Military history of Italy
Encyclopedia
The military history of Italy chronicles a vast time period, lasting from the overthrow of Tarquinius Superbus in 509 BC, through the Roman Empire
, Italian unification
, and into the modern day. The Italian peninsula
has been a centre of military conflict throughout European history
.
in the west, Sabine
s in the upper valley of the Tiber, Umbrian
s in the north-east, Samnites
in the South, Oscans
and others) shared the Italian peninsula with two other major ethnic groups: the Etruscans
in the North, and the Greeks
in the south.
The Etruscan
s (Etrusci or Tusci in Latin
) were settled north of Rome in Etruria
(modern northern Lazio, Tuscany
and part of Umbria
). They founded cities like Tarquinia
, Veii and Volterra and deeply influenced Roman culture, as clearly shown by the Etruscan origin of some of the mythical Roman kings. The origins of the Etruscans are lost in prehistory. Historians have no literature, no texts of religion or philosophy; therefore much of what is known about this civilisation is derived from grave goods and tomb findings.
The Italics were war-like as the Etruscans (the gladiator
ial displays actually evolved out of Etruscan funerary customs). The Italics and the Etruscans had a significant military tradition. In addition to marking the rank and power of certain individuals in their culture, warfare was a considerable economic boon to their civilization. Like many ancient societies, the Italics and the Etruscans conducted campaigns during summer months, raiding neighboring areas, attempting to gain territory and combating piracy/banditism as a means of acquiring valuable resources such as land, prestige and goods. It is also likely individuals taken in battle would be ransomed back to their families and clans at high cost.
The Greeks had founded many colonies in Southern Italy
(that the Romans later called Magna Graecia
), such as Cumae
, Naples
and Taranto
, as well as in the eastern two-thirds of Sicily
, between 750
and 550 BC
.
After 650 BC
, the Etruscan
s became dominant in central Italy, and expanded into north Italy founding cities like Mutina (actual Modena
) and Felsina (actual Bologna
). Roman tradition claimed that Rome had been under the control of seven "etruscan" kings
from 753
to 509 BC beginning with the mythic Romulus
who along with his brother Remus
were said to have founded the city of Rome
.
s influenced by Greek civilization, a citizen militia
which practiced hoplite
tactics. It was small (the population of free males of military age was then about 9,000) and organized in five classes (in parallel to the comitia centuriata
, the body of citizens organized politically), with three providing hoplites and two providing light infantry. The early Roman army was tactically limited and its stance during this period was essentially defensive. By the 3rd century BC, the Romans abandoned the hoplite formation in favor of a more flexible system in which smaller groups of 120 (or in some cases 60) men called maniples
could maneuver more independently on the battlefield. Thirty maniples arranged in three lines with supporting troops constituted a legion
, totaling between 4,000 and 5,000 men. The early Republican legion consisted of five sections, each of which was equipped differently and had different places in formation: the three lines of manipular heavy infantry (hastati
, principes
and triarii
), a force of light infantry (velites
), and the cavalry (equites). With the new organization came a new orientation toward the offensive and a much more aggressive posture toward adjoining city-states.
At nominal full strength, an early Republican legion would have included 3,600 to 4,800 heavy infantry, several hundred light infantry and several hundred cavalrymen, for a total of 4,000 to 5,000 men. Legions were often significantly understrength from recruitment failures or following periods of active service due to accidents, battle casualties, disease and desertion. During the Civil War, Pompey's legions in the east were at full strength because recently recruited, while Caesar's legions were in many cases well below nominal strength after long active service in Gaul. This pattern also held true for auxiliary forces.
Until the late Republican period, the typical legionary was a property-owning citizen farmer from a rural area (an adsiduus) who served for particular (often annual) campaigns, and who supplied his own equipment and, in the case of equites, his own mount. Harris suggests that down to 200 BC, the average rural farmer (who survived) might participate in six or seven campaigns. Freedmen and slaves (wherever resident) and urban citizens did not serve except in rare emergencies. After 200 BC, economic conditions in rural areas deteriorated as manpower needs increased, so that the property qualifications for service were gradually reduced. Beginning with Gaius Marius
in 107 BC, citizens without property and some urban-dwelling citizens (proletarii) were enlisted and provided with equipment, although most legionaries continued to come from rural areas. Terms of service became continuous and long—up to twenty years if emergencies required it although Brunt argues that six or seven years was more typical. Beginning in the 3rd century BC, legionaries were paid stipendium (amounts are disputed but Caesar famously "doubled" payments to his troops to 225 denarii
a year), could anticipate booty and donatives (distributions of plunder by commanders) from successful campaigns and, beginning at the time of Marius, often were granted allotments of land upon retirement. Cavalry and light infantry attached to a legion (the auxilia) were often recruited in the areas where the legion served. Caesar formed a legion, the Fifth Alaudae, from non-citizens in Transalpine Gaul to serve in his campaigns in Gaul. By the time of Caesar Augustus, the ideal of the citizen-soldier had been abandoned and the legions had become fully professional. Legionaries were paid 900 sesterces
a year and could expect a payment of 12,000 sesterces on retirement.
At the end of the Civil War
, Augustus reorganized Roman military forces, discharging soldiers and disbanding legions. He retained 28 legions, distributed through the provinces of the Empire. During the Principate
, the tactical organization of the Army continued to evolve. The auxilia remained independent cohorts, and legionary troops often operated as groups of cohorts rather than as full legions. A new versatile type of unit, the cohortes equitatae, combining cavalry and legionaries in a single formation could be stationed at garrisons or outposts, could fight on their own as balanced small forces or could combine with other similar units as a larger legion-sized force. This increase in organizational flexibility over time helped ensure the long-term success of Roman military forces.
The Emperor Gallienus
(253–268 AD) began a reorganization that created the final military structure of the late Empire. Withdrawing some legionaries from the fixed bases on the border, Gallienus created mobile forces (the Comitatenses
or field armies) and stationed them behind and at some distance from the borders as a strategic reserve. The border troops (limitanei) stationed at fixed bases continued to be the first line of defense. The basic unit of the field army was the "regiment", legiones or auxilia for infantry and vexellationes for cavalry. Evidence suggests that nominal strengths may have been 1,200 men for infantry regiments and 600 for cavalry, although many records show lower actual troop levels (800 and 400). Many infantry and cavalry regiments operated in pairs under the command of a comes
. In addition to Roman troops, the field armies included regiments of "barbarians" recruited from allied tribes and known as foederati
. By 400 AD, foederati regiments had become permanently established units of the Roman army, paid and equipped by the Empire, led by a Roman tribune and used just as Roman units were used. In addition to the foederati, the Empire also used groups of barbarians to fight along with the legions as "allies" without integration into the field armies. Under the command of the senior Roman general present, they were led at lower levels by their own officers.
Military leadership evolved greatly over the course of the history of Rome. Under the monarchy, the hoplite armies would have been led by the kings of Rome. During the early and middle Roman Republic, military forces were under the command of one of the two elected consuls
for the year. During the later Republic, members of the Roman Senatorial elite, as part of the normal sequence of elected public offices known as the cursus honorum
, would have served first as quaestor
(often posted as deputies to field commanders), then as praetor
. Following the end of a term as praetor or consul, a Senator might be appointed by the Senate as a propraetor
or proconsul
(depending on the highest office previously held) to govern a foreign province. More junior officers (down to but not including the level of centurion) were selected by their commanders from their own clientelae
or those recommended by political allies among the Senatorial elite. Under Augustus, whose most important political priority was to place the military under a permanent and unitary command, the Emperor was the legal commander of each legion but exercised that command through a legatus
(legate) he appointed from the Senatorial elite. In a province with a single legion, the legate would command the legion (legatus legionis
) and also serve as provincial governor, while in a province with more than one legion, each legion would be commanded by a legate and the legates would be commanded by the provincial governor (also a legate but of higher rank). During the later stages of the Imperial period (beginning perhaps with Diocletian
), the Augustan model was abandoned. Provincial governors were stripped of military authority, and command of the armies in a group of provinces was given to generals (duces
) appointed by the Emperor. These were no longer members of the Roman elite but men who came up through the ranks and had seen much practical soldiering. With increasing frequency, these men attempted (sometimes successfully) to usurp the positions of the Emperors who had appointed them. Decreased resources, increasing political chaos and civil war eventually left the Western Empire vulnerable to attack and takeover by neighboring barbarian peoples.
Comparatively less is known about the Roman navy than the Roman army. Prior to the middle of the 3rd century BC, officials known as duumviri navales commanded a fleet of twenty ships used mainly to control piracy. This fleet was given up in 278 AD and replaced by allied forces. The First Punic War
required that Rome build large fleets, and it did so largely with the assistance of and financing from allies. This reliance on allies continued to the end of the Roman Republic. The quinquereme
was the main warship on both sides of the Punic Wars and remained the mainstay of Roman naval forces until replaced by the time of Caesar Augustus by lighter and more maneuverable vessels. As compared with a trireme
, the quinquereme permitted the use of a mix of experienced and inexperienced crewmen (an advantage for a primarily land-based power), and its lesser maneuverability permitted the Romans to adopt and perfect boarding tactics
using a troop of approximately 40 marines in lieu of the ram
. Ships were commanded by a navarch
, a rank equivalent to a centurion, who were usually not citizens. Potter suggests that because the fleet was dominated by non-Romans, the navy was considered non-Roman and allowed to atrophy in times of peace.
Available information suggests that by the time of the late Empire (350 AD), the Roman navy comprised a number of fleets including both warships and merchant vessels for transportation and supply. Warships were oared sailing galleys with three to five banks of oarsmen. Fleet bases included such ports as Ravenna, Arles, Aquilea, Misenum and the mouth of the Somme River in the West and Alexandria and Rhodes in the East. Flotillas of small river craft (classes) were part of the limitanei (border troops) during this period, based at fortified river harbors along the Rhine and the Danube. The fact that prominent generals commanded both armies and fleets suggests that naval forces were treated as auxiliaries to the army and not as an independent service. The details of command structure and fleet strengths during this period are not well known although it is known that fleets were commanded by prefects.
, from the collapse of a central Roman government in the late 5th century to the Italian Wars
of the Renaissance
, Italy was constantly divided between opposing factions fighting for control. At the time of the deposition of Romulus Augustulus (476), the Heruli Confederation
governed Italy, but it was displaced by the Ostrogoths, who fought a long war with the Byzantine army
in Italy (the Gothic War
). The Byzantine came out of the war victorious only to find Italy invaded by a new wave of barbarians led by the Lombards
.
The Lombards diminished Byzantine territory to the Exarchate of Ravenna
, the Duchy of Rome
, the Duchy of Naples
, and the far south of Apulia
and Calabria
. They established a kingdom centred on Pavia
in the north. During the interregnum called the Rule of the Dukes
(574 – 584), the dukes of the Lombards invaded Burgundy, but were repulsed by the Merovingian king Guntram
, who in turn invaded Italy and took the region of Savoy
. The Lombards were forced to elect a new king to organise their defence. For the next two centuries, the Byzantine power in the peninsula was reduced by the Lombard kings, the greatest of which was Liutprand
, until it consisted of little more than the tips of the Italian toe and heel, Rome and its environs being practically independent under the popes and the Neapolitan coast under its dukes.
In 774, Charlemagne
of the Franks
invaded and conquered the Lombard kingdom. In the south of the peninsula, the Duchy of Benevento
remained independent of Frankish dominion, however. During the period of Carolingian
strength, Charlemagne's descendants governed the north of Italy in relative peace, except for the brief period of the rebellion of Bernard
and the constant raids from the Slavs to the east and the Saracens to the south. Pirates harassed the Adriatic and Liguria
n coasts and the islands of Corsica
and Sardinia
. The south was very different, as the Lombards were at the height of there power there. Warfare between Lombard and Greek, especially the Greek city-states of the Tyrrhenian
, was endemic. The Greek cities fell out of the orbit of Constantinople and Byzantine possessions shrank to their smallest mark as the Lombards and the Saracens increased their predations. In 831, the Arabs conquered Palermo
and in 902 they conquered Taormina
, ending the conquest of Sicily. They likewise established their presence on the peninsula, especially on the Garigliano and in Bari
. The story of the incessant conflicts of the states of the Mezzogiorno is chaotic until the arrival of the Normans
in the early eleventh century (1016). Under their leadership, the Jews of the south found themselves eventually united, the Arabs expelled, and the whole Mezzogiorno subjugated to the Hauteville dynasty
of kings of Sicily (1130).
The second half of the Middle Ages in Italy was marked by frequent conflict between the Holy Roman Empire
and the Papacy, the latter eventually emerging victorious in that it ultimately prevented political unification of northern Italy under Imperial rule. Imperial invasions were led by more or less all medieval Emperors, the most notable episodes being the end of the Investiture controversy
by the pilgrimage of Henry IV, Holy Roman Emperor
at Canossa
in 1077 and the no less than five major invasions staged by Frederick Barbarossa
against the Lombard League
, culminating in the sack of Milan
in 1162, after which every building in the city was demolished, except the churches. The lasting conflict led to the emergence of the Guelph and the Ghibelline
parties in northern Italy, supporting respectively the Pope (and the independent cities) and the Emperor, though siding with a party was often dictated by other political considerations (more or less each city has belonged to both parties). In May 1176, the Lombard League, led by a revived Milan, defeated the Emperor Frederick Barbarossa at Legnano.
The victory of the Guelph party meant the end of Imperial overlordship over northern Italy, and the formation of city-state
s such as Florence
, Venice
, Milan, Genoa
or Siena
. While Venice was turning to the seas, supporting, and acquiring large loot from, the 1204 Fourth Crusade
's sack of Constantinople, the other city-states were struggling for control of mainland, Florence being the rising power of the time (annexation of Pisa
in 1406).
Sicily was invaded in 1266 by Charles I, duke of Anjou; the Angevines were however toppled in the 1282 Sicilian Vespers
, and Peter III of Aragon
invaded the island. This set the background for later French claims over Naples and Sicily.
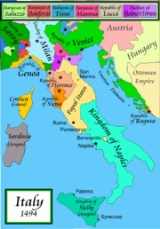
Disintegration of the Holy Roman Empire and the Hundred Years War in neighbouring France
meant that Italy was more or less left in peace during the fifteenth century; this allowed its cities to grow rich and to become attractive preys for its neighbours during the sixteenth century.
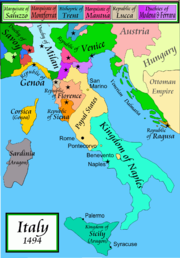 The relative peace that had prevailed in Italy following the Treaty of Lodi
The relative peace that had prevailed in Italy following the Treaty of Lodi
was shattered by the beginning of the Italian Wars in 1494. Ludovico Sforza
, seeking allies, suggested to Charles VIII of France
that the latter press his claim to the throne of Naples
; Charles obliged and launched an invasion of the peninsula
. The French march to, and capture of, Naples was accomplished with relative ease—the Italian states being shocked at the brutality of French tactics and the efficacy of the new French artillery
—but Charles was forced to withdraw from Italy in 1495, after a hastily-constructed alliance fought him at the Battle of Fornovo
. Charles died in 1498, but the conflict he started would be continued by his successors; the Italian Wars would last until 1559, involving, at various times, all the major states of western Europe (France
, Spain
, the Holy Roman Empire
, England
, Scotland
, the Republic of Venice
, the Papal States
, and most of the city-states of Italy
) as well as the Ottoman Empire
, and rapidly becoming a general struggle for power and territory among the various participants, marked with an increasing degree of alliances, counter-alliances, and regular betrayals.
In 1499, Louis XII of France
launched the Second Italian War
, invading Lombardy
and seizing the Duchy of Milan
. He then reached an agreement with Ferdinand I of Spain to divide Naples. By 1502, combined French and Spanish forces had seized control of the Kingdom; disagreements about the terms of the partition led to a war between Louis and Ferdinand. By 1503, Louis, having been defeated at the Battle of Cerignola
and Battle of Garigliano
, was forced to withdraw from Naples, which was left under the control of the Spanish viceroy, Gonzalo Fernández de Córdoba
. Meanwhile, Pope Alexander VI
attempted to carve a Borgia
state from the Romagna
through the efforts of Cesare Borgia
.
In 1508, Pope Julius II
formed the League of Cambrai, in which France, the Papacy, Spain and the Holy Roman Empire
agreed to attack the Republic of Venice
and partition her mainland territories. The resulting War of the League of Cambrai
was a kaleidoscope of shifting alliances. The French defeated the Venetian army at the Battle of Agnadello
, capturing extensive territories; but Julius, now regarding France as a greater threat, left the League and allied himself with Venice. After a year of fighting over the Romagna
, he proclaimed a Holy League against the French; this rapidly grew to include England, Spain, and the Holy Roman Empire. The French were driven from Italy in late 1512, despite their victory at the Battle of Ravenna
earlier that year, leaving Milan in the hands of Maximilian Sforza
and his Swiss mercenaries
; but the Holy League fell apart over the subject of dividing the spoils, and in 1513 Venice allied with France, agreeing to partition Lombardy between them. The French invasion of Milan in 1513 was defeated at the Battle of Novara
, which was followed by a series of defeats for the French alliance; but Francis I of France
defeated the Swiss at the Battle of Marignano
in 1515, and the treaties of Noyon and Brussels left France and Venice in control of northern Italy.
The election of Charles of Spain
as Holy Roman Emperor
in 1519 led to a collapse of relations between France and the Habsburgs which resulted in the Italian War of 1521
, in which France and Venice were pitted against England, the Papacy, and Charles's Habsburg possessions. Prosper Colonna defeated the French at the Battle of Bicocca
, driving them from Lombardy. A series of abortive invasions of France by the allies and of Italy by the French continued until 1524, when Francis personally led a French army into Lombardy, only to be defeated and captured at the Battle of Pavia
; imprisoned in Madrid
, Francis was forced to agree to extensive concessions. Released in 1526, Francis repudiated the terms of the agreement, allied himself with Venice, the Papacy, Milan, and England, and launched the War of the League of Cognac
. In 1527, Imperial troops sacked Rome itself
; the French expedition to capture Naples the next year failed, leading Francis and Charles to conclude the Treaty of Cambrai. Charles then concluded a series of treaties at Barcelona and Bologna
which eliminated all his opponents save the Florentine Republic, which was subdued by the Siege of Florence
and returned to the Medici
.
The remainder of the Italian Wars—which flared up again in 1535—was primarily a struggle between the Habsburg
s and the Valois; while Italy was, at times, a battlefield, the Italian states played little further role in the fighting. The French managed to seize and hold Turin
, defeating an Imperial army at the Battle of Ceresole
in 1544; but the warfare continued (primarily in northern France) until Henry II of France
was forced to accept the Peace of Cateau-Cambrésis in 1559, in which he renounced any further claims to Italy.
By the end of the wars in 1559, Habsburg Spain
had been established as the premier power of Europe, to the detriment of France
. The states of Italy, which had wielded power disproportionate to their size during the Middle Ages
and the Renaissance
, were reduced to second-rate powers or destroyed entirely.
The Italian Wars had a number of consequences for the work and workplace of Leonardo da Vinci
; his plans for a "Gran Cavallo" horse statue in 1495 were dropped when the seventy tons of bronze intended for the statue were instead cast into weapons to save Milan
. Later, following a chance encounter with Francis I after the Battle of Marignano
, Leonardo agreed to move to France, where he spent his final years.
In France, Henry II
was fatally wounded in a joust held during the celebrations of the peace. His death led to the accession of his 15-year-old son Francis II
, who in turn soon died. The French monarchy was thrown into turmoil, which increased further with the outbreak of the French Wars of Religion
in 1562.
There is a lack of consensus on the exact dates for the beginning and the end of Italian reunification, but many scholars agree that the process began with the end of Napoleonic rule and the Congress of Vienna in 1815, and approximately ended with the Franco-Prussian War in 1871 and the conquest of Rome, though the last città irredente (Trento
and Triest) did not join the Kingdom of Italy until after World War I.
and Italian Somalia were formed, but the conquest of Ethiopia
was stopped at the Battle of Adwa in 1896.
(1911–1912) Italy occupied Tripolitania
and Cyrenaica
that later were unified in the colony of Libya
.
together with Germany
and Austria-Hungary
, in the years before the outbreak of the conflict the Italian government had enhanced its diplomatic efforts towards United Kingdom
and France
. This was because the Italian government had grown convinced that a support of Austria (which had been also the traditional enemy of Italy during the 19th century Risorgimento) would not grant to Italy the Italian-speaking lands the country was aiming for in its territorial expansion: Trieste
, Istria
, Zara
and Dalmatia
, all Austrian possessions. In fact, a secret agreement signed with France in 1902 practically nullified Italy's membership in the Triple Alliance.
A few days after the outbreak of the conflict, on 3 August 1914, the government, led by the conservative Antonio Salandra
, declared that Italy would not commit its troops, maintaining that the Triple Alliance had only a defensive stance, whereas Austria-Hungary had been the aggressor. In reality, both Salandra and the minister of Foreign Affairs, Sidney Sonnino
, started diplomatic activities to probe which side was ready to grant the best reward for Italy's entrance in the war. Although the majority of the cabinet (including former Prime Minister Giovanni Giolitti
) was firmly contrary to the intervention, numerous intellectuals, including socialists
such as Ivanoe Bonomi
, Leonida Bissolati
and Benito Mussolini
, declared in favour of the intervention, which was then mostly supported by the Nationalist and the Liberal parties.
The diplomatic moves led to the London Pact
(26 April 1915), signed by Sonnino without the approval of the Italian Parliament. By the Pact, in case of victory Italy was to be given Trentino and the South Tyrol
up to the Brenner Pass
, the entire Austrian Littoral
(with Trieste
, Gorizia-Gradisca
and Istria
, but without Fiume), parts of western Carniola
(Idrija
and Ilirska Bistrica
) and north-western Dalmatia
with Zadar
and most of the islands, but without Split
. Other agreements concerned the sovereignty of the port of Valona
, the province of Antalya
in Turkey
and part of the German colonies in Africa.
Germany and Austria-Hungary had only advanced the possibility of negotiating parts of the Trentino and Eastern Friuli
, without Gorizia
and Trieste. The offer of the French colony of Tunisia
was deemed unsatisfactory.
In April 1915 Italy joined the Entente
and on 3 May 1915 officially rejected the Triple Alliance. In the following days Giolitti and the neutralist majority of the Parliament fought to keep Italy out of the conflict, while the nationalists demonstrated in the squares in favour of entrance into the war (the nationalist poet Gabriele D'Annunzio
defined them le radiose giornate di Maggio - "the sunny days of May"). On 13 May Salandra presented his resignation to King Victor Emmanuel III. Giolitti, fearful of a further blow to governing institutions, declined to succeed as prime minister and also resigned. Italy thenceforth entered the war under the impetus of a relative minority of its population and politicians.

brought the fascist party
to power in Italy with his March on Rome
on 28 October. Mussolini repeatedly stated his dream of the Mediterranean Sea
becoming an "Italian lake" and valued war, saying "Though words are beautiful things, rifles, machine guns, planes, and cannon are still more beautiful".
was to be Mussolini's way of making up for Italy's embarrassing defeat at the hands of the Ethiopians in the First Italo–Ethiopian War in 1896, and was also a chance to build Italian empire in the last unoccupied region of Africa and divert the populace from economic woes. General Emilio de Bono
put on record that preparations for the invasion of Ethiopia
(Abyssinia) had been going on since 1932 as roads were being built from Italian Somalia
into Ethiopian territory, though Mussolini constantly claimed that he was not a "collector of deserts" and would never think of invading. Ethiopians protested this build-up to war which eventually led up to a border clash at Walwal. Mussolini called this clash "unprovoked aggression" by Ethiopia and invaded on 3 October 1935, led by De Bono. In only three days the Italians had captured Adwa
where the former disgraceful defeat had happened. In December Pietro Badoglio
replaced De Bono as commander of the invasion because of De Bono's cautious advance. On 31 March 1936, a desperate final counter-attack by Haile Selassie, king of Ethiopia, was carried out, though word of the attack had already gotten to the Italians, giving them victory in the Battle of Maychew
. Only a few days later the Ethiopian capital Addis Ababa
was conquered, allowing Italy to annex the country on 7 May, proclaiming Victor Emmanuel III Emperor of Italian East Africa
.
 On 17 July 1936, Francisco Franco
On 17 July 1936, Francisco Franco
and the rest of Nationalist Spain's forces began a rebellion against Republican Spain that was to last three years, called the Spanish Civil War
. Franco was fairly sure that he would be able to secure German and Italian help for his National Faction
, sending emissaries out on 20 July to achieve this. Both did indeed pledge support, sending in the Corpo Truppe Volontarie
from Italy and the Legión Cóndor from Nazi Germany
, as well as weapons and aircraft. Mussolini was very devoted, eventually sending in 37,000 men and huge amounts of planes to ensure that this "campaign against communism
" would succeed. The foreign press started to heap pressure on Mussolini when Italian troops suffered a major defeat at Guadalajara
, which led to Mussolini sending in normal troops rather than militia to fight in Spain, eventually ruining the Italian economy with the expense of a war Mussolini thought would end any day. This war also distracted Italy, allowing Germany to carry out the annexation of Austria with the Anschluss
, a move that otherwise may have been a breaking point between the two powers, due to Austria's alliance with Fascist Italy. The war was supposed to be a staging ground for Italian tactics, potential time to fix any creases out of the system, but Italy continued during World War II
to use the same tactics as long before that, unlike Germany's new revolutionary war tactics.
, Mussolini decided to accompany that invasion with his own invasion of Albania
. Albania had long been nearly a puppet state of Italy, several of its military officers actually being Italian themselves. However, King Zog was currently in fairly serious debt and wanted help from Italy, so Mussolini sent foreign minister Gian Galeazzo Ciano
with a list of demands, which Ciano described as impossible to accept. Once King Zog declined, Mussolini said that he must accept these demands by 7 April 1939, or Italy would invade. The invaders had already disembarked to invade before that time. General Alfredo Guzzoni
would lead two Bersaglieri
divisions with a battalion of tanks in the invasion, where most resistance was extremely minor, though various organizational problems in the Italian military showed themselves. King Zog fled the country to Greece
, granted asylum in Athens
, then eventually to get to London
. On 12 April, the Albanian parliament voted to unite their country with Italy, giving Victor Emmanuel III the Albanian crown.
was signed by Galeazzo Ciano and Joachim von Ribbentrop
of Germany, effectively allying the two powers. Despite the fairly good relations the two forces had had, many Italians were against this alliance, thinking of it as more of a submission to Germany, knowing that Italian interests were likely not to be favored in the relationship. The alliance also technically forced Italy to join in any war that Germany had entered, so that Germany could at any time present the paper and force Mussolini to enter, though they did not end up using this right.
invaded Poland
on 1 September 1939, but Italy
remained neutral for the following ten months even though it was one of the Axis powers
.
Italian dictator Benito Mussolini
's Under-Secretary for War Production, Carlo Favagrossa
, had estimated that Italy could not possibly be prepared for such a war until at least October 1942. This had been made clear during Italo-German negotiations for the Pact of Steel
whereby it was stipulated that neither signatory was to make war without the other earlier than 1943. Although considered a major power, the Italian industrial sector was relatively weak compared to other Europe
an major powers. Italian industry did not equal more than 15% of that of France
or of Britain in militarily critical areas such as automobile
production: the number of automobiles in Italy before the war ranged at ca. 372,000, in comparison to ca. 2,500,000 in Britain and France. The lack of a stronger automotive industry made it difficult for Italy to mechanize
its military. Italy still had a predominantly agricultural-based economy, with demographics more akin to a developing country
(high illiteracy, poverty, rapid population growth and a high proportion of adolescents) and a proportion of GNP derived from industry less than that of Czechoslovakia, Hungary and Sweden, in addition to the other great powers. In terms of strategic materials, in 1940, Italy produced 4.4, 0.01, 1.2 and 2.1 Mt of coal, crude oil, iron ore and steel, respectively. By comparison, Great Britain produced 224.3, 11.9, 17.7, and 13.0 Mt and Germany produced 364.8, 8.0, 29.5 and 21.5 Mt of coal, crude oil, iron ore and steel, respectively. Most of the raw material needs could only be fulfilled through importation and no effort was made to stockpile key materials before the entry into war. Also, approximately one quarter of Italy’s merchant fleet were present at foreign ports and given no forewarning of Mussolini’s rash decision to enter the war and were immediately impounded. Another handicap was the large number of weapons and supplies given by Italy practically for free to the Spanish forces fighting under Franco
during the Spanish Civil War
between 1936 and 1939. The Italians also sent the "Corps of Volunteer Troops
" (Corpo Truppe Volontarie) to fight for Franco. The financial cost of this war was between 6 and 8.5 billion lire, approximately 14 to 20% of annual expenditure. Added to these issues was Italy's extreme debt position. When Benito Mussolini
took office in 1921 the government debt was 93 billion lire
, un-repayable in the short to medium term. Yet only two years later this debt increased to 405 billion lire.
The Italian Royal Army (Regio Esercito) therefore remained comparatively depleted and weak at the commencement of the war. The Italian tanks were of poor quality, and radios were few in number. The bulk of the Italian artillery
dated from World War I
. The Italian Air Force (Regia Aeronautica
's) primary fighter was the Fiat CR-42, though an advanced design for a biplane
with excellent performance characteristics, it was obsolete compared to the then current generation monoplane
fighters of other nations. The Italian Royal Navy (Regia Marina
) had no aircraft carrier
s. In addition, the Royal Air Force (Regia Aeronautica
) could field approximately 1,760 aircraft, of which only 900 of them could be considered as "front-line machines".
Yet whilst equipment was lacking and outdated, Italian authorities were acutely aware of the need to maintain a modern army and were taking the necessary steps to modernize in accordance with their very own relatively advanced tactical principles. Almost 40% of the 1939 budget was allocated to military spending. Awareness existed, albeit belatedly, of the need to have close air support for the Navy and the decision to build carriers was taken And whilst the majority of equipment was obsolescent and poor, appropriate steps were being taken whereby quality equipment was being developed. For example, the three series 5 fighters were capable of meeting the best allied fighters on equal terms, but only a few hundred of each were produced; The Fiat G55 Centauro received much German interest and was defined by Oberst Petersen, advisor to Goering
, as the “best Axis fighter.” The Carro Armato P40 tank, roughly equivalent to the M4 Sherman
and Panzer IV
, was designed in 1940, but no prototype was produced until 1942 and developers/manufacturers not able to roll out any of these tanks before Armistice. This was owing, in part, to the lack of sufficiently powerful engines, which were themselves undergoing a development push. Unlike the Allies, Italian tank designers did not think to use old aircraft engines, which were available in relative abundance, and would have certainly facilitated more rapid tank development. Total tank production for the war (~ 3,500) was less than the number of tanks used by Germany in its invasion of France. The Italians were also reported to be the first to use self-propelled guns, both in close support and anti-tank roles, and their, for example, 75/46
(& 75/32
) , 90/53
(a peer of the German 88/55
), 102/35 and 47/32
mm, and 20 mm AA
guns were not obsolete. Also of note were the AB 41
and the Camionetta AS 42 which were regarded as excellent vehicles of their type. None of these developments precluded the fact that the bulk of the equipment was obsolescent and poor. However, it was this relatively weak economy, lack of suitable raw materials and inability to produce suitable quantities of armaments and supplies which was predominant reason for Italian military failure.
On paper, Italy had one of the largest armies, but this was far from reality. According to the estimates of Bierman and Smith, the Italian regular army could field only about 200,000 troops at the start of World War II. Irrespective of the attempts to modernize, the majority of Italian army personnel were lightly armed infantry lacking sufficient motor transport. There was insufficient budget to train the men in the services such that in World War II the bulk of the personnel received much of their training at the front, when it was too late to be of use. Air units had not been trained to operate with the naval fleet and the majority of ships had been built for fleet actions, not the convoy protection duties which they were mostly employed for during the war. Regardless, a critical lack of fuel kept naval activities to a minimum.
Senior leadership was also an issue. Mussolini personally assumed control of all three individual military service ministries with the intention of influencing detailed planning. Comando Supremo (the Italian High Command) consisted of only a small complement of staff that could do little more than inform the individual service commands of Mussolini’s intentions, after which it was up to the individual service commands to develop these into proper plans and execute. The result was that there was no central direction for operations and the three military services tended to work independently, focusing only on their fields, with little inter-service cooperation. The Army itself was essentially split into two different institutions; those institutionally loyal to the king (Regio Esercito
) and those to Mussolini, and discrepancies in pay existed for personnel of equal rank, but from different units.
Following the German conquest of Poland, Mussolini would change his mind repeatedly as to whether he would enter the war. The British
commander in Africa
, General Archibald Wavell, correctly predicted that Mussolini's pride would ultimately cause him to enter the war. Wavell would compare Mussolini's situation to that of someone at the top of a diving board: "I think he must do something. If he cannot make a graceful dive, he will at least have to jump in somehow; he can hardly put on his dressing-gown and walk down the stairs again."
Some historians believe that Italian leader Benito Mussolini
was induced to enter the war against the Allies
by secret negotiations with British Prime Minister Winston Churchill
, with whom he had an active mail correspondence between September 1939 and June 1940. The journalist Luciano Garibaldi wrote that "in those letters (which disappeared at Lake Como in 1945) Churchill may have extorted Mussolini to enter the war to mitigate Hitler's demands and dissuade him from continuing hostilities against Great Britain as France was inexorably moving toward defeat. In light of this, Mussolini could urge Hitler turn against the USSR, the common enemy of both Churchill and Mussolini".
Initially, the entry into the war was clearly political opportunism, which led to a lack of consistency in planning, with principal objectives and enemies being changed with little regard for the consequences. Mussolini was well aware of the military and material deficiencies but thought the war would be over soon and did not expect to do much fighting. This led to confusion amongst ordinary Italians and soldiers who had little idea of what they were fighting for and, hence, had little conviction and saw little justification for it. As the war progressed and one disaster followed another, Comando Supremo were forced to take more serious steps in their planning.
, with the impending German conquest of Belgium
, the Netherlands
, and France
, Mussolini could no longer hold himself back and declared war on the allies on 10 June 1940. To Mussolini it seemed that the war was already nearly over, and he wanted to make sure that Italy at least got a position at the peace tables at the end and obtained such lands as Corsica
, Nice
, and more North African territory. The Italian offensive against France did not actually begin until ten days after the declaration of war, and Italian troops were very slow to capture territory, while Germany had already taken hold of Paris
. By 25 June, the armistice with France had already been arranged, though Italian troops made virtually no progress into French territory.
, as the Regia Marina
would now oppose them in Mediterranean waters. Italian armies in Libya and East Africa could also potentially have knocked British troops completely out of Egypt
, having half a million men in Africa compared to the United Kingdom's fifty thousand. However, British troops took the initiative in Africa while Italy was still having trouble pacifying Ethiopia and General Wavell
kept up a constantly moving front of raids on Italian positions that proved to be successful. On 14 June a successful surprise attack was made on Fort Capuzzo
by the British, though it was not meant as a permanent gain as the British were using far more mobile tactics at the time. By mid-September, casualty listings indicate that Italy had lost 3,000 troops where the United Kingdom had only lost slightly over 490, despite Italy's land numbers and air superiority at the time.
On 13 September 1940, Italy began a very slow advance
eastward into Egypt
. The Italians advanced with six divisions. After three days, they stopped and set up a chain of fortified camps near Sidi Barrani
. However, the chain of camps were too far apart from one another. This allowed Wavell make a crippling blow to the Italian forces around Sidi Barrani
right at the start of what was to become Operation Compass
. Richard O'Connor
led the initial attack against the Italian camps. O'Connor moved between the camps and around to the Italian rear. This greatly surprised the Italians and the British were able to immediately capture four thousand prisoners. This attack alone could have effectively annihilated the Italian army in North Africa. But the British commanders did not foresee such a large victory. Instead, the initial attack was thought of as a large-scale raid. For this reason, no infantry division was available to press home the British opportunity at Sidi Barrani
. So the remaining Italian troops managed to escape safely to Bardia
. However, Bardia
was captured by the British within three weeks.
The Italian campaign in East Africa
was perhaps even less successful. The Italians captured small parts of Sudan
, Kenya
, and British Somaliland
, then took up a defensive posture against an expected counterattack. This counterattack came from the Indian 4th Infantry Division, which drove into Ethiopia with help from an amphibious assault and forces in Kenya, capturing Eritrea in February, Somalia in March, and Addis Ababa, capital of Ethiopia, in April. Forces in Italian East Africa
were somewhat cut short by the Regia Aeronautica
's forced presence in the Battle of Britain
at the time, leaving only 150 planes in Ethiopia.
Campaigning in North Africa then fell to Erwin Rommel
over any Italian generals, as many Panzer
units came into the theatre from Germany as the Afrika Korps
. However, the bulk of the Axis army in North Africa was still Italian. Rommel was at first very successful, reaching the Egyptian border again in less than a fortnight as he caught Wavell off-guard. Another British offensive was crushed, and Rommel made his way to El Alamein
. This made Mussolini believe the end was near, as he flew to Africa, planning to enter the capital of Egypt triumphantly, only to wait three weeks, then fly back to Rome. Field Marshal Montgomery won at El Alamein in October 1942 for the British. This victory coincided with Operation Torch
, America's landing in French North Africa, and the Battle of Stalingrad
's outcome, destroying axis morale.
, Mussolini then decided on an invasion of Greece
as his next move to keep in pace with Germany's recent occupation of Romania
. After large propaganda campaigns and even the sinking of a Greek light cruiser, Mussolini then handed an ultimatum to Ioannis Metaxas
, Prime Minister of Greece, which would initiate the Greco-Italian War
. Hitler was against Mussolini's invasion, (as it would require German troops' help later on), but Mussolini continued without German knowledge, as he felt that the Nazis had invaded countries too many times without telling Mussolini beforehand.
Mussolini was very unsure of what date to invade, as he changed his mind many times, even five times in one segment of fifteen minutes. Eventually he decided on 28 October, the anniversary of the March on Rome
, though staff headquarters was not aware until they heard the date on London radio. In about two weeks, the Italian army was already retreating back into Albania, for conditions at this time of year were very detrimental to mountain warfare and general organization problems continued throughout the military. Franco of the recently victorious Fascist side in the Spanish Civil War was pondering entrance into World War II, but Italy's failure in Greece put him off of the idea. Hitler then came in to rescue Mussolini's troops, gaining him the upper hand in all politics and military operations for the rest of the war.
when Hitler invaded his former ally in fighting Poland. However, Mussolini was taken once again by Hitler's promise of quick victory and would eventually send a total of 200,000 troops as the Italian Eighth Army to the Russian front for Operation Barbarossa
, organized as the CSIR, Italian Expeditionary Corps in Russia. To begin with, three whole divisions were sent, though only one division at all motorized, but having no tanks.
After some large initial losses in the "Celere" Division, Mussolini sent four new infantry divisions and three Alpini
(alpine) divisions to the Soviet Union to officially make his forces an army. But instead of being deployed in the Caucasus Mountains as expected, the Italian units were tasked with holding the front in the Don river plains. As a result of this disastrous strategic decision, the Alpine troops armed, trained and equipped for mountain warfare and the under strength Italian infantry divisions were pitted against tanks and mechanized infantry, to counter which they were neither equipped nor trained. The Soviet offensive Operation Little Saturn wiped out the majority of the Italian troops, with only the 2nd "Tridentina" Alpine division
escaping annihilation. By the end of February 1943, the few remaining Italian troops were being withdrawn, a huge blow to public opinion of the Fascist government in Italy.
in Operation Husky. German generals again took the lead in the defence and, although they lost the island, they succeeded in ferrying large numbers of German and Italian forces safely off Sicily to the Italian mainland. With the loss of Sicily, popular support for the war diminished in Italy. On 25 July 1943, the Grand Council of Fascism
ousted Italian dictator Benito Mussolini
and a new Italian government, led by General Pietro Badoglio
and King Victor Emmanuel III
, took over in Italy. The new Italian government immediately began secret negotiations with the Allies to end the fighting and to come over to the Allied side. On 3 September, a secret armistice was signed with the Allies at Fairfield Camp in Sicily. The armistice was announced on 8 September. By then, the Allies were on the Italian mainland.
, Italian forces deployed in Lebanon
, together with United States
and France
, a force of around 3000 troops, led by then Brigadier General Angioni, whose in the end was the most successful of the three deployed forces, raising the confidence of Italian leadership and people in the Armed Forces, recovering the low esteem in the public opinion caused by the defeat in World War II
and paving the way to the subsequent increase in overseas missions for the Italian military.
, Italy contributed to the international operation in Afghanistan
. Italian forces have contributed to ISAF
, the NATO force in Afghanistan
, and a Provincial reconstruction team
and five Italian soldiers have died under ISAF. Italy has sent 411 troops, based on one infantry company from the 2nd Alpini Regiment
tasked to protect the ISAF HQ, one engineer company, one NBC platoon, one logistic unit, as well as liaison and staff elements integrated into the operation chain of command. Italian forces also command a multinational engineer task force and have deployed a platoon of Italian military police
. Three AB 212 helicopters also were deployed to Kabul and four Tornado
.
The Italian Army did not take part in combat operations of the 2003 Second Gulf War, dispatching troops only after May 1, 2003 – when major combat operations were declared over by the U.S. President
George W. Bush
. Subsequently Italian troops arrived in the late summer of 2003, and began patrolling Nasiriyah
and the surrounding area. On 26 May 2006, Italian foreign minister Massimo D'Alema
announced that the Italian forces would be reduced to 1,600 by June; Italian participation in the military operations in Iraq was concluded by the end of 2006, with full withdrawal of Italian military personnel except for a small group of about 30 soldiers engaged in providing security for the Italian embassy in Baghdad
, and about 87 soldiers stationing in bases in the Persian Gulf
(but not in Iraqi territory). As of June 2006 32 Italian troops have been killed in Iraq – with the greatest single loss of life coming on November 12, 2003 – a suicide car bombing of the Italian Carabinieri
Corps HQ left a dozen Carabinieri, five Army soldiers, two Italian civilians, and eight Iraqi civilians dead.
George W. Bush
. Subsequently Italian troops arrived in the late summer of 2003, and began patrolling Nasiriyah
and the surrounding area. On 26 May 2006, Italian foreign minister Massimo D'Alema announced that the Italian forces would be reduced to 1,600 by June. As of June 2006 32 Italian troops have been killed in Iraq - with the greatest single loss of life coming on November 12, 2004 - a suicide car bombing of the Italian Carabinieri Corps HQ left a dozen Carabinieri, five Army soldiers, two Italian civilians, and eight Iraqi civilians dead.
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of the ancient Roman civilization, characterised by an autocratic form of government and large territorial holdings in Europe and around the Mediterranean....
, Italian unification
Italian unification
Italian unification was the political and social movement that agglomerated different states of the Italian peninsula into the single state of Italy in the 19th century...
, and into the modern day. The Italian peninsula
Italian Peninsula
The Italian Peninsula or Apennine Peninsula is one of the three large peninsulas of Southern Europe , spanning from the Po Valley in the north to the central Mediterranean Sea in the south. The peninsula's shape gives it the nickname Lo Stivale...
has been a centre of military conflict throughout European history
History of Europe
History of Europe describes the history of humans inhabiting the European continent since it was first populated in prehistoric times to present, with the first human settlement between 45,000 and 25,000 BC.-Overview:...
.
Ancient Italy
In the 8th century BC, a group of Italic tribes (LatinsLatins
"Latins" refers to different groups of people and the meaning of the word changes for where and when it is used.The original Latins were an Italian tribe inhabiting central and south-central Italy. Through conquest by their most populous city-state, Rome, the original Latins culturally "Romanized"...
in the west, Sabine
Sabine
The Sabines were an Italic tribe that lived in the central Appennines of ancient Italy, also inhabiting Latium north of the Anio before the founding of Rome...
s in the upper valley of the Tiber, Umbrian
Umbrian language
Umbrian is an extinct Italic language formerly spoken by the Umbri in the ancient Italian region of Umbria. Within the Italic languages it is closely related to the Oscan group and is therefore associated with it in the group of Osco-Umbrian languages...
s in the north-east, Samnites
Samnium
Samnium is a Latin exonym for a region of south or south and central Italy in Roman times. The name survives in Italian today, but today's territory comprising it is only a small portion of what it once was. The populations of Samnium were called Samnites by the Romans...
in the South, Oscans
Osci
The Osci , were an Italic people of Campania and Latium adiectum during Roman times. They spoke the Oscan language, also spoken by the Samnites of Southern Italy. Although the language of the Samnites was called Oscan, the Samnites were never called Osci, or the Osci Samnites...
and others) shared the Italian peninsula with two other major ethnic groups: the Etruscans
Etruscan civilization
Etruscan civilization is the modern English name given to a civilization of ancient Italy in the area corresponding roughly to Tuscany. The ancient Romans called its creators the Tusci or Etrusci...
in the North, and the Greeks
Greeks
The Greeks, also known as the Hellenes , are a nation and ethnic group native to Greece, Cyprus and neighboring regions. They also form a significant diaspora, with Greek communities established around the world....
in the south.
The Etruscan
Etruscan
-Etruscan civilization:*Etruscan alphabet*Etruscan architecture*Etruscan art*Etruscan cities*Etruscan civilization*Etruscan coins*Etruscan language*Etruscan mythology*Etruscan numerals*Etruscan society*Etruscan terracotta warriors*Etruscan warfare...
s (Etrusci or Tusci in Latin
Latin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
) were settled north of Rome in Etruria
Etruria
Etruria—usually referred to in Greek and Latin source texts as Tyrrhenia—was a region of Central Italy, an area that covered part of what now are Tuscany, Latium, Emilia-Romagna, and Umbria. A particularly noteworthy work dealing with Etruscan locations is D. H...
(modern northern Lazio, Tuscany
Tuscany
Tuscany is a region in Italy. It has an area of about 23,000 square kilometres and a population of about 3.75 million inhabitants. The regional capital is Florence ....
and part of Umbria
Umbria
Umbria is a region of modern central Italy. It is one of the smallest Italian regions and the only peninsular region that is landlocked.Its capital is Perugia.Assisi and Norcia are historical towns associated with St. Francis of Assisi, and St...
). They founded cities like Tarquinia
Tarquinia
Tarquinia, formerly Corneto and in Antiquity Tarquinii, is an ancient city in the province of Viterbo, Lazio, Italy.- History :Tarquinii is said to have been already a flourishing city when Demaratus of Corinth brought in Greek workmen...
, Veii and Volterra and deeply influenced Roman culture, as clearly shown by the Etruscan origin of some of the mythical Roman kings. The origins of the Etruscans are lost in prehistory. Historians have no literature, no texts of religion or philosophy; therefore much of what is known about this civilisation is derived from grave goods and tomb findings.
The Italics were war-like as the Etruscans (the gladiator
Gladiator
A gladiator was an armed combatant who entertained audiences in the Roman Republic and Roman Empire in violent confrontations with other gladiators, wild animals, and condemned criminals. Some gladiators were volunteers who risked their legal and social standing and their lives by appearing in the...
ial displays actually evolved out of Etruscan funerary customs). The Italics and the Etruscans had a significant military tradition. In addition to marking the rank and power of certain individuals in their culture, warfare was a considerable economic boon to their civilization. Like many ancient societies, the Italics and the Etruscans conducted campaigns during summer months, raiding neighboring areas, attempting to gain territory and combating piracy/banditism as a means of acquiring valuable resources such as land, prestige and goods. It is also likely individuals taken in battle would be ransomed back to their families and clans at high cost.
The Greeks had founded many colonies in Southern Italy
Italy
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
(that the Romans later called Magna Graecia
Magna Graecia
Magna Græcia is the name of the coastal areas of Southern Italy on the Tarentine Gulf that were extensively colonized by Greek settlers; particularly the Achaean colonies of Tarentum, Crotone, and Sybaris, but also, more loosely, the cities of Cumae and Neapolis to the north...
), such as Cumae
Cumae
Cumae is an ancient Greek settlement lying to the northwest of Naples in the Italian region of Campania. Cumae was the first Greek colony on the mainland of Italy , and the seat of the Cumaean Sibyl...
, Naples
Naples
Naples is a city in Southern Italy, situated on the country's west coast by the Gulf of Naples. Lying between two notable volcanic regions, Mount Vesuvius and the Phlegraean Fields, it is the capital of the region of Campania and of the province of Naples...
and Taranto
Taranto
Taranto is a coastal city in Apulia, Southern Italy. It is the capital of the Province of Taranto and is an important commercial port as well as the main Italian naval base....
, as well as in the eastern two-thirds of Sicily
Sicily
Sicily is a region of Italy, and is the largest island in the Mediterranean Sea. Along with the surrounding minor islands, it constitutes an autonomous region of Italy, the Regione Autonoma Siciliana Sicily has a rich and unique culture, especially with regard to the arts, music, literature,...
, between 750
750s BC
-Events and trends:* 756 BC—Founding of Cyzicus.* 754 BC—Latins move into Italy* 755 BC—Ashur-nirari V succeeds Ashur-Dan III as king of Assyria* 755 BC—Aeschylus, King of Athens, dies after a reign of 23 years and is succeeded by Alcmaeon....
and 550 BC
550s BC
-Events and trends:*Carthage conquers Sicily, Sardinia and Corsica.*559 BC—King Cambyses I of Anshan dies and is succeeded by his son Cyrus II the Great.*558 BC—Hegesias is removed as Archon of Athens....
.
After 650 BC
650s BC
-Events and trends:*Occupation begins at Maya site of Piedras Negras, Guatemala.*657 BC—Cypselus becomes the first tyrant of Corinth.*656 BC—Psamtik I extends his control over all of Egypt...
, the Etruscan
Etruscan
-Etruscan civilization:*Etruscan alphabet*Etruscan architecture*Etruscan art*Etruscan cities*Etruscan civilization*Etruscan coins*Etruscan language*Etruscan mythology*Etruscan numerals*Etruscan society*Etruscan terracotta warriors*Etruscan warfare...
s became dominant in central Italy, and expanded into north Italy founding cities like Mutina (actual Modena
Modena
Modena is a city and comune on the south side of the Po Valley, in the Province of Modena in the Emilia-Romagna region of Italy....
) and Felsina (actual Bologna
Bologna
Bologna is the capital city of Emilia-Romagna, in the Po Valley of Northern Italy. The city lies between the Po River and the Apennine Mountains, more specifically, between the Reno River and the Savena River. Bologna is a lively and cosmopolitan Italian college city, with spectacular history,...
). Roman tradition claimed that Rome had been under the control of seven "etruscan" kings
Roman Kingdom
The Roman Kingdom was the period of the ancient Roman civilization characterized by a monarchical form of government of the city of Rome and its territories....
from 753
750s BC
-Events and trends:* 756 BC—Founding of Cyzicus.* 754 BC—Latins move into Italy* 755 BC—Ashur-nirari V succeeds Ashur-Dan III as king of Assyria* 755 BC—Aeschylus, King of Athens, dies after a reign of 23 years and is succeeded by Alcmaeon....
to 509 BC beginning with the mythic Romulus
Romulus and Remus
Romulus and Remus are Rome's twin founders in its traditional foundation myth, although the former is sometimes said to be the sole founder...
who along with his brother Remus
Romulus and Remus
Romulus and Remus are Rome's twin founders in its traditional foundation myth, although the former is sometimes said to be the sole founder...
were said to have founded the city of Rome
Founding of Rome
The founding of Rome is reported by many legends, which in recent times are beginning to be supplemented by scientific reconstructions.- Development of the city :...
.
Rome
The early Roman army (c. 500 BC) was, like those of other contemporary city-stateCity-state
A city-state is an independent or autonomous entity whose territory consists of a city which is not administered as a part of another local government.-Historical city-states:...
s influenced by Greek civilization, a citizen militia
Militia
The term militia is commonly used today to refer to a military force composed of ordinary citizens to provide defense, emergency law enforcement, or paramilitary service, in times of emergency without being paid a regular salary or committed to a fixed term of service. It is a polyseme with...
which practiced hoplite
Hoplite
A hoplite was a citizen-soldier of the Ancient Greek city-states. Hoplites were primarily armed as spearmen and fought in a phalanx formation. The word "hoplite" derives from "hoplon" , the type of the shield used by the soldiers, although, as a word, "hopla" could also denote weapons held or even...
tactics. It was small (the population of free males of military age was then about 9,000) and organized in five classes (in parallel to the comitia centuriata
Roman assemblies
The Legislative Assemblies of the Roman Republic were political institutions in the ancient Roman Republic. According to the contemporary historian Polybius, it was the people who had the final say regarding the election of magistrates, the enactment of new statutes, the carrying out of capital...
, the body of citizens organized politically), with three providing hoplites and two providing light infantry. The early Roman army was tactically limited and its stance during this period was essentially defensive. By the 3rd century BC, the Romans abandoned the hoplite formation in favor of a more flexible system in which smaller groups of 120 (or in some cases 60) men called maniples
Maniple (military unit)
Maniple was a tactical unit of the Roman legion adopted from the Samnites during the Samnite Wars . It was also the name of the military insignia carried by such unit....
could maneuver more independently on the battlefield. Thirty maniples arranged in three lines with supporting troops constituted a legion
Roman legion
A Roman legion normally indicates the basic ancient Roman army unit recruited specifically from Roman citizens. The organization of legions varied greatly over time but they were typically composed of perhaps 5,000 soldiers, divided into maniples and later into "cohorts"...
, totaling between 4,000 and 5,000 men. The early Republican legion consisted of five sections, each of which was equipped differently and had different places in formation: the three lines of manipular heavy infantry (hastati
Hastati
Hastatii were a class of infantry in the armies of the early Roman Republic who originally fought as spearmen, and later as swordsmen. They were originally some of the poorest men in the legion, and could afford only modest equipment — light armour and a large shield, in their service as the...
, principes
Principes
Principes were spearmen, and later swordsmen, in the armies of the early Roman Republic. They were men in the prime of their lives who were fairly wealthy, and could afford decent equipment. They were the heavier infantry of the legion who carried large shields and wore good quality armour. Their...
and triarii
Triarii
Triarii were one of the elements of the early Roman military Manipular legions of the early Roman Republic . They were the oldest and among the wealthiest men in the army, and could afford good quality equipment. They wore heavy metal armour and carried large shields, their usual position being...
), a force of light infantry (velites
Velites
Velites were a class of infantry in the Polybian legions of the early Roman republic. Velites were light infantry and skirmishers who were armed with a number of light javelins, or hastae velitares, to fling at the enemy, and also carried short thrusting swords, or gladii for use in melee...
), and the cavalry (equites). With the new organization came a new orientation toward the offensive and a much more aggressive posture toward adjoining city-states.
At nominal full strength, an early Republican legion would have included 3,600 to 4,800 heavy infantry, several hundred light infantry and several hundred cavalrymen, for a total of 4,000 to 5,000 men. Legions were often significantly understrength from recruitment failures or following periods of active service due to accidents, battle casualties, disease and desertion. During the Civil War, Pompey's legions in the east were at full strength because recently recruited, while Caesar's legions were in many cases well below nominal strength after long active service in Gaul. This pattern also held true for auxiliary forces.
Until the late Republican period, the typical legionary was a property-owning citizen farmer from a rural area (an adsiduus) who served for particular (often annual) campaigns, and who supplied his own equipment and, in the case of equites, his own mount. Harris suggests that down to 200 BC, the average rural farmer (who survived) might participate in six or seven campaigns. Freedmen and slaves (wherever resident) and urban citizens did not serve except in rare emergencies. After 200 BC, economic conditions in rural areas deteriorated as manpower needs increased, so that the property qualifications for service were gradually reduced. Beginning with Gaius Marius
Gaius Marius
Gaius Marius was a Roman general and statesman. He was elected consul an unprecedented seven times during his career. He was also noted for his dramatic reforms of Roman armies, authorizing recruitment of landless citizens, eliminating the manipular military formations, and reorganizing the...
in 107 BC, citizens without property and some urban-dwelling citizens (proletarii) were enlisted and provided with equipment, although most legionaries continued to come from rural areas. Terms of service became continuous and long—up to twenty years if emergencies required it although Brunt argues that six or seven years was more typical. Beginning in the 3rd century BC, legionaries were paid stipendium (amounts are disputed but Caesar famously "doubled" payments to his troops to 225 denarii
Denarius
In the Roman currency system, the denarius was a small silver coin first minted in 211 BC. It was the most common coin produced for circulation but was slowly debased until its replacement by the antoninianus...
a year), could anticipate booty and donatives (distributions of plunder by commanders) from successful campaigns and, beginning at the time of Marius, often were granted allotments of land upon retirement. Cavalry and light infantry attached to a legion (the auxilia) were often recruited in the areas where the legion served. Caesar formed a legion, the Fifth Alaudae, from non-citizens in Transalpine Gaul to serve in his campaigns in Gaul. By the time of Caesar Augustus, the ideal of the citizen-soldier had been abandoned and the legions had become fully professional. Legionaries were paid 900 sesterces
Sestertius
The sestertius, or sesterce, was an ancient Roman coin. During the Roman Republic it was a small, silver coin issued only on rare occasions...
a year and could expect a payment of 12,000 sesterces on retirement.
At the end of the Civil War
Final war of the Roman Republic
The final war of the Roman Republic, also known as Antony's civil war or the war between Antony and Octavian, was the last of the Roman civil wars of the republic, fought between Cleopatra and Octavian...
, Augustus reorganized Roman military forces, discharging soldiers and disbanding legions. He retained 28 legions, distributed through the provinces of the Empire. During the Principate
Principate
The Principate is the first period of the Roman Empire, extending from the beginning of the reign of Caesar Augustus to the Crisis of the Third Century, after which it was replaced with the Dominate. The Principate is characterized by a concerted effort on the part of the Emperors to preserve the...
, the tactical organization of the Army continued to evolve. The auxilia remained independent cohorts, and legionary troops often operated as groups of cohorts rather than as full legions. A new versatile type of unit, the cohortes equitatae, combining cavalry and legionaries in a single formation could be stationed at garrisons or outposts, could fight on their own as balanced small forces or could combine with other similar units as a larger legion-sized force. This increase in organizational flexibility over time helped ensure the long-term success of Roman military forces.
The Emperor Gallienus
Gallienus
Gallienus was Roman Emperor with his father Valerian from 253 to 260, and alone from 260 to 268. He took control of the Empire at a time when it was undergoing great crisis...
(253–268 AD) began a reorganization that created the final military structure of the late Empire. Withdrawing some legionaries from the fixed bases on the border, Gallienus created mobile forces (the Comitatenses
Comitatenses
Comitatenses is the Latin plural of comitatensis, originally the adjective derived from comitatus , itself rooting in Comes .However, historically it became the accepted name for...
or field armies) and stationed them behind and at some distance from the borders as a strategic reserve. The border troops (limitanei) stationed at fixed bases continued to be the first line of defense. The basic unit of the field army was the "regiment", legiones or auxilia for infantry and vexellationes for cavalry. Evidence suggests that nominal strengths may have been 1,200 men for infantry regiments and 600 for cavalry, although many records show lower actual troop levels (800 and 400). Many infantry and cavalry regiments operated in pairs under the command of a comes
Comes
Comes , plural comites , is the Latin word for companion, either individually or as a member of a collective known as comitatus, especially the suite of a magnate, in some cases large and/or formal enough to have a specific name, such as a cohors amicorum. The word comes derives from com- "with" +...
. In addition to Roman troops, the field armies included regiments of "barbarians" recruited from allied tribes and known as foederati
Foederati
Foederatus is a Latin term whose definition and usage drifted in the time between the early Roman Republic and the end of the Western Roman Empire...
. By 400 AD, foederati regiments had become permanently established units of the Roman army, paid and equipped by the Empire, led by a Roman tribune and used just as Roman units were used. In addition to the foederati, the Empire also used groups of barbarians to fight along with the legions as "allies" without integration into the field armies. Under the command of the senior Roman general present, they were led at lower levels by their own officers.
Military leadership evolved greatly over the course of the history of Rome. Under the monarchy, the hoplite armies would have been led by the kings of Rome. During the early and middle Roman Republic, military forces were under the command of one of the two elected consuls
Roman consul
A consul served in the highest elected political office of the Roman Republic.Each year, two consuls were elected together, to serve for a one-year term. Each consul was given veto power over his colleague and the officials would alternate each month...
for the year. During the later Republic, members of the Roman Senatorial elite, as part of the normal sequence of elected public offices known as the cursus honorum
Cursus honorum
The cursus honorum was the sequential order of public offices held by aspiring politicians in both the Roman Republic and the early Empire. It was designed for men of senatorial rank. The cursus honorum comprised a mixture of military and political administration posts. Each office had a minimum...
, would have served first as quaestor
Quaestor
A Quaestor was a type of public official in the "Cursus honorum" system who supervised financial affairs. In the Roman Republic a quaestor was an elected official whereas, with the autocratic government of the Roman Empire, quaestors were simply appointed....
(often posted as deputies to field commanders), then as praetor
Praetor
Praetor was a title granted by the government of Ancient Rome to men acting in one of two official capacities: the commander of an army, usually in the field, or the named commander before mustering the army; and an elected magistratus assigned varied duties...
. Following the end of a term as praetor or consul, a Senator might be appointed by the Senate as a propraetor
Promagistrate
A promagistrate is a person who acts in and with the authority and capacity of a magistrate, but without holding a magisterial office. A legal innovation of the Roman Republic, the promagistracy was invented in order to provide Rome with governors of overseas territories instead of having to elect...
or proconsul
Promagistrate
A promagistrate is a person who acts in and with the authority and capacity of a magistrate, but without holding a magisterial office. A legal innovation of the Roman Republic, the promagistracy was invented in order to provide Rome with governors of overseas territories instead of having to elect...
(depending on the highest office previously held) to govern a foreign province. More junior officers (down to but not including the level of centurion) were selected by their commanders from their own clientelae
Patronage in ancient Rome
Patronage was the distinctive relationship in ancient Roman society between the patronus and his client . The relationship was hierarchical, but obligations were mutual. The patronus was the protector, sponsor, and benefactor of the client...
or those recommended by political allies among the Senatorial elite. Under Augustus, whose most important political priority was to place the military under a permanent and unitary command, the Emperor was the legal commander of each legion but exercised that command through a legatus
Legatus
A legatus was a general in the Roman army, equivalent to a modern general officer. Being of senatorial rank, his immediate superior was the dux, and he outranked all military tribunes...
(legate) he appointed from the Senatorial elite. In a province with a single legion, the legate would command the legion (legatus legionis
Legatus legionis
Legatus legionis was a title awarded to legion commanders in Ancient Rome.-History:By the time of the Roman Republic, the term legatus delegated authority...
) and also serve as provincial governor, while in a province with more than one legion, each legion would be commanded by a legate and the legates would be commanded by the provincial governor (also a legate but of higher rank). During the later stages of the Imperial period (beginning perhaps with Diocletian
Diocletian
Diocletian |latinized]] upon his accession to Diocletian . c. 22 December 244 – 3 December 311), was a Roman Emperor from 284 to 305....
), the Augustan model was abandoned. Provincial governors were stripped of military authority, and command of the armies in a group of provinces was given to generals (duces
Dux
Dux is Latin for leader and later for Duke and its variant forms ....
) appointed by the Emperor. These were no longer members of the Roman elite but men who came up through the ranks and had seen much practical soldiering. With increasing frequency, these men attempted (sometimes successfully) to usurp the positions of the Emperors who had appointed them. Decreased resources, increasing political chaos and civil war eventually left the Western Empire vulnerable to attack and takeover by neighboring barbarian peoples.
Comparatively less is known about the Roman navy than the Roman army. Prior to the middle of the 3rd century BC, officials known as duumviri navales commanded a fleet of twenty ships used mainly to control piracy. This fleet was given up in 278 AD and replaced by allied forces. The First Punic War
Punic Wars
The Punic Wars were a series of three wars fought between Rome and Carthage from 264 B.C.E. to 146 B.C.E. At the time, they were probably the largest wars that had ever taken place...
required that Rome build large fleets, and it did so largely with the assistance of and financing from allies. This reliance on allies continued to the end of the Roman Republic. The quinquereme
Quinquereme
From the 4th century BC on, new types of oared warships appeared in the Mediterranean Sea, superseding the trireme and transforming naval warfare. Ships became increasingly bigger and heavier, including some of the largest wooden ships ever constructed...
was the main warship on both sides of the Punic Wars and remained the mainstay of Roman naval forces until replaced by the time of Caesar Augustus by lighter and more maneuverable vessels. As compared with a trireme
Trireme
A trireme was a type of galley, a Hellenistic-era warship that was used by the ancient maritime civilizations of the Mediterranean, especially the Phoenicians, ancient Greeks and Romans.The trireme derives its name from its three rows of oars on each side, manned with one man per oar...
, the quinquereme permitted the use of a mix of experienced and inexperienced crewmen (an advantage for a primarily land-based power), and its lesser maneuverability permitted the Romans to adopt and perfect boarding tactics
Corvus (weapon)
The corvus or harpago was a Roman military boarding device used in naval warfare during the First Punic War against Carthage....
using a troop of approximately 40 marines in lieu of the ram
Naval tactics in the Age of Galleys
Naval tactics in the age of galleys were used from antiquity to the early 17th century when sailing ships replaced oared galleys.-Weapons in the age of galleys:Throughout antiquity and the Middle Ages until the 16th century, the weapons relied on were:...
. Ships were commanded by a navarch
Navarch
Navarch is a Greek word meaning "leader of the ships", which in some states became the title of an office equivalent to that of a modern admiral.- Historical usage :...
, a rank equivalent to a centurion, who were usually not citizens. Potter suggests that because the fleet was dominated by non-Romans, the navy was considered non-Roman and allowed to atrophy in times of peace.
Available information suggests that by the time of the late Empire (350 AD), the Roman navy comprised a number of fleets including both warships and merchant vessels for transportation and supply. Warships were oared sailing galleys with three to five banks of oarsmen. Fleet bases included such ports as Ravenna, Arles, Aquilea, Misenum and the mouth of the Somme River in the West and Alexandria and Rhodes in the East. Flotillas of small river craft (classes) were part of the limitanei (border troops) during this period, based at fortified river harbors along the Rhine and the Danube. The fact that prominent generals commanded both armies and fleets suggests that naval forces were treated as auxiliaries to the army and not as an independent service. The details of command structure and fleet strengths during this period are not well known although it is known that fleets were commanded by prefects.
Middle Ages
Throughout the Middle AgesMiddle Ages
The Middle Ages is a periodization of European history from the 5th century to the 15th century. The Middle Ages follows the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 and precedes the Early Modern Era. It is the middle period of a three-period division of Western history: Classic, Medieval and Modern...
, from the collapse of a central Roman government in the late 5th century to the Italian Wars
Italian Wars
The Italian Wars, often referred to as the Great Italian Wars or the Great Wars of Italy and sometimes as the Habsburg–Valois Wars, were a series of conflicts from 1494 to 1559 that involved, at various times, most of the city-states of Italy, the Papal States, most of the major states of Western...
of the Renaissance
Renaissance
The Renaissance was a cultural movement that spanned roughly the 14th to the 17th century, beginning in Italy in the Late Middle Ages and later spreading to the rest of Europe. The term is also used more loosely to refer to the historical era, but since the changes of the Renaissance were not...
, Italy was constantly divided between opposing factions fighting for control. At the time of the deposition of Romulus Augustulus (476), the Heruli Confederation
Heruli
The Heruli were an East Germanic tribe who are famous for their naval exploits. Migrating from Northern Europe to the Black Sea in the third century They were part of the...
governed Italy, but it was displaced by the Ostrogoths, who fought a long war with the Byzantine army
Byzantine army
The Byzantine army was the primary military body of the Byzantine armed forces, serving alongside the Byzantine navy. A direct descendant of the Roman army, the Byzantine army maintained a similar level of discipline, strategic prowess and organization...
in Italy (the Gothic War
Gothic War (535–552)
The Gothic War between the Eastern Roman Empire and the Ostrogothic Kingdom of Italy was fought from 535 until 554 in Italy, Dalmatia, Sardinia, Sicily and Corsica. It is commonly divided into two phases. The first phase lasted from 535 to 540 and ended with the fall of Ravenna and the apparent...
). The Byzantine came out of the war victorious only to find Italy invaded by a new wave of barbarians led by the Lombards
Lombards
The Lombards , also referred to as Longobards, were a Germanic tribe of Scandinavian origin, who from 568 to 774 ruled a Kingdom in Italy...
.
The Lombards diminished Byzantine territory to the Exarchate of Ravenna
Exarchate of Ravenna
The Exarchate of Ravenna or of Italy was a centre of Byzantine power in Italy, from the end of the 6th century to 751, when the last exarch was put to death by the Lombards.-Introduction:...
, the Duchy of Rome
Duchy of Rome
The Duchy of Rome was a Byzantine district in the Exarchate of Ravenna. Like other Byzantine states in Italy, it was ruled by an imperial functionary with the title dux...
, the Duchy of Naples
Duchy of Naples
The Duchy of Naples began as a Byzantine province that was constituted in the seventh century, in the reduced coastal lands that the Lombards had not conquered during their invasion of Italy in the sixth century...
, and the far south of Apulia
Apulia
Apulia is a region in Southern Italy bordering the Adriatic Sea in the east, the Ionian Sea to the southeast, and the Strait of Òtranto and Gulf of Taranto in the south. Its most southern portion, known as Salento peninsula, forms a high heel on the "boot" of Italy. The region comprises , and...
and Calabria
Calabria
Calabria , in antiquity known as Bruttium, is a region in southern Italy, south of Naples, located at the "toe" of the Italian Peninsula. The capital city of Calabria is Catanzaro....
. They established a kingdom centred on Pavia
Pavia
Pavia , the ancient Ticinum, is a town and comune of south-western Lombardy, northern Italy, 35 km south of Milan on the lower Ticino river near its confluence with the Po. It is the capital of the province of Pavia. It has a population of c. 71,000...
in the north. During the interregnum called the Rule of the Dukes
Rule of the Dukes
The Rule of the Dukes was an interregnum in the Lombard Kingdom of Italy during which Italy was ruled by the Lombard dukes of the old Roman provinces and urban centres...
(574 – 584), the dukes of the Lombards invaded Burgundy, but were repulsed by the Merovingian king Guntram
Guntram
Saint Guntram was the king of Burgundy from 561 to 592. He was a son of Chlothar I and Ingunda...
, who in turn invaded Italy and took the region of Savoy
Savoy
Savoy is a region of France. It comprises roughly the territory of the Western Alps situated between Lake Geneva in the north and Monaco and the Mediterranean coast in the south....
. The Lombards were forced to elect a new king to organise their defence. For the next two centuries, the Byzantine power in the peninsula was reduced by the Lombard kings, the greatest of which was Liutprand
Liutprand, King of the Lombards
Liutprand was the King of the Lombards from 712 to 744 and is chiefly remembered for his Donation of Sutri, in 728, and his long reign, which brought him into a series of conflicts, mostly successful, with most of Italy. He profited by Byzantine weakness to enlarge his domains in Emilia and the...
, until it consisted of little more than the tips of the Italian toe and heel, Rome and its environs being practically independent under the popes and the Neapolitan coast under its dukes.
In 774, Charlemagne
Charlemagne
Charlemagne was King of the Franks from 768 and Emperor of the Romans from 800 to his death in 814. He expanded the Frankish kingdom into an empire that incorporated much of Western and Central Europe. During his reign, he conquered Italy and was crowned by Pope Leo III on 25 December 800...
of the Franks
Franks
The Franks were a confederation of Germanic tribes first attested in the third century AD as living north and east of the Lower Rhine River. From the third to fifth centuries some Franks raided Roman territory while other Franks joined the Roman troops in Gaul. Only the Salian Franks formed a...
invaded and conquered the Lombard kingdom. In the south of the peninsula, the Duchy of Benevento
Duchy of Benevento
The Duchy and later Principality of Benevento was the southernmost Lombard duchy in medieval Italy, centred on Benevento, a city central in the Mezzogiorno. Owing to the Ducatus Romanus of the popes, which cut it off from the rest of Lombard Italy, Benevento was from the first practically...
remained independent of Frankish dominion, however. During the period of Carolingian
Carolingian
The Carolingian dynasty was a Frankish noble family with origins in the Arnulfing and Pippinid clans of the 7th century AD. The name "Carolingian", Medieval Latin karolingi, an altered form of an unattested Old High German *karling, kerling The Carolingian dynasty (known variously as the...
strength, Charlemagne's descendants governed the north of Italy in relative peace, except for the brief period of the rebellion of Bernard
Bernard of Italy
Bernard was the King of the Lombards from 810 to 818. He plotted against his uncle, Emperor Louis the Pious, when the latter's Ordinatio Imperii made Bernard a vassal of his cousin Lothair...
and the constant raids from the Slavs to the east and the Saracens to the south. Pirates harassed the Adriatic and Liguria
Liguria
Liguria is a coastal region of north-western Italy, the third smallest of the Italian regions. Its capital is Genoa. It is a popular region with tourists for its beautiful beaches, picturesque little towns, and good food.-Geography:...
n coasts and the islands of Corsica
Corsica
Corsica is an island in the Mediterranean Sea. It is located west of Italy, southeast of the French mainland, and north of the island of Sardinia....
and Sardinia
Sardinia
Sardinia is the second-largest island in the Mediterranean Sea . It is an autonomous region of Italy, and the nearest land masses are the French island of Corsica, the Italian Peninsula, Sicily, Tunisia and the Spanish Balearic Islands.The name Sardinia is from the pre-Roman noun *sard[],...
. The south was very different, as the Lombards were at the height of there power there. Warfare between Lombard and Greek, especially the Greek city-states of the Tyrrhenian
Tyrrhenian
Tyrrhenian may refer to the:* Tyrrhenian Stage, a faunal stage from 0.26 to 0.01143 million years ago* Tyrrhenians, an ancient ethnonym associated variously with Pelasgians, Etruscans or Lemnians* Tyrrhenian Sea* Tyrrhenian languages...
, was endemic. The Greek cities fell out of the orbit of Constantinople and Byzantine possessions shrank to their smallest mark as the Lombards and the Saracens increased their predations. In 831, the Arabs conquered Palermo
Palermo
Palermo is a city in Southern Italy, the capital of both the autonomous region of Sicily and the Province of Palermo. The city is noted for its history, culture, architecture and gastronomy, playing an important role throughout much of its existence; it is over 2,700 years old...
and in 902 they conquered Taormina
Taormina
Taormina is a comune and small town on the east coast of the island of Sicily, Italy, in the Province of Messina, about midway between Messina and Catania. Taormina has been a very popular tourist destination since the 19th century...
, ending the conquest of Sicily. They likewise established their presence on the peninsula, especially on the Garigliano and in Bari
Bari
Bari is the capital city of the province of Bari and of the Apulia region, on the Adriatic Sea, in Italy. It is the second most important economic centre of mainland Southern Italy after Naples, and is well known as a port and university city, as well as the city of Saint Nicholas...
. The story of the incessant conflicts of the states of the Mezzogiorno is chaotic until the arrival of the Normans
Normans
The Normans were the people who gave their name to Normandy, a region in northern France. They were descended from Norse Viking conquerors of the territory and the native population of Frankish and Gallo-Roman stock...
in the early eleventh century (1016). Under their leadership, the Jews of the south found themselves eventually united, the Arabs expelled, and the whole Mezzogiorno subjugated to the Hauteville dynasty
Hauteville family
The family of the Hauteville was a petty baronial Norman family from the Cotentin which rose to prominence in Europe, Asia, and Africa through its conquests in the Mediterranean, especially Southern Italy and Sicily...
of kings of Sicily (1130).
The second half of the Middle Ages in Italy was marked by frequent conflict between the Holy Roman Empire
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a realm that existed from 962 to 1806 in Central Europe.It was ruled by the Holy Roman Emperor. Its character changed during the Middle Ages and the Early Modern period, when the power of the emperor gradually weakened in favour of the princes...
and the Papacy, the latter eventually emerging victorious in that it ultimately prevented political unification of northern Italy under Imperial rule. Imperial invasions were led by more or less all medieval Emperors, the most notable episodes being the end of the Investiture controversy
Investiture Controversy
The Investiture Controversy or Investiture Contest was the most significant conflict between Church and state in medieval Europe. In the 11th and 12th centuries, a series of Popes challenged the authority of European monarchies over control of appointments, or investitures, of church officials such...
by the pilgrimage of Henry IV, Holy Roman Emperor
Henry IV, Holy Roman Emperor
Henry IV was King of the Romans from 1056 and Holy Roman Emperor from 1084 until his forced abdication in 1105. He was the third emperor of the Salian dynasty and one of the most powerful and important figures of the 11th century...
at Canossa
Canossa
Canossa is a comune and castle town in Emilia-Romagna, famous as the site where Holy Roman Emperor Henry IV did penance in 1077, standing three days bare-headed in the snow, in order to reverse his excommunication by Pope Gregory VII...
in 1077 and the no less than five major invasions staged by Frederick Barbarossa
Frederick I, Holy Roman Emperor
Frederick I Barbarossa was a German Holy Roman Emperor. He was elected King of Germany at Frankfurt on 4 March 1152 and crowned in Aachen on 9 March, crowned King of Italy in Pavia in 1155, and finally crowned Roman Emperor by Pope Adrian IV, on 18 June 1155, and two years later in 1157 the term...
against the Lombard League
Lombard League
The Lombard League was an alliance formed around 1167, which at its apex included most of the cities of northern Italy , including, among others, Crema, Cremona, Mantua, Piacenza, Bergamo, Brescia, Milan, Genoa, Bologna, Padua, Modena, Reggio Emilia, Treviso, Venice, Vercelli, Vicenza, Verona,...
, culminating in the sack of Milan
Milan
Milan is the second-largest city in Italy and the capital city of the region of Lombardy and of the province of Milan. The city proper has a population of about 1.3 million, while its urban area, roughly coinciding with its administrative province and the bordering Province of Monza and Brianza ,...
in 1162, after which every building in the city was demolished, except the churches. The lasting conflict led to the emergence of the Guelph and the Ghibelline
Guelphs and Ghibellines
The Guelphs and Ghibellines were factions supporting the Pope and the Holy Roman Emperor, respectively, in central and northern Italy. During the 12th and 13th centuries, the split between these two parties was a particularly important aspect of the internal policy of the Italian city-states...
parties in northern Italy, supporting respectively the Pope (and the independent cities) and the Emperor, though siding with a party was often dictated by other political considerations (more or less each city has belonged to both parties). In May 1176, the Lombard League, led by a revived Milan, defeated the Emperor Frederick Barbarossa at Legnano.
The victory of the Guelph party meant the end of Imperial overlordship over northern Italy, and the formation of city-state
City-state
A city-state is an independent or autonomous entity whose territory consists of a city which is not administered as a part of another local government.-Historical city-states:...
s such as Florence
Florence
Florence is the capital city of the Italian region of Tuscany and of the province of Florence. It is the most populous city in Tuscany, with approximately 370,000 inhabitants, expanding to over 1.5 million in the metropolitan area....
, Venice
Venice
Venice is a city in northern Italy which is renowned for the beauty of its setting, its architecture and its artworks. It is the capital of the Veneto region...
, Milan, Genoa
Genoa
Genoa |Ligurian]] Zena ; Latin and, archaically, English Genua) is a city and an important seaport in northern Italy, the capital of the Province of Genoa and of the region of Liguria....
or Siena
Siena
Siena is a city in Tuscany, Italy. It is the capital of the province of Siena.The historic centre of Siena has been declared by UNESCO a World Heritage Site. It is one of the nation's most visited tourist attractions, with over 163,000 international arrivals in 2008...
. While Venice was turning to the seas, supporting, and acquiring large loot from, the 1204 Fourth Crusade
Fourth Crusade
The Fourth Crusade was originally intended to conquer Muslim-controlled Jerusalem by means of an invasion through Egypt. Instead, in April 1204, the Crusaders of Western Europe invaded and conquered the Christian city of Constantinople, capital of the Eastern Roman Empire...
's sack of Constantinople, the other city-states were struggling for control of mainland, Florence being the rising power of the time (annexation of Pisa
Pisa
Pisa is a city in Tuscany, Central Italy, on the right bank of the mouth of the River Arno on the Tyrrhenian Sea. It is the capital city of the Province of Pisa...
in 1406).
Sicily was invaded in 1266 by Charles I, duke of Anjou; the Angevines were however toppled in the 1282 Sicilian Vespers
Sicilian Vespers
The Sicilian Vespers is the name given to the successful rebellion on the island of Sicily that broke out on the Easter of 1282 against the rule of the French/Angevin king Charles I, who had ruled the Kingdom of Sicily since 1266. Within six weeks three thousand French men and women were slain by...
, and Peter III of Aragon
Peter III of Aragon
Peter the Great was the King of Aragon of Valencia , and Count of Barcelona from 1276 to his death. He conquered Sicily and became its king in 1282. He was one of the greatest of medieval Aragonese monarchs.-Youth and succession:Peter was the eldest son of James I of Aragon and his second wife...
invaded the island. This set the background for later French claims over Naples and Sicily.
Disintegration of the Holy Roman Empire and the Hundred Years War in neighbouring France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
meant that Italy was more or less left in peace during the fifteenth century; this allowed its cities to grow rich and to become attractive preys for its neighbours during the sixteenth century.
Italian Wars

Treaty of Lodi
The Treaty of Lodi, also known as the Peace of Lodi was a peace agreement between Milan, Naples, and Florence signed on April 9, 1454 at Lodi in Lombardy, on the banks of the Adda...
was shattered by the beginning of the Italian Wars in 1494. Ludovico Sforza
Ludovico Sforza
Ludovico Sforza , was Duke of Milan from 1489 until his death. A member of the Sforza family, he was the fourth son of Francesco Sforza. He was famed as a patron of Leonardo da Vinci and other artists, and presided over the final and most productive stage of the Milanese Renaissance...
, seeking allies, suggested to Charles VIII of France
Charles VIII of France
Charles VIII, called the Affable, , was King of France from 1483 to his death in 1498. Charles was a member of the House of Valois...
that the latter press his claim to the throne of Naples
Naples
Naples is a city in Southern Italy, situated on the country's west coast by the Gulf of Naples. Lying between two notable volcanic regions, Mount Vesuvius and the Phlegraean Fields, it is the capital of the region of Campania and of the province of Naples...
; Charles obliged and launched an invasion of the peninsula
First Italian War
The First Italian War , sometimes referred to as the Italian War of 1494 or Charles VIII's Italian War, was the opening phase of the Italian Wars...
. The French march to, and capture of, Naples was accomplished with relative ease—the Italian states being shocked at the brutality of French tactics and the efficacy of the new French artillery
Artillery
Originally applied to any group of infantry primarily armed with projectile weapons, artillery has over time become limited in meaning to refer only to those engines of war that operate by projection of munitions far beyond the range of effect of personal weapons...
—but Charles was forced to withdraw from Italy in 1495, after a hastily-constructed alliance fought him at the Battle of Fornovo
Battle of Fornovo
The Battle of Fornovo took place 30 km southwest of the city of Parma on 6 July 1495. The League of Venice was able to temporarily expel the French from the Italian Peninsula. It was the first major battle of the Italian Wars.-Antecedents:...
. Charles died in 1498, but the conflict he started would be continued by his successors; the Italian Wars would last until 1559, involving, at various times, all the major states of western Europe (France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
, Spain
Spain
Spain , officially the Kingdom of Spain languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Spain's official name is as follows:;;;;;;), is a country and member state of the European Union located in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula...
, the Holy Roman Empire
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a realm that existed from 962 to 1806 in Central Europe.It was ruled by the Holy Roman Emperor. Its character changed during the Middle Ages and the Early Modern period, when the power of the emperor gradually weakened in favour of the princes...
, England
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
, Scotland
Scotland
Scotland is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Occupying the northern third of the island of Great Britain, it shares a border with England to the south and is bounded by the North Sea to the east, the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, and the North Channel and Irish Sea to the...
, the Republic of Venice
Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice or Venetian Republic was a state originating from the city of Venice in Northeastern Italy. It existed for over a millennium, from the late 7th century until 1797. It was formally known as the Most Serene Republic of Venice and is often referred to as La Serenissima, in...
, the Papal States
Papal States
The Papal State, State of the Church, or Pontifical States were among the major historical states of Italy from roughly the 6th century until the Italian peninsula was unified in 1861 by the Kingdom of Piedmont-Sardinia .The Papal States comprised territories under...
, and most of the city-states of Italy
Italian city-states
The Italian city-states were a political phenomenon of small independent states mostly in the central and northern Italian peninsula between the 10th and 15th centuries....
) as well as the Ottoman Empire
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman EmpireIt was usually referred to as the "Ottoman Empire", the "Turkish Empire", the "Ottoman Caliphate" or more commonly "Turkey" by its contemporaries...
, and rapidly becoming a general struggle for power and territory among the various participants, marked with an increasing degree of alliances, counter-alliances, and regular betrayals.
In 1499, Louis XII of France
Louis XII of France
Louis proved to be a popular king. At the end of his reign the crown deficit was no greater than it had been when he succeeded Charles VIII in 1498, despite several expensive military campaigns in Italy. His fiscal reforms of 1504 and 1508 tightened and improved procedures for the collection of taxes...
launched the Second Italian War
Second Italian War
The Second Italian War , sometimes known as Louis XII's Italian War or the War over Naples, was the second of the Italian Wars; it was fought primarily by Louis XII of France and Ferdinand II of Aragon, with the participation of several Italian powers...
, invading Lombardy
Lombardy
Lombardy is one of the 20 regions of Italy. The capital is Milan. One-sixth of Italy's population lives in Lombardy and about one fifth of Italy's GDP is produced in this region, making it the most populous and richest region in the country and one of the richest in the whole of Europe...
and seizing the Duchy of Milan
Duchy of Milan
The Duchy of Milan , was created on the 1st of may 1395, when Gian Galeazzo Visconti, Lord of Milan, purchased a diploma for 100,000 Florins from King Wenceslaus. It was this diploma that installed, Gian Galeazzo as Duke of Milan and Count of Pavia...
. He then reached an agreement with Ferdinand I of Spain to divide Naples. By 1502, combined French and Spanish forces had seized control of the Kingdom; disagreements about the terms of the partition led to a war between Louis and Ferdinand. By 1503, Louis, having been defeated at the Battle of Cerignola
Battle of Cerignola
The Battle of Cerignola was fought on April 28, 1503, between Spanish and French armies, in Cerignola, next Bari, Southern Italy. It is noted as the first battle in history won by gunpowder small arms....
and Battle of Garigliano
Battle of Garigliano (1503)
The Battle of Garigliano was fought on December 29, 1503 between a Spanish army under Gonzalo Fernández de Córdoba and a French army commanded by Ludovico II, Marquis of Saluzzo.-Preliminary phase:...
, was forced to withdraw from Naples, which was left under the control of the Spanish viceroy, Gonzalo Fernández de Córdoba
Gonzalo Fernández de Córdoba
Gonzalo Fernández de Córdoba known as The Great Captain, Duke of Terranova and Santangelo, Andria, Montalto and Sessa, also known as Gonzalo de Córdoba, Italian: Gonsalvo or Consalvo Ernandes di Cordova was a Spanish general fighting in the times of the Conquest of Granada and the Italian Wars...
. Meanwhile, Pope Alexander VI
Pope Alexander VI
Pope Alexander VI , born Roderic Llançol i Borja was Pope from 1492 until his death on 18 August 1503. He is one of the most controversial of the Renaissance popes, and his Italianized surname—Borgia—became a byword for the debased standards of the Papacy of that era, most notoriously the Banquet...
attempted to carve a Borgia
Borgia
The Borgias, also known as the Borjas, Borjia, were a European Papal family of Italian and Spanish origin with the name stemming from the familial fief seat of Borja belonging to their Aragonese Lords; they became prominent during the Renaissance. The Borgias were patrons of the arts, and their...
state from the Romagna
Romagna
Romagna is an Italian historical region that approximately corresponds to the south-eastern portion of present-day Emilia-Romagna. Traditionally, it is limited by the Apennines to the south-west, the Adriatic to the east, and the rivers Reno and Sillaro to the north and west...
through the efforts of Cesare Borgia
Cesare Borgia
Cesare Borgia , Duke of Valentinois, was an Italian condottiero, nobleman, politician, and cardinal. He was the son of Pope Alexander VI and his long-term mistress Vannozza dei Cattanei. He was the brother of Lucrezia Borgia; Giovanni Borgia , Duke of Gandia; and Gioffre Borgia , Prince of Squillace...
.
In 1508, Pope Julius II
Pope Julius II
Pope Julius II , nicknamed "The Fearsome Pope" and "The Warrior Pope" , born Giuliano della Rovere, was Pope from 1503 to 1513...
formed the League of Cambrai, in which France, the Papacy, Spain and the Holy Roman Empire
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a realm that existed from 962 to 1806 in Central Europe.It was ruled by the Holy Roman Emperor. Its character changed during the Middle Ages and the Early Modern period, when the power of the emperor gradually weakened in favour of the princes...
agreed to attack the Republic of Venice
Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice or Venetian Republic was a state originating from the city of Venice in Northeastern Italy. It existed for over a millennium, from the late 7th century until 1797. It was formally known as the Most Serene Republic of Venice and is often referred to as La Serenissima, in...
and partition her mainland territories. The resulting War of the League of Cambrai
War of the League of Cambrai
The War of the League of Cambrai, sometimes known as the War of the Holy League and by several other names, was a major conflict in the Italian Wars...
was a kaleidoscope of shifting alliances. The French defeated the Venetian army at the Battle of Agnadello
Battle of Agnadello
The Battle of Agnadello, also known as Vailà, was one of the more significant battles of the War of the League of Cambrai and one of the major battles of the Italian Wars....
, capturing extensive territories; but Julius, now regarding France as a greater threat, left the League and allied himself with Venice. After a year of fighting over the Romagna
Romagna
Romagna is an Italian historical region that approximately corresponds to the south-eastern portion of present-day Emilia-Romagna. Traditionally, it is limited by the Apennines to the south-west, the Adriatic to the east, and the rivers Reno and Sillaro to the north and west...
, he proclaimed a Holy League against the French; this rapidly grew to include England, Spain, and the Holy Roman Empire. The French were driven from Italy in late 1512, despite their victory at the Battle of Ravenna
Battle of Ravenna (1512)
The Battle of Ravenna, fought on 11 April 1512, by forces of the Holy League and France, was a major battle of the War of the League of Cambrai in the Italian Wars...
earlier that year, leaving Milan in the hands of Maximilian Sforza
Maximilian Sforza
Maximilian Sforza was a Duke of Milan from the Sforza family, the son of Lodovico Sforza. He ruled between the occupations of Louis XII of France , and Francis I of France in 1515...
and his Swiss mercenaries
Swiss mercenaries
Swiss mercenaries were notable for their service in foreign armies, especially the armies of the Kings of France, throughout the Early Modern period of European history, from the Later Middle Ages into the Age of the European Enlightenment...
; but the Holy League fell apart over the subject of dividing the spoils, and in 1513 Venice allied with France, agreeing to partition Lombardy between them. The French invasion of Milan in 1513 was defeated at the Battle of Novara
Battle of Novara (1513)
The Battle of Novara was a battle of the War of the League of Cambrai fought on June 6, 1513, near Novara, in Northern Italy.The French had been victorious at Ravenna the previous year. Nevertheless, the French under King Louis XII were driven out of the city of Milan the following month by the...
, which was followed by a series of defeats for the French alliance; but Francis I of France
Francis I of France
Francis I was King of France from 1515 until his death. During his reign, huge cultural changes took place in France and he has been called France's original Renaissance monarch...
defeated the Swiss at the Battle of Marignano
Battle of Marignano
The Battle of Marignano was fought during the phase of the Italian Wars called the War of the League of Cambrai, between France and the Old Swiss Confederacy. It took place on September 13 and 15, 1515, near the town today called Melegnano, 16 km southeast of Milan...
in 1515, and the treaties of Noyon and Brussels left France and Venice in control of northern Italy.
The election of Charles of Spain
Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor
Charles V was ruler of the Holy Roman Empire from 1519 and, as Charles I, of the Spanish Empire from 1516 until his voluntary retirement and abdication in favor of his younger brother Ferdinand I and his son Philip II in 1556.As...
as Holy Roman Emperor
Holy Roman Emperor
The Holy Roman Emperor is a term used by historians to denote a medieval ruler who, as German King, had also received the title of "Emperor of the Romans" from the Pope...
in 1519 led to a collapse of relations between France and the Habsburgs which resulted in the Italian War of 1521
Italian War of 1521
The Italian War of 1521–26, sometimes known as the Four Years' War, was a part of the Italian Wars. The war pitted Francis I of France and the Republic of Venice against the Holy Roman Emperor Charles V, Henry VIII of England, and the Papal States...
, in which France and Venice were pitted against England, the Papacy, and Charles's Habsburg possessions. Prosper Colonna defeated the French at the Battle of Bicocca
Battle of Bicocca
The Battle of Bicocca or La Bicocca was fought on April 27, 1522, during the Italian War of 1521–26. A combined French and Venetian force under Odet de Foix, Vicomte de Lautrec, was decisively defeated by a Spanish-Imperial and Papal army under the overall command of Prospero Colonna...
, driving them from Lombardy. A series of abortive invasions of France by the allies and of Italy by the French continued until 1524, when Francis personally led a French army into Lombardy, only to be defeated and captured at the Battle of Pavia
Battle of Pavia
The Battle of Pavia, fought on the morning of 24 February 1525, was the decisive engagement of the Italian War of 1521–26.A Spanish-Imperial army under the nominal command of Charles de Lannoy attacked the French army under the personal command of Francis I of France in the great hunting preserve...
; imprisoned in Madrid
Madrid
Madrid is the capital and largest city of Spain. The population of the city is roughly 3.3 million and the entire population of the Madrid metropolitan area is calculated to be 6.271 million. It is the third largest city in the European Union, after London and Berlin, and its metropolitan...
, Francis was forced to agree to extensive concessions. Released in 1526, Francis repudiated the terms of the agreement, allied himself with Venice, the Papacy, Milan, and England, and launched the War of the League of Cognac
War of the League of Cognac
The War of the League of Cognac was fought between the Habsburg dominions of Charles V—primarily Spain and the Holy Roman Empire—and the League of Cognac, an alliance including France, Pope Clement VII, the Republic of Venice, England, the Duchy of Milan and Republic of Florence.- Prelude :Shocked...
. In 1527, Imperial troops sacked Rome itself
Sack of Rome (1527)
The Sack of Rome on 6 May 1527 was a military event carried out by the mutinous troops of Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor in Rome, then part of the Papal States...
; the French expedition to capture Naples the next year failed, leading Francis and Charles to conclude the Treaty of Cambrai. Charles then concluded a series of treaties at Barcelona and Bologna
Bologna
Bologna is the capital city of Emilia-Romagna, in the Po Valley of Northern Italy. The city lies between the Po River and the Apennine Mountains, more specifically, between the Reno River and the Savena River. Bologna is a lively and cosmopolitan Italian college city, with spectacular history,...
which eliminated all his opponents save the Florentine Republic, which was subdued by the Siege of Florence
Siege of Florence (1529)
The Siege of Florence took place from October 24, 1529 to August 10, 1530, at the end of the War of the League of Cognac. A large Imperial and Spanish army under Philibert of Châlon, Prince of Orange and Pier Maria III de' Rossi surrounded the city, and, after a siege of nearly ten months,...
and returned to the Medici
Medici
The House of Medici or Famiglia de' Medici was a political dynasty, banking family and later royal house that first began to gather prominence under Cosimo de' Medici in the Republic of Florence during the late 14th century. The family originated in the Mugello region of the Tuscan countryside,...
.
The remainder of the Italian Wars—which flared up again in 1535—was primarily a struggle between the Habsburg
Habsburg
The House of Habsburg , also found as Hapsburg, and also known as House of Austria is one of the most important royal houses of Europe and is best known for being an origin of all of the formally elected Holy Roman Emperors between 1438 and 1740, as well as rulers of the Austrian Empire and...
s and the Valois; while Italy was, at times, a battlefield, the Italian states played little further role in the fighting. The French managed to seize and hold Turin
Turin
Turin is a city and major business and cultural centre in northern Italy, capital of the Piedmont region, located mainly on the left bank of the Po River and surrounded by the Alpine arch. The population of the city proper is 909,193 while the population of the urban area is estimated by Eurostat...
, defeating an Imperial army at the Battle of Ceresole
Battle of Ceresole
The Battle of Ceresole was an encounter between a French army and the combined forces of Spain and the Holy Roman Empire during the Italian War of 1542–46...
in 1544; but the warfare continued (primarily in northern France) until Henry II of France
Henry II of France
Henry II was King of France from 31 March 1547 until his death in 1559.-Early years:Henry was born in the royal Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye, near Paris, the son of Francis I and Claude, Duchess of Brittany .His father was captured at the Battle of Pavia in 1525 by his sworn enemy,...
was forced to accept the Peace of Cateau-Cambrésis in 1559, in which he renounced any further claims to Italy.
By the end of the wars in 1559, Habsburg Spain
Habsburg Spain
Habsburg Spain refers to the history of Spain over the 16th and 17th centuries , when Spain was ruled by the major branch of the Habsburg dynasty...
had been established as the premier power of Europe, to the detriment of France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
. The states of Italy, which had wielded power disproportionate to their size during the Middle Ages
Middle Ages
The Middle Ages is a periodization of European history from the 5th century to the 15th century. The Middle Ages follows the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 and precedes the Early Modern Era. It is the middle period of a three-period division of Western history: Classic, Medieval and Modern...
and the Renaissance
Renaissance
The Renaissance was a cultural movement that spanned roughly the 14th to the 17th century, beginning in Italy in the Late Middle Ages and later spreading to the rest of Europe. The term is also used more loosely to refer to the historical era, but since the changes of the Renaissance were not...
, were reduced to second-rate powers or destroyed entirely.
The Italian Wars had a number of consequences for the work and workplace of Leonardo da Vinci
Leonardo da Vinci
Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci was an Italian Renaissance polymath: painter, sculptor, architect, musician, scientist, mathematician, engineer, inventor, anatomist, geologist, cartographer, botanist and writer whose genius, perhaps more than that of any other figure, epitomized the Renaissance...
; his plans for a "Gran Cavallo" horse statue in 1495 were dropped when the seventy tons of bronze intended for the statue were instead cast into weapons to save Milan
Milan
Milan is the second-largest city in Italy and the capital city of the region of Lombardy and of the province of Milan. The city proper has a population of about 1.3 million, while its urban area, roughly coinciding with its administrative province and the bordering Province of Monza and Brianza ,...
. Later, following a chance encounter with Francis I after the Battle of Marignano
Battle of Marignano
The Battle of Marignano was fought during the phase of the Italian Wars called the War of the League of Cambrai, between France and the Old Swiss Confederacy. It took place on September 13 and 15, 1515, near the town today called Melegnano, 16 km southeast of Milan...
, Leonardo agreed to move to France, where he spent his final years.
In France, Henry II
Henry II of France
Henry II was King of France from 31 March 1547 until his death in 1559.-Early years:Henry was born in the royal Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye, near Paris, the son of Francis I and Claude, Duchess of Brittany .His father was captured at the Battle of Pavia in 1525 by his sworn enemy,...
was fatally wounded in a joust held during the celebrations of the peace. His death led to the accession of his 15-year-old son Francis II
Francis II of France
Francis II was aged 15 when he succeeded to the throne of France after the accidental death of his father, King Henry II, in 1559. He reigned for 18 months before he died in December 1560...
, who in turn soon died. The French monarchy was thrown into turmoil, which increased further with the outbreak of the French Wars of Religion
French Wars of Religion
The French Wars of Religion is the name given to a period of civil infighting and military operations, primarily fought between French Catholics and Protestants . The conflict involved the factional disputes between the aristocratic houses of France, such as the House of Bourbon and House of Guise...
in 1562.
Italian Unification and colonial period
Italian Unification (Italian: il Risorgimento, or "The Resurgence") was the political and social movement that unified different states of the Italian peninsula into the single nation of Italy.There is a lack of consensus on the exact dates for the beginning and the end of Italian reunification, but many scholars agree that the process began with the end of Napoleonic rule and the Congress of Vienna in 1815, and approximately ended with the Franco-Prussian War in 1871 and the conquest of Rome, though the last città irredente (Trento
Trento
Trento is an Italian city located in the Adige River valley in Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol. It is the capital of Trentino...
and Triest) did not join the Kingdom of Italy until after World War I.
Italian conquest of Eritrea and Somalia
Between 1881 and 1905 Italy colonized a portion in the Horn of Africa, so the colonies of EritreaEritrea
Eritrea , officially the State of Eritrea, is a country in the Horn of Africa. Eritrea derives it's name from the Greek word Erethria, meaning 'red land'. The capital is Asmara. It is bordered by Sudan in the west, Ethiopia in the south, and Djibouti in the southeast...
and Italian Somalia were formed, but the conquest of Ethiopia
Ethiopia
Ethiopia , officially known as the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a country located in the Horn of Africa. It is the second-most populous nation in Africa, with over 82 million inhabitants, and the tenth-largest by area, occupying 1,100,000 km2...
was stopped at the Battle of Adwa in 1896.
The conquest of Libya
During the Italo-Turkish WarItalo-Turkish War
The Italo-Turkish or Turco-Italian War was fought between the Ottoman Empire and the Kingdom of Italy from September 29, 1911 to October 18, 1912.As a result of this conflict, Italy was awarded the Ottoman provinces of Tripolitania, Fezzan, and...
(1911–1912) Italy occupied Tripolitania
Tripolitania
Tripolitania or Tripolitana is a historic region and former province of Libya.Tripolitania was a separate Italian colony from 1927 to 1934...
and Cyrenaica
Cyrenaica
Cyrenaica is the eastern coastal region of Libya.Also known as Pentapolis in antiquity, it was part of the Creta et Cyrenaica province during the Roman period, later divided in Libia Pentapolis and Libia Sicca...
that later were unified in the colony of Libya
Libya
Libya is an African country in the Maghreb region of North Africa bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to the east, Sudan to the southeast, Chad and Niger to the south, and Algeria and Tunisia to the west....
.
World War I
In spite of its official status as member of the Triple AllianceTriple Alliance (1882)
The Triple Alliance was the military alliance between Germany, Austria–Hungary, and Italy, , that lasted from 1882 until the start of World War I in 1914...
together with Germany
German Empire
The German Empire refers to Germany during the "Second Reich" period from the unification of Germany and proclamation of Wilhelm I as German Emperor on 18 January 1871, to 1918, when it became a federal republic after defeat in World War I and the abdication of the Emperor, Wilhelm II.The German...
and Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary , more formally known as the Kingdoms and Lands Represented in the Imperial Council and the Lands of the Holy Hungarian Crown of Saint Stephen, was a constitutional monarchic union between the crowns of the Austrian Empire and the Kingdom of Hungary in...
, in the years before the outbreak of the conflict the Italian government had enhanced its diplomatic efforts towards United Kingdom
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
and France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
. This was because the Italian government had grown convinced that a support of Austria (which had been also the traditional enemy of Italy during the 19th century Risorgimento) would not grant to Italy the Italian-speaking lands the country was aiming for in its territorial expansion: Trieste
Trieste
Trieste is a city and seaport in northeastern Italy. It is situated towards the end of a narrow strip of land lying between the Adriatic Sea and Italy's border with Slovenia, which lies almost immediately south and east of the city...
, Istria
Istria
Istria , formerly Histria , is the largest peninsula in the Adriatic Sea. The peninsula is located at the head of the Adriatic between the Gulf of Trieste and the Bay of Kvarner...
, Zara
Zadar
Zadar is a city in Croatia on the Adriatic Sea. It is the centre of Zadar county and the wider northern Dalmatian region. Population of the city is 75,082 citizens...
and Dalmatia
Dalmatia
Dalmatia is a historical region on the eastern coast of the Adriatic Sea. It stretches from the island of Rab in the northwest to the Bay of Kotor in the southeast. The hinterland, the Dalmatian Zagora, ranges from fifty kilometers in width in the north to just a few kilometers in the south....
, all Austrian possessions. In fact, a secret agreement signed with France in 1902 practically nullified Italy's membership in the Triple Alliance.
A few days after the outbreak of the conflict, on 3 August 1914, the government, led by the conservative Antonio Salandra
Antonio Salandra
Antonio Salandra was a conservative Italian politician who served as the 33rd Prime Minister of Italy between 1914 and 1916...
, declared that Italy would not commit its troops, maintaining that the Triple Alliance had only a defensive stance, whereas Austria-Hungary had been the aggressor. In reality, both Salandra and the minister of Foreign Affairs, Sidney Sonnino
Sidney Sonnino
Baron Sidney Costantino Sonnino was an Italian politician.Sonnino was born in Pisa to an Italian father of Jewish heritage and a Welsh mother...
, started diplomatic activities to probe which side was ready to grant the best reward for Italy's entrance in the war. Although the majority of the cabinet (including former Prime Minister Giovanni Giolitti
Giovanni Giolitti
Giovanni Giolitti was an Italian statesman. He was the 19th, 25th, 29th, 32nd and 37th Prime Minister of Italy between 1892 and 1921. A left-wing liberal, Giolitti's periods in office were notable for the passage of a wide range of progressive social reforms which improved the living standards of...
) was firmly contrary to the intervention, numerous intellectuals, including socialists
Italian Socialist Party
The Italian Socialist Party was a socialist and later social-democratic political party in Italy founded in Genoa in 1892.Once the dominant leftist party in Italy, it was eclipsed in status by the Italian Communist Party following World War II...
such as Ivanoe Bonomi
Ivanoe Bonomi
Ivanoe Bonomi was an Italian politician and statesman before and after World War II.Bonomi was born in Mantua. He was elected to the Italian Chamber of Deputies in 1909, representing Mantua as a member of the Italian Socialist Party...
, Leonida Bissolati
Leonida Bissolati
Leonida Bissolati was a leading exponent of the Italian socialist movement at the turn of the nineteenth century.- Biography :...
and Benito Mussolini
Benito Mussolini
Benito Amilcare Andrea Mussolini was an Italian politician who led the National Fascist Party and is credited with being one of the key figures in the creation of Fascism....
, declared in favour of the intervention, which was then mostly supported by the Nationalist and the Liberal parties.
The diplomatic moves led to the London Pact
London Pact
London Pact , or more correctly, the Treaty of London, 1915, was a secret pact between Italy and Triple Entente, signed in London on 26 April 1915 by the Kingdom of Italy, Great Britain, France and Russia....
(26 April 1915), signed by Sonnino without the approval of the Italian Parliament. By the Pact, in case of victory Italy was to be given Trentino and the South Tyrol
South Tyrol
South Tyrol , also known by its Italian name Alto Adige, is an autonomous province in northern Italy. It is one of the two autonomous provinces that make up the autonomous region of Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol. The province has an area of and a total population of more than 500,000 inhabitants...
up to the Brenner Pass
Brenner Pass
- Roadways :The motorway E45 leading from Innsbruck via Bolzano to Verona and Modena uses this pass, and is one of the most important north-south connections in Europe...
, the entire Austrian Littoral
Austrian Littoral
The Austrian Littoral was established as a crown land of the Austrian Empire in 1849. In 1861 it was divided into the three crown lands of the Imperial Free City of Trieste and its suburbs, the Margraviate of Istria, and the Princely County of Gorizia and Gradisca, which each had separate...
(with Trieste
Trieste
Trieste is a city and seaport in northeastern Italy. It is situated towards the end of a narrow strip of land lying between the Adriatic Sea and Italy's border with Slovenia, which lies almost immediately south and east of the city...
, Gorizia-Gradisca
Gorizia and Gradisca
The County of Gorizia and Gradisca was a Habsburg county in Central Europe, in what is now a multilingual border area of Italy and Slovenia. It was named for its two major urban centers, Gorizia and Gradisca d'Isonzo.-Province of the Habsburg Empire:...
and Istria
Istria
Istria , formerly Histria , is the largest peninsula in the Adriatic Sea. The peninsula is located at the head of the Adriatic between the Gulf of Trieste and the Bay of Kvarner...
, but without Fiume), parts of western Carniola
Carniola
Carniola was a historical region that comprised parts of what is now Slovenia. As part of Austria-Hungary, the region was a crown land officially known as the Duchy of Carniola until 1918. In 1849, the region was subdivided into Upper Carniola, Lower Carniola, and Inner Carniola...
(Idrija
Idrija
Idrija is a small town and municipality in the Goriška region of Slovenia. It is known for its mercury mine and lace....
and Ilirska Bistrica
Ilirska Bistrica
Ilirska Bistrica is a town and a municipality in Slovenia. It belongs to the traditional region of Primorska.The town of Ilirska Bistrica is the major economic centre of the district of the same name...
) and north-western Dalmatia
Dalmatia
Dalmatia is a historical region on the eastern coast of the Adriatic Sea. It stretches from the island of Rab in the northwest to the Bay of Kotor in the southeast. The hinterland, the Dalmatian Zagora, ranges from fifty kilometers in width in the north to just a few kilometers in the south....
with Zadar
Zadar
Zadar is a city in Croatia on the Adriatic Sea. It is the centre of Zadar county and the wider northern Dalmatian region. Population of the city is 75,082 citizens...
and most of the islands, but without Split
Split (city)
Split is a Mediterranean city on the eastern shores of the Adriatic Sea, centered around the ancient Roman Palace of the Emperor Diocletian and its wide port bay. With a population of 178,192 citizens, and a metropolitan area numbering up to 467,899, Split is by far the largest Dalmatian city and...
. Other agreements concerned the sovereignty of the port of Valona
Vlorë
Vlorë is one of the biggest towns and the second largest port city of Albania, after Durrës, with a population of about 94,000 . It is the city where the Albanian Declaration of Independence was proclaimed on November 28, 1912...
, the province of Antalya
Antalya
Antalya is a city on the Mediterranean coast of southwestern Turkey. With a population 1,001,318 as of 2010. It is the eighth most populous city in Turkey and country's biggest international sea resort.- History :...
in Turkey
Turkey
Turkey , known officially as the Republic of Turkey , is a Eurasian country located in Western Asia and in East Thrace in Southeastern Europe...
and part of the German colonies in Africa.
Germany and Austria-Hungary had only advanced the possibility of negotiating parts of the Trentino and Eastern Friuli
Gorizia and Gradisca
The County of Gorizia and Gradisca was a Habsburg county in Central Europe, in what is now a multilingual border area of Italy and Slovenia. It was named for its two major urban centers, Gorizia and Gradisca d'Isonzo.-Province of the Habsburg Empire:...
, without Gorizia
Gorizia
Gorizia is a town and comune in northeastern Italy, in the autonomous region of Friuli Venezia Giulia. It is located at the foot of the Julian Alps, bordering Slovenia. It is the capital of the Province of Gorizia, and it is a local center of tourism, industry, and commerce. Since 1947, a twin...
and Trieste. The offer of the French colony of Tunisia
Tunisia
Tunisia , officially the Tunisian RepublicThe long name of Tunisia in other languages used in the country is: , is the northernmost country in Africa. It is a Maghreb country and is bordered by Algeria to the west, Libya to the southeast, and the Mediterranean Sea to the north and east. Its area...
was deemed unsatisfactory.
In April 1915 Italy joined the Entente
Triple Entente
The Triple Entente was the name given to the alliance among Britain, France and Russia after the signing of the Anglo-Russian Entente in 1907....
and on 3 May 1915 officially rejected the Triple Alliance. In the following days Giolitti and the neutralist majority of the Parliament fought to keep Italy out of the conflict, while the nationalists demonstrated in the squares in favour of entrance into the war (the nationalist poet Gabriele D'Annunzio
Gabriele D'Annunzio
Gabriele D'Annunzio or d'Annunzio was an Italian poet, journalist, novelist, and dramatist...
defined them le radiose giornate di Maggio - "the sunny days of May"). On 13 May Salandra presented his resignation to King Victor Emmanuel III. Giolitti, fearful of a further blow to governing institutions, declined to succeed as prime minister and also resigned. Italy thenceforth entered the war under the impetus of a relative minority of its population and politicians.

Interwar period
In 1922, Benito MussoliniBenito Mussolini
Benito Amilcare Andrea Mussolini was an Italian politician who led the National Fascist Party and is credited with being one of the key figures in the creation of Fascism....
brought the fascist party
Italian Fascism
Italian Fascism also known as Fascism with a capital "F" refers to the original fascist ideology in Italy. This ideology is associated with the National Fascist Party which under Benito Mussolini ruled the Kingdom of Italy from 1922 until 1943, the Republican Fascist Party which ruled the Italian...
to power in Italy with his March on Rome
March on Rome
The March on Rome was a march by which Italian dictator Benito Mussolini's National Fascist Party came to power in the Kingdom of Italy...
on 28 October. Mussolini repeatedly stated his dream of the Mediterranean Sea
Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean surrounded by the Mediterranean region and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Anatolia and Europe, on the south by North Africa, and on the east by the Levant...
becoming an "Italian lake" and valued war, saying "Though words are beautiful things, rifles, machine guns, planes, and cannon are still more beautiful".
Ethiopia
The Second Italo-Abyssinian WarSecond Italo-Abyssinian War
The Second Italo–Abyssinian War was a colonial war that started in October 1935 and ended in May 1936. The war was fought between the armed forces of the Kingdom of Italy and the armed forces of the Ethiopian Empire...
was to be Mussolini's way of making up for Italy's embarrassing defeat at the hands of the Ethiopians in the First Italo–Ethiopian War in 1896, and was also a chance to build Italian empire in the last unoccupied region of Africa and divert the populace from economic woes. General Emilio de Bono
Emilio De Bono
Emilio De Bono was an Italian General, fascist activist, Marshal, and member of the Fascist Grand Council . De Bono fought in the Italo-Turkish War, World War I, and the Second Italo-Abyssinian War.-Early life:De Bono was born in Cassano d'Adda...
put on record that preparations for the invasion of Ethiopia
Ethiopia
Ethiopia , officially known as the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a country located in the Horn of Africa. It is the second-most populous nation in Africa, with over 82 million inhabitants, and the tenth-largest by area, occupying 1,100,000 km2...
(Abyssinia) had been going on since 1932 as roads were being built from Italian Somalia
Somalia
Somalia , officially the Somali Republic and formerly known as the Somali Democratic Republic under Socialist rule, is a country located in the Horn of Africa. Since the outbreak of the Somali Civil War in 1991 there has been no central government control over most of the country's territory...
into Ethiopian territory, though Mussolini constantly claimed that he was not a "collector of deserts" and would never think of invading. Ethiopians protested this build-up to war which eventually led up to a border clash at Walwal. Mussolini called this clash "unprovoked aggression" by Ethiopia and invaded on 3 October 1935, led by De Bono. In only three days the Italians had captured Adwa
Adwa
Adwa is a market town in northern Ethiopia, and best known as the community closest to the decisive Battle of Adowa fought in 1896 with Italian troops. Notably, Ethiopian soldiers won the battle, thus being the only African nation to thwart European colonialism...
where the former disgraceful defeat had happened. In December Pietro Badoglio
Pietro Badoglio
Pietro Badoglio, 1st Duke of Addis Abeba, 1st Marquess of Sabotino was an Italian soldier and politician...
replaced De Bono as commander of the invasion because of De Bono's cautious advance. On 31 March 1936, a desperate final counter-attack by Haile Selassie, king of Ethiopia, was carried out, though word of the attack had already gotten to the Italians, giving them victory in the Battle of Maychew
Battle of Maychew
The Battle of Maychew was the last major battle fought on the northern front during the Second Italo-Abyssinian War. The battle consisted of a failed counterattack by the Ethiopian forces under Emperor Haile Selassie making frontal assaults against prepared Italian defensive positions under the...
. Only a few days later the Ethiopian capital Addis Ababa
Addis Ababa
Addis Ababa is the capital city of Ethiopia...
was conquered, allowing Italy to annex the country on 7 May, proclaiming Victor Emmanuel III Emperor of Italian East Africa
Italian East Africa
Italian East Africa was an Italian colonial administrative subdivision established in 1936, resulting from the merger of the Ethiopian Empire with the old colonies of Italian Somaliland and Italian Eritrea. In August 1940, British Somaliland was conquered and annexed to Italian East Africa...
.
Spain

Francisco Franco
Francisco Franco y Bahamonde was a Spanish general, dictator and head of state of Spain from October 1936 , and de facto regent of the nominally restored Kingdom of Spain from 1947 until his death in November, 1975...
and the rest of Nationalist Spain's forces began a rebellion against Republican Spain that was to last three years, called the Spanish Civil War
Spanish Civil War
The Spanish Civil WarAlso known as The Crusade among Nationalists, the Fourth Carlist War among Carlists, and The Rebellion or Uprising among Republicans. was a major conflict fought in Spain from 17 July 1936 to 1 April 1939...
. Franco was fairly sure that he would be able to secure German and Italian help for his National Faction
National Faction (Spanish Civil War)
The National faction also known as Nationalists or Nationals , was a major faction in the Spanish Civil War of 1936 to 1939. It was composed of a variety of political groups opposed to the Second Spanish Republic, including the Falange, the CEDA, and two rival monarchist claimants: the Alfonsists...
, sending emissaries out on 20 July to achieve this. Both did indeed pledge support, sending in the Corpo Truppe Volontarie
Corpo Truppe Volontarie
The Corps of Volunteer Troops was an Italian expeditionary force which was sent to Spain to support General Francisco Franco and the Spanish Nationalist forces during the Spanish Civil War...
from Italy and the Legión Cóndor from Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany , also known as the Third Reich , but officially called German Reich from 1933 to 1943 and Greater German Reich from 26 June 1943 onward, is the name commonly used to refer to the state of Germany from 1933 to 1945, when it was a totalitarian dictatorship ruled by...
, as well as weapons and aircraft. Mussolini was very devoted, eventually sending in 37,000 men and huge amounts of planes to ensure that this "campaign against communism
Communism
Communism is a social, political and economic ideology that aims at the establishment of a classless, moneyless, revolutionary and stateless socialist society structured upon common ownership of the means of production...
" would succeed. The foreign press started to heap pressure on Mussolini when Italian troops suffered a major defeat at Guadalajara
Battle of Guadalajara
The Battle of Guadalajara saw the Republican People's Army defeat Italian and Nationalist forces attempting to encircle Madrid during the Spanish Civil War...
, which led to Mussolini sending in normal troops rather than militia to fight in Spain, eventually ruining the Italian economy with the expense of a war Mussolini thought would end any day. This war also distracted Italy, allowing Germany to carry out the annexation of Austria with the Anschluss
Anschluss
The Anschluss , also known as the ', was the occupation and annexation of Austria into Nazi Germany in 1938....
, a move that otherwise may have been a breaking point between the two powers, due to Austria's alliance with Fascist Italy. The war was supposed to be a staging ground for Italian tactics, potential time to fix any creases out of the system, but Italy continued during World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
to use the same tactics as long before that, unlike Germany's new revolutionary war tactics.
Albania
As Germany was invading CzechoslovakiaCzechoslovakia
Czechoslovakia or Czecho-Slovakia was a sovereign state in Central Europe which existed from October 1918, when it declared its independence from the Austro-Hungarian Empire, until 1992...
, Mussolini decided to accompany that invasion with his own invasion of Albania
Albania
Albania , officially known as the Republic of Albania , is a country in Southeastern Europe, in the Balkans region. It is bordered by Montenegro to the northwest, Kosovo to the northeast, the Republic of Macedonia to the east and Greece to the south and southeast. It has a coast on the Adriatic Sea...
. Albania had long been nearly a puppet state of Italy, several of its military officers actually being Italian themselves. However, King Zog was currently in fairly serious debt and wanted help from Italy, so Mussolini sent foreign minister Gian Galeazzo Ciano
Galeazzo Ciano
Gian Galeazzo Ciano, 2nd Count of Cortellazzo and Buccari was an Italian Minister of Foreign Affairs and Benito Mussolini's son-in-law. In early 1944 Count Ciano was shot by firing squad at the behest of his father-in-law, Mussolini under pressure from Nazi Germany.-Early life:Ciano was born in...
with a list of demands, which Ciano described as impossible to accept. Once King Zog declined, Mussolini said that he must accept these demands by 7 April 1939, or Italy would invade. The invaders had already disembarked to invade before that time. General Alfredo Guzzoni
Alfredo Guzzoni
Alfredo Guzzoni was an Italian military officer who served in both World War I and World War II.-Italian Army:Guzzoni joined the Italian Royal Army and fought in World War I....
would lead two Bersaglieri
Bersaglieri
The Bersaglieri are a corps of the Italian Army originally created by General Alessandro La Marmora on 18 June 1836 to serve in the Piedmontese Army, later to become the Royal Italian Army...
divisions with a battalion of tanks in the invasion, where most resistance was extremely minor, though various organizational problems in the Italian military showed themselves. King Zog fled the country to Greece
Greece
Greece , officially the Hellenic Republic , and historically Hellas or the Republic of Greece in English, is a country in southeastern Europe....
, granted asylum in Athens
Athens
Athens , is the capital and largest city of Greece. Athens dominates the Attica region and is one of the world's oldest cities, as its recorded history spans around 3,400 years. Classical Athens was a powerful city-state...
, then eventually to get to London
London
London is the capital city of :England and the :United Kingdom, the largest metropolitan area in the United Kingdom, and the largest urban zone in the European Union by most measures. Located on the River Thames, London has been a major settlement for two millennia, its history going back to its...
. On 12 April, the Albanian parliament voted to unite their country with Italy, giving Victor Emmanuel III the Albanian crown.
Pact of Steel
On May 22, 1939, the Pact of SteelPact of Steel
The Pact of Steel , known formally as the Pact of Friendship and Alliance between Germany and Italy, was an agreement between Fascist Italy and Nazi Germany signed on May 22, 1939, by the foreign ministers of each country and witnessed by Count Galeazzo Ciano for Italy and Joachim von Ribbentrop...
was signed by Galeazzo Ciano and Joachim von Ribbentrop
Joachim von Ribbentrop
Ulrich Friedrich Wilhelm Joachim von Ribbentrop was Foreign Minister of Germany from 1938 until 1945. He was later hanged for war crimes after the Nuremberg Trials.-Early life:...
of Germany, effectively allying the two powers. Despite the fairly good relations the two forces had had, many Italians were against this alliance, thinking of it as more of a submission to Germany, knowing that Italian interests were likely not to be favored in the relationship. The alliance also technically forced Italy to join in any war that Germany had entered, so that Germany could at any time present the paper and force Mussolini to enter, though they did not end up using this right.
World War II
Nazi GermanyNazi Germany
Nazi Germany , also known as the Third Reich , but officially called German Reich from 1933 to 1943 and Greater German Reich from 26 June 1943 onward, is the name commonly used to refer to the state of Germany from 1933 to 1945, when it was a totalitarian dictatorship ruled by...
invaded Poland
Poland
Poland , officially the Republic of Poland , is a country in Central Europe bordered by Germany to the west; the Czech Republic and Slovakia to the south; Ukraine, Belarus and Lithuania to the east; and the Baltic Sea and Kaliningrad Oblast, a Russian exclave, to the north...
on 1 September 1939, but Italy
Italy
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
remained neutral for the following ten months even though it was one of the Axis powers
Axis Powers
The Axis powers , also known as the Axis alliance, Axis nations, Axis countries, or just the Axis, was an alignment of great powers during the mid-20th century that fought World War II against the Allies. It began in 1936 with treaties of friendship between Germany and Italy and between Germany and...
.
Italian dictator Benito Mussolini
Benito Mussolini
Benito Amilcare Andrea Mussolini was an Italian politician who led the National Fascist Party and is credited with being one of the key figures in the creation of Fascism....
's Under-Secretary for War Production, Carlo Favagrossa
Carlo Favagrossa
Carlo Secillano Favagrossa, during the World War II-era, was the Italian Under-Secretary for War Production. Participated in the Spanish civil war on the side of Francisco Franco....
, had estimated that Italy could not possibly be prepared for such a war until at least October 1942. This had been made clear during Italo-German negotiations for the Pact of Steel
Pact of Steel
The Pact of Steel , known formally as the Pact of Friendship and Alliance between Germany and Italy, was an agreement between Fascist Italy and Nazi Germany signed on May 22, 1939, by the foreign ministers of each country and witnessed by Count Galeazzo Ciano for Italy and Joachim von Ribbentrop...
whereby it was stipulated that neither signatory was to make war without the other earlier than 1943. Although considered a major power, the Italian industrial sector was relatively weak compared to other Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
an major powers. Italian industry did not equal more than 15% of that of France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
or of Britain in militarily critical areas such as automobile
Automobile
An automobile, autocar, motor car or car is a wheeled motor vehicle used for transporting passengers, which also carries its own engine or motor...
production: the number of automobiles in Italy before the war ranged at ca. 372,000, in comparison to ca. 2,500,000 in Britain and France. The lack of a stronger automotive industry made it difficult for Italy to mechanize
Mechanization
Mechanization or mechanisation is providing human operators with machinery that assists them with the muscular requirements of work or displaces muscular work. In some fields, mechanization includes the use of hand tools...
its military. Italy still had a predominantly agricultural-based economy, with demographics more akin to a developing country
Developing country
A developing country, also known as a less-developed country, is a nation with a low level of material well-being. Since no single definition of the term developing country is recognized internationally, the levels of development may vary widely within so-called developing countries...
(high illiteracy, poverty, rapid population growth and a high proportion of adolescents) and a proportion of GNP derived from industry less than that of Czechoslovakia, Hungary and Sweden, in addition to the other great powers. In terms of strategic materials, in 1940, Italy produced 4.4, 0.01, 1.2 and 2.1 Mt of coal, crude oil, iron ore and steel, respectively. By comparison, Great Britain produced 224.3, 11.9, 17.7, and 13.0 Mt and Germany produced 364.8, 8.0, 29.5 and 21.5 Mt of coal, crude oil, iron ore and steel, respectively. Most of the raw material needs could only be fulfilled through importation and no effort was made to stockpile key materials before the entry into war. Also, approximately one quarter of Italy’s merchant fleet were present at foreign ports and given no forewarning of Mussolini’s rash decision to enter the war and were immediately impounded. Another handicap was the large number of weapons and supplies given by Italy practically for free to the Spanish forces fighting under Franco
Francisco Franco
Francisco Franco y Bahamonde was a Spanish general, dictator and head of state of Spain from October 1936 , and de facto regent of the nominally restored Kingdom of Spain from 1947 until his death in November, 1975...
during the Spanish Civil War
Spanish Civil War
The Spanish Civil WarAlso known as The Crusade among Nationalists, the Fourth Carlist War among Carlists, and The Rebellion or Uprising among Republicans. was a major conflict fought in Spain from 17 July 1936 to 1 April 1939...
between 1936 and 1939. The Italians also sent the "Corps of Volunteer Troops
Corpo Truppe Volontarie
The Corps of Volunteer Troops was an Italian expeditionary force which was sent to Spain to support General Francisco Franco and the Spanish Nationalist forces during the Spanish Civil War...
" (Corpo Truppe Volontarie) to fight for Franco. The financial cost of this war was between 6 and 8.5 billion lire, approximately 14 to 20% of annual expenditure. Added to these issues was Italy's extreme debt position. When Benito Mussolini
Benito Mussolini
Benito Amilcare Andrea Mussolini was an Italian politician who led the National Fascist Party and is credited with being one of the key figures in the creation of Fascism....
took office in 1921 the government debt was 93 billion lire
Italian lira
The lira was the currency of Italy between 1861 and 2002. Between 1999 and 2002, the Italian lira was officially a “national subunit” of the euro...
, un-repayable in the short to medium term. Yet only two years later this debt increased to 405 billion lire.
The Italian Royal Army (Regio Esercito) therefore remained comparatively depleted and weak at the commencement of the war. The Italian tanks were of poor quality, and radios were few in number. The bulk of the Italian artillery
Artillery
Originally applied to any group of infantry primarily armed with projectile weapons, artillery has over time become limited in meaning to refer only to those engines of war that operate by projection of munitions far beyond the range of effect of personal weapons...
dated from World War I
World War I
World War I , which was predominantly called the World War or the Great War from its occurrence until 1939, and the First World War or World War I thereafter, was a major war centred in Europe that began on 28 July 1914 and lasted until 11 November 1918...
. The Italian Air Force (Regia Aeronautica
Regia Aeronautica
The Italian Royal Air Force was the name of the air force of the Kingdom of Italy. It was established as a service independent of the Royal Italian Army from 1923 until 1946...
's) primary fighter was the Fiat CR-42, though an advanced design for a biplane
Biplane
A biplane is a fixed-wing aircraft with two superimposed main wings. The Wright brothers' Wright Flyer used a biplane design, as did most aircraft in the early years of aviation. While a biplane wing structure has a structural advantage, it produces more drag than a similar monoplane wing...
with excellent performance characteristics, it was obsolete compared to the then current generation monoplane
Monoplane
A monoplane is a fixed-wing aircraft with one main set of wing surfaces, in contrast to a biplane or triplane. Since the late 1930s it has been the most common form for a fixed wing aircraft.-Types of monoplane:...
fighters of other nations. The Italian Royal Navy (Regia Marina
Regia Marina
The Regia Marina dates from the proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy in 1861 after Italian unification...
) had no aircraft carrier
Aircraft carrier
An aircraft carrier is a warship designed with a primary mission of deploying and recovering aircraft, acting as a seagoing airbase. Aircraft carriers thus allow a naval force to project air power worldwide without having to depend on local bases for staging aircraft operations...
s. In addition, the Royal Air Force (Regia Aeronautica
Regia Aeronautica
The Italian Royal Air Force was the name of the air force of the Kingdom of Italy. It was established as a service independent of the Royal Italian Army from 1923 until 1946...
) could field approximately 1,760 aircraft, of which only 900 of them could be considered as "front-line machines".
Yet whilst equipment was lacking and outdated, Italian authorities were acutely aware of the need to maintain a modern army and were taking the necessary steps to modernize in accordance with their very own relatively advanced tactical principles. Almost 40% of the 1939 budget was allocated to military spending. Awareness existed, albeit belatedly, of the need to have close air support for the Navy and the decision to build carriers was taken And whilst the majority of equipment was obsolescent and poor, appropriate steps were being taken whereby quality equipment was being developed. For example, the three series 5 fighters were capable of meeting the best allied fighters on equal terms, but only a few hundred of each were produced; The Fiat G55 Centauro received much German interest and was defined by Oberst Petersen, advisor to Goering
Hermann Göring
Hermann Wilhelm Göring, was a German politician, military leader, and a leading member of the Nazi Party. He was a veteran of World War I as an ace fighter pilot, and a recipient of the coveted Pour le Mérite, also known as "The Blue Max"...
, as the “best Axis fighter.” The Carro Armato P40 tank, roughly equivalent to the M4 Sherman
M4 Sherman
The M4 Sherman, formally Medium Tank, M4, was the primary tank used by the United States during World War II. Thousands were also distributed to the Allies, including the British Commonwealth and Soviet armies, via lend-lease...
and Panzer IV
Panzer IV
The Panzerkampfwagen IV , commonly known as the Panzer IV, was a medium tank developed in Nazi Germany in the late 1930s and used extensively during the Second World War. Its ordnance inventory designation was Sd.Kfz...
, was designed in 1940, but no prototype was produced until 1942 and developers/manufacturers not able to roll out any of these tanks before Armistice. This was owing, in part, to the lack of sufficiently powerful engines, which were themselves undergoing a development push. Unlike the Allies, Italian tank designers did not think to use old aircraft engines, which were available in relative abundance, and would have certainly facilitated more rapid tank development. Total tank production for the war (~ 3,500) was less than the number of tanks used by Germany in its invasion of France. The Italians were also reported to be the first to use self-propelled guns, both in close support and anti-tank roles, and their, for example, 75/46
Cannone da 75/46 C.A. modello 34
The Cannone da 75/46 C.A. modello 34 was an Italian anti-aircraft gun used during World War II. The designation means it had a caliber of 75 mm, the barrel was 46 caliber-lengths long and it was accepted in service in 1934.- See also :...
(& 75/32
Cannone da 75/32 modello 37
The Cannone da 75/32 modello 37 was an Italian field gun used during World War II. .- History :...
) , 90/53
Cannone da 90/53
The Cannone da 90/53 was an Italian designed cannon, and one of the most successful anti-aircraft guns to see service during World War II. It was used both in an anti-aircraft role and as an anti-tank gun...
(a peer of the German 88/55
88 mm gun
The 88 mm gun was a German anti-aircraft and anti-tank artillery gun from World War II. It was widely used by Germany throughout the war, and was one of the most recognizable German weapons of the war...
), 102/35 and 47/32
Cannone da 47/32 M35
The Cannone da 47/32 M35 was an Austrian artillery piece produced under license in Italy during World War II. It was used both as an infantry gun and an anti-tank gun....
mm, and 20 mm AA
Breda Model 35
The Cannone-Mitragliera da 20/65 modello 35 , also known as Breda Model 35, was a 20 mm anti-aircraft gun produced by the Società Italiana Ernesto Breda of Brescia company in Italy and used during World War II. It was designed in 1932 and was adopted by the Italian armed forces in 1935...
guns were not obsolete. Also of note were the AB 41
AB 41
The Autoblinda 41 was an Italian armored car in use during World War II. It was armed with a 20 mm Breda 35 autocannon and a coaxial 8mm machine gun in a turret similar to the one fitted to the Fiat L6/40, and another hull mounted rear-facing 8mm machine gun.-Description:The AB 41 was based...
and the Camionetta AS 42 which were regarded as excellent vehicles of their type. None of these developments precluded the fact that the bulk of the equipment was obsolescent and poor. However, it was this relatively weak economy, lack of suitable raw materials and inability to produce suitable quantities of armaments and supplies which was predominant reason for Italian military failure.
On paper, Italy had one of the largest armies, but this was far from reality. According to the estimates of Bierman and Smith, the Italian regular army could field only about 200,000 troops at the start of World War II. Irrespective of the attempts to modernize, the majority of Italian army personnel were lightly armed infantry lacking sufficient motor transport. There was insufficient budget to train the men in the services such that in World War II the bulk of the personnel received much of their training at the front, when it was too late to be of use. Air units had not been trained to operate with the naval fleet and the majority of ships had been built for fleet actions, not the convoy protection duties which they were mostly employed for during the war. Regardless, a critical lack of fuel kept naval activities to a minimum.
Senior leadership was also an issue. Mussolini personally assumed control of all three individual military service ministries with the intention of influencing detailed planning. Comando Supremo (the Italian High Command) consisted of only a small complement of staff that could do little more than inform the individual service commands of Mussolini’s intentions, after which it was up to the individual service commands to develop these into proper plans and execute. The result was that there was no central direction for operations and the three military services tended to work independently, focusing only on their fields, with little inter-service cooperation. The Army itself was essentially split into two different institutions; those institutionally loyal to the king (Regio Esercito
Royal Italian Army (1940–1946)
This article is about the Italian Royal Army which participated in World War II.The Italian Royal Army was reformed in 1861 and lasted until 1946. The Royal Army started with the unification of Italy and the formation of the Kingdom of Italy . It ended with the dissolution of the monarchy...
) and those to Mussolini, and discrepancies in pay existed for personnel of equal rank, but from different units.
Following the German conquest of Poland, Mussolini would change his mind repeatedly as to whether he would enter the war. The British
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
commander in Africa
Africa
Africa is the world's second largest and second most populous continent, after Asia. At about 30.2 million km² including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of the Earth's total surface area and 20.4% of the total land area...
, General Archibald Wavell, correctly predicted that Mussolini's pride would ultimately cause him to enter the war. Wavell would compare Mussolini's situation to that of someone at the top of a diving board: "I think he must do something. If he cannot make a graceful dive, he will at least have to jump in somehow; he can hardly put on his dressing-gown and walk down the stairs again."
Some historians believe that Italian leader Benito Mussolini
Benito Mussolini
Benito Amilcare Andrea Mussolini was an Italian politician who led the National Fascist Party and is credited with being one of the key figures in the creation of Fascism....
was induced to enter the war against the Allies
Allies of World War II
The Allies of World War II were the countries that opposed the Axis powers during the Second World War . Former Axis states contributing to the Allied victory are not considered Allied states...
by secret negotiations with British Prime Minister Winston Churchill
Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer-Churchill, was a predominantly Conservative British politician and statesman known for his leadership of the United Kingdom during the Second World War. He is widely regarded as one of the greatest wartime leaders of the century and served as Prime Minister twice...
, with whom he had an active mail correspondence between September 1939 and June 1940. The journalist Luciano Garibaldi wrote that "in those letters (which disappeared at Lake Como in 1945) Churchill may have extorted Mussolini to enter the war to mitigate Hitler's demands and dissuade him from continuing hostilities against Great Britain as France was inexorably moving toward defeat. In light of this, Mussolini could urge Hitler turn against the USSR, the common enemy of both Churchill and Mussolini".
Initially, the entry into the war was clearly political opportunism, which led to a lack of consistency in planning, with principal objectives and enemies being changed with little regard for the consequences. Mussolini was well aware of the military and material deficiencies but thought the war would be over soon and did not expect to do much fighting. This led to confusion amongst ordinary Italians and soldiers who had little idea of what they were fighting for and, hence, had little conviction and saw little justification for it. As the war progressed and one disaster followed another, Comando Supremo were forced to take more serious steps in their planning.
France
As the war looked increasingly bad for the alliesAllies of World War II
The Allies of World War II were the countries that opposed the Axis powers during the Second World War . Former Axis states contributing to the Allied victory are not considered Allied states...
, with the impending German conquest of Belgium
Belgium
Belgium , officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a federal state in Western Europe. It is a founding member of the European Union and hosts the EU's headquarters, and those of several other major international organisations such as NATO.Belgium is also a member of, or affiliated to, many...
, the Netherlands
Netherlands
The Netherlands is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, located mainly in North-West Europe and with several islands in the Caribbean. Mainland Netherlands borders the North Sea to the north and west, Belgium to the south, and Germany to the east, and shares maritime borders...
, and France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
, Mussolini could no longer hold himself back and declared war on the allies on 10 June 1940. To Mussolini it seemed that the war was already nearly over, and he wanted to make sure that Italy at least got a position at the peace tables at the end and obtained such lands as Corsica
Corsica
Corsica is an island in the Mediterranean Sea. It is located west of Italy, southeast of the French mainland, and north of the island of Sardinia....
, Nice
Nice
Nice is the fifth most populous city in France, after Paris, Marseille, Lyon and Toulouse, with a population of 348,721 within its administrative limits on a land area of . The urban area of Nice extends beyond the administrative city limits with a population of more than 955,000 on an area of...
, and more North African territory. The Italian offensive against France did not actually begin until ten days after the declaration of war, and Italian troops were very slow to capture territory, while Germany had already taken hold of Paris
Paris
Paris is the capital and largest city in France, situated on the river Seine, in northern France, at the heart of the Île-de-France region...
. By 25 June, the armistice with France had already been arranged, though Italian troops made virtually no progress into French territory.
Africa
Mussolini's entry into the war was at least bad news for the United KingdomUnited Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
, as the Regia Marina
Regia Marina
The Regia Marina dates from the proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy in 1861 after Italian unification...
would now oppose them in Mediterranean waters. Italian armies in Libya and East Africa could also potentially have knocked British troops completely out of Egypt
Egypt
Egypt , officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, Arabic: , is a country mainly in North Africa, with the Sinai Peninsula forming a land bridge in Southwest Asia. Egypt is thus a transcontinental country, and a major power in Africa, the Mediterranean Basin, the Middle East and the Muslim world...
, having half a million men in Africa compared to the United Kingdom's fifty thousand. However, British troops took the initiative in Africa while Italy was still having trouble pacifying Ethiopia and General Wavell
Archibald Wavell, 1st Earl Wavell
Field Marshal Archibald Percival Wavell, 1st Earl Wavell GCB, GCSI, GCIE, CMG, MC, PC was a British field marshal and the commander of British Army forces in the Middle East during the Second World War. He led British forces to victory over the Italians, only to be defeated by the German army...
kept up a constantly moving front of raids on Italian positions that proved to be successful. On 14 June a successful surprise attack was made on Fort Capuzzo
Fort Capuzzo
Fort Capuzzo was a fort in the Italiancolony of Libya, near the Libyan-Egyptian border. It is famous for its role during the World War II.Within a week of Italy's 10 June 1940 declaration of war upon Britain, the British Army's 11th Hussars captured Fort Capuzzo...
by the British, though it was not meant as a permanent gain as the British were using far more mobile tactics at the time. By mid-September, casualty listings indicate that Italy had lost 3,000 troops where the United Kingdom had only lost slightly over 490, despite Italy's land numbers and air superiority at the time.
On 13 September 1940, Italy began a very slow advance
Italian invasion of Egypt
The Italian Invasion of Egypt was an Italian offensive action against British, Commonwealth and Free French forces during the Western Desert Campaign of the Second World War. Initially, the goal of the offensive was to seize the Suez Canal. To accomplish this, Italian forces from Libya would have...
eastward into Egypt
Egypt
Egypt , officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, Arabic: , is a country mainly in North Africa, with the Sinai Peninsula forming a land bridge in Southwest Asia. Egypt is thus a transcontinental country, and a major power in Africa, the Mediterranean Basin, the Middle East and the Muslim world...
. The Italians advanced with six divisions. After three days, they stopped and set up a chain of fortified camps near Sidi Barrani
Sidi Barrani
Sidi Barrani is a town in Egypt, near the Mediterranean Sea, about east of the border with Libya, and around from Tobruk, Libya.Probably named after Sidi Mohammed el Barrani, a Senussi fighter in the early 1900s, the village is mainly a Bedouin community...
. However, the chain of camps were too far apart from one another. This allowed Wavell make a crippling blow to the Italian forces around Sidi Barrani
Sidi Barrani
Sidi Barrani is a town in Egypt, near the Mediterranean Sea, about east of the border with Libya, and around from Tobruk, Libya.Probably named after Sidi Mohammed el Barrani, a Senussi fighter in the early 1900s, the village is mainly a Bedouin community...
right at the start of what was to become Operation Compass
Operation Compass
Operation Compass was the first major Allied military operation of the Western Desert Campaign during World War II. British and Commonwealth forces attacked Italian forces in western Egypt and eastern Libya in December 1940 to February 1941. The attack was a complete success...
. Richard O'Connor
Richard O'Connor
General Sir Richard Nugent O'Connor KT, GCB, DSO & Bar, MC, ADC was a British Army general who commanded the Western Desert Force in the early years of World War II...
led the initial attack against the Italian camps. O'Connor moved between the camps and around to the Italian rear. This greatly surprised the Italians and the British were able to immediately capture four thousand prisoners. This attack alone could have effectively annihilated the Italian army in North Africa. But the British commanders did not foresee such a large victory. Instead, the initial attack was thought of as a large-scale raid. For this reason, no infantry division was available to press home the British opportunity at Sidi Barrani
Sidi Barrani
Sidi Barrani is a town in Egypt, near the Mediterranean Sea, about east of the border with Libya, and around from Tobruk, Libya.Probably named after Sidi Mohammed el Barrani, a Senussi fighter in the early 1900s, the village is mainly a Bedouin community...
. So the remaining Italian troops managed to escape safely to Bardia
Bardia
Bardia is a geographic region in the Democratic Republic of Nepal.Bardia comprises a portion of the Terai, or lowland hills and valleys of southern Nepal. The Terai is over 1,000 feet in elevation, and extends all along the Indian border...
. However, Bardia
Bardia
Bardia is a geographic region in the Democratic Republic of Nepal.Bardia comprises a portion of the Terai, or lowland hills and valleys of southern Nepal. The Terai is over 1,000 feet in elevation, and extends all along the Indian border...
was captured by the British within three weeks.
The Italian campaign in East Africa
East African Campaign (World War II)
The East African Campaign was a series of battles fought in East Africa during World War II by the British Empire, the British Commonwealth of Nations and several allies against the forces of Italy from June 1940 to November 1941....
was perhaps even less successful. The Italians captured small parts of Sudan
Sudan
Sudan , officially the Republic of the Sudan , is a country in North Africa, sometimes considered part of the Middle East politically. It is bordered by Egypt to the north, the Red Sea to the northeast, Eritrea and Ethiopia to the east, South Sudan to the south, the Central African Republic to the...
, Kenya
Kenya
Kenya , officially known as the Republic of Kenya, is a country in East Africa that lies on the equator, with the Indian Ocean to its south-east...
, and British Somaliland
British Somaliland
British Somaliland was a British protectorate in the northern part of present-day Somalia. For much of its existence, British Somaliland was bordered by French Somaliland, Ethiopia, and Italian Somaliland. From 1940 to 1941, it was occupied by the Italians and was part of Italian East Africa...
, then took up a defensive posture against an expected counterattack. This counterattack came from the Indian 4th Infantry Division, which drove into Ethiopia with help from an amphibious assault and forces in Kenya, capturing Eritrea in February, Somalia in March, and Addis Ababa, capital of Ethiopia, in April. Forces in Italian East Africa
Italian East Africa
Italian East Africa was an Italian colonial administrative subdivision established in 1936, resulting from the merger of the Ethiopian Empire with the old colonies of Italian Somaliland and Italian Eritrea. In August 1940, British Somaliland was conquered and annexed to Italian East Africa...
were somewhat cut short by the Regia Aeronautica
Regia Aeronautica
The Italian Royal Air Force was the name of the air force of the Kingdom of Italy. It was established as a service independent of the Royal Italian Army from 1923 until 1946...
's forced presence in the Battle of Britain
Battle of Britain
The Battle of Britain is the name given to the World War II air campaign waged by the German Air Force against the United Kingdom during the summer and autumn of 1940...
at the time, leaving only 150 planes in Ethiopia.
Campaigning in North Africa then fell to Erwin Rommel
Erwin Rommel
Erwin Johannes Eugen Rommel , popularly known as the Desert Fox , was a German Field Marshal of World War II. He won the respect of both his own troops and the enemies he fought....
over any Italian generals, as many Panzer
Panzer
A Panzer is a German language word that, when used as a noun, means "tank". When it is used as an adjective, it means either tank or "armoured" .- Etymology :...
units came into the theatre from Germany as the Afrika Korps
Afrika Korps
The German Africa Corps , or the Afrika Korps as it was popularly called, was the German expeditionary force in Libya and Tunisia during the North African Campaign of World War II...
. However, the bulk of the Axis army in North Africa was still Italian. Rommel was at first very successful, reaching the Egyptian border again in less than a fortnight as he caught Wavell off-guard. Another British offensive was crushed, and Rommel made his way to El Alamein
First Battle of El Alamein
The First Battle of El Alamein was a battle of the Western Desert Campaign of the Second World War, fought between Axis forces of the Panzer Army Africa commanded by Field Marshal Erwin Rommel, and Allied forces The First Battle of El Alamein (1–27 July 1942) was a battle of the Western Desert...
. This made Mussolini believe the end was near, as he flew to Africa, planning to enter the capital of Egypt triumphantly, only to wait three weeks, then fly back to Rome. Field Marshal Montgomery won at El Alamein in October 1942 for the British. This victory coincided with Operation Torch
Operation Torch
Operation Torch was the British-American invasion of French North Africa in World War II during the North African Campaign, started on 8 November 1942....
, America's landing in French North Africa, and the Battle of Stalingrad
Battle of Stalingrad
The Battle of Stalingrad was a major battle of World War II in which Nazi Germany and its allies fought the Soviet Union for control of the city of Stalingrad in southwestern Russia. The battle took place between 23 August 1942 and 2 February 1943...
's outcome, destroying axis morale.
Greece
With very little preparation after this disaster in Africa and the ensuing retirement of Rodolfo GrazianiRodolfo Graziani
Rodolfo Graziani, 1st Marquis of Neghelli , was an officer in the Italian Regio Esercito who led military expeditions in Africa before and during World War II.-Rise to prominence:...
, Mussolini then decided on an invasion of Greece
Greece
Greece , officially the Hellenic Republic , and historically Hellas or the Republic of Greece in English, is a country in southeastern Europe....
as his next move to keep in pace with Germany's recent occupation of Romania
Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central and Southeastern Europe, on the Lower Danube, within and outside the Carpathian arch, bordering on the Black Sea...
. After large propaganda campaigns and even the sinking of a Greek light cruiser, Mussolini then handed an ultimatum to Ioannis Metaxas
Ioannis Metaxas
Ioannis Metaxas was a Greek general, politician, and dictator, serving as Prime Minister of Greece from 1936 until his death in 1941...
, Prime Minister of Greece, which would initiate the Greco-Italian War
Greco-Italian War
The Greco-Italian War was a conflict between Italy and Greece which lasted from 28 October 1940 to 23 April 1941. It marked the beginning of the Balkans Campaign of World War II...
. Hitler was against Mussolini's invasion, (as it would require German troops' help later on), but Mussolini continued without German knowledge, as he felt that the Nazis had invaded countries too many times without telling Mussolini beforehand.
Mussolini was very unsure of what date to invade, as he changed his mind many times, even five times in one segment of fifteen minutes. Eventually he decided on 28 October, the anniversary of the March on Rome
March on Rome
The March on Rome was a march by which Italian dictator Benito Mussolini's National Fascist Party came to power in the Kingdom of Italy...
, though staff headquarters was not aware until they heard the date on London radio. In about two weeks, the Italian army was already retreating back into Albania, for conditions at this time of year were very detrimental to mountain warfare and general organization problems continued throughout the military. Franco of the recently victorious Fascist side in the Spanish Civil War was pondering entrance into World War II, but Italy's failure in Greece put him off of the idea. Hitler then came in to rescue Mussolini's troops, gaining him the upper hand in all politics and military operations for the rest of the war.
Soviet Union
Mussolini was actually in the middle of negotiating a commercial treaty with the Soviet UnionSoviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
when Hitler invaded his former ally in fighting Poland. However, Mussolini was taken once again by Hitler's promise of quick victory and would eventually send a total of 200,000 troops as the Italian Eighth Army to the Russian front for Operation Barbarossa
Operation Barbarossa
Operation Barbarossa was the code name for Germany's invasion of the Soviet Union during World War II that began on 22 June 1941. Over 4.5 million troops of the Axis powers invaded the USSR along a front., the largest invasion in the history of warfare...
, organized as the CSIR, Italian Expeditionary Corps in Russia. To begin with, three whole divisions were sent, though only one division at all motorized, but having no tanks.
After some large initial losses in the "Celere" Division, Mussolini sent four new infantry divisions and three Alpini
Alpini
The Alpini, , are the elite mountain warfare soldiers of the Italian Army. They are currently organized in two operational brigades, which are subordinated to the Alpini Corps Command. The singular is Alpino ....
(alpine) divisions to the Soviet Union to officially make his forces an army. But instead of being deployed in the Caucasus Mountains as expected, the Italian units were tasked with holding the front in the Don river plains. As a result of this disastrous strategic decision, the Alpine troops armed, trained and equipped for mountain warfare and the under strength Italian infantry divisions were pitted against tanks and mechanized infantry, to counter which they were neither equipped nor trained. The Soviet offensive Operation Little Saturn wiped out the majority of the Italian troops, with only the 2nd "Tridentina" Alpine division
2 Alpine Division Tridentina
The 2nd Alpine Division Tridentina was a World War II Mountain Infantry division of the Italian Army. The Alpini that formed the divisions are a highly decorated and elite mountain corps of the Italian Army comprising both infantry and artillery units...
escaping annihilation. By the end of February 1943, the few remaining Italian troops were being withdrawn, a huge blow to public opinion of the Fascist government in Italy.
Sicily and armistice
On 10 July 1943, a combined force of American and British Commonwealth troops invaded SicilySicily
Sicily is a region of Italy, and is the largest island in the Mediterranean Sea. Along with the surrounding minor islands, it constitutes an autonomous region of Italy, the Regione Autonoma Siciliana Sicily has a rich and unique culture, especially with regard to the arts, music, literature,...
in Operation Husky. German generals again took the lead in the defence and, although they lost the island, they succeeded in ferrying large numbers of German and Italian forces safely off Sicily to the Italian mainland. With the loss of Sicily, popular support for the war diminished in Italy. On 25 July 1943, the Grand Council of Fascism
Grand Council of Fascism
The Grand Council of Fascism was the main body of Mussolini's Fascist government in Italy. A body which held and applied great power to control the institutions of government, it was created as a party body in 1923 and became a state body on 9 December 1928....
ousted Italian dictator Benito Mussolini
Benito Mussolini
Benito Amilcare Andrea Mussolini was an Italian politician who led the National Fascist Party and is credited with being one of the key figures in the creation of Fascism....
and a new Italian government, led by General Pietro Badoglio
Pietro Badoglio
Pietro Badoglio, 1st Duke of Addis Abeba, 1st Marquess of Sabotino was an Italian soldier and politician...
and King Victor Emmanuel III
Victor Emmanuel III of Italy
Victor Emmanuel III was a member of the House of Savoy and King of Italy . In addition, he claimed the crowns of Ethiopia and Albania and claimed the titles Emperor of Ethiopia and King of Albania , which were unrecognised by the Great Powers...
, took over in Italy. The new Italian government immediately began secret negotiations with the Allies to end the fighting and to come over to the Allied side. On 3 September, a secret armistice was signed with the Allies at Fairfield Camp in Sicily. The armistice was announced on 8 September. By then, the Allies were on the Italian mainland.
Lebanon Intervention (1982-1984)
In 1982, after the Sabra and Chatila MassacreSabra and Shatila massacre
The Sabra and Shatila massacre took place in the Sabra and Shatila Palestinian refugee camps in Beirut, Lebanon between September 16 and September 18, 1982, during the Lebanese civil war. Palestinian and Lebanese civilians were massacred in the camps by Christian Lebanese Phalangists while the camp...
, Italian forces deployed in Lebanon
Lebanon
Lebanon , officially the Republic of LebanonRepublic of Lebanon is the most common term used by Lebanese government agencies. The term Lebanese Republic, a literal translation of the official Arabic and French names that is not used in today's world. Arabic is the most common language spoken among...
, together with United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
and France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
, a force of around 3000 troops, led by then Brigadier General Angioni, whose in the end was the most successful of the three deployed forces, raising the confidence of Italian leadership and people in the Armed Forces, recovering the low esteem in the public opinion caused by the defeat in World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
and paving the way to the subsequent increase in overseas missions for the Italian military.
War on Terrorism
As part of Operation Enduring Freedom in response to the September 11, 2001 attacksSeptember 11, 2001 attacks
The September 11 attacks The September 11 attacks The September 11 attacks (also referred to as September 11, September 11th or 9/119/11 is pronounced "nine eleven". The slash is not part of the pronunciation...
, Italy contributed to the international operation in Afghanistan
Afghanistan
Afghanistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located in the centre of Asia, forming South Asia, Central Asia and the Middle East. With a population of about 29 million, it has an area of , making it the 42nd most populous and 41st largest nation in the world...
. Italian forces have contributed to ISAF
International Security Assistance Force
The International Security Assistance Force is a NATO-led security mission in Afghanistan established by the United Nations Security Council on 20 December 2001 by Resolution 1386 as envisaged by the Bonn Agreement...
, the NATO force in Afghanistan
Afghanistan
Afghanistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located in the centre of Asia, forming South Asia, Central Asia and the Middle East. With a population of about 29 million, it has an area of , making it the 42nd most populous and 41st largest nation in the world...
, and a Provincial reconstruction team
Provincial reconstruction team
A Provincial Reconstruction Team is a unit introduced by the United States government, consisting of military officers, diplomats, and reconstruction subject matter experts, working to support reconstruction efforts in unstable states. PRTs were first established in Afghanistan in late 2001 or...
and five Italian soldiers have died under ISAF. Italy has sent 411 troops, based on one infantry company from the 2nd Alpini Regiment
2 Alpini Regiment
The 2nd Alpini Regiment is a light Infantry regiment of the Italian Army, specializing in mountain combat. The Alpini are a mountain infantry corps of the Italian Army, that distinguished itself in combat during World War I and World War II...
tasked to protect the ISAF HQ, one engineer company, one NBC platoon, one logistic unit, as well as liaison and staff elements integrated into the operation chain of command. Italian forces also command a multinational engineer task force and have deployed a platoon of Italian military police
Military police
Military police are police organisations connected with, or part of, the military of a state. The word can have different meanings in different countries, and may refer to:...
. Three AB 212 helicopters also were deployed to Kabul and four Tornado
Tornado
A tornado is a violent, dangerous, rotating column of air that is in contact with both the surface of the earth and a cumulonimbus cloud or, in rare cases, the base of a cumulus cloud. They are often referred to as a twister or a cyclone, although the word cyclone is used in meteorology in a wider...
.
The Italian Army did not take part in combat operations of the 2003 Second Gulf War, dispatching troops only after May 1, 2003 – when major combat operations were declared over by the U.S. President
President of the United States
The President of the United States of America is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president leads the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces....
George W. Bush
George W. Bush
George Walker Bush is an American politician who served as the 43rd President of the United States, from 2001 to 2009. Before that, he was the 46th Governor of Texas, having served from 1995 to 2000....
. Subsequently Italian troops arrived in the late summer of 2003, and began patrolling Nasiriyah
Nasiriyah
Nasiriyah is a city in Iraq. It is on the Euphrates about 225 miles southeast of Baghdad, near the ruins of the ancient city of Ur. It is the capital of the province of Dhi Qar...
and the surrounding area. On 26 May 2006, Italian foreign minister Massimo D'Alema
Massimo D'Alema
Massimo D'Alema is an Italian politician. He is also a journalist and a former national secretary of the Democratic Party of the Left...
announced that the Italian forces would be reduced to 1,600 by June; Italian participation in the military operations in Iraq was concluded by the end of 2006, with full withdrawal of Italian military personnel except for a small group of about 30 soldiers engaged in providing security for the Italian embassy in Baghdad
Baghdad
Baghdad is the capital of Iraq, as well as the coterminous Baghdad Governorate. The population of Baghdad in 2011 is approximately 7,216,040...
, and about 87 soldiers stationing in bases in the Persian Gulf
Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf, in Southwest Asia, is an extension of the Indian Ocean located between Iran and the Arabian Peninsula.The Persian Gulf was the focus of the 1980–1988 Iran-Iraq War, in which each side attacked the other's oil tankers...
(but not in Iraqi territory). As of June 2006 32 Italian troops have been killed in Iraq – with the greatest single loss of life coming on November 12, 2003 – a suicide car bombing of the Italian Carabinieri
Carabinieri
The Carabinieri is the national gendarmerie of Italy, policing both military and civilian populations, and is a branch of the armed forces.-Early history:...
Corps HQ left a dozen Carabinieri, five Army soldiers, two Italian civilians, and eight Iraqi civilians dead.
Multinational force in Iraq
The multinational force in Iraq, also known as the 'Coalition' or 'US-led coalition', refers to the nations whose governments have military personnel in Iraq. The Italian Army did not take part in initial combat operations of the 2003 Second Gulf War, despatching troops only after May 1, 2003 - when major combat operations were declared over by the U.S. PresidentPresident of the United States
The President of the United States of America is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president leads the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces....
George W. Bush
George W. Bush
George Walker Bush is an American politician who served as the 43rd President of the United States, from 2001 to 2009. Before that, he was the 46th Governor of Texas, having served from 1995 to 2000....
. Subsequently Italian troops arrived in the late summer of 2003, and began patrolling Nasiriyah
Nasiriyah
Nasiriyah is a city in Iraq. It is on the Euphrates about 225 miles southeast of Baghdad, near the ruins of the ancient city of Ur. It is the capital of the province of Dhi Qar...
and the surrounding area. On 26 May 2006, Italian foreign minister Massimo D'Alema announced that the Italian forces would be reduced to 1,600 by June. As of June 2006 32 Italian troops have been killed in Iraq - with the greatest single loss of life coming on November 12, 2004 - a suicide car bombing of the Italian Carabinieri Corps HQ left a dozen Carabinieri, five Army soldiers, two Italian civilians, and eight Iraqi civilians dead.

