanuel Kant
Immanuel Kant was a German philosopher from Königsberg , researching, lecturing and writing on philosophy and anthropology at the end of the 18th Century Enlightenment....
, the universal law of reason
Reason
Reason is a term that refers to the capacity human beings have to make sense of things, to establish and verify facts, and to change or justify practices, institutions, and beliefs. It is closely associated with such characteristically human activities as philosophy, science, language, ...
guided the way towards total emancipation from any kind of tyranny. These ideas were challenged. The young Karl Marx
Young Marx
Some theorists consider Karl Marx's thought to be divided into a "young" period and a "mature" one. There is disagreement to when Marx's thought began to mature, and the problem of the idea of a "Young Marx" is the problem of tracking the development of Marx's works and of its possible unity...
criticized the project of political emancipation (embodied in the form of human rights
Human rights
Human rights are "commonly understood as inalienable fundamental rights to which a person is inherently entitled simply because she or he is a human being." Human rights are thus conceived as universal and egalitarian . These rights may exist as natural rights or as legal rights, in both national...
), asserting it to be symptomatic of the very dehumanization it is supposed to oppose. For Friedrich Nietzsche
Friedrich Nietzsche
Friedrich Wilhelm Nietzsche was a 19th-century German philosopher, poet, composer and classical philologist...
, humanism was nothing more than a secular version of theism
Theism
Theism, in the broadest sense, is the belief that at least one deity exists.In a more specific sense, theism refers to a doctrine concerning the nature of a monotheistic God and God's relationship to the universe....
. In his Genealogy of Morals, he argues that human rights exist as a means for the weak to collectively constrain the strong. On this view, such rights do not facilitate emancipation of life, but rather deny it. In the 20th century, the notion that human beings are rationally autonomous was challenged by the concept that humans were driven by unconscious irrational desires.
Notable persons
Sigmund FreudSigmund Freud
Sigmund Freud , born Sigismund Schlomo Freud , was an Austrian neurologist who founded the discipline of psychoanalysis...
is renowned for his redefinition of sexual desire as the primary motivational energy of human life, as well as his therapeutic techniques, including the use of free association
Free association (psychology)
Free association is a technique used in psychoanalysis which was originally devised by Sigmund Freud out of the hypnotic method of his mentor and coworker, Josef Breuer....
, his theory of transference
Transference
Transference is a phenomenon in psychoanalysis characterized by unconscious redirection of feelings from one person to another. One definition of transference is "the inappropriate repetition in the present of a relationship that was important in a person's childhood." Another definition is "the...
in the therapeutic relationship, and the interpretation of dreams
Dream interpretation
Dream interpretation is the process of assigning meaning to dreams. In many ancient societies, such as those of Egypt and Greece, dreaming was considered a supernatural communication or a means of divine intervention, whose message could be unravelled by people with certain powers...
as sources of insight into unconscious desires.
Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein was a German-born theoretical physicist who developed the theory of general relativity, effecting a revolution in physics. For this achievement, Einstein is often regarded as the father of modern physics and one of the most prolific intellects in human history...
is known for his theories of special relativity
Special relativity
Special relativity is the physical theory of measurement in an inertial frame of reference proposed in 1905 by Albert Einstein in the paper "On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies".It generalizes Galileo's...
and general relativity
General relativity
General relativity or the general theory of relativity is the geometric theory of gravitation published by Albert Einstein in 1916. It is the current description of gravitation in modern physics...
. He also made important contributions to statistical mechanics
Statistical mechanics
Statistical mechanics or statistical thermodynamicsThe terms statistical mechanics and statistical thermodynamics are used interchangeably...
, especially his mathematical treatment of Brownian motion
Brownian motion
Brownian motion or pedesis is the presumably random drifting of particles suspended in a fluid or the mathematical model used to describe such random movements, which is often called a particle theory.The mathematical model of Brownian motion has several real-world applications...
, his resolution of the paradox of specific heats
Einstein solid
The Einstein solid is a model of a solid based on two assumptions:* Each atom in the lattice is an independent 3D quantum harmonic oscillator* All atoms oscillate with the same frequency...
, and his connection of fluctuations and dissipation
Fluctuation dissipation theorem
The fluctuation-dissipation theorem is a powerful tool in statistical physics for predicting the behavior of non-equilibrium thermodynamical systems. These systems involve the irreversible dissipation of energy into heat from their reversible thermal fluctuations at thermodynamic equilibrium...
. Despite his reservations about its interpretation, Einstein also made contributions to quantum mechanics and, indirectly, quantum field theory
Quantum field theory
Quantum field theory provides a theoretical framework for constructing quantum mechanical models of systems classically parametrized by an infinite number of dynamical degrees of freedom, that is, fields and many-body systems. It is the natural and quantitative language of particle physics and...
, primarily through his theoretical studies of the photon
Photon
In physics, a photon is an elementary particle, the quantum of the electromagnetic interaction and the basic unit of light and all other forms of electromagnetic radiation. It is also the force carrier for the electromagnetic force...
.
Social Darwinism
At the end of the 19th century, Social DarwinismSocial Darwinism
Social Darwinism is a term commonly used for theories of society that emerged in England and the United States in the 1870s, seeking to apply the principles of Darwinian evolution to sociology and politics...
was promoted and included the various ideologies based on a concept that competition among all individuals, groups, nations, or ideas was the framework of social evolution in human societies. In this view, society's advancement was dependent on the "survival of the fittest
Survival of the fittest
"Survival of the fittest" is a phrase originating in evolutionary theory, as an alternative description of Natural selection. The phrase is today commonly used in contexts that are incompatible with the original meaning as intended by its first two proponents: British polymath philosopher Herbert...
", the term was in fact coined by Herbert Spencer
Herbert Spencer
Herbert Spencer was an English philosopher, biologist, sociologist, and prominent classical liberal political theorist of the Victorian era....
and referred to in "The Gospel of Wealth
The Gospel of Wealth
"Wealth", more commonly known as "The Gospel of Wealth", "the Richest man in the World," is an essay written by Andrew Carnegie in 1889 that described the responsibility of philanthropy by the new upper class of self-made rich...
" theory written by Andrew Carnegie
Andrew Carnegie
Andrew Carnegie was a Scottish-American industrialist, businessman, and entrepreneur who led the enormous expansion of the American steel industry in the late 19th century...
.
Marxism's society

Karl Marx
Karl Heinrich Marx was a German philosopher, economist, sociologist, historian, journalist, and revolutionary socialist. His ideas played a significant role in the development of social science and the socialist political movement...
summarized his approach to history and politics in the opening line of the first chapter of The Communist Manifesto
The Communist Manifesto
The Communist Manifesto, originally titled Manifesto of the Communist Party is a short 1848 publication written by the German Marxist political theorists Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels. It has since been recognized as one of the world's most influential political manuscripts. Commissioned by the...
(1848). He wrote:
- The history of all hitherto existing society is the history of class struggleClass struggleClass struggle is the active expression of a class conflict looked at from any kind of socialist perspective. Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels wrote "The [written] history of all hitherto existing society is the history of class struggle"....
s.
The Manifesto went through a number of editions from 1872 to 1890; notable new prefaces were written by Marx and Engels for the 1872 German edition, the 1882 Russian edition, the 1883 German edition, and the 1888 English edition. In general, Marxism
Marxism
Marxism is an economic and sociopolitical worldview and method of socioeconomic inquiry that centers upon a materialist interpretation of history, a dialectical view of social change, and an analysis and critique of the development of capitalism. Marxism was pioneered in the early to mid 19th...
identified five (and one transitional) successive stages of development in Western Europe.
- Primitive CommunismPrimitive communismPrimitive communism is a term used by Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels to describe what they interpreted as early forms of communism: As a model, primitive communism is usually used to describe early hunter-gatherer societies, that had no hierarchical social class structures or capital accumulation...
: as seen in cooperative tribal societies. - Slave Society: which develops when the tribe becomes a city-state. Aristocracy is born.
- FeudalismFeudalismFeudalism was a set of legal and military customs in medieval Europe that flourished between the 9th and 15th centuries, which, broadly defined, was a system for ordering society around relationships derived from the holding of land in exchange for service or labour.Although derived from the...
: aristocracy is the ruling class. Merchants develop into capitalists. - CapitalismCapitalismCapitalism is an economic system that became dominant in the Western world following the demise of feudalism. There is no consensus on the precise definition nor on how the term should be used as a historical category...
: capitalists are the ruling class, who create and employ the true working class. - Dictatorship of the proletariatDictatorship of the proletariatIn Marxist socio-political thought, the dictatorship of the proletariat refers to a socialist state in which the proletariat, or the working class, have control of political power. The term, coined by Joseph Weydemeyer, was adopted by the founders of Marxism, Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels, in the...
: workers gain class consciousness, overthrowProletarian revolutionA proletarian revolution is a social and/or political revolution in which the working class attempts to overthrow the bourgeoisie. Proletarian revolutions are generally advocated by socialists, communists, and most anarchists....
the capitalists and take control over the stateSocialist stateA socialist state generally refers to any state constitutionally dedicated to the construction of a socialist society. It is closely related to the political strategy of "state socialism", a set of ideologies and policies that believe a socialist economy can be established through government...
. - CommunismCommunismCommunism is a social, political and economic ideology that aims at the establishment of a classless, moneyless, revolutionary and stateless socialist society structured upon common ownership of the means of production...
: a classless and stateless society.
European decline and the 20th century
Major political developments saw the former British EmpireBritish Empire
The British Empire comprised the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom. It originated with the overseas colonies and trading posts established by England in the late 16th and early 17th centuries. At its height, it was the...
lose most of its remaining political power over commonwealth countries. The Trans-Siberian Railway
Trans-Siberian Railway
The Trans-Siberian Railway is a network of railways connecting Moscow with the Russian Far East and the Sea of Japan. It is the longest railway in the world...
, crossing Asia by train, was complete by 1916. Other events include the Israeli–Palestinian conflict
Israeli–Palestinian conflict
The Israeli–Palestinian conflict is the ongoing conflict between Israelis and Palestinians. The conflict is wide-ranging, and the term is also used in reference to the earlier phases of the same conflict, between Jewish and Zionist yishuv and the Arab population living in Palestine under Ottoman or...
, two world wars, and the Cold War
Cold War
The Cold War was the continuing state from roughly 1946 to 1991 of political conflict, military tension, proxy wars, and economic competition between the Communist World—primarily the Soviet Union and its satellite states and allies—and the powers of the Western world, primarily the United States...
.
Australian Constitution
In 1901, the Federation of AustraliaFederation of Australia
The Federation of Australia was the process by which the six separate British self-governing colonies of New South Wales, Queensland, South Australia, Tasmania, Victoria and Western Australia formed one nation...
was the process by which the six separate British self-governing colonies
Self-governing colony
A self-governing colony is a colony with an elected legislature, in which politicians are able to make most decisions without reference to the colonial power with formal or nominal control of the colony...
of New South Wales
New South Wales
New South Wales is a state of :Australia, located in the east of the country. It is bordered by Queensland, Victoria and South Australia to the north, south and west respectively. To the east, the state is bordered by the Tasman Sea, which forms part of the Pacific Ocean. New South Wales...
, Queensland
Queensland
Queensland is a state of Australia, occupying the north-eastern section of the mainland continent. It is bordered by the Northern Territory, South Australia and New South Wales to the west, south-west and south respectively. To the east, Queensland is bordered by the Coral Sea and Pacific Ocean...
, South Australia
South Australia
South Australia is a state of Australia in the southern central part of the country. It covers some of the most arid parts of the continent; with a total land area of , it is the fourth largest of Australia's six states and two territories.South Australia shares borders with all of the mainland...
, Tasmania
Tasmania
Tasmania is an Australian island and state. It is south of the continent, separated by Bass Strait. The state includes the island of Tasmania—the 26th largest island in the world—and the surrounding islands. The state has a population of 507,626 , of whom almost half reside in the greater Hobart...
, Victoria
Victoria (Australia)
Victoria is the second most populous state in Australia. Geographically the smallest mainland state, Victoria is bordered by New South Wales, South Australia, and Tasmania on Boundary Islet to the north, west and south respectively....
and Western Australia
Western Australia
Western Australia is a state of Australia, occupying the entire western third of the Australian continent. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, the Great Australian Bight and Indian Ocean to the south, the Northern Territory to the north-east and South Australia to the south-east...
formed one nation. They kept the systems of government that they had developed as separate colonies but also would have a federal government that was responsible for matters concerning the whole nation. When the Constitution of Australia
Constitution of Australia
The Constitution of Australia is the supreme law under which the Australian Commonwealth Government operates. It consists of several documents. The most important is the Constitution of the Commonwealth of Australia...
came into force, the colonies collectively became states
States and territories of Australia
The Commonwealth of Australia is a union of six states and various territories. The Australian mainland is made up of five states and three territories, with the sixth state of Tasmania being made up of islands. In addition there are six island territories, known as external territories, and a...
of the Commonwealth of Australia
Australia
Australia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area...
.
Eastern warlords
The last days of the Qing DynastyQing Dynasty
The Qing Dynasty was the last dynasty of China, ruling from 1644 to 1912 with a brief, abortive restoration in 1917. It was preceded by the Ming Dynasty and followed by the Republic of China....
were marked by civil unrest and foreign invasions. Responding to these civil failures and discontent, the Qing Imperial Court did attempt to reform the government in various ways, such as the decision to draft a constitution in 1906, the establishment of provincial legislatures in 1909, and the preparation for a national parliament in 1910. However, many of these measures were opposed by the conservatives of the Qing Court, and many reformers were either imprisoned or executed outright. The failures of the Imperial Court to enact such reforming measures of political liberalization and modernization caused the reformists to steer toward the road of revolution.
In 1912, the Republic of China was established and was inaugurated in Nanjing
Nanjing
' is the capital of Jiangsu province in China and has a prominent place in Chinese history and culture, having been the capital of China on several occasions...
as the first Provisional President
President of the Republic of China
The President of the Republic of China is the head of state and commander-in-chief of the Republic of China . The Republic of China was founded on January 1, 1912, to govern all of China...
. But power in Beijing
Beijing
Beijing , also known as Peking , is the capital of the People's Republic of China and one of the most populous cities in the world, with a population of 19,612,368 as of 2010. The city is the country's political, cultural, and educational center, and home to the headquarters for most of China's...
already had passed to Yuan Shikai
Yuan Shikai
Yuan Shikai was an important Chinese general and politician famous for his influence during the late Qing Dynasty, his role in the events leading up to the abdication of the last Qing Emperor of China, his autocratic rule as the second President of the Republic of China , and his short-lived...
, who had effective control of the Beiyang Army
Beiyang Army
The Beiyang Army was a powerful, Western-style Chinese military force created by the Qing Dynasty government in the late 19th century. It was the centerpiece of a general reconstruction of China's military system. The Beiyang Army played a major role in Chinese politics for at least three decades...
, the most powerful military force in China at the time. To prevent civil war
Civil war
A civil war is a war between organized groups within the same nation state or republic, or, less commonly, between two countries created from a formerly-united nation state....
and possible foreign intervention from undermining the infant republic, leaders agreed to Army's demand that China be united under a Beijing government. On March 10, in Beijing, Shikai was sworn in as the second Provisional President of the Republic of China.
After the early 1900s revolutions, shifting alliances of China's regional warlords fought for control of the Beijing government. Despite the fact that various warlords gained control of the government in Beijing during the warlord era, this did not constitute a new era of control or governance, because other warlords did not acknowledge the transitory governments in this period and were a law unto themselves. These military-dominated governments were collectively known as the Beiyang government
Beiyang Government
The Beiyang government or warlord government collectively refers to a series of military regimes that ruled from Beijing from 1912 to 1928 at Zhongnanhai. It was internationally recognized as the legitimate Government of the Republic of China. The name comes from the Beiyang Army which dominated...
. The warlord era is ends around in 1927.
Turn of the 20th century
Begun at the Battle of Port Arthur
Battle of Port Arthur
The Battle of Port Arthur was the starting battle of the Russo-Japanese War...
, the Russo-Japanese War
Russo-Japanese War
The Russo-Japanese War was "the first great war of the 20th century." It grew out of rival imperial ambitions of the Russian Empire and Japanese Empire over Manchuria and Korea...
establishes the Empire of Japan
Empire of Japan
The Empire of Japan is the name of the state of Japan that existed from the Meiji Restoration on 3 January 1868 to the enactment of the post-World War II Constitution of...
as a world power. The Russians were in constant pursuit of a warm water port on the Pacific Ocean, for their navy as well as for maritime trade. The Manchurian Campaign of the Russian Empire
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was a state that existed from 1721 until the Russian Revolution of 1917. It was the successor to the Tsardom of Russia and the predecessor of the Soviet Union...
was fought against the Japanese over Manchuria
Manchuria
Manchuria is a historical name given to a large geographic region in northeast Asia. Depending on the definition of its extent, Manchuria usually falls entirely within the People's Republic of China, or is sometimes divided between China and Russia. The region is commonly referred to as Northeast...
and Korea
Korea
Korea ) is an East Asian geographic region that is currently divided into two separate sovereign states — North Korea and South Korea. Located on the Korean Peninsula, Korea is bordered by the People's Republic of China to the northwest, Russia to the northeast, and is separated from Japan to the...
. The major theatres of operations were Southern Manchuria, specifically the area around the Liaodong Peninsula and Mukden, and the seas around Korea, Japan, and the Yellow Sea
Yellow Sea
The Yellow Sea is the name given to the northern part of the East China Sea, which is a marginal sea of the Pacific Ocean. It is located between mainland China and the Korean Peninsula. Its name comes from the sand particles from Gobi Desert sand storms that turn the surface of the water golden...
. The resulting campaigns, in which the fledgling Japanese military consistently attained victory over the Russian forces arrayed against them, were unexpected by world observers. These victories, as time transpired, would dramatically transform the distribution of power in East Asia, resulting in a reassessment of Japan's recent entry onto the world stage. The embarrassing string of defeats increased Russian popular dissatisfaction with the inefficient and corrupt Tsarist government.
The Russian Revolution of 1905
Russian Revolution of 1905
The 1905 Russian Revolution was a wave of mass political and social unrest that spread through vast areas of the Russian Empire. Some of it was directed against the government, while some was undirected. It included worker strikes, peasant unrest, and military mutinies...
was a wave of mass political unrest through vast areas of the Russian Empire
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was a state that existed from 1721 until the Russian Revolution of 1917. It was the successor to the Tsardom of Russia and the predecessor of the Soviet Union...
. Some of it was directed against the government, while some was undirected. It included terrorism
Terrorism
Terrorism is the systematic use of terror, especially as a means of coercion. In the international community, however, terrorism has no universally agreed, legally binding, criminal law definition...
, worker strikes, peasant unrests, and military mutinies. It led to the establishment of the limited constitutional monarchy, the establishment of State Duma of the Russian Empire
State Duma of the Russian Empire
The State Duma of the Russian Empire was a legislative assembly in the late Russian Empire, which met in the Taurida Palace in St. Petersburg. It was convened four times between 1906 and the collapse of the Empire in 1917.-History:...
, the multi-party system
Multi-party system
A multi-party system is a system in which multiple political parties have the capacity to gain control of government separately or in coalition, e.g.The Conservative-Liberal Democrat coalition in the United Kingdom formed in 2010. The effective number of parties in a multi-party system is normally...
and Russian Constitution of 1906
Russian Constitution of 1906
The Russian Constitution of 1906 refers to a major revision of the 1832 Fundamental Laws of the Russian Empire, which transformed the formerly absolutist state into one in which the emperor agreed for the first time to share his autocratic power with a parliament. It was enacted on April 23, 1906,...
.
In China, the Qing Dynasty was overthrown following the Xinhai Revolution
Xinhai Revolution
The Xinhai Revolution or Hsinhai Revolution, also known as Revolution of 1911 or the Chinese Revolution, was a revolution that overthrew China's last imperial dynasty, the Qing , and established the Republic of China...
. The Xinhai Revolution began with the Wuchang Uprising
Wuchang Uprising
The Wuchang Uprising began with the dissatisfaction of the handling of a railway crisis. The crisis then escalated to an uprising where the revolutionaries went up against Qing government officials. The uprising was then assisted by the New Army in a coup against their own authorities in the city...
on October 10, 1911 and ended with the abdication of Emperor Puyi on February 12, 1912. The primary parties to the conflict were the Imperial forces of the Qing Dynasty
Qing Dynasty
The Qing Dynasty was the last dynasty of China, ruling from 1644 to 1912 with a brief, abortive restoration in 1917. It was preceded by the Ming Dynasty and followed by the Republic of China....
(1644–1911), and the revolutionary forces of the Chinese Revolutionary Alliance
Tongmenghui
The Tongmenghui, also known as the Chinese United League, United League, Chinese Revolutionary Alliance, Chinese Alliance and United Allegiance Society, was a secret society and underground resistance movement formed when merging many Chinese revolutionary groups together by Sun Yat-sen, Song...
(Tongmenghui).
Edwardian Britain
The Edwardian era in the United Kingdom is the period spanning the reign of King Edward VII
Edward VII of the United Kingdom
Edward VII was King of the United Kingdom and the British Dominions and Emperor of India from 22 January 1901 until his death in 1910...
up to the end of the First World War, including the years surrounding the sinking of the RMS Titanic. In the early years of the period, the Second Boer War
Second Boer War
The Second Boer War was fought from 11 October 1899 until 31 May 1902 between the British Empire and the Afrikaans-speaking Dutch settlers of two independent Boer republics, the South African Republic and the Orange Free State...
in South Africa split the country into anti- and pro-war factions. The imperial policies of the Conservatives eventually proved unpopular and in the general election of 1906
United Kingdom general election, 1906
-Seats summary:-See also:*MPs elected in the United Kingdom general election, 1906*The Parliamentary Franchise in the United Kingdom 1885-1918-External links:***-References:*F. W. S. Craig, British Electoral Facts: 1832-1987**...
the Liberals won a huge landslide. The Liberal government was unable to proceed with all of its radical programme without the support of the House of Lords
House of Lords
The House of Lords is the upper house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Like the House of Commons, it meets in the Palace of Westminster....
, which was largely Conservative. Conflict between the two Houses of Parliament over the People's Budget
People's Budget
The 1909 People's Budget was a product of then British Prime Minister H. H. Asquith's Liberal government, introducing many unprecedented taxes on the wealthy and radical social welfare programmes to Britain's political life...
led to a reduction in the power of the peers in 1910. The general election in January that year returned a hung parliament
Hung parliament
In a two-party parliamentary system of government, a hung parliament occurs when neither major political party has an absolute majority of seats in the parliament . It is also less commonly known as a balanced parliament or a legislature under no overall control...
with the balance of power held by Labour
Labour Party (UK)
The Labour Party is a centre-left democratic socialist party in the United Kingdom. It surpassed the Liberal Party in general elections during the early 1920s, forming minority governments under Ramsay MacDonald in 1924 and 1929-1931. The party was in a wartime coalition from 1940 to 1945, after...
and Irish Nationalist
Nationalist Party (Ireland)
The Nationalist Party was a term commonly used to describe a number of parliamentary political parties and constituency organisations supportive of Home Rule for Ireland from 1874 to 1922...
members.
World War I
The causes of World War I
Causes of World War I
The causes of World War I, which began in central Europe in July 1914, included many intertwined factors, such as the conflicts and hostility of the four decades leading up to the war. Militarism, alliances, imperialism, and nationalism played major roles in the conflict as well...
included many factors, including the conflicts and antagonisms of the four decades leading up to the war. The Triple Entente
Triple Entente
The Triple Entente was the name given to the alliance among Britain, France and Russia after the signing of the Anglo-Russian Entente in 1907....
was the name given to the loose alignment between the United Kingdom
British Empire
The British Empire comprised the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom. It originated with the overseas colonies and trading posts established by England in the late 16th and early 17th centuries. At its height, it was the...
, France
French Third Republic
The French Third Republic was the republican government of France from 1870, when the Second French Empire collapsed due to the French defeat in the Franco-Prussian War, to 1940, when France was overrun by Nazi Germany during World War II, resulting in the German and Italian occupations of France...
, and Russia
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was a state that existed from 1721 until the Russian Revolution of 1917. It was the successor to the Tsardom of Russia and the predecessor of the Soviet Union...
after the signing of the Anglo-Russian Entente
Anglo-Russian Entente
Signed on August 31, 1907, in St. Petersburg, Russia, the Anglo-Russian Convention of 1907 brought shaky British-Russian relations to the forefront by solidifying boundaries that identified respective control in Persia, Afghanistan, and Tibet...
in 1907. The alignment of the three powers, supplemented by various agreements with Japan
Empire of Japan
The Empire of Japan is the name of the state of Japan that existed from the Meiji Restoration on 3 January 1868 to the enactment of the post-World War II Constitution of...
, the United States, and Spain
Spain under the Restoration
The Restoration was the name given to the period that began on December 29, 1874 after the First Spanish Republic ended with the restoration of Alfonso XII to the throne after a coup d'état by Martinez Campos, and ended on April 14, 1931 with the proclamation of the Second Spanish Republic.After...
, constituted a powerful counterweight to the Triple Alliance
Triple Alliance (1882)
The Triple Alliance was the military alliance between Germany, Austria–Hungary, and Italy, , that lasted from 1882 until the start of World War I in 1914...
of Germany
German Empire
The German Empire refers to Germany during the "Second Reich" period from the unification of Germany and proclamation of Wilhelm I as German Emperor on 18 January 1871, to 1918, when it became a federal republic after defeat in World War I and the abdication of the Emperor, Wilhelm II.The German...
, Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary , more formally known as the Kingdoms and Lands Represented in the Imperial Council and the Lands of the Holy Hungarian Crown of Saint Stephen, was a constitutional monarchic union between the crowns of the Austrian Empire and the Kingdom of Hungary in...
, and Italy
Kingdom of Italy (1861–1946)
The Kingdom of Italy was a state forged in 1861 by the unification of Italy under the influence of the Kingdom of Sardinia, which was its legal predecessor state...
, the third having concluded an additional secret agreement with France effectively nullifying her Alliance commitments. Militarism, alliances, imperialism, and nationalism played major roles in the conflict. The immediate origins of the war lay in the decisions taken by statesmen and generals during the July crisis of 1914, the spark (or casus belli) for which was the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria.
However, the crisis did not exist in a void; it came after a long series of diplomatic clashes between the Great Powers over European and colonial issues in the decade prior to 1914 which had left tensions high. The diplomatic clashes can be traced to changes in the balance of power in Europe since 1870. An example is the Baghdad Railway
Baghdad Railway
The Baghdad Railway , was built from 1903 to 1940 to connect Berlin with the Ottoman Empire city of Baghdad with a line through modern-day Turkey, Syria, and Iraq....
which was planned to connect the Ottoman Empire
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman EmpireIt was usually referred to as the "Ottoman Empire", the "Turkish Empire", the "Ottoman Caliphate" or more commonly "Turkey" by its contemporaries...
cities of Konya
Konya
Konya is a city in the Central Anatolia Region of Turkey. The metropolitan area in the entire Konya Province had a population of 1,036,027 as of 2010, making the city seventh most populous in Turkey.-Etymology:...
and Baghdad
Baghdad
Baghdad is the capital of Iraq, as well as the coterminous Baghdad Governorate. The population of Baghdad in 2011 is approximately 7,216,040...
with a line through modern-day Turkey, Syria and Iraq. The railway became a source of international disputes during the years immediately preceding World War I. Although it has been argued that they were resolved in 1914 before the war began, it has also been argued that the railroad was a cause of the First World War. Fundamentally the war was sparked by tensions over territory in the Balkans
Balkans
The Balkans is a geopolitical and cultural region of southeastern Europe...
. Austria-Hungary competed with Serbia and Russia for territory and influence in the region and they pulled the rest of the great powers into the conflict through their various alliances and treaties. The Balkan Wars
Balkan Wars
The Balkan Wars were two conflicts that took place in the Balkans in south-eastern Europe in 1912 and 1913.By the early 20th century, Montenegro, Bulgaria, Greece and Serbia, the countries of the Balkan League, had achieved their independence from the Ottoman Empire, but large parts of their ethnic...
were two wars in South-eastern Europe in 1912–1913 in the course of which the Balkan League (Bulgaria, Montenegro, Greece, and Serbia) first captured Ottoman-held remaining part of Thessaly, Macedonia, Epirus, Albania and most of Thrace and then fell out over the division of the spoils, with incorporation of Romania this time.

Armistice with Germany (Compiègne)
The armistice between the Allies and Germany was an agreement that ended the fighting in the First World War. It was signed in a railway carriage in Compiègne Forest on 11 November 1918 and marked a victory for the Allies and a complete defeat for Germany, although not technically a surrender...
in 1918. The Allied Powers
Allies of World War I
The Entente Powers were the countries at war with the Central Powers during World War I. The members of the Triple Entente were the United Kingdom, France, and the Russian Empire; Italy entered the war on their side in 1915...
, led by the British Empire, France
French Third Republic
The French Third Republic was the republican government of France from 1870, when the Second French Empire collapsed due to the French defeat in the Franco-Prussian War, to 1940, when France was overrun by Nazi Germany during World War II, resulting in the German and Italian occupations of France...
, Russia until March 1918, Japan and the United States after 1917, defeated the Central Powers
Central Powers
The Central Powers were one of the two warring factions in World War I , composed of the German Empire, the Austro-Hungarian Empire, the Ottoman Empire, and the Kingdom of Bulgaria...
, led by the German Empire
German Empire
The German Empire refers to Germany during the "Second Reich" period from the unification of Germany and proclamation of Wilhelm I as German Emperor on 18 January 1871, to 1918, when it became a federal republic after defeat in World War I and the abdication of the Emperor, Wilhelm II.The German...
, Austro-Hungarian Empire and the Ottoman Empire
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman EmpireIt was usually referred to as the "Ottoman Empire", the "Turkish Empire", the "Ottoman Caliphate" or more commonly "Turkey" by its contemporaries...
. The war caused the disintegration of four empires — the Austro-Hungarian, German, Ottoman, and Russian ones — as well as radical change in the European and Middle Eastern maps. The Allied powers before 1917 are sometimes referred to as the Triple Entente
Triple Entente
The Triple Entente was the name given to the alliance among Britain, France and Russia after the signing of the Anglo-Russian Entente in 1907....
, and the Central Powers are sometimes referred to as the Triple Alliance
Triple Alliance (1882)
The Triple Alliance was the military alliance between Germany, Austria–Hungary, and Italy, , that lasted from 1882 until the start of World War I in 1914...
.
Much of the fighting in World War I took place along the Western Front
Western Front (World War I)
Following the outbreak of World War I in 1914, the German Army opened the Western Front by first invading Luxembourg and Belgium, then gaining military control of important industrial regions in France. The tide of the advance was dramatically turned with the Battle of the Marne...
, within a system of opposing manned trenches and fortifications (separated by a "No man's land
No man's land
No man's land is a term for land that is unoccupied or is under dispute between parties that leave it unoccupied due to fear or uncertainty. The term was originally used to define a contested territory or a dumping ground for refuse between fiefdoms...
") running from the North Sea
North Sea
In the southwest, beyond the Straits of Dover, the North Sea becomes the English Channel connecting to the Atlantic Ocean. In the east, it connects to the Baltic Sea via the Skagerrak and Kattegat, narrow straits that separate Denmark from Norway and Sweden respectively...
to the border of Switzerland. On the Eastern Front
Eastern Front (World War I)
The Eastern Front was a theatre of war during World War I in Central and, primarily, Eastern Europe. The term is in contrast to the Western Front. Despite the geographical separation, the events in the two theatres strongly influenced each other...
, the vast eastern plains and limited rail network prevented a trench warfare stalemate from developing, although the scale of the conflict was just as large. Hostilities also occurred on and under the sea and — for the first time — from the air. More than 9 million soldiers died on the various battlefields, and nearly that many more in the participating countries' home fronts on account of food shortages and genocide
Genocide
Genocide is defined as "the deliberate and systematic destruction, in whole or in part, of an ethnic, racial, religious, or national group", though what constitutes enough of a "part" to qualify as genocide has been subject to much debate by legal scholars...
committed under the cover of various civil wars and internal conflicts. Notably, more people died of the worldwide influenza outbreak
Spanish flu
The 1918 flu pandemic was an influenza pandemic, and the first of the two pandemics involving H1N1 influenza virus . It was an unusually severe and deadly pandemic that spread across the world. Historical and epidemiological data are inadequate to identify the geographic origin...
at the end of the war and shortly after than died in the hostilities. The unsanitary conditions engendered by the war, severe overcrowding in barracks, wartime propaganda interfering with public health warnings, and migration of so many soldiers around the world helped the outbreak become a pandemic
Pandemic
A pandemic is an epidemic of infectious disease that is spreading through human populations across a large region; for instance multiple continents, or even worldwide. A widespread endemic disease that is stable in terms of how many people are getting sick from it is not a pandemic...
.
Ultimately, World War I created a decisive break with the old world order that had emerged after the Napoleonic Wars
Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars were a series of wars declared against Napoleon's French Empire by opposing coalitions that ran from 1803 to 1815. As a continuation of the wars sparked by the French Revolution of 1789, they revolutionised European armies and played out on an unprecedented scale, mainly due to...
, which was modified by the mid-19th century's nationalistic revolutions. The results of World War I would be important factors in the development of World War II approximately 20 years later. More immediate to the time, the partitioning of the Ottoman Empire
Partitioning of the Ottoman Empire
The Partitioning of the Ottoman Empire was a political event that occurred after World War I. The huge conglomeration of territories and peoples formerly ruled by the Sultan of the Ottoman Empire was divided into several new nations.The partitioning was planned from the early days of the war,...
was a political event that redrew the political boundaries of the Middle East. The huge conglomeration of territories and peoples formerly ruled by the Sultan of the Ottoman Empire was divided into several new nations. The partitioning brought the creation of the modern Arab world
Arab world
The Arab world refers to Arabic-speaking states, territories and populations in North Africa, Western Asia and elsewhere.The standard definition of the Arab world comprises the 22 states and territories of the Arab League stretching from the Atlantic Ocean in the west to the Arabian Sea in the...
and the Republic of Turkey. The League of Nations
League of Nations
The League of Nations was an intergovernmental organization founded as a result of the Paris Peace Conference that ended the First World War. It was the first permanent international organization whose principal mission was to maintain world peace...
granted France mandates over Syria
French Mandate of Syria
Officially the French Mandate for Syria and the Lebanon was a League of Nations mandate founded after the First World War and the partitioning of the Ottoman Empire...
and Lebanon
French Mandate of Lebanon
The state of Greater Lebanon, the predecessor of modern Lebanon, was created in 1920 as part of the French scheme of dividing the French Mandate of Syria into six states....
and granted the United Kingdom mandates over Mesopotamia and Palestine (which was later divided into two regions: Palestine
Palestine
Palestine is a conventional name, among others, used to describe the geographic region between the Mediterranean Sea and the Jordan River, and various adjoining lands....
and Transjordan
Transjordan
The Emirate of Transjordan was a former Ottoman territory in the Southern Levant that was part of the British Mandate of Palestine...
). Parts of the Ottoman Empire on the Arabian Peninsula
Arabian Peninsula
The Arabian Peninsula is a land mass situated north-east of Africa. Also known as Arabia or the Arabian subcontinent, it is the world's largest peninsula and covers 3,237,500 km2...
became parts of what are today Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia
The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia , commonly known in British English as Saudi Arabia and in Arabic as as-Sa‘ūdiyyah , is the largest state in Western Asia by land area, constituting the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and the second-largest in the Arab World...
and Yemen
Yemen
The Republic of Yemen , commonly known as Yemen , is a country located in the Middle East, occupying the southwestern to southern end of the Arabian Peninsula. It is bordered by Saudi Arabia to the north, the Red Sea to the west, and Oman to the east....
.
Revolutions and war

Tsarist autocracy
The Tsarist autocracy |transcr.]] tsarskoye samoderzhaviye) refers to a form of autocracy specific to the Grand Duchy of Muscovy . In a tsarist autocracy, all power and wealth is controlled by the tsar...
and led to the creation of the Soviet Union. Following the abdication of Nicholas II of Russia
Nicholas II of Russia
Nicholas II was the last Emperor of Russia, Grand Prince of Finland, and titular King of Poland. His official short title was Nicholas II, Emperor and Autocrat of All the Russias and he is known as Saint Nicholas the Passion-Bearer by the Russian Orthodox Church.Nicholas II ruled from 1894 until...
, the Russian Provisional Government
Russian Provisional Government
The Russian Provisional Government was the short-lived administrative body which sought to govern Russia immediately following the abdication of Tsar Nicholas II . On September 14, the State Duma of the Russian Empire was officially dissolved by the newly created Directorate, and the country was...
was established. In October 1917, a red faction revolution
October Revolution
The October Revolution , also known as the Great October Socialist Revolution , Red October, the October Uprising or the Bolshevik Revolution, was a political revolution and a part of the Russian Revolution of 1917...
occurred in which the Red Guard
Red Guards (Russia)
In the context of the history of Russia and Soviet Union, Red Guards were paramilitary formations consisting of workers and partially of soldiers and sailors formed in the time frame of the Russian Revolution of 1917...
, armed groups of workers and deserting soldiers directed by the Bolshevik Party, seized control of Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg is a city and a federal subject of Russia located on the Neva River at the head of the Gulf of Finland on the Baltic Sea...
(then known as Petrograd) and began an immediate armed takeover of cities and villages throughout the former Russian Empire
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was a state that existed from 1721 until the Russian Revolution of 1917. It was the successor to the Tsardom of Russia and the predecessor of the Soviet Union...
.
Another action in 1917 that is of note was the armistice signed between Russia and the Central Powers at Brest-Litovsk. As a condition for peace, the treaty by the Central Powers
Central Powers
The Central Powers were one of the two warring factions in World War I , composed of the German Empire, the Austro-Hungarian Empire, the Ottoman Empire, and the Kingdom of Bulgaria...
conceded huge portions of the former Russian Empire to Imperial Germany
German Empire
The German Empire refers to Germany during the "Second Reich" period from the unification of Germany and proclamation of Wilhelm I as German Emperor on 18 January 1871, to 1918, when it became a federal republic after defeat in World War I and the abdication of the Emperor, Wilhelm II.The German...
and the Ottoman Empire, greatly upsetting nationalists and conservative
Conservatism
Conservatism is a political and social philosophy that promotes the maintenance of traditional institutions and supports, at the most, minimal and gradual change in society. Some conservatives seek to preserve things as they are, emphasizing stability and continuity, while others oppose modernism...
s. The Bolsheviks made peace with the German Empire
German Empire
The German Empire refers to Germany during the "Second Reich" period from the unification of Germany and proclamation of Wilhelm I as German Emperor on 18 January 1871, to 1918, when it became a federal republic after defeat in World War I and the abdication of the Emperor, Wilhelm II.The German...
and the Central Powers
Central Powers
The Central Powers were one of the two warring factions in World War I , composed of the German Empire, the Austro-Hungarian Empire, the Ottoman Empire, and the Kingdom of Bulgaria...
, as they had promised the Russian people prior to the Revolution. Vladimir Lenin's decision has been attributed to his sponsorship by the foreign office of Wilhelm II, German Emperor, offered by the latter in hopes that with a revolution, Russia would withdraw from World War I. This suspicion was bolstered by the German Foreign Ministry's sponsorship of Lenin's return to Petrograd
Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg is a city and a federal subject of Russia located on the Neva River at the head of the Gulf of Finland on the Baltic Sea...
. The Western Allies
Triple Entente
The Triple Entente was the name given to the alliance among Britain, France and Russia after the signing of the Anglo-Russian Entente in 1907....
, expressed their dismay at the Bolsheviks, upset at:
- the withdrawal of Russia from the war effort,
- worried about a possible Russo-German alliance, and
- galvanized by the prospect of the Bolsheviks making good their threats to assume no responsibility for, and so default on, Imperial Russia's massive foreign loansExternal debtExternal debt is that part of the total debt in a country that is owed to creditors outside the country. The debtors can be the government, corporations or private households. The debt includes money owed to private commercial banks, other governments, or international financial institutions such...
.
In addition, there was a concern, shared by many Central Powers
Central Powers
The Central Powers were one of the two warring factions in World War I , composed of the German Empire, the Austro-Hungarian Empire, the Ottoman Empire, and the Kingdom of Bulgaria...
as well, that the socialist revolutionary ideas would spread to the West. Hence, many of these countries expressed their support for the Whites, including the provision of troops and supplies. Winston Churchill
Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer-Churchill, was a predominantly Conservative British politician and statesman known for his leadership of the United Kingdom during the Second World War. He is widely regarded as one of the greatest wartime leaders of the century and served as Prime Minister twice...
declared that Bolshevism must be "strangled in its cradle".
The Russian Civil War
Russian Civil War
The Russian Civil War was a multi-party war that occurred within the former Russian Empire after the Russian provisional government collapsed to the Soviets, under the domination of the Bolshevik party. Soviet forces first assumed power in Petrograd The Russian Civil War (1917–1923) was a...
was a multi-party war that occurred within the former Russian Empire
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was a state that existed from 1721 until the Russian Revolution of 1917. It was the successor to the Tsardom of Russia and the predecessor of the Soviet Union...
after the Russian provisional government
Russian Provisional Government
The Russian Provisional Government was the short-lived administrative body which sought to govern Russia immediately following the abdication of Tsar Nicholas II . On September 14, the State Duma of the Russian Empire was officially dissolved by the newly created Directorate, and the country was...
collapsed and the Soviets
Soviet republic (system of government)
A Soviet Republic is a system of government in which the whole state power belongs to the Soviets . Although the term is usually associated with communist states, it was not initially intended to represent only one political force, but merely a form of democracy and representation.In the classic...
under the domination of the Bolshevik
Bolshevik
The Bolsheviks, originally also Bolshevists , derived from bol'shinstvo, "majority") were a faction of the Marxist Russian Social Democratic Labour Party which split apart from the Menshevik faction at the Second Party Congress in 1903....
party assumed power, first in Petrograd (St. Petersburg)
Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg is a city and a federal subject of Russia located on the Neva River at the head of the Gulf of Finland on the Baltic Sea...
and then in other places. In the wake of the October Revolution
October Revolution
The October Revolution , also known as the Great October Socialist Revolution , Red October, the October Uprising or the Bolshevik Revolution, was a political revolution and a part of the Russian Revolution of 1917...
, the old Russian Imperial Army had been demobilized; the volunteer-based Red Guard was the Bolsheviks' main military force, augmented by an armed military component of the Cheka
Cheka
Cheka was the first of a succession of Soviet state security organizations. It was created by a decree issued on December 20, 1917, by Vladimir Lenin and subsequently led by aristocrat-turned-communist Felix Dzerzhinsky...
, the Bolshevik state security apparatus. There was an instituted mandatory conscription of the rural peasantry into the Red Army. Opposition of rural Russians to Red Army conscription units was overcome by taking hostages and shooting them when necessary in order to force compliance. Former Tsarist officers were utilized as "military specialists" (voenspetsy), sometimes taking their families hostage in order to ensure loyalty. At the start of the war, three-fourths of the Red Army officer corps was composed of former Tsarist officers. By its end, 83% of all Red Army divisional and corps commanders were ex-Tsarist soldiers.
The principal fighting occurred between the Bolshevik
Bolshevik
The Bolsheviks, originally also Bolshevists , derived from bol'shinstvo, "majority") were a faction of the Marxist Russian Social Democratic Labour Party which split apart from the Menshevik faction at the Second Party Congress in 1903....
Red Army
Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army started out as the Soviet Union's revolutionary communist combat groups during the Russian Civil War of 1918-1922. It grew into the national army of the Soviet Union. By the 1930s the Red Army was among the largest armies in history.The "Red Army" name refers to...
and the forces of the White Army
White movement
The White movement and its military arm the White Army - known as the White Guard or the Whites - was a loose confederation of Anti-Communist forces.The movement comprised one of the politico-military Russian forces who fought...
. Many foreign armies warred against the Red Army, notably the Allied Forces
Allied Intervention in the Russian Civil War
The Allied intervention was a multi-national military expedition launched in 1918 during World War I which continued into the Russian Civil War. Its operations included forces from 14 nations and were conducted over a vast territory...
, yet many volunteer foreigners fought in both sides of the Russian Civil War. Other nationalist and regional political groups also participated in the war, including the Ukrainian nationalist Green Army, the Ukrainian anarchist Black Army
Revolutionary Insurrectionary Army of Ukraine
The Revolutionary Insurrectionary Army of Ukraine , popularly called Makhnovshchina, less correctly Makhnovchina, and also known as the Black Army, was an anarchist army formed largely of Ukrainian and Crimean peasants and workers under the command of the famous anarchist Nestor Makhno during the...
and Black Guards
Black Guards
Black Guards were armed groups of workers formed after the Russian Revolution and before the Third Russian Revolution. They were the main strike force of the anarchists...
, and warlords such as Ungern von Sternberg. The most intense fighting took place from 1918 to 1920. Major military operations ended on 25 October 1922 when the Red Army occupied Vladivostok
Vladivostok
The city is located in the southern extremity of Muravyov-Amursky Peninsula, which is about 30 km long and approximately 12 km wide.The highest point is Mount Kholodilnik, the height of which is 257 m...
, previously held by the Provisional Priamur Government. The last enclave of the White Forces was the Ayano-Maysky District
Ayano-Maysky District
Ayano-Maysky District is an administrative and municipal district , one of the seventeen in Khabarovsk Krai, Russia. Its administrative center is the rural locality of Ayan. District's population: Population of Ayan accounts for 40.5% of the district's population.-Geography:The district has...
on the Pacific coast. The majority of the fighting ended in 1920 with the defeat of General Pyotr Wrangel in the Crimea
Crimea
Crimea , or the Autonomous Republic of Crimea , is a sub-national unit, an autonomous republic, of Ukraine. It is located on the northern coast of the Black Sea, occupying a peninsula of the same name...
, but a notable resistance in certain areas continued until 1923 (e.g., Kronstadt Uprising, Tambov Rebellion
Tambov Rebellion
The Tambov Rebellion which occurred between 1920 and 1921 was one of the largest and best-organized peasant rebellions challenging the Bolshevik regime during the Russian Civil War. The uprising took place in the territories of the modern Tambov Oblast and part of the Voronezh Oblast, less than...
, Basmachi Revolt
Basmachi Revolt
The Basmachi movement or Basmachi Revolt was an uprising against Russian Imperial and Soviet rule by the Muslim, largely Turkic peoples of Central Asia....
, and the final resistance of the White movement
White movement
The White movement and its military arm the White Army - known as the White Guard or the Whites - was a loose confederation of Anti-Communist forces.The movement comprised one of the politico-military Russian forces who fought...
in the Far East
Russian Far East
Russian Far East is a term that refers to the Russian part of the Far East, i.e., extreme east parts of Russia, between Lake Baikal in Eastern Siberia and the Pacific Ocean...
).
In 1917, China declared war on Germany in the hope of recovering its lost province, then under Japanese control. The New Culture Movement
New Culture Movement
The New Culture Movement of the mid 1910s and 1920s sprang from the disillusionment with traditional Chinese culture following the failure of the Chinese Republic, founded in 1912 to address China’s problems. Scholars like Chen Duxiu, Cai Yuanpei, Li Dazhao, Lu Xun, Zhou Zuoren, and Hu Shi, had...
occupied the period from 1917 to 1923. Chinese representatives refused to sign the Treaty of Versailles
Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles was one of the peace treaties at the end of World War I. It ended the state of war between Germany and the Allied Powers. It was signed on 28 June 1919, exactly five years after the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand. The other Central Powers on the German side of...
, due to intense pressure from the student protesters and public opinion alike.
The May Fourth Movement helped to rekindle the then-fading cause of republican revolution. In 1917 Sun Yat-sen
Sun Yat-sen
Sun Yat-sen was a Chinese doctor, revolutionary and political leader. As the foremost pioneer of Nationalist China, Sun is frequently referred to as the "Father of the Nation" , a view agreed upon by both the People's Republic of China and the Republic of China...
had become commander-in-chief of a rival military government in Guangzhou
Guangzhou
Guangzhou , known historically as Canton or Kwangchow, is the capital and largest city of the Guangdong province in the People's Republic of China. Located in southern China on the Pearl River, about north-northwest of Hong Kong, Guangzhou is a key national transportation hub and trading port...
in collaboration with southern warlords. Sun efforts to obtain aid from the Western democracies were ignored, however, and in 1920 he turned to the Soviet Union, which had recently achieved its own revolution. The Soviets sought to befriend the Chinese revolutionists by offering scathing attacks on Western imperialism. But for political expediency, the Soviet leadership initiated a dual policy of support for both Sun and the newly established Chinese Communist Party (CCP).

Kuomintang
The Kuomintang of China , sometimes romanized as Guomindang via the Pinyin transcription system or GMD for short, and translated as the Chinese Nationalist Party is a founding and ruling political party of the Republic of China . Its guiding ideology is the Three Principles of the People, espoused...
and Chiang Kai-shek
Chiang Kai-shek
Chiang Kai-shek was a political and military leader of 20th century China. He is known as Jiǎng Jièshí or Jiǎng Zhōngzhèng in Mandarin....
had been recommended by the Dutch
Netherlands
The Netherlands is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, located mainly in North-West Europe and with several islands in the Caribbean. Mainland Netherlands borders the North Sea to the north and west, Belgium to the south, and Germany to the east, and shares maritime borders...
Communist Henk Sneevliet
Henk Sneevliet
Hendricus Josephus Franciscus Marie Sneevliet, known as Henk Sneevliet or the pseudonym Maring , was a Dutch Communist, who was active in both the Netherlands and the Dutch East-Indies...
, chosen in 1923 to be the Comintern
Comintern
The Communist International, abbreviated as Comintern, also known as the Third International, was an international communist organization initiated in Moscow during March 1919...
representative in China due to his revolutionary experience in the Dutch Indies, where he had a major role in founding the Partai Komunis Indonesia (PKI) - and who felt that the Chinese party was too small and weak to undertake a major effort on its own (see Henk Sneevliet's work for the Comintern).
In early 1927, the Kuomintang-CCP rivalry led to a split in the revolutionary ranks. The CCP and the left wing of the Kuomintang had decided to move the seat of the Nationalist government from Guangzhou to Wuhan
Wuhan
Wuhan is the capital of Hubei province, People's Republic of China, and is the most populous city in Central China. It lies at the east of the Jianghan Plain, and the intersection of the middle reaches of the Yangtze and Han rivers...
. But Chiang Kai-shek
Chiang Kai-shek
Chiang Kai-shek was a political and military leader of 20th century China. He is known as Jiǎng Jièshí or Jiǎng Zhōngzhèng in Mandarin....
, whose Northern Expedition was proving successful, set his forces to destroying the Shanghai CCP apparatus and established an anti-Communist government at Nanjing in April 1927 - bloody events
April 12 Incident
The April 12 Incident of 1927 refers to the violent suppression of Chinese Communist Party organizations in Shanghai by the military forces of Chiang Kai-shek and conservative factions in the Kuomintang...
.
The Twenties and the Depression
The interwar period
Interwar period
Interwar period can refer to any period between two wars. The Interbellum is understood to be the period between the end of the Great War or First World War and the beginning of the Second World War in Europe....
was the period between the end of the First World War and the beginning of the Second World War. This period was marked by turmoil in much of the world, as Europe struggled to recover from the devastation of the First World War.
In North America, especially the first half of this period, people experienced considerable prosperity in the Roaring Twenties
Roaring Twenties
The Roaring Twenties is a phrase used to describe the 1920s, principally in North America, but also in London, Berlin and Paris for a period of sustained economic prosperity. The phrase was meant to emphasize the period's social, artistic, and cultural dynamism...
. The social and societal upheaval known as the Roaring Twenties began in North America and spread to Europe in the aftermath of World War I
Aftermath of World War I
The fighting in World War I ended in western Europe when the Armistice took effect at 11:00 am GMT on November 11, 1918, and in eastern Europe by the early 1920s. During and in the aftermath of the war the political, cultural, and social order was drastically changed in Europe, Asia and Africa,...
. The Roaring Twenties, often called "The Jazz Age
Jazz Age
The Jazz Age was a movement that took place during the 1920s or the Roaring Twenties from which jazz music and dance emerged. The movement came about with the introduction of mainstream radio and the end of the war. This era ended in the 1930s with the beginning of The Great Depression but has...
", saw a exposition of social, artistic, and cultural dynamism. 'Normalcy
Normalcy
"A return to normalcy" was United States presidential candidate Warren G. Harding’s campaign promise in the election of 1920...
' returned to politics, jazz music blossomed, the flapper
Flapper
Flapper in the 1920s was a term applied to a "new breed" of young Western women who wore short skirts, bobbed their hair, listened to jazz, and flaunted their disdain for what was then considered acceptable behavior...
redefined modern womanhood, Art Deco
Art Deco
Art deco , or deco, is an eclectic artistic and design style that began in Paris in the 1920s and flourished internationally throughout the 1930s, into the World War II era. The style influenced all areas of design, including architecture and interior design, industrial design, fashion and...
peaked. The spirit of the Roaring Twenties was marked by a general feeling of discontinuity associated with modernity, a break with traditions. Everything seemed to be feasible through modern technology. New technologies, especially automobiles, movies and radio proliferated 'modernity' to a large part of the population. The Twenties saw the general favor of practicality, in architecture as well as in daily life. The Twenties was further distinguished by several inventions and discoveries, extensive industrial growth and the rise in consumer demand and aspirations, and significant changes in lifestyle.
Europe spent these years rebuilding and coming to terms with the vast human cost of the conflict. The economy of the United States became increasingly intertwined with that of Europe. In Germany, the Weimar Republic
Weimar Republic
The Weimar Republic is the name given by historians to the parliamentary republic established in 1919 in Germany to replace the imperial form of government...
gave way to episodes of political and economic turmoil, which culminated with the German hyperinflation
Hyperinflation
In economics, hyperinflation is inflation that is very high or out of control. While the real values of the specific economic items generally stay the same in terms of relatively stable foreign currencies, in hyperinflationary conditions the general price level within a specific economy increases...
of 1923 and the failed Beer Hall Putsch
Beer Hall Putsch
The Beer Hall Putsch was a failed attempt at revolution that occurred between the evening of 8 November and the early afternoon of 9 November 1923, when Nazi Party leader Adolf Hitler, Generalquartiermeister Erich Ludendorff, and other heads of the Kampfbund unsuccessfully tried to seize power...
of that same year. When Germany could no longer afford war payments, Wall Street invested heavily in European debts to keep the European economy afloat as a large consumer market for American mass produced goods. By the middle of the decade, economic development
Economic development
Economic development generally refers to the sustained, concerted actions of policymakers and communities that promote the standard of living and economic health of a specific area...
soared in Europe, and the Roaring Twenties broke out in Germany, Britain and France, the second half of the decade becoming known as the "Golden Twenties
Golden Twenties
Golden Twenties or Happy Twenties is a term, mostly used in Europe, to describe the 1920s, in which most of the continent had an economic boom following the First World War and the severe economic downturns that took place between 1919–1923, and before the Wall Street Crash in 1929.It is often...
". In France and francophone Canada, they were also called the "années folles" ("Crazy Years").
Worldwide prosperity changed dramatically with the onset of the Great Depression
Great Depression
The Great Depression was a severe worldwide economic depression in the decade preceding World War II. The timing of the Great Depression varied across nations, but in most countries it started in about 1929 and lasted until the late 1930s or early 1940s...
in 1929. The Wall Street Crash of 1929
Wall Street Crash of 1929
The Wall Street Crash of 1929 , also known as the Great Crash, and the Stock Market Crash of 1929, was the most devastating stock market crash in the history of the United States, taking into consideration the full extent and duration of its fallout...
served to punctuate the end of the previous era, as The Great Depression set in. The Great Depression was a worldwide economic downturn
Recession
In economics, a recession is a business cycle contraction, a general slowdown in economic activity. During recessions, many macroeconomic indicators vary in a similar way...
starting in most places in 1929 and ending at different times in the 1930s or early 1940s for different countries. It was the largest and most important economic depression
Depression (economics)
In economics, a depression is a sustained, long-term downturn in economic activity in one or more economies. It is a more severe downturn than a recession, which is seen by some economists as part of the modern business cycle....
in the 20th century, and is used in the 21st century as an example of how far the world's economy can fall.
The depression had devastating effects in virtually every country, rich or poor. International trade plunged by half to two-thirds, as did personal income, tax revenue, prices and profits. Cities all around the world
Cities in the Great Depression
Throughout the industrial world, cities in the Great Depression were hit hard, beginning in 1929 and lasting through most of the 1930s. Worst hit were ports and cities dependent on heavy industry, such as steel and automobiles. Service-oriented cities were less hurt...
were hit hard, especially those dependent on heavy industry
Heavy industry
Heavy industry does not have a single fixed meaning as compared to light industry. It can mean production of products which are either heavy in weight or in the processes leading to their production. In general, it is a popular term used within the name of many Japanese and Korean firms, meaning...
. Construction was virtually halted in many countries. Farming and rural areas suffered as crop prices fell by roughly 60 percent. Facing plummeting demand with few alternate sources of jobs, areas dependent on primary sector industries suffered the most.
The Great Depression ended at different times in different countries with the effect lasting into the next era
Home front during World War II
The home front covers the activities of the civilians in a nation at war. World War II was a total war; homeland production became even more invaluable to both the Allied and Axis powers. Life on the home front during World War II was a significant part of the war effort for all participants and...
. America's Great Depression ended in 1941 with America's entry into World War II. The majority of countries set up relief programs, and most underwent some sort of political upheaval, pushing them to the left or right. In some world states, the desperate citizens turned toward nationalist demagogues
Demagogy
Demagogy or demagoguery is a strategy for gaining political power by appealing to the prejudices, emotions, fears, vanities and expectations of the public—typically via impassioned rhetoric and propaganda, and often using nationalist, populist or religious themes...
— the most infamous being Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler was an Austrian-born German politician and the leader of the National Socialist German Workers Party , commonly referred to as the Nazi Party). He was Chancellor of Germany from 1933 to 1945, and head of state from 1934 to 1945...
— setting the stage for the next era of war. The convulsion brought on by the worldwide depression resulted in the rise of Nazism
Nazism
Nazism, the common short form name of National Socialism was the ideology and practice of the Nazi Party and of Nazi Germany...
. In Asia, Japan became an ever more assertive power, especially with regards to China.
Nanjing period

Nanjing decade
The Nanjing decade was the decade from 1927 to 1937 in the Republic of China. It began when Nationalist Generalissimo Chiang Kai-shek took the city from Zhili clique warlord Sun Chuanfang halfway through the Northern Expedition in 1927. He declared it to be the national capital despite the...
" of 1928-37 was one of consolidation and accomplishment under the leadership of the Nationalists, with a mixed but generally positive record in the economy, social progress, development of democracy
Democracy in China
Democracy was a major concept introduced to China in the late nineteenth century. The debate over its form and definition as well as application was one of the major ideological battlegrounds in Chinese politics for well over a century. It is still a contentious subject...
, and cultural creativity. Some of the harsh aspects of foreign concessions and privileges in China were moderated through diplomacy.
The League and crises
The interwar period was also marked by a radical change in the international order, away from the balance of power
Balance of power in international relations
In international relations, a balance of power exists when there is parity or stability between competing forces. The concept describes a state of affairs in the international system and explains the behavior of states in that system...
that had dominated pre–World War I Europe. One main institution that was meant to bring stability was the League of Nations
League of Nations
The League of Nations was an intergovernmental organization founded as a result of the Paris Peace Conference that ended the First World War. It was the first permanent international organization whose principal mission was to maintain world peace...
, which was created after the First World War with the intention of maintaining world security and peace and encouraging economic growth between member countries. The League was undermined by the bellicosity of Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany , also known as the Third Reich , but officially called German Reich from 1933 to 1943 and Greater German Reich from 26 June 1943 onward, is the name commonly used to refer to the state of Germany from 1933 to 1945, when it was a totalitarian dictatorship ruled by...
, Imperial Japan, the Soviet Union, and Mussolini's
Benito Mussolini
Benito Amilcare Andrea Mussolini was an Italian politician who led the National Fascist Party and is credited with being one of the key figures in the creation of Fascism....
Italy, and by the non-participation of the United States, leading many to question its effectiveness and legitimacy.
A series of international crises strained the League to its limits, the earliest being the invasion of Manchuria by Japan and the Abyssinian crisis of 1935/36 in which Italy invaded Abyssinia
Ethiopian Empire
The Ethiopian Empire also known as Abyssinia, covered a geographical area that the present-day northern half of Ethiopia and Eritrea covers, and included in its peripheries Zeila, Djibouti, Yemen and Western Saudi Arabia...
, one of the only free African nations at that time. The League tried to enforce economic sanctions upon Italy, but to no avail. The incident highlighted French and British weakness, exemplified by their reluctance to alienate Italy and lose her as their ally. The limited actions taken by the Western powers pushed Mussolini's Italy towards alliance with Hitler's Germany anyway. The Abyssinian war showed Hitler how weak the League was and encouraged the remilitarization of the Rhineland in flagrant disregard of the Treaty of Versailles. This was the first in a series of provocative acts culminating in the invasion of Poland
Invasion of Poland (1939)
The Invasion of Poland, also known as the September Campaign or 1939 Defensive War in Poland and the Poland Campaign in Germany, was an invasion of Poland by Germany, the Soviet Union, and a small Slovak contingent that marked the start of World War II in Europe...
in September 1939 and the beginning of the Second World War.
Few Chinese had any illusions about Japanese designs on China. Hungry for raw materials and pressed by a growing population, Japan initiated the seizure of Manchuria
Manchuria
Manchuria is a historical name given to a large geographic region in northeast Asia. Depending on the definition of its extent, Manchuria usually falls entirely within the People's Republic of China, or is sometimes divided between China and Russia. The region is commonly referred to as Northeast...
in September 1931 and established ex-Qing emperor Puyi
Puyi
Puyi , of the Manchu Aisin Gioro clan, was the last Emperor of China, and the twelfth and final ruler of the Qing Dynasty. He ruled as the Xuantong Emperor from 1908 until his abdication on 12 February 1912. From 1 to 12 July 1917 he was briefly restored to the throne as a nominal emperor by the...
as head of the puppet state
Puppet state
A puppet state is a nominal sovereign of a state who is de facto controlled by a foreign power. The term refers to a government controlled by the government of another country like a puppeteer controls the strings of a marionette...
of Manchukuo
Manchukuo
Manchukuo or Manshū-koku was a puppet state in Manchuria and eastern Inner Mongolia, governed under a form of constitutional monarchy. The region was the historical homeland of the Manchus, who founded the Qing Empire in China...
in 1932. During the Sino-Japanese War (1937-1945), the loss of Manchuria, and its vast potential for industrial development and war industries, was a blow to the Kuomintang economy. The League of Nations
League of Nations
The League of Nations was an intergovernmental organization founded as a result of the Paris Peace Conference that ended the First World War. It was the first permanent international organization whose principal mission was to maintain world peace...
, established at the end of World War I, was unable to act in the face of the Japanese defiance. After 1940, conflicts between the Kuomintang and Communists became more frequent in the areas not under Japanese control
Free China (Second Sino-Japanese War)
The term Free China, in the context of the Second Sino-Japanese War, refers to those areas of China not under the control of the Imperial Japanese Army or any of its puppet governments, such as Manchukuo, the Mengjiang government in Suiyuan and Chahar, or the Provisional Government of the Republic...
. The Communists expanded their influence wherever opportunities presented themselves through mass organizations, administrative reforms, and the land- and tax-reform measures favoring the peasants — while the Kuomintang attempted to neutralize the spread of Communist influence.
Tripartite Pact
The Second Sino-Japanese War
Second Sino-Japanese War
The Second Sino-Japanese War was a military conflict fought primarily between the Republic of China and the Empire of Japan. From 1937 to 1941, China fought Japan with some economic help from Germany , the Soviet Union and the United States...
had seen tensions rise between Imperial Japan and the United States; events such as the Panay incident
Panay incident
The USS Panay Incident was a Japanese attack on the American gunboat while she was anchored in the Yangtze River outside Nanking , China on December 12, 1937. Japan and the United States were not at war at the time. The Japanese claimed that they did not see the American flags painted on the deck...
and the Nanking Massacre
Nanking Massacre
The Nanking Massacre or Nanjing Massacre, also known as the Rape of Nanking, was a mass murder, genocide and war rape that occurred during the six-week period following the Japanese capture of the city of Nanjing , the former capital of the Republic of China, on December 13, 1937 during the Second...
turned American public opinion against Japan. With the occupation of French Indochina
French Indochina
French Indochina was part of the French colonial empire in southeast Asia. A federation of the three Vietnamese regions, Tonkin , Annam , and Cochinchina , as well as Cambodia, was formed in 1887....
in the years of 1940–41, and with the continuing war in China, the United States placed embargoes on Japan of strategic materials such as scrap metal and oil, which were vitally needed for the war effort. The Japanese were faced with the option of either withdrawing from China and losing face or seizing and securing new sources of raw materials in the resource-rich, European-controlled colonies of South East Asia—specifically British Malaya
British Malaya
British Malaya loosely described a set of states on the Malay Peninsula and the Island of Singapore that were brought under British control between the 18th and the 20th centuries...
and the Dutch East Indies
Dutch East Indies
The Dutch East Indies was a Dutch colony that became modern Indonesia following World War II. It was formed from the nationalised colonies of the Dutch East India Company, which came under the administration of the Netherlands government in 1800....
(modern-day Indonesia
Indonesia
Indonesia , officially the Republic of Indonesia , is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania. Indonesia is an archipelago comprising approximately 13,000 islands. It has 33 provinces with over 238 million people, and is the world's fourth most populous country. Indonesia is a republic, with an...
). In 1940, Imperial Japan signed the Tripartite Pact
Tripartite Pact
The Tripartite Pact, also the Three-Power Pact, Axis Pact, Three-way Pact or Tripartite Treaty was a pact signed in Berlin, Germany on September 27, 1940, which established the Axis Powers of World War II...
with Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy.
World War II
The Second World War was a global
World war
A world war is a war affecting the majority of the world's most powerful and populous nations. World wars span multiple countries on multiple continents, with battles fought in multiple theaters....
military conflict
War
War is a state of organized, armed, and often prolonged conflict carried on between states, nations, or other parties typified by extreme aggression, social disruption, and usually high mortality. War should be understood as an actual, intentional and widespread armed conflict between political...
that took place in 1939–1945. It was the largest and deadliest war in history, culminating in the Holocaust and ending with the dropping of the atom bomb.

Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany , also known as the Third Reich , but officially called German Reich from 1933 to 1943 and Greater German Reich from 26 June 1943 onward, is the name commonly used to refer to the state of Germany from 1933 to 1945, when it was a totalitarian dictatorship ruled by...
invaded Poland, the Drang nach Osten
Drang nach Osten
Drang nach Osten was a term coined in the 19th century to designate German expansion into Slavic lands. The term became a motto of the German nationalist movement in the late nineteenth century...
. Within two days the United Kingdom and France declared war on Germany, even though the fighting was confined to Poland. Pursuant to a then-secret provision of its non-aggression Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact
Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact
The Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact, named after the Soviet foreign minister Vyacheslav Molotov and the German foreign minister Joachim von Ribbentrop, was an agreement officially titled the Treaty of Non-Aggression between Germany and the Soviet Union and signed in Moscow in the late hours of 23 August 1939...
, the Soviet Union joined with Germany on September 17, 1939, to conquer Poland and to divide Eastern Europe.
The Allies
Allies of World War II
The Allies of World War II were the countries that opposed the Axis powers during the Second World War . Former Axis states contributing to the Allied victory are not considered Allied states...
were initially made up of Poland, the United Kingdom, France, Australia, Canada, New Zealand, South Africa, as well as British Commonwealth
Commonwealth of Nations
The Commonwealth of Nations, normally referred to as the Commonwealth and formerly known as the British Commonwealth, is an intergovernmental organisation of fifty-four independent member states...
countries which were controlled directly by the UK, such as the Indian Empire
British Raj
British Raj was the British rule in the Indian subcontinent between 1858 and 1947; The term can also refer to the period of dominion...
. All of these countries declared war on Germany in September 1939.
Following the lull in fighting, known as the "Phoney War", Germany invaded western Europe in May 1940. Six weeks later, France, in the mean time attacked by Italy as well, surrendered to Germany, which then tried unsuccessfully to conquer Britain. On September 27, Germany, Italy, and Japan signed a mutual defense agreement, the Tripartite Pact
Tripartite Pact
The Tripartite Pact, also the Three-Power Pact, Axis Pact, Three-way Pact or Tripartite Treaty was a pact signed in Berlin, Germany on September 27, 1940, which established the Axis Powers of World War II...
, and were known as the Axis Powers
Axis Powers
The Axis powers , also known as the Axis alliance, Axis nations, Axis countries, or just the Axis, was an alignment of great powers during the mid-20th century that fought World War II against the Allies. It began in 1936 with treaties of friendship between Germany and Italy and between Germany and...
.
Nine months later, on June 22, 1941, Germany launched a massive invasion of the Soviet Union, which promptly joined the Allies. Germany was now engaged in fighting a war on two fronts. This proved to be a mistake by Germany - Germany had not successfully carried out the invasion of Britain and the war turned against of the Axis.

Attack on Pearl Harbor
The attack on Pearl Harbor was a surprise military strike conducted by the Imperial Japanese Navy against the United States naval base at Pearl Harbor, Hawaii, on the morning of December 7, 1941...
, bringing it too into the war on the Allied side. China also joined the Allies, as eventually did most of the rest of the world. China was in turmoil at the time, and attacked Japanese armies through guerilla-type warfare. By the beginning of 1942, the major combatants were aligned as follows: the British Commonwealth, the United States, and the Soviet Union were fighting Germany and Italy; and the British Commonwealth, China, and the United States were fighting Japan. From then through August 1945, battles raged across all of Europe, in the North Atlantic Ocean, across North Africa, throughout Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, South-East Asia, South East Asia or Southeastern Asia is a subregion of Asia, consisting of the countries that are geographically south of China, east of India, west of New Guinea and north of Australia. The region lies on the intersection of geological plates, with heavy seismic...
, throughout China, across the Pacific Ocean and in the air over Japan.
Italy surrendered in September 1943 and split in a northern Germany-occupied puppet state
Puppet state
A puppet state is a nominal sovereign of a state who is de facto controlled by a foreign power. The term refers to a government controlled by the government of another country like a puppeteer controls the strings of a marionette...
and in an Allies-friendly state in the South; Germany surrendered in May 1945. Following the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki
Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki
During the final stages of World War II in 1945, the United States conducted two atomic bombings against the cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki in Japan, the first on August 6, 1945, and the second on August 9, 1945. These two events are the only use of nuclear weapons in war to date.For six months...
, Japan surrendered
Surrender of Japan
The surrender of Japan in 1945 brought hostilities of World War II to a close. By the end of July 1945, the Imperial Japanese Navy was incapable of conducting operations and an Allied invasion of Japan was imminent...
, marking the end of the war on September 2, 1945.
It is possible that around 62 million people died in the war
World War II casualties
World War II was the deadliest military conflict in history. Over 60 million people were killed, which was over 2.5% of the world population. The tables below give a detailed country-by-country count of human losses.-Total dead:...
; estimates vary greatly. About 60% of all casualties were civilians, who died as a result of disease, starvation, genocide
Genocide
Genocide is defined as "the deliberate and systematic destruction, in whole or in part, of an ethnic, racial, religious, or national group", though what constitutes enough of a "part" to qualify as genocide has been subject to much debate by legal scholars...
(in particular, the Holocaust), and aerial bombing. The former Soviet Union and China suffered the most casualties. Estimates place deaths in the Soviet Union at around 23 million, while China suffered about 10 million. No country lost a greater portion of its population than Poland: approximately 5.6 million, or 16%, of its pre-war population of 34.8 million died.
The Holocaust (which roughly means "burnt whole") was the deliberate and systematic murder of millions of Jews and other "unwanted" during World War II by the Nazi regime in Germany. Several differing views exist regarding whether it was intended to occur from the war's beginning, or if the plans for it came about later. Regardless, persecution of Jews extended well before the war even started, such as in the Kristallnacht
Kristallnacht
Kristallnacht, also referred to as the Night of Broken Glass, and also Reichskristallnacht, Pogromnacht, and Novemberpogrome, was a pogrom or series of attacks against Jews throughout Nazi Germany and parts of Austria on 9–10 November 1938.Jewish homes were ransacked, as were shops, towns and...
(Night of Broken Glass). The Nazis used propaganda to great effect to stir up anti-Semitic feelings within ordinary Germans.
After World War II, Europe was informally split into Western and Soviet spheres of influence
Sphere of influence
In the field of international relations, a sphere of influence is a spatial region or conceptual division over which a state or organization has significant cultural, economic, military or political influence....
. Western Europe
Western Europe
Western Europe is a loose term for the collection of countries in the western most region of the European continents, though this definition is context-dependent and carries cultural and political connotations. One definition describes Western Europe as a geographic entity—the region lying in the...
later aligned as North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) and Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is the eastern part of Europe. The term has widely disparate geopolitical, geographical, cultural and socioeconomic readings, which makes it highly context-dependent and even volatile, and there are "almost as many definitions of Eastern Europe as there are scholars of the region"...
as the Warsaw Pact
Warsaw Pact
The Warsaw Treaty Organization of Friendship, Cooperation, and Mutual Assistance , or more commonly referred to as the Warsaw Pact, was a mutual defense treaty subscribed to by eight communist states in Eastern Europe...
. There was a shift in power from Western Europe and the British Empire
British Empire
The British Empire comprised the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom. It originated with the overseas colonies and trading posts established by England in the late 16th and early 17th centuries. At its height, it was the...
to the two new superpowers, the United States and the Soviet Union. These two rivals would later face off in the Cold War
Cold War
The Cold War was the continuing state from roughly 1946 to 1991 of political conflict, military tension, proxy wars, and economic competition between the Communist World—primarily the Soviet Union and its satellite states and allies—and the powers of the Western world, primarily the United States...
. In Asia, the defeat of Japan led to its democratization
Democratization
Democratization is the transition to a more democratic political regime. It may be the transition from an authoritarian regime to a full democracy, a transition from an authoritarian political system to a semi-democracy or transition from a semi-authoritarian political system to a democratic...
. China's civil war
Chinese Civil War
The Chinese Civil War was a civil war fought between the Kuomintang , the governing party of the Republic of China, and the Communist Party of China , for the control of China which eventually led to China's division into two Chinas, Republic of China and People's Republic of...
continued through and after the war, resulting eventually in the establishment of the People's Republic of China
People's Republic of China
China , officially the People's Republic of China , is the most populous country in the world, with over 1.3 billion citizens. Located in East Asia, the country covers approximately 9.6 million square kilometres...
. The former colonies of the European powers began their road to independence.
Post-1945 World

Over the course of the 20th century, the world's per-capita gross domestic product
Gross domestic product
Gross domestic product refers to the market value of all final goods and services produced within a country in a given period. GDP per capita is often considered an indicator of a country's standard of living....
grew by a factor of five, much more than all earlier centuries combined (including the 19th with its Industrial Revolution). Many economists make the case that this understates the magnitude of growth, as many of the goods and services consumed at the end of the century, such as improved medicine (causing world life expectancy to increase by more than two decades) and communications technologies, were not available at any price at its beginning. However, the gulf between the world's rich and poor grew wider, and the majority of the global population remained in the poor side of the divide.
Still, advancing technology and medicine has had a great impact even in the Global South. Large-scale industry and more centralized media
Mass media
Mass media refers collectively to all media technologies which are intended to reach a large audience via mass communication. Broadcast media transmit their information electronically and comprise of television, film and radio, movies, CDs, DVDs and some other gadgets like cameras or video consoles...
made brutal dictatorships possible on an unprecedented scale in the middle of the century, leading to wars that were also unprecedented. However, the increased communications contributed to democratization
Democratization
Democratization is the transition to a more democratic political regime. It may be the transition from an authoritarian regime to a full democracy, a transition from an authoritarian political system to a semi-democracy or transition from a semi-authoritarian political system to a democratic...
. Technological developments included the development of airplanes and space exploration
Space exploration
Space exploration is the use of space technology to explore outer space. Physical exploration of space is conducted both by human spaceflights and by robotic spacecraft....
, nuclear technology
Nuclear technology
Nuclear technology is technology that involves the reactions of atomic nuclei. Among the notable nuclear technologies are nuclear power, nuclear medicine, and nuclear weapons...
, advancement in genetics
Genetics
Genetics , a discipline of biology, is the science of genes, heredity, and variation in living organisms....
, and the dawning of the Information Age
Information Age
The Information Age, also commonly known as the Computer Age or Digital Age, is an idea that the current age will be characterized by the ability of individuals to transfer information freely, and to have instant access to knowledge that would have been difficult or impossible to find previously...
.
American Peace

Pax Americana
Pax Americana is an appellation applied to the historical concept of relative peace in the Western hemisphere and, later, the Western world, resulting from the preponderance of power enjoyed by the United States of America starting around the turn of the 20th century...
is an appellation applied to the historical concept of relative liberal peace in the Western world, resulting from the preponderance of power enjoyed by the United States of America starting around the turn of the 20th century. Although the term finds its primary utility in the latter half of the 20th century, it has been used in various places and eras. Its modern connotations concern the peace established after the end of World War II in 1945.
Cold War era
The Cold War
Cold War
The Cold War was the continuing state from roughly 1946 to 1991 of political conflict, military tension, proxy wars, and economic competition between the Communist World—primarily the Soviet Union and its satellite states and allies—and the powers of the Western world, primarily the United States...
began in the mid-1940s and lasted into the early 1990s. Throughout this period, the conflict was expressed through military coalitions, espionage, weapons development, invasions, propaganda, and competitive technological development. The conflict included costly defense spending, a massive conventional
Conventional weapon
The terms conventional weapons or conventional arms generally refer to weapons that are in relatively wide use that are not weapons of mass destruction, such as nuclear, chemical, and biological weapons. Conventional weapons include small arms and light weapons, sea and land mines, as well as ...
and nuclear
Nuclear weapon
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission or a combination of fission and fusion. Both reactions release vast quantities of energy from relatively small amounts of matter. The first fission bomb test released the same amount...
arms race
Arms race
The term arms race, in its original usage, describes a competition between two or more parties for the best armed forces. Each party competes to produce larger numbers of weapons, greater armies, or superior military technology in a technological escalation...
, and numerous proxy war
Proxy war
A proxy war or proxy warfare is a war that results when opposing powers use third parties as substitutes for fighting each other directly. While powers have sometimes used governments as proxies, violent non-state actors, mercenaries, or other third parties are more often employed...
s; the two superpower
Superpower
A superpower is a state with a dominant position in the international system which has the ability to influence events and its own interests and project power on a worldwide scale to protect those interests...
s never fought one another directly.
.png)
Eastern bloc
The term Eastern Bloc or Communist Bloc refers to the former communist states of Eastern and Central Europe, generally the Soviet Union and the countries of the Warsaw Pact...
of countries that it occupied, annexing some as Soviet Socialist Republics and maintaining others as satellite states that would later form the Warsaw Pact
Warsaw Pact
The Warsaw Treaty Organization of Friendship, Cooperation, and Mutual Assistance , or more commonly referred to as the Warsaw Pact, was a mutual defense treaty subscribed to by eight communist states in Eastern Europe...
. The United States and various western European countries began a policy of "containment
Containment
Containment was a United States policy using military, economic, and diplomatic strategies to stall the spread of communism, enhance America’s security and influence abroad, and prevent a "domino effect". A component of the Cold War, this policy was a response to a series of moves by the Soviet...
" of communism
Communism
Communism is a social, political and economic ideology that aims at the establishment of a classless, moneyless, revolutionary and stateless socialist society structured upon common ownership of the means of production...
and forged myriad alliances to this end, including NATO. Several of these western countries also coordinated efforts regarding the rebuilding of western Europe, including western Germany, which the Soviets opposed. In other regions of the world, such as Latin America and Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, South-East Asia, South East Asia or Southeastern Asia is a subregion of Asia, consisting of the countries that are geographically south of China, east of India, west of New Guinea and north of Australia. The region lies on the intersection of geological plates, with heavy seismic...
, the Soviet Union fostered communist revolution
Communist revolution
A communist revolution is a proletarian revolution inspired by the ideas of Marxism that aims to replace capitalism with communism, typically with socialism as an intermediate stage...
ary movements, which the United States and many of its allies opposed and, in some cases, attempted to "roll back
Rollback
In political science, rollback is the strategy of forcing change in the major policies of a state, usually by replacing its ruling regime. It contrasts with containment, which means preventing the expansion of that state; and with détente, which means a working relationship with that state...
". Many countries were prompted to align themselves with the nations that would later form either NATO or the Warsaw Pact, though other movements would also emerge.
The Cold War saw periods of both heightened tension and relative calm. International crises arose, such as the Berlin Blockade
Berlin Blockade
The Berlin Blockade was one of the first major international crises of the Cold War and the first resulting in casualties. During the multinational occupation of post-World War II Germany, the Soviet Union blocked the Western Allies' railway and road access to the sectors of Berlin under Allied...
(1948–1949), the Korean War
Korean War
The Korean War was a conventional war between South Korea, supported by the United Nations, and North Korea, supported by the People's Republic of China , with military material aid from the Soviet Union...
(1950–1953), the Berlin Crisis of 1961
Berlin Crisis of 1961
The Berlin Crisis of 1961 was the last major politico-military European incident of the Cold War about the occupational status of the German capital city, Berlin, and of post–World War II Germany. The U.S.S.R...
, the Vietnam War
Vietnam War
The Vietnam War was a Cold War-era military conflict that occurred in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia from 1 November 1955 to the fall of Saigon on 30 April 1975. This war followed the First Indochina War and was fought between North Vietnam, supported by its communist allies, and the government of...
(1959–1975), the Cuban Missile Crisis
Cuban Missile Crisis
The Cuban Missile Crisis was a confrontation among the Soviet Union, Cuba and the United States in October 1962, during the Cold War...
(1962), the Soviet war in Afghanistan
Soviet war in Afghanistan
The Soviet war in Afghanistan was a nine-year conflict involving the Soviet Union, supporting the Marxist-Leninist government of the Democratic Republic of Afghanistan against the Afghan Mujahideen and foreign "Arab–Afghan" volunteers...
(1979–1989) and NATO exercises in November 1983
Able Archer 83
Able Archer 83 was a ten-day NATO command post exercise starting on November 2, 1983 that spanned Western Europe, centred on the Supreme Headquarters Allied Powers Europe Headquarters situated at Casteau, north of the Belgian city of Mons. Able Archer exercises simulated a period of conflict...
. There were also periods of reduced tension as both sides sought détente
Détente
Détente is the easing of strained relations, especially in a political situation. The term is often used in reference to the general easing of relations between the Soviet Union and the United States in the 1970s, a thawing at a period roughly in the middle of the Cold War...
. Direct military attacks on adversaries were deterred by the potential for mutual assured destruction
Mutual assured destruction
Mutual Assured Destruction, or mutually assured destruction , is a doctrine of military strategy and national security policy in which a full-scale use of high-yield weapons of mass destruction by two opposing sides would effectively result in the complete, utter and irrevocable annihilation of...
using deliverable nuclear weapon
Nuclear weapon
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission or a combination of fission and fusion. Both reactions release vast quantities of energy from relatively small amounts of matter. The first fission bomb test released the same amount...
s. In the Cold War era, the Generation of Love
Generation of Love
"Generation of Love" is a 1995 song recorded by German band Masterboy. It was one of the singles from its album of the same name and band's one of the most successful singles in terms of peak positions on the charts. It achieved success in many European countries where it was a top twenty hit,...
and the rise of computer
Computer
A computer is a programmable machine designed to sequentially and automatically carry out a sequence of arithmetic or logical operations. The particular sequence of operations can be changed readily, allowing the computer to solve more than one kind of problem...
s changed society in very different, complex ways, including higher social and local mobility.
 |
The Cold War drew to a close in the late 1980s and the early 1990s. The United States under President Ronald Reagan
Ronald Reagan
Ronald Wilson Reagan was the 40th President of the United States , the 33rd Governor of California and, prior to that, a radio, film and television actor....
increased diplomatic, military, and economic pressure on the Soviet Union, which was already suffering from severe economic stagnation
Brezhnev stagnation
The Era of Stagnation, also known as Brezhnev stagnation or the Stagnation Period, refers to a period of economic stagnation under the rules of Leonid Brezhnev, Yuri Andropov and Konstantin Chernenko in the history of the Soviet Union which started in the mid-1970s.-Terminology:Various authors...
. In the second half of the 1980s, newly appointed Soviet leader Mikhail Gorbachev
Mikhail Gorbachev
Mikhail Sergeyevich Gorbachev is a former Soviet statesman, having served as General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union from 1985 until 1991, and as the last head of state of the USSR, having served from 1988 until its dissolution in 1991...
introduced the perestroika
Perestroika
Perestroika was a political movement within the Communist Party of the Soviet Union during 1980s, widely associated with the Soviet leader Mikhail Gorbachev...
and glasnost
Glasnost
Glasnost was the policy of maximal publicity, openness, and transparency in the activities of all government institutions in the Soviet Union, together with freedom of information, introduced by Mikhail Gorbachev in the second half of the 1980s...
reforms. The Soviet Union collapsed in 1991, leaving the United States as the dominant military power, though Russia retained much of the massive Soviet nuclear arsenal.
Latin America polarization
In Latin America, the 1970s saw leftists acquire a significant political influence which prompted the right-wing, ecclesiastical authorities and a large portion of the individual country's upper class to support coup d'états to avoid what they perceived as a communist threat. This was further fueled by Cuban and United States intervention which led to a political polarization. Most South American countries were in some periods ruled by military dictatorship
Military dictatorship
A military dictatorship is a form of government where in the political power resides with the military. It is similar but not identical to a stratocracy, a state ruled directly by the military....
s that were supported by the United States of America. Around the 1970s, the regimes of the Southern Cone
Southern Cone
Southern Cone is a geographic region composed of the southernmost areas of South America, south of the Tropic of Capricorn. Although geographically this includes part of Southern and Southeast of Brazil, in terms of political geography the Southern cone has traditionally comprised Argentina,...
collaborated in Operation Condor
Operation Condor
Operation Condor , was a campaign of political repression involving assassination and intelligence operations officially implemented in 1975 by the right-wing dictatorships of the Southern Cone of South America...
killing many leftist dissidents, including some urban guerrillas. However, by the early 1990s all countries had restored their democracies.
Space Age

Space Age
The Space Age is a time period encompassing the activities related to the Space Race, space exploration, space technology, and the cultural developments influenced by these events. The Space Age is generally considered to have begun with Sputnik...
is a period encompassing the activities related to the Space Race
Space Race
The Space Race was a mid-to-late 20th century competition between the Soviet Union and the United States for supremacy in space exploration. Between 1957 and 1975, Cold War rivalry between the two nations focused on attaining firsts in space exploration, which were seen as necessary for national...
, space exploration
Space exploration
Space exploration is the use of space technology to explore outer space. Physical exploration of space is conducted both by human spaceflights and by robotic spacecraft....
, space technology, and the cultural developments influenced by these events. The Space Age began with the development of several technologies that culminated with the launch of Sputnik 1
Sputnik 1
Sputnik 1 ) was the first artificial satellite to be put into Earth's orbit. It was launched into an elliptical low Earth orbit by the Soviet Union on 4 October 1957. The unanticipated announcement of Sputnik 1s success precipitated the Sputnik crisis in the United States and ignited the Space...
by the Soviet Union. This was the world's first artificial satellite, orbiting the Earth in 98.1 minutes and weighing in at 83 kg. The launch of Sputnik 1 ushered a new era of political, scientific and technological achievements that became known as the Space Age. The Space Age was characterized by rapid development of new technology in a close race mostly between the United States and the Soviet Union. The Space Age reached its peak with the Apollo program which captured the imagination of much of the world's population. The landing of Apollo 11
Apollo 11
In early 1969, Bill Anders accepted a job with the National Space Council effective in August 1969 and announced his retirement as an astronaut. At that point Ken Mattingly was moved from the support crew into parallel training with Anders as backup Command Module Pilot in case Apollo 11 was...
was an event watched by over 500 million people around the world and is widely recognized as one of the defining moments of the 20th century. Since then and with the end of the space race due to the dissolution of the Soviet Union
Dissolution of the Soviet Union
The dissolution of the Soviet Union was the disintegration of the federal political structures and central government of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , resulting in the independence of all fifteen republics of the Soviet Union between March 11, 1990 and December 25, 1991...
, public attention has largely moved to other areas.
Contemporary era
In the Contemporary era, there were various socio-technological trends, among the challenges and problems the modern world faces is climate change. Regarding the 21st century and the late modern world, the Information age and computers were forefront in use, not completely ubiquitous but often present in daily life. The development of Eastern powers was of note, with China and India becoming more powerful. In the Eurasian theater, the European Union and Russian Federation were two forces recently developed. A concern for Western world, if not the whole world, was the late modern form of terrorism and the warfare that has resulted from the contemporary terrorist acts.Modern History education and schools
The humanitiesHumanities
The humanities are academic disciplines that study the human condition, using methods that are primarily analytical, critical, or speculative, as distinguished from the mainly empirical approaches of the natural sciences....
are academic disciplines which study the human condition
Human condition
The human condition encompasses the experiences of being human in a social, cultural, and personal context. It can be described as the irreducible part of humanity that is inherent and not connected to gender, race, class, etc. — a search for purpose, sense of curiosity, the inevitability of...
, using methods that are primarily analytic
Analytic induction
Analytic induction refers to a systematic examination of similarities between various social phenomena in order to develop concepts or ideas. Social scientists doing social research use analytic induction to search for those similarities in broad categories and then develop subcategories...
, critical, or speculative, as distinguished from the mainly empirical
Empirical
The word empirical denotes information gained by means of observation or experimentation. Empirical data are data produced by an experiment or observation....
approaches of the natural
Natural science
The natural sciences are branches of science that seek to elucidate the rules that govern the natural world by using empirical and scientific methods...
and social sciences
Social sciences
Social science is the field of study concerned with society. "Social science" is commonly used as an umbrella term to refer to a plurality of fields outside of the natural sciences usually exclusive of the administrative or managerial sciences...
. Although many of the subjects of modern history coincide with that of standard history, the subject is taught independently by various systems of education in the world.
British education
Students can choose the subject at UniversityUniversity
A university is an institution of higher education and research, which grants academic degrees in a variety of subjects. A university is an organisation that provides both undergraduate education and postgraduate education...
. The material covered includes from the mid-18th century, to analysis of the present day
Present day
The term "present day" is used to describe the approximate period of time that surrounds the present. Depending on the context, this period may be as narrow as referring to the immediate moment, or as broad as referring to the current year or decade...
. Virtually all colleges and sixth forms that do teach modern history do it alongside standard history; very few teach the subject exclusively.
Universities
At the University of OxfordUniversity of Oxford
The University of Oxford is a university located in Oxford, United Kingdom. It is the second-oldest surviving university in the world and the oldest in the English-speaking world. Although its exact date of foundation is unclear, there is evidence of teaching as far back as 1096...
'Modern History' has a somewhat different meaning. The contrast is not with the Middle Ages but with Antiquity. The earliest period that can be studied in the Final Honour School of Modern History begins in 285.
See also
Religious: IrreligionIrreligion
Irreligion is defined as an absence of religion or an indifference towards religion. Sometimes it may also be defined more narrowly as hostility towards religion. When characterized as hostility to religion, it includes antitheism, anticlericalism and antireligion. When characterized as...
, Atheism
Atheism
Atheism is, in a broad sense, the rejection of belief in the existence of deities. In a narrower sense, atheism is specifically the position that there are no deities...
, Ancestor worship, Muslim
Muslim
A Muslim, also spelled Moslem, is an adherent of Islam, a monotheistic, Abrahamic religion based on the Quran, which Muslims consider the verbatim word of God as revealed to prophet Muhammad. "Muslim" is the Arabic term for "submitter" .Muslims believe that God is one and incomparable...
s and the Muslim world
Muslim world
The term Muslim world has several meanings. In a religious sense, it refers to those who adhere to the teachings of Islam, referred to as Muslims. In a cultural sense, it refers to Islamic civilization, inclusive of non-Muslims living in that civilization...
, Christian
Christian
A Christian is a person who adheres to Christianity, an Abrahamic, monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth as recorded in the Canonical gospels and the letters of the New Testament...
s and Christendom
Christendom
Christendom, or the Christian world, has several meanings. In a cultural sense it refers to the worldwide community of Christians, adherents of Christianity...
, Huguenots, Puritan
Puritan
The Puritans were a significant grouping of English Protestants in the 16th and 17th centuries. Puritanism in this sense was founded by some Marian exiles from the clergy shortly after the accession of Elizabeth I of England in 1558, as an activist movement within the Church of England...
s, Church Missionary Society, Robert College
Robert College
Robert College of Istanbul , is one of the most selective independent private high schools in Turkey. Robert College is a co-educational, boarding school with a wooded campus on the European side of Istanbul between the two bridges on the Bosphorus, with the Arnavutköy district to the east, and...
, Pietist, London Missionary Society
London Missionary Society
The London Missionary Society was a non-denominational missionary society formed in England in 1795 by evangelical Anglicans and Nonconformists, largely Congregationalist in outlook, with missions in the islands of the South Pacific and Africa...
, Society of Jesus
Society of Jesus
The Society of Jesus is a Catholic male religious order that follows the teachings of the Catholic Church. The members are called Jesuits, and are also known colloquially as "God's Army" and as "The Company," these being references to founder Ignatius of Loyola's military background and a...
(Jesuits), European wars of religion
European wars of religion
The European wars of religion were a series of wars waged in Europe from ca. 1524 to 1648, following the onset of the Protestant Reformation in Western and Northern Europe...
People and groups: Andreas Karlstadt
Andreas Karlstadt
Andreas Rudolph Bodenstein von Karlstadt , better known as Andreas Karlstadt or Andreas Carlstadt or Karolostadt, was a German Christian theologian during the Protestant Reformation. He was born in Karlstadt, Franconia.-Education:Karlstadt received his doctorate of theology in 1510 from the...
, Anne Boleyn
Anne Boleyn
Anne Boleyn ;c.1501/1507 – 19 May 1536) was Queen of England from 1533 to 1536 as the second wife of Henry VIII of England and Marquess of Pembroke in her own right. Henry's marriage to Anne, and her subsequent execution, made her a key figure in the political and religious upheaval that was the...
, Menocchio
Menocchio
Menocchio, also known as Domenico Scandella, was a Friulian miller born in 1532 in the village of Montereale, twenty-five kilometers north of Pordenone...
, Descartes, Goethe, Voltaire
Voltaire
François-Marie Arouet , better known by the pen name Voltaire , was a French Enlightenment writer, historian and philosopher famous for his wit and for his advocacy of civil liberties, including freedom of religion, free trade and separation of church and state...
, Nostradamus
Nostradamus
Michel de Nostredame , usually Latinised to Nostradamus, was a French apothecary and reputed seer who published collections of prophecies that have since become famous worldwide. He is best known for his book Les Propheties , the first edition of which appeared in 1555...
, Isaac Newton
Isaac Newton
Sir Isaac Newton PRS was an English physicist, mathematician, astronomer, natural philosopher, alchemist, and theologian, who has been "considered by many to be the greatest and most influential scientist who ever lived."...
, Fugger
Fugger
The Fugger family was a historically prominent group of European bankers, members of the fifteenth and sixteenth-century mercantile patriciate of Augsburg, international mercantile bankers, and venture capitalists like the Welser and the Höchstetter families. This banking family replaced the de'...
, Charles VII, Holy Roman Emperor
Charles VII, Holy Roman Emperor
Charles VII Albert a member of the Wittelsbach family, was Prince-elector of Bavaria from 1726 and Holy Roman Emperor from 24 January 1742 until his death in 1745...
, Boers, Congress of Berlin
Congress of Berlin
The Congress of Berlin was a meeting of the European Great Powers' and the Ottoman Empire's leading statesmen in Berlin in 1878. In the wake of the Russo-Turkish War of 1877–78, the meeting's aim was to reorganize the countries of the Balkans...
, Lenin, Yamagata Aritomo
Yamagata Aritomo
Field Marshal Prince , also known as Yamagata Kyōsuke, was a field marshal in the Imperial Japanese Army and twice Prime Minister of Japan. He is considered one of the architects of the military and political foundations of early modern Japan. Yamagata Aritomo can be seen as the father of Japanese...
, Tojo Hideki, Balkan League
Balkan League
The Balkan League was an alliance formed by a series of bilateral treaties concluded in 1912 between the Balkan states of Bulgaria, Greece, Montenegro and Serbia, and directed against the Ottoman Empire, which at the time still controlled much of the Balkan peninsula...
, Tutsi
Tutsi
The Tutsi , or Abatutsi, are an ethnic group in Central Africa. Historically they were often referred to as the Watussi or Watusi. They are the second largest caste in Rwanda and Burundi, the other two being the Hutu and the Twa ....
, William Paley
William Paley
William Paley was a British Christian apologist, philosopher, and utilitarian. He is best known for his exposition of the teleological argument for the existence of God in his work Natural Theology, which made use of the watchmaker analogy .-Life:Paley was Born in Peterborough, England, and was...
, British Whig Party and the Radical Whigs
Radical Whigs
The Radical Whigs were "a group of British political commentators" associated with the British Whig faction who were at the forefront of Radicalism...
, US Whig Party
Whig Party (United States)
The Whig Party was a political party of the United States during the era of Jacksonian democracy. Considered integral to the Second Party System and operating from the early 1830s to the mid-1850s, the party was formed in opposition to the policies of President Andrew Jackson and his Democratic...
, John Stuart Mill
John Stuart Mill
John Stuart Mill was a British philosopher, economist and civil servant. An influential contributor to social theory, political theory, and political economy, his conception of liberty justified the freedom of the individual in opposition to unlimited state control. He was a proponent of...
, John Partridge
John Partridge (artist)
John Partridge was a British artist and portrait painter. Named 'portrait painter-extraordinary' to Queen Victoria, his pictures depict many of the notable figures of his time....
, Sir Frederick Pollock, William Ashley, American Historical Association
American Historical Association
The American Historical Association is the oldest and largest society of historians and professors of history in the United States. Founded in 1884, the association promotes historical studies, the teaching of history, and the preservation of and access to historical materials...
, John Adams
John Adams
John Adams was an American lawyer, statesman, diplomat and political theorist. A leading champion of independence in 1776, he was the second President of the United States...
, Andrew Jackson
Andrew Jackson
Andrew Jackson was the seventh President of the United States . Based in frontier Tennessee, Jackson was a politician and army general who defeated the Creek Indians at the Battle of Horseshoe Bend , and the British at the Battle of New Orleans...
and Jacksonian Democracy
Jacksonian democracy
Jacksonian democracy is the political movement toward greater democracy for the common man typified by American politician Andrew Jackson and his supporters. Jackson's policies followed the era of Jeffersonian democracy which dominated the previous political era. The Democratic-Republican Party of...
, United States Republican party, Joseph Galloway
Joseph Galloway
Joseph Galloway was an American Loyalist during the American Revolution, after serving as delegate to the First Continental Congress from Pennsylvania.-Early life:...
, Frederick Jackson Turner
Frederick Jackson Turner
Frederick Jackson Turner was an American historian in the early 20th century. He is best known for his essay "The Significance of the Frontier in American History", whose ideas are referred to as the Frontier Thesis. He is also known for his theories of geographical sectionalism...
, American Anti-Slavery Society
American Anti-Slavery Society
The American Anti-Slavery Society was an abolitionist society founded by William Lloyd Garrison and Arthur Tappan. Frederick Douglass was a key leader of this society and often spoke at its meetings. William Wells Brown was another freed slave who often spoke at meetings. By 1838, the society had...
, A. P. Herbert
A. P. Herbert
Sir Alan Patrick Herbert, CH was an English humorist, novelist, playwright and law reform activist...
, Rosa Parks
Rosa Parks
Rosa Louise McCauley Parks was an African-American civil rights activist, whom the U.S. Congress called "the first lady of civil rights", and "the mother of the freedom movement"....
, Jackie Robinson
Jackie Robinson
Jack Roosevelt "Jackie" Robinson was the first black Major League Baseball player of the modern era. Robinson broke the baseball color line when he debuted with the Brooklyn Dodgers in 1947...
, Institute of Contemporary History
Institute of Contemporary History
The name "Institute of Contemporary History" is used by the following institutions:* The Wiener Library and Institute of Contemporary History, London, England* Institut für Zeitgeschichte, Munich, Germany* Inštitut za novejšo zgodovino, Ljubljana, Slovenia...
Companies and businesses: Laissez-faire
Laissez-faire
In economics, laissez-faire describes an environment in which transactions between private parties are free from state intervention, including restrictive regulations, taxes, tariffs and enforced monopolies....
, Marconi Company
Marconi Company
The Marconi Company Ltd. was founded by Guglielmo Marconi in 1897 as The Wireless Telegraph & Signal Company...
, Electric Vehicle Company
Electric Vehicle Company
-History:The Electric Vehicle Company was founded as a holding company of battery-powered electric automobile manufacturers made up of several car companies assembled by Isaac L. Rice beginning in 1897. It was taken over in 1899 by William C. Whitney and P. A. B...
, Henry Ford
Henry Ford
Henry Ford was an American industrialist, the founder of the Ford Motor Company, and sponsor of the development of the assembly line technique of mass production. His introduction of the Model T automobile revolutionized transportation and American industry...
and the Ford Motor Company
Ford Motor Company
Ford Motor Company is an American multinational automaker based in Dearborn, Michigan, a suburb of Detroit. The automaker was founded by Henry Ford and incorporated on June 16, 1903. In addition to the Ford and Lincoln brands, Ford also owns a small stake in Mazda in Japan and Aston Martin in the UK...
, AT&T
AT&T
AT&T Inc. is an American multinational telecommunications corporation headquartered in Whitacre Tower, Dallas, Texas, United States. It is the largest provider of mobile telephony and fixed telephony in the United States, and is also a provider of broadband and subscription television services...
, Bechtel
Bechtel
Bechtel Corporation is the largest engineering company in the United States, ranking as the 5th-largest privately owned company in the U.S...
, Asahi Shimbun
Asahi Shimbun
The is the second most circulated out of the five national newspapers in Japan. Its circulation, which was 7.96 million for its morning edition and 3.1 million for its evening edition as of June 2010, was second behind that of Yomiuri Shimbun...
, Daily Mail
Daily Mail
The Daily Mail is a British daily middle-market tabloid newspaper owned by the Daily Mail and General Trust. First published in 1896 by Lord Northcliffe, it is the United Kingdom's second biggest-selling daily newspaper after The Sun. Its sister paper The Mail on Sunday was launched in 1982...
Areas and histories: List of World Map changes, Duchy of Warsaw
Duchy of Warsaw
The Duchy of Warsaw was a Polish state established by Napoleon I in 1807 from the Polish lands ceded by the Kingdom of Prussia under the terms of the Treaties of Tilsit. The duchy was held in personal union by one of Napoleon's allies, King Frederick Augustus I of Saxony...
, Bohemia
Bohemia
Bohemia is a historical region in central Europe, occupying the western two-thirds of the traditional Czech Lands. It is located in the contemporary Czech Republic with its capital in Prague...
, Cape Colony
Cape Colony
The Cape Colony, part of modern South Africa, was established by the Dutch East India Company in 1652, with the founding of Cape Town. It was subsequently occupied by the British in 1795 when the Netherlands were occupied by revolutionary France, so that the French revolutionaries could not take...
, Transvaal, History of the Netherlands
History of the Netherlands
The history of the Netherlands is the history of a maritime people thriving on a watery lowland river delta at the edge of northwestern Europe. When the Romans and written history arrived in 57 BC, the country was sparsely populated by various tribal groups at the periphery of the empire...
, History of Iran
History of Iran
The history of Iran has been intertwined with the history of a larger historical region, comprising the area from the Danube River in the west to the Indus River and Jaxartes in the east and from the Caucasus, Caspian Sea, and Aral Sea in the north to the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman and Egypt...
, History of Korea
History of Korea
The Korean Peninsula was inhabited from the Lower Paleolithic about 400,000-500,000 years ago. Archeological evidence indicates that the presence of modern humans in northeast Asia dates to 39,000 years ago. The earliest known Korean pottery dates to around 8000 BC, and the Neolithic period began...
, History of Manchuria, History of Vladivostok
History of Vladivostok
The history of Vladivostok can roughly be divided into the history of the territory where Vladivostok is located and into the history of the city per se.- Influences :...
, History of Pakistan
History of Pakistan
The 1st known inhabitants of the modern-day Pakistan region are believed to have been the Soanian , who settled in the Soan Valley and Riwat almost 2 million years ago. Over the next several thousand years, the region would develop into various civilizations like Mehrgarh and the Indus Valley...
, History of Saudi Arabia
History of Saudi Arabia
The modern state of Saudi Arabia was founded in 1932 with the union of the kingdoms of the Hejaz and Nejd. Although the territory within the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia's boundaries is largely arid desert or rocky infertile terrain – home for much of its history to tribal nomadic societies with...
, History of Kuwait
History of Kuwait
The country of Kuwait has a history which dates to ancient times.-The Greeks:In 3rd century BC, the Ancient Greeks colonized the island, Failaka, on today's Kuwait coast under Alexander and named it "Ikaros". Some believe the name came from an island off the Greek coast, where it is believed that...
, History of Cambodia
History of Cambodia
- Prehistory and early history :Carbon 14 dating of a cave at Laang Spean in northwest Cambodia reveals people who made pots were living in Cambodia as early as 4200 BCE . Further archaeological evidence indicates that other parts of the region now called Cambodia were inhabited from around...
, Kansas-Nebraska Act
Kansas-Nebraska Act
The Kansas–Nebraska Act of 1854 created the territories of Kansas and Nebraska, opening new lands for settlement, and had the effect of repealing the Missouri Compromise of 1820 by allowing settlers in those territories to determine through Popular Sovereignty if they would allow slavery within...
, History of New York City
History of New York City
The history of New York, New York begins with the first European documentation of the area by Giovanni da Verrazzano, in command of the French ship, La Dauphine, when he visited the region in 1524. It is believed he sailed in Upper New York Bay where he encountered native Lenape, returned through...
, Moabit
Moabit
Moabit is an inner city locality of Berlin. Since Berlin's 2001 administrative reform it belongs to the newly regrouped governmental borough of Mitte. Previously, from 1920 to 2001, it belonged to the borough of Tiergarten. Moabit's borders are defined by three watercourses, the Spree, the...
, Levittown
Willingboro Township, New Jersey
Willingboro is a Township in Burlington County, New Jersey, United States and a suburb of Philadelphia. As of the United States 2010 Census, the township population was 31,629....
Culture and society: Iconoclasm
Iconoclasm
Iconoclasm is the deliberate destruction of religious icons and other symbols or monuments, usually with religious or political motives. It is a frequent component of major political or religious changes...
, Le Corbusier
Le Corbusier
Charles-Édouard Jeanneret, better known as Le Corbusier , was a Swiss-born French architect, designer, urbanist, writer and painter, famous for being one of the pioneers of what now is called modern architecture. He was born in Switzerland and became a French citizen in 1930...
, Apsley House
Apsley House
Apsley House, also known as Number One, London, is the former London residence of the Dukes of Wellington. It stands alone at Hyde Park Corner, on the south-east corner of Hyde Park, facing south towards the busy traffic interchange and Wellington Arch...
, Yosano Akiko
Yosano Akiko
was the pen-name of a Japanese author, poet, pioneering feminist, pacifist, and social reformer, active in the late Meiji period as well as the Taishō and early Showa periods of Japan. Her name at birth was Otori Shô. She is one of the most famous, and most controversial, post-classical woman poets...
, Romanticist, Television
Television
Television is a telecommunication medium for transmitting and receiving moving images that can be monochrome or colored, with accompanying sound...
and Cable television
Cable television
Cable television is a system of providing television programs to consumers via radio frequency signals transmitted to televisions through coaxial cables or digital light pulses through fixed optical fibers located on the subscriber's property, much like the over-the-air method used in traditional...
, History of modern literature
History of modern literature
The history of literature in the Modern period in Europe begins with the Age of Enlightenment and the conclusion of the Baroque period in the 18th century, succeeding the Renaissance and Early Modern periods....
, Symbolist
Symbolism (arts)
Symbolism was a late nineteenth-century art movement of French, Russian and Belgian origin in poetry and other arts. In literature, the style had its beginnings with the publication Les Fleurs du mal by Charles Baudelaire...
, The Beatles, Rodgers and Hammerstein
Rodgers and Hammerstein
Richard Rodgers and Oscar Hammerstein II were a well-known American songwriting duo, usually referred to as Rodgers and Hammerstein. They created a string of popular Broadway musicals in the 1940s and 1950s during what is considered the golden age of the medium...
, I Love Lucy
I Love Lucy
I Love Lucy is an American television sitcom starring Lucille Ball, Desi Arnaz, Vivian Vance, and William Frawley. The black-and-white series originally ran from October 15, 1951, to May 6, 1957, on the Columbia Broadcasting System...
, Mass Observation
Legal:letter of credence
Letter of Credence
A letter of credence is a formal letter usually sent by one head of state to another that formally grants diplomatic accreditation to a named individual to be their ambassador in the country of the head of state receiving the letter...
, prisoner of war
Prisoner of war
A prisoner of war or enemy prisoner of war is a person, whether civilian or combatant, who is held in custody by an enemy power during or immediately after an armed conflict...
, laws of war
Laws of war
The law of war is a body of law concerning acceptable justifications to engage in war and the limits to acceptable wartime conduct...
, exequatur
Exequatur
An exequatur is a legal document issued by a sovereign authority allowing a right to be enforced in the authority's domain of competence. The word is a form of the Latin verb exequi, and means let it be executed in Latin.-International relations:...
, extradition
Extradition
Extradition is the official process whereby one nation or state surrenders a suspected or convicted criminal to another nation or state. Between nation states, extradition is regulated by treaties...
, right of asylum
Right of asylum
Right of asylum is an ancient juridical notion, under which a person persecuted for political opinions or religious beliefs in his or her own country may be protected by another sovereign authority, a foreign country, or church sanctuaries...
, jus soli
Jus soli
Jus soli , also known as birthright citizenship, is a right by which nationality or citizenship can be recognized to any individual born in the territory of the related state...
, jus sanguinis
Jus sanguinis
Ius sanguinis is a social policy by which citizenship is not determined by place of birth, but by having a parent who are citizens of the nation...
, exterritoriality
Other: Modernity
Modernity
Modernity typically refers to a post-traditional, post-medieval historical period, one marked by the move from feudalism toward capitalism, industrialization, secularization, rationalization, the nation-state and its constituent institutions and forms of surveillance...
, Postmodernity
Postmodernity
Postmodernity is generally used to describe the economic or cultural state or condition of society which is said to exist after modernity...
, Romanticism
Romanticism
Romanticism was an artistic, literary and intellectual movement that originated in the second half of the 18th century in Europe, and gained strength in reaction to the Industrial Revolution...
, Free silver
Free Silver
Free Silver was an important United States political policy issue in the late 19th century and early 20th century. Its advocates were in favor of an inflationary monetary policy using the "free coinage of silver" as opposed to the less inflationary Gold Standard; its supporters were called...
, political consciousness
Political consciousness
Following the work of Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel, Karl Marx outlined the workings of a political consciousness.-The politics of consciousness:...
, Sophisms, Fire of London, Tower of London
Tower of London
Her Majesty's Royal Palace and Fortress, more commonly known as the Tower of London, is a historic castle on the north bank of the River Thames in central London, England. It lies within the London Borough of Tower Hamlets, separated from the eastern edge of the City of London by the open space...
, utilitarian, Uitlanders, Pan-Slavism
Pan-Slavism
Pan-Slavism was a movement in the mid-19th century aimed at unity of all the Slavic peoples. The main focus was in the Balkans where the South Slavs had been ruled for centuries by other empires, Byzantine Empire, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman Empire, and Venice...
, Sinn Féin
Sinn Féin
Sinn Féin is a left wing, Irish republican political party in Ireland. The name is Irish for "ourselves" or "we ourselves", although it is frequently mistranslated as "ourselves alone". Originating in the Sinn Féin organisation founded in 1905 by Arthur Griffith, it took its current form in 1970...
, UNESCO
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations...
, Women's suffrage
Women's suffrage
Women's suffrage or woman suffrage is the right of women to vote and to run for office. The expression is also used for the economic and political reform movement aimed at extending these rights to women and without any restrictions or qualifications such as property ownership, payment of tax, or...
, The Nobel
Nobel Prize
The Nobel Prizes are annual international awards bestowed by Scandinavian committees in recognition of cultural and scientific advances. The will of the Swedish chemist Alfred Nobel, the inventor of dynamite, established the prizes in 1895...
and the Peace Prize
Nobel Peace Prize
The Nobel Peace Prize is one of the five Nobel Prizes bequeathed by the Swedish industrialist and inventor Alfred Nobel.-Background:According to Nobel's will, the Peace Prize shall be awarded to the person who...
, Origin of Species, human evolution
Human evolution
Human evolution refers to the evolutionary history of the genus Homo, including the emergence of Homo sapiens as a distinct species and as a unique category of hominids and mammals...
, Social evolution
Social evolution
Social evolution is a subdiscipline of evolutionary biology that is concerned with social behaviors that have fitness consequences for individuals other than the actor...
, Bakelite, Transistor
Transistor
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify and switch electronic signals and power. It is composed of a semiconductor material with at least three terminals for connection to an external circuit. A voltage or current applied to one pair of the transistor's terminals changes the current...
s, Infidelity
Infidelity
In many intimate relationships in many cultures there is usually an express or implied expectation of exclusivity, especially in sexual matters. Infidelity most commonly refers to a breach of the expectation of sexual exclusivity.Infidelity can occur in relation to physical intimacy and/or...
, Penicillin
Penicillin
Penicillin is a group of antibiotics derived from Penicillium fungi. They include penicillin G, procaine penicillin, benzathine penicillin, and penicillin V....
, Ethanol
Ethanol
Ethanol, also called ethyl alcohol, pure alcohol, grain alcohol, or drinking alcohol, is a volatile, flammable, colorless liquid. It is a psychoactive drug and one of the oldest recreational drugs. Best known as the type of alcohol found in alcoholic beverages, it is also used in thermometers, as a...
, Gasoline
Gasoline
Gasoline , or petrol , is a toxic, translucent, petroleum-derived liquid that is primarily used as a fuel in internal combustion engines. It consists mostly of organic compounds obtained by the fractional distillation of petroleum, enhanced with a variety of additives. Some gasolines also contain...
, Fuel Cell
Fuel cell
A fuel cell is a device that converts the chemical energy from a fuel into electricity through a chemical reaction with oxygen or another oxidizing agent. Hydrogen is the most common fuel, but hydrocarbons such as natural gas and alcohols like methanol are sometimes used...
, Automobile
Automobile
An automobile, autocar, motor car or car is a wheeled motor vehicle used for transporting passengers, which also carries its own engine or motor...
, personal computers, mobile phone
Mobile phone
A mobile phone is a device which can make and receive telephone calls over a radio link whilst moving around a wide geographic area. It does so by connecting to a cellular network provided by a mobile network operator...
, Falklands War
Falklands War
The Falklands War , also called the Falklands Conflict or Falklands Crisis, was fought in 1982 between Argentina and the United Kingdom over the disputed Falkland Islands and South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands...
Modernism Framework
Western Philosophy
Further reading
21st century sources- Boyd, Andrew, Joshua Comenetz. An atlas of world affairs. Routledge, 2007. ISBN 0415391695
- Black, Edwin. Internal Combustion: How Corporations and Governments Addicted the World to Oil and Derailed the Alternatives. New York: St. Martin's Press, 2006.
- Briggs, Asa, and Peter Burke. A Social History of the Media: From Gutenberg to the Internet. Cambridge: Polity, 2002.
- Barzun, Jacques. From Dawn to Decadence: 500 Years of Western Cultural Life : 1500 to the Present. New York: HarperCollins, 2001.
20th century sources
- Burke, Peter. A Social History of Knowledge: From Gutenberg to Diderot. Cambridge, UK: Polity, 2000.
- CBS News. People of the century. Simon and Schuster, 1999. ISBN 0684870932
- Wang, Ke-wen. Modern China: an encyclopedia of history, culture, and nationalism. Taylor & Francis, 1998. ISBN 0815307209
- Huffman, James L. Modern Japan: an encyclopedia of history, culture, and nationalism. Taylor & Francis, 1998. ISBN 0815325258
- Schlesinger, Arthur M. New Viewpoints in American History. New York: Macmillan, 1922.
- Bakeless, John Edwin. The Economic Causes of Modern War; A Study of the Period: 1878-1918. New York: Printed for the Department of political science of Williams college, by Moffat, Yard and Co, 1921
- Day, Clive. A History of Commerce. New York [etc.]: Longmans, Green, and Co, 1921.
- Moore, Edward Caldwell. The Spread of Christianity in the Modern World. Chicago, Ill: University of Chicago Press, 1919.
- Muir, Ramsay. The Expansion of Europe; The Culmination of Modern History. Boston: Houghton Mifflin Company, 1917.
- Palat, Madhavan K., Social Identities in Revolutionary Russia, ed. (Macmillan, Palgrave, UK, and St Martin’s Press, New York, 2001).
- Palat, Madhavan K., History of Civilizations of Central Asia, ed. , vol. 6, Towards the Contemporary Period: From The Mid-Nineteenth Century To The End Of The Twentieth Century, UNESCO, Paris 2005.
- Robinson, James Harvey, and Charles Austin Beard. Readings in Modern European History; A Collection of Extracts from the Sources Chosen with the Purpose of Illustrating Some of the Chief Phases of Development of Europe During the Last Two Hundred Years. Boston: Ginn & Co, 1908.
- McCarthy, Michael J. F. The Coming Power; A Contemporary History of the Far East, 1898-1905. London: Hodder and Stoughton, 1905.
- Kidd, Benjamin. Principles of Western Civilisation. London: Macmillan and Co., Limited, 1902.
- Acton, John Emerich Edward Dalberg Acton, Adolphus William Ward, G. W. Prothero, Stanley Mordaunt Leathes, and E. A. Benians. The Cambridge Modern History. New York: Macmillan Co, 1902
- Wilson, George Grafton, and George Fox Tucker. International Law. New York: Silver, Burdett and co, 1901.
19th century sources
- Stubbs, William. Seventeen Lectures on the Study of Medieval and Modern History and Kindred Subjects; Delivered at Oxford, Under Statutory Obligation in the Years 1867-1884; with Two Addresses Given at Oxford and Reading. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1900.
- Duruy, Victor, and Edwin A. Grosvenor. History of Modern Times, From the Fall of Constantinople to the French Revolution. New York: H. Holt and company, 1894.
- Fredet, Peter. Modern History; From the Coming of Christ and Change of the Roman Republic into an Empire, to the Year of Our Lord 1888. Baltimore: J. Murphy & Co, 1888.
- Thalheimer, M. E. An Outline of General History: For the Use of Schools. Cincinnati: Van Antwerp, Bragg & Co, 1883.
- Lord, John. A Modern History, From the Time of Luther to the Fall of Napoleon. Philadelphia: C. Desilver & Sons [etc.], 1877.
- Michelet, Jules, and M. C. M. Simpson. A Summary of Modern History. London: Macmillan, 1875.
- Timbs, John. Predictions Realized in Modern Times.: Now First Collected by Horace Welby. London: Kent and Co. Paternoster Row, 1862.
- Post, Truman M. The Skeptical Era in Modern History; Or, The Infidelity of the Eighteenth Century, the Product of Spiritual Despotism. New York: C. Scribner, 1856.
- Modern history. Chambers W. and R., ltd. 1856.
- Michelet, Jules, and Alonzo Potter. Modern History. New York: Harper & Brothers, 82 Cliff-St, 1846.
- Goodrich, Samuel G. Famous Men of Modern Times. Boston: Bradbury, Soden & Co, 1843.
- General History of the World: Abridged. Huddersfield: Brook and Lancaster, 1802.
External links
- Journal of Contemporary History. SAGE Publications. ISSN 1461-7250 (Print ISSN 0022-0094)
- Contemporary History Institute (CHI). ohiou.edu (ed., Analyzes the contemporary period in world affairs — the period from World War II to the present — from an interdisciplinary historical perspective.)
- China and Europe, 1500–2000 and Beyond: What is Modern?. Columbia UniversityColumbia UniversityColumbia University in the City of New York is a private, Ivy League university in Manhattan, New York City. Columbia is the oldest institution of higher learning in the state of New York, the fifth oldest in the United States, and one of the country's nine Colonial Colleges founded before the...

