
List of Russian explorers
Encyclopedia
This is a list of explorers from the Russian Federation, Soviet Union
, Russian Empire
, Tsardom of Russia
and other Russian predecessor states, including ethnic Russians
and people of other ethnicities. This list also includes those who were born in Russia but later emigrated, and those who were born elsewhere but immigrated to the country and participated in its exploration activities.
At 17075400 square kilometres (6,592,848.8 sq mi), Russia is the largest country in the world, covering more than a ninth of the Earth
’s land mass. In the times of the Soviet Union
and the Russian Empire
the country's share in the world's land mass reached 1/6. Most of these territories were first discovered by Russian explorers (if, of course, we don't count indigenous peoples of inhabited territories). Apart from their discoveries in Siberia
, Alaska
, Central Asia
and the Extreme North, Russians have made significant contributions to the exploration of the Arctic
and Antarctic
, the Pacific islands, as well as deep-sea
and space
exploration.
For the full plain list of Russian explorers on Wikipedia, see :Category:Russian explorers. See also the list of Russian and Soviet cosmonauts; several cosmonauts, who've set important records, are listed here.
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
, Russian Empire
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was a state that existed from 1721 until the Russian Revolution of 1917. It was the successor to the Tsardom of Russia and the predecessor of the Soviet Union...
, Tsardom of Russia
Tsardom of Russia
The Tsardom of Russia was the name of the centralized Russian state from Ivan IV's assumption of the title of Tsar in 1547 till Peter the Great's foundation of the Russian Empire in 1721.From 1550 to 1700, Russia grew 35,000 km2 a year...
and other Russian predecessor states, including ethnic Russians
Russians
The Russian people are an East Slavic ethnic group native to Russia, speaking the Russian language and primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries....
and people of other ethnicities. This list also includes those who were born in Russia but later emigrated, and those who were born elsewhere but immigrated to the country and participated in its exploration activities.
At 17075400 square kilometres (6,592,848.8 sq mi), Russia is the largest country in the world, covering more than a ninth of the Earth
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
’s land mass. In the times of the Soviet Union
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
and the Russian Empire
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was a state that existed from 1721 until the Russian Revolution of 1917. It was the successor to the Tsardom of Russia and the predecessor of the Soviet Union...
the country's share in the world's land mass reached 1/6. Most of these territories were first discovered by Russian explorers (if, of course, we don't count indigenous peoples of inhabited territories). Apart from their discoveries in Siberia
Siberia
Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th...
, Alaska
Alaska
Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait...
, Central Asia
Central Asia
Central Asia is a core region of the Asian continent from the Caspian Sea in the west, China in the east, Afghanistan in the south, and Russia in the north...
and the Extreme North, Russians have made significant contributions to the exploration of the Arctic
Arctic
The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost...
and Antarctic
Antarctic
The Antarctic is the region around the Earth's South Pole, opposite the Arctic region around the North Pole. The Antarctic comprises the continent of Antarctica and the ice shelves, waters and island territories in the Southern Ocean situated south of the Antarctic Convergence...
, the Pacific islands, as well as deep-sea
Deep-sea exploration
Deep-sea exploration is the investigation of physical, chemical, and biological conditions on the sea bed, for scientific or commercial purposes. Deep-sea exploration is considered as a relatively recent human activity compared to the other areas of geophysical research, as the depths of the sea...
and space
Space exploration
Space exploration is the use of space technology to explore outer space. Physical exploration of space is conducted both by human spaceflights and by robotic spacecraft....
exploration.
For the full plain list of Russian explorers on Wikipedia, see :Category:Russian explorers. See also the list of Russian and Soviet cosmonauts; several cosmonauts, who've set important records, are listed here.
Alphabetical list
Areas primarily explored:A
| Portrait | Person | Achievements | Image |
|---|---|---|---|
| Valerian Albanov Valerian Albanov Valerian Ivanovich Albanov was a Russian navigator, best known for being one of only two survivors of the ill-fated Brusilov expedition of 1912.-Biography:... (1881–1919)  Russian Empire Russian EmpireImperial Russian Navy Imperial Russian Navy The Imperial Russian Navy refers to the Tsarist fleets prior to the February Revolution.-First Romanovs:Under Tsar Mikhail Feodorovich, construction of the first three-masted ship, actually built within Russia, was completed in 1636. It was built in Balakhna by Danish shipbuilders from Holstein... officer, lieutenant, Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... explorer |
Albanov was one of the only two survivors of the ill-fated 1912-14 Brusilov expedition Georgy Brusilov Georgy Lvovich Brusilov or Hryhoriy Brusylov was a Ukrainian Russian naval officer of the Imperial Russian Navy and an Arctic explorer... , the other being Alexander Konrad Alexander Konrad Alexander Eduardovich Konrad was a Russian sailor. Along with Valerian Albanov, he was one of the only two survivors, and the only surviving sailor of the ill-fated Brusilov expedition.-Biography:... . They left ice-bound ship St. Anne and by ski Ski A ski is a long, flat device worn on the foot, usually attached through a boot, designed to help the wearer slide smoothly over snow. Originally intended as an aid to travel in snowy regions, they are now mainly used for recreational and sporting purposes... , sledge, and kayak Kayak A kayak is a small, relatively narrow, human-powered boat primarily designed to be manually propelled by means of a double blade paddle.The traditional kayak has a covered deck and one or more cockpits, each seating one paddler... crossed the Kara Sea Kara Sea The Kara Sea is part of the Arctic Ocean north of Siberia. It is separated from the Barents Sea to the west by the Kara Strait and Novaya Zemlya, and the Laptev Sea to the east by the Severnaya Zemlya.... , reached Franz Josef Land Franz Josef Land Franz Josef Land, Franz Joseph Land, or Francis Joseph's Land is an archipelago located in the far north of Russia. It is found in the Arctic Ocean north of Novaya Zemlya and east of Svalbard, and is administered by Arkhangelsk Oblast. Franz Josef Land consists of 191 ice-covered islands with a... and finally were rescued by Georgy Sedov Georgy Sedov Georgy Yakovlevich Sedov was a Russian Arctic explorer.Born in the village of Krivaya Kosa of Taganrog district in a fisherman's family. In 1898, Sedov finished navigation courses in Rostov-on-Don and acquired the rank of long voyage navigator... 's Saint Phocas. The data about ice drift of St. Anna, provided by Albanov, helped Vladimir Vize to calculate the coordinates of previously unknown Vize Island Vize Island Vize Island or Wiese Island is an isolated island located in the Arctic Ocean at the northern end of the Kara Sea, roughly midway between Franz Josef Land and Severnaya Zemlya, its latitude is 79° 30' N and its longitude 76° 54' E... . A glacier in Severnaya Zemlya Severnaya Zemlya Severnaya Zemlya is an archipelago in the Russian high Arctic at around . It is located off mainland Siberia's Taymyr Peninsula across the Vilkitsky Strait... is named after Albanov. Either Albanov or Konrad is a prototype for a hero in the novel The Two Captains The Two Captains The Two Captains is a novel written by Soviet author Veniamin Kaverin between 1938 and 1944. It is Kaverin's best known work and is considered one of the most popular works of Soviet literature, winning the USSR State Prize in 1946 being reissued 42 times in 25 years... by Veniamin Kaverin Veniamin Kaverin Veniamin Alexandrovich Kaverin was a Soviet writer associated with the early 1920s movement of the Serapion Brothers. The immunologist Lev Zilber was his older brother, and the critic Yury Tynyanov was his brother-in-law.... . |
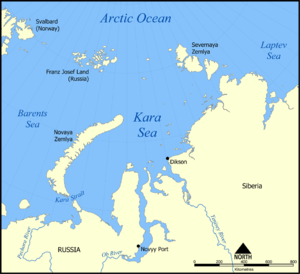 |
|
| Pyotr Anjou (1796–1869)  Russian Empire Russian EmpireImperial Russian Navy Imperial Russian Navy The Imperial Russian Navy refers to the Tsarist fleets prior to the February Revolution.-First Romanovs:Under Tsar Mikhail Feodorovich, construction of the first three-masted ship, actually built within Russia, was completed in 1636. It was built in Balakhna by Danish shipbuilders from Holstein... officer, Admiral Admiral Admiral is the rank, or part of the name of the ranks, of the highest naval officers. It is usually considered a full admiral and above vice admiral and below admiral of the fleet . It is usually abbreviated to "Adm" or "ADM"... , hero of the Battle of Navarino Battle of Navarino The naval Battle of Navarino was fought on 20 October 1827, during the Greek War of Independence in Navarino Bay , on the west coast of the Peloponnese peninsula, in the Ionian Sea. A combined Ottoman and Egyptian armada was destroyed by a combined British, French and Russian naval force... , Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... explorer |
In 1820, as a lieutenant, Anjou described the coastline and the islands of Eastern Siberia between Olenek and Indigirka rivers and mapped the New Siberian Islands New Siberian Islands The New Siberian Islands are an archipelago, located to the North of the East Siberian coast between the Laptev Sea and the East Siberian Sea north of the Sakha Republic.... . In 1825-26 he participated in describing the northeastern coast of the Caspian Sea Caspian Sea The Caspian Sea is the largest enclosed body of water on Earth by area, variously classed as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. The sea has a surface area of and a volume of... and the western coast of the Aral Sea Aral Sea The Aral Sea was a lake that lay between Kazakhstan in the north and Karakalpakstan, an autonomous region of Uzbekistan, in the south... . Anjou Islands, the largest group in the New Siberian Islands, bear Anjou's name. |
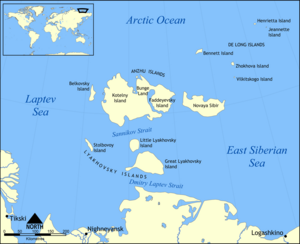 |
|
| Danila Antsiferov Danila Antsiferov Danila Yakovlevich Antsiferov was a Russian explorer.Upon the death of Vladimir Atlasov in 1711, Danila Antsiferov was elected Cossack ataman of the Kamchatka. Together with Ivan Kozyrevsky, he was one of the first Russian Cossacks to visit the Shumshu and Paramushir Islands of the Kuril Islands... (?–1712) Tsardom of Russia Tsardom of Russia The Tsardom of Russia was the name of the centralized Russian state from Ivan IV's assumption of the title of Tsar in 1547 till Peter the Great's foundation of the Russian Empire in 1721.From 1550 to 1700, Russia grew 35,000 km2 a year... Siberian Cossack Siberian Cossacks Siberian Cossacks were Cossacks who settled in the Siberian region of Russia from the end of the 16th century, following the Yermak Timofeyevich's conquest of Siberia. In early Siberia practically the whole Russian population, especially the serving-men were called Cossacks, but only in the loose... ataman Ataman Ataman was a commander title of the Ukrainian People's Army, Cossack, and haidamak leaders, who were in essence the Cossacks... , explorer of Kamchatka and Kuril Islands Kuril Islands The Kuril Islands , in Russia's Sakhalin Oblast region, form a volcanic archipelago that stretches approximately northeast from Hokkaidō, Japan, to Kamchatka, Russia, separating the Sea of Okhotsk from the North Pacific Ocean. There are 56 islands and many more minor rocks. It consists of Greater... |
Danila Antsiferov was elected Cossack Cossack Cossacks are a group of predominantly East Slavic people who originally were members of democratic, semi-military communities in what is today Ukraine and Southern Russia inhabiting sparsely populated areas and islands in the lower Dnieper and Don basins and who played an important role in the... ataman on Kamchatka after the death of Vladimir Atlasov Vladimir Atlasov Vladimir Vasilyevich Atlasov or Otlasov was a Siberian Cossack who was the first Russian to explore the Kamchatka Peninsula. Atlasov Island, an uninhabited volcanic island off the southern tip of Kamchatka, is named after him.... . He was one of the first Russians to visit Kuril Islands Kuril Islands The Kuril Islands , in Russia's Sakhalin Oblast region, form a volcanic archipelago that stretches approximately northeast from Hokkaidō, Japan, to Kamchatka, Russia, separating the Sea of Okhotsk from the North Pacific Ocean. There are 56 islands and many more minor rocks. It consists of Greater... and describe them in writing, including Shumshu Shumshu Shumshu , is the northernmost island of Kuril Islands chain in the Sea of Okhotsk in the northwest Pacific Ocean. The name of the island is derived from the Ainu language meaning “good island”. It is separated from Paramushir by the very narrow Second Kuril Strait in the northeast , its northern... and Paramushir Island. A cape and a volcano on the Paramushir Island and one of the Kuril Islands bear Antsiferov's name. |
 |
|
| Dmitry Anuchin Dmitry Nikolayevich Anuchin Dmitry Nikolayevich Anuchin was a Russian anthropologist, ethnographist, archaeologist, and geographer. He was a member of the Russian GeographicaL Society and convened the ethnographic sub-section of the Twelfth Congress of Russian Natural Scientists and Physicians held in Moscow in 1909... (1843–1923)  Russian Empire Russian Empire Soviet Union Soviet Uniongeographer, anthropologist, ethnographer, archaeologist, explorer of European Russia European Russia European Russia refers to the western areas of Russia that lie within Europe, comprising roughly 3,960,000 square kilometres , larger in area than India, and spanning across 40% of Europe. Its eastern border is defined by the Ural Mountains and in the south it is defined by the border with... |
In 1880 Anuchin researched Valday Hills and Lake Seliger Lake Seliger Seliger is a lake in Tver Oblast and, in the extreme northern part, Novgorod Oblast of Russia, in the northwest of the Valdai Hills, a part of the Volga basin. Absolute height: 205 m, area 212 km², average depth 5.8 m.... . In 1894-95, joining the expedition of Alexei Tillo, he again studied Valday. Anuchin finally determined the location of the source of Volga, the largest European river. He published a major work about the relief Relief Relief is a sculptural technique. The term relief is from the Latin verb levo, to raise. To create a sculpture in relief is thus to give the impression that the sculpted material has been raised above the background plane... of European Russia European Russia European Russia refers to the western areas of Russia that lie within Europe, comprising roughly 3,960,000 square kilometres , larger in area than India, and spanning across 40% of Europe. Its eastern border is defined by the Ural Mountains and in the south it is defined by the border with... and founded the Geography Museum at Moscow State University Moscow State University Lomonosov Moscow State University , previously known as Lomonosov University or MSU , is the largest university in Russia. Founded in 1755, it also claims to be one of the oldest university in Russia and to have the tallest educational building in the world. Its current rector is Viktor Sadovnichiy... . Anuchin Anuchin (crater) Anuchin is a lunar impact crater that lies on the southern hemisphere on the far side of the Moon. It is located to the south of the larger crater Lamb, and to the north-northwest of Kugler.... crater on the Moon Moon The Moon is Earth's only known natural satellite,There are a number of near-Earth asteroids including 3753 Cruithne that are co-orbital with Earth: their orbits bring them close to Earth for periods of time but then alter in the long term . These are quasi-satellites and not true moons. For more... , a glacier in Novaya Zemlya Novaya Zemlya Novaya Zemlya , also known in Dutch as Nova Zembla and in Norwegian as , is an archipelago in the Arctic Ocean in the north of Russia and the extreme northeast of Europe, the easternmost point of Europe lying at Cape Flissingsky on the northern island... , one of the Kuril Islands Kuril Islands The Kuril Islands , in Russia's Sakhalin Oblast region, form a volcanic archipelago that stretches approximately northeast from Hokkaidō, Japan, to Kamchatka, Russia, separating the Sea of Okhotsk from the North Pacific Ocean. There are 56 islands and many more minor rocks. It consists of Greater... , a mountain in Ural Ural (region) Ural is a geographical region located around the Ural Mountains, between the East European and West Siberian plains. It extends approximately from north to south, from the Arctic Ocean to the bend of Ural River near Orsk city. The boundary between Europe and Asia runs along the eastern side of... and Anuchin Institute of Anthropology of Moscow State University Moscow State University Lomonosov Moscow State University , previously known as Lomonosov University or MSU , is the largest university in Russia. Founded in 1755, it also claims to be one of the oldest university in Russia and to have the tallest educational building in the world. Its current rector is Viktor Sadovnichiy... are named after Anuchin. |
||
 |
Vladimir Arsenyev Vladimir Arsenyev Vladimir Klavdiyevich Arsenyev was a Russian explorer of the Far East who recounted his travels in a series of books - "По Уссурийскому Краю" and "Дерсу Узала" - telling of his military journeys to the Ussuri basin with Dersu Uzala, a native hunter, from 1902 to 1907... (1872–1930)  Russian Empire Russian Empire Soviet Union Soviet Unionmilitary topographer, explorer of the Far East Far East The Far East is an English term mostly describing East Asia and Southeast Asia, with South Asia sometimes also included for economic and cultural reasons.The term came into use in European geopolitical discourse in the 19th century,... , writer |
Arsenyev wrote a number of popular books about his journeys to the Ussuri basin in 1902-07, where he was accompanied by Dersu Uzala Dersu Uzala Dersu Uzala is the title of a 1923 book by the Russian explorer Vladimir Arsenyev.-Plot:Arsenyev's book tells of his travels in the Ussuri basin in the Russian Far East. Dersu was the name of a Nanai hunter who acted as a guide for Arsenyev's surveying crew from 1902 to 1907, and saved them from... , a native Nanai hunter. Arsenyev was the first to describe numerous species of Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... n flora; he produced some 60 works on the geography, wildlife and ethnography of the regions he traveled. In 1975, the joint Japanese-Soviet movie Dersu Uzala Dersu Uzala (1975 film) Dersu Uzala is a 1975 Soviet-Japanese co-production film directed by Akira Kurosawa, his first non-Japanese-language film and his first and only 70 mm film. The film won the Grand Prix at the Moscow Film Festival and the 1975 Oscar for Best Foreign Language Film... by Akira Kurosawa Akira Kurosawa was a Japanese film director, producer, screenwriter and editor. Regarded as one of the most important and influential filmmakers in the history of cinema, Kurosawa directed 30 filmsIn 1946, Kurosawa co-directed, with Hideo Sekigawa and Kajiro Yamamoto, the feature Those Who Make Tomorrow ;... won the Oscar for the Best Foreign-Language Film. A glacier on volcano Avachinskaya Sopka and Arsenyev Arsenyev Arsenyev is a town in Primorsky Krai, Russia, located about northeast of Vladivostok. Population: -History:The history of Arsenyev begins in 1895, when the settlement of Semyonovka was founded. The first settlement dwellers were the Old Believers. In 1901 the migrant peasants from what is now... town in Primorsky Krai Primorsky Krai Primorsky Krai , informally known as Primorye , is a federal subject of Russia . Primorsky means "maritime" in Russian, hence the region is sometimes referred to as Maritime Province or Maritime Territory. Its administrative center is in the city of Vladivostok... are named after Arsenyev. |
 |
| Vladimir Atlasov Vladimir Atlasov Vladimir Vasilyevich Atlasov or Otlasov was a Siberian Cossack who was the first Russian to explore the Kamchatka Peninsula. Atlasov Island, an uninhabited volcanic island off the southern tip of Kamchatka, is named after him.... (1661–64 – 1711) Tsardom of Russia Tsardom of Russia The Tsardom of Russia was the name of the centralized Russian state from Ivan IV's assumption of the title of Tsar in 1547 till Peter the Great's foundation of the Russian Empire in 1721.From 1550 to 1700, Russia grew 35,000 km2 a year... Siberian Cossack Siberian Cossacks Siberian Cossacks were Cossacks who settled in the Siberian region of Russia from the end of the 16th century, following the Yermak Timofeyevich's conquest of Siberia. In early Siberia practically the whole Russian population, especially the serving-men were called Cossacks, but only in the loose... ataman Ataman Ataman was a commander title of the Ukrainian People's Army, Cossack, and haidamak leaders, who were in essence the Cossacks... , explorer of Kamchatka, Kuril Islands Kuril Islands The Kuril Islands , in Russia's Sakhalin Oblast region, form a volcanic archipelago that stretches approximately northeast from Hokkaidō, Japan, to Kamchatka, Russia, separating the Sea of Okhotsk from the North Pacific Ocean. There are 56 islands and many more minor rocks. It consists of Greater... , Chukotka Chukchi Peninsula The Chukchi Peninsula, Chukotka Peninsula or Chukotski Peninsula , at about 66° N 172° W, is the northeastern extremity of Asia. Its eastern end is at Cape Dezhnev near the village of Uelen. It is bordered by the Chukchi Sea to the north, the Bering Sea to the south, and the Bering Strait to the... and Japan Japan Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south... |
Atlasov established the first permanent Russian settlements on Kamchatka Peninsula Kamchatka Peninsula The Kamchatka Peninsula is a peninsula in the Russian Far East, with an area of . It lies between the Pacific Ocean to the east and the Sea of Okhotsk to the west... and led its colonisation. He was the first to present a detailed description of the region's nature and people, and also accounted on the lands near Kamchatka – Chukotka Chukchi Peninsula The Chukchi Peninsula, Chukotka Peninsula or Chukotski Peninsula , at about 66° N 172° W, is the northeastern extremity of Asia. Its eastern end is at Cape Dezhnev near the village of Uelen. It is bordered by the Chukchi Sea to the north, the Bering Sea to the south, and the Bering Strait to the... and Japan Japan Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south... . Atlasov brought Dembei Dembei Dembei was a Japanese castaway who, through Vladimir Atlasov, provided Russia with some of its first knowledge of Japan. He was a fisherman who, along with a number of others, had been caught in a storm; they found their way to Kamchatka, where Dembei was found by Atlasov in 1701 or 1702. Despite... , a shipwrecked Japanese merchant, to Moscow, where he become the first to teach Japanese to Russians Japanese language education in Russia Japanese language education in Russia formally dates back to December 1701 or January 1702, when Dembei, a shipwrecked Japanese merchant, was taken to Moscow and ordered to begin teaching the language as soon as possible... . Atlasov Island Atlasov Island Atlasov Island, known in Russian as Ostrov Atlasova , or in Japanese as Araido , is the northernmost island and volcano and also the highest volcano of the Kuril islands, part of the Sakhalin Oblast in Russia. The Russian name is sometimes rendered in English as Atlasova Island... off the southern tip of Kamchatka, a bay and a volcano on Kuril Islands Kuril Islands The Kuril Islands , in Russia's Sakhalin Oblast region, form a volcanic archipelago that stretches approximately northeast from Hokkaidō, Japan, to Kamchatka, Russia, separating the Sea of Okhotsk from the North Pacific Ocean. There are 56 islands and many more minor rocks. It consists of Greater... are named after Atlasov. |
 |
B
| Portrait | Person | Achievements | Image |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mikhail Babushkin Mikhail Babushkin Mikhail Babushkin was a Soviet polar aviator, a Hero of the Soviet Union .Mikhail Babushkin was born in a village of Bordino , started military service in 1914, graduated from Gatchina aviation school in 1915. Since 1923 he served in the Arctic aviation... (1893–1938)  Russian Empire Russian Empire Soviet Union Soviet Unionmilitary pilot, polar aviator, Hero of the Soviet Union Hero of the Soviet Union The title Hero of the Soviet Union was the highest distinction in the Soviet Union, awarded personally or collectively for heroic feats in service to the Soviet state and society.-Overview:... (a monument in Moscow Moscow Moscow is the capital, the most populous city, and the most populous federal subject of Russia. The city is a major political, economic, cultural, scientific, religious, financial, educational, and transportation centre of Russia and the continent... ) |
Babushkin took part in an a expedition to rescue Umberto Nobile Umberto Nobile Umberto Nobile was an Italian aeronautical engineer and Arctic explorer. Nobile was a developer and promoter of semi-rigid airships during the Golden Age of Aviation between the two World Wars... in 1928, and in the rescue of SS Chelyuskin crew in 1933. He performed the flights to the first drifting ice station North Pole-1 North Pole-1 North Pole-1 was the first Soviet manned drifting station, primarily used for research.North Pole-1 was established on May 21, 1937, and officially opened on June 6, some from the North Pole by the expedition into the high latitudes Sever-1, led by Otto Schmidt. The expedition had been airlifted... in 1937. In 1937-38 he participated in a search for Sigizmund Levanevsky Sigizmund Levanevsky Sigizmund Aleksandrovich Levanevsky was a Soviet aircraft pilot of Polish origin and a Hero of the Soviet Union .-Life and career:... . A district and a street of Moscow Moscow Moscow is the capital, the most populous city, and the most populous federal subject of Russia. The city is a major political, economic, cultural, scientific, religious, financial, educational, and transportation centre of Russia and the continent... (in the area where he was born) and the Babushkinskaya Babushkinskaya Babushkinskaya is a Moscow Metro station in the Babushkinsky District, North-Eastern Administrative Okrug, Moscow. It is on the Kaluzhsko-Rizhskaya Line, between Sviblovo and Medvedkovo stations.- Name & Design :... station of the Moscow Metro Moscow Metro The Moscow Metro is a rapid transit system serving Moscow and the neighbouring town of Krasnogorsk. Opened in 1935 with one line and 13 stations, it was the first underground railway system in the Soviet Union. As of 2011, the Moscow Metro has 182 stations and its route length is . The system is... are named after Babushkin. |
 |
|
| Konstantin Badygin Konstantin Badygin Captain Konstantin Sergeyevich Badygin , sometimes also transliterated "Badigin", was a Soviet naval officer, explorer, author, and scientist.Konstantin Sergeyevich Badygin began his naval career in 1928 as a sailor on Soviet ships in the Pacific Ocean... (1910–1984)  Russian Empire Russian Empire Soviet Union Soviet UnionSoviet navy Soviet Navy The Soviet Navy was the naval arm of the Soviet Armed Forces. Often referred to as the Red Fleet, the Soviet Navy would have played an instrumental role in a Warsaw Pact war with NATO, where it would have attempted to prevent naval convoys from bringing reinforcements across the Atlantic Ocean... officer, writer, scientist, Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... explorer, Hero of the Soviet Union Hero of the Soviet Union The title Hero of the Soviet Union was the highest distinction in the Soviet Union, awarded personally or collectively for heroic feats in service to the Soviet state and society.-Overview:... (Badygin left, Sedov Icebreaker Sedov The Sedov was a Soviet ice-breaker fitted with steam engines. She was originally the Newfoundland sealing steamer Beothic and was renamed after Russian Captain and Polar explorer Georgy Yakovlevich Sedov.... 's mechanic D.G. Trofimov right on the Soviet postage stamp) |
In 1938 Badygin became the captain of the ice-captured icebreaker Icebreaker An icebreaker is a special-purpose ship or boat designed to move and navigate through ice-covered waters. Although the term usually refers to ice-breaking ships, it may also refer to smaller vessels .For a ship to be considered an icebreaker, it requires three traits most... Sedov Icebreaker Sedov The Sedov was a Soviet ice-breaker fitted with steam engines. She was originally the Newfoundland sealing steamer Beothic and was renamed after Russian Captain and Polar explorer Georgy Yakovlevich Sedov.... , turned into a kind of drifting ice station Soviet and Russian manned drifting ice stations Soviet and Russian manned drifting ice stations are important contributors to exploration of the Arctic. The stations are named North Pole Soviet and Russian manned drifting ice stations are important contributors to exploration of the Arctic. The stations are named North Pole Soviet and... . Most of the crew was evacuated, but 15 sailors and scientists, including Vladimir Vize, stayed aboard and carried out a valuable scientific research during their 812 days on Sedov. After drifting from New Siberian Islands New Siberian Islands The New Siberian Islands are an archipelago, located to the North of the East Siberian coast between the Laptev Sea and the East Siberian Sea north of the Sakha Republic.... across the North Pole North Pole The North Pole, also known as the Geographic North Pole or Terrestrial North Pole, is, subject to the caveats explained below, defined as the point in the northern hemisphere where the Earth's axis of rotation meets its surface... , they were finally freed between Greenland Greenland Greenland is an autonomous country within the Kingdom of Denmark, located between the Arctic and Atlantic Oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Though physiographically a part of the continent of North America, Greenland has been politically and culturally associated with Europe for... and Svalbard Svalbard Svalbard is an archipelago in the Arctic, constituting the northernmost part of Norway. It is located north of mainland Europe, midway between mainland Norway and the North Pole. The group of islands range from 74° to 81° north latitude , and from 10° to 35° east longitude. Spitsbergen is the... by icebreaker Joseph Stalin Icebreaker Joseph Stalin The Icebreaker Joseph Stalin was the first Soviet icebreaker built at a domestic shipyard.Owing to many delays, it took over two years to finish. It was built at the Ordzhonikidze Yard in Leningrad between 1937 and 1938.... in 1940. |
 |
|
| Karl Ernst von Baer Karl Ernst von Baer Karl Ernst Ritter von Baer, Edler von Huthorn also known in Russia as Karl Maksimovich Baer was an Estonian naturalist, biologist, geologist, meteorologist, geographer, a founding father of embryology, explorer of European Russia and Scandinavia, a member of the Russian Academy of Sciences, a... (1792–1876)  Russian Empire Russian Empire(born in Estonia Estonia Estonia , officially the Republic of Estonia , is a state in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea, to the south by Latvia , and to the east by Lake Peipsi and the Russian Federation . Across the Baltic Sea lies... , Baltic German Baltic German The Baltic Germans were mostly ethnically German inhabitants of the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea, which today form the countries of Estonia and Latvia. The Baltic German population never made up more than 10% of the total. They formed the social, commercial, political and cultural élite in... descent) naturalist Naturalist Naturalist may refer to:* Practitioner of natural history* Conservationist* Advocate of naturalism * Naturalist , autobiography-See also:* The American Naturalist, periodical* Naturalism... , a founder of embryology Embryology Embryology is a science which is about the development of an embryo from the fertilization of the ovum to the fetus stage... , explorer of European Russia European Russia European Russia refers to the western areas of Russia that lie within Europe, comprising roughly 3,960,000 square kilometres , larger in area than India, and spanning across 40% of Europe. Its eastern border is defined by the Ural Mountains and in the south it is defined by the border with... , Northern Europe Northern Europe Northern Europe is the northern part or region of Europe. Northern Europe typically refers to the seven countries in the northern part of the European subcontinent which includes Denmark, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Norway, Finland and Sweden... and Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... |
A prominent naturalist Naturalist Naturalist may refer to:* Practitioner of natural history* Conservationist* Advocate of naturalism * Naturalist , autobiography-See also:* The American Naturalist, periodical* Naturalism... , Karl Ernst von Baer was also an explorer. In 1830-40 he researched Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... meteorology. He was interested in the Northern part of Russia Russia Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects... and explored Novaya Zemlya Novaya Zemlya Novaya Zemlya , also known in Dutch as Nova Zembla and in Norwegian as , is an archipelago in the Arctic Ocean in the north of Russia and the extreme northeast of Europe, the easternmost point of Europe lying at Cape Flissingsky on the northern island... in 1837 collecting specimens. Other travels led him to the North Cape North Cape, Norway North Cape is a cape on the island of Magerøya in Northern Norway, in the municipality of Nordkapp. Its 307 m high, steep cliff is often referred to as the northernmost point of Europe, located at , 2102.3 km from the North Pole. However, the neighbouring point Knivskjellodden is actually... , Lapland, and the Caspian Sea Caspian Sea The Caspian Sea is the largest enclosed body of water on Earth by area, variously classed as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. The sea has a surface area of and a volume of... . After his explorations of Volga he formulated the geological Baer's law Baer's law In geology, Baer's law, named after Karl Ernst von Baer, says that, because of the rotation of the earth, in the Northern Hemisphere, erosion occurs mostly on the right banks of rivers and in the Southern Hemisphere on the left banks... , stating that in the northern hemisphere Northern Hemisphere The Northern Hemisphere is the half of a planet that is north of its equator—the word hemisphere literally means “half sphere”. It is also that half of the celestial sphere north of the celestial equator... erosion Erosion Erosion is when materials are removed from the surface and changed into something else. It only works by hydraulic actions and transport of solids in the natural environment, and leads to the deposition of these materials elsewhere... occurs mostly on the right banks of rivers, and in the southern hemisphere Southern Hemisphere The Southern Hemisphere is the part of Earth that lies south of the equator. The word hemisphere literally means 'half ball' or "half sphere"... on the left banks. Baer was one of the founders of the Russian Geographical Society Russian Geographical Society The Russian Geographical Society is a learned society, founded on 6 August 1845 in Saint Petersburg, Russia.-Imperial Geographical Society:Prior to the Russian Revolution of 1917, it was known as the Imperial Russian Geographical Society.... in 1845, and also a co-founder and the first President of the Russian Entomological Society Russian Entomological Society The Russian Entomological Society is a Russian scientific society devoted to entomology.The Society was founded in 1859 in St. Petersburg by Karl Ernst von Baer , Johann Friedrich von Brandt who was then the director of the Zoological Museum of the Russian Academy of Science , Ya. A... . Baer Island in the Taymyr Gulf Taymyr Gulf The Taymyr Gulf is a gulf in the Kara Sea that includes the estuary of the Lower Taymyr River. The estuary opens roughly northwestwise from the western coast of the Taymyr Peninsula into the eastern expanses of the Kara Sea, widening from about 4 km at the river's mouth to about 20 km... of the Kara Sea Kara Sea The Kara Sea is part of the Arctic Ocean north of Siberia. It is separated from the Barents Sea to the west by the Kara Strait and Novaya Zemlya, and the Laptev Sea to the east by the Severnaya Zemlya.... is named after Karl Baer. |
 |
|
| Georgiy Baidukov Georgiy Baidukov Georgy Filippovich Baydukov was a Soviet aircraft test pilot and a Hero of the Soviet Union .- Early years :Georgy Baydukov had been born in Taryshta railway station to a railway worker. He became an orphan in the age of 9 and had been homeless for some time... (1904–1994)  Russian Empire Russian Empire Soviet Union Soviet Union Russia Russiaaircraft test pilot, Hero of the Soviet Union Hero of the Soviet Union The title Hero of the Soviet Union was the highest distinction in the Soviet Union, awarded personally or collectively for heroic feats in service to the Soviet state and society.-Overview:... (Baidukov, Chkalov and Belyakov in 1937) |
Baidukov was involved in a number of Soviet ultralong flights. In 1936 Valery Chkalov Valery Chkalov Valery Pavlovich Chkalov was a Russian aircraft test pilot and a Hero of the Soviet Union .-Early life:... , Baidukov and A.V.Belyakov on ANT-25 flew 9,374 km from Moscow Moscow Moscow is the capital, the most populous city, and the most populous federal subject of Russia. The city is a major political, economic, cultural, scientific, religious, financial, educational, and transportation centre of Russia and the continent... through the North Pole North Pole The North Pole, also known as the Geographic North Pole or Terrestrial North Pole, is, subject to the caveats explained below, defined as the point in the northern hemisphere where the Earth's axis of rotation meets its surface... to follow-up Chkalov Island Chkalov Island Chkalov Island , formerly Udd Island , is a coastal island in the southern end of the Sea of Okhotsk. It is located off Schastya Bay, between the shorebound lagoon and the sea. Baydukov Island lies only 2 km off its ESE tip.Chkalov Island is long and narrow... in Okhotsk Sea, which took 56 h 20 min. In 1937, also on ANT-25, the same crew flew 8,504 km from Moscow through the North Pole North Pole The North Pole, also known as the Geographic North Pole or Terrestrial North Pole, is, subject to the caveats explained below, defined as the point in the northern hemisphere where the Earth's axis of rotation meets its surface... to Vancouver, Washington Vancouver, Washington Vancouver is a city on the north bank of the Columbia River in the U.S. state of Washington. Incorporated in 1857, it is the fourth largest city in the state with a 2010 census population of 161,791 as of April 1, 2010... , which was the first transpolar flight between Europe Europe Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting... and North America North America North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas... on airplane, rather than on dirigible. Baydukov Island Baydukov Island Baydukov Island , formerly Langr Island or Bol'shoy Langr Island, is a coastal island in the southern end of the Sea of Okhotsk... near Chkalov Island Chkalov Island Chkalov Island , formerly Udd Island , is a coastal island in the southern end of the Sea of Okhotsk. It is located off Schastya Bay, between the shorebound lagoon and the sea. Baydukov Island lies only 2 km off its ESE tip.Chkalov Island is long and narrow... in the Okhotsk Sea and a number of streets are named after Baidukov. |
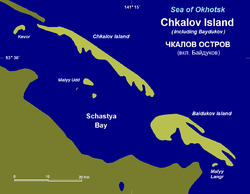 |
|
 |
Alexander Baranov (1746–1819)  Russian Empire Russian Empiremerchant in Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... and Alaska Alaska Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait... , first Governor of Russian America |
Baranov was hired to head the Shelikhov-Golikov Company, which was in 1799 transformed into Russian-American Company Russian-American Company The Russian-American Company was a state-sponsored chartered company formed largely on the basis of the so-called Shelekhov-Golikov Company of Grigory Shelekhov and Ivan Larionovich Golikov The Russian-American Company (officially: Under His Imperial Majesty's Highest Protection (patronage)... . Thus Baranov became the first Governor of Russian America and held this post in 1799-1818. He explored the coast areas of northwestern North America North America North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas... , helped Russian Orthodox missionaries and improved relations with Alaska Alaska Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait... natives. He established trade with China China Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture... , Hawaii Hawaii Hawaii is the newest of the 50 U.S. states , and is the only U.S. state made up entirely of islands. It is the northernmost island group in Polynesia, occupying most of an archipelago in the central Pacific Ocean, southwest of the continental United States, southeast of Japan, and northeast of... and also with California California California is a state located on the West Coast of the United States. It is by far the most populous U.S. state, and the third-largest by land area... , where he founded Fort Ross. Baranof Island Baranof Island Baranof Island, also sometimes called Baranov Island, Shee or Sitka Island, is an island in the northern Alexander Archipelago in the Alaska Panhandle, in Alaska. The name Baranof was given in 1805 by Imperial Russian Navy captain U. F. Lisianski to honor Alexander Andreyevich Baranov... in Alaska Alaska Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait... and U.S. liberty ship Liberty ship Liberty ships were cargo ships built in the United States during World War II. Though British in conception, they were adapted by the U.S. as they were cheap and quick to build, and came to symbolize U.S. wartime industrial output. Based on vessels ordered by Britain to replace ships torpedoed by... SS Alexander Baranof have been named after Baranov. |
 |
| Nikifor Begichev (1874–1927)  Russian Empire Russian Empire Soviet Union Soviet UnionRussian Imperial Navy officer, Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... explorer (forensic facial reconstruction) |
Begichev was the bosun of ship Zarya Zarya (polar ship) Zarya was a steam- and sail-powered brig used by the Russian Academy of Sciences for a polar exploration during 1900–1903.Toward the end of the 19th century, the Russian Academy of Sciences sought to build a general-purpose research vessel for long-term expeditions. The first such Russian... , carrying Baron Eduard Toll Eduard Toll Eduard Gustav von Toll was a Baltic German geologist and Arctic explorer in Russian service. Often referred to as Baron von Toll or as Eduard v. Toll, in Russia he is known as Eduard Vasiliyevich Toll . Eduard Toll was born on and he died in 1902 in an unknown location in the Arctic Ocean)... 's expedition in 1900-03. In 1922, at the request of Norway Norway Norway , officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic unitary constitutional monarchy whose territory comprises the western portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula, Jan Mayen, and the Arctic archipelago of Svalbard and Bouvet Island. Norway has a total area of and a population of about 4.9 million... , Begichev led a Soviet expedition in search for lost crew members of Roald Amundsen Roald Amundsen Roald Engelbregt Gravning Amundsen was a Norwegian explorer of polar regions. He led the first Antarctic expedition to reach the South Pole between 1910 and 1912 and he was the first person to reach both the North and South Poles. He is also known as the first to traverse the Northwest Passage.... 's 1918 expedition on ship Maud Maud (ship) The Maud, named for Queen Maud of Norway, was a ship built for Roald Amundsen for his second expedition to the Arctic. Designed for his intended voyage through the Northeast Passage, the vessel was specially built at a shipyard in Asker, Norway on the Oslofjord.The Maud was launched in June 1916... Peter Tessem and Paul Knutsen Peter Tessem and Paul Knutsen Peter Tessem and Paul Knutsen were two young men from Norway who went with fellow Norwegian explorer Roald Amundsen on his 1918 Arctic expedition aboard ship Maud. Peter Tessem was a carpenter and Paul Knutsen was an able-bodiedseaman... , but he was not successful. In 1923-24.Begichev explored the Taymyr Peninsula Taymyr Peninsula The Taymyr Peninsula is a peninsula in the Far North of Russia, in the Siberian Federal District, that forms the northernmost part of mainland Eurasia and Asia... with Nikolay Urvantsev Nikolay Urvantsev Nikolay Nikolayevich Urvantsev was a Soviet geologist and explorer. He was born in the town of Lukoyanov of Nizhny Novgorod Governorate, Russian Empire to the family of a merchant... . Bolshoy Begichev Island Bolshoy Begichev Island Bolshoy Begichev is an island in the Laptev Sea, Russia. Its area is 1764 km². The island is situated within the Khatanga Gulf , splitting the gulf into two straits.... and Maliy Begichev Island Maliy Begichev Island Maliy Begichev is an island in the Laptev Sea, Russia. Its area is 15 km². This small island is situated within the Khatanga Gulf .... , explored by Begichev, have been named after him. |
 |
|
| Pyotr Beketov Pyotr Beketov Pyotr Beketov was a prominent Cossack explorer of Siberia and founder of many cities such as Yakutsk, Chita, and Nerchinsk.Beketov started his military service as a guardsman in 1624 and was sent to Siberia in 1627. He was appointed Enisei voevoda and proceeded on his first voyage in order to... (c. 1600 – c. 1661) Tsardom of Russia Tsardom of Russia The Tsardom of Russia was the name of the centralized Russian state from Ivan IV's assumption of the title of Tsar in 1547 till Peter the Great's foundation of the Russian Empire in 1721.From 1550 to 1700, Russia grew 35,000 km2 a year... Siberian Cossack Siberian Cossacks Siberian Cossacks were Cossacks who settled in the Siberian region of Russia from the end of the 16th century, following the Yermak Timofeyevich's conquest of Siberia. In early Siberia practically the whole Russian population, especially the serving-men were called Cossacks, but only in the loose... voevoda, explorer of Zabaykalye and Yakutia (a monument in Chita) |
Beketov, initially a strelets, was appointed Enisei voevoda in Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... after 1627. He successfully carried out the voyage to collect taxes from Zabaykalye Buryats Buryats The Buryats or Buriyads , numbering approximately 436,000, are the largest ethnic minority group in Siberia and are mainly concentrated in their homeland, the Buryat Republic, a federal subject of Russia... , becoming the first Russian to step in Buryatia. He founded there the first Russian settlement, Rybinsky ostrog Ostrog (fortress) Ostrog was a Russian term for a small fort, typically wooden and often non-permanently manned. Ostrogs were encircled by 4-6 metres high palisade walls made from sharpened trunks. The name derives from the Russian word строгать , "to shave the wood". Ostrogs were smaller and exclusively military... . Beketov was sent to the Lena River Lena River The Lena is the easternmost of the three great Siberian rivers that flow into the Arctic Ocean . It is the 11th longest river in the world and has the 9th largest watershed... in 1631, where in 1632 he founded Yakutsk Yakutsk With a subarctic climate , Yakutsk is the coldest city, though not the coldest inhabited place, on Earth. Average monthly temperatures range from in July to in January. The coldest temperatures ever recorded on the planet outside Antarctica occurred in the basin of the Yana River to the northeast... , a startpoint of further Russian expeditions eastward. He sent his Cossacks to explore Aldan Aldan River The Aldan River is the second-longest tributary of the Lena River in the Sakha Republic in eastern Siberia. The river is 2,273 km long, of which around 1,600 km is navigable. It was part of the River Route to Okhotsk... and Kolyma Kolyma River The Kolyma River is a river in northeastern Siberia, whose basin covers parts of the Sakha Republic, Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, and Magadan Oblast of Russia. Itrises in the mountains north of Okhotsk and Magadan, in the area of and... rivers, to found new fortresses, and to collect taxes. In 1652 he launched another voyage to Buryatia, and in 1653 Beketov's Cossacks founded follow-up Chita and then future Nerchinsk Nerchinsk Nerchinsk is a town and the administrative center of Nerchinsky District of Zabaykalsky Krai, Russia, located east of Lake Baikal, east of Chita, and about west of the Chinese border on the left bank of the Nercha River, above its confluence with the Shilka River, which flows into the Amur... in 1654. |
 |
|
 |
Alexander Bekovich-Cherkassky Alexander Bekovich-Cherkassky Prince Alexander Bekovich-Cherkassky was a Russian officer of Circassian origin who led the first Russian military expedition into Central Asia.-Background:... (?–1717) Tsardom of Russia Tsardom of Russia The Tsardom of Russia was the name of the centralized Russian state from Ivan IV's assumption of the title of Tsar in 1547 till Peter the Great's foundation of the Russian Empire in 1721.From 1550 to 1700, Russia grew 35,000 km2 a year... (Circassia Circassia Circassia was an independent mountainous country located in the Caucasus region of Eurasia and was the largest and most important country in the Caucasus. Circassia was located at the crossroads of Western Asia and Eastern Europe between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea... n origin) Russian officer, explorer of Central Asia Central Asia Central Asia is a core region of the Asian continent from the Caspian Sea in the west, China in the east, Afghanistan in the south, and Russia in the north... |
Bekovich-Cherkassky, a Circassia Circassia Circassia was an independent mountainous country located in the Caucasus region of Eurasia and was the largest and most important country in the Caucasus. Circassia was located at the crossroads of Western Asia and Eastern Europe between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea... n Muslim Muslim A Muslim, also spelled Moslem, is an adherent of Islam, a monotheistic, Abrahamic religion based on the Quran, which Muslims consider the verbatim word of God as revealed to prophet Muhammad. "Muslim" is the Arabic term for "submitter" .Muslims believe that God is one and incomparable... converted into Christianity Christianity Christianity is a monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus as presented in canonical gospels and other New Testament writings... , was made by Tsar Tsar Tsar is a title used to designate certain European Slavic monarchs or supreme rulers. As a system of government in the Tsardom of Russia and Russian Empire, it is known as Tsarist autocracy, or Tsarism... Peter I the leader of the first Russian military expeditions into Central Asia Central Asia Central Asia is a core region of the Asian continent from the Caspian Sea in the west, China in the east, Afghanistan in the south, and Russia in the north... in 1714-17, with the aim to conquer the Khanate of Khiva Khanate of Khiva The Khanate of Khiva was the name of a Uzbek state that existed in the historical region of Khwarezm from 1511 to 1920, except for a period of Persian occupation by Nadir Shah between 1740–1746. It was the patrilineal descendants of Shayban , the fifth son of Jochi and grandson of Genghis Khan... and the golden sands of the Oxus River. Bekovich received these orders in Astrakhan Astrakhan Astrakhan is a major city in southern European Russia and the administrative center of Astrakhan Oblast. The city lies on the left bank of the Volga River, close to where it discharges into the Caspian Sea at an altitude of below the sea level. Population:... , where he was engaged in preparing the first Russian map of the Caspian Sea Caspian Sea The Caspian Sea is the largest enclosed body of water on Earth by area, variously classed as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. The sea has a surface area of and a volume of... . He commanded a preliminary expedition to Turkmenistan and set up the forts in Krasnovodsk and Alexandrovsk. In 1717 he won the battle against Khiva Khiva Khiva is a city of approximately 50,000 people located in Xorazm Province, Uzbekistan. It is the former capital of Khwarezmia and the Khanate of Khiva... n Khan, but was tricked into separating his men, betrayed by Khan, defeated and killed. |
 |
 |
Fabian Gottlieb von Bellingshausen Fabian Gottlieb von Bellingshausen Fabian Gottlieb Thaddeus von Bellingshausen was an officer in the Imperial Russian Navy, cartographer and explorer, who ultimately rose to the rank of Admiral... (1778–1852)  Russian Empire Russian Empire(born in Estonia Estonia Estonia , officially the Republic of Estonia , is a state in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea, to the south by Latvia , and to the east by Lake Peipsi and the Russian Federation . Across the Baltic Sea lies... , Baltic German Baltic German The Baltic Germans were mostly ethnically German inhabitants of the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea, which today form the countries of Estonia and Latvia. The Baltic German population never made up more than 10% of the total. They formed the social, commercial, political and cultural élite in... descent) Russian Imperial Navy officer, circumnavigator, Antarctic Antarctic The Antarctic is the region around the Earth's South Pole, opposite the Arctic region around the North Pole. The Antarctic comprises the continent of Antarctica and the ice shelves, waters and island territories in the Southern Ocean situated south of the Antarctic Convergence... and Pacific explorer |
Bellingshausen took part in the first Russian circumnavigation First Russian circumnavigation The first Russian circumnavigation of the Earth took place from August 1803 to August 1806. It was sponsored by Count Nikolay Rumyantsev and was headed by Adam Johann von Krusenstern.-Events:... under Ivan Krusenstern on Nadezhda Russian warship Nadezhda The Russian warship Nadezhda was a three-masted sloop-of-war frigate, commonly called "frigate Nadezhda" in Russia.It was built in London in the spring of 1800 as a 425-ton sloop named , and sold to Russia... in 1803-06. He led himself another Russian circumnavigation in 1819-21 on the corvette Vostok Vostok Station Vostok Station was a Russian Antarctic research station. It was at the southern Pole of Cold, with the lowest reliably measured natural temperature on Earth of −89.2 °C . Research includes ice core drilling and magnetometry... , together with Mikhail Lazarev Mikhail Petrovich Lazarev Admiral Mikhail Petrovich Lazarev was a Russian fleet commander and explorer who discovered Antarctica.-Education and early career:Lazarev was born in Vladimir, a scion of the old Russian nobility from the Vladimir province. In 1800, he enrolled in Russia's Naval College. Three years later he... on Mirny Mirny Station Mirny is a Russian science station in Antarctica, located on the Antarctic coast of the Davis Sea in the Australian Antarctic Territory. Named after support vessel of the Bellingshausen's expedition.... – this expedition was the first to discover the contenent of Antarctica on January 28, 1820 (New Style). They also discovered and named Peter I Island Peter I Island Peter I Island is an uninhabited volcanic island in the Bellingshausen Sea, from Antarctica. It is claimed as a dependency of Norway, and along with Queen Maud Land and Bouvet Island comprises one of the three Norwegian dependent territories in the Antarctic and sub-Antarctic. Peter I Island is ... , Zavodovski Zavodovski Island Zavodovski Island is an uninhabited volcanic island in the Traversay Islands group of the South Sandwich Islands. It lies southeast of South Georgia Island... , Leskov Leskov Island Leskov Island is a small uninhabited island in the Traversay Islands group of the South Sandwich Islands. It is less than long, and lies west of Visokoi Island... and Visokoi Island Visokoi Island Visokoi Island is an uninhabited island in the Traversay Islands group of the South Sandwich Islands. It was discovered in 1819 by a Russian expedition under Fabian Gottlieb von Bellingshausen, who named the island Visokoi because of its conspicuous height.The island is long and wide, capped by... s, Antarctic peninsula Antarctic Peninsula The Antarctic Peninsula is the northernmost part of the mainland of Antarctica. It extends from a line between Cape Adams and a point on the mainland south of Eklund Islands.... mainland and Alexander Island Alexander Island Alexander Island or Alexander I Island or Alexander I Land or Alexander Land is the largest island of Antarctica, with an area of lying in the Bellingshausen Sea west of the base of the Antarctic Peninsula, from which it is separated by Marguerite Bay and George VI Sound. Alexander Island lies off... (Alexander Coast), and made some discoveries in the tropical waters of the Pacific. Bellingshausen Island Bellingshausen Island The island is a basaltic andesite stratovolcano, and the latest crater, about across and deep, formed explosively some time between 1968 and 1984.-References:*... in the Atlantic, Bellingshausen Sea Bellingshausen Sea The Bellingshausen Sea is an area along the west side of the Antarctic Peninsula, west of Alexander Island, east of Cape Flying Fish on Thurston Island, and south of Peter I Island . In the south are, from west to east, Eights Coast, Bryan Coast and English Coast of West Antarctica... , Bellingshausen Station Bellingshausen Station thumb|right|Bellingshausen is one of Antarctica's most polluted places. Old vehicles, rusting barrels and other refuse litter the shorelinethumb|right|Muddy scene around the base. On the hilltop an orthodox church was built in 2004... , Bellinshausen Island Motu One (Society Islands) Motu One, also known as Bellinghausen, is an atoll in the Leeward group of the Society Islands. Motu One is located 550 km northwest from Tahiti and 72 km northeast of Manuae, its closest neighbor.... in the Pacific, Faddey Islands Faddey Islands The Faddey Islands is a group of islands covered with tundra vegetation, shingle and ice. It is located in the Laptev Sea coastal region, off Faddey Bay in the coast of Siberia, east of the Taymyr Peninsula.The Main islands are:* Ostrov Faddeyya-Severnyy, latitude 76° 59' N and longitude 108° 02’... in the Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... , ancient Bellingshausen Plate Bellingshausen Plate The Bellingshausen Plate was an ancient tectonic plate that fused onto the Antarctic Plate. It is named after the Baltic German-Russian explorer of Antarctica, Fabian Gottlieb von Bellingshausen.... , Bellinsgauzen crater Bellinsgauzen (crater) Bellinsgauzen is a lunar impact crater that lies in the southern part of Moon, on the far side from the Earth. It is attached to the northern rim of the larger crater Berlage, and within a half crater diameter of Cabannes to the west. North of Bellinsgauzen is the crater Bhabha.The outer rim of... (Moon Moon The Moon is Earth's only known natural satellite,There are a number of near-Earth asteroids including 3753 Cruithne that are co-orbital with Earth: their orbits bring them close to Earth for periods of time but then alter in the long term . These are quasi-satellites and not true moons. For more... ) and minor planet Minor planet An asteroid group or minor-planet group is a population of minor planets that have a share broadly similar orbits. Members are generally unrelated to each other, unlike in an asteroid family, which often results from the break-up of a single asteroid... 3659 Bellingshausen 3659 Bellingshausen 3659 Bellingshausen is a main-belt asteroid discovered on October 8, 1969, by Chernykh, L. at Nauchnyj.- External links :*... are named in honor of Bellinsgausen. |
 |
 |
Lev Berg (1876–1950)  Russian Empire Russian Empire Soviet Union Soviet Uniongeographer, biologist, explorer of Central Asia Central Asia Central Asia is a core region of the Asian continent from the Caspian Sea in the west, China in the east, Afghanistan in the south, and Russia in the north... |
Berg studied and determined the depth of the lakes of Central Asia Central Asia Central Asia is a core region of the Asian continent from the Caspian Sea in the west, China in the east, Afghanistan in the south, and Russia in the north... , including Balkhash Lake and Issyk Kul Issyk Kul Issyk Kul is an endorheic lake in the northern Tian Shan mountains in eastern Kyrgyzstan. It is the tenth largest lake in the world by volume and the second largest saline lake after the Caspian Sea. Although it is surrounded by snow-capped peaks, it never freezes; hence its name, which means "hot... . He researched the ichthyology Ichthyology Ichthyology is the branch of zoology devoted to the study of fish. This includes skeletal fish , cartilaginous fish , and jawless fish... of Central Asia Central Asia Central Asia is a core region of the Asian continent from the Caspian Sea in the west, China in the east, Afghanistan in the south, and Russia in the north... and European Russia European Russia European Russia refers to the western areas of Russia that lie within Europe, comprising roughly 3,960,000 square kilometres , larger in area than India, and spanning across 40% of Europe. Its eastern border is defined by the Ural Mountains and in the south it is defined by the border with... . He developed Dokuchaev's doctrine of biome Biome Biomes are climatically and geographically defined as similar climatic conditions on the Earth, such as communities of plants, animals, and soil organisms, and are often referred to as ecosystems. Some parts of the earth have more or less the same kind of abiotic and biotic factors spread over a... s and climatology Climatology Climatology is the study of climate, scientifically defined as weather conditions averaged over a period of time, and is a branch of the atmospheric sciences... and was one of the founders of the Geographical Institute, now a Faculty of Geography of the Saint Petersburg University. In 1940-50 Berg was the President of the Soviet Geographical Society. |
 |
| Vitus Bering Vitus Bering Vitus Jonassen Bering Vitus Jonassen Bering Vitus Jonassen Bering (also, less correNavy]], a captain-komandor known among the Russian sailors as Ivan Ivanovich. He is noted for being the first European to discover Alaska and its Aleutian Islands... (1681–1741)  Denmark DenmarkTsardom of Russia Tsardom of Russia The Tsardom of Russia was the name of the centralized Russian state from Ivan IV's assumption of the title of Tsar in 1547 till Peter the Great's foundation of the Russian Empire in 1721.From 1550 to 1700, Russia grew 35,000 km2 a year...  Russian Empire Russian EmpireRussian Imperial Navy officer, captain-komandor, explorer of Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... , the Russian Far East Russian Far East Russian Far East is a term that refers to the Russian part of the Far East, i.e., extreme east parts of Russia, between Lake Baikal in Eastern Siberia and the Pacific Ocean... and Alaska Alaska Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait... |
Returning from the East Indies East Indies East Indies is a term used by Europeans from the 16th century onwards to identify what is now known as Indian subcontinent or South Asia, Southeastern Asia, and the islands of Oceania, including the Malay Archipelago and the Philippines... , Bering joined the Russian Navy in 1703. He became the main organiser of the Great Northern Expedition Great Northern Expedition The Great Northern Expedition or Second Kamchatka expedition was one of the largest organised exploration enterprises in history, resulting in mapping of the most of the Arctic coast of Siberia and some parts of the North America coastline, greatly reducing the "white areas" on the maps... to explore the northern Asia. In 1725, Bering went overland to Okhotsk Okhotsk Okhotsk is an urban locality and a seaport at the mouth of the Okhota River on the Sea of Okhotsk, in Okhotsky District, Khabarovsk Krai, Russia. Population: 4,470 ;... , crossed to Kamchatka, and aboard Sviatoi Gavriil mapped some 3500 km of the Bering Sea Bering Sea The Bering Sea is a marginal sea of the Pacific Ocean. It comprises a deep water basin, which then rises through a narrow slope into the shallower water above the continental shelves.... coast and passed Bering Strait Bering Strait The Bering Strait , known to natives as Imakpik, is a sea strait between Cape Dezhnev, Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, Russia, the easternmost point of the Asian continent and Cape Prince of Wales, Alaska, USA, the westernmost point of the North American continent, with latitude of about 65°40'N,... in 1728-29. Later, Ivan Fyodorov Ivan Fyodorov (navigator) Ivan Fedorov , was a Russian navigator and commanding officer of the expedition to northern Alaska in 1732.After the first Kamchatka expedition of Vitus Bering the Russian exploration efforts were continued by Lieutenant Martin Shpanberg and Navigator I... and Mikhail Gvozdev Mikhail Gvozdev Mikhail Spiridonovich Gvozdev was a Russian military geodesist and a commander of the expedition to northern Alaska in 1732, when Alaskan shore was for the first time sited by Russians.... aboard the same Sv. Gavriil sighted Alaska Alaska Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait... shore in 1732. Having organised a major Second Kamchatka expedition, Bering and Aleksei Chirikov Aleksei Chirikov Aleksei Ilyich Chirikov was a Russian navigator and captain who along with Bering was the first Russian to reach North-West coast of North America. He discovered and charted some of the Aleutian Islands while he was deputy to Vitus Bering during the Great Northern Expedition.- Life and work :In... sailed from Okhotsk Okhotsk Okhotsk is an urban locality and a seaport at the mouth of the Okhota River on the Sea of Okhotsk, in Okhotsky District, Khabarovsk Krai, Russia. Population: 4,470 ;... in 1740 aboard Sv. Piotr and Sv. Pavel Paul of Tarsus Paul the Apostle , also known as Saul of Tarsus, is described in the Christian New Testament as one of the most influential early Christian missionaries, with the writings ascribed to him by the church forming a considerable portion of the New Testament... , founded Petropavlovsk Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky is the main city and the administrative, industrial, scientific, and cultural center of Kamchatka Krai, Russia. Population: .-History:It was founded by Danish navigator Vitus Bering, in the service of the Russian Navy... in Kamchatka, and headed together to North America North America North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas... in 1741, until separated by storm. Bering discovered the southern coast of Alaska Alaska Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait... , landed near Kayak Kayak Island Kayak Island , which includes the Bering Expedition Landing Site, is located in the Gulf of Alaska, 100 km SE of Cordova, Alaska Malaspina Coastal Plain. It has a land area of 73.695 km² and no population.... and discovered the Aleutian Islands. Chirikov Aleksei Chirikov Aleksei Ilyich Chirikov was a Russian navigator and captain who along with Bering was the first Russian to reach North-West coast of North America. He discovered and charted some of the Aleutian Islands while he was deputy to Vitus Bering during the Great Northern Expedition.- Life and work :In... discovered the shores of America near Aleksander Archipelago and safely returned to Asia. Bering, however, became very ill and his ship was driven to an uninhabited follow-up Bering Island Bering Island Bering Island is located off the Kamchatka Peninsula in the Bering Sea. At long by wide, it is the largest of the Commander Islands with the area of .... of the Commander group. Bering died there, along with part of his crew. The rest built a vessel out of the wreckage of Sv. Piotr and escaped to Petropavlovsk Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky is the main city and the administrative, industrial, scientific, and cultural center of Kamchatka Krai, Russia. Population: .-History:It was founded by Danish navigator Vitus Bering, in the service of the Russian Navy... . The Bering Strait Bering Strait The Bering Strait , known to natives as Imakpik, is a sea strait between Cape Dezhnev, Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, Russia, the easternmost point of the Asian continent and Cape Prince of Wales, Alaska, USA, the westernmost point of the North American continent, with latitude of about 65°40'N,... , the Bering Sea Bering Sea The Bering Sea is a marginal sea of the Pacific Ocean. It comprises a deep water basin, which then rises through a narrow slope into the shallower water above the continental shelves.... , Bering Island Bering Island Bering Island is located off the Kamchatka Peninsula in the Bering Sea. At long by wide, it is the largest of the Commander Islands with the area of .... , Bering Glacier Bering Glacier Bering Glacier is a glacier in the U.S. state of Alaska. It currently terminates in Vitus Lake south of Alaska’s Wrangell-St. Elias National Park, about from the Gulf of Alaska. Combined with the Bagley Icefield, where the snow that feeds the glacier accumulates, the Bering is the largest glacier... and the Bering Land Bridge Bering land bridge The Bering land bridge was a land bridge roughly 1,000 miles wide at its greatest extent, which joined present-day Alaska and eastern Siberia at various times during the Pleistocene ice ages. Like most of Siberia and all of Manchuria, Beringia was not glaciated because snowfall was extremely light... bear the Bering's name. |
||
| Joseph Billings Joseph Billings Joseph Billings was an English navigator and explorer who spent the most significant part of his life in Russian service.In 1785, the Russian government of Catherine II commissioned a new expedition in search for the Northeast Passage, led by English officer Joseph Billings, who had previously... (c. 1758–1806)  United Kingdom United Kingdom Russian Empire Russian EmpireRoyal Navy Royal Navy The Royal Navy is the naval warfare service branch of the British Armed Forces. Founded in the 16th century, it is the oldest service branch and is known as the Senior Service... and Russian Imperial Navy officer, explorer of Chukotka Chukchi Peninsula The Chukchi Peninsula, Chukotka Peninsula or Chukotski Peninsula , at about 66° N 172° W, is the northeastern extremity of Asia. Its eastern end is at Cape Dezhnev near the village of Uelen. It is bordered by the Chukchi Sea to the north, the Bering Sea to the south, and the Bering Strait to the... and Alaska Alaska Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait... |
In 1785-95 Billings, previously an English officer who had sailed with Captain Cook, led a Russian expedition in search for the Northeast Passage, with Gavril Sarychev Gavril Sarychev Gavril Andreyevich Sarychev , spelt "Sarichef" in the United States, was a Russian navigator, hydrographer, admiral and Honorable Member of the Russian Academy of Sciences in Saint Petersburg.Sarychev started his career in the Imperial Russian Navy in 1775... as his deputy. They made accurate maps of the Chukotka Chukchi Peninsula The Chukchi Peninsula, Chukotka Peninsula or Chukotski Peninsula , at about 66° N 172° W, is the northeastern extremity of Asia. Its eastern end is at Cape Dezhnev near the village of Uelen. It is bordered by the Chukchi Sea to the north, the Bering Sea to the south, and the Bering Strait to the... , the west coast of Alaska Alaska Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait... , and the Aleutian Islands. They landed on Kodiak Island Kodiak Island Kodiak Island is a large island on the south coast of the U.S. state of Alaska, separated from the Alaska mainland by the Shelikof Strait. The largest island in the Kodiak Archipelago, Kodiak Island is the second largest island in the United States and the 80th largest island in the world, with an... , examined the area of Prince William Sound Prince William Sound Prince William Sound is a sound off the Gulf of Alaska on the south coast of the U.S. state of Alaska. It is located on the east side of the Kenai Peninsula. Its largest port is Valdez, at the southern terminus of the Trans-Alaska Pipeline System... and compiled a census of the native population of the Aleutian Islands. Billings crossed Chukotka Chukchi Peninsula The Chukchi Peninsula, Chukotka Peninsula or Chukotski Peninsula , at about 66° N 172° W, is the northeastern extremity of Asia. Its eastern end is at Cape Dezhnev near the village of Uelen. It is bordered by the Chukchi Sea to the north, the Bering Sea to the south, and the Bering Strait to the... on reindeer Reindeer The reindeer , also known as the caribou in North America, is a deer from the Arctic and Subarctic, including both resident and migratory populations. While overall widespread and numerous, some of its subspecies are rare and one has already gone extinct.Reindeer vary considerably in color and size... and made the first elaborate description of the Chukchi people Chukchi people The Chukchi, or Chukchee , ) are an indigenous people inhabiting the Chukchi Peninsula and the shores of the Chukchi Sea and the Bering Sea region of the Arctic Ocean within the Russian Federation. They speak the Chukchi language... . Cape Billings Cape Billings Cape Billings , is a headland on the northern coast of Chukotka, Russian Federation to the west of Cape Schmidt. The shore in the area around cape Billings is bounded by narrow landspits, beach ridges and swales enclosing a series of coastal inshore lagoons.... , a bay and a settlement in Chukotka Chukchi Peninsula The Chukchi Peninsula, Chukotka Peninsula or Chukotski Peninsula , at about 66° N 172° W, is the northeastern extremity of Asia. Its eastern end is at Cape Dezhnev near the village of Uelen. It is bordered by the Chukchi Sea to the north, the Bering Sea to the south, and the Bering Strait to the... have been named after Billings. |
 |
|
| Georgy Brusilov Georgy Brusilov Georgy Lvovich Brusilov or Hryhoriy Brusylov was a Ukrainian Russian naval officer of the Imperial Russian Navy and an Arctic explorer... (1884–1914?)  Russian Empire Russian EmpireRussian Imperial Navy captain, Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... explorer |
In 1910-11, Brusilov took part in a hydrographic expedition on the icebreakers Taymyr Icebreaker Taymyr Icebreaker Taymyr was an icebreaking steamer of 1200 tons built for the Russian Imperial Navy at St. Petersburg in 1909. It was named after the Taymyr Peninsula.... and Vaygach Icebreaker Vaygach Icebreaker Vaygach was an icebreaking steamer of moderate size built for the Russian Imperial Navy at St. Petersburg in 1909. It was named after Vaygach Island in the Russian Arctic.... to the Chukchi Chukchi Sea Chukchi Sea is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It is bounded on the west by the De Long Strait, off Wrangel Island, and in the east by Point Barrow, Alaska, beyond which lies the Beaufort Sea. The Bering Strait forms its southernmost limit and connects it to the Bering Sea and the Pacific... and East Siberian East Siberian Sea The East Siberian Sea is a marginal sea in the Arctic Ocean. It is located between the Arctic Cape to the north, the coast of Siberia to the south, the New Siberian Islands to the west and Cape Billings, close to Chukotka, and Wrangel Island to the east... seas. In 1912-14 he led an expedition on the brig St.Anna Svyataya Anna The ship Svyataya Anna , named after Saint Anne, was the Philomel-class gunvessel HMS Newport launched in England in 1867. She was sold in 1881 and renamed Pandora II. She was purchased again in about 1890 and renamed Blencathra, taking part in expeditions to the north coast of Russia... , which aimed to travel by the Northern Sea Route Northern Sea Route The Northern Sea Route is a shipping lane officially defined by Russian legislation from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean specifically running along the Russian Arctic coast from Murmansk on the Barents Sea, along Siberia, to the Bering Strait and Far East. The entire route lies in Arctic... from the Atlantic to the Pacific. St.Anna became icebound west of Yamal Yamal Peninsula The Yamal Peninsula , located in Yamal-Nenets autonomous district of northwest Siberia, Russia, extends roughly 700 km and is bordered principally by the Kara Sea, Baydaratskaya Bay on the west, and by the Gulf of Ob on the east... and drifted to the North Pole North Pole The North Pole, also known as the Geographic North Pole or Terrestrial North Pole, is, subject to the caveats explained below, defined as the point in the northern hemisphere where the Earth's axis of rotation meets its surface... since 1913. Brusilov became ill and many of the crew succumbed to scurvy. In 1914 a group led by lieutenant Valerian Albanov Valerian Albanov Valerian Ivanovich Albanov was a Russian navigator, best known for being one of only two survivors of the ill-fated Brusilov expedition of 1912.-Biography:... abandoned the ship and walked south over the drifting ice. Only Albanov and Alexander Konrad Alexander Konrad Alexander Eduardovich Konrad was a Russian sailor. Along with Valerian Albanov, he was one of the only two survivors, and the only surviving sailor of the ill-fated Brusilov expedition.-Biography:... managed to reach Franz Joseph Land, where they were rescued by Georgy Sedov Georgy Sedov Georgy Yakovlevich Sedov was a Russian Arctic explorer.Born in the village of Krivaya Kosa of Taganrog district in a fisherman's family. In 1898, Sedov finished navigation courses in Rostov-on-Don and acquired the rank of long voyage navigator... 's St. Foka. The efforts to find St. Anna were unsuccessful. Brusilov and his ship are among the prototypes for the novel The Two Captains The Two Captains The Two Captains is a novel written by Soviet author Veniamin Kaverin between 1938 and 1944. It is Kaverin's best known work and is considered one of the most popular works of Soviet literature, winning the USSR State Prize in 1946 being reissued 42 times in 25 years... by Veniamin Kaverin Veniamin Kaverin Veniamin Alexandrovich Kaverin was a Soviet writer associated with the early 1920s movement of the Serapion Brothers. The immunologist Lev Zilber was his older brother, and the critic Yury Tynyanov was his brother-in-law.... , where the fictional St. Maria repeats the drift of St. Anna. |
 |
|
 |
Alexander Bulatovich Alexander Bulatovich Alexander Ksaverievich Bulatovich tonsured Father Antony was a Russian military officer, explorer of Africa, writer, hieromonk and the leader of imiaslavie movement in Eastern Orthodox Christianity.-Biography:... (1870–1919)  Russian Empire Russian EmpireRussian military officer, explorer of Africa Africa Africa is the world's second largest and second most populous continent, after Asia. At about 30.2 million km² including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of the Earth's total surface area and 20.4% of the total land area... , writer, hieromonk (tonsured Father Antony) |
In 1897 Bulatovich was a member of the Russian mission of the Red Cross in Ethiopia Ethiopia Ethiopia , officially known as the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a country located in the Horn of Africa. It is the second-most populous nation in Africa, with over 82 million inhabitants, and the tenth-largest by area, occupying 1,100,000 km2... , where he became a confidant of Negus Menelek II of Ethiopia Menelek II of Ethiopia Emperor Menelik II GCB, GCMG, baptized as Sahle Maryam , was Negus of Shewa , then of Ethiopia from 1889 to his death. At the height of his internal power and external prestige, the process of territorial expansion and creation of the modern empire-state had been completed by 1898... and his military aide in the war with Italy Italy Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and... and the southern tribes. He became the first European to provide a description of the Kaffa province Kaffa Province, Ethiopia Kaffa was a province on the southwestern side of Ethiopia; its capital city was Jimma. It was named after the former Kingdom of Kaffa.Kaffa was bordered on the west by Sudan, on the northwest by Illubabor, on the north by Walega, on the northeast by Shewa, on the east by Sidamo, and on the... (conquered by Menelek II with Bulatovich's help) and among the first to reach the mouth of the Omo River Omo River The Omo River is an important river of southern Ethiopia. Its course is entirely contained within the boundaries of Ethiopia, and empties into Lake Turkana on the border with Kenya... . Among the places named by Bulatovich was the Nicholas II Mountain range. Back in Russia, he became a monk and one of the leaders of the imiaslavie Imiaslavie Imiaslavie or Imiabozhie , also spelled imyaslavie and imyabozhie, and also referred to as onomatodoxy, is a dogmatic movement which was condemned by the Russian Orthodox Church, but that is still promoted by some affiliated with Gregory Lourie of the "Russian Orthodox Autonomous Church" , and by... Russian Orthodox Russian Orthodox Church The Russian Orthodox Church or, alternatively, the Moscow Patriarchate The ROC is often said to be the largest of the Eastern Orthodox churches in the world; including all the autocephalous churches under its umbrella, its adherents number over 150 million worldwide—about half of the 300 million... movement; later he distinguished himself during World War I World War I World War I , which was predominantly called the World War or the Great War from its occurrence until 1939, and the First World War or World War I thereafter, was a major war centred in Europe that began on 28 July 1914 and lasted until 11 November 1918... . Bulatovich was a prototype for the grotesque Schema-Hussar Alexei Bulanovich in the novel The Twelve Chairs The Twelve Chairs The Twelve Chairs is a classic satirical novel by the Soviet authors Ilf and Petrov, released in 1928. Its main character Ostap Bender reappears in the book's sequel The Little Golden Calf.-Plot:... by Ilf and Petrov Ilf and Petrov Ilya Ilf Ilya Ilf Ilya Ilf (Ilya Arnoldovich Faynzilberg and Evgeny or Yevgeni Petrov (Yevgeniy Petrovich Kataev or Katayev were two Soviet prose authors of the 1920s and 1930s... ; he was the hero of Valentin Pikul Valentin Pikul Valentin Savvich Pikul was a popular and prolific Soviet historical novelist of Ukrainian-Russian heritage. He lived and worked in Riga.... 's story The Hussar on a Camel and the hero of The Name of Hero by Richard Seltzer. |
|
 |
Alexander Bunge (1803–1890)  Russian Empire Russian Empirebotanist, explorer of European Russia European Russia European Russia refers to the western areas of Russia that lie within Europe, comprising roughly 3,960,000 square kilometres , larger in area than India, and spanning across 40% of Europe. Its eastern border is defined by the Ural Mountains and in the south it is defined by the border with... , Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... , China China Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture... and Persia |
In 1825-29 Bunge studied the flora of Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... and Altai Mountains. In 1830 he made research in China China Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture... and in 1832-33 again on Altai. In 1835 he researched Volga steppe Steppe In physical geography, steppe is an ecoregion, in the montane grasslands and shrublands and temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biomes, characterized by grassland plains without trees apart from those near rivers and lakes... s and Astrakhan Astrakhan Astrakhan is a major city in southern European Russia and the administrative center of Astrakhan Oblast. The city lies on the left bank of the Volga River, close to where it discharges into the Caspian Sea at an altitude of below the sea level. Population:... region. In 1857-59 he traveled in Persia, exploring little known territories and collecting plants. A crater on Mars Mars Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun in the Solar System. The planet is named after the Roman god of war, Mars. It is often described as the "Red Planet", as the iron oxide prevalent on its surface gives it a reddish appearance... and more than a hundred of plants are named after Bunge. |
 |
C
| Portrait | Person | Achievements | Image |
|---|---|---|---|
| Semion Chelyuskin Semion Chelyuskin Semyon Ivanovich Chelyuskin was a Russian polar explorer and naval officer.Chelyuskin graduated from the Navigation School in Moscow. He first became a deputy navigator while serving in the Baltic Fleet and later promoted to navigator . Chelyuskin was chosen for the Second Kamchatka Expedition,... (c. 1700–1764) Tsardom of Russia Tsardom of Russia The Tsardom of Russia was the name of the centralized Russian state from Ivan IV's assumption of the title of Tsar in 1547 till Peter the Great's foundation of the Russian Empire in 1721.From 1550 to 1700, Russia grew 35,000 km2 a year...  Russian Empire Russian EmpireRussian Imperial Navy officer, Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... explorer (Malygin Stepan Malygin Stepan Gavrilovich Malygin was a Russian Arctic explorer.In 1711–1717, Stepan Malygin was a student at the Moscow School of Mathematical and Navigational Sciences. After his graduation, Malygin began his career as a naval cadet and was then promoted to the rank of lieutenant four years later... , Ovtsyn Dmitry Ovtsyn Dmitry Leontiyevich Ovtsyn was a Russian hydrographer and Arctic explorer.In 1734-1738, Ovtsyn led one of the units of the Second Kamchatka expedition that charted the coastline of the Kara Sea east of the river Ob. In summer of 1737, his unit made its way from Ob to Yenisei and made the first... , Chelyuskin, K.Laptev Khariton Laptev Khariton Prokofievich Laptev was a Russian naval officer and Arctic explorer.Khariton Laptev was born in a gentry family in the village of Pokarevo near Velikiye Luki , just a year before his cousin Dmitry Laptev was born in the nearby village of Bolotovo.Khariton Laptev started his career in the... and D.Laptev Dmitry Laptev Dmitry Yakovlevich Laptev was a Russian Arctic explorer and Vice Admiral .Dmitry Laptev was born in the village of Bolotovo, near Velikie Luki, in 1701. Bolotovo was the estate of his father, Yakov Laptev... on a modern commemorative coin) |
Chelyuskin participated in the Great Northern Expedition Great Northern Expedition The Great Northern Expedition or Second Kamchatka expedition was one of the largest organised exploration enterprises in history, resulting in mapping of the most of the Arctic coast of Siberia and some parts of the North America coastline, greatly reducing the "white areas" on the maps... in 1733-43. He traveled in the groups led by Vasily Pronchischev and Khariton Laptev Khariton Laptev Khariton Prokofievich Laptev was a Russian naval officer and Arctic explorer.Khariton Laptev was born in a gentry family in the village of Pokarevo near Velikiye Luki , just a year before his cousin Dmitry Laptev was born in the nearby village of Bolotovo.Khariton Laptev started his career in the... . In 1741 he led an own voyage from the Khatanga River Khatanga River The Khatanga River is a river in Krasnoyarsk Krai in Russia. It begins at the confluence of the rivers Kotuy and Kheta. The Khatanga River is long; the area of its basin is 364,000 km². It flows into the Khatanga Gulf of the Laptev Sea, forming an estuary... to the Pyasina River Pyasina River Pyasina River is a river in Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russia. The length of the river is . The area of its basin is 182,000 km². The Pyasina River originates in the Lake Pyasino and flows into the Pyasino Gulf of the Kara Sea. There are more than 60,000 lakes in the basin of the Pyasina covering... by land. He explored and described the western coastline of Taimyr Peninsula and the mouths of Pyasina and Yenisei River Yenisei River Yenisei , also written as Yenisey, is the largest river system flowing to the Arctic Ocean. It is the central of the three great Siberian rivers that flow into the Arctic Ocean... s. In 1741-42, he traveled from Turukhansk Turukhansk Turukhansk is a village in Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russia. It is located 1474 km north of Krasnoyarsk, at the confluence of the Yenisei and Lower Tunguska rivers. The Turukhan River joins the Yenisei about 20 km northwest. Population: 4,849 ; 8,900 ; 200... to the mouth of the Khatanga and described the northern coastline of Taimyr from the Cape Faddey in the east to the mouth of the Taimyra River in the west. Chelyuskin discovered the northern extremity of Asia Asia Asia is the world's largest and most populous continent, located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres. It covers 8.7% of the Earth's total surface area and with approximately 3.879 billion people, it hosts 60% of the world's current human population... , Cape Chelyuskin Cape Chelyuskin Cape Chelyuskin is the northernmost point of the Eurasian continent , and the northernmost point of mainland Russia. It is situated at the tip of the Taymyr Peninsula, south of Severnaya Zemlya archipelago, in Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russia... . Cape Chelyuskin Cape Chelyuskin Cape Chelyuskin is the northernmost point of the Eurasian continent , and the northernmost point of mainland Russia. It is situated at the tip of the Taymyr Peninsula, south of Severnaya Zemlya archipelago, in Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russia... (the northernmost cape of Eurasia Eurasia Eurasia is a continent or supercontinent comprising the traditional continents of Europe and Asia ; covering about 52,990,000 km2 or about 10.6% of the Earth's surface located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres... ), Chelyuskin Peninsula (northern tip of Taymyr Taymyr Peninsula The Taymyr Peninsula is a peninsula in the Far North of Russia, in the Siberian Federal District, that forms the northernmost part of mainland Eurasia and Asia... ), Chelyuskin Island near Taymyr Taymyr Peninsula The Taymyr Peninsula is a peninsula in the Far North of Russia, in the Siberian Federal District, that forms the northernmost part of mainland Eurasia and Asia... , famous Soviet Chelyuskin steamship Chelyuskin steamship SS Chelyuskin was a Soviet steamship reinforced to navigate through polar ice that became ice-bound in Arctic waters during navigation along the Northern Maritime Route from Murmansk to Vladivostok... and some streets and settlements have been named after Chelyuskin. |
 |
|
| Ivan Chersky (1845–1892)  Russian Empire Russian Empire(Belorussian and Polish descent) paleontologist, geologist, geographer, explorer of Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... |
Exiled to Transbaikalia for participation in the January Uprising January Uprising The January Uprising was an uprising in the former Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth against the Russian Empire... and pardoned only in 1883, Chersky became a self-taught scientist in Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... . He traveled to Sayan Mountains Sayan Mountains The Sayan Mountains are a mountain range between northwestern Mongolia and southern Siberia, Russia.The Eastern Sayan extends from the Yenisei River at 92° E to the southwest end of Lake Baikal at 106° E... , Irkut River Irkut River Irkut is a river in the Buryat Republic and Irkutsk Oblast of Russia; Angara's left tributary. The length of the river is . The area of its basin is . The Irkut River freezes up in late October - mid-November and stays icebound until late April - early May. The city of Irkutsk is located at the... Valley and Lower Tunguska Lower Tunguska Nizhnyaya Tunguska — is a river in Siberia, Russia, flows through the Irkutsk Oblast and the Krasnoyarsk Krai. The river is a right tributary of the Yenisei joining it at Turukhansk . Settlements on the river include Tura, Yukti and Simenga... . During four expeditions in 1877-81 Chersky explored Selenga Selenga The Selenge is a major river in Mongolia and Buryatia, Russia. Its source rivers are the Ider River and the Delgermörön river. It flows into Lake Baikal and has a length of 616 miles... river. He explained the origin of Lake Baikal Lake Baikal Lake Baikal is the world's oldest at 30 million years old and deepest lake with an average depth of 744.4 metres.Located in the south of the Russian region of Siberia, between Irkutsk Oblast to the northwest and the Buryat Republic to the southeast, it is the most voluminous freshwater lake in the... , made the first geological map of its coast and described the geological structure of East Siberia. He analysed the tectonics of Inner Asia and pioneered the geomorphological Geomorphology Geomorphology is the scientific study of landforms and the processes that shape them... evolution theory. He collected over 2,500 of ancient bones. In 1892 he explored Kolyma Kolyma River The Kolyma River is a river in northeastern Siberia, whose basin covers parts of the Sakha Republic, Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, and Magadan Oblast of Russia. Itrises in the mountains north of Okhotsk and Magadan, in the area of and... , Yana Yana River The Yana River , is a river in Sakha in Russia, located between the Lena to the west and the Indigirka to the east.It is 872 km in length. The area of its basin is 238,000 km², whilst its annual discharge totals approximately . Most of this discharge occurs in May and June as the ice on the... and Indigirka River Indigirka River The Indigirka River is a river in the Sakha Republic in Russia between the Yana River and the Kolyma River. It is in length. The area of its basin is 360,000 km²... s and died from illness there. Chersky Mountain Range Chersky Range The Chersky Range is a chain of mountains in northeastern Siberia between the Yana River and the Indigirka River. It generally runs from northwest to southeast through the Sakha Republic and Magadan Oblast. The tallest mountain in the range is Peak Pobeda, which is 3,003 meters tall. The range... , Chersky (settlement) Chersky (settlement) Chersky is an urban locality and the administrative center of Nizhnekolymsky District of the Sakha Republic, Russia, located on the Kolyma River east of Yakutsk. Population:... in Yakutia, another mountain range in Chita Oblast Chita Oblast Chita Oblast was a federal subject of Russia in southeast Siberia, Russia. Its administrative center was the city of Chita. It had extensive international borders with China and Mongolia and internal borders with Irkutsk and Amur Oblasts, as well as with the Buryat and the Sakha Republics. Its... , Chersky Mountain (highest peak of the Baikal Range), a pass and a peak in the Chamar-Daban Chamar-Daban Khamar-Daban is a mountain range near Baikal Mountains in Siberia, Russia at the Lake Baikal. The highest peak is the Utulinskaya podkova at 2396 metres.... , Chersky Stone (a peak in near Listvyanka, Irkutsk Oblast), a valley and a plateau in the Sayan Mountains Sayan Mountains The Sayan Mountains are a mountain range between northwestern Mongolia and southern Siberia, Russia.The Eastern Sayan extends from the Yenisei River at 92° E to the southwest end of Lake Baikal at 106° E... , a waterfall Waterfall A waterfall is a place where flowing water rapidly drops in elevation as it flows over a steep region or a cliff.-Formation:Waterfalls are commonly formed when a river is young. At these times the channel is often narrow and deep. When the river courses over resistant bedrock, erosion happens... near Baikal, an inactive volcano, a site near Irkutsk Irkutsk Irkutsk is a city and the administrative center of Irkutsk Oblast, Russia, one of the largest cities in Siberia. Population: .-History:In 1652, Ivan Pokhabov built a zimovye near the site of Irkutsk for gold trading and for the collection of fur taxes from the Buryats. In 1661, Yakov Pokhabov... with ancient human remains and a number of species have been named after Chersky. |
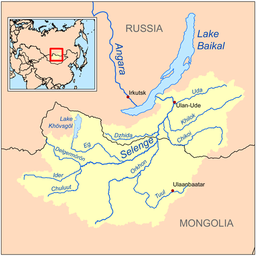 |
|
| Vasili Chichagov Vasili Chichagov Vasili Yakovlevich Chichagov was an admiral in the Russian Navy and an explorer. He was the father of Pavel Chichagov, a Russian admiral during the Napoleonic Wars.-Background:... (1726–1809)  Russian Empire Russian EmpireRussian Imperial Navy officer, Admiral Admiral Admiral is the rank, or part of the name of the ranks, of the highest naval officers. It is usually considered a full admiral and above vice admiral and below admiral of the fleet . It is usually abbreviated to "Adm" or "ADM"... , Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... explorer |
In 1764-66 Chichagov led two expeditions to find the Northeast Passage between the Atlantic and the Pacific along the northern coast of Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... , a project of Mikhail Lomonosov Mikhail Lomonosov Mikhail Vasilyevich Lomonosov was a Russian polymath, scientist and writer, who made important contributions to literature, education, and science. Among his discoveries was the atmosphere of Venus. His spheres of science were natural science, chemistry, physics, mineralogy, history, art,... . Although he sailed past Svalbard Svalbard Svalbard is an archipelago in the Arctic, constituting the northernmost part of Norway. It is located north of mainland Europe, midway between mainland Norway and the North Pole. The group of islands range from 74° to 81° north latitude , and from 10° to 35° east longitude. Spitsbergen is the... , reached 80°26'N in 1765 and 80°30'N in 1766, and made valuable research, both expeditions failed to find the route. Later he distinguished himself as victorious Commander-in-chief of the Baltic Fleet Baltic Fleet The Twice Red Banner Baltic Fleet - is the Russian Navy's presence in the Baltic Sea. In previous historical periods, it has been part of the navy of Imperial Russia and later the Soviet Union. The Fleet gained the 'Twice Red Banner' appellation during the Soviet period, indicating two awards of... in the Russo-Swedish War (1788–1790). Islands near Novaya Zemlya Novaya Zemlya Novaya Zemlya , also known in Dutch as Nova Zembla and in Norwegian as , is an archipelago in the Arctic Ocean in the north of Russia and the extreme northeast of Europe, the easternmost point of Europe lying at Cape Flissingsky on the northern island... , Chichagof Island Chichagof Island Chichagof Island, or Shee Kaax, is an island in the Alexander Archipelago of the Alaska Panhandle. At long and wide, it has a land area of , making it the fifth largest island in the United States and the 109th largest island in the world. It's coastline measures 742 miles. There was a 2000... in the Alexander Archipelago Alexander Archipelago The Alexander Archipelago is a long archipelago, or group of islands, of North America off the southeastern coast of Alaska. It contains about 1,100 islands, which are the tops of the submerged coastal mountains that rise steeply from the Pacific Ocean. Deep channels and fjords separate the... near Alaska Alaska Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait... , a bay and a cape of Nuka Hiva in French Polynesia French Polynesia French Polynesia is an overseas country of the French Republic . It is made up of several groups of Polynesian islands, the most famous island being Tahiti in the Society Islands group, which is also the most populous island and the seat of the capital of the territory... , and a mountain at Svalbard Svalbard Svalbard is an archipelago in the Arctic, constituting the northernmost part of Norway. It is located north of mainland Europe, midway between mainland Norway and the North Pole. The group of islands range from 74° to 81° north latitude , and from 10° to 35° east longitude. Spitsbergen is the... are named after Chichagov. |
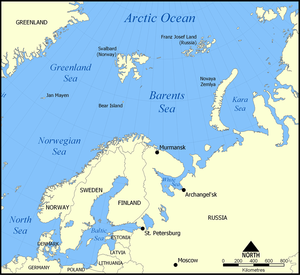 |
|
 |
Pyotr Chikhachyov (1808–1890)  Russian Empire Russian Empirenaturalist, geologist, explorer of Central Asia Central Asia Central Asia is a core region of the Asian continent from the Caspian Sea in the west, China in the east, Afghanistan in the south, and Russia in the north... and Asia Minor Asia Minor Asia Minor is a geographical location at the westernmost protrusion of Asia, also called Anatolia, and corresponds to the western two thirds of the Asian part of Turkey... |
In 1839-41 Chikhachyov researched geology of Italy. In 1842 he led an expedition to the unknown territories of the Altai and Sayan Mountains Sayan Mountains The Sayan Mountains are a mountain range between northwestern Mongolia and southern Siberia, Russia.The Eastern Sayan extends from the Yenisei River at 92° E to the southwest end of Lake Baikal at 106° E... . He discovered Kuznetsk Coal Basin, reached the sources of the rivers Abakan Abakan Abakan is the capital city of the Republic of Khakassia, Russia, located in the central part of Minusinsk Depression, at the confluence of the Yenisei and Abakan Rivers. Population: -History:... , Chu Chu River "Chui River" redirects here. For the South American Chuí or Chuy River, on the Brazil-Uruguay border and Brazil's southernmost point, see Chuí River. For the Nam Sam River or Chu River, on the Lao-Vietnam border, see Nam Sam River.... and Chulyshman, and entered Tuva Tuva The Tyva Republic , or Tuva , is a federal subject of Russia . It lies in the geographical center of Asia, in southern Siberia. The republic borders with the Altai Republic, the Republic of Khakassia, Krasnoyarsk Krai, Irkutsk Oblast, and the Republic of Buryatia in Russia and with Mongolia to the... . In 1845 he published works on geology of Altai and Xinjiang Xinjiang Xinjiang is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China. It is the largest Chinese administrative division and spans over 1.6 million km2... . In 1848-63 he led eight expeditions in Asia Minor Asia Minor Asia Minor is a geographical location at the westernmost protrusion of Asia, also called Anatolia, and corresponds to the western two thirds of the Asian part of Turkey... , Armenia Armenia Armenia , officially the Republic of Armenia , is a landlocked mountainous country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia... , Kurdistan and East Thrace East Thrace East Thrace or Eastern Thrace , also known as Turkish Thrace, is the part of the modern republic of Turkey that is geographically part of Europe, all in the eastern part of the historical region of Thrace; most of Turkey is in Anatolia, also known as Asia Minor. Turkish Thrace is also called... . In 1853-69 he conducted a major study of Asia Minor Asia Minor Asia Minor is a geographical location at the westernmost protrusion of Asia, also called Anatolia, and corresponds to the western two thirds of the Asian part of Turkey... , while being the attaché of the Russian embassy in Constantinople Constantinople Constantinople was the capital of the Roman, Eastern Roman, Byzantine, Latin, and Ottoman Empires. Throughout most of the Middle Ages, Constantinople was Europe's largest and wealthiest city.-Names:... . In 1878, at the age of 71, he visited Algeria and Tunis. He published many works in geography, natural history and politics of the Eastern Question Eastern Question The "Eastern Question", in European history, encompasses the diplomatic and political problems posed by the decay of the Ottoman Empire. The expression does not apply to any one particular problem, but instead includes a variety of issues raised during the 18th, 19th, and 20th centuries, including... . A mountain range in Altai is named after Chikhachyov. |
  |
| Artur Chilingarov Artur Chilingarov Artur Nikolayevich Chilingarov is a Russian polar explorer. He is a corresponding member of the Russian Academy of Sciences, was awarded the title Hero of the Soviet Union in 1986 and the title Hero of the Russian Federation in 2008. Chilingarov is also a member of State Duma from Nenets... (born 1939)  Soviet Union Soviet Union Russia RussiaArctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... , Antarctic Antarctic The Antarctic is the region around the Earth's South Pole, opposite the Arctic region around the North Pole. The Antarctic comprises the continent of Antarctica and the ice shelves, waters and island territories in the Southern Ocean situated south of the Antarctic Convergence... and deep-sea Deep-sea exploration Deep-sea exploration is the investigation of physical, chemical, and biological conditions on the sea bed, for scientific or commercial purposes. Deep-sea exploration is considered as a relatively recent human activity compared to the other areas of geophysical research, as the depths of the sea... explorer, Hero of the Soviet Union Hero of the Soviet Union The title Hero of the Soviet Union was the highest distinction in the Soviet Union, awarded personally or collectively for heroic feats in service to the Soviet state and society.-Overview:... , Hero of the Russian Federation Hero of the Russian Federation Hero of the Russian Federation is a Russian decoration and the highest honorary title that can be bestowed on a citizen by the Russian Federation. The President of the Russian Federation is the main conferring authority of the medal, which is bestowed on those committing actions or deeds that... , politician |
In 1969 Chilingarov became the head of the research station “North Pole-19 Soviet and Russian manned drifting ice stations Soviet and Russian manned drifting ice stations are important contributors to exploration of the Arctic. The stations are named North Pole Soviet and Russian manned drifting ice stations are important contributors to exploration of the Arctic. The stations are named North Pole Soviet and... ” and in 1971 the head of Bellingshausen Station Bellingshausen Station thumb|right|Bellingshausen is one of Antarctica's most polluted places. Old vehicles, rusting barrels and other refuse litter the shorelinethumb|right|Muddy scene around the base. On the hilltop an orthodox church was built in 2004... during the 17-th Soviet Antarctic Expedition Soviet Antarctic Expedition The Soviet Antarctic Expedition was part of the Arctic and Antarctic Research Institute of the Soviet Committee on Antarctic Research of the Academy of Sciences of the USSR.... . In 1985 he successfully led the mission to rescue the research vessel Mikhail Somov Mikhail Somov Mikhail Mikhailovich Somov was a Soviet oceanologist, polar explorer, Doctor of Geographical Sciences .... , which had been ice-blocked in the Southern Ocean Southern Ocean The Southern Ocean comprises the southernmost waters of the World Ocean, generally taken to be south of 60°S latitude and encircling Antarctica. It is usually regarded as the fourth-largest of the five principal oceanic divisions... . During the Russian Arktika 2007 Arktika 2007 Arktika 2007 was a 2007 expedition in which Russia performed the first ever crewed descent to the ocean bottom at the North Pole, as part of research related to the 2001 Russian territorial claim, one of many territorial claims in the Arctic, made possible, in part, because of Arctic shrinkage... expedition, Chilingarov, accompanied by other explorers from different countries, descended to the seabed 13,980 feet below the North Pole North Pole The North Pole, also known as the Geographic North Pole or Terrestrial North Pole, is, subject to the caveats explained below, defined as the point in the northern hemisphere where the Earth's axis of rotation meets its surface... in order to plant there the Russian flag and gather the specimens of the bottom ground, using MIR submersibles MIR (submersible) Mir is a self-propelled Deep Submergence Vehicle. The project was initially developed by the USSR Academy of Sciences along with Design Bureau Lazurith. Later two vehicles were ordered from Finland... . In 2008 he took part in the expedition which on MIRs to descend one mile to the bottom of Lake Baikal Lake Baikal Lake Baikal is the world's oldest at 30 million years old and deepest lake with an average depth of 744.4 metres.Located in the south of the Russian region of Siberia, between Irkutsk Oblast to the northwest and the Buryat Republic to the southeast, it is the most voluminous freshwater lake in the... . |
 |
|
 |
Aleksei Chirikov Aleksei Chirikov Aleksei Ilyich Chirikov was a Russian navigator and captain who along with Bering was the first Russian to reach North-West coast of North America. He discovered and charted some of the Aleutian Islands while he was deputy to Vitus Bering during the Great Northern Expedition.- Life and work :In... (1703–1748) Tsardom of Russia Tsardom of Russia The Tsardom of Russia was the name of the centralized Russian state from Ivan IV's assumption of the title of Tsar in 1547 till Peter the Great's foundation of the Russian Empire in 1721.From 1550 to 1700, Russia grew 35,000 km2 a year...  Russian Empire Russian EmpireRussian Imperial Navy officer, captain, explorer of the Russian Far East Russian Far East Russian Far East is a term that refers to the Russian part of the Far East, i.e., extreme east parts of Russia, between Lake Baikal in Eastern Siberia and the Pacific Ocean... and Alaska Alaska Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait... |
In 1725-30 and in 1733-43, Chirikov was Vitus Bering Vitus Bering Vitus Jonassen Bering Vitus Jonassen Bering Vitus Jonassen Bering (also, less correNavy]], a captain-komandor known among the Russian sailors as Ivan Ivanovich. He is noted for being the first European to discover Alaska and its Aleutian Islands... 's deputy during the 1st and the 2nd Kamchatka expeditions. On July 15, 1741 Chirikov, the captain of Sv. Pavel Paul of Tarsus Paul the Apostle , also known as Saul of Tarsus, is described in the Christian New Testament as one of the most influential early Christian missionaries, with the writings ascribed to him by the church forming a considerable portion of the New Testament... , became the first European to land on the northwestern coast of North America North America North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas... near Alexander Archipelago Alexander Archipelago The Alexander Archipelago is a long archipelago, or group of islands, of North America off the southeastern coast of Alaska. It contains about 1,100 islands, which are the tops of the submerged coastal mountains that rise steeply from the Pacific Ocean. Deep channels and fjords separate the... . Thereafter he discovered some of the Aleutian Islands. In 1742 Chirikov specified the location of the Attu Island Attu Island Attu is the westernmost and largest island in the Near Islands group of the Aleutian Islands of Alaska, making it the westernmost point of land relative to Alaska and the United States. It was the site of the only World War II land battle fought on the incorporated territory of the United States ,... during the search for the lost Bering Vitus Bering Vitus Jonassen Bering Vitus Jonassen Bering Vitus Jonassen Bering (also, less correNavy]], a captain-komandor known among the Russian sailors as Ivan Ivanovich. He is noted for being the first European to discover Alaska and its Aleutian Islands... 's ship. In 1746 Chirikov took part in creating the final map of the Russian discoveries in the northern Pacific Ocean Pacific Ocean The Pacific Ocean is the largest of the Earth's oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, bounded by Asia and Australia in the west, and the Americas in the east.At 165.2 million square kilometres in area, this largest division of the World... . Capes of the Kyūshū Kyushu is the third largest island of Japan and most southwesterly of its four main islands. Its alternate ancient names include , , and . The historical regional name is referred to Kyushu and its surrounding islands.... and Attu Attu Island Attu is the westernmost and largest island in the Near Islands group of the Aleutian Islands of Alaska, making it the westernmost point of land relative to Alaska and the United States. It was the site of the only World War II land battle fought on the incorporated territory of the United States ,... islands, capes in Anadyr Bay and Tauyskaya Bay, and an underwater mountain in the Pacific bear Chirikov's name. |
 |
 |
Valery Chkalov Valery Chkalov Valery Pavlovich Chkalov was a Russian aircraft test pilot and a Hero of the Soviet Union .-Early life:... (1904–1938)  Russian Empire Russian Empire Soviet Union Soviet Unionaircraft test pilot, Hero of the Soviet Union Hero of the Soviet Union The title Hero of the Soviet Union was the highest distinction in the Soviet Union, awarded personally or collectively for heroic feats in service to the Soviet state and society.-Overview:... |
Chkalov developed several new figures of aerobatics Aerobatics Aerobatics is the practice of flying maneuvers involving aircraft attitudes that are not used in normal flight. Aerobatics are performed in airplanes and gliders for training, recreation, entertainment and sport... . He was involved in a number of Soviet ultralong flights. In 1936 Chkalov, Georgiy Baidukov Georgiy Baidukov Georgy Filippovich Baydukov was a Soviet aircraft test pilot and a Hero of the Soviet Union .- Early years :Georgy Baydukov had been born in Taryshta railway station to a railway worker. He became an orphan in the age of 9 and had been homeless for some time... and A.V.Belyakov on ANT-25 flew 9,374 km from Moscow Moscow Moscow is the capital, the most populous city, and the most populous federal subject of Russia. The city is a major political, economic, cultural, scientific, religious, financial, educational, and transportation centre of Russia and the continent... through the North Pole North Pole The North Pole, also known as the Geographic North Pole or Terrestrial North Pole, is, subject to the caveats explained below, defined as the point in the northern hemisphere where the Earth's axis of rotation meets its surface... to follow-up Chkalov Island Chkalov Island Chkalov Island , formerly Udd Island , is a coastal island in the southern end of the Sea of Okhotsk. It is located off Schastya Bay, between the shorebound lagoon and the sea. Baydukov Island lies only 2 km off its ESE tip.Chkalov Island is long and narrow... in Okhotsk Sea, which took 56 h 20 min. In 1937, also on ANT-25, the same crew flew 8,504 km from Moscow through the North Pole North Pole The North Pole, also known as the Geographic North Pole or Terrestrial North Pole, is, subject to the caveats explained below, defined as the point in the northern hemisphere where the Earth's axis of rotation meets its surface... to Vancouver, Washington Vancouver, Washington Vancouver is a city on the north bank of the Columbia River in the U.S. state of Washington. Incorporated in 1857, it is the fourth largest city in the state with a 2010 census population of 161,791 as of April 1, 2010... , which was the first transpolar flight between Europe Europe Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting... and North America North America North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas... on airplane, rather than on dirigible. Chkalovsk Chkalovsk, Russia Chkalovsk is a town and the administrative center of Chkalovsky District of Nizhny Novgorod Oblast, Russia, situated on the right bank of the Volga River, northwest of Nizhny Novgorod. Population: -History:... city, Chkalov Island Chkalov Island Chkalov Island , formerly Udd Island , is a coastal island in the southern end of the Sea of Okhotsk. It is located off Schastya Bay, between the shorebound lagoon and the sea. Baydukov Island lies only 2 km off its ESE tip.Chkalov Island is long and narrow... in the Okhotsk Sea and a number of streets and metro stations are named after Chkalov. |
 |
D
| Portrait | Person | Achievements | Image |
|---|---|---|---|
| Semyon Dezhnyov (c. 1605–1672) Tsardom of Russia Tsardom of Russia The Tsardom of Russia was the name of the centralized Russian state from Ivan IV's assumption of the title of Tsar in 1547 till Peter the Great's foundation of the Russian Empire in 1721.From 1550 to 1700, Russia grew 35,000 km2 a year... Siberian Cossack Siberian Cossacks Siberian Cossacks were Cossacks who settled in the Siberian region of Russia from the end of the 16th century, following the Yermak Timofeyevich's conquest of Siberia. In early Siberia practically the whole Russian population, especially the serving-men were called Cossacks, but only in the loose... leader, explorer of Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... and the Russian Far East Russian Far East Russian Far East is a term that refers to the Russian part of the Far East, i.e., extreme east parts of Russia, between Lake Baikal in Eastern Siberia and the Pacific Ocean... |
In 1638 Dezhnyov came to Yakutsk Yakutsk With a subarctic climate , Yakutsk is the coldest city, though not the coldest inhabited place, on Earth. Average monthly temperatures range from in July to in January. The coldest temperatures ever recorded on the planet outside Antarctica occurred in the basin of the Yana River to the northeast... and then to the Indigirka River Indigirka River The Indigirka River is a river in the Sakha Republic in Russia between the Yana River and the Kolyma River. It is in length. The area of its basin is 360,000 km²... where he served under Mikhail Stadukhin Mikhail Stadukhin Mikhail Vasilyevich Stadukhin was a Russian explorer of far northeast Siberia, one of the first to reach the Kolyma, Anadyr, Penzhina and Gizhiga Rivers and the northern Sea of Okhotsk. He was a Pomor, probably born in the village of Pinega, and the nephew of a Moscow merchant... . Together they discovered Kolyma River Kolyma River The Kolyma River is a river in northeastern Siberia, whose basin covers parts of the Sakha Republic, Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, and Magadan Oblast of Russia. Itrises in the mountains north of Okhotsk and Magadan, in the area of and... and founded Srednekolymsk Srednekolymsk Srednekolymsk is a town and the administrative center of Srednekolymsky District of the Sakha Republic, Russia, located northeast of Yakutsk on the left bank of the Kolyma River. Population: -History:... there in 1643. Fedot Popov Fedot Alekseyev Popov Fedot Alekseyevich Popov , date of birth unknown, died between 1648 and 1654) was a Russian explorer who organized the first European expedition through the Bering Strait.He was normally known as Fedot Alekseyev. Only a few sources call him the son of Popov... organized the further expedition eastward, and Dezhnyov became a captain of one koch Koch (boat) The Koch was a special type of small one or two mast wooden sailing ships designed and used in Russia for transpolar voyages in ice conditions of the Arctic seas, popular among the Pomors.... . In 1648 they sailed from Srednekolymsk Srednekolymsk Srednekolymsk is a town and the administrative center of Srednekolymsky District of the Sakha Republic, Russia, located northeast of Yakutsk on the left bank of the Kolyma River. Population: -History:... down to the Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... and after some time they rounded a 'great rocky projection', thus becoming the first to pass through the Bering Strait Bering Strait The Bering Strait , known to natives as Imakpik, is a sea strait between Cape Dezhnev, Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, Russia, the easternmost point of the Asian continent and Cape Prince of Wales, Alaska, USA, the westernmost point of the North American continent, with latitude of about 65°40'N,... and to discover Chukotka Chukchi Peninsula The Chukchi Peninsula, Chukotka Peninsula or Chukotski Peninsula , at about 66° N 172° W, is the northeastern extremity of Asia. Its eastern end is at Cape Dezhnev near the village of Uelen. It is bordered by the Chukchi Sea to the north, the Bering Sea to the south, and the Bering Strait to the... and Bering Sea Bering Sea The Bering Sea is a marginal sea of the Pacific Ocean. It comprises a deep water basin, which then rises through a narrow slope into the shallower water above the continental shelves.... . All their kochs and most of their men (including Popov himself) were lost in storms and clashes with the natives. A small group led by Dezhnyov reached the mouth of Anadyr River Anadyr River Anadyr is a river in the far northeast Siberia which flows into Anadyr Bay of the Bering Sea and drains much of the interior of Chukotka Autonomous Okrug. Its basin corresponds to the Anadyrsky District of Chukotka.... and sailed up it in 1649, having built new boats of the wreckage. They founded Anadyrsk Anadyrsk thumb|Anadyrsk was on the east-west part of the Anadyr River at the point where it swings northAnadyrsk was an important Russian ostrog in far northeastern Siberia from 1649 to 1764... and were stranded there, until Stadukhin found them, coming from Kolyma by land. A mountain ridge in Chukotka Chukchi Peninsula The Chukchi Peninsula, Chukotka Peninsula or Chukotski Peninsula , at about 66° N 172° W, is the northeastern extremity of Asia. Its eastern end is at Cape Dezhnev near the village of Uelen. It is bordered by the Chukchi Sea to the north, the Bering Sea to the south, and the Bering Strait to the... , a bay of the Bering Sea Bering Sea The Bering Sea is a marginal sea of the Pacific Ocean. It comprises a deep water basin, which then rises through a narrow slope into the shallower water above the continental shelves.... , a settlement on Amur River, and Cape Dezhnyov (the easternmost cape of Eurasia Eurasia Eurasia is a continent or supercontinent comprising the traditional continents of Europe and Asia ; covering about 52,990,000 km2 or about 10.6% of the Earth's surface located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres... ) are named after Dezhnyov. |
||
 |
Vasily Dokuchaev (1846–1903)  Russian Empire Russian Empiregeographer, geologist, pedologist Pedology (soil study) Pedology is the study of soils in their natural environment. It is one of two main branches of soil science, the other being edaphology... , explorer of European Russia European Russia European Russia refers to the western areas of Russia that lie within Europe, comprising roughly 3,960,000 square kilometres , larger in area than India, and spanning across 40% of Europe. Its eastern border is defined by the Ural Mountains and in the south it is defined by the border with... |
Dokuchaev led numerous expeditions to study soil Soil Soil is a natural body consisting of layers of mineral constituents of variable thicknesses, which differ from the parent materials in their morphological, physical, chemical, and mineralogical characteristics... s and geology of European Russia European Russia European Russia refers to the western areas of Russia that lie within Europe, comprising roughly 3,960,000 square kilometres , larger in area than India, and spanning across 40% of Europe. Its eastern border is defined by the Ural Mountains and in the south it is defined by the border with... . In 1871-77 he traveled through Finland Finland Finland , officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country situated in the Fennoscandian region of Northern Europe. It is bordered by Sweden in the west, Norway in the north and Russia in the east, while Estonia lies to its south across the Gulf of Finland.Around 5.4 million people reside... and Northern and Central Russia, and in 1877-81 through Chernozem Region. In 1897-1900 he traveled to the Caucasus Caucasus The Caucasus, also Caucas or Caucasia , is a geopolitical region at the border of Europe and Asia, and situated between the Black and the Caspian sea... , Bessarabia Bessarabia Bessarabia is a historical term for the geographic region in Eastern Europe bounded by the Dniester River on the east and the Prut River on the west.... and Central Asia Central Asia Central Asia is a core region of the Asian continent from the Caspian Sea in the west, China in the east, Afghanistan in the south, and Russia in the north... . As a result of his long research of Russian soils, he founded the modern soil science Soil science Soil science is the study of soil as a natural resource on the surface of the earth including soil formation, classification and mapping; physical, chemical, biological, and fertility properties of soils; and these properties in relation to the use and management of soils.Sometimes terms which... , developed the conception of biome Biome Biomes are climatically and geographically defined as similar climatic conditions on the Earth, such as communities of plants, animals, and soil organisms, and are often referred to as ecosystems. Some parts of the earth have more or less the same kind of abiotic and biotic factors spread over a... s and proposed ways to improve soil productivity. Dokuchaevsk town and a village in Ukraine Ukraine Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It has an area of 603,628 km², making it the second largest contiguous country on the European continent, after Russia... , a number of streets and soil research institutions have been named after Dokuchaev. |
 |
E
| Portrait | Person | Achievements | Image |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adolf Etolin Adolf Etolin Adolf Karlovich Etolin, lso Arvid Adolf Etholén, Russian: Адольф Карлович Этолин was a naval officer, explorer and administrator who was employed by the Russian-American Company. He was a Swedish-speaking Finn who was born in Helsinki, Finland... (1799–1876)  Sweden Sweden Russian Empire Russian Empire(born in Finland Finland Finland , officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country situated in the Fennoscandian region of Northern Europe. It is bordered by Sweden in the west, Norway in the north and Russia in the east, while Estonia lies to its south across the Gulf of Finland.Around 5.4 million people reside... ) Russian Imperial Navy officer, explorer of Alaska Alaska Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait... , governor of Russian America |
Etolin sailed to Alaska Alaska Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait... with Vasily Golovnin Vasily Golovnin Vasily Mikhailovich Golovnin .-Early life and career:Vasily Mikhailovich Golovnin was born in April 1776, in the village of Gulyniki in Ryazan Oblast, on his father's country estate. Both his father and grandfather had served in the Russian military as officers in the elite Preobrazhensky... on Kamchatka Russian frigate Kamchatka At least two frigates of the Imperial Russian Navy have been named Kamchatka* Russian sloop-of-war Kamchatka circumnavigated the globe between 1817 and 1819 under Captain Vasily Golovnin.... and entered the service of the Russian-American Company Russian-American Company The Russian-American Company was a state-sponsored chartered company formed largely on the basis of the so-called Shelekhov-Golikov Company of Grigory Shelekhov and Ivan Larionovich Golikov The Russian-American Company (officially: Under His Imperial Majesty's Highest Protection (patronage)... . He was part of a group that surveyed the Aleutian Islands in 1822-24. In 1833 he explored the Gulf of Alaska Gulf of Alaska The Gulf of Alaska is an arm of the Pacific Ocean defined by the curve of the southern coast of Alaska, stretching from the Alaska Peninsula and Kodiak Island in the west to the Alexander Archipelago in the east, where Glacier Bay and the Inside Passage are found.The entire shoreline of the Gulf is... . Etolin was the governor of Russian America in 1840-45, and continued to explore Alaska and Bering Sea Bering Sea The Bering Sea is a marginal sea of the Pacific Ocean. It comprises a deep water basin, which then rises through a narrow slope into the shallower water above the continental shelves.... . Etolin Island Etolin Island Etolin Island is an island in the Alexander Archipelago of southeastern Alaska, USA, at . It is between Prince of Wales Island, to its west, and the Alaska mainland, to its east. It is southwest of Wrangell Island. It was first charted in 1793 by James Johnstone, one of George Vancouver's... , Etolin Strait Etolin Strait Etolin Strait is a strait in the western region of the U.S. state of Alaska, at about . It is between Nunivak Island to its west and Nelson Island and the Alaska mainland to its east... , a cape and a bay at Nunivak Island Nunivak Island Nunivak Island , the second largest island in the Bering Sea, is a permafrost-covered volcanic island lying about 30 miles offshore from the delta of the Yukon and Kuskokwim rivers in the state of Alaska, at about 60° North latitude... , a mountain in Alaska Alaska Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait... and a cape on Urup Island are named after Etolin. |
||
| Eduard Eversmann Eduard Friedrich Eversmann Alexander Eduard Friedrich Eversmann was a biologist and explorer.Eversmann was born in Westphalia and studied at the universities of Marburg, Halle, Berlin and Dorpat. He received his degree of Philosophy and Master of Liberal Sciences at Halle in 1814, and at Dorpat graduated as a Doctor of... (1794–1860)  Holy Roman Empire Holy Roman Empire Russian Empire Russian Empirenaturalist Naturalist Naturalist may refer to:* Practitioner of natural history* Conservationist* Advocate of naturalism * Naturalist , autobiography-See also:* The American Naturalist, periodical* Naturalism... , explorer of Southern Urals and Central Asia Central Asia Central Asia is a core region of the Asian continent from the Caspian Sea in the west, China in the east, Afghanistan in the south, and Russia in the north... |
In 1817 Eversmann came to Russia and started his travels in the southern Urals to collect specimens. In 1820 he traveled to Bukhara Bukhara Bukhara , from the Soghdian βuxārak , is the capital of the Bukhara Province of Uzbekistan. The nation's fifth-largest city, it has a population of 263,400 . The region around Bukhara has been inhabited for at least five millennia, and the city has existed for half that time... disguised as a merchant and in 1825 traveled with a military expedition to Khiva Khiva Khiva is a city of approximately 50,000 people located in Xorazm Province, Uzbekistan. It is the former capital of Khwarezmia and the Khanate of Khiva... . In 1828 he became a professor of zoology Zoology Zoology |zoölogy]]), is the branch of biology that relates to the animal kingdom, including the structure, embryology, evolution, classification, habits, and distribution of all animals, both living and extinct... and botany Botany Botany, plant science, or plant biology is a branch of biology that involves the scientific study of plant life. Traditionally, botany also included the study of fungi, algae and viruses... at the university of Kazan. He wrote numerous publications and pioneered the research of the flora and fauna of the southeast steppes of Russia between Volga and Urals. A number of birds, such as Eversmann's Redstart, butterflies, such as Eversmann's Parnassian, and moths, such as Eversmann's Rustic are named after Eversmann. |
 |
F
| Portrait | Person | Achievements | Image |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
Alexei Fedchenko Alexei Pavlovich Fedchenko Alexei Pavlovich Fedchenko was a Russian naturalist and explorer well known for his travels in central Asia.... (1844–1873)  Russian Empire Russian Empirenaturalist Naturalist Naturalist may refer to:* Practitioner of natural history* Conservationist* Advocate of naturalism * Naturalist , autobiography-See also:* The American Naturalist, periodical* Naturalism... , explorer of Central Asia Central Asia Central Asia is a core region of the Asian continent from the Caspian Sea in the west, China in the east, Afghanistan in the south, and Russia in the north... |
In 1868 Fedchenko traveled through Turkestan Turkestan Turkestan, spelled also as Turkistan, literally means "Land of the Turks".The term Turkestan is of Persian origin and has never been in use to denote a single nation. It was first used by Persian geographers to describe the place of Turkish peoples... , including Samarkand Samarkand Although a Persian-speaking region, it was not united politically with Iran most of the times between the disintegration of the Seleucid Empire and the Arab conquest . In the 6th century it was within the domain of the Turkic kingdom of the Göktürks.At the start of the 8th century Samarkand came... , Panjkent and the upper Zarafshan River valley. In 1870 he explored the Fan Mountains south of the Zarafshan. In 1871 he reached the Alay Valley Alay Valley The Alay Valley is a broad, dry valley running east-west across most of southern Osh Province, Kyrgyzstan. . It is about 180km east-west and about 40km north-south and 2500-3500m in altitude. The north side is the Alay Mountains which slope down to the Ferghana Valley... at Daroot-Korgan and explored the northern Pamir Mountains Pamir Mountains The Pamir Mountains are a mountain range in Central Asia formed by the junction or knot of the Himalayas, Tian Shan, Karakoram, Kunlun, and Hindu Kush ranges. They are among the world’s highest mountains and since Victorian times they have been known as the "Roof of the World" a probable... but was unable to penetrate southward. He perished on Mont Blanc Mont Blanc Mont Blanc or Monte Bianco , meaning "White Mountain", is the highest mountain in the Alps, Western Europe and the European Union. It rises above sea level and is ranked 11th in the world in topographic prominence... while engaged in an exploring tour in France France The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France... . Fedchenko Glacier Fedchenko Glacier The Fedchenko Glacier is a large glacier in the Pamir Mountains of north-central Gorno-Badakhshan province, Tajikistan. The glacier is long and narrow, currently extending for and covering over . It is the longest glacier in the world outside of the polar regions... in the Pamir Mountains Pamir Mountains The Pamir Mountains are a mountain range in Central Asia formed by the junction or knot of the Himalayas, Tian Shan, Karakoram, Kunlun, and Hindu Kush ranges. They are among the world’s highest mountains and since Victorian times they have been known as the "Roof of the World" a probable... and the asteroid 3195 Fedchenko 3195 Fedchenko 3195 Fedchenko is a main-belt asteroid discovered on August 8, 1978 by Chernykh, N. at Nauchnyj.- External links :*... are named after Fedchenko. |
 |
| Alexander Fersman Alexander Fersman Alexander Yevgenyevich Fersman was a prominent Soviet geochemist and mineralogist, academician of the Soviet Academy of Sciences .... (1883–1945)  Russian Empire Russian Empire Soviet Union Soviet Uniongeologist, geochemist, explorer of European Russia European Russia European Russia refers to the western areas of Russia that lie within Europe, comprising roughly 3,960,000 square kilometres , larger in area than India, and spanning across 40% of Europe. Its eastern border is defined by the Ural Mountains and in the south it is defined by the border with... |
Fersman founded geochemistry Geochemistry The field of geochemistry involves study of the chemical composition of the Earth and other planets, chemical processes and reactions that govern the composition of rocks, water, and soils, and the cycles of matter and energy that transport the Earth's chemical components in time and space, and... , the science about chemical composition of the Earth Earth Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets... . He led numerous expeditions in Crimea Crimea Crimea , or the Autonomous Republic of Crimea , is a sub-national unit, an autonomous republic, of Ukraine. It is located on the northern coast of the Black Sea, occupying a peninsula of the same name... , Kola Peninsula Kola Peninsula The Kola Peninsula is a peninsula in the far northwest of Russia. Constituting the bulk of the territory of Murmansk Oblast, it lies almost completely to the north of the Arctic Circle and is washed by the Barents Sea in the north and the White Sea in the east and southeast... and the Urals. He discovered copper Copper Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29. It is a ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. Pure copper is soft and malleable; an exposed surface has a reddish-orange tarnish... and nickel Nickel Nickel is a chemical element with the chemical symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel belongs to the transition metals and is hard and ductile... in Monchegorsk Monchegorsk Monchegorsk is a town in Murmansk Oblast, Russia, located on the Kola Peninsula, south of Murmansk, the administrative center of the oblast. Administratively, it is incorporated as Monchegorsk Town with Jurisdictional Territory—a unit of administrative division equal in status to that of a district... , apatite Apatite Apatite is a group of phosphate minerals, usually referring to hydroxylapatite, fluorapatite, chlorapatite and bromapatite, named for high concentrations of OH−, F−, Cl− or Br− ions, respectively, in the crystal... reserves in Khibiny and sulfur Sulfur Sulfur or sulphur is the chemical element with atomic number 16. In the periodic table it is represented by the symbol S. It is an abundant, multivalent non-metal. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow... in Central Asia Central Asia Central Asia is a core region of the Asian continent from the Caspian Sea in the west, China in the east, Afghanistan in the south, and Russia in the north... . A pass and a mountain in Murmansk Oblast Murmansk Oblast Murmansk Oblast is a federal subject of Russia , located in the northwestern part of Russia. Its administrative center is the city of Murmansk.-Geography:... , a settlement in Crimea Crimea Crimea , or the Autonomous Republic of Crimea , is a sub-national unit, an autonomous republic, of Ukraine. It is located on the northern coast of the Black Sea, occupying a peninsula of the same name... , the Fersman Mineralogical Museum Fersman Mineralogical Museum Fersman Mineralogical Museum is one of the largest mineral museums of the world. Its collections include more than 135,000 items. Among them natural crystals, geodes, druzes and other kinds of mineral treasures. The museum was named after Alexander Fersman.... in the Urals, the mineral Mineral A mineral is a naturally occurring solid chemical substance formed through biogeochemical processes, having characteristic chemical composition, highly ordered atomic structure, and specific physical properties. By comparison, a rock is an aggregate of minerals and/or mineraloids and does not... s fersmite and fersmanite, a crater Fersman (crater) Fersman is a large lunar impact crater on the Moon's far side. It lies to the east of the crater Poynting, and west-northwest of Weyl. To the south is the huge walled plain Hertzsprung.... on the Moon Moon The Moon is Earth's only known natural satellite,There are a number of near-Earth asteroids including 3753 Cruithne that are co-orbital with Earth: their orbits bring them close to Earth for periods of time but then alter in the long term . These are quasi-satellites and not true moons. For more... , and a number of streets are named after Fersman. |
||
| Ivan Fyodorov Ivan Fyodorov (navigator) Ivan Fedorov , was a Russian navigator and commanding officer of the expedition to northern Alaska in 1732.After the first Kamchatka expedition of Vitus Bering the Russian exploration efforts were continued by Lieutenant Martin Shpanberg and Navigator I... (?–1733) Tsardom of Russia Tsardom of Russia The Tsardom of Russia was the name of the centralized Russian state from Ivan IV's assumption of the title of Tsar in 1547 till Peter the Great's foundation of the Russian Empire in 1721.From 1550 to 1700, Russia grew 35,000 km2 a year...  Russian Empire Russian EmpireRussian Imperial Navy officer, navigator, explorer of the Russian Far East Russian Far East Russian Far East is a term that refers to the Russian part of the Far East, i.e., extreme east parts of Russia, between Lake Baikal in Eastern Siberia and the Pacific Ocean... and Alaska Alaska Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait... |
Fyodorov, a navigator, took part in the 1st Kamchatka expedition of Vitus Bering Vitus Bering Vitus Jonassen Bering Vitus Jonassen Bering Vitus Jonassen Bering (also, less correNavy]], a captain-komandor known among the Russian sailors as Ivan Ivanovich. He is noted for being the first European to discover Alaska and its Aleutian Islands... in 1725-30. In 1732 Fyodorov and geodesist Mikhail Gvozdev Mikhail Gvozdev Mikhail Spiridonovich Gvozdev was a Russian military geodesist and a commander of the expedition to northern Alaska in 1732, when Alaskan shore was for the first time sited by Russians.... aboard Sviatoi Gavriil (Bering's ship) sailed to Cape Dezhnyov, the easternmost point of Asia Asia Asia is the world's largest and most populous continent, located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres. It covers 8.7% of the Earth's total surface area and with approximately 3.879 billion people, it hosts 60% of the world's current human population... . From there they sailed east and soon discovered Alaska Alaska Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait... mainland near the Cape Prince of Wales Cape Prince of Wales Cape Prince of Wales is the westernmost point on the mainland of the Americas.Located on the Seward Peninsula of the U.S. state of Alaska near the city of Wales, Cape Prince of Wales is the terminus of the Continental Divide, marking the division between the Pacific and Arctic coasts, as well as... , the westernmost point of North America North America North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas... . They charted the north-western coast of Alaska. By doing this, Fyodorov and Gvozdev completed the discovery of the Bering Strait Bering Strait The Bering Strait , known to natives as Imakpik, is a sea strait between Cape Dezhnev, Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, Russia, the easternmost point of the Asian continent and Cape Prince of Wales, Alaska, USA, the westernmost point of the North American continent, with latitude of about 65°40'N,... , once started by Semyon Dezhnyov and Fedot Alekseyev Popov Fedot Alekseyev Popov Fedot Alekseyevich Popov , date of birth unknown, died between 1648 and 1654) was a Russian explorer who organized the first European expedition through the Bering Strait.He was normally known as Fedot Alekseyev. Only a few sources call him the son of Popov... and continued by Bering. Their expedition also discovered three previously unknown islands. |
 |
|
| Johan Hampus Furuhjelm Johan Hampus Furuhjelm Johan Hampus Furuhjelm, was a Finnish-Russian vice-admiral and explorer, commander of the Russian Baltic Fleet, Governor of the Russian Far East, Taganrog and Russian America.-Early years:... (1821–1909)  Russian Empire Russian Empire(born in Finland Finland Finland , officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country situated in the Fennoscandian region of Northern Europe. It is bordered by Sweden in the west, Norway in the north and Russia in the east, while Estonia lies to its south across the Gulf of Finland.Around 5.4 million people reside... , Swedish descent) Russian Imperial Navy officer, Vice-Admiral, Governor of the Russian Far East Russian Far East Russian Far East is a term that refers to the Russian part of the Far East, i.e., extreme east parts of Russia, between Lake Baikal in Eastern Siberia and the Pacific Ocean... , Taganrog Taganrog Taganrog is a seaport city in Rostov Oblast, Russia, located on the north shore of Taganrog Bay , several kilometers west of the mouth of the Don River. Population: -History of Taganrog:... and Russian America, explorer of Alaska Alaska Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait... (on photo with his wife Anna) |
In 1850 Furuhjelm became a commander of Novoarkhangelsk port (now Sitka, Alaska Alaska Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait... ) and in 1854 of Ayan port. In 1858-64 he was the Governor of Russian America. He improved relations with natives, once using the Columbus Christopher Columbus Christopher Columbus was an explorer, colonizer, and navigator, born in the Republic of Genoa, in northwestern Italy. Under the auspices of the Catholic Monarchs of Spain, he completed four voyages across the Atlantic Ocean that led to general European awareness of the American continents in the... -like trick with an eclipse of the moon to impress the Indians. In 1865-72 Furuhjelm served as military governor of Primorsky Krai Primorsky Krai Primorsky Krai , informally known as Primorye , is a federal subject of Russia . Primorsky means "maritime" in Russian, hence the region is sometimes referred to as Maritime Province or Maritime Territory. Its administrative center is in the city of Vladivostok... and chief of Russian seaports on Pacific, where he contributed a lot to development and exploration of the whole region. Mount Furuhelm Mount Furuhelm Mount Furuhelm is a 3,620 foot peak located on Baranof Island just east and adjacent to Peak 5390 in Alaska. It is located at .Mount Furuhelm was named for Johan Hampus Furuhjelm , who was governor of Russian America from 1859 to 1863.Mount Furuhelm actually has both an east and west peak less... in Alexander Archipelago Alexander Archipelago The Alexander Archipelago is a long archipelago, or group of islands, of North America off the southeastern coast of Alaska. It contains about 1,100 islands, which are the tops of the submerged coastal mountains that rise steeply from the Pacific Ocean. Deep channels and fjords separate the... , Furugelm Island Furugelm Island Furugelm Island is an island in the southwest part of Peter the Great Gulf in the Sea of Japan, 110 km southwest of Vladivostok. It belongs to Khasansky District of Primorsky Krai, Russia.- History :... in the Sea of Japan Sea of Japan The Sea of Japan is a marginal sea of the western Pacific Ocean, between the Asian mainland, the Japanese archipelago and Sakhalin. It is bordered by Japan, North Korea, Russia and South Korea. Like the Mediterranean Sea, it has almost no tides due to its nearly complete enclosure from the Pacific... , Furuhelm Street in Sitka (Alaska Alaska Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait... ) were named after Ivan Furuhjelm. Furugelm point and Furugelm island near Sakhalin Sakhalin Sakhalin or Saghalien, is a large island in the North Pacific, lying between 45°50' and 54°24' N.It is part of Russia, and is Russia's largest island, and is administered as part of Sakhalin Oblast... in the Sea of Japan Sea of Japan The Sea of Japan is a marginal sea of the western Pacific Ocean, between the Asian mainland, the Japanese archipelago and Sakhalin. It is bordered by Japan, North Korea, Russia and South Korea. Like the Mediterranean Sea, it has almost no tides due to its nearly complete enclosure from the Pacific... were named for Carl Furuhjelm, brother of Ivan Furuhjelm. |
 |
G
| Portrait | Person | Achievements | Image |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yury Gagarin (1934–1968)  Soviet Union Soviet UnionSoviet Air Force Soviet Air Force The Soviet Air Force, officially known in Russian as Военно-воздушные силы or Voenno-Vozdushnye Sily and often abbreviated VVS was the official designation of one of the air forces of the Soviet Union. The other was the Soviet Air Defence Forces... pilot, cosmonaut, the Hero of the Soviet Union Hero of the Soviet Union The title Hero of the Soviet Union was the highest distinction in the Soviet Union, awarded personally or collectively for heroic feats in service to the Soviet state and society.-Overview:... |
On 12 April 1961 Cosmonautics Day Cosmonautics Day is a holiday celebrated in Russia and some other former USSR countries on April 12. This holiday celebrates the first manned space flight made on April 12, 1961 by the 27-year old Soviet cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin. Gagarin circled the Earth for 1 hour and 48 minutes aboard the Vostok... , Gagarin became the first ever human to travel into space Space Space is the boundless, three-dimensional extent in which objects and events occur and have relative position and direction. Physical space is often conceived in three linear dimensions, although modern physicists usually consider it, with time, to be part of a boundless four-dimensional continuum... , launching to orbit aboard the Vostok 3KA-3 (Vostok 1 Vostok 1 Vostok 1 was the first spaceflight in the Vostok program and the first human spaceflight in history. The Vostok 3KA spacecraft was launched on April 12, 1961. The flight took Yuri Gagarin, a cosmonaut from the Soviet Union, into space. The flight marked the first time that a human entered outer... ). Gagarin town near the place of Gagarin's birth, Gagarin Gagarin, Armenia Gagarin is a town in the Gegharkunik Province of Armenia. The town was founded in 1955 and named after cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin.- References :* – World-Gazetteer.com... town in Armenia, Gagarin crater Gagarin (crater) Gagarin is a large lunar impact crater that is located in the southern hemisphere on the far side of the Moon. To the southwest is the crater Pavlov and to the northeast lies Keeler. Closer to the rim are the craters Levi-Civita to the southwest, and Beijerinck to the north-northeast. Isaev lies... on the far side of the Moon Moon The Moon is Earth's only known natural satellite,There are a number of near-Earth asteroids including 3753 Cruithne that are co-orbital with Earth: their orbits bring them close to Earth for periods of time but then alter in the long term . These are quasi-satellites and not true moons. For more... , asteroid 1772 Gagarin 1772 Gagarin 1772 Gagarin is a main-belt asteroid discovered on February 6, 1968 by Chernykh, L. at Nauchnyj.The asteroid is named after the Soviet cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin.- External links :*... , a scientific ship Kosmonaut Yuri Gagarin Kosmonaut Yuri Gagarin Kosmonavt Yuri Gagarin was a Soviet space control-monitoring ship that was devoted to detecting and receiving satellite communications. Named after cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin, she was completed in December 1971 to support the Soviet space program... , a vast number of settlements, streets, squares and other places in the Soviet Union Soviet Union The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991.... and Russia Russia Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects... , along with many other objects ranging from bars and clubs to Gagarin Cup Gagarin Cup The Gagarin Cup is the trophy presented to the winner of the Kontinental Hockey League playoffs, and is named after cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin, the first human in space... , are named in honor of Yury Gagarin. Cosmonautics Day Cosmonautics Day Cosmonautics Day is a holiday celebrated in Russia and some other former USSR countries on April 12. This holiday celebrates the first manned space flight made on April 12, 1961 by the 27-year old Soviet cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin. Gagarin circled the Earth for 1 hour and 48 minutes aboard the Vostok... aka Yuri's Night Yuri's Night Yuri's Night is an international celebration held on April 12 every year to commemorate space exploration milestones. The event is named for the first human to launch into space, Yuri Gagarin, who flew the Vostok 1 spaceship on April 12, 1961. In 2004, people celebrated Yuri's Night in 34... is a yearly held celebration of Gagarin's flight on 12 April. |
||
| Yakov Gakkel Yakov Gakkel Yakov Yakovlevich Gakkel was a Soviet oceanographer, doctor of geographical sciences , professor, director of the geography department of the Arctic and Antarctic Research Institute, son of a scientist Yakov Modestovich Gakkel.Yakov Gakkel participated in numerous Arctic expeditions, including... (1901–1965)  Russian Empire Russian Empire Soviet Union Soviet Unionoceanographer, Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... explorer |
Gakkel was a director of the geography department of the Arctic and Antarctic Research Institute Arctic and Antarctic Research Institute The Arctic and Antarctic Research Institute, or AARI is the oldest and largest Russian research institute in the field of comprehensive studies of Arctic and Antarctica... . He participated in numerous Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... expeditions, including the ones on the icebreakers Sibiryakov Icebreaker Sibiryakov The icebreaker Sibiryakov was a Soviet ship which was active in the Russian Arctic during the 1930s. She was built in 1909 in Glasgow and was originally the Newfoundland sealing steamer Bellaventure. After being purchased by Russia in 1916, she was renamed the Sibiryakov... in 1932 and Chelyuskin Chelyuskin steamship SS Chelyuskin was a Soviet steamship reinforced to navigate through polar ice that became ice-bound in Arctic waters during navigation along the Northern Maritime Route from Murmansk to Vladivostok... in 1934. He was the first to create a bathymetric map of the Arctic basin Arctic Ocean The Arctic Ocean, located in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Arctic north polar region, is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceanic divisions... . In 1966, the Gakkel Ridge Gakkel Ridge The Gakkel Ridge is a mid-oceanic ridge, a divergent tectonic plate boundary between the North American Plate and the Eurasian Plate. It is located in the Arctic Ocean between Greenland and Siberia, and has a length of about 1,800 kilometers... , a mid-oceanic ridge in the Arctic Ocean Arctic Ocean The Arctic Ocean, located in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Arctic north polar region, is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceanic divisions... , was named after Gakkel. |
 |
|
| Matvei Gedenschtrom Matvei Gedenschtrom Matvei Matveyevich Gedenschtrom was a Russian explorer of Northern Siberia, writer, and public servant.Matvei Gedenschtrom attended University of Tartu. He did not finish his studies and left his alma mater in favor of work at Tallinn customs. Soon, however, he was arrested in connection with a... (1780–1845)  Russian Empire Russian Empirepublic servant, writer, explorer of Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... and Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... |
Gedenschtrom was sent to serve in Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... for connection with a smuggling Smuggling Smuggling is the clandestine transportation of goods or persons, such as out of a building, into a prison, or across an international border, in violation of applicable laws or other regulations.There are various motivations to smuggle... affair at Tallinn Tallinn Tallinn is the capital and largest city of Estonia. It occupies an area of with a population of 414,940. It is situated on the northern coast of the country, on the banks of the Gulf of Finland, south of Helsinki, east of Stockholm and west of Saint Petersburg. Tallinn's Old Town is in the list... customs Customs Customs is an authority or agency in a country responsible for collecting and safeguarding customs duties and for controlling the flow of goods including animals, transports, personal effects and hazardous items in and out of a country... . In 1809-10 together with Yakov Sannikov Yakov Sannikov Yakov Sannikov was a Russian merchant and explorer of the New Siberian Islands.In 1800, Sannikov discovered and charted Stolbovoy Island, and in 1805 Faddeyevsky Island. In 1809-1810, he took part in the expedition led by Matvei Gedenschtrom. In 1810, Sannikov crossed the island of New Siberia... he led the cartographic expedition to the Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... shores of Yakutia. They explored and named the New Siberian Islands New Siberian Islands The New Siberian Islands are an archipelago, located to the North of the East Siberian coast between the Laptev Sea and the East Siberian Sea north of the Sakha Republic.... (earlier discovered by Yakov Permyakov Yakov Permyakov Yakov Permyakov was a Russian seafarer, explorer, merchant, and Cossack.In 1710, while sailing from the Lena River to the Kolyma River, Permyakov observed the silhouette of two unknown island groups in the sea... ). This expedition established a theory about the existence of the legendary Sannikov Land Sannikov Land Sannikov Land was a phantom island in the Arctic Ocean. Its supposed existence became something of a myth in 19th-century Russia.Yakov Sannikov and Matvei Gedenschtrom claimed to have seen it during their 1809-1810 cartographic expedition to the New Siberian Islands... somewhere northwest of the Kotelny Island. Gedenschtrom discovered the presence of Siberian polynya (patches of open water at the edge of the drifting ice and continental fast ice Fast ice Fast ice is sea ice that has frozen along coasts along the shoals, or to the sea floor over shallow parts of the continental shelf, and extends out from land into sea. In Antarctica, fast ice may also extend between grounded icebergs... ). He charted the coastline between the Yana and Kolyma River Kolyma River The Kolyma River is a river in northeastern Siberia, whose basin covers parts of the Sakha Republic, Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, and Magadan Oblast of Russia. Itrises in the mountains north of Okhotsk and Magadan, in the area of and... s. He made numerous trips across Yakutia and the areas east of Lake Baikal Lake Baikal Lake Baikal is the world's oldest at 30 million years old and deepest lake with an average depth of 744.4 metres.Located in the south of the Russian region of Siberia, between Irkutsk Oblast to the northwest and the Buryat Republic to the southeast, it is the most voluminous freshwater lake in the... . |
 |
|
 |
Johann Gottlieb Georgi Johann Gottlieb Georgi Johann Gottlieb Georgi was a German geographer and chemist.Georgi was professor of chemistry at St Petersburg. He accompanied both Johann Peter Falck and Peter Simon Pallas on their respective journeys through Siberia. Gergi was particularly interested in Lake Baikal... (1729–1802)  Kingdom of Prussia Kingdom of Prussia Russian Empire Russian Empiregeographer, naturalist, ethnographer, physician, chemist, explorer of European Russia European Russia European Russia refers to the western areas of Russia that lie within Europe, comprising roughly 3,960,000 square kilometres , larger in area than India, and spanning across 40% of Europe. Its eastern border is defined by the Ural Mountains and in the south it is defined by the border with... and Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... |
Georgi accompanied both Johann Peter Falck and Peter Simon Pallas Peter Simon Pallas Peter Simon Pallas was a German zoologist and botanist who worked in Russia.- Life and work :Pallas was born in Berlin, the son of Professor of Surgery Simon Pallas. He studied with private tutors and took an interest in natural history, later attending the University of Halle and the University... on their respective journeys through European Russia European Russia European Russia refers to the western areas of Russia that lie within Europe, comprising roughly 3,960,000 square kilometres , larger in area than India, and spanning across 40% of Europe. Its eastern border is defined by the Ural Mountains and in the south it is defined by the border with... and Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... . In 1772 he mapped Lake Baikal Lake Baikal Lake Baikal is the world's oldest at 30 million years old and deepest lake with an average depth of 744.4 metres.Located in the south of the Russian region of Siberia, between Irkutsk Oblast to the northwest and the Buryat Republic to the southeast, it is the most voluminous freshwater lake in the... and was the first to describe omul Omul The omul, Coregonus migratorius, also known as Baikal omul , is a whitefish species of the salmon family endemic to Lake Baikal in Siberia, Russia. It is considered a delicacy and is the object of one of the largest commercial fisheries on Lake Baikal... fish, as well as other fauna and flora of Baikal region. He amassed a large collection of minerals and in 1776-80 published the first comprehensive work on ethnography of indigenous peoples of Russia. Georgia Dahlia Dahlia is a genus of bushy, tuberous, perennial plants native to Mexico, Central America, and Colombia. There are at least 36 species of dahlia, some like D. imperialis up to 10 metres tall. Dahlia hybrids are commonly grown as garden plants... flower was named after Georgi. |
|
 |
Johann Georg Gmelin Johann Georg Gmelin Johann Georg Gmelin was a German naturalist, botanist and geographer.- Early life and education :Gmelin was born in Tübingen, the son of an professor at the University of Tübingen. He was a gifted child and begun attending university lectures at the age of 14. In 1727, he graduated with a medical... (1709–1755)  Holy Roman Empire Holy Roman Empire Russian Empire Russian Empirenaturalist, botanist, geographer, explorer of European Russia European Russia European Russia refers to the western areas of Russia that lie within Europe, comprising roughly 3,960,000 square kilometres , larger in area than India, and spanning across 40% of Europe. Its eastern border is defined by the Ural Mountains and in the south it is defined by the border with... and Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... |
In 1733-43 Gmelin participated in the Great Northern Expedition Great Northern Expedition The Great Northern Expedition or Second Kamchatka expedition was one of the largest organised exploration enterprises in history, resulting in mapping of the most of the Arctic coast of Siberia and some parts of the North America coastline, greatly reducing the "white areas" on the maps... and made a number of journeys through Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... , covering more than 34,000 km in the total. He discovered that the Caspian Sea Caspian Sea The Caspian Sea is the largest enclosed body of water on Earth by area, variously classed as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. The sea has a surface area of and a volume of... lies below the ocean level. He published two major works about his travels in Russia and the flora of Siberia, and described more than 500 previously unknown plants. The settlement of Gmelinka, Gmelina Gmelina Gmelina is a genus of plant in family Lamiaceae. It was named in honour of botanist Johann Georg Gmelin.Species include:* Gmelina arborea* Gmelina asiatica* Gmelina fasciculiflora - Northern White Beech, Australia... plant genus, Larix gmelinii tree and other plants are named after Gmelin. |
 |
 |
Vasily Golovnin Vasily Golovnin Vasily Mikhailovich Golovnin .-Early life and career:Vasily Mikhailovich Golovnin was born in April 1776, in the village of Gulyniki in Ryazan Oblast, on his father's country estate. Both his father and grandfather had served in the Russian military as officers in the elite Preobrazhensky... (1776–1831)  Russian Empire Russian EmpireRussian Imperial Navy officer, Vice Admiral Vice Admiral Vice admiral is a senior naval rank of a three-star flag officer, which is equivalent to lieutenant general in the other uniformed services. A vice admiral is typically senior to a rear admiral and junior to an admiral... , circumnavigator, explorer of the Far East Far East The Far East is an English term mostly describing East Asia and Southeast Asia, with South Asia sometimes also included for economic and cultural reasons.The term came into use in European geopolitical discourse in the 19th century,... |
He made two circumnavigation Circumnavigation Circumnavigation – literally, "navigation of a circumference" – refers to travelling all the way around an island, a continent, or the entire planet Earth.- Global circumnavigation :... s on the sloop Diana (1807–09) and the frigate Kamchatka Russian frigate Kamchatka At least two frigates of the Imperial Russian Navy have been named Kamchatka* Russian sloop-of-war Kamchatka circumnavigated the globe between 1817 and 1819 under Captain Vasily Golovnin.... (1817–19). In 1811 Golovnin described and mapped part of the Kuril Islands Kuril Islands The Kuril Islands , in Russia's Sakhalin Oblast region, form a volcanic archipelago that stretches approximately northeast from Hokkaidō, Japan, to Kamchatka, Russia, separating the Sea of Okhotsk from the North Pacific Ocean. There are 56 islands and many more minor rocks. It consists of Greater... . At that time he was taken prisoner for two years by the Japanese. He described in books his years in captivity, life in Japan Japan Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south... , and his voyages around the world. Later he was athe General Quartermaster Quartermaster Quartermaster refers to two different military occupations depending on if the assigned unit is land based or naval.In land armies, especially US units, it is a term referring to either an individual soldier or a unit who specializes in distributing supplies and provisions to troops. The senior... of Russian Navy and supervised the building of the first Russian steamships. He tutored Fyodor Litke Fyodor Petrovich Litke Count Fyodor Petrovich Litke , born Friedrich Benjamin Lütke, was a Russian navigator, geographer, and Arctic explorer. He became a count in 1866, and an admiral in 1855. He was a Corresponding Member , Honorable Member , and President of the Russian Academy of Science in St.Petersburg... , Ferdinand von Wrangel Ferdinand von Wrangel Baron Ferdinand Friedrich Georg Ludwig von Wrangel – May 25 , 1870) was a Russian explorer and seaman, Honorable Member of the Saint Petersburg Academy of Sciences, a founder of the Russian Geographic Society... and other famous seafarers. The village of Golovin, Alaska Golovin, Alaska Golovin is a city in Nome Census Area, Alaska, United States. At the 2000 census the population was 144.-Geography:Golovin is located at .... , a cape in the west of North America North America North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas... , a bay in the Bering Sea Bering Sea The Bering Sea is a marginal sea of the Pacific Ocean. It comprises a deep water basin, which then rises through a narrow slope into the shallower water above the continental shelves.... , a strait between two of the Kuril Islands Kuril Islands The Kuril Islands , in Russia's Sakhalin Oblast region, form a volcanic archipelago that stretches approximately northeast from Hokkaidō, Japan, to Kamchatka, Russia, separating the Sea of Okhotsk from the North Pacific Ocean. There are 56 islands and many more minor rocks. It consists of Greater... , a volcano on Kunashir Island Kunashir Island Kunashir Island , possibly meaning Black Island or Grass Island in Ainu, is the southernmost island of the Kuril Islands, which are controlled by Russia and claimed by Japan .... , mountains on Novaya Zemlya Novaya Zemlya Novaya Zemlya , also known in Dutch as Nova Zembla and in Norwegian as , is an archipelago in the Arctic Ocean in the north of Russia and the extreme northeast of Europe, the easternmost point of Europe lying at Cape Flissingsky on the northern island... and on Franz Josef Land Franz Josef Land Franz Josef Land, Franz Joseph Land, or Francis Joseph's Land is an archipelago located in the far north of Russia. It is found in the Arctic Ocean north of Novaya Zemlya and east of Svalbard, and is administered by Arkhangelsk Oblast. Franz Josef Land consists of 191 ice-covered islands with a... are named after Golovnin. He is a character in Patrick O'Brian's Patrick O'Brian Patrick O'Brian, CBE , born Richard Patrick Russ, was an English novelist and translator, best known for his Aubrey–Maturin series of novels set in the Royal Navy during the Napoleonic Wars and centred on the friendship of English Naval Captain Jack Aubrey and the Irish–Catalan physician Stephen... The Mauritius Command The Mauritius Command The Mauritius Command is a historical naval novel by British author Patrick O'Brian. It is fourth in the Aubrey-Maturin series of stories that follow the partnership of Captain Jack Aubrey and the naval surgeon Stephen Maturin. It retells in fictional form the real campaign carried out by the Royal... . |
|
| Bronislav Gromchevsky Bronislav Gromchevsky Bronislav Grombchevsky, , , was an ethnic Polish officer in the Imperial Russian Army and an explorer famous for his participation in the The Great Game.... (1855–1926)  Russian Empire Russian Empire Soviet Union Soviet Union(Polish descent) Imperial Russian Army Imperial Russian Army The Imperial Russian Army was the land armed force of the Russian Empire, active from around 1721 to the Russian Revolution of 1917. In the early 1850s, the Russian army consisted of around 938,731 regular soldiers and 245,850 irregulars . Until the time of military reform of Dmitry Milyutin in... officer, explorer of Central Asia Central Asia Central Asia is a core region of the Asian continent from the Caspian Sea in the west, China in the east, Afghanistan in the south, and Russia in the north... |
Gromchevsky participated in the Russian conquest of Central Asia Central Asia Central Asia is a core region of the Asian continent from the Caspian Sea in the west, China in the east, Afghanistan in the south, and Russia in the north... and then led reconnaissance expeditions in the surrounding regions. In 1885-86 he explored Kashgar Kashgar Kashgar or Kashi is an oasis city with approximately 350,000 residents in the western part of the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region of the People's Republic of China. Kashgar is the administrative centre of Kashgar Prefecture which has an area of 162,000 km² and a population of approximately... and Tian Shan Tian Shan The Tian Shan , also spelled Tien Shan, is a large mountain system located in Central Asia. The highest peak in the Tian Shan is Victory Peak , .... . In 1888-89 he explored the Pamirs, Kafiristan Kafiristan Kāfiristān or Kāfirstān was a historic name of Nurestan , a province in the Hindu Kush region of Afghanistan and Pakistan, prior to 1896. This historic region lies on, and mainly comprises, basins of the rivers Alingar, Pech , Landai Sin, and Kunar, and the intervening mountain ranges... , Kashmir Kashmir Kashmir is the northwestern region of the Indian subcontinent. Until the mid-19th century, the term Kashmir geographically denoted only the valley between the Great Himalayas and the Pir Panjal mountain range... and northwestern Tibet Tibet Tibet is a plateau region in Asia, north-east of the Himalayas. It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people as well as some other ethnic groups such as Monpas, Qiang, and Lhobas, and is now also inhabited by considerable numbers of Han and Hui people... and went as far as into the British India. He is regarded as the Russian counterpart to the British military-explorer Francis Younghusband Francis Younghusband Lieutenant Colonel Sir Francis Edward Younghusband, KCSI, KCIE was a British Army officer, explorer, and spiritual writer... . The two Great Game The Great Game The Great Game or Tournament of Shadows in Russia, were terms for the strategic rivalry and conflict between the British Empire and the Russian Empire for supremacy in Central Asia. The classic Great Game period is generally regarded as running approximately from the Russo-Persian Treaty of 1813... rivals famously met in 1889 when they were exploring the Hunza Valley Hunza Valley The Hunza Valley is a mountainous valley in the Gilgit-Baltistan region of Pakistan. The Hunza valley is situated to the north of the Hunza River, at an elevation of around . The territory of Hunza is about... for their respective governments. In 1900 Gromchevsky explored North Eastern China China Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture... . |
||
| Grigory Grumm-Grzhimaylo Grigory Grumm-Grzhimaylo Grigory Yefimovich Grumm-Grzhimaylo was a Russian entomologist, best known for his expeditions to Central Asia , West Mongolia and Tuva, and the Russian Far East.-Life and work:... (1860–1936)  Russian Empire Russian Empire Soviet Union Soviet Unionzoologist, entomologist, ethnographer, geographer, explorer of Central Asia Central Asia Central Asia is a core region of the Asian continent from the Caspian Sea in the west, China in the east, Afghanistan in the south, and Russia in the north... |
In 1884 Grumm-Grzhimaylo started his first Pamir expedition on which he explored the Alai Mountains and reached as far as Lake Karakul. In 1885-87 he extensively traveled through Central Asia Central Asia Central Asia is a core region of the Asian continent from the Caspian Sea in the west, China in the east, Afghanistan in the south, and Russia in the north... , reaching the Great Silk Route Silk Road The Silk Road or Silk Route refers to a historical network of interlinking trade routes across the Afro-Eurasian landmass that connected East, South, and Western Asia with the Mediterranean and European world, as well as parts of North and East Africa... , Lake Chatyr-Kul Chatyr-Kul Chatyr-Kul is an endorheic alpine lake in the Tian Shan mountains in At-Bashi District of Naryn Province, Kyrgyzstan; it lies in the lower part of Chatyr-Kul Depression near the Torugart Pass border crossing into China. The name of the lake means “Celestial Lake” in Kyrgyz... and Kashgar Kashgar Kashgar or Kashi is an oasis city with approximately 350,000 residents in the western part of the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region of the People's Republic of China. Kashgar is the administrative centre of Kashgar Prefecture which has an area of 162,000 km² and a population of approximately... . In this expedition he collected tens of thousands of insects and other specimens. In 1889-90 he discovered the Ayding Lake, the second lowest land point Table of elevation extremes by country The following sortable table lists land surface elevation extremes by country.Elevation is the vertical distance above the reference geoid, an equipotential gravitational surface model of the Earth's sea level.-Table:-National elevation ranges:... on Earth, at 130 m below the sea level. He obtained two Przewalski's Horse Przewalski's Horse Przewalski's Horse or Dzungarian Horse, is a rare and endangered subspecies of wild horse native to the steppes of central Asia, specifically China and Mongolia.At one time extinct in the wild, it has been reintroduced to its native habitat in Mongolia at the Khustain Nuruu... s and more than 1000 bird specimens during 8600 km long travel. In 1903 he explored Mongolia Mongolia Mongolia is a landlocked country in East and Central Asia. It is bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south, east and west. Although Mongolia does not share a border with Kazakhstan, its western-most point is only from Kazakhstan's eastern tip. Ulan Bator, the capital and largest... and Tuva Tuva The Tyva Republic , or Tuva , is a federal subject of Russia . It lies in the geographical center of Asia, in southern Siberia. The republic borders with the Altai Republic, the Republic of Khakassia, Krasnoyarsk Krai, Irkutsk Oblast, and the Republic of Buryatia in Russia and with Mongolia to the... and later traveled in the Far East Far East The Far East is an English term mostly describing East Asia and Southeast Asia, with South Asia sometimes also included for economic and cultural reasons.The term came into use in European geopolitical discourse in the 19th century,... . A pass in Sikhote-Alin Sikhote-Alin The Sikhote-Alin is a mountain range in Primorsky and Khabarovsk Krais, Russia, extending about 900 km to the northeast of the Russian Pacific seaport of Vladivostok... Mountains, a glacier he discovered in the Pamirs and a glacier in Bogdo Ula Bogd Khan Uul The Bogd Khan Mountain is a mountain in Mongolia that overlooks the nation's capital, Ulaanbaatar, from a height of 3000 feet above and to the south of the city.- World Heritage Status :... are named after Grumm-Grzhimaylo. |
||
| Mikhail Gvozdev Mikhail Gvozdev Mikhail Spiridonovich Gvozdev was a Russian military geodesist and a commander of the expedition to northern Alaska in 1732, when Alaskan shore was for the first time sited by Russians.... (1700-04 – after 1759) Tsardom of Russia Tsardom of Russia The Tsardom of Russia was the name of the centralized Russian state from Ivan IV's assumption of the title of Tsar in 1547 till Peter the Great's foundation of the Russian Empire in 1721.From 1550 to 1700, Russia grew 35,000 km2 a year...  Russian Empire Russian Empiremilitary geodesist, explorer of the Far East Far East The Far East is an English term mostly describing East Asia and Southeast Asia, with South Asia sometimes also included for economic and cultural reasons.The term came into use in European geopolitical discourse in the 19th century,... , co-discoverer of Alaska Alaska Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait... |
Gvozdev took part in the 1st Kamchatka expedition of Vitus Bering Vitus Bering Vitus Jonassen Bering Vitus Jonassen Bering Vitus Jonassen Bering (also, less correNavy]], a captain-komandor known among the Russian sailors as Ivan Ivanovich. He is noted for being the first European to discover Alaska and its Aleutian Islands... . In 1732 together with Ivan Fedorov aboard Sviatoi Gavriil (Bering's ship) they reached Dezhnev Cape (the easternmost point of Asia Asia Asia is the world's largest and most populous continent, located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres. It covers 8.7% of the Earth's total surface area and with approximately 3.879 billion people, it hosts 60% of the world's current human population... ), sailed east and soon discovered Alaska Alaska Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait... mainland near the Cape Prince of Wales Cape Prince of Wales Cape Prince of Wales is the westernmost point on the mainland of the Americas.Located on the Seward Peninsula of the U.S. state of Alaska near the city of Wales, Cape Prince of Wales is the terminus of the Continental Divide, marking the division between the Pacific and Arctic coasts, as well as... (the westernmost point of North America North America North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas... ). They charted the part of Alaska coast and discovered three new islands. Thus they completed the discovery of the Bering Strait Bering Strait The Bering Strait , known to natives as Imakpik, is a sea strait between Cape Dezhnev, Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, Russia, the easternmost point of the Asian continent and Cape Prince of Wales, Alaska, USA, the westernmost point of the North American continent, with latitude of about 65°40'N,... , once started by Semyon Dezhnyov and Fedot Alekseyev Popov Fedot Alekseyev Popov Fedot Alekseyevich Popov , date of birth unknown, died between 1648 and 1654) was a Russian explorer who organized the first European expedition through the Bering Strait.He was normally known as Fedot Alekseyev. Only a few sources call him the son of Popov... and continued by Bering. Subsequently in 1741-42 Gvozdev participated in the expedition led by Alexey Shelting and mapped most of the western and southern shores of the Okhotsk Sea, and the eastern shore of Sakhalin Sakhalin Sakhalin or Saghalien, is a large island in the North Pacific, lying between 45°50' and 54°24' N.It is part of Russia, and is Russia's largest island, and is administered as part of Sakhalin Oblast... . A cape on Sakhalin Sakhalin Sakhalin or Saghalien, is a large island in the North Pacific, lying between 45°50' and 54°24' N.It is part of Russia, and is Russia's largest island, and is administered as part of Sakhalin Oblast... island is named after Gvozdev. |
 |
H
| Portrait | Person | Achievements | Image |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ludwig von Hagemeister (1780–1833)  Russian Empire Russian Empire(born in Latvia Latvia Latvia , officially the Republic of Latvia , is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by Estonia , to the south by Lithuania , to the east by the Russian Federation , to the southeast by Belarus and shares maritime borders to the west with Sweden... , Baltic German Baltic German The Baltic Germans were mostly ethnically German inhabitants of the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea, which today form the countries of Estonia and Latvia. The Baltic German population never made up more than 10% of the total. They formed the social, commercial, political and cultural élite in... descent) Russian Imperial Navy captain, governor of Russian America, circumnavigator, explorer of the Pacific and Alaska Alaska Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait... |
After taking part in Napoleonic Wars Napoleonic Wars The Napoleonic Wars were a series of wars declared against Napoleon's French Empire by opposing coalitions that ran from 1803 to 1815. As a continuation of the wars sparked by the French Revolution of 1789, they revolutionised European armies and played out on an unprecedented scale, mainly due to... , at which point his abilities were praised by admiral Nelson, in 1806-07 Hagemeister journeyed to Russian America on his ship Neva. In 1808-09, he explored the shores of Alaska Alaska Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait... and waters of the North Pacific. In 1812-15 he supervised the building of the first tall ship Tall ship A tall ship is a large, traditionally-rigged sailing vessel. Popular modern tall ship rigs include topsail schooners, brigantines, brigs and barques. "Tall Ship" can also be defined more specifically by an organization, such as for a race or festival.... s to sail on Lake Baikal Lake Baikal Lake Baikal is the world's oldest at 30 million years old and deepest lake with an average depth of 744.4 metres.Located in the south of the Russian region of Siberia, between Irkutsk Oblast to the northwest and the Buryat Republic to the southeast, it is the most voluminous freshwater lake in the... . In 1816-19 he was in charge of Kutuzov, on which he made his first full circumnavigation Circumnavigation Circumnavigation – literally, "navigation of a circumference" – refers to travelling all the way around an island, a continent, or the entire planet Earth.- Global circumnavigation :... of the globe, with a stop in Alaska Alaska Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait... , where he was a governor of Russian America in 1818-19. In 1828-29, Hagemeister made his second circumnavigation aboard Krotky. Among other islands he surveyed the Menshikov Atoll (Kwajalein) Kwajalein Kwajalein Atoll , is part of the Republic of the Marshall Islands . The southernmost and largest island in the atoll is named Kwajalein Island. English-speaking residents of the U.S... in the Marshall Islands Marshall Islands The Republic of the Marshall Islands , , is a Micronesian nation of atolls and islands in the middle of the Pacific Ocean, just west of the International Date Line and just north of the Equator. As of July 2011 the population was 67,182... group. Hagemeister Island Hagemeister Island Hagemeister Island is an island in the U.S. state of Alaska, located on the north shore of Bristol Bay at the entrance to Togiak Bay.The island is long, has a land area of , and its highest point is... and a strait in Alaska Alaska Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait... , a mountain in Alexander Archipelago Alexander Archipelago The Alexander Archipelago is a long archipelago, or group of islands, of North America off the southeastern coast of Alaska. It contains about 1,100 islands, which are the tops of the submerged coastal mountains that rise steeply from the Pacific Ocean. Deep channels and fjords separate the... and an atoll group in the Pacific were named after Hagemeister. |
I
| Portrait | Person | Achievements | Image |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kurbat Ivanov Kurbat Ivanov Kurbat Afanasyevich Ivanov was among the greatest Cossack explorers of Siberia. He was the first Russian to discover Lake Baikal, and to create the first map of the Russian Far East... (?–1666) Tsardom of Russia Tsardom of Russia The Tsardom of Russia was the name of the centralized Russian state from Ivan IV's assumption of the title of Tsar in 1547 till Peter the Great's foundation of the Russian Empire in 1721.From 1550 to 1700, Russia grew 35,000 km2 a year... Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... n Cossack Cossack Cossacks are a group of predominantly East Slavic people who originally were members of democratic, semi-military communities in what is today Ukraine and Southern Russia inhabiting sparsely populated areas and islands in the lower Dnieper and Don basins and who played an important role in the... voevoda, explorer of East Siberia and the Russian Far East Russian Far East Russian Far East is a term that refers to the Russian part of the Far East, i.e., extreme east parts of Russia, between Lake Baikal in Eastern Siberia and the Pacific Ocean... |
Initially Kurbat Ivanov was a Yeniseyan Cossack Cossack Cossacks are a group of predominantly East Slavic people who originally were members of democratic, semi-military communities in what is today Ukraine and Southern Russia inhabiting sparsely populated areas and islands in the lower Dnieper and Don basins and who played an important role in the... . In 1642, on the basis of explorations made by Ivan Moskvitin Ivan Moskvitin Ivan Yuryevich Moskvitin was a Russian explorer, presumably a native of Moscow, who led a Russian reconnaissance party to the Pacific Ocean, becoming the first Russian to reach the Sea of Okhotsk.... , he made the earliest known map of the Russian Far East Russian Far East Russian Far East is a term that refers to the Russian part of the Far East, i.e., extreme east parts of Russia, between Lake Baikal in Eastern Siberia and the Pacific Ocean... . In 1643 With a group of Cossacks he sailed up Lena River Lena River The Lena is the easternmost of the three great Siberian rivers that flow into the Arctic Ocean . It is the 11th longest river in the world and has the 9th largest watershed... from Verkholensky ostrog Ostrog (fortress) Ostrog was a Russian term for a small fort, typically wooden and often non-permanently manned. Ostrogs were encircled by 4-6 metres high palisade walls made from sharpened trunks. The name derives from the Russian word строгать , "to shave the wood". Ostrogs were smaller and exclusively military... , having decided to check the rumors of large body of water to the south. They crossed Baikal Mountains Baikal Mountains thumb|right|300px|The mountains and lake in the summer, as seen from [[Bolshiye Koty]] on the southwest shoreThe Baikal Mountains or Baikal Range rise steeply over the northwestern shore of Lake Baikal in southern Siberia, Russia... by foot, descended down the Sarma River Sarma River Sarma is a river in Irkutsk Oblast, Russia. It runs from the Baikal Range into the Small Sea Strait of Lake Baikal.The valley and estuary of Sarma is the source of the strongest of Baikal winds, the Sarma wind. Its speed may exceed 40 meters per second.... and discovered Lake Baikal Lake Baikal Lake Baikal is the world's oldest at 30 million years old and deepest lake with an average depth of 744.4 metres.Located in the south of the Russian region of Siberia, between Irkutsk Oblast to the northwest and the Buryat Republic to the southeast, it is the most voluminous freshwater lake in the... and visited its Olkhon Island. Ivanov made the first chart and description of Baikal Baikal Baykal commonly refers to Lake Baikal in southern Siberia, Russia.Baykal or Baikal may also refer to:-Russia:*Baykal, Irkutsk Oblast, an urban-type settlement*Baykal, Aurgazinsky District, Republic of Bashkortostan, a village... . In 1659-65 Ivanov was the next head of Anadyrsk Anadyrsk thumb|Anadyrsk was on the east-west part of the Anadyr River at the point where it swings northAnadyrsk was an important Russian ostrog in far northeastern Siberia from 1649 to 1764... y ostrog after Semyon Dezhnyov. In 1660 he sailed from Anadyr Bay to Cape Dezhnyov. He is credited with creation of the early map of Chukotka Chukchi Peninsula The Chukchi Peninsula, Chukotka Peninsula or Chukotski Peninsula , at about 66° N 172° W, is the northeastern extremity of Asia. Its eastern end is at Cape Dezhnev near the village of Uelen. It is bordered by the Chukchi Sea to the north, the Bering Sea to the south, and the Bering Strait to the... and Bering Strait Bering Strait The Bering Strait , known to natives as Imakpik, is a sea strait between Cape Dezhnev, Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, Russia, the easternmost point of the Asian continent and Cape Prince of Wales, Alaska, USA, the westernmost point of the North American continent, with latitude of about 65°40'N,... , which was the first to show on paper (very schematically) the yet undiscovered Wrangel Island Wrangel Island Wrangel Island is an island in the Arctic Ocean, between the Chukchi Sea and East Siberian Sea. Wrangel Island lies astride the 180° meridian. The International Date Line is displaced eastwards at this latitude to avoid the island as well as the Chukchi Peninsula on the Russian mainland... , both Diomede Islands Diomede Islands The Diomede Islands , also known in Russia as Gvozdev Islands , consist of two rocky, tuya-like islands:* The U.S. island of Little Diomede or, in its native language, Ignaluk , and* The Russian island of Big Diomede , also known as Imaqliq,... and Alaska Alaska Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait... . |
 |
|
| Gerasim Izmailov Gerasim Izmailov Gerasim Grigoryevich Izmaylov was a Russian navigator involved in the Russian colonization of the Americas and in the establishment of the colonies of Russian America in Alaska. He was responsible for the first detailed maps of the Aleutian Islands.... (c. 1745 – after 1795)  Russian Empire Russian EmpireRussian Imperial Navy officer, explorer of Alaska Alaska Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait... |
In 1771 Izmailov was caught up in the Benevsky mutiny while serving on Kamchatka. After an attempt to break away from the mutineers he was marooned on Simushir Simushir Simushir is an uninhabited volcanic island near the center of the Kuril Islands chain in the Sea of Okhotsk in the northwest Pacific Ocean. Its name is derived from the Ainu language for “large island”.-Geology:... , an uninhabited isle in the Kurils. For a year he lived as Robinson Robinson Crusoe Robinson Crusoe is a novel by Daniel Defoe that was first published in 1719. Epistolary, confessional, and didactic in form, the book is a fictional autobiography of the title character—a castaway who spends 28 years on a remote tropical island near Trinidad, encountering cannibals, captives, and... there before being rescued, tried on charges of mutiny and cleared. Starting in 1775 he created the first detailed map of the Aleutian Islands. In 1778 he met with Captain James Cook James Cook Captain James Cook, FRS, RN was a British explorer, navigator and cartographer who ultimately rose to the rank of captain in the Royal Navy... in Unalaska. In 1783-85 Izmaylov and Grigory Shelikhov Grigory Shelikhov Grigory Ivanovich Shelekhov Grigory Ivanovich Shelekhov Grigory Ivanovich Shelekhov (Григорий Иванович Шелехов in Russian; (1747–July 20, 1795 (July 31, 1795 N.S.)) was a Russian seafarer and merchant born in Rylsk.... founded the first permanent Russian settlement in North America North America North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas... on Kodiak Island Kodiak Island Kodiak Island is a large island on the south coast of the U.S. state of Alaska, separated from the Alaska mainland by the Shelikof Strait. The largest island in the Kodiak Archipelago, Kodiak Island is the second largest island in the United States and the 80th largest island in the world, with an... . In 1789 Izmaylov became the first to explore and map the Kenai Peninsula Kenai Peninsula The Kenai Peninsula is a large peninsula jutting from the southern coast of Alaska in the United States. The name Kenai is probably derived from Kenayskaya, the Russian name for Cook Inlet, which borders the peninsula to the west.-Geography:... . Later he helped Alexander Baranov to fight off the Tlingit natives and saved a lost crew of a Russian ship from Saint Paul Island Saint Paul Island, Alaska Saint Paul Island is the largest of the Pribilof Islands, a group of five Alaskan volcanic islands located in the Bering Sea between the United States and Russia. The city of St. Paul is the only residential area on the island. The two nearest islands to Saint Paul Island are Otter Island to the... . |
J
| Portrait | Person | Achievements | Image |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wilhelm Junker Wilhelm Junker Wilhelm Junker was a Russian explorer of Africa. He was of German descent.He was born in Moscow. He studied medicine at Dorpat, Göttingen, Berlin and Prague, but did not practise for long... (1840–1892)  Russian Empire Russian Empire(German descent) physician, etnographer, explorer of Africa Africa Africa is the world's second largest and second most populous continent, after Asia. At about 30.2 million km² including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of the Earth's total surface area and 20.4% of the total land area... |
Born in a rich family of Moscow Moscow Moscow is the capital, the most populous city, and the most populous federal subject of Russia. The city is a major political, economic, cultural, scientific, religious, financial, educational, and transportation centre of Russia and the continent... banker, Junker journeyed to Iceland Iceland Iceland , described as the Republic of Iceland, is a Nordic and European island country in the North Atlantic Ocean, on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. Iceland also refers to the main island of the country, which contains almost all the population and almost all the land area. The country has a population... , Tunis Tunis Tunis is the capital of both the Tunisian Republic and the Tunis Governorate. It is Tunisia's largest city, with a population of 728,453 as of 2004; the greater metropolitan area holds some 2,412,500 inhabitants.... and Lower Egypt Lower Egypt Lower Egypt is the northern-most section of Egypt. It refers to the fertile Nile Delta region, which stretches from the area between El-Aiyat and Zawyet Dahshur, south of modern-day Cairo, and the Mediterranean Sea.... for his own money. Then he carried out a major exploration of Eastern and Equatorial Africa Equatorial Africa Equatorial Africa is an ambiguous term that is sometimes used to refer to tropical Africa, or the region of Sub-Saharan Africa traversed by the equator.... in 1875-86, with Khartoum Khartoum Khartoum is the capital and largest city of Sudan and of Khartoum State. It is located at the confluence of the White Nile flowing north from Lake Victoria, and the Blue Nile flowing west from Ethiopia. The location where the two Niles meet is known as "al-Mogran"... and then Lado as bases for his expeditions. He researched African peoples, including Azande Azande The Azande are a tribe of north Central Africa. Their number is estimated by various sources at between 1 and 4 million.... from Niam-Niam, and collected plant and animal specimens. He explored the Nile Nile The Nile is a major north-flowing river in North Africa, generally regarded as the longest river in the world. It is long. It runs through the ten countries of Sudan, South Sudan, Burundi, Rwanda, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Tanzania, Kenya, Ethiopia, Uganda and Egypt.The Nile has two major... -Congo Congo River The Congo River is a river in Africa, and is the deepest river in the world, with measured depths in excess of . It is the second largest river in the world by volume of water discharged, though it has only one-fifth the volume of the world's largest river, the Amazon... watershed, where he established the identity of the Uele Uele River The Uele River, also spelled Welle River, is a river in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It originates in the mountains near Lake Albert and flows west for about to join the Mbomou River at Yakoma.... and Ubangi rivers. The Mahdist rising prevented his return to Europe through the Sudan Sudan Sudan , officially the Republic of the Sudan , is a country in North Africa, sometimes considered part of the Middle East politically. It is bordered by Egypt to the north, the Red Sea to the northeast, Eritrea and Ethiopia to the east, South Sudan to the south, the Central African Republic to the... , and in 1884-86 he went south, traveled through Uganda Uganda Uganda , officially the Republic of Uganda, is a landlocked country in East Africa. Uganda is also known as the "Pearl of Africa". It is bordered on the east by Kenya, on the north by South Sudan, on the west by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, on the southwest by Rwanda, and on the south by... and Tabora Tabora Tabora is the capital city of Tanzania's Tabora Region with a population of 127,880 . Tabora region is one of the largest geographical regions of Tanzania.- History :... , reached Zanzibar Zanzibar Zanzibar ,Persian: زنگبار, from suffix bār: "coast" and Zangi: "bruin" ; is a semi-autonomous part of Tanzania, in East Africa. It comprises the Zanzibar Archipelago in the Indian Ocean, off the coast of the mainland, and consists of numerous small islands and two large ones: Unguja , and Pemba... and finally returned to St. Petersburg. |
K
| Portrait | Person | Achievements | Image |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
Johann Karl Ehrenfried Kegel Johann Karl Ehrenfried Kegel Johann Karl Ehrenfried Kegel was a German agronomist and explorer of the Kamchatka Peninsula.Kegel was born in Rammelburg and studied in Copenhagen... (1784–1863)  Holy Roman Empire Holy Roman Empire Russian Empire Russian Empireagronomist Agronomist An agronomist is a scientist who specializes in agronomy, which is the science of utilizing plants for food, fuel, feed, and fiber. An agronomist is an expert in agricultural and allied sciences, with the exception veterinary sciences.Agronomists deal with interactions between plants, soils, and... , explorer of Kamchatka |
1841 Kegel was sent to Kamchatka Peninsula Kamchatka Peninsula The Kamchatka Peninsula is a peninsula in the Russian Far East, with an area of . It lies between the Pacific Ocean to the east and the Sea of Okhotsk to the west... to investigate possibilities of agriculture and mining. In 1841-47 he traveled extensively through Kamchatka, crossed it several times and subsequently wrote the most detailed account of Kamchatka's nature and ethnography at that time. |
 |
| Yerofey Khabarov Yerofey Khabarov Yerofey Pavlovich Khabarov or Svyatitsky Erofej Pavlovič Chabarov , was a Russian entrepreneur and adventurer, best known for his exploring the Amur river region and his attempts to colonize the area for Russia... (1603 – after 1671) Tsardom of Russia Tsardom of Russia The Tsardom of Russia was the name of the centralized Russian state from Ivan IV's assumption of the title of Tsar in 1547 till Peter the Great's foundation of the Russian Empire in 1721.From 1550 to 1700, Russia grew 35,000 km2 a year... Siberian Cossack Siberian Cossacks Siberian Cossacks were Cossacks who settled in the Siberian region of Russia from the end of the 16th century, following the Yermak Timofeyevich's conquest of Siberia. In early Siberia practically the whole Russian population, especially the serving-men were called Cossacks, but only in the loose... ataman Ataman Ataman was a commander title of the Ukrainian People's Army, Cossack, and haidamak leaders, who were in essence the Cossacks... , explorer of East Siberia and Amur River region |
A manager for the merchants Stroganovs Stroganovs The Stroganovs or Strogonovs , also spelled in French manner as Stroganoffs, were a family of highly successful Russian merchants, industrialists, landowners, and statesmen of the 16th – 20th centuries who eventually earned nobility.-Origins:... , Khabarov went to Siberia and in 1641 founded a settlement and saltworks on the Lena River Lena River The Lena is the easternmost of the three great Siberian rivers that flow into the Arctic Ocean . It is the 11th longest river in the world and has the 9th largest watershed... . In 1649-50 he became the second Russian to explore the Amur river (after Vassili Poyarkov Vassili Poyarkov Vassili Danilovich Poyarkov was the first Russian explorer of the Amur region.The Russian expansion into Siberia began with the conquest of the Khanate of Sibir in 1582. By 1643 they reached the Pacific at Okhotsk... ). Through Olyokma, Tungur and Shilka River Shilka River Shilka is a river in Zabaykalsky Krai, south-eastern Russia. It has a length . It originates as a confluence of the Onon and Ingoda rivers. Its confluence with the Ergune on the Russia-China border gives rise to the Amur River. The river is navigable for its entire length.... s he reached Amur (Dauria), returned to Yakutsk Yakutsk With a subarctic climate , Yakutsk is the coldest city, though not the coldest inhabited place, on Earth. Average monthly temperatures range from in July to in January. The coldest temperatures ever recorded on the planet outside Antarctica occurred in the basin of the Yana River to the northeast... and then back to Amur with a larger force. This time he was met with armed resistance Russian-Manchu border conflicts The Russian–Manchu border conflicts were a series of intermittent skirmishes between the Manchus and the Cossacks in which the Cossacks tried and failed to gain the land north of the Amur River... . He built winter quarters at Albazin Albazin Albazino is a village in Skovorodinsky District of Amur Oblast, Russia, noted as the site of Albazin , the first Russian settlement on the Amur River.... , then sailed down Amur and found Achansk, which preceded the present-day Khabarovsk Khabarovsk Khabarovsk is the largest city and the administrative center of Khabarovsk Krai, Russia. It is located some from the Chinese border. It is the second largest city in the Russian Far East, after Vladivostok. The city became the administrative center of the Far Eastern Federal District of Russia... , defeating or evading large armies of Daurian Manchu Manchu The Manchu people or Man are an ethnic minority of China who originated in Manchuria . During their rise in the 17th century, with the help of the Ming dynasty rebels , they came to power in China and founded the Qing Dynasty, which ruled China until the Xinhai Revolution of 1911, which... Chinese China Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture... and Koreans on his way. There was a mutiny against him, then he mutined himself when a nobleman Dimitry Zinoviev appeared with new reinforcements and demanded full command. Zinoviev was unable to deal with the Manchus, and finally withdrew, leaving Onufriy Stepanov Onufriy Stepanov Onufriy Stepanov was a Siberian Cossack and explorer of the Amur River. For background see Russian–Manchu border conflicts.... in charge. Khabarov was sent to Moscow, acquitted and returned to Siberia. He charted the Amur in his Draft of the Amur river. The major city of Khabarovsk Khabarovsk Khabarovsk is the largest city and the administrative center of Khabarovsk Krai, Russia. It is located some from the Chinese border. It is the second largest city in the Russian Far East, after Vladivostok. The city became the administrative center of the Far Eastern Federal District of Russia... , a town and a railway station Yerofey Pavlovich on the Trans-Siberian railroad in Amur Oblast Amur Oblast Amur Oblast is a federal subject of Russia , situated about east of Moscow on the banks of the Amur and Zeya Rivers. It shares its border with the Sakha Republic in the north, Khabarovsk Krai and the Jewish Autonomous Oblast in the east, People's Republic of China in the south, and Zabaykalsky... bear Khabarov's name. |
 |
|
| Maria Klenova Maria Klenova Maria Vasilyevna Klenova was a Russian and Soviet marine geologist and one of the founders of Russian marine science.Klenova studied to become a professor and later on worked as a member of the Council for Antarctic Research of the USSR Academy of Sciences... (1898–1976)  Russian Empire Russian Empire Soviet Union Soviet Unionmarine geologist Marine geology Marine geology or geological oceanography involves geophysical, geochemical, sedimentological and paleontological investigations of the ocean floor and coastal margins... , Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... and Antarctic Antarctic The Antarctic is the region around the Earth's South Pole, opposite the Arctic region around the North Pole. The Antarctic comprises the continent of Antarctica and the ice shelves, waters and island territories in the Southern Ocean situated south of the Antarctic Convergence... explorer |
Klenova was one of the founders of marine geology Marine geology Marine geology or geological oceanography involves geophysical, geochemical, sedimentological and paleontological investigations of the ocean floor and coastal margins... . She began her career in 1925 aboard the Soviet research vessel Persey in the Barents Sea Barents Sea The Barents Sea is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean, located north of Norway and Russia. Known in the Middle Ages as the Murman Sea, the sea takes its current name from the Dutch navigator Willem Barents... , visiting Novaya Zemlya Novaya Zemlya Novaya Zemlya , also known in Dutch as Nova Zembla and in Norwegian as , is an archipelago in the Arctic Ocean in the north of Russia and the extreme northeast of Europe, the easternmost point of Europe lying at Cape Flissingsky on the northern island... , Spitsbergen Spitsbergen Spitsbergen is the largest and only permanently populated island of the Svalbard archipelago in Norway. Constituting the western-most bulk of the archipelago, it borders the Arctic Ocean, the Norwegian Sea and the Greenland Sea... and Franz Josef Land Franz Josef Land Franz Josef Land, Franz Joseph Land, or Francis Joseph's Land is an archipelago located in the far north of Russia. It is found in the Arctic Ocean north of Novaya Zemlya and east of Svalbard, and is administered by Arkhangelsk Oblast. Franz Josef Land consists of 191 ice-covered islands with a... . In 1933 Klenova made the first complete seabed map of the Barents Sea. Her later work included the research of seabed geology in the Atlantic and the Antarctic Antarctic The Antarctic is the region around the Earth's South Pole, opposite the Arctic region around the North Pole. The Antarctic comprises the continent of Antarctica and the ice shelves, waters and island territories in the Southern Ocean situated south of the Antarctic Convergence... , and in the Caspian Caspian Sea The Caspian Sea is the largest enclosed body of water on Earth by area, variously classed as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. The sea has a surface area of and a volume of... and White Sea White Sea The White Sea is a southern inlet of the Barents Sea located on the northwest coast of Russia. It is surrounded by Karelia to the west, the Kola Peninsula to the north, and the Kanin Peninsula to the northeast. The whole of the White Sea is under Russian sovereignty and considered to be part of... s. She was one of the earliest women explorers of Antarctic Antarctic The Antarctic is the region around the Earth's South Pole, opposite the Arctic region around the North Pole. The Antarctic comprises the continent of Antarctica and the ice shelves, waters and island territories in the Southern Ocean situated south of the Antarctic Convergence... . The Klenova Valley in the Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... and a crater on Venus are named after Klenova. |
||
 |
Aleksandr Kolchak Aleksandr Kolchak Aleksandr Vasiliyevich Kolchak was a Russian naval commander, polar explorer and later - Supreme ruler . Supreme ruler of Russia , was recognized in this position by all the heads of the White movement, "De jure" - Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes, "De facto" - Entente States... (1874–1920)  Russian Empire Russian EmpireRussian Imperial Navy officer, Admiral Admiral Admiral is the rank, or part of the name of the ranks, of the highest naval officers. It is usually considered a full admiral and above vice admiral and below admiral of the fleet . It is usually abbreviated to "Adm" or "ADM"... , Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... explorer |
Kolchak joined the expedition of Eduard Toll Eduard Toll Eduard Gustav von Toll was a Baltic German geologist and Arctic explorer in Russian service. Often referred to as Baron von Toll or as Eduard v. Toll, in Russia he is known as Eduard Vasiliyevich Toll . Eduard Toll was born on and he died in 1902 in an unknown location in the Arctic Ocean)... on ship Zarya Zarya (polar ship) Zarya was a steam- and sail-powered brig used by the Russian Academy of Sciences for a polar exploration during 1900–1903.Toward the end of the 19th century, the Russian Academy of Sciences sought to build a general-purpose research vessel for long-term expeditions. The first such Russian... in 1900 as a hydrologist. He took part in two further Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... expeditions and explored the shores of Taymyr Taymyr Peninsula The Taymyr Peninsula is a peninsula in the Far North of Russia, in the Siberian Federal District, that forms the northernmost part of mainland Eurasia and Asia... . For a while was nickname Nickname A nickname is "a usually familiar or humorous but sometimes pointed or cruel name given to a person or place, as a supposedly appropriate replacement for or addition to the proper name.", or a name similar in origin and pronunciation from the original name.... d "Kolchak-Poliarnyi" ("Kolchak the Polar"). Then he distinguished himself in the Russo-Japanese War Russo-Japanese War The Russo-Japanese War was "the first great war of the 20th century." It grew out of rival imperial ambitions of the Russian Empire and Japanese Empire over Manchuria and Korea... and in World War I World War I World War I , which was predominantly called the World War or the Great War from its occurrence until 1939, and the First World War or World War I thereafter, was a major war centred in Europe that began on 28 July 1914 and lasted until 11 November 1918... , and during the Russian Civil War Russian Civil War The Russian Civil War was a multi-party war that occurred within the former Russian Empire after the Russian provisional government collapsed to the Soviets, under the domination of the Bolshevik party. Soviet forces first assumed power in Petrograd The Russian Civil War (1917–1923) was a... he was one of the main leaders of the White movement White movement The White movement and its military arm the White Army - known as the White Guard or the Whites - was a loose confederation of Anti-Communist forces.The movement comprised one of the politico-military Russian forces who fought... . He published a number of important works on Arctic ice. Kolchak Island Kolchak Island Kolchak Island or Kolchaka Island , is an island in the Kara Sea located NE of the Shturmanov Peninsula, in an area of skerries south of the Nordenskiöld Archipelago. Compared to other large islands in the area it has a quite regular shape.... , discovered and explored by Kolchak is named after him. |
 |
| Nikolai Kolomeitsev (1867–1944)  Russian Empire Russian Empire Early Modern France Early Modern FranceRussian Imperial Navy officer, Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... explorer |
After several expeditions in the Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... , Kolomeitsev became a commander of Eduard Toll Eduard Toll Eduard Gustav von Toll was a Baltic German geologist and Arctic explorer in Russian service. Often referred to as Baron von Toll or as Eduard v. Toll, in Russia he is known as Eduard Vasiliyevich Toll . Eduard Toll was born on and he died in 1902 in an unknown location in the Arctic Ocean)... 's Zarya Zarya (polar ship) Zarya was a steam- and sail-powered brig used by the Russian Academy of Sciences for a polar exploration during 1900–1903.Toward the end of the 19th century, the Russian Academy of Sciences sought to build a general-purpose research vessel for long-term expeditions. The first such Russian... during Russian Polar Expedition in 1900. They aimed to explore the area north of the New Siberian Islands New Siberian Islands The New Siberian Islands are an archipelago, located to the North of the East Siberian coast between the Laptev Sea and the East Siberian Sea north of the Sakha Republic.... and to find the Sannikov Land Sannikov Land Sannikov Land was a phantom island in the Arctic Ocean. Its supposed existence became something of a myth in 19th-century Russia.Yakov Sannikov and Matvei Gedenschtrom claimed to have seen it during their 1809-1810 cartographic expedition to the New Siberian Islands... . There was a disagreement between Kolomeitsev and Toll over the treatment of the crew, and finally Fyodor Matisen was made captain, while Kolomeitsev was sent with Stepan Rastorguyev Stepan Rastorguyev Stepan Innokentyevich Rastorguyev was an officer of the Yakut Cossack Regiment and an explorer.As Rastorguyev's parents died early, he was reared by his kindred. Then he was sent to the Okhotsk Sea coast, Kamchatka and Chukotka... to organize coal depots and carry the post to the mainland. They made a number of discoveries on the 800 km long sledge trip over Taymyr Taymyr Peninsula The Taymyr Peninsula is a peninsula in the Far North of Russia, in the Siberian Federal District, that forms the northernmost part of mainland Eurasia and Asia... . Later he became a hero of the Russo-Japanese War Russo-Japanese War The Russo-Japanese War was "the first great war of the 20th century." It grew out of rival imperial ambitions of the Russian Empire and Japanese Empire over Manchuria and Korea... . Kolomeitsev Islands Kolomeitsev Islands The Kolomeytseva Islands is a group of two small islands, part of the Nordenskjold Archipelago in the Kara Sea coastal region, off the coast of Siberia... , a bay and a strait in the Kara Sea Kara Sea The Kara Sea is part of the Arctic Ocean north of Siberia. It is separated from the Barents Sea to the west by the Kara Strait and Novaya Zemlya, and the Laptev Sea to the east by the Severnaya Zemlya.... , a river on Taymyr Taymyr Peninsula The Taymyr Peninsula is a peninsula in the Far North of Russia, in the Siberian Federal District, that forms the northernmost part of mainland Eurasia and Asia... , a mountain and a Soviet ship have been named after Kolomeitsev. |
 |
|
| Alexander Konrad Alexander Konrad Alexander Eduardovich Konrad was a Russian sailor. Along with Valerian Albanov, he was one of the only two survivors, and the only surviving sailor of the ill-fated Brusilov expedition.-Biography:... (?–1940)  Russian Empire Russian Empire Soviet Union Soviet Unionsailor in the Russian Imperial Navy and the Soviet Navy Soviet Navy The Soviet Navy was the naval arm of the Soviet Armed Forces. Often referred to as the Red Fleet, the Soviet Navy would have played an instrumental role in a Warsaw Pact war with NATO, where it would have attempted to prevent naval convoys from bringing reinforcements across the Atlantic Ocean... , Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... explorer |
Konrad was one of the only two survivors of the ill-fated 1912-14 Brusilov expedition Georgy Brusilov Georgy Lvovich Brusilov or Hryhoriy Brusylov was a Ukrainian Russian naval officer of the Imperial Russian Navy and an Arctic explorer... , the other being lieutenant Valerian Albanov Valerian Albanov Valerian Ivanovich Albanov was a Russian navigator, best known for being one of only two survivors of the ill-fated Brusilov expedition of 1912.-Biography:... . They left ice-bound ship St. Anna Svyataya Anna The ship Svyataya Anna , named after Saint Anne, was the Philomel-class gunvessel HMS Newport launched in England in 1867. She was sold in 1881 and renamed Pandora II. She was purchased again in about 1890 and renamed Blencathra, taking part in expeditions to the north coast of Russia... and by ski Ski A ski is a long, flat device worn on the foot, usually attached through a boot, designed to help the wearer slide smoothly over snow. Originally intended as an aid to travel in snowy regions, they are now mainly used for recreational and sporting purposes... , sledge, and kayak Kayak A kayak is a small, relatively narrow, human-powered boat primarily designed to be manually propelled by means of a double blade paddle.The traditional kayak has a covered deck and one or more cockpits, each seating one paddler... crossed the Kara Sea Kara Sea The Kara Sea is part of the Arctic Ocean north of Siberia. It is separated from the Barents Sea to the west by the Kara Strait and Novaya Zemlya, and the Laptev Sea to the east by the Severnaya Zemlya.... , reached Franz Josef Land Franz Josef Land Franz Josef Land, Franz Joseph Land, or Francis Joseph's Land is an archipelago located in the far north of Russia. It is found in the Arctic Ocean north of Novaya Zemlya and east of Svalbard, and is administered by Arkhangelsk Oblast. Franz Josef Land consists of 191 ice-covered islands with a... and finally were rescued by Georgy Sedov Georgy Sedov Georgy Yakovlevich Sedov was a Russian Arctic explorer.Born in the village of Krivaya Kosa of Taganrog district in a fisherman's family. In 1898, Sedov finished navigation courses in Rostov-on-Don and acquired the rank of long voyage navigator... 's Saint Foka. The data about ice drift of St. Anna, provided by Albanov, helped Vladimir Vize to calculate the coordinates of previously unknown Vize Island Vize Island Vize Island or Wiese Island is an isolated island located in the Arctic Ocean at the northern end of the Kara Sea, roughly midway between Franz Josef Land and Severnaya Zemlya, its latitude is 79° 30' N and its longitude 76° 54' E... . In 1939, serving on a Soviet ship, Konrad completed the full passage of the Northern Sea Route Northern Sea Route The Northern Sea Route is a shipping lane officially defined by Russian legislation from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean specifically running along the Russian Arctic coast from Murmansk on the Barents Sea, along Siberia, to the Bering Strait and Far East. The entire route lies in Arctic... , which had been the main goal of St. Anna. A glacier in Severnaya Zemlya Severnaya Zemlya Severnaya Zemlya is an archipelago in the Russian high Arctic at around . It is located off mainland Siberia's Taymyr Peninsula across the Vilkitsky Strait... is named after Albanov. Either Albanov or Konrad is a prototype fora hero in the novel The Two Captains The Two Captains The Two Captains is a novel written by Soviet author Veniamin Kaverin between 1938 and 1944. It is Kaverin's best known work and is considered one of the most popular works of Soviet literature, winning the USSR State Prize in 1946 being reissued 42 times in 25 years... by Veniamin Kaverin Veniamin Kaverin Veniamin Alexandrovich Kaverin was a Soviet writer associated with the early 1920s movement of the Serapion Brothers. The immunologist Lev Zilber was his older brother, and the critic Yury Tynyanov was his brother-in-law.... . |
||
| Fyodor Konyukhov Fyodor Konyukhov Fyodor Filippovich Konyukhov is a Russian survivalist, traveller and yacht captain. Eventually turned East Orthodox priest.- Military service :... (born 1951)  Soviet Union Soviet Union Russia Russiayacht captain, traveler, painter, writer |
By the age of 50 Konyukhov has made more than 40 unique trips and climbs expressing his vision of the world in more than 3000 paintings and 9 books. He set a record of crossing the Atlantic on a single row-boat in 46 days. He also crossed 800 km for record 15 days and 22 hours during a Trans-Greenland Greenland Greenland is an autonomous country within the Kingdom of Denmark, located between the Arctic and Atlantic Oceans, east of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Though physiographically a part of the continent of North America, Greenland has been politically and culturally associated with Europe for... dog sleigh ride. He was the first Russian to complete the Three Poles Challenge Three Poles Challenge The Three Poles is an adventurer’s challenge to reach all three of the North Pole, the South Pole, and Mount Everest.The Norwegian explorer Erling Kagge was the first in recorded history to accomplish this challenge in 1994. Kagge reached the North Pole on May 8 1990 with Børge Ousland; the South... and Explorers Grand Slam Explorers Grand Slam The Explorers Grand Slam or Adventurers Grand Slam is an adventurers challenge to reach the North Pole, the South Pole and all of the Seven Summits.... . He is the first and so far the only person in the world to have reached the five extreme Poles Geographical pole A geographical pole is either of the two points—the north pole and the south pole—on the surface of a rotating planet where the axis of rotation meets the surface of the body... of the planet: North Pole North Pole The North Pole, also known as the Geographic North Pole or Terrestrial North Pole, is, subject to the caveats explained below, defined as the point in the northern hemisphere where the Earth's axis of rotation meets its surface... (3 times), South Pole South Pole The South Pole, also known as the Geographic South Pole or Terrestrial South Pole, is one of the two points where the Earth's axis of rotation intersects its surface. It is the southernmost point on the surface of the Earth and lies on the opposite side of the Earth from the North Pole... , Pole of inaccessibility Pole of inaccessibility A pole of inaccessibility marks a location that is the most challenging to reach owing to its remoteness from geographical features that could provide access... in the Arctic Ocean Arctic Ocean The Arctic Ocean, located in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Arctic north polar region, is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceanic divisions... , Mt. Everest (Alpinist Alpinist Alpinist is a quarterly American magazine focused on mountaineering ascents worldwide. It was originally published out of Jackson, Wyoming and was founded in 2002... s pole) and Cape Horn Cape Horn Cape Horn is the southernmost headland of the Tierra del Fuego archipelago of southern Chile, and is located on the small Hornos Island... (Yachtsmen pole). He set a record for the solo yacht circumnavigation of Antarctica in 2008, making it in 102 days. |
 |
|
| Nikolai Korzhenevskiy Nikolai Korzhenevskiy Nikolai Leopol'dovich Korzhenevskiy , 1879 – October 31, 1958), born in Vitebsk Guberniya, Russia , died in Tashkent, Uzbekistan. A famous Russian and Soviet geographer, glaciologist, Pamir explorer. His exploration of Pamir began in 1903, with support from the military command in the region... (1879–1958)  Russian Empire Russian Empire Soviet Union Soviet UnionRussian Imperial Army officer, geographer, glaciologist, explorer of Central Asia Central Asia Central Asia is a core region of the Asian continent from the Caspian Sea in the west, China in the east, Afghanistan in the south, and Russia in the north... |
In 1903-28 Korzhenevskiy organized eleven expeditions to explore the Pamir Mountains Pamir Mountains The Pamir Mountains are a mountain range in Central Asia formed by the junction or knot of the Himalayas, Tian Shan, Karakoram, Kunlun, and Hindu Kush ranges. They are among the world’s highest mountains and since Victorian times they have been known as the "Roof of the World" a probable... . He discovered a number of glaciers and the highest peaks in the Pamirs, including Peak Korzhenevskaya Peak Korzhenevskaya Peak Korzhenevskaya is the third highest peak in the Pamir Mountains of Tajikistan. It is one of the five "Snow Leopard Peaks" in the territory of theformer Soviet Union. It is named after Evgenia Korzhenevskaya, the wife of Russiangeographer Nikolai L... which he named after his wife Evgeniya. He discovered and called Akademiya Nauk Range Akademiya Nauk Range Akademiya Nauk Range is a mountain range in the Western Pamirs of Tajikistan. It is stretched in the meridianal direction and considered to be the core of the Pamir mountain system.... (in honor of the Academy of Sciences of the USSR) and made a catalogue of all glaciers in Central Asia Central Asia Central Asia is a core region of the Asian continent from the Caspian Sea in the west, China in the east, Afghanistan in the south, and Russia in the north... , himself having discovered 70 of them. Three glaciers in different Central Asia Central Asia Central Asia is a core region of the Asian continent from the Caspian Sea in the west, China in the east, Afghanistan in the south, and Russia in the north... mountain ridges and a peak in the Pamirs have been named after Korzhenevskiy. |
 |
|
 |
Otto von Kotzebue Otto von Kotzebue Otto von Kotzebue was a Baltic German navigator in Russian service.... (1787–1846)  Russian Empire Russian Empire(born in Estonia Estonia Estonia , officially the Republic of Estonia , is a state in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea, to the south by Latvia , and to the east by Lake Peipsi and the Russian Federation . Across the Baltic Sea lies... , Baltic German Baltic German The Baltic Germans were mostly ethnically German inhabitants of the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea, which today form the countries of Estonia and Latvia. The Baltic German population never made up more than 10% of the total. They formed the social, commercial, political and cultural élite in... descent) Russian Imperial Navy officer, circumnavigator, explorer of Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... , Alaska Alaska Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait... and Pacific |
Kotzebue accompanied Ivan Krusenstern in the first Russian circumnavigation First Russian circumnavigation The first Russian circumnavigation of the Earth took place from August 1803 to August 1806. It was sponsored by Count Nikolay Rumyantsev and was headed by Adam Johann von Krusenstern.-Events:... in 1803-06. On the brig Rurik Rurik Rurik, or Riurik , was a semilegendary 9th-century Varangian who founded the Rurik dynasty which ruled Kievan Rus and later some of its successor states, most notably the Tsardom of Russia, until 1598.... he himself led another Russian circumnavigation in 1815-18. Proceeding via Cape Horn Cape Horn Cape Horn is the southernmost headland of the Tierra del Fuego archipelago of southern Chile, and is located on the small Hornos Island... , he discovered the Romanzov Islands, Rurik Islands and Krusenstern Islands Tuamotus The Tuamotus or the Tuamotu Archipelago are a chain of islands and atolls in French Polynesia. They form the largest chain of atolls in the world, spanning an area of the Pacific Ocean roughly the size of Western Europe... (today Tikehau Tikehau -External links:* * * * * * * * * * *... ) in Pacific, then made for Kamchatka Peninsula Kamchatka Peninsula The Kamchatka Peninsula is a peninsula in the Russian Far East, with an area of . It lies between the Pacific Ocean to the east and the Sea of Okhotsk to the west... and proceeded along the north-west coast of North America North America North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas... to the Chukchi Sea Chukchi Sea Chukchi Sea is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It is bounded on the west by the De Long Strait, off Wrangel Island, and in the east by Point Barrow, Alaska, beyond which lies the Beaufort Sea. The Bering Strait forms its southernmost limit and connects it to the Bering Sea and the Pacific... . He discovered and named Kotzebue Sound Kotzebue Sound Kotzebue Sound is an arm of the Chukchi Sea in the western region of the U.S. state of Alaska. It is on the north side of the Seward Peninsula and bounded the east by the Baldwin Peninsula. It is long and wide.... and Cape Krusenstern Cape Krusenstern Cape Krusenstern is a cape on the northwestern coast of the U.S. state of Alaska, located near the village of Kivalina at .It is bounded by Kotzebue Sound to the south and the Chukchi Sea to the west, and consists of a series of beach ridges and swales with numerous ponds and lakes... . Returning south he discovered the New Year Island in Pacific. In 1823-26 he made another world cruise on the sloop "Enterprise"making several discoveries. Kotzebue Sound Kotzebue Sound Kotzebue Sound is an arm of the Chukchi Sea in the western region of the U.S. state of Alaska. It is on the north side of the Seward Peninsula and bounded the east by the Baldwin Peninsula. It is long and wide.... and the city of Kotzebue, Alaska Kotzebue, Alaska As of the census of 2000, there were 3,082 people, 889 households, and 656 families residing in the city. The population density was 114.1 people per square mile . There were 1,007 housing units at an average density of 37.3 per square mile... are named after Otto von Kotzebue. |
|
 |
Pyotr Kozlov Pyotr Kozlov Pyotr Kuzmich Kozlov was a Russian and Soviet traveler and explorer who continued the studies of Nikolai Przhevalsky in Mongolia and Tibet.Although prepared by his parents for military career, Kozlov chose to join Przhevalsky's expedition. After his mentor's death, Kozlov continued travelling in... (1863–1935)  Russian Empire Russian Empire Soviet Union Soviet UnionRussian Imperial Army officer, explorer of Central Asia Central Asia Central Asia is a core region of the Asian continent from the Caspian Sea in the west, China in the east, Afghanistan in the south, and Russia in the north... |
Kozlov started travelling in the Central Asia Central Asia Central Asia is a core region of the Asian continent from the Caspian Sea in the west, China in the east, Afghanistan in the south, and Russia in the north... with Nikolai Przhevalsky Nikolai Przhevalsky Nikolai Mikhaylovich Przhevalsky and Prjevalsky, ; —), was a Russian geographer of Polish background and explorer of Central and Eastern Asia. Although he never reached his final goal, Lhasa in Tibet, he travelled through regions unknown to the west, such as northern Tibet, modern Qinghai and... , and after the death of his mentor he continued his work. From 1899 to 1901 he explored the upper reaches of Huang He, Yangtze, and Mekong Mekong The Mekong is a river that runs through China, Burma, Laos, Thailand, Cambodia and Vietnam. It is the world's 10th-longest river and the 7th-longest in Asia. Its estimated length is , and it drains an area of , discharging of water annually.... rivers. Kozlov rivalled Sven Hedin Sven Hedin Sven Anders Hedin KNO1kl RVO was a Swedish geographer, topographer, explorer, photographer, and travel writer, as well as an illustrator of his own works... and Aurel Stein as the foremost researcher of Xinjiang Xinjiang Xinjiang is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China. It is the largest Chinese administrative division and spans over 1.6 million km2... at the historical peak of the Great Game The Great Game The Great Game or Tournament of Shadows in Russia, were terms for the strategic rivalry and conflict between the British Empire and the Russian Empire for supremacy in Central Asia. The classic Great Game period is generally regarded as running approximately from the Russo-Persian Treaty of 1813... . In 1907 he visited the Dalai Lama Dalai Lama The Dalai Lama is a high lama in the Gelug or "Yellow Hat" branch of Tibetan Buddhism. The name is a combination of the Mongolian word далай meaning "Ocean" and the Tibetan word bla-ma meaning "teacher"... in Urga. In 1907-09, Kozlov explored the Gobi Desert Gobi Desert The Gobi is a large desert region in Asia. It covers parts of northern and northwestern China, and of southern Mongolia. The desert basins of the Gobi are bounded by the Altai Mountains and the grasslands and steppes of Mongolia on the north, by the Hexi Corridor and Tibetan Plateau to the... and discovered remains of the ancient Tangut Tibetan people The Tibetan people are an ethnic group that is native to Tibet, which is mostly in the People's Republic of China. They number 5.4 million and are the 10th largest ethnic group in the country. Significant Tibetan minorities also live in India, Nepal, and Bhutan... city of Khara-Khoto Khara-Khoto Khara-Khoto was a Tangut city in the Ejin khoshuu of Alxa League, in western Inner Mongolia, near the former Gashun Lake. It has been identified as the city of Etzina, which appears in The Travels of Marco Polo.-History:... . He excavated the site and uncovered no less than 2,000 books in Tangut language Tangut language Tangut is an ancient northeastern Tibeto-Burman language once spoken in the Western Xia Dynasty, also known as the Tangut Empire. It is classified by some linguists as one of the Qiangic languages, which also include Qiang and rGyalrong, among others... . In 1923-26 he explored Mongolia Mongolia Mongolia is a landlocked country in East and Central Asia. It is bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south, east and west. Although Mongolia does not share a border with Kazakhstan, its western-most point is only from Kazakhstan's eastern tip. Ulan Bator, the capital and largest... and Tibet Tibet Tibet is a plateau region in Asia, north-east of the Himalayas. It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people as well as some other ethnic groups such as Monpas, Qiang, and Lhobas, and is now also inhabited by considerable numbers of Han and Hui people... and discovered an unprecedented number of Xiongnu Xiongnu The Xiongnu were ancient nomadic-based people that formed a state or confederation north of the agriculture-based empire of the Han Dynasty. Most of the information on the Xiongnu comes from Chinese sources... royal burials at Noin-Ula. |
|
| Stepan Krasheninnikov Stepan Krasheninnikov Stepan Petrovich Krasheninnikov was a Russian explorer of Siberia, naturalist and geographer who gave the first full description of Kamchatka in the early 18th century. He was elected to the Russian Academy of Sciences in 1745... (1711–1755) Tsardom of Russia Tsardom of Russia The Tsardom of Russia was the name of the centralized Russian state from Ivan IV's assumption of the title of Tsar in 1547 till Peter the Great's foundation of the Russian Empire in 1721.From 1550 to 1700, Russia grew 35,000 km2 a year...  Russian Empire Russian Empiregeographer and explorer of Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... and Kamchatka |
Krashennikov was a classmate of Mikhail Lomonosov Mikhail Lomonosov Mikhail Vasilyevich Lomonosov was a Russian polymath, scientist and writer, who made important contributions to literature, education, and science. Among his discoveries was the atmosphere of Venus. His spheres of science were natural science, chemistry, physics, mineralogy, history, art,... . He embarked upon a major Second Kamchatka Expedition, organised by Vitus Bering Vitus Bering Vitus Jonassen Bering Vitus Jonassen Bering Vitus Jonassen Bering (also, less correNavy]], a captain-komandor known among the Russian sailors as Ivan Ivanovich. He is noted for being the first European to discover Alaska and its Aleutian Islands... . Krashennikov traveled in Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... in 1733-36 and on Kamchatka Peninsula Kamchatka Peninsula The Kamchatka Peninsula is a peninsula in the Russian Far East, with an area of . It lies between the Pacific Ocean to the east and the Sea of Okhotsk to the west... in 1737-41. He gave the first full description of Kamchatka in his book An Account of the Land of Kamchatka, with detailed report of the plants and animals of the region, and also the language and culture of the indigenous Itelmen and Koryak Koryaks Koryaks are an indigenous people of Kamchatka Krai in the Russian Far East, who inhabit the coastlands of the Bering Sea to the south of the Anadyr basin and the country to the immediate north of the Kamchatka Peninsula, the southernmost limit of their range being Tigilsk. They are akin to the... peoples. The Krasheninnikov Volcano on Kamchatka and more than 20 species are named after Krasheninnikov. |
.jpg) |
|
| Pyotr Krenitsyn Pyotr Krenitsyn Pyotr Kuzmich Krenitsyn , spelt "Krenitzin" in the United States, was a Russian explorer and Captain/Lieutenant of the Imperial Russian Navy. Following Vitus Bering's 1741 tragic venture he was the first to conduct an expedition to Alaska and the Aleutians... (1728–1770)  Russian Empire Russian EmpireRussian Imperial Navy officer, explorer of Alaska Alaska Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait... and Pacific |
In 1766-70 Krenitsyn led the "secret" expedition to the North Pacific together with Mikhail Levashov Mikhail Levashev Mikhail D. Levashev was a Russian explorer and Lieutenant of the Imperial Russian Navy... , as ordered by Catherine II. They explored the Aleutian Islands and part of Alaska Alaska Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait... shore, discovering good haven in Unalaska and many features of Alaska Alaska Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait... n coast. Krenitsyn died drowning in Kamchatka River Kamchatka River The Kamchatka River runs eastward for through Kamchatka Krai in the Russian Far East towards the Pacific Ocean. The river is rich with salmon, millions of which spawn yearly and which once supported the settlements of the native Itelmen.... . On the basis of his explorations the first general map of the Aleutian Islands was created. The Krenitzin Islands Krenitzin Islands The Krenitzin Islands are a group of small islands located in the eastern portion of the Fox Islands group of the eastern Aleutian Islands, Alaska. The Krenitizins are situated between Unalaska Island to the southwest and Unimak Island to the northeast... in Aleutian chain, a strait between Onekotan Onekotan Onekotan Island is an uninhabited volcanic island located near the northern end of the Kuril Islands chain in the Sea of Okhotsk in the northwest Pacific Ocean. Its name is derived from the Ainu language for "large village".-Geology:... and Kharimkotan Kharimkotan Kharimkotan ; Japanese 春牟古丹島; Harimukotan-tō, alternatively Harumukotan-tō or 加林古丹; Karinkotan-tō) is an uninhabited volcanic island located km from Onekotan near the northern end of the Kuril Islands chain in the Sea of Okhotsk in the northwest Pacific Ocean... islands in the Kurils, the highest volcano on Onekotan, a cape and a volcano on Kharimkotan and a cape in Bristol Bay Bristol Bay Bristol Bay is the eastern-most arm of the Bering Sea, at 57° to 59° North 157° to 162° West in Southwest Alaska. Bristol Bay is 400 km long and 290 km, wide at its mouth... of the Bering Sea Bering Sea The Bering Sea is a marginal sea of the Pacific Ocean. It comprises a deep water basin, which then rises through a narrow slope into the shallower water above the continental shelves.... are named after Krenitsyn. |
||
| Sergei Krikalyov (born 1958)  Soviet Union Soviet Union Russia Russiacosmonaut and mechanical engineer, Hero of the Soviet Union Hero of the Soviet Union The title Hero of the Soviet Union was the highest distinction in the Soviet Union, awarded personally or collectively for heroic feats in service to the Soviet state and society.-Overview:... , Hero of the Russian Federation Hero of the Russian Federation Hero of the Russian Federation is a Russian decoration and the highest honorary title that can be bestowed on a citizen by the Russian Federation. The President of the Russian Federation is the main conferring authority of the medal, which is bestowed on those committing actions or deeds that... |
Krikalyov has spent in space Space Space is the boundless, three-dimensional extent in which objects and events occur and have relative position and direction. Physical space is often conceived in three linear dimensions, although modern physicists usually consider it, with time, to be part of a boundless four-dimensional continuum... a record 803 days and 9 hours and 39 minutes during his six spaceflights. As a Soviet cosmonaut he traveled in space and back aboard Soyuz TM-7 Soyuz TM-7 -Mission parameters:*Mass: 7,000 kg 15,400 lb*Perigee: 194 km *Apogee: 235 km *Inclination: 51.6°*Period: 88.8 minutes-Mission highlights:... in 1988 and then launched upon Soyuz TM-12 Soyuz TM-12 -Mission highlights:12th expedition to Mir. Included first Briton in space.The Derbents welcomed aboard Mir Anatoli Artsebarski, Sergei Krikalev , and British cosmonaut-researcher Helen Sharman, who was aboard as part of Project Juno, a cooperative venture partly sponsored by British private... in 1991, both times working on the Soviet Space Station Space station A space station is a spacecraft capable of supporting a crew which is designed to remain in space for an extended period of time, and to which other spacecraft can dock. A space station is distinguished from other spacecraft used for human spaceflight by its lack of major propulsion or landing... Mir Mir Mir was a space station operated in low Earth orbit from 1986 to 2001, at first by the Soviet Union and then by Russia. Assembled in orbit from 1986 to 1996, Mir was the first modular space station and had a greater mass than that of any previous spacecraft, holding the record for the... . "The last Citizen of the USSR", Krikalev landed back on Earth Earth Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets... aboard Soyuz TM-13 Soyuz TM-13 -Mission highlights:13th expedition to Mir. Included astronaut from Austria and cosmonaut from soon to be independent Kazakhstan.Soyuz-TM 13 carried Austrian cosmonaut-researcher Franz Viehböck and still Soviet-Kazakh cosmonaut-researcher Toktar Aubakirov. The flight was unusual for carrying no... in 1992 to turn into a Russia Russia Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects... n cosmonaut. He became the first Russian to travel on the American Space Shuttle Space Shuttle The Space Shuttle was a manned orbital rocket and spacecraft system operated by NASA on 135 missions from 1981 to 2011. The system combined rocket launch, orbital spacecraft, and re-entry spaceplane with modular add-ons... during STS-60 STS-60 STS-60 was the first mission of the US/Russian Shuttle-Mir Program, which carried Sergei K. Krikalev, the first Russian cosmonaut to fly aboard a Space Shuttle. The mission used Space Shuttle Discovery, which lifted off from Launch Pad 39A on 3 February 1994 from Kennedy Space Center, Florida... mission to Mir Mir Mir was a space station operated in low Earth orbit from 1986 to 2001, at first by the Soviet Union and then by Russia. Assembled in orbit from 1986 to 1996, Mir was the first modular space station and had a greater mass than that of any previous spacecraft, holding the record for the... in 1994, and then he made another Shuttle flight STS-88 STS-88 -Mission parameters:*Weight*Liftoff: *Landing: *Perigee: *Apogee: *Orbital Period: 92.4min-Launch attempts:-Mission highlights:Node 1, named Unity, was the first space station hardware delivered by the space shuttle. It has two Pressurized Mating Adapters , one attached to either end... , which was the first Shuttle mission to International Space Station International Space Station The International Space Station is a habitable, artificial satellite in low Earth orbit. The ISS follows the Salyut, Almaz, Cosmos, Skylab, and Mir space stations, as the 11th space station launched, not including the Genesis I and II prototypes... . He again traveled to ISS ISS The ISS is the International Space Station.ISS may also refer to:* I See Stars, an American electronic rock band* ISS A/S, a Danish service company* Idea Star Singer, a Malayalam music reality show by Asianet TV... on Soyuz TM-31 Soyuz TM-31 Soyuz TM-31 was the first Soyuz spacecraft to dock with the International Space Station . Launched near the end of 2000 the Soyuz-TM spacecraft brought to ISS Expedition 1, the first long-duration ISS crew... in 2000 and returned back on STS-102 STS-102 STS-102 was a Space Shuttle mission to the International Space Station flown by Space Shuttle Discovery and launched from Kennedy Space Center, Florida... in 2001. And yet again he traveled to ISS and back on Soyuz TMA-6 Soyuz TMA-6 Soyuz TMA-6 was a Soyuz mission to the International Space Station launched by a Soyuz-FG launch vehicle.-Crew:-Docking with ISS:*Docked to ISS: April 17, 2005, 02:20 UTC... in 2005. |
 |
|
| Pyotr Kropotkin (1842–1921)  Russian Empire Russian EmpireRussian Imperial Army officer, geographer, zoologist, anarchist, explorer of Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... , the Far East Far East The Far East is an English term mostly describing East Asia and Southeast Asia, with South Asia sometimes also included for economic and cultural reasons.The term came into use in European geopolitical discourse in the 19th century,... and the Northern Europe Northern Europe Northern Europe is the northern part or region of Europe. Northern Europe typically refers to the seven countries in the northern part of the European subcontinent which includes Denmark, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Norway, Finland and Sweden... |
While serving in Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... , in 1864 Kropotkin led survey expedition crossing North Manchuria Manchuria Manchuria is a historical name given to a large geographic region in northeast Asia. Depending on the definition of its extent, Manchuria usually falls entirely within the People's Republic of China, or is sometimes divided between China and Russia. The region is commonly referred to as Northeast... from Transbaikalia to the Amur River. Subsequently he took part in the expedition which proceeded up the Sungari River into central Manchuria Manchuria Manchuria is a historical name given to a large geographic region in northeast Asia. Depending on the definition of its extent, Manchuria usually falls entirely within the People's Republic of China, or is sometimes divided between China and Russia. The region is commonly referred to as Northeast... , yielding valuable geographical results. In 1871 he explored the glacial deposits of Finland Finland Finland , officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country situated in the Fennoscandian region of Northern Europe. It is bordered by Sweden in the west, Norway in the north and Russia in the east, while Estonia lies to its south across the Gulf of Finland.Around 5.4 million people reside... and Sweden Sweden Sweden , officially the Kingdom of Sweden , is a Nordic country on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. Sweden borders with Norway and Finland and is connected to Denmark by a bridge-tunnel across the Öresund.... . He published several important works on geography of Asia. Kropotkin was also one of the most prominent Russian anarchists and revolutionaries Revolutionary A revolutionary is a person who either actively participates in, or advocates revolution. Also, when used as an adjective, the term revolutionary refers to something that has a major, sudden impact on society or on some aspect of human endeavor.-Definition:... . The town of Kropotkin, Krasnodar Krai Kropotkin, Krasnodar Krai Kropotkin is a town in Krasnodar Krai, Russia, located on the right bank of the Kuban River. Population: 70,000 ; 42,000 ; 27,000 .... , a settlement in Irkutsk Oblast Irkutsk Oblast Irkutsk Oblast is a federal subject of Russia , located in southeastern Siberia in the basins of Angara River, Lena, and Nizhnyaya Tunguska Rivers. The administrative center is the city of Irkutsk. Population: -History:... , an inactive volcano in Buryatia, Kropotkinskaya Kropotkinskaya Kropotkinskaya is a station on the Sokolnicheskaya Line of the Moscow Metro. One of the better-known Metro stations, it was designed by Alexey Dushkin and Ya... station of Moscow metro Moscow Metro The Moscow Metro is a rapid transit system serving Moscow and the neighbouring town of Krasnogorsk. Opened in 1935 with one line and 13 stations, it was the first underground railway system in the Soviet Union. As of 2011, the Moscow Metro has 182 stations and its route length is . The system is... and many streets in Soviet and Russian cities have been named after Kropotkin. |
 |
|
| Adam Johann von Krusenstern Adam Johann von Krusenstern Adam Johann Ritter von Krusenstern , was an admiral and explorer, who led the first Russian circumnavigation of the globe.- Life :... (1770–1846)  Russian Empire Russian Empire(born in Estonia Estonia Estonia , officially the Republic of Estonia , is a state in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea, to the south by Latvia , and to the east by Lake Peipsi and the Russian Federation . Across the Baltic Sea lies... , Baltic German Baltic German The Baltic Germans were mostly ethnically German inhabitants of the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea, which today form the countries of Estonia and Latvia. The Baltic German population never made up more than 10% of the total. They formed the social, commercial, political and cultural élite in... descent) Russian Imperial Navy officer, circumnavigator, explorer of Pacific |
In 1803-06, under the patronage of Tsar Alexander I Alexander I of Russia Alexander I of Russia , served as Emperor of Russia from 23 March 1801 to 1 December 1825 and the first Russian King of Poland from 1815 to 1825. He was also the first Russian Grand Duke of Finland and Lithuania.... and Baron Nikolai Rezanov Nikolai Rezanov Nikolay Petrovich Rezanov was a Russian nobleman and statesman who promoted the project of Russian colonization of Alaska and California. One of the ten barons of Russia, he was the first Russian ambassador to Japan , and participated in the first Russian circumnavigation of the globe ,... , Krusenstern led the first Russian circumnavigation First Russian circumnavigation The first Russian circumnavigation of the Earth took place from August 1803 to August 1806. It was sponsored by Count Nikolay Rumyantsev and was headed by Adam Johann von Krusenstern.-Events:... of the world aboard Nadezhda together with Yuri Lisianski on Neva. The purpose of the expedition was to establish trade with China China Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture... and Japan Japan Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south... , and examine California California California is a state located on the West Coast of the United States. It is by far the most populous U.S. state, and the third-largest by land area... for a possible colony. They sailed from Kronstadt, rounded Cape Horn Cape Horn Cape Horn is the southernmost headland of the Tierra del Fuego archipelago of southern Chile, and is located on the small Hornos Island... , and reached the northern Pacific. Krusenstern's account of his journey was published in Russia and many European countries. He made an atlas of the Pacific, receiving an honorary membership in the Russian Academy of Sciences for that. The Russian training tall ship Tall ship A tall ship is a large, traditionally-rigged sailing vessel. Popular modern tall ship rigs include topsail schooners, brigantines, brigs and barques. "Tall Ship" can also be defined more specifically by an organization, such as for a race or festival.... Kruzenshtern Kruzenshtern (ship) The Kruzenshtern or Krusenstern is a four masted barque and tall ship that was built in 1926 at Geestemünde in Bremerhaven, Germany as the Padua . She was surrendered to the USSR in 1946 as war reparation and renamed after the early 19th century Baltic German explorer in Russian service, Adam... , crater Krusenstern Krusenstern (crater) Krusenstern is a lunar crater that lies amidst the battered terrain in the southern part of the Moon's near side. Nearly attached to the east-southeast rim is the crater Apianus. Less than one crater diameter to the southwest is the prominent Werner. Krusenstern is intruding into a large circular... on the Moon Moon The Moon is Earth's only known natural satellite,There are a number of near-Earth asteroids including 3753 Cruithne that are co-orbital with Earth: their orbits bring them close to Earth for periods of time but then alter in the long term . These are quasi-satellites and not true moons. For more... , Krusenstern Island Ailuk Atoll Ailuk Atoll is a coral atoll of 57 islets in the Pacific Ocean, and forms a legislative district of the Ratak Chain of the Marshall Islands. It is located approximately north from Wotje. Its total land area is only , but it encloses a lagoon with an area of... in the Marshall Islands Marshall Islands The Republic of the Marshall Islands , , is a Micronesian nation of atolls and islands in the middle of the Pacific Ocean, just west of the International Date Line and just north of the Equator. As of July 2011 the population was 67,182... , Krusenstern Island Tikehau -External links:* * * * * * * * * * *... in the Tuamotus Tuamotus The Tuamotus or the Tuamotu Archipelago are a chain of islands and atolls in French Polynesia. They form the largest chain of atolls in the world, spanning an area of the Pacific Ocean roughly the size of Western Europe... , Krusenstern Island Little Diomede Island Little Diomede Island is an island of Alaska, United States. It is the smaller of the two Diomede Islands located in the middle of the Bering Strait between the Alaska mainland and Siberia... in the Bering Strait Bering Strait The Bering Strait , known to natives as Imakpik, is a sea strait between Cape Dezhnev, Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, Russia, the easternmost point of the Asian continent and Cape Prince of Wales, Alaska, USA, the westernmost point of the North American continent, with latitude of about 65°40'N,... , as well as Krusenstern Islands in the Kara Sea Kara Sea The Kara Sea is part of the Arctic Ocean north of Siberia. It is separated from the Barents Sea to the west by the Kara Strait and Novaya Zemlya, and the Laptev Sea to the east by the Severnaya Zemlya.... have been named after Krusenstern. |
||
 |
Alexander Kuchin Alexander Kuchin Alexander Stepanovich Kuchin was a young Russian oceanographer and Arctic explorer.... (1888–1913?)  Russian Empire Russian EmpireRussian Imperial Navy officer, oceanographer, Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... and Antarctic Antarctic The Antarctic is the region around the Earth's South Pole, opposite the Arctic region around the North Pole. The Antarctic comprises the continent of Antarctica and the ice shelves, waters and island territories in the Southern Ocean situated south of the Antarctic Convergence... explorer |
Kuchin's life was bound with Norway Norway Norway , officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic unitary constitutional monarchy whose territory comprises the western portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula, Jan Mayen, and the Arctic archipelago of Svalbard and Bouvet Island. Norway has a total area of and a population of about 4.9 million... : he started as a seaman on a Norwegian ship, created a Small Russian-Norwegian dictionary, studied oceanography Oceanography Oceanography , also called oceanology or marine science, is the branch of Earth science that studies the ocean... from Bjorn Helland-Hansen Bjorn Helland-Hansen Bjørn Helland-Hansen was a Norwegian pioneer in the field of modern oceanography. He studied the variation patterns of the weather in the northern Atlantic Ocean and of the atmosphere.... , participated in Amundsen Amundsen -People:*Arthur Amundsen , Norwegian gymnast who competed in the 1908 and 1912 Summer Olympics*Asle Amundsen, Norwegian politician for the Socialist Left Party*Carl Morten Amundsen, Norwegian dramaturg and theatre director... ’s expedition to the South Pole South Pole The South Pole, also known as the Geographic South Pole or Terrestrial South Pole, is one of the two points where the Earth's axis of rotation intersects its surface. It is the southernmost point on the surface of the Earth and lies on the opposite side of the Earth from the North Pole... on the Fram Fram Fram is a ship that was used in expeditions of the Arctic and Antarctic regions by the Norwegian explorers Fridtjof Nansen, Otto Sverdrup, Oscar Wisting, and Roald Amundsen between 1893 and 1912... , and married Aslaug Poulson, a Norwegian. In 1912-13 he took part in Vladimir Rusanov Vladimir Rusanov Vladimir Alexandrovich Rusanov was an experienced Russian geologist who specialized in the Arctic.In 1909–1911 V. A. Rusanov carried out explorations in Novaya Zemlya. He was helped by Tyko Vylka, his guide, who later became the Chairman of the Novaya Zemlya Soviet.In 1912 Rusanov had been... ’s expedition to Svalbard Svalbard Svalbard is an archipelago in the Arctic, constituting the northernmost part of Norway. It is located north of mainland Europe, midway between mainland Norway and the North Pole. The group of islands range from 74° to 81° north latitude , and from 10° to 35° east longitude. Spitsbergen is the... as the captain of their ship Gerkules Hercules Hercules is the Roman name for Greek demigod Heracles, son of Zeus , and the mortal Alcmene... . After the successful research of the coal reserves on Svalbard, without consultation with the Russian authorities they made an incredibly rash attempt to pass via the Northern Sea Route Northern Sea Route The Northern Sea Route is a shipping lane officially defined by Russian legislation from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean specifically running along the Russian Arctic coast from Murmansk on the Barents Sea, along Siberia, to the Bering Strait and Far East. The entire route lies in Arctic... , and were lost in the Kara Sea Kara Sea The Kara Sea is part of the Arctic Ocean north of Siberia. It is separated from the Barents Sea to the west by the Kara Strait and Novaya Zemlya, and the Laptev Sea to the east by the Severnaya Zemlya.... . Relics of Gerkules were found near Kolosovykh Islands Kolosovykh Islands The Kolosovykh Island is a island, in the Kara Sea off the coast of Siberia.This coastal archipelago, is located north of the small Kolosovykh peninsula, which is almost an island itself. This island group is located between 74° 45' and 75° N and between 85° and 87° 30'E... . Two islets off Salisbury Island Salisbury Island (Russia) Salisbury Island, is an island located in the central area of Franz Josef Land, Russia.Salisbury Island is relatively large and long, having a surface of 960 km²... in Franz Josef Land Franz Josef Land Franz Josef Land, Franz Joseph Land, or Francis Joseph's Land is an archipelago located in the far north of Russia. It is found in the Arctic Ocean north of Novaya Zemlya and east of Svalbard, and is administered by Arkhangelsk Oblast. Franz Josef Land consists of 191 ice-covered islands with a... have been named after Kuchin. |
 |
L
| Portrait | Person | Achievements | Image |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grigory Langsdorff Grigori Ivanovitch Langsdorff Georg Heinrich von Langsdorff, Baron de Langsdorff was a Prussian aristocrat, politician and naturalist. He lived in Russia and was better known by his Russian name, Grigori Ivanovitch... (1774–1852)  Holy Roman Empire Holy Roman Empire Russian Empire Russian Empirephysician, naturalist, consul Consul Consul was the highest elected office of the Roman Republic and an appointive office under the Empire. The title was also used in other city states and also revived in modern states, notably in the First French Republic... general of Russia in Rio de Janeiro Rio de Janeiro Rio de Janeiro , commonly referred to simply as Rio, is the capital city of the State of Rio de Janeiro, the second largest city of Brazil, and the third largest metropolitan area and agglomeration in South America, boasting approximately 6.3 million people within the city proper, making it the 6th... , explorer of the Aleutian Islands and Brazil Brazil Brazil , officially the Federative Republic of Brazil , is the largest country in South America. It is the world's fifth largest country, both by geographical area and by population with over 192 million people... |
Langsdorff participated as naturalist and physician in the first Russian circumnavigation First Russian circumnavigation The first Russian circumnavigation of the Earth took place from August 1803 to August 1806. It was sponsored by Count Nikolay Rumyantsev and was headed by Adam Johann von Krusenstern.-Events:... commanded by Ivan Kruzenshtern in 1803-05. Independently, he explored the Aleutians, Kodiak Kodiak Island Kodiak Island is a large island on the south coast of the U.S. state of Alaska, separated from the Alaska mainland by the Shelikof Strait. The largest island in the Kodiak Archipelago, Kodiak Island is the second largest island in the United States and the 80th largest island in the world, with an... and Sitka in 1805-07. In 1813 he was nominated consul Consul Consul was the highest elected office of the Roman Republic and an appointive office under the Empire. The title was also used in other city states and also revived in modern states, notably in the First French Republic... general of Russia in Rio de Janeiro Rio de Janeiro Rio de Janeiro , commonly referred to simply as Rio, is the capital city of the State of Rio de Janeiro, the second largest city of Brazil, and the third largest metropolitan area and agglomeration in South America, boasting approximately 6.3 million people within the city proper, making it the 6th... , Brazil Brazil Brazil , officially the Federative Republic of Brazil , is the largest country in South America. It is the world's fifth largest country, both by geographical area and by population with over 192 million people... . There he explored the flora, fauna and geography of the province of Minas Gerais Minas Gerais Minas Gerais is one of the 26 states of Brazil, of which it is the second most populous, the third richest, and the fourth largest in area. Minas Gerais is the Brazilian state with the largest number of Presidents of Brazil, the current one, Dilma Rousseff, being one of them. The capital is the... with French naturalist Augustin Saint-Hilaire Augustin Saint-Hilaire Augustin François César Prouvençal de Saint-Hilaire , French botanist and traveler, was born at Orléans, France, on 4 October 1779. He began to publish memoirs on botanical subjects at an early age... in 1813-20. In 1821-22 he led an exploratory and scientific expedition from São Paulo São Paulo São Paulo is the largest city in Brazil, the largest city in the southern hemisphere and South America, and the world's seventh largest city by population. The metropolis is anchor to the São Paulo metropolitan area, ranked as the second-most populous metropolitan area in the Americas and among... to Pará Pará Pará is a state in the north of Brazil. It borders the Brazilian states of Amapá, Maranhão, Tocantins, Mato Grosso, Amazonas and Roraima. To the northwest it also borders Guyana and Suriname, and to the northeast it borders the Atlantic Ocean. The capital is Belém.Pará is the most populous state... in the Amazon Amazon Rainforest The Amazon Rainforest , also known in English as Amazonia or the Amazon Jungle, is a moist broadleaf forest that covers most of the Amazon Basin of South America... via a fluvial route, accompanied by an international team of scientists. In 1826-29 he led a 6000 km long expedition from Porto Feliz Porto Feliz Porto Feliz is a municipality in the Brazilian state of São Paulo. As of 2004, The population was 49,915, the density was 89.5/km², the area is 557.98 km², and the elevation is 523 m... to Amazon River Amazon River The Amazon of South America is the second longest river in the world and by far the largest by waterflow with an average discharge greater than the next seven largest rivers combined... and back. As a consequence of the tropical fever, he became insane and went to Europe for healing. Still he and his companions were able to emass huge scientific collections now deposited in Kunstkamera Kunstkamera The Kunstkamera was the first museum in Russia. Established by Peter the Great and completed in 1727, the Kunstkammer Building hosts the Peter the Great Museum of Anthropology and Ethnography, with a collection of almost 2,000,000 items... , St. Petersburg, including much valuable material on Brazilian nature and ethnography. |
 |
|
| Dmitry Laptev Dmitry Laptev Dmitry Yakovlevich Laptev was a Russian Arctic explorer and Vice Admiral .Dmitry Laptev was born in the village of Bolotovo, near Velikie Luki, in 1701. Bolotovo was the estate of his father, Yakov Laptev... (1701–1771) Tsardom of Russia Tsardom of Russia The Tsardom of Russia was the name of the centralized Russian state from Ivan IV's assumption of the title of Tsar in 1547 till Peter the Great's foundation of the Russian Empire in 1721.From 1550 to 1700, Russia grew 35,000 km2 a year...  Russian Empire Russian EmpireRussian Imperial Navy officer, Vice Admiral Vice Admiral Vice admiral is a senior naval rank of a three-star flag officer, which is equivalent to lieutenant general in the other uniformed services. A vice admiral is typically senior to a rear admiral and junior to an admiral... , explorer of Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... and Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... (Malygin Stepan Malygin Stepan Gavrilovich Malygin was a Russian Arctic explorer.In 1711–1717, Stepan Malygin was a student at the Moscow School of Mathematical and Navigational Sciences. After his graduation, Malygin began his career as a naval cadet and was then promoted to the rank of lieutenant four years later... , Ovtsyn Dmitry Ovtsyn Dmitry Leontiyevich Ovtsyn was a Russian hydrographer and Arctic explorer.In 1734-1738, Ovtsyn led one of the units of the Second Kamchatka expedition that charted the coastline of the Kara Sea east of the river Ob. In summer of 1737, his unit made its way from Ob to Yenisei and made the first... , Chelyuskin Semion Chelyuskin Semyon Ivanovich Chelyuskin was a Russian polar explorer and naval officer.Chelyuskin graduated from the Navigation School in Moscow. He first became a deputy navigator while serving in the Baltic Fleet and later promoted to navigator . Chelyuskin was chosen for the Second Kamchatka Expedition,... , K.Laptev and D.Laptev on a modern commemorative coin) |
A cousine of Khariton Laptev Khariton Laptev Khariton Prokofievich Laptev was a Russian naval officer and Arctic explorer.Khariton Laptev was born in a gentry family in the village of Pokarevo near Velikiye Luki , just a year before his cousin Dmitry Laptev was born in the nearby village of Bolotovo.Khariton Laptev started his career in the... , Dmitry Laptev led one of the parties of the Great Northern Expedition Great Northern Expedition The Great Northern Expedition or Second Kamchatka expedition was one of the largest organised exploration enterprises in history, resulting in mapping of the most of the Arctic coast of Siberia and some parts of the North America coastline, greatly reducing the "white areas" on the maps... in 1739-42. He described the sea coastline from the mouth of the Lena River Lena River The Lena is the easternmost of the three great Siberian rivers that flow into the Arctic Ocean . It is the 11th longest river in the world and has the 9th largest watershed... to the Cape Bolshoy Baranov east of the mouth of Kolyma Kolyma River The Kolyma River is a river in northeastern Siberia, whose basin covers parts of the Sakha Republic, Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, and Magadan Oblast of Russia. Itrises in the mountains north of Okhotsk and Magadan, in the area of and... , the basin and the mouth of the Anadyr River Anadyr River Anadyr is a river in the far northeast Siberia which flows into Anadyr Bay of the Bering Sea and drains much of the interior of Chukotka Autonomous Okrug. Its basin corresponds to the Anadyrsky District of Chukotka.... , and land route from the Anadyr fortress to the Penzhin Bay. In 1741-42, Laptev surveyed the rivers of Bolshoy Anyuy Bolshoy Anyuy River The Bolshoy Anyuy River or Bolshoy Anyui River is a river in the Kolyma River basin in Far East Siberia. It flows roughly westwards and passes through the sparsely populated areas of Chukotka... and Anadyr. Later he continued his service in the Baltic Fleet Baltic Fleet The Twice Red Banner Baltic Fleet - is the Russian Navy's presence in the Baltic Sea. In previous historical periods, it has been part of the navy of Imperial Russia and later the Soviet Union. The Fleet gained the 'Twice Red Banner' appellation during the Soviet period, indicating two awards of... and became Vice Admiral Vice Admiral Vice admiral is a senior naval rank of a three-star flag officer, which is equivalent to lieutenant general in the other uniformed services. A vice admiral is typically senior to a rear admiral and junior to an admiral... . A cape in the delta of the Lena River and a strait between the Bolshoy Lyakhovsky Island and Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... n mainland bear Dmitry Laptev's name. The Laptev Sea Laptev Sea The Laptev Sea is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It is located between the northern coast of Siberia, the Taimyr Peninsula, Severnaya Zemlya and the New Siberian Islands. Its northern boundary passes from the Arctic Cape to a point with co-ordinates of 79°N and 139°E, and ends at the Anisiy... is named after Dmitry Laptev and Khariton Laptev. |
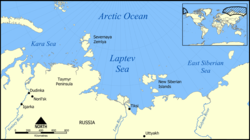 |
|
| Khariton Laptev Khariton Laptev Khariton Prokofievich Laptev was a Russian naval officer and Arctic explorer.Khariton Laptev was born in a gentry family in the village of Pokarevo near Velikiye Luki , just a year before his cousin Dmitry Laptev was born in the nearby village of Bolotovo.Khariton Laptev started his career in the... (1700–1763) Tsardom of Russia Tsardom of Russia The Tsardom of Russia was the name of the centralized Russian state from Ivan IV's assumption of the title of Tsar in 1547 till Peter the Great's foundation of the Russian Empire in 1721.From 1550 to 1700, Russia grew 35,000 km2 a year...  Russian Empire Russian EmpireRussian Imperial Navy officer, explorer of Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... and Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... (Malygin Stepan Malygin Stepan Gavrilovich Malygin was a Russian Arctic explorer.In 1711–1717, Stepan Malygin was a student at the Moscow School of Mathematical and Navigational Sciences. After his graduation, Malygin began his career as a naval cadet and was then promoted to the rank of lieutenant four years later... , Ovtsyn Dmitry Ovtsyn Dmitry Leontiyevich Ovtsyn was a Russian hydrographer and Arctic explorer.In 1734-1738, Ovtsyn led one of the units of the Second Kamchatka expedition that charted the coastline of the Kara Sea east of the river Ob. In summer of 1737, his unit made its way from Ob to Yenisei and made the first... , Chelyuskin Semion Chelyuskin Semyon Ivanovich Chelyuskin was a Russian polar explorer and naval officer.Chelyuskin graduated from the Navigation School in Moscow. He first became a deputy navigator while serving in the Baltic Fleet and later promoted to navigator . Chelyuskin was chosen for the Second Kamchatka Expedition,... , K.Laptev and D.Laptev on a modern commemorative coin) |
A cousine of Dmitry Laptev Dmitry Laptev Dmitry Yakovlevich Laptev was a Russian Arctic explorer and Vice Admiral .Dmitry Laptev was born in the village of Bolotovo, near Velikie Luki, in 1701. Bolotovo was the estate of his father, Yakov Laptev... , Khariton Laptev led one of the parties of the Great Northern Expedition Great Northern Expedition The Great Northern Expedition or Second Kamchatka expedition was one of the largest organised exploration enterprises in history, resulting in mapping of the most of the Arctic coast of Siberia and some parts of the North America coastline, greatly reducing the "white areas" on the maps... in 1739-42. Together with Semion Chelyuskin Semion Chelyuskin Semyon Ivanovich Chelyuskin was a Russian polar explorer and naval officer.Chelyuskin graduated from the Navigation School in Moscow. He first became a deputy navigator while serving in the Baltic Fleet and later promoted to navigator . Chelyuskin was chosen for the Second Kamchatka Expedition,... , N. Chekin, and G. Medvedev, Laptev described the Taimyr Peninsula from the mouth of the Khatanga River Khatanga River The Khatanga River is a river in Krasnoyarsk Krai in Russia. It begins at the confluence of the rivers Kotuy and Kheta. The Khatanga River is long; the area of its basin is 364,000 km². It flows into the Khatanga Gulf of the Laptev Sea, forming an estuary... to the mouth of the Pyasina river and discovered several islands. He participated in the creation of the "General Map of the Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... n and Kamchatka Coast", and then continued his service in the Baltic Fleet Baltic Fleet The Twice Red Banner Baltic Fleet - is the Russian Navy's presence in the Baltic Sea. In previous historical periods, it has been part of the navy of Imperial Russia and later the Soviet Union. The Fleet gained the 'Twice Red Banner' appellation during the Soviet period, indicating two awards of... . The sea coastline of the Taimyr Peninsula, a cape on the Chelyuskin Cape Chelyuskin Cape Chelyuskin is the northernmost point of the Eurasian continent , and the northernmost point of mainland Russia. It is situated at the tip of the Taymyr Peninsula, south of Severnaya Zemlya archipelago, in Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russia... Peninsula and other landmarks bear Khariton Laptev's name. The Laptev Sea Laptev Sea The Laptev Sea is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It is located between the northern coast of Siberia, the Taimyr Peninsula, Severnaya Zemlya and the New Siberian Islands. Its northern boundary passes from the Arctic Cape to a point with co-ordinates of 79°N and 139°E, and ends at the Anisiy... is named after Dmitry Laptev and Khariton Laptev. |
 |
|
 |
Mikhail Lavrov Mikhail Lavrov Mikhail Andrianovich Lavrov was a Russian rear-admiral and Arctic explorer.Mikhail Lavrov was born on September 13, 1799 in the city of Arkhangelsk. He graduated from Cadets Corps in Saint Petersburg and served at the Baltic Fleet. He participated in the voyage of the cargo ship Mezen from... (1799–1882)  Russian Empire Russian EmpireRussian Imperial Navy officer, Rear Admiral Rear Admiral Rear admiral is a naval commissioned officer rank above that of a commodore and captain, and below that of a vice admiral. It is generally regarded as the lowest of the "admiral" ranks, which are also sometimes referred to as "flag officers" or "flag ranks"... , Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... explorer |
Lavrov participated in the voyage of the cargo ship Mezen from Kronstadt Kronstadt Kronstadt , also spelled Kronshtadt, Cronstadt |crown]]" and Stadt for "city"); is a municipal town in Kronshtadtsky District of the federal city of St. Petersburg, Russia, located on Kotlin Island, west of Saint Petersburg proper near the head of the Gulf of Finland. Population: It is also... to Arkhangelsk Arkhangelsk Arkhangelsk , formerly known as Archangel in English, is a city and the administrative center of Arkhangelsk Oblast, Russia. It lies on both banks of the Northern Dvina River near its exit into the White Sea in the north of European Russia. The city spreads for over along the banks of the river... and back in 1819-20. In 1821-24 he participated in the expedition of Fyodor Litke to Novaya Zemlya Novaya Zemlya Novaya Zemlya , also known in Dutch as Nova Zembla and in Norwegian as , is an archipelago in the Arctic Ocean in the north of Russia and the extreme northeast of Europe, the easternmost point of Europe lying at Cape Flissingsky on the northern island... , making description of its shores and the coastline near Murmansk Murmansk Murmansk is a city and the administrative center of Murmansk Oblast, Russia. It serves as a seaport and is located in the extreme northwest part of Russia, on the Kola Bay, from the Barents Sea on the northern shore of the Kola Peninsula, not far from Russia's borders with Norway and Finland... . In 1825-27, he sailed around the world on board of sloop Krotkiy led by Ferdinand Wrangel, visiting Kamchatka and Russian America. Later he became Rear Admiral for his feats of arms. A cape to in the Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... and an island in Severnaya Zemlya Severnaya Zemlya Severnaya Zemlya is an archipelago in the Russian high Arctic at around . It is located off mainland Siberia's Taymyr Peninsula across the Vilkitsky Strait... were named after Lavrov. |
 |
| Adam Laxman (1766–1806?)  Russian Empire Russian Empire(Finland-Swedish descent) Russian Imperial Army officer, diplomat, explorer of Japan Japan Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south... |
Son of Kirill Laxman, Adam Laxman was sent to Japan Japan Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south... on a diplomatic mission in 1791-92, with the aim to return Daikokuya Kōdayū Daikokuya Kōdayū was a Japanese castaway who spent eleven years in Russia.His ship landed at Amchitka, Aleutian Islands. They managed to escape to the Russian mainland and had Catherine the Great allow them to go back to Japan by Kirill Laxman's effort with Alexander Bezborodko and Alexander Vorontsov... and another Japanese castaway in exchange for trade concessions from Tokugawa shogunate Tokugawa shogunate The Tokugawa shogunate, also known as the and the , was a feudal regime of Japan established by Tokugawa Ieyasu and ruled by the shoguns of the Tokugawa family. This period is known as the Edo period and gets its name from the capital city, Edo, which is now called Tokyo, after the name was... . He made valuable observations, but returned to Russia essentially empty-handed, though he possibly obtained the first official Japanese documents granting very limited permission to trade, to a nation other than China or the Netherlands. |
 |
|
| Kirill Laxman (1737–1796)  Sweden Sweden Russian Empire Russian Empire(Finland-Swedish origin) clergyman, naturalist, explorer of Northern Europe Northern Europe Northern Europe is the northern part or region of Europe. Northern Europe typically refers to the seven countries in the northern part of the European subcontinent which includes Denmark, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Norway, Finland and Sweden... and Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... |
Kirill Laxman became a priest first in St. Petersburg and then in Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... n town of Barnaul Barnaul -Russian Empire:Barnaul was one of the earlier cities established in Siberia. Originally chosen for its proximity to the mineral-rich Altai Mountains and its location on a major river, the site was founded by the wealthy Demidov family in the 1730s. In addition to the copper which had originally... . In 1764-68 he explored Siberia, reaching Irkutsk Irkutsk Irkutsk is a city and the administrative center of Irkutsk Oblast, Russia, one of the largest cities in Siberia. Population: .-History:In 1652, Ivan Pokhabov built a zimovye near the site of Irkutsk for gold trading and for the collection of fur taxes from the Buryats. In 1661, Yakov Pokhabov... , Baikal Baikal Baykal commonly refers to Lake Baikal in southern Siberia, Russia.Baykal or Baikal may also refer to:-Russia:*Baykal, Irkutsk Oblast, an urban-type settlement*Baykal, Aurgazinsky District, Republic of Bashkortostan, a village... , Kiakhta and the border with China China Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture... and researching the Siberian flora and fauna. In 1782 he founded the oldest museum in Siberia in Irkutsk, where he settled earlier and was a business partner of Alexander Baranov (the future governor of Russian America). Laxman was engaged in attempts to establish relationships between Russia and Japan Japan Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south... . He brought Daikokuya Kōdayū Daikokuya Kōdayū was a Japanese castaway who spent eleven years in Russia.His ship landed at Amchitka, Aleutian Islands. They managed to escape to the Russian mainland and had Catherine the Great allow them to go back to Japan by Kirill Laxman's effort with Alexander Bezborodko and Alexander Vorontsov... , a Japanese Japanese people The are an ethnic group originating in the Japanese archipelago and are the predominant ethnic group of Japan. Worldwide, approximately 130 million people are of Japanese descent; of these, approximately 127 million are residents of Japan. People of Japanese ancestry who live in other countries... castaway, to the court of empress Catherine II, and after that his son Adam Laxman was sent with Kōdayū to Japan. A number of plant species have been named after Laxman. |
||
| Mikhail Lazarev Mikhail Petrovich Lazarev Admiral Mikhail Petrovich Lazarev was a Russian fleet commander and explorer who discovered Antarctica.-Education and early career:Lazarev was born in Vladimir, a scion of the old Russian nobility from the Vladimir province. In 1800, he enrolled in Russia's Naval College. Three years later he... (1788–1851)  Russian Empire Russian EmpireRussian Imperial Navy officer, Admiral Admiral Admiral is the rank, or part of the name of the ranks, of the highest naval officers. It is usually considered a full admiral and above vice admiral and below admiral of the fleet . It is usually abbreviated to "Adm" or "ADM"... , circumnavigator, Antarctic Antarctic The Antarctic is the region around the Earth's South Pole, opposite the Arctic region around the North Pole. The Antarctic comprises the continent of Antarctica and the ice shelves, waters and island territories in the Southern Ocean situated south of the Antarctic Convergence... and Pacific explorer |
Lazarev thrice circumnavigated the globe. He led 1813-16 circumnavigation Circumnavigation Circumnavigation – literally, "navigation of a circumference" – refers to travelling all the way around an island, a continent, or the entire planet Earth.- Global circumnavigation :... aboard the vessel Suvorov and discovered Suvorov Atoll Suwarrow Suwarrow is a low coral atoll in the Cook Islands in the Pacific Ocean. It is about 1,300 km south of the equator and 930 km NNW of Rarotonga, from which it is administered.... . He commanded Mirny Mirny Station Mirny is a Russian science station in Antarctica, located on the Antarctic coast of the Davis Sea in the Australian Antarctic Territory. Named after support vessel of the Bellingshausen's expedition.... , the second ship in the Russian circumnavigation of 1819-21 under the leadership of Fabian Gottlieb von Bellingshausen Fabian Gottlieb von Bellingshausen Fabian Gottlieb Thaddeus von Bellingshausen was an officer in the Imperial Russian Navy, cartographer and explorer, who ultimately rose to the rank of Admiral... aboard Vostok Vostok Station Vostok Station was a Russian Antarctic research station. It was at the southern Pole of Cold, with the lowest reliably measured natural temperature on Earth of −89.2 °C . Research includes ice core drilling and magnetometry... – this expedition was the first to discover the contenent of Antarctica on January 28, 1820 (New Style). They also discovered and named Peter I Island Peter I Island Peter I Island is an uninhabited volcanic island in the Bellingshausen Sea, from Antarctica. It is claimed as a dependency of Norway, and along with Queen Maud Land and Bouvet Island comprises one of the three Norwegian dependent territories in the Antarctic and sub-Antarctic. Peter I Island is ... , Zavodovski Zavodovski Island Zavodovski Island is an uninhabited volcanic island in the Traversay Islands group of the South Sandwich Islands. It lies southeast of South Georgia Island... , Leskov Leskov Island Leskov Island is a small uninhabited island in the Traversay Islands group of the South Sandwich Islands. It is less than long, and lies west of Visokoi Island... and Visokoi Island Visokoi Island Visokoi Island is an uninhabited island in the Traversay Islands group of the South Sandwich Islands. It was discovered in 1819 by a Russian expedition under Fabian Gottlieb von Bellingshausen, who named the island Visokoi because of its conspicuous height.The island is long and wide, capped by... s, Antarctic peninsula Antarctic Peninsula The Antarctic Peninsula is the northernmost part of the mainland of Antarctica. It extends from a line between Cape Adams and a point on the mainland south of Eklund Islands.... mainland and Alexander Island Alexander Island Alexander Island or Alexander I Island or Alexander I Land or Alexander Land is the largest island of Antarctica, with an area of lying in the Bellingshausen Sea west of the base of the Antarctic Peninsula, from which it is separated by Marguerite Bay and George VI Sound. Alexander Island lies off... (Alexander Coast), and made some discoveries in the tropical waters of the Pacific. In 1822-25 Lazarev sailed around the globe for the third time on his frigate Frigate A frigate is any of several types of warship, the term having been used for ships of various sizes and roles over the last few centuries.In the 17th century, the term was used for any warship built for speed and maneuverability, the description often used being "frigate-built"... Kreyser. Lazarev was a hero of the Battle of Navarino Battle of Navarino The naval Battle of Navarino was fought on 20 October 1827, during the Greek War of Independence in Navarino Bay , on the west coast of the Peloponnese peninsula, in the Ionian Sea. A combined Ottoman and Egyptian armada was destroyed by a combined British, French and Russian naval force... , the commander of the Russian Black Sea Fleet for 20 years and the tutor of famous Admirals and war heroes Pavel Nakhimov Pavel Nakhimov Pavel Stepanovich Nakhimov |Siege of Sevastopol]] during the Crimean War.-Biography:Born in the Gorodok village of Vyazma district of Smolensk region. Nakhimov entered the Naval Academy for the Nobility in Saint Petersburg in 1815. He made his first sea voyage in 1817, aboard the frigate Feniks ,... , Vladimir Kornilov and Vladimir Istomin Vladimir Istomin Vladimir Ivanovich Istomin was a Russian rear admiral and hero of the Siege of Sevastopol.... . Lazarev Mountains Lazarev Mountains Lazarev Mountains is a chain of mountains along the west side of Matusevich Glacier southward of Eld Peak, about 40 km long. Photographed from the air by Operation Highjump , the Soviet Antarctic Expedition and ANARE . Named by the Soviet expedition after Lieutenant M.P... , Lazarev and Novolazarevskaya Station Novolazarevskaya Station Novolazarevskaya Station is a Russian, formerly Soviet, Antarctic research station. The station is located at Schirmacher Oasis, Queen Maud Land, 75 km from the Antarctic coast, from which it is separated by Lazarev Ice Shelf. It was opened on January 18, 1961 by the 6th Soviet Antarctic... s in Antarctic, Lazarev Atoll in the Pacific Russian Islands Tuamotus The Tuamotus or the Tuamotu Archipelago are a chain of islands and atolls in French Polynesia. They form the largest chain of atolls in the world, spanning an area of the Pacific Ocean roughly the size of Western Europe... , capes in the Amur Liman Amur Liman The Amur Liman is a liman of the Amur River, the northern part of the Strait of Tartary between Eurasia and Sakhalin. It connects the Sakhalin Gulf of the Sea of Okhotsk with the main body of the Strait of Tartary via the Nevelskoy Strait.... and on the Unimak Island Unimak Island Unimak Island is the largest island in the Aleutian Islands chain of the U.S. state of Alaska. It is the easternmost island in the Aleutians and, with an area of 1,571.41 mi² , the ninth largest island in the United States and the 134th largest island in the world. It is home to Mount... , an island in the Aral Sea Aral Sea The Aral Sea was a lake that lay between Kazakhstan in the north and Karakalpakstan, an autonomous region of Uzbekistan, in the south... , a bay and a port in the Sea of Japan Sea of Japan The Sea of Japan is a marginal sea of the western Pacific Ocean, between the Asian mainland, the Japanese archipelago and Sakhalin. It is bordered by Japan, North Korea, Russia and South Korea. Like the Mediterranean Sea, it has almost no tides due to its nearly complete enclosure from the Pacific... , Lazarevskoye Lazarevskoye Lazarevskoye is a microdistrict of Lazarevsky City District of the city of Sochi, Krasnodar Krai, Russia. It was a resort settlement before 1961, when it was merged into Sochi.-Geography:... settlement near Sochi and other locations, a number of streets and vessels, and minor planet Minor planet An asteroid group or minor-planet group is a population of minor planets that have a share broadly similar orbits. Members are generally unrelated to each other, unlike in an asteroid family, which often results from the break-up of a single asteroid... 3660 Lazarev 3660 Lazarev 3660 Lazarev is an outer main-belt asteroid discovered on August 31, 1978 by N. Chernykh at Nauchnyj. It is named after the 19th century Russian explorer Mikhail Petrovich Lazarev.- External links :*... are named in honor of Lazarev. |
 |
|
| Alexei Leonov (born 1934)  Soviet Union Soviet Union Russia Russiacosmonaut and Soviet Air Force Soviet Air Force The Soviet Air Force, officially known in Russian as Военно-воздушные силы or Voenno-Vozdushnye Sily and often abbreviated VVS was the official designation of one of the air forces of the Soviet Union. The other was the Soviet Air Defence Forces... General General A general officer is an officer of high military rank, usually in the army, and in some nations, the air force. The term is widely used by many nations of the world, and when a country uses a different term, there is an equivalent title given.... , twice the Hero of the Soviet Union Hero of the Soviet Union The title Hero of the Soviet Union was the highest distinction in the Soviet Union, awarded personally or collectively for heroic feats in service to the Soviet state and society.-Overview:... , painter, writer |
On March 18, 1965, connected to the spacecraft Voskhod 2 Voskhod 2 Voskhod 2 was a Soviet manned space mission in March 1965. Vostok-based Voskhod 3KD spacecraft with two crew members on board, Pavel Belyaev and Alexei Leonov, was equipped with an inflatable airlock... by a 5.35 meter tether, Leonov became the first person to make a spacewalk, or extra-vehicular activity Extra-vehicular activity Extra-vehicular activity is work done by an astronaut away from the Earth, and outside of a spacecraft. The term most commonly applies to an EVA made outside a craft orbiting Earth , but also applies to an EVA made on the surface of the Moon... . He was in the open space for 12 min 9 sec. At the end of the spacewalk, Leonov's spacesuit had inflated in the vacuum to the point where he could not reenter the airlock. He opened a valve to allow some of the suit's pressure to bleed off, and was barely able to get back inside the capsule, where his companion Pavel Belyayev Pavel Belyayev Pavel Ivanovich Belyayev , , was a Soviet fighter pilot with extensive experience in piloting different types of aircraft... assisted him. Subsequently Leonov made a second spaceflight Spaceflight Spaceflight is the act of travelling into or through outer space. Spaceflight can occur with spacecraft which may, or may not, have humans on board. Examples of human spaceflight include the Russian Soyuz program, the U.S. Space shuttle program, as well as the ongoing International Space Station... on Soyuz 19 spacecraft, a part of Apollo–Soyuz Test Project in 1975. Thus Leonov participated in the first joint flight of the U.S. and Soviet space programs. He published several books and albums of paintings, some of which he created in space. Arthur C. Clarke Arthur C. Clarke Sir Arthur Charles Clarke, CBE, FRAS was a British science fiction author, inventor, and futurist, famous for his short stories and novels, among them 2001: A Space Odyssey, and as a host and commentator in the British television series Mysterious World. For many years, Robert A. Heinlein,... 's book 2010: Odyssey Two 2010: Odyssey Two 2010: Odyssey Two is a 1982 best-selling science fiction novel by Arthur C. Clarke. It is the sequel to the 1968 novel 2001: A Space Odyssey, but continues the story of Stanley Kubrick's film adaptation with the same title and not Clarke's original novel. The book is a part of Clarke's... was dedicated to Leonov and Andrei Sakharov Andrei Sakharov Andrei Dmitrievich Sakharov was a Soviet nuclear physicist, dissident and human rights activist. He earned renown as the designer of the Soviet Union's Third Idea, a codename for Soviet development of thermonuclear weapons. Sakharov was an advocate of civil liberties and civil reforms in the... ; the fictional spaceship Cosmonaut Alexei Leonov in the book was named after him. |
||
| Mikhail Levashov Mikhail Levashev Mikhail D. Levashev was a Russian explorer and Lieutenant of the Imperial Russian Navy... (c. 1738–1774-76)  Russian Empire Russian EmpireRussian Imperial Navy officer, explorer of Alaska Alaska Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait... and Pacific |
In 1766-70 Levashov was second-in-command in the "secret" expedition to the North Pacific led by Pyotr Krenitsyn Pyotr Krenitsyn Pyotr Kuzmich Krenitsyn , spelt "Krenitzin" in the United States, was a Russian explorer and Captain/Lieutenant of the Imperial Russian Navy. Following Vitus Bering's 1741 tragic venture he was the first to conduct an expedition to Alaska and the Aleutians... , as ordered by Catherine II. They explored the Aleutian Islands and part of Alaska Alaska Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait... shore, discovering good haven in Unalaska and many features of Alaska Alaska Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait... n coast. Levashov also explored and described the Commander Islands. On the basis of their explorations the first general map of the Aleutian Islands was created. Port Levashef (the harbor in Unalaska), one of the straits between Kuril Islands Kuril Islands The Kuril Islands , in Russia's Sakhalin Oblast region, form a volcanic archipelago that stretches approximately northeast from Hokkaidō, Japan, to Kamchatka, Russia, separating the Sea of Okhotsk from the North Pacific Ocean. There are 56 islands and many more minor rocks. It consists of Greater... , a cape and a volcano on Paramushir Island, and a cape in the west of Kamchatka have been named after Levashov. |
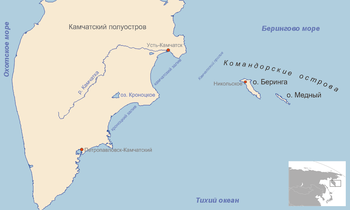 |
|
| Yuri Lisyansky Yuri Lisyansky Yuri Fyodorovich Lisyansky was an officer in the Imperial Russian Navy and explorer of Ukrainian origin.... (1773–1837)  Russian Empire Russian EmpireRussian Imperial Navy officer, circumnavigator, explorer of the Pacific |
In 1803-06 Lisyansky aboard Neva together with Ivan Krusenstern on Nadezhda led the first Russian circumnavigation First Russian circumnavigation The first Russian circumnavigation of the Earth took place from August 1803 to August 1806. It was sponsored by Count Nikolay Rumyantsev and was headed by Adam Johann von Krusenstern.-Events:... of the world. The purpose of the expedition was to establish trade with China China Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture... and Japan Japan Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south... and examine California California California is a state located on the West Coast of the United States. It is by far the most populous U.S. state, and the third-largest by land area... for a possible colony. They sailed from Kronstadt, rounded Cape Horn Cape Horn Cape Horn is the southernmost headland of the Tierra del Fuego archipelago of southern Chile, and is located on the small Hornos Island... , and reached the northern Pacific. The ships split near Hawaii Hawaii Hawaii is the newest of the 50 U.S. states , and is the only U.S. state made up entirely of islands. It is the northernmost island group in Polynesia, occupying most of an archipelago in the central Pacific Ocean, southwest of the continental United States, southeast of Japan, and northeast of... and Lisyanski headed to Russian Alaska Russian Alaska Russian America was the name of Russian colonial possessions in the Americas from 1733 to 1867 that today is the U.S. state of Alaska and settlements farther south in California and Hawaii... , where Neva became essential in defeating the Tlingit in the Battle of Sitka Battle of Sitka The Battle of Sitka was the last major armed conflict between Europeans and Alaska Natives, and was initiated in response to the destruction of a Russian trading post two years prior... . Lisyansky was the first to describe the Hawaiian monk seal Hawaiian Monk Seal The Hawaiian monk seal, Monachus schauinslandi, is an endangered species of earless seal in the Phocidae family that is endemic to the Hawaiian Islands.... on the island which now bears his name. He met Krusenstern again in Macau Macau Macau , also spelled Macao , is, along with Hong Kong, one of the two special administrative regions of the People's Republic of China... , but they soon separated. Eventually, Lisyansky was the first to return to Kronstadt. Lisianski Island Lisianski Island Lisianski Island is one of the Northwestern Hawaiian Islands, with a land area of and a maximum elevation of above sea level. Honolulu is away, to the southeast. Linked to Lisianski are the extensive Neva Shoals... in the Northwestern Hawaiian Islands Northwestern Hawaiian Islands The Northwestern Hawaiian Islands or the Leeward Islands are the small islands and atolls in the Hawaiian island chain located northwest of the islands of Kauai and Niihau. They are administered by the U.S. state of Hawaii except Midway Atoll, which has temporary residential facilities and is... , a peninsula of the Baranof Island Baranof Island Baranof Island, also sometimes called Baranov Island, Shee or Sitka Island, is an island in the northern Alexander Archipelago in the Alaska Panhandle, in Alaska. The name Baranof was given in 1805 by Imperial Russian Navy captain U. F. Lisianski to honor Alexander Andreyevich Baranov... near Alaska Alaska Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait... , a bay, a strait, a river, a cape in North America North America North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas... , an undersea mountain in Okhotsk Sea and a peninsula there have been named after Lisyansky. |
  |
|
 |
Fyodor Litke Fyodor Petrovich Litke Count Fyodor Petrovich Litke , born Friedrich Benjamin Lütke, was a Russian navigator, geographer, and Arctic explorer. He became a count in 1866, and an admiral in 1855. He was a Corresponding Member , Honorable Member , and President of the Russian Academy of Science in St.Petersburg... (1797–1882)  Russian Empire Russian EmpireRussian Imperial Navy officer, Admiral Admiral Admiral is the rank, or part of the name of the ranks, of the highest naval officers. It is usually considered a full admiral and above vice admiral and below admiral of the fleet . It is usually abbreviated to "Adm" or "ADM"... , circumnavigator, Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... explorer |
Litke took part in Vasily Golovnin Vasily Golovnin Vasily Mikhailovich Golovnin .-Early life and career:Vasily Mikhailovich Golovnin was born in April 1776, in the village of Gulyniki in Ryazan Oblast, on his father's country estate. Both his father and grandfather had served in the Russian military as officers in the elite Preobrazhensky... 's world cruise on the ship Kamchatka in 1817-19. In 1821-24, Litke explored the coastline of Novaya Zemlya Novaya Zemlya Novaya Zemlya , also known in Dutch as Nova Zembla and in Norwegian as , is an archipelago in the Arctic Ocean in the north of Russia and the extreme northeast of Europe, the easternmost point of Europe lying at Cape Flissingsky on the northern island... , the White Sea White Sea The White Sea is a southern inlet of the Barents Sea located on the northwest coast of Russia. It is surrounded by Karelia to the west, the Kola Peninsula to the north, and the Kanin Peninsula to the northeast. The whole of the White Sea is under Russian sovereignty and considered to be part of... , and the eastern Barents Sea Barents Sea The Barents Sea is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean, located north of Norway and Russia. Known in the Middle Ages as the Murman Sea, the sea takes its current name from the Dutch navigator Willem Barents... . In 1826-29, he led the circumnavigation on the ship Senyavin and accompanied by Mikhail Staniukovich on the sloop Moller. During this voyage they explored the Bering Sea Bering Sea The Bering Sea is a marginal sea of the Pacific Ocean. It comprises a deep water basin, which then rises through a narrow slope into the shallower water above the continental shelves.... (including Pribilof Islands Pribilof Islands The Pribilof Islands are a group of four volcanic islands off the coast of mainland Alaska, in the Bering Sea, about north of Unalaska and 200 miles southwest of Cape Newenham. The Siberia coast is roughly northwest... , St. Matthew Island St. Matthew Island St. Matthew Island is a remote island in the Bering Sea in Alaska, WNW of Nunivak Island. The island has a land area of , making it the 43rd largest island in the United States. Its most southerly point is Cape Upright which features cliff faces which exceed... and the Commander Islands), the Bonin Islands off Japan Japan Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south... , and the Carolines Caroline Islands The Caroline Islands are a widely scattered archipelago of tiny islands in the western Pacific Ocean, to the north of New Guinea. Politically they are divided between the Federated States of Micronesia in the eastern part of the group, and Palau at the extreme western end... , discovering 12 new islands. Litke was a co-fouder and the president of the Russian Geographic Society in 1845-50 and 1857-72. He was the president of the Russian Academy of Sciences Russian Academy of Sciences The Russian Academy of Sciences consists of the national academy of Russia and a network of scientific research institutes from across the Russian Federation as well as auxiliary scientific and social units like libraries, publishers and hospitals.... in 1864-82, and occupied a number of major military and state offices. Litke gold medal of the Russian Geographical Society Russian Geographical Society The Russian Geographical Society is a learned society, founded on 6 August 1845 in Saint Petersburg, Russia.-Imperial Geographical Society:Prior to the Russian Revolution of 1917, it was known as the Imperial Russian Geographical Society.... , Cape Lutke, Alaska Cape Lutke, Alaska Cape Lutke is a landhead in Unimak Island, the largest island in the Aleutian Islands chain of the U.S. state of Alaska. It is located on the southern central coast of the island.... , Litke Strait Litke Strait Litke Strait is a strait in the Bering Sea off the northeastern coast of Kamchatka, Russia, which separates the Karaginsky Island from the mainland. It is named after explorer Fyodor Petrovich Litke.... between Kamchatka Kamchatka Peninsula The Kamchatka Peninsula is a peninsula in the Russian Far East, with an area of . It lies between the Pacific Ocean to the east and the Sea of Okhotsk to the west... and Karaginsky Island Karaginsky Island Karaginsky Island or Karaginskiy Island is an island in the Karaginsky Gulf of the Bering Sea. The 40 km wide strait between the Kamchatka Peninsula and this island is called Litke Strait.... , a cape, a peninsula, a mountain and a bay in Novaya Zemlya Novaya Zemlya Novaya Zemlya , also known in Dutch as Nova Zembla and in Norwegian as , is an archipelago in the Arctic Ocean in the north of Russia and the extreme northeast of Europe, the easternmost point of Europe lying at Cape Flissingsky on the northern island... , a number of islands in the Franz Josef Land Franz Josef Land Franz Josef Land, Franz Joseph Land, or Francis Joseph's Land is an archipelago located in the far north of Russia. It is found in the Arctic Ocean north of Novaya Zemlya and east of Svalbard, and is administered by Arkhangelsk Oblast. Franz Josef Land consists of 191 ice-covered islands with a... , Baydaratskaya Bay Baydaratskaya Bay Baydaratskaya Bay is a gulf in Russia, located in the southern part of the Kara Sea between the coastline of the Northern termination of the Ural Mountains and Yamal Peninsula. The length of the gulf is approx. 180 km, mouth width - 78 km, depth - up to 20 m. Surface water temperature... , and Nordenskiöld Archipelago Nordenskiöld Archipelago The Nordenskiöld Archipelago or Nordenskjold Archipelago is a very large and complex cluster of islands in the eastern region of the Kara Sea. Its eastern limit lies west of the Taymyr Peninsula.... , as well as a Russian icebreaker Icebreaker An icebreaker is a special-purpose ship or boat designed to move and navigate through ice-covered waters. Although the term usually refers to ice-breaking ships, it may also refer to smaller vessels .For a ship to be considered an icebreaker, it requires three traits most... Feodor Litke Icebreaker Feodor Litke The icebreaker Fyodor Litke was active in the Soviet era in the Arctic, until the late 1950s. It was built in 1909 in England for the Saint Lawrence River service and initially named CGC Earl Grey after Albert Grey, Governor General of Canada... have been named after Litke. |
|
| Fyodor Luzhin Fyodor Luzhin Fyodor Fyodorovich Luzhin was a Russian geodesist and cartographer.Fyodor Luzhin was first a student at the School for Mathematical and Navigational Sciences in Moscow and then in a geodesic class of the Naval Academy in St. Petersburg... (?–1727) Tsardom of Russia Tsardom of Russia The Tsardom of Russia was the name of the centralized Russian state from Ivan IV's assumption of the title of Tsar in 1547 till Peter the Great's foundation of the Russian Empire in 1721.From 1550 to 1700, Russia grew 35,000 km2 a year...  Russian Empire Russian Empirecartographer, geodesist, explorer of Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... and the Russian Far East Russian Far East Russian Far East is a term that refers to the Russian part of the Far East, i.e., extreme east parts of Russia, between Lake Baikal in Eastern Siberia and the Pacific Ocean... |
In 1719-1721, together Ivan Yevreinov Ivan Yevreinov Ivan Mikhaylovich Yevreinov was a Russian geodesist and explorer.Ivan Yevreinov was born in Poland, then brought to Russia and baptized into Orthodox Christianity.... , Luzhin made the first instrumental mapping of Kamchatka and the first map of the Kuril Islands Kuril Islands The Kuril Islands , in Russia's Sakhalin Oblast region, form a volcanic archipelago that stretches approximately northeast from Hokkaidō, Japan, to Kamchatka, Russia, separating the Sea of Okhotsk from the North Pacific Ocean. There are 56 islands and many more minor rocks. It consists of Greater... during the "secret expedition", as ordered by Peter I of Russia Peter I of Russia Peter the Great, Peter I or Pyotr Alexeyevich Romanov Dates indicated by the letters "O.S." are Old Style. All other dates in this article are New Style. ruled the Tsardom of Russia and later the Russian Empire from until his death, jointly ruling before 1696 with his half-brother, Ivan V... . In 1723-24 he made surveys Surveying See Also: Public Land Survey SystemSurveying or land surveying is the technique, profession, and science of accurately determining the terrestrial or three-dimensional position of points and the distances and angles between them... of different parts of East Siberia near Irkutsk Irkutsk Irkutsk is a city and the administrative center of Irkutsk Oblast, Russia, one of the largest cities in Siberia. Population: .-History:In 1652, Ivan Pokhabov built a zimovye near the site of Irkutsk for gold trading and for the collection of fur taxes from the Buryats. In 1661, Yakov Pokhabov... . In 1725-27, Luzhin participated in the 1st Kamchatka Expedition led by Vitus Bering Vitus Bering Vitus Jonassen Bering Vitus Jonassen Bering Vitus Jonassen Bering (also, less correNavy]], a captain-komandor known among the Russian sailors as Ivan Ivanovich. He is noted for being the first European to discover Alaska and its Aleutian Islands... . Luzhin Strait which separates Paramushir Paramushir Paramushir , is a volcanic island in the northern portion of Kuril Islands chain in the Sea of Okhotsk in the northwest Pacific Ocean. It is separated from Shumshu by the very narrow Second Kuril Strait in the northeast , from Antsiferov by the Luzhin Strait to the southwest, from Atlasov in the... and Antsiferov Islands in the Kurils, and a cape in Taui Bay of Okhotsk Sea are named after Luzhin. |
 |
|
| Ivan Lyakhov Ivan Lyakhov Ivan Lyakhov , died around 1800, was a Russian merchant who explored large sections of the New Siberian Islands in the 18th century.Lyakhov began his explorations in the spring of 1770 on dogsleds in order to explore the islands off the northern Siberian coast reported by Yakov Permyakov and... (? – c. 1800)  Russian Empire Russian Empiremerchant, Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... explorer |
Lyakhov, a merchant, investigated the New Siberian Islands New Siberian Islands The New Siberian Islands are an archipelago, located to the North of the East Siberian coast between the Laptev Sea and the East Siberian Sea north of the Sakha Republic.... in three expeditions on dogsleds in 1770, 1773–74 and 1775. He hoped to find mammoth Mammoth A mammoth is any species of the extinct genus Mammuthus. These proboscideans are members of Elephantidae, the family of elephants and mammoths, and close relatives of modern elephants. They were often equipped with long curved tusks and, in northern species, a covering of long hair... ivory there as he believed the islands were mainly formed by a substratum of bones and tusks of mammoths. He explored the follow-up Lyakhovsky Islands Lyakhovsky Islands The Lyakhovsky Islands are the southernmost group of the New Siberian Islands in the arctic seas of eastern Russia. They are separated from the mainland by the Laptev Strait , and from the Anzhu Islands group by the Sannikov Strait... , crossed the Sannikov Strait Sannikov Strait Sannikov Strait is a 50 km-wide strait in Russia. It separates Anzhu Islands from Lyakhovsky Islands, and connects the Laptev Sea in the west with the East Siberian Sea in the east. It is named after Russian explorer Yakov Sannikov.-References:* Location: * Geographical names:... and discovered Kotelny Island. Lyakhovsky Islands Lyakhovsky Islands The Lyakhovsky Islands are the southernmost group of the New Siberian Islands in the arctic seas of eastern Russia. They are separated from the mainland by the Laptev Strait , and from the Anzhu Islands group by the Sannikov Strait... group in the south of New Siberian Islands New Siberian Islands The New Siberian Islands are an archipelago, located to the North of the East Siberian coast between the Laptev Sea and the East Siberian Sea north of the Sakha Republic.... are named after Lyakhov. |
 |
M
| Portrait | Person | Achievements | Image |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
Richard Maack Richard Maack Richard Otto Maack was a 19th century Russian naturalist, geographer, and anthropologist. He is most known for his exploration of the Russian Far East and Siberia, particularly the Ussuri and Amur River valleys... (1825–1886)  Russian Empire Russian Empire(born in Estonia Estonia Estonia , officially the Republic of Estonia , is a state in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea, to the south by Latvia , and to the east by Lake Peipsi and the Russian Federation . Across the Baltic Sea lies... ) naturalist, geographer, anthropologist, explorer of East Siberia and the Russian Far East Russian Far East Russian Far East is a term that refers to the Russian part of the Far East, i.e., extreme east parts of Russia, between Lake Baikal in Eastern Siberia and the Pacific Ocean... |
Maack participated in the first expedition to describe the orography, geology and population of the Vilyuy River basin in 1853-55. He explored the Amur River and the Ussuri River Ussuri River The Usuri ula is a river in the south of the Outer Manchuria and east of Inner Manchuria . It rises in the Sikhote-Alin range, flowing north, forming part of the Sino-Russian border based on the Sino-Russian Convention of Peking in 1860, until it joins the Amur River at Khabarovsk . It is... in 1855-56 and in 1859 correspondingly. He discovered a number if unknown species and wrote some of the first scientific descriptions of remote Siberia regions. Maackia amurensis Maackia amurensis The tree species Maackia amurensis is commonly known as the Amur maackia. The species epithet and common names are from the Amur River region, where the tree originated.... , Lonicera maackii Lonicera maackii Lonicera maackii is a species of honeysuckle in the family Caprifoliaceae, native to temperate Asia in northern and western China , Mongolia, Japan , Korea, and southeastern Russia .It is listed as an endangered species in Japan... , Prunus maackii Prunus maackii Prunus maackii, commonly called the Manchurian cherry or Amur chokecherry, is a species of cherry native to Korea and both banks of the Amur River, in Manchuria in northeastern China, and Amur Oblast and Primorye in southeastern Russia.... and other plant species have been named after Maack. |
 |
 |
Stepan Makarov Stepan Makarov Stepan Osipovich Makarov was a Ukrainian - born Russian vice-admiral, a highly accomplished and decorated commander of the Imperial Russian Navy, an oceanographer, awarded by the Russian Academy of Sciences, and author of several books. Makarov also designed a small number of ships... (1849–1904)  Russian Empire Russian EmpireRussian Imperial Navy officer, vice-Admiral, oceanographer, Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... explorer |
Makarov was highly decorated for his service as a captain of the Russian torpedo boat tender Torpedo boat tender The torpedo boat tender was a type of warship developed at the end of the 19th century to help bring small torpedo boat to the high seas, and launch them for attack.... Velikiy Knyaz Konstantin in the Russo-Turkish War of 1877–78. On January 16, 1877 he was the first in the world to successfully launch torpedo Torpedo The modern torpedo is a self-propelled missile weapon with an explosive warhead, launched above or below the water surface, propelled underwater towards a target, and designed to detonate either on contact with it or in proximity to it.The term torpedo was originally employed for... es (against the Turkish Turkey Turkey , known officially as the Republic of Turkey , is a Eurasian country located in Western Asia and in East Thrace in Southeastern Europe... armed ship Intibah). He was one of the developers of Russian Flag semaphore Flag semaphore Semaphore Flags is the system for conveying information at a distance by means of visual signals with hand-held flags, rods, disks, paddles, or occasionally bare or gloved hands. Information is encoded by the position of the flags; it is read when the flag is in a fixed position... system. Makarov directed two round-the-world oceanographic expeditions on the corvette Corvette A corvette is a small, maneuverable, lightly armed warship, originally smaller than a frigate and larger than a coastal patrol craft or fast attack craft , although many recent designs resemble frigates in size and role... Vityaz in 1886–89 and in 1894–96. He proposed the idea and oversaw the construction of Yermak Icebreaker Yermak Yermak was a Russian and later Soviet icebreaker, the first polar icebreaker in the world, having a strengthened hull shaped to ride over and crush pack ice.... , the world's first true icebreaker Icebreaker An icebreaker is a special-purpose ship or boat designed to move and navigate through ice-covered waters. Although the term usually refers to ice-breaking ships, it may also refer to smaller vessels .For a ship to be considered an icebreaker, it requires three traits most... , which was able to ride over and crash pack ice. He commanded Yermak in two Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... expeditions in 1899 and in 1901. Promoted to Commander of the Russian Pacific Fleet, Admiral Makarov was killed in action during the Russo-Japanese War Russo-Japanese War The Russo-Japanese War was "the first great war of the 20th century." It grew out of rival imperial ambitions of the Russian Empire and Japanese Empire over Manchuria and Korea... of 1904–05 on the battleship Petropavlovsk Russian battleship Petropavlovsk (1897) The Petropavlovsk was the lead ship of the Petropavlovsk class of battleships built for the Imperial Russian Navy. During the Russo-Japanese War, Petropavlovsk was a flagship of the First Pacific Squadron, taking part in battles against the Imperial Japanese Navy. On March 31, 1904, the battleship... after his ship struck a mine Naval mine A naval mine is a self-contained explosive device placed in water to destroy surface ships or submarines. Unlike depth charges, mines are deposited and left to wait until they are triggered by the approach of, or contact with, an enemy vessel... . An island in the Tsivolk group of the Nordenskiöld Archipelago Nordenskiöld Archipelago The Nordenskiöld Archipelago or Nordenskjold Archipelago is a very large and complex cluster of islands in the eastern region of the Kara Sea. Its eastern limit lies west of the Taymyr Peninsula.... , a town on Sakhalin Sakhalin Sakhalin or Saghalien, is a large island in the North Pacific, lying between 45°50' and 54°24' N.It is part of Russia, and is Russia's largest island, and is administered as part of Sakhalin Oblast... , a number of naval institutions, an embankment in St. Petersburg and other places were named after Stepan Makarov, as well as number of ships called Admiral Makarov. |
 |
| Stepan Malygin Stepan Malygin Stepan Gavrilovich Malygin was a Russian Arctic explorer.In 1711–1717, Stepan Malygin was a student at the Moscow School of Mathematical and Navigational Sciences. After his graduation, Malygin began his career as a naval cadet and was then promoted to the rank of lieutenant four years later... (?–1764) Tsardom of Russia Tsardom of Russia The Tsardom of Russia was the name of the centralized Russian state from Ivan IV's assumption of the title of Tsar in 1547 till Peter the Great's foundation of the Russian Empire in 1721.From 1550 to 1700, Russia grew 35,000 km2 a year...  Russian Empire Russian EmpireRussian Imperial Navy officer, navigator, captain, cartographer, Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... explorer (Malygin, Ovtsyn Dmitry Ovtsyn Dmitry Leontiyevich Ovtsyn was a Russian hydrographer and Arctic explorer.In 1734-1738, Ovtsyn led one of the units of the Second Kamchatka expedition that charted the coastline of the Kara Sea east of the river Ob. In summer of 1737, his unit made its way from Ob to Yenisei and made the first... , Chelyuskin Semion Chelyuskin Semyon Ivanovich Chelyuskin was a Russian polar explorer and naval officer.Chelyuskin graduated from the Navigation School in Moscow. He first became a deputy navigator while serving in the Baltic Fleet and later promoted to navigator . Chelyuskin was chosen for the Second Kamchatka Expedition,... , K.Laptev Khariton Laptev Khariton Prokofievich Laptev was a Russian naval officer and Arctic explorer.Khariton Laptev was born in a gentry family in the village of Pokarevo near Velikiye Luki , just a year before his cousin Dmitry Laptev was born in the nearby village of Bolotovo.Khariton Laptev started his career in the... and D.Laptev Dmitry Laptev Dmitry Yakovlevich Laptev was a Russian Arctic explorer and Vice Admiral .Dmitry Laptev was born in the village of Bolotovo, near Velikie Luki, in 1701. Bolotovo was the estate of his father, Yakov Laptev... on a modern commemorative coin) |
Malygin was the first one to write a manual on navigation Navigation Navigation is the process of monitoring and controlling the movement of a craft or vehicle from one place to another. It is also the term of art used for the specialized knowledge used by navigators to perform navigation tasks... in Russian language Russian language Russian is a Slavic language used primarily in Russia, Belarus, Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan, Tajikistan and Kyrgyzstan. It is an unofficial but widely spoken language in Ukraine, Moldova, Latvia, Turkmenistan and Estonia and, to a lesser extent, the other countries that were once constituent republics... in 1733. In the early 1736, he was appointed leader of the western unit of the Great Northern Expedition Great Northern Expedition The Great Northern Expedition or Second Kamchatka expedition was one of the largest organised exploration enterprises in history, resulting in mapping of the most of the Arctic coast of Siberia and some parts of the North America coastline, greatly reducing the "white areas" on the maps... . In 1736-37, two boats Perviy (First) and Vtoroy (Second) under the command of Malygin and A. Skuratov undertook a voyage from the Dolgiy Island Dolgiy Island Dolgy Island is an island in the Pechora Sea, east of the Khaypudyr Bay. Long and narrow, this island is in length, with an average width of... in the Barents Sea Barents Sea The Barents Sea is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean, located north of Norway and Russia. Known in the Middle Ages as the Murman Sea, the sea takes its current name from the Dutch navigator Willem Barents... to the mouth of the Ob River Ob River The Ob River , also Obi, is a major river in western Siberia, Russia and is the world's seventh longest river. It is the westernmost of the three great Siberian rivers that flow into the Arctic Ocean .The Gulf of Ob is the world's longest estuary.-Names:The Ob is known to the Khanty people as the... . During this trip, Malygin for the first time described and mapped the part of the Russian Arctic coastline between the Pechora Pechora River The Pechora River is a river in northwest Russia which flows north into the Arctic Ocean on the west side of the Ural Mountains. It lies mostly in the Komi Republic but the northernmost part crosses the Nenets Autonomous Okrug. It is 1,809 km long and its basin is 322,000 square kilometers... and Ob River Ob River The Ob River , also Obi, is a major river in western Siberia, Russia and is the world's seventh longest river. It is the westernmost of the three great Siberian rivers that flow into the Arctic Ocean .The Gulf of Ob is the world's longest estuary.-Names:The Ob is known to the Khanty people as the... s. Later he commanded ships on the Baltic Baltic Sea The Baltic Sea is a brackish mediterranean sea located in Northern Europe, from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from 20°E to 26°E longitude. It is bounded by the Scandinavian Peninsula, the mainland of Europe, and the Danish islands. It drains into the Kattegat by way of the Øresund, the Great Belt and... , prepared navigators for the Russian Navy, and was in charge of Riga Riga Riga is the capital and largest city of Latvia. With 702,891 inhabitants Riga is the largest city of the Baltic states, one of the largest cities in Northern Europe and home to more than one third of Latvia's population. The city is an important seaport and a major industrial, commercial,... port during the Seven Years War. Malygin Strait between Yamal Peninsula Yamal Peninsula The Yamal Peninsula , located in Yamal-Nenets autonomous district of northwest Siberia, Russia, extends roughly 700 km and is bordered principally by the Kara Sea, Baydaratskaya Bay on the west, and by the Gulf of Ob on the east... and Bely Island Bely Island Bely Island is a relatively large island in the Kara Sea off the tip of the Yamal Peninsula, Siberia, Russia.Bely Island covers an area of . It is covered by tundra, but some dwarf shrubs also grow on this island... , a number of ships (including icebreaker Malygin) and several streets bear Malygin's name. |
||
| Fyodor Matisen (1872–1921)  Russian Empire Russian EmpireRussian Imperial Navy officer, hydrographer, Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... explorer |
Matisen replaced Nikolai Kolomeitsev as a commander of Eduard Toll Eduard Toll Eduard Gustav von Toll was a Baltic German geologist and Arctic explorer in Russian service. Often referred to as Baron von Toll or as Eduard v. Toll, in Russia he is known as Eduard Vasiliyevich Toll . Eduard Toll was born on and he died in 1902 in an unknown location in the Arctic Ocean)... 's Zarya Zarya (polar ship) Zarya was a steam- and sail-powered brig used by the Russian Academy of Sciences for a polar exploration during 1900–1903.Toward the end of the 19th century, the Russian Academy of Sciences sought to build a general-purpose research vessel for long-term expeditions. The first such Russian... during Russian Polar Expedition in 1900-03. He was the first to make a thorough geographical survey of the Nordenskiöld Archipelago Nordenskiöld Archipelago The Nordenskiöld Archipelago or Nordenskjold Archipelago is a very large and complex cluster of islands in the eastern region of the Kara Sea. Its eastern limit lies west of the Taymyr Peninsula.... , exploring it on dogsled Dog sled A dog sled is a sled pulled by one or more sled dogs used to travel over ice and through snow. Numerous types of sleds are used, depending on their function. They can be used for dog sled racing.-History:... and discovering and naming 40 of its islands. Subsequently Toll and Matisen led Zarya across the Laptev Sea Laptev Sea The Laptev Sea is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It is located between the northern coast of Siberia, the Taimyr Peninsula, Severnaya Zemlya and the New Siberian Islands. Its northern boundary passes from the Arctic Cape to a point with co-ordinates of 79°N and 139°E, and ends at the Anisiy... to the New Siberian Islands New Siberian Islands The New Siberian Islands are an archipelago, located to the North of the East Siberian coast between the Laptev Sea and the East Siberian Sea north of the Sakha Republic.... . The ship was trapped in fast ice, and Toll and three companions went in search of the elusive Sannikov Land Sannikov Land Sannikov Land was a phantom island in the Arctic Ocean. Its supposed existence became something of a myth in 19th-century Russia.Yakov Sannikov and Matvei Gedenschtrom claimed to have seen it during their 1809-1810 cartographic expedition to the New Siberian Islands... on foot and kayaks, and were lost. When Zarya became able to set sail, Matisen made it towards the Lena Lena River The Lena is the easternmost of the three great Siberian rivers that flow into the Arctic Ocean . It is the 11th longest river in the world and has the 9th largest watershed... river delta. A strait in the Nordenskiöld Archipelago Nordenskiöld Archipelago The Nordenskiöld Archipelago or Nordenskjold Archipelago is a very large and complex cluster of islands in the eastern region of the Kara Sea. Its eastern limit lies west of the Taymyr Peninsula.... and a coastal survey ship bear Matisen's name. |
||
| Fyodor Matyushkin Fyodor Matyushkin Fyodor Fyodorovich Matyushkin was a Russian navigator, Admiral , and a close friend of Aleksandr Pushkin.Matyushkin graduated from Tsarskoselskiy College in 1817... (1799–1872)  Russian Empire Russian EmpireRussian Imperial Navy officer, Admiral Admiral Admiral is the rank, or part of the name of the ranks, of the highest naval officers. It is usually considered a full admiral and above vice admiral and below admiral of the fleet . It is usually abbreviated to "Adm" or "ADM"... , circumnavigator, Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... explorer |
Matyushkin studied in Tsarskoselskiy College together with Alexander Pushkin. He participated in Vassili Golovnin's world cruise aboard Kamchatka in 1817-19. In 1820-24 he took part in Ferdinand Wrangel's Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... expedition to the East Siberian Sea East Siberian Sea The East Siberian Sea is a marginal sea in the Arctic Ocean. It is located between the Arctic Cape to the north, the coast of Siberia to the south, the New Siberian Islands to the west and Cape Billings, close to Chukotka, and Wrangel Island to the east... and the Chukchi Sea Chukchi Sea Chukchi Sea is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It is bounded on the west by the De Long Strait, off Wrangel Island, and in the east by Point Barrow, Alaska, beyond which lies the Beaufort Sea. The Bering Strait forms its southernmost limit and connects it to the Bering Sea and the Pacific... . They explored and mapped the Medvyezhi Islands Medvyezhi Islands The Medvezhyi Islands, or Bear Islands is an uninhabited group of islands at the western end of the Kolyma Gulf of the East Siberian Sea. It is located about to the north of the mouths of the Kolyma River. The coast of Siberia is about to the southwest of the largest island, which is about km... . Following this survey, Matyushkin on his own explored a vast tundra Tundra In physical geography, tundra is a biome where the tree growth is hindered by low temperatures and short growing seasons. The term tundra comes through Russian тундра from the Kildin Sami word tūndâr "uplands," "treeless mountain tract." There are three types of tundra: Arctic tundra, alpine... area east of the Kolyma Kolyma The Kolyma region is located in the far north-eastern area of Russia in what is commonly known as Siberia but is actually part of the Russian Far East. It is bounded by the East Siberian Sea and the Arctic Ocean in the north and the Sea of Okhotsk to the south... river. In 1825-27, he joined Wrangel in his world cruise aboard Krotky. Later he took part in the Russo-Turkish War, 1828-1829 Russo-Turkish War, 1828-1829 The Russo–Turkish War of 1828–1829 was sparked by the Greek War of Independence. The war broke out after the Sultan, incensed by the Russian participation in the Battle of Navarino, closed the Dardanelles for Russian ships and revoked the Akkerman Convention.... and became Admiral Admiral Admiral is the rank, or part of the name of the ranks, of the highest naval officers. It is usually considered a full admiral and above vice admiral and below admiral of the fleet . It is usually abbreviated to "Adm" or "ADM"... . |
 |
|
 |
Alexander Middendorff Alexander von Middendorff Alexander Theodor von Middendorff was a Baltic German zoologist and explorer.- Early life :Middendorff's mother Sophia Johanson was an Estonian peasant girl who had been sent to Saint Petersburg for education by her parents. There she met with the future director of the St... (1815–1894)  Russian Empire Russian Empire(Baltic German Baltic German The Baltic Germans were mostly ethnically German inhabitants of the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea, which today form the countries of Estonia and Latvia. The Baltic German population never made up more than 10% of the total. They formed the social, commercial, political and cultural élite in... descent) zoologist, botanist, geographer, explorer of the Northern Europe Northern Europe Northern Europe is the northern part or region of Europe. Northern Europe typically refers to the seven countries in the northern part of the European subcontinent which includes Denmark, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Norway, Finland and Sweden... , Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... , Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... , the Russian Far East Russian Far East Russian Far East is a term that refers to the Russian part of the Far East, i.e., extreme east parts of Russia, between Lake Baikal in Eastern Siberia and the Pacific Ocean... and Central Asia Central Asia Central Asia is a core region of the Asian continent from the Caspian Sea in the west, China in the east, Afghanistan in the south, and Russia in the north... |
In 1840 Middendorff took part in Karl Baer's expedition to the Kola Peninsula Kola Peninsula The Kola Peninsula is a peninsula in the far northwest of Russia. Constituting the bulk of the territory of Murmansk Oblast, it lies almost completely to the north of the Arctic Circle and is washed by the Barents Sea in the north and the White Sea in the east and southeast... and Lapland Lapland (region) Lapland is a region in northern Fennoscandia, largely within the Arctic Circle. It streches across Norway, Sweden, Finland and the Kola Peninsula . On the North it is bounded by the Barents Sea, on the West by the Norwegian Sea and on the East by the White Sea... . In 1843-45 he pioneered the scientific exploration of the Taimyr Peninsula and discovered Putorana Plateau in the Central Siberia Central Siberian Plateau The Central Siberian Plateau is made up of sharply demarcated surfaces of varying altitudes occupying most of Siberia between the Yenisei and Lena rivers. It extends over an area of 3.5 million km². The highest point is the Putoran Mountains rising to 1701 m. To the north of the plateau are... . Then he traveled along the coast of the Sea of Okhotsk Sea of Okhotsk The Sea of Okhotsk is a marginal sea of the western Pacific Ocean, lying between the Kamchatka Peninsula on the east, the Kuril Islands on the southeast, the island of Hokkaidō to the far south, the island of Sakhalin along the west, and a long stretch of eastern Siberian coast along the west and... and entered the lower Amur River valley. He studied the ethnography of Siberian peoples, the climate, animals and plants of Siberia. He was a founder of the permafrost Permafrost In geology, permafrost, cryotic soil or permafrost soil is soil at or below the freezing point of water for two or more years. Ice is not always present, as may be in the case of nonporous bedrock, but it frequently occurs and it may be in amounts exceeding the potential hydraulic saturation of... science and the Vice President of the Russian Geographical Society Russian Geographical Society The Russian Geographical Society is a learned society, founded on 6 August 1845 in Saint Petersburg, Russia.-Imperial Geographical Society:Prior to the Russian Revolution of 1917, it was known as the Imperial Russian Geographical Society.... . He determined the southern border of permafrost Permafrost In geology, permafrost, cryotic soil or permafrost soil is soil at or below the freezing point of water for two or more years. Ice is not always present, as may be in the case of nonporous bedrock, but it frequently occurs and it may be in amounts exceeding the potential hydraulic saturation of... and explained the high sinuosity Sinuosity Sinuosity or sinuosity index is a measure of deviation of a path between two points from the shortest possible path... of the northern boundary of taiga Taiga Taiga , also known as the boreal forest, is a biome characterized by coniferous forests.Taiga is the world's largest terrestrial biome. In North America it covers most of inland Canada and Alaska as well as parts of the extreme northern continental United States and is known as the Northwoods... zone. In 1870 he accompanied Grand Duke Alexei Alexandrovich to Novaya Zemlya Novaya Zemlya Novaya Zemlya , also known in Dutch as Nova Zembla and in Norwegian as , is an archipelago in the Arctic Ocean in the north of Russia and the extreme northeast of Europe, the easternmost point of Europe lying at Cape Flissingsky on the northern island... and discovered the North Cape sea current North Cape, Norway North Cape is a cape on the island of Magerøya in Northern Norway, in the municipality of Nordkapp. Its 307 m high, steep cliff is often referred to as the northernmost point of Europe, located at , 2102.3 km from the North Pole. However, the neighbouring point Knivskjellodden is actually... (a part of Norwegian Current Norwegian Current The Norwegian Current is a water current that flows north-easterly along the Atlantic coast of Norway at depths of between 50 and 100 meters... ). In 1870 he also explored the Baraba steppe Baraba steppe The Baraba steppe, also known as Barabinsk steppe, , is a grassland steppe and wooded flat plain situated in western Siberia.The steppe has an area of 117,000 km² and stretches between the Irtysh and the Ob Rivers. Barabinsk is the largest city on the steppe. The Baraba steppe also contains... , and in 1878 he travelled in Fergana Valley Fergana Valley The Fergana Valley or Farghana Valley is a region in Central Asia spreading across eastern Uzbekistan, Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan. Divided across three subdivisions of the former Soviet Union, the valley is ethnically diverse, and in the early 21st century was the scene of ethnic conflict... . He was also a prominent hippologist Hippology Hippology is the study of the horse.Today, Hippology is the title of an Equine Knowledge Contest that is used in 4-H, FFA and many horse breed contests... and contributed in the development of agriculture in Russia. Cape Middendorff in Novaya Zemlya Novaya Zemlya Novaya Zemlya , also known in Dutch as Nova Zembla and in Norwegian as , is an archipelago in the Arctic Ocean in the north of Russia and the extreme northeast of Europe, the easternmost point of Europe lying at Cape Flissingsky on the northern island... , Middendorff Bay Middendorff Bay The Middendorff Bay, is a deeply indented bay in the shores of the Taymyr Peninsula. It is located southwest of the Nordenskiöld Archipelago in the Kara Sea and it is open towards the west. This bay is limited on its eastern side by the Zarya Peninsula, named after Baron Eduard von Toll's ship Zarya... (Taymyr Peninsula Taymyr Peninsula The Taymyr Peninsula is a peninsula in the Far North of Russia, in the Siberian Federal District, that forms the northernmost part of mainland Eurasia and Asia... ), Middendorff's Grasshopper Warbler, Ursus arctos middendorffi (Kodiak Bear Kodiak Bear The Kodiak bear , also known as the Kodiak brown bear or the Alaskan grizzly bear or American brown bear, occupies the islands of the Kodiak Archipelago in South-Western Alaska. Its name in the Alutiiq language is Taquka-aq. It is the largest subspecies of brown bear.- Taxonomy :Taxonomist C.H... ) and some other species are named after Middendorff. |
  |
 |
Nicholas Miklouho-Maclay (1846–1888)  Russian Empire Russian Empire(Ukrainian, German and Polish descent) ethnologist, anthropologist and biologist Biologist A biologist is a scientist devoted to and producing results in biology through the study of life. Typically biologists study organisms and their relationship to their environment. Biologists involved in basic research attempt to discover underlying mechanisms that govern how organisms work... , explorer of Australia Australia Australia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area... , New Guinea New Guinea New Guinea is the world's second largest island, after Greenland, covering a land area of 786,000 km2. Located in the southwest Pacific Ocean, it lies geographically to the east of the Malay Archipelago, with which it is sometimes included as part of a greater Indo-Australian Archipelago... and Oceania Oceania Oceania is a region centered on the islands of the tropical Pacific Ocean. Conceptions of what constitutes Oceania range from the coral atolls and volcanic islands of the South Pacific to the entire insular region between Asia and the Americas, including Australasia and the Malay Archipelago... |
Miklouho-Maclay visited the north-eastern New Guinea New Guinea New Guinea is the world's second largest island, after Greenland, covering a land area of 786,000 km2. Located in the southwest Pacific Ocean, it lies geographically to the east of the Malay Archipelago, with which it is sometimes included as part of a greater Indo-Australian Archipelago... , Philippines Philippines The Philippines , officially known as the Republic of the Philippines , is a country in Southeast Asia in the western Pacific Ocean. To its north across the Luzon Strait lies Taiwan. West across the South China Sea sits Vietnam... , Indonesia Indonesia Indonesia , officially the Republic of Indonesia , is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania. Indonesia is an archipelago comprising approximately 13,000 islands. It has 33 provinces with over 238 million people, and is the world's fourth most populous country. Indonesia is a republic, with an... and Melanesia Melanesia Melanesia is a subregion of Oceania extending from the western end of the Pacific Ocean to the Arafura Sea, and eastward to Fiji. The region comprises most of the islands immediately north and northeast of Australia... on a number of occasions starting from 1870, and for a long time he lived amongst the native Oceania Oceania Oceania is a region centered on the islands of the tropical Pacific Ocean. Conceptions of what constitutes Oceania range from the coral atolls and volcanic islands of the South Pacific to the entire insular region between Asia and the Americas, including Australasia and the Malay Archipelago... n tribes, writing a comprehensive treatise on their way of life and customs. One of the earliest followers of Darwin Charles Darwin Charles Robert Darwin FRS was an English naturalist. He established that all species of life have descended over time from common ancestry, and proposed the scientific theory that this branching pattern of evolution resulted from a process that he called natural selection.He published his theory... , he was a humanist Humanism Humanism is an approach in study, philosophy, world view or practice that focuses on human values and concerns. In philosophy and social science, humanism is a perspective which affirms some notion of human nature, and is contrasted with anti-humanism.... scholar who, on the basis of comparative anatomical research, was among the first to refute the then prevailing view that the different 'races' of mankind belonged to different species. He arrived to Sydney Sydney Sydney is the most populous city in Australia and the state capital of New South Wales. Sydney is located on Australia's south-east coast of the Tasman Sea. As of June 2010, the greater metropolitan area had an approximate population of 4.6 million people... in 1878 and organised a zoological centre known as the Marine Biological Station, the first marine biological research institute in Australia Australia Australia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area... . He married a daughter of the Premier of New South Wales, John Robertson, and returned to Russia. Being in poor health after the trip he died, and left his skull to the St. Petersburg Military and Medical Academy. Maclay Coast is still used as the name for the North-East of Papua New Guinea Papua New Guinea Papua New Guinea , officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea, is a country in Oceania, occupying the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and numerous offshore islands... . A street in Papua New Guinea Papua New Guinea Papua New Guinea , officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea, is a country in Oceania, occupying the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and numerous offshore islands... n Madang Madang Madang is the capital of Madang Province and is a town with a population of 27,420 on the north coast of Papua New Guinea. It was first settled by the Germans in the 19th century.... not far from where the explorer stayed, plant species Pouteria maclayana, Australia Australia Australia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area... n Miklouho-Maclay Prize and Macleay Museum Macleay Museum The Macleay Museum in Sydney, Australia, is a natural history museum located on the main campus of the University of Sydney.- History :The building in which the museum is housed was built off Science Lane in 1887... , Miklukho-Maklai Institute of Ethnology and Anthropology and a street in South-West Moscow Moscow Moscow is the capital, the most populous city, and the most populous federal subject of Russia. The city is a major political, economic, cultural, scientific, religious, financial, educational, and transportation centre of Russia and the continent... (near the Peoples' Friendship University of Russia Peoples' Friendship University of Russia The Peoples' Friendship University of Russia is an educational and research institution located in the South of Moscow and is ranked by the Ministry of Education of Russia as the country's third-best university after Moscow State University and Saint Petersburg State University... ) are named after Miklukho-Maklai. |
 |
| Nicolae Milescu Nicolae Milescu Nicolae Milescu was a Moldavian writer, traveler, geographer, and diplomat. Milescu spoke 9 languages: Romanian, Latin, Greek, Modern Greek, French, German, Turkish, Swedish and Russian... (1636–1708)  Moldavia MoldaviaTsardom of Russia Tsardom of Russia The Tsardom of Russia was the name of the centralized Russian state from Ivan IV's assumption of the title of Tsar in 1547 till Peter the Great's foundation of the Russian Empire in 1721.From 1550 to 1700, Russia grew 35,000 km2 a year... writer, traveler, geographer, diplomat, explorer of Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... and China China Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture... |
Born in Moldavia Moldavia Moldavia is a geographic and historical region and former principality in Eastern Europe, corresponding to the territory between the Eastern Carpathians and the Dniester river... n noble family, Milescu traveled extensively through Europe Europe Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting... and Ottoman Empire Ottoman Empire The Ottoman EmpireIt was usually referred to as the "Ottoman Empire", the "Turkish Empire", the "Ottoman Caliphate" or more commonly "Turkey" by its contemporaries... , first on education purposes and then as diplomat serving for Moldavia and Wallachia Wallachia Wallachia or Walachia is a historical and geographical region of Romania. It is situated north of the Danube and south of the Southern Carpathians... . In 1671 he went to live in Russia, working for its foreign ministry. He wrote several important works there, including the first arithmetics textbook in Russian language Russian language Russian is a Slavic language used primarily in Russia, Belarus, Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan, Tajikistan and Kyrgyzstan. It is an unofficial but widely spoken language in Ukraine, Moldova, Latvia, Turkmenistan and Estonia and, to a lesser extent, the other countries that were once constituent republics... , Arithmologion. He led Russian diplomatic mission to China China Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture... in 1675-78, for the first time among Russian ambassadors travelling to Beijing Beijing Beijing , also known as Peking , is the capital of the People's Republic of China and one of the most populous cities in the world, with a population of 19,612,368 as of 2010. The city is the country's political, cultural, and educational center, and home to the headquarters for most of China's... through the East Siberia rather than through Mongolia Mongolia Mongolia is a landlocked country in East and Central Asia. It is bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south, east and west. Although Mongolia does not share a border with Kazakhstan, its western-most point is only from Kazakhstan's eastern tip. Ulan Bator, the capital and largest... . After his assistant Ignatiy Milovanov (sent beforehand) Milescu was the first known European to cross the Amur River from north and reach Beijing by that way. Milescu made the first detailed description of Lake Baikal Lake Baikal Lake Baikal is the world's oldest at 30 million years old and deepest lake with an average depth of 744.4 metres.Located in the south of the Russian region of Siberia, between Irkutsk Oblast to the northwest and the Buryat Republic to the southeast, it is the most voluminous freshwater lake in the... and all the rivers feeding the lake, and he was the first to point out Baikal's unfathomable depth. His travel notes also contain valuable descriptions of major Siberian rivers and the first ever orthographic Orthographic projection (cartography) An orthographic projection is a map projection of cartography. Like the stereographic projection and gnomonic projection, orthographic projection is a perspective projection, in which the sphere is projected onto a tangent plane or secant plane. The point of perspective for the orthographic... scheme of the East Siberia. |
||
| Fyodor Minin Fyodor Minin Fyodor Alekseyevich Minin was a Russian Arctic explorer.In 1730s, Minin participated in the Second Kamchatka expedition. In 1736, he joined the unit led by Dmitry Ovtsyn. In 1738, he was in charge of a group of explorers, that would chart the Arctic Ocean coastline east of the Yenisei river... (c. 1709 – after 1742) Tsardom of Russia Tsardom of Russia The Tsardom of Russia was the name of the centralized Russian state from Ivan IV's assumption of the title of Tsar in 1547 till Peter the Great's foundation of the Russian Empire in 1721.From 1550 to 1700, Russia grew 35,000 km2 a year...  Russian Empire Russian EmpireRussian Imperial Navy officer, Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... explorer |
In 1730s, Minin participated in the Great Northern Expedition Great Northern Expedition The Great Northern Expedition or Second Kamchatka expedition was one of the largest organised exploration enterprises in history, resulting in mapping of the most of the Arctic coast of Siberia and some parts of the North America coastline, greatly reducing the "white areas" on the maps... . In 1736, he joined the unit led by Dmitry Ovtsyn Dmitry Ovtsyn Dmitry Leontiyevich Ovtsyn was a Russian hydrographer and Arctic explorer.In 1734-1738, Ovtsyn led one of the units of the Second Kamchatka expedition that charted the coastline of the Kara Sea east of the river Ob. In summer of 1737, his unit made its way from Ob to Yenisei and made the first... . In 1738 together with Dmitry Sterlegov he led the group that charted the Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... coastline east of the Yenisei river for some 250 km. In 1738-42, Minin made several vain attempts to sail around the Taimyr Peninsula. He also mapped and described Dikson Island. A cape at Khalmyer Bay Khalmyer Bay The Khalmyer Bay is a bay on the Siberian coast in the Kara Sea. It is located in the Gydan Peninsula and it is roughly 185 km long and 47 km wide at its widest point. Lat 71°30′ N, long 76° E.... , the Minina Skerries Minina Skerries The Minina Skerries are located in the Kara Sea, in the northwestern shores of Siberia. They stretch between the Mikhailov Peninsula and the mouths of the river Pyasina... in the Kara Sea Kara Sea The Kara Sea is part of the Arctic Ocean north of Siberia. It is separated from the Barents Sea to the west by the Kara Strait and Novaya Zemlya, and the Laptev Sea to the east by the Severnaya Zemlya.... , a gulf, a bay, a cape and a mountain on the shores of the Taimyr Peninsula bear Minin's name. |
 |
|
| Ivan Moskvitin Ivan Moskvitin Ivan Yuryevich Moskvitin was a Russian explorer, presumably a native of Moscow, who led a Russian reconnaissance party to the Pacific Ocean, becoming the first Russian to reach the Sea of Okhotsk.... (? – after 1645) Tsardom of Russia Tsardom of Russia The Tsardom of Russia was the name of the centralized Russian state from Ivan IV's assumption of the title of Tsar in 1547 till Peter the Great's foundation of the Russian Empire in 1721.From 1550 to 1700, Russia grew 35,000 km2 a year... Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... n Cossack Cossack Cossacks are a group of predominantly East Slavic people who originally were members of democratic, semi-military communities in what is today Ukraine and Southern Russia inhabiting sparsely populated areas and islands in the lower Dnieper and Don basins and who played an important role in the... ataman Ataman Ataman was a commander title of the Ukrainian People's Army, Cossack, and haidamak leaders, who were in essence the Cossacks... , explorer of East Siberia and the Russian Far East Russian Far East Russian Far East is a term that refers to the Russian part of the Far East, i.e., extreme east parts of Russia, between Lake Baikal in Eastern Siberia and the Pacific Ocean... |
Presumably a native of Moscow Moscow Moscow is the capital, the most populous city, and the most populous federal subject of Russia. The city is a major political, economic, cultural, scientific, religious, financial, educational, and transportation centre of Russia and the continent... , Moskvitin appeared in Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... around 1626 in Tomsk Tomsk Tomsk is a city and the administrative center of Tomsk Oblast, Russia, located on the Tom River. One of the oldest towns in Siberia, Tomsk celebrated its 400th anniversary in 2004... . He accompanied the Cossack Cossack Cossacks are a group of predominantly East Slavic people who originally were members of democratic, semi-military communities in what is today Ukraine and Southern Russia inhabiting sparsely populated areas and islands in the lower Dnieper and Don basins and who played an important role in the... ataman Ataman Ataman was a commander title of the Ukrainian People's Army, Cossack, and haidamak leaders, who were in essence the Cossacks... Dmitry Kopylov to Yakutsk Yakutsk With a subarctic climate , Yakutsk is the coldest city, though not the coldest inhabited place, on Earth. Average monthly temperatures range from in July to in January. The coldest temperatures ever recorded on the planet outside Antarctica occurred in the basin of the Yana River to the northeast... . In 1638 Kopylov founded a small fort on the Aldan River Aldan River The Aldan River is the second-longest tributary of the Lena River in the Sakha Republic in eastern Siberia. The river is 2,273 km long, of which around 1,600 km is navigable. It was part of the River Route to Okhotsk... and in 1639 dispatched Moskvitin in command of 20 Tomsk Cossacks and 29 Krasnoyarsk Krasnoyarsk Krasnoyarsk is a city and the administrative center of Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russia, located on the Yenisei River. It is the third largest city in Siberia, with the population of 973,891. Krasnoyarsk is an important junction of the Trans-Siberian Railway and one of Russia's largest producers of... Cossacks to look for silver ore further to the east. Leading this party, Moskvitin became the first Russian to reach the Pacific Ocean Pacific Ocean The Pacific Ocean is the largest of the Earth's oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, bounded by Asia and Australia in the west, and the Americas in the east.At 165.2 million square kilometres in area, this largest division of the World... and to discover the Sea of Okhotsk Sea of Okhotsk The Sea of Okhotsk is a marginal sea of the western Pacific Ocean, lying between the Kamchatka Peninsula on the east, the Kuril Islands on the southeast, the island of Hokkaidō to the far south, the island of Sakhalin along the west, and a long stretch of eastern Siberian coast along the west and... , building a winter camp on its shore at the Ulya River Ulya River Ulya River is a river in northern Khabarovsk Krai in Russia. The length of the river is 325 km, the area of its drainage basin is 15,500 km². The Ulya originates in the Dzhugdzhur Mountains, flows northeast parallel to the coast and turns east to reach the Sea of Okhotsk about 100km southwest of... mouth. The Cossacks learned from the locals about the proximity of the Amur River. In 1640 they apparently sailed south, explored the south-eastern shores of the Okhotsk Sea and probably reached the mouth of the Amur River. On their way back they discovered the Shantar Islands Shantar Islands The Shantar Islands are a group of fifteen islands that lie in Uda Bay, in the southwestern zone of the Sea of Okhotsk. These islands are located close to the shores of the Siberian mainland... . Based on Moskvitin's account, Kurbat Ivanov Kurbat Ivanov Kurbat Afanasyevich Ivanov was among the greatest Cossack explorers of Siberia. He was the first Russian to discover Lake Baikal, and to create the first map of the Russian Far East... draw the first Russian map of the Far East Far East The Far East is an English term mostly describing East Asia and Southeast Asia, with South Asia sometimes also included for economic and cultural reasons.The term came into use in European geopolitical discourse in the 19th century,... in 1642. Moskvitin personally brought the news of the discovery of the eastern ocean to Moscow Moscow Moscow is the capital, the most populous city, and the most populous federal subject of Russia. The city is a major political, economic, cultural, scientific, religious, financial, educational, and transportation centre of Russia and the continent... . A cape in Luzhin Bay of the Okhotsk Sea is named after Moskvitin. |
 |
|
| Gerhard Friedrich Müller (1705–1783)  Holy Roman Empire Holy Roman Empire Russian Empire Russian Empirehistorian, ethnologist, explorer of Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... |
Müller came to St. Petersburg in 1725 and became a co-founder of the Russian Academy of Sciences Russian Academy of Sciences The Russian Academy of Sciences consists of the national academy of Russia and a network of scientific research institutes from across the Russian Federation as well as auxiliary scientific and social units like libraries, publishers and hospitals.... . In 1733-43 he participated in the academic unit of the Great Northern Expedition Great Northern Expedition The Great Northern Expedition or Second Kamchatka expedition was one of the largest organised exploration enterprises in history, resulting in mapping of the most of the Arctic coast of Siberia and some parts of the North America coastline, greatly reducing the "white areas" on the maps... and traveled extensively through Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... , studying Siberian geography and peoples. Müller is considered to be one of the fathers of ethnography Ethnography Ethnography is a qualitative method aimed to learn and understand cultural phenomena which reflect the knowledge and system of meanings guiding the life of a cultural group... . He collected the vernacular stories and archival documents about Russian explorers of Siberia, including Demid Pyanda Demid Pyanda Demid Sofonovich Pyanda or, according to some sources, Panteley Demidovich Pyanda , also spelled Penda was among the first and most important Russian explorers of Siberia... , Fedot Alekseyev Popov Fedot Alekseyev Popov Fedot Alekseyevich Popov , date of birth unknown, died between 1648 and 1654) was a Russian explorer who organized the first European expedition through the Bering Strait.He was normally known as Fedot Alekseyev. Only a few sources call him the son of Popov... and Semyon Dezhnyov. He was one of the first historians to write a general account of Russian history based on extensive examination of documentary sources. He put forth the so-called Normanist theory, a controversial accentuation of the role of Scandinavians and Germans in the history of Russia. |
 |
|
 |
Nikolay Muravyov-Amursky Nikolay Muravyov-Amursky Nikolay Nikolayevich Muravyov-Amursky was a Russian statesman and diplomat, who played a major role in the expansion of the Russian Empire into the Amur River basin and to the shores of the Sea of Japan.-Surname spelling:The surname Muravyov has also been transcribed as Muravyev or Murav'ev.-Early... (1809–1881)  Russian Empire Russian Empirestatesman, diplomat, explorer of the Russian Far East Russian Far East Russian Far East is a term that refers to the Russian part of the Far East, i.e., extreme east parts of Russia, between Lake Baikal in Eastern Siberia and the Pacific Ocean... |
In 1847 Nikolay Muravyov was appointed the Governor General of Eastern Siberia. He pursued the Russian exploration and settlement of the territories north of the Amur River. He assisted in organisation of Gennady Nevelskoy Gennady Nevelskoy Gennady Ivanovich Nevelskoy was a Russian navigator.In 1848 Nevelskoy led the expedition in the Russian Far East, exploring the area of the Sakhalin and the outlet of the Amur River. He proved that the Strait of Tartary was not a gulf, but indeed a strait, connected to Amur's estuary by a narrow... 's expeditions, which led to the Russian presence near Amur estuary and on Sakhalin. In 1854 the military troops sailed down the Amur, and in 1855 the first settlers reached the river mouth. In 1856 the city of Blagoveshchensk Blagoveshchensk Blagoveshchensk is a city and the administrative center of Amur Oblast, Russia. Population: -Early history of the region:The early residents of both sides of the Amur in the region of today's Blagoveshchensk were the Daurs and Duchers... was founded on Amur. During the last expedition of 1858, Muravyov concluded the Treaty of Aigun Treaty of Aigun The Treaty of Aigun was a 1858 treaty between the Russian Empire, and the empire of the Qing Dynasty, the sinicized-Manchu rulers of China, that established much of the modern border between the Russian Far East and Manchuria , which is now known as Northeast China... with China China Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture... , which recognised Amur River as a border between the two countries and granted Russia an easier access to the Pacific Ocean Pacific Ocean The Pacific Ocean is the largest of the Earth's oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, bounded by Asia and Australia in the west, and the Americas in the east.At 165.2 million square kilometres in area, this largest division of the World... . The new territories acquired by Russia included Priamurye and most of the territories of modern Primorsky Primorsky Krai Primorsky Krai , informally known as Primorye , is a federal subject of Russia . Primorsky means "maritime" in Russian, hence the region is sometimes referred to as Maritime Province or Maritime Territory. Its administrative center is in the city of Vladivostok... and Khabarovsk Krai Khabarovsk Krai Khabarovsk Krai is a federal subject of Russia , located in the Russian Far East. It lies mostly in the basin of the lower Amur River, but also occupies a vast mountainous area along the coastline of the Sea of Okhotsk, an arm of the Pacific Ocean. The administrative center of the krai is the... s. For this achievement Muravyov was granted the title of Count Amursky (i.e., "of the Amur River"). The Treaty of Aigun was confirmed and expanded by the provisions of the Beijing Treaty Convention of Peking The Convention of Peking or the First Convention of Peking is the name used for three different unequal treaties, which were concluded between Qing China and the United Kingdom, France, and Russia.-Background:... of 1860, which granted Russia right to the Ussuri krai Ussuri krai Ussuri krai is an unofficial name for a part of Primorsky Krai and Khabarovsky Krai that consisted of Ussuri and South-Ussuri Okrugs. The name was often used in late Imperial Russia... and southern parts of Primorye Primorsky Krai Primorsky Krai , informally known as Primorye , is a federal subject of Russia . Primorsky means "maritime" in Russian, hence the region is sometimes referred to as Maritime Province or Maritime Territory. Its administrative center is in the city of Vladivostok... . To defend the new lands Muravyov created the Amur Cossacks Amur Cossacks The Amur Cossack Host , a Cossack host created in the Amur region and Primorye in the 1850s on the basis of the Cossacks relocated from the Transbaikal region and freed miners of Nerchinsk region.... corps. Muravyov-Amursky Peninsula Muravyov-Amursky Peninsula The Muravyov-Amursky Peninsula is a peninsula in the Peter the Great Gulf, which it subdivides into the Amur Bay to the west and the Ussuri Bay to the east. It is approximately 30 km long and 12 km wide.... has been named after Muravyov-Amursky. |
 _front.jpg) |
| Ivan Mushketov Ivan Mushketov Ivan Vasilʹevich Mushketov was a famous Russian geologist, tectonist, explorer, and geographer who was born in the Don region and entered Saint Petersburg University in 1867, but soon transferred to the Mining Institute where he was a student of A. P. Karpinsky, and graduated from there in 1872... (1850–1902)  Russian Empire Russian Empiregeologist, geographer, explorer of Central Asia Central Asia Central Asia is a core region of the Asian continent from the Caspian Sea in the west, China in the east, Afghanistan in the south, and Russia in the north... , Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... , the Urals and the Caucasus Caucasus The Caucasus, also Caucas or Caucasia , is a geopolitical region at the border of Europe and Asia, and situated between the Black and the Caspian sea... |
In 1873-79 Mushketov traveled extensively in the Central Asia Central Asia Central Asia is a core region of the Asian continent from the Caspian Sea in the west, China in the east, Afghanistan in the south, and Russia in the north... , discovering and cataloguing mineral deposits. He produced the first geological map of Turkestan Turkestan Turkestan, spelled also as Turkistan, literally means "Land of the Turks".The term Turkestan is of Persian origin and has never been in use to denote a single nation. It was first used by Persian geographers to describe the place of Turkish peoples... (together with S. Romanovsky). Mushketov also started observations of earthquakes in Kazakhstan Kazakhstan Kazakhstan , officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country in Central Asia and Eastern Europe. Ranked as the ninth largest country in the world, it is also the world's largest landlocked country; its territory of is greater than Western Europe... , organized regular observation of the glaciers of the Caucasus Caucasus The Caucasus, also Caucas or Caucasia , is a geopolitical region at the border of Europe and Asia, and situated between the Black and the Caspian sea... , and researched the gold mines of the Urals. He led the team that surveyed the territory for the future Circum-Baikal Railway Circum-Baikal Railway The Circum-Baikal Railway is a historical railway in Irkutsk region of Russia. It runs along the Northern shore of the Southern extremity of the lake from the town of Slyudyanka to the Baikal settlement. Until the middle of the 20th century Circum-Baikal railway was part of the main line of... . A glacier and a mountain in Antarctica, a glacier in the Tian Shan Tian Shan The Tian Shan , also spelled Tien Shan, is a large mountain system located in Central Asia. The highest peak in the Tian Shan is Victory Peak , .... Mountains, and a mountain in Buryatia are named after Mushketov. |
 |
N
| Portrait | Person | Achievements | Image |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
Ivan Nagurski (1888–1976)  Russian Empire Russian Empire Poland Polandengineer, Russian Imperial Navy officer, pioneer of aviation, Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... explorer |
Nagurski was among the first pilots Aviator An aviator is a person who flies an aircraft. The first recorded use of the term was in 1887, as a variation of 'aviation', from the Latin avis , coined in 1863 by G. de la Landelle in Aviation Ou Navigation Aérienne... of the Imperial Russian Navy Imperial Russian Navy The Imperial Russian Navy refers to the Tsarist fleets prior to the February Revolution.-First Romanovs:Under Tsar Mikhail Feodorovich, construction of the first three-masted ship, actually built within Russia, was completed in 1636. It was built in Balakhna by Danish shipbuilders from Holstein... . In 1914 Nagurski was tasked with the difficult mission of locating the expeditions of Georgy Sedov Georgy Sedov Georgy Yakovlevich Sedov was a Russian Arctic explorer.Born in the village of Krivaya Kosa of Taganrog district in a fisherman's family. In 1898, Sedov finished navigation courses in Rostov-on-Don and acquired the rank of long voyage navigator... , Georgy Brusilov Georgy Brusilov Georgy Lvovich Brusilov or Hryhoriy Brusylov was a Ukrainian Russian naval officer of the Imperial Russian Navy and an Arctic explorer... , and Vladimir Rusanov Vladimir Rusanov Vladimir Alexandrovich Rusanov was an experienced Russian geologist who specialized in the Arctic.In 1909–1911 V. A. Rusanov carried out explorations in Novaya Zemlya. He was helped by Tyko Vylka, his guide, who later became the Chairman of the Novaya Zemlya Soviet.In 1912 Rusanov had been... in the Russian Arctic. Between August 21 and September 13, 1914, he flew five missions, spending more than ten hours in the air and travelling more than a thousand kilometres over land and the Barents Sea Barents Sea The Barents Sea is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean, located north of Norway and Russia. Known in the Middle Ages as the Murman Sea, the sea takes its current name from the Dutch navigator Willem Barents... reaching as far as the 76th parallel north 76th parallel north The 76th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 76 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane, in the Arctic. It crosses the Atlantic Ocean, Europe, Asia, the Arctic Ocean and North America.... . Nagurski failed to find the expeditions, but he became the first polar aviator in history, and his experience was of much value to the subsequent polar flights. Later Nagurski performed the first ever loop with a flying boat, took part in the First World War and the Russian Civil War Russian Civil War The Russian Civil War was a multi-party war that occurred within the former Russian Empire after the Russian provisional government collapsed to the Soviets, under the domination of the Bolshevik party. Soviet forces first assumed power in Petrograd The Russian Civil War (1917–1923) was a... , and was thought dead for several decades until regaining his fame in 1950s. Nagurskoye meteorological station in Franz Josef Land Franz Josef Land Franz Josef Land, Franz Joseph Land, or Francis Joseph's Land is an archipelago located in the far north of Russia. It is found in the Arctic Ocean north of Novaya Zemlya and east of Svalbard, and is administered by Arkhangelsk Oblast. Franz Josef Land consists of 191 ice-covered islands with a... was named after Nagurski. |
|
| Gennady Nevelskoy Gennady Nevelskoy Gennady Ivanovich Nevelskoy was a Russian navigator.In 1848 Nevelskoy led the expedition in the Russian Far East, exploring the area of the Sakhalin and the outlet of the Amur River. He proved that the Strait of Tartary was not a gulf, but indeed a strait, connected to Amur's estuary by a narrow... (1813–1876)  Russian Empire Russian EmpireRussian Imperial Navy officer, Admiral Admiral Admiral is the rank, or part of the name of the ranks, of the highest naval officers. It is usually considered a full admiral and above vice admiral and below admiral of the fleet . It is usually abbreviated to "Adm" or "ADM"... , explorer of the Russian Far East Russian Far East Russian Far East is a term that refers to the Russian part of the Far East, i.e., extreme east parts of Russia, between Lake Baikal in Eastern Siberia and the Pacific Ocean... |
In 1848 Nevelskoy led the expedition in the Russian Far East Russian Far East Russian Far East is a term that refers to the Russian part of the Far East, i.e., extreme east parts of Russia, between Lake Baikal in Eastern Siberia and the Pacific Ocean... , exploring the area of Sakhalin Sakhalin Sakhalin or Saghalien, is a large island in the North Pacific, lying between 45°50' and 54°24' N.It is part of Russia, and is Russia's largest island, and is administered as part of Sakhalin Oblast... and the Amur Liman Amur Liman The Amur Liman is a liman of the Amur River, the northern part of the Strait of Tartary between Eurasia and Sakhalin. It connects the Sakhalin Gulf of the Sea of Okhotsk with the main body of the Strait of Tartary via the Nevelskoy Strait.... (which he found possible to sail through on the tall ship Tall ship A tall ship is a large, traditionally-rigged sailing vessel. Popular modern tall ship rigs include topsail schooners, brigantines, brigs and barques. "Tall Ship" can also be defined more specifically by an organization, such as for a race or festival.... s). He proved that the Strait of Tartary Strait of Tartary Strait of Tartary is a strait in the Pacific Ocean dividing the Russian island of Sakhalin from mainland Asia , connecting the Sea of Okhotsk on the north with... was not a gulf, but indeed a strait, connected to Amur's estuary by a narrow section later called Nevelskoy Strait Nevelskoy Strait The Nevelskoy Strait is a strait between Eurasia and Sakhalin that connects the main body of the Strait of Tartary with the Amur Liman . It was named in memory of Capt... . Not knowing about the efforts of Japan Japan Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south... ese navigator Mamiya Rinzo Mamiya Rinzō was a Japanese explorer of the late Edo period.Mamiya was born in 1775 in Tsukuba District, Hitachi Province, in what is now Tsukubamirai, Ibaraki Prefecture. Later in his life he would become an undercover agent for the Tokugawa shogunate... who explored the same area forty years earlier, the Russians took Nevelskoy's report as the first proof that Sakhalin is indeed an island. In 1850 Nevelskoy founded Nikolayevsk-on-Amur Nikolayevsk-on-Amur Nikolayevsk-on-Amur often romanized as Nikolayevsk-na-Amure, is a town and the administrative center of Nikolayevsky District of Khabarovsk Krai, Russia located on the Amur River close to its liman in the Pacific Ocean... , the first Russian settlement in the lower Amur River region. He also founded several military posts on Sakhalin Sakhalin Sakhalin or Saghalien, is a large island in the North Pacific, lying between 45°50' and 54°24' N.It is part of Russia, and is Russia's largest island, and is administered as part of Sakhalin Oblast... . For that Nevelskoy is credited as one of the key figures in the Russian colonisation of Primorsky Krai Primorsky Krai Primorsky Krai , informally known as Primorye , is a federal subject of Russia . Primorsky means "maritime" in Russian, hence the region is sometimes referred to as Maritime Province or Maritime Territory. Its administrative center is in the city of Vladivostok... and Sakhalin Sakhalin Sakhalin or Saghalien, is a large island in the North Pacific, lying between 45°50' and 54°24' N.It is part of Russia, and is Russia's largest island, and is administered as part of Sakhalin Oblast... . Nevelskoy Strait Nevelskoy Strait The Nevelskoy Strait is a strait between Eurasia and Sakhalin that connects the main body of the Strait of Tartary with the Amur Liman . It was named in memory of Capt... , a city of Nevelsk Nevelsk Nevelsk is a port town in Sakhalin Oblast, Russia. Population 18,639 .-Geography:The town is located on the southwest coast of Sakhalin, 123 km from Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk, on the Sea of Japan.-History:... on Sakhalin Sakhalin Sakhalin or Saghalien, is a large island in the North Pacific, lying between 45°50' and 54°24' N.It is part of Russia, and is Russia's largest island, and is administered as part of Sakhalin Oblast... and Nevelskoy Marine State University in Vladivostok Vladivostok The city is located in the southern extremity of Muravyov-Amursky Peninsula, which is about 30 km long and approximately 12 km wide.The highest point is Mount Kholodilnik, the height of which is 257 m... have been named after Gennady Nevelskoy. |
 |
|
| Afanasy Nikitin Afanasy Nikitin Afanasy Nikitin was a Russian merchant and one of the first Europeans to travel to and document his visit to India. He described his trip in a narrative known as The Journey Beyond Three Seas .-The voyage:In 1466, Nikitin left his hometown of Tver on a commercial trip to India... (?–1472) Principality of Tver merchant, early European traveler to Persia and India India India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world... |
In 1466, Nikitin left his hometown of Tver Tver Tver is a city and the administrative center of Tver Oblast, Russia. Population: 403,726 ; 408,903 ;... on a commercial Commerce While business refers to the value-creating activities of an organization for profit, commerce means the whole system of an economy that constitutes an environment for business. The system includes legal, economic, political, social, cultural, and technological systems that are in operation in any... trip to India India India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world... . He traveled down the Volga River Volga River The Volga is the largest river in Europe in terms of length, discharge, and watershed. It flows through central Russia, and is widely viewed as the national river of Russia. Out of the twenty largest cities of Russia, eleven, including the capital Moscow, are situated in the Volga's drainage... , reached Derbent Derbent Derbent |Lak]]: Чурул, Churul; Persian: دربند; Judæo-Tat: דארבּאנד/Дэрбэнд/Dərbənd) is a city in the Republic of Dagestan, Russia, close to the Azerbaijani border. It is the southernmost city in Russia, and it is the second most important city of Dagestan... , then Baku Baku Baku , sometimes spelled as Baki or Bakou, is the capital and largest city of Azerbaijan, as well as the largest city on the Caspian Sea and of the Caucasus region. It is located on the southern shore of the Absheron Peninsula, which projects into the Caspian Sea. The city consists of two principal... and later Persia by crossing the Caspian Sea Caspian Sea The Caspian Sea is the largest enclosed body of water on Earth by area, variously classed as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. The sea has a surface area of and a volume of... , where he lived for a year. In 1469 Nikitin arrived to Ormus Ormus The Kingdom of Ormus was a 10th to 17th century kingdom located within the Persian Gulf and extending as far as the Strait of Hormuz... and then, crossing the Arabian Sea Arabian Sea The Arabian Sea is a region of the Indian Ocean bounded on the east by India, on the north by Pakistan and Iran, on the west by the Arabian Peninsula, on the south, approximately, by a line between Cape Guardafui in northeastern Somalia and Kanyakumari in India... , reached the sultanate of Bahmani, where he lived for 3 years. On his way back, Nikitin visited the Africa Africa Africa is the world's second largest and second most populous continent, after Asia. At about 30.2 million km² including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of the Earth's total surface area and 20.4% of the total land area... n continent (Somalia Somalia Somalia , officially the Somali Republic and formerly known as the Somali Democratic Republic under Socialist rule, is a country located in the Horn of Africa. Since the outbreak of the Somali Civil War in 1991 there has been no central government control over most of the country's territory... ), Muscat Muscat, Oman Muscat is the capital of Oman. It is also the seat of government and largest city in the Governorate of Muscat. As of 2008, the population of the Muscat metropolitan area was 1,090,797. The metropolitan area spans approximately and includes six provinces called wilayats... , Trabzon Trabzon Trabzon is a city on the Black Sea coast of north-eastern Turkey and the capital of Trabzon Province. Trabzon, located on the historical Silk Road, became a melting pot of religions, languages and culture for centuries and a trade gateway to Iran in the southeast and the Caucasus to the northeast... and in 1472 arrived at Feodosiya by crossing the Black Sea Black Sea The Black Sea is bounded by Europe, Anatolia and the Caucasus and is ultimately connected to the Atlantic Ocean via the Mediterranean and the Aegean seas and various straits. The Bosphorus strait connects it to the Sea of Marmara, and the strait of the Dardanelles connects that sea to the Aegean... . Thus Nikitin became one of the first Europe Europe Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting... ans to travel to and to document his visit to India India India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world... . He described his trip in a narrative known as A Journey Beyond the Three Seas A Journey Beyond the Three Seas A Journey Beyond the Three Seas is a Russian literary monument in the form of travel notes, made by a merchant from Tver Afanasiy Nikitin during his journey to India in 1466-1472.... (Khozheniye za tri morya). Nikitin had studied the population of India, its social Social The term social refers to a characteristic of living organisms... system, government Government Government refers to the legislators, administrators, and arbitrators in the administrative bureaucracy who control a state at a given time, and to the system of government by which they are organized... , military (he witnessed war-games featuring war elephant War elephant A war elephant was an elephant trained and guided by humans for combat. Their main use was to charge the enemy, trampling them and breaking their ranks. A division of war elephants is known as elephantry.... s), its economy Economic system An economic system is the combination of the various agencies, entities that provide the economic structure that defines the social community. These agencies are joined by lines of trade and exchange along which goods, money etc. are continuously flowing. An example of such a system for a closed... , religion Religion Religion is a collection of cultural systems, belief systems, and worldviews that establishes symbols that relate humanity to spirituality and, sometimes, to moral values. Many religions have narratives, symbols, traditions and sacred histories that are intended to give meaning to life or to... , lifestyles, and natural resources. Nikitin's book provide a valuable source of information about India at that time. There are monuments to Nikitin in his hometown of Tver Tver Tver is a city and the administrative center of Tver Oblast, Russia. Population: 403,726 ; 408,903 ;... and in Revdanda Revdanda Revdanda is a village near Alibag, India. It is 17 km away from Alibag and 125 km away from Mumbai.-Directions:Till a few years ago the coastal road that goes south from Alibag used to terminate at Revdanda where it encountered the Kundalika creek. A bridge now spans the creek and the... near Mumbai Mumbai Mumbai , formerly known as Bombay in English, is the capital of the Indian state of Maharashtra. It is the most populous city in India, and the fourth most populous city in the world, with a total metropolitan area population of approximately 20.5 million... in India India India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world... . In 1958, Mosfilm Mosfilm Mosfilm is a film studio, which is often described as the largest and oldest in Russia and in Europe. Its output includes most of the more widely-acclaimed Soviet films, ranging from works by Tarkovsky and Eisenstein , to Red Westerns, to the Akira Kurosawa co-production and the epic Война и Мир... produced a film A Journey Beyond the Three Seas A Journey Beyond the Three Seas A Journey Beyond the Three Seas is a Russian literary monument in the form of travel notes, made by a merchant from Tver Afanasiy Nikitin during his journey to India in 1466-1472.... . In 2006-07, the Indian organization "Adventures & Explorers" sponsored the "Nikitin Expedition", in which 14 travellers set out from Tver Tver Tver is a city and the administrative center of Tver Oblast, Russia. Population: 403,726 ; 408,903 ;... to retrace Nikitin's journey beyond the three seas A Journey Beyond the Three Seas A Journey Beyond the Three Seas is a Russian literary monument in the form of travel notes, made by a merchant from Tver Afanasiy Nikitin during his journey to India in 1466-1472.... . |
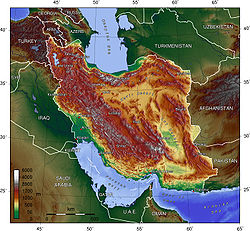  |
O
| Portrait | Person | Achievements | Image |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vladimir Obruchev Vladimir Obruchev Vladimir Afanasyevich Obruchev was a Russian and Soviet geologist who specialized in the study of Siberia and Central Asia. He was also one of the first Russian science fiction authors.- Scientific research :... (1863–1956)  Russian Empire Russian Empire Soviet Union Soviet Uniongeologist Geologist A geologist is a scientist who studies the solid and liquid matter that constitutes the Earth as well as the processes and history that has shaped it. Geologists usually engage in studying geology. Geologists, studying more of an applied science than a theoretical one, must approach Geology using... , geographer, explorer of Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... and Central Asia Central Asia Central Asia is a core region of the Asian continent from the Caspian Sea in the west, China in the east, Afghanistan in the south, and Russia in the north... , science fiction Science fiction Science fiction is a genre of fiction dealing with imaginary but more or less plausible content such as future settings, futuristic science and technology, space travel, aliens, and paranormal abilities... author |
Having graduated from the Petersburg Mining Institute in 1886, Obruchev went to Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... . He studied gold-mining and assisted in constructing Central Asian and Trans-Siberian Railway Trans-Siberian Railway The Trans-Siberian Railway is a network of railways connecting Moscow with the Russian Far East and the Sea of Japan. It is the longest railway in the world... s. In Central Asia Central Asia Central Asia is a core region of the Asian continent from the Caspian Sea in the west, China in the east, Afghanistan in the south, and Russia in the north... he explored the Kara Kum Desert, the shores of the Amu Darya Amu Darya The Amu Darya , also called Oxus and Amu River, is a major river in Central Asia. It is formed by the junction of the Vakhsh and Panj rivers... River, and the old riverbeds of the Uzbois. In 1892-94 Obruchev took part in the Grigory Potanin Grigory Potanin Grigory Nikolayaevich Potanin was a Russian explorer of Inner Asia who aligned himself with the Siberian separatist movement... 's expedition to Mongolia Mongolia Mongolia is a landlocked country in East and Central Asia. It is bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south, east and west. Although Mongolia does not share a border with Kazakhstan, its western-most point is only from Kazakhstan's eastern tip. Ulan Bator, the capital and largest... and North China North China thumb|250px|Northern [[People's Republic of China]] region.Northern China or North China is a geographical region of China. The heartland of North China is the North China Plain.... . He explored the Transbaikal Transbaikal Transbaikal, Trans-Baikal, Transbaikalia , or Dauria is a mountainous region to the east of or "beyond" Lake Baikal in Russia. The alternative name, Dauria, is derived from the ethnonym of the Daur people. It stretches for almost 1000 km from north to south from the Patomskoye Plateau and North... area, Dzhungaria and Altai Mountains. Having spent half a century in exploring Siberia and Inner Asia, Obruchev summarized his findings in the extensive work The Geology of Siberia. He studied the origins of loess Loess Loess is an aeolian sediment formed by the accumulation of wind-blown silt, typically in the 20–50 micrometre size range, twenty percent or less clay and the balance equal parts sand and silt that are loosely cemented by calcium carbonate... , the ice Ice Ice is water frozen into the solid state. Usually ice is the phase known as ice Ih, which is the most abundant of the varying solid phases on the Earth's surface. It can appear transparent or opaque bluish-white color, depending on the presence of impurities or air inclusions... formation and permafrost Permafrost In geology, permafrost, cryotic soil or permafrost soil is soil at or below the freezing point of water for two or more years. Ice is not always present, as may be in the case of nonporous bedrock, but it frequently occurs and it may be in amounts exceeding the potential hydraulic saturation of... , and the tectonics Tectonics Tectonics is a field of study within geology concerned generally with the structures within the lithosphere of the Earth and particularly with the forces and movements that have operated in a region to create these structures.Tectonics is concerned with the orogenies and tectonic development of... of Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... . All together, he authored over a thousand scientific works. Obruchev is also known as the author of two popular science fiction Science fiction Science fiction is a genre of fiction dealing with imaginary but more or less plausible content such as future settings, futuristic science and technology, space travel, aliens, and paranormal abilities... novels, Plutonia Hollow Earth The Hollow Earth hypothesis proposes that the planet Earth is either entirely hollow or otherwise contains a substantial interior space. The hypothesis has been shown to be wrong by observational evidence, as well as by the modern understanding of planet formation; the scientific community has... (1915) and Sannikov Land Sannikov Land Sannikov Land was a phantom island in the Arctic Ocean. Its supposed existence became something of a myth in 19th-century Russia.Yakov Sannikov and Matvei Gedenschtrom claimed to have seen it during their 1809-1810 cartographic expedition to the New Siberian Islands... (1924). These stories, imitating the pattern of Arthur Conan Doyle Arthur Conan Doyle Sir Arthur Ignatius Conan Doyle DL was a Scottish physician and writer, most noted for his stories about the detective Sherlock Holmes, generally considered a milestone in the field of crime fiction, and for the adventures of Professor Challenger... 's The Lost World The Lost World (Arthur Conan Doyle) The Lost World is a novel released in 1912 by Sir Arthur Conan Doyle concerning an expedition to a plateau in the Amazon basin of South America where prehistoric animals still survive. It was originally published serially in the popular Strand Magazine during the months of April 1912-November 1912... , depict in vivid detail the discovery of an isolated world of prehistoric animals in hitherto unexplored large islands in the Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... . Obruchevite mineral, Akademik Obruchev Range in Tuva Tuva The Tyva Republic , or Tuva , is a federal subject of Russia . It lies in the geographical center of Asia, in southern Siberia. The republic borders with the Altai Republic, the Republic of Khakassia, Krasnoyarsk Krai, Irkutsk Oblast, and the Republic of Buryatia in Russia and with Mongolia to the... , a mountain near the upper Vitim River Vitim River Vitim River is a major tributary of the Lena River. With its source east of Lake Baikal, the Vitim flows 1,978 km north through the Transbaykalian Mountains and the town of Bodaybo. The river peaks in June and freezes from November to May. It is navigable from the Lena to Bodaybo. Upstream,... , an oasis Oasis In geography, an oasis or cienega is an isolated area of vegetation in a desert, typically surrounding a spring or similar water source... in Antarctica, Obruchev crater Obruchev (crater) Obruchev is a disintegrating lunar crater that lies along the southern shore of Mare Ingenii, on the far side of the Moon. Less than three crater diameters to the south of Obruchev is the crater Chrétien, and about the same distance to the southeast lies Oresme.The outer rim of this crater has been... on the Moon Moon The Moon is Earth's only known natural satellite,There are a number of near-Earth asteroids including 3753 Cruithne that are co-orbital with Earth: their orbits bring them close to Earth for periods of time but then alter in the long term . These are quasi-satellites and not true moons. For more... , the Obruchev Prize for works in the field of Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... n geology, Vladimir Obruchev oil and gas research vessel and many streets and other places have been named after Obruchev. |
 |
|
| Dmitry Ovtsyn Dmitry Ovtsyn Dmitry Leontiyevich Ovtsyn was a Russian hydrographer and Arctic explorer.In 1734-1738, Ovtsyn led one of the units of the Second Kamchatka expedition that charted the coastline of the Kara Sea east of the river Ob. In summer of 1737, his unit made its way from Ob to Yenisei and made the first... (? – after 1757) Tsardom of Russia Tsardom of Russia The Tsardom of Russia was the name of the centralized Russian state from Ivan IV's assumption of the title of Tsar in 1547 till Peter the Great's foundation of the Russian Empire in 1721.From 1550 to 1700, Russia grew 35,000 km2 a year...  Russian Empire Russian EmpireRussian Imperial Navy officer, hydrographer, Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... explorer |
In 1737-38 Ovtsyn led one of the units of the Great Northern Expedition Great Northern Expedition The Great Northern Expedition or Second Kamchatka expedition was one of the largest organised exploration enterprises in history, resulting in mapping of the most of the Arctic coast of Siberia and some parts of the North America coastline, greatly reducing the "white areas" on the maps... that charted the coastline of the Kara Sea Kara Sea The Kara Sea is part of the Arctic Ocean north of Siberia. It is separated from the Barents Sea to the west by the Kara Strait and Novaya Zemlya, and the Laptev Sea to the east by the Severnaya Zemlya.... east of the Ob River Ob River The Ob River , also Obi, is a major river in western Siberia, Russia and is the world's seventh longest river. It is the westernmost of the three great Siberian rivers that flow into the Arctic Ocean .The Gulf of Ob is the world's longest estuary.-Names:The Ob is known to the Khanty people as the... , making the first hydrographic description of the large Gydan Peninsula Gydan Peninsula The Gydan Peninsula is a geographical feature of the Siberian coast in the Kara Sea. It is roughly 500 km long and 260 km wide. This wide peninsula lies between the estuaries of the Ob and Yenisei Rivers , which are two of the most important rivers of Russia and the world... and part of Taymyr Taymyr Peninsula The Taymyr Peninsula is a peninsula in the Far North of Russia, in the Siberian Federal District, that forms the northernmost part of mainland Eurasia and Asia... . In 1741-42 Ovtsyn took part in Vitus Bering Vitus Bering Vitus Jonassen Bering Vitus Jonassen Bering Vitus Jonassen Bering (also, less correNavy]], a captain-komandor known among the Russian sailors as Ivan Ivanovich. He is noted for being the first European to discover Alaska and its Aleutian Islands... 's voyage to the shores of North America North America North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas... . A cape on the Taimyr Peninsula and a strait Strait A strait or straits is a narrow, typically navigable channel of water that connects two larger, navigable bodies of water. It most commonly refers to a channel of water that lies between two land masses, but it may also refer to a navigable channel through a body of water that is otherwise not... between the islands Oleniy and Sibiryakov bear Ovtsyn's name. |
 |
P
| Portrait | Person | Achievements | Image |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
Pyotr Pakhtusov Pyotr Pakhtusov Pyotr Kuzmich Pakhtusov was a Russian surveyor and Arctic explorer. He is credited with the first thorough survey of Novaya Zemlya.... (1800–1835)  Russian Empire Russian EmpireRussian Imperial Navy officer, hydrographer, Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... explorer (a monument in Kronstadt Kronstadt Kronstadt , also spelled Kronshtadt, Cronstadt |crown]]" and Stadt for "city"); is a municipal town in Kronshtadtsky District of the federal city of St. Petersburg, Russia, located on Kotlin Island, west of Saint Petersburg proper near the head of the Gulf of Finland. Population: It is also... ) |
A participant of the earlier explorations by Fyodor Litke, Pakhtusov led two expeditions to Novaya Zemlya Novaya Zemlya Novaya Zemlya , also known in Dutch as Nova Zembla and in Norwegian as , is an archipelago in the Arctic Ocean in the north of Russia and the extreme northeast of Europe, the easternmost point of Europe lying at Cape Flissingsky on the northern island... in 1832 and 1835. He twice wintered on the islands and took detailed meteorological observations. Together with fellow explorer and cartographer Avgust Tsivolko Avgust Tsivolko Avgust Karlovich Tsivolko, also spelled as Tsivolka was a Russian navigator and Arctic explorer.... , Pakhtusov made the first reliable maps of Novaya Zemlya's southern shores. An island on the eastern shore of Novaya Zemlya Novaya Zemlya Novaya Zemlya , also known in Dutch as Nova Zembla and in Norwegian as , is an archipelago in the Arctic Ocean in the north of Russia and the extreme northeast of Europe, the easternmost point of Europe lying at Cape Flissingsky on the northern island... and a group of islands in the Nordenskiöld Archipelago Nordenskiöld Archipelago The Nordenskiöld Archipelago or Nordenskjold Archipelago is a very large and complex cluster of islands in the eastern region of the Kara Sea. Its eastern limit lies west of the Taymyr Peninsula.... are named after Pakhtusov. |
 |
| Peter Simon Pallas Peter Simon Pallas Peter Simon Pallas was a German zoologist and botanist who worked in Russia.- Life and work :Pallas was born in Berlin, the son of Professor of Surgery Simon Pallas. He studied with private tutors and took an interest in natural history, later attending the University of Halle and the University... (1741–1811)  Kingdom of Prussia Kingdom of Prussia Russian Empire Russian Empirenaturalist, zoologist and botanist, geographer, explorer of European Russia European Russia European Russia refers to the western areas of Russia that lie within Europe, comprising roughly 3,960,000 square kilometres , larger in area than India, and spanning across 40% of Europe. Its eastern border is defined by the Ural Mountains and in the south it is defined by the border with... and Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... |
Born in Berlin Berlin Berlin is the capital city of Germany and is one of the 16 states of Germany. With a population of 3.45 million people, Berlin is Germany's largest city. It is the second most populous city proper and the seventh most populous urban area in the European Union... and educated at German universities, Pallas was ivited by Catherine II of Russia Catherine II of Russia Catherine II, also known as Catherine the Great , Empress of Russia, was born in Stettin, Pomerania, Prussia on as Sophie Friederike Auguste von Anhalt-Zerbst-Dornburg... to became a professor at the St Petersburg Academy of Sciences. In 1768-74, he led an academic expedition to central Russian provinces Central economic region Central economic region is one of twelve economic regions of Russia.Area: 484,000 km²; population: 30.5 million . Average population density—63/km². Over 80% of the population is urban.... , Povolzhye, Caspian Sea Caspian Sea The Caspian Sea is the largest enclosed body of water on Earth by area, variously classed as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. The sea has a surface area of and a volume of... , Urals, and Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... , reaching as far east as Transbaikal Transbaikal Transbaikal, Trans-Baikal, Transbaikalia , or Dauria is a mountainous region to the east of or "beyond" Lake Baikal in Russia. The alternative name, Dauria, is derived from the ethnonym of the Daur people. It stretches for almost 1000 km from north to south from the Patomskoye Plateau and North... . The regular reports which Pallas sent to St. Petersburg covered a wide range of topics, including geology and mineralogy, native peoples and religions, new plants and animals. Pallas became a favourite of Catherine II, and was provided with the specimens collected by other naturalists to compile the Flora Rossica (publ. 1784-1815) and Zoographica Rosso-Asiatica (1811–31). He also published an account of Johann Anton Güldenstädt Johann Anton Güldenstädt Johann Anton Güldenstädt was a Baltic German naturalist and explorer in Russian service.... 's travels in the Caucasus and journals of Georg Wilhelm Steller Georg Wilhelm Steller Georg Wilhelm Steller was a German botanist, zoologist, physician and explorer, who worked in Russia and is considered the discoverer of Alaska and a pioneer of Alaskan natural history.-Biography:... from Kamchatka and Alaska Alaska Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait... . In 1793-94 Pallas led an expedition to southern Russia, visiting the Crimea Crimea Crimea , or the Autonomous Republic of Crimea , is a sub-national unit, an autonomous republic, of Ukraine. It is located on the northern coast of the Black Sea, occupying a peninsula of the same name... and the Black Sea Black Sea The Black Sea is bounded by Europe, Anatolia and the Caucasus and is ultimately connected to the Atlantic Ocean via the Mediterranean and the Aegean seas and various straits. The Bosphorus strait connects it to the Sea of Marmara, and the strait of the Dardanelles connects that sea to the Aegean... , the Caucasus Caucasus The Caucasus, also Caucas or Caucasia , is a geopolitical region at the border of Europe and Asia, and situated between the Black and the Caspian sea... and the valley of the Dnieper. He discovered and described a large number of new specimen and amassed a vast natural history collection. Streets in Berlin and Castrop-Rauxel Castrop-Rauxel -Geography:Castrop-Rauxel is between Dortmund to the east, Bochum , Herne , and to the north, Recklinghausen, Datteln and Waltrop.- Urban Area :The urban area of Castrop-Rauxel has an total expanse of... , a city of Pallasovka Pallasovka Pallasovka is a town and the administrative center of Pallasovsky District of Volgograd Oblast, Russia, located on the Torgun River , northeast of Volgograd. Population: -History:... in Volgograd Oblast Volgograd Oblast Volgograd Oblast is a federal subject of Russia . Its administrative center is the city of Volgograd. Population: -Geography:*Area: 113,900 km²;*Borders length: 2221,9 km².... , an asteroid Asteroid Asteroids are a class of small Solar System bodies in orbit around the Sun. They have also been called planetoids, especially the larger ones... 21087 Petsimpallas 21087 Petsimpallas 21087 Petsimpallas is a main-belt asteroid discovered on January 30, 1992 by E. W. Elst at the European Southern Observatory. It is named after botanist and zoologist Peter Simon Pallas.... were named after Pallas, as well as many animals, including Pallas's Cat, Pallas's Squirrel, Pallas's Gull and others. |
  |
|
| Ivan Papanin Ivan Papanin Ivan Dmitrievich Papanin was a Russian Polar Explorer, Scientist,Counter Admiral, twice Hero of the Soviet Union awarded nine Orders of Lenin... (1894–1986)  Russian Empire Russian Empire Soviet Union Soviet UnionSoviet Navy Soviet Navy The Soviet Navy was the naval arm of the Soviet Armed Forces. Often referred to as the Red Fleet, the Soviet Navy would have played an instrumental role in a Warsaw Pact war with NATO, where it would have attempted to prevent naval convoys from bringing reinforcements across the Atlantic Ocean... officer, Counter Admiral Counter Admiral Counter admiral is a rank found in many navies of the world, but no longer used in English-speaking countries, where the equivalent rank is rear admiral... , twice Hero of the Soviet Union Hero of the Soviet Union The title Hero of the Soviet Union was the highest distinction in the Soviet Union, awarded personally or collectively for heroic feats in service to the Soviet state and society.-Overview:... , Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... explorer (On photo: a monument to Ivan Papanin on the street of his name in Murmansk Murmansk Murmansk is a city and the administrative center of Murmansk Oblast, Russia. It serves as a seaport and is located in the extreme northwest part of Russia, on the Kola Bay, from the Barents Sea on the northern shore of the Kola Peninsula, not far from Russia's borders with Norway and Finland... ) |
In 1931 Papanin took part in the expedition of the icebreaker Icebreaker An icebreaker is a special-purpose ship or boat designed to move and navigate through ice-covered waters. Although the term usually refers to ice-breaking ships, it may also refer to smaller vessels .For a ship to be considered an icebreaker, it requires three traits most... Malygin to the Franz Josef Land Franz Josef Land Franz Josef Land, Franz Joseph Land, or Francis Joseph's Land is an archipelago located in the far north of Russia. It is found in the Arctic Ocean north of Novaya Zemlya and east of Svalbard, and is administered by Arkhangelsk Oblast. Franz Josef Land consists of 191 ice-covered islands with a... . In 1932-33 he was the chief of a polar expedition in the Tikhaya Bay Hooker Island Hooker Island is one of the most important islands of Franz Josef Land. It is located in the central area of the archipelago at . It is administered by the Arkhangelsk Oblast, Russia.... on the Franz Josef Land. In 1934-35 he was the head of a polar station on the Cape Chelyuskin Cape Chelyuskin Cape Chelyuskin is the northernmost point of the Eurasian continent , and the northernmost point of mainland Russia. It is situated at the tip of the Taymyr Peninsula, south of Severnaya Zemlya archipelago, in Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russia... . In 1937-38 he was the head of the first Soviet manned drifting ice station Soviet and Russian manned drifting ice stations Soviet and Russian manned drifting ice stations are important contributors to exploration of the Arctic. The stations are named North Pole Soviet and Russian manned drifting ice stations are important contributors to exploration of the Arctic. The stations are named North Pole Soviet and... North Pole-1 North Pole-1 North Pole-1 was the first Soviet manned drifting station, primarily used for research.North Pole-1 was established on May 21, 1937, and officially opened on June 6, some from the North Pole by the expedition into the high latitudes Sever-1, led by Otto Schmidt. The expedition had been airlifted... , the world's first expedition of such kind. Together with Ernest Krenkel, Evgeny Fedorov Evgeny Fedorov Evgeny Fedorov is a Russian professional ice hockey centre currently playing for Yugra Khanty-Mansiysk of the Kontinental Hockey League .... and Petr Shirshov he landed on to the Arctic drifting ice-floes in an airplane flown by Mikhail Vodopyanov Mikhail Vasilyevich Vodopianov Mikhail Vasilyevich Vodopianov was a Soviet aircraft pilot, one of the first Heroes of the Soviet Union, and a Major General of the Soviet Air Force.... . For 234 days the team carried out a wide range of scientific observations in the near-polar zone, until taken back. In 1939-46 Papanin became the head of the Glavsevmorput' Chief Directorate of the Northern Sea Route The Chief Directorate of the Northern Sea Route , also known as Glavsevmorput, was a Soviet government organization in charge of the naval Northern Sea Route, established in January 1932 and dissolved in 1964.-History:The organization traces its roots to AO Komseveroput, a shipping company... , an establishment that oversaw operations on the Northern Sea Route Northern Sea Route The Northern Sea Route is a shipping lane officially defined by Russian legislation from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean specifically running along the Russian Arctic coast from Murmansk on the Barents Sea, along Siberia, to the Bering Strait and Far East. The entire route lies in Arctic... . In 1940 he organized the expedition that rescued ice-trapped icebreaker Icebreaker An icebreaker is a special-purpose ship or boat designed to move and navigate through ice-covered waters. Although the term usually refers to ice-breaking ships, it may also refer to smaller vessels .For a ship to be considered an icebreaker, it requires three traits most... "Sedov Icebreaker Sedov The Sedov was a Soviet ice-breaker fitted with steam engines. She was originally the Newfoundland sealing steamer Beothic and was renamed after Russian Captain and Polar explorer Georgy Yakovlevich Sedov.... ", and subsequently he headed various naval institutions. A cape on the Taymyr Peninsula Taymyr Peninsula The Taymyr Peninsula is a peninsula in the Far North of Russia, in the Siberian Federal District, that forms the northernmost part of mainland Eurasia and Asia... , a mountain in Antarctica, an underwater mountain in the Pacific Ocean Pacific Ocean The Pacific Ocean is the largest of the Earth's oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, bounded by Asia and Australia in the west, and the Americas in the east.At 165.2 million square kilometres in area, this largest division of the World... , a number of streets and an ice-class cargo and research ship have been named after Papanin. |
 |
|
| Maksim Perfilyev Maksim Perfilyev Maksim Perfilyev was a Cossack explorer of Eastern Siberia and the first Russian to reach Transbaikalia. He was renowned for his diplomatic skills in negotiations with Tunguses, Mongols and Chinese.... (? – after 1638) Tsardom of Russia Tsardom of Russia The Tsardom of Russia was the name of the centralized Russian state from Ivan IV's assumption of the title of Tsar in 1547 till Peter the Great's foundation of the Russian Empire in 1721.From 1550 to 1700, Russia grew 35,000 km2 a year... Siberian Cossack Siberian Cossacks Siberian Cossacks were Cossacks who settled in the Siberian region of Russia from the end of the 16th century, following the Yermak Timofeyevich's conquest of Siberia. In early Siberia practically the whole Russian population, especially the serving-men were called Cossacks, but only in the loose... voevoda, explorer of Eastern Siberia |
In 1618-19 Perfilyev became a co-founder of Yeniseysk Yeniseysk Yeniseysk is a town in Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russia, located on the Yenisei River. Population: 20,000 .Yeniseysk was founded in 1619 as a stockaded town—the first town on the Yenisei River. It played an important role in Russian colonization of East Siberia in the 17th–18th centuries... y ostrog, the first Russian fortress at the central Yenisey River and a major standpoint for further expeditions eastward. In 1618-27 Perfilyev made several journeys on Angara Angara River The Angara River is a long river in Irkutsk Oblast and Krasnoyarsk Krai, south-east Siberia, Russia. It is the only river flowing out of Lake Baikal, and is the headwater tributary of the Yenisei River.... , Ilim Ilim River Ilim River is a river in Irkutsk Oblast in Russia, a right tributary of the Angara River. It flows north between and parallel to the Angara and Lena Rivers, and then swings west to join the Angara 40km south of Ust-Ilimsk.... , Lena Lena River The Lena is the easternmost of the three great Siberian rivers that flow into the Arctic Ocean . It is the 11th longest river in the world and has the 9th largest watershed... and Vitim Vitim River Vitim River is a major tributary of the Lena River. With its source east of Lake Baikal, the Vitim flows 1,978 km north through the Transbaykalian Mountains and the town of Bodaybo. The river peaks in June and freezes from November to May. It is navigable from the Lena to Bodaybo. Upstream,... rivers, and built several new ostrogs Ostrog (fortress) Ostrog was a Russian term for a small fort, typically wooden and often non-permanently manned. Ostrogs were encircled by 4-6 metres high palisade walls made from sharpened trunks. The name derives from the Russian word строгать , "to shave the wood". Ostrogs were smaller and exclusively military... . In 1631 he founded Bratsk Bratsk Bratsk is a city in Irkutsk Oblast, Russia, located on the Angara River near the vast Bratsk Reservoir. Population: Although the name sounds like the Russian word for 'brother' , it actually comes from 'bratskiye lyudi', an old name for the Buryats.-History:The first Europeans in the area arrived... y ostrog (follow-up Bratsk Bratsk Bratsk is a city in Irkutsk Oblast, Russia, located on the Angara River near the vast Bratsk Reservoir. Population: Although the name sounds like the Russian word for 'brother' , it actually comes from 'bratskiye lyudi', an old name for the Buryats.-History:The first Europeans in the area arrived... ). In 1638 he became the first Russian to step in Transbaikalia. The Maksimikha Bay at Lake Baikal Lake Baikal Lake Baikal is the world's oldest at 30 million years old and deepest lake with an average depth of 744.4 metres.Located in the south of the Russian region of Siberia, between Irkutsk Oblast to the northwest and the Buryat Republic to the southeast, it is the most voluminous freshwater lake in the... (part of Barguzin Bay), Cape Maksimin and a village Maksimikha there (founded by Perfilyev ans his Buryat Buryats The Buryats or Buriyads , numbering approximately 436,000, are the largest ethnic minority group in Siberia and are mainly concentrated in their homeland, the Buryat Republic, a federal subject of Russia... wife), as well as the village of Maksimovschina on Irkut River Irkut River Irkut is a river in the Buryat Republic and Irkutsk Oblast of Russia; Angara's left tributary. The length of the river is . The area of its basin is . The Irkut River freezes up in late October - mid-November and stays icebound until late April - early May. The city of Irkutsk is located at the... are named after Maksim Perfilyev. |
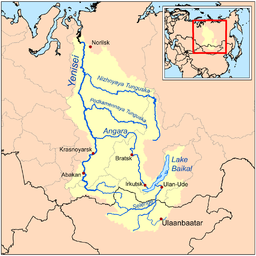 |
|
| Yakov Permyakov Yakov Permyakov Yakov Permyakov was a Russian seafarer, explorer, merchant, and Cossack.In 1710, while sailing from the Lena River to the Kolyma River, Permyakov observed the silhouette of two unknown island groups in the sea... (? – 1712) Tsardom of Russia Tsardom of Russia The Tsardom of Russia was the name of the centralized Russian state from Ivan IV's assumption of the title of Tsar in 1547 till Peter the Great's foundation of the Russian Empire in 1721.From 1550 to 1700, Russia grew 35,000 km2 a year... Siberian Cossack, seafarer, merchant, Arctic explorer |
In 1710, while sailing from the Lena River Lena River The Lena is the easternmost of the three great Siberian rivers that flow into the Arctic Ocean . It is the 11th longest river in the world and has the 9th largest watershed... to the Kolyma River Kolyma River The Kolyma River is a river in northeastern Siberia, whose basin covers parts of the Sakha Republic, Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, and Magadan Oblast of Russia. Itrises in the mountains north of Okhotsk and Magadan, in the area of and... , Permyakov discovered the Medvyezhi Islands Medvyezhi Islands The Medvezhyi Islands, or Bear Islands is an uninhabited group of islands at the western end of the Kolyma Gulf of the East Siberian Sea. It is located about to the north of the mouths of the Kolyma River. The coast of Siberia is about to the southwest of the largest island, which is about km... , siting them from afar. During the same voyage he also observed the follow-up Bolshoy Lyakhovsky island, known to the earlier explorers but never reached so far. In 1712, Permyakov and his companion Merkury Vagin Merkury Vagin Merkury Vagin was a Russian Arctic explorer.In 1712, together with Yakov Permyakov, Merkury Vagin explored the region of the eastern Laptev Sea coast, including Bolshoy Lyakhovsky Island, the southermost of the New Siberian Archipelago... crossed the Yana Bay Yana Bay The Yana Bay is the most important gulf of the Laptev Sea. It is located between Cape Buor-Khaya on its western side and the Ebelyakh Bay at its eastern end.... from the mouth of the Yana Yana River The Yana River , is a river in Sakha in Russia, located between the Lena to the west and the Indigirka to the east.It is 872 km in length. The area of its basin is 238,000 km², whilst its annual discharge totals approximately . Most of this discharge occurs in May and June as the ice on the... over the ice and explored Bolshoy Lyakhovsky island, the southernmost of the New Siberian Islands New Siberian Islands The New Siberian Islands are an archipelago, located to the North of the East Siberian coast between the Laptev Sea and the East Siberian Sea north of the Sakha Republic.... . Thus they initiated the exploration of the large New Siberian archipelago. On their way back Permyakov and Vagin were murdered by mutineering expedition members. |
 |
|
| Ivan Petlin Ivan Petlin Ivan Petlin Petlin), a Siberian Cossack, was the first Russian to have reached China on an official mission . His expedition may have been the second European expedition to reach China from the west by an overland route since the fall of the Yuan Dynasty... (? – after 1619) Tsardom of Russia Tsardom of Russia The Tsardom of Russia was the name of the centralized Russian state from Ivan IV's assumption of the title of Tsar in 1547 till Peter the Great's foundation of the Russian Empire in 1721.From 1550 to 1700, Russia grew 35,000 km2 a year... Siberian Cossack Siberian Cossacks Siberian Cossacks were Cossacks who settled in the Siberian region of Russia from the end of the 16th century, following the Yermak Timofeyevich's conquest of Siberia. In early Siberia practically the whole Russian population, especially the serving-men were called Cossacks, but only in the loose... , diplomat, explorer of Central Asia Central Asia Central Asia is a core region of the Asian continent from the Caspian Sea in the west, China in the east, Afghanistan in the south, and Russia in the north... and China China Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture... |
Petlin was the first Russian to reach China China Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture... on an official diplomatic mission in 1618-19. His expedition may have been the second European expedition to reach China from the west by an overland route (after that of Bento de Góis) since the fall of the Yuan Dynasty Yuan Dynasty The Yuan Dynasty , or Great Yuan Empire was a ruling dynasty founded by the Mongol leader Kublai Khan, who ruled most of present-day China, all of modern Mongolia and its surrounding areas, lasting officially from 1271 to 1368. It is considered both as a division of the Mongol Empire and as an... . Together with Andrei Mundov and 10 other men, Petlin went south up the Ob River Ob River The Ob River , also Obi, is a major river in western Siberia, Russia and is the world's seventh longest river. It is the westernmost of the three great Siberian rivers that flow into the Arctic Ocean .The Gulf of Ob is the world's longest estuary.-Names:The Ob is known to the Khanty people as the... , crossed the Abakan Range Abakan Range Abakan Range is a metamorphic rock mountain range in the Southwestern Siberia, Russia: length: , elevation: up to . It is mostly covered by taiga, up to , followed by mountainous tundra.... , went south to Tuva Tuva The Tyva Republic , or Tuva , is a federal subject of Russia . It lies in the geographical center of Asia, in southern Siberia. The republic borders with the Altai Republic, the Republic of Khakassia, Krasnoyarsk Krai, Irkutsk Oblast, and the Republic of Buryatia in Russia and with Mongolia to the... and rounding Lake Ubsa Uvs Nuur Uvs Lake is a highly saline lake in an endorheic basin - Uvs Nuur Basin in Mongolia with a small part in Russia. It is the largest lake in Mongolia by surface area, covering 3,350 km² at 759 m above sea level.... reached the court of the Altyn Khan. Then they passed through Mongolia Mongolia Mongolia is a landlocked country in East and Central Asia. It is bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south, east and west. Although Mongolia does not share a border with Kazakhstan, its western-most point is only from Kazakhstan's eastern tip. Ulan Bator, the capital and largest... to the Great Wall of China Great Wall of China The Great Wall of China is a series of stone and earthen fortifications in northern China, built originally to protect the northern borders of the Chinese Empire against intrusions by various nomadic groups... and Peking. He was not allowed to see the Wanli Emperor Wanli Emperor The Wanli Emperor was emperor of China between 1572 and 1620. His era name means "Ten thousand calendars". Born Zhu Yijun, he was the Longqing Emperor's third son... because of not bringing proper tribute, so he returned back. He brought back a letter in Chinese inviting Russians to open trade, but no one in Russia was able to read it until 1675. A vague but still valuable account of Petlin's expedition was translated into English and published in Samuel Purchas Samuel Purchas Samuel Purchas , was an English travel writer, a near-contemporary of Richard Hakluyt.Purchas was born at Thaxted, Essex, and graduated at St John's College, Cambridge, in 1600; later he became a B.D., and with this degree was admitted at Oxford in 1615. In 1604 he was presented by James I to the... ' Pilgrims in 1625, and then translated to other European languages. |
 |
|
| Valeri Polyakov (born 1942)  Soviet Union Soviet Union Russia Russiacosmonaut and physician Physician A physician is a health care provider who practices the profession of medicine, which is concerned with promoting, maintaining or restoring human health through the study, diagnosis, and treatment of disease, injury and other physical and mental impairments... , Hero of the Soviet Union Hero of the Soviet Union The title Hero of the Soviet Union was the highest distinction in the Soviet Union, awarded personally or collectively for heroic feats in service to the Soviet state and society.-Overview:... , Hero of the Russian Federation Hero of the Russian Federation Hero of the Russian Federation is a Russian decoration and the highest honorary title that can be bestowed on a citizen by the Russian Federation. The President of the Russian Federation is the main conferring authority of the medal, which is bestowed on those committing actions or deeds that... |
Polyakov holds the world record for the longest continuous spaceflight Spaceflight Spaceflight is the act of travelling into or through outer space. Spaceflight can occur with spacecraft which may, or may not, have humans on board. Examples of human spaceflight include the Russian Soyuz program, the U.S. Space shuttle program, as well as the ongoing International Space Station... in history, 437 days 18 hours (more than 14 months), which he spent aboard Soyuz TM-18 Soyuz TM-18 Soyuz TM-18 was launch from Baikonur Cosmodrome and landing 112 km north of Arkalyk. TM-18 was a two day solo flight that docked with the Mir space station on January 10, 1994. The three cosmonauts became the 15th resident crew of the MIR... , Mir Mir Mir was a space station operated in low Earth orbit from 1986 to 2001, at first by the Soviet Union and then by Russia. Assembled in orbit from 1986 to 1996, Mir was the first modular space station and had a greater mass than that of any previous spacecraft, holding the record for the... space station Space station A space station is a spacecraft capable of supporting a crew which is designed to remain in space for an extended period of time, and to which other spacecraft can dock. A space station is distinguished from other spacecraft used for human spaceflight by its lack of major propulsion or landing... and Soyuz TM-20 Soyuz TM-20 -Crew:-Mission highlights:20th expedition to Mir.Carried 10 kg of equipment for use by Merbold in ESA’s month-long Euromir94 experiment program. During automatic approach to Mir’s front port, the... in 1994-95. With his earlier expedition to Mir on Soyuz TM-6 Soyuz TM-6 Dr. Valeri Polyakov remained behind on Mir with cosmonauts Musa Manarov and Vladimir Titov when Mohmand and Lyakhov returned to Earth in Soyuz TM-5.... and back on Soyuz TM-7 Soyuz TM-7 -Mission parameters:*Mass: 7,000 kg 15,400 lb*Perigee: 194 km *Apogee: 235 km *Inclination: 51.6°*Period: 88.8 minutes-Mission highlights:... in 1988-89, his combined space experience is more than 22 months. |
 |
|
| Fedot Popov Fedot Alekseyev Popov Fedot Alekseyevich Popov , date of birth unknown, died between 1648 and 1654) was a Russian explorer who organized the first European expedition through the Bering Strait.He was normally known as Fedot Alekseyev. Only a few sources call him the son of Popov... (? – 1648-54) Tsardom of Russia Tsardom of Russia The Tsardom of Russia was the name of the centralized Russian state from Ivan IV's assumption of the title of Tsar in 1547 till Peter the Great's foundation of the Russian Empire in 1721.From 1550 to 1700, Russia grew 35,000 km2 a year... merchant, explorer of Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... and the Russian Far East Russian Far East Russian Far East is a term that refers to the Russian part of the Far East, i.e., extreme east parts of Russia, between Lake Baikal in Eastern Siberia and the Pacific Ocean... |
An agent of Moscow Moscow Moscow is the capital, the most populous city, and the most populous federal subject of Russia. The city is a major political, economic, cultural, scientific, religious, financial, educational, and transportation centre of Russia and the continent... merchant Alexey Usov, Fedot Popov came to Srednekolymsk Srednekolymsk Srednekolymsk is a town and the administrative center of Srednekolymsky District of the Sakha Republic, Russia, located northeast of Yakutsk on the left bank of the Kolyma River. Population: -History:... in Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... in 1645. There he organized an expedition eastward, and carried in Semyon Dezhnev Semyon Dezhnev Semyon Ivanovich Dezhnyov was a Russian explorer of Siberia and the first European to sail through the Bering Strait. In 1648 he sailed from the Kolyma River on the Arctic Ocean to the Anadyr River on the Pacific... . In 1648 they sailed down to the Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... and became the first to pass through the Bering Strait Bering Strait The Bering Strait , known to natives as Imakpik, is a sea strait between Cape Dezhnev, Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, Russia, the easternmost point of the Asian continent and Cape Prince of Wales, Alaska, USA, the westernmost point of the North American continent, with latitude of about 65°40'N,... and to discover Chukotka Chukchi Peninsula The Chukchi Peninsula, Chukotka Peninsula or Chukotski Peninsula , at about 66° N 172° W, is the northeastern extremity of Asia. Its eastern end is at Cape Dezhnev near the village of Uelen. It is bordered by the Chukchi Sea to the north, the Bering Sea to the south, and the Bering Strait to the... and Bering Sea Bering Sea The Bering Sea is a marginal sea of the Pacific Ocean. It comprises a deep water basin, which then rises through a narrow slope into the shallower water above the continental shelves.... . All their kochs Koch (boat) The Koch was a special type of small one or two mast wooden sailing ships designed and used in Russia for transpolar voyages in ice conditions of the Arctic seas, popular among the Pomors.... and most of their men (including Popov himself) were lost in storms and clashes with the natives. A small group led by Dezhnyov reached the Anadyr River Anadyr River Anadyr is a river in the far northeast Siberia which flows into Anadyr Bay of the Bering Sea and drains much of the interior of Chukotka Autonomous Okrug. Its basin corresponds to the Anadyrsky District of Chukotka.... . In 1653-54, while fighting with Koryaks Koryaks Koryaks are an indigenous people of Kamchatka Krai in the Russian Far East, who inhabit the coastlands of the Bering Sea to the south of the Anadyr basin and the country to the immediate north of the Kamchatka Peninsula, the southernmost limit of their range being Tigilsk. They are akin to the... near Anadyrsk Anadyrsk thumb|Anadyrsk was on the east-west part of the Anadyr River at the point where it swings northAnadyrsk was an important Russian ostrog in far northeastern Siberia from 1649 to 1764... , Dezhnyov captured Popov's Yakut Yakuts Yakuts , are a Turkic people associated with the Sakha Republic.The Yakut or Sakha language belongs to the Northern branch of the Turkic family of languages.... wife, who confirmed him dead. When Vladimir Atlasov Vladimir Atlasov Vladimir Vasilyevich Atlasov or Otlasov was a Siberian Cossack who was the first Russian to explore the Kamchatka Peninsula. Atlasov Island, an uninhabited volcanic island off the southern tip of Kamchatka, is named after him.... came to conquer Kamchatka in 1697, he heard from the locals about a certain Fedotov, who had lived with his men near Kamchatka River Kamchatka River The Kamchatka River runs eastward for through Kamchatka Krai in the Russian Far East towards the Pacific Ocean. The river is rich with salmon, millions of which spawn yearly and which once supported the settlements of the native Itelmen.... and had married local women - so the Fedotov legend appeared. Gerhardt Friedrich Müller Gerhardt Friedrich Müller Gerhard Friedrich Müller was a historian and pioneer ethnologist.-Biography:He was educated at Leipzig.In 1725, he was invited to St. Petersburg to co-found the Imperial Academy of Sciences... thought he was probably Fedot's son, while Stepan Krasheninnikov Stepan Krasheninnikov Stepan Petrovich Krasheninnikov was a Russian explorer of Siberia, naturalist and geographer who gave the first full description of Kamchatka in the early 18th century. He was elected to the Russian Academy of Sciences in 1745... thought he was Fedot himself, thus deeming Fedot Popov to be the possible discoverer of Kamchatka. |
||
 |
Konstantin Posyet Konstantin Posyet Constantine Possiet was a Russian statesman and admiral who served as Minister of Transport Communications between 1874 and 1888.... (1819–1899)  Russian Empire Russian EmpireRussian Imperial Navy officer, Admiral Admiral Admiral is the rank, or part of the name of the ranks, of the highest naval officers. It is usually considered a full admiral and above vice admiral and below admiral of the fleet . It is usually abbreviated to "Adm" or "ADM"... , military writer, statesman, diplomat, explorer of Pacific, Japan Japan Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south... and the Russian Far East Russian Far East Russian Far East is a term that refers to the Russian part of the Far East, i.e., extreme east parts of Russia, between Lake Baikal in Eastern Siberia and the Pacific Ocean... |
In 1852-54, Possiet journeyed on the frigate Pallas to Japan Japan Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south... under the command of admirals Yevfimy Putyatin Yevfimy Putyatin Yevfimy Vasilyevich Putyatin was a Russian admiral noted for his diplomatic missions to Japan and China which resulted in the signing of the Treaty of Shimoda in 1855.-Early life:... and Ivan Unkovsky. Accompanied also by novelist Ivan Goncharov Ivan Goncharov Ivan Alexandrovich Goncharov was a Russian novelist best known as the author of Oblomov .- Biography :Ivan Goncharov was born in Simbirsk ; his father was a wealthy grain merchant and respected official who was elected mayor of Simbirsk several times... and inventor Alexander Mozhaisky, Possiet explored and mapped the northern coastline of the Sea of Japan Sea of Japan The Sea of Japan is a marginal sea of the western Pacific Ocean, between the Asian mainland, the Japanese archipelago and Sakhalin. It is bordered by Japan, North Korea, Russia and South Korea. Like the Mediterranean Sea, it has almost no tides due to its nearly complete enclosure from the Pacific... , including Possiet Bay, which now bears his name. In 1856 he carried to Japan the news of the ratification of the Treaty of Shimoda Treaty of Shimoda The Treaty of Shimoda of 1855, formally Treaty of Commerce and Navigation between Japan and Russia , was signed between the Russian Vice-Admiral Euphimy Vasil'evich Putiatin and Toshiakira Kawaji of Japan in the city of Shimoda, Izu Province, Japan, on February 7, 1855... . Possiet's journeys and published observations made an expert on Japan in Russia. In 1875, already a Minister of Ways and Communications of Russia, he negotiated with Enomoto Takeaki Enomoto Takeaki Viscount was a samurai and admiral of the Tokugawa navy of Bakumatsu period Japan, who remained faithful to the Tokugawa shogunate who fought against the new Meiji government until the end of the Boshin War... the Treaty of Saint Petersburg, which brought entire Sakhalin Island into the Russian fold. He prepared the construction of the Trans-Siberian Railway Trans-Siberian Railway The Trans-Siberian Railway is a network of railways connecting Moscow with the Russian Far East and the Sea of Japan. It is the longest railway in the world... and was a leading advocate for the restoration of the familiar white-blue-red tricolor as the official flag of Russia Flag of Russia The flag of Russia is a tricolour flag of three equal horizontal fields, white on the top, blue in the middle and red on the bottom. The flag was first used as an ensign for Russian merchant and war ships and only became official in 1896... in 1896. Possiet Bay in the Sea of Japan Sea of Japan The Sea of Japan is a marginal sea of the western Pacific Ocean, between the Asian mainland, the Japanese archipelago and Sakhalin. It is bordered by Japan, North Korea, Russia and South Korea. Like the Mediterranean Sea, it has almost no tides due to its nearly complete enclosure from the Pacific... , Posyet Posyet Posyet is an urban locality in Khasansky District of Primorsky Krai, Russia, and an ice-free port on the Possiet Bay. Population:... port there, and a street in Vladivostok Vladivostok The city is located in the southern extremity of Muravyov-Amursky Peninsula, which is about 30 km long and approximately 12 km wide.The highest point is Mount Kholodilnik, the height of which is 257 m... are named after Konstantin Posyet. |
 |
| Grigory Potanin Grigory Potanin Grigory Nikolayaevich Potanin was a Russian explorer of Inner Asia who aligned himself with the Siberian separatist movement... (1835–1920)  Russian Empire Russian Empiregeographer, ethnographer, botanist, explorer of Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... , Central Asia Central Asia Central Asia is a core region of the Asian continent from the Caspian Sea in the west, China in the east, Afghanistan in the south, and Russia in the north... and China China Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture... |
Potanin traveled extensively through Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... , studying its nature and peoples, once accompanied by Nikolai Yadrintsev Nikolai Yadrintsev Nikolai Mikhailovich Yadrintsev was a Russian public figure, explorer, archaeologist, and turkologist. His discoveries include the Orkhon script, Genghis Khan's capital Karakorum and Ordu-Baliq, the capital of the Uyghur Khaganate. He was also one of the founding fathers of Siberian separatism.-... . In 1876 and 1879 Potanin led two expeditions into Mongolia, obtaining valuable material in all fields of geography. In 1884-86 Potanin explored the Northern China China Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture... and Tibet Tibet Tibet is a plateau region in Asia, north-east of the Himalayas. It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people as well as some other ethnic groups such as Monpas, Qiang, and Lhobas, and is now also inhabited by considerable numbers of Han and Hui people... , returning to Russia through Qilian Mountains and Mongolia. They encountered a Turkish people Turkish people Turkish people, also known as the "Turks" , are an ethnic group primarily living in Turkey and in the former lands of the Ottoman Empire where Turkish minorities had been established in Bulgaria, Cyprus, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Georgia, Greece, Kosovo, Macedonia, and Romania... called the Salars and made other ethnographic and geographic discoveries, including the first account of East and West Uighur languages. In 1989 Potanin became one of the founders of Tomsk University, the first university in Asian Russia. In 1892-93 he again explored the Northern China China Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture... and Sichuan Sichuan ' , known formerly in the West by its postal map spellings of Szechwan or Szechuan is a province in Southwest China with its capital in Chengdu... accompanied by geologist Vladimir Obruchev Vladimir Obruchev Vladimir Afanasyevich Obruchev was a Russian and Soviet geologist who specialized in the study of Siberia and Central Asia. He was also one of the first Russian science fiction authors.- Scientific research :... . Before reaching Tibet, Potanin was forced to turn back because of the illness and death of his wife Alexandra, who was the first woman in the Russian Geographical Society Russian Geographical Society The Russian Geographical Society is a learned society, founded on 6 August 1845 in Saint Petersburg, Russia.-Imperial Geographical Society:Prior to the Russian Revolution of 1917, it was known as the Imperial Russian Geographical Society.... . In 1899 Potanin travelled onto Greater Khingan Greater Khingan The Greater Khingan Range , also called the Greater Hing'an Range or Greater Hinggan Range, is a volcanic mountain range in the northeastern part of the People's Republic of China. The range extends roughly 1,200 km from north to south, narrowing towards the south... . A ridge in Qilian Mountains in China China Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture... , the largest glacier Potanin Glacier The Potanin Glacier is the longest glacier in Mongolia, its long about 14 kilometres and located through in the Altai Tavan Bogd mountain in Altai Mountains. The glacier is named after explorer Grigory Potanin.... in Altai Tavan Bogd (Altai Mountains), a number of streets in Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... n cities, several dozens of plants and 9915 Potanin 9915 Potanin 9915 Potanin is a C-type main belt asteroid. It orbits the Sun once every 5.05 years.Discovered on September 8, 1977 by Nikolai Chernykh, it was given the provisional designation "". It was later renamed "Potanin" after Grigorij Potanin, a Russian explorer of Siberia.- References :... asteroid were named after Potanin. |
||
| Vassili Poyarkov Vassili Poyarkov Vassili Danilovich Poyarkov was the first Russian explorer of the Amur region.The Russian expansion into Siberia began with the conquest of the Khanate of Sibir in 1582. By 1643 they reached the Pacific at Okhotsk... (? – after 1668) Tsardom of Russia Tsardom of Russia The Tsardom of Russia was the name of the centralized Russian state from Ivan IV's assumption of the title of Tsar in 1547 till Peter the Great's foundation of the Russian Empire in 1721.From 1550 to 1700, Russia grew 35,000 km2 a year... Siberian Cossack Siberian Cossacks Siberian Cossacks were Cossacks who settled in the Siberian region of Russia from the end of the 16th century, following the Yermak Timofeyevich's conquest of Siberia. In early Siberia practically the whole Russian population, especially the serving-men were called Cossacks, but only in the loose... ataman Ataman Ataman was a commander title of the Ukrainian People's Army, Cossack, and haidamak leaders, who were in essence the Cossacks... , explorer of Eastern Siberia and the Russian Far East Russian Far East Russian Far East is a term that refers to the Russian part of the Far East, i.e., extreme east parts of Russia, between Lake Baikal in Eastern Siberia and the Pacific Ocean... |
In 1643, Poyarkov with 133 men were sent from Yakutsk Yakutsk With a subarctic climate , Yakutsk is the coldest city, though not the coldest inhabited place, on Earth. Average monthly temperatures range from in July to in January. The coldest temperatures ever recorded on the planet outside Antarctica occurred in the basin of the Yana River to the northeast... to explore new lands south of Stanovoy Ridge. Having no idea of the proper route, Poyarkov traveled up the rivers Lena Lena River The Lena is the easternmost of the three great Siberian rivers that flow into the Arctic Ocean . It is the 11th longest river in the world and has the 9th largest watershed... , Aldan Aldan River The Aldan River is the second-longest tributary of the Lena River in the Sakha Republic in eastern Siberia. The river is 2,273 km long, of which around 1,600 km is navigable. It was part of the River Route to Okhotsk... , Uchur, Gonam and passed over the Stanovoy watershed only by winter, reaching the upper Zeya River Zeya River Zeya River , 1,242 km long, is a northern tributary of the Amur River. It rises in the Tokiysky Stanovik mountain ridge, a part of the Stanovoy Range. The first Russian to enter the area was Vassili Poyarkov.... in the country of Daurs, who were paying tribute to Manchu Manchu The Manchu people or Man are an ethnic minority of China who originated in Manchuria . During their rise in the 17th century, with the help of the Ming dynasty rebels , they came to power in China and founded the Qing Dynasty, which ruled China until the Xinhai Revolution of 1911, which... Chinese China Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture... . After wintering, in 1644 Poyarkov pushed down the Zeya and became the first Russian to reach the Amur River. He reached the Gilyak country and discovered the mouth of the Amur River from land. Since his Cossacks provoked the enmity of the locals behind, Poyarkov chose different way back. They built boats and in 1645 sailed along the Sea of Okhotsk Sea of Okhotsk The Sea of Okhotsk is a marginal sea of the western Pacific Ocean, lying between the Kamchatka Peninsula on the east, the Kuril Islands on the southeast, the island of Hokkaidō to the far south, the island of Sakhalin along the west, and a long stretch of eastern Siberian coast along the west and... coast to the Ulia River and spent the next winter in the huts that had been built by explorer Ivan Moskvitin Ivan Moskvitin Ivan Yuryevich Moskvitin was a Russian explorer, presumably a native of Moscow, who led a Russian reconnaissance party to the Pacific Ocean, becoming the first Russian to reach the Sea of Okhotsk.... six years earlier. In 1646 they returned to Yakutsk. |
||
| Gavriil Pribylov (? – 1796)  Russian Empire Russian Empirenavigator, explorer of Alaska Alaska Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait... and Bering Sea Bering Sea The Bering Sea is a marginal sea of the Pacific Ocean. It comprises a deep water basin, which then rises through a narrow slope into the shallower water above the continental shelves.... |
Pribylov, a commander of the ship St. George, led an expedition funded jointly by Grigory Shelikhov Grigory Shelikhov Grigory Ivanovich Shelekhov Grigory Ivanovich Shelekhov Grigory Ivanovich Shelekhov (Григорий Иванович Шелехов in Russian; (1747–July 20, 1795 (July 31, 1795 N.S.)) was a Russian seafarer and merchant born in Rylsk.... and Pavel Lebedev-Lastochkin with an aim to find the lucrative breeding grounds of fur seals, long sought by Siberian merchants. Pribylov discovered St. George Island St. George Island (Alaska) St. George Island is one of the Pribilof Islands of the state of Alaska, USA, in the Bering Sea off the western coast of the state. The island has a land area of 90 km² and a population of about 100 people, all living in its only community, the city of St... in the Bering Sea Bering Sea The Bering Sea is a marginal sea of the Pacific Ocean. It comprises a deep water basin, which then rises through a narrow slope into the shallower water above the continental shelves.... in 1786, by following the sounds of barking northern fur seal Northern Fur Seal The Northern fur seal is an eared seal found along the north Pacific Ocean, the Bering Sea and the Sea of Okhotsk. It is the largest member of the fur seal subfamily and the only species in the genus Callorhinus.-Physical description:Northern fur seals have extreme sexual dimorphism, with males... s and possibly hinted by Aleutian natives. Mixed Russian and Aleut crew of St. George established the international hunting for northern fur seals (continued for over a century until banned by international treaty in 1911 North Pacific Fur Seal Convention of 1911 The North Pacific Fur Seal Convention of 1911, formally known as the Convention between the United States and Other Powers Providing for the Preservation and Protection of Fur Seals, was an international treaty signed on July 7, 1911 designed to manage the commercial harvest of fur bearing mammals ... ). A year later in 1787, Pribylov discovered St. Paul Island 50 miles to the north of St. George. Pribilof Islands Pribilof Islands The Pribilof Islands are a group of four volcanic islands off the coast of mainland Alaska, in the Bering Sea, about north of Unalaska and 200 miles southwest of Cape Newenham. The Siberia coast is roughly northwest... (St. George Island St. George Island (Alaska) St. George Island is one of the Pribilof Islands of the state of Alaska, USA, in the Bering Sea off the western coast of the state. The island has a land area of 90 km² and a population of about 100 people, all living in its only community, the city of St... and St. Paul Island) are named after Pribylov. |
 |
|
| Vasili Pronchishchev Vasili Pronchishchev Vasili Vasilyevich Pronchishchev was a Russian explorer.In 1718, Vasili Pronchishchev graduated from Moscow School of Mathematics and Navigation and was promoted to naval cadet... (1702–1736) Tsardom of Russia Tsardom of Russia The Tsardom of Russia was the name of the centralized Russian state from Ivan IV's assumption of the title of Tsar in 1547 till Peter the Great's foundation of the Russian Empire in 1721.From 1550 to 1700, Russia grew 35,000 km2 a year...  Russian Empire Russian EmpireRussian Imperial Navy officer, Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... explorer (forensic facial reconstruction) |
In 1735-36 Pronchishchev led one of the units of the Great Northern Expedition Great Northern Expedition The Great Northern Expedition or Second Kamchatka expedition was one of the largest organised exploration enterprises in history, resulting in mapping of the most of the Arctic coast of Siberia and some parts of the North America coastline, greatly reducing the "white areas" on the maps... that discovered and mapped more than 500 of the Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... shore to the west of the mouth of Lena River Lena River The Lena is the easternmost of the three great Siberian rivers that flow into the Arctic Ocean . It is the 11th longest river in the world and has the 9th largest watershed... . He took his wife Maria Pronchishcheva Maria Pronchishcheva Maria Pronchishcheva - a Russian explorer.In 1735 with her husband, Vasili Pronchishchev, went down the Lena River on Vasili's sloop Yakutsk, doubled its delta, and stopped for wintering at the mouth of the Olenek River. Unfortunately many members of the crew fell ill and died, mainly owing to... with himself, aboard the sloop Sloop A sloop is a sail boat with a fore-and-aft rig and a single mast farther forward than the mast of a cutter.... Yakutsk. Despite the difficulties, they reached Taymyr Taymyr Peninsula The Taymyr Peninsula is a peninsula in the Far North of Russia, in the Siberian Federal District, that forms the northernmost part of mainland Eurasia and Asia... in 1736, having discovered the follow-up Faddey Islands Faddey Islands The Faddey Islands is a group of islands covered with tundra vegetation, shingle and ice. It is located in the Laptev Sea coastal region, off Faddey Bay in the coast of Siberia, east of the Taymyr Peninsula.The Main islands are:* Ostrov Faddeyya-Severnyy, latitude 76° 59' N and longitude 108° 02’... , Komsomolskoy Pravdy Islands, Saint Peter Islands Saint Peter Islands The Saint Peter Islands, also known as Saint Petra Islands or Petra Islands are two islands covered with tundra vegetation, shingle and ice. These islands, as well as some other islands nearby were originally named after Christian Apostles.The Saint Peter Islands are surrounded by narrow beach... , and the east of Byrranga Mountains Byrranga Mountains The Byrranga Mountains are a mountain range in the middle of the Taymyr Peninsula, Siberia, Russia, located north and west of Lake Taymyr. They run for about 1,100 km, forming a looping curve that runs roughly in a southwest to northeast direction... on Taymyr. Pronchishchev and his wife died from illness on the way back and were buried in the mouth of the Olenek River A part of the eastern coastline of the Taymyr Peninsula Taymyr Peninsula The Taymyr Peninsula is a peninsula in the Far North of Russia, in the Siberian Federal District, that forms the northernmost part of mainland Eurasia and Asia... , a lake and a cape in the east of Taymyr Taymyr Peninsula The Taymyr Peninsula is a peninsula in the Far North of Russia, in the Siberian Federal District, that forms the northernmost part of mainland Eurasia and Asia... , a ridge between the mouths of the Olenek and Anabar River Anabar River The Anabar River is a river in Sakha, Russia, located just west of the Lena River. Its catchment extends into the Putoran Mountains that form the highest part of the Central Siberian Plateau.... s, and icebreaker Icebreaker An icebreaker is a special-purpose ship or boat designed to move and navigate through ice-covered waters. Although the term usually refers to ice-breaking ships, it may also refer to smaller vessels .For a ship to be considered an icebreaker, it requires three traits most... Vasili Pronchishchev bear Pronchishchev's name. |
 |
|
| Maria Pronchishcheva Maria Pronchishcheva Maria Pronchishcheva - a Russian explorer.In 1735 with her husband, Vasili Pronchishchev, went down the Lena River on Vasili's sloop Yakutsk, doubled its delta, and stopped for wintering at the mouth of the Olenek River. Unfortunately many members of the crew fell ill and died, mainly owing to... (1710–1736) Tsardom of Russia Tsardom of Russia The Tsardom of Russia was the name of the centralized Russian state from Ivan IV's assumption of the title of Tsar in 1547 till Peter the Great's foundation of the Russian Empire in 1721.From 1550 to 1700, Russia grew 35,000 km2 a year...  Russian Empire Russian Empirefirst female Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... explorer (forensic facial reconstruction) |
Maria Pronchishcheva (or Tatiana according to some sources) accompanied her husband Vasili Pronchishchev Vasili Pronchishchev Vasili Vasilyevich Pronchishchev was a Russian explorer.In 1718, Vasili Pronchishchev graduated from Moscow School of Mathematics and Navigation and was promoted to naval cadet... in 1735-36, during the Great Northern Expedition Great Northern Expedition The Great Northern Expedition or Second Kamchatka expedition was one of the largest organised exploration enterprises in history, resulting in mapping of the most of the Arctic coast of Siberia and some parts of the North America coastline, greatly reducing the "white areas" on the maps... , when they explored the coastline west of the mouth of Lena River Lena River The Lena is the easternmost of the three great Siberian rivers that flow into the Arctic Ocean . It is the 11th longest river in the world and has the 9th largest watershed... , making many discoveries. She is considered to be the first female explorer of Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... . Maria died from illness on the way back, only 14 days after the death of her husband Vasili. Maria Pronchishcheva Bay Maria Pronchishcheva Bay Maria Pronchishcheva Bay is a deep gulf in the Laptev Sea. It is located about 75 km north of the mouth of the Khatanga Gulf, on the eastern side of the Taymyr Peninsula.... of Taymyr Taymyr Peninsula The Taymyr Peninsula is a peninsula in the Far North of Russia, in the Siberian Federal District, that forms the northernmost part of mainland Eurasia and Asia... in the Laptev Sea Laptev Sea The Laptev Sea is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It is located between the northern coast of Siberia, the Taimyr Peninsula, Severnaya Zemlya and the New Siberian Islands. Its northern boundary passes from the Arctic Cape to a point with co-ordinates of 79°N and 139°E, and ends at the Anisiy... is named after Pronchishcheva. |
||
 |
Nikolai Przhevalsky Nikolai Przhevalsky Nikolai Mikhaylovich Przhevalsky and Prjevalsky, ; —), was a Russian geographer of Polish background and explorer of Central and Eastern Asia. Although he never reached his final goal, Lhasa in Tibet, he travelled through regions unknown to the west, such as northern Tibet, modern Qinghai and... (1839–1888)  Russian Empire Russian Empire(Polish descent) Imperial Russian Army Imperial Russian Army The Imperial Russian Army was the land armed force of the Russian Empire, active from around 1721 to the Russian Revolution of 1917. In the early 1850s, the Russian army consisted of around 938,731 regular soldiers and 245,850 irregulars . Until the time of military reform of Dmitry Milyutin in... officer, Major General Major General Major general or major-general is a military rank used in many countries. It is derived from the older rank of sergeant major general. A major general is a high-ranking officer, normally subordinate to the rank of lieutenant general and senior to the ranks of brigadier and brigadier general... , geographer Geographer A geographer is a scholar whose area of study is geography, the study of Earth's natural environment and human society.Although geographers are historically known as people who make maps, map making is actually the field of study of cartography, a subset of geography... , naturalist Naturalist Naturalist may refer to:* Practitioner of natural history* Conservationist* Advocate of naturalism * Naturalist , autobiography-See also:* The American Naturalist, periodical* Naturalism... , explorer of Central Asia Central Asia Central Asia is a core region of the Asian continent from the Caspian Sea in the west, China in the east, Afghanistan in the south, and Russia in the north... and China China Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture... |
In 1867-69 Przhevalsky led an expedition to the basin of Ussuri River Ussuri River The Usuri ula is a river in the south of the Outer Manchuria and east of Inner Manchuria . It rises in the Sikhote-Alin range, flowing north, forming part of the Sino-Russian border based on the Sino-Russian Convention of Peking in 1860, until it joins the Amur River at Khabarovsk . It is... in the Far East Russian Far East Russian Far East is a term that refers to the Russian part of the Far East, i.e., extreme east parts of Russia, between Lake Baikal in Eastern Siberia and the Pacific Ocean... . Subsequently he made a four major journeys to largely unknown parts of Central Asia Central Asia Central Asia is a core region of the Asian continent from the Caspian Sea in the west, China in the east, Afghanistan in the south, and Russia in the north... , in the total covering more than 40,000 km in length. In 1870-73 he crossed the Gobi desert to Beijing Beijing Beijing , also known as Peking , is the capital of the People's Republic of China and one of the most populous cities in the world, with a population of 19,612,368 as of 2010. The city is the country's political, cultural, and educational center, and home to the headquarters for most of China's... , explored the upper Yangtze River Yangtze River The Yangtze, Yangzi or Cháng Jiāng is the longest river in Asia, and the third-longest in the world. It flows for from the glaciers on the Tibetan Plateau in Qinghai eastward across southwest, central and eastern China before emptying into the East China Sea at Shanghai. It is also one of the... , and crossed into Tibet Tibet Tibet is a plateau region in Asia, north-east of the Himalayas. It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people as well as some other ethnic groups such as Monpas, Qiang, and Lhobas, and is now also inhabited by considerable numbers of Han and Hui people... , surveying over 18,000 km2 and collecting some 5,000 plants species, 1000 birds, 3,000 insects, 70 reptiles and the skins of 130 different mammals. The results of this journey were highly appreciated in Russia, both by Geographical Society Russian Geographical Society The Russian Geographical Society is a learned society, founded on 6 August 1845 in Saint Petersburg, Russia.-Imperial Geographical Society:Prior to the Russian Revolution of 1917, it was known as the Imperial Russian Geographical Society.... and Russian military. In 1876-77, travelling through Eastern Turkestan and the Tian Shan range, he visited Lake Lop Nor. In 1879-80 he traveled via Hami and the Qaidam Qaidam Qaidam Basin, also spelled Tsaidam is an hyperarid basin that occupies a large part of the Haixi Mongol and Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture in Qinghai Province, western China... basin to Lake Koko Nor. Passing over Tian Shan Tian Shan The Tian Shan , also spelled Tien Shan, is a large mountain system located in Central Asia. The highest peak in the Tian Shan is Victory Peak , .... into Tibet, he was short of 260 km from Lhasa Lhasa Lhasa is the administrative capital of the Tibet Autonomous Region in the People's Republic of China and the second most populous city on the Tibetan Plateau, after Xining. At an altitude of , Lhasa is one of the highest cities in the world... before being turned back by Tibetan officials. In 1883-85 Przhevalsky traveled across Gobi to Alashan Alashan, Kyrgyzstan Alashan is a village in the Osh Province of Kyrgyzstan.... and Tian Shan, then back to Koko Nor, and westwards to Lake Issyk Kul Issyk Kul Issyk Kul is an endorheic lake in the northern Tian Shan mountains in eastern Kyrgyzstan. It is the tenth largest lake in the world by volume and the second largest saline lake after the Caspian Sea. Although it is surrounded by snow-capped peaks, it never freezes; hence its name, which means "hot... . His journeys opened a new era for the study of geography, fauna and flora of Central Asia. He was the first to report on the wild population of Bactrian Camel Bactrian camel The Bactrian camel is a large, even-toed ungulate native to the steppes of central Asia. It is presently restricted in the wild to remote regions of the Gobi and Taklamakan Deserts of Mongolia and Xinjiang. A small number of wild Bactrian camels still roam the Mangystau Province of southwest... s, to describe the Przewalski's Gazelle Przewalski's Gazelle Przewalski's Gazelle is a member of the Bovidae family and, in the wild, is found only in China. Once widespread, its range has declined to six populations near Qinghai Lake. The Przewalski's Gazelle was named after Nikolai Przhevalsky, a Russian explorer who collected a specimen and brought it... and the Przewalski's Horse Przewalski's Horse Przewalski's Horse or Dzungarian Horse, is a rare and endangered subspecies of wild horse native to the steppes of central Asia, specifically China and Mongolia.At one time extinct in the wild, it has been reintroduced to its native habitat in Mongolia at the Khustain Nuruu... (the only extant wild horse Wild Horse The wild horse is a species of the genus Equus, which includes as subspecies the domesticated horse as well as the undomesticated Tarpan and Przewalski's Horse. The Tarpan became extinct in the 19th century, and Przewalski's Horse was saved from the brink of extinction and reintroduced... ). Przewalski's Gazelle Przewalski's Gazelle Przewalski's Gazelle is a member of the Bovidae family and, in the wild, is found only in China. Once widespread, its range has declined to six populations near Qinghai Lake. The Przewalski's Gazelle was named after Nikolai Przhevalsky, a Russian explorer who collected a specimen and brought it... , Przewalski's Horse Przewalski's Horse Przewalski's Horse or Dzungarian Horse, is a rare and endangered subspecies of wild horse native to the steppes of central Asia, specifically China and Mongolia.At one time extinct in the wild, it has been reintroduced to its native habitat in Mongolia at the Khustain Nuruu... and other species, a ridge in Kunlun Kunlun Mountains The Kunlun Mountains are one of the longest mountain chains in Asia, extending more than 3,000 km. In the broadest sense, it forms the northern edge of the Tibetan Plateau south of the Tarim Basin and the Gansu Corridor and continues east south of the Wei River to end at the North China Plain.The... , a glacier in Altai, Przhevalsk town (now Karakol Karakol Karakol , formerly Przhevalsk, is fourth largest city in Kyrgyzstan, near the eastern tip of Issyk Kul Lake in Kyrgyzstan, about from the Kyrgyzstan-China border and from the capital Bishkek. It is the administrative capital of Issyk Kul Province... ) in Kyrgyzstan Kyrgyzstan Kyrgyzstan , officially the Kyrgyz Republic is one of the world's six independent Turkic states . Located in Central Asia, landlocked and mountainous, Kyrgyzstan is bordered by Kazakhstan to the north, Uzbekistan to the west, Tajikistan to the southwest and China to the east... and his native Przhevalskoye Przhevalskoye Przhevalskoye is an urban locality in Demidovsky District of Smolensk Oblast, Russia. It is situated northeast of Demidov in the northwestern part of the oblast, on Lake Sapsho. Population: Area :... viilage in near Smolensk Smolensk Smolensk is a city and the administrative center of Smolensk Oblast, Russia, located on the Dnieper River. Situated west-southwest of Moscow, this walled city was destroyed several times throughout its long history since it was on the invasion routes of both Napoleon and Hitler. Today, Smolensk... have been named after Przhevalsky. |
 |
 |
Yevfimy Putyatin Yevfimy Putyatin Yevfimy Vasilyevich Putyatin was a Russian admiral noted for his diplomatic missions to Japan and China which resulted in the signing of the Treaty of Shimoda in 1855.-Early life:... (1803–1883)  Russian Empire Russian EmpireRussian Imperial Navy officer, Admiral Admiral Admiral is the rank, or part of the name of the ranks, of the highest naval officers. It is usually considered a full admiral and above vice admiral and below admiral of the fleet . It is usually abbreviated to "Adm" or "ADM"... , diplomat, explorer of Pacific, Japan Japan Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south... and the Russian Far East Russian Far East Russian Far East is a term that refers to the Russian part of the Far East, i.e., extreme east parts of Russia, between Lake Baikal in Eastern Siberia and the Pacific Ocean... |
In 1822-25 Putyatin sailed with Mikhail Lazarev around the world aboard Suvorov. Later he led diplomatic missions to Iran Iran Iran , officially the Islamic Republic of Iran , is a country in Southern and Western Asia. The name "Iran" has been in use natively since the Sassanian era and came into use internationally in 1935, before which the country was known to the Western world as Persia... and the Caucasus Caucasus The Caucasus, also Caucas or Caucasia , is a geopolitical region at the border of Europe and Asia, and situated between the Black and the Caspian sea... . Together with Admiral Ivan Unkovsky they led a scientific expedition on the frigate Pallada through the Atlantic Atlantic Ocean The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's oceanic divisions. With a total area of about , it covers approximately 20% of the Earth's surface and about 26% of its water surface area... , Indian Indian Ocean The Indian Ocean is the third largest of the world's oceanic divisions, covering approximately 20% of the water on the Earth's surface. It is bounded on the north by the Indian Subcontinent and Arabian Peninsula ; on the west by eastern Africa; on the east by Indochina, the Sunda Islands, and... and Pacific Ocean Pacific Ocean The Pacific Ocean is the largest of the Earth's oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, bounded by Asia and Australia in the west, and the Americas in the east.At 165.2 million square kilometres in area, this largest division of the World... s to Japan Japan Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south... in 1852-55. This expedition contributed many important discoveries in oceanography Oceanography Oceanography , also called oceanology or marine science, is the branch of Earth science that studies the ocean... . One of the results achieved was the Treaty of Shimoda Treaty of Shimoda The Treaty of Shimoda of 1855, formally Treaty of Commerce and Navigation between Japan and Russia , was signed between the Russian Vice-Admiral Euphimy Vasil'evich Putiatin and Toshiakira Kawaji of Japan in the city of Shimoda, Izu Province, Japan, on February 7, 1855... between Japan and Russia. In 1857-58 Putyatin twice traveled to both Japan and China and explored Peter the Great Gulf Peter the Great Gulf The Peter the Great Gulf is the largest gulf of the Sea of Japan adjoining the coast of Russia's Primorski Krai... , Russky Island Russky Island Russky Island is a Russian island off Vladivostok, in the Peter the Great Gulf, Sea of Japan. It is located about 9,334 kilometres east of Moscow. The Eastern Bosphorus separates the island from the Muravyov-Amursky Peninsula.... , Eastern Bosphorus Eastern Bosphorus Eastern Bosphorus is a strait that separates the Muravyov-Amursky Peninsula and Russky Island, and connects Amur Bay and Ussuri Bay.The depth is up to 50 m... and other features of the Russian shores of the Sea of Japan Sea of Japan The Sea of Japan is a marginal sea of the western Pacific Ocean, between the Asian mainland, the Japanese archipelago and Sakhalin. It is bordered by Japan, North Korea, Russia and South Korea. Like the Mediterranean Sea, it has almost no tides due to its nearly complete enclosure from the Pacific... . An island in the Peter the Great Gulf Peter the Great Gulf The Peter the Great Gulf is the largest gulf of the Sea of Japan adjoining the coast of Russia's Primorski Krai... (Russian Far East Russian Far East Russian Far East is a term that refers to the Russian part of the Far East, i.e., extreme east parts of Russia, between Lake Baikal in Eastern Siberia and the Pacific Ocean... ), a cape in Anadyr Bay (Bering Sea Bering Sea The Bering Sea is a marginal sea of the Pacific Ocean. It comprises a deep water basin, which then rises through a narrow slope into the shallower water above the continental shelves.... ) and a number of ships have been named after Putyatin. |
 |
| Demid Pyanda Demid Pyanda Demid Sofonovich Pyanda or, according to some sources, Panteley Demidovich Pyanda , also spelled Penda was among the first and most important Russian explorers of Siberia... (? – after 1637) Tsardom of Russia Tsardom of Russia The Tsardom of Russia was the name of the centralized Russian state from Ivan IV's assumption of the title of Tsar in 1547 till Peter the Great's foundation of the Russian Empire in 1721.From 1550 to 1700, Russia grew 35,000 km2 a year... Siberian Cossack Siberian Cossacks Siberian Cossacks were Cossacks who settled in the Siberian region of Russia from the end of the 16th century, following the Yermak Timofeyevich's conquest of Siberia. In early Siberia practically the whole Russian population, especially the serving-men were called Cossacks, but only in the loose... ataman Ataman Ataman was a commander title of the Ukrainian People's Army, Cossack, and haidamak leaders, who were in essence the Cossacks... , explorer of Eastern Siberia |
Coming from Mangazeya Mangazeya Mangazeya was a Northwest Siberian trans-Ural trade colony and later city in the 16-17th centuries. Founded in 1600, it was situated on the Taz River, between the lower courses of the Ob and Yenisei Rivers flowing into the Arctic Ocean.... , Demid Pyanda was a great hunter for Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... n fur Fur Fur is a synonym for hair, used more in reference to non-human animals, usually mammals; particularly those with extensives body hair coverage. The term is sometimes used to refer to the body hair of an animal as a complete coat, also known as the "pelage". Fur is also used to refer to animal... s. Starting his long journey from Turukhansk Turukhansk Turukhansk is a village in Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russia. It is located 1474 km north of Krasnoyarsk, at the confluence of the Yenisei and Lower Tunguska rivers. The Turukhan River joins the Yenisei about 20 km northwest. Population: 4,849 ; 8,900 ; 200... , in three and a half years from 1620 to 1624 Pyanda passed the total of 8000 km of hitherto unknown large Siberian rivers. He explored some 2300 km of Lower Tunguska Lower Tunguska Nizhnyaya Tunguska — is a river in Siberia, Russia, flows through the Irkutsk Oblast and the Krasnoyarsk Krai. The river is a right tributary of the Yenisei joining it at Turukhansk . Settlements on the river include Tura, Yukti and Simenga... (Nizhnyaya Tunguska in Russian Russian language Russian is a Slavic language used primarily in Russia, Belarus, Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan, Tajikistan and Kyrgyzstan. It is an unofficial but widely spoken language in Ukraine, Moldova, Latvia, Turkmenistan and Estonia and, to a lesser extent, the other countries that were once constituent republics... ) and, having reached the upper part of Tunguska, he discovered the great Siberian river Lena Lena River The Lena is the easternmost of the three great Siberian rivers that flow into the Arctic Ocean . It is the 11th longest river in the world and has the 9th largest watershed... and explored some 2400 km of its length. When doing this, he became the first Russian to reach Yakutia and meet Yakuts Yakuts Yakuts , are a Turkic people associated with the Sakha Republic.The Yakut or Sakha language belongs to the Northern branch of the Turkic family of languages.... . He returned back up Lena until it became too rocky and shallow, and by land reached Angara Angara The Angara River is a long river in Irkutsk Oblast and Krasnoyarsk Krai, south-east Siberia, Russia. It is the only river flowing out of Lake Baikal, and is the headwater tributary of the Yenisei River.... . On this way, Pyanda became the first Russian to meet Buryats Buryats The Buryats or Buriyads , numbering approximately 436,000, are the largest ethnic minority group in Siberia and are mainly concentrated in their homeland, the Buryat Republic, a federal subject of Russia... . He built new boats and explored some 1400 km of Angara Angara The Angara River is a long river in Irkutsk Oblast and Krasnoyarsk Krai, south-east Siberia, Russia. It is the only river flowing out of Lake Baikal, and is the headwater tributary of the Yenisei River.... , finally discovering that Angara Angara The Angara River is a long river in Irkutsk Oblast and Krasnoyarsk Krai, south-east Siberia, Russia. It is the only river flowing out of Lake Baikal, and is the headwater tributary of the Yenisei River.... (a Buryat Buryats The Buryats or Buriyads , numbering approximately 436,000, are the largest ethnic minority group in Siberia and are mainly concentrated in their homeland, the Buryat Republic, a federal subject of Russia... name) and Upper Tunguska (Verkhnyaya Tunguska, as initially known by Russians) are one and the same river. |
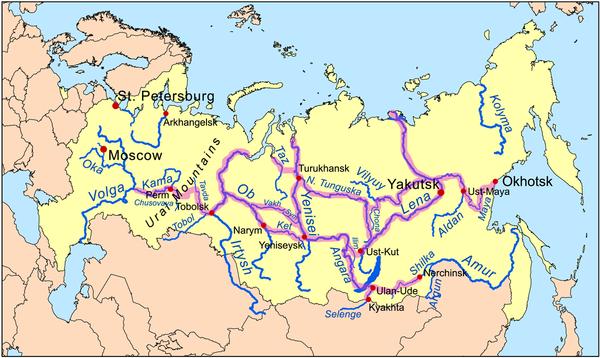 |
R
| Portrait | Person | Achievements | Image |
|---|---|---|---|
| Semyon Remezov Semyon Remezov Semyon Ulyanovich Remezov was a Russian historian, architect and geographer of Siberia.He is known as the compiler of the Remezov Chronicle, and as the author of some of the earliest extant maps of Siberia, including the , 1667 and , the originals of which are both part of the Houghton Library... (c. 1642 – after 1720) Tsardom of Russia Tsardom of Russia The Tsardom of Russia was the name of the centralized Russian state from Ivan IV's assumption of the title of Tsar in 1547 till Peter the Great's foundation of the Russian Empire in 1721.From 1550 to 1700, Russia grew 35,000 km2 a year... cartographer, geographer, historian, explorer of Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... (a monument in the Tobolsk Tobolsk Tobolsk is a town in Tyumen Oblast, Russia, located at the confluence of the Tobol and Irtysh Rivers. It is a historic capital of Siberia. Population: -History:... Kremlin) |
In 1683-1710 Remezov described and mapped the Tobolsk Tobolsk Tobolsk is a town in Tyumen Oblast, Russia, located at the confluence of the Tobol and Irtysh Rivers. It is a historic capital of Siberia. Population: -History:... region, where he was born. He wrote the Remezov Chronicle Remezov Chronicle The Remezov Chronicle is one of the Siberian Chronicles, compiled by a Russian historian Semyon Remezov in the late 17th century.... , one of the earliest historical accounts of Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... and its exploration, a part of Siberian Chronicles Siberian Chronicles The Siberian Chronicles are the Russian chronicles of the late 16th - 18th centuries on the history of Siberia. They include the Yesipov Chronicle, Kungur Chronicle, Remezov Chronicle, Stroganov Chronicle, and others. These chronicles represent a valuable source on the early history of the Russian... . In 1699-1701 he created the Chart book of Siberia, the first large format cartographic atlas Atlas An atlas is a collection of maps; it is typically a map of Earth or a region of Earth, but there are atlases of the other planets in the Solar System. Atlases have traditionally been bound into book form, but today many atlases are in multimedia formats... of Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... . Apart from that he made more than two hundreds of charts and maps of eastern Russian regions. |
||
 |
Nikolai Rezanov Nikolai Rezanov Nikolay Petrovich Rezanov was a Russian nobleman and statesman who promoted the project of Russian colonization of Alaska and California. One of the ten barons of Russia, he was the first Russian ambassador to Japan , and participated in the first Russian circumnavigation of the globe ,... (1764–1807)  Russian Empire Russian Empirestatesman, diplomat, explorer of Alaska Alaska Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait... and North Pacific |
Rezanov was one of the founders of Russian-American Company Russian-American Company The Russian-American Company was a state-sponsored chartered company formed largely on the basis of the so-called Shelekhov-Golikov Company of Grigory Shelekhov and Ivan Larionovich Golikov The Russian-American Company (officially: Under His Imperial Majesty's Highest Protection (patronage)... in 1799, formed on the basis of Shelikhov-Golikov Company. In 1803-06, made an ambassador to Japan Japan Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south... by Emperor Alexander I Alexander I of Russia Alexander I of Russia , served as Emperor of Russia from 23 March 1801 to 1 December 1825 and the first Russian King of Poland from 1815 to 1825. He was also the first Russian Grand Duke of Finland and Lithuania.... , Rezanov co-led the first Russian circumnavigation First Russian circumnavigation The first Russian circumnavigation of the Earth took place from August 1803 to August 1806. It was sponsored by Count Nikolay Rumyantsev and was headed by Adam Johann von Krusenstern.-Events:... of the world, aboard Nadezhda under the captaincy of Ivan Krusenstern, together with Yuri Lisianski on Neva. Rezanov was in command as far as Kamchatka. After his embassy to Japan failed, he was made an inspector of Russian colonies in America. In 1806 he sailed to San Francisco and managed to open a trade with Spanish California, concluded a treaty and engaged with Concepción Argüello Concepción Argüello María Concepción Argüello was the daughter of José Darío Argüello, the Spanish governor of Alta California and Presidio Commandante.... , the daughter of the comandante of San Francisco. Rezanov died in Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... , however, on journey back to St. Petersburg carrying the treaty to the capital. Rezanov's love affair with Concepción Argüello Concepción Argüello María Concepción Argüello was the daughter of José Darío Argüello, the Spanish governor of Alta California and Presidio Commandante.... inspired a ballad by the San Francisco author, Francis Bret Harte, and a 1937 novel, Rezánov and Doña Concha, by another SF author, Gertrude Atherton Gertrude Atherton Gertrude Franklin Horn Atherton was an American writer.-Early Childhood:Gertrude Franklin Horn was born on October 30, 1857 in San Francisco to Thomas Ludovich Horn and his wife, the former Gertrude Franklin... , as well as a very successful Russian rock opera Rock opera A rock opera is a work of rock music that presents a storyline told over multiple parts, songs or sections in the manner of opera. A rock opera differs from a conventional rock album, which usually includes songs that are not unified by a common theme or narrative. More recent developments include... Juno and Avos Juno and Avos (opera) Juno and Avos is a Russian rock opera written by Alexey Rybnikov, poetry by Andrei Voznesensky. It was first performed in 1981 in the Lenkom Theatre, Moscow, directed by Mark Zakharov.... by the composer Alexei Rybnikov Alexei Rybnikov Alexey Lvovich Rybnikov is a modern Russian composer.He is the author of music for the first Soviet and Russian musicals "Star and Death of Joaquin Murrieta" and "Juno and Avos" , for numerous plays and operas, for more than 80 Russian movies. More than 10 millions discs with his music have... and the poet Andrey Voznesensky Andrey Voznesensky Andrei Andreyevich Voznesensky was a Soviet and Russian poet and writer who had been referred to by Robert Lowell as "one of the greatest living poets in any language." He was one of the "Children of the '60s," a new wave of iconic Russian intellectuals led by the Khrushchev Thaw.Voznesensky was... in 1979. |
.jpg) |
| Voin Rimsky-Korsakov Voin Rimsky-Korsakov Voin Andreyevich Rimsky-Korsakov was a Russian navigator, hydrographer and geographer. He was an elder brother of composer and conductor Nikolai Rimsky-Korsakov.... (1822–1871)  Russian Empire Russian EmpireRussian Imperial Navy officer, hydroghafer and geographer, explorer of the Russian Far East Russian Far East Russian Far East is a term that refers to the Russian part of the Far East, i.e., extreme east parts of Russia, between Lake Baikal in Eastern Siberia and the Pacific Ocean... |
A senior brother of Nikolai Rimsky-Korsakov Nikolai Rimsky-Korsakov Nikolai Andreyevich Rimsky-Korsakov was a Russian composer, and a member of the group of composers known as The Five.The Five, also known as The Mighty Handful or The Mighty Coterie, refers to a circle of composers who met in Saint Petersburg, Russia, in the years 1856–1870: Mily Balakirev , César... (famous composer and conductor), Voin Rimsky-Korsakov became a naval officer. In 1839 he took part in the describing of Finland Finland Finland , officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country situated in the Fennoscandian region of Northern Europe. It is bordered by Sweden in the west, Norway in the north and Russia in the east, while Estonia lies to its south across the Gulf of Finland.Around 5.4 million people reside... shores. Later he was the commander of schooner Schooner A schooner is a type of sailing vessel characterized by the use of fore-and-aft sails on two or more masts with the forward mast being no taller than the rear masts.... Vostok in flotilla Flotilla A flotilla , or naval flotilla, is a formation of small warships that may be part of a larger fleet. A flotilla is usually composed of a homogeneous group of the same class of warship, such as frigates, destroyers, torpedo boats, submarines, gunboats, or minesweepers... under administration of Admiral Admiral Admiral is the rank, or part of the name of the ranks, of the highest naval officers. It is usually considered a full admiral and above vice admiral and below admiral of the fleet . It is usually abbreviated to "Adm" or "ADM"... Yevfimy Putyatin Yevfimy Putyatin Yevfimy Vasilyevich Putyatin was a Russian admiral noted for his diplomatic missions to Japan and China which resulted in the signing of the Treaty of Shimoda in 1855.-Early life:... . In 1850s and 1860s Rimsky-Korsakov explored the area of the Sea of Japan Sea of Japan The Sea of Japan is a marginal sea of the western Pacific Ocean, between the Asian mainland, the Japanese archipelago and Sakhalin. It is bordered by Japan, North Korea, Russia and South Korea. Like the Mediterranean Sea, it has almost no tides due to its nearly complete enclosure from the Pacific... near Ussuri Krai Ussuri krai Ussuri krai is an unofficial name for a part of Primorsky Krai and Khabarovsky Krai that consisted of Ussuri and South-Ussuri Okrugs. The name was often used in late Imperial Russia... , including the Sakhalin Island, the Amur Liman Amur Liman The Amur Liman is a liman of the Amur River, the northern part of the Strait of Tartary between Eurasia and Sakhalin. It connects the Sakhalin Gulf of the Sea of Okhotsk with the main body of the Strait of Tartary via the Nevelskoy Strait.... and the Strait of Tartary Strait of Tartary Strait of Tartary is a strait in the Pacific Ocean dividing the Russian island of Sakhalin from mainland Asia , connecting the Sea of Okhotsk on the north with... . Later he also surveyed the shores of Kamchatka and Kuril Islands Kuril Islands The Kuril Islands , in Russia's Sakhalin Oblast region, form a volcanic archipelago that stretches approximately northeast from Hokkaidō, Japan, to Kamchatka, Russia, separating the Sea of Okhotsk from the North Pacific Ocean. There are 56 islands and many more minor rocks. It consists of Greater... . Rimsky-Korsakov Archipelago Rimsky-Korsakov Archipelago Rimsky-Korsakov Archipelago is a group of six small islands and few kekurs in Peter the Great Gulf of Sea of Japan under administration of Khasansky District. Islands are located approximately to southwest of Vladivostok.... in the Sea of Japan Sea of Japan The Sea of Japan is a marginal sea of the western Pacific Ocean, between the Asian mainland, the Japanese archipelago and Sakhalin. It is bordered by Japan, North Korea, Russia and South Korea. Like the Mediterranean Sea, it has almost no tides due to its nearly complete enclosure from the Pacific... has been named after Voin Rimsky-Korsakov. |
||
 |
Helena Roerich Helena Roerich Helena Ivanovna Roerich was a Russian philosopher, writer, and public figure. In the early 20th century, she created, in cooperation with the Teachers of the East, a philosophic teaching of Living Ethics . She was an organizer and participant of cultural and enlightened creativity in the U.S.,... (1879–1955)  Russian Empire Russian Empire United States United States India Indiaphilosopher, writer, public figure, traveler, explorer of Central Asia Central Asia Central Asia is a core region of the Asian continent from the Caspian Sea in the west, China in the east, Afghanistan in the south, and Russia in the north... , China China Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture... and India India India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world... |
Helena Roerich was an organizer and participant of cultural and enlightened creativity in the U. S., conducted under the guidance of her husband, Nicholas Roerich Nicholas Roerich Nicholas Roerich, also known as Nikolai Konstantinovich Rerikh , was a Russian mystic, painter, philosopher, scientist, writer, traveler, and public figure. A prolific artist, he created thousands of paintings and about 30 literary works... . Along with her husband, she took part in expedition to the little-investigated regions of Central Asia Central Asia Central Asia is a core region of the Asian continent from the Caspian Sea in the west, China in the east, Afghanistan in the south, and Russia in the north... in 1924-28. She was an Honorary President-Founder of the Institute of Himalayan Studies «Urusvati» in India and co-author of idea of the International Treaty for Protection of Artistic and Scientific Institutions and Historical Monuments (Roerich’s Pact). Various institutions, minor planet Minor planet An asteroid group or minor-planet group is a population of minor planets that have a share broadly similar orbits. Members are generally unrelated to each other, unlike in an asteroid family, which often results from the break-up of a single asteroid... 4426 Roerich 4426 Roerich 4426 Roerich is a main-belt asteroid discovered on October 15, 1969 by L. I. Chernykh at Nauchnyj.- External links :*-References:... , peak Urusvati in Altai Mountains and pass in Tian Shan Tian Shan The Tian Shan , also spelled Tien Shan, is a large mountain system located in Central Asia. The highest peak in the Tian Shan is Victory Peak , .... were named after Helena Roerich. |
 |
 |
Nicholas Roerich Nicholas Roerich Nicholas Roerich, also known as Nikolai Konstantinovich Rerikh , was a Russian mystic, painter, philosopher, scientist, writer, traveler, and public figure. A prolific artist, he created thousands of paintings and about 30 literary works... (1874–1947)  Russian Empire Russian Empire United States United States India Indiapainter, philosopher, archeologist, writer, public figure, traveler, explorer of Central Asia Central Asia Central Asia is a core region of the Asian continent from the Caspian Sea in the west, China in the east, Afghanistan in the south, and Russia in the north... , China China Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture... and India India India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world... |
A famous Russian painter, Roerich emigrated to the U. S. after Russian Revolution. By sale of his paintings and writings, and gain from activity of his cultural and enlightener organizations in America, Roerich was able to collect the finance and led a major expedition to Central Asia Central Asia Central Asia is a core region of the Asian continent from the Caspian Sea in the west, China in the east, Afghanistan in the south, and Russia in the north... in 1924-28. The expedition went through Sikkim Sikkim Sikkim is a landlocked Indian state nestled in the Himalayan mountains... , Kashmir Kashmir Kashmir is the northwestern region of the Indian subcontinent. Until the mid-19th century, the term Kashmir geographically denoted only the valley between the Great Himalayas and the Pir Panjal mountain range... , Ladakh Ladakh Ladakh is a region of Jammu and Kashmir, the northernmost state of the Republic of India. It lies between the Kunlun mountain range in the north and the main Great Himalayas to the south, inhabited by people of Indo-Aryan and Tibetan descent... , China China Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture... (Xinjiang Xinjiang Xinjiang is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China. It is the largest Chinese administrative division and spans over 1.6 million km2... ), Russia Russia Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects... (including Moscow Moscow Moscow is the capital, the most populous city, and the most populous federal subject of Russia. The city is a major political, economic, cultural, scientific, religious, financial, educational, and transportation centre of Russia and the continent... ), Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... , Altai Altai Krai Altai Krai is a federal subject of Russia . It borders with, clockwise from the south, Kazakhstan, Novosibirsk and Kemerovo Oblasts, and the Altai Republic. The krai's administrative center is the city of Barnaul... , Mongolia Mongolia Mongolia is a landlocked country in East and Central Asia. It is bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south, east and west. Although Mongolia does not share a border with Kazakhstan, its western-most point is only from Kazakhstan's eastern tip. Ulan Bator, the capital and largest... , Tibet Tibet Tibet is a plateau region in Asia, north-east of the Himalayas. It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people as well as some other ethnic groups such as Monpas, Qiang, and Lhobas, and is now also inhabited by considerable numbers of Han and Hui people... , unstudied areas of the Himalayas Himalayas The Himalaya Range or Himalaya Mountains Sanskrit: Devanagari: हिमालय, literally "abode of snow"), usually called the Himalayas or Himalaya for short, is a mountain range in Asia, separating the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau... . Archeological and ethnographical investigations were conducted, dozens of new mountain peaks and passes were marked on maps, rarest manuscripts were found, and some of the best series of Roerich's paintings were created. In 1934–35 Roerich conducted an expedition in Inner Mongolia Inner Mongolia Inner Mongolia is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China, located in the northern region of the country. Inner Mongolia shares an international border with the countries of Mongolia and the Russian Federation... , Manchuria Manchuria Manchuria is a historical name given to a large geographic region in northeast Asia. Depending on the definition of its extent, Manchuria usually falls entirely within the People's Republic of China, or is sometimes divided between China and Russia. The region is commonly referred to as Northeast... and China China Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture... , collecting nearly 300 species of xerophytes, herbs, manuscript and archeological relics. Roerich was an author and initiator of an international pact for the protection of artistic and academic institutions and historical sites (Roerich’s Pact, 1935) and a founder of an international movement for the defence of culture. He created about 7,000 paintings and founded a number of scientific and cultural institutions in the United States United States The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district... , Europe Europe Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting... and India India India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world... . Roerich’s Pact, various institutions, minor planet Minor planet An asteroid group or minor-planet group is a population of minor planets that have a share broadly similar orbits. Members are generally unrelated to each other, unlike in an asteroid family, which often results from the break-up of a single asteroid... 4426 Roerich 4426 Roerich 4426 Roerich is a main-belt asteroid discovered on October 15, 1969 by L. I. Chernykh at Nauchnyj.- External links :*-References:... , a peak and a pass in Altai Mountains, two passes and a glacier in Tian Shan Tian Shan The Tian Shan , also spelled Tien Shan, is a large mountain system located in Central Asia. The highest peak in the Tian Shan is Victory Peak , .... were named after Nicholas Roerich. |
  |
 |
Vladimir Rusanov Vladimir Rusanov Vladimir Alexandrovich Rusanov was an experienced Russian geologist who specialized in the Arctic.In 1909–1911 V. A. Rusanov carried out explorations in Novaya Zemlya. He was helped by Tyko Vylka, his guide, who later became the Chairman of the Novaya Zemlya Soviet.In 1912 Rusanov had been... (1875–1913?)  Russian Empire Russian Empiregeologist, Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... explorer |
In 1909-11 Rusanov carried out explorations in Novaya Zemlya Novaya Zemlya Novaya Zemlya , also known in Dutch as Nova Zembla and in Norwegian as , is an archipelago in the Arctic Ocean in the north of Russia and the extreme northeast of Europe, the easternmost point of Europe lying at Cape Flissingsky on the northern island... archipelago. In 1912 he commanded a government expedition to Svalbard Svalbard Svalbard is an archipelago in the Arctic, constituting the northernmost part of Norway. It is located north of mainland Europe, midway between mainland Norway and the North Pole. The group of islands range from 74° to 81° north latitude , and from 10° to 35° east longitude. Spitsbergen is the... to investigate its coal Coal Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock usually occurring in rock strata in layers or veins called coal beds or coal seams. The harder forms, such as anthracite coal, can be regarded as metamorphic rock because of later exposure to elevated temperature and pressure... reserves. They sailed on a small ship Herkules under Captain Alexander Kuchin Alexander Kuchin Alexander Stepanovich Kuchin was a young Russian oceanographer and Arctic explorer.... , Roald Amundsen Roald Amundsen Roald Engelbregt Gravning Amundsen was a Norwegian explorer of polar regions. He led the first Antarctic expedition to reach the South Pole between 1910 and 1912 and he was the first person to reach both the North and South Poles. He is also known as the first to traverse the Northwest Passage.... 's South Pole South Pole The South Pole, also known as the Geographic South Pole or Terrestrial South Pole, is one of the two points where the Earth's axis of rotation intersects its surface. It is the southernmost point on the surface of the Earth and lies on the opposite side of the Earth from the North Pole... expedition navigator. Concluding the work, part of the expedition members returned to Russia Russia Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects... via Norway Norway Norway , officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic unitary constitutional monarchy whose territory comprises the western portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula, Jan Mayen, and the Arctic archipelago of Svalbard and Bouvet Island. Norway has a total area of and a population of about 4.9 million... , while the rest without consultation with the authorities in St. Petersburg, set off with Rusanov in an incredibly rash attempt at reaching the Pacific via the Northern Sea Route Northern Sea Route The Northern Sea Route is a shipping lane officially defined by Russian legislation from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean specifically running along the Russian Arctic coast from Murmansk on the Barents Sea, along Siberia, to the Bering Strait and Far East. The entire route lies in Arctic... , and disappeared in the Kara Sea Kara Sea The Kara Sea is part of the Arctic Ocean north of Siberia. It is separated from the Barents Sea to the west by the Kara Strait and Novaya Zemlya, and the Laptev Sea to the east by the Severnaya Zemlya.... . The relics of the expedition were found in 1937 in Kolosovykh Islands Kolosovykh Islands The Kolosovykh Island is a island, in the Kara Sea off the coast of Siberia.This coastal archipelago, is located north of the small Kolosovykh peninsula, which is almost an island itself. This island group is located between 74° 45' and 75° N and between 85° and 87° 30'E... group. Soviet coal mining on Svalbard Svalbard Svalbard is an archipelago in the Arctic, constituting the northernmost part of Norway. It is located north of mainland Europe, midway between mainland Norway and the North Pole. The group of islands range from 74° to 81° north latitude , and from 10° to 35° east longitude. Spitsbergen is the... began in 1932. A glacier on Severnaya Zemlya Severnaya Zemlya Severnaya Zemlya is an archipelago in the Russian high Arctic at around . It is located off mainland Siberia's Taymyr Peninsula across the Vilkitsky Strait... , a bay and a peninsula on Novaya Zemlya Novaya Zemlya Novaya Zemlya , also known in Dutch as Nova Zembla and in Norwegian as , is an archipelago in the Arctic Ocean in the north of Russia and the extreme northeast of Europe, the easternmost point of Europe lying at Cape Flissingsky on the northern island... , a mountain in Antarctic Antarctic The Antarctic is the region around the Earth's South Pole, opposite the Arctic region around the North Pole. The Antarctic comprises the continent of Antarctica and the ice shelves, waters and island territories in the Southern Ocean situated south of the Antarctic Convergence... , streets in Moscow Moscow Moscow is the capital, the most populous city, and the most populous federal subject of Russia. The city is a major political, economic, cultural, scientific, religious, financial, educational, and transportation centre of Russia and the continent... , Severodvinsk Severodvinsk Severodvinsk is a city in the north of Arkhangelsk Oblast, Russia, located in the delta of the Northern Dvina River, west of Arkhangelsk. Administratively, it is incorporated as a town of oblast significance . Municipally, it is incorporated as Severodvinsk Urban Okrug. The city was founded as... and Oryol Oryol Oryol or Orel is a city and the administrative center of Oryol Oblast, Russia, located on the Oka River, approximately south-southwest of Moscow... (the city of Rusanov's birth) and several ships were named after Rusanov. Rusanov and his expedition are among the prototypes for the novel The Two Captains The Two Captains The Two Captains is a novel written by Soviet author Veniamin Kaverin between 1938 and 1944. It is Kaverin's best known work and is considered one of the most popular works of Soviet literature, winning the USSR State Prize in 1946 being reissued 42 times in 25 years... by Veniamin Kaverin Veniamin Kaverin Veniamin Alexandrovich Kaverin was a Soviet writer associated with the early 1920s movement of the Serapion Brothers. The immunologist Lev Zilber was his older brother, and the critic Yury Tynyanov was his brother-in-law.... , where the search proceedings for fictional captain Tatarinov resemble the search for Rusanov. |
|
| Georgy Rybin Georgy Rybin Georgy Nikolaevich Rybin . was a Russian hуdrographer; explorer of the Arctic seas and the Baltic Sea.- Biography :- Family and Childhood :... (1901–1974)  Russian Empire Russian Empire Soviet Union Soviet UnionSoviet Navy Soviet Navy The Soviet Navy was the naval arm of the Soviet Armed Forces. Often referred to as the Red Fleet, the Soviet Navy would have played an instrumental role in a Warsaw Pact war with NATO, where it would have attempted to prevent naval convoys from bringing reinforcements across the Atlantic Ocean... officer, hydrographer, explorer of the Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... and the Baltic Sea Baltic Sea The Baltic Sea is a brackish mediterranean sea located in Northern Europe, from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from 20°E to 26°E longitude. It is bounded by the Scandinavian Peninsula, the mainland of Europe, and the Danish islands. It drains into the Kattegat by way of the Øresund, the Great Belt and... |
In 1922-33 Rybin participated in hydrographic works on Ob Ob River The Ob River , also Obi, is a major river in western Siberia, Russia and is the world's seventh longest river. It is the westernmost of the three great Siberian rivers that flow into the Arctic Ocean .The Gulf of Ob is the world's longest estuary.-Names:The Ob is known to the Khanty people as the... and Yenisey Rivers. In 1922 he found the remnants of Peter Tessem Peter Tessem and Paul Knutsen Peter Tessem and Paul Knutsen were two young men from Norway who went with fellow Norwegian explorer Roald Amundsen on his 1918 Arctic expedition aboard ship Maud. Peter Tessem was a carpenter and Paul Knutsen was an able-bodiedseaman... , a lost member of Amundsen's Roald Amundsen Roald Engelbregt Gravning Amundsen was a Norwegian explorer of polar regions. He led the first Antarctic expedition to reach the South Pole between 1910 and 1912 and he was the first person to reach both the North and South Poles. He is also known as the first to traverse the Northwest Passage.... expedition on Maud Maud (ship) The Maud, named for Queen Maud of Norway, was a ship built for Roald Amundsen for his second expedition to the Arctic. Designed for his intended voyage through the Northeast Passage, the vessel was specially built at a shipyard in Asker, Norway on the Oslofjord.The Maud was launched in June 1916... . Since 1933 he made hydrographic works on the Baltic Baltic Sea The Baltic Sea is a brackish mediterranean sea located in Northern Europe, from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from 20°E to 26°E longitude. It is bounded by the Scandinavian Peninsula, the mainland of Europe, and the Danish islands. It drains into the Kattegat by way of the Øresund, the Great Belt and... , which became especially important during World War II World War II World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis... and the Siege of Leningrad Siege of Leningrad The Siege of Leningrad, also known as the Leningrad Blockade was a prolonged military operation resulting from the failure of the German Army Group North to capture Leningrad, now known as Saint Petersburg, in the Eastern Front theatre of World War II. It started on 8 September 1941, when the last... . Rybin-yaha River, flowing into the Gulf of Ob Gulf of Ob The Gulf of Ob is a gigantic bay of the Arctic Ocean, located in Northern Russia at the head the mouth of the Ob River.... and charted by Rybin, and Rybin seamount in the Atlantic west of the Canary Islands Canary Islands The Canary Islands , also known as the Canaries , is a Spanish archipelago located just off the northwest coast of mainland Africa, 100 km west of the border between Morocco and the Western Sahara. The Canaries are a Spanish autonomous community and an outermost region of the European Union... , are named after Rybin. |
||
 |
Alexander Nevsky Alexander Nevsky Alexander Nevsky was the Prince of Novgorod and Grand Prince of Vladimir during some of the most trying times in the city's history. Commonly regarded as the key figure of medieval Rus, Alexander was the grandson of Vsevolod the Big Nest and rose to legendary status on account of his military... (Rurikid) (1220–1263)  Novgorod Republic Novgorod RepublicNovgorod Republic The Novgorod Republic was a large medieval Russian state which stretched from the Baltic Sea to the Ural Mountains between the 12th and 15th centuries, centred on the city of Novgorod...  Vladimir-Suzdal Vladimir-SuzdalVladimir-Suzdal The Vladimir-Suzdal Principality or Vladimir-Suzdal Rus’ was one of the major principalities which succeeded Kievan Rus' in the late 12th century and lasted until the late 14th century. For a long time the Principality was a vassal of the Mongolian Golden Horde... medieval Grand Prince of Novgorod Prince of Novgorod The Prince of Novgorod was the chief executive of Novgorod the Great. The office was originally an appointed one until the late eleventh or early twelfth century, then became something of an elective one until the fourteenth century, after which the Prince of Vladimir was almost invariably the... and Vladimir Vladimir-Suzdal The Vladimir-Suzdal Principality or Vladimir-Suzdal Rus’ was one of the major principalities which succeeded Kievan Rus' in the late 12th century and lasted until the late 14th century. For a long time the Principality was a vassal of the Mongolian Golden Horde... , national hero and saint of Russia Russia Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects... , traveler to Central Asia Central Asia Central Asia is a core region of the Asian continent from the Caspian Sea in the west, China in the east, Afghanistan in the south, and Russia in the north... |
A famous warrior, Russian Prince Alexander Yaroslavich Nevsky Alexander Nevsky Alexander Nevsky was the Prince of Novgorod and Grand Prince of Vladimir during some of the most trying times in the city's history. Commonly regarded as the key figure of medieval Rus, Alexander was the grandson of Vsevolod the Big Nest and rose to legendary status on account of his military... traveled into Mongolian capital Karakorum Karakorum Karakorum was the capital of the Mongol Empire in the 13th century, and of the Northern Yuan in the 14-15th century. Its ruins lie in the northwestern corner of the Övörkhangai Province of Mongolia, near today's town of Kharkhorin, and adjacent to the Erdene Zuu monastery... in Central Asia Central Asia Central Asia is a core region of the Asian continent from the Caspian Sea in the west, China in the east, Afghanistan in the south, and Russia in the north... , between 1247–49, accompanied by his brother Andrey Yaroslavich. They were summoned there by Genghisid Khans Khan (title) Khan is an originally Altaic and subsequently Central Asian title for a sovereign or military ruler, widely used by medieval nomadic Turko-Mongol tribes living to the north of China. 'Khan' is also seen as a title in the Xianbei confederation for their chief between 283 and 289... who had conquered Rus' Rus' (region) Rus' is an ethno-cultural region in Eastern Europe inhabited by Eastern Slavs. Historically, it comprises the northern part of Ukraine, the north-western part of Russia, Belarus and some eastern parts of Poland and Slovakia.The name comes from Old East Slavic , and remains the same in modern... a few years before. Unlike their father Yaroslav II of Vladimir Yaroslav II of Vladimir Yaroslav II , Christian name Theodor was the Grand Prince of Vladimir who helped to restore his country and capital after the Mongol invasion of Russia.-Prince of Pereyaslav:... , who had come into Karakorum in 1245-46 and was poisoned by the Mongols, princes Alexander and Andrey were able to get back to Rus', confirmed in power by their new overlords. Russian princes were among the first known Europeans to travel so far into Asia Asia Asia is the world's largest and most populous continent, located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres. It covers 8.7% of the Earth's total surface area and with approximately 3.879 billion people, it hosts 60% of the world's current human population... , making their journey around the same time as Italian monk Plano Carpini traveled to Mongolia Mongolia Mongolia is a landlocked country in East and Central Asia. It is bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south, east and west. Although Mongolia does not share a border with Kazakhstan, its western-most point is only from Kazakhstan's eastern tip. Ulan Bator, the capital and largest... . Multiple churches, monasteries, streets, squares, ships and other objects are named after Alexander Nevsky Alexander Nevsky Alexander Nevsky was the Prince of Novgorod and Grand Prince of Vladimir during some of the most trying times in the city's history. Commonly regarded as the key figure of medieval Rus, Alexander was the grandson of Vsevolod the Big Nest and rose to legendary status on account of his military... in Russia. |
S
| Portrait | Person | Achievements | Image |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anatoly Sagalevich Anatoly Sagalevich Anatoly Mikhailovich Sagalevich is a Russian explorer, who works at the Shirshov Institute of Oceanology of the Russian Academy of Sciences since 1965.... (born 1938)  Soviet Union Soviet Union Russia Russiadeepwater explorer, Hero of the Russian Federation Hero of the Russian Federation Hero of the Russian Federation is a Russian decoration and the highest honorary title that can be bestowed on a citizen by the Russian Federation. The President of the Russian Federation is the main conferring authority of the medal, which is bestowed on those committing actions or deeds that... (right on photo with Vladimir Putin Vladimir Putin Vladimir Vladimirovich Putin served as the second President of the Russian Federation and is the current Prime Minister of Russia, as well as chairman of United Russia and Chairman of the Council of Ministers of the Union of Russia and Belarus. He became acting President on 31 December 1999, when... ) |
Since 1979 Sagalevich is the head of Deepwater Submersibles Laboratory at Shirshov Institute of Oceanology Shirshov Institute of Oceanology Shirshov Institute of Oceanology in Moscow, is the largest institute for ocean and earth science research, in Russia, established in 1946.- Fleet :* RV Akademik Ioffe... . He took part in the construction of Pisces VIII, Pisces IX and MIR MIR (submersible) Mir is a self-propelled Deep Submergence Vehicle. The project was initially developed by the USSR Academy of Sciences along with Design Bureau Lazurith. Later two vehicles were ordered from Finland... Deep Submergence Vehicle Deep Submergence Vehicle A Deep Sea Submergence Vehicle is a deep diving manned submarine that is self-propelled. The term DSV is generally one used by the United States Navy, though several navies operate vehicles that can be accurately described as DSVs... s (DSV) and completed more than 300 submersions as the chief pilot of DSVs. He piloted MIRs during expeditions to RMS Titanic, German battleship Bismarck German battleship Bismarck Bismarck was the first of two s built for the German Kriegsmarine during World War II. Named after Chancellor Otto von Bismarck, the primary force behind the German unification in 1871, the ship was laid down at the Blohm & Voss shipyard in Hamburg in July 1936 and launched nearly three years later... , Soviet and Russian submarines K-278 Komsomolets and K-141 Kursk, and Japanese I-52. Sagalevich holds the world record for the deepest fresh water dive at 1637 m in Lake Baikal Lake Baikal Lake Baikal is the world's oldest at 30 million years old and deepest lake with an average depth of 744.4 metres.Located in the south of the Russian region of Siberia, between Irkutsk Oblast to the northwest and the Buryat Republic to the southeast, it is the most voluminous freshwater lake in the... aboard a Pisces in 1990. On August 2, 2007, he was the pilot of MIR-1 DSV that reached the seabed Seabed The seabed is the bottom of the ocean.- Ocean structure :Most of the oceans have a common structure, created by common physical phenomena, mainly from tectonic movement, and sediment from various sources... at the North Pole North Pole The North Pole, also known as the Geographic North Pole or Terrestrial North Pole, is, subject to the caveats explained below, defined as the point in the northern hemisphere where the Earth's axis of rotation meets its surface... during Arktika 2007 Arktika 2007 Arktika 2007 was a 2007 expedition in which Russia performed the first ever crewed descent to the ocean bottom at the North Pole, as part of research related to the 2001 Russian territorial claim, one of many territorial claims in the Arctic, made possible, in part, because of Arctic shrinkage... expedition. |
||
| Rudolf Samoylovich Rudolf Samoylovich Rudolf Lazarevich Samoylovich was a Soviet polar explorer, professor , and doctor of geographic sciences .... (1881–1940?)  Russian Empire Russian Empire Soviet Union Soviet Uniongeographer, Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... explorer |
In 1912 Samoylovich took part in Vladimir Rusanov Vladimir Rusanov Vladimir Alexandrovich Rusanov was an experienced Russian geologist who specialized in the Arctic.In 1909–1911 V. A. Rusanov carried out explorations in Novaya Zemlya. He was helped by Tyko Vylka, his guide, who later became the Chairman of the Novaya Zemlya Soviet.In 1912 Rusanov had been... 's geological expedition to Spitsbergen Spitsbergen Spitsbergen is the largest and only permanently populated island of the Svalbard archipelago in Norway. Constituting the western-most bulk of the archipelago, it borders the Arctic Ocean, the Norwegian Sea and the Greenland Sea... . He was one of the initiators and the first director of the Arctic and Antarctic Research Institute Arctic and Antarctic Research Institute The Arctic and Antarctic Research Institute, or AARI is the oldest and largest Russian research institute in the field of comprehensive studies of Arctic and Antarctica... in 1920-30 and 1932-38. He was also the founder and the first chairman of the Polar Countries' Department at Leningrad State University. In 1928 he was the head of the rescue party on the Krasin Krasin (1916 icebreaker) The first icebreaker Krasin was built for the Imperial Russian Navy as Svyatogor. She had a long, distinguished career in rescue operations, as well as a pathfinder and explorer of the Northern Sea Route... icebreaker, that saved most of the crew of Airship Italia Airship Italia Airship Italia was a semi-rigid airship used by Italian engineer Umberto Nobile in his second series of flights around the North Pole.-Design and specifications:... of Umberto Nobile Umberto Nobile Umberto Nobile was an Italian aeronautical engineer and Arctic explorer. Nobile was a developer and promoter of semi-rigid airships during the Golden Age of Aviation between the two World Wars... . Also, he participated in the polar flight of Graf Zeppelin LZ 127 Graf Zeppelin LZ 127 Graf Zeppelin was a German built and operated passenger-carrying hydrogen-filled rigid airship which operated commercially from 1928 to 1937. It was named after the German pioneer of airships, Ferdinand von Zeppelin, who was a Graf or Count in the German nobility. During its operating life,... in 1931 and headed expeditions on icebreakers Vladimir Rusanov (1932), Georgy Sedov (1934), and Sadko Icebreaker Sadko Icebreaker Sadko was a Russian and Soviet icebreaker ship of 3,800 tonnes displacement. She was named after Sadko, a hero of a Russian bylina.... (1936 and 1937–38). A strait and a glacier top on Franz Josef Land Franz Josef Land Franz Josef Land, Franz Joseph Land, or Francis Joseph's Land is an archipelago located in the far north of Russia. It is found in the Arctic Ocean north of Novaya Zemlya and east of Svalbard, and is administered by Arkhangelsk Oblast. Franz Josef Land consists of 191 ice-covered islands with a... , a bay on Novaya Zemlya Novaya Zemlya Novaya Zemlya , also known in Dutch as Nova Zembla and in Norwegian as , is an archipelago in the Arctic Ocean in the north of Russia and the extreme northeast of Europe, the easternmost point of Europe lying at Cape Flissingsky on the northern island... , an island in Severnaya Zemlya Severnaya Zemlya Severnaya Zemlya is an archipelago in the Russian high Arctic at around . It is located off mainland Siberia's Taymyr Peninsula across the Vilkitsky Strait... , a mountain and a peninsula in the Antarctica bear Rudolf Samoylovich's name. |
 |
|
| Yakov Sannikov Yakov Sannikov Yakov Sannikov was a Russian merchant and explorer of the New Siberian Islands.In 1800, Sannikov discovered and charted Stolbovoy Island, and in 1805 Faddeyevsky Island. In 1809-1810, he took part in the expedition led by Matvei Gedenschtrom. In 1810, Sannikov crossed the island of New Siberia... (1780 – after 1812)  Russian Empire Russian Empiremerchant, Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... explorer |
Sannikov is known for his explorations of the New Siberian Islands New Siberian Islands The New Siberian Islands are an archipelago, located to the North of the East Siberian coast between the Laptev Sea and the East Siberian Sea north of the Sakha Republic.... . In 1800, he discovered and charted Stolbovoy Island Stolbovoy Island Stolbovoy Island is a long and narrow island off the southwest side of the New Siberian archipelago in the eastern part of the Laptev Sea. It is located 184 km away from the Siberian coast and 100 km southwest of Kotelny Island, being thus quite detached from the New Siberian island... , and then Faddeyevsky Island in 1805. In 1809-1810, he took part in the expedition led by Matvei Gedenschtrom Matvei Gedenschtrom Matvei Matveyevich Gedenschtrom was a Russian explorer of Northern Siberia, writer, and public servant.Matvei Gedenschtrom attended University of Tartu. He did not finish his studies and left his alma mater in favor of work at Tallinn customs. Soon, however, he was arrested in connection with a... . During this expedition, in 1810, Sannikov crossed the island of New Siberia New Siberia New Siberia is the easternmost of the Anzhu Islands, the northern subgroup of the New Siberian Islands lying between the Laptev Sea and East Siberian Sea. Its area of approximately 6,200 km² places it just outside the 100 largest islands in the world. New Siberia Island is low lying, rising... and a year later explored Faddeyevsky Island. He also discovered Bunge Land Bunge Land Bunge Land or Zemlya Bunge is a huge empty and almost barren intermediate zone. It is located between Kotelny and Faddeyevsky, which, unlike Bunge Land, could be described as proper islands. Sandy and flat, its area is 6,200 km²... . He suggested that there was a vast land north of the Kotelny Island. Thus he introduced a theory about the existence of the legendary Sannikov Land Sannikov Land Sannikov Land was a phantom island in the Arctic Ocean. Its supposed existence became something of a myth in 19th-century Russia.Yakov Sannikov and Matvei Gedenschtrom claimed to have seen it during their 1809-1810 cartographic expedition to the New Siberian Islands... . The legendary Sannikov Land Sannikov Land Sannikov Land was a phantom island in the Arctic Ocean. Its supposed existence became something of a myth in 19th-century Russia.Yakov Sannikov and Matvei Gedenschtrom claimed to have seen it during their 1809-1810 cartographic expedition to the New Siberian Islands... , the Sannikov Strait Sannikov Strait Sannikov Strait is a 50 km-wide strait in Russia. It separates Anzhu Islands from Lyakhovsky Islands, and connects the Laptev Sea in the west with the East Siberian Sea in the east. It is named after Russian explorer Yakov Sannikov.-References:* Location: * Geographical names:... strait between Maly Lyakhovsky Lyakhovsky Islands The Lyakhovsky Islands are the southernmost group of the New Siberian Islands in the arctic seas of eastern Russia. They are separated from the mainland by the Laptev Strait , and from the Anzhu Islands group by the Sannikov Strait... and Kotelny islands and a street in Moscow Moscow Moscow is the capital, the most populous city, and the most populous federal subject of Russia. The city is a major political, economic, cultural, scientific, religious, financial, educational, and transportation centre of Russia and the continent... bear Sannikov's name. |
 |
|
| Gavriil Sarychev Gavril Sarychev Gavril Andreyevich Sarychev , spelt "Sarichef" in the United States, was a Russian navigator, hydrographer, admiral and Honorable Member of the Russian Academy of Sciences in Saint Petersburg.Sarychev started his career in the Imperial Russian Navy in 1775... (1763–1831)  Russian Empire Russian EmpireRussian Imperial Navy officer, navigator, Admiral Admiral Admiral is the rank, or part of the name of the ranks, of the highest naval officers. It is usually considered a full admiral and above vice admiral and below admiral of the fleet . It is usually abbreviated to "Adm" or "ADM"... , cartographer, explorer of the Russian Far East Russian Far East Russian Far East is a term that refers to the Russian part of the Far East, i.e., extreme east parts of Russia, between Lake Baikal in Eastern Siberia and the Pacific Ocean... and Alaska Alaska Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait... |
In 1785-94 Sarychev took part in the expedition sponsored by Catherine II of Russia Catherine II of Russia Catherine II, also known as Catherine the Great , Empress of Russia, was born in Stettin, Pomerania, Prussia on as Sophie Friederike Auguste von Anhalt-Zerbst-Dornburg... and led by Joseph Billings Joseph Billings Joseph Billings was an English navigator and explorer who spent the most significant part of his life in Russian service.In 1785, the Russian government of Catherine II commissioned a new expedition in search for the Northeast Passage, led by English officer Joseph Billings, who had previously... . Sarychev, a commander of ship Slava Rossii (Glory of Russia), described and mapped the coastline of the Sea of Okhotsk Sea of Okhotsk The Sea of Okhotsk is a marginal sea of the western Pacific Ocean, lying between the Kamchatka Peninsula on the east, the Kuril Islands on the southeast, the island of Hokkaidō to the far south, the island of Sakhalin along the west, and a long stretch of eastern Siberian coast along the west and... from Okhotsk Okhotsk Okhotsk is an urban locality and a seaport at the mouth of the Okhota River on the Sea of Okhotsk, in Okhotsky District, Khabarovsk Krai, Russia. Population: 4,470 ;... to Aldoma Aldoma Aldoma is a rural locality in Ayano-Maysky District of Khabarovsk Krai, Russia, located on the shore of the Aldoma Bay .... and many of the Aleutian Islands (especially Unalaska). He also described the islands of Pribylov Pribilof Islands The Pribilof Islands are a group of four volcanic islands off the coast of mainland Alaska, in the Bering Sea, about north of Unalaska and 200 miles southwest of Cape Newenham. The Siberia coast is roughly northwest... , St. Matthew Island St. Matthew Island St. Matthew Island is a remote island in the Bering Sea in Alaska, WNW of Nunivak Island. The island has a land area of , making it the 43rd largest island in the United States. Its most southerly point is Cape Upright which features cliff faces which exceed... , St. Lawrence Island St. Lawrence Island St. Lawrence Island is located west of mainland Alaska in the Bering Sea, just south of the Bering Strait, at about 63°30' North 173°20' West. The village of Gambell is located on the northwest cape, from the Chukchi Peninsula in the Russian Far East. The island is part of Alaska, but closer to... , Gvozdev Diomede Islands The Diomede Islands , also known in Russia as Gvozdev Islands , consist of two rocky, tuya-like islands:* The U.S. island of Little Diomede or, in its native language, Ignaluk , and* The Russian island of Big Diomede , also known as Imaqliq,... , and King Island King Island, Alaska King Island is an island in the Bering Sea, west of Alaska. It is about west of Cape Douglas and is south of Wales, Alaska.... . In 1802-06, Sarychev led the hydrographic expedition on the Baltic Baltic Sea The Baltic Sea is a brackish mediterranean sea located in Northern Europe, from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from 20°E to 26°E longitude. It is bounded by the Scandinavian Peninsula, the mainland of Europe, and the Danish islands. It drains into the Kattegat by way of the Øresund, the Great Belt and... . He was also in charge of hydrographic research in Russia Russia Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects... since 1808 and led the compilation of the Atlas of the Northern Part of the Pacific Ocean Pacific Ocean The Pacific Ocean is the largest of the Earth's oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, bounded by Asia and Australia in the west, and the Americas in the east.At 165.2 million square kilometres in area, this largest division of the World... in 1826. Sarychev Peak Sarychev Peak Sarychev Peak Fuyō-san, Fuyō-yama, Fuyo-zan, Huyō San), is a stratovolcano covering almost the entirety of Matua Island in the Kuril Islands, Russia. It is a young, highly symmetrical stratovolcanic cone.- History :... of Matua Island Matua Island Matua is an uninhabited volcanic island near the center of the Kuril Islands chain in the Sea of Okhotsk in the northwest Pacific Ocean, 16 kilometers across Golovnin Strait from Raikoke... in the Kuril Islands Kuril Islands The Kuril Islands , in Russia's Sakhalin Oblast region, form a volcanic archipelago that stretches approximately northeast from Hokkaidō, Japan, to Kamchatka, Russia, separating the Sea of Okhotsk from the North Pacific Ocean. There are 56 islands and many more minor rocks. It consists of Greater... , as well as Cape Sarichef Cape Sarichef Airport Cape Sarichef Airport was a small landing strip located on the western end of Unimak Island in the Aleutian Islands of the U.S. state of Alaska. It was used to supply and support a United States Coast Guard LORAN station and U.S. Air Force DEW Line site during the Cold War.It is now a private-use... , Sarichef Strait and Sarichef Island Sarichef Island Sarichef Island is a long and narrow coastal island on the Chukchi Sea-facing coast of Alaska. It is located at the mouth of the Shishmaref Inlet, Kotzebue-Kobuk LowSarichef Island is in length. The highest point on the island is above sea level.... in Alaska Alaska Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait... were named after Gavril Sarychev. The Soviet ship Gavril Sarychev also was named after this explorer. |
 |
|
| Svetlana Savitskaya Svetlana Savitskaya Svetlana Yevgenyevna Savitskaya She started training as a cosmonaut in 1980. Upon returning to Earth, Savitskaya was assigned as the commander of an all-female Soyuz crew to Salyut 7 in commemoration of the International Women's Day, a mission that was later canceled.She was twice awarded the Hero... (born 1948)  Soviet Union Soviet Union Russia Russiafemale cosmonaut, aviator, twice the Hero of the Soviet Union Hero of the Soviet Union The title Hero of the Soviet Union was the highest distinction in the Soviet Union, awarded personally or collectively for heroic feats in service to the Soviet state and society.-Overview:... , politician (Savitskaya Svetlana Savitskaya Svetlana Yevgenyevna Savitskaya She started training as a cosmonaut in 1980. Upon returning to Earth, Savitskaya was assigned as the commander of an all-female Soyuz crew to Salyut 7 in commemoration of the International Women's Day, a mission that was later canceled.She was twice awarded the Hero... with her 1982 crew fellows Popov Leonid Popov Leonid Ivanovich Popov is a former Soviet cosmonaut.Popov was born in Oleksandriia, Kirovohrad Oblast, Ukrainian SSR. He was selected as a cosmonaut on April 27, 1970, and flew as Commander on Soyuz 35, Soyuz 40 and Soyuz T-7, logging 200 days, 14 hours, and 45 minutes in space before his... and Serebrov Aleksandr Serebrov Aleksandr Aleksandrovich Serebrov is a former Soviet cosmonaut. He was born in Moscow, on February 15, 1944, graduated from Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology , and was selected as a cosmonaut on December 1, 1978. He retired on May 10, 1995... ) |
Savitskaya was the second woman in space Outer space Outer space is the void that exists between celestial bodies, including the Earth. It is not completely empty, but consists of a hard vacuum containing a low density of particles: predominantly a plasma of hydrogen and helium, as well as electromagnetic radiation, magnetic fields, and neutrinos.... (after Valentina Tereshkova Valentina Tereshkova Valentina Vladimirovna Tereshkova is a retired Soviet cosmonaut, and was the first woman in space. She was selected out of more than four hundred applicants, and then out of five finalists, to pilot Vostok 6 on the 16 June, 1963, becoming both the first woman and the first civilian to fly in... ) and the first woman to conduct an extra-vehicular activity Extra-vehicular activity Extra-vehicular activity is work done by an astronaut away from the Earth, and outside of a spacecraft. The term most commonly applies to an EVA made outside a craft orbiting Earth , but also applies to an EVA made on the surface of the Moon... . She achieved this during the two successful expeditions to Salyut 7 Salyut 7 Salyut 7 was a space station in low Earth orbit from April 1982 to February 1991. It was first manned in May 1982 with two crew via Soyuz T-5, and last visited in June 1986, by Soyuz T-15. Various crew and modules were used over its lifetime, including a total of 12 manned and 15 unmanned launches... space station Space station A space station is a spacecraft capable of supporting a crew which is designed to remain in space for an extended period of time, and to which other spacecraft can dock. A space station is distinguished from other spacecraft used for human spaceflight by its lack of major propulsion or landing... in 1982 and 1984, making her spacewalk on July 25, 1984. Two minor planet Minor planet An asteroid group or minor-planet group is a population of minor planets that have a share broadly similar orbits. Members are generally unrelated to each other, unlike in an asteroid family, which often results from the break-up of a single asteroid... s № 4118 Sveta and № 4303 Savitskaya have been named after Svetlana Savitskaya. |
||
 |
Otto Schmidt Otto Schmidt Otto Yulyevich Schmidt was a Soviet scientist, mathematician, astronomer, geophysicist, statesman, academician, Hero of the USSR , and member of the Communist Party.-Biography:He was born in Mogilev, Russian Empire... (1891–1956)  Russian Empire Russian Empire Soviet Union Soviet Unionmathematician, astronomer, geophysicist, statesman, Hero of the Soviet Union Hero of the Soviet Union The title Hero of the Soviet Union was the highest distinction in the Soviet Union, awarded personally or collectively for heroic feats in service to the Soviet state and society.-Overview:... , Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... explorer |
In 1932-39 Schmidt was the head of Chief Directorate of the Northern Sea Route Chief Directorate of the Northern Sea Route The Chief Directorate of the Northern Sea Route , also known as Glavsevmorput, was a Soviet government organization in charge of the naval Northern Sea Route, established in January 1932 and dissolved in 1964.-History:The organization traces its roots to AO Komseveroput, a shipping company... . In 1929-30, travelling on the icebreaker Icebreaker An icebreaker is a special-purpose ship or boat designed to move and navigate through ice-covered waters. Although the term usually refers to ice-breaking ships, it may also refer to smaller vessels .For a ship to be considered an icebreaker, it requires three traits most... Georgy Sedov, he established the first research station on the Franz Josef Land Franz Josef Land Franz Josef Land, Franz Joseph Land, or Francis Joseph's Land is an archipelago located in the far north of Russia. It is found in the Arctic Ocean north of Novaya Zemlya and east of Svalbard, and is administered by Arkhangelsk Oblast. Franz Josef Land consists of 191 ice-covered islands with a... , explored the northwestern Kara Sea Kara Sea The Kara Sea is part of the Arctic Ocean north of Siberia. It is separated from the Barents Sea to the west by the Kara Strait and Novaya Zemlya, and the Laptev Sea to the east by the Severnaya Zemlya.... and western Severnaya Zemlya Severnaya Zemlya Severnaya Zemlya is an archipelago in the Russian high Arctic at around . It is located off mainland Siberia's Taymyr Peninsula across the Vilkitsky Strait... , discovering a few islands. In 1932 his expedition on the icebreaker Sibiryakov Icebreaker Sibiryakov The icebreaker Sibiryakov was a Soviet ship which was active in the Russian Arctic during the 1930s. She was built in 1909 in Glasgow and was originally the Newfoundland sealing steamer Bellaventure. After being purchased by Russia in 1916, she was renamed the Sibiryakov... with Captain Vladimir Voronin made first non-stop voyage through the Northern Sea Route Northern Sea Route The Northern Sea Route is a shipping lane officially defined by Russian legislation from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean specifically running along the Russian Arctic coast from Murmansk on the Barents Sea, along Siberia, to the Bering Strait and Far East. The entire route lies in Arctic... from Arkhangelsk Arkhangelsk Arkhangelsk , formerly known as Archangel in English, is a city and the administrative center of Arkhangelsk Oblast, Russia. It lies on both banks of the Northern Dvina River near its exit into the White Sea in the north of European Russia. The city spreads for over along the banks of the river... to the Pacific Ocean Pacific Ocean The Pacific Ocean is the largest of the Earth's oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, bounded by Asia and Australia in the west, and the Americas in the east.At 165.2 million square kilometres in area, this largest division of the World... without wintering. In 1933-34 Schmidt and Voronin led the voyage on the steamship Cheliuskin, that resulted in the loss of the ship and evacuation of the crew. In 1937 Schmidt supervised an airborne expedition that established a drift-ice station North Pole-1 North Pole-1 North Pole-1 was the first Soviet manned drifting station, primarily used for research.North Pole-1 was established on May 21, 1937, and officially opened on June 6, some from the North Pole by the expedition into the high latitudes Sever-1, led by Otto Schmidt. The expedition had been airlifted... , and in 1938 he was in charge of evacuating its personnel from the ice. An island in the Kara Sea Kara Sea The Kara Sea is part of the Arctic Ocean north of Siberia. It is separated from the Barents Sea to the west by the Kara Strait and Novaya Zemlya, and the Laptev Sea to the east by the Severnaya Zemlya.... , a cape on in the Chukchi Sea Chukchi Sea Chukchi Sea is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It is bounded on the west by the De Long Strait, off Wrangel Island, and in the east by Point Barrow, Alaska, beyond which lies the Beaufort Sea. The Bering Strait forms its southernmost limit and connects it to the Bering Sea and the Pacific... , minor planet Minor planet An asteroid group or minor-planet group is a population of minor planets that have a share broadly similar orbits. Members are generally unrelated to each other, unlike in an asteroid family, which often results from the break-up of a single asteroid... 2108 Otto Schmidt 2108 Otto Schmidt 2108 Otto Schmidt is a main-belt asteroid discovered on October 4, 1948 by P. F. Shajn at Simeis.- External links :*... , an icebreaker, a number of scientific institutions and streets bear Schmidt's name. |
 |
| Leopold von Schrenck Leopold von Schrenck Leopold Ivanovich von Schrenck was a Russian zoologist, geographer and ethnographer.-Biography:Schrenck was a Baltic German born and brought up near Chotenj, south-west of St Petersburg. He received his doctorate from the University of Tartu, and then studied natural science in Berlin and Königsberg... (1826–1894)  Russian Empire Russian Empirezoologist, geographer, ethnographer, explorer of the Russian Far East Russian Far East Russian Far East is a term that refers to the Russian part of the Far East, i.e., extreme east parts of Russia, between Lake Baikal in Eastern Siberia and the Pacific Ocean... |
On behalf of the Russian Academy of Sciences Russian Academy of Sciences The Russian Academy of Sciences consists of the national academy of Russia and a network of scientific research institutes from across the Russian Federation as well as auxiliary scientific and social units like libraries, publishers and hospitals.... , Schrenck explored fauna of the Russian Far East Russian Far East Russian Far East is a term that refers to the Russian part of the Far East, i.e., extreme east parts of Russia, between Lake Baikal in Eastern Siberia and the Pacific Ocean... , in Amurland between 1853–54, and on Sakhalin Sakhalin Sakhalin or Saghalien, is a large island in the North Pacific, lying between 45°50' and 54°24' N.It is part of Russia, and is Russia's largest island, and is administered as part of Sakhalin Oblast... in 1854-55, discovering a number of animals. Later he turned to the study of native peoples of Russia. He coined the term Paleo-Asiatic peoples and was a director of Peter the Great Museum of Anthropology and Ethnography in St Petersburg. A mountain ridge on the Sakhalin Sakhalin Sakhalin or Saghalien, is a large island in the North Pacific, lying between 45°50' and 54°24' N.It is part of Russia, and is Russia's largest island, and is administered as part of Sakhalin Oblast... and a number of animals including Amur sturgeon Amur sturgeon The Amur sturgeon is a species of fish in the Acipenseridae family. It is found in China, Mongolia, Russia and Japan.-References:* Sturgeon Specialist Group 1996. . Downloaded on 3 August 2007.... , Manchurian Black Water Snake and Manchurian Black Water Snake are named after Schrenck. |
||
| Georgiy Sedov (1877–1914)  Russian Empire Russian EmpireRussian Imperial Navy officer, Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... explorer |
In 1902-03, Sedov took part in a hydrographic Hydrography Hydrography is the measurement of the depths, the tides and currents of a body of water and establishment of the sea, river or lake bed topography and morphology. Normally and historically for the purpose of charting a body of water for the safe navigation of shipping... expedition in the Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... . In 1909, he led the expedition that described the mouth of the Kolyma Kolyma The Kolyma region is located in the far north-eastern area of Russia in what is commonly known as Siberia but is actually part of the Russian Far East. It is bounded by the East Siberian Sea and the Arctic Ocean in the north and the Sea of Okhotsk to the south... river. In 1910 he explored the Krestovaya Bay on Novaya Zemlya Novaya Zemlya Novaya Zemlya , also known in Dutch as Nova Zembla and in Norwegian as , is an archipelago in the Arctic Ocean in the north of Russia and the extreme northeast of Europe, the easternmost point of Europe lying at Cape Flissingsky on the northern island... . He suggested a sleigh expedition to the North Pole North Pole The North Pole, also known as the Geographic North Pole or Terrestrial North Pole, is, subject to the caveats explained below, defined as the point in the northern hemisphere where the Earth's axis of rotation meets its surface... and found the independent sponsors, as the government refused in the finance. In 1912 Sedov's ship "Svyatoy Muchenik Foka" (Saint Martyr Foka) sailed north but had to stay for the winter near Novaya Zemlya Novaya Zemlya Novaya Zemlya , also known in Dutch as Nova Zembla and in Norwegian as , is an archipelago in the Arctic Ocean in the north of Russia and the extreme northeast of Europe, the easternmost point of Europe lying at Cape Flissingsky on the northern island... because of impassable ice. Sv. Foka reached Franz Josef Land Franz Josef Land Franz Josef Land, Franz Joseph Land, or Francis Joseph's Land is an archipelago located in the far north of Russia. It is found in the Arctic Ocean north of Novaya Zemlya and east of Svalbard, and is administered by Arkhangelsk Oblast. Franz Josef Land consists of 191 ice-covered islands with a... , but had to stop for another winter due to lack of coal. In early 1914, Sedov, sick with scurvy Scurvy Scurvy is a disease resulting from a deficiency of vitamin C, which is required for the synthesis of collagen in humans. The chemical name for vitamin C, ascorbic acid, is derived from the Latin name of scurvy, scorbutus, which also provides the adjective scorbutic... , with two companions set off for the North Pole North Pole The North Pole, also known as the Geographic North Pole or Terrestrial North Pole, is, subject to the caveats explained below, defined as the point in the northern hemisphere where the Earth's axis of rotation meets its surface... with the draft dogs. Near Rudolf Island Rudolf Island Prince Rudolf Land, Crown Prince Rudolf Land, Prince Rudolf Island or Rudolf Island is the northernmost island of the Franz Josef Archipelago, Russia. The island was named by the Austro-Hungarian North Pole Expedition in honor of Archduke Rudolf , Crown Prince of Austria, Hungary and Bohemia... Sedov died and was buried there, at Cape Auk. On the way back, at Franz Josef Land, the Sv. Foka rescued two survivors of the Georgy Brusilov Georgy Brusilov Georgy Lvovich Brusilov or Hryhoriy Brusylov was a Ukrainian Russian naval officer of the Imperial Russian Navy and an Arctic explorer... expedition, Valerian Albanov Valerian Albanov Valerian Ivanovich Albanov was a Russian navigator, best known for being one of only two survivors of the ill-fated Brusilov expedition of 1912.-Biography:... and Alexander Konrad Alexander Konrad Alexander Eduardovich Konrad was a Russian sailor. Along with Valerian Albanov, he was one of the only two survivors, and the only surviving sailor of the ill-fated Brusilov expedition.-Biography:... . Two gulfs Headlands and bays Headlands and bays are two related features of the coastal environment.- Geology and geography :Headlands and bays are often found on the same coastline. A bay is surrounded by land on three sides, whereas a headland is surrounded by water on three sides. Headlands are characterized by high,... and a peak Mountain Image:Himalaya_annotated.jpg|thumb|right|The Himalayan mountain range with Mount Everestrect 58 14 160 49 Chomo Lonzorect 200 28 335 52 Makalurect 378 24 566 45 Mount Everestrect 188 581 920 656 Tibetan Plateaurect 250 406 340 427 Rong River... on Novaya Zemlya Novaya Zemlya Novaya Zemlya , also known in Dutch as Nova Zembla and in Norwegian as , is an archipelago in the Arctic Ocean in the north of Russia and the extreme northeast of Europe, the easternmost point of Europe lying at Cape Flissingsky on the northern island... , a glacier Glacier A glacier is a large persistent body of ice that forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. At least 0.1 km² in area and 50 m thick, but often much larger, a glacier slowly deforms and flows due to stresses induced by its weight... and a cape on Franz Josef Land Franz Josef Land Franz Josef Land, Franz Joseph Land, or Francis Joseph's Land is an archipelago located in the far north of Russia. It is found in the Arctic Ocean north of Novaya Zemlya and east of Svalbard, and is administered by Arkhangelsk Oblast. Franz Josef Land consists of 191 ice-covered islands with a... , an island in the Barents Sea Barents Sea The Barents Sea is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean, located north of Norway and Russia. Known in the Middle Ages as the Murman Sea, the sea takes its current name from the Dutch navigator Willem Barents... , a cape in Antarctica and a steam icebreaker Icebreaker An icebreaker is a special-purpose ship or boat designed to move and navigate through ice-covered waters. Although the term usually refers to ice-breaking ships, it may also refer to smaller vessels .For a ship to be considered an icebreaker, it requires three traits most... Sedov Icebreaker Sedov The Sedov was a Soviet ice-breaker fitted with steam engines. She was originally the Newfoundland sealing steamer Beothic and was renamed after Russian Captain and Polar explorer Georgy Yakovlevich Sedov.... were named after Sedov. He and his last expedition are among the prototypes for the novel The Two Captains The Two Captains The Two Captains is a novel written by Soviet author Veniamin Kaverin between 1938 and 1944. It is Kaverin's best known work and is considered one of the most popular works of Soviet literature, winning the USSR State Prize in 1946 being reissued 42 times in 25 years... by Veniamin Kaverin Veniamin Kaverin Veniamin Alexandrovich Kaverin was a Soviet writer associated with the early 1920s movement of the Serapion Brothers. The immunologist Lev Zilber was his older brother, and the critic Yury Tynyanov was his brother-in-law.... , where the fictional captain Tatarinov has Sedov-like appearance and shares his passion for Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... exploration. |
 |
|
 |
Pyotr Semyonov-Tyan-Shansky (1827–1914)  Russian Empire Russian Empiregeographer, statistician, entomologist, explorer of Central Asia Central Asia Central Asia is a core region of the Asian continent from the Caspian Sea in the west, China in the east, Afghanistan in the south, and Russia in the north... |
Semyonov is known for his explorations of the then largely unknown mountains of the Tian Shan Tian Shan The Tian Shan , also spelled Tien Shan, is a large mountain system located in Central Asia. The highest peak in the Tian Shan is Victory Peak , .... . In 1856-57 he passed through the Altay Mountains Altay Mountains The Altai Mountains are a mountain range in East-Central Asia, where Russia, China, Mongolia and Kazakhstan come together, and where the rivers Irtysh and Ob have their sources. The Altai Mountains are known as the original locus of the speakers of Turkic as well as other members of the proposed... , visited the Issyk Kul Issyk Kul Issyk Kul is an endorheic lake in the northern Tian Shan mountains in eastern Kyrgyzstan. It is the tenth largest lake in the world by volume and the second largest saline lake after the Caspian Sea. Although it is surrounded by snow-capped peaks, it never freezes; hence its name, which means "hot... and came to the Tian Shan. Semyonov was the first European to see the peak of Khan Tengri Khan Tengri Khan Tengri is a mountain of the Tian Shan mountain range. It is located on the China—Kyrgyzstan—Kazakhstan border, east of lake Issyk Kul. Its geologic elevation is , but its glacial cap rises to... . He disproved Humboldt's earlier claims about Tian Shan's supposed volcanic origins. The next year, he published the first systematic description of the Tian Shan Tian Shan The Tian Shan , also spelled Tien Shan, is a large mountain system located in Central Asia. The highest peak in the Tian Shan is Victory Peak , .... . The reputation of this monograph was such that half a century later Nicholas II of Russia Nicholas II of Russia Nicholas II was the last Emperor of Russia, Grand Prince of Finland, and titular King of Poland. His official short title was Nicholas II, Emperor and Autocrat of All the Russias and he is known as Saint Nicholas the Passion-Bearer by the Russian Orthodox Church.Nicholas II ruled from 1894 until... authorized him to add the epithet "Tian-Shansky" (that is, "of Tian Shan") to his last name. For many years Semyonov served as Chairman of the Russia's Central Committee for Statistics. It was largely due to his efforts that the first census Census A census is the procedure of systematically acquiring and recording information about the members of a given population. It is a regularly occurring and official count of a particular population. The term is used mostly in connection with national population and housing censuses; other common... of the Russian Empire Russian Empire The Russian Empire was a state that existed from 1721 until the Russian Revolution of 1917. It was the successor to the Tsardom of Russia and the predecessor of the Soviet Union... was held in 1897. Semyonov amassed a large collection of old Dutch masters, which now belongs to the Hermitage Museum Hermitage Museum The State Hermitage is a museum of art and culture in Saint Petersburg, Russia. One of the largest and oldest museums of the world, it was founded in 1764 by Catherine the Great and has been opened to the public since 1852. Its collections, of which only a small part is on permanent display,... as well as insect collection of ca. 700,000 specimens. He was a member of 53 learned societies and headed the Russian Geographical Society Russian Geographical Society The Russian Geographical Society is a learned society, founded on 6 August 1845 in Saint Petersburg, Russia.-Imperial Geographical Society:Prior to the Russian Revolution of 1917, it was known as the Imperial Russian Geographical Society.... for 40 years from 1873 until his death, using this position to encourage the exploration of inland Asia Asia Asia is the world's largest and most populous continent, located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres. It covers 8.7% of the Earth's total surface area and with approximately 3.879 billion people, it hosts 60% of the world's current human population... , notably by Nikolai Przhevalsky Nikolai Przhevalsky Nikolai Mikhaylovich Przhevalsky and Prjevalsky, ; —), was a Russian geographer of Polish background and explorer of Central and Eastern Asia. Although he never reached his final goal, Lhasa in Tibet, he travelled through regions unknown to the west, such as northern Tibet, modern Qinghai and... and Pyotr Kozlov Pyotr Kozlov Pyotr Kuzmich Kozlov was a Russian and Soviet traveler and explorer who continued the studies of Nikolai Przhevalsky in Mongolia and Tibet.Although prepared by his parents for military career, Kozlov chose to join Przhevalsky's expedition. After his mentor's death, Kozlov continued travelling in... . More than 100 plant and animal species as well as a number of geographical objects in Central Asia Central Asia Central Asia is a core region of the Asian continent from the Caspian Sea in the west, China in the east, Afghanistan in the south, and Russia in the north... , Alaska Alaska Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait... , the Caucasus Caucasus The Caucasus, also Caucas or Caucasia , is a geopolitical region at the border of Europe and Asia, and situated between the Black and the Caspian sea... and Svalbard Svalbard Svalbard is an archipelago in the Arctic, constituting the northernmost part of Norway. It is located north of mainland Europe, midway between mainland Norway and the North Pole. The group of islands range from 74° to 81° north latitude , and from 10° to 35° east longitude. Spitsbergen is the... were named after Semyonov. |
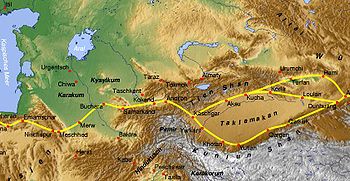  |
| Yuri Senkevich Yuri Senkevich Yuri Aleksandrovich Senkevich was a Soviet doctor, scientist. He is Candidate of Sciences. He became famous in the USSR and worldwide for his participation in the Ra Expedition, in which he sailed together with Thor Heyerdahl.Senkevich was born of Russian parents in Mongolia... (1937–2003)  Soviet Union Soviet Union Russia Russiaphysician, scientist, traveler, TV anchorman (photo of Senkevich on the cover of his memoirs A Lifelong Travel) |
Senkevich, being a Soviet military physician, participated in the 12th Soviet Antarctic expedition at Vostok station in 1966-67. In 1969 Senkevich sailed with Thor Heyerdahl Thor Heyerdahl Thor Heyerdahl was a Norwegian ethnographer and adventurer with a background in zoology and geography. He became notable for his Kon-Tiki expedition, in which he sailed by raft from South America to the Tuamotu Islands... on the Ra papyrus Papyrus Papyrus is a thick paper-like material produced from the pith of the papyrus plant, Cyperus papyrus, a wetland sedge that was once abundant in the Nile Delta of Egypt.... boat, and later on the Ra II across the Atlantic Ocean Atlantic Ocean The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's oceanic divisions. With a total area of about , it covers approximately 20% of the Earth's surface and about 26% of its water surface area... in 1970. He also sailed with Heyerdahl on another reed Reed (plant) Reed is a generic polyphyletic botanical term used to describe numerous tall, grass-like plants of wet places, which are the namesake vegetation of reed beds... boat Tigris across the Indian Ocean Indian Ocean The Indian Ocean is the third largest of the world's oceanic divisions, covering approximately 20% of the water on the Earth's surface. It is bounded on the north by the Indian Subcontinent and Arabian Peninsula ; on the west by eastern Africa; on the east by Indochina, the Sunda Islands, and... in 1978. In 1973-2003, Senkevich was a host of the "Travelers' Club" show on the Soviet Television for the record 30 years, making it into the Guinness Book of Records. He visited more than 200 countries as a journalist and TV anchorman. |
 |
|
| Nikolai Severtzov (1827–1885)  Russian Empire Russian Empirenaturalist Naturalist Naturalist may refer to:* Practitioner of natural history* Conservationist* Advocate of naturalism * Naturalist , autobiography-See also:* The American Naturalist, periodical* Naturalism... , explorer of Central Asia Central Asia Central Asia is a core region of the Asian continent from the Caspian Sea in the west, China in the east, Afghanistan in the south, and Russia in the north... |
Severtzov started as naturalist Naturalist Naturalist may refer to:* Practitioner of natural history* Conservationist* Advocate of naturalism * Naturalist , autobiography-See also:* The American Naturalist, periodical* Naturalism... in his native Voronezh Voronezh Voronezh is a city in southwestern Russia, the administrative center of Voronezh Oblast. It is located on both sides of the Voronezh River, away from where it flows into the Don. It is an operating center of the Southeastern Railway , as well as the center of the Don Highway... gubernia. In 1857-58, on an expedition to the Syr Darya Syr Darya The Syr Darya , also transliterated Syrdarya or Sirdaryo, is a river in Central Asia, sometimes known as the Jaxartes or Yaxartes from its Ancient Greek name . The Greek name is derived from Old Persian, Yakhsha Arta , a reference to the color of the river's water... in Central Asia Central Asia Central Asia is a core region of the Asian continent from the Caspian Sea in the west, China in the east, Afghanistan in the south, and Russia in the north... , he was captured by Kokand Khanate of Kokand The Khanate of Kokand was a state in Central Asia that existed from 1709–1883 within the territory of modern eastern Uzbekistan, southern Kazakhstan, Tajikistan and Kyrgyzstan... bandits and severely wounded. He was freed after a month by the Russian military and continued his studies. In 1865-68 he explored the Tian Shan Tian Shan The Tian Shan , also spelled Tien Shan, is a large mountain system located in Central Asia. The highest peak in the Tian Shan is Victory Peak , .... and Lake Issyk Kul Issyk Kul Issyk Kul is an endorheic lake in the northern Tian Shan mountains in eastern Kyrgyzstan. It is the tenth largest lake in the world by volume and the second largest saline lake after the Caspian Sea. Although it is surrounded by snow-capped peaks, it never freezes; hence its name, which means "hot... . In 1877-78 he explored the unknown areas of Pamir Mountains Pamir Mountains The Pamir Mountains are a mountain range in Central Asia formed by the junction or knot of the Himalayas, Tian Shan, Karakoram, Kunlun, and Hindu Kush ranges. They are among the world’s highest mountains and since Victorian times they have been known as the "Roof of the World" a probable... following a route close to the current Pamir Highway Pamir Highway The M41, known informally and more commonly as the Pamir Highway is a road traversing the Pamir Mountains through Afghanistan, Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, and Kyrgyzstan in Central Asia... as far as Lake Yashil Kul on the Ghunt River. Severtzov wrote a major study of Turkestan Turkestan Turkestan, spelled also as Turkistan, literally means "Land of the Turks".The term Turkestan is of Persian origin and has never been in use to denote a single nation. It was first used by Persian geographers to describe the place of Turkish peoples... zoology called Vertical and horizontal distribution of Turkestan wildlife (1873), which included the first description of a number of animals. The Severtzov Argali Argali The argali, or the mountain sheep is a wild sheep, which roams the highlands of Central Asia . It is the biggest wild sheep, standing at the shoulder, measuring long and weighing , with a maximum known weight of... (a wild sheep) has been named after Severtzov. |
 |
|
 |
Grigory Shelikhov Grigory Shelikhov Grigory Ivanovich Shelekhov Grigory Ivanovich Shelekhov Grigory Ivanovich Shelekhov (Григорий Иванович Шелехов in Russian; (1747–July 20, 1795 (July 31, 1795 N.S.)) was a Russian seafarer and merchant born in Rylsk.... (1747–1795)  Russian Empire Russian Empireseafarer, merchant, explorer of the Russian Far East Russian Far East Russian Far East is a term that refers to the Russian part of the Far East, i.e., extreme east parts of Russia, between Lake Baikal in Eastern Siberia and the Pacific Ocean... and Alaska Alaska Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait... |
Shelikhov organized commercial trips of the merchant ships to the Kuril Islands Kuril Islands The Kuril Islands , in Russia's Sakhalin Oblast region, form a volcanic archipelago that stretches approximately northeast from Hokkaidō, Japan, to Kamchatka, Russia, separating the Sea of Okhotsk from the North Pacific Ocean. There are 56 islands and many more minor rocks. It consists of Greater... and the Aleutian Islands starting from 1775. Together with Ivan Golikov, Shelikhov founded the precursor of Russian-American Company Russian-American Company The Russian-American Company was a state-sponsored chartered company formed largely on the basis of the so-called Shelekhov-Golikov Company of Grigory Shelekhov and Ivan Larionovich Golikov The Russian-American Company (officially: Under His Imperial Majesty's Highest Protection (patronage)... (this name appeared in 1799 after Shelikhov death). In 1783-86, he led an expedition to the shores of Russian America, during which he founded the first permanent Russian settlements in North America North America North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas... . In 1784 Shelikhov arrived in Three Saints Bay on Kodiak Island Kodiak Island Kodiak Island is a large island on the south coast of the U.S. state of Alaska, separated from the Alaska mainland by the Shelikof Strait. The largest island in the Kodiak Archipelago, Kodiak Island is the second largest island in the United States and the 80th largest island in the world, with an... . Having established the authority there, he founded the first permanent Russian settlement in Alaska Alaska Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait... . In 1790, Shelikhov, back in Russia, hired Aleksandr Baranov to manage his fur enterprise in Russian America. Shelikhov Bay Shelikhov Bay The Shelikhov Gulf is a large gulf off the northwestern coast of Kamchatka, Russia. It is located in the NE corner of the Sea of Okhotsk and it branches into two main arms, the Gizhigin Bay on the west and the Penzhin Bay on the east... in the Sea of Okhotsk Sea of Okhotsk The Sea of Okhotsk is a marginal sea of the western Pacific Ocean, lying between the Kamchatka Peninsula on the east, the Kuril Islands on the southeast, the island of Hokkaidō to the far south, the island of Sakhalin along the west, and a long stretch of eastern Siberian coast along the west and... , a strait between Alaska Alaska Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait... and Kodiak Island Kodiak Island Kodiak Island is a large island on the south coast of the U.S. state of Alaska, separated from the Alaska mainland by the Shelikof Strait. The largest island in the Kodiak Archipelago, Kodiak Island is the second largest island in the United States and the 80th largest island in the world, with an... , and a town Shelekhov Shelekhov Shelekhov is a town in Irkutsk Oblast, Russia, located southwest of Irkutsk. Population: It was founded in the early 1950s due to the construction of an aluminum plant. In 1956, it was named Shelekhov after a Russian explorer Grigory Shelekhov. For some reason, the authorities used the incorrect ... in Irkutsk Oblast Irkutsk Oblast Irkutsk Oblast is a federal subject of Russia , located in southeastern Siberia in the basins of Angara River, Lena, and Nizhnyaya Tunguska Rivers. The administrative center is the city of Irkutsk. Population: -History:... in Russia Russia Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects... bear Shelikhov's name. |
 |
| Pyotr Shirshov Pyotr Shirshov Pyotr Petrovich Shirshov was a Ukrainian Soviet oceanographer, hydrobiologist, polar explorer, statesman, academician , and Hero of the Soviet Union .Pyotr Shirshov graduated from the Odessa Public Education Institute in 1929... (1905–1953)  Russian Empire Russian Empire Soviet Union Soviet Unionoceanographer, hydrobiologist Hydrobiology Hydrobiology is the science of life and life processes in water. Much of modern hydrobiology can be viewed as a sub-discipline of ecology but the sphere of hydrobiology includes taxonomy, economic biology, industrial biology, morphology, physiology etc. The one distinguishing aspect is that all... , statesman, academician, Hero of the Soviet Union Hero of the Soviet Union The title Hero of the Soviet Union was the highest distinction in the Soviet Union, awarded personally or collectively for heroic feats in service to the Soviet state and society.-Overview:... , Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... explorer |
Shirshov participated in numerous Arctic expeditions, including the famous ones on icebreakers Sibiryakov Icebreaker Sibiryakov The icebreaker Sibiryakov was a Soviet ship which was active in the Russian Arctic during the 1930s. She was built in 1909 in Glasgow and was originally the Newfoundland sealing steamer Bellaventure. After being purchased by Russia in 1916, she was renamed the Sibiryakov... (1932) and Chelyuskin Chelyuskin steamship SS Chelyuskin was a Soviet steamship reinforced to navigate through polar ice that became ice-bound in Arctic waters during navigation along the Northern Maritime Route from Murmansk to Vladivostok... (1934). He was among the crew of the drifting ice station North Pole-1 Soviet and Russian manned drifting ice stations Soviet and Russian manned drifting ice stations are important contributors to exploration of the Arctic. The stations are named North Pole Soviet and Russian manned drifting ice stations are important contributors to exploration of the Arctic. The stations are named North Pole Soviet and... in 1937-38. In 1942-48, Shirshov was a Maritime Minister of the Soviet Union. In 1946-53, he became the founder and the first director of the Institute of Oceanology of the Soviet Academy of Sciences Shirshov Institute of Oceanology Shirshov Institute of Oceanology in Moscow, is the largest institute for ocean and earth science research, in Russia, established in 1946.- Fleet :* RV Akademik Ioffe... . He wrote numerous works about plankton Plankton Plankton are any drifting organisms that inhabit the pelagic zone of oceans, seas, or bodies of fresh water. That is, plankton are defined by their ecological niche rather than phylogenetic or taxonomic classification... in the polar regions and proved that there is life in high latitudes of the Arctic Ocean Arctic Ocean The Arctic Ocean, located in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Arctic north polar region, is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceanic divisions... . A bay and a lake in the Franz Josef Land Franz Josef Land Franz Josef Land, Franz Joseph Land, or Francis Joseph's Land is an archipelago located in the far north of Russia. It is found in the Arctic Ocean north of Novaya Zemlya and east of Svalbard, and is administered by Arkhangelsk Oblast. Franz Josef Land consists of 191 ice-covered islands with a... , an underwater range in the Bering Sea Bering Sea The Bering Sea is a marginal sea of the Pacific Ocean. It comprises a deep water basin, which then rises through a narrow slope into the shallower water above the continental shelves.... , a street in Dnepropetrovsk (the native city of Shirshov), two scientific vessels and Shirshov Institute of Oceanology Shirshov Institute of Oceanology Shirshov Institute of Oceanology in Moscow, is the largest institute for ocean and earth science research, in Russia, established in 1946.- Fleet :* RV Akademik Ioffe... bear Shirshov's name. |
 |
|
| Gleb Shishmaryov Gleb Shishmaryov Gleb Semyonovich Shishmaryov was a rear admiral of the Imperial Russian Navy. He is reputed for having surveyed the then little-known coast of Alaska as navigator... (1781–1835)  Russian Empire Russian EmpireRussian Imperial Navy officer, circumnavigator, explorer of the Alaska Alaska Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait... |
In 1815-18 Shishmaryov accompanied Otto von Kotzebue Otto von Kotzebue Otto von Kotzebue was a Baltic German navigator in Russian service.... on his circumnavigation, including the visit to Alaska Alaska Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait... . During this voyage a new-discovered inlet on Chukotka was named after Shishmaryov. In 1820 he returned to Alaska in command of ship Blagonamierennie, accompanied by Lt. Mikhail Vasiliev Ensign Mikhail Vasiliev Mikhail Nikolayevich Vasilyev was a Russian explorer and vice admiral of the Imperial Russian Navy. He is reputed for having surveyed the then little-known coast of Alaska as navigator. Vasiliev was sent by the Russian Imperial Hydrographic Service in 1819 to explore the northern parts of the... on ship Otkrietie. Shishmaref and Vasiliev entered the Chukchi Sea Chukchi Sea Chukchi Sea is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It is bounded on the west by the De Long Strait, off Wrangel Island, and in the east by Point Barrow, Alaska, beyond which lies the Beaufort Sea. The Bering Strait forms its southernmost limit and connects it to the Bering Sea and the Pacific... and explored the coast of Alaska from Kotzebue Sound Kotzebue Sound Kotzebue Sound is an arm of the Chukchi Sea in the western region of the U.S. state of Alaska. It is on the north side of the Seward Peninsula and bounded the east by the Baldwin Peninsula. It is long and wide.... to Icy Cape Icy Cape, Alaska The Icy Cape is a headland on the Chukchi Sea side of the North Slope Borough, Alaska, United States. It was discovered and named by James Cook on August 17, 1778.... and later from Norton Sound Norton Sound Norton Sound is an inlet of the Bering Sea on the western coast of the U.S. state of Alaska, south of the Seward Peninsula. It is about 240 km long and 200 km wide. The Yukon River delta forms a portion of the south shore and water from the Yukon influences this body of water... to Cape Newenham. St. Lawrence Island St. Lawrence Island St. Lawrence Island is located west of mainland Alaska in the Bering Sea, just south of the Bering Strait, at about 63°30' North 173°20' West. The village of Gambell is located on the northwest cape, from the Chukchi Peninsula in the Russian Far East. The island is part of Alaska, but closer to... was mapped on the return way. The town of Shishmaref, Alaska Shishmaref, Alaska Shishmaref is a village in the Nome Census Area, Alaska, United States, located on Sarichef Island in the Chukchi Sea, just north of the Bering Strait and five miles from the mainland. It lies within the Bering Land Bridge National Preserve... , and the Shishmaref Inlet Shishmaref Inlet The Shishmaref Inlet is a coastal lagoon on the Chukchi Sea-facing shores of Alaska. It is 5 miles in length.The location of the Shishmaref Inlet is SW 17 mi. to the SW from Sarichef Island, at the mouth of the Serpentine River, Kotzebue-Kobuk Low.... in Chukotka Chukchi Peninsula The Chukchi Peninsula, Chukotka Peninsula or Chukotski Peninsula , at about 66° N 172° W, is the northeastern extremity of Asia. Its eastern end is at Cape Dezhnev near the village of Uelen. It is bordered by the Chukchi Sea to the north, the Bering Sea to the south, and the Bering Strait to the... bear Shishmaryov's name. |
 |
|
| Nikolay Shkot Nikolay Shkot Nikolay Yakovlevich Shkot , was a war veteran of Siege of Sevastopol during the Crimean War. He was badly wounded in the battle.After the War he commanded corvette America and troopship Yaponets on Far East. The expedition made geographic discoveries at a coast of modern Primorsky Krai and Sakhalin... (1829–1870)  Russian Empire Russian EmpireRussian Imperial Navy officer, explorer of the Russian Far East Russian Far East Russian Far East is a term that refers to the Russian part of the Far East, i.e., extreme east parts of Russia, between Lake Baikal in Eastern Siberia and the Pacific Ocean... |
After being wounded in the Siege of Sevastopol during the Crimean War Crimean War The Crimean War was a conflict fought between the Russian Empire and an alliance of the French Empire, the British Empire, the Ottoman Empire, and the Kingdom of Sardinia. The war was part of a long-running contest between the major European powers for influence over territories of the declining... , Shkot served on the Far East Far East The Far East is an English term mostly describing East Asia and Southeast Asia, with South Asia sometimes also included for economic and cultural reasons.The term came into use in European geopolitical discourse in the 19th century,... . In 1956-63 he explored Sakhalin Sakhalin Sakhalin or Saghalien, is a large island in the North Pacific, lying between 45°50' and 54°24' N.It is part of Russia, and is Russia's largest island, and is administered as part of Sakhalin Oblast... (especially the Moneron Island Moneron Island Moneron Island, is a Russian possession located off Sakhalin Island.-Description:Moneron has an area of about and a highest point of . It is approximately long by wide, and is located from Sakhalin's port of Nevelsk and about directly southwest of Sakhalin Island itself at the northeastern... ) and the coast of Primorsky Krai Primorsky Krai Primorsky Krai , informally known as Primorye , is a federal subject of Russia . Primorsky means "maritime" in Russian, hence the region is sometimes referred to as Maritime Province or Maritime Territory. Its administrative center is in the city of Vladivostok... in the area of Peter the Great Gulf Peter the Great Gulf The Peter the Great Gulf is the largest gulf of the Sea of Japan adjoining the coast of Russia's Primorski Krai... and Nakhodka Bay Nakhodka Bay Nakhodka Bay or Nakhodka Gulf is a bay of the Peter the Great Gulf of the Sea of Japan, on which is sited the port of Nakhodka. It is part of the Primorsky Krai of Russia. The Lisy Island protects the bay from open sea waves... , making a number of discoveries. He founded hydrograph Hydrograph A hydrograph is a graph showing the rate of flow versus time past a specific point in a river, or other channel or conduit carrying flow... ic post on a place of modern Nakhodka Nakhodka Nakhodka is a port city in Primorsky Krai, Russia, situated on the Trudny Peninsula jutting into the Nakhodka Bay of the Sea of Japan, about east of Vladivostok... , and was one of the founders of Vladivostok Vladivostok The city is located in the southern extremity of Muravyov-Amursky Peninsula, which is about 30 km long and approximately 12 km wide.The highest point is Mount Kholodilnik, the height of which is 257 m... in 1860. Shkot Island Shkot Island Shkot Island is a one of five big islands of Eugénie de Montijo Archipelago under Vladivostok administration.... in the Sea of Japan Sea of Japan The Sea of Japan is a marginal sea of the western Pacific Ocean, between the Asian mainland, the Japanese archipelago and Sakhalin. It is bordered by Japan, North Korea, Russia and South Korea. Like the Mediterranean Sea, it has almost no tides due to its nearly complete enclosure from the Pacific... , Shkotovo Shkotovo Shkotovo is an urban locality and a railway station in Shkotovsky District of Primorsky Krai, Russia. Population:... village and Shkotovka River Shkotovka River Shkotovka River is a river in Primorsky Krai.It is 59 km long, its drainage basin area is 714 square kilometres. It rises in South Sikhote-Alin and flow into Ussuri Bay of Sea of Japan near settlement Shkotovo.It was named after Nikolay Shkot in 1972... in Primorsky Krai Primorsky Krai Primorsky Krai , informally known as Primorye , is a federal subject of Russia . Primorsky means "maritime" in Russian, hence the region is sometimes referred to as Maritime Province or Maritime Territory. Its administrative center is in the city of Vladivostok... , and a cape in Olga Bay Olga Bay Olga Bay is a small bay in the Sea of Japan at the east coast of Primorsky Krai.Olga Bay was discovered in 1859 by the Russian corvette Amerika and named after Saint Olga.... are named after Shkot. |
||
 |
Yuly Shokalsky Yuly Shokalsky Yuly Mikhailovich Shokalsky was a Russian oceanographer, cartographer, and geographer.A grandson of Anna Kern, Pushkin's celebrated mistress, Shokalsky graduated from the Naval Academy in 1880 and made a career in the Imperial Russian Navy, helping establish the Sevastopol Marine Observatory and... (1856–1940)  Russian Empire Russian Empire Soviet Union Soviet UnionImperial Russian Navy Imperial Russian Navy The Imperial Russian Navy refers to the Tsarist fleets prior to the February Revolution.-First Romanovs:Under Tsar Mikhail Feodorovich, construction of the first three-masted ship, actually built within Russia, was completed in 1636. It was built in Balakhna by Danish shipbuilders from Holstein... officer, oceanographer, meteorologist, cartographer, geographer, explorer of European Russia European Russia European Russia refers to the western areas of Russia that lie within Europe, comprising roughly 3,960,000 square kilometres , larger in area than India, and spanning across 40% of Europe. Its eastern border is defined by the Ural Mountains and in the south it is defined by the border with... |
In 1897-1901 Shokalsky researched Lake Ladoga Lake Ladoga Lake Ladoga is a freshwater lake located in the Republic of Karelia and Leningrad Oblast in northwestern Russia, not far from Saint Petersburg. It is the largest lake in Europe, and the 14th largest lake by area in the world.-Geography:... . Since 1907 he supervised all oceanographic works in Russia. He coined the term World Ocean World Ocean The World Ocean, world ocean, or global ocean, is the interconnected system of the Earth's oceanic waters, and comprises the bulk of the hydrosphere, covering almost 71% of the Earth's surface, with a total volume of 1.332 billion cubic kilometres.The unity and continuity of the World Ocean, with... . In 1919 he headed the commission that set up time zones in Russia Time in Russia There are nine time zones in Russia, which currently observe times ranging from UTC+03:00 to UTC+12:00. UTC+05:00 is not used.-List of zones:Since March 2011, the time zones are as follows:-Daylight saving time:... . In 1918-31 he was the head of Russian Geographical Society Russian Geographical Society The Russian Geographical Society is a learned society, founded on 6 August 1845 in Saint Petersburg, Russia.-Imperial Geographical Society:Prior to the Russian Revolution of 1917, it was known as the Imperial Russian Geographical Society.... and contributed a lot to the Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... exploration on this post. Shokalsky Strait Shokalsky Strait Shokalsky Strait is a 50 km-wide strait in Russia. It separates Bolshevik Island from October Revolution Island, and connects the Laptev Sea in the west with the East Siberian Sea in the east. It is named after Russian oceanographer Yuly Shokalsky.... in the Severnaya Zemlya Severnaya Zemlya Severnaya Zemlya is an archipelago in the Russian high Arctic at around . It is located off mainland Siberia's Taymyr Peninsula across the Vilkitsky Strait... , Shokalsky Island in the Kara Sea Kara Sea The Kara Sea is part of the Arctic Ocean north of Siberia. It is separated from the Barents Sea to the west by the Kara Strait and Novaya Zemlya, and the Laptev Sea to the east by the Severnaya Zemlya.... , two islands in the Kara Strait Kara Strait The Kara Strait or Kara Gates is a 56 km wide channel of water between the southern end of Novaya Zemlya and the northern tip of Vaygach Island... , a lake on Kanin Peninsula Kanin Peninsula Kanin Peninsula is a large peninsula in Nenets Autonomous Okrug, Russia. Latitude : 68° Longitude : 45°It is surrounded by the White Sea to the west and by the Barents Sea to the north and east. Shoyna is one of the few communities on the peninsula.... , a glacier in Novaya Zemlya Novaya Zemlya Novaya Zemlya , also known in Dutch as Nova Zembla and in Norwegian as , is an archipelago in the Arctic Ocean in the north of Russia and the extreme northeast of Europe, the easternmost point of Europe lying at Cape Flissingsky on the northern island... and an ocean current Ocean current An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of ocean water generated by the forces acting upon this mean flow, such as breaking waves, wind, Coriolis effect, cabbeling, temperature and salinity differences and tides caused by the gravitational pull of the Moon and the Sun... around Svalbard Svalbard Svalbard is an archipelago in the Arctic, constituting the northernmost part of Norway. It is located north of mainland Europe, midway between mainland Norway and the North Pole. The group of islands range from 74° to 81° north latitude , and from 10° to 35° east longitude. Spitsbergen is the... are named after Shokalsky. |
 |
| Martin Shpanberg Martin Shpanberg Martin Petrovich Shpanberg was a Danish born naval lieutenant who took part in Berings two Kamchatka expeditions as second in command. He is best known for exploring the Kuril Islands and finding the sea route to Japan.... (?–1761)  Denmark Denmark Tsardom of Russia Tsardom of Russia The Tsardom of Russia was the name of the centralized Russian state from Ivan IV's assumption of the title of Tsar in 1547 till Peter the Great's foundation of the Russian Empire in 1721.From 1550 to 1700, Russia grew 35,000 km2 a year...  Russian Empire Russian EmpireRussian Imperial Navy officer, navigator, explorer of the Russian Far East Russian Far East Russian Far East is a term that refers to the Russian part of the Far East, i.e., extreme east parts of Russia, between Lake Baikal in Eastern Siberia and the Pacific Ocean... and Japan Japan Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south... |
Shpanberg was born in Denmark Denmark Denmark is a Scandinavian country in Northern Europe. The countries of Denmark and Greenland, as well as the Faroe Islands, constitute the Kingdom of Denmark . It is the southernmost of the Nordic countries, southwest of Sweden and south of Norway, and bordered to the south by Germany. Denmark... and like Vitus Bering Vitus Bering Vitus Jonassen Bering Vitus Jonassen Bering Vitus Jonassen Bering (also, less correNavy]], a captain-komandor known among the Russian sailors as Ivan Ivanovich. He is noted for being the first European to discover Alaska and its Aleutian Islands... (another Danish Denmark Denmark is a Scandinavian country in Northern Europe. The countries of Denmark and Greenland, as well as the Faroe Islands, constitute the Kingdom of Denmark . It is the southernmost of the Nordic countries, southwest of Sweden and south of Norway, and bordered to the south by Germany. Denmark... ) he joined the Russian Navy. He took part in the Russian exploration efforts in the Northern Pacific during the first Kamchatka expedition of Vitus Bering Vitus Bering Vitus Jonassen Bering Vitus Jonassen Bering Vitus Jonassen Bering (also, less correNavy]], a captain-komandor known among the Russian sailors as Ivan Ivanovich. He is noted for being the first European to discover Alaska and its Aleutian Islands... (1725–30). During the Second Kamchatka Expedition, also organised by Bering, Shpanberg was made a leader of expedition to find a sea route to Japan. In 1738-39 he explored and mapped most of Kuril islands Kuril Islands The Kuril Islands , in Russia's Sakhalin Oblast region, form a volcanic archipelago that stretches approximately northeast from Hokkaidō, Japan, to Kamchatka, Russia, separating the Sea of Okhotsk from the North Pacific Ocean. There are 56 islands and many more minor rocks. It consists of Greater... and reached Japan Japan Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south... , however he failed to establish the relations with Japanese and soon returned back. |
 |
|
| Alexander Sibiryakov Alexander Sibiryakov Alexander Mikhaylovich Sibiryakov was a Russian gold mine owner and explorer of Siberia.... (1849–1933)  Russian Empire Russian Empire Early Modern France Early Modern Francegold mine owner, explorer of Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... and Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... , sponsor of many expeditions |
A rich gold mine owner from an ancient family of Siberian merchants, Sibiryakov financed the polar expeditions of Adolf Erik Nordenskiöld Adolf Erik Nordenskiöld Freiherr Nils Adolf Erik Nordenskiöld , also known as A. E. Nordenskioeld was a Finnish baron, geologist, mineralogist and arctic explorer of Finnish-Swedish origin. He was a member of the prominent Finland-Swedish Nordenskiöld family of scientists... and A.V.Grigoriev. He also sponsored the publication of works on Siberia's history. In 1880, he made an attempt to enter the Yenisei estuary Estuary An estuary is a partly enclosed coastal body of water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea.... through the Kara Sea Kara Sea The Kara Sea is part of the Arctic Ocean north of Siberia. It is separated from the Barents Sea to the west by the Kara Strait and Novaya Zemlya, and the Laptev Sea to the east by the Severnaya Zemlya.... on a schooner Schooner A schooner is a type of sailing vessel characterized by the use of fore-and-aft sails on two or more masts with the forward mast being no taller than the rear masts.... . In 1884, Sibiryakov reached the Pechora Pechora River The Pechora River is a river in northwest Russia which flows north into the Arctic Ocean on the west side of the Ural Mountains. It lies mostly in the Komi Republic but the northernmost part crosses the Nenets Autonomous Okrug. It is 1,809 km long and its basin is 322,000 square kilometers... estuary on the steamer Steamboat A steamboat or steamship, sometimes called a steamer, is a ship in which the primary method of propulsion is steam power, typically driving propellers or paddlewheels... "Nordenskiöld" and proceeded up the river River A river is a natural watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, a lake, a sea, or another river. In a few cases, a river simply flows into the ground or dries up completely before reaching another body of water. Small rivers may also be called by several other names, including... . He also crossed the Urals using reindeer Reindeer The reindeer , also known as the caribou in North America, is a deer from the Arctic and Subarctic, including both resident and migratory populations. While overall widespread and numerous, some of its subspecies are rare and one has already gone extinct.Reindeer vary considerably in color and size... s and reached Tobolsk Tobolsk Tobolsk is a town in Tyumen Oblast, Russia, located at the confluence of the Tobol and Irtysh Rivers. It is a historic capital of Siberia. Population: -History:... by the Tobol River Tobol River Tobol is a river in Kurgan and Tyumen Oblasts in Russia and Kazakhstan, left tributary of the Irtysh. The length of the Tobol River is 1591 km. The area of its drainage basin is 426,000 km². Average discharge at mouth is 805 m³/s. The lower reaches of the river freeze up in late October -... . Sibiryakov contributed significantly to Siberia's economic development. Sibiryakow Island in the Kara Sea Kara Sea The Kara Sea is part of the Arctic Ocean north of Siberia. It is separated from the Barents Sea to the west by the Kara Strait and Novaya Zemlya, and the Laptev Sea to the east by the Severnaya Zemlya.... near the mouth of the Yenisey, Sibiryakov Island in the Sea of Japan Sea of Japan The Sea of Japan is a marginal sea of the western Pacific Ocean, between the Asian mainland, the Japanese archipelago and Sakhalin. It is bordered by Japan, North Korea, Russia and South Korea. Like the Mediterranean Sea, it has almost no tides due to its nearly complete enclosure from the Pacific... , Russian icebreaker Icebreaker An icebreaker is a special-purpose ship or boat designed to move and navigate through ice-covered waters. Although the term usually refers to ice-breaking ships, it may also refer to smaller vessels .For a ship to be considered an icebreaker, it requires three traits most... s Alexander Sibiryakov Icebreaker Sibiryakov The icebreaker Sibiryakov was a Soviet ship which was active in the Russian Arctic during the 1930s. She was built in 1909 in Glasgow and was originally the Newfoundland sealing steamer Bellaventure. After being purchased by Russia in 1916, she was renamed the Sibiryakov... (the first to pass the Northern Sea Route Northern Sea Route The Northern Sea Route is a shipping lane officially defined by Russian legislation from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean specifically running along the Russian Arctic coast from Murmansk on the Barents Sea, along Siberia, to the Bering Strait and Far East. The entire route lies in Arctic... in one navigation) and Sibiryakov have been named after Alexander Sibiryakov. |
 |
|
| Anatoly Solovyev Anatoly Solovyev Anatoly Yakovlevich Solovyev is a former Soviet pilot, cosmonaut, and Colonel. Solovyev holds the world record on the number of spacewalks performed , and accumulated time spent spacewalking .- Family :... (born 1948)  Soviet Union Soviet Union Russia Russiacosmonaut, aviator, Hero of the Soviet Union Hero of the Soviet Union The title Hero of the Soviet Union was the highest distinction in the Soviet Union, awarded personally or collectively for heroic feats in service to the Soviet state and society.-Overview:... |
Solovyev holds the world record on the number of spacewalks Extra-vehicular activity Extra-vehicular activity is work done by an astronaut away from the Earth, and outside of a spacecraft. The term most commonly applies to an EVA made outside a craft orbiting Earth , but also applies to an EVA made on the surface of the Moon... (16), and accumulated time spent spacewalking (over 82 hours), which he performed during his five spaceflights. In 1988 he traveled on Soyuz TM-5 Soyuz TM-5 -Launch:Soyuz TM-5 launched on 1988 June 7 and arrived at Mir on June 9 carrying the second Bulgarian in space, Alexandrov . He became the first Bulgarian to reach a Soviet space station... to Mir Mir Mir was a space station operated in low Earth orbit from 1986 to 2001, at first by the Soviet Union and then by Russia. Assembled in orbit from 1986 to 1996, Mir was the first modular space station and had a greater mass than that of any previous spacecraft, holding the record for the... space station Space station A space station is a spacecraft capable of supporting a crew which is designed to remain in space for an extended period of time, and to which other spacecraft can dock. A space station is distinguished from other spacecraft used for human spaceflight by its lack of major propulsion or landing... and back on Soyuz TM-4 Soyuz TM-4 -Mission parameters:*Mass: 7070 kg*Perigee: 337 km*Apogee: 357 km*Inclination: 51.6°*Period: 91.5 minutes-Mission highlights:... . In 1990 he again traveled to Mir and back on Soyuz TM-9 Soyuz TM-9 -Mission highlights:During docking, cosmonauts aboard Mir noticed that three of the eight thermal blankets on the descent module of the approaching Soyuz-TM 9 spacecraft had come loose from their attachments near the heat shield, yet remained attached at their top ends... , and in 1990 made the similar journey on Soyuz TM-15 Soyuz TM-15 -Crew:-Mission highlights:15th expedition to Mir. Included astronaut Michel Tognini from France.Michel Tognini, passenger aboard Soyuz- TM 15, was the third Frenchman to visit a space station. He conducted ten experiments using 300 kg of equipment delivered by Progress-M flights. Tognini spent... . In 1995 he got to Mir on Space Shuttle Space Shuttle The Space Shuttle was a manned orbital rocket and spacecraft system operated by NASA on 135 missions from 1981 to 2011. The system combined rocket launch, orbital spacecraft, and re-entry spaceplane with modular add-ons... STS-71 STS-71 STS-71 was the third mission of the US/Russian Shuttle-Mir Program, which carried out the first Space Shuttle docking to Mir, a Russian space station. The mission used Space Shuttle Atlantis, which lifted off from launch pad 39A on 27 June 1995 from Kennedy Space Center, Florida... and went back on Soyuz TM-21 Soyuz TM-21 Soyuz TM-21 was Soyuz mission, a human spaceflight mission transporting personnel to the Russian space station Mir. Part of the US/Russian Shuttle-Mir Program, the mission launched from Baikonur Cosmodrome, atop a Soyuz-U2 carrier rocket, at 06:11:34 UTC on March 14, 1995... , and in 1997-98 again traveled to Mir and back on Soyuz TM-26 Soyuz TM-26 Soyuz TM-26 is a Russian spacecraft that ferried cosmonauts and supplies to the Mir, the Russian space station. It was the 32nd expedition to Mir. It was launched by a Soyuz-U rocket from Baikonur Cosmodrome on August 5, 1997... . |
 |
|
| Mikhail Somov Mikhail Somov Mikhail Mikhailovich Somov was a Soviet oceanologist, polar explorer, Doctor of Geographical Sciences .... (1908–1973)  Russian Empire Russian Empire Soviet Union Soviet Uniongeographer, oceanologist, Hero of the Soviet Union Hero of the Soviet Union The title Hero of the Soviet Union was the highest distinction in the Soviet Union, awarded personally or collectively for heroic feats in service to the Soviet state and society.-Overview:... , Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... and Antarctic Antarctic The Antarctic is the region around the Earth's South Pole, opposite the Arctic region around the North Pole. The Antarctic comprises the continent of Antarctica and the ice shelves, waters and island territories in the Southern Ocean situated south of the Antarctic Convergence... explorer |
Mikhail Somov graduated from the Moscow Hydrometeorological Institute in 1937. In 1939, he was appointed senior researcher at the Arctic and Antarctic Research Institute Arctic and Antarctic Research Institute The Arctic and Antarctic Research Institute, or AARI is the oldest and largest Russian research institute in the field of comprehensive studies of Arctic and Antarctica... . In 1950-51, Mikhail Somov headed a second Soviet drifting ice station Soviet and Russian manned drifting ice stations Soviet and Russian manned drifting ice stations are important contributors to exploration of the Arctic. The stations are named North Pole Soviet and Russian manned drifting ice stations are important contributors to exploration of the Arctic. The stations are named North Pole Soviet and... North Pole-2. In 1955-57, he became a leader of the 1st Soviet Antarctic Expedition 1st Soviet Antarctic Expedition The First Soviet Antarctic Expedition was led by Mikhail Somov; his scientific deputy was V. G. Kort. The expedition lasted from 30 November 1955 to 1957 and involved 127 expedition members and 75 crew members.... on icebreaker Icebreaker An icebreaker is a special-purpose ship or boat designed to move and navigate through ice-covered waters. Although the term usually refers to ice-breaking ships, it may also refer to smaller vessels .For a ship to be considered an icebreaker, it requires three traits most... s Ob Ob River The Ob River , also Obi, is a major river in western Siberia, Russia and is the world's seventh longest river. It is the westernmost of the three great Siberian rivers that flow into the Arctic Ocean .The Gulf of Ob is the world's longest estuary.-Names:The Ob is known to the Khanty people as the... and Lena Lena River The Lena is the easternmost of the three great Siberian rivers that flow into the Arctic Ocean . It is the 11th longest river in the world and has the 9th largest watershed... . The expedition established the first Soviet Antarctic station, Mirny Mirny Station Mirny is a Russian science station in Antarctica, located on the Antarctic coast of the Davis Sea in the Australian Antarctic Territory. Named after support vessel of the Bellingshausen's expedition.... , performed some observations and reconnaissance, and researched oceanography of the Indian ocean Indian Ocean The Indian Ocean is the third largest of the world's oceanic divisions, covering approximately 20% of the water on the Earth's surface. It is bounded on the north by the Indian Subcontinent and Arabian Peninsula ; on the west by eastern Africa; on the east by Indochina, the Sunda Islands, and... . Somov was also the first Soviet delegate to the international Scientific Committee for Antarctic Research. A glacier Glacier A glacier is a large persistent body of ice that forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. At least 0.1 km² in area and 50 m thick, but often much larger, a glacier slowly deforms and flows due to stresses induced by its weight... in East Antarctica East Antarctica East Antarctica, also called Greater Antarctica, constitutes the majority of the Antarctic continent, lying on the Indian Ocean side of the Transantarctic Mountains... (Queen Maud Land Queen Maud Land Queen Maud Land is a c. 2.7 million-square-kilometre region of Antarctica claimed as a dependent territory by Norway. The territory lies between 20° west and 45° east, between the British Antarctic Territory to the west and the Australian Antarctic Territory to the east. The latitudinal... ), a scientific icebreaker Icebreaker An icebreaker is a special-purpose ship or boat designed to move and navigate through ice-covered waters. Although the term usually refers to ice-breaking ships, it may also refer to smaller vessels .For a ship to be considered an icebreaker, it requires three traits most... and a minor planet Minor planet An asteroid group or minor-planet group is a population of minor planets that have a share broadly similar orbits. Members are generally unrelated to each other, unlike in an asteroid family, which often results from the break-up of a single asteroid... 3334 Somov 3334 Somov 3334 Somov is a main-belt asteroid discovered on December 20, 1981 by A. Mrkos at Klet.- External links :*... bear Somov's name. |
||
| Mikhail Stadukhin Mikhail Stadukhin Mikhail Vasilyevich Stadukhin was a Russian explorer of far northeast Siberia, one of the first to reach the Kolyma, Anadyr, Penzhina and Gizhiga Rivers and the northern Sea of Okhotsk. He was a Pomor, probably born in the village of Pinega, and the nephew of a Moscow merchant... (?–1666) Tsardom of Russia Tsardom of Russia The Tsardom of Russia was the name of the centralized Russian state from Ivan IV's assumption of the title of Tsar in 1547 till Peter the Great's foundation of the Russian Empire in 1721.From 1550 to 1700, Russia grew 35,000 km2 a year... Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... n cossack Cossack Cossacks are a group of predominantly East Slavic people who originally were members of democratic, semi-military communities in what is today Ukraine and Southern Russia inhabiting sparsely populated areas and islands in the lower Dnieper and Don basins and who played an important role in the... leader, explorer of the north-eastern Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... and the Russian Far East Russian Far East Russian Far East is a term that refers to the Russian part of the Far East, i.e., extreme east parts of Russia, between Lake Baikal in Eastern Siberia and the Pacific Ocean... |
In 1633 Stadukhin came to the Lena River Lena River The Lena is the easternmost of the three great Siberian rivers that flow into the Arctic Ocean . It is the 11th longest river in the world and has the 9th largest watershed... and then to Indigirka. With Semyon Dezhnyov he led a group to the Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... coast and then to the east. They discovered Kolyma River Kolyma River The Kolyma River is a river in northeastern Siberia, whose basin covers parts of the Sakha Republic, Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, and Magadan Oblast of Russia. Itrises in the mountains north of Okhotsk and Magadan, in the area of and... and founded Srednekolymsk Srednekolymsk Srednekolymsk is a town and the administrative center of Srednekolymsky District of the Sakha Republic, Russia, located northeast of Yakutsk on the left bank of the Kolyma River. Population: -History:... there in 1643. In 1649 he followed by Arctic Ocean Arctic Ocean The Arctic Ocean, located in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Arctic north polar region, is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceanic divisions... the traces of Dezhnyov's and Fedot Alekseyev Fedot Alekseyev Popov Fedot Alekseyevich Popov , date of birth unknown, died between 1648 and 1654) was a Russian explorer who organized the first European expedition through the Bering Strait.He was normally known as Fedot Alekseyev. Only a few sources call him the son of Popov... 's expedition to the east, which started earlier in 1648 (and reached the Bering Strait Bering Strait The Bering Strait , known to natives as Imakpik, is a sea strait between Cape Dezhnev, Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, Russia, the easternmost point of the Asian continent and Cape Prince of Wales, Alaska, USA, the westernmost point of the North American continent, with latitude of about 65°40'N,... ). He learned from the captive natives that two of Dezhnyov's koches Koch (boat) The Koch was a special type of small one or two mast wooden sailing ships designed and used in Russia for transpolar voyages in ice conditions of the Arctic seas, popular among the Pomors.... had been wrecked and the crews killed by the natives. Facing shortages in provision, Stadukhin returned to Srednekolymsk Srednekolymsk Srednekolymsk is a town and the administrative center of Srednekolymsky District of the Sakha Republic, Russia, located northeast of Yakutsk on the left bank of the Kolyma River. Population: -History:... . Later he found the connection of Kolyma Kolyma The Kolyma region is located in the far north-eastern area of Russia in what is commonly known as Siberia but is actually part of the Russian Far East. It is bounded by the East Siberian Sea and the Arctic Ocean in the north and the Sea of Okhotsk to the south... watershed to that of Anadyr Anadyr River Anadyr is a river in the far northeast Siberia which flows into Anadyr Bay of the Bering Sea and drains much of the interior of Chukotka Autonomous Okrug. Its basin corresponds to the Anadyrsky District of Chukotka.... and thus explored the land way to Chukotka Chukchi Peninsula The Chukchi Peninsula, Chukotka Peninsula or Chukotski Peninsula , at about 66° N 172° W, is the northeastern extremity of Asia. Its eastern end is at Cape Dezhnev near the village of Uelen. It is bordered by the Chukchi Sea to the north, the Bering Sea to the south, and the Bering Strait to the... . On Anadyr Anadyr River Anadyr is a river in the far northeast Siberia which flows into Anadyr Bay of the Bering Sea and drains much of the interior of Chukotka Autonomous Okrug. Its basin corresponds to the Anadyrsky District of Chukotka.... he found Dezhnyov in 1650. In 1651 he set off south and discovered the Penzhin Bay of northern Okhotsk Sea. He also may have explored the western shores of Kamchatka. |
 |
|
| Georg Wilhelm Steller Georg Wilhelm Steller Georg Wilhelm Steller was a German botanist, zoologist, physician and explorer, who worked in Russia and is considered the discoverer of Alaska and a pioneer of Alaskan natural history.-Biography:... (1709–1746)  Holy Roman Empire Holy Roman Empire Russian Empire Russian Empirebotanist, zoologist, physician, explorer of the Russian Far East Russian Far East Russian Far East is a term that refers to the Russian part of the Far East, i.e., extreme east parts of Russia, between Lake Baikal in Eastern Siberia and the Pacific Ocean... and Alaska Alaska Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait... |
In 1734 Steller, a naturalist, moved from Bavaria Bavaria Bavaria, formally the Free State of Bavaria is a state of Germany, located in the southeast of Germany. With an area of , it is the largest state by area, forming almost 20% of the total land area of Germany... to Russia to work at the Saint Petersburg Academy of Sciences. Steller traveled trough Siberia, researching its nature, and in 1740 reached Okhotsk Okhotsk Okhotsk is an urban locality and a seaport at the mouth of the Okhota River on the Sea of Okhotsk, in Okhotsky District, Khabarovsk Krai, Russia. Population: 4,470 ;... and Kamchatka. He joined Vitus Bering Vitus Bering Vitus Jonassen Bering Vitus Jonassen Bering Vitus Jonassen Bering (also, less correNavy]], a captain-komandor known among the Russian sailors as Ivan Ivanovich. He is noted for being the first European to discover Alaska and its Aleutian Islands... on the voyage to North America North America North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas... . The expedition landed in Alaska Alaska Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait... at Kayak Island Kayak Island Kayak Island , which includes the Bering Expedition Landing Site, is located in the Gulf of Alaska, 100 km SE of Cordova, Alaska Malaspina Coastal Plain. It has a land area of 73.695 km² and no population.... in 1741, staying only long enough to take on fresh water. During this time Steller became the first European naturalist to describe a number of North American plants and animals, including the Steller's Jay Steller's Jay The Steller's Jay is a jay native to western North America, closely related to the Blue Jay found in the rest of the continent, but with a black head and upper body. It is also known as the Long-crested Jay, Mountain Jay, and Pine Jay... . On the return journey the expedition was shipwrecked on Bering Island Bering Island Bering Island is located off the Kamchatka Peninsula in the Bering Sea. At long by wide, it is the largest of the Commander Islands with the area of .... . Here Bering died, and almost half of the crew perished from scurvy Scurvy Scurvy is a disease resulting from a deficiency of vitamin C, which is required for the synthesis of collagen in humans. The chemical name for vitamin C, ascorbic acid, is derived from the Latin name of scurvy, scorbutus, which also provides the adjective scorbutic... . Despite the hardships, Steller studied the flora and fauna of the island in great detail. He collected the only existing detailed observations of the now extinct Steller sea cow, a large sirenian mammal. In the spring the crew constructed a new vessel and returned to Kamchatka, where Steller continued his research. He died on the journey to St. Petersburg, but his journals were published by Peter Simon Pallas Peter Simon Pallas Peter Simon Pallas was a German zoologist and botanist who worked in Russia.- Life and work :Pallas was born in Berlin, the son of Professor of Surgery Simon Pallas. He studied with private tutors and took an interest in natural history, later attending the University of Halle and the University... and were later used by other explorers, including Captain Cook. Steller's Jay Steller's Jay The Steller's Jay is a jay native to western North America, closely related to the Blue Jay found in the rest of the continent, but with a black head and upper body. It is also known as the Long-crested Jay, Mountain Jay, and Pine Jay... , Steller's (or Northern) Sea Lion Steller's Sea Lion The Steller sea lion also known as the northern sea lion, is a threatened species of sea lion in the northern Pacific. It is the sole member of the genus Eumetopias and the largest of the eared seals . Among pinnipeds, it is inferior in size only to the walrus and the two elephant seals... , Steller's Sea Cow Steller's Sea Cow Steller's sea cow was a large herbivorous marine mammal. In historical times, it was the largest member of the order Sirenia, which includes its closest living relative, the dugong , and the manatees... , Steller's Eider Steller's Eider The Steller's Eider is a medium-large sea duck that breeds along the Arctic coasts of eastern Siberia and Alaska. The lined nest is built on tundra close to the sea, and 6-10 eggs are laid.... , the marine cryptid Cryptid In cryptozoology and sometimes in cryptobotany, a cryptid is a creature or plant whose existence has been suggested but is unrecognized by scientific consensus and often regarded as highly unlikely. Famous examples include the Yeti in the Himalayas and the Loch Ness Monster in... Steller's Sea Ape (never sighted by anyone but Steller), Steller's Sea Eagle Steller's Sea Eagle The Steller's Sea Eagle, Haliaeetus pelagicus, is a large bird of prey in the family Accipitridae. It lives in coastal northeastern Asia and mainly preys on fish. It is, on average, the heaviest eagle in the world, at about , but often lags behind the Harpy Eagle and Philippine Eagle in other... and other animals have been named after Steller. |
  |
|
| Anikey Stroganov Anikey Stroganov Anikey Stroganov was a founder of numerous salterns in Solvychegodsk and Perm, a colonizer of the basin of the Kama and Chusovaya Rivers. He was the progenitor of the family of highly successful Russian merchants, industrialists, landowners, and statesmen.Anikey Stroganov was the fourth and... (1488–1570) Grand Duchy of Moscow Grand Duchy of Moscow The Grand Duchy of Moscow or Grand Principality of Moscow, also known in English simply as Muscovy , was a late medieval Rus' principality centered on Moscow, and the predecessor state of the early modern Tsardom of Russia.... Tsardom of Russia Tsardom of Russia The Tsardom of Russia was the name of the centralized Russian state from Ivan IV's assumption of the title of Tsar in 1547 till Peter the Great's foundation of the Russian Empire in 1721.From 1550 to 1700, Russia grew 35,000 km2 a year... rich merchant and landowner, colonizer of Perm Krai Perm Krai Perm Krai is a federal subject of Russia that came into existence on December 1, 2005 as a result of the 2004 referendum on the merger of Perm Oblast and Komi-Permyak Autonomous Okrug. The city of Perm became the administrative center of the new federal subject... and Urals |
Anikey Stroganov was a progenitor of the famous Stroganovs Stroganovs The Stroganovs or Strogonovs , also spelled in French manner as Stroganoffs, were a family of highly successful Russian merchants, industrialists, landowners, and statesmen of the 16th – 20th centuries who eventually earned nobility.-Origins:... family of highly successful Russian merchant Merchant A merchant is a businessperson who trades in commodities that were produced by others, in order to earn a profit.Merchants can be one of two types:# A wholesale merchant operates in the chain between producer and retail merchant... s, industrialists, landowners, and statesmen. He was a founder of numerous saltern Saltern Saltern is a word with a number of differing meanings. In English archaeology, a saltern is an area used for salt making, especially in the East Anglian fenlands.... s in Solvychegodsk Solvychegodsk Solvychegodsk is a town in the southern part of Arkhangelsk Oblast, Russia, located on the right-hand bank of the Vychegda River northeast of Kotlas. Administratively, it is a part of Kotlassky District. Municipally, it is incorporated as Solvychegodskoye Urban Settlement of Kotlassky Municipal... , Kola Peninsula Kola Peninsula The Kola Peninsula is a peninsula in the far northwest of Russia. Constituting the bulk of the territory of Murmansk Oblast, it lies almost completely to the north of the Arctic Circle and is washed by the Barents Sea in the north and the White Sea in the east and southeast... and Perm Perm Perm is a city and the administrative center of Perm Krai, Russia, located on the banks of the Kama River, in the European part of Russia near the Ural Mountains. From 1940 to 1957 it was named Molotov .... . He colonized the basin Drainage basin A drainage basin is an extent or an area of land where surface water from rain and melting snow or ice converges to a single point, usually the exit of the basin, where the waters join another waterbody, such as a river, lake, reservoir, estuary, wetland, sea, or ocean... of the Kama Kama River Kama is a major river in Russia, the longest left tributary of the Volga and the largest one in discharge; in fact, it is larger than the Volga before junction.... and Chusovaya Rivers. In the beginning of the reign of Tsar Tsar Tsar is a title used to designate certain European Slavic monarchs or supreme rulers. As a system of government in the Tsardom of Russia and Russian Empire, it is known as Tsarist autocracy, or Tsarism... Ivan IV he received the right to control the trade with English England England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental... merchants, traveling from Arkhangelsk Arkhangelsk Arkhangelsk , formerly known as Archangel in English, is a city and the administrative center of Arkhangelsk Oblast, Russia. It lies on both banks of the Northern Dvina River near its exit into the White Sea in the north of European Russia. The city spreads for over along the banks of the river... to Moscow Moscow Moscow is the capital, the most populous city, and the most populous federal subject of Russia. The city is a major political, economic, cultural, scientific, religious, financial, educational, and transportation centre of Russia and the continent... . Stroganov established trade routes with Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... n tribes. Tsar Ivan granted large estates near the Urals as well as tax privileges to Stroganovs, and they organized large scale migration to their new lands. They developed farming, hunting Hunting Hunting is the practice of pursuing any living thing, usually wildlife, for food, recreation, or trade. In present-day use, the term refers to lawful hunting, as distinguished from poaching, which is the killing, trapping or capture of the hunted species contrary to applicable law... , saltworks, fishing Fishing Fishing is the activity of trying to catch wild fish. Fish are normally caught in the wild. Techniques for catching fish include hand gathering, spearing, netting, angling and trapping.... , and ore mining Mining Mining is the extraction of valuable minerals or other geological materials from the earth, from an ore body, vein or seam. The term also includes the removal of soil. Materials recovered by mining include base metals, precious metals, iron, uranium, coal, diamonds, limestone, oil shale, rock... . They built new towns and fortresses and annexed new lands in the Urals and Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... in favor of Russia Russia Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects... . |
 |
|
| Semyon Stroganov Semyon Stroganov Semyon Stroganov was a Russian merchant from the family of Stroganov who financed Yermak's Siberian campaign in 1581.Semyon was the younger son of Anikey Stroganov. His date of birth is unknown, but most likely he reached adulthood before 1559... (?–1586) Grand Duchy of Moscow Grand Duchy of Moscow The Grand Duchy of Moscow or Grand Principality of Moscow, also known in English simply as Muscovy , was a late medieval Rus' principality centered on Moscow, and the predecessor state of the early modern Tsardom of Russia.... Tsardom of Russia Tsardom of Russia The Tsardom of Russia was the name of the centralized Russian state from Ivan IV's assumption of the title of Tsar in 1547 till Peter the Great's foundation of the Russian Empire in 1721.From 1550 to 1700, Russia grew 35,000 km2 a year... rich merchant and landowner, coloniser of the Urals and Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... |
Semyon was the younger son of Anikey Stroganov Anikey Stroganov Anikey Stroganov was a founder of numerous salterns in Solvychegodsk and Perm, a colonizer of the basin of the Kama and Chusovaya Rivers. He was the progenitor of the family of highly successful Russian merchants, industrialists, landowners, and statesmen.Anikey Stroganov was the fourth and... . After the death of his father in 1570, Semyon quarreled with his brothers. Initially he was deprived of family wealth, however after the deaths of his brothers he received an appropriate part. He is most famous for the fact that together with his nephews he sponsored and prepared Yermak's expedition to conquer Siberia Khanate Siberia Khanate The Khanate of Sibir were the patrilineal descendants of Shayban , the fifth son of Jochi and grandson of Genghis Khan. The Khanate had an ethnically diverse population of Siberian Tatars, Khanty, Mansi, Nenets and Selkup people. Along with the Khanate of Kazan it was the northernmost Muslim state.... in 1581-85. After the success of Yermak and his followers, the Tsar Tsar Tsar is a title used to designate certain European Slavic monarchs or supreme rulers. As a system of government in the Tsardom of Russia and Russian Empire, it is known as Tsarist autocracy, or Tsarism... granted new Siberian lands to the Stroganovs. |
 |
T
| Portrait | Person | Achievements | Image |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
Vasily Tatishchev Vasily Tatishchev Vasily Nikitich Tatishchev was a prominent Russian statesman, and ethnographer, best remembered as the author of the first full-scale Russian history... (1686–1750) Tsardom of Russia Tsardom of Russia The Tsardom of Russia was the name of the centralized Russian state from Ivan IV's assumption of the title of Tsar in 1547 till Peter the Great's foundation of the Russian Empire in 1721.From 1550 to 1700, Russia grew 35,000 km2 a year...  Russian Empire Russian Empirestatesman, geographer, ethnographer, historian, explorer of European Russia European Russia European Russia refers to the western areas of Russia that lie within Europe, comprising roughly 3,960,000 square kilometres , larger in area than India, and spanning across 40% of Europe. Its eastern border is defined by the Ural Mountains and in the south it is defined by the border with... and the Urals |
In the service of Peter the Great Peter I of Russia Peter the Great, Peter I or Pyotr Alexeyevich Romanov Dates indicated by the letters "O.S." are Old Style. All other dates in this article are New Style. ruled the Tsardom of Russia and later the Russian Empire from until his death, jointly ruling before 1696 with his half-brother, Ivan V... Tatishchev was sent to the Urals and there supervised the works on general geographical description of Russia. Subsequently new Empress Anna entrusted him with a lucrative office of the management of Ural Ural (region) Ural is a geographical region located around the Ural Mountains, between the East European and West Siberian plains. It extends approximately from north to south, from the Arctic Ocean to the bend of Ural River near Orsk city. The boundary between Europe and Asia runs along the eastern side of... factories. At that post he founded the cities of Perm Perm Perm is a city and the administrative center of Perm Krai, Russia, located on the banks of the Kama River, in the European part of Russia near the Ural Mountains. From 1940 to 1957 it was named Molotov .... and Yekaterinburg Yekaterinburg Yekaterinburg is a major city in the central part of Russia, the administrative center of Sverdlovsk Oblast. Situated on the eastern side of the Ural mountain range, it is the main industrial and cultural center of the Urals Federal District with a population of 1,350,136 , making it Russia's... , which have since grown into the veritable capitals of Ural. Tatischev finished his career as a governor of Astrakhan Astrakhan Astrakhan is a major city in southern European Russia and the administrative center of Astrakhan Oblast. The city lies on the left bank of the Volga River, close to where it discharges into the Caspian Sea at an altitude of below the sea level. Population:... (1741–44) and dedicated himself to Russian geography and historiography Historiography Historiography refers either to the study of the history and methodology of history as a discipline, or to a body of historical work on a specialized topic... . He discovered and published several documents of great interest, e.g., Russkaya Pravda Russkaya Pravda Russkaya Pravda was the legal code of Kievan Rus' and the subsequent Rus' principalities during the times of feudal division.In spite of great influence of Byzantine legislation on the contemporary world, and in... and Sudebnik Sudebnik Sudebnik of 1497 , a collection of laws, which was introduced by Ivan III and played a big part in the centralisation of the Russian state, creation of the nationwide Russian Law and elimination of feudal division.... of 1550. His magnum opus Masterpiece Masterpiece in modern usage refers to a creation that has been given much critical praise, especially one that is considered the greatest work of a person's career or to a work of outstanding creativity, skill or workmanship.... was the first sketch of Russian history, entitled Russian History Dating Back to the Most Ancient Times. He also compiled the first encyclopedic dictionary Dictionary A dictionary is a collection of words in one or more specific languages, often listed alphabetically, with usage information, definitions, etymologies, phonetics, pronunciations, and other information; or a book of words in one language with their equivalents in another, also known as a lexicon... of the Russian language Russian language Russian is a Slavic language used primarily in Russia, Belarus, Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan, Tajikistan and Kyrgyzstan. It is an unofficial but widely spoken language in Ukraine, Moldova, Latvia, Turkmenistan and Estonia and, to a lesser extent, the other countries that were once constituent republics... . A settlement and a district Tatishchevsky District Tatishchevsky District is a district in Saratov Oblast, Russia . Named after historiographer and state figure V. N. Tatischev... was named in his honour in Saratov Oblast Saratov Oblast Saratov Oblast is a federal subject of Russia , located in the Volga Federal District. Its administrative center is the city of Saratov. Population: -Demographics:Population:... . |
.jpg) |
| Mikhail Tebenkov Mikhail Tebenkov Mikhail Dmitriyevich Tebenkov, spelt Tebenkof in the United States , was a Russian hydrographer and vice admiral of the Imperial Russian Navy... (1802–1872)  Russian Empire Russian EmpireRussian Imperial Navy officer, Vice Admiral Vice Admiral Vice admiral is a senior naval rank of a three-star flag officer, which is equivalent to lieutenant general in the other uniformed services. A vice admiral is typically senior to a rear admiral and junior to an admiral... , hydrographer, explorer of Alaska Alaska Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait... |
Tebenkov surveyed Norton Sound Norton Sound Norton Sound is an inlet of the Bering Sea on the western coast of the U.S. state of Alaska, south of the Seward Peninsula. It is about 240 km long and 200 km wide. The Yukon River delta forms a portion of the south shore and water from the Yukon influences this body of water... on behalf of the Russian Imperial Hydrographic Service in 1831 and was the first European to sight the bay that now bears his name. In 1845-50 he was the director of the Russian American Company and the governor of Russian America. Tebenkov created a detailed atlas of the western shores of Alaska Alaska Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait... , published in 1852. A bay, a glacier, a mount and a point on Alaska Alaska Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait... have been named after Tebenkov. |
 |
|
 |
Valentina Tereshkova Valentina Tereshkova Valentina Vladimirovna Tereshkova is a retired Soviet cosmonaut, and was the first woman in space. She was selected out of more than four hundred applicants, and then out of five finalists, to pilot Vostok 6 on the 16 June, 1963, becoming both the first woman and the first civilian to fly in... (born 1937)  Soviet Union Soviet Union Russia Russiafemale cosmonaut, Hero of the Soviet Union Hero of the Soviet Union The title Hero of the Soviet Union was the highest distinction in the Soviet Union, awarded personally or collectively for heroic feats in service to the Soviet state and society.-Overview:... , Major General Major General Major general or major-general is a military rank used in many countries. It is derived from the older rank of sergeant major general. A major general is a high-ranking officer, normally subordinate to the rank of lieutenant general and senior to the ranks of brigadier and brigadier general... , politician and public figure |
Aboard Vostok 6 Vostok 6 -Backup crew:-Reserve crew:Vostok VI-Mission parameters:*Mass: *Apogee: *Perigee: *Inclination: 64.9°*Period: 87.8 minutes9090... on 16 June 1963 Tereshkova became the first woman as well as the first civilian to travel into space. On this mission, lasting almost three days in space, she performed various tests on herself to collect data on the female body's reaction to spaceflight. She also maintained a flight log and took photographs of the horizon Horizon The horizon is the apparent line that separates earth from sky, the line that divides all visible directions into two categories: those that intersect the Earth's surface, and those that do not. At many locations, the true horizon is obscured by trees, buildings, mountains, etc., and the resulting... , which were later used to identify aerosol Aerosol Technically, an aerosol is a suspension of fine solid particles or liquid droplets in a gas. Examples are clouds, and air pollution such as smog and smoke. In general conversation, aerosol usually refers to an aerosol spray can or the output of such a can... layers within the atmosphere Atmosphere An atmosphere is a layer of gases that may surround a material body of sufficient mass, and that is held in place by the gravity of the body. An atmosphere may be retained for a longer duration, if the gravity is high and the atmosphere's temperature is low... . Tereshkova crater Tereshkova (crater) Tereshkova is a relatively small lunar impact crater on the far side of the Moon. It is located along the western perimeter of the Mare Moscoviense, and to the southeast of the crater Feoktistov. It is named for cosmonaut Valentina Tereshkova, the first woman in space.The rim of this crater... on the far side of the Moon Moon The Moon is Earth's only known natural satellite,There are a number of near-Earth asteroids including 3753 Cruithne that are co-orbital with Earth: their orbits bring them close to Earth for periods of time but then alter in the long term . These are quasi-satellites and not true moons. For more... and minor planet Minor planet An asteroid group or minor-planet group is a population of minor planets that have a share broadly similar orbits. Members are generally unrelated to each other, unlike in an asteroid family, which often results from the break-up of a single asteroid... 1671 Chaika (her call sign in the flight, meaning seagull), as well as many streets and other places have been named after Valentina Tereshkova. |
|
| Aleksey Tillo (1839–1900)  Russian Empire Russian Empiregeographer, cartographer, land surveyor, lieutenant general Lieutenant General Lieutenant General is a military rank used in many countries. The rank traces its origins to the Middle Ages where the title of Lieutenant General was held by the second in command on the battlefield, who was normally subordinate to a Captain General.... of the Russian Imperial Army, explorer of European Russia European Russia European Russia refers to the western areas of Russia that lie within Europe, comprising roughly 3,960,000 square kilometres , larger in area than India, and spanning across 40% of Europe. Its eastern border is defined by the Ural Mountains and in the south it is defined by the border with... |
Tillo created the first correct hypsometric Cartographic relief depiction Terrain or relief is an essential aspect of physical geography, and as such its portrayal presents a central problem in cartography, and more recently GIS and 3D Visualization.... map of European Russia European Russia European Russia refers to the western areas of Russia that lie within Europe, comprising roughly 3,960,000 square kilometres , larger in area than India, and spanning across 40% of Europe. Its eastern border is defined by the Ural Mountains and in the south it is defined by the border with... , published in 1889. He is known to have coined the term Central Russian Upland Central Russian Upland Central Russian Upland is an area of approximately 200,000 miles² in Southern European Russia and Northeast of Ukraine, located inside East European Plain.... . Also, he measured the length of the main Russian rivers and conducted work on level difference of Caspian Sea Caspian Sea The Caspian Sea is the largest enclosed body of water on Earth by area, variously classed as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. The sea has a surface area of and a volume of... and Sea of Aral. He authored a number of works on geomagnetism and meteorology Meteorology Meteorology is the interdisciplinary scientific study of the atmosphere. Studies in the field stretch back millennia, though significant progress in meteorology did not occur until the 18th century. The 19th century saw breakthroughs occur after observing networks developed across several countries... . The Tillo Islands Tillo Islands The Tillo Islands is a group of small islands covered with tundra vegetation. They stretch along the Kara Sea coastal region, right off the bleak coast of Siberia's Taymyr Peninsula. Most of the islands of the group are a mere 3 or 4 km from the continental shore.The largest island of the... in the Kara Sea Kara Sea The Kara Sea is part of the Arctic Ocean north of Siberia. It is separated from the Barents Sea to the west by the Kara Strait and Novaya Zemlya, and the Laptev Sea to the east by the Severnaya Zemlya.... and an island near Wilczek Land Wilczek Land Wilczek Land , is a large-sized island located at . It is a part of Franz Josef Land, Russia.Wilczek Land is the second largest island of the Franz Josef Archipelago. It is almost completely glaciarized except for two narrow areas along its western shores. The highest point on the island is 606... in Franz Josef Land Franz Josef Land Franz Josef Land, Franz Joseph Land, or Francis Joseph's Land is an archipelago located in the far north of Russia. It is found in the Arctic Ocean north of Novaya Zemlya and east of Svalbard, and is administered by Arkhangelsk Oblast. Franz Josef Land consists of 191 ice-covered islands with a... , were named after Tillo. |
||
| Gherman Titov Gherman Titov Gherman Stepanovich Titov was a Soviet cosmonaut who, on August 6, 1961, became the second human to orbit the Earth aboard Vostok 2, preceded by Yuri Gagarin on Vostok 1... (1935–2000)  Soviet Union Soviet Union Russia Russiacosmonaut, Hero of the Soviet Union Hero of the Soviet Union The title Hero of the Soviet Union was the highest distinction in the Soviet Union, awarded personally or collectively for heroic feats in service to the Soviet state and society.-Overview:... |
Aboard Vostok 2 Vostok 2 Vostok 2 was a Soviet space mission which carried cosmonaut Gherman Titov into orbit for a full day in order to study the effects of a more prolonged period of weightlessness on the human body... on August 6, 1961, Titov became the fourth man in space after Yury Gagarin, Alan Shepard Alan Shepard Alan Bartlett Shepard, Jr. was an American naval aviator, test pilot, flag officer, and NASA astronaut who in 1961 became the second person, and the first American, in space. This Mercury flight was designed to enter space, but not to achieve orbit... and Gus Grissom Gus Grissom Virgil Ivan Grissom , , better known as Gus Grissom, was one of the original NASA Project Mercury astronauts and a United States Air Force pilot... , and the second man to orbit the Earth, the first to do it multiple times (a total of 17), the first to spent more than a day in space, and the first person to drive a spaceship manually. He also was the first person to sleep in space and to suffer from space sickness. He made the first manual photographs from orbit, thus setting a record for modern space photography. A month short of 26 years old at launch, until this day he remains the youngest person to fly in space. A crater Titov (crater) Titov is a relatively small lunar impact crater on the far side of the Moon. The most unusual aspect of this crater is that it is located entirely within the Mare Moscoviense, one of the few maria found on the far side of the Moon. It lies to the northwest of the crater Komarov, in the northern... on the far side of the Moon and an island in Halong Bay Halong Bay Ha Long Bay is a UNESCO World Heritage Site, and a popular travel destination, located in Quang Ninh province, Vietnam. Administratively, the bay belongs to Hạ Long City, Cẩm Phả town, and part of Van Don district. The bay features thousands of limestone karsts and isles in various sizes and shapes... are named after Titov. |
||
| Eduard Toll Eduard Toll Eduard Gustav von Toll was a Baltic German geologist and Arctic explorer in Russian service. Often referred to as Baron von Toll or as Eduard v. Toll, in Russia he is known as Eduard Vasiliyevich Toll . Eduard Toll was born on and he died in 1902 in an unknown location in the Arctic Ocean)... (1858–1902)  Russian Empire Russian Empire(born in Estonia Estonia Estonia , officially the Republic of Estonia , is a state in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea, to the south by Latvia , and to the east by Lake Peipsi and the Russian Federation . Across the Baltic Sea lies... , Baltic German Baltic German The Baltic Germans were mostly ethnically German inhabitants of the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea, which today form the countries of Estonia and Latvia. The Baltic German population never made up more than 10% of the total. They formed the social, commercial, political and cultural élite in... descent) zoologist, paleontologist, geologist, Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... and Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... explorer |
In 1885–86, Baron Toll took part in an expedition of Russian Academy of Sciences Russian Academy of Sciences The Russian Academy of Sciences consists of the national academy of Russia and a network of scientific research institutes from across the Russian Federation as well as auxiliary scientific and social units like libraries, publishers and hospitals.... to the New Siberian Islands New Siberian Islands The New Siberian Islands are an archipelago, located to the North of the East Siberian coast between the Laptev Sea and the East Siberian Sea north of the Sakha Republic.... led by Alexander Bunge. In 1893 Toll led a major academic expedition to Yakutia and explored the region between lower Lena Lena River The Lena is the easternmost of the three great Siberian rivers that flow into the Arctic Ocean . It is the 11th longest river in the world and has the 9th largest watershed... and Khatanga Khatanga River The Khatanga River is a river in Krasnoyarsk Krai in Russia. It begins at the confluence of the rivers Kotuy and Kheta. The Khatanga River is long; the area of its basin is 364,000 km². It flows into the Khatanga Gulf of the Laptev Sea, forming an estuary... , the basins of Yana Yana River The Yana River , is a river in Sakha in Russia, located between the Lena to the west and the Indigirka to the east.It is 872 km in length. The area of its basin is 238,000 km², whilst its annual discharge totals approximately . Most of this discharge occurs in May and June as the ice on the... , Indigirka, and Kolyma Kolyma River The Kolyma River is a river in northeastern Siberia, whose basin covers parts of the Sakha Republic, Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, and Magadan Oblast of Russia. Itrises in the mountains north of Okhotsk and Magadan, in the area of and... , the plateau Plateau In geology and earth science, a plateau , also called a high plain or tableland, is an area of highland, usually consisting of relatively flat terrain. A highly eroded plateau is called a dissected plateau... between the Anabar Anabar River The Anabar River is a river in Sakha, Russia, located just west of the Lena River. Its catchment extends into the Putoran Mountains that form the highest part of the Central Siberian Plateau.... and Popigay Rivers, and the Vasily Pronchischev mountain ridge (named by Toll) between Olenek and Anabar. In 1899, Toll took part in a voyage of the icebreaker Yermak Icebreaker Yermak Yermak was a Russian and later Soviet icebreaker, the first polar icebreaker in the world, having a strengthened hull shaped to ride over and crush pack ice.... to Spitsbergen Spitsbergen Spitsbergen is the largest and only permanently populated island of the Svalbard archipelago in Norway. Constituting the western-most bulk of the archipelago, it borders the Arctic Ocean, the Norwegian Sea and the Greenland Sea... , led by Stepan Makarov Stepan Makarov Stepan Osipovich Makarov was a Ukrainian - born Russian vice-admiral, a highly accomplished and decorated commander of the Imperial Russian Navy, an oceanographer, awarded by the Russian Academy of Sciences, and author of several books. Makarov also designed a small number of ships... . In 1900–02, Toll led an expedition on ship Zarya Zarya (polar ship) Zarya was a steam- and sail-powered brig used by the Russian Academy of Sciences for a polar exploration during 1900–1903.Toward the end of the 19th century, the Russian Academy of Sciences sought to build a general-purpose research vessel for long-term expeditions. The first such Russian... to find the legendary Sannikov Land Sannikov Land Sannikov Land was a phantom island in the Arctic Ocean. Its supposed existence became something of a myth in 19th-century Russia.Yakov Sannikov and Matvei Gedenschtrom claimed to have seen it during their 1809-1810 cartographic expedition to the New Siberian Islands... . Due to severe ice conditions the expedition was forced to spend two winters in the Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... . Toll traveled to Bennett Island Bennett Island Bennett Island is the largest of the islands of the De Long group in the northern part of the East Siberian Sea. The area of this island is approximately 150 km² ... by sledge and kayak with three companions, and they were lost. In 1903 the search led by Mikhail Brusnev Mikhail Brusnev Mikhail Ivanovich Brusnev was a Russian explorer and Bolshevik activist.Mikhail was born 13 January 1864, in Storozhevaia, a stanitsa in the Kuban’. He became active as a revolutionary in 1881. He developed links between students at the St... and Aleksandr Kolchak Aleksandr Kolchak Aleksandr Vasiliyevich Kolchak was a Russian naval commander, polar explorer and later - Supreme ruler . Supreme ruler of Russia , was recognized in this position by all the heads of the White movement, "De jure" - Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes, "De facto" - Entente States... brought out only the diaries and the collections of Toll's party. A bay at the north-west of Taymyr Taymyr Peninsula The Taymyr Peninsula is a peninsula in the Far North of Russia, in the Siberian Federal District, that forms the northernmost part of mainland Eurasia and Asia... , Tollievaya River, a cape on Tsirkul Island Kolosovykh Islands The Kolosovykh Island is a island, in the Kara Sea off the coast of Siberia.This coastal archipelago, is located north of the small Kolosovykh peninsula, which is almost an island itself. This island group is located between 74° 45' and 75° N and between 85° and 87° 30'E... , mountains in Novaya Zemlya Novaya Zemlya Novaya Zemlya , also known in Dutch as Nova Zembla and in Norwegian as , is an archipelago in the Arctic Ocean in the north of Russia and the extreme northeast of Europe, the easternmost point of Europe lying at Cape Flissingsky on the northern island... , the northern cape at Stolbovoy Island Stolbovoy Island Stolbovoy Island is a long and narrow island off the southwest side of the New Siberian archipelago in the eastern part of the Laptev Sea. It is located 184 km away from the Siberian coast and 100 km southwest of Kotelny Island, being thus quite detached from the New Siberian island... , the strait and a plateau at Kotelny Island, the central ice cap of Bennett Island Bennett Island Bennett Island is the largest of the islands of the De Long group in the northern part of the East Siberian Sea. The area of this island is approximately 150 km² ... , and many specimens of fauna and flora are named after Baron Eduard Von Toll. |
||
| Yevgeny Tolstikov Yevgeny Tolstikov Yevgeny Ivanovich Tolstikov was a Soviet polar explorer, awarded by the Hero of the Soviet Union title. He led the Third Soviet Antarctic Expedition and one of the first manned drifting ice station in the Arctic.... (1913–1987)  Russian Empire Russian Empire Soviet Union Soviet Uniongeographer, Hero of the Soviet Union Hero of the Soviet Union The title Hero of the Soviet Union was the highest distinction in the Soviet Union, awarded personally or collectively for heroic feats in service to the Soviet state and society.-Overview:... , Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... and Antarctic Antarctic The Antarctic is the region around the Earth's South Pole, opposite the Arctic region around the North Pole. The Antarctic comprises the continent of Antarctica and the ice shelves, waters and island territories in the Southern Ocean situated south of the Antarctic Convergence... explorer |
Tolstikov was involved in defending the Northern Sea Route Northern Sea Route The Northern Sea Route is a shipping lane officially defined by Russian legislation from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean specifically running along the Russian Arctic coast from Murmansk on the Barents Sea, along Siberia, to the Bering Strait and Far East. The entire route lies in Arctic... during World War II World War II World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis... . In 1954 he was the head of the drifting ice station Soviet and Russian manned drifting ice stations Soviet and Russian manned drifting ice stations are important contributors to exploration of the Arctic. The stations are named North Pole Soviet and Russian manned drifting ice stations are important contributors to exploration of the Arctic. The stations are named North Pole Soviet and... North Pole-3 in the Arctic Ocean Arctic Ocean The Arctic Ocean, located in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Arctic north polar region, is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceanic divisions... . In 1957-59 he became the leader of the 3rd Soviet Antarctic Expedition 3rd Soviet Antarctic Expedition The Third Soviet Antarctic Expedition was led by Yevgeny Tolstikov on the continent; the marine expedition on the Ob was led by I V Maksimov.... and the founder of Sovetskaya Sovetskaya (Antarctic Research Station) Sovetskaya was a Soviet research station in Antarctica at . The surface elevation was initially reported to be 3,570 m; however, it was later revised to 3,662 m. Reached on 16 February 1958 by the 3rd Soviet Antarctic Expedition for International Geophysical Year research work, it closed on 3... and Pole of inaccessibility Pole of inaccessibility (Antarctic research station) Pole of inaccessibility is a now defunct Soviet research station in Antarctica, located near the southern pole of inaccessibility — the point in Antarctica furthest from any ocean. . It performed meteorological observations from 14 December 1958 to 26 December 1958... research stations. This expedition discovered Gamburtsev Mountain Range Gamburtsev Mountain Range The Gamburtsev Mountain Range is a subglacial mountain range located in Eastern Antarctica, near Dome A. The range was discovered by the 3rd Soviet Antarctic Expedition in 1958 and is named for Soviet geophysicist Grigoriy A. Gamburtsev... and other features of Antarctica relief under the ice. He was the chief editor of the general atlas of Antarctic Antarctic The Antarctic is the region around the Earth's South Pole, opposite the Arctic region around the North Pole. The Antarctic comprises the continent of Antarctica and the ice shelves, waters and island territories in the Southern Ocean situated south of the Antarctic Convergence... . A minor planet Minor planet An asteroid group or minor-planet group is a population of minor planets that have a share broadly similar orbits. Members are generally unrelated to each other, unlike in an asteroid family, which often results from the break-up of a single asteroid... 3357 Tolstikov 3357 Tolstikov 3357 Tolstikov is a main-belt asteroid discovered on March 21, 1984 by A. Mrkos at Klet.Was named in honour of Yevgeny Tolstikov.- External links :... is named after Tolstikov. |
 |
|
| Fyodor Ivanovich Tolstoy Fyodor Ivanovich Tolstoy Count Fyodor Ivanovich Tolstoy , also known as the "American" was a Russian nobleman from the well-known Tolstoy family. Possessed of an unusual temper, he became famous for his gambling, his passion for duels, and his voyage to North America, where he earned his nickname... (1782–1846)  Russian Empire Russian Empirenobleman, adventurer, traveler to Alaska Alaska Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait... and around the world |
A count from the well-known Tolstoy Tolstoy Tolstoy, or Tolstoi is a prominent family of Russian nobility, descending from Andrey Kharitonovich Tolstoy who served under Vasily II of Moscow... family, Fyodor Tolstoy was famous for his unusual temper, gambling and passion for duels. In 1803 Tolstoy took part in the first Russian circumnavigation of the world on sloop Sloop-of-war In the 18th and most of the 19th centuries, a sloop-of-war was a warship with a single gun deck that carried up to eighteen guns. As the rating system covered all vessels with 20 guns and above, this meant that the term sloop-of-war actually encompassed all the unrated combat vessels including the... Nadezhda , captained by Ivan Krusenstern. However, multiple quarrels with other members of the team and very bad behaviour, including the successful teaching a pet orangutan Orangutan Orangutans are the only exclusively Asian genus of extant great ape. The largest living arboreal animals, they have proportionally longer arms than the other, more terrestrial, great apes. They are among the most intelligent primates and use a variety of sophisticated tools, also making sleeping... of how to cover the captain's longbook in ink, caused Tolstoy to be abandoned on a stop in Kamchatka with aforementioned ape, whose later fate is unknown. On a different ship Tolstoy managed to get into Sitka, Alaska, where he spent several months among Alaskan natives of the Tlinkit tribe and acquired multiple tattoo Tattoo A tattoo is made by inserting indelible ink into the dermis layer of the skin to change the pigment. Tattoos on humans are a type of body modification, and tattoos on other animals are most commonly used for identification purposes... s. Finally he returned to St Petersburg via Kamchatka and Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... . His voyage to North America North America North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas... earned him nickname the American and a legendary celebrity due to the tales and gossip of his adventures. Tolstoy served as a prototype for a number of characters in the Russian literature Russian literature Russian literature refers to the literature of Russia or its émigrés, and to the Russian-language literature of several independent nations once a part of what was historically Russia or the Soviet Union... , including the duellist Zaretsky in Eugene Onegin Eugene Onegin Eugene Onegin is a novel in verse written by Alexander Pushkin.It is a classic of Russian literature, and its eponymous protagonist has served as the model for a number of Russian literary heroes . It was published in serial form between 1825 and 1832... of Aleksandr Pushkin Aleksandr Pushkin Alexander Sergeyevich Pushkin was a Russian author of the Romantic era who is considered by many to be the greatest Russian poet and the founder of modern Russian literature.... . |
.jpg) |
|
| Alexey Tryoshnikov (1914–1991)  Russian Empire Russian Empire Soviet Union Soviet Uniongeographer, oceanologist, Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... and Antarctic Antarctic The Antarctic is the region around the Earth's South Pole, opposite the Arctic region around the North Pole. The Antarctic comprises the continent of Antarctica and the ice shelves, waters and island territories in the Southern Ocean situated south of the Antarctic Convergence... explorer |
Tryoshnikov was involved in defending the Northern Sea Route Northern Sea Route The Northern Sea Route is a shipping lane officially defined by Russian legislation from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean specifically running along the Russian Arctic coast from Murmansk on the Barents Sea, along Siberia, to the Bering Strait and Far East. The entire route lies in Arctic... during World War II World War II World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis... and participated in the 1948 Soviet expedition to the North Pole North Pole The North Pole, also known as the Geographic North Pole or Terrestrial North Pole, is, subject to the caveats explained below, defined as the point in the northern hemisphere where the Earth's axis of rotation meets its surface... . In 1954-55, he was the leader of the drifting ice station Soviet and Russian manned drifting ice stations Soviet and Russian manned drifting ice stations are important contributors to exploration of the Arctic. The stations are named North Pole Soviet and Russian manned drifting ice stations are important contributors to exploration of the Arctic. The stations are named North Pole Soviet and... North Pole-3 in the Arctic Ocean Arctic Ocean The Arctic Ocean, located in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Arctic north polar region, is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceanic divisions... . In 1956-58 he was a leader of the 2nd 2nd Soviet Antarctic Expedition The Second Soviet Antarctic Expedition was led by Aleksei Treshnikov on the continent; the marine expedition on the "Ob" was led by I. V. Maksimov. The "Ob" left Kaliningrad on 7 November, 1956.... and in 1967-69 he led the 13th Soviet Antarctic Expedition 13th Soviet Antarctic Expedition The 13th Soviet Antarctic Expedition was the Soviet Antarctic Expedition that ran from 1967 to 1969.The leader of the expedition was Aleksei Treshnikov. American scientists on the expedition researched the accessible ice-free locations on the west coast of Enderby Land.-References:* MacNamara, E. E... . During the latter expedition Bellingshausen Station Bellingshausen Station thumb|right|Bellingshausen is one of Antarctica's most polluted places. Old vehicles, rusting barrels and other refuse litter the shorelinethumb|right|Muddy scene around the base. On the hilltop an orthodox church was built in 2004... was founded. Tryoshnikov took part in the creation of the general atlas of Antarctic Antarctic The Antarctic is the region around the Earth's South Pole, opposite the Arctic region around the North Pole. The Antarctic comprises the continent of Antarctica and the ice shelves, waters and island territories in the Southern Ocean situated south of the Antarctic Convergence... and then he was the main editor of the atlas of Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... . He also was the president of the Geographical Society of the USSR Russian Geographical Society The Russian Geographical Society is a learned society, founded on 6 August 1845 in Saint Petersburg, Russia.-Imperial Geographical Society:Prior to the Russian Revolution of 1917, it was known as the Imperial Russian Geographical Society.... since 1977 and the director of the Arctic and Antarctic Research Institute Arctic and Antarctic Research Institute The Arctic and Antarctic Research Institute, or AARI is the oldest and largest Russian research institute in the field of comprehensive studies of Arctic and Antarctica... of the Soviet Union Soviet Union The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991.... in 1960-81. A minor planet Minor planet An asteroid group or minor-planet group is a population of minor planets that have a share broadly similar orbits. Members are generally unrelated to each other, unlike in an asteroid family, which often results from the break-up of a single asteroid... 3339 Treshnikov 3339 Treshnikov 3339 Treshnikov is a main-belt asteroid discovered on June 6, 1978 by A. Mrkos at Klet.- External links :*... and a scientific vessel named after Tryoshnikov. |
 |
|
| Avgust Tsivolko Avgust Tsivolko Avgust Karlovich Tsivolko, also spelled as Tsivolka was a Russian navigator and Arctic explorer.... (1810–1839)  Russian Empire Russian EmpireRussian Imperial Navy officer, hydrographer, Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... explorer |
In 1832-34 Tsivolko participated in the Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... expeditions led by Pyotr Pakhtusov Pyotr Pakhtusov Pyotr Kuzmich Pakhtusov was a Russian surveyor and Arctic explorer. He is credited with the first thorough survey of Novaya Zemlya.... . They made the first reliable maps of Novaya Zemlya's southern shores. It was Tsivolko who first mapped the Matochkin Strait Matochkin Strait Matochkin Strait or Matochkin Shar is a strait between the Severny and Yuzhny Islands of Novaya Zemlya. It connects the Barents Sea and the Kara Sea. The banks along the strait are high and steep. Its length is approximately and its width in its narrowest part is approximately . The strait is... between two main islands of Novaya Zemlya Novaya Zemlya Novaya Zemlya , also known in Dutch as Nova Zembla and in Norwegian as , is an archipelago in the Arctic Ocean in the north of Russia and the extreme northeast of Europe, the easternmost point of Europe lying at Cape Flissingsky on the northern island... . In 1837 he commanded a schooner Schooner A schooner is a type of sailing vessel characterized by the use of fore-and-aft sails on two or more masts with the forward mast being no taller than the rear masts.... Krotov during the Karl Baer Karl Ernst von Baer Karl Ernst Ritter von Baer, Edler von Huthorn also known in Russia as Karl Maksimovich Baer was an Estonian naturalist, biologist, geologist, meteorologist, geographer, a founding father of embryology, explorer of European Russia and Scandinavia, a member of the Russian Academy of Sciences, a... 's expedition to Novaya Zemlya. In 1838 he was sent to map the northern and northeastern shores of Novaya Zemlya, but died from scurvy before this work was completed. A gulf in the Kara Sea Kara Sea The Kara Sea is part of the Arctic Ocean north of Siberia. It is separated from the Barents Sea to the west by the Kara Strait and Novaya Zemlya, and the Laptev Sea to the east by the Severnaya Zemlya.... and a group of islands in the Nordenskiöld Archipelago Nordenskiöld Archipelago The Nordenskiöld Archipelago or Nordenskjold Archipelago is a very large and complex cluster of islands in the eastern region of the Kara Sea. Its eastern limit lies west of the Taymyr Peninsula.... are named after Tsivolko. |
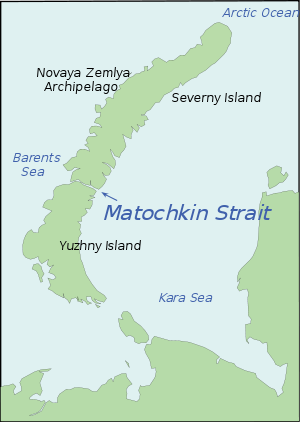 |
|
| Gombojab Tsybikov Gombojab Tsybikov Gombojab Tsybikov , was a Russian explorer of Tibet from 1899 to 1902. Tsybikov specialized in social anthropology, ethnography, Buddhist Studies, and for some time after 1917 was an important educator and statesman in Siberia and Mongolia.... (1873–1930)  Russian Empire Russian Empire Soviet Union Soviet Unionanthropologist, ethnographer, statesmen, explorer of Tibet Tibet Tibet is a plateau region in Asia, north-east of the Himalayas. It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people as well as some other ethnic groups such as Monpas, Qiang, and Lhobas, and is now also inhabited by considerable numbers of Han and Hui people... |
A native Buryat Buryats The Buryats or Buriyads , numbering approximately 436,000, are the largest ethnic minority group in Siberia and are mainly concentrated in their homeland, the Buryat Republic, a federal subject of Russia... , Tsybikov studied in Tomsk and St Petersburg Universities. In 1899-1902 he traveled to Tibet Tibet Tibet is a plateau region in Asia, north-east of the Himalayas. It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people as well as some other ethnic groups such as Monpas, Qiang, and Lhobas, and is now also inhabited by considerable numbers of Han and Hui people... in a group of Buryat Buryats The Buryats or Buriyads , numbering approximately 436,000, are the largest ethnic minority group in Siberia and are mainly concentrated in their homeland, the Buryat Republic, a federal subject of Russia... and Kalmyk Kalmyk people Kalmyk people is the name given to the Oirats, western Mongols in Russia, whose descendants migrated from Dzhungaria in 1607. Today they form a majority in the autonomous Republic of Kalmykia on the western shore of the Caspian Sea. Kalmykia is Europe's only Buddhist government... Bhuddist pilgrims. He became the first photographer of Tibet Tibet Tibet is a plateau region in Asia, north-east of the Himalayas. It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people as well as some other ethnic groups such as Monpas, Qiang, and Lhobas, and is now also inhabited by considerable numbers of Han and Hui people... , taking pictures in secret. These pictures were widely celebrated throughout the world, printed also by the National Geographic in the U. S. In 1904 Tsybikov served as a translator on Russian talks with Dalai Lama Thubten Gyatso, 13th Dalai Lama Thubten Gyatso was the 13th Dalai Lama of Tibet.During 1878 he was recognized as the reincarnation of the Dalai Lama. He was escorted to Lhasa and given his pre-novice vows by the Panchen Lama, Tenpai Wangchuk, and named "Ngawang Lobsang Thupten Gyatso Jigdral Chokley Namgyal"... in Urga, Mongolia Mongolia Mongolia is a landlocked country in East and Central Asia. It is bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south, east and west. Although Mongolia does not share a border with Kazakhstan, its western-most point is only from Kazakhstan's eastern tip. Ulan Bator, the capital and largest... , presenting Dalai Lama with an edition of his pictures. Later Tsybikov published his travelogue with much valuable translations from Tibetan Tibetan language The Tibetan languages are a cluster of mutually-unintelligible Tibeto-Burman languages spoken primarily by Tibetan peoples who live across a wide area of eastern Central Asia bordering the Indian subcontinent, including the Tibetan Plateau and the northern Indian subcontinent in Baltistan, Ladakh,... included. A number of streets in Buryatian settlements and a museum are named after Tsybikov. |
 |
U
| Portrait | Person | Achievements | Image |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ivan Unkovsky (1822–1886)  Russian Empire Russian EmpireRussian Imperial Navy officer, Admiral Admiral Admiral is the rank, or part of the name of the ranks, of the highest naval officers. It is usually considered a full admiral and above vice admiral and below admiral of the fleet . It is usually abbreviated to "Adm" or "ADM"... , circumnavigator, explorer of North Pacific and Japan Japan Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south... |
Unkovsky led a scientific expedition on the frigate Pallada, together with Admiral Yevfimy Putyatin Yevfimy Putyatin Yevfimy Vasilyevich Putyatin was a Russian admiral noted for his diplomatic missions to Japan and China which resulted in the signing of the Treaty of Shimoda in 1855.-Early life:... , through the Atlantic Atlantic Ocean The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's oceanic divisions. With a total area of about , it covers approximately 20% of the Earth's surface and about 26% of its water surface area... , Indian Indian Ocean The Indian Ocean is the third largest of the world's oceanic divisions, covering approximately 20% of the water on the Earth's surface. It is bounded on the north by the Indian Subcontinent and Arabian Peninsula ; on the west by eastern Africa; on the east by Indochina, the Sunda Islands, and... and Pacific Ocean Pacific Ocean The Pacific Ocean is the largest of the Earth's oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, bounded by Asia and Australia in the west, and the Americas in the east.At 165.2 million square kilometres in area, this largest division of the World... s to Japan Japan Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south... in 1852-55. This expedition contributed many important discoveries in oceanography Oceanography Oceanography , also called oceanology or marine science, is the branch of Earth science that studies the ocean... . Described in the book of famous writer Ivan Goncharov Ivan Goncharov Ivan Alexandrovich Goncharov was a Russian novelist best known as the author of Oblomov .- Biography :Ivan Goncharov was born in Simbirsk ; his father was a wealthy grain merchant and respected official who was elected mayor of Simbirsk several times... , who also sailed on Pallada, it was a dangerous voyage since it coincided in time with the Crimean War Crimean War The Crimean War was a conflict fought between the Russian Empire and an alliance of the French Empire, the British Empire, the Ottoman Empire, and the Kingdom of Sardinia. The war was part of a long-running contest between the major European powers for influence over territories of the declining... between Russia and the Franco France The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France... -British United Kingdom The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages... alliance. One of the results achieved was the Treaty of Shimoda Treaty of Shimoda The Treaty of Shimoda of 1855, formally Treaty of Commerce and Navigation between Japan and Russia , was signed between the Russian Vice-Admiral Euphimy Vasil'evich Putiatin and Toshiakira Kawaji of Japan in the city of Shimoda, Izu Province, Japan, on February 7, 1855... with Japan. An island in the Nordenskiöld Archipelago Nordenskiöld Archipelago The Nordenskiöld Archipelago or Nordenskjold Archipelago is a very large and complex cluster of islands in the eastern region of the Kara Sea. Its eastern limit lies west of the Taymyr Peninsula.... , a bay and a shallow in the Sea of Japan Sea of Japan The Sea of Japan is a marginal sea of the western Pacific Ocean, between the Asian mainland, the Japanese archipelago and Sakhalin. It is bordered by Japan, North Korea, Russia and South Korea. Like the Mediterranean Sea, it has almost no tides due to its nearly complete enclosure from the Pacific... have been named after Unkovsky. |
 |
|
| Nikolay Urvantsev Nikolay Urvantsev Nikolay Nikolayevich Urvantsev was a Soviet geologist and explorer. He was born in the town of Lukoyanov of Nizhny Novgorod Governorate, Russian Empire to the family of a merchant... (1893–1985)  Russian Empire Russian Empire Soviet Union Soviet Uniongeologist Geologist A geologist is a scientist who studies the solid and liquid matter that constitutes the Earth as well as the processes and history that has shaped it. Geologists usually engage in studying geology. Geologists, studying more of an applied science than a theoretical one, must approach Geology using... , Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... explorer |
Urvantsev was among the discoverers of a coal Coal Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock usually occurring in rock strata in layers or veins called coal beds or coal seams. The harder forms, such as anthracite coal, can be regarded as metamorphic rock because of later exposure to elevated temperature and pressure... basin and a copper Copper Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu and atomic number 29. It is a ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. Pure copper is soft and malleable; an exposed surface has a reddish-orange tarnish... -nickel Nickel Nickel is a chemical element with the chemical symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel belongs to the transition metals and is hard and ductile... ore region in Norilsk Norilsk Norilsk is an industrial city in Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russia, located between the Yenisei River and the Taymyr Peninsula. Population: It was granted city status in 1953. It is the northernmost city in Siberia and the world's second largest city north of the Arctic Circle... in 1919-22 and was among the founders of Norilsk town. In 1922 he found evidence of the mysteriously disappeared Amundsen Roald Amundsen Roald Engelbregt Gravning Amundsen was a Norwegian explorer of polar regions. He led the first Antarctic expedition to reach the South Pole between 1910 and 1912 and he was the first person to reach both the North and South Poles. He is also known as the first to traverse the Northwest Passage.... 's 1918 Arctic expedition crew members Peter Tessem and Paul Knutsen Peter Tessem and Paul Knutsen Peter Tessem and Paul Knutsen were two young men from Norway who went with fellow Norwegian explorer Roald Amundsen on his 1918 Arctic expedition aboard ship Maud. Peter Tessem was a carpenter and Paul Knutsen was an able-bodiedseaman... on the Kara Sea Kara Sea The Kara Sea is part of the Arctic Ocean north of Siberia. It is separated from the Barents Sea to the west by the Kara Strait and Novaya Zemlya, and the Laptev Sea to the east by the Severnaya Zemlya.... shore. In 1930-32 Urvantsev and Georgy Ushakov Georgy Ushakov Georgy Alexeyevich Ushakov was a Soviet explorer of the Arctic, Doctor of Geographic Sciences .... explored and completely mapped the Severnaya Zemlya Severnaya Zemlya Severnaya Zemlya is an archipelago in the Russian high Arctic at around . It is located off mainland Siberia's Taymyr Peninsula across the Vilkitsky Strait... and established that it was an archipelago, discovering a number or islands and obliterating enormous "white spaces" on the Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... map. Urvantsev also explored Taimyr Taymyr Peninsula The Taymyr Peninsula is a peninsula in the Far North of Russia, in the Siberian Federal District, that forms the northernmost part of mainland Eurasia and Asia... and Central Siberian Plateau Central Siberian Plateau The Central Siberian Plateau is made up of sharply demarcated surfaces of varying altitudes occupying most of Siberia between the Yenisei and Lena rivers. It extends over an area of 3.5 million km². The highest point is the Putoran Mountains rising to 1701 m. To the north of the plateau are... . In 1933-34 aboard the Pravda Steamer Pravda Steamer Pravda was a Soviet merchant freighter of about 3,100 tonnes displacement, which was active in the Soviet Arctic during the 1930s. This ship had been normally used for carrying timber. It was named after Soviet newspaper Pravda.... Urvantsev led the first Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... oil exploration Oil exploration Hydrocarbon exploration is the search by petroleum geologists and geophysicists for hydrocarbon deposits beneath the Earth's surface, such as oil and natural gas... expedition to Nordvik (Laptev Sea) Nordvik (Laptev Sea) Nordvik was a harbor-port in the Khatanga Gulf at the mouth of the Khatanga River. It was located on the Uryung Tumus Peninsula, west of a bay called Nordvik Bay . Formerly there was a small town and a penal colony next to the harbour, called Nordvik... . |
 |
|
| Georgy Ushakov Georgy Ushakov Georgy Alexeyevich Ushakov was a Soviet explorer of the Arctic, Doctor of Geographic Sciences .... (1901–1963)  Russian Empire Russian Empire Soviet Union Soviet Uniongeographer, Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... explorer |
In 1926 Ushakov founded the first Soviet settlement on the Wrangel Island Wrangel Island Wrangel Island is an island in the Arctic Ocean, between the Chukchi Sea and East Siberian Sea. Wrangel Island lies astride the 180° meridian. The International Date Line is displaced eastwards at this latitude to avoid the island as well as the Chukchi Peninsula on the Russian mainland... . In 1930-32 Ushakov and Nikolay Urvantsev Nikolay Urvantsev Nikolay Nikolayevich Urvantsev was a Soviet geologist and explorer. He was born in the town of Lukoyanov of Nizhny Novgorod Governorate, Russian Empire to the family of a merchant... explored and completely mapped the Severnaya Zemlya Severnaya Zemlya Severnaya Zemlya is an archipelago in the Russian high Arctic at around . It is located off mainland Siberia's Taymyr Peninsula across the Vilkitsky Strait... and established that it was an archipelago. Severnaya Zemlya was a last archipelago on Earth to be explored. In 1935-36 Ushakov led the first Soviet high-latitude expedition on an icebreaker Sadko Icebreaker Sadko Icebreaker Sadko was a Russian and Soviet icebreaker ship of 3,800 tonnes displacement. She was named after Sadko, a hero of a Russian bylina.... , examined the last unexplored areas in the northern Kara Sea Kara Sea The Kara Sea is part of the Arctic Ocean north of Siberia. It is separated from the Barents Sea to the west by the Kara Strait and Novaya Zemlya, and the Laptev Sea to the east by the Severnaya Zemlya.... and discovered Ushakov Island Ushakov Island Ushakov Island is an isolated island located in the Arctic Ocean, midway between Franz Josef Land and Severnaya Zemlya, at the northern limit of the Kara Sea. Its latitude is 80° 48' N and its longitude 79° 29' E.... , the last unknown island in the Russian Arctic outside any archipelago. In 1937 Sadko was ice-trapped and wintered in the Laptev Sea Laptev Sea The Laptev Sea is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It is located between the northern coast of Siberia, the Taimyr Peninsula, Severnaya Zemlya and the New Siberian Islands. Its northern boundary passes from the Arctic Cape to a point with co-ordinates of 79°N and 139°E, and ends at the Anisiy... . Ushakov died in Moscow Moscow Moscow is the capital, the most populous city, and the most populous federal subject of Russia. The city is a major political, economic, cultural, scientific, religious, financial, educational, and transportation centre of Russia and the continent... , but was buried in Severnaya Zemlya. Mountains in the Antarctica, a spit, a cape and a settlement on Wrangel Island Wrangel Island Wrangel Island is an island in the Arctic Ocean, between the Chukchi Sea and East Siberian Sea. Wrangel Island lies astride the 180° meridian. The International Date Line is displaced eastwards at this latitude to avoid the island as well as the Chukchi Peninsula on the Russian mainland... , a river in Severnaya Zemlya Severnaya Zemlya Severnaya Zemlya is an archipelago in the Russian high Arctic at around . It is located off mainland Siberia's Taymyr Peninsula across the Vilkitsky Strait... , and Ushakov Island Ushakov Island Ushakov Island is an isolated island located in the Arctic Ocean, midway between Franz Josef Land and Severnaya Zemlya, at the northern limit of the Kara Sea. Its latitude is 80° 48' N and its longitude 79° 29' E.... bear Ushakov's name. |
||
| Tatyana Ustinova Tatyana Ustinova Tatyana Ustinova was a Soviet geologist, who discovered Valley of Geysers in Kamchatka.- Biography :... (1913–2009)  Russian Empire Russian Empire Soviet Union Soviet Union Canada Canadageologist Geologist A geologist is a scientist who studies the solid and liquid matter that constitutes the Earth as well as the processes and history that has shaped it. Geologists usually engage in studying geology. Geologists, studying more of an applied science than a theoretical one, must approach Geology using... , explorer of Kamchatka |
In 1940 Ustinova came to Kronotsky Nature Reserve Kronotsky Nature Reserve Kronotsky Nature Reserve is a nature area reserved for the study of natural sciences in the remote Russian Far East, on the coast of the Kamchatka Peninsula. It was created in 1934 and its current boundary contains an area of... in Kamchatka. In 1941, with the help of the local guide Anysyfor Krupenin, she discovered the Valley of Geysers Valley of Geysers The Valley of Geysers is a geyser field in Russia, and has the second largest concentration of geysers in the world. This 6 km long basin with approximately ninety geysers and many hot springs is situated on the Kamchatka Peninsula in the Russian Far East, predominantly on the left bank of... , the second largest concentration of geysers in the world. She researched the geysers until 1946 and gave the names to the most notable of them. Before she died, in a testament she wished that her ashes were buried in the Valley of Geysers. |
V
| Portrait | Person | Achievements | Image | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Merkury Vagin Merkury Vagin Merkury Vagin was a Russian Arctic explorer.In 1712, together with Yakov Permyakov, Merkury Vagin explored the region of the eastern Laptev Sea coast, including Bolshoy Lyakhovsky Island, the southermost of the New Siberian Archipelago... (?–1712) Tsardom of Russia Tsardom of Russia The Tsardom of Russia was the name of the centralized Russian state from Ivan IV's assumption of the title of Tsar in 1547 till Peter the Great's foundation of the Russian Empire in 1721.From 1550 to 1700, Russia grew 35,000 km2 a year... Siberian Cossack, seafarer, merchant, Arctic explorer |
In 1712, Vagin and his companion Yakov Permyakov Yakov Permyakov Yakov Permyakov was a Russian seafarer, explorer, merchant, and Cossack.In 1710, while sailing from the Lena River to the Kolyma River, Permyakov observed the silhouette of two unknown island groups in the sea... crossed the Yana Bay Yana Bay The Yana Bay is the most important gulf of the Laptev Sea. It is located between Cape Buor-Khaya on its western side and the Ebelyakh Bay at its eastern end.... from the mouth of the Yana Yana River The Yana River , is a river in Sakha in Russia, located between the Lena to the west and the Indigirka to the east.It is 872 km in length. The area of its basin is 238,000 km², whilst its annual discharge totals approximately . Most of this discharge occurs in May and June as the ice on the... over the ice and explored Bolshoy Lyakhovsky island, the southernmost of the New Siberian Islands New Siberian Islands The New Siberian Islands are an archipelago, located to the North of the East Siberian coast between the Laptev Sea and the East Siberian Sea north of the Sakha Republic.... (the island was sited two years earlier by Permyakov). From Bolshoy Lyakhovsky they spotted Maly Lyakhovsky island. Thus they initiated the exploration of the large New Siberian archipelago. On the way back Permyakov and Vagin were murdered by mutineering expedition members. Merkuriya Island in the Arctic was named after Merkury Vagin. |
 |
||
 |
Nikolai Vavilov Nikolai Vavilov Nikolai Ivanovich Vavilov was a prominent Russian and Soviet botanist and geneticist best known for having identified the centres of origin of cultivated plants... (1887–1943)  Russian Empire Russian Empire Soviet Union Soviet Unionbotanist and geneticist Geneticist A geneticist is a biologist who studies genetics, the science of genes, heredity, and variation of organisms. A geneticist can be employed as a researcher or lecturer. Some geneticists perform experiments and analyze data to interpret the inheritance of skills. A geneticist is also a Consultant or... ,explorer of the centres of origin of cultivated plants |
Vavilov devoted his life to the study and improvement of wheat Wheat Wheat is a cereal grain, originally from the Levant region of the Near East, but now cultivated worldwide. In 2007 world production of wheat was 607 million tons, making it the third most-produced cereal after maize and rice... , corn Maize Maize known in many English-speaking countries as corn or mielie/mealie, is a grain domesticated by indigenous peoples in Mesoamerica in prehistoric times. The leafy stalk produces ears which contain seeds called kernels. Though technically a grain, maize kernels are used in cooking as a vegetable... , and other crops that sustain the global population. In 1924-35 he was the director of the All-Union Institute of Agricultural Sciences at Leningrad Leningrad Leningrad is the former name of Saint Petersburg, Russia.Leningrad may also refer to:- Places :* Leningrad Oblast, a federal subject of Russia, around Saint Petersburg* Leningrad, Tajikistan, capital of Muminobod district in Khatlon Province... . Vavilov organized a series of botanical-agronomic expeditions, collected seeds from every corner of the globe, and created the world's largest collection of plant seeds in Leningrad Leningrad Leningrad is the former name of Saint Petersburg, Russia.Leningrad may also refer to:- Places :* Leningrad Oblast, a federal subject of Russia, around Saint Petersburg* Leningrad, Tajikistan, capital of Muminobod district in Khatlon Province... . As a result of his long work and explorations he identified the centres of origin of main cultivated plants. During his journeys he had visited a number of virtually unknown regions of the world. N.I. Vavilov Institute of Plant Industry Institute of Plant Industry The Institute of Plant Industry, Vavilov Institute of Plant Industry or All-Russian Research Institute of Plant Industry , as it is officially called, is a research institute of plant genetics, located in Saint Petersburg, Russia.-History:... in St. Petersburg, the Vavilov Award and the Vavilov Medal of the USSR Academy of Sciences, Vavilovian mimicry Vavilovian mimicry Vavilovian mimicry is a form of mimicry in plants where a weed comes to share one or more characteristics with a domesticated plant through generations of artificial selection. It is named after Nikolai Vavilov, a prominent Russian plant geneticist who identified the centres of origin of... , Vavilov Center, many plant species, scientific institutions, streets and settlements are named after Nikolai Vavilov Nikolai Vavilov Nikolai Ivanovich Vavilov was a prominent Russian and Soviet botanist and geneticist best known for having identified the centres of origin of cultivated plants... . A meteostation and a glacier in October Revolution Island October Revolution Island October Revolution Island is the largest island of the Severnaya Zemlya group in the Russian Arctic.... (Severnaya Zemlya Severnaya Zemlya Severnaya Zemlya is an archipelago in the Russian high Arctic at around . It is located off mainland Siberia's Taymyr Peninsula across the Vilkitsky Strait... ), a minor planet Minor planet An asteroid group or minor-planet group is a population of minor planets that have a share broadly similar orbits. Members are generally unrelated to each other, unlike in an asteroid family, which often results from the break-up of a single asteroid... 2862 Vavilov 2862 Vavilov 2862 Vavilov is a main-belt asteroid discovered on May 15, 1977 by N. Chernykh at Nauchnyj.- External links :*... and the Vavilov crater Vavilov (crater) Vavilov is a prominent impact crater that is located to the west of the walled plain Hertzsprung. It is located on the far side of the Moon and cannot be viewed directly from the Earth. About a crater diameter to the northwest is the smaller Chaucer, and farther to the southwest is Sechenov.This is... on the Moon Moon The Moon is Earth's only known natural satellite,There are a number of near-Earth asteroids including 3753 Cruithne that are co-orbital with Earth: their orbits bring them close to Earth for periods of time but then alter in the long term . These are quasi-satellites and not true moons. For more... are also named after him and his brother physicist Sergey Vavilov Sergey Ivanovich Vavilov Sergey Ivanovich Vavilov -Biography:Vavilov founded the Soviet school of physical optics, known by his works in luminescence. In 1934 he co-discovered the Vavilov-Cherenkov effect, a discovery for which Pavel Cherenkov was awarded a Nobel Prize in Physics in 1958... . |
||
 |
Boris Vilkitsky Boris Vilkitsky Boris Andreyevich Vilkitsky was a Russian hydrographer and surveyor. He was the son of Andrey Ippolitovich Vilkitsky.... (1885–1961)  Russian Empire Russian Empire United Kingdom United Kingdom Belgium BelgiumRussian Imperial Navy officer, hydrographer, Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... explorer |
In 1913-15 Vilkitsky led the Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... hydrographic expedition on the icebreaker Icebreaker An icebreaker is a special-purpose ship or boat designed to move and navigate through ice-covered waters. Although the term usually refers to ice-breaking ships, it may also refer to smaller vessels .For a ship to be considered an icebreaker, it requires three traits most... s Taimyr Icebreaker Taymyr Icebreaker Taymyr was an icebreaking steamer of 1200 tons built for the Russian Imperial Navy at St. Petersburg in 1909. It was named after the Taymyr Peninsula.... and Vaigach Icebreaker Vaygach Icebreaker Vaygach was an icebreaking steamer of moderate size built for the Russian Imperial Navy at St. Petersburg in 1909. It was named after Vaygach Island in the Russian Arctic.... , exploring the parts of the Northern Sea Route Northern Sea Route The Northern Sea Route is a shipping lane officially defined by Russian legislation from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean specifically running along the Russian Arctic coast from Murmansk on the Barents Sea, along Siberia, to the Bering Strait and Far East. The entire route lies in Arctic... . In 1913, the expedition discovered Severnaya Zemlya Severnaya Zemlya Severnaya Zemlya is an archipelago in the Russian high Arctic at around . It is located off mainland Siberia's Taymyr Peninsula across the Vilkitsky Strait... , the last archipelago on Earth to be explored. Vilkitsky Island also was discovered then, as well as Maly Taymyr and Starokadomsky Island Starokadomsky Island Starokadomsky Island is an hourglass-shaped island in the Laptev Sea, Russian Arctic.It is located off the southeastern end of the Severnaya Zemlya archipelago and northeast of the Taymyr Peninsula. Maly Taymyr Island lies on its southeastern side, separated by a 6 km wide sound.The maximum... s. In 1914-15, Vilkitsky's expedition made the first through voyage from Vladivostok Vladivostok The city is located in the southern extremity of Muravyov-Amursky Peninsula, which is about 30 km long and approximately 12 km wide.The highest point is Mount Kholodilnik, the height of which is 257 m... to Arkhangelsk Arkhangelsk Arkhangelsk , formerly known as Archangel in English, is a city and the administrative center of Arkhangelsk Oblast, Russia. It lies on both banks of the Northern Dvina River near its exit into the White Sea in the north of European Russia. The city spreads for over along the banks of the river... , discovered Novopashenniy Island (now Zhokhova Island), and described the southern coastline of Severnaya Zemlya. In 1920 Vilkitsky emigrated to Britain United Kingdom The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages... . Later he led commercial expeditions in the Kara Sea Kara Sea The Kara Sea is part of the Arctic Ocean north of Siberia. It is separated from the Barents Sea to the west by the Kara Strait and Novaya Zemlya, and the Laptev Sea to the east by the Severnaya Zemlya.... and was employed as a hydrographer in the Belgian Congo Belgian Congo The Belgian Congo was the formal title of present-day Democratic Republic of the Congo between King Leopold II's formal relinquishment of his personal control over the state to Belgium on 15 November 1908, and Congolese independence on 30 June 1960.-Congo Free State, 1884–1908:Until the latter... . Vilkitsky Strait Vilkitsky Strait Vilkitsky Strait is a strait between the Taimyr Peninsula and Bolshevik Island in the Severnaya Zemlya archipelago. The strait connects the Kara and Laptev Seas. The length of the Vilkitsky Strait is 104 km, the width – approx. 55 km, and the depth – between 32 and 210 m. It is... between Severnaya Zemlya and Taimyr Peninsula, Vilkitsky bay of Novaya Zemlya Novaya Zemlya Novaya Zemlya , also known in Dutch as Nova Zembla and in Norwegian as , is an archipelago in the Arctic Ocean in the north of Russia and the extreme northeast of Europe, the easternmost point of Europe lying at Cape Flissingsky on the northern island... , two different Vilkitsky Islands subgroups of the Komsomolskaya Pravda Islands Komsomolskaya Pravda Islands The Komsomolskaya Pravda Islands are a group of islands covered with tundra vegetation, shingle and ice. They were known as Ostrova Samuila before the 1917 Russian Revolution and then they were renamed after Komsomolskaya Pravda, being for a while the only island group in the world named after a... and Nordenskjold Archipelago, Vilkitsky Island (Kara Sea) Vilkitsky Island (Kara Sea) Vilkitsky Island, is an island in the Kara Sea. It is located 40 km northeast of Shokalskogo Island, off the tip of the Gydan Peninsula in North Siberia. This island is bleak and windswept and is covered with tundra. Vilkitsky Island is crescent-shaped and it is divided in two by a narrow... , Vilkitsky Island (East Siberian Sea) and other objects were named after Vilkitsky. |
||
| Vladimir Vize (1886–1954)  Russian Empire Russian Empire Soviet Union Soviet Unionoceanographer, Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... explorer |
In 1912-14 Vize took part in the Georgiy Sedov's expedition to Novaya Zemlya Novaya Zemlya Novaya Zemlya , also known in Dutch as Nova Zembla and in Norwegian as , is an archipelago in the Arctic Ocean in the north of Russia and the extreme northeast of Europe, the easternmost point of Europe lying at Cape Flissingsky on the northern island... and Franz Josef Land Franz Josef Land Franz Josef Land, Franz Joseph Land, or Francis Joseph's Land is an archipelago located in the far north of Russia. It is found in the Arctic Ocean north of Novaya Zemlya and east of Svalbard, and is administered by Arkhangelsk Oblast. Franz Josef Land consists of 191 ice-covered islands with a... . In 1924 he studied the drift of Georgy Brusilov Georgy Brusilov Georgy Lvovich Brusilov or Hryhoriy Brusylov was a Ukrainian Russian naval officer of the Imperial Russian Navy and an Arctic explorer... 's ill-fated Russian ship St. Anna Svyataya Anna The ship Svyataya Anna , named after Saint Anne, was the Philomel-class gunvessel HMS Newport launched in England in 1867. She was sold in 1881 and renamed Pandora II. She was purchased again in about 1890 and renamed Blencathra, taking part in expeditions to the north coast of Russia... , trapped on the pack ice. As a result of this study he predicted the location of yet unseen Vize Island Vize Island Vize Island or Wiese Island is an isolated island located in the Arctic Ocean at the northern end of the Kara Sea, roughly midway between Franz Josef Land and Severnaya Zemlya, its latitude is 79° 30' N and its longitude 76° 54' E... , based on the analysys of ice movement in the Kara Sea Kara Sea The Kara Sea is part of the Arctic Ocean north of Siberia. It is separated from the Barents Sea to the west by the Kara Strait and Novaya Zemlya, and the Laptev Sea to the east by the Severnaya Zemlya.... . Vize took part in a number of Soviet polar expeditions, including the first successful crossing of the Northern Sea Route Northern Sea Route The Northern Sea Route is a shipping lane officially defined by Russian legislation from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean specifically running along the Russian Arctic coast from Murmansk on the Barents Sea, along Siberia, to the Bering Strait and Far East. The entire route lies in Arctic... in a single navigation on icebreaker Sibiryakov Icebreaker Sibiryakov The icebreaker Sibiryakov was a Soviet ship which was active in the Russian Arctic during the 1930s. She was built in 1909 in Glasgow and was originally the Newfoundland sealing steamer Bellaventure. After being purchased by Russia in 1916, she was renamed the Sibiryakov... in 1932. In 1938-40 Vize conducted the scientific research on the ice-captured icebreaker Icebreaker An icebreaker is a special-purpose ship or boat designed to move and navigate through ice-covered waters. Although the term usually refers to ice-breaking ships, it may also refer to smaller vessels .For a ship to be considered an icebreaker, it requires three traits most... Sedov Icebreaker Sedov The Sedov was a Soviet ice-breaker fitted with steam engines. She was originally the Newfoundland sealing steamer Beothic and was renamed after Russian Captain and Polar explorer Georgy Yakovlevich Sedov.... , turned into a drifting ice station Soviet and Russian manned drifting ice stations Soviet and Russian manned drifting ice stations are important contributors to exploration of the Arctic. The stations are named North Pole Soviet and Russian manned drifting ice stations are important contributors to exploration of the Arctic. The stations are named North Pole Soviet and... . Vize Island Vize Island Vize Island or Wiese Island is an isolated island located in the Arctic Ocean at the northern end of the Kara Sea, roughly midway between Franz Josef Land and Severnaya Zemlya, its latitude is 79° 30' N and its longitude 76° 54' E... in the Kara Sea Kara Sea The Kara Sea is part of the Arctic Ocean north of Siberia. It is separated from the Barents Sea to the west by the Kara Strait and Novaya Zemlya, and the Laptev Sea to the east by the Severnaya Zemlya.... , a bay, a glacier and a point on Novaya Zemlya Novaya Zemlya Novaya Zemlya , also known in Dutch as Nova Zembla and in Norwegian as , is an archipelago in the Arctic Ocean in the north of Russia and the extreme northeast of Europe, the easternmost point of Europe lying at Cape Flissingsky on the northern island... , and a scientific vessel have been named after Vize. |
 |
||
| Vladimir Voronin Vladimir Voronin (Captain) Vladimir Ivanovich Voronin was a Soviet Navy captain, born in Sumsky Posad, in the present Republic of Karelia, Russia. In 1932 he commanded the expedition of the Soviet icebreaker Alexander Sibiryakov which made the first successful crossing of the Northern Sea Route in a single navigation... (1890–1952)  Russian Empire Russian Empire Soviet Union Soviet UnionSoviet Navy Soviet Navy The Soviet Navy was the naval arm of the Soviet Armed Forces. Often referred to as the Red Fleet, the Soviet Navy would have played an instrumental role in a Warsaw Pact war with NATO, where it would have attempted to prevent naval convoys from bringing reinforcements across the Atlantic Ocean... captain, Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... explorer |
In 1932 Voronin commanded the expedition of the Soviet icebreaker Alexander Sibiryakov Icebreaker Sibiryakov The icebreaker Sibiryakov was a Soviet ship which was active in the Russian Arctic during the 1930s. She was built in 1909 in Glasgow and was originally the Newfoundland sealing steamer Bellaventure. After being purchased by Russia in 1916, she was renamed the Sibiryakov... which made the first successful crossing of the Northern Sea Route Northern Sea Route The Northern Sea Route is a shipping lane officially defined by Russian legislation from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean specifically running along the Russian Arctic coast from Murmansk on the Barents Sea, along Siberia, to the Bering Strait and Far East. The entire route lies in Arctic... in a single navigation without wintering. In 65 days Sibiryakov sailed from Archangelsk to Yokohama Yokohama is the capital city of Kanagawa Prefecture and the second largest city in Japan by population after Tokyo and most populous municipality of Japan. It lies on Tokyo Bay, south of Tokyo, in the Kantō region of the main island of Honshu... in Japan Japan Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south... , having covered more than 2500 miles in the Arctic seas. In 1933-34 Voronin commanded less fortunate Cheliuskin Chelyuskin steamship SS Chelyuskin was a Soviet steamship reinforced to navigate through polar ice that became ice-bound in Arctic waters during navigation along the Northern Maritime Route from Murmansk to Vladivostok... steamship with scientific expedition of Otto Schmidt Otto Schmidt Otto Yulyevich Schmidt was a Soviet scientist, mathematician, astronomer, geophysicist, statesman, academician, Hero of the USSR , and member of the Communist Party.-Biography:He was born in Mogilev, Russian Empire... aboard. The sheep became ice-bound in the Chukchi Sea Chukchi Sea Chukchi Sea is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It is bounded on the west by the De Long Strait, off Wrangel Island, and in the east by Point Barrow, Alaska, beyond which lies the Beaufort Sea. The Bering Strait forms its southernmost limit and connects it to the Bering Sea and the Pacific... , but almost all the crew was resqued by planes from their camp on ice. Voronina Island Voronina Island Voronina Island or Voronina Islands is an isolated two-island group composed of a larger island and a narrow island on its northern side separated by a 3 km wide sound.The main Voronina Island is about 9 km long and 6 km wide and is covered with tundra vegetation and ice... in the Kara Sea Kara Sea The Kara Sea is part of the Arctic Ocean north of Siberia. It is separated from the Barents Sea to the west by the Kara Strait and Novaya Zemlya, and the Laptev Sea to the east by the Severnaya Zemlya.... , Voronina shoal Shoal Shoal, shoals or shoaling may mean:* Shoal, a sandbank or reef creating shallow water, especially where it forms a hazard to shipping* Shoal draught , of a boat with shallow draught which can pass over some shoals: see Draft... in the Gulf of Finland Gulf of Finland The Gulf of Finland is the easternmost arm of the Baltic Sea. It extends between Finland and Estonia all the way to Saint Petersburg in Russia, where the river Neva drains into it. Other major cities around the gulf include Helsinki and Tallinn... , Voronin bay at Novaya Zemlya Novaya Zemlya Novaya Zemlya , also known in Dutch as Nova Zembla and in Norwegian as , is an archipelago in the Arctic Ocean in the north of Russia and the extreme northeast of Europe, the easternmost point of Europe lying at Cape Flissingsky on the northern island... , underwater Voronin Trough in the Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... basin. |
W
| Portrait | Person | Achievements | Image |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
Ferdinand von Wrangel Ferdinand von Wrangel Baron Ferdinand Friedrich Georg Ludwig von Wrangel – May 25 , 1870) was a Russian explorer and seaman, Honorable Member of the Saint Petersburg Academy of Sciences, a founder of the Russian Geographic Society... (1797–1870)  Russian Empire Russian Empire(born in Estonia Estonia Estonia , officially the Republic of Estonia , is a state in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea, to the south by Latvia , and to the east by Lake Peipsi and the Russian Federation . Across the Baltic Sea lies... , Baltic German Baltic German The Baltic Germans were mostly ethnically German inhabitants of the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea, which today form the countries of Estonia and Latvia. The Baltic German population never made up more than 10% of the total. They formed the social, commercial, political and cultural élite in... descent) Russian Imperial Navy officer, Admiral Admiral Admiral is the rank, or part of the name of the ranks, of the highest naval officers. It is usually considered a full admiral and above vice admiral and below admiral of the fleet . It is usually abbreviated to "Adm" or "ADM"... , Arctic Arctic The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost... explorer |
Ferdinand Petrovich Wrangel took part in Vasily Golovnin Vasily Golovnin Vasily Mikhailovich Golovnin .-Early life and career:Vasily Mikhailovich Golovnin was born in April 1776, in the village of Gulyniki in Ryazan Oblast, on his father's country estate. Both his father and grandfather had served in the Russian military as officers in the elite Preobrazhensky... 's world cruise on the ship Kamchatka in 1817-19. Subsequently Wrangel led the Kolymskaya expedition in 1820-24 in search of northern lands. He established that north of the Kolyma River Kolyma River The Kolyma River is a river in northeastern Siberia, whose basin covers parts of the Sakha Republic, Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, and Magadan Oblast of Russia. Itrises in the mountains north of Okhotsk and Magadan, in the area of and... there was an open sea, not dry land, as previously thought. Together with Fyodor Matyushkin Fyodor Matyushkin Fyodor Fyodorovich Matyushkin was a Russian navigator, Admiral , and a close friend of Aleksandr Pushkin.Matyushkin graduated from Tsarskoselskiy College in 1817... and P. Kuzmin, Wrangel described the Medvyezhi Islands Medvyezhi Islands The Medvezhyi Islands, or Bear Islands is an uninhabited group of islands at the western end of the Kolyma Gulf of the East Siberian Sea. It is located about to the north of the mouths of the Kolyma River. The coast of Siberia is about to the southwest of the largest island, which is about km... and East Siberian Sea East Siberian Sea The East Siberian Sea is a marginal sea in the Arctic Ocean. It is located between the Arctic Cape to the north, the coast of Siberia to the south, the New Siberian Islands to the west and Cape Billings, close to Chukotka, and Wrangel Island to the east... coastline from the Indigirka River Indigirka River The Indigirka River is a river in the Sakha Republic in Russia between the Yana River and the Kolyma River. It is in length. The area of its basin is 360,000 km²... to the Kolyuchinskaya Bay Kolyuchinskaya Bay Kolyuchinskaya Bay is a large bay in the Chukchi Sea on the northern shore of the Chukotka Peninsula, Russia. To the west is Cape Vankarem and to the east Neskynpil'gyn Lagoon and Cape Serdtse-Kamen. The length of the bay is 100 km. Its mouth is only 2.8 km because of the Serykh Gusey... in the Chukchi Sea Chukchi Sea Chukchi Sea is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It is bounded on the west by the De Long Strait, off Wrangel Island, and in the east by Point Barrow, Alaska, beyond which lies the Beaufort Sea. The Bering Strait forms its southernmost limit and connects it to the Bering Sea and the Pacific... . After noticing swarm Swarm Swarm behaviour, or swarming, is a collective behaviour exhibited by animals of similar size which aggregate together, perhaps milling about the same spot or perhaps moving en masse or migrating in some direction. As a term, swarming is applied particularly to insects, but can also be applied to... s of birds flying north and questioning the native population, he determined that there must be an undiscovered island in the Arctic Ocean Arctic Ocean The Arctic Ocean, located in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Arctic north polar region, is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceanic divisions... . Even though his search for it was unsuccessful the island was later named Wrangel Island Wrangel Island Wrangel Island is an island in the Arctic Ocean, between the Chukchi Sea and East Siberian Sea. Wrangel Island lies astride the 180° meridian. The International Date Line is displaced eastwards at this latitude to avoid the island as well as the Chukchi Peninsula on the Russian mainland... to honour his endeavor. Wrangel led the Russian world voyage on the ship Krotky in 1825-27. He was the governor of Russian America in 1829-35, the president of the Russian-American Company Russian-American Company The Russian-American Company was a state-sponsored chartered company formed largely on the basis of the so-called Shelekhov-Golikov Company of Grigory Shelekhov and Ivan Larionovich Golikov The Russian-American Company (officially: Under His Imperial Majesty's Highest Protection (patronage)... in 1840-49 and the Minister of the Navy in 1855-57. In 1845 he became one of the founders of the Russian Geographic Society. Wrangel Island Wrangel Island Wrangel Island is an island in the Arctic Ocean, between the Chukchi Sea and East Siberian Sea. Wrangel Island lies astride the 180° meridian. The International Date Line is displaced eastwards at this latitude to avoid the island as well as the Chukchi Peninsula on the Russian mainland... north of Chukotka Chukchi Peninsula The Chukchi Peninsula, Chukotka Peninsula or Chukotski Peninsula , at about 66° N 172° W, is the northeastern extremity of Asia. Its eastern end is at Cape Dezhnev near the village of Uelen. It is bordered by the Chukchi Sea to the north, the Bering Sea to the south, and the Bering Strait to the... , Wrangell Island Wrangell Island Wrangell Island is in the Alexander Archipelago in the Alaska Panhandle of southeastern Alaska. It is long and 8–23 km wide. It has a land area of , making it the 29th largest island in the United States... in Alexander Archipelago Alexander Archipelago The Alexander Archipelago is a long archipelago, or group of islands, of North America off the southeastern coast of Alaska. It contains about 1,100 islands, which are the tops of the submerged coastal mountains that rise steeply from the Pacific Ocean. Deep channels and fjords separate the... near Alaska Alaska Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait... and a city Wrangell, Alaska Wrangell is a city and borough in the U.S. state of Alaska. At the 2000 census the population was 2,308.Its Tlingit name is Ḵaachx̱aana.áakʼw . The Tlingit people residing in the Wrangell area, who were there centuries before Europeans, call themselves the Shtaxʼhéen Ḵwáan after the nearby Stikine... there, Wrangell Narrows Wrangell Narrows The Wrangell Narrows is a winding, 35-km-long channel between Mitkof Island and Kupreanof Island in the Alexander Archipelago in Southeast Alaska. The Wrangell Narrows is one of the six Listed narrows in Southeast Alaska. There are about 60 lights and buoys to mark it because of its winding nature... channel in the Alexander Archipelago, Cape Wrangell Cape Wrangell Cape Wrangell is the westernmost point of the U.S. state of Alaska from the geographic center of the United States. It is located on the island of Attu which is situated in the Near Islands.-External links:*... of Attu Island Attu Island Attu is the westernmost and largest island in the Near Islands group of the Aleutian Islands of Alaska, making it the westernmost point of land relative to Alaska and the United States. It was the site of the only World War II land battle fought on the incorporated territory of the United States ,... (the westernmost point of Alaska and the continental USA) and Mount Wrangell Mount Wrangell Mount Wrangell is a massive shield volcano located in Wrangell-St. Elias National Park and Preserve in southeastern Alaska, United States. The shield rises over above the Copper River to its southwest. Its volume is over , making it more than twice as massive as Mount Shasta in California, the... (a volcano Volcano 2. Bedrock3. Conduit 4. Base5. Sill6. Dike7. Layers of ash emitted by the volcano8. Flank| 9. Layers of lava emitted by the volcano10. Throat11. Parasitic cone12. Lava flow13. Vent14. Crater15... in Alaska) were named after Wrangel. |
  |
Y
| Portrait | Person | Achievements | Image |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nikolai Yadrintsev Nikolai Yadrintsev Nikolai Mikhailovich Yadrintsev was a Russian public figure, explorer, archaeologist, and turkologist. His discoveries include the Orkhon script, Genghis Khan's capital Karakorum and Ordu-Baliq, the capital of the Uyghur Khaganate. He was also one of the founding fathers of Siberian separatism.-... (1842–1894)  Russian Empire Russian Empirepublic figure, archaeologist, and turkologist, explorer of Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... and Central Asia Central Asia Central Asia is a core region of the Asian continent from the Caspian Sea in the west, China in the east, Afghanistan in the south, and Russia in the north... |
Under a contract with Russian Geographical Society, Yadrintsev twice traveled across Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... and Altai Altai Republic Altai Republic is a federal subject of Russia . Its capital is the town of Gorno-Altaysk. The area of the republic is . Population: -Geography:... , researching economy and geography, archeology and ethnography, anthropology and linguistics. In 1889 he located the remains of medieval city Hara-Balgas and the Genghis Khan Genghis Khan Genghis Khan , born Temujin and occasionally known by his temple name Taizu , was the founder and Great Khan of the Mongol Empire, which became the largest contiguous empire in history after his death.... 's capital Karakorum Karakorum Karakorum was the capital of the Mongol Empire in the 13th century, and of the Northern Yuan in the 14-15th century. Its ruins lie in the northwestern corner of the Övörkhangai Province of Mongolia, near today's town of Kharkhorin, and adjacent to the Erdene Zuu monastery... in Mongolia Mongolia Mongolia is a landlocked country in East and Central Asia. It is bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south, east and west. Although Mongolia does not share a border with Kazakhstan, its western-most point is only from Kazakhstan's eastern tip. Ulan Bator, the capital and largest... . In the valley of the Orkhon River Yadrintsev discovered the Orkhon script Orkhon script The Old Turkic script is the alphabet used by the Göktürk and other early Turkic Khanates from at least the 7th century to record the Old Turkic language. It was later used by the Uyghur Empire... of ancient Türks on two petroglyphic monuments with runiform writing, later decoded by the Danish scientist Vilhelm Thomsen Vilhelm Thomsen Vilhelm Ludwig Peter Thomsen was a Danish linguist. In 1893, he deciphered the Turkish Orkhon inscriptions in advance of his rival, Wilhelm Radloff... . In 1891 Yadrintsev took part in the expedition led by turkologist academician Vasily Radlov Vasily Radlov Vasily Vasilievich Radlov or Friedrich Wilhelm Radloff was a German-born Russian founder of Turkology, a scientific study of Turkic peoples.... , finding more monuments of Türkic runiform writing. A number of streets in Siberian cities and a settlement in Omsk Oblast Omsk Oblast Omsk Oblast is a federal subject of Russia , located in southwestern Siberia. The oblast has an area of and a population of with the majority, 1.15 million, living in Omsk, the administrative center.... were named after Yadrintsev. |
||
 |
Yermak Timofeyevich Yermak Timofeyevich Yermak Timofeyevich , Cossack leader, Russian folk hero and explorer of Siberia. His exploration of Siberia marked the beginning of the expansion of Russia towards this region and its colonization... (1532-42 – 1585) Grand Duchy of Moscow Grand Duchy of Moscow The Grand Duchy of Moscow or Grand Principality of Moscow, also known in English simply as Muscovy , was a late medieval Rus' principality centered on Moscow, and the predecessor state of the early modern Tsardom of Russia.... Tsardom of Russia Tsardom of Russia The Tsardom of Russia was the name of the centralized Russian state from Ivan IV's assumption of the title of Tsar in 1547 till Peter the Great's foundation of the Russian Empire in 1721.From 1550 to 1700, Russia grew 35,000 km2 a year... Cossack Cossack Cossacks are a group of predominantly East Slavic people who originally were members of democratic, semi-military communities in what is today Ukraine and Southern Russia inhabiting sparsely populated areas and islands in the lower Dnieper and Don basins and who played an important role in the... ataman Ataman Ataman was a commander title of the Ukrainian People's Army, Cossack, and haidamak leaders, who were in essence the Cossacks... , folk hero Folk hero A folk hero is a type of hero, real, fictional, or mythological. The single salient characteristic which makes a character a folk hero is the imprinting of the name, personality and deeds of the character in the popular consciousness. This presence in the popular consciousness is evidenced by... , explorer of West Siberia West Siberian Plain The West Siberian Plain is a large plain that occupies the western portion of Siberia, between the Ural Mountains in the west and the Yenisei River in the east, and by the Altay Mountains on the South-East. Much of the plain is poorly drained and consists of some of the world's largest swamps and... and conqueror of Siberia Khanate Siberia Khanate The Khanate of Sibir were the patrilineal descendants of Shayban , the fifth son of Jochi and grandson of Genghis Khan. The Khanate had an ethnically diverse population of Siberian Tatars, Khanty, Mansi, Nenets and Selkup people. Along with the Khanate of Kazan it was the northernmost Muslim state.... |
Around 1577, the merchants Stroganovs Stroganovs The Stroganovs or Strogonovs , also spelled in French manner as Stroganoffs, were a family of highly successful Russian merchants, industrialists, landowners, and statesmen of the 16th – 20th centuries who eventually earned nobility.-Origins:... , who were the main colonisers of the Urals, hired the Cossack Cossack Cossacks are a group of predominantly East Slavic people who originally were members of democratic, semi-military communities in what is today Ukraine and Southern Russia inhabiting sparsely populated areas and islands in the lower Dnieper and Don basins and who played an important role in the... leader Yermak to protect their lands from attacks of the Siberian Khan Khan (title) Khan is an originally Altaic and subsequently Central Asian title for a sovereign or military ruler, widely used by medieval nomadic Turko-Mongol tribes living to the north of China. 'Khan' is also seen as a title in the Xianbei confederation for their chief between 283 and 289... Kuchum Kuchum Kuchum khan Kuchum khan (Tatar: Küçüm, Күчүм, Russian: Кучум; in Sybyr Küçüm is pronounced approximately as /kytsym/ - Күцүм, English name comes from standard Tatar pronunciation)Kuchum khan (Tatar: Küçüm, Күчүм, Russian: Кучум; in Sybyr Küçüm is pronounced approximately as /kytsym/ - Күцүм,... . In 1581 Yermak began his voyage into the depths of Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... . After a few victories over the khan's army, Yermak's people defeated Kuchum's main forces on Irtysh River after a 3-day battle Battle of Chuvash Cape Battle of Chuvash Cape The Battle of Chuvash Cape led to the victory of a Russian expedition under Yermak Timofeyevich and the fall of Siberia Khanate and the end of Khan Kuchum's power. The battle took place near Qashliq .-Context:... in 1582. The remains of the khan's army retreated to the steppes and Yermak captured the Siberia Khanate Siberia Khanate The Khanate of Sibir were the patrilineal descendants of Shayban , the fifth son of Jochi and grandson of Genghis Khan. The Khanate had an ethnically diverse population of Siberian Tatars, Khanty, Mansi, Nenets and Selkup people. Along with the Khanate of Kazan it was the northernmost Muslim state.... , including its capital Qashliq Qashliq Qashliq, Isker or Sibir was a medieval Siberian Tatar fortress, in the 16th century the capital of the Khanate of Sibir, located on the right bank of the Irtysh River at its confluence with the Sibirka rivulet, some 17 km from the modern city of Tobolsk.The fortress is first mentioned in... near modern Tobolsk Tobolsk Tobolsk is a town in Tyumen Oblast, Russia, located at the confluence of the Tobol and Irtysh Rivers. It is a historic capital of Siberia. Population: -History:... . Kuchum still was strong and suddenly attacked Yermak in 1585 in the dead of night, killing most of his people. Yermak was wounded and tried to swim across the Wagay River (Irtysh Irtysh The Irtysh River is a river in Siberia and is the chief tributary of the Ob River. Its name means White River. Irtysh's main affluent is the Tobol River... 's tributary), but drowned under the weight of his own chain mail Mail (armour) Mail is a type of armour consisting of small metal rings linked together in a pattern to form a mesh.-History:Mail was a highly successful type of armour and was used by nearly every metalworking culture.... . Russians had to withdraw from Siberia completely, but thanks to Yermak's having explored all the main river routes of central West Siberia West Siberian Plain The West Siberian Plain is a large plain that occupies the western portion of Siberia, between the Ural Mountains in the west and the Yenisei River in the east, and by the Altay Mountains on the South-East. Much of the plain is poorly drained and consists of some of the world's largest swamps and... , they successfully returned all Yermak's conquests just several years later. Yermak Icebreaker Yermak Yermak was a Russian and later Soviet icebreaker, the first polar icebreaker in the world, having a strengthened hull shaped to ride over and crush pack ice.... , the first true icebreaker Icebreaker An icebreaker is a special-purpose ship or boat designed to move and navigate through ice-covered waters. Although the term usually refers to ice-breaking ships, it may also refer to smaller vessels .For a ship to be considered an icebreaker, it requires three traits most... able to crush pack ice, was named after Yermak, as well as Yermak Stone Yermak Stone The Yermak Stone is a cliff in Kungursky District of Perm Krai, at the territory of Preduralye Reserve. It is situated at the right bank of Sylva River opposite the Chikali Station... in Perm Krai Perm Krai Perm Krai is a federal subject of Russia that came into existence on December 1, 2005 as a result of the 2004 referendum on the merger of Perm Oblast and Komi-Permyak Autonomous Okrug. The city of Perm became the administrative center of the new federal subject... and a number of streets and settlements. Yermak's life and death have been subjects for numerous Russian songs, books, and paintings since the 16th century. In 1995 a historical biopic Yermak was shot. |
 |
| Ivan Yevreinov Ivan Yevreinov Ivan Mikhaylovich Yevreinov was a Russian geodesist and explorer.Ivan Yevreinov was born in Poland, then brought to Russia and baptized into Orthodox Christianity.... (?–1724) Poland-Lithuania Tsardom of Russia Tsardom of Russia The Tsardom of Russia was the name of the centralized Russian state from Ivan IV's assumption of the title of Tsar in 1547 till Peter the Great's foundation of the Russian Empire in 1721.From 1550 to 1700, Russia grew 35,000 km2 a year...  Russian Empire Russian Empirecartographer, geodesist, explorer of Siberia Siberia Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th... and the Russian Far East Russian Far East Russian Far East is a term that refers to the Russian part of the Far East, i.e., extreme east parts of Russia, between Lake Baikal in Eastern Siberia and the Pacific Ocean... |
In 1719-1721, together with Fyodor Luzhin Fyodor Luzhin Fyodor Fyodorovich Luzhin was a Russian geodesist and cartographer.Fyodor Luzhin was first a student at the School for Mathematical and Navigational Sciences in Moscow and then in a geodesic class of the Naval Academy in St. Petersburg... , Yevreinov made the first instrumental mapping of Kamchatka and the first map of the Kuril Islands Kuril Islands The Kuril Islands , in Russia's Sakhalin Oblast region, form a volcanic archipelago that stretches approximately northeast from Hokkaidō, Japan, to Kamchatka, Russia, separating the Sea of Okhotsk from the North Pacific Ocean. There are 56 islands and many more minor rocks. It consists of Greater... during the "secret expedition", as ordered by Peter I of Russia Peter I of Russia Peter the Great, Peter I or Pyotr Alexeyevich Romanov Dates indicated by the letters "O.S." are Old Style. All other dates in this article are New Style. ruled the Tsardom of Russia and later the Russian Empire from until his death, jointly ruling before 1696 with his half-brother, Ivan V... . In 1723-24 he mapped Khlynov region near Vyatka Kirov Oblast Kirov Oblast is a federal subject of Russia . Its administrative center is the city of Kirov. Population: -History:In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, Vyatka remained a place of exile for opponents of the tsarist regime, including many prominent revolutionary figures.In 1920, a number of... . A strait between Makanrushi Makanrushi Makanrushi is an uninhabited volcanic island located near the northern end of the Kuril Islands chain in the Sea of Okhotsk in the northwest Pacific Ocean. Its name is derived from the Ainu language.-Geology:... and Onekotan Onekotan Onekotan Island is an uninhabited volcanic island located near the northern end of the Kuril Islands chain in the Sea of Okhotsk in the northwest Pacific Ocean. Its name is derived from the Ainu language for "large village".-Geology:... in the Kurils, a mountain, and a peninsula in the Okhotsk Sea are named after Yevreinov. |
Z
| Portrait | Person | Achievements | Image |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
Lavrenty Zagoskin Lavrenty Zagoskin Lavrenty Alekseyevich Zagoskin was a Russian naval officer and explorer of Alaska.Zagoskin was born in 1808 in the Russian district of Penza in a village named Nikolayevka. Even though Nikolayevka was not near the ocean, Zagoskin would eventually train for the Russian Navy and served as a naval... (1808–1890)  Russian Empire Russian EmpireRussian Imperial Navy officer, naturalist, explorer of Alaska Alaska Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait... |
Commissioned by Russian America Company, in 1842-44 Zagoskin traveled extensively in Alaska Alaska Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait... , covering more than 3300 miles. He explored and mapped the Yukon Yukon River The Yukon River is a major watercourse of northwestern North America. The source of the river is located in British Columbia, Canada. The next portion lies in, and gives its name to Yukon Territory. The lower half of the river lies in the U.S. state of Alaska. The river is long and empties into... , Kuskokwim Kuskokwim River The Kuskokwim River or Kusko River is a river, long, in Southwest Alaska in the United States. It is the ninth largest river in the United States by average discharge volume at its mouth and seventeenth largest by basin drainage area.The river provides the principal drainage for an area of the... , Innoko Innoko River The Innoko River is a river in western Alaska. It flows north from its origin south of Cloudy Mountain in the Kuskoswim Mountains and then flows southwest to its end at the Yukon River, across from Holy Cross, Alaska.... and Koyukuk River Koyukuk River The Koyukuk River is a principal tributary of the Yukon River, approximately 500 mi long, in northern Alaska in the United States.It drains an area north of the Yukon on the southern side of the Brooks Range... s, researched the native peoples and nature of the region. He published the first detailed description of the inner areas of Alaska Alaska Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait... . |
 |
| Vasily Zavoyko Vasily Zavoyko Vasily Stepanovich Zavoyko was an admiral in the Russian navy.Born to a noble family of Poltava Governorate, in 1827 he took part in the Battle of Navarino, and in 1835-1838 he twice circumnavigated the Earth.... (1809–1898)  Russian Empire Russian EmpireRussian Imperial Navy officer, Admiral Admiral Admiral is the rank, or part of the name of the ranks, of the highest naval officers. It is usually considered a full admiral and above vice admiral and below admiral of the fleet . It is usually abbreviated to "Adm" or "ADM"... , circumnavigator, explorer of the Russian Far East Russian Far East Russian Far East is a term that refers to the Russian part of the Far East, i.e., extreme east parts of Russia, between Lake Baikal in Eastern Siberia and the Pacific Ocean... |
In 1835–38 Zavoyko twice circumnavigated the globe. After 1840, during his service for the Russian-American Company Russian-American Company The Russian-American Company was a state-sponsored chartered company formed largely on the basis of the so-called Shelekhov-Golikov Company of Grigory Shelekhov and Ivan Larionovich Golikov The Russian-American Company (officially: Under His Imperial Majesty's Highest Protection (patronage)... in the Okhotsk Sea, Zavoyko explored the estuary Estuary An estuary is a partly enclosed coastal body of water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea.... of the Amur River. His reports led to further expeditions and ultimately the incorporation of Primorsky Krai Primorsky Krai Primorsky Krai , informally known as Primorye , is a federal subject of Russia . Primorsky means "maritime" in Russian, hence the region is sometimes referred to as Maritime Province or Maritime Territory. Its administrative center is in the city of Vladivostok... into Russia. In 1854, at the time of Crimean War Crimean War The Crimean War was a conflict fought between the Russian Empire and an alliance of the French Empire, the British Empire, the Ottoman Empire, and the Kingdom of Sardinia. The war was part of a long-running contest between the major European powers for influence over territories of the declining... , as a governor of Kamchatka Zavoyko led the successful defence during the Siege of Petropavlovsk Siege of Petropavlovsk The Siege of Petropavlovsk was the main operation on the Pacific Theatre of the Crimean War. The Russian casualties are estimated at 100 soldiers; the Allies lost five times as many.... . He repelled the superior allied British United Kingdom The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages... -French France The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France... forces and even captured the British banner. In 1855, making the way through the frozen seas and successfully avoiding the large enemy fleet, he supervised the transfer of the Russian Pacific Fleet from Petropavlovsk to Nikolayevsk-on-Amur Nikolayevsk-on-Amur Nikolayevsk-on-Amur often romanized as Nikolayevsk-na-Amure, is a town and the administrative center of Nikolayevsky District of Khabarovsk Krai, Russia located on the Amur River close to its liman in the Pacific Ocean... . A settlement near Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky is the main city and the administrative, industrial, scientific, and cultural center of Kamchatka Krai, Russia. Population: .-History:It was founded by Danish navigator Vitus Bering, in the service of the Russian Navy... (now a city district) is named after Zavoyko. |
 |
See also
- 1966 Soviet submarine global circumnavigation1966 Soviet submarine global circumnavigationThe 1966 Soviet submarine global circumnavigation was announced to be the first submerged around-the-world voyage by a group of Soviet nuclear-powered submarines. The voyage was an early example of blue-water operations by the Soviet Navy's nuclear-powered submarine fleet, and it paved the way for...
- Arctic policy of RussiaArctic policy of RussiaThe Arctic policy of Russia is the domestic and foreign policy of the Russian Federation with respect to the Russian region of the Arctic. The Russian region of the Arctic is defined in the "Russian Arctic Policy" as all Russian possessions located north of the Arctic Circle...
- First Russian circumnavigationFirst Russian circumnavigationThe first Russian circumnavigation of the Earth took place from August 1803 to August 1806. It was sponsored by Count Nikolay Rumyantsev and was headed by Adam Johann von Krusenstern.-Events:...
- Geography of RussiaGeography of RussiaThe geography of Russia entails the physical and human geography of Russia, a country extending over much of northern Eurasia. Comprising much of eastern Europe and northern Asia, it is the world's largest country in total area. Due to its size, Russia displays both monotony and diversity. As with...
- Great Northern ExpeditionGreat Northern ExpeditionThe Great Northern Expedition or Second Kamchatka expedition was one of the largest organised exploration enterprises in history, resulting in mapping of the most of the Arctic coast of Siberia and some parts of the North America coastline, greatly reducing the "white areas" on the maps...
- List of explorers
- List of Russian Admirals
- List of Russian aviators
- Northern Sea RouteNorthern Sea RouteThe Northern Sea Route is a shipping lane officially defined by Russian legislation from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean specifically running along the Russian Arctic coast from Murmansk on the Barents Sea, along Siberia, to the Bering Strait and Far East. The entire route lies in Arctic...
- Russian cultureRussian cultureRussian culture is associated with the country of Russia and, sometimes, specifically with ethnic Russians. It has a rich history and can boast a long tradition of excellence in every aspect of the arts, especially when it comes to literature and philosophy, classical music and ballet, architecture...
- Russian Geographical SocietyRussian Geographical SocietyThe Russian Geographical Society is a learned society, founded on 6 August 1845 in Saint Petersburg, Russia.-Imperial Geographical Society:Prior to the Russian Revolution of 1917, it was known as the Imperial Russian Geographical Society....
- Soviet Antarctic ExpeditionSoviet Antarctic ExpeditionThe Soviet Antarctic Expedition was part of the Arctic and Antarctic Research Institute of the Soviet Committee on Antarctic Research of the Academy of Sciences of the USSR....
s - Siberian river routesSiberian River RoutesSiberian River Routes were the main ways of communication in the Russian Siberia before the 1730s, when roads began to be built. The rivers also were of primary importance in the process of Russian exploration and colonisation of vast Siberian territories...
- Soviet space programSoviet space programThe Soviet space program is the rocketry and space exploration programs conducted by the former Union of Soviet Socialist Republics from the 1930s until its dissolution in 1991...

