
Pericope Adulteræ
Encyclopedia

or Pericope de Adultera is a traditional name for a famous passage (pericope
Pericope
A pericope in rhetoric is a set of verses that forms one coherent unit or thought, thus forming a short passage suitable for public reading from a text, now usually of sacred scripture....
) about Jesus and the woman taken in adultery from verses
Chapters and verses of the Bible
The Bible is a compilation of many shorter books written at different times and later assembled into the Biblical canon. All but the shortest of these books have been divided into chapters, generally a page or so in length, since the early 13th century. Since the mid-16th century, each chapter has...
of the Gospel of John
Gospel of John
The Gospel According to John , commonly referred to as the Gospel of John or simply John, and often referred to in New Testament scholarship as the Fourth Gospel, is an account of the public ministry of Jesus...
. The passage describes a confrontation between Jesus
Jesus
Jesus of Nazareth , commonly referred to as Jesus Christ or simply as Jesus or Christ, is the central figure of Christianity...
and the scribe
Scribe
A scribe is a person who writes books or documents by hand as a profession and helps the city keep track of its records. The profession, previously found in all literate cultures in some form, lost most of its importance and status with the advent of printing...
s and Pharisees
Pharisees
The Pharisees were at various times a political party, a social movement, and a school of thought among Jews during the Second Temple period beginning under the Hasmonean dynasty in the wake of...
over whether a woman, caught in an act of adultery
Adultery
Adultery is sexual infidelity to one's spouse, and is a form of extramarital sex. It originally referred only to sex between a woman who was married and a person other than her spouse. Even in cases of separation from one's spouse, an extramarital affair is still considered adultery.Adultery is...
, ought to be stoned
Stoning
Stoning, or lapidation, is a form of capital punishment whereby a group throws stones at a person until the person dies. No individual among the group can be identified as the one who kills the subject, yet everyone involved plainly bears some degree of moral culpability. This is in contrast to the...
. Jesus shames the crowd into dispersing, and averts the execution.
Although in line with many stories in the Gospels and probably primitive (Didascalia Apostolorum
Didascalia Apostolorum
Didascalia Apostolorum is a Christian treatise which belongs to genre of the Church Orders. It presents itself as being written by the Twelve Apostles at the time of the Council of Jerusalem, however, scholars agree that it was actually a composition of the 3rd century CE, perhaps around 230...
refers to it, possibly Papias also), most scholars argue that it was "certainly not part of the original text of St John's Gospel." On the other hand, the Council of Trent declared that the Latin Vulgate was authentic and authoritative. The Latin Vulgate includes the adultery episode in John 7:53-8:11.
The parable, and its messages of not being quick to condemn when one is not blameless and tempering justice with mercy, have endured in Christian thought. Both "he that is without sin, cast the first stone" and "go, and sin no more" have found their way into common usage.
The English idiomatic phrase to "cast the first stone" is derived from this passage. The subject was fairly common in art, especially from the Renaissance
Renaissance
The Renaissance was a cultural movement that spanned roughly the 14th to the 17th century, beginning in Italy in the Late Middle Ages and later spreading to the rest of Europe. The term is also used more loosely to refer to the historical era, but since the changes of the Renaissance were not...
onwards; Christ and the Woman Taken in Adultery by Pieter Bruegel is a famous example. There was a medieval tradition, originating in a comment attributed to Ambrose
Ambrose
Aurelius Ambrosius, better known in English as Saint Ambrose , was a bishop of Milan who became one of the most influential ecclesiastical figures of the 4th century. He was one of the four original doctors of the Church.-Political career:Ambrose was born into a Roman Christian family between about...
, that the words written were terra terram accusat ("earth accuses earth"), which is shown in some depictions in art, for example the Codex Egberti. There have also been other suggestions as to what was written. To some Christians not concerned with textual disputes, the passage has been taken as confirmation of the literacy of Jesus, otherwise only suggested by implication in the Gospels, but the word "εγραφεν" in 8:8 could mean "draw" as well as "write".
The passage
in the Authorized Version:
7:53 And every man went unto his own house.
8:1 ¶ Jesus went unto the mount of Olives.
8:2 And early in the morning he came again into the temple, and all the people came unto him; and he sat down, and taught them.
8:3 And the scribes and Pharisees brought unto him a woman taken in adultery; and when they had set her in the midst,
8:4 They say unto him, Master, this woman was taken in adultery, in the very act.
8:5 Now Moses in the law commanded us, that such should be stoned: but what sayest thou?
8:6 This they said, tempting him, that they might have to accuse him. But Jesus stooped down, and with his finger wrote on the ground, as though he heard them not.
8:7 So when they continued asking him, he lifted up himself, and said unto them, He that is without sin among you, let him first cast a stone at her.
8:8 And again he stooped down, and wrote on the ground.
8:9 And they which heard it, being convicted by their own conscience, went out one by one, beginning at the eldest, even unto the last: and Jesus was left alone, and the woman standing in the midst.
8:10 When Jesus had lifted up himself, and saw none but the woman, he said unto her, Woman, where are those thine accusers? hath no man condemned thee?
8:11 She said, No man, Lord. And Jesus said unto her, Neither do I condemn thee: go, and sin no more.
Textual history
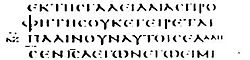
Pericope
A pericope in rhetoric is a set of verses that forms one coherent unit or thought, thus forming a short passage suitable for public reading from a text, now usually of sacred scripture....
is not found in any place in any of the earliest surviving Greek Gospel manuscripts; neither in the two 3rd century papyrus
Papyrus
Papyrus is a thick paper-like material produced from the pith of the papyrus plant, Cyperus papyrus, a wetland sedge that was once abundant in the Nile Delta of Egypt....
witnesses to John - P66
Papyrus 66
Papyrus 66 is a near complete codex of the Gospel of John, and part of the collection known as the Bodmer Papyri.-Description:...
and P75
Papyrus 75
Papyrus 75 is an early Greek New Testament papyrus.- Description :Originally '[it] contained about 144 pages ... of which 102 have survived, either in whole or in part.' It 'contains about half the text of ... two Gospels' – Luke and John in Greek...
; nor in the 4th century Codex Sinaiticus
Codex Sinaiticus
Codex Sinaiticus is one of the four great uncial codices, an ancient, handwritten copy of the Greek Bible. It is an Alexandrian text-type manuscript written in the 4th century in uncial letters on parchment. Current scholarship considers the Codex Sinaiticus to be one of the best Greek texts of...
and Vaticanus, although all four of these manuscripts may acknowledge the existence of the passage via diacritical marks at the spot. The first surviving Greek manuscript to contain the pericope is the Latin/Greek diglot Codex Bezae
Codex Bezae
The Codex Bezae Cantabrigensis, designated by siglum Dea or 05 , δ 5 , is a codex of the New Testament dating from the 5th century written in an uncial hand on vellum. It contains, in both Greek and Latin, most of the four Gospels and Acts, with a small fragment of the 3 John...
of the late 4th or early 5th century. It is also the earliest surviving Latin manuscript to contain it; 17 of the 23 Old Latin manuscripts of John 7-8 contain at least part of the Pericope. Papias (circa AD 125) refers to a story of Jesus and a woman "accused of many sins" as being found in the Gospel of the Hebrews
Gospel of the Hebrews
The Gospel of the Hebrews , commonly shortened from the Gospel according to the Hebrews or simply called the Hebrew Gospel, is a hypothesised lost gospel preserved in fragments within the writings of the Church Fathers....
, which may well refer to this passage; there is a very certain quotation of the pericope adulterae in the 3rd Century Syriac Didascalia Apostolorum
Didascalia Apostolorum
Didascalia Apostolorum is a Christian treatise which belongs to genre of the Church Orders. It presents itself as being written by the Twelve Apostles at the time of the Council of Jerusalem, however, scholars agree that it was actually a composition of the 3rd century CE, perhaps around 230...
; though without indicating John's Gospel. The Constitutions of the Holy Apostles
Apostolic Constitutions
The Apostolic Constitutions is a Christian collection of eight treatises which belongs to genre of the Church Orders. The work can be dated from 375 to 380 AD. The provenience is usually regarded as Syria, probably Antioch...
Book II.24 refers to the passage “And when the elders had set another woman who had sinned before Him, and had left the sentence to Him, and were gone out, our Lord, the Searcher of the hearts, inquiring of her whether the elders had condemned her, and being answered No, He said unto her: “Go thy way therefore, for neither do I condemn thee.” Book II is generally dated to the late third century (Von Drey, Krabbe, Bunsen, Funk). Codex Fuldensis
Codex Fuldensis
The Codex Fuldensis, designated by F, is a New Testament manuscript based on the Latin Vulgate made between 541 and 546. The codex is considered the second most important witness to the Vulgate text; and is also the oldest complete manuscript witness to the order of the Diatessaron. It is an...
, which is positively dated to AD 546 contains the adulterae pericope. The Second Epistle of Pope Callistus section 6 contains a quote that may be from John 8:11 - "Let him see to it that he sin no more, that the sentence of the Gospel may abide in him: “Go, and sin no more.”" However the epistle quotes from eighth century writings and is not thought to be genuine.
Until recently, it was not thought that any Greek Church Father had taken note of the passage before the 12th Century; but in 1941 a large collection of the writings of Didymus the Blind
Didymus the Blind
Didymus the Blind was a Coptic Church theologian of Alexandria, whose famous Catechetical School he led for about half a century. He became blind at a very young age, and therefore ignorant of the rudiments of learning...
(ca. 313- 398) was discovered in Egypt, including a reference to the pericope adulterae as being found in "several copies"; and it is now considered established that this passage was present in its usual place in some Greek manuscripts known in Alexandria and elsewhere from the 4th Century onwards. In support of this it is noted that the 4th century Codex Vaticanus, which was written in Egypt, marks the end of John chapter 7 with an "umlaut", indicating that an alternative reading was known at this point.
Jerome
Jerome
Saint Jerome was a Roman Christian priest, confessor, theologian and historian, and who became a Doctor of the Church. He was the son of Eusebius, of the city of Stridon, which was on the border of Dalmatia and Pannonia...
reports that the pericope adulterae was to be found in its usual place in "many Greek and Latin manuscripts" in Rome and the Latin West in the late 4th Century. This is confirmed by some of Latin Fathers of the 4th and 5th Centuries CE; including Ambrose
Ambrose
Aurelius Ambrosius, better known in English as Saint Ambrose , was a bishop of Milan who became one of the most influential ecclesiastical figures of the 4th century. He was one of the four original doctors of the Church.-Political career:Ambrose was born into a Roman Christian family between about...
, and Augustine
Augustine of Hippo
Augustine of Hippo , also known as Augustine, St. Augustine, St. Austin, St. Augoustinos, Blessed Augustine, or St. Augustine the Blessed, was Bishop of Hippo Regius . He was a Latin-speaking philosopher and theologian who lived in the Roman Africa Province...
. The latter claimed that the passage may have been improperly excluded from some manuscripts in order to avoid the impression that Christ had sanctioned adultery:
"Certain persons of little faith, or rather enemies of the true faith, fearing, I suppose, lest their wives should be given impunity in sinning, removed from their manuscripts the Lord's act of forgiveness toward the adulteress, as if he who had said, Sin no more, had granted permission to sin."
History of textual criticism on John 7:53-8:11
The first to systematically apply the critical marks of the Alexandrian critics was OrigenOrigen
Origen , or Origen Adamantius, 184/5–253/4, was an early Christian Alexandrian scholar and theologian, and one of the most distinguished writers of the early Church. As early as the fourth century, his orthodoxy was suspect, in part because he believed in the pre-existence of souls...
:
"In the Septuagint column [Origen] used the system of diacritical marks which was in use with the Alexandrian critics of Homer, especially Aristarchus, marking with an obelusObelusAn obelus is a symbol consisting of a short horizontal line with a dot above and below. It is mainly used to represent the mathematical operation of division. It is therefore commonly referred to as the division sign.- History :The word "obelus" comes from the Greek word for a sharpened stick,...
under different forms, as "./.", called lemniscus, and "/.", called a hypolemniscus, those passages of the Septuagint which had nothing to correspond to in Hebrew, and inserting, chiefly from Theodotion under an asterisk (*), those which were missing in the Septuagint; in both cases a metobelus (Y) marked the end of the notation."
Early textual critics familiar with the use and meaning of these marks in classical Greek works like Homer
Homer
In the Western classical tradition Homer , is the author of the Iliad and the Odyssey, and is revered as the greatest ancient Greek epic poet. These epics lie at the beginning of the Western canon of literature, and have had an enormous influence on the history of literature.When he lived is...
, interpreted the signs to mean that the section (John 7:53-8:11) was an interpolation
Interpolation (manuscripts)
An interpolation, in relation to literature and especially ancient manuscripts, is an entry or passage in a text that was not written by the original author...
and not an original part of the Gospel.
During the 16th Century, Western European scholars – both Catholic
Catholic
The word catholic comes from the Greek phrase , meaning "on the whole," "according to the whole" or "in general", and is a combination of the Greek words meaning "about" and meaning "whole"...
and Protestant – sought to recover the most correct Greek text of the New Testament
New Testament
The New Testament is the second major division of the Christian biblical canon, the first such division being the much longer Old Testament....
, rather than relying on the Vulgate
Vulgate
The Vulgate is a late 4th-century Latin translation of the Bible. It was largely the work of St. Jerome, who was commissioned by Pope Damasus I in 382 to make a revision of the old Latin translations...
Latin translation. At this time, it was noticed that a number of early manuscripts containing John's Gospel lacked John 7:53-8:11 inclusive; and also that some manuscripts containing the verses marked them with critical signs, usually a lemniscus or asterisk
Asterisk
An asterisk is a typographical symbol or glyph. It is so called because it resembles a conventional image of a star. Computer scientists and mathematicians often pronounce it as star...
. It was also noted that, in the lectionary of the Greek church, the set gospel reading for Pentecost runs from John 7:37 to 8:12, but skips over the twelve verses of this pericope.
Beginning with Lachmann (in Germany, 1840), reservations about the pericope became more strongly argued in the modern period, and these opinions were carried into the English world by Samuel Davidson
Samuel Davidson
Samuel Davidson was an Irish biblical scholar who was born near Ballymena in Ireland.He was educated at the Royal College of Belfast, entered the Presbyterian ministry in 1835, and was appointed professor of biblical criticism at his own college...
(1848–1851), Tregelles
Samuel Prideaux Tregelles
Samuel Prideaux Tregelles was an English biblical scholar, textual critic, and theologian.- Life :Tregelles was born at Wodehouse Place, Falmouth, of Quaker parents, but he himself for many years was in communion with the Plymouth Brethren and then later in life became a Presbyterian...
(1862), and others; the argument against the verses being given body and final expression in Hort
Fenton John Anthony Hort
Fenton John Anthony Hort was an Irish theologian and editor, with Brooke Westcott of a critical edition of The New Testament in the Original Greek.-Life:...
(1886). Those opposing the authenticity of the verses as part of John are represented in the 20th century by men like Cadbury (1917), Colwell (1935), and Metzger (1971).
According to Henry Alford
Henry Alford
Henry Alford was an English churchman, theologian, textual critic, scholar, poet, hymnodist, and writer.-Life:...
and Scrivener the passage was added by John in a second edition of the Gospel along with 5:3.4 and the 21st chapter.
On the other hand, many scholars strongly defend the Johannine authorship of these verses, and present opposing arguments and counter-analysis. This group of critics is typified by such scholars as Nolan (1865), and Burgon
John William Burgon
John William Burgon was an English Anglican divine who became the Dean of Chichester Cathedral in 1876. He is remembered for his passionate defence of the historicity and Mosaic authorship of Genesis and of Biblical inerrancy in general.-Biography:Burgon was born at Smyrna, the son of an English...
(1886); and find modern counterparts and apologists in Hoskier (1920), O.T. Fuller (1978), Pickering (1980), Hodges & Farstad (1985), Pierpont, and Robinson (2005).
Almost all modern translations now include the Pericope de Adultera at John 7:53-8:11; but some enclose it in brackets, and/or add a note concerning the oldest and most reliable witnesses.
Arguments against Johannine authorship
Bishop J.B. LightfootJoseph Barber Lightfoot
Joseph Barber Lightfoot was an English theologian and Bishop of Durham, usually known as J.B. Lightfoot....
wrote that absence of the passage from the earliest manuscripts, combined with the occurrence of stylistic characteristics atypical of John, together implied that the passage was an interpolation
Interpolation (manuscripts)
An interpolation, in relation to literature and especially ancient manuscripts, is an entry or passage in a text that was not written by the original author...
. Nevertheless, he considered the story to be authentic history. As a result, based on Eusebius' mention that the writings of Papias contained a story "about a woman falsely accused before the Lord of many sins" (H.E. 3.39), he argued that this section originally was part of Papias' Interpretations of the Sayings of the Lord, and included it in his collection of Papias' fragments. However, Michael W. Holmes has pointed out that it is not certain "that Papias knew the story in precisely this form, inasmuch as it now appears that at least two independent stories about Jesus and a sinful woman circulated among Christians in the first two centuries of the church, so that the traditional form found in many New Testament manuscripts may well represent a conflation of two independent shorter, earlier versions of the incident."
Arguments for Johannine authorship
Zane C. HodgesZane C. Hodges
Zane Clark Hodges was an American pastor, seminary professor, and Bible scholar. He was reared in Chambersburg, Pennsylvania, and came to Dallas, Texas in 1954 after receiving a bachelor's degree from Wheaton College. He received master of theology degree from Dallas Theological Seminary in 1958...
and Arthur L. Farstad argue for Johannine authorship of the pericope. They suggest points of similarity between the pericope's style and the style of the rest of the gospel. They claim that the details of the encounter fit very well into the context of the surrounding verses. They argue that the pericope's appearance in the majority of manuscripts, if not in the oldest ones, is evidence of its authenticity.
Manuscript evidence

Novum Testamentum Graece
Novum Testamentum Graece is the Latin name editions of the original Greek-language version of the New Testament.The first printed edition was the Complutensian Polyglot Bible by Cardinal Francisco Jiménez de Cisneros, printed in 1514, but not published until 1520...
(NA27) and the United Bible Societies
United Bible Societies
The United Bible Societies is a worldwide association of Bible societies. In 1946 delegates from 13 countries formed the UBS, as an effort to coordinate the activities of the bible societies. The first headquarters were London and in Geneva...
(UBS4) provide critical text for the pericope, but mark this off with
However, UBS4 rates its reconstruction of the wording of the pericope as { A }, meaning "virtually certain" to reflect the original text of the addition.
- Exclude pericope. Papyri 66Papyrus 66Papyrus 66 is a near complete codex of the Gospel of John, and part of the collection known as the Bodmer Papyri.-Description:...
(c. 200) and 75Papyrus 75Papyrus 75 is an early Greek New Testament papyrus.- Description :Originally '[it] contained about 144 pages ... of which 102 have survived, either in whole or in part.' It 'contains about half the text of ... two Gospels' – Luke and John in Greek...
(early 3rd century); Codices SinaiticusCodex SinaiticusCodex Sinaiticus is one of the four great uncial codices, an ancient, handwritten copy of the Greek Bible. It is an Alexandrian text-type manuscript written in the 4th century in uncial letters on parchment. Current scholarship considers the Codex Sinaiticus to be one of the best Greek texts of...
and Vaticanus (4th century), also apparently AlexandrinusCodex AlexandrinusThe Codex Alexandrinus is a 5th century manuscript of the Greek Bible,The Greek Bible in this context refers to the Bible used by Greek-speaking Christians who lived in Egypt and elsewhere during the early history of Christianity...
and EphraemiCodex Ephraemi RescriptusCodex Ephraemi Rescriptus is an early 5th century Greek manuscript of the Bible, the last in the group of the four great uncial manuscripts...
(5th), Codices WashingtonianusCodex WashingtonianusThe Codex Washingtonianus or Codex Washingtonensis, designated by W or 032 , ε 014 , also called the Washington Manuscript of the Gospels, and The Freer Gospel, contains the four biblical gospels and was written in Greek on vellum in the fourth or fifth century...
and BorgianusCodex BorgianusCodex Borgianus, designated by T or 029 , ε 5 , is a Greek and Sahidic uncial manuscript of the Gospels, dated palaeographically to the 5th century...
also from the 5th century, RegiusCodex Regius (New Testament)Codex Regius designated by siglum Le or 019 , ε 56 , is a Greek uncial manuscript of the New Testament, dated paleographically to the 8th century. The manuscript is lacunose. It has marginalia....
from the 8th, Athous Lavrensis (c. 800), Petropolitanus PurpureusCodex Petropolitanus PurpureusCodex Petropolitanus Purpureus, designated by N or 022 , ε 19 , is a 6th century Greek New Testament codex gospel book. Written in majuscules , on 231 parchment leaves, measuring 32 x 27 cm...
, MacedoniensisCodex MacedoniensisCodex Macedoniensis or Macedonianus designated by Y or 034 , ε 073 , is a Greek uncial manuscript of the Gospels, dated palaeographically to the 9th century. The manuscript is lacunose....
, Sangallensis and KoridethiCodex KoridethiThe Codex Koridethi, also named Codex Coridethianus, designated by Θ, 038, or Theta , ε 050 , is a 9th century manuscript of the four Gospels. It is written in Greek with uncial script in two columns per page, in 25 lines per page...
from the 9th century and MonacensisCodex MonacensisCodex Monacensis designated by X or 033 , A3 , is a Greek uncial manuscript of the Gospels, dated palaeographically to the 9th or 10th century...
from the 10th; Uncials 0141Uncial 0141Uncial 0141 , CL13 , is a Greek uncial manuscript of the New Testament, dated palaeographically to the 10th century.- Description :...
and 0211Uncial 0211Uncial 0211 , ε 051 , is a Greek uncial manuscript of the New Testament, dated paleographically to the 7th century.- Description :...
; Minuscules 3Minuscule 3Minuscule 3 , δ 253 . It is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on a parchment. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 12th century...
, 12Minuscule 12Minuscule 12 , A137 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment, dated palaeographically to the 14th century.- Description :...
, 15Minuscule 15Minuscule 15 , ε 283 . It is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on 225 parchment leaves , dated palaeographically to the 12th century. It has full marginalia.- Description :...
, 21Minuscule 21Minuscule 21 , ε 286 . It is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament. Written on parchment. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 12th century. According to Scrivener it was written in the 10th century...
, 22Minuscule 22Minuscule 22 , ε 288 , known also as Codex Colbertinus 2467. It is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, written on vellum. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 12th century. Formerly it was assigned to the 11th century...
, 32Minuscule 32Minuscule 32 , ε 296 . It is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, written on vellum, on 244 leaves . Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 12th century...
, 33Minuscule 33Minuscule 33 , δ 48 , formerly it was called Codex Colbertinus 2844, is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament on parchment, dated palaeographically to the 9th century. The manuscript is lacunose. It has marginalia...
, 36Minuscule 36Minuscule 36 , A20 . It is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, written on vellum. Paleographically it has been assigned to the 12th century. It has complex contents and full marginalia.- Description :...
, 39Minuscule 39Minuscule 39 , A140 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, written on vellum. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 11th century. It has complex contents and some marginalia.- Description :...
, 44Minuscule 44Minuscule 44 , ε 239 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment leaves. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 12th century. It has complex contents and full marginalia....
, 49Minuscule 49Minuscule 49 , ε 155 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment leaves. Paleographically it has been assigned to the 12th century. It has complex contents and full marginalia....
, 63Minuscule 63Minuscule 63 , A 118 , formerly known as Ussher 1, is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment leaves. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 10th century. It has marginalia....
, 72Minuscule 72Minuscule 72 , ε 110 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment leaves. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 11th century. John Mill called it Codex Ephesinus...
, 87Minuscule 87Minuscule 87 , CL22 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment leaves. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 11th century. Formerly it was dated to the 12 century Minuscule 87 (in the Gregory-Aland numbering), CL22 (Soden), is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the...
, 96Minuscule 96Minuscule 96 , ε 514 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on paper leaves. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 15th century. It has marginalia.- Description :...
, 97Minuscule 97Minuscule 97 , α 260 , is a Greek language minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment leaves. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 12th century. The manuscript is lacunose...
, 106Minuscule 106Minuscule 106 , ε 1380 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment leaves. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 10th century.- Description :...
, 108Minuscule 108Minuscule 108 , A144 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment leaves. Paleographically it has been assigned to the 11th century. It has complex contents with some marginalia.- Description :...
, 124Minuscule 124Minuscule 124 , ε 1211 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on 188 thick parchment leaves . Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 11th century. It has marginalia....
, 131Minuscule 131Minuscule 131 , δ 467 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment leaves. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 15th century. It has marginalia.- Description :...
, 134Minuscule 134Minuscule 134 , ε 200 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment leaves. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 12th century. It has marginalia.- Description :...
, 139Minuscule 139Minuscule 139 , A202 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment leaves. It is dated by a colophon to 1173.- Description :...
, 151Minuscule 151Minuscule 151 , A17 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment leaves. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 10th century. The manuscript has complex contents...
, 157Minuscule 157Minuscule 157 , ε 207 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on vellum. According to the colophon it is dated to the year 1122. Formerly date was wrongly deciphered as 1128?...
, 169Minuscule 169Minuscule 169 , ε 305 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 11th century. It has marginalia.- Description :...
, 209Minuscule 209Minuscule 209 , δ 457 and α 1581 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment. Paleographically it has been assigned to the 14th century, with an exception to the Book of Revelation which was added to the codex in the 15th century...
, 213Minuscule 213Minuscule 213 , ε 129 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 11th century...
, 228Minuscule 228Minuscule 228 , δ 458 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment. Palaeographicaly it has been assigned to the 14th century. Formerly it was labelled by 109a and 229p.- Description :...
, 297Minuscule 297Minuscule 297 , ε 1200 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 12th century.It has marginalia- Description :...
, 388Minuscule 388Minuscule 388 , ε 302 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 13th century.It has marginalia.- Description :...
, 391Minuscule 391Minuscule 391 , A128 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment. The text represents the Byzantine textual tradition. It is dated by a colophon to the year 1055. It has marginalia....
, 401Minuscule 401Minuscule 401 , ε 236 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 12th century. It has marginalia.- Description :...
, 416Minuscule 416Minuscule 416 , ε 422 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment...
, 445Minuscule 445Minuscule 445 , ε 603 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on paper. It is dated by a colophon to the year 1506.- Description :...
, 488Minuscule 488Minuscule 488 , ε 4006 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on paper. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 14th century.Scrivener labeled it by number 514....
, 496Minuscule 496Minuscule 496 , δ 360 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 13th century. Scrivener labelled it by number 582...
, 499Minuscule 499Minuscule 499 , ε 244 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment...
, 501Minuscule 501Minuscule 501 , 588 , ε 324 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 13th century....
, 523Minuscule 523Minuscule 523 , ε 145 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on a parchment. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 14th century.Scrivener labelled it by number 489...
, 537Minuscule 537Minuscule 537 , ε 334 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on a parchment. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 12th century. Scrivener labelled it by number 550. The manuscript was prepared for liturgical use, its marginalia are not complete...
, 542Minuscule 542Minuscule 542 , ε 336 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on a parchment. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 13th century.Scrivener labelled it by number 555....
, 554Minuscule 554Minuscule 554 , ε 332 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment. It is dated by a Colophon to the year 1271 or 1272.Scrivener labelled it by number 541.- Description :...
, 565Minuscule 565Minuscule 565 , ε 93 , also known as the Empress Theodora's Codex. It is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on purple parchment, dated palaeographically to the 9th century...
, 578Minuscule 578Minuscule 578 , ε 453 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on paper. It is dated by a colophon to the year 1361.The manuscript has complex contents.- Description :...
, 584Minuscule 584Minuscule 584 , ε 1010 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 10th century. The manuscript is lacunose. It was labelled by Scrivener as 453....
, 703Minuscule 703Minuscule 703 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 11th century. The manuscript has complex contents...
, 719Minuscule 719 (Gregory-Aland)Minuscule 719 , Θε24 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on paper. It is dated by a Colophon to the year 1196. The manuscript has complex contents...
, 723Minuscule 723 (Gregory-Aland)Minuscule 723 , Θε53 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on paper. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 15th century...
, 730Minuscule 730 (Gregory-Aland)Minuscule 730 , Zε32 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament written on paper. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 14th century. The manuscript has no complex contents...
, 731Minuscule 731 (Gregory-Aland)Minuscule 731 , Θε415 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament written on paper. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 14th century. The manuscript has no complex contents...
, 736Minuscule 736 (Gregory-Aland)Minuscule 736 , Θε320 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament written on parchment. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 12th century. The manuscript has no complex contents...
, 741Minuscule 741 (Gregory-Aland)Minuscule 741 , Θε417 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament written on paper. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 14th century. The manuscript has complex contents. Scrivener labelled it as 762e.- Description :The codex contains the text of the Gospel of Luke, on 362...
, 742Minuscule 742 (Gregory-Aland)Minuscule 742 , Θε414 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament written on paper. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 15th century. The manuscript has no complex contents...
, 768Minuscule 768 (Gregory-Aland)Minuscule 768 , ε480 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament written on parchment. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 12th century. The manuscript has no complex contents. Scrivener labelled it as 859e.- Description :The codex contains the text of the four Gospels, on 222...
, 770Minuscule 770 (Gregory-Aland)Minuscule 770 , A148 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament written on parchment. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 12th century. The manuscript has no complex contents...
, 772Minuscule 772 (Gregory-Aland)Minuscule 772 , Θε418 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament written on parchment. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 14th century. The manuscript has no complex contents. Scrivener labelled it as 867e.- Description :The codex contains the text of the four Gospels, on 387...
, 773Minuscule 773 (Gregory-Aland)Minuscule 773 , A14 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament written on parchment. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 10th century. The manuscript has no complex contents. Scrivener labelled it as 868e.- Description :The codex contains the text of the four Gospels, on 285...
, 776Minuscule 776 (Gregory-Aland)Minuscule 776 , ε1228 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament written on parchment. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 11th century. The manuscript has complex contents.- Description :...
, 777Minuscule 777 (Gregory-Aland)Minuscule 777 , ε469 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament written on parchment. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 12th century. The manuscript has complex contents.- Description :...
, 780Minuscule 780 (Gregory-Aland)Minuscule 780 , ε198 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament written on parchment. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 11th century. The manuscript has complex contents.- Description :...
, 799Minuscule 799 (Gregory-Aland)Minuscule 799 , ε196 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament written on parchment. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 11th century...
, 800Minuscule 800 (Gregory-Aland)Minuscule 800 , A407 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament written on parchment. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 12th century. The manuscript is lacunose.- Description :...
, 817Minuscule 817 (Gregory-Aland)Minuscule 817 , Θε52 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament written on paper, with a commentary. It was used by Erasmus...
, 827Minuscule 827 (Gregory-Aland)Minuscule 827 , ε309 , is a 13th-century Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament on parchment.- Description :...
, 828Minuscule 828 (Gregory-Aland)Minuscule 828 , ε219 , is a 12th-century Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament on parchment.- Description :The codex contains the text of the four Gospels, on 176 parchment leaves...
, 843Minuscule 843 (Gregory-Aland)Minuscule 843 , ε237 , is a 12th-century Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament on parchment. The manuscript is lacunose.- Description :...
, 896, 989, 1077, 1100, 1178, 1230, 1241, 1242, 1253, 1333, 2193 and 2768; the majority of lectionaries; some Old LatinVetus LatinaVetus Latina is a collective name given to the Biblical texts in Latin that were translated before St Jerome's Vulgate Bible became the standard Bible for Latin-speaking Western Christians. The phrase Vetus Latina is Latin for Old Latin, and the Vetus Latina is sometimes known as the Old Latin Bible...
, the majority of the Syriac, the Sahidic dialect of the CopticCoptic languageCoptic or Coptic Egyptian is the current stage of the Egyptian language, a northern Afro-Asiatic language spoken in Egypt until at least the 17th century. Egyptian began to be written using the Greek alphabet in the 1st century...
, the GothicGothic languageGothic is an extinct Germanic language that was spoken by the Goths. It is known primarily from the Codex Argenteus, a 6th-century copy of a 4th-century Bible translation, and is the only East Germanic language with a sizable Text corpus...
, some ArmenianArmenian languageThe Armenian language is an Indo-European language spoken by the Armenian people. It is the official language of the Republic of Armenia as well as in the region of Nagorno-Karabakh. The language is also widely spoken by Armenian communities in the Armenian diaspora...
, Georgian mss. of Adysh (IX c.)Adysh GospelsThe Adysh Gospels is an important early medieval Gospel Book from Georgia.The oldest dated extant manuscript of the Georgian version of the Gospels, it was created at Shatberdi Monastery in the southwestern Georgian princedom of Klarjeti in AD 897, and later removed thence to be preserved in the...
; DiatessaronDiatessaronThe Diatessaron is the most prominent Gospel harmony created by Tatian, an early Christian apologist and ascetic. The term "diatessaron" is from Middle English by way of Latin, diatessarōn , and ultimately Greek, διὰ τεσσάρων The Diatessaron (c 160 - 175) is the most prominent Gospel harmony...
(2nd century); apparently Clement of AlexandriaClement of AlexandriaTitus Flavius Clemens , known as Clement of Alexandria , was a Christian theologian and the head of the noted Catechetical School of Alexandria. Clement is best remembered as the teacher of Origen...
(died 215), other Church FathersChurch FathersThe Church Fathers, Early Church Fathers, Christian Fathers, or Fathers of the Church were early and influential theologians, eminent Christian teachers and great bishops. Their scholarly works were used as a precedent for centuries to come...
namely TertullianTertullianQuintus Septimius Florens Tertullianus, anglicised as Tertullian , was a prolific early Christian author from Carthage in the Roman province of Africa. He is the first Christian author to produce an extensive corpus of Latin Christian literature. He also was a notable early Christian apologist and...
(died 220), OrigenOrigenOrigen , or Origen Adamantius, 184/5–253/4, was an early Christian Alexandrian scholar and theologian, and one of the most distinguished writers of the early Church. As early as the fourth century, his orthodoxy was suspect, in part because he believed in the pre-existence of souls...
(died 254), CyprianCyprianCyprian was bishop of Carthage and an important Early Christian writer, many of whose Latin works are extant. He was born around the beginning of the 3rd century in North Africa, perhaps at Carthage, where he received a classical education...
(died 258), NonnusNonnusNonnus of Panopolis , was a Greek epic poet. He was a native of Panopolis in the Egyptian Thebaid, and probably lived at the end of the 4th or early 5th century....
(died 431), Cyril of AlexandriaCyril of AlexandriaCyril of Alexandria was the Patriarch of Alexandria from 412 to 444. He came to power when the city was at its height of influence and power within the Roman Empire. Cyril wrote extensively and was a leading protagonist in the Christological controversies of the later 4th and 5th centuries...
(died 444) and CosmasCosmasCosmas or Kosmas is a Greek name and may refer to:Saints:* Saints Cosmas and Damian , Christian martyrs and physicians* Cosmas the Monk, a Sicilian monk and tutor to John of Damascus and Cosmas of Maiuma* Cosmas of Maiuma Cosmas or Kosmas is a Greek name and may refer to:Saints:* Saints Cosmas and...
(died 550). - Shorter pericope exclude. Minuscule 759Minuscule 759 (Gregory-Aland)Minuscule 759 , ε397 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament written on parchment. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 13th century. The manuscript has complex contents. Scrivener labelled it as 848e.It has marginalia.- Description :The codex contains the text of the four...
contains John 7:53-8:2 but excludes 8:3-11. - Shorter pericope include (8:3-11). ℓ 4Lectionary 4Lectionary 4, designated by siglum ℓ 4 , is a Greek manuscript of the New Testament, on vellum leaves. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 11th century.- Description :...
, ℓ 67Lectionary 67Lectionary 67, designated by siglum ℓ 675 , is a Greek manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment leaves. It is a lectionary...
, ℓ 69Lectionary 69Lectionary 69, designated by siglum ℓ 69 , is a Greek manuscript of the New Testament, on vellum leaves. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 12th century.- Description :...
, ℓ 70Lectionary 70Lectionary 70, designated by siglum ℓ 70 , is a Greek manuscript of the New Testament, on vellum leaves. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 12th century.- Description :...
, ℓ 71Lectionary 71Lectionary 71, designated by siglum ℓ 71 . It is a Greek manuscript of the New Testament, on vellum leaves. It is dated by a colophon to the year 1066.- Description :...
, ℓ 75Lectionary 75Lectionary 75, designated by siglum ℓ 75 , is a Greek manuscript of the New Testament, on vellum leaves. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the year 12th century.- Description :...
, ℓ 81Lectionary 81Lectionary 81, designated by siglum ℓ 81 , is a Greek manuscript of the New Testament, on vellum leaves. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 14th century.- Description :...
, ℓ 89Lectionary 89Lectionary 89, designated by siglum ℓ 89 , is a Greek manuscript of the New Testament, on cotton paper leaves. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 14th century.- Description :...
, ℓ 90Lectionary 90Lectionary 90, designated by siglum ℓ 90 , is a Greek manuscript of the New Testament, on paper leaves. It is dated by a colophon to the year 1553.- Description :...
, ℓ 98Lectionary 98Lectionary 98, designated by siglum ℓ 98 , is a Greek manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment leaves...
, ℓ 101Lectionary 101Lectionary 101, designated by siglum ℓ 101 , is a Greek manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment leaves...
, ℓ 107Lectionary 107Lectionary 107, designated by siglum ℓ 107 is a Greek manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment leaves. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 12th century.- Description :...
, ℓ 125Lectionary 125Lectionary 125, designated by siglum ℓ 125 is a Greek manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment leaves. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 11th century.- Description :...
, ℓ 126Lectionary 126Lectionary 126, designated by siglum ℓ 126 is a Greek manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment leaves. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 11th century.- Description :...
, ℓ 139Lectionary 139Lectionary 139, designated by siglum ℓ 139 is a Greek manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment leaves...
, ℓ 146Lectionary 146Lectionary 146, designated by sigla ℓ 146 is a Greek manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment leaves...
, ℓ 185Lectionary 185Lectionary 185, designated by siglum ℓ 185 is a Greek manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment leaves...
, ℓ 211Lectionary 211Lectionary 211, designated by siglum ℓ 211 is a Greek manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment...
, ℓ 217Lectionary 217Lectionary 217, designated by siglum ℓ 217 is a Greek manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment...
, ℓ 229Lectionary 229Lectionary 229, designated by siglum ℓ 229 is a Greek manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment...
, ℓ 267Lectionary 267Lectionary 267, designated by siglum ℓ 267 is a Greek manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment. It is dated by a colophon to the year 1046.Scrivener labelled it as 173e,Gregory by 267e...
, ℓ 280Lectionary 280Lectionary 280, designated by siglum ℓ 280 is a Greek manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment...
, ℓ 282Lectionary 282Lectionary 282, designated by siglum ℓ 282 is a Greek manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment...
, ℓ 287Lectionary 287Lectionary 287, designated by siglum ℓ 287 is a Greek manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment...
, ℓ 376, ℓ 381, ℓ 386, ℓ 390, ℓ 396, ℓ 398, ℓ 402, ℓ 405, ℓ 409, ℓ 417, ℓ 422, ℓ 430, ℓ 431, ℓ 435 (8:2-11), ℓ 462, ℓ 464, ℓ 465, ℓ 520 (8:2-11). - Include pericope. Codex BezaeCodex BezaeThe Codex Bezae Cantabrigensis, designated by siglum Dea or 05 , δ 5 , is a codex of the New Testament dating from the 5th century written in an uncial hand on vellum. It contains, in both Greek and Latin, most of the four Gospels and Acts, with a small fragment of the 3 John...
(5th century), Codex BasilensisCodex BasilensisCodex Basilensis designated by Ee or 07 , ε 55 , is a Greek uncial manuscript of the four Gospels, dated paleographically to the 8th century...
, 9th century Codices BoreelianusCodex BoreelianusCodex Boreelianus, Codex Boreelianus Rheno-Trajectinus , designated by Fe or 09 in the Gregory-Aland numbering and ε 86 in von Soden numbering, is a 9th century uncial manuscript of the four Gospels in Greek. The manuscript, written on parchment, is full of lacunae , many of which arose between...
, Seidelianus ICodex Seidelianus ICodex Seidelianus I, designated by siglum Ge or 011 , ε 87 is a Greek uncial manuscript of the Gospels, dated palaeographically to the 9th century . The codex contains 252 parchment leaves...
, Seidelianus IICodex Seidelianus IICodex Seidelianus II designated by He or 013 , ε 88 , is a Greek uncial manuscript of the four Gospels, dated palaeographically to the 9th century. The manuscript is lacunose.- Description :...
, CypriusCodex CypriusCodex Cyprius, designated by Ke or 017 , ε 71 , is a Greek uncial manuscript of the four Gospels, on parchment. It was variously dated in the past , currently it is dated to the 9th century. It was brought from Cyprus to Paris...
, CampianusCodex CampianusCodex Campianus designated by M or 021 , ε 72 , is a Greek uncial manuscript of the New Testament, dated palaeographically to the 9th century...
, NanianusCodex NanianusCodex Nanianus, designated by siglum U or 030 , ε 90 , is a Greek uncial manuscripts of the New Testament on parchment, dated palaeographically to the 9th century. The manuscript has complex contents, with full marginalia . The codex is named after its last owner...
, also Tischendorfianus IVCodex Tischendorfianus IVCodex Tischendorfianus IV – designated by Γ or 036 , ε 70 – is a Greek uncial manuscript of the Gospels, dated palaeographically to the 10th century...
from the 10th, Codex PetropolitanusCodex Petropolitanus (New Testament)Codex Petropolitanus, designated by Π or 041 , ε 73 , is a Greek uncial manuscript of the Gospels, dated palaeographically to the 9th century...
; Minuscule 28Minuscule 28Minuscule 28 , ε 168 , formerly known as Colbertinus 4705, is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, written on vellum. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 11th century. It has marginalia. It is lacunose.- Description :The codex contains the text of the four Gospels on 292...
, 318Minuscule 318Minuscule 318 , Θε409 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 14th century.- Description :...
, 700Minuscule 700Minuscule 700 , ε 133 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the Gospels. Formerly it was labelled as 604 in all catalogues , Gregory gave it the number 700....
, 892Minuscule 892Minuscule 892 , ε 1016 . It is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on 353 parchment leaves . It is dated palaeografically to the 9th century.- Description :...
, 1009, 1010, 1071, 1079, 1195, 1216, 1344, 1365, 1546, 1646, 2148, 2174; the Byzantine majority textByzantine text-typeThe Byzantine text-type is one of several text-types used in textual criticism to describe the textual character of Greek New Testament manuscripts. It is the form found in the largest number of surviving manuscripts, though not in the oldest...
; ℓ 79Lectionary 79Lectionary 79, designated by siglum ℓ 79 , is a Greek manuscript of the New Testament, on vellum leaves...
, ℓ 100Lectionary 100Lectionary 100, designated by siglum ℓ 100 , is a Greek manuscript of the New Testament, on paper leaves. It is dated by a colophon to the year 1550.- Description :...
(John 8:1-11), ℓ 118Lectionary 118Lectionary 118, designated by siglum ℓ 118 is a Greek manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment leaves. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 14th century.- Description :...
, ℓ 130Lectionary 130Lectionary 130, designated by siglum ℓ 130 is a Greek manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment leaves. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 10th century.- Description :...
(8:1-11), ℓ 221Lectionary 221Lectionary 221, designated by siglum ℓ 221 is a Greek manuscript of the New Testament, on paper. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 15th century.Scrivener labelled it by 245evl....
, ℓ 274Lectionary 274Lectionary 274, designated by siglum ℓ 274 is a Greek manuscript of the New Testament, on paper. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 16th century.Formerly it was known as Nanianus 202...
, ℓ 281Lectionary 281Lectionary 281, designated by siglum ℓ 281 is a Greek manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment...
, ℓ 411, ℓ 421, ℓ 429 (8:1-11), ℓ 442 (8:1-11), ℓ 445 (8:1-11), ℓ 459; the majority of the Old LatinVetus LatinaVetus Latina is a collective name given to the Biblical texts in Latin that were translated before St Jerome's Vulgate Bible became the standard Bible for Latin-speaking Western Christians. The phrase Vetus Latina is Latin for Old Latin, and the Vetus Latina is sometimes known as the Old Latin Bible...
, the VulgateVulgateThe Vulgate is a late 4th-century Latin translation of the Bible. It was largely the work of St. Jerome, who was commissioned by Pope Damasus I in 382 to make a revision of the old Latin translations...
(Codex FuldensisCodex FuldensisThe Codex Fuldensis, designated by F, is a New Testament manuscript based on the Latin Vulgate made between 541 and 546. The codex is considered the second most important witness to the Vulgate text; and is also the oldest complete manuscript witness to the order of the Diatessaron. It is an...
), some Syriac, the Bohairic dialect of the Coptic, some Armenian, and the Ethopian translations; Didascalia (3rd century), Didymus the BlindDidymus the BlindDidymus the Blind was a Coptic Church theologian of Alexandria, whose famous Catechetical School he led for about half a century. He became blind at a very young age, and therefore ignorant of the rudiments of learning...
(4th century), AmbrosiasterAmbrosiasterAmbrosiaster is the name given to the writer of a commentary on St Paul's epistles, "brief in words but weighty in matter," and valuable for the criticism of the Latin text of the New Testament...
(4th century), AmbroseAmbroseAurelius Ambrosius, better known in English as Saint Ambrose , was a bishop of Milan who became one of the most influential ecclesiastical figures of the 4th century. He was one of the four original doctors of the Church.-Political career:Ambrose was born into a Roman Christian family between about...
(died 397), John ChrysostomJohn ChrysostomJohn Chrysostom , Archbishop of Constantinople, was an important Early Church Father. He is known for his eloquence in preaching and public speaking, his denunciation of abuse of authority by both ecclesiastical and political leaders, the Divine Liturgy of St. John Chrysostom, and his ascetic...
(died 407), JeromeJeromeSaint Jerome was a Roman Christian priest, confessor, theologian and historian, and who became a Doctor of the Church. He was the son of Eusebius, of the city of Stridon, which was on the border of Dalmatia and Pannonia...
(died 420), AugustineAugustine of HippoAugustine of Hippo , also known as Augustine, St. Augustine, St. Austin, St. Augoustinos, Blessed Augustine, or St. Augustine the Blessed, was Bishop of Hippo Regius . He was a Latin-speaking philosopher and theologian who lived in the Roman Africa Province...
(died 430). - Question pericope. Marked with asterisks (*) or obeli (÷). Codex Vaticanus 354Codex Vaticanus 354Codex Vaticanus, designated by S or 028 , ε 1027 , formerly called Codex Guelpherbytanus, is a Greek manuscript of the four Gospels which can be dated to a specific year instead of an estimated range. The colophon of the codex lists the date as 949...
(S) and the Minuscules 4Minuscule 4Minuscule 4 , ε 371 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on 212 parchment leaves , dated palaeographically to the 13th century. Formerly it was named Codex Regius 84.It has full marginalia...
, 8Minuscule 8Minuscule 8 , ε 164 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament on parchment. It is dated palaeographically to the 11th century. The manuscript has complex contents. It has complex contents anbd full marginalia.- Description :The codex contains the complete text of the four Gospels, on...
, 14Minuscule 14Minuscule 14 , ε 1021 . It is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on 392 parchment leaves , dated by a colophon to the year 964 CE.- Description :...
, 18Minuscule 18Minuscule 18 , δ 411 . It is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament. According to the colophon it was written in the year 1364 CE. The manuscript has complex contents. It has marginalia.- Description :...
, 24Minuscule 24Minuscule 24 , A18 . It is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, written on vellum. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 10th century.- Description :...
, 35Minuscule 35Minuscule 35 , δ309 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, written on 328 parchment leaves . Paleographically it has been assigned to the 11th century. The manuscript has complex contents, marginalia, and many corrections.- Description :The codex contains the entire New Testament...
, 83Minuscule 83Minuscule 83 , ε 1218 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment leaves. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 11th century. It was adapted for liturgical use. It has marginalia....
, 95Minuscule 95Minuscule 95 , A212 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment leaves. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 12th century. It has marginalia.- Description :...
(questionable scholion), 109Minuscule 109Minuscule 109 , ε 431 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment leaves. It is dated by a colophon to the year 1326. The manuscript has complex contents.- Description :...
, 125Minuscule 125Minuscule 125 , ε 1028 . It is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament on a parchment. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 11th century...
, 141Minuscule 141Minuscule 141 , δ 408 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment leaves. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 13th century. The manuscript has complex contents...
, 148Minuscule 148Minuscule 148 , ε 132 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment leaves. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 11th century...
, 156Minuscule 156Minuscule 156 , ε 206 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment. Paleographically it has been assigned to the 12th century. It has marginalia.- Description :...
, 161Minuscule 161Minuscule 161 , ε 1005 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 10th century...
, 164Minuscule 164Minuscule 164 , ε 116 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment. It is dated by its colophon to the year 1039. It has complex contents, with full marginalia.- Description :...
, 165Minuscule 165Minuscule 165 , ε 1320 , is a Greek-Latin minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment. It is dated by its colophon to the year 1292. It has complex contents. It has marginalia.- Description :...
, 166Minuscule 166Minuscule 166 , ε 306 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 11th or 12th centuries. It has marginalia.- Description :...
, 167Minuscule 167Minuscule 167 , ε 305 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 13th century. It has marginalia.-Description:...
, 178Minuscule 178Minuscule 178 , ε 210 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 12th century. It has marginalia.- Description :...
, 179Minuscule 179Minuscule 179 , ε 211 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 12th century. It has marginalia.- Description :...
, 200Minuscule 200Minuscule 200 , ε 118 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 11th century. It has marginalia.- Description :...
, 202Minuscule 202Minuscule 202 , ε 242 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment. Paleographically it has been assigned to the 12th century. It has marginalia.- Description :...
, 285Minuscule 285Minuscule 285 , ε 527 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment. Paleographically it has been assigned to the 15th century.It has marginalia.- Description :...
, 338Minuscule 338Minuscule 338 , ε 1006 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 10th century. The manuscript has complex contents.It has marginalia....
, 348Minuscule 348Minuscule 348 , ε 227 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment. Dated by a colophon to the year 1022 .It has full marginalia.- Description :...
, 363Minuscule 363Minuscule 363 , δ 455 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment. Paleographically it has been assigned to the 14th century.It was adapted for liturgical use.- Description :...
, 367Minuscule 367Minuscule 367 , δ 400 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on paper. It is dated by a Colophon to the year 1331 .It has marginalia.- Description :...
, 376Minuscule 376Minuscule 376 , ε 100 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment. Paleographically it has been assigned to the 11th century.It has marginalia.- Description :...
, 386Minuscule 386Minuscule 386 , δ 401 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment. Paleographically it has been assigned to the 14th century.It has complex context and some marginalia.- Description :...
, 407Minuscule 407Minuscule 407 , ε 320 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment. Paleographically it has been assigned to the 12th century.It contains marginalia.- Description :...
, 443Minuscule 443Minuscule 443 , ε 270 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 12th century.- Description :...
, 478Minuscule 478Minuscule 478 , α 1126 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 10th century. Scrivener labeled it by number 575...
, 479Minuscule 479Minuscule 479 , δ 2491 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 13th century. Scrivener labelled it by number 542. It was adapted for liturgical use...
, 510Minuscule 510Minuscule 510 , 496 , ε 259 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment. It has been assigned to the 12th century. The manuscript has complex contents. Marginalia are incomplete...
, 532Minuscule 532Minuscule 532 , ε 255 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 12th century.Scrivener labeled it number 545....
, 547Minuscule 547Minuscule 547 , δ 157 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment...
, 553Minuscule 553Minuscule 553 , ε 331 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 13th century.Scrivener labelled it by number 540....
, 645Minuscule 645Minuscule 645 , ε 434 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment. It is dated by a colophon to the year 1304 . The manuscript has complex contents. Scrivener labelled it by 591e....
, 655Minuscule 655Minuscule 655 , ε 177 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 12th century. The manuscript has complex contents. Scrivener labelled it by 635e.- Description :The codex contains the text of the four Gospels, on 324 parchment...
, 656Minuscule 656Minuscule 656 , δ 463 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 12th century. The manuscript is lacunose...
, 661Minuscule 661Minuscule 661 , ε 179 , is a Greek language minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 11th century. The manuscript has complex contents. Scrivener labelled it by 639e.-Description:The codex contains a complete text of the four Gospels, on...
, 662Minuscule 662Minuscule 662 , ε 298 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 12th century. The manuscript is lacunose...
, 685Minuscule 685Minuscule 685 ε 339 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament on a parchment. It is dated palaeographically to the 13th century. Scrivener labelled it by 1147e.- Description :...
, 757Minuscule 757 (Gregory-Aland)Minuscule 757 , δ304 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament written on paper. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 13th century. The manuscript has no complex contents...
, 758Minuscule 758 (Gregory-Aland)Minuscule 758 , ε474 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament written on parchment. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 14th century. The manuscript has complex contents. Scrivener labelled it as 847e.- Description :The codex contains the text of the four Gospels, on 301...
, 763Minuscule 763 (Gregory-Aland)Minuscule 763 , ε539 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament written on parchment. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 14th century. The manuscript has complex contents. Scrivener labelled it as 854e.- Description :The codex contains the text of the four Gospels, on 324...
, 769Minuscule 769 (Gregory-Aland)Minuscule 769 , ε540 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament written on paper. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 14th century. The manuscript has complex contents. Scrivener labelled it as 861e.- Description :The codex contains the text of the four Gospels, on 253 paper...
, 781Minuscule 781 (Gregory-Aland)Minuscule 781 , ε354 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament written on paper. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 14th century. The manuscript has no complex contents.- Description :...
, 797Minuscule 797 (Gregory-Aland)Minuscule 797 , ε535 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament written on paper. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 14th century. The manuscript has complex contents.- Description :...
, 801Minuscule 801 (Gregory-Aland)Minuscule 801 , δ553 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament written on paper. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 15th century. The manuscript has complex contents.- Description :...
, 824Minuscule 824 (Gregory-Aland)Minuscule 824 , δ404 , is a 14th-century Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament on paper.- Description :The codex contains the entire New Testament, on 366 paper leaves...
, 825Minuscule 825 (Gregory-Aland)Minuscule 825 , ε308 , is a 13th-century Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament on parchment.- Description :The codex contains the text of the four Gospels, on 337 parchment leaves...
, 829Minuscule 829 (Gregory-Aland)Minuscule 829 , ε220 , is a 12th-century Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament on parchment.- Description :...
, 844Minuscule 844 (Gregory-Aland)Minuscule 844 , ε505 , is a 15th-century Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament on parchment...
, 845Minuscule 845 (Gregory-Aland)Minuscule 845 , ε412 , is a 14th-century Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament on parchment. The manuscript has complex context.- Description :...
, 867Minuscule 867 (Gregory-Aland)Minuscule 867 , ε400 , is a 14th-century Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament on parchment. The manuscript has no complex context, and some marginalia.- Description :...
, 873, 897, 922, 1073, 1077, 1092 (later hand), 1099, 1187, 1189, 1443 and 1445 include entire pericope from 7:53; the menologion of Lectionary 185 includes 8:1ff; Codex Basilensis (E) includes 8:2ff; Codex Tischendorfianus IIICodex Tischendorfianus IIICodex Tischendorfianus III – designated by siglum Λ or 039 , ε 77 – is a Greek uncial manuscript of the Gospels on parchment...
(Λ) and Petropolitanus (П)Codex Petropolitanus (New Testament)Codex Petropolitanus, designated by Π or 041 , ε 73 , is a Greek uncial manuscript of the Gospels, dated palaeographically to the 9th century...
also the menologia of Lectionaries ℓ 86Lectionary 86Lectionary 86, designated by siglum ℓ 86 , is a Greek manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment leaves. It is dated by a colophon to the year 1336.- Description :...
, ℓ 211, ℓ 1579 and ℓ 1761 include 8:3ff. Minuscule 807 is a manuscript with a Catena, but only in John 7:53-8:11 without catena. It is a characteristic of late Byzantine manuscripts conforming to the sub-type Family KrFamily KrFamily Kr is a large group of the New Testament manuscripts. It belongs to the Byzantine text-type as one of the textual families of this group. It has no uncials, no early minuscules, it has only hundreds of minuscules.- Description :...
, that this pericope is marked with obeliObelusAn obelus is a symbol consisting of a short horizontal line with a dot above and below. It is mainly used to represent the mathematical operation of division. It is therefore commonly referred to as the division sign.- History :The word "obelus" comes from the Greek word for a sharpened stick,...
; although Maurice Robinson argues that these marks are intended to remind lectors that these verses are to be omitted from the Gospel lection for PentecostPentecostPentecost is a prominent feast in the calendar of Ancient Israel celebrating the giving of the Law on Sinai, and also later in the Christian liturgical year commemorating the descent of the Holy Spirit upon the disciples of Christ after the Resurrection of Jesus...
, not to question the authenticity of the passage. - Shorter pericope questioned (8:3-11). Marked with asterisks (*) or obeli (÷). 707Minuscule 707Minuscule 707 , ε152 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 11th century. The manuscript is lacunose...
- Relocate pericope. Family 1Family 1Family 1 is a group of Greek Gospel manuscripts, varying in date from the 12th to the 15th century. The group takes its name from the minuscule codex 1, now in the Basel University Library. "Family 1" is also known as "the Lake Group", symbolized as f1. Hermann von Soden calls the group Ih...
, minuscules 20Minuscule 20Minuscule 20 , A138 . It is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, dated paleographically to the 11th century. The manuscript has complex contents and full marginalia. It was prepared for the church reading....
, 37Minuscule 37Minuscule 37 , A154 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, written on vellum. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 11th century.- Description :...
, 135Minuscule 135Minuscule 135 , ε 1000 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment leaves. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 10th century. The codex has complex contents. It has marginalia....
, 207Minuscule 207Minuscule 207 , ε 126 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 11th century. The manuscript is lacunose...
, 301Minuscule 301Minuscule 301 , A156 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 11th century.It has marginalia.- Description :...
, 347Minuscule 347Minuscule 347 , ε 226 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment. Paleographically it has been assigned to the 12th century. It has full marginalia.- Description :...
, and nearly all Armenian translations place the pericope after John 21:25; Family 13Family 13Family 13, also known Ferrar Group , is a group of Greek Gospel manuscripts, varying in date from the 11th to the 15th century, which display a distinctive pattern of variant readings — especially in placing the story of Jesus and the woman taken in adultery in the Gospel of Luke, rather than in...
place it after Luke 24:53; a corrector to Minuscule 1333 added 8:3–11 after Luke 24:53; and Minuscule 225Minuscule 225Minuscule 225 , ε 1210 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment. It is dated by a colophon to the year 1192. It was adapted for liturgical use.- Description :...
includes the pericope after John 7:36. Minuscule 129Minuscule 129Minuscule 129 , A200 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment leaves. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 12th century. The manuscript has complex contents. It has complex contents, and full marginalia.- Description :The codex contains a complete text of the...
, 135Minuscule 135Minuscule 135 , ε 1000 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment leaves. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 10th century. The codex has complex contents. It has marginalia....
, 259Minuscule 259Minuscule 259 , A122 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment. Paleographically it has been assigned to the 11th century...
, 470Minuscule 470Minuscule 470 , α 136 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 11th century. Scrivener labelled it number 509...
, 564Minuscule 564Minuscule 564 , ε 1026 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 10th century.Scrivener labelled it by number 478....
, 831Minuscule 831 (Gregory-Aland)Minuscule 831 , ε117 , is a 11th-century Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament on parchment. The manuscript is lacunose.- Description :...
, 1076Minuscule 1076 (Gregory-Aland)Minuscule 1076 , ε1140 , is a 10th-century Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament on parchment. The manuscript does not contain gaps.- Description :...
, 1078Minuscule 1078 (Gregory-Aland)Minuscule 1078 , A159 , is a 10th-century Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament on parchment. It was adapted for liturgical use. The manuscript is not lacunose.- Description :...
, and 1356Minuscule 1356 (Gregory-Aland)Minuscule 1356 , ε1087 , is a 11th-century Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament on parchment. The manuscript has complex contents.- Description :...
place John 8:3-11 after John 21:25. 788Minuscule 788 (Gregory-Aland)Minuscule 788 , ε1033 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament written on parchment. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 11th century...
and Minuscule 826Minuscule 826 (Gregory-Aland)Minuscule 826 , ε218 , is a 12th-century Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament on parchment.- Description :The codex contains the text of the four Gospels, on 233 parchment leaves...
placed pericope after Luke 21:38 - Added by a later hand. Codex EbnerianusCodex EbnerianusCodex Ebnerianus, Minuscule 105 , δ 257 , is a Greek language illuminated manuscript of the New Testament, though missing the Book of Revelation.Formerly it was labeled by 105e, 48a, and 24p.- Description :...
, 284Minuscule 284Minuscule 284 , ε 374 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment. Paleographically it has been assigned to the 13th century.It has marginalia.- Description :...
, 431Minuscule 431Minuscule 431 , δ 268 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 12th century....
, 461, 470Minuscule 470Minuscule 470 , α 136 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment. Palaeographically it has been assigned to the 11th century. Scrivener labelled it number 509...
, 578Minuscule 578Minuscule 578 , ε 453 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on paper. It is dated by a colophon to the year 1361.The manuscript has complex contents.- Description :...
, 2174Minuscule 2174Minuscule 2174 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment leaves. Paleographically it has been assigned to the 13th century. It has marginalia.- Description :...
.
The pericope was never read as a part of the lesson for Pentecost
Pentecost
Pentecost is a prominent feast in the calendar of Ancient Israel celebrating the giving of the Law on Sinai, and also later in the Christian liturgical year commemorating the descent of the Holy Spirit upon the disciples of Christ after the Resurrection of Jesus...
(John 7:37-8:12), but was reserved for the festivals of such saints as Theodora, September 18, or Pelagia, October 8.
Some of the textual variants
8:4 – εκπειραζοντες αυτον οι ιερεις ινα εχωσιν κατηγοριαν αυτου – D
8:5 – λιθαζειν ] λιθοβολεισθαι – K Π
8:6 – ενος εκαστου αυτων τας αμαρτιας – 264
Minuscule 264
Minuscule 264 , ε 284 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment. Paleographically it has been assigned to the 12th century. It has marginalia.- Description :...
8:6 – μη προσποιουμενος – K
8:7 – ανακυψας ] αναβλεψας – Κ Γ ] U Λ f13 700
8:8 – κατω κυψας – f13
8:8 – ενος εκαστου αυτων τας αμαρτιας – U, 73, 95, 331, 413
Minuscule 413
Minuscule 413 , ε 420 , is a Greek minuscule manuscript of the New Testament, on parchment. It is dated by a colophon to the year 1302.It has marginalia.- Description :...
, 700
8:9 – και υπο της συνειδησεως αλεγχομενοι εξρχοντο εις καθ' εις – K
8:9 – εως των εσχατων – U Λ f13
8:10 – και μηδενα θασαμενος πλην της γυναικος – K
8:11 – τουτο δε ειπαν πειραζοντες αυτον ινα εχωσιν κατηγοριαν κατ αυτου – M
See also
Other questioned passages- Comma JohanneumComma JohanneumThe Comma Johanneum is a comma in the First Epistle of John according to the Latin Vulgate text as transmitted since the Early Middle Ages, based on Vetus Latina minority readings dating to the 7th century...
- The Longer Ending of Mark
- Matthew 16:2b–3
- Christ's agony at GethsemaneChrist's agony at GethsemaneChrist's agony at Gethsemane is a passage in the Gospel of Luke , describing a prayer of Jesus, after which he receives strength from an angel, on the Mount of Olives prior to his betrayal and arrest...
- John 5:3b-4
- Doxology to the Lord's Prayer
- Luke 22:19b-20
Sortable articles
- List of omitted Bible verses
- John 21John 21The chapter John 21 in the Bible contains an account of the post-Resurrection appearance in Galilee, which the text describes as the third time Jesus had appeared to his disciples...
- Textual criticismTextual criticismTextual criticism is a branch of literary criticism that is concerned with the identification and removal of transcription errors in the texts of manuscripts...
- The Woman Taken in Adultery (Rembrandt)The Woman Taken in Adultery (Rembrandt)The Woman Taken in Adultery is a painting of 1644 by Rembrandt, bought by the National Gallery, London in 1824, as one of their foundation batch of paintings. It is in oil on oak, and 83.8 x 65.4 cm....
External links
(NIV) (KJV)- Pericope Adulterae in Manuscript Comparator — allows two or more New Testament manuscript editions' readings of the passage to be compared in side-by-side and unified views (similar to diffDiffIn computing, diff is a file comparison utility that outputs the differences between two files. It is typically used to show the changes between one version of a file and a former version of the same file. Diff displays the changes made per line for text files. Modern implementations also...
output) - The Pericope de Adultera Homepage Site dedicated to proving that the passage is authentic, with links to a wide range of scholarly published material on both sides about all aspects of this text, and dozens of new articles.
- Jesus and the Adultress, a detailed study by Wieland Willker.
- Concerning the Story of the Adulteress in the Eighth Chapter of John, list marginal notes from several versions, extended discussion taken from Samuel P. Tregelles, lists extended excerpts from An Account of the Printed Text of the Greek New Testament (London, 1854), F.H.A. Scrivener, A Plain Introduction to the Criticism of the New Testament (4th edition. London, 1894), Bruce Metzger, A Textual Commentary on the Greek New Testament (Stuttgart, 1971), Raymond E. Brown, The Gospel According to John (i-xii), in the Anchor Bible series (Garden City, New York: Doubleday, 1966).
- The Woman Taken In Adultery (John 7:53-8:11), in defense of the pericope de adultera by Edward F. Hills, taken from chapter 6 of his book, The King James Version Defended, 4th edition (Des Moines: Christian Research Press, 1984).
- David Robert Palmer, John 5:3b and the Pericope Adulterae

